
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write an Essay Introduction (with Examples)

The introduction of an essay plays a critical role in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. It sets the stage for the rest of the essay, establishes the tone and style, and motivates the reader to continue reading.
Table of Contents
What is an essay introduction , what to include in an essay introduction, how to create an essay structure , step-by-step process for writing an essay introduction , how to write an introduction paragraph , how to write a hook for your essay , how to include background information , how to write a thesis statement .
- Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
- Expository Essay Introduction Example
Literary Analysis Essay Introduction Example
Check and revise – checklist for essay introduction , key takeaways , frequently asked questions .
An introduction is the opening section of an essay, paper, or other written work. It introduces the topic and provides background information, context, and an overview of what the reader can expect from the rest of the work. 1 The key is to be concise and to the point, providing enough information to engage the reader without delving into excessive detail.
The essay introduction is crucial as it sets the tone for the entire piece and provides the reader with a roadmap of what to expect. Here are key elements to include in your essay introduction:
- Hook : Start with an attention-grabbing statement or question to engage the reader. This could be a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or a compelling anecdote.
- Background information : Provide context and background information to help the reader understand the topic. This can include historical information, definitions of key terms, or an overview of the current state of affairs related to your topic.
- Thesis statement : Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic. Your thesis should be concise and specific, providing a clear direction for your essay.
Before we get into how to write an essay introduction, we need to know how it is structured. The structure of an essay is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting them clearly and logically. It is divided as follows: 2
- Introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention with a hook, provide context, and include a thesis statement that presents the main argument or purpose of the essay.
- Body: The body should consist of focused paragraphs that support your thesis statement using evidence and analysis. Each paragraph should concentrate on a single central idea or argument and provide evidence, examples, or analysis to back it up.
- Conclusion: The conclusion should summarize the main points and restate the thesis differently. End with a final statement that leaves a lasting impression on the reader. Avoid new information or arguments.

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to write an essay introduction:
- Start with a Hook : Begin your introduction paragraph with an attention-grabbing statement, question, quote, or anecdote related to your topic. The hook should pique the reader’s interest and encourage them to continue reading.
- Provide Background Information : This helps the reader understand the relevance and importance of the topic.
- State Your Thesis Statement : The last sentence is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be clear, concise, and directly address the topic of your essay.
- Preview the Main Points : This gives the reader an idea of what to expect and how you will support your thesis.
- Keep it Concise and Clear : Avoid going into too much detail or including information not directly relevant to your topic.
- Revise : Revise your introduction after you’ve written the rest of your essay to ensure it aligns with your final argument.
Here’s an example of an essay introduction paragraph about the importance of education:
Education is often viewed as a fundamental human right and a key social and economic development driver. As Nelson Mandela once famously said, “Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” It is the key to unlocking a wide range of opportunities and benefits for individuals, societies, and nations. In today’s constantly evolving world, education has become even more critical. It has expanded beyond traditional classroom learning to include digital and remote learning, making education more accessible and convenient. This essay will delve into the importance of education in empowering individuals to achieve their dreams, improving societies by promoting social justice and equality, and driving economic growth by developing a skilled workforce and promoting innovation.
This introduction paragraph example includes a hook (the quote by Nelson Mandela), provides some background information on education, and states the thesis statement (the importance of education).
This is one of the key steps in how to write an essay introduction. Crafting a compelling hook is vital because it sets the tone for your entire essay and determines whether your readers will stay interested. A good hook draws the reader in and sets the stage for the rest of your essay.
- Avoid Dry Fact : Instead of simply stating a bland fact, try to make it engaging and relevant to your topic. For example, if you’re writing about the benefits of exercise, you could start with a startling statistic like, “Did you know that regular exercise can increase your lifespan by up to seven years?”
- Avoid Using a Dictionary Definition : While definitions can be informative, they’re not always the most captivating way to start an essay. Instead, try to use a quote, anecdote, or provocative question to pique the reader’s interest. For instance, if you’re writing about freedom, you could begin with a quote from a famous freedom fighter or philosopher.
- Do Not Just State a Fact That the Reader Already Knows : This ties back to the first point—your hook should surprise or intrigue the reader. For Here’s an introduction paragraph example, if you’re writing about climate change, you could start with a thought-provoking statement like, “Despite overwhelming evidence, many people still refuse to believe in the reality of climate change.”
Including background information in the introduction section of your essay is important to provide context and establish the relevance of your topic. When writing the background information, you can follow these steps:
- Start with a General Statement: Begin with a general statement about the topic and gradually narrow it down to your specific focus. For example, when discussing the impact of social media, you can begin by making a broad statement about social media and its widespread use in today’s society, as follows: “Social media has become an integral part of modern life, with billions of users worldwide.”
- Define Key Terms : Define any key terms or concepts that may be unfamiliar to your readers but are essential for understanding your argument.
- Provide Relevant Statistics: Use statistics or facts to highlight the significance of the issue you’re discussing. For instance, “According to a report by Statista, the number of social media users is expected to reach 4.41 billion by 2025.”
- Discuss the Evolution: Mention previous research or studies that have been conducted on the topic, especially those that are relevant to your argument. Mention key milestones or developments that have shaped its current impact. You can also outline some of the major effects of social media. For example, you can briefly describe how social media has evolved, including positives such as increased connectivity and issues like cyberbullying and privacy concerns.
- Transition to Your Thesis: Use the background information to lead into your thesis statement, which should clearly state the main argument or purpose of your essay. For example, “Given its pervasive influence, it is crucial to examine the impact of social media on mental health.”

A thesis statement is a concise summary of the main point or claim of an essay, research paper, or other type of academic writing. It appears near the end of the introduction. Here’s how to write a thesis statement:
- Identify the topic: Start by identifying the topic of your essay. For example, if your essay is about the importance of exercise for overall health, your topic is “exercise.”
- State your position: Next, state your position or claim about the topic. This is the main argument or point you want to make. For example, if you believe that regular exercise is crucial for maintaining good health, your position could be: “Regular exercise is essential for maintaining good health.”
- Support your position: Provide a brief overview of the reasons or evidence that support your position. These will be the main points of your essay. For example, if you’re writing an essay about the importance of exercise, you could mention the physical health benefits, mental health benefits, and the role of exercise in disease prevention.
- Make it specific: Ensure your thesis statement clearly states what you will discuss in your essay. For example, instead of saying, “Exercise is good for you,” you could say, “Regular exercise, including cardiovascular and strength training, can improve overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.”
Examples of essay introduction
Here are examples of essay introductions for different types of essays:
Argumentative Essay Introduction Example:
Topic: Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
“The question of whether the voting age should be lowered to 16 has sparked nationwide debate. While some argue that 16-year-olds lack the requisite maturity and knowledge to make informed decisions, others argue that doing so would imbue young people with agency and give them a voice in shaping their future.”
Expository Essay Introduction Example
Topic: The benefits of regular exercise
“In today’s fast-paced world, the importance of regular exercise cannot be overstated. From improving physical health to boosting mental well-being, the benefits of exercise are numerous and far-reaching. This essay will examine the various advantages of regular exercise and provide tips on incorporating it into your daily routine.”
Text: “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
“Harper Lee’s novel, ‘To Kill a Mockingbird,’ is a timeless classic that explores themes of racism, injustice, and morality in the American South. Through the eyes of young Scout Finch, the reader is taken on a journey that challenges societal norms and forces characters to confront their prejudices. This essay will analyze the novel’s use of symbolism, character development, and narrative structure to uncover its deeper meaning and relevance to contemporary society.”
- Engaging and Relevant First Sentence : The opening sentence captures the reader’s attention and relates directly to the topic.
- Background Information : Enough background information is introduced to provide context for the thesis statement.
- Definition of Important Terms : Key terms or concepts that might be unfamiliar to the audience or are central to the argument are defined.
- Clear Thesis Statement : The thesis statement presents the main point or argument of the essay.
- Relevance to Main Body : Everything in the introduction directly relates to and sets up the discussion in the main body of the essay.

Writing a strong introduction is crucial for setting the tone and context of your essay. Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3
- Hook the Reader : Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader’s attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote.
- Provide Background : Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
- Thesis Statement : State your thesis, which is the main argument or point of your essay. It should be concise, clear, and specific.
- Preview the Structure : Outline the main points or arguments to help the reader understand the organization of your essay.
- Keep it Concise : Avoid including unnecessary details or information not directly related to your thesis.
- Revise and Edit : Revise your introduction to ensure clarity, coherence, and relevance. Check for grammar and spelling errors.
- Seek Feedback : Get feedback from peers or instructors to improve your introduction further.
The purpose of an essay introduction is to give an overview of the topic, context, and main ideas of the essay. It is meant to engage the reader, establish the tone for the rest of the essay, and introduce the thesis statement or central argument.
An essay introduction typically ranges from 5-10% of the total word count. For example, in a 1,000-word essay, the introduction would be roughly 50-100 words. However, the length can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the overall length of the essay.
An essay introduction is critical in engaging the reader and providing contextual information about the topic. To ensure its effectiveness, consider incorporating these key elements: a compelling hook, background information, a clear thesis statement, an outline of the essay’s scope, a smooth transition to the body, and optional signposting sentences.
The process of writing an essay introduction is not necessarily straightforward, but there are several strategies that can be employed to achieve this end. When experiencing difficulty initiating the process, consider the following techniques: begin with an anecdote, a quotation, an image, a question, or a startling fact to pique the reader’s interest. It may also be helpful to consider the five W’s of journalism: who, what, when, where, why, and how. For instance, an anecdotal opening could be structured as follows: “As I ascended the stage, momentarily blinded by the intense lights, I could sense the weight of a hundred eyes upon me, anticipating my next move. The topic of discussion was climate change, a subject I was passionate about, and it was my first public speaking event. Little did I know , that pivotal moment would not only alter my perspective but also chart my life’s course.”
Crafting a compelling thesis statement for your introduction paragraph is crucial to grab your reader’s attention. To achieve this, avoid using overused phrases such as “In this paper, I will write about” or “I will focus on” as they lack originality. Instead, strive to engage your reader by substantiating your stance or proposition with a “so what” clause. While writing your thesis statement, aim to be precise, succinct, and clear in conveying your main argument.
To create an effective essay introduction, ensure it is clear, engaging, relevant, and contains a concise thesis statement. It should transition smoothly into the essay and be long enough to cover necessary points but not become overwhelming. Seek feedback from peers or instructors to assess its effectiveness.
References
- Cui, L. (2022). Unit 6 Essay Introduction. Building Academic Writing Skills .
- West, H., Malcolm, G., Keywood, S., & Hill, J. (2019). Writing a successful essay. Journal of Geography in Higher Education , 43 (4), 609-617.
- Beavers, M. E., Thoune, D. L., & McBeth, M. (2023). Bibliographic Essay: Reading, Researching, Teaching, and Writing with Hooks: A Queer Literacy Sponsorship. College English, 85(3), 230-242.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
- How to Cite Social Media Sources in Academic Writing?
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
Similarity Checks: The Author’s Guide to Plagiarism and Responsible Writing
Types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid it in your writing , you may also like, leveraging generative ai to enhance student understanding of..., how to write a good hook for essays,..., addressing peer review feedback and mastering manuscript revisions..., how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., what is the importance of a concept paper..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how to write a high-quality conference paper.
How To Write A Solid Assignment Introduction
By: Derek Jansen | December 2017

I’ll kick off this post by making a bold assertion:
The introduction chapter of your assignment is the single most important section in your entire assignment.
Yip. Not the analysis chapter. Not the recommendations chapter. The introduction chapter. Yip, that short 200/300/400-word chapter that so many students rush through to get to the meatier chapters. Why do I say this? There are a few reasons:
It creates the first impression.
Apart from the executive summary (which some assignments don’t have), the introduction creates the very first impression on your marker. It sets the tone in terms of the quality of the assignment.
It introduces your industry.
You might have decades of experience in your industry – but your marker won’t. This means that the simplest concepts can be misunderstood (and thereby cost you marks) if not explained right at the beginning of your assignment. A good introduction lays the foundation so that the marker can understand your upcoming arguments.
It defines and justifies your topic.
The introduction, if developed correctly, clearly outlines what the assignment will be about (and what it won’t) and why that’s important (i.e. a justification). In other words, it makes it clear what the focus of the assignment will be about, and why that is worth investigating. This clarity and justification of the topic are essential to earning good marks and keeping you focused on the purpose of the assignment.
It clarifies your approach.
Beyond the what and why, a good introduction also briefly explains how you’ll approach the research, both from a theoretical and practical perspective. This lays a clear roadmap both for the marker and for yourself. For the marker, this improves the readability and digestibility of the document (which is essential for earning marks). And for you, this big-picture view of the approach keeps you from digressing into a useless analysis.
In short, a good introduction lays a solid foundation and a clear direction for the rest of your assignment. Hopefully, you’re convinced…

The 5 essential ingredients.
In this post, I’ll outline the key components of a strong introduction chapter/section. But first, I want to discuss the structure.
Some assignment briefs will provide a proposed structure which combines the introduction and analysis chapters. I always encourage my clients to split this up into two chapters, as it provides a clearer, more logical structure. You’ll see why once I discuss the core components.
#1 – The Four Ws
A logical starting point is to assume the marker knows nothing about your business . Make sure you cover the basics:
- Who – what is the name of the business? If its multiple words, you should take the opportunity to introduce an acronym here. Then, stick to the acronym throughout the rest of the assignment. It’s also good practice to provide a list of acronyms in the appendix.
- What – explain what the business does, in simple English. Avoid industry jargon and explain the basic operating model of the business.
- Where – explain where the business operates from and where its customers operate. If you have multiple offices and serve multiple markets, a visual representation can save you some words.
- When – mention the age of the business, and how many staff it employs. You can also note the ownership structure (private company, listed entity, JV, etc).
If you’re only going to focus on one country/branch/department, make mention of this now. Also, be sure to justify why you’re focusing on that (for example, due to limited access to data).
If done right, you will have now painted a very clear (but concise) picture of the organisation for the marker. The next step is to discuss the context that the business operates in.
#2 – A brief discussion of the context.
Now that you’ve introduced the business, you need to move towards identifying the key issue(s) that will form the focus of the assignment. To do this, you need to lay a context, which will then lead to the issue(s). This will vary between assignments, and could be something like:
- The entry of new competitors resulting in reduced market share (STR, SM)
- A merger leading to a culture clash and poor performance (MP)
- A corporate scandal resulting in reputation damage (R&R)
- Changing regulation leading to the opening of a new potential country market (IB)
In other words, you need to present a (brief) story of how the key issue(s) or opportunity has arisen – X has lead to Y, which caused Z.
#3 – Identification of the key issue and research question(s).
With the context set, you need to clearly state what the key issue(s) or opportunity is, and why this is worth investigating (for example, due to the financial impact if left unresolved). This is pretty straightforward, but it is a critical step often missed by students, and results in the marker questioning the quality of the entire assignment.
With the key issue identified, its time to lay out your research question(s). In other words, state in question format, what question(s) your assignment will seek to answer.
For example:
- “What has changed in Organisation X’s competitive context, and how should it best respond to ensure sustainable competitive advantage?”
- “Should Organisation X internationalise to Country Y?”
- “What segments exist within Industry X and which segment should Organisation Y target?”
- “Which digital business model should Organisation X adopt?”
By stating your research question(s) up front, you are providing a very clear, focused direction for your assignment, thereby reducing your risk of getting distracted by the shiny objects that will invariably pop up along the way. You are stating clearly what you will and won’t focus on, and ring-fencing the assignment to a manageable breadth. This is critically important for earning marks, as it allows you to go deep into a highly relevant set of theories and develop meaningful insights, rather than superficially fluttering with numerous less-relevant ones.
What’s critically important is that you achieve alignment between the context, the issue(s) and the research question(s). They should all flow in a logical fashion, as shown below.

If you achieve this alignment, you have a rock-solid foundation for your assignment, and your marker will be crystal clear regarding your direction, and why you chose that direction.
#4 – A brief outline of your theoretical approach.
Now that you’ve made it clear what your assignment is aiming to achieve (i.e. what research question(s) it wants to answer), it is very good practice to briefly mention:
- How you will approach the analysis.
- What key theory you will draw on.
In other words, you should give the marker an indication of how you approached the analysis, and on what theoretical basis. For example:
“The report begins by briefly looking at the organisation’s broader strategy, as well as values using Schwartz’s model (1994). It then reviews stakeholders using Mitchell et al.’s framework (1997) and identifies a key group with which reputation needs to be managed to achieve strategic alignment. It then analyses antecedents, reputation, and outcomes of the said group using Money et al.’s (2012) RELATE framework. This is followed by proposed strategic actions.”
As you can see, this excerpt clearly outlines how the analysis was approached, and what key theory was used in the relevant sections. This gives the marker a big-picture view of the assignment, which aids the digestibility of the document.
#5 – A brief outline of your fieldwork.
Now that you’ve communicated the approach, structure and underpinning theory, it’s best practice to make a quick mention of your fieldwork. Yes, you’re typically supposed to collect some primary data (for example, undertake some semi-structured interviews or a survey), as well as secondary data (for example, review industry reports, company data, etc), for your assignments – especially in Stage 2 and 3 of the program.
In this final section, you should very briefly outline what you did in this respect so that the marker can rest assured that your assignment is not an opinion piece. A quality assignment draws on multiple data sources to make well-informed, data-backed arguments. Show that you’ve done this, and be sure to refer the reader to the appendices for evidence of this work (for example, interview transcripts, survey results, etc.).
Lastly, make mention of your relationship with the business, and your broad responsibilities. Remember to keep this in third-person language. For example:
“The author is employed as the [INSERT YOUR TITLE] and is responsible for X, Y and Z.”
Let’s recap.
In this article, I’ve hopefully convinced you of the critical importance of writing a strong introduction chapter. I’ve also presented 5 essential ingredients that you should bake into your intro in every assignment. By incorporating these ingredients (ideally, in this order), you will set the foundation for a strong assignment.
To recap the 5 essentials:
- A (plain language) explanation of the organisation.
- A brief discussion of the context.
- Identification of the key issue and research question(s).
- A brief outline of your theoretical approach.
- A brief outline of your fieldwork and your professional position.
You Might Also Like:

Informative and easy to apply advice…tx D
You’re welcome, Rishen 🙂
It is a very useful and understandable explanation of writing a research paper. Thank you so much for the sharing free such a useful example.
Yours sincerely Tara
This is really good, thank you.
Thanks for the feedback, Paul. Best of luck with your Henley MBA.
Very useful guide for the MBA. You mention that it’s good practice to use a range of sources to support arguments. If an assignment task isn’t that strategic (e.g. reviewing a process for a particular team within the business), can the assignment be supported purely by ‘fieldwork’ and models/theory? Thank you.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Introductions
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain the functions of introductions, offer strategies for creating effective introductions, and provide some examples of less effective introductions to avoid.
The role of introductions
Introductions and conclusions can be the most difficult parts of papers to write. Usually when you sit down to respond to an assignment, you have at least some sense of what you want to say in the body of your paper. You might have chosen a few examples you want to use or have an idea that will help you answer the main question of your assignment; these sections, therefore, may not be as hard to write. And it’s fine to write them first! But in your final draft, these middle parts of the paper can’t just come out of thin air; they need to be introduced and concluded in a way that makes sense to your reader.
Your introduction and conclusion act as bridges that transport your readers from their own lives into the “place” of your analysis. If your readers pick up your paper about education in the autobiography of Frederick Douglass, for example, they need a transition to help them leave behind the world of Chapel Hill, television, e-mail, and The Daily Tar Heel and to help them temporarily enter the world of nineteenth-century American slavery. By providing an introduction that helps your readers make a transition between their own world and the issues you will be writing about, you give your readers the tools they need to get into your topic and care about what you are saying. Similarly, once you’ve hooked your readers with the introduction and offered evidence to prove your thesis, your conclusion can provide a bridge to help your readers make the transition back to their daily lives. (See our handout on conclusions .)
Note that what constitutes a good introduction may vary widely based on the kind of paper you are writing and the academic discipline in which you are writing it. If you are uncertain what kind of introduction is expected, ask your instructor.
Why bother writing a good introduction?
You never get a second chance to make a first impression. The opening paragraph of your paper will provide your readers with their initial impressions of your argument, your writing style, and the overall quality of your work. A vague, disorganized, error-filled, off-the-wall, or boring introduction will probably create a negative impression. On the other hand, a concise, engaging, and well-written introduction will start your readers off thinking highly of you, your analytical skills, your writing, and your paper.
Your introduction is an important road map for the rest of your paper. Your introduction conveys a lot of information to your readers. You can let them know what your topic is, why it is important, and how you plan to proceed with your discussion. In many academic disciplines, your introduction should contain a thesis that will assert your main argument. Your introduction should also give the reader a sense of the kinds of information you will use to make that argument and the general organization of the paragraphs and pages that will follow. After reading your introduction, your readers should not have any major surprises in store when they read the main body of your paper.
Ideally, your introduction will make your readers want to read your paper. The introduction should capture your readers’ interest, making them want to read the rest of your paper. Opening with a compelling story, an interesting question, or a vivid example can get your readers to see why your topic matters and serve as an invitation for them to join you for an engaging intellectual conversation (remember, though, that these strategies may not be suitable for all papers and disciplines).
Strategies for writing an effective introduction
Start by thinking about the question (or questions) you are trying to answer. Your entire essay will be a response to this question, and your introduction is the first step toward that end. Your direct answer to the assigned question will be your thesis, and your thesis will likely be included in your introduction, so it is a good idea to use the question as a jumping off point. Imagine that you are assigned the following question:
Drawing on the Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass , discuss the relationship between education and slavery in 19th-century America. Consider the following: How did white control of education reinforce slavery? How did Douglass and other enslaved African Americans view education while they endured slavery? And what role did education play in the acquisition of freedom? Most importantly, consider the degree to which education was or was not a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
You will probably refer back to your assignment extensively as you prepare your complete essay, and the prompt itself can also give you some clues about how to approach the introduction. Notice that it starts with a broad statement and then narrows to focus on specific questions from the book. One strategy might be to use a similar model in your own introduction—start off with a big picture sentence or two and then focus in on the details of your argument about Douglass. Of course, a different approach could also be very successful, but looking at the way the professor set up the question can sometimes give you some ideas for how you might answer it. (See our handout on understanding assignments for additional information on the hidden clues in assignments.)
Decide how general or broad your opening should be. Keep in mind that even a “big picture” opening needs to be clearly related to your topic; an opening sentence that said “Human beings, more than any other creatures on earth, are capable of learning” would be too broad for our sample assignment about slavery and education. If you have ever used Google Maps or similar programs, that experience can provide a helpful way of thinking about how broad your opening should be. Imagine that you’re researching Chapel Hill. If what you want to find out is whether Chapel Hill is at roughly the same latitude as Rome, it might make sense to hit that little “minus” sign on the online map until it has zoomed all the way out and you can see the whole globe. If you’re trying to figure out how to get from Chapel Hill to Wrightsville Beach, it might make more sense to zoom in to the level where you can see most of North Carolina (but not the rest of the world, or even the rest of the United States). And if you are looking for the intersection of Ridge Road and Manning Drive so that you can find the Writing Center’s main office, you may need to zoom all the way in. The question you are asking determines how “broad” your view should be. In the sample assignment above, the questions are probably at the “state” or “city” level of generality. When writing, you need to place your ideas in context—but that context doesn’t generally have to be as big as the whole galaxy!
Try writing your introduction last. You may think that you have to write your introduction first, but that isn’t necessarily true, and it isn’t always the most effective way to craft a good introduction. You may find that you don’t know precisely what you are going to argue at the beginning of the writing process. It is perfectly fine to start out thinking that you want to argue a particular point but wind up arguing something slightly or even dramatically different by the time you’ve written most of the paper. The writing process can be an important way to organize your ideas, think through complicated issues, refine your thoughts, and develop a sophisticated argument. However, an introduction written at the beginning of that discovery process will not necessarily reflect what you wind up with at the end. You will need to revise your paper to make sure that the introduction, all of the evidence, and the conclusion reflect the argument you intend. Sometimes it’s easiest to just write up all of your evidence first and then write the introduction last—that way you can be sure that the introduction will match the body of the paper.
Don’t be afraid to write a tentative introduction first and then change it later. Some people find that they need to write some kind of introduction in order to get the writing process started. That’s fine, but if you are one of those people, be sure to return to your initial introduction later and rewrite if necessary.
Open with something that will draw readers in. Consider these options (remembering that they may not be suitable for all kinds of papers):
- an intriguing example —for example, Douglass writes about a mistress who initially teaches him but then ceases her instruction as she learns more about slavery.
- a provocative quotation that is closely related to your argument —for example, Douglass writes that “education and slavery were incompatible with each other.” (Quotes from famous people, inspirational quotes, etc. may not work well for an academic paper; in this example, the quote is from the author himself.)
- a puzzling scenario —for example, Frederick Douglass says of slaves that “[N]othing has been left undone to cripple their intellects, darken their minds, debase their moral nature, obliterate all traces of their relationship to mankind; and yet how wonderfully they have sustained the mighty load of a most frightful bondage, under which they have been groaning for centuries!” Douglass clearly asserts that slave owners went to great lengths to destroy the mental capacities of slaves, yet his own life story proves that these efforts could be unsuccessful.
- a vivid and perhaps unexpected anecdote —for example, “Learning about slavery in the American history course at Frederick Douglass High School, students studied the work slaves did, the impact of slavery on their families, and the rules that governed their lives. We didn’t discuss education, however, until one student, Mary, raised her hand and asked, ‘But when did they go to school?’ That modern high school students could not conceive of an American childhood devoid of formal education speaks volumes about the centrality of education to American youth today and also suggests the significance of the deprivation of education in past generations.”
- a thought-provoking question —for example, given all of the freedoms that were denied enslaved individuals in the American South, why does Frederick Douglass focus his attentions so squarely on education and literacy?
Pay special attention to your first sentence. Start off on the right foot with your readers by making sure that the first sentence actually says something useful and that it does so in an interesting and polished way.
How to evaluate your introduction draft
Ask a friend to read your introduction and then tell you what they expect the paper will discuss, what kinds of evidence the paper will use, and what the tone of the paper will be. If your friend is able to predict the rest of your paper accurately, you probably have a good introduction.
Five kinds of less effective introductions
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don’t have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don’t really say much. They exist just to take up the “introduction space” in your paper. If you had something more effective to say, you would probably say it, but in the meantime this paragraph is just a place holder.
Example: Slavery was one of the greatest tragedies in American history. There were many different aspects of slavery. Each created different kinds of problems for enslaved people.
2. The restated question introduction. Restating the question can sometimes be an effective strategy, but it can be easy to stop at JUST restating the question instead of offering a more specific, interesting introduction to your paper. The professor or teaching assistant wrote your question and will be reading many essays in response to it—they do not need to read a whole paragraph that simply restates the question.
Example: The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass discusses the relationship between education and slavery in 19th century America, showing how white control of education reinforced slavery and how Douglass and other enslaved African Americans viewed education while they endured. Moreover, the book discusses the role that education played in the acquisition of freedom. Education was a major force for social change with regard to slavery.
3. The Webster’s Dictionary introduction. This introduction begins by giving the dictionary definition of one or more of the words in the assigned question. Anyone can look a word up in the dictionary and copy down what Webster says. If you want to open with a discussion of an important term, it may be far more interesting for you (and your reader) if you develop your own definition of the term in the specific context of your class and assignment. You may also be able to use a definition from one of the sources you’ve been reading for class. Also recognize that the dictionary is also not a particularly authoritative work—it doesn’t take into account the context of your course and doesn’t offer particularly detailed information. If you feel that you must seek out an authority, try to find one that is very relevant and specific. Perhaps a quotation from a source reading might prove better? Dictionary introductions are also ineffective simply because they are so overused. Instructors may see a great many papers that begin in this way, greatly decreasing the dramatic impact that any one of those papers will have.
Example: Webster’s dictionary defines slavery as “the state of being a slave,” as “the practice of owning slaves,” and as “a condition of hard work and subjection.”
4. The “dawn of man” introduction. This kind of introduction generally makes broad, sweeping statements about the relevance of this topic since the beginning of time, throughout the world, etc. It is usually very general (similar to the placeholder introduction) and fails to connect to the thesis. It may employ cliches—the phrases “the dawn of man” and “throughout human history” are examples, and it’s hard to imagine a time when starting with one of these would work. Instructors often find them extremely annoying.
Example: Since the dawn of man, slavery has been a problem in human history.
5. The book report introduction. This introduction is what you had to do for your elementary school book reports. It gives the name and author of the book you are writing about, tells what the book is about, and offers other basic facts about the book. You might resort to this sort of introduction when you are trying to fill space because it’s a familiar, comfortable format. It is ineffective because it offers details that your reader probably already knows and that are irrelevant to the thesis.
Example: Frederick Douglass wrote his autobiography, Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, An American Slave , in the 1840s. It was published in 1986 by Penguin Books. In it, he tells the story of his life.
And now for the conclusion…
Writing an effective introduction can be tough. Try playing around with several different options and choose the one that ends up sounding best to you!
Just as your introduction helps readers make the transition to your topic, your conclusion needs to help them return to their daily lives–but with a lasting sense of how what they have just read is useful or meaningful. Check out our handout on conclusions for tips on ending your paper as effectively as you began it!
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Douglass, Frederick. 1995. Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave, Written by Himself . New York: Dover.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How to Write An Assignment Introduction Like A Pro

Assignments become a crucial part of students’ academic lives as they have to encounter writing assignments daily. Writing an assignment in itself is a big and tough task, but most students face problems in writing an introduction for such assignments.
An introduction has to be precise and complete to give a brief about your assignment, and there is a fixed word limit for writing an introduction of an assignment. That is why the most searched question about the assignment is
How To Write An Assignment Introduction!
Table of Contents
If you want to make sure that your assignment’s introduction is eye-catching and précis, then follow the following guidelines on how to write an introduction for an assignment.
What is the Assignment Introduction?
The introduction gives an outline of the whole paper. It is the presentation of key ideas and also the purpose of your work. The introduction tells the readers about what you are going to tell in the assignment. An introduction has its own grading rules as it is counted distinctly from the body.
Significance of Writing Assignment Introduction
First, we need to understand the significance of writing a good introduction to an assignment. So you must have heard that the first impression is the last impression, and an introduction of your assignment works as a first impression for your assignment.
Thus, if you wish to attract your examiner’s attention or your readers, you should write a good introduction for your assignment. Moreover, the important role of the introduction is to give an overview of the assignment, which helps the reader determine whether they want to read it.
Hence, before writing an assignment, it is very important to understand how to write an introduction of an assignment .
Strategies: How to write an assignment introduction
- A good introduction to the assignment manifests the following strategies –
- It must show the main objective and purpose of the assignment.
- The importance of assignment.
- The purview of the assignment’s study that is what it includes.
- A brief description of the assignment’s content and its organization.
Characteristics of Good Introduction
Before knowing how to write an assignment introduction, the most crucial thing is to know the characteristics of a good introduction. Because then only you can write a good introduction. So following are the essential characteristics of a good introduction-
- A good introduction is written precisely and clearly so that everyone can understand it. In short, there must not be any language errors.
- It must be written while remembering that it should be attention-grabbing so that it can grab the attention of its readers.
- A good introduction always shows the purpose of the study and what the study is about.
- A Good Assignment should be grammatical error free and plagiarism free. It will be a wise decision to take help from AI Content Detector tool like Content at Scale’s AI detector.
- Best Guide on How to Write a Case Study Assignment?
- Useful Guide on How to Submit Assignment on Google Classroom
- Handy Tips on How to Write an Assignment From Scratch
Elements: How to Write Introduction For Assignment
1. background.
The first thing you have to write in an introduction is a brief background of the study. You have to give an overview of your assignment, what your assignment is about, its impact, and its area of study.
2. Context in brief
You have to include a gist of the context of your assignment. It helps the readers to get information about the scope of the study in the assignment. But, including a summarizer tool can automate this process for your convenience.
3. Your Contention
You have to write your stance on the question involved in the statement. It should be limited to one statement. It will help the readers understand your stance on such points and that the assignment is based on such points.
4. Main points of study
You will write one line on the main points of your study as it will help the readers circumscribe the assignment’s limits.
5. Definition of the Topic
The most important step in how to write an introduction for an assignment is to write a definition of the topic of the assignment very briefly. So that readers can understand the title of the study at once.
6. Why are you writing on this topic only
It is always suggested that you write in the introduction of an assignment why you are writing on this topic only.
7. Outline
Write briefly about the outline or structure of the assignment so that readers can read accordingly, and also it will help you to define the scope of the assignment in short.
However, students often look for how to write assignment pdf. So, below we provide the assignment introduction pdf.
How To Write An Introduction Of An Assignment Pdf
Download this PDF of how to write an introduction on an assignment:
How Long Should An Assignment Introduction Be?
It is true that students find this question while looking for an answer on the assignment’s introduction page. Let’s state that while writing an assignment, the introduction section should not be too long. Furthermore, the context should not be more than a few pages long.
Keep your assignment’s introduction simple and readable. Replace difficult words with simpler ones to fix readability issues (if any). To save time and effort, online paraphrasing tools such as Editpad or Paraphraser can be used to paraphrase text in a simple way.
If you are writing a 2000-word assignment, the introduction should be 200-250 words long.
But if you are writing a 3000-word assignment, the introduction should be 350-400 words long.
Guidelines/Tips On How To Write An Assignment Introduction
- Always start your assignment’s introduction with a broad idea about the topic of the assignment. After giving a broader picture of the study, you have to narrow down the discussion and write the main object of the study.
- Don’t forget to state the significance of your assignment in brief. It is the prominent part of the introduction.
- You have to smartly write about the tasks you are dealing with in the assignment in brief.
- Make sure you use easy and understandable language so that readers don’t find it difficult to understand the introduction; otherwise, they will not read the other parts of the assignment as well.
- Double-check and proofread your assignment introduction to ensure it is free from spelling mistakes and grammar mistakes.
These guidelines are very important in writing a good introduction to your assignment. If you want to be well-versed in writing an assignment introduction, it is mandatory first to be acquainted with these tips and guidelines.
Assignment Introduction Example
For more clarity, you can see the following assignment example;

Is There Any Other Way To Write Or Get An Effective Assignment Introduction?
Yes, there is!
It has been seen that there are several writers who are confused when it comes to the assignment’s introduction writing. And it is true that they struggle to summarise the broad issue and write an introduction without conducting sufficient research. However, because the subject experts or online assignments help provide experts who are well-versed in the field, they easily write the introduction in minutes.
- The majority of students do not properly understand the English language. The experts who work in the writing industry have years of experience in writing assignments. That is why they always make sure to write an engaging introduction that also seems professional.
- Furthermore, the requirements of the writer are always given priority by the professionals. After that, they write a professional article that will, without a doubt, engage the reader.
- The expert not only helps the student in preparing the assignment’s introduction. They offer their support in completing the entire home task and guarantee that they will get an A+ grade.
- Besides that, the professionals’ support is available 24/7/365/366 days. So you won’t have to worry about coming up with a solution for your writing task.
What Makes A Good Introduction?
As you already know that, the rules are always subject to change, and our perspectives may be different. However, the academic standards for writing an introduction are quite clear. When creating a great introduction for an assignment, you have to make sure some of the points that are given below:
- Motivates the audience.
- Introduces your thesis statement.
- Defines the topic you’re talking about.
- Emphasizes the significance of your topic.
- Highlights the main points you want to discuss.
- Provides your reasoning for approaching your topic.
- Gives a high-level overview of your methodology.
- Provides statistical information and the purpose of your methodology.
Note: Remember that even creative writing tasks require an inspiring introduction that discusses your purpose for writing.
On the other hand, writing an introduction is relatively easy. Some important things must be clear, including:
- Your topic’s importance.
- The goal of your paper.
- An element of explanation.
- A powerful opening hook sentence.
- Include a link to your thesis statement.
Quick recap
To write an engaging assignment introduction, remember to:
- Make their introduction interesting,
- outline the reasons,
- make the audience curious about your assignment,
- and keep the audience guessing.
Experts warn that rephrasing the assignment question or telling everything in the opening like a story synopsis is not a good idea. You must stick to your tutor’s specified word limit for the assignment introduction and write it with a clear, focused approach.
Since the time assignments have become a crucial part of our studies and grades, and the need to learn the concept and structure of assignments has arisen.
An introduction is the important part of the assignment to grab readers’ attention and tell in brief about the background and information of the assignment. Thus it is very important to learn how to write assignment introductions. The introduction of an assignment should be eye-catching and alluring to capture the audience and make them read the whole assignment.
Browse related content
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. what are the 3 parts of an introduction paragraph.
Following are the three parts of an introduction: 1. Parts of an introduction 2. The opening statement 3. The supporting sentences 4. The introductory topic sentence.
Q2. What are the key elements of an introduction?
The introduction must have the following responsibilities: 1. Get the audience’s attention 2. Introduce the topic 3. Explain its relevance to the audience 4. State a thesis or purpose 5. Outline the main points.
Q3. How to write introduction for assignment?
A good introduction shows the reader that the essay will provide a relevant answer to the assignment question. As a result, the introduction should link back to the question. That is done by writing a paragraph that deals with all the key content mentioned in the assignment question.
Related Posts

7+ Tips On How To Get Higher Grades In Exams In 2023

How to Write a Research Paper- A guide From Professionals

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write an introduction paragraph in 3 steps.
General Education

It’s the roadmap to your essay, it’s the forecast for your argument, it’s...your introduction paragraph, and writing one can feel pretty intimidating. The introduction paragraph is a part of just about every kind of academic writing , from persuasive essays to research papers. But that doesn’t mean writing one is easy!
If trying to write an intro paragraph makes you feel like a Muggle trying to do magic, trust us: you aren’t alone. But there are some tips and tricks that can make the process easier—and that’s where we come in.
In this article, we’re going to explain how to write a captivating intro paragraph by covering the following info:
- A discussion of what an introduction paragraph is and its purpose in an essay
- An overview of the most effective introduction paragraph format, with explanations of the three main parts of an intro paragraph
- An analysis of real intro paragraph examples, with a discussion of what works and what doesn’t
- A list of four top tips on how to write an introduction paragraph
Are you ready? Let’s begin!

What Is an Introduction Paragraph?
An introduction paragraph is the first paragraph of an essay , paper, or other type of academic writing. Argumentative essays , book reports, research papers, and even personal essays are common types of writing that require an introduction paragraph. Whether you’re writing a research paper for a science course or an argumentative essay for English class , you’re going to have to write an intro paragraph.
So what’s the purpose of an intro paragraph? As a reader’s first impression of your essay, the intro paragraph should introduce the topic of your paper.
Your introduction will also state any claims, questions, or issues that your paper will focus on. This is commonly known as your paper’s thesis . This condenses the overall point of your paper into one or two short sentences that your reader can come back and reference later.
But intro paragraphs need to do a bit more than just introduce your topic. An intro paragraph is also supposed to grab your reader’s attention. The intro paragraph is your chance to provide just enough info and intrigue to make your reader say, “Hey, this topic sounds interesting. I think I’ll keep reading this essay!” That can help your essay stand out from the crowd.
In most cases, an intro paragraph will be relatively short. A good intro will be clear, brief, purposeful, and focused. While there are some exceptions to this rule, it’s common for intro paragraphs to consist of three to five sentences .
Effectively introducing your essay’s topic, purpose, and getting your reader invested in your essay sounds like a lot to ask from one little paragraph, huh? In the next section, we’ll demystify the intro paragraph format by breaking it down into its core parts . When you learn how to approach each part of an intro, writing one won’t seem so scary!

Once you figure out the three parts of an intro paragraph, writing one will be a piece of cake!
The 3 Main Parts of an Intro Paragraph
In general, an intro paragraph is going to have three main parts: a hook, context, and a thesis statement . Each of these pieces of the intro plays a key role in acquainting the reader with the topic and purpose of your essay.
Below, we’ll explain how to start an introduction paragraph by writing an effective hook, providing context, and crafting a thesis statement. When you put these elements together, you’ll have an intro paragraph that does a great job of making a great first impression on your audience!
Intro Paragraph Part 1: The Hook
When it comes to how to start an introduction paragraph, o ne of the most common approaches is to start with something called a hook.
What does hook mean here, though? Think of it this way: it’s like when you start a new Netflix series: you look up a few hours (and a few episodes) later and you say, “Whoa. I guess I must be hooked on this show!”
That’s how the hook is supposed to work in an intro paragrap h: it should get your reader interested enough that they don’t want to press the proverbial “pause” button while they’re reading it . In other words, a hook is designed to grab your reader’s attention and keep them reading your essay!
This means that the hook comes first in the intro paragraph format—it’ll be the opening sentence of your intro.
It’s important to realize that there are many different ways to write a good hook. But generally speaking, hooks must include these two things: what your topic is, and the angle you’re taking on that topic in your essay.
One approach to writing a hook that works is starting with a general, but interesting, statement on your topic. In this type of hook, you’re trying to provide a broad introduction to your topic and your angle on the topic in an engaging way .
For example, if you’re writing an essay about the role of the government in the American healthcare system, your hook might look something like this:
There's a growing movement to require that the federal government provide affordable, effective healthcare for all Americans.
This hook introduces the essay topic in a broad way (government and healthcare) by presenting a general statement on the topic. But the assumption presented in the hook can also be seen as controversial, which gets readers interested in learning more about what the writer—and the essay—has to say.
In other words, the statement above fulfills the goals of a good hook: it’s intriguing and provides a general introduction to the essay topic.
Intro Paragraph Part 2: Context
Once you’ve provided an attention-grabbing hook, you’ll want to give more context about your essay topic. Context refers to additional details that reveal the specific focus of your paper. So, whereas the hook provides a general introduction to your topic, context starts helping readers understand what exactly you’re going to be writing about
You can include anywhere from one to several sentences of context in your intro, depending on your teacher’s expectations, the length of your paper, and complexity of your topic. In these context-providing sentences, you want to begin narrowing the focus of your intro. You can do this by describing a specific issue or question about your topic that you’ll address in your essay. It also helps readers start to understand why the topic you’re writing about matters and why they should read about it.
So, what counts as context for an intro paragraph? Context can be any important details or descriptions that provide background on existing perspectives, common cultural attitudes, or a specific situation or controversy relating to your essay topic. The context you include should acquaint your reader with the issues, questions, or events that motivated you to write an essay on your topic...and that your reader should know in order to understand your thesis.
For instance, if you’re writing an essay analyzing the consequences of sexism in Hollywood, the context you include after your hook might make reference to the #metoo and #timesup movements that have generated public support for victims of sexual harassment.
The key takeaway here is that context establishes why you’re addressing your topic and what makes it important. It also sets you up for success on the final piece of an intro paragraph: the thesis statement.
Elle Woods' statement offers a specific point of view on the topic of murder...which means it could serve as a pretty decent thesis statement!
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis
The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way . The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Whether it’s making a claim, outlining key points, or stating a hypothesis, your thesis statement will tell your reader exactly what idea(s) are going to be addressed in your essay. A good thesis statement will be clear, straightforward, and highlight the overall point you’re trying to make.
Some instructors also ask students to include an essay map as part of their thesis. An essay map is a section that outlines the major topics a paper will address. So for instance, say you’re writing a paper that argues for the importance of public transport in rural communities. Your thesis and essay map might look like this:
Having public transport in rural communities helps people improve their economic situation by giving them reliable transportation to their job, reducing the amount of money they spend on gas, and providing new and unionized work .
The underlined section is the essay map because it touches on the three big things the writer will talk about later. It literally maps out the rest of the essay!
So let’s review: Your thesis takes the idea you’ve introduced in your hook and context and wraps it up. Think of it like a television episode: the hook sets the scene by presenting a general statement and/or interesting idea that sucks you in. The context advances the plot by describing the topic in more detail and helping readers understand why the topic is important. And finally, the thesis statement provides the climax by telling the reader what you have to say about the topic.
The thesis statement is the most important part of the intro. Without it, your reader won’t know what the purpose of your essay is! And for a piece of writing to be effective, it needs to have a clear purpose. Your thesis statement conveys that purpose , so it’s important to put careful thought into writing a clear and compelling thesis statement.

How To Write an Introduction Paragraph: Example and Analysis
Now that we’ve provided an intro paragraph outline and have explained the three key parts of an intro paragraph, let’s take a look at an intro paragraph in action.
To show you how an intro paragraph works, we’ve included a sample introduction paragraph below, followed by an analysis of its strengths and weaknesses.
Example of Introduction Paragraph
While college students in the U.S. are struggling with how to pay for college, there is another surprising demographic that’s affected by the pressure to pay for college: families and parents. In the face of tuition price tags that total more than $100,000 (as a low estimate), families must make difficult decisions about how to save for their children’s college education. Charting a feasible path to saving for college is further complicated by the FAFSA’s estimates for an “Expected Family Contribution”—an amount of money that is rarely feasible for most American families. Due to these challenging financial circumstances and cultural pressure to give one’s children the best possible chance of success in adulthood, many families are going into serious debt to pay for their children’s college education. The U.S. government should move toward bearing more of the financial burden of college education.
Example of Introduction Paragraph: Analysis
Before we dive into analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of this example intro paragraph, let’s establish the essay topic. The sample intro indicates that t he essay topic will focus on one specific issue: who should cover the cost of college education in the U.S., and why. Both the hook and the context help us identify the topic, while the thesis in the last sentence tells us why this topic matters to the writer—they think the U.S. Government needs to help finance college education. This is also the writer’s argument, which they’ll cover in the body of their essay.
Now that we’ve identified the essay topic presented in the sample intro, let’s dig into some analysis. To pin down its strengths and weaknesses, we’re going to use the following three questions to guide our example of introduction paragraph analysis:
- Does this intro provide an attention-grabbing opening sentence that conveys the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide relevant, engaging context about the essay topic?
- Does this intro provide a thesis statement that establishes the writer’s point of view on the topic and what specific aspects of the issue the essay will address?
Now, let’s use the questions above to analyze the strengths and weaknesses of this sample intro paragraph.
Does the Intro Have a Good Hook?
First, the intro starts out with an attention-grabbing hook . The writer starts by presenting an assumption (that the U.S. federal government bears most of the financial burden of college education), which makes the topic relatable to a wide audience of readers. Also note that the hook relates to the general topic of the essay, which is the high cost of college education.
The hook then takes a surprising turn by presenting a counterclaim : that American families, rather than students, feel the true burden of paying for college. Some readers will have a strong emotional reaction to this provocative counterclaim, which will make them want to keep reading! As such, this intro provides an effective opening sentence that conveys the essay topic.
Does the Intro Give Context?
T he second, third, and fourth sentences of the intro provide contextual details that reveal the specific focus of the writer’s paper . Remember: the context helps readers start to zoom in on what the paper will focus on, and what aspect of the general topic (college costs) will be discussed later on.
The context in this intro reveals the intent and direction of the paper by explaining why the issue of families financing college is important. In other words, the context helps readers understand why this issue matters , and what aspects of this issue will be addressed in the paper.
To provide effective context, the writer refers to issues (the exorbitant cost of college and high levels of family debt) that have received a lot of recent scholarly and media attention. These sentences of context also elaborate on the interesting perspective included in the hook: that American families are most affected by college costs.
Does the Intro Have a Thesis?
Finally, this intro provides a thesis statement that conveys the writer’s point of view on the issue of financing college education. This writer believes that the U.S. government should do more to pay for students’ college educations.
However, the thesis statement doesn’t give us any details about why the writer has made this claim or why this will help American families . There isn’t an essay map that helps readers understand what points the writer will make in the essay.
To revise this thesis statement so that it establishes the specific aspects of the topic that the essay will address, the writer could add the following to the beginning of the thesis statement:
The U.S. government should take on more of the financial burden of college education because other countries have shown this can improve education rates while reducing levels of familial poverty.
Check out the new section in bold. Not only does it clarify that the writer is talking about the pressure put on families, it touches on the big topics the writer will address in the paper: improving education rates and reduction of poverty. So not only do we have a clearer argumentative statement in this thesis, we also have an essay map!
So, let’s recap our analysis. This sample intro paragraph does an effective job of providing an engaging hook and relatable, interesting context, but the thesis statement needs some work ! As you write your own intro paragraphs, you might consider using the questions above to evaluate and revise your work. Doing this will help ensure you’ve covered all of your bases and written an intro that your readers will find interesting!

4 Tips for How To Write an Introduction Paragraph
Now that we’ve gone over an example of introduction paragraph analysis, let’s talk about how to write an introduction paragraph of your own. Keep reading for four tips for writing a successful intro paragraph for any essay.
Tip 1: Analyze Your Essay Prompt
If you’re having trouble with how to start an introduction paragraph, analyze your essay prompt! Most teachers give you some kind of assignment sheet, formal instructions, or prompt to set the expectations for an essay they’ve assigned, right? Those instructions can help guide you as you write your intro paragraph!
Because they’ll be reading and responding to your essay, you want to make sure you meet your teacher’s expectations for an intro paragraph . For instance, if they’ve provided specific instructions about how long the intro should be or where the thesis statement should be located, be sure to follow them!
The type of paper you’re writing can give you clues as to how to approach your intro as well. If you’re writing a research paper, your professor might expect you to provide a research question or state a hypothesis in your intro. If you’re writing an argumentative essay, you’ll need to make sure your intro overviews the context surrounding your argument and your thesis statement includes a clear, defensible claim.
Using the parameters set out by your instructor and assignment sheet can put some easy-to-follow boundaries in place for things like your intro’s length, structure, and content. Following these guidelines can free you up to focus on other aspects of your intro... like coming up with an exciting hook and conveying your point of view on your topic!
Tip 2: Narrow Your Topic
You can’t write an intro paragraph without first identifying your topic. To make your intro as effective as possible, you need to define the parameters of your topic clearly—and you need to be specific.
For example, let’s say you want to write about college football. “NCAA football” is too broad of a topic for a paper. There is a lot to talk about in terms of college football! It would be tough to write an intro paragraph that’s focused, purposeful, and engaging on this topic. In fact, if you did try to address this whole topic, you’d probably end up writing a book!
Instead, you should narrow broad topics to identify a specific question, claim, or issue pertaining to some aspect of NCAA football for your intro to be effective. So, for instance, you could frame your topic as, “How can college professors better support NCAA football players in academics?” This focused topic pertaining to NCAA football would give you a more manageable angle to discuss in your paper.
So before you think about writing your intro, ask yourself: Is my essay topic specific, focused, and logical? Does it convey an issue or question that I can explore over the course of several pages? Once you’ve established a good topic, you’ll have the foundation you need to write an effective intro paragraph .

Once you've figured out your topic, it's time to hit the books!
Tip 3: Do Your Research
This tip is tightly intertwined with the one above, and it’s crucial to writing a good intro: do your research! And, guess what? This tip applies to all papers—even ones that aren’t technically research papers.
Here’s why you need to do some research: getting the lay of the land on what others have said about your topic—whether that’s scholars and researchers or the mass media— will help you narrow your topic, write an engaging hook, and provide relatable context.
You don't want to sit down to write your intro without a solid understanding of the different perspectives on your topic. Whether those are the perspectives of experts or the general public, these points of view will help you write your intro in a way that is intriguing and compelling for your audience of readers.
Tip 4: Write Multiple Drafts
Some say to write your intro first; others say write it last. The truth is, there isn’t a right or wrong time to write your intro—but you do need to have enough time to write multiple drafts .
Oftentimes, your professor will ask you to write multiple drafts of your paper, which gives you a built-in way to make sure you revise your intro. Another approach you could take is to write out a rough draft of your intro before you begin writing your essay, then revise it multiple times as you draft out your paper.
Here’s why this approach can work: as you write your paper, you’ll probably come up with new insights on your topic that you didn’t have right from the start. You can use these “light bulb” moments to reevaluate your intro and make revisions that keep it in line with your developing essay draft.
Once you’ve written your entire essay, consider going back and revising your intro again . You can ask yourself these questions as you evaluate your intro:
- Is my hook still relevant to the way I’ve approached the topic in my essay?
- Do I provide enough appropriate context to introduce my essay?
- Now that my essay is written, does my thesis statement still accurately reflect the point of view that I present in my essay?
Using these questions as a guide and putting your intro through multiple revisions will help ensure that you’ve written the best intro for the final draft of your essay. Also, revising your writing is always a good thing to do—and this applies to your intro, too!

What's Next?
Your college essays also need great intro paragraphs. Here’s a guide that focuses on how to write the perfect intro for your admissions essays.
Of course, the intro is just one part of your college essay . This article will teach you how to write a college essay that makes admissions counselors sit up and take notice.
Are you trying to write an analytical essay? Our step-by-step guide can help you knock it out of the park.

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Have a language expert improve your writing
Check your paper for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- College essay
How to Write a Great College Essay Introduction | Examples
Published on October 4, 2021 by Meredith Testa . Revised on August 14, 2023 by Kirsten Courault.
Admissions officers read thousands of essays each application season, and they may devote as little as five minutes to reviewing a student’s entire application. That means it’s critical to have a well-structured essay with a compelling introduction. As you write and revise your essay , look for opportunities to make your introduction more engaging.
There’s one golden rule for a great introduction: don’t give too much away . Your reader shouldn’t be able to guess the entire trajectory of the essay after reading the first sentence. A striking or unexpected opening captures the reader’s attention, raises questions, and makes them want to keep reading to the end .
Table of contents
Start with a surprise, start with a vivid, specific image, avoid clichés, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about college application essays.
A great introduction often has an element of mystery. Consider the following opening statement.
This opener is unexpected, even bizarre—what could this student be getting at? How can you be bad at breathing?
The student goes on to describe her experience with asthma and how it has affected her life. It’s not a strange topic, but the introduction is certainly intriguing. This sentence keeps the admissions officer reading, giving the student more of an opportunity to keep their attention and make her point.
In a sea of essays with standard openings such as “One life-changing experience for me was …” or “I overcame an obstacle when …,” this introduction stands out. The student could have used either of those more generic introductions, but neither would have been as successful.
This type of introduction is a true “hook”—it’s highly attention-grabbing, and the reader has to keep reading to understand.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If your topic doesn’t lend itself to such a surprising opener, you can also start with a vivid, specific description.
Many essays focus on a particular experience, and describing one moment from that experience can draw the reader in. You could focus on small details of what you could see and feel, or drop the reader right into the middle of the story with dialogue or action.
Some students choose to write more broadly about themselves and use some sort of object or metaphor as the focus. If that’s the type of essay you’d like to write, you can describe that object in vivid detail, encouraging the reader to imagine it.
Cliché essay introductions express ideas that are stereotypical or generally thought of as conventional wisdom. Ideas like “My family made me who I am today” or “I accomplished my goals through hard work and determination” may genuinely reflect your life experience, but they aren’t unique or particularly insightful.
Unoriginal essay introductions are easily forgotten and don’t demonstrate a high level of creative thinking. A college essay is intended to give insight into the personality and background of an applicant, so a standard, one-size-fits-all introduction may lead admissions officers to think they are dealing with a standard, unremarkable applicant.
Quotes can often fall into the category of cliché essay openers. There are some circumstances in which using a quote might make sense—for example, you could quote an important piece of advice or insight from someone important in your life. But for most essays, quotes aren’t necessary, and they may make your essay seem uninspired.
If you want to know more about academic writing , effective communication , or parts of speech , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Academic writing
- Writing process
- Transition words
- Passive voice
- Paraphrasing
Communication
- How to end an email
- Ms, mrs, miss
- How to start an email
- I hope this email finds you well
- Hope you are doing well
Parts of speech
- Personal pronouns
- Conjunctions
The introduction of your college essay is the first thing admissions officers will read and therefore your most important opportunity to stand out. An excellent introduction will keep admissions officers reading, allowing you to tell them what you want them to know.
The key to a strong college essay introduction is not to give too much away. Try to start with a surprising statement or image that raises questions and compels the reader to find out more.
Cliché openers in a college essay introduction are usually general and applicable to many students and situations. Most successful introductions are specific: they only work for the unique essay that follows.
In most cases, quoting other people isn’t a good way to start your college essay . Admissions officers want to hear your thoughts about yourself, and quotes often don’t achieve that. Unless a quote truly adds something important to your essay that it otherwise wouldn’t have, you probably shouldn’t include it.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Testa, M. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Great College Essay Introduction | Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/college-essay/introduction-college-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Meredith Testa
Other students also liked, college essay format & structure | example outlines, how to end a college admissions essay | 4 winning strategies, what do colleges look for in an essay | examples & tips, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Essay writing: Introductions
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- Analysing questions
- Planning & drafting
- Revising & editing
- Proofreading
- Essay writing videos
Jump to content on this page:
“A relevant and coherent beginning is perhaps your best single guarantee that the essay as a whole will achieve its object.” Gordon Taylor, A Student's Writing Guide
Your introduction is the first thing your marker will read and should be approximately 10% of your word count. Within the first minute they should know if your essay is going to be a good one or not. An introduction has several components but the most important of these are the last two we give here. You need to show the reader what your position is and how you are going to argue the case to get there so that the essay becomes your answer to the question rather than just an answer.
What an introduction should include:
- A little basic background about the key subject area (just enough to put your essay into context, no more or you'll bore the reader).
- Explanation of how you are defining any key terms . Confusion on this could be your undoing.
- A road-map of how your essay will answer the question. What is your overall argument and how will you develop it?
- A confirmation of your position .
Background information
It is good to start with a statement that fixes your essay topic and focus in a wider context so that the reader is sure of where they are within the field. This is a very small part of the introduction though - do not fall into the trap of writing a whole paragraph that is nothing but background information.
Beware though, this only has to be a little bit wider, not completely universal. That is, do not start with something like "In the whole field of nursing...." or "Since man could write, he has always...". Instead, simply situate the area that you are writing about within a slightly bigger area. For example, you could start with a general statement about a topic, outlining some key issues but explain that your essay will focus on only one. Here is an example:
The ability to communicate effectively and compassionately is a key skill within nursing. Communication is about more than being able to speak confidently and clearly, it is about effective listening (Singh, 2019), the use of gesture, body language and tone (Adebe et al., 2016) and the ability to tailor language and messaging to particular situations (Smith & Jones, 2015). This essay will explore the importance of non-verbal communication ...
The example introduction at the bottom of this page also starts with similar, short background information.

Defining key terms
This does not mean quoting dictionary definitions - we all have access to dictionary.com with a click or two. There are many words we use in academic work that can have multiple or nuanced definitions. You have to write about how you are defining any potentially ambiguous terms in relation to your essay topic. This is really important for your reader, as it will inform them how you are using such words in the context of your essay and prevent confusion or misunderstanding.

Stating your case (road mapping)
The main thing an introduction will do is...introduce your essay! That means you need to tell the reader what your conclusion is and how you will get there.
There is no need to worry about *SPOILER ALERTS* - this is not a detective novel you can give away the ending! Sorry, but building up suspense is just going to irritate the reader rather than eventually satisfy. Simply outline how your main arguments (give them in order) lead to your conclusion. In American essay guides you will see something described as the ‘thesis statement’ - although we don't use this terminology in the UK, it is still necessary to state in your introduction what the over-arching argument of your essay will be. Think of it as the mega-argument , to distinguish it from the mini-arguments you make in each paragraph. Look at the example introduction at the bottom of this page which includes both of these elements.

Confirming your position
To some extent, this is covered in your roadmap (above), but it is so important, it deserves some additional attention here. Setting out your position is an essential component of all essays. Brick et al. (2016:143) even suggest
"The purpose of an essay is to present a clear position and defend it"
It is, however, very difficult to defend a position if you have not made it clear in the first place. This is where your introduction comes in. In stating your position, you are ultimately outlining the answer to the question. You can then make the rest of your essay about providing the evidence that supports your answer. As such, if you make your position clear, you will find all subsequent paragraphs in your essay easier to write and join together. As you have already told your reader where the essay is going, you can be explicit in how each paragraph contributes to your mega-argument.
In establishing your position and defending it, you are ultimately engaging in scholarly debate. This is because your positions are supported by academic evidence and analysis. It is in your analysis of the academic evidence that should lead your reader to understand your position. Once again - this is only possible if your introduction has explained your position in the first place.

An example introduction
(Essay title = Evaluate the role of stories as pedagogical tools in higher education)
Stories have been an essential communication technique for thousands of years and although teachers and parents still think they are important for educating younger children, they have been restricted to the role of entertainment for most of us since our teenage years. This essay will claim that stories make ideal pedagogical tools, whatever the age of the student, due to their unique position in cultural and cognitive development. To argue this, it will consider three main areas: firstly, the prevalence of stories across time and cultures and how the similarity of story structure suggests an inherent understanding of their form which could be of use to academics teaching multicultural cohorts when organising lecture material; secondly, the power of stories to enable listeners to personally relate to the content and how this increases the likelihood of changing thoughts, behaviours and decisions - a concept that has not gone unnoticed in some fields, both professional and academic; and finally, the way that different areas of the brain are activated when reading, listening to or watching a story unfold, which suggests that both understanding and ease of recall, two key components of learning, are both likely to be increased . Each of these alone could make a reasoned argument for including more stories within higher education teaching – taken together, this argument is even more compelling.
Key: Background information (scene setting) Stating the case (r oad map) Confirming a position (in two places). Note in this introduction there was no need to define key terms.
Brick, J., Herke, M., and Wong, D., (2016) Academic Culture, A students guide to studying at university, 3rd edition. Victoria, Australia: Palgrave Macmillan.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Main body >>
- Last Updated: Nov 3, 2023 3:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/essays
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
- Most popular requests
- See full list of services at order form
- Essay Writing Service
- British Essay Writers
- Write My Essay
- Law Essay Help
- Dissertation Service
- Write My Dissertation
- Buy Dissertation
- Thesis Service
- Literature Review Service
- Assignment Service
- Buy Assignments
- Do My Assignment
- Do My Homework
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Coursework Service
- Do My Coursework
- Research Paper Service
- Lab Report Service
- Personal Statement Service
- How it works
- Prices & discounts
- Client reviews
This site uses cookies to make sure you get the best experience. By continuing you are agreeing with our cookie policy .
- How to Start an Assignment Introduction Like an Expert

Every student wonders how to start an assignment introduction because this knowledge can keep them afloat through their endless years of school, college, and university. If you're here, you probably wonder that as well. Thankfully, there is nothing complicated about writing an introduction. This is how one starts an essay that teases the topics to come and explains your work’s final goal. Its importance is absolute.
Think about it. You open someone’s essay and see a very boring assignment introduction. Chances are, it’ll inform your opinion about the whole text right then and there, and even if the body has some fascinating facts, you might stay unimpressed anyway. First impressions usually stick with people. The guide prepared by StateOfWriting’s experts will teach you how you can grab your audience’s attention from the first seconds. In it, you’ll find explanations, examples, tips, and even common grading criteria that will help you start most compellingly.
How to Start an Assignment Introduction and What to Include
The introduction plays the same role in every paper, regardless of its topic. It must briefly address the content you will explore in the body and outline the needed steps. Its more subtle purpose is triggering genuine interest in your audience, motivating them to keep reading.
5 Elements of Every Introduction
Include these components in the introduction for assignment you’re working on:
- Hook. This would be the first sentence of your introduction. Does the word itself evoke any associations in you? When you hook someone, be it a fish or a person, you get to hold onto them. They become yours, and that’s exactly what you should strive for when writing your paper. Hit your readers with the very first line as powerfully as you can. It could be a piece of astonishing statistics that will make people gape in shock. Alternatively, you could go for an emotional approach, writing something that clenches your readers’ hearts in their chests. Whatever you choose, make it count.
- Background. The second element you’ll need for learning to know how to write introduction for assignment is the background. Professional tips for college application essay will show you how essential it is to make it interesting. This background represents your topic — it must explain what you’re investigating and how this subject came to be. For example, we’re analysing a TV show, Devil Judge. To present its background properly, we’d mention its title, airing date, and key figures. Then we’d briefly describe its plot.
- Justification. Next in figuring out how to write an introduction for assignment is deciding why you picked your topic. What makes it relevant to your subject? How can people benefit from reading about it? No need for much detail; just make a few references.
- Steps. This and the next component are interchangeable. In most cases, students need either one or another, depending on your professor's request. Outline the steps you’ll be undertaking when exploring your topic. If you will analyse the plot in the first body paragraph and dissect the characters in the second one, explain it to your readers. Provide a roadmap of your intentions. This approach is more suitable for really long papers.
- Thesis. How to write a good introduction for an assignment? By creating a powerful thesis. Most academic papers require it. It concludes your introduction, functioning as its last sentence. A thesis is a direct claim that embodies your essay’s entire essence. Even if people read it and nothing else, they should understand your work.

Specific Moments to Cover in Your Intro
You have a general picture of how to start writing an assignment now. It’s time to learn about the smaller and more specific details you should include in your introduction!
- Context. Always give your readers context. Disclose it carefully, bit by bit, instead of jumping straight to your main point. Using our TV show example, saying “Devil Judge is about revenge and power abuse” would be a bad start. It dumps too much information on a person and discloses too many relevant points. Be gradual and untangle your topic.
- Overview. When writing an introduction for an assignment, include a content overview. As mentioned above, it could be present as steps or a thesis. Either way, just demonstrate your plans to your readers — no introduction can function without it.
- Your perspective. Share your opinion about your topic. It doesn’t mean that you should use personal pronouns, just show what your position is by focusing your readers’ attention on a specific angle. Going back to our example, we could mention how the affection of Judge Kang toward his deceased brother coloured his perception of Ga On, who closely resembled him physically. This would narrow the focus down, displaying what we want to explore.
- Your goal. This aspect is closely linked to the previous one. Specify the end point of your essay by teasing the conclusion you plan to achieve.
Avoid These Mistakes When Writing Your Introduction
- Repetitions. Some students choose to repeat their title word by word in their paper. It’s not a good idea! Your assignment introduction sentence starters should be more unique. Come up with new words and phrases instead of engaging in self-plagiarism.
- General statements. Avoid vague sentences that suit any topic. An individual and relevant introduction will help make your paper look special. Be specific.
- Rambling paragraphs. Don’t try to introduce all possible information in your first paragraph. Being specific doesn’t mean talking non-stop. You should briefly present your ideas in the introduction and develop them in the body.
- Personal pronouns. Never use personal pronouns unless your task allows them. This covers “I, my, we, us, our,” etc.

5 Tips from Our Academic Experts
StateOfWriting’s British experts have written more essays than they can ever count. This extensive experience fuels their professionalism: they know how to create amazing papers, and they shared some key introduction-related insights with you.
- Create an introduction last. How to start an assignment for university? By writing it last. Yes, it may sound surprising, but this is how you can ensure you don’t need to rewrite anything later. An introduction has to reflect your whole paper. You should understand your findings and conclusions before crafting it.
- Size matters. Introduction shouldn’t take more than 10% of your total word count.
- Keep a balance between teasing and informing. Remember our assignment introduction writing tips from above? It’s important to share just the right details with readers.
- Edit this intro. Re-read your introduction a couple of times. Clean it thoroughly, removing all accidental mistakes and typos.
- Seek help. If any of these rules frustrate you, simply buy assignment online from professionals. Our writers could give you extra tips or take over the task completely.
Grading Criteria to Guide You on How to Write an Assignment Introduction
StateOfWriting’s experience spans across various fields. We know how college professors operate and what they expect to see in students’ papers. Take a look at their common grading points below. Remember them when you work on your introduction and adjust it accordingly.
- Conciseness. Professors want a short yet succinct introduction that covers all the necessary points without being overly long or overwhelming.
- Relevance. An introduction must be relevant to the subject and prompt. If the connection is loose, some points may be removed.
- Suspense. Not all professors pay attention to this aspect, but you’ll benefit from intriguing your audience and instilling a sense of anticipation in them.
- Research. Most essays require the use of credible academic studies. Cite at least the most important one in your intro to demonstrate your thoughtful approach. Get help with assignments if you’re struggling with this part.
- Thesis. All professors award separate points for a strong thesis statement.
Lack of inspiration? Want to Enjoy Free Time?
GRAB A 20% DISCOUNT
Practical Example of Effective Essay Introduction
We will provide you with a practical assignment introduction example to secure your theoretical knowledge. One of our top writers created it on the topic we already mentioned, the Devil Judge show. Find its analysis below and use this text as a template for your introduction!
The Dangers of Affection Transference in ‘Devil Judge’ Losing a loved one and then suddenly seeing a stranger with their face is the sharpest and most overwhelming experience. It can bring devastation and joy simultaneously, and this topic lies at the heart of ‘Devil Judge.’ This Korean show aired in 2021; it was written by Moon Yoo-Seok, who worked as a judge for over two decades (Livson, 2023). Kang Yohan, one of the protagonists, has lost his beloved older brother ten years before the show's start. When he meets Ga On, a junior judge sent to spy on him, he feels torn because Ga On bears a striking physical resemblance to his brother. The topic of affection transference is interesting because it is easy to use as a form of emotional manipulation. Moreover, the research in this area is lacking. As Joilis (2022) notes, when a person automatically attributes the qualities of their loved one to someone else over their resemblance, they face the risk of being emotionally compromised. Kang Yohan feels drawn to Ga On because he reminds him of his brother, and he becomes a victim of unwilling manipulation by starting to perceive Ga On as a part of his family sooner than naturally.
Analysis of Successful Assignment Introduction
Hook: The essay begins by thrusting the readers into a complicated emotional scenario and shortly describing the feelings it evokes. Background: In the next several sentences, we explore the meaning of ‘Devil Judge’, address its main characters, and show our willingness to focus on one specific theme, affection transference. Justification: The paper underlines how transference can be emotionally harmful to people and notes how scarce research is in this area, elevating our study's value. Thesis: We make a final claim that unites the show's plot with our chosen psychological phenomenon and introduces the points we’ll tackle, such as the resemblance between Ga On and Yohan’s brother, accidental manipulation, and the strengths of their feelings.

FAQ on How to Write an Introduction for an Assignment
- How many words should my introduction have?
The average introduction should be between 7% and 10% of your final word count. So, if your essay has 600 words, dedicate 60 of them to your first section.
- What sentence should I start my introduction with?
It could be a shocking statement, statistics, a quote, and even a question.
- What should I do when writing an introduction for a report?
Stay precise and objective. In this task, you don’t need to develop an individual position on a specific topic, just summarise it properly.
- How to write an introduction for a case study?
Address the details from this case study. Depending on your prompt, mention the situation and offer ways of analysing or resolving it.
- What should I do when writing an introduction for a dissertation?
This introduction will be longer. Follow our tips above, but be more detailed. Demonstrate your plan of action and research questions.
- How to write an introduction for a maths assignment?
The rules don’t change based on assignments. Be formal and thoughtful, and introduce your topic properly by mentioning some of its background.
- Other articles
- Unique Discursive Essay Topics To Try In 2024
- Vital Tips on How to Write a Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write a Personal Statement for College
- Top Tourist Attractions in England for Students
Writers are verified and tested to comply with quality standards.
Work is completed in time and delivered before deadline.
Wide range of subjects and topics of any difficulty covered.
Read testimonials to learn why customers trust us.
See how it works from order placement to delivery.
Client id #: 000229
You managed to please my supervisor on the first try! Whoa, I've been working with him for over a year and never turned in a paper without having to rewrite it at least once, lol I wonder if he thinks something's wrong with me now.
Client id #: 000154
Your attention to details cannot but makes me happy. Your professional writer followed every single instruction I gave and met the deadline. The text itself is full of sophisticated lexis and well-structured. I was on cloud nine when I looked through it. And my professor is satisfied as well. Million thanks!
Client id #: 000234
I contacted their call-center to specify the possible custom deadline dates prior to making an order decision and it felt like they hadn't even considered a possibility of going beyond the standard urgency. I didn't even want an additional discount for the extended time, just want to make sure I'll have enough time for editing if necessary. Made an order for standard 14 days, we'll see.
Client id #: 000098
I have no idea how you managed to do this research paper so quickly and professionally. But the result is magnificent. Well-structured, brilliantly written and with all the elements I asked for. I am already filling out my next order from you.
How to Write a Good Introduction: Examples & Tips [2024 Upd.]
A five-paragraph essay is one of the most common academic assignments a student may face. It has a well-defined structure: an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Writing an introduction can be the most challenging part of the entire piece. It aims to introduce the main ideas and present a reason for the essay’s existence. Besides, it helps the writer to capture the reader’s interest and attention. A good start is a great way to make a lasting first impression.
So, let’s see what our team found a standard essay introduction paragraph format should include:
- “The attention grabber” is the first part of the introduction;
- Some relevant background information;
- Your thesis statement—it states what you will argue in the body paragraphs;
- A “road map”—an explanation of how you will defend your thesis statement.
The following tips and guidance will help you to learn how to start an essay.
- 🛎️ Create a Hook
📚 Provide Context
- ✍️ Write a Thesis
- 🙅♀️ Dos and Dont’s
📜 Introduction Examples
📍 step-by-step guide.
Memorizing the introduction paragraph outline is a great way to learn how to write an introduction. For every type of essay, its structure will be almost identical.
This guide will show you each step of writing an introduction, using a sample from the argumentative essay about school uniforms.
🛎️Create a Hook
The first sentence sets the tone not only for the introductory paragraph but for the entire essay. In it, you aim to grab your readers’ attention from the very beginning. So, avoid long sentences that are too generic. You can try to implement some of these techniques for a good way to start an essay:
- Offer a surprising fact or thought-provoking idea;
- Start with a question;
- Introduce a quotation;
- Tell a short story;
- Start with a broad summary.
However, for an academic essay, do not try to come up with something too creative. For instance, a short story or an anecdote is not going to work for a serious topic.
Writing a hook that introduces an issue without giving too much information is essential. In our sample essay, the first sentence is quite general, but it concisely presents the problem.
For many decades, the idea of wearing a school uniform has been a topic for heated discussions.
The next step in writing your essay introduction is to provide the reader with some background information. This part will help them to understand the topic and the arguments you will be making further.
A lot will depend on the subject itself and the type of essay, but the background information can be given in one of these ways:
- Through geographic, historical, or social context;
- Via a brief analysis of scholarly debate;
- By defining terms and language.
The information and the context is needed to explain why this problem is essential and needs attention. However, do not give too many details. Keep the most relevant and interesting facts for the essay’s body.A rule of thumb is to start your opening paragraph broadly and go to a specific point later. In the sample, the writer presents the background information with these two sentences:
It is common for students to wear distinctive clothes in schools, but by the time they reach adolescence, they tend to despise the enforcement of uniforms. The opposition creates controversies on school grounds, with teachers demanding coordinated outfits and students refusing to oblige.
This statement introduces the problem and shows two opinions on the matter. It also gives an insight into a social context and an issue that both sides face.
✍️ Write a Thesis Statement
This part of the introductory paragraph aims to establish your position and narrow down the essay’s focus. The writer does it to let the reader know what exactly will become the scope of the piece.
A thesis statement does not have to be too long. Usually, a sentence or two is more than enough to explain the fundamental idea of the essay. In the sample essay, the thesis statement sets the limits for the discussion in this way:
School uniforms are meant to ensure equality and discipline; however, they mostly are seen as an infringement of human rights limiting students’ self-esteem and adding financial losses to low-income families.
🔺 Outline Your Argumentation
For more extended essays, you should also provide an outline of what you will be arguing further. However, it is not obligatory for the shorter works because the introduction has to be concise: about 5%-10% of the entire essay.
It is also the case for the essay introduction example used in this guide. It does not provide a preview for the arguments because of its length.
It is also recommended to write this part after you finish developing your arguments. Remember that even though the introduction is the first thing the reader reads, it does not have to be the first part you compose. Even if something in your writing doesn’t click, you can always use help in a form of a sentence rewrite generator that can improve your content right away.
🙅♀️ Do’s and Don’ts
These do’s and don’ts are a general list of recommendations that will help you write an outstanding introduction.
| 👍 Do’s | 👎 Don’ts |
|---|---|
| When you write an introduction, you should think about space. Therefore, do not waste it with unnecessary and vague information. | Generalizations can be hazardous. Not only it demonstrates a lack of reasoning, but it also makes untruthful statements. It can make readers feel skeptical about your whole essay. |
| It will help you have a roadmap for your essay. Also, it will allow the reader to get accustomed to the main themes, terms, and information. | It is crucial to prepare the reader for the thesis statement. First, catch the attention, give the background information. Only then can you introduce your thesis statement. |
| Writing an essay is not a thesaurus competition. Your main goal is to explain your point of view. Therefore, use language that the general reader will understand. | State your position clearly and don’t use vague language because it will undermine your authority on the matter. |
| The principal goal of the introduction is to make an impact. For that, you should not be afraid to use verbs. | You have to make sure that the introduction is written in your own words. Later in the essay, you can use quotes, but it is better to avoid it in the beginning. |
Keep in mind:
These tips apply solely to an introductory paragraph. For more information on five-paragraph essays, check other articles.
You should always aim to see the essay as a unified piece of writing. The role of the introduction is to prepare the reader for the rest of the work. Make sure you read and revise your introductory paragraph, and see if it accomplishes this purpose.
Here’s a good introduction for a research paper example :
For many decades, the idea of wearing a school uniform has been a topic for heated discussions. It is common for students to wear distinctive clothes in schools, but by the time they reach adolescence, they tend to despise the enforcement of uniforms. The opposition creates controversies on school grounds, with teachers demanding coordinated outfits and students refusing to oblige. School uniforms are meant to ensure equality and discipline; however, they mostly are seen as an infringement of human rights limiting students’ self-esteem and adding financial losses to low-income families.
Thank you for reading this article and don’t hesitate to share it with your peers. If you want to improve your essay-writing skills, look at the materials provided on our website. We have plenty of tips on how to write better essays!
- Beginning the Academic Essay: Patricia Kain, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
- Introductions: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Introductions and Conclusions: Leora Freedman and Jerry Plotnick, University of Toronto College Writing Centre
- Introductions & Conclusions: Ashford University Writing Center
- Writing an Essay Introduction: Research & Learning Online, Monash University
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Exemplification essays, also called illustration essays, are one of the easiest papers to write. However, even the simplest tasks require experience and practice. It is a good idea to find and analyze free exemplification essay examples. You can also ask your teacher to give you some sample exemplification essays from...
![how to write an introduction for an assignment sample How to Write about a Topic You Lack Interest in [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Frustrated-exhausted-young-woman-blogger-284x153.jpg)
During their school years, students may not always have the opportunity to select a topic for their essay or research paper. Instructors tend to assign one or offer a list of ideas that might not seem engaging. Moreover, even the topic that you choose yourself can sometimes end up being...

Sorry to disappoint you, but if you think that your high scores and grades would be enough to get accepted into the university of your dreams, you’re wrong… The best colleges worldwide, such as the Ivy League schools receive applications from thousands and thousands of talented students. You gotta stand...

Writing an essay is a task that everyone has to deal with. The first encounter most likely happens at primary school. Compositions in primary school are quite basic and only require a good imagination and somewhat decent writing skills. But… As time passes, essay writing becomes more and more complicated....

Often when you’re completing academic writing, especially essays, you need to use pronouns. In academic writing, the use of the word you is unacceptable. You can find yourself in a sticky situation, deciding upon gender-neutral pronouns in your academic writing. How can students deal with it? In most situations today,...

A divorce is a life-changing experience that affects spouses and their children (if there are any). Since divorce rates are relatively high in modern society, more and more people face this problem nowadays. When you are assigned to compose an argumentative essay about divorce, you should be as careful as...
![how to write an introduction for an assignment sample How to Stop Corruption Essay: Guide & Topics [+4 Samples]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/close-up-two-hands-while-paying-money-284x153.jpeg)
Corruption is an abuse of power that was entrusted to a person or group of people for personal gain. It can appear in various settings and affect different social classes, leading to unemployment and other economic issues. This is why writing an essay on corruption can become a challenge. One...

Do you have to write an essay for the first time? Or maybe you’ve only written essays with less than 1000 words? Someone might think that writing a 1000-word essay is a rather complicated and time-consuming assignment. Others have no idea how difficult thousand-word essays can be. Well, we have...

To write an engaging “If I Could Change the World” essay, you have to get a few crucial elements: Let us help you a bit and give recommendations for “If I Could Change the World” essays with examples. And bookmark our writing company website for excellent academic assistance and study...
![how to write an introduction for an assignment sample Why I Want to be a Pharmacist Essay: How to Write [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/cut-out-medicament-drug-doctor-medical-1-284x153.jpg)
Why do you want to be a pharmacist? An essay on this topic can be challenging, even when you know the answer. The most popular reasons to pursue this profession are the following:

How to write a film critique essay? To answer this question, you should clearly understand what a movie critique is. It can be easily confused with a movie review. Both paper types can become your school or college assignments. However, they are different. A movie review reveals a personal impression...

Are you getting ready to write your Language Proficiency Index Exam essay? Well, your mission is rather difficult, and you will have to work hard. One of the main secrets of successful LPI essays is perfect writing skills. So, if you practice writing, you have a chance to get the...

How to Write an Introduction for an Assignment: Easy Student Guide
Table of Contents
Why Assignment Introduction Matters?
Writing an introduction is not that hard, what makes a good introduction, an example of introduction for assignment, useful resources to get ease your intro writing.
Knowing how to start writing an assignment is basically knowing how to write an introduction for an assignment. No matter how easy it sounds, it can often become tricky. An introduction is a part of academic writing that always differs depending on initial instructions and the subject in question. For example, writing a reflective journal for your Nursing course would be different from some research paper.
We can sum it up by saying that introductions should always follow a clear purpose, which is to provide your target audience with a definite idea regarding your essay’s content.
It all comes down to the purpose of your introduction. It will either catch your reader’s interest or make them feel confused. Your introduction should focus on providing certain general data or statistics before narrowing things down . It makes it essential. It works as the preface to your thesis statement by making it sound valid. For example, if your thesis statement discusses the negative effects of modern video games, your introduction part will have to provide clear stats along with the significance of this problem for society and/or educators.
It is a well-known fact that college professors start paper evaluation by taking a closer look at your introduction, thesis statement, and the final part of the paper. It is another reason why setting the clear purpose of the introduction matters for your paper’s success and recognition.
Your assignment can be completed in 3 hours!
Has your deadline come quicker than you expected? No worries! We have what you need – a 3-hours deadline option! All features available for any other order applied, including:
- 100% original assignment
- Free formatting and reference list
- 24/7 online support
The most important is to understand your assignment structure. It means that you should not apply the same methods when dealing with your research paper or writing a compare-and-contrast essay.
Most importantly, it must be clear and convincing, including:
- A Strong Introductory Hook Sentence.
- Your Paper’s Purpose.
- An Explanatory Element.
- The Importance of Your Topic.
- Link to Your Thesis Statement.
If this kind of work sounds too confusing, you should ask yourself why this topic matters to you and why you have chosen it. Remember that your introduction should be about 10% of the total paper, not counting your thesis statement sentence. If you are not sure about your introduction’s content or do not know which structure would fit better, consider approaching assignment writing help . It is only natural to feel lost when starting with your paper.
Of course, the rules always differ, and we have our opinions that will not match everyone’s taste. Yet, the academic standards regarding how to write an introduction are quite clear. Coming up with a great introduction for assignment, make sure that it:
- Highlights the importance of your subject.
- Provides a definition of the topic you discuss.
- Offers the reasoning why you approach your topic.
- Provides an overview of your methodology or scientific approach.
- Highlights the major points you would like to discuss.
- Introduces your thesis.
- Provides statistical data and the purpose of your methodology.
- Makes the audience inspired.
Do not forget that even your creative writing tasks must have an inspiring introduction that talks about your purpose of writing.
By following the initial instructions outlined in this guide, you’ll be able to provide impactful statistics, introduce your topic effectively, and lead your readers towards a compelling thesis in your assignment’s introduction.
Let us take the topic of Special Education and Dyslexia as an introduction example:

As you can see, the introduction provides statistics and introduces the topic by leading it to a strong thesis (the last sentence).
Here is the list of helpful resources that you can use as you are brainstorming various ideas or think about how to come up with a perfect introduction for your essay:
- Quillbot . A paraphrasing tool that can help when your introduction just doesn’t feel right.
- Grammarly . A great tool to shape your introduction and bring it to perfection by polishing all the messy ot incorrect parts..
- Wordsmith . It helps to turn statistics into an insightful narrative. Try it out!
Alternatively, if you need something stylish or you are facing challenges with your grammar as an ESL student, consider checking an affordable assignment service in the UAE . It can provide you with all kinds of writing assistance and proofreading to keep you safe and your introduction perfect!
Find the writer according to your requirements
- AssignmentBro is a team of experienced writers in any field of academic research
- We thoroughly choose writers with advanced multistep selection process
- Our writers work according to the highest academic standards

Knowing how to avoid plagiarism in the assignment is one of those skills that many college students learn the hard way when they face high similarity plagiarism reports. It doesn't even...
Knowing how to avoid plagiarism in the assignment is one of those...
Knowing how to structure an assignment is half the battle. Once you understand what sections need to be included, you can begin to organize your thoughts and materials easily. Assignment...
Knowing how to structure an assignment is half the battle. Once you...
What is an Assignment Plan? In simple terms, an assignment plan is what helps college and university students come up with a clear outline and preparation before they start writing. Even...
What is an Assignment Plan? In simple terms, an assignment plan is...
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .

Let's start a new assignment project together, Get Exclusive Free Assistance Now!

Need Help? Call Us :
- Assignment Writing Service
- Assignment Editing Service
- Assignment Masters
- Assignment Provider
- Buy Assignment Online
- Do My Assignment
- Assignment Writers
- College Assignment Help
- Essay Writing Service
- Online Essay Help
- Do My Essay
- Write My Essay
- Essay Assignment Help
- Essay Writer
- Essay Typer
- College Essay Help
- Essay Editor
- Types Of Essays
- Expository Essays
- Types Of Expository Essays
- Narrative Essays
- Narrative Essay Examples
- Narrative Essay Hooks
- Narrative Essay Childhood Memory
- Descriptive Essay About An Event
- Types Of Essays In Ielts
- Application Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Essay Writing
- Essay Types
- Paper Writing Service
- Research Paper Help
- Term Paper Help
- Write My paper
- Paper Editor
- Research Proposal Help
- Thesis Writing Help
- Thesis Statement Help
- Homework Help
- Do My Homework
- Statistics Homework Help
- Physics Homework Help
- Word Problem Solver
- Accounting Homework Help
- Math Homework Help
- Solve my Math Problem
- College Homework Help
- Online Tutoring Service
- Algebra Homework Help
- CPM Homework Help
- Homework Answers
- Lab Report Help
- Pestel Analysis Help
- Business Report Help
- Book Review Help
- Book Report Help
- University Assignment Help
- Capstone Project Help
- Resume Writing Services
- Annotated Bibliography
- Ghostwriter
- Personal Statement Help
- Speech Writer
- Proofreading
- computation assignment help
- dbms assignment help
- microprocessor assignment help
- oracle assignment help
- pascal assignment help
- perl assignment help
- ruby assignment help
- sql assignment help
- uml assignment help
- web designing assignment help
- epidemiology assignment help
- nursing assignment help
- pharmacology assignment help
- psychology assignment help
- brand management assignment help
- construction management assignment help
- customer relationship management
- healthcare management assignment help
- mba assignment help
- myob assignment help
- recruitment assignment help
- strategy analysis assignment help
- pricing strategy assignment help
- business analytics assignment help
- business communication assignment help
- e commerce assignment help
- international finance assignment help
- quantitative analysis assignment help
- engineering mathematics assignment help
- civil engineering assignment help
- transportation assignment
- electronics assignment help
- geotechnical engineering assignment help
- telecommunication assignment help
- biomedical engineering assignment help
- mechanical engineering assignment help
- system analysis and design assignment help
- rationalism assignment help
- religion assignment help
- physics assignment help
- biology assignment help
- botany assignment help
- bioinformatics assignment help
- eviews assignment help
- linear programming assignment help
- minitab assignment help
- probability assignment help
- spss assignment help
- stata assignment help
- android assignment help
- c programing assignment help
- c sharp assignment help
- c plus plus assignment help
- fortran assignment help
- haskell assignment help
- html assignment help
- java assignment help
- python programming assignment help
- sap assignment help
- web programming assignment help
- Taxation Law Aassignment Help
- Constitutional Law Assignment help
- contract law assignment help
- civil law assignment help
- company law assignment help
- property law assignment help
- international law assignment help
- human rights law assignment help
- agriculture assignment help
- anthropology assignment help
- childcare assignment help
- english assignment help
- fashion assignment help
- music assignment help
- How It Works
- Assignment Help
How to Write an Introduction for Assignment?
Academic writing is an important part of every curriculum whether you are in high school or you are a university student. You might always be discussing the several issues and concerns about various academic writing projects you get with your friends and mentors. The objective of all such assignments is to see how better you can express yourself through words and how much you know about a subject. The best part about writing is that you can always learn and evolve. In this article, you will learn an important aspect of assignment writing that is the art of writing the introduction of an assignment.
Why an Introduction is Important in Academic Writing Assignments?
As a student, you might not be able to develop clear and concise paragraphs. If you often wonder who can do my assignment more academically then you should start with learning how to write an introduction for an assignment. Whether you are writing an essay, report or dissertation, an introductory paragraph is always required. If you prepare that paragraph well you might impress your readers from the very beginning.
Also Read : Experts Tips on College Assignment Formats & Structure with Examples
The main aim of the introductory paragraph is to provide the readers with a clear idea about the topic of your assignment. Â The introduction gives a generalization about the topic before a writer narrows down their discussion. It is just like a guide to your assignment. It must also include some background details of the assignment topic and an outline of what is your opinion or argument. You will understand in a deeper sense if you go through some introduction examples.
The Ingredients of An Introduction
There are some points that one should consider to provide a good introduction to their assignment. You may not incorporate all of them but, in general, you should try including some of these points in your introductory paragraph. While you read some introduction paragraph examples try identifying which points had the writer included in them.
- Highlight the importance of the subject
- The definition of the topic being discussed
- The reason why you are writing on this topic
- An overview of your approach on the topic
- Highlight the points that you want to discuss in the assignment
- State some previous works about the topic
- State some limitations about the topic
Consider the sample introductory paragraph given below. You may see that the paragraph starts with a central issue. It gives a little background of the topic and establishes the argument that will be discussed further in the essay.

How to Write An Introduction for A Report?
So above we discussed some generalized points about the introduction of an academic assignment. Now let us see how to write an introduction for a report.
Establish A Background
You may mention something about the previous research on the topic. You may mention all the issues that you have researched about the topic and you want to discuss further in the report. This will give your readers a reason why they should read your report.
Bridging The Gap
You should also mention the gaps in the previous research and how you are making efforts to bridge those gaps. Mention what all extra information you are going to provide that will expand your reader’s knowledge.
State Your Objective
Once you have established a background state your objectives. Write your thesis statement or the hypothesis. You may discuss the structure of your report here and list all the findings of the report. The following example gives a clear idea of the format that we are discussing.

How to Write an Introduction for A Dissertation/ Thesis?
The procedure to write an introduction for a long piece of writing is generally similar to what we have discussed so far. Still, it is important to know the little details that you should take care of. Our experts always suggest the students go through the introduction example for assignment before starting their writing process. Many times students have a lot of ideas in mind but they just cannot paraphrase them. They may avail our affordable writing services at such times to seek clarity. Our writers will help them convert their ideas into a powerful piece of writing.
As far as dissertations are concerned you must focus on writing an attention-grabbing introduction because then only you will be able to convince the reader to read your paper further. If you will consider any introduction paragraph examples of dissertations you will find that the writers generally maintain suspense. They never reveal everything about their research straightaway in the introductory paragraph. Apart from the general introduction of the dissertation, you can also provide an introduction to each chapter. This will widen your scope of including references and you can always remind the reader of your purpose of writing this dissertation.
Also Read: Tips and Examples of The Conclusion Section of Assignments
Some Extra Tips from Our Experts
By now we expect that you might have understood what an introduction is, what all points you should include in an introduction and how to write an introduction for an assignment whether it is an essay, report or a dissertation. You should always remember that the introduction should be eye-catching. It should build up curiosity among the readers. Your introduction should not just restate the question of your assignment title . It should rather give your readers an outline of what is there in your assignment.
Most importantly, introduction writing is not storytelling. It should be written with a focused approach. Consider your instructor’s guidelines about the word limit of the assignment introduction and stick to it if you want to gain better marks. Do not forget to consider our experts for fresh ideas and different introduction writing examples.
Need Help with writing an introduction for an assignment?
An introduction task segment is a key element of any task or item. It’s your task’s main area. Generally, this region has only a few passages.
We at GoAssignmentHelp, a leading assignment help services with the best and experienced assignment Writers based in Brisbane operating online in Sydney , Melbourne , Perth , Canberra , Adelaide , Darwin and across the major cities of Australia can help you with assignment writing services in essays , research papers , thesis , dissertation , homework .
0 responses on "How to Write an Introduction for Assignment?"
Leave a message cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Figurative Language and Its Importance
- A’s and B’s: The True Story Behind The Letter Grades
- How to Write an Article Review: Tips, Outline, Format
- Explanatory Essay Writing Guide
- Poem Analysis Essay Guide: Outline, Template, Structure
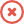
Securing Higher Grades is no more expensive!
We can help you boost your grades at best price., get exclusive 20% off.

[email protected] | (+1)617-933-5480
187 Wolf Road, Albany, New York, 12205, USA
100% Secure Payment

We offer assignment writing services in :
- Los Angeles
Disclaimer: Any material such as academic assignments, essays, articles, term and research papers, dissertations, coursework, case studies, PowerPoint presentations, reviews, etc. is solely for referential purposes. We do not encourage plagiarism in any form. We trust that our clients will use the provided material purely as a reference point in their own writing efforts.
GoAssignmentHelp Rated 4.4/5 based on 123 Reviews Copyright © 2010-2024 | www.goassignmenthelp.com | All rights reserved.

Tap to Chat
Get instant assignment help

How to Write an Assignment Introduction – 6 Best Tips
In essence, the writing tasks in academic tenure students are an integral part of any curriculum. Whether in high school, college, or university, they may also address the various issues and concerns with their friends and mentors about different academic writing assignments they receive.
The main purpose of all these assignments is to recognize how you can adequately express yourself through words and how much you understand a particular subject.
An introduction is a base of an assignment. It is challenging to prepare, and many students struggle to write an assignment.
Some students have doubts about how to write assignment introduction. The current educational system has neglected to teach this vitally necessary writing method.
The best thing about writing is that you can learn and grow all the time by practicing. In this blog, I will discover significant tips for assignment writing, which is the art of writing an assignment introduction.
If you are struggling with your assignment, then you can get top-notch assignment help online service from our experts who will help you with any type of assignment.
What Is The Introduction Section?
Table of Contents
An assignment introduction segment is a crucial piece of any task or article. It is the main area of your task. This area generally has not more than a few passages.
Why is an introduction section important?
It is a fact that your “ first impression is your last impression .” So, if you write a good introduction to your assignment, you catch your examiner’s eye and get good grades.
The primary purpose of the introductory paragraph is to give the readers a real understanding of the topic of your assignment. The introduction gives the subject a generalization until the author narrows the discussion.
It is just like your assignment guide. It also provides context information regarding the assignment topic and an outline of your view or claim.
You can understand it more deeply if you go through some introduction examples. It gives the reader an overview of your essay and what it’s all about.

What Are The Characteristics Of A Good Introduction?
- Ensure your writing is clear and precise, and there must be no language errors.
- The introduction section should be attention-grabbing to browse and attracts the reader to continue reading the rest of the assignment.
- The introduction should tell the reader what the full assignment is all concerning.
Still, Need help with your assignments writing? Click the banner above & get a free quote for your assignments.
Hope that you find this information useful. Happy learning, and best of luck with your assignment.
If you need any type of help regarding your assignments, contact us & get affordable assignment help .
Points To Remember Before Write Assignment Introduction
Before you searching the answer to your question about how to write an assignment introduction, you must keep these things in mind before writing it:
Proper introduction for a process documentation creates your experience a lot easier. It frees you from evaluating whether readers would be excited to continue your work. If you want to attract more readers, keep a few parameters before creating the introduction section It is a strong recommendation for the serious writers to take help from AI Content Detector Tools which are much efficient to secure your website ranking factor. You have a choice to check the best solution on Originality.AI in this regard.
1. Understand Your Readers
To present a valid assignment to your audience, you must use audience-centric language rather than writer-centric. Ask yourself what the audience needs to understand from your writing. Are your audience expected to have an emotional reply to your writing? What do you need the audience to act, think, or feel about it? No matter how well-educated, we all bear the challenge of getting into someone’s shoes. Audience information is one of the keys to efficient completion.
2. Think About The Good Ideas
The thesis statement is your essay’s most significant sentence. So you’ve got to work over and over to get it accurate. Get assured you explain the research question acutely while writing your thesis statement. In the sentence of the thesis statement, your point of view should be clear. Avoid a lengthy, wordy, and complex statement of the thesis.
3. Avoid Explanation
Don’t try to explain anything to make your argument in the introduction section. You should drop the information part to the principal body. Just mention the primary points of the argument you plan to make later in the assignment. This point is important while searching for how to write an assignment introduction, as the introduction must be written in brief only.
4. Volume Matters
There is no doubt that the duration of the introduction depends on the subject, the format of the assignment, and the research work. However, it will be written in one paragraph.
Remember that your introductory section should be more or less half a page long so that the audience can finish it one day. The introduction should be one-tenth of the entire assignment.
- The introduction must be 200-250 words when writing a 2000 words assignment.
- The introduction must be 350-400 words when writing a 3000 words assignment.
5. Don’t Act In The Dark
None of this comes as a surprise in academic writing. Academic writing is unlike writing fiction, where you can keep the audience in suspense. The entire assignment should be outlined in the introduction in academic literature, followed by a description in the central body. The following points will comprise an overview,
a. Related background data
b. A Map of Essay
c. A Sentence of Thesis
d. Your opinion.
Note: This is the rule for writing an introduction in the assignment. But there is no fast and robust rule for introduction writing. You need to be careful about the criteria you need to fulfill. Nevertheless, the above suggestions certainly will enable you to write a useful introduction.
6 Tips For How To Write An Assignment Introduction?
These are the following tips and tricks to write assignment introduction.
Tip 1:- Try to Find A Good Idea To Write An Assignments
Your whole assignment should often be based on the assignment question’s answer, and the introduction is the first step of your assignment. Your direct response to your question on the assignment is your idea statement that should be involved in your introduction. Your assignment problem often starts with a large view and narrows down to some topic field. You should follow assignmentguru.com for an identical pattern while writing the introduction. Begin with a broad picture to attract readers, then give the readers particular information to engage in more reading.
Tip 2:- Choose Specific And General Perspectives
Remember, the subject needs an effective ‘big opening.’ For instance, an opening sentence that explains, ‘Human beings are capable of learning more than any other entity on earth’ would not be appropriate for the subject of ‘work and study.’ In another instance, the opening statement does not provide a world perspective in an assignment focusing on the city or state. So when you think about how to write an assignment introduction, you must take care of the opening statement as the success of the assignment introduction depends on it.
Tip 3:- Try To Write Assignment Introduction At The Beginning
The best method to write assignment introduction is to write it at the beginning. The explanation for this is very clear when you write the introduction, you may have an indefinite view of the key points of the argument. Yet when you finish the material, you have good ideas about what you’ve written in your writing so far. When you follow all the rules, first write all of your proof and, finally, the introduction. Please ensure that your facts, conclusion, and introduction represent the claim you plan to bring forward.
Tip 4:- Use Creativity As An Opportunity
Don’t be scared to make and alter an experimental introduction in the first as you proceed with the subject. Writing an introduction is often the most challenging for any student since this is the first thing readers can search for. All you should do is write a normal introduction to get the work started. Complete the task, return to the introduction section again, and thoroughly review it. If rewriting is required, do not hesitate to do so.
Tip 5:- Give Earlier Attention To All Sentences
You may start with a quotation, short story, analogy, or even subject-related statistics. Create a strong impression on the audience by making that relevant information accessible. This is the point of thinking outside the box and using new skills. The reader won’t want to read the truth they already know. Uniquely, you need to find specific ways of expressing details or opinions. The students who want to know how to write an assignment introduction are searching for a unique way and methods to write it.

Tip 6:- Be Optimistic
Avoid phrases like “I will address about- in this article. Such sentences are of no concern to the reader’s mind. First of all, you need to leap in confidence in your story. Readers will find it hard to connect when you don’t believe in your content. So be sure of what you’re writing; only the readers will be involved in more reading.
- The purpose and objectives of your assignment .
- Why this assignment task is valuable?
- The scope of the assignment or what the assignment covers.
- A brief description of the organization of the assignment content.
All the above strategies help you in writing an effective and engaging introduction.
What Are The Most Common Strategies To Write Assignment Introduction?
These are the following most common strategies for writing assignment introductions.
- Start with a board idea about the topic. After that, narrow down the discussion to the area you focus on in your assignment. We also need to explain why this assignment is useful and important.
- Then briefly discuss the tasks to be tackled, which usually includes the objectives and purpose of an assignment.
- Finally, give the reader a brief preview of your homework, which you will include in subsequent sections.
What Are The Elements Important To Write Assignment Introduction?
Here the following elements are crucial to write an assignment introduction.
- The first and foremost most important element to writing the school or college assignment is the brief background of the study.
- Apart from this, you need to add the context of your assignment in the introduction.
- Also, the other major elements to writing an assignment introduction are adding the contention, major points to study, the definition of the topic, why you are writing on this topic only, giving an outline, etc.
Assignment Introduction Examples
These are the following assignment introduction examples;

Quick links
- How To Attach Assignment In Google Classroom
- How To Make An Assignment On MS Word With Easy Steps
Conclusion (Write Assignment Introduction)
From the above discussion, now you get the answer to your question, “how to write an assignment introduction.” All the above strategies and points help you in improving your writing. We hope that you find this information useful. Happy learning, and best of luck with your assignment.
If you need any help regarding your assignments, then you can contact CallTutors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you say in a quick introduction.
The personal introductions should include the name, expected graduation date, major career goals, experience in projects, internship, co-op, etc.
How To Start An Assignment Introduction?
Follow these steps to start a good assignment introduction :
1. Define the main purpose of writing 2. Discuss the problems and try to solve them 3. What will be the tone and style of writing?
How Long Should An Assignment Introduction Be?
The introduction for the assignment should be three to five sentences long or 50-80 words.
Similar Articles

13 Best Tips To Write An Assignment
Whenever the new semester starts, you will get a lot of assignment writing tasks. Now you enter the new academic…

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Introduction for a Psychology Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
- Writing Tips
If you are writing a psychology paper, it is essential to kick things off with a strong introduction. The introduction to a psychology research paper helps your readers understand why the topic is important and what they need to know before they delve deeper.
Your goal in this section is to introduce the topic to the reader, provide an overview of previous research on the topic, and identify your own hypothesis .
At a Glance
Writing a great introduction can be a great foundation for the rest of your psychology paper. To create a strong intro:
- Research your topic
- Outline your paper
- Introduce your topic
- Summarize the previous research
- Present your hypothesis or main argument
Before You Write an Introduction
There are some important steps you need to take before you even begin writing your introduction. To know what to write, you need to collect important background information and create a detailed plan.
Research Your Topic
Search a journal database, PsychInfo or ERIC, to find articles on your subject. Once you have located an article, look at the reference section to locate other studies cited in the article. As you take notes from these articles, be sure to write down where you found the information.
A simple note detailing the author's name, journal, and date of publication can help you keep track of sources and avoid plagiarism.
Create a Detailed Outline
This is often one of the most boring and onerous steps, so students tend to skip outlining and go straight to writing. Creating an outline might seem tedious, but it can be an enormous time-saver down the road and will make the writing process much easier.
Start by looking over the notes you made during the research process and consider how you want to present all of your ideas and research.
Introduce the Topic
Once you are ready to write your introduction, your first task is to provide a brief description of the research question. What is the experiment or study attempting to demonstrate? What phenomena are you studying? Provide a brief history of your topic and explain how it relates to your current research.
As you are introducing your topic, consider what makes it important. Why should it matter to your reader? The goal of your introduction is not only to let your reader know what your paper is about, but also to justify why it is important for them to learn more.
If your paper tackles a controversial subject and is focused on resolving the issue, it is important to summarize both sides of the controversy in a fair and impartial way. Consider how your paper fits in with the relevant research on the topic.
The introduction of a research paper is designed to grab interest. It should present a compelling look at the research that already exists and explain to readers what questions your own paper will address.
Summarize Previous Research
The second task of your introduction is to provide a well-rounded summary of previous research that is relevant to your topic. So, before you begin to write this summary, it is important to research your topic thoroughly.
Finding appropriate sources amid thousands of journal articles can be a daunting task, but there are several steps you can take to simplify your research. If you have completed the initial steps of researching and keeping detailed notes, writing your introduction will be much easier.
It is essential to give the reader a good overview of the historical context of the issue you are writing about, but do not feel like you must provide an exhaustive review of the subject. Focus on hitting the main points, and try to include the most relevant studies.
You might describe previous research findings and then explain how the current study differs or expands upon earlier research.
Provide Your Hypothesis
Once you have summarized the previous research, explain areas where the research is lacking or potentially flawed. What is missing from previous studies on your topic? What research questions have yet to be answered? Your hypothesis should lead to these questions.
At the end of your introduction, offer your hypothesis and describe what you expected to find in your experiment or study.
The introduction should be relatively brief. You want to give your readers an overview of a topic, explain why you are addressing it, and provide your arguments.
Tips for Writing Your Psychology Paper Intro
- Use 3x5 inch note cards to write down notes and sources.
- Look in professional psychology journals for examples of introductions.
- Remember to cite your sources.
- Maintain a working bibliography with all of the sources you might use in your final paper. This will make it much easier to prepare your reference section later on.
- Use a copy of the APA style manual to ensure that your introduction and references are in proper APA format .
What This Means For You
Before you delve into the main body of your paper, you need to give your readers some background and present your main argument in the introduction of you paper. You can do this by first explaining what your topic is about, summarizing past research, and then providing your thesis.
Armağan A. How to write an introduction section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):8-9. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.046
Fried T, Foltz C, Lendner M, Vaccaro AR. How to write an effective introduction . Clin Spine Surg . 2019;32(3):111-112. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000714
Jawaid SA, Jawaid M. How to write introduction and discussion . Saudi J Anaesth . 2019;13(Suppl 1):S18-S19. doi:10.4103/sja.SJA_584_18
American Psychological Association. Information Recommended for Inclusion in Manuscripts That Report New Data Collections Regardless of Research Design . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Search entire site
- Search for a course
- Browse study areas
Analytics and Data Science
- Data Science and Innovation
- Postgraduate Research Courses
- Business Research Programs
- Undergraduate Business Programs
- Entrepreneurship
- MBA Programs
- Postgraduate Business Programs
Communication
- Animation Production
- Business Consulting and Technology Implementation
- Digital and Social Media
- Media Arts and Production
- Media Business
- Media Practice and Industry
- Music and Sound Design
- Social and Political Sciences
- Strategic Communication
- Writing and Publishing
- Postgraduate Communication Research Degrees
Design, Architecture and Building
- Architecture
- Built Environment
- DAB Research
- Public Policy and Governance
- Secondary Education
- Education (Learning and Leadership)
- Learning Design
- Postgraduate Education Research Degrees
- Primary Education
Engineering
- Civil and Environmental
- Computer Systems and Software
- Engineering Management
- Mechanical and Mechatronic
- Systems and Operations
- Telecommunications
- Postgraduate Engineering courses
- Undergraduate Engineering courses
- Sport and Exercise
- Palliative Care
- Public Health
- Nursing (Undergraduate)
- Nursing (Postgraduate)
- Health (Postgraduate)
- Research and Honours
- Health Services Management
- Child and Family Health
- Women's and Children's Health
Health (GEM)
- Coursework Degrees
- Clinical Psychology
- Genetic Counselling
- Good Manufacturing Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Speech Pathology
- Research Degrees
Information Technology
- Business Analysis and Information Systems
- Computer Science, Data Analytics/Mining
- Games, Graphics and Multimedia
- IT Management and Leadership
- Networking and Security
- Software Development and Programming
- Systems Design and Analysis
- Web and Cloud Computing
- Postgraduate IT courses
- Postgraduate IT online courses
- Undergraduate Information Technology courses
- International Studies
- Criminology
- International Relations
- Postgraduate International Studies Research Degrees
- Sustainability and Environment
- Practical Legal Training
- Commercial and Business Law
- Juris Doctor
- Legal Studies
- Master of Laws
- Intellectual Property
- Migration Law and Practice
- Overseas Qualified Lawyers
- Postgraduate Law Programs
- Postgraduate Law Research
- Undergraduate Law Programs
- Life Sciences
- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- Postgraduate Science Programs
- Science Research Programs
- Undergraduate Science Programs
Transdisciplinary Innovation
- Creative Intelligence and Innovation
- Diploma in Innovation
- Postgraduate Research Degree
- Transdisciplinary Learning
Sample written assignments
Look at sample assignments to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills.
How to use this page
This page features authentic sample assignments that you can view or download to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills.
PLEASE NOTE: Comments included in these sample written assignments are intended as an educational guide only. Always check with academic staff which referencing convention you should follow. All sample assignments have been submitted using Turnitin® (anti-plagiarism software). Under no circumstances should you copy from these or any other texts.
Annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliography: Traditional Chinese Medicine (PDF, 103KB)
Essay: Business - "Culture is a Tool Used by Management" (PDF, 496KB)
Essay: Business - "Integrating Business Perspectives - Wicked Problem" (PDF, 660KB)
Essay: Business - "Overconsumption and Sustainability" (PDF, 762KB)
Essay: Business - "Post bureaucracy vs Bureaucracy" (PDF, 609KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "Ideas in History - Postmodernism" (PDF, 545KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "The Context of Visual Communication Design Research Project" (PDF, 798KB)
Essay: Design, Architecture & Building - "Ideas in History - The Nurses Walk and Postmodernism" (PDF, 558KB)
Essay: Health (Childhood Obesity ) (PDF, 159KB)
Essay: Health (Improving Quality and Safety in Healthcare) (PDF, 277KB)
Essay: Health (Organisational Management in Healthcare) (PDF, 229KB)
UTS HELPS annotated Law essay
(PDF, 250KB)
Essay: Science (Traditional Chinese Medicine) (PDF, 153KB)
Literature review
Literature Review: Education (Critical Pedagogy) (PDF, 165KB)
Reflective writing
Reflective Essay: Business (Simulation Project) (PDF, 119KB)
Reflective Essay: Nursing (Professionalism in Context) (PDF, 134KB)
Report: Business (Management Decisions and Control) (PDF, 244KB)
Report: Education (Digital Storytelling) (PDF, 145KB)
Report: Education (Scholarly Practice) (PDF, 261KB)
Report: Engineering Communication (Flood Mitigation & Water Storage) (PDF, 1MB)
UTS acknowledges the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation, the Boorooberongal people of the Dharug Nation, the Bidiagal people and the Gamaygal people, upon whose ancestral lands our university stands. We would also like to pay respect to the Elders both past and present, acknowledging them as the traditional custodians of knowledge for these lands.


Self-introduction for Students [With Sample Intros]
- Updated on Jan 13, 2023
- shares
You would want to make a good impression on your friends when you introduce yourself on the first day in class at your school or college – or at some other gathering. Wouldn’t you?
A small note before we dive into thick of things: Self-introductions can be context-driven, implying that because of unique situation you’re in, you may have to customize some part of the introduction. So, feel free to add or subtract to what’s covered here.
What to include in self-introduction?
Is there a format (for the introduction) to follow? The organizer, for example, may ask to include your name, place you come from, and your hobbies in the introduction.
If there is a format, follow it, but feel free to venture into areas that aren’t included in the format if they provide a more complete picture of yours.
You may include following in your introduction:
1. The start
You can start with the obvious – your name.
But that’s a common start. You can be bit innovative by starting with an attention-grabber. Watch the beginning of this video on marketing to get a feel of what I’m saying (watch the first 15 seconds):
Neil didn’t start with his name. He started with things that will grab people’s attention immediately and came to his name later on.
You can follow the same strategy to stand out among your classmates, most of whom would be following the standard ‘name first’ approach. You can start with a unique experience or a peculiar fact about your city or your uncommon hobby. The first sample intro (later in the post) follows this strategy.
More resources on conversations and introductions:
- How to introduce yourself in different settings?
- How to say ‘thank you’?
- How to respond when someone asks ‘how are you’?
2. Where are you from?
Mention the city you come from. You may add a sentence or two about the city as well if there is something interesting to talk about. Maybe the city is known for historic monuments. Maybe it’s known for natural resources.
And if you’ve lived in multiple cities, you may briefly mention the names and, as mentioned above, a sentence or two on the most interesting of them.
3. Where did you last attend the school?
If you recently moved to a new school (or college) and are introducing yourself there, you can briefly talk about your last school. Are there any interesting facts about your last school? If yes, mention them. Maybe it was established a long, long time ago. Maybe it has produced few famous alumni.
If you’re continuing in the same school, you may mention how many years you’ve been studying there.
4. Interests, hobbies, and achievements
What are your interests and hobbies?
Playing a sport? Traveling? Hiking? Reading? Kite flying? Or something unusual, say bull fighting?
Go into details if you’ve pursued the hobby with serious interest. For example, if you’re into reading, mention what genres you read, your favorite books, your favorite author, and how reading has affected you.
Don’t forget to mention your participation in extracurricular activities in school, if you did. Don’t forget to mention any significant achievements you’ve had?
5. Which stream/department/subject have you enrolled in?
You can briefly talk about which subjects (math, science, arts, commerce, biology, and so on) you’ve picked or you intend to pick in future. Optionally, you may also mention why you made the choice you have. Was it because you love it? Was it because it’ll help you achieve your career goals?
If you’re a college student, you can mention the department you’ve enrolled in. Are you in Arts, Commerce, Mechanical Engineering, Science, or Economics?
This doesn’t apply though if you’re introducing yourself to students who’re all from the same stream/department/subject.
6. Do you’ve clarity on interests/goals you want to pursue in future?
If you’re in K-12, you may not have seriously evaluated what career path you want to follow, and that’s fine. But if you’ve certain career aspiration and if you want to talk about it, you can. Some want to become engineer. Some, astronaut. Some, doctor. Some, model. Speak out what you aspire to become.
Most college students though have more concrete idea on post-college career. If you’ve decided the career path you want to pursue after college, you can share it with your classmates. You never know few of your classmates harboring same career aspirations may just approach you to be friends. You may also mention professional clubs you want to join to hone your skills.
Leave feedback on this post
Was anything not explained well in this post? Was any topic not covered? Do you have any other suggestion? Your feedback will help improve this post for you and for others.
( Note : In the first field below, simply copy-paste url/link of this post from the search bar. In the second field, feel free to refer to parts of this post to explain.)
Participate in a short survey
If you’re a learner or teacher of English language, you can help improve website’s content for the visitors through a short survey.
7. Where can you help others?
If you’ve a strength others in your class can benefit from, feel free to share it. For example, if you’re good in dancing, you can offer to teach the ropes to anyone interested. If you’re strong in a particular subject that is part of your syllabus, you can offer to help others in that subject.
If people know of your strengths, they’ll readily approach you when they need help. This is an easy way to make friends in college. And if you think helping others may be a time waster, you should remember that you too may need help in areas where others are stronger.
This is also a good stage – by offering help – to finish your intro. (See the first sample intro.)
Should I talk about my family?
Avoid it unless the format of the intro requires you to talk about your family as well. You need not go into what your parents do and which class your siblings study in.
Should I mention my last year’s grades?
You shouldn’t unless specifically asked to or others are mentioning it. Top grades can lend a snobbish air to your intro, even if you’re otherwise. Students may make an impression that you’re flaunting your grades, even if you aren’t.
Remember, the primary goal of your intro is to make friends, find people with shared interests.
Four do’s and don’ts when introducing yourself
1. listen to other intros.
Listen to intros that come before yours. If you can refer to someone else’s point or two seamlessly in your intro, you’ll impress people around.
2. Practice, but don’t cram
People often go blank on some of the points or get nervous when they stand up to speak. The best long-term way to overcome this is exposure to such speaking experiences . But in the immediate term, practice what you want to say few times (don’t cram though) to increase your odds of speaking with confidence.
3. Appear confident even if you’re not
After the presentations by executives and entrepreneurs (presumably confident speakers) as part of an executive program at Harvard University, Carmine Gallo , one of the judges, asked them how their presentations went. He heard following comments:
“I was so nervous. I was shaking.”
“I forgot what to say about a slide.”
“I stumbled over my words.”
“I totally lost my place.”
But, no one in the audience spotted those mistakes.
This phenomenon is called spotlight effect , which in nutshell means that people overestimate how much others are noticing their actions and appearance.
What’s the lesson?
If you’re nervous or you make few mistakes, don’t let them rattle you. Most won’t even notice them. Caroline Goyder captures this sentiment aptly in her book Find Your Voice: The Secret to Talking with Confidence in Any Situation :
When you dive into contribution [speaking], and move beyond the anxious competing, you realize that all the worry was such a waste of time. No one is ever judging you as harshly as you judge yourself. Because the truth is that most people are thinking about themselves.
But if you let nervousness and mistakes overpower you, you may make a mistake or display body language that will be noticed by all. And once you’re through the first few lines in your intro, your nerves will start easing.
So, stay composed and carry on. Many in the audience in fact wouldn’t even be listening to most introductions, as they would be busy silently rehearsing their own lines.
4. Make eye contact and be enthusiastic
Make eye contact with other students while speaking. Don’t fix your eyes on a familiar section of the audience. Move your eyes around. And, last but important, your voice and body language should show enthusiasm.
Here are few sample self-introductions for you to get a hang of how they’re done:
Sample self-introductions
Introduction 1
I once spent an entire night in a dense forest with a friend. Well, this act was not to show off how brave I was, but it was forced on me… by my foolishness. During a trek in [name of the region], I and a friend got too adventurous and strayed from our regular route despite instructions to the contrary by our trek guide. We got lost. We survived somehow (that’s a story for another day), but I haven’t given up on my adventure streak and love for outdoors.
Friends, I’m [your first name] and I love outdoors. I’ve been to treks in Himalayas on multiple occasions. These outdoor expeditions have also forced me to learn basic cooking. Well, I don’t boast of cooking dishes you’ll relish, but yes when you’re dying of hunger in the middle of night, you can count on me. I also love cycling long distances – 20+ kilometers in a stretch – and I can manage singing which some may find intolerable.
I’m from [name of the city]. It’s not a big place, but it somehow exists on the map. I’m really excited to be here. I look forward to having some fun, making friends, and building myself up for college. If you’re organizing any outdoor event in future, you can always count on me for help.
Thanks for giving me this opportunity to introduce myself.
Introduction 2
My name is [your first name]. I’m from [name of the city] where I finished my schooling last year from [name of the school]. Is there anyone here from my city? (Changes tack to engage with the audience.) OK, few.
I like watching movies, at least once a month. I play basketball on weekends and chess whenever I get time. I’m into reading thriller novels as well, Dan Brown being my favorite novelist.
I’m happy to step into college life, which provides more freedom and where, finally, I don’t have to come in a uniform. Post-college, I aspire to work in consulting industry.
I’m particularly strong in Excel worksheets and creating well-designed banners and documents. If anyone requires support in these areas, I’ll be glad to help. I look forward to meeting each one of you in the coming days.
Thanks. Have a great day.

Anil is the person behind content on this website, which is visited by 3,000,000+ learners every year. He writes on most aspects of English Language Skills. More about him here:
15 Comments
This really helped me… Thank you so so much.
Thank u….this is quite helpful to overcome my nervousness and get into action..Cheers?
Man, I was so nervous about my interview for school admission. But after reading this, I felt comfortable. Thanks, this was a great explanation.
It helped me a lot. Thank you so much. It was like I was the center of attraction. Thank you again.
Thanx…. It really helped on my first day of college.
Dude, this is another level. Thanks a lot.
Thanks a lot. It was useful. Now, I should be able to introduce my self without nerves ????
Thank you. Now I get some ideas for self intro and thank you for your brief explanation.
I was a little nervous about my varsity first introduction and my confidence increased after watching it.
Intro 2 was like fire…. It helped me a lot, thanx!!
Thanks, dude!!!! I am a school-level student and the introduction part really helped me.
I have a virtual introduction meeting with my seniors in college. I am so nervous about it. This piece is so helpful. Thanks.
Excellent. I like this a lot. I searched for this type of introduction on many websites, but this post is so interesting and good enough to impress my teacher and classmates.
My name is Yeabkal Solomon. I’m a first year student at Arba minch University. It helped me when I was gave my oral presentation.
I was very scared. I was really scared. Thank you very much for helping with the interview. It was very helpful for me
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The On-Campus and Online versions of Purdue OWL assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue OWL serves the Purdue West Lafayette and Indianapolis campuses and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

The Learning Strategies Center
- Meet the Staff
- –Supplemental Course Schedule
- AY Course Offerings
- Anytime Online Modules
- Winter Session Workshop Courses
- –About Tutoring
- –Office Hours and Tutoring Schedule
- –LSC Tutoring Opportunities
- –How to Use Office Hours
- –Campus Resources and Support
- –Student Guide for Studying Together
- –Find Study Partners
- –Productivity Power Hour
- –Effective Study Strategies
- –Concept Mapping
- –Guidelines for Creating a Study Schedule
- –Five-Day Study Plan
- –What To Do With Practice Exams
- –Consider Exam Logistics
- –Online Exam Checklist
- –Open-Book Exams
- –How to Tackle Exam Questions
- –What To Do When You Get Your Graded Test (or Essay) Back
- –The Cornell Note Taking System
- –Learning from Digital Materials
- –3 P’s for Effective Reading
- –Textbook Reading Systems
- –Online Learning Checklist
- –Things to Keep in Mind as you Participate in Online Classes
- –Learning from Online Lectures and Discussions
- –Online Group Work
- –Learning Online Resource Videos
- –Start Strong!
- –Effectively Engage with Classes
- –Plans if you Need to Miss Class
- –Managing Time
- –Managing Stress
- –The Perils of Multitasking
- –Break the Cycle of Procrastination!
- –Finish Strong
- –Neurodiversity at Cornell
- –LSC Scholarship
- –Pre-Collegiate Summer Scholars Program
- –Study Skills Workshops
- –Private Consultations
- –Resources for Advisors and Faculty
- –Presentation Support (aka Practice Your Talk on a Dog)
- –About LSC
- –Meet The Team
- –Contact Us
The Cornell Note Taking System
Why do you take notes? What do you hope to get from your notes? What are Cornell Notes and how do you use the Cornell note-taking system?
There are many ways to take notes. It’s helpful to try out different methods and determine which work best for you in different situations. Whether you are learning online or in person, the physical act of writing can help you remember better than just listening or reading. Research shows that taking notes by hand is more effective than typing on a laptop. This page and our Canvas module will teach you about different note-taking systems and styles and help you determine what will work best for your situation.
In our Cornell Note Taking System module you will:
- Examine your current note taking system
- Explore different note taking strategies (including the Cornell Notes system)
- Assess which strategies work best for you in different situations
The best way to explore your current note-taking strategies and learn about the Cornell note taking system is to go through our Canvas note taking module. The module will interactively guide you through how to use Cornell Notes – click on the link here or the button below. This module is publicly available.

Just want to see a bit more about Cornell Notes? You can view the videos below.
Watch: What are Cornell Notes?
Watch: Learn how students use the Cornell Note Taking System
The Cornell Note-Taking System was originally developed by Cornell education professor, Walter Pauk. Prof. Pauk outlined this effective note-taking method in his book, How to Study in College (1).
- Pauk, Walter; Owens, Ross J. Q. (2010). How to Study in College (10 ed.). Boston, MA: Wadsworth. ISBN 978-1-4390-8446-5 . Chapter 10: “The Cornell System: Take Effective Notes”, pp. 235-277

Blog about Writing Case Study and Coursework
dudestudy.com

How to Write an Introduction for a Case Study Report
If you’re looking for examples of how to write an introduction for a case-study report, you’ve come to the right place. Here you’ll find a sample, guidelines for writing a case-study introduction, and tips on how to make it clear. In five minutes or less, recruiters will read your case study and decide whether you’re a good fit for the job.
Example of a case study introduction
An example of a case study introduction should be written to provide a roadmap for the reader. It should briefly summarize the topic, identify the problem, and discuss its significance. It should include previous case studies and summarize the literature review. In addition, it should include the purpose of the study, and the issues that it addresses. Using this example as a guideline, writers can make their case study introductions. Here are some tips:
The first paragraph of the introduction should summarize the entire article, and should include the following sections: the case presentation, the examinations performed, and the working diagnosis, the management of the case, and the outcome. The final section, the discussion, should summarize the previous subsections, explain any apparent inconsistencies, and describe the lessons learned. The body of the paper should also summarize the introduction and include any notes for the instructor.
The last section of a case study introduction should summarize the findings and limitations of the study, as well as suggestions for further research. The conclusion section should restate the thesis and main findings of the case study. The conclusion should summarize previous case studies, summarize the findings, and highlight the possibilities for future study. It is important to note that not all educational institutions require the case study analysis format, so it is important to check ahead of time.
The introductory paragraph should outline the overall strategy for the study. It should also describe the short-term and long-term goals of the case study. Using this method will ensure clarity and reduce misunderstandings. However, it is important to consider the end goal. After all, the objective is to communicate the benefits of the product. And, the solution should be measurable. This can be done by highlighting the benefits and minimizing the negatives.
Structure of a case study introduction
The structure of a case study introduction is different from the general introduction of a research paper. The main purpose of the introduction is to set the stage for the rest of the case study. The problem statement must be short and precise to convey the main point of the study. Then, the introduction should summarize the literature review and present the previous case studies that have dealt with the topic. The introduction should end with a thesis statement.
The thesis statement should contain facts and evidence related to the topic. Include the method used, the findings, and discussion. The solution section should describe specific strategies for solving the problem. It should conclude with a call to action for the reader. When using quotations, be sure to cite them properly. The thesis statement must include the problem statement, the methods used, and the expected outcome of the study. The conclusion section should state the case study’s importance.
In the discussion section, state the limitations of the study and explain why they are not significant. In addition, mention any questions unanswered and issues that the study was unable to address. For more information, check out the APA, Harvard, Chicago, and MLA citation styles. Once you know how to structure a case study introduction, you’ll be ready to write it! And remember, there’s always a right and wrong way to write a case study introduction.
During the writing process, you’ll need to make notes on the problems and issues of the case. Write down any ideas and directions that come to mind. Avoid writing neatly. It may impede your creative process, so write down a rough draft first, and then draw it up for your educational instructor. The introduction is an overview of the case study. Include the thesis statement. If you’re writing a case study for an assignment, you’ll also need to provide an overview of the assignment.
Guidelines for writing a case study introduction
A case study is not a formal scientific research report, but it is written for a lay audience. It should be readable and follow the general narrative that was determined in the first step. The introduction should provide background information about the case and its main topic. It should be short, but should introduce the topic and explain its context in just one or two paragraphs. An ideal case study introduction is between three and five sentences.
The case study must be well-designed and logical. It cannot contain opinions or assumptions. The research question must be a logical conclusion based on the findings. This can be done through a spreadsheet program or by consulting a linguistics expert. Once you have identified the major issues, you need to revise the paper. Once you have revised it twice, it should be well-written, concise, and logical.
The conclusion should state the findings, explain their significance, and summarize the main points. The conclusion should move from the detailed to the general level of consideration. The conclusion should also briefly state the limitations of the case study and point out the need for further research in order to fully address the problem. This should be done in a manner that will keep the reader interested in reading the paper. It should be clear about what the case study found and what it means for the research community.
The case study begins with a cover page and an executive summary, depending on your professor’s instructions. It’s important to remember that this is not a mandatory element of the case study. Instead, the executive summary should be brief and include the key points of the study’s analysis. It should be written as if an executive would read it on the run. Ultimately, the executive summary should include all the key points of the case study.
Clarity in a case study introduction
Clarity in a case study introduction should be at the heart of the paper. This section should explain why the case was chosen and how you decided to use it. The case study introduction varies according to the type of subject you are studying and the goals of the study. Here are some examples of clear and effective case study introductions. Read on to find out how to write a successful one. Clarity in a case study introduction begins with a strong thesis statement and ends with a compelling conclusion.
The conclusion of the case study should restate the research question and emphasize its importance. Identify and restate the key findings and describe how they address the research question. If the case study has limitations, discuss the potential for further research. In addition, document the limitations of the case study. Include any limitations of the case study in the conclusion. This will allow readers to make informed decisions about whether or not the findings are relevant to their own practices.
A case study introduction should include a brief discussion of the topic and selected case. It should explain how the study fits into current knowledge. A reader may question the validity of the analysis if it fails to consider all possible outcomes. For example, a case study on railroad crossings may fail to document the obvious outcome of improving the signage at these intersections. Another example would be a study that failed to document the impact of warning signs and speed limits on railroad crossings.
As a conclusion, the case study should also contain a discussion of how the research was conducted. While it may be a case study, the results are not necessarily applicable to other situations. In addition to describing how a solution has solved the problem, a case study should also discuss the causes of the problem. A case study should be based on real data and information. If the case study is not valid, it will not be a good fit for the audience.
Sample of a case study introduction
A good case study introduction serves as a map for the reader to follow. It should identify the research problem and discuss its significance. It should be based on extensive research and should incorporate relevant issues and facts. For example, it may include a short but precise problem statement. The next section of the introduction should include a description of the solution. The final part of the introduction should conclude with the recommended action. Once the reader has a sense of the direction the study will take, they will feel confident in pursuing the study further.
In the case of social sciences, case studies cannot be purely empirical. The results of a case study can be compared with those of other studies, so that the case study’s findings can be assessed against previous research. A case study’s results can help support general conclusions and build theories, while their practical value lies in generating hypotheses. Despite their utility, case studies often contain a bias toward verification and tend to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions.
In the case of case studies, the conclusions section should state the significance of the findings, stating how the findings of the study differ from other previous studies. Likewise, the conclusion section should summarize the key findings, and make the reader understand how they address the research problem. In the case of a case study, it is crucial to document any limitations that have been identified. After all, a case study is not complete without further research.
After the introduction, the main body of the paper is the case presentation. It should provide information about the case, such as the history, examination results, working diagnosis, management, and outcome. It should conclude with a discussion, explaining the correlations, apparent inconsistencies, and lessons learned. Finally, the conclusion should state whether the case study presented the results in the desired way. The findings should not be overgeneralized, and the conclusions must be derived from this information.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Coursework Help
- Thesis Help
- Case Study Help
- Referencing Style Help
- Proofreading Services
- Rewrite Services
- Assessment Help
- Submenu item 1
- Submenu item 2
- Referencing Style Help
- Nursing Assignment Helper
- Management Assignment Helper
- Marketing Assignment Helper
- Programming Assignment Helper
- Finance Assignment Helper
- Accounting Assignment Helper
- Law Assignment Helper
- Computer Science Assignment
- Statistics Assignment Helper
- Engineering Assignment Helper
- Science Assignment Helper
- TAFE Assignment Helper
- Economics Assignment Helper
- Dissertation Proposal
- Dissertation Writing
- Dissertation Experts
- Research Writing
- Dissertation Proofreding
- Thesis Writing
- Law Dissertation
- Nursing Dissertation
- Accounting Dissertation
- Finance Dissertation
- Economics Dissertation
- Statistics Dissertation
- Chemistry Dissertation
- Accounting Exam Quiz
- Finance Exam Quiz
- Statisics Exam Quiz
- Economics Exam Quiz
- Biology Exam Quiz
- History Exam Quiz
- Maths Exam Quiz
- Reviews 4.95/5

Informative Essay Topics
- The Student Helpline
- Academic Blog

A Guide To Mastering Informative Essay: Sample And Topics
Are you a student who has to complete an informative essay but have no idea how to start with it? Then relax, The Student Helpline experts are going to help you with this short guide on how to write an informative essay! Indeed, you can learn a lot about informative essay topics and share your knowledge with others by writing an informational essay, which can be a rewarding process. It is important to understand the details of an informative essay, no matter if you are trying to get better at writing or just writing for yourself. So, go ahead and read on!
What Is An Informative Essay?
Writing to educate the reader about a certain subject is known as an informative essay. Informative essays offer information, analysis, and justifications to help the reader understand the subject matter. The primary goal of assignment writing help such an essay is to inform or explain without influencing the content from the views of the writer.
Major Features of Informative Essay Writing
So, thinking about what is an informative essay? (refer to figure 2), then it is more likely an essay writing that aims to impart knowledge to readers. Besides, here are the key features of an informative essay!
- Goal Style: The information in your informative essays should be presented without errors and in terms of objectives.
- Strong Structure: You must follow a proper informative essay format that should contain an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a summary.
- Complete Information: Moreover, you may ensure the reliability, of the informative essays by doing effective research based on reliable information.
- Learning Purpose: The main goal of writing an informative essay is to educate the readers effectively.
Informative Essay Structure
There is nothing hard and fast in terms of the structure of informative essay. It includes the following main components:
- Introduction: The informative essay introduction explains the subject of your essay, provides a little history, and states your thesis.
- Body: The next part of an informative essay structure is its body or description. Every body paragraph centres on specific aspects of the subject. By offering proof, an example of an informative essay, and reasoning to support your thesis.
- Summary: At last, we add an informative essay conclusion, which freshly restates the thesis for an informative essay, highlights the key ideas covered throughout the essay, and gives the reader a closing remark or call to action.
You Can Also Read:- Diagnostic Essay Examples
How To Start An Informative Essay?
Certainly, there are various steps involved in writing an informative essay and here is how to write an impactful informative essay. It goes as
- Pick a Good Topic: Pick the topics for informative essays that are clear, appealing, and easily studied. Make sure that it is focused enough to give specific details that are important to your target.
- Do Deep Research: Look for reliable sources that give the right information on writing an informational essay. Start by making notes and arrange your research to support your major points.
- Work on an Outline: You should put your thoughts into an organized informative essay outline by dividing them into an introduction, some body paragraphs, and a summary. Since a clear and logical flow is improved by the use of an informative essay outline.
- Revise and Edit: Last but not least, the final draft needs to be proofread on the terms of keeping it free from all sorts of informational essay mistakes. You should ensure that there are no spelling mistakes or incorrect sentences.
Informative Essay Examples
To get a better understanding of informative essays, it is required that you go through some of the example of an informative essay. They are!
Example 1: Why Excercing Daily is Good?
Introduction - There is no doubt that exercising regularly is essential for maintaining general health and well-being. In fact, it is an essential part of an active way of life because it provides many kinds of mental and physical rewards.
Description - When writing an informative essay, you can write about walking, running, and swimming as they are examples of physical activities that develop muscles and enhance heart function. In addition to reducing the risk of serious diseases like heart failure and diabetes, fitness also helps control weight and releases endorphins. Thus, this improves mood and lower stress and exercise on a regular basis increases energy and improves the quantity of sleep.
Conclusion - Thus, exercise is an essential part of a healthy lifestyle since it may significantly enhance your health and quality of life when included in your daily schedule.
Example 2: Social Media: Its Influence on Modern Society
Introduction - In the present day, social media has entirely altered the way people interact and acquire information.
Description - This informative essay on immediate global interaction is made possible by networks like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, which have an impact on business, politics, and education. They offer an avenue for sparking social movements and raising awareness. On the other hand, excessive use of social media can have unfavourable effects like reduced output, mental health problems, and privacy issues.
Conclusion - Hence, social media has a lot to provide in terms of uniting and informing people, but to keep a positive connection with the internet. It is important to use social media tools properly and be aware of any possible hazards.
Check Our Recent Post:- Rhetorical Analysis Essays
Best Informative Essay Topics
You can find a short list of the 10 best informative essay topics are:
- The Internet: Its Development and History
- Informative Essay on How Climate Change Affects World Ecosystems.
- Recycling: The Method and Advantages!
- Artificial Intelligence: Its Role in Healthcare
- Social Media: Its Impact on Mental Health
- Why is Vaccination Significant for Public Health
- The Space Exploration: An informative essay about its History!
- Genetic Engineering: The Advantages and Dangers
- The Photosynthesis Process in Plants
- Greek Culture: Its Impact on Contemporary Society
Top Informative Essay Ideas in 2024
No doubt, informative essay ideas are hard to find, so here is a compiled list of top such ideas that are blooming in 2024!
- Renewable Energy: An Informative Essay on the Future
- Digital Age Mental Health Awareness
- Virtual Reality: Its Effect on Education
- Informative Essays on Sustainable Urban Planning
- Globalization: Its Effects on Cultural Diversity
- Plant-Based Diets: Their Ascent
- An informative essay on Health and Artificial Intelligence
- Cybersecurity in 21st-century
- Progress in Space Exploration
- The Development of Green Clothing
A List of Top Management Informative Essay Topics
So, have no idea which will be the suitable informative essay topics for management, then read this out to find the best one.
- An Informative Essay help on the Development of Contemporary Organizational Leadership Styles
- Using Technology to Help Managers Make Better Decisions
- Initiatives for Diversity and Inclusion: Fueling Organizational Success
- Emotional Intelligence: Significance for Effective Leadership
- Sustainability Practices: Combining Management Strategies with Environmental Responsibility
- Balancing Innovation and Risk Management in the Modern Business Environment
- Crisis Management: Navigating Challenges in an Uncertain World
- Globalization: Management Techniques and Plans
- Informative Essay on Building and Maintaining Effective Teams
- Ethical Leadership: Establishing Integrity and Trust in Institutions
Some Best Informative Essay Topics on Nursing
The top 10 best informative essay ideas for nursing students are as follows:
- The Value of Evidence-Based Nursing Practice
- Nursing Informative Essay: Using Technology to Improve Patient Care
- Nurse Practitioners: Function in Primary Healthcare
- Nursing Practice Informational Essay: Mental Health Needs
- Palliative Care: Offering Solace and Assistance Towards the End of Life
- Cultural Competence in Nursing: Providing Care That Is Culturally Appropriate
- Nursing Shortages informative essay: Origins, Consequences, and Remedies
- An information essay on Nursing Practice Patient Safety
- How Nursing Education Affects Patient Results
- Holistic Nursing: Unifying the Body, Mind, and Spirit in Medical Practice
Top Engineering Informative Essay Topics
Some of the top engineering informational essay topics for grabbing goods are:
- Sustainable Engineering: Innovative Approaches for a More Eco-Friendly Future
- Informational Essay on AI: Function in Engineering Automation and Design
- Technological Developments and Applications in Renewable Energy
- Constructing Disaster-Resilient Infrastructure for Planning and Reaction
- Ethical Engineering Informative Essay: Juggling Innovation and Accountability
- Aerospace Engineering: Extending the Limits of Air Travel
- Biomedical Engineering: Using Technology to Revolutionize Healthcare
- Smart Cities: Engineering Answers to Urban Challenges
- The Future of Transportation: Hyperloop Technology to Electric Vehicles
- Nanotechnology: Small-Scale Engineering Solutions with Large Effects
A Short Informative Essay Sample
Besides, the informative essay examples, you can get better insights into how to start an informative essay by understanding this informative essay sample. It is!
Recycling: Why is it Important?
Introduction: Recycling supports the preservation of the environment by cutting the production of waste and saving resources.
Body: To analyse this informative essay sample, you should understand certain benefits of the recycling process. And they are!
- Environment Impact: Recycling helps with energy efficiency, decreases pollution, and ecosystem restoration.
- Protection of Resources: Humans may reduce the demand for essential supplies and reduce the strain on natural resources by recycling products like paper, glass, and plastic.
- Financial Gains: Recycling minimizes the costs of trash disposal, improves economic growth, and provides employment.
Summary: So, recycling is an essential process that helps the economy, the planet, and society at large. Generations to come may have a more sustainable and healthy future if recycling is embraced.
To sum up, it is like from how to start an innovative essay to proofreading, things will be very hard for you to handle. However, a regular writing routine will help you get the necessary resources to become a skilled good profile essay writer. It starts by outlining the definition and salient features of an informative essay format. The guide then describes an organized approach to writing about different informative essay topic ideas is certainly hectic. Thus, this includes topic selection, outline design, interesting introduction development, informative body paragraph development, and strong conclusion creation. So turn to innovative essay writers experts at The university Helpline!
Looking For a Clue to Start? We Are There to Guide You
Yes, it must be at times, daunting to start writing an informative essay, but do not worry! We, the professional writers of The Students Helpline are here to give you a well-defined path. While picking a topic that interests you and is relevant to your mentors to start. So, after gathering trustworthy information through extensive research, arrange your ideas into an informative essay format. Once you have a strong base in place, write your introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion, making sure that each piece flows naturally into the next. Recall that balance and clarity are essential in writing an informational essay. So, just have faith in the process, and express in your writing your passion and enthusiasm for the subject.
Why Is It Important to Learn Informative Essay Writing?
Stop thinking that what is the main purpose of writing an informative essay. Its main objective is to write an informative essay has only the primary goal of informing the reader about a certain subject. It does not include the writer's viewpoints or arguments in favour of offering information that is truthful, clear, and fully researched.
How to Start With an Informative Essay? Tell the Pointers.
So to begin writing an informative essay, you need to keep in mind the following pointers!
- Start with a riveting innovative essay hook to draw the reader in.
- Give background details to your informational essay so that the topic has meaning.
- Clearly describe the goals of informational essay writing in your thesis statement.
What Is the First Step in Writing an Informative Essay?
Stoop thinking about what is the first step in writing an informative essay, rather than getting back to research. Finding a focused and interesting topic is the first stage in creating an informative essay. So, you have to look for a topic that fascinates you and about which there is a wealth of study to guarantee that you can give your audience thorough information.
How to Write a Conclusion for an Informative Essay?
Do you have no idea how to write a conclusion of an informative essay? Then, your informational essay should end with an overview of the main ideas, an update of the thesis, and a closing statement or call to action. Take care to provide impact and clarity in a few succinct lines.
Can We Add Visuals to the Informative Essays?
Yes, you can definitely add visuals to your informative essays. Since by adding visuals like diagrams, charts, tables and images can make your informative essay structure more impactful. This helps readers with visual interest, aces written content and simplifies difficult concepts for better understanding and retention.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Mathematics
- Engineering
- Programming
- Agriculture
- Dissertation
- Writing Skills
Recent Posts

You may also like
Acknowledgement For Dissertation

Most Interesting And Pivotal Dissertation Topics For Law Students

Why Do Students Fail In Their Dissertation Writing

Writing An Abstract For A Dissertation

How To Write Your Findings In A Dissertation
How to Introduce Yourself in an Email (With Examples!)
Learn all the most important tricks and tools to introduce yourself in an email so the recipient gets back to you.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
The average professional spends over two hours a day 1 https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/technology-media-and-telecommunications/our-insights/the-social-economy responding to emails. If you are introducing yourself to someone in an email, there is a reasonable chance they won’t open it or will delete it before responding. But if you take the proper steps, you can significantly increase your likelihood of getting a response.
In this article, we’ll go over how to write a masterful introduction email that can help the relationship start on a positive note.
What Is a Self-Introduction Email?
A self-introduction email is a way to meet someone virtually. Think of it as the email version of shaking someone’s hand and telling them a few sentences about yourself. Often, people send self-introduction emails when they want to ask for something—to apply for a job, offer a service, get feedback, etc. Here is a template of a typical self-introduction email:
Subject: Pleasure to meet you!
It’s so great to meet you virtually. My name is ___. I specialize in / My role is ___.
I want to reach out because ___.
My goal is for us to grab coffee / hop on zoom / connect on LinkedIn.
Next step is ___.
[Your name]
Depending on the person you’re “meeting,” you would probably mention different details. For example, if you’re meeting a new team member, you might tell them a bit about your role and how long you’ve been at the Company, whereas if you are meeting a potential client, you might focus on the product you represent and how you believe it could benefit them.
Just like an in-person meeting, keep the introduction short and to the point. You don’t need to say everything in the first minute—more details can emerge as the conversation progresses.
Watch our video below to learn 7 tips for better emails:
Here is a quick 9-step guide for introducing yourself in an email.
- Seek to build a connection; don’t just ask for something
- Make the subject line clear
- Set the tone with a friendly email greeting
- Open with a genuine compliment
- Be clear and upfront about what you want
- Share something valuable
- Give a (non-pushy) call to action
- End with a pleasant signoff
- Always proofread the email
Now, let’s dive into each tip with more detail and go over some example scripts.
10 Tips for Writing a Great Introduction Email
Introducing yourself can be stressful, no matter the context. One nice aspect of doing it via email is that you can take the time to reread and edit as much as needed to make sure it sounds exactly how you envision it.
Use it to demonstrate your competence and charisma (yes, you can show appeal via email!) even if you feel like Anne Hathaway when she first walks into the office in The Devil Wears Prada .
#1 Build a connection; don’t just ask for something
This is a mindset to write from. The rest of the tips are more practical, but if you approach the email as trying to create a connection with a new person, it’s more likely to feel good to both of you and to bear mutual fruit in the future.
I’ve received plenty of emails from people who pasted my name into a pre-written template. When I get emails like this, they feel insincere and unprofessional. Like the other person just wants something from me.
Don’t write emails like that! Come from a place of connection.
A generic email to avoid might be:
“Hi, Mike! I came across your website and thought you had some great content. Do you think I might be able to write a guest post?”
A more personal email might look like:
“ Hi, Mike! I just finished your article on the meaning of love, and I was thoroughly impressed! Especially when you went into the Greek ideas about love—that gave me a lot to think about. I actually enjoy writing about similar topics, and I was wondering if you accept guest posts on your site?”
With that said, let’s get into some more specific tips.
#2 Make the subject a specific one
Only 21.5% of all emails 2 https://www.campaignmonitor.com/resources/guides/email-marketing-benchmarks/ get opened. So, a good subject line is crucial!
The subject of your email should give the email recipient a good idea of what to expect when they read your email. It should also be relatively concise. People read over 40% of emails 3 https://www.litmus.com/blog/email-client-market-share-august-2021/ on mobile devices, and it’ll help the reader if they can see the entire email subject line.
Here are a few different subject lines you can use for an introduction email:
- [Your name]: Letter of Introduction
- Hello from [your name] at [company name]
- Greetings from an English 201 Student
- Introducing: [Person one] to [Person two]
- Confirming the Time and Location of our Interview
Pro Tip: If you’re having difficulty writing a compelling subject line, wait until the very end. Write the body of the email first, read through it, and think about what the core idea of your email is.
And there you have it—your email subject!
#3 Set the tone with your email greeting
The first sentence sets the tone of your email correspondence. For an introduction email, it’s best to err on being more formal. This is one way to show respect and create an excellent first impression. If you can, try to add a small positive word. This kicks off the email with some optimism.
Here are some email greetings you can use:
- A pleasure to meet you, [name],
- Good morning/afternoon/evening,
- I hope this email finds you well,
- Happy Monday, [name]
- [Mutual connection’s name] gave me your contact info and recommended I reach out.
#4 Open with genuine compliments
While you’ll want to cut to the chase as soon as possible (which we’ll get to in the next tip), it can be helpful to open with a genuine appreciation for the other person’s work.
Maybe you resonated with a blog post they wrote or have long admired their marketing campaigns.
Starting with a personal touch can build trust and rapport from the get-go. If done well, the recipient will feel more open to the rest of your email.
But be careful because if you send a generic or insincere compliment, then you might come off as sleazy, and this can cause the recipient to put the guard up.
Here are a few examples of a genuine compliment that works:
Dear Steve,
First, I want to express gratitude. I took your online course Amplify last year, and it completely rewired how I think about creativity and productivity. I’ve recommended it to several friends.
Here’s another:
Dear Tanya,
I LOVED your recent webinar on negotiation. I legitimately had 5 or 6 lightbulb moments. So, I wanted to thank you for the work you’re putting out into the world and attest to your positive impact.
Pro Tip: If you already know this person’s work, share a specific way how it has impacted you.
If you don’t yet know their work, take some time to research them online before sending your email, and then give a compliment that is specific and genuine enough to show that you’ve actually taken in what they’ve put out.
#5 Be clear and upfront about what you want
Take inspiration from the BLUF method (Bottom Line Up Front), which is how military personnel communicate.
Very few people will thoroughly read a 2,000-word introduction email. In the best-case scenario, they might skim over it, but depending on how busy they are, they might not even have the time to do that. Writing a concise email demonstrates your respect for their time.
Try to keep the email to two or three paragraphs max. And clearly state the purpose of the email as soon as possible. In some cases, this will be right after you say hello, and in other cases, you might want to build rapport with a sentence or two first.
Here are some non-BLUF method communication practices and how you can transform them to make the communication stronger.
Don’t: “Hi Dan, I have a quick question. Do you have a minute?”
Don’t: “Hi Dan, could you send me the research you quoted in the meeting today?”
Do: “Hi Dan, I was wondering if you would be willing to share the research on ABC you cited in the meeting today. I think it will be helpful to me with a project on XYZ that I’m working on.
Why did that help? In the first instance, you’re creating extra work for you and the recipient by necessitating additional communication. There is no way for Dan to know if your question is quick or if you’ll end up calling him for 30 minutes.
The second option is better, but still not great. Dan doesn’t know why you’re asking for the research, so he might get confused and send you the wrong files.
The third option is the strongest. Notice how it starts with the request followed by some context, all while staying short and sweet!
Don’t: “Hi Anne, Jaimie and I were talking about you earlier today and were wondering if you would consider helping with a bake sale we are planning for next week. The proceeds would go to help refugees.”
Do: “Hi Anne, Would you like to participate in a bake sale next Saturday from 3-5 pm? All proceeds go towards helping refugee families acclimate to the US. If you’re willing, we could use a few gluten-free desserts.”
Why did that help? Notice how, in the first instance, Anne wouldn’t know what you’re talking about until the end of the message—the fact that you and Jaimie were talking about her is pretty irrelevant to the end goal of the correspondence.
The second message gives her all the information she will need—the date, time, and type of baked goods you want her to bring. She would be able to respond to that message with a definitive yes or no response.
#6 Share value
If you can do so in a way that doesn’t feel forced, consider sending something valuable to the recipient.
There are a few good reasons to do so.
- To support the other person. Being generous is always a good idea. If you are able to share something that could benefit another person (whether in this email or any email!), then why not?
- The reciprocity principle 4 https://news.wpcarey.asu.edu/20061206-gentle-science-persuasion-part-two-reciprocity . This is a psychological observation that states that when we receive something from another person (even if we don’t want the thing they give us), we feel compelled to give something back to them.
- It shows you to be generous. Offering something valuable in a cold email demonstrates that the interaction isn’t just one-sided. It shows that you’re not only seeking help but also willing to provide something in return.
- Differentiates your email. A cold email that offers something valuable stands out in a crowded inbox. It shows that you’ve done your homework and are genuinely interested in creating a meaningful connection, not just asking for a favor.
So, with that said, here are a couple of things you could consider sending:
- Industry insights: Share a recent study, article, or trend report that is relevant to the recipient’s industry or field of interest. Make sure it’s something they might not have come across yet.
- Helpful tools: If you know of a tool, app, or resource that could benefit their work, mention it. But don’t send something they’ve probably already heard of.
- Offer an introduction: If there’s a contact you have where you think both parties could benefit from knowing each other, consider trying to connect the two people (if your other contact has already agreed, of course)
- Rate their book on Amazon: You could try something like, “By the way, I loved your book and was happy to give it the 5-star Amazon review it deserved.”
If you send them something valuable in your email, do so with no strings attached.
If you choose to send something their way, make sure it feels like a natural part of the conversation, not a forced insertion. You don’t want it to feel like you’re offering a trade and that you’ll only do something nice if they fulfill your request first.
Make sure that you’re willing to provide value to them whether or not they give you anything in return.
#7 Give a (non-pushy) call to action
Finishing your email with a clear call to action ( CTA ) can help guide the recipient towards your desired response.
The clearer you are on what you want in a response, the more likely you are to get it! Without a CTA, your email might be well-received but may not lead to action.
A good CTA is specific and easy to follow. It could be as simple as requesting a brief reply, scheduling a call, or asking for feedback on a specific question.
But make sure not to be pushy with your CTA! You don’t want to come off as demanding or entitled.
Pro Tip: Try to frame your CTA as a suggestion or invitation rather than a demand. Use phrases like:
- “I’d appreciate your thoughts on…”
- “Would you be open to…”
- “I’d be honored if…”
#8 End with a memorable signoff
While the email greeting sets the tone of the conversation, the signoff determines the final tone you leave the email recipient with.
“A race isn’t won until it’s over.” —Niki Lauda
So don’t write a great letter and let it flop at the last moment!
Try a professional closing from the list below in your email:
- Thank you,
Sincerely,
- Kind regards,
- Have a great rest of your week,
With gratitude,
- Best regards,
- Let me know if you have any further questions about [topic discussed in the email],
- Enjoy the snowy weekend!
For more professional introduction emails, add your contact information, LinkedIn link, and job title at the end of the email.
Here’s a template you can use to create a comprehensive email signature:
[Email sign-off],
[Your full name]
[Job title], [Company name]
[Phone number]
[LinkedIn link]
[Personal portfolio website—if relevant]
#9 Proofread before you send!
Before you hit send, always take a moment to reread and spell-check what you’ve written. We all make mistakes! By reading through the email one more time, you can fix any typos or other errors.
Sending an email with typos, grammatical errors, or (possibly worst of all) a misspelled name can hurt your credibility or offend the email recipient.
Pro Tip: Read your email out loud. This can help you notice little errors that might slip by if you’re just reading it in your head. If you’re more tech-savvy, you can download a grammar checker like Grammarly to correct your errors in real-time.
Bonus Pro Tip: If the email doesn’t need to go out immediately, wait an hour or two after writing it to read through it again. Sometimes, fresh eyes can help you notice little mistakes that would otherwise slip past.
#10 If you don’t succeed at first, try again!
If all you got back from your email were crickets, don’t be afraid to follow up!
After all, most corporate employees receive over 120 emails per day 1 https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/technology-media-and-telecommunications/our-insights/the-social-economy . So it’s possible that you simply got lost in the sauce.
A follow-up serves as a gentle reminder and increases the likelihood that your email will get read and responded to.
And if they did read your first email but weren’t impressed, your follow-up could show both persistence and give you another chance to make your case.
If you’re going to send a follow-up, wait a minimum of one week. And consider more time if you’re intersecting the holidays.
To write a follow-up email, consider these tips:
- Politely reference your first email: “Last week I mentioned…”
- Include a new piece of information that wasn’t in the first email
- Share your call to action again.
- Close on a positive, non-pushy note like: “hoping to connect soon” or “keeping the door open for future communication.”
Bonus #11 Professional development
Sending a good introduction email is a key skill in your professional toolbelt. And if you want to cultivate more skills and advance your career, you might appreciate this free training to help boost your professional development.
Ready to start planning your professional development?
Use our free worksheet to get started on your Professional Development Plan.
Scripts, Templates, and Examples of How to Introduce Yourself by Email for Any Situation
There can be so many different types of introduction emails. Here’s a range of settings you might find yourself in, with some tips and email templates for each!
How to pitch your service
One of the most common introduction emails is if you are reaching out to a potential client to offer them your service or product.
Try to work this template around your specific needs.
Subject: A crazy idea for [Company]
First, I want to tell you that I’ve been a fan of your personal brand for years. Your recent newsletter on growth tactics gave me a real ah-ha, so thank you 🙂
I’m working on an email productivity app that can save you 2.3 hours a week (that’s what we’ve found from our clients).
If you’d like to hear more, let me know, and I’d love to set up a time to share more.
PS I was thinking a lot about [Company] recently and thought you might be interested in this tech development I just came across.
This email works because it creates a personal connection and gives a compliment to start. It then goes right into the ask with a CTA. And it closes with a value offer.
How to introduce yourself in an email for a job
Sending an introduction email to the hiring manager or recruiter for a job that you’re interested in can help you give an excellent first impression.
If you have a mutual connection who told you about the job posting, mention that to the hiring manager. This can help you get your foot in the door.
Here’s a template you can use to introduce yourself with a referral:
Subject: [Michael Smith], a referral from [Margie Sullivan]
Good morning, Annette,
I hope your week is going well.
I am a recent graduate from [UCLA] with a degree in [business marketing]. I was speaking with my friend, [Maggie], who works in the [IT department] at [this Company]. She told me you might be looking for a few new team members to join the [marketing department].
She recommended that I reach out to you to learn more specifics about the position to see if I’m a good fit for it.
Thank you for your time. I appreciate any insight and direction you can offer me.
It’s common to send a job application without a mutual acquaintance—that’s okay!
You can still make a great first impression by sending a quick introductory email to either the head of the department or the hiring manager.
It’s typically best to address the email to a specific individual, but sometimes it’s hard to find that information.
If you don’t know who will be handling the interview process, try checking LinkedIn. If you can’t find the information there, try using one of the following formal email greetings that don’t require a name:
Greetings,
- Hello,
- Good morning/afternoon/evening
Here’s a template you can use to introduce yourself for a potential job if you don’t have a shared contact:
Subject: Introduction from [Caroline Oliveros], [Creative Director Applicant]
I hope this email finds you well.
I just completed my application for the [Creative Director] position you are looking to fill at [company name]. I believe my past work experience has prepared me well for this position, and I would be honored if you consider me for it. Although I already submitted it in the application process, I am attaching a copy of my resume to this email as well.
This position would be an excellent fit for me because I love working in teams, have strong time-management skills, and have experience using all relevant software. I enjoy the products you all create and would love to work alongside you.
Thank you for your time, and please let me know of any next steps in this process.
How to introduce yourself in an email to clients
When you’re introducing yourself to a new client, they likely fall into one of three categories:
- Someone who has already been working with your Company but is working with you for the first time
- Someone who has reached out to your Company
- Someone you are cold emailing in hopes of working with them
Let’s say your coworker is retiring, and as a result, they will pass some of their clients to you. That’s awesome! In this instance, you’ll be introducing yourself to a client who has already been working with your Company for some time but is working with you for the first time.
You want to start this new client relationship off on a good foot.
Think about how they may be feeling. They could be feeling:
- Nervous
- Disoriented
- Or otherwise!
Use the introduction email to put their nerves at ease. Tell them a little about you, mention your retiring coworker, and let them know that you’ve been briefed on their file and look forward to working with them.
Here’s an example of what that could look like:
Subject: [Janice], your new point person at [company name]
Dear [Javier],
We haven’t had the privilege of meeting yet, but I’m one of [Ryan’s] coworkers. My name is [Janice], and I will be the new point person working with you now that [Ryan] is retiring.
I have been working with [company name] for three years now, and throughout that time, I have helped out on several projects for your Company. We have a very collaborative office environment, which helps us serve our clients to the best of our ability.
I have just finished reading through your file and think it would be nice if we could arrange a time to chat on the phone so that I can answer any questions you may have about this transition.
I look forward to working together.
In the second instance, when you’re introducing yourself to someone who has reached out to your Company, you have the benefit that you don’t need to convince them that they need your service or product.
Use your email to show them why you’re the person they want to work with. After all, they may have also reached out to your competitor!
Subject: [Billie], responding to [SEO] request
Dear [Annalise],
I’m writing in response to your request about [optimizing your website for SEO]. You’re right—optimizing your website can make a huge difference and help to increase sales.
I’ve had over [five years] of experience in this space and have optimized around [100 websites]. I am proud to say that my clients are happy with the work I provide for them. I am attaching a link to my portfolio to look at some of the fantastic businesses I’ve had the privilege to work with.
If you’re interested in discussing what working together could look like, I’d be happy to arrange a call sometime later this week. Let me know what works for you.
Warm regards,
When sending a cold email introduction to a prospective client, try to tailor the email specifically to them!
Remember that this will be a professional introduction email, so lean towards more formal language. Also, where relevant, include industry-specific jargon to demonstrate that you know what you’re talking about.
Subject: [Adam] from [Company name]
Hello [Lyzette],
I am writing to you to discuss the possibility of working together.
I work as part of a [data analyst] organization that takes pride in seeing our clients’ businesses grow as they reach more of their ideal clients. I’m attaching a link to my portfolio to see some of the fantastic people I’ve had the privilege to work with.
I love what you at [their Company] are doing with [product/service they provide] to help people better [specific aspect of their product].
I hope to hear from you soon.
Best,
Pro Tip: You may not know much about someone’s product or service before you begin working with them. It’s still good to name something specific that you notice about their work—it helps the reader know that you took the time to personalize the email.
Go to the Company’s “About” page and read up on its mission and vision. This should give you an idea of the heart of their Company and will help you know what to say.
How to introduce yourself in an email to a professor
Before you send your professor an email, take a moment to look them up in the school directory or through LinkedIn and see if they have their doctorate or not. If they do, address the email to “Dr. [last name];” if not, stick with “Professor [last name].”
Earning a doctorate takes a lot of time, effort, and investment. It’s good to start the email off by acknowledging their expertise!
Let’s say you’ll be taking their Anatomy 101 class that starts in a few weeks, and you want to check in and introduce yourself.
Here’s one way that you can go about that:
Subject: Greetings from a new student
Hello, [Dr. Howard],
I have enrolled in the [Anatomy 101] class that you will be teaching [this fall] and wanted to take a moment to introduce myself. I took a [Anatomy] class in high school that helped me see how interesting the human body is. I am currently deciding whether I should major in [Pre-Med] or [Kinesiology]—I love [the idea of being able to help people who are sick or injured].
I am looking forward to learning from you this term. Is there any reading you recommend I do before class begins in a few weeks?
Thank you for your time.
All the best,
[Anne]
How to introduce yourself in an email to a new team
Woohoo—you landed a new job!
How should you present yourself to the team you’re working with?
Depending on the industry, this can be slightly less formal than other introductory emails. But you can keep things professional by leaving out conjunctions and slang terms.
Also, include a few fun facts about yourself. That way, when you meet your teammates, they’ll know what conversations to strike up with you.
Here’s a template you can use for emailing your new team:
Subject: Excited to be joining the team
Hello all,
My name is [Luca]. I am very excited to work with a team of hard-working and creative people! I look forward to getting to know each of you better over the coming weeks.
When I am not at work, I love [spending time with my family (wife and two kids)], [going for runs], and [traveling to new corners of the world]. I am currently [working on Spanish and am hoping to visit Guatemala in the next year to see some of my wife’s family].
I am looking forward to meeting you in person on Monday.
Have a great weekend,
Final Takeaways
Introducing yourself by email can be a great way to start a new professional relationship. Whether you’re writing to a hiring manager, a professor, a new team, or a prospective client, sending a friendly and professional email can be a great way to start the relationship off on a positive note.
Here are a few things to remember:
- Build a connection, don’t just ask for something: Approaching your email with the intent to create a connection, rather than just asking for something, increases the likelihood of a mutually beneficial relationship.
- Make the subject line clear: This will make it easier for the recipient to know what to expect when they open your email. It can also help them reference back to your email in their inbox later.
- Set the tone with a friendly email greeting: The first line of an email will set the tone for how the reader “hears” the rest of the message.
- Open with genuine compliments: Starting your email with a sincere compliment can build trust and rapport, making the recipient more receptive to your message.
- Be clear and upfront about what you want: Using a direct approach like the BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front) method shows respect for the recipient’s time and makes your intentions clear.
- Share value: Offering something of value in your email, like industry insights or helpful tools, can demonstrate generosity and set your email apart.
- Give a (non-pushy) call to action: A clear, specific, and respectful call to action guides the recipient toward your desired response without coming off as demanding.
- End with a pleasant signoff: Leave your reader with a pleasant well-wish at the end of the email.
- Always proofread the email: Before you hit “send,” make sure you don’t have any spelling or grammatical errors and are saying what you want to say in the email. Double-check that you’ve spelled the recipient’s name and company name correctly.
- Consider reading it out loud or waiting and rereading it after an hour or two has passed. This can help you catch any mistakes that you might otherwise skim over.
Writing an introduction email can be stressful, but you’ve got this!
Are you looking to up your communication skills (and not just by email)? Check out these Communication Skills Training Tips .
Article sources
Popular guides, how to deal with difficult people at work.
Do you have a difficult boss? Colleague? Client? Learn how to transform your difficult relationship. I’ll show you my science-based approach to building a strong, productive relationship with even the most difficult people.
Related Articles
Science of People offers over 1000+ articles on people skills and nonverbal behavior.
Get our latest insights and advice delivered to your inbox.
It’s a privilege to be in your inbox. We promise only to send the good stuff.
Docker overview
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly. With Docker, you can manage your infrastructure in the same ways you manage your applications. By taking advantage of Docker's methodologies for shipping, testing, and deploying code, you can significantly reduce the delay between writing code and running it in production.
The Docker platform
Docker provides the ability to package and run an application in a loosely isolated environment called a container. The isolation and security lets you run many containers simultaneously on a given host. Containers are lightweight and contain everything needed to run the application, so you don't need to rely on what's installed on the host. You can share containers while you work, and be sure that everyone you share with gets the same container that works in the same way.
Docker provides tooling and a platform to manage the lifecycle of your containers:
- Develop your application and its supporting components using containers.
- The container becomes the unit for distributing and testing your application.
- When you're ready, deploy your application into your production environment, as a container or an orchestrated service. This works the same whether your production environment is a local data center, a cloud provider, or a hybrid of the two.
What can I use Docker for?
Fast, consistent delivery of your applications.
Docker streamlines the development lifecycle by allowing developers to work in standardized environments using local containers which provide your applications and services. Containers are great for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) workflows.
Consider the following example scenario:
- Your developers write code locally and share their work with their colleagues using Docker containers.
- They use Docker to push their applications into a test environment and run automated and manual tests.
- When developers find bugs, they can fix them in the development environment and redeploy them to the test environment for testing and validation.
- When testing is complete, getting the fix to the customer is as simple as pushing the updated image to the production environment.
Responsive deployment and scaling
Docker's container-based platform allows for highly portable workloads. Docker containers can run on a developer's local laptop, on physical or virtual machines in a data center, on cloud providers, or in a mixture of environments.
Docker's portability and lightweight nature also make it easy to dynamically manage workloads, scaling up or tearing down applications and services as business needs dictate, in near real time.
Running more workloads on the same hardware
Docker is lightweight and fast. It provides a viable, cost-effective alternative to hypervisor-based virtual machines, so you can use more of your server capacity to achieve your business goals. Docker is perfect for high density environments and for small and medium deployments where you need to do more with fewer resources.
Docker architecture
Docker uses a client-server architecture. The Docker client talks to the Docker daemon, which does the heavy lifting of building, running, and distributing your Docker containers. The Docker client and daemon can run on the same system, or you can connect a Docker client to a remote Docker daemon. The Docker client and daemon communicate using a REST API, over UNIX sockets or a network interface. Another Docker client is Docker Compose, that lets you work with applications consisting of a set of containers.
The Docker daemon
The Docker daemon ( dockerd ) listens for Docker API requests and manages Docker objects such as images, containers, networks, and volumes. A daemon can also communicate with other daemons to manage Docker services.
The Docker client
The Docker client ( docker ) is the primary way that many Docker users interact with Docker. When you use commands such as docker run , the client sends these commands to dockerd , which carries them out. The docker command uses the Docker API. The Docker client can communicate with more than one daemon.
Docker Desktop
Docker Desktop is an easy-to-install application for your Mac, Windows or Linux environment that enables you to build and share containerized applications and microservices. Docker Desktop includes the Docker daemon ( dockerd ), the Docker client ( docker ), Docker Compose, Docker Content Trust, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper. For more information, see Docker Desktop .
Docker registries
A Docker registry stores Docker images. Docker Hub is a public registry that anyone can use, and Docker looks for images on Docker Hub by default. You can even run your own private registry.
When you use the docker pull or docker run commands, Docker pulls the required images from your configured registry. When you use the docker push command, Docker pushes your image to your configured registry.
Docker objects
When you use Docker, you are creating and using images, containers, networks, volumes, plugins, and other objects. This section is a brief overview of some of those objects.
An image is a read-only template with instructions for creating a Docker container. Often, an image is based on another image, with some additional customization. For example, you may build an image which is based on the ubuntu image, but installs the Apache web server and your application, as well as the configuration details needed to make your application run.
You might create your own images or you might only use those created by others and published in a registry. To build your own image, you create a Dockerfile with a simple syntax for defining the steps needed to create the image and run it. Each instruction in a Dockerfile creates a layer in the image. When you change the Dockerfile and rebuild the image, only those layers which have changed are rebuilt. This is part of what makes images so lightweight, small, and fast, when compared to other virtualization technologies.
A container is a runnable instance of an image. You can create, start, stop, move, or delete a container using the Docker API or CLI. You can connect a container to one or more networks, attach storage to it, or even create a new image based on its current state.
By default, a container is relatively well isolated from other containers and its host machine. You can control how isolated a container's network, storage, or other underlying subsystems are from other containers or from the host machine.
A container is defined by its image as well as any configuration options you provide to it when you create or start it. When a container is removed, any changes to its state that aren't stored in persistent storage disappear.
Example docker run command
The following command runs an ubuntu container, attaches interactively to your local command-line session, and runs /bin/bash .
When you run this command, the following happens (assuming you are using the default registry configuration):
If you don't have the ubuntu image locally, Docker pulls it from your configured registry, as though you had run docker pull ubuntu manually.
Docker creates a new container, as though you had run a docker container create command manually.
Docker allocates a read-write filesystem to the container, as its final layer. This allows a running container to create or modify files and directories in its local filesystem.
Docker creates a network interface to connect the container to the default network, since you didn't specify any networking options. This includes assigning an IP address to the container. By default, containers can connect to external networks using the host machine's network connection.
Docker starts the container and executes /bin/bash . Because the container is running interactively and attached to your terminal (due to the -i and -t flags), you can provide input using your keyboard while Docker logs the output to your terminal.
When you run exit to terminate the /bin/bash command, the container stops but isn't removed. You can start it again or remove it.
The underlying technology
Docker is written in the Go programming language and takes advantage of several features of the Linux kernel to deliver its functionality. Docker uses a technology called namespaces to provide the isolated workspace called the container. When you run a container, Docker creates a set of namespaces for that container.
These namespaces provide a layer of isolation. Each aspect of a container runs in a separate namespace and its access is limited to that namespace.
- Install Docker
- Get started with Docker

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When you are stuck with how to start a writing assignment, writing an introduction can solve most of your problems. Different types of assignments have different types of introductory paragraphs. The student introduction assignment example mentioned above is suitable for an essay. Now, we will see an example of an assignment introduction for a ...
Here are the key takeaways for how to write essay introduction: 3. Hook the Reader: Start with an engaging hook to grab the reader's attention. This could be a compelling question, a surprising fact, a relevant quote, or an anecdote. Provide Background: Give a brief overview of the topic, setting the context and stage for the discussion.
Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
A brief discussion of the context. Identification of the key issue and research question (s). A brief outline of your theoretical approach. A brief outline of your fieldwork and your professional position. In this post, I'll outline the 5 key components of a strong introduction chapter/section in a mark-earning Henley MBA assignment.
Some people find it easiest to write the introduction first, whereas others leave it until the end. Neither approach is right or wrong, so write the assignment in whichever order feels best for you. The introduction might be up to around 10% of the word count (e.g. up to 200 words for a 2000 word assignment). Don't forget your conclusion
Tips for writing introductions • If you are writing in a new discipline, you should always make sure to ask about conventions and expectations for introductions, just as you would for any other aspect of the essay. For example, while it may be acceptable to write a two-paragraph (or longer) introduction for your papers in some courses ...
1. The placeholder introduction. When you don't have much to say on a given topic, it is easy to create this kind of introduction. Essentially, this kind of weaker introduction contains several sentences that are vague and don't really say much. They exist just to take up the "introduction space" in your paper.
1. Background. The first thing you have to write in an introduction is a brief background of the study. You have to give an overview of your assignment, what your assignment is about, its impact, and its area of study. 2. Context in brief. You have to include a gist of the context of your assignment.
Intro Paragraph Part 3: The Thesis. The final key part of how to write an intro paragraph is the thesis statement. The thesis statement is the backbone of your introduction: it conveys your argument or point of view on your topic in a clear, concise, and compelling way. The thesis is usually the last sentence of your intro paragraph.
Good example. I wiped the sweat from my head and tried to catch my breath. I was nearly there—just one more back tuck and a strong dismount and I'd have nailed a perfect routine. Some students choose to write more broadly about themselves and use some sort of object or metaphor as the focus.
Essay writing: Introductions. "A relevant and coherent beginning is perhaps your best single guarantee that the essay as a whole will achieve its object.". Gordon Taylor, A Student's Writing Guide. Your introduction is the first thing your marker will read and should be approximately 10% of your word count. Within the first minute they ...
Category: Writing Date: 16 April, 2024. Every student wonders how to start an assignment introduction because this knowledge can keep them afloat through their endless years of school, college, and university. If you're here, you probably wonder that as well. Thankfully, there is nothing complicated about writing an introduction.
Smart Student FREE Resources https://www.mysmartstudent.com/tools-and-resourcesSMART WRITERS MASTERCLASS 💻https://www.mysmartstudent.com/registration-page-...
Offer a surprising fact or thought-provoking idea; Start with a question; Introduce a quotation; Tell a short story; Start with a broad summary. However, for an academic essay, do not try to come up with something too creative. For instance, a short story or an anecdote is not going to work for a serious topic.
Coming up with a great introduction for assignment, make sure that it: Highlights the importance of your subject. Provides a definition of the topic you discuss. Offers the reasoning why you approach your topic. Provides an overview of your methodology or scientific approach. Highlights the major points you would like to discuss.
Highlight the importance of the subject. The definition of the topic being discussed. The reason why you are writing on this topic. An overview of your approach on the topic. Highlight the points that you want to discuss in the assignment. State some previous works about the topic. State some limitations about the topic.
Avoid a lengthy, wordy, and complex statement of the thesis. 3. Avoid Explanation. Don't try to explain anything to make your argument in the introduction section. You should drop the information part to the principal body. Just mention the primary points of the argument you plan to make later in the assignment.
At a Glance. Writing a great introduction can be a great foundation for the rest of your psychology paper. To create a strong intro: Research your topic. Outline your paper. Introduce your topic. Summarize the previous research. Present your hypothesis or main argument.
This page features authentic sample assignments that you can view or download to help you develop and enhance your academic writing skills. PLEASE NOTE: Comments included in these sample written assignments are intended as an educational guide only. Always check with academic staff which referencing convention you should follow. All sample ...
1. Listen to other intros. Listen to intros that come before yours. If you can refer to someone else's point or two seamlessly in your intro, you'll impress people around. 2. Practice, but don't cram. People often go blank on some of the points or get nervous when they stand up to speak.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects.
There are many ways to take notes. It's helpful to try out different methods and determine which work best for you in different situations. Whether you are learning online or in person, the physical act of writing can help you remember better than just listening or reading.
Here we will help you write an introduction for a good assignment. Highlight the importance of the subject. Put down the definition of the topic that you will be discussing. Provide reasoning why ...
The body of the paper should also summarize the introduction and include any notes for the instructor. The last section of a case study introduction should summarize the findings and limitations of the study, as well as suggestions for further research. The conclusion section should restate the thesis and main findings of the case study.
Writing to educate the reader about a certain subject is known as an informative essay. Informative essays offer information, analysis, and justifications to help the reader understand the subject matter. The primary goal of assignment writing help such an essay is to inform or explain without influencing the content from the views of the writer.
Teacher's assistant cover letter sample To support your understanding of cover letters, here's a sample cover letter for a teacher's assistant: Marcus Ong Beng Chin Singapore (65) 9555 5555 [email protected] 4 March 2024 Mr. Robert Chan Wavewood School Dear Mr Chan, I am writing to express my interest in the available teacher's assistant position at your school, as highlighted in your ...
Write the body of the email first, read through it, and think about what the core idea of your email is. And there you have it—your email subject! #3 Set the tone with your email greeting. The first sentence sets the tone of your email correspondence. For an introduction email, it's best to err on being more formal.
When you run this command, the following happens (assuming you are using the default registry configuration): If you don't have the ubuntu image locally, Docker pulls it from your configured registry, as though you had run docker pull ubuntu manually.. Docker creates a new container, as though you had run a docker container create command manually.. Docker allocates a read-write filesystem to ...