

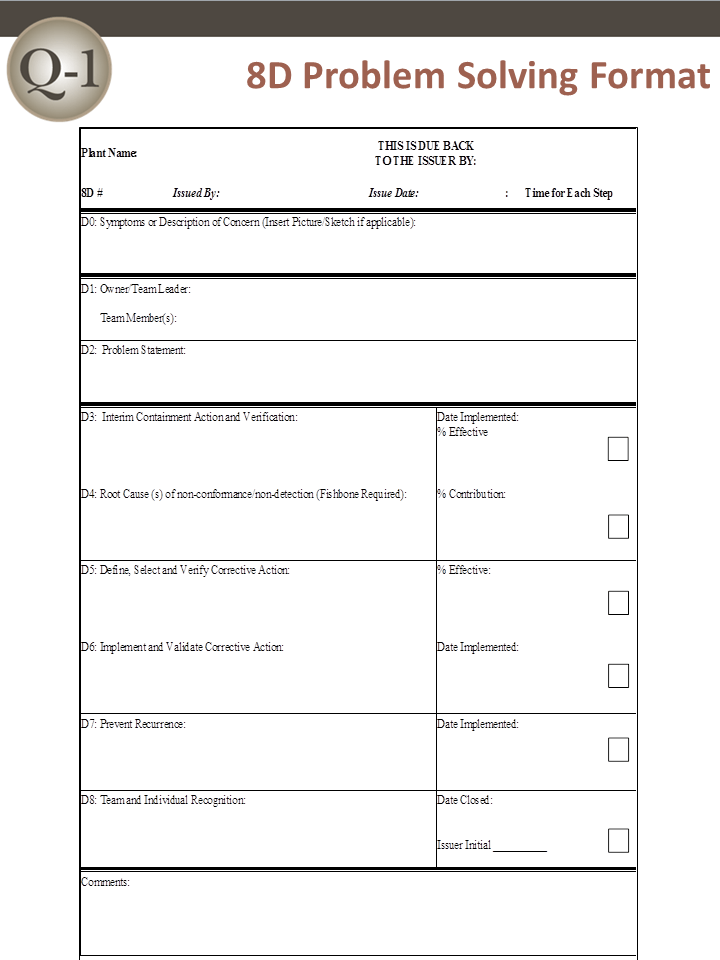
Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
– Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving –
⇓ Introduction to 8D
⇓ What is 8D
⇓ Why Apply 8D
⇓ When to Apply 8D
⇓ How to Apply 8D

Introduction to Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D) is a problem solving methodology designed to find the root cause of a problem, devise a short-term fix and implement a long-term solution to prevent recurring problems. When it’s clear that your product is defective or isn’t satisfying your customers, an 8D is an excellent first step to improving Quality and Reliability.
Ford Motor Company developed this problem solving methodology, then known as Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS), in the 1980s. The early usage of 8D proved so effective that it was adopted by Ford as the primary method of documenting problem solving efforts, and the company continues to use 8D today.
8D has become very popular among manufacturers because it is effective and reasonably easy to teach. Below you’ll find the benefits of an 8D, when it is appropriate to perform and how it is performed.
What is Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future.
The strength of the 8D process lies in its structure, discipline and methodology. 8D uses a composite methodology, utilizing best practices from various existing approaches. It is a problem solving method that drives systemic change, improving an entire process in order to avoid not only the problem at hand but also other issues that may stem from a systemic failure.
8D has grown to be one of the most popular problem solving methodologies used for Manufacturing, Assembly and Services around the globe. Read on to learn about the reasons why the Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving may be a good fit for your company.
Why Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D methodology is so popular in part because it offers your engineering team a consistent, easy-to-learn and thorough approach to solving whatever problems might arise at various stages in your production process. When properly applied, you can expect the following benefits:
- Improved team oriented problem solving skills rather than reliance on the individual
- Increased familiarity with a structure for problem solving
- Creation and expansion of a database of past failures and lessons learned to prevent problems in the future
- Better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools required for problem solving
- Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem solving
- A practical understanding of Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
- Problem solving effort may be adopted into the processes and methods of the organization
- Improved skills for implementing corrective action
- Better ability to identify necessary systemic changes and subsequent inputs for change
- More candid and open communication in problem solving discussion, increasing effectiveness
- An improvement in management’s understanding of problems and problem resolution
8D was created to represent the best practices in problem solving. When performed correctly, this methodology not only improves the Quality and Reliability of your products but also prepares your engineering team for future problems.
When to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D problem solving process is typically required when:
- Safety or Regulatory issues has been discovered
- Customer complaints are received
- Warranty Concerns have indicated greater-than-expected failure rates
- Internal rejects, waste, scrap, poor performance or test failures are present at unacceptable levels
How to Apply Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
The 8D process alternates inductive and deductive problem solving tools to relentlessly move forward toward a solution. The Quality-One approach uses a core team of three individuals for inductive activities with data driven tools and then a larger Subject Matter Expert (SME) group for the deductive activities through brainstorming, data-gathering and experimentation.
D0: Prepare and Plan for the 8D
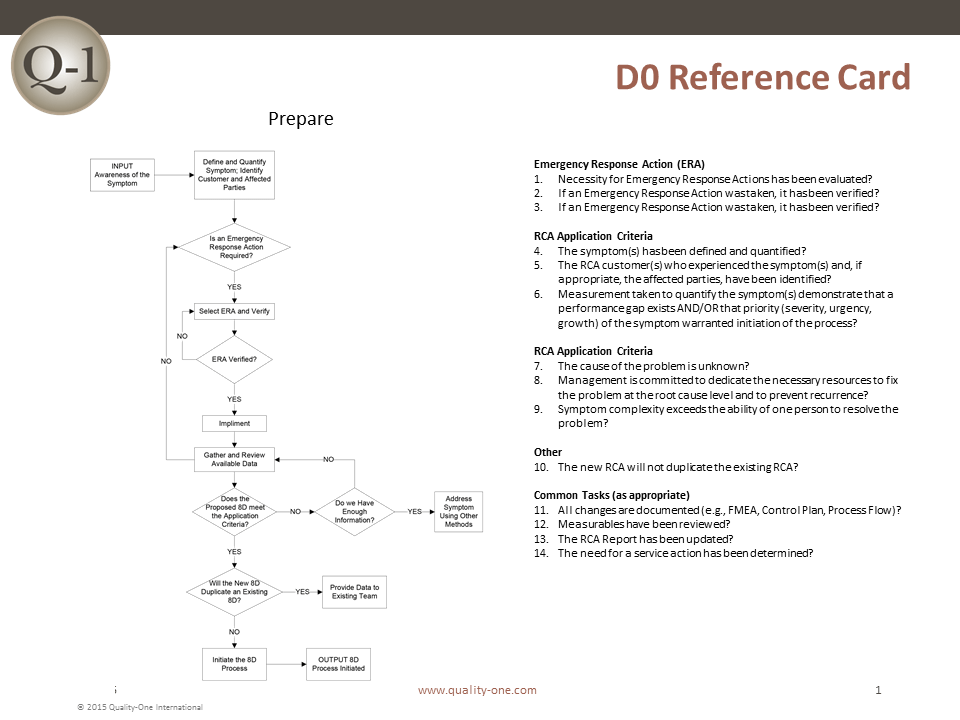
Proper planning will always translate to a better start. Thus, before 8D analysis begins, it is always a good idea to ask an expert first for their impressions. After receiving feedback, the following criterion should be applied prior to forming a team:
Collect information on the symptoms
Use a Symptoms Checklist to ask the correct questions
Identify the need for an Emergency Response Action (ERA), which protects the customer from further exposure to the undesired symptoms
D1: Form a Team
A Cross Functional Team (CFT) is made up of members from many disciplines. Quality-One takes this principle one step further by having two levels of CFT:
- The Core Team Structure should involve three people on the respective subjects: product, process and data
- Additional Subject Matter Experts are brought in at various times to assist with brainstorming, data collection and analysis
Teams require proper preparation. Setting the ground rules is paramount. Implementation of disciplines like checklists, forms and techniques will ensure steady progress. 8D must always have two key members: a Leader and a Champion / Sponsor:
- The Leader is the person who knows the 8D process and can lead the team through it (although not always the most knowledgeable about the problem being studied)
- The Champion or Sponsor is the one person who can affect change by agreeing with the findings and can provide final approval on such changes
D2: Describe the Problem
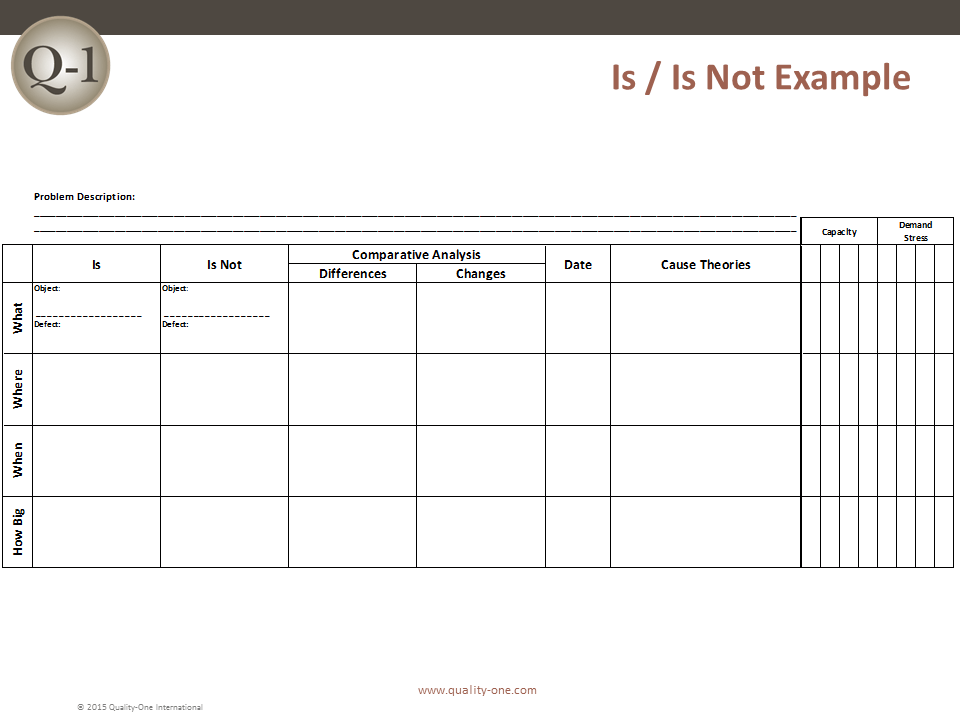
The 8D method’s initial focus is to properly describe the problem utilizing the known data and placing it into specific categories for future comparisons. The “Is” data supports the facts whereas the “Is Not” data does not. As the “Is Not” data is collected, many possible reasons for failure are able to be eliminated. This approach utilizes the following tools:
- Problem Statement
- Affinity Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Fishbone/Ishikawa Diagram (Deductive tool)
- Problem Description
D3: Interim Containment Action
In the interim, before the permanent corrective action has been determined, an action to protect the customer can be taken. The Interim Containment Action (ICA) is temporary and is typically removed after the Permanent Correct Action (PCA) is taken.
- Verification of effectiveness of the ICA is always recommended to prevent any additional customer dissatisfaction calls
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
The root cause must be identified to take permanent action to eliminate it. The root cause definition requires that it can be turned on or off, at will. Activities in D4 include:
- Comparative Analysis listing differences and changes between “Is” and “Is Not”
- Development of Root Cause Theories based on remaining items
- Verification of the Root Cause through data collection
- Review Process Flow Diagram for location of the root cause
- Determine Escape Point, which is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been found but was not
D5: Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)
The PCA is directed toward the root cause and removes / changes the conditions of the product or process that was responsible for the problem. Activities in D5 include:
- Establish the Acceptance Criteria which include Mandatory Requirements and Wants
- Perform a Risk Assessment / Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) on the PCA choices
- Based on risk assessment, make a balanced choice for PCA
- Select control-point improvement for the Escape Point
- Verification of Effectiveness for both the PCA and the Escape Point are required
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
To successfully implement a permanent change, proper planning is essential. A project plan should encompass: communication, steps to complete, measurement of success and lessons learned. Activities in D6 include:
- Develop Project Plan for Implementation
- Communicate the plan to all stakeholders
- Validation of improvements using measurement
D7: Prevent Recurrence
D7 affords the opportunity to preserve and share the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, locations or families. Updating documents and procedures / work instructions are expected at this step to improve future use. Activities in D7 include:
- Review Similar Products and Processes for problem prevention
- Develop / Update Procedures and Work Instructions for Systems Prevention
- Capture Standard Work / Practice and reuse
- Assure FMEA updates have been completed
- Assure Control Plans have been updated
D8: Closure and Team Celebration
Teams require feedback to allow for satisfactory closure. Recognizing both team and individual efforts and allowing the team to see the previous and new state solidifies the value of the 8D process. Activities in D8 include:
- Archive the 8D Documents for future reference
- Document Lessons Learned on how to make problem solving better
- Before and After Comparison of issue
- Celebrate Successful Completion
8D and Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
The 8D process has Root Cause Analysis (RCA) imbedded within it. All problem solving techniques include RCA within their structure. The steps and techniques within 8D which correspond to Root Cause Analysis are as follows:
- Problem Symptom is quantified and converted to “Object and Defect”
- Problem Symptom is converted to Problem Statement using Repeated Whys
- Possible and Potential Causes are collected using deductive tools (i.e. Fishbone or Affinity Diagram)
- Problem Statement is converted into Problem Description using Is / Is Not
- Problem Description reduces the number of items on the deductive tool (from step 3)
- Comparative Analysis between the Is and Is Not items (note changes and time)
- Root Cause theories are developed from remaining possible causes on deductive tool and coupled with changes from Is / Is Not
- Compare theories with current data and develop experiments for Root Cause Verification
- Test and confirm the Root Causes
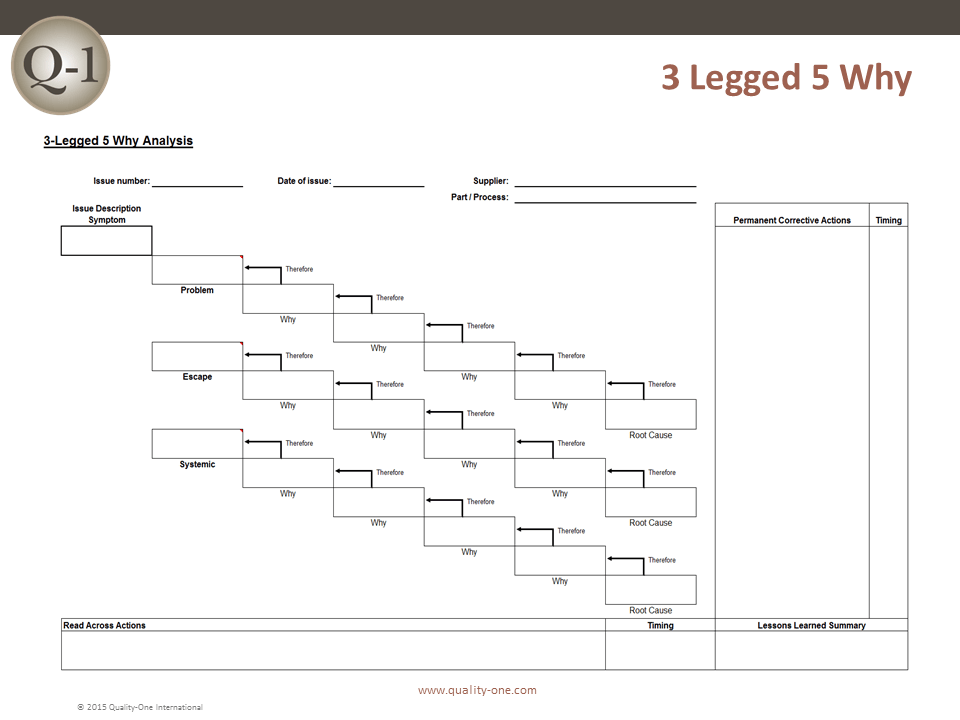
Example: Multiple Why Technique
The Multiple / Repeated Why (Similar to 5 Why) is an inductive tool, which means facts are required to proceed to a more detailed level. The steps required to determine problem statement are:
- Problem Symptom is defined as an Object and Defect i.e. “Passenger Injury”
- Why? In every case “SUV’s Roll Over”
- Why? In every case, it was preceded by a “Blown Tire”
- Why? Many explanations may be applied, therefore the team cannot continue with another repeated why past “Blown Tire”
- Therefore, the Problem Statement is “Blown Tire”
- Why? Low (Air) Pressure, Tire Defect (Degradation of an Interface) and High (Ambient) Temperature
- Counter measures assigned to low pressure and tire defect
This example uses only 4 of the 5 Whys to determine the root causes without going further into the systemic reasons that supported the failure. The Repeated Why is one way to depict this failure chain. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) could also be used.
Learn More About Eight Disciplines of Problem Solving (8D)
Quality-One offers Quality and Reliability Support for Product and Process Development through Consulting, Training and Project Support. Quality-One provides Knowledge, Guidance and Direction in Quality and Reliability activities, tailored to your unique wants, needs and desires. Let us help you Discover the Value of 8D Consulting , 8D Training or 8D Project Support .
Contact Us | Discover the Value!
(248) 280-4800 | [email protected]
Remember Me
- Don't have an account? Register
- Lost your password? Click here
- Already have an account? Log in
Lean Six Sigma Training Certification
- Facebook Instagram Twitter LinkedIn YouTube
- (877) 497-4462

8D Corrective Action: Mastering Problem-Solving for Continuous Improvement
May 13th, 2024
Businesses constantly refine products, services, and workflows to stay ahead. But issues can still pop up, angering customers and jacking costs while hurting a company’s image. This is where the 8D corrective action problem-solving method earns its stripes.
It was developed by Ford in the 80s and has since spread widely across manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, and more.
The 8D approach is a methodical process combining pros from different parts of the company, analytical tools, and fact-based decision-making.
By following its eight systematic steps, organizations can expertly handle thorny problems. They uncover root causes and implement lasting fixes addressing immediate concerns while fueling constant upgrades to prevent repeat issues.
Key Highlights
- Understanding the origins and history of the 8D corrective action methodology, its benefits, and when to apply it for optimal results.
- Exploring the eight disciplined steps of the 8D corrective action process.
- Integrating the 8D methodology with quality management systems, leveraging Enterprise Quality Management Software (EQMS) to streamline workflows.
- Examining case studies and examples from various industries, including manufacturing, service, healthcare, and the automotive sector.
Understanding the 8D Corrective Action Problem-Solving Methodology
The Eight Disciplines (8D) methodology is a structured, team-based approach to problem-solving that aims to identify the root causes of issues and implement effective corrective actions.
It is a comprehensive framework that combines analytical tools, cross-functional collaboration, and a disciplined mindset to tackle complex problems systematically.
The 8D process establishes a step-by-step approach that guides organizations through eight distinct disciplines, each building upon the previous one.
Origins and History of 8D Corrective Action
The origins of the 8D methodology can be traced back to the 1980s when it was developed and pioneered by Ford Motor Company.
Initially referred to as “ Team Oriented Problem Solving ” (TOPS), this approach was designed to address the recurring quality issues that plagued the automotive industry at the time.
Recognizing the limitations of traditional problem-solving techniques, Ford sought to establish a more robust and effective framework that would not only resolve immediate concerns but also drive continuous improvement and prevent future issues.
The 8D methodology quickly gained traction within Ford and was subsequently adopted as the company’s primary approach for documenting and addressing problem-solving efforts.
As the benefits of the 8D corrective action process became evident, it rapidly gained popularity among other manufacturers and industries, transcending its automotive roots.
Today, the 8D methodology is widely employed across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, and service industries, among others.
Benefits of Using 8D Corrective Action
Implementing the 8D problem-solving methodology offers numerous benefits to organizations, including:
1. Systematic Approach : The structured nature of the 8D process ensures a consistent and comprehensive approach to problem-solving, reducing the risk of overlooking critical factors or jumping to premature conclusions.
2. Root Cause Identification : By emphasizing root cause analysis , the 8D methodology goes beyond addressing surface-level symptoms and focuses on identifying and eliminating the underlying causes of problems.
3. Cross-Functional Collaboration : The team-based approach fosters cross-functional collaboration, leveraging diverse perspectives and expertise from various departments, leading to more robust and well-rounded solutions.
4. Preventive Measures : The 8D corrective action process incorporates preventive actions to mitigate the recurrence of similar issues, promoting a culture of continuous improvement and proactive problem-solving.
5. Improved Quality and Reliability : By addressing root causes and implementing corrective actions, organizations can enhance the quality and reliability of their products, services, and processes, leading to increased customer satisfaction and cost savings.
6. Knowledge Sharing and Organizational Learning : The documentation and archiving of 8D processes facilitate knowledge sharing and organizational learning, enabling teams to build upon past experiences and lessons learned.
When to Apply 8D Corrective Action
The 8D problem-solving methodology is particularly valuable in situations where:
- Root Cause Analysis is Required: When issues persist despite initial troubleshooting efforts, or when the underlying causes are not immediately apparent, the 8D process can provide a structured approach to root cause analysis.
- Recurring Problems: If an organization experiences recurring problems or quality issues, the 8D methodology can help identify and eliminate the root causes, preventing future occurrences.
- Quality Issues with Significant Impact: When quality issues have a substantial impact on customer satisfaction, safety, regulatory compliance, or financial performance, the rigorous 8D approach can be employed to address the problem comprehensively.
- Complex Problems: For intricate problems involving multiple factors, processes, or departments, the cross-functional nature of the 8D team and the systematic approach can facilitate a thorough investigation and effective solution development.
By understanding the core principles, benefits, and appropriate application scenarios of the 8D problem-solving methodology, organizations can leverage this powerful framework to drive continuous improvement , enhance quality, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
The Eight Disciplines (8D) Process
At the heart of the 8D corrective action methodology lies a structured, step-by-step approach that guides organizations through eight distinct disciplines.
Each discipline builds upon the previous one, ensuring a thorough investigation, analysis, and resolution of the problem at hand.
The eight disciplines of the 8D process are designed to facilitate a systematic and disciplined approach to problem-solving, leveraging cross-functional collaboration, analytical tools, and data-driven decision-making.
D0: Planning and Preparation
Before embarking on the 8D corrective action journey, proper planning and preparation are crucial. This initial step, often referred to as Discipline Zero (D0), lays the foundation for a successful problem-solving effort.
During D0, the team gathers relevant information about the problem, assesses the need for interim containment actions, and establishes the prerequisites for forming an effective cross-functional team.
This stage involves collecting data on symptoms, identifying potential risks, and ensuring that the necessary resources and support are in place to execute the 8D process effectively.
D1: Team Formation
The first formal discipline of the 8D process focuses on assembling a cross-functional team with the collective knowledge, skills, and expertise required to tackle the problem at hand.
Effective team formation is critical to the success of the 8D corrective action effort, as it ensures diverse perspectives and a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
During D1, team members are carefully selected from various departments or functions, such as product engineering, process engineering, quality assurance, and data analysis.
Best practices in team formation involve considering factors such as technical expertise, problem-solving skills, interpersonal abilities, and the availability and commitment of potential team members.
Establishing ground rules, communication protocols, and team-building exercises can further enhance collaboration and effective teamwork.
D2: Problem Description
In Discipline 2, the team focuses on accurately describing the problem, utilizing quantitative data and evidence-based approaches.
This step is crucial, as it establishes a shared understanding of the issue and guides the subsequent steps of the 8D process.
The problem description involves defining the problem statement in specific, measurable terms, identifying the affected product or process, and quantifying the impact on operations, quality, customer satisfaction, and costs.
Tools such as the “ 5 Whys ” technique, Ishikawa (fishbone) diagrams , and “ Is/Is Not ” analysis can aid in this process, helping to capture relevant details and categorize information.
D3: Interim Containment Actions
While the team works towards identifying and implementing permanent solutions, Discipline 3 focuses on implementing interim containment actions to mitigate the immediate impact of the problem and protect customers from further exposure.
Interim containment actions are temporary measures designed to isolate the problem and prevent it from causing further harm or spreading to other areas, processes, or products.
These actions may include segregating defective products, implementing additional inspections or checks, or introducing manual oversight until permanent corrective actions are in place.
It is essential to verify the effectiveness of interim containment actions and monitor their implementation to ensure that they are successful in containing the problem and minimizing its impact on operations and customers.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
At the core of the 8D corrective action process lies Discipline 4, which focuses on identifying the root causes of the problem through rigorous analysis and data-driven investigation.
This step is crucial, as it lays the foundation for developing effective and sustainable corrective actions.
During root cause analysis, the team employs various analytical tools and techniques, such as comparative analysis , fault tree analysis , and root cause verification experiments.
These methods help to isolate and verify the underlying causes of the problem, separating symptoms from true root causes.
Thorough documentation and verification of root causes are essential in this discipline, ensuring that the team has a solid foundation for developing effective corrective actions.
D5: Permanent Corrective Actions (PCAs)
Building upon the insights gained from root cause analysis , Discipline 5 focuses on selecting and verifying permanent corrective actions (PCAs) that address the identified root causes and mitigate the risk of future occurrences.
During this stage, the team evaluates potential corrective actions based on their effectiveness in addressing the root causes, as well as their feasibility, cost, and potential impact on other processes or systems.
Risk assessment tools, such as Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), can aid in this evaluation process.
Once the most appropriate corrective actions have been selected, the team verifies their effectiveness through pilot testing , simulations, or other validation methods.
This step ensures that the proposed solutions will indeed resolve the problem and prevent its recurrence without introducing unintended consequences.
Detailed planning and documentation of the corrective actions, including acceptance criteria, implementation timelines, and responsibilities, are critical components of Discipline 5.
D6: Implementation and Validation
In Discipline 6, the team focuses on implementing the selected permanent corrective actions and validating their effectiveness in resolving the problem and preventing future occurrences.
This stage involves developing a comprehensive project plan that outlines the steps, timelines, and resources required for successful implementation.
Effective communication and coordination with all relevant stakeholders, including cross-functional teams and management, are essential to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions.
During implementation, the team closely monitors the progress and performance of the corrective actions, gathering data and feedback to validate their effectiveness.
This validation process may involve conducting simulations, inspections, or collecting performance metrics to assess the impact of the implemented solutions.
If the validation process reveals any shortcomings or unintended consequences, the team may need to revisit the corrective actions, make adjustments, or conduct further root cause analysis to address any remaining issues.
D7: Preventive Actions
Discipline 7 of the 8D process focuses on taking preventive measures to ensure that the lessons learned and improvements made during the problem-solving journey are embedded into the organization’s processes, systems, and culture.
In this stage, the team reviews similar products, processes, or areas that could be affected by the same or similar root causes, identifying opportunities to apply preventive actions more broadly.
This proactive approach helps to mitigate the risk of future occurrences and promotes a culture of continuous improvement .
Effective implementation of preventive actions requires cross-functional collaboration, clear communication, and ongoing monitoring to ensure their sustained effectiveness.
D8: Closure and Celebration
The final discipline of the 8D process, D8, serves as a critical step in recognizing the team’s efforts, sharing lessons learned, and celebrating the successful resolution of the problem.
During this stage, the team conducts a final review of the problem-solving journey, documenting key lessons and insights that can be applied to future projects.
This documentation not only preserves institutional knowledge but also facilitates continuous improvement by enabling the organization to build upon past experiences.
Equally important is the recognition and celebration of the team’s achievements. By acknowledging the collective efforts, dedication, and collaboration of team members, organizations can foster a positive and supportive culture that values problem-solving and continuous improvement.
Formal recognition events, such as team presentations or awards ceremonies, can be organized to showcase the team’s accomplishments and highlight the impact of their work on the organization’s quality, customer satisfaction, and overall performance.
By completing the eight disciplines of the 8D process, organizations can effectively navigate complex problems, identify root causes, implement sustainable solutions, and establish a foundation for continuous improvement and organizational learning.
Integrating 8D Corrective Action with Quality Management Systems
While the 8D problem-solving methodology offers a robust framework for addressing quality issues and driving continuous improvement, its effectiveness can be further amplified by integrating it with an organization’s quality management systems .
Leveraging enterprise-level software solutions can streamline the 8D process, enhance collaboration, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
The Role of EQMS in 8D Corrective Action
Enterprise Quality Management Software (EQMS) plays a pivotal role in supporting the successful implementation of the 8D corrective action methodology.
By utilizing an EQMS, teams can benefit from features such as:
- Standardized 8D Workflows: Pre-configured 8D workflows and templates ensure consistency and adherence to best practices, guiding teams through each discipline with clearly defined tasks, responsibilities, and timelines.
- Collaboration and Communication: EQMS platforms facilitate cross-functional collaboration by providing secure document sharing, real-time updates, and centralized communication channels, ensuring that all stakeholders remain informed and engaged throughout the 8D process.
- Data Management and Reporting: Comprehensive data management capabilities within an EQMS enable teams to easily capture, analyze, and report on quality data, facilitating data-driven decision-making and root cause analysis during the 8D process.
- Integration with Quality Systems: EQMS solutions often integrate with other quality management systems, such as corrective and preventive action (CAPA) systems, enabling seamless information sharing and ensuring that the insights gained from the 8D process are incorporated into broader quality improvement initiatives.
Automating 8D Corrective Action Workflows
One of the key advantages of leveraging an EQMS is the ability to automate 8D workflows, streamlining the process and reducing the administrative burden on teams.
Automated workflows also facilitate consistent documentation and record-keeping, which is essential for maintaining compliance with industry regulations and standards, as well as enabling knowledge sharing and organizational learning.
Data-Driven Decision-making
The 8D corrective action methodology heavily relies on data-driven decision-making, particularly during the root cause analysis and corrective action selection phases.
An EQMS provides teams with powerful data analysis and reporting capabilities, enabling them to quickly identify trends, patterns, and correlations that can inform their decision-making process.
Continuous Improvement Culture
Ultimately, the integration of the 8D methodology with an EQMS fosters a culture of continuous improvement within an organization.
The insights gained from the 8D process, coupled with the robust reporting and analytics capabilities of an EQMS, provide organizations with a wealth of data and knowledge that can be leveraged to drive ongoing process optimization and quality enhancement initiatives.
Case Studies and Examples of 8D Corrective Action
To illustrate the practical application and impact of the 8D problem-solving methodology, let us explore a few real-world case studies and examples from various industries.
These examples will showcase how organizations have successfully leveraged the 8D approach to address quality issues, resolve complex problems, and drive continuous improvement.
Manufacturing Quality Issues
In the manufacturing sector, where quality and reliability are paramount, the 8D methodology has proven invaluable in addressing a wide range of issues.
One notable example is a leading automotive parts manufacturer that faced recurring quality issues with a critical component, resulting in costly rework and customer dissatisfaction.
By implementing the 8D process, a cross-functional team was assembled to investigate the problem. Through root cause analysis , they identified a flaw in the supplier’s raw material handling processes, leading to inconsistencies in the component’s material properties.
The team implemented interim containment actions to segregate and inspect incoming materials, while also working with the supplier to implement permanent corrective actions, such as upgrading their material handling equipment and revising their quality control procedures.
Service Industry Applications of 8D Corrective Action
While the 8D corrective action approach is often associated with manufacturing, it has also proven valuable in the service industry, where quality and process excellence are equally critical.
A prominent financial institution faced challenges with excessive customer complaints related to billing errors and account discrepancies.
By implementing the 8D methodology, a cross-functional team analyzed the problem, identifying root causes such as outdated software systems, inadequate training for customer service representatives, and inefficient data entry processes.
The team implemented interim containment actions, including manual account audits and increased customer communication, while also developing permanent corrective actions, such as upgrading their billing software, revising training programs, and streamlining data entry procedures.
Healthcare and Life Sciences
In the healthcare and life sciences industries, where patient safety and regulatory compliance are paramount, the 8D methodology has proven invaluable in addressing quality issues and mitigating risks.
A prominent pharmaceutical company faced a recurring issue with contamination in one of its drug products, posing potential health risks and regulatory concerns.
By implementing the 8D corrective action process, a cross-functional team investigated the issue, identifying root causes related to inadequate environmental controls in the manufacturing facility and inconsistencies in the cleaning and sterilization procedures.
Interim containment actions included quarantining and recalling affected product batches, while permanent corrective actions focused on upgrading the facility’s HVAC systems, revising cleaning and sterilization protocols, and implementing enhanced environmental monitoring.
Automotive Industry (origin of 8D Corrective Action)
It is fitting to revisit the automotive industry, where the 8D methodology originated. In a recent case study, a major automaker faced recurring issues with engine failures in one of their popular vehicle models, leading to costly warranty claims and customer dissatisfaction.
By implementing the 8D process, a cross-functional team investigated the issue, identifying root causes related to a design flaw in the engine’s cooling system and inadequate testing procedures during the product development phase.
Interim containment actions included issuing technical service bulletins and providing temporary cooling system modifications for affected vehicles.
Permanent corrective actions focused on redesigning the engine’s cooling system, implementing more rigorous testing protocols, and enhancing communication between the engineering and manufacturing teams.
Through the 8D process and integration with their quality management practices, the automaker successfully resolved the engine failure issue, regained customer trust, and enhanced their overall product quality and reliability.
The 8D corrective action problem-solving method has proven extremely useful for handling thorny quality issues, continuously upgrading workflows, and cultivating an excellence culture in businesses.
By pairing its structured team approach with analytical tools and fact-based choices, the 8D process empowers companies to uncover root causes. It also helps implement lasting fixes and prevent repeating mistakes through establishing protective measures.
As the case studies and examples show, it’s been put to great use across many industries from manufacturing to healthcare where it originated in automotive.
Its flexibility and power have made 8D valued for boosting quality, improving customer satisfaction and staying ahead competitively no matter the market.
The Eight Disciplines methodology remains a strong tool for companies serious about excellence, innovation, and customer focus.
By wholeheartedly embracing this robust framework and blending it with modern quality practices, businesses can expertly handle complex problems. They can also unlock fresh opportunities and build the foundation for sustainable success.
In other words, don’t sleep on 8D corrective action problem-solving. Its fact-based, team-centric transformation approach strengthens any organization now and into the future.
SixSigma.us offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Virtual Classroom Training Programs Self-Paced Online Training Programs
SixSigma.us Accreditation & Affiliations

Monthly Management Tips
- Be the first one to receive the latest updates and information from 6Sigma
- Get curated resources from industry-experts
- Gain an edge with complete guides and other exclusive materials
- Become a part of one of the largest Six Sigma community
- Unlock your path to become a Six Sigma professional
" * " indicates required fields

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
8D Problem Solving Process
Solving major problems in a disciplined way.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
(Also known as Global 8D Problem Solving)

When your company runs into a major problem, you need to address it quickly. However, you also need to deal with it thoroughly and ensure that it doesn't recur – and this can take a lot of effort and elapsed time.
The 8D Problem Solving Process helps you do both of these seemingly-contradictory things, in a professional and controlled way. In this article, we'll look at the 8D Problem Solving Process, and we'll discuss how you can use it to help your team solve major problems.
Origins of the Tool
The Ford Motor Company® developed the 8D (8 Disciplines) Problem Solving Process, and published it in their 1987 manual, "Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS)." In the mid-90s, Ford added an additional discipline, D0: Plan. The process is now Ford's global standard, and is called Global 8D.
Ford created the 8D Process to help teams deal with quality control and safety issues; develop customized, permanent solutions to problems; and prevent problems from recurring. Although the 8D Process was initially applied in the manufacturing, engineering, and aerospace industries, it's useful and relevant in any industry.
The eight disciplines are shown in figure 1, below:
Figure 1: The 8D Problem Solving Process

The 8D Process works best in teams tasked with solving a complex problem with identifiable symptoms. However, you can also use this process on an individual level, as well.
Applying the Tool
To use the 8D Process, address each of the disciplines listed below, in order. Take care not to skip steps, even when time is limited; the process is only effective when you follow every step.
Discipline 0: Plan
Before you begin to assemble a team to address the problem, you need to plan your approach. This means thinking about who will be on the team, what your time frame is, and what resources you'll need to address the problem at hand.
Discipline 1: Build the Team
You should aim to put together a team that has the skills needed to solve the problem, and that has the time and energy to commit to the problem solving process.
Keep in mind that a diverse team is more likely to find a creative solution than a team of people with the same outlook (although if outlooks are too diverse, people can spend so much time disagreeing that nothing gets done).
Create a team charter that outlines the team's goal and identifies each person's role. Then, do what you can to build trust and get everyone involved in the process that's about to happen.
If your team is made up of professionals who haven't worked together before, consider beginning with team-building activities to ensure that everyone is comfortable working with one another.
Discipline 2: Describe the Problem
Once your team has settled in, describe the problem in detail. Specify the who, what, when, where, why, how, and how many; and use techniques like CATWOE and the Problem-Definition Process to ensure that you're focusing on the right problem.
Start by doing a Risk Analysis – if the problem is causing serious risks, for example, to people's health or life, then you need to take appropriate action. (This may include stopping people using a product or process until the problem is resolved.)
If the problem is with a process, use a Flow Chart , Swim Lane Diagram , or Storyboard to map each step out; these tools will help your team members understand how the process works, and, later on, think about how they can best fix it.
Discovering the root cause of the problem comes later in the process, so don't spend time on this here. Right now, your goal is to look at what's going wrong and to make sure that your team understands the full extent of the problem.
Discipline 3: Implement a Temporary Fix
Once your team understands the problem, come up with a temporary fix. This is particularly important if the problem is affecting customers, reducing product quality, or slowing down work processes.
Harness the knowledge of everyone on the team. To ensure that each person's ideas are heard, consider using brainstorming techniques such as Round Robin Brainstorming or Crawford's Slip Writing Method , alongside more traditional team problem solving discussions.
Once the group has identified possible temporary fixes, address issues such as cost, implementation time, and relevancy. The short-term solution should be quick, easy to implement, and worth the effort.
Discipline 4: Identify and Eliminate the Root Cause
Once your temporary fix is in place, it's time to discover the root cause of the problem.
Conduct a Cause and Effect Analysis to identify the likely causes of the problem. This tool is useful because it helps you uncover many possible causes, and it can highlight other problems that you might not have been aware of. Next, apply Root Cause Analysis to find the root causes of the problems you've identified.
Once you identify the source of the problem, develop several permanent solutions to it.
If your team members are having trouble coming up with viable permanent solutions, use the Straw Man Concept to generate prototype solutions that you can then discuss, tear apart, and rebuild into stronger solutions.
Discipline 5: Verify the Solution
Once your team agrees on a permanent solution, make sure that you test it thoroughly before you fully implement it, in the next step.
- Conducting a Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) to spot any potential problems.
- Using Impact Analysis to make sure that there will be no unexpected future consequences.
- Using Six Thinking Hats to examine the fix from several different emotional perspectives.
Last, conduct a Blind Spot Analysis to confirm that you and your team haven't overlooked a key factor, or made an incorrect assumption about this solution.
Discipline 6: Implement a Permanent Solution
Once your team reaches a consensus on the solution, roll your fix out. Monitor this new solution closely for an appropriate period of time to make sure that it's working correctly, and ensure that there are no unexpected side effects.
Discipline 7: Prevent the Problem From Recurring
When you're sure that the permanent solution has solved the problem, gather your team together again to identify how you'll prevent the problem from recurring in the future.
You might need to update your organization's standards, policies, procedures, or training manual to reflect the new fix. You'll likely also need to train others on the new process or standard. Finally, you'll need to consider whether to change your management practices or procedures to prevent a recurrence.
Discipline 8: Celebrate Team Success
The last step in the process is to celebrate and reward your team's success . Say "thank you" to everyone involved, and be specific about how each person's hard work has made a difference. If appropriate, plan a party or celebration to communicate your appreciation.
Before the team disbands, conduct a Post-Implementation Review to analyze whether your solution is working as you thought, and to improve the way that you solve problems in the future.
In the late 1980s, Ford Motor Company developed the 8D (8 Disciplines) Problem Solving Process to help manufacturing and engineering teams diagnose, treat, and eliminate quality problems. However, teams in any industry can use this problem solving process.
The eight disciplines are:
- Build the Team.
- Describe the Problem.
- Implement a Temporary Fix.
- Identify and Eliminate the Root Cause.
- Verify the Solution.
- Implement a Permanent Solution.
- Prevent the Problem From Recurring.
- Celebrate Team Success.
The 8D Problem Solving Process is best used with a team solving complex problems; however, individuals can also use it to solve problems on their own.
Ford is a registered trademark of the Ford Motor Company: https://www.ford.com/
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Win-win negotiation.
Finding Solutions That Work for Everyone
Thomas Davenport and Larry Prusak: Working Knowledge
The Five Modes of Knowledge Generation According to Davenport and Prusak
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Gain essential management and leadership skills
Busy schedule? No problem. Learn anytime, anywhere.
Subscribe to unlimited access to meticulously researched, evidence-based resources.
Join today and take advantage of our 30% offer, available until May 31st .
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Winning Body Language

Business Stripped Bare
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Nine ways to get the best from x (twitter).
Growing Your Business Quickly and Safely on Social Media
Managing Your Emotions at Work
Controlling Your Feelings... Before They Control You
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Breaking the glass ceiling video.
How to Smash Through Invisible Barriers
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

What is Eight Disciplines (8D)
Provided By: Management and Strategy Institute
Download This Free eBook Here: What is Eight Disciplines (8D)
Table of Contents

Eight Disciplines (8D) is a problem-solving methodology designed to address, correct, and eliminate recurring problems impacting business operations, manufacturing, and product development.
Developed by Ford Motor Company in the 1980s, the 8D method has since been widely adopted across various industries as a comprehensive quality and process improvement tool. It combines teamwork, analytical tools, and a systematic approach to identify, solve, and prevent problems.
How & When 8D Methodology is Used
The 8D methodology is used when a recurring or significant problem has been identified and needs a structured approach to resolve. It is advantageous in scenarios where the root cause of the problem is not immediately apparent and requires thorough analysis to identify.
Industries like automotive, manufacturing, aerospace, and healthcare, among others, leverage 8D for its systematic approach to problem-solving and its emphasis on prevention.
The process is typically initiated once a problem is recognized and can significantly impact quality, safety, customer satisfaction, or costs. The 8D approach is about resolving the issue at hand and implementing a continuous improvement system that prevents similar problems from occurring.
The Eight Disciplines Explained
The 8D methodology consists of the following steps:
D1: Establish the Team
The first formal step of the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving methodology, D1, focuses on establishing the team that will work on identifying, analyzing, and solving the problem at hand. This step is critical to the success of the 8D process, as the team’s composition, skills, and collaboration will significantly impact the effectiveness of the problem-solving efforts. Here’s a detailed look at D1, including its objectives, key considerations, and best practices for assembling an effective team.
Objectives of D1
- Form a Cross-functional Team : The primary objective is to assemble a team with members from various departments or functions relevant to the problem. This diversity ensures a broad range of perspectives and expertise, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of the problem and the development of effective solutions.
- Define Roles and Responsibilities : Clearly outline each team member’s roles, responsibilities, and expectations. This clarity helps in ensuring accountability and efficient collaboration throughout the 8D process.
- Empower the Team : Equip the team with the authority, resources, and support needed to investigate the problem thoroughly and implement solutions effectively. This includes access to data, tools, and decision-making authority.
Key Considerations for Establishing the Team
- Expertise and Knowledge : Select members with the relevant technical knowledge, problem-solving skills, and experience related to the problem area. Including experts who understand the processes, products, or services involved is crucial.
- Interpersonal Skills : Consider potential team members’ interpersonal skills and teamwork capabilities. Effective communication, collaboration, and conflict-resolution skills are essential for the team’s success.
- Representation from Affected Areas : Ensure that the team includes representation from all areas affected by the problem. This can include manufacturing, quality assurance, engineering, customer service, and other relevant departments.
- Leadership : Appoint a team leader with strong leadership skills and the ability to guide the team through the 8D process. The team leader should be capable of facilitating meetings, keeping the team focused, and ensuring progress.
Best Practices for Assembling an Effective Team
- Size of the Team : Aim for a manageable team size, typically between 4 to 8 members. This size allows for diverse input while maintaining efficient communication and decision-making.
- Training : Provide training or orientation on the 8D methodology and problem-solving tools to team members unfamiliar with the process. This ensures that all members are aligned and can contribute effectively.
- Commitment and Availability : Ensure selected team members are available and committed to participating in the 8D process. This may require securing support from management to allocate time and resources for the team’s activities.
- Communication Plan : Establish a communication plan outlining how the team will communicate internally and with external stakeholders. Regular updates and meetings should be scheduled to keep everyone informed and engaged.
In summary, D1 is about carefully selecting and preparing a team with the right mix of skills, knowledge, and perspectives to tackle the problem effectively. A well-established team sets the foundation for a successful 8D process, enabling thorough analysis, creative solutions, and sustainable improvements.
D2: Describe the Problem
After establishing a well-composed team in D1, the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving methodology progresses to D2, which focuses on accurately and comprehensively describing the problem. This step is crucial as it lays the foundation for understanding the issue and guides the subsequent steps in the 8D process. An effective problem description ensures that the team has a clear and shared understanding of what needs to be addressed. Here’s a closer look at D2, including its objectives, key elements, and best practices.
Objectives of D2
- Define the Problem Clearly : Provide a clear, concise description of the problem, emphasizing specific, measurable details about what is happening, where, when, and to what extent.
- Establish Baseline Data : Gather and document quantitative data related to the problem to establish a baseline for future comparisons. This data helps in understanding the severity, frequency, and trends of the problem.
- Identify the Impact : Assess and describe the impact of the problem on operations, quality, customer satisfaction, costs, and safety. Understanding the impact helps prioritize the problem-solving efforts.
Key Elements of an Effective Problem Description
- Specificity : Avoid vague descriptions. Be specific about the details of the problem, including the affected product or process, locations, time frames, and quantities.
- Quantitative Data : Use data and evidence to describe the problem. Quantifiable information such as defect rates, downtime, and customer complaints provides a clearer picture of the problem’s magnitude.
- Use of Visuals : Where possible, use charts, graphs, photographs, or diagrams to illustrate the problem. Visual aids can enhance understanding and communication among team members and stakeholders.
- 5W2H Method : Employ the 5W2H method (Who, What, Where, When, Why, How, How Much) to ensure a comprehensive description. While not all elements may be known at this stage, addressing as many as possible strengthens the problem statement.

Best Practices for Describing the Problem
- Involve Relevant Stakeholders : Engage with individuals who are directly affected by the problem or who have firsthand knowledge of it. Their insights can contribute to a more accurate and detailed problem description.
- Avoid Assuming Causes : Focus on describing the problem without jumping to conclusions about its causes. The analysis of root causes is addressed in later stages of the 8D process.
- Initial Problem Statement Revision : Be prepared to revise the problem statement as more information becomes available. An iterative approach ensures the problem description remains accurate and relevant throughout the process.
- Document Everything : Maintain thorough documentation of the problem description, including all data, visuals, and stakeholder inputs. This documentation will be invaluable as the team progresses through the 8D steps.
In summary, D2 is about defining the problem in clear, specific, and measurable terms, utilizing data and evidence to outline the scope and impact of the issue. A well-articulated problem statement is essential for guiding the team’s efforts in investigating root causes, developing corrective actions, and ultimately resolving the problem effectively.
D3: Develop Interim Containment Plan
Following the establishment of the team and the detailed description of the problem, the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving methodology advances to D3, which involves developing an interim containment plan. This step is crucial for preventing the problem from causing further harm or spreading while the team works on identifying and implementing a permanent solution. Here’s a deeper look at D3, its objectives, key considerations, and best practices.
Objectives of D3
- Minimize Impact : Implement immediate, temporary measures to contain the problem, minimizing its impact on customers, operations, and quality.
- Prevent Spread : Ensure that the problem does not escalate or spread to other areas, processes, or products.
- Maintain Operations : Keep operations running as smoothly as possible while the team works on identifying and implementing a long-term solution.
Key Considerations for Developing an Interim Containment Plan
- Quick and Effective Measures : The containment actions should be quick to implement and effective in addressing the immediate impacts of the problem. They don’t have to be the long-term solution but should provide immediate relief.
- Assessment of Risks and Side Effects : Evaluate the potential risks and side effects of the containment actions. It’s vital to ensure that these actions do not introduce new problems or significantly disrupt operations.
- Resource Allocation : Determine what resources (e.g., personnel, equipment, materials) are needed to implement the containment actions and ensure they are readily available.
Best Practices for Interim Containment
- Identify Containment Actions : Containment actions can vary widely depending on the nature of the problem. Manufacturing issues might involve segregating and inspecting inventory to remove defective products. In service-oriented processes, it might entail additional checks or temporary manual oversight.
- Communication and Documentation : Clearly communicate the need for, and details of, the containment actions to all affected parties. Document all actions taken, including who is responsible for implementing and monitoring these actions’ effectiveness.
- Monitor and Adjust : Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the containment actions. Be prepared to adjust or implement additional measures if the problem persists or side effects are observed.
- Link to Root Cause Analysis : While D3 focuses on immediate containment, it should be implemented with an understanding that it is a temporary fix. Insights gained during this stage can be valuable for the root cause analysis in D4.
Example of Containment Actions
For a manufacturing defect identified in a product line, containment actions might include:
- Inspecting All Current Inventory : Perform a thorough inspection of all current inventory to identify and segregate any defective products.
- Halting Production : Temporarily stop production of the affected product line until the root cause is identified and addressed.
- Notifying Customers : If defective products have reached customers, inform them of the issue, and offer replacements, repairs, or refunds as appropriate.
In summary, D3 is about quickly responding to the problem with effective interim measures that contain its impact. These actions are crucial for maintaining customer trust and operational stability while the team works on a permanent solution. Properly executed, the containment plan sets the stage for a thorough analysis and resolution of the underlying issue in the subsequent steps of the 8D process.
D4: Determine Root Cause(s)
After establishing an interim containment plan to manage the immediate impacts of the problem, the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving process moves to D4, which focuses on identifying the root cause(s) of the problem. This critical step involves a deep dive into the problem to understand why it occurred in the first place, setting the stage for developing effective, long-lasting solutions. Here’s a closer look at D4, including its objectives, methodologies, and best practices.
Objectives of D4
- Identify Underlying Causes : The primary objective of D4 is to determine the fundamental reasons behind the problem, going beyond superficial symptoms to understand the underlying causes.
- Systematic Analysis : Employ a systematic approach to analyze the problem and its contributing factors, ensuring that all possible causes are considered.
- Evidence-Based Conclusions : Base conclusions on data and evidence, rather than assumptions or speculation, to ensure that the identified root causes accurately represent the source of the problem.
Methodologies for Root Cause Analysis
Several tools and techniques can be employed during D4 to facilitate thorough and systematic root cause analysis:
- 5 Whys : A questioning technique used to drill down into the details of the problem and uncover the root cause by repeatedly asking “Why?” until the fundamental cause is identified. [ Learn More ]
- Ishikawa (Fishbone) Diagram : A visual tool that helps identify and categorize potential causes of a problem across various categories (e.g., People, Processes, Materials, Equipment), facilitating a comprehensive analysis.
- Pareto Analysis : A statistical technique that applies the 80/20 rule to identify the few critical causes that contribute to most of the problem, helping prioritize focus areas. [ Learn More ]
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) : A top-down, deductive analysis method used to explore the causes of a specific problem or undesired event.
Best Practices for Root Cause Analysis
- Cross-functional Collaboration : Engage team members from different functions or departments to ensure a broad perspective is considered during the analysis. Different viewpoints can uncover aspects of the problem that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Data Collection and Analysis : Gather and analyze data related to the problem, including historical data, to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies that might point to root causes.
- Verification of Root Causes : Before concluding the analysis, verify that the identified root causes, when addressed, would prevent the recurrence of the problem. This might involve experimentation, additional data analysis, or consulting with subject matter experts.
- Document Findings : Thoroughly document the analysis process, findings, and evidence supporting the identification of root causes. This documentation is crucial for justifying the corrective actions in later stages and for future reference.
Example of Root Cause Identification
If a manufacturing process is producing a high rate of defective products, root cause analysis might reveal that the root cause is outdated equipment that cannot maintain the necessary precision for production. Alternatively, the analysis might uncover that the real issue is a lack of operator training, leading to improper machine setup.
In summary, D4 is about rigorously identifying the root cause(s) of the problem through systematic analysis and evidence-based conclusions. Understanding the underlying reasons why a problem occurred is essential for developing effective corrective actions that prevent recurrence, setting the stage for D5, where these solutions are selected and planned.
D5: Choose and Verify Permanent Corrective Actions (PCAs)
After identifying the root cause(s) of the problem in D4, the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving process progresses to D5. This crucial step involves selecting, verifying, and planning the implementation of permanent corrective actions (PCAs) to address the root causes identified. The goal is to ensure that the problem is resolved in a way that prevents its recurrence. Here’s a detailed look at D5, including its objectives, considerations, and best practices.
Objectives of D5
- Select Effective Solutions : Choose corrective actions that directly address the root causes of the problem to ensure that it is effectively resolved.
- Prevent Recurrence : Ensure that the chosen solutions not only fix the problem but also prevent it from happening again in the future.
- Consider Impact : Evaluate the potential impact of the corrective actions on other processes, systems, or products to avoid creating new problems.
Key Considerations for Choosing Corrective Actions
- Effectiveness : Assess the potential effectiveness of each corrective action in addressing the root cause. This often involves a cost-benefit analysis to determine the most efficient solution.
- Feasibility : Evaluate the feasibility of implementing each corrective action, considering factors such as time, resources, and organizational constraints.
- Side Effects : Consider any potential side effects or negative impacts of corrective actions on other processes or areas.
Best Practices for Selecting and Verifying PCAs
- Brainstorming and Collaboration : Engage the team in brainstorming sessions to generate a wide range of potential corrective actions. Collaboration ensures diverse perspectives and innovative solutions.
- Pilot Testing : Where feasible, conduct pilot tests of the proposed corrective actions. This allows the team to assess their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments before full-scale implementation.
- Stakeholder Input : Involve stakeholders, including those who will be affected by the corrective actions, in the selection process. Their insights can provide valuable input on the practicality and potential impact of the proposed solutions.
- Documentation : Thoroughly document the decision-making process, including the rationale for selecting specific corrective actions and the results of any tests or evaluations conducted.
Example of Verifying Corrective Actions
If the root cause of a manufacturing defect was identified as outdated equipment unable to maintain precision, a potential corrective action might be to upgrade or replace the equipment. Before implementing this solution across the board, a pilot test could be conducted with one production line to verify the effectiveness of the new equipment in reducing defects. The results would inform whether this solution should be applied more broadly or adjusted.
Implementation Planning
Once the corrective actions have been selected and verified, the next step is to plan their implementation. This involves:
- Developing a Detailed Action Plan : Outline the steps needed to implement the corrective actions, including timelines, responsibilities, and required resources.
- Setting Milestones and Metrics for Success : Establish clear milestones and performance metrics to monitor the effectiveness of the corrective actions over time.
- Communication : Communicate the plan and expected outcomes to all stakeholders, ensuring alignment and support for the implementation phase.
In summary, D5 is a critical step in the 8D process, where the team selects and verifies corrective actions that will effectively address the root causes of the problem. By carefully considering each solution’s impact, effectiveness, and feasibility, and involving stakeholders in the process, the team can ensure that the chosen actions will provide a lasting resolution to the problem, paving the way for successful implementation in D6.
D6: Implement and Validate Corrective Actions
Following the selection and verification of permanent corrective actions (PCAs) in D5, the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving process moves on to D6, which focuses on implementing and validating these corrective actions. This crucial step ensures that the solutions are effectively put into place and that they effectively resolve the problem and prevent its recurrence. Here’s an in-depth look at D6, including its objectives, implementation strategies, and best practices for validation.
Objectives of D6
- Implement Solutions : Execute the plan developed in D5 to implement the corrective actions that address the root causes of the problem.
- Monitor Implementation : Closely monitor the implementation process to ensure corrective actions are executed as planned and identify any issues or barriers to successful implementation.
- Validate Effectiveness : Verify that the implemented corrective actions have effectively resolved the problem and that there are no unintended negative impacts on other processes or areas.
Strategies for Implementing Corrective Actions
- Detailed Implementation Plan : Utilize the detailed plan developed in D5, which outlines the steps, timelines, responsibilities, and resources required for implementation. This plan serves as a roadmap, guiding the implementation process.
- Communication and Training : Communicate the implementation plan to all relevant parties, ensuring everyone understands their role. Provide training or support as necessary to facilitate effective implementation.
- Resource Allocation : Ensure that all necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, and financial resources, are available and allocated to support the implementation of corrective actions.
Best Practices for Validating Corrective Actions
- Establish Validation Criteria : Define clear criteria for evaluating the success of the corrective actions. These criteria should be directly linked to the metrics and goals established during the planning phase.
- Collect and Analyze Data : Gather data to assess the effectiveness of the corrective actions. This may involve measuring performance indicators, conducting inspections, or gathering stakeholder feedback.
- Adjust and Optimize : If the data indicates that the corrective actions are not fully effective, or if there are unforeseen negative impacts, be prepared to make adjustments. This may involve revising the actions, implementing additional measures, or conducting further analysis to identify additional root causes.
- Document Results : Thoroughly document the implementation process, the validation efforts, and the outcomes. This documentation should include data analysis, adjustments, and final assessment of the effectiveness of corrective actions.
Example of Implementation and Validation
If the corrective action involved upgrading equipment to address manufacturing defects, the implementation phase would include purchasing and installing the new equipment, training operators on its use, and integrating it into the production process. Validation would involve monitoring defect rates before and after the implementation, assessing production efficiency, and gathering feedback from operators to ensure that the problem has been resolved and that no new issues are arising from the change.
In summary, D6 is about taking the corrective actions from plan to action, ensuring they are implemented effectively, and validating their success in solving the original problem. This step requires careful planning, coordination, and data-driven validation to confirm that the problem has been addressed and to prevent its recurrence, setting the stage for preventive measures in D7.
D7: Take Preventive Measures
After implementing and validating the effectiveness of the corrective actions in D6, the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving process advances to D7. This step focuses on taking preventive measures to ensure that the problem and similar issues do not recur in the future. D7 is about embedding long-term solutions into the organization’s processes, systems, and culture. Here’s a detailed look at D7, including its objectives, key activities, and best practices.
Objectives of D7
- Prevent Recurrence : Establish measures that prevent the original problem and similar issues from occurring again in the future.
- Systemic Improvement : Identify and implement changes to systems, processes, and practices to improve overall quality and performance, based on the learnings from the problem-solving process.
- Enhance Organizational Learning : Promote a culture of continuous improvement and learning by sharing insights and best practices derived from the problem-solving process across the organization.
Key Activities for Taking Preventive Measures
- Review of Related Processes and Systems : Examine other processes and systems that could be affected by the same or similar root causes. This broad review helps identify areas where preventive measures can be applied more widely.
- Modification of Standards and Procedures : Update existing standards, procedures, and documentation to incorporate the learnings and preventive measures identified during the problem-solving process. This may include revising work instructions, quality standards, training materials, and maintenance schedules.
- Training and Education : Conduct training sessions to educate employees on the new or revised standards and procedures. Ensure that all relevant personnel understand the changes and the reasons behind them.
- Change Management : Implement change management practices to facilitate the adoption of new or revised processes and systems. This includes communicating the benefits of the changes, addressing concerns, and providing support during the transition.
Best Practices for Taking Preventive Measures
- Root Cause Analysis for Prevention : Use the insights gained from the root cause analysis in D4 to identify potential vulnerabilities in other areas. By understanding the underlying causes, organizations can proactively address issues before they become problems.
- Engagement and Ownership : Involve employees at all levels in developing and implementing preventive measures. Foster a sense of ownership and accountability for quality and continuous improvement.
- Monitoring and Feedback Loops : Establish mechanisms for ongoing monitoring of the effectiveness of preventive measures. Encourage feedback from employees and stakeholders to identify opportunities for further improvement.
- Continuous Improvement Culture : Promote a culture that values learning from mistakes and proactively seeks improvement opportunities. Recognize and celebrate the contributions of teams and individuals to fostering continuous improvement.
Example of Preventive Measures
Suppose the problem-solving process revealed that a manufacturing defect was due to inadequate training on new equipment. In that case, preventive measures might include developing a comprehensive training program for all operators on existing and future equipment, revising the onboarding process for new hires to include hands-on training sessions, and scheduling regular refresher courses to ensure skills remain up-to-date.
In summary, D7 is about solidifying the gains made through the problem-solving process by implementing systemic changes that prevent recurrence of the problem and similar issues. By taking preventive measures, organizations can improve their resilience, enhance quality and performance, and build a culture of continuous improvement that drives long-term success.
D8: Congratulate Your Team
The final step in the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving process, D8, serves a crucial role in recognizing and celebrating the efforts and achievements of the team that has worked through the complex process of resolving a problem. This step is about acknowledging the hard work, dedication, and collaboration that contributed to the successful outcome. Here’s an in-depth look at D8, including its objectives, significance, and best practices for effectively congratulating the team.
Objectives of D8
- Recognize and Reward Effort : Acknowledge the individual and collective efforts of the team members who contributed to identifying and implementing the solution to the problem.
- Reinforce Teamwork and Collaboration : Highlight the importance of teamwork, collaboration, and cross-functional engagement as key factors in problem-solving.
- Promote a Positive Culture : Foster a positive organizational culture that values problem-solving, continuous improvement, and employee contributions.
- Encourage Future Participation : Motivate team members and others within the organization to actively participate in future problem-solving efforts by demonstrating that their contributions will be recognized and valued.
Significance of Congratulating the Team
- Morale and Motivation : Celebrating successes boosts team morale and motivation, making members feel valued and appreciated. This positive reinforcement encourages continued engagement and commitment to excellence.
- Learning and Development : Recognizing the team’s achievements provides an opportunity to reflect on what was learned during the process, reinforcing best practices and lessons that can be applied to future challenges.
- Visibility and Communication : Publicly acknowledging the team’s work communicates to the wider organization the importance of the problem-solving process and the positive outcomes that can be achieved, promoting a culture of transparency and accountability.
Best Practices for Congratulating the Team
- Personalized Recognition : Tailor recognition to the team and its members, acknowledging specific contributions and achievements. Personalized recognition can be more meaningful and impactful.
- Formal and Informal Acknowledgment : Use formal and informal channels to congratulate the team. Formal recognition might include awards or commendations, while informal recognition could be a team lunch or handwritten notes.
- Involve Leadership : Involvement of senior leadership in the recognition process can significantly enhance its impact. Leadership acknowledgment underscores the value placed on problem-solving and continuous improvement efforts at the highest levels of the organization.
- Share Success Stories : Share the team’s success story across the organization through internal newsletters, meetings, or intranet posts. Highlighting the problem-solving journey and its outcomes can inspire others and promote a proactive problem-solving culture.
- Continuous Feedback Loop : Integrate recognition into a continuous feedback loop where teams are regularly acknowledged for their contributions to problem-solving and improvement initiatives, not just at the conclusion of an 8D process.
Example of Congratulating the Team
After successfully implementing corrective actions to resolve a production issue, a company might organize an all-hands meeting where senior management formally recognizes the team. Each team member could receive a certificate of appreciation, and the team leader might share insights from the problem-solving journey, highlighting key contributions from team members. Additionally, the team could be treated to a celebratory lunch or team-building activity, reinforcing the sense of camaraderie and achievement.
In summary, D8 is a vital step that closes the 8D problem-solving process on a high note, reinforcing the value of teamwork, dedication, and continuous improvement. By effectively congratulating the team, organizations recognize the immediate achievements and foster a positive culture that encourages ongoing engagement, learning, and excellence in problem-solving.
What about D0 (Discipline Zero)?
In some organizations, the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving process includes an additional preliminary step known as D0 (Discipline Zero). D0 serves as a preparatory phase before the formal 8D process begins and is crucial for setting the stage for effective problem-solving.
The main objective of D0 is to plan and prepare for the 8D process. This involves identifying the need for an 8D, gathering initial information about the problem, and ensuring that the necessary resources and commitments are in place to support the process. It’s about getting ready to tackle the problem efficiently and effectively.
What are some Negatives associated with the Eight Discipline Method?
While the Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving method is widely regarded for its structured approach and effectiveness in addressing complex problems, some potential drawbacks and challenges are associated with its implementation and application. Here are some of the negatives or limitations that organizations might encounter when using the 8D method:
1. Resource Intensive:
The 8D process requires significant time and resources, including assembling a cross-functional team and dedicating time for detailed analysis and implementation of corrective actions. Smaller organizations or teams with limited resources may find it challenging to commit to the process fully.
Strategies to Overcome :
- Prioritize Problems : Use the 8D method for issues that have a significant impact on quality, cost, or customer satisfaction, ensuring that resources are allocated to problems that warrant the investment.
- Efficient Team Composition : Form smaller, more focused teams that include key personnel with the necessary expertise and authority to make decisions, reducing the resource burden.
- Leverage Technology : Utilize project management and collaboration tools to streamline communication and documentation, making the process more efficient.
2. Complexity and Overhead:
The structured and rigorous nature of the 8D process can add complexity and administrative overhead, particularly for relatively simple problems that might be resolved more efficiently with less formal approaches.
- Simplify Documentation : While thorough documentation is crucial, focus on streamlining and simplifying documentation requirements to the essentials, avoiding unnecessary complexity.
- Tailor the Process : Adapt the 8D methodology to fit the organization’s specific needs and problem types, simplifying steps where possible without compromising the effectiveness of the problem-solving effort.
- Incremental Implementation : Start with a pilot project to implement the 8D process on a smaller scale, allowing the organization to adjust and refine the approach before wider adoption.
3. Resistance to Change:
Introducing a structured problem-solving process like 8D can encounter resistance from employees accustomed to more informal approaches. Overcoming this resistance and fostering buy-in can require significant effort and change management.
- Communicate Benefits : Clearly communicate the benefits of the 8D process, including real-world examples of how it has successfully resolved problems, to build buy-in and enthusiasm.
- Involve Employees Early : Involve employees in implementing the 8D process from the beginning, seeking their input and addressing their concerns, to foster a sense of ownership and commitment.
- Celebrate Successes : Publicly recognize and celebrate the successes achieved through the 8D process, reinforcing its value and encouraging wider acceptance and participation.
- Change Management : Implement change management practices , including leadership endorsement, open communication, and training, to support employees through the transition to the new process.
The Eight Disciplines (8D) problem-solving methodology offers a structured and practical approach to identifying, solving, and preventing organizational problems. By emphasizing teamwork, systematic analysis, and continuous improvement, 8D helps organizations enhance their quality management practices, improve operations, and increase customer satisfaction. Through its disciplined approach, 8D equips teams with the tools and processes necessary to tackle complex issues, ensuring long-term success and stability in today’s competitive business environment.
Download this FREE eBook here: What is Eight Disciplines (8D)
Earn a FREE Eight Disciplines (8D) Certificate of Completion
Learn more:.
Learn more about process improvement methods through these programs:
- Lean Six Sigma Black belt Certification
- Continuous Improvement Manager Certification
- All Certifications
- Accessibility
Connect With Us
Copyright © 2022 MSI. All Rights Reserved.

8D: Tools and Techniques

- Learn Lean Sigma
- 8D Problem Solving
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way to resolve them once and for all? Look no further than the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology —a comprehensive eight-step approach initially developed in the automotive industry but widely applicable across various sectors.
This systematic method not only aids in diagnosing the root cause of a problem but also offers a roadmap for effective solutions. However, maximizing the potential of the 8D process involves more than just following its steps. It requires the strategic application of specific tools and techniques at each stage. In this educational blog post, we will guide you through the tools and techniques best suited for each of the 8 Disciplines, empowering you to turn challenges into opportunities for improvement. So, let’s delve into this toolkit and make your problem-solving journey as efficient and effective as possible.
Table of Contents
D1: form a team.
The first step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is to form a cross-functional team. A well-assembled team is the backbone of any successful problem-solving initiative. While it may be tempting to rush through this step, investing time and effort here can pay dividends later. Let’s explore some of the key tools that can assist you in forming an effective team.
Suggested Tools:
1. raci matrix.
The RACI Matrix is an invaluable tool for defining roles and responsibilities within the team. The acronym stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. By using this matrix, you can clearly specify:
- Responsible : Who is doing the task?
- Accountable : Who is ensuring the task gets completed?
- Consulted : Who needs to provide input?
- Informed : Who needs to know the outcome?
Clear delineation of roles prevents overlap, ensures accountability, and minimizes confusion later in the process.

2. Skills Matrix
Selecting team members with the right set of skills is crucial. A Skills Matrix can help you in this aspect by providing a visual representation of each potential team member’s skills and competencies. You can rate skills on a scale (e.g., 1 to 5) and identify gaps that need to be filled. The matrix can include both technical and soft skills like communication, leadership, and domain expertise.
Key Takeaway:
An effective problem-solving team is not just a group of people; it’s a carefully chosen set of individuals with complementary skills and clearly defined roles. Utilizing tools like the RACI Matrix and Skills Matrix can immensely help in this phase, setting the stage for a successful problem-solving endeavor.
By taking the time to carefully form your team and define everyone’s roles and responsibilities, you lay a strong foundation for the rest of the 8D process. Remember, a well-prepared team is more likely to find sustainable solutions and less likely to encounter roadblocks down the line.
D2: Define the Problem
After assembling a competent team, the next critical step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is defining the problem. A well-defined problem serves as a clear roadmap, guiding your team in the right direction from the start. Ambiguity at this stage can lead to misdirection and wasted resources. So what tools can help you clearly and concisely articulate the problem?
1. 5W2H Method
The 5W2H method is a powerful tool for problem definition. It involves asking a series of questions to gain a comprehensive understanding of the issue at hand. These questions include:
- Who is involved or affected?
- What exactly is the problem?
- When did it occur?
- Where did it occur?
- Why is it a problem?
- How did it happen?
- How much is it affecting?
By systematically answering these questions, you define the problem in a manner that is both comprehensive and easily understandable for everyone involved.

2. SMART Criteria
The SMART criteria focus on setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals for the problem-solving effort. This approach helps ensure that the problem is clearly defined and that the team has a focused, achievable objective to aim for.
- Specific : Clearly define what needs to be achieved.
- Measurable : Set criteria for measuring progress and success.
- Achievable : Ensure the goals are realistic given the resources.
- Relevant : Align the goals with broader organizational objectives.
- Time-bound : Establish a timeline for solving the problem.

Defining the problem is not a mere formality; it is a necessity for effective problem-solving. A well-defined problem ensures that everyone is on the same page and focused on the right issues. Tools like the 5W2H method and SMART criteria offer invaluable frameworks for achieving this clarity. They help dissect the problem into manageable parts, setting the stage for focused root cause analysis.
D3: Contain the Problem
Once you have a team in place and a well-defined problem, the next step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is containment. This stage is often overlooked but is crucial for limiting the damage and preventing the problem from exacerbating. Containment actions are essentially short-term solutions aimed at halting the spread of the issue while you work on finding a permanent fix. Let’s delve into some tools that can guide you in this phase.
1. Check Sheet
A Check Sheet is a simple yet effective tool for collecting and organizing data. It’s often a paper-and-pencil tool that allows for quick data collection in real-time. For example, if the problem is a high rate of defects in a manufacturing line, a Check Sheet could be used to tally the number of defects by type or time of occurrence. This provides valuable insights into the scope and pattern of the problem, aiding in containment.
2. SWIFT Checklist
The SWIFT (Short Window Immediate Fix Technique) Checklist is a tool designed for rapid assessment. It outlines immediate actions that should be taken to contain the issue. The checklist could include questions like:
- Are there safety issues that need immediate attention?
- Can the affected products be quarantined?
- Do stakeholders need to be informed?
By quickly going through the SWIFT Checklist, you can prioritize the most critical containment actions and implement them without delay.
Containment is not just about putting a temporary fix; it’s about preventing the problem from causing further harm or affecting other processes. Tools like the Check Sheet and SWIFT Checklist can be instrumental in quickly assessing the situation and implementing immediate containment actions.
Utilizing these tools allows you to create a rapid response mechanism, thereby minimizing the impact and scope of the problem. As you transition to finding a long-term solution, these containment measures ensure that the situation remains under control.
D4: Root Cause Analysis
Reaching the root cause analysis stage in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology signifies a pivotal moment. Here, you transition from understanding and containing the problem to actually solving it. Identifying the root cause(s) is fundamental to ensuring that the issue doesn’t recur. While containment measures provide short-term relief, it’s the root cause analysis that offers a long-term solution. Let’s examine some essential tools that can assist in uncovering the underlying issues.
The “ 5 Whys ” is a powerful questioning technique that helps you drill down into the root cause of a problem by asking “Why?” repeatedly. Often, the apparent issue is just a symptom of a deeper problem. The 5 Whys technique encourages you to move beyond the symptoms and discover the underlying cause.
For instance, if the issue is frequent machine breakdowns, asking “Why?” might reveal:
- Why is the machine breaking down? Because of excessive wear and tear.
- Why is there excessive wear and tear? Because maintenance isn’t performed regularly.
- Why isn’t maintenance regular? Because there’s no schedule.
- Why is there no schedule? Because it was never made a priority.
- Why was it never a priority? Because of a lack of awareness about its importance.

2. Pareto Analysis
Pareto Analysis is based on the Pareto Principle, which states that 80% of problems are often due to 20% of causes. By identifying and focusing on these significant causes, you can resolve the majority of issues with minimum effort. Pareto Analysis typically involves collecting data and creating a Pareto Chart to visualize which factors are most impactful.

3. Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa)
Though also used in problem definition, the Fishbone Diagram is invaluable for root cause analysis as well. It allows you to categorize potential causes and delve deeper into each, often in combination with other tools like the 5 Whys or Pareto Analysis.

Identifying the root cause is not merely a step in the process; it’s the cornerstone for effective corrective action. Tools like the 5 Whys, Pareto Analysis, and Fishbone Diagram provide a structured approach to dig deep into the problem and unearth its roots. Only by understanding the root cause can you implement solutions that are not just quick fixes but long-lasting remedies.
D5: Choose and Verify Corrective Actions
After identifying the root cause of the problem, the next logical step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is to choose and verify corrective actions. It’s crucial to remember that not all solutions are created equal. Some may offer a quick fix but not a long-lasting one, while others could inadvertently introduce new issues. Therefore, this stage involves a delicate balance of selecting an effective solution and ensuring it doesn’t have unintended consequences. Let’s explore some of the tools that can guide you in making informed decisions.
1. FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis)
FMEA is a structured approach for evaluating the potential failure modes of a proposed solution and their impact. By predicting how things could go wrong, you can proactively address these issues before they occur. The FMEA process involves the identification of failure modes, assessment of their effects, and prioritization based on their severity, occurrence, and detectability. This prioritization helps you focus your resources where they’ll be most effective.

2. Pilot Testing
Before implementing a corrective action on a full scale, it’s prudent to test it on a smaller scale to verify its effectiveness. Pilot testing allows you to:
- Evaluate the impact of the solution without large-scale commitment.
- Identify any adjustments or optimizations needed.
- Collect data to validate the solution’s efficacy.
Pilot tests should be carefully designed to mimic the conditions under which the full-scale implementation will occur. This way, the results are indicative of what you can expect in the broader application.
Choosing a corrective action is a significant milestone, but verifying its effectiveness is equally crucial. Tools like FMEA and Pilot Testing enable you to rigorously evaluate your chosen solutions, mitigating risks and ensuring that the corrective actions will address the root cause without creating new problems.
By diligently applying these tools, you not only select the right corrective action but also build a robust verification mechanism. This two-pronged approach ensures that your solution is not just theoretically sound but practically effective as well.
D6: Implement Corrective Actions
Reaching the implementation phase of the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is a big step. You’ve formed a team, defined the problem, contained it, identified its root cause, and chosen and verified corrective actions. Now, it’s time to put those actions into play. However, effective implementation is easier said than done. It requires meticulous planning, execution, and monitoring to ensure the corrective actions yield the desired results. Let’s look at some of the tools that can help you master this crucial stage.
1. Gantt Chart
A Gantt Chart is an excellent tool for project planning and tracking. It provides a visual timeline for the tasks involved in implementing the corrective actions. The chart specifies:
- Start and end dates
- Responsible parties
- Dependencies between tasks
This visual representation makes it easier to manage resources and timelines, ensuring that implementation stays on track.

2. PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act)
The PDCA cycle is a four-step approach for implementing changes in a controlled manner. Each step serves a specific purpose:
- Plan : Establish the objectives, processes, and metrics for the corrective action.
- Do : Execute the plan on a small scale initially.
- Check : Measure the outcomes against the planned objectives and analyze the results.
- Act : Make adjustments based on the analysis and either scale the implementation or revisit the plan.
By cycling through these steps, you can continually refine your implementation approach, ensuring it aligns with your objectives.

Implementation is the stage where your problem-solving efforts come to fruition, but it’s not a one-and-done deal. Effective implementation requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Tools like the Gantt Chart and PDCA cycle provide you with the means to implement corrective actions in a structured, controlled, and measurable way.
Remember, a well-planned implementation not only solves the current problem but also equips your organization with the knowledge and experience to tackle future challenges more effectively.
D7: Prevent Recurrence
Successfully implementing corrective actions is an accomplishment, but the 8D Problem-Solving journey doesn’t end there. The next crucial step is to ensure that the problem doesn’t recur. This phase focuses on institutionalizing the improvements you’ve made, ensuring they are sustainable over the long term. It involves both documentation of new best practices and ongoing monitoring. Let’s explore the tools that can help solidify these new standards.
1. Standard Work
Standard Work refers to the documentation of the new best practices that led to the resolution of the problem. These could be new procedures, guidelines, or checklists that need to be followed. Standard Work serves multiple purposes:
- It provides a clear and easy-to-follow guide for team members.
- It ensures that the successful corrective actions are repeated, thereby making the improvements sustainable.
- It serves as a training resource for new employees or for refresher training for existing staff.

2. Control Charts
Control Charts are used to monitor process performance over time. These charts can help you:
- Identify any variations in the process.
- Distinguish between normal variations and those that need attention.
- Trigger corrective actions if the process goes out of the defined control limits.
Regularly updating and reviewing the Control Charts ensures that you catch any deviations before they turn into bigger problems.

Prevention is indeed better than cure. The most effective problem-solving initiatives are those that not only solve the immediate issue but also prevent its recurrence. Tools like Standard Work and Control Charts offer a structured way to document and monitor the improvements, making them a part of your organizational culture.
By diligently using these tools, you not only secure the gains made but also create a proactive environment where potential issues are identified and addressed before they escalate.
D8: Congratulate the Team
The final step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is often the most overlooked but is crucial for long-term success: congratulating the team. After navigating through a complex problem-solving journey, taking a moment to acknowledge and celebrate the hard work is vital. It not only boosts morale but also encourages a culture of continuous improvement. Let’s delve into some tools and practices that can help you effectively close out your problem-solving initiative.
1. Recognition and Rewards
Acknowledging the hard work and dedication of the team is essential for maintaining a motivated and engaged workforce. Recognition can take various forms:
- Public acknowledgment in team meetings or company-wide announcements.
- Certificates or plaques to commemorate the achievement.
- Small rewards or bonuses, where appropriate.
This recognition serves as a reminder that efforts are appreciated, which in turn fosters a positive work environment.
2. Lessons Learned Document
Closing out a problem-solving initiative offers a prime opportunity to capture what worked and what didn’t. A Lessons Learned Document serves this purpose:
- It details the challenges faced, how they were overcome, and any roadblocks encountered.
- It captures best practices for future reference.
- It identifies areas for improvement, offering a starting point for future problem-solving endeavors.
Sharing this document organization-wide can serve as a valuable resource for other teams facing similar challenges.

A job well done indeed deserves recognition, but it also lays the groundwork for future improvements. Tools like Recognition and Rewards and the Lessons Learned Document not only celebrate success but also institutionalize the knowledge gained. This twofold approach not only marks the successful completion of one problem-solving initiative but sets the stage for ongoing improvements and future successes.
By taking the time to celebrate and reflect, you not only acknowledge the efforts made but also capture valuable insights that can guide your organization’s continuous improvement journey.
Successfully navigating the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is a commendable achievement, but the journey doesn’t end with implementing a solution. Each step, from forming a team to congratulating them, is a building block in your organization’s culture of continuous improvement.
Employing specific tools like RACI Matrix, 5 Whys, FMEA, and Control Charts at different stages ensures that your problem-solving efforts are not just effective but also sustainable. These tools offer more than just a way to tackle issues; they provide a structured approach to learning from them. Remember, the goal isn’t just to solve a single problem but to refine a system that becomes increasingly resilient and efficient over time. So, take a moment to celebrate your achievements, and then gear up for your next challenge, armed with the knowledge and tools that will make your problem-solving journey even more impactful.
- Sharma, M., Sharma, S. and Sahni, S., 2020. Structured Problem Solving: combined approach using 8D and Six Sigma case study. Engineering Management in Production and Services , 12 (1), pp.57-69.
- Broday, E.E. and Júnior, P.P.A., 2013. Application of a quality management tool (8D) for solving industrial problems. Independent Journal of Management & Production , 4 (2), pp.377-390.
- Engineer, A.T.D., 2016. Managing project using 8D technique. Management , 7 (6), p.67œ76.

Daniel Croft
Daniel Croft is a seasoned continuous improvement manager with a Black Belt in Lean Six Sigma. With over 10 years of real-world application experience across diverse sectors, Daniel has a passion for optimizing processes and fostering a culture of efficiency. He's not just a practitioner but also an avid learner, constantly seeking to expand his knowledge. Outside of his professional life, Daniel has a keen Investing, statistics and knowledge-sharing, which led him to create the website learnleansigma.com, a platform dedicated to Lean Six Sigma and process improvement insights.

Is Minitab Worth it?

Reducing Transport Waste: Mastering the ‘T’ in TIMWOODS
Free lean six sigma templates.
Improve your Lean Six Sigma projects with our free templates. They're designed to make implementation and management easier, helping you achieve better results.

5S Floor Marking Best Practices
In lean manufacturing, the 5S System is a foundational tool, involving the steps: Sort, Set…
How to Measure the ROI of Continuous Improvement Initiatives
When it comes to business, knowing the value you’re getting for your money is crucial,…
8D Problem-Solving: Common Mistakes to Avoid
In today’s competitive business landscape, effective problem-solving is the cornerstone of organizational success. The 8D…
The Evolution of 8D Problem-Solving: From Basics to Excellence
In a world where efficiency and effectiveness are more than just buzzwords, the need for…
Are you grappling with recurring problems in your organization and searching for a structured way…
How to Select the Right Lean Six Sigma Projects: A Comprehensive Guide
Going on a Lean Six Sigma journey is an invigorating experience filled with opportunities for…
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project management |
- What is 8D? A template for efficient pr ...
What is 8D? A template for efficient problem-solving
How you respond when problems arise is one of the most defining qualities of a manager. Luckily, there are tools you can use to master problem-solving. The 8D method of problem-solving combines teamwork and basic statistics to help you reach a logical solution and prevent new issues from arising.
You’ve spent months overseeing the development of your company's newest project. From initiation, planning, and execution, you’re confident this may be your best work yet.
Until the feedback starts rolling in.
There’s no sugar-coating it—things don’t always go as planned. But production or process issues are hardly a signal to throw in the towel. Instead, focus on honing your problem-solving skills to find a solution that keeps it from happening again.
The 8D method of problem solving emphasizes the importance of teamwork to not only solve your process woes but prevent new ones from occurring. In this guide, we’ll break down what 8D is, how to use this methodology, and the benefits it can give to you and your team. Plus, get an 8D template to make solving your issue easier.
What is 8D?
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues.
How do you use the 8D method?
The 8D method is a proven strategy for avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems. If you’re noticing issues in your workflow or processes, then it’s a good time to give this problem-solving method a try.
To complete an 8D analysis, follow “the eight disciplines” to construct a statistical analysis of the problem and determine the best solution.
The eight disciplines of problem-solving
8D stands for the eight disciplines you will use to establish an 8D report. As you may notice, this outline starts with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. The “zero stage” was developed later as an initial planning stage.
To illustrate these steps, imagine your organization experienced a decline in team innovation and productivity this past year. Your stakeholders have noticed and want to see changes implemented within the next six months. Below, we’ll use the 8D process to uncover a morale-boosting solution.
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D8 problem solving approach (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/6ab7c188-3258-4d2e-afe6-9a4a084cc09f/inline-productivity-8d-template-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
D0: Prepare and plan
Before starting the problem-solving process, evaluate the problem you want to solve. Understanding the background of the problem will help you identify the root cause in later steps.
Collect information about how the problem has affected a process or product and what the most severe consequences may be. Planning can include:
Gathering data
Determining the prerequisites for solving the problem
Collecting feedback from others involved
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D0 Planning (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/abc3621d-e1ae-47ff-b731-0ee38cff99e9/inline-productivity-8d-template-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If we look back at our example, you may want to figure out whether this decline in morale is organization-wide or only applies to a few departments. Consider interviewing a few employees from different departments and levels of management to gain some perspective. Next, determine what knowledge and skills you will need to solve this lapse in productivity.
D1: Form your team
Create a cross-functional team made up of people who have knowledge of the various products and workflows involved. These team members should have the skills needed to solve the problem and put corrective actions in place.
Steps in this discipline may include:
Appointing a team leader
Developing and implementing team guidelines
Determining team goals and priorities
Assigning individual roles
Arranging team-building activities
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D1 Team members (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/51986017-5150-4dd4-940c-252cd0eb8ba5/inline-productivity-8d-template-3-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
From our example, a solid team would consist of people with first-hand experience with the issues—like representatives from all departments and key people close to workshop-level work. You may also want to pull someone in from your HR department to help design and implement a solution. Most importantly, make sure the people you choose want to be involved and contribute to the solution.

D2: Identify the problem
You may have a good understanding of your problem by now, but this phase aims to break it down into clear and quantifiable terms by identifying the five W’s a and two H’s (5W2H):
Who first reported the problem?
What is the problem about?
When did it occur and how often?
Where did it occur (relating to the sector, supplier, machine, or production line involved)?
Why is solving the problem important?
How was the problem first detected?
How many parts/units/customers are affected?
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D2 Problem statement & description (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9825ecd6-2bd3-4559-a68c-b1ae8aca2e52/inline-productivity-8d-template-4-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Use your team’s insights to answer these questions. From our example, your team may conclude that:
Employees feel overwhelmed with their current workload.
There is no real structure or opportunity to share new ideas.
Managers have had no training for meetings or innovation settings.
Disgruntled employees know they can achieve more—and want to achieve more—even if they seem disengaged.
Once you answer these questions, record an official problem statement to describe the issue. If possible, include photos, videos, and diagrams to ensure all parties have a clear understanding of the problem. It may also help to create a flowchart of the process that includes various steps related to the problem description.
D3: Develop an interim containment plan
Much like we can expect speedy first aid after an accident, your team should take immediate actions to ensure you contain the problem—especially if the problem is related to customer safety.
An interim containment plan will provide a temporary solution to isolate the problem from customers and clients while your team works to develop a permanent corrective action. This band-aid will help keep your customers informed and safe—and your reputation intact.
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D3 Interim containment action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d6279c36-ccc6-4de3-89d2-f221632a1059/inline-productivity-8d-template-5-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Because your findings revealed workers were overworked and managers lacked training, your team suggests scheduling a few mandatory training sessions for leaders of each department covering time and stress management and combating burnout . You may also want to have a presentation outlining the topics of this training to get key managers and stakeholders interested and primed for positive upcoming changes.
D4: Verify root causes and escape points
Refer back to your findings and consult with your team about how the problem may have occurred. The root cause analysis involves mapping each potential root cause against the problem statement and its related test data. Make sure to test all potential causes—fuzzy brainstorming and sloppy analyses may cause you to overlook vital information.
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D4 Root cause & escape points (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/301717c6-0434-4c88-addf-d500dc23ae87/inline-productivity-8d-template-6-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
In our example, focus on the “why” portion of the 5W2H. You and your team identify six root causes:
Managers have never had any training
There is a lack of trust and psychological safety
Employees don’t understand the objectives and goals
Communication is poor
Time management is poor
Employees lack confidence
In addition to identifying the root causes, try to pinpoint where you first detected the problem in the process, and why it went unnoticed. This is called the escape point, and there may be more than one.
D5: Choose permanent corrective actions
Work with your team to determine the most likely solution to remove the root cause of the problem and address the issues with the escape points. Quantitatively confirm that the selected permanent corrective action(s) (PCA) will resolve the problem for the customer.
Steps to choosing a PCA may include:
Determining if you require further expertise
Ensuring the 5W2Hs are defined correctly
Carrying out a decision analysis and risk assessment
Considering alternative measures
Collecting evidence to prove the PCA will be effective
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D5 Permanent corrective action (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/53509966-18dd-4bb4-88a1-c7ca940fde3f/inline-productivity-8d-template-7-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your team decides to roll out the training used in the interim plan to all employees, with monthly company-wide workshops on improving well-being. You also plan to implement meetings, innovation sessions, and team-coaching training for managers. Lastly, you suggest adopting software to improve communication and collaboration.
D6: Implement your corrective actions
Once all parties have agreed on a solution, the next step is to create an action plan to remove the root causes and escape points. Once the solution is in effect, you can remove your interim containment actions.
After seeing success with the training in the interim phase, your stakeholders approve all of your team’s proposed PCAs. Your representative from HR also plans to implement periodic employee wellness checks to track employee morale .
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D6 PCA implementation plan (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/ca68af4a-afa7-4be4-93cb-8a8321eb5172/inline-productivity-8d-template-8-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
To ensure your corrective action was a success, monitor the results, customer, or employee feedback over a long period of time and take note of any negative effects. Setting up “controls” like employee wellness checks will help you validate whether your solution is working or more needs to be done.
D7: Take preventive measures
One of the main benefits of using the 8D method is the improved ability to identify necessary systematic changes to prevent future issues from occurring. Look for ways to improve your management systems, operating methods, and procedures to not only eliminate your current problem, but stop similar problems from developing later on.
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] D7 Preventive measure (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/cdd7b133-fb80-4db7-8935-1285a6b62b69/inline-productivity-8d-template-9-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Based on our example, the training your team suggested is now adopted in the new manager onboarding curriculum. Every manager now has a “meeting system” that all meetings must be guided by, and workloads and projects are managed as a team within your new collaboration software . Innovation is improving, and morale is at an all-time high!
D8: Celebrate with your team
The 8D method of problem-solving is impossible to accomplish without dedicated team members and first-class collaboration. Once notes, lessons, research, and test data are documented and saved, congratulate your teammates on a job well done! Make an effort to recognize each individual for their contribution to uncovering a successful solution.
![explain 8d problem solving its steep [inline illustration] 8D Team congratulations & reward (example)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d2055965-bf3d-4bf4-a1ea-a0a7c4bf8a32/inline-productivity-8d-template-10-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
8D report template and example
Check out our 8D report template below to help you record your findings as you navigate through the eight disciplines of problem solving. This is a formal report that can be used as a means of communication within companies, which makes for transparent problem-solving that you can apply to the entire production or process chain.
Benefits of using the 8D method
The 8D method is one of the most popular problem-solving strategies for good reason. Its strength lies in teamwork and fact-based analyses to create a culture of continuous improvement —making it one of the most effective tools for quality managers. The benefits of using the 8D method include:
Improved team-oriented problem-solving skills rather than relying on an individual to provide a solution
Increased familiarity with a problem-solving structure
A better understanding of how to use basic statistical tools for problem-solving
Open and honest communication in problem-solving discussions
Prevent future problems from occurring by identifying system weaknesses and solutions
Improved effectiveness and efficiency at problem-solving
Better collaboration = better problem solving
No matter how good a manager you are, production and process issues are inevitable. It’s how you solve them that separates the good from the great. The 8D method of problem solving allows you to not only solve the problem at hand but improve team collaboration, improve processes, and prevent future issues from arising.
Try Asana’s project management tool to break communication barriers and keep your team on track.
Related resources
What are story points? Six easy steps to estimate work in Agile
What is a flowchart? Symbols and types explained

How to choose project management software for your team

7 steps to complete a social media audit (with template)

8D Chess: How to Use The 8 Disciplines for Problem Solving
Hospitals have developed something of a reputation for being rife with bad processes . When processes aren’t adequate, the result is an abundance of “workarounds”.
For example, when equipment or supplies are missing, a nurse might waste time running around searching for what is needed, and once the item is found, return to their previous duties.
One study indicates that nurses spend 33 minutes of a 7.5-hour shift completing workarounds that are not part of their job description.
This may well “put out the fire” so-to-speak, but really it is just a hastily applied band-aid that does nothing to treat the root cause of the problem.
More time is wasted and more problems will arise in the future because nothing has been done to prevent the initial problem from happening again.
Individual nurses are not at fault here; workplace culture often values expertise in the form of those who “get the job done”, which tends to pull against the notion of spending time building good processes (time in which the job is perhaps not “getting done”).
So how to approach the problem of problem solving ?
In a lean context, problem solving can be distilled into two simple questions:
- What is the problem and how did it happen?
- How can we make sure that it doesn’t happen again?
The 8D, or eight disciplines methodology, is a problem solving process – most likely one of the most widely used problem solving processes out there. It is used by many different countries, in many different industries, and many different organizations.
8D is designed to help you put out those fires, and make sure they don’t happen again.
In this article, I’ll introduce you to the 8D problem solving methodology and provide you with an outline of the basic process that you can hopefully apply in your own business, plus how you can enhance 8D with other tools and methodologies like Six Sigma , FMEA , and Process Street .
Here’s what I hope you’ll take away after reading:
- An understanding of the basics of 8D
- Advantages of using 8D
- The purpose and objectives of each phase of the 8D process
- An understanding of how to use 8D for problem solving
- How 8D works with other problem solving tools
- How you can use Process Street to maximize the potential of the 8D framework
Let’s begin with the origins of 8D – what is it, and where did it come from?
What is 8D?
8D (sometimes Global 8D or G8D) stands for eight disciplines, and is a problem solving methodology. It’s basically a process for understanding and preventing problems.
Much like how risk management seeks to take a proactive, preventative stance, 8D aims to gain insight into the root causes of why the problems happen, so they won’t happen again.
The 8D process involves eight (sometimes nine) steps to solve difficult, recurring problems. It’s a transparent, team-based approach that will help you solve more problems in your business.
8D origins: Where did it come from?

Despite the popular story that 8D originated at Ford, it was in fact developed in 1974 by the US Department of Defence, ultimately taking the form of the military standard 1520 Corrective Action and Disposition System for Nonconforming Material .
Ford took this military standard, which was essentially a process for quality management , and expanded on it to include more robust problem solving methods.
In 1987, Ford Motor Company published their manual, Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS) , which included their first iteration of the 8D methodology.
Initially termed Global 8D (or G8D) standard, it is currently used by Ford and many other companies in the automotive supply chain.
8D, PDSA, & other problem solving processes
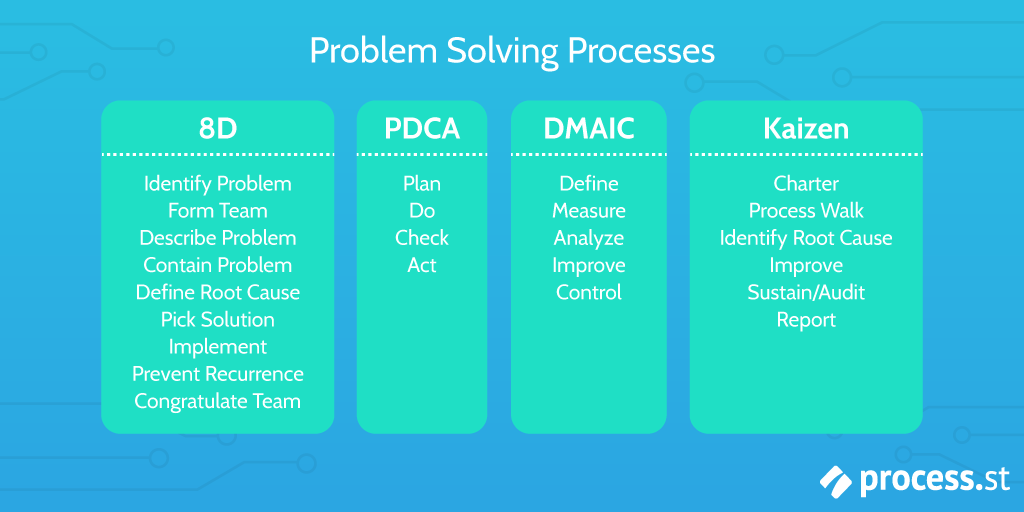
The disciplines of 8D follow the same logic as the Deming Cycle (also known as PDSA, and sometimes PDCA).
PDSA stands for Plan, Do, Study, Act (or Check, in the case of PDCA).
The similarity lies in the fact that both PDSA and 8D are designed to be used to improve processes. They’re both examples of cycles of continuous improvement.
Whereas 8D may be painted as a more generic problem-solving framework, structurally speaking both 8D and PDSA share a lot in common.
The simple idea of beginning with a clear objective, or desired output, and then testing, analyzing , and iteratively tweaking in a continuous cycle is the basis for both methodologies.
There are, of course, differences. We’ll cover the different applications of both 8D and PDSA in this article.
8D advantages

One of the main strengths of 8D is its focus on teamwork. 8D philosophy encourages the idea that teams, as a whole, are more powerful than the sum of the individual qualities of each team member.
It’s also an empirical methodology; that is to say that it is a fact-based problem solving process.
A branch of continuous improvement, proper use of 8D will help you coordinate your entire team for effective problem solving and improved implementation of just about all of the processes used in your business.
The 8 disciplines for problem solving
As you may have noticed, we’re starting with zero, which makes nine total disciplines. This “zero” stage was developed as an initial planning step.
D0: Plan adequately
Make comprehensive plans for solving the problem including any prerequisites you might determine.
Be sure to include emergency response actions.
D1: Establish your team
Establish your core team with relevant product or process knowledge. This team will provide you with the perspective and ideas needed for the problem solving process.
The team should consist of about five people, from various cross-functional departments. All individuals should have relevant process knowledge.
A varied group will offer you a variety of different perspectives from which to observe the problem.
It is advisable to establish team structure, roles, and objectives as far ahead in advance as possible so that corrective action can begin as quickly and effectively as possible.
D2: Describe the problem
Have your team gather information and data related to the problem or symptom. Using clear, quantifiable terms, unpack the problem by asking:
D3: Contain the problem (temporary damage control)
Depending on the circumstances, you may need to mobilize some kind of temporary fix, or “firefighting”.
The focus of this stage should be on preventing the problem from getting worse, until a more permanent solution can be identified and implemented.
D4: Identify, describe, and verify root causes
In preparation for permanent corrective action, you must identify, describe, and verify all possible causes that could contribute to the problem happening.
You can use various techniques for this, including a Failure Modes and Effects Analysis , or Ishikawa (fishbone) diagram .
It’s important that the root causes are systematically identified, described in detail, and promptly verified (or proved). How each cause is verified will depend on the data type and the nature of the problem.
Take a look at the section towards the end of this article for some more problem solving tools to help you decide the right approach.
D5: Identify corrective actions
You must verify that the corrective action you identified will in fact solve the problem and prevent it from happening again in the future (or whatever is your desired threshold of recurrence).
The best way to do this is to collect as much data as possible and by performing smaller-scale “pilot” tests to get an idea of the corrective action’s impact.
You can’t begin to identify the optimal corrective action until you have identified the root cause(s) of the problem.
D6: Implement and validate corrective actions
Carry out the corrective actions, and monitor short and long term effects. During this stage, you should assess and validate the corrective actions with empirical evidence.
Discuss and review results with your team.
D7: Take preventative measures (to avoid the problem happening again)
Here is where you make any necessary changes to your processes, standard operating procedures , policies , and anything else to make sure the problem does not happen again.
It may not be possible to completely eliminate any chance of the problem recurring; in that case, efforts should focus on minimizing possibility of recurrence as much as possible.
D8: Congratulate your team
It’s important to recognize the joint contribution of each and every one of the individuals that were involved in the process.
Team members should feel valued and rewarded for their efforts; this is crucial and perhaps the most important step – after all, without the team, the problem would not have been fixed.
Providing positive feedback and expressing appreciation helps to keep motivation high, which in turn improves the sense of process ownership and simply increases the likelihood your team will actually want to improve internal processes in the future.
How to use 8D for problem solving
The 8D method above outlines a proven strategy for identifying and dealing with problems. It’s an effective problem solving and problem prevention process.
In addition to avoiding long-term damage from recurring problems, 8D also helps to mitigate customer impact as much as possible.
More than just a problem-solving methodology, 8D sits alongside Six Sigma and other lean frameworks and can easily be integrated with them to minimize training and maximize efficacy.
8D is definitely a powerful framework on its own, but it really shines when combined with other synergistic concepts of lean and continuous improvement.
More problem solving tools that synergize well with 8D
8D has become a leading framework for process improvement, and in many ways it is more prescriptive and robust than other more simplistic Six Sigma approaches.
However, there are many Six Sigma methodologies, and even more frameworks for problem solving and process improvement .
The following improvement tools are often used within or alongside the 8D methodology.
DMAIC: Lean Six Sigma

DMAIC stands for:
The DMAIC process is a data-driven cycle of process improvement designed for businesses to help identify flaws or inefficiencies in processes.
Simply put, the goal with DMAIC is to improve and optimize existing processes.
Interestingly, the development of the DMAIC framework is credited to Motorola , whose work built upon the systems initially developed by Toyota .
In terms of working alongside 8D, you could use DMAIC to identify root causes as in D4; you could also implement the same techniques to better understand prospects for corrective actions as in D5, and D6.
We have a whole article on the DMAIC process, if you’re interested.
SWOT analysis

Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. You can use a SWOT analysis to gain insight into your organization as a whole, or on individual processes.
The main synergy with 8D is in the identification of opportunities, threats, and weaknesses.
These can represent opportunities for process improvements, weaknesses in your process that could produce problems further down the line, and threats, both internal and external, that may be out of your direct control but that could cause problems for you.
Here’s a SWOT analysis checklist you can use to structure your own analysis:
FMEA: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis

FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) is a way of understanding the potential for problems and making preemptive preparations in order to avoid them. It is a method of risk management .
It is a type of preventative risk management process, and so works well in the context of identifying causes of problems so you can better deal with them.
FMEA and 8D work well together because:
- 8D can make use of information gathered during an FMEA process, like brainstorming sessions, to identify potential problems and their root causes.
- You can reuse possible cause information gathered during an FMEA process to feed into different representational diagrams like the Ishikawa (fishbone) diagram, which will help in the 8D process.
- 8D brainstorming data is useful for new process design. This allows the FMEA to take actual process failures into account, which produces more effective results.
- FMEA completed in the past can be used as databases of potential root causes of problems to inform 8D process development.
Here’s a free FMEA template for you to get started ASAP:
The Pareto Chart
The Pareto Chart helps us understand the impact of different variations of input on our output.
In relation to 8D, Pareto Charts can help us prioritize which root cause to target, based on which will have the greatest impact on improvement (where improvement is the desired output of the 8D process).
Here’s the Six Sigma Institute’s example Pareto Chart :
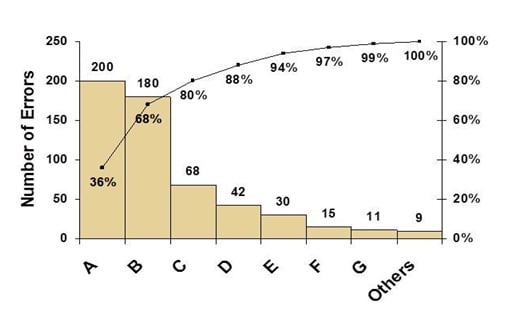
Here we have a simple deductive reasoning technique that asks “why?” five times to dig into the root cause of a problem.
The logic here is that by asking the same question five times, you work progressively “deeper” into the complexity of the problem from a single point of focus.
Ideally, by the fifth question you should have something that has a high likelihood of being a root cause.
This example from Wikipedia does a great job of conveying how the process works:
- The vehicle will not start. (the problem)
- Why? – The battery is dead. (First why)
- Why? – The alternator is not functioning. (Second why)
- Why? – The alternator belt has broken. (Third why)
- Why? – The alternator belt was well beyond its useful service life and not replaced. (Fourth why)
- Why? – The vehicle was not maintained according to the recommended service schedule. (Fifth why, a root cause)
Ishikawa diagrams (fishbone diagrams)
Sometimes called “cause-and-effect diagrams”, they are as such used to visualize the cause and effect of problems.
The approach takes six different categories and places information about the problem into different categories to help you understand what factors could be contributing to the problem.
One advantage over the 5 Whys approach is the way this method forces a more holistic perspective, as opposed to the potentially narrow vantage point offered by zooming in on a single aspect or question.
According to the Six Sigma Institute, the 6 key variables pertaining to root causes of problems are:
- Machine: Root causes related to tools used to execute the process.
- Material: Root causes related to information and forms needed to execute the process.
- Nature: Root causes related to our work environment, market conditions, and regulatory issues.
- Measure: Root causes related to the process measurement.
- Method: Root causes related to procedures, hand-offs, input-output issues.
- People: Root causes related people and organizations.
There’s also this useful illustration of a company using a fishbone diagram to better understand what factors contribute to a company’s high turn around time.
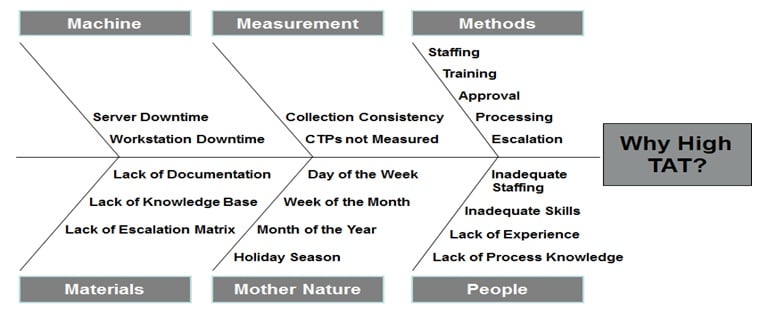
Gap analysis

A gap analysis is concerned with three key elements:
- The current situation, or “performance”
- The ideal situation, or “potential”
- What needs to be done in order to get from performance to potential, or “bridging the gap”
The “gap” is what separates your current situation from your ideal situation.
Businesses that perform a gap analysis can improve their efficiency and better understand how to improve processes and products.
They can help to better optimize how time, money, and human resources are spent in business.
There’s a lot that goes into a gap analysis, and quite a few different ways to approach it. Check out our article for a deeper dive into the gap analysis process.
Superpowered checklists
Checklists can be a great way to simplify a complex process into a series of smaller, easy-to-manage tasks. They’re one of the best ways to start using processes in your business.
By using checklists, you can reduce the amount of error in your workflow , while saving time and money by eliminating confusion and uncertainty.
What’s more, if you’re using Process Street, you have access to advanced features like conditional logic , rich form fields and streamlined template editing .
How to use Process Street for 8D problem solving
Good problem solving relies on good process. If you’re trying to solve problems effectively, the last thing you want is your tools getting in your way.
What you want is a seamless experience from start to finish of the 8D methodology.
The best kinds of processes are actionable. That’s why you should consider using a BPM software like Process Street to streamline recurring tasks and eliminate manual work with automation .
Process Street’s mission statement is to make recurring work fun, fast, and faultless. By breaking down a process into bite-sized tasks , you can get more done and stay on top of your workload.
Sign up today for a free Process Street trial!
Problem solving is an invaluable skill. What’s your go-to process for problem solving? We’d love to know how it compares with the 8D method. Let us know in the comments!
Get our posts & product updates earlier by simply subscribing
Oliver Peterson
Oliver Peterson is a content writer for Process Street with an interest in systems and processes, attempting to use them as tools for taking apart problems and gaining insight into building robust, lasting solutions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Take control of your workflows today
What is 8D (Eight Disciplines)? – Problem Solving Process
Eight Disciplines ( 8D Method) – 8 Disciplines Process, which can be translated as the Eight-Step Process of Responding to a Quality Problem. This method aims to treat defects quickly and consistently and to prevent such problems by preventing them. It boosts customer satisfaction and, despite the possible high costs at first, reduces costs in the medium term.
The eight steps of 8D Method are:

Step 1 (D1) – Formation of a working group on the decision trouble.
This is the first step in the8D process and the first part of Report 8D method. In this step, you determine the composition of Working Group 8D. Working Group8D shall be cross-functional and shall include technologist, designer, representative of the Quality Control Department and other specialists who will be involved in the localization of the problem, determining the causes of the occurrence defect, elimination, and prevention of the problem.
Step 2 (D2) – A detailed description of the defect : 8D.
This step includes a detailed description of the problem specified by the consumer. The problem should be described clearly and unambiguously. It is necessary to consider the data on the operation of the last one to two years, as well as 8D reports with the same defect (if any). in this step report 8d lists the problem information from the data Consumer. The information should contain the following items:
- Name consumer organization;
- Description claims;
- Information about the product (name, batch, date of delivery, etc.);
- When the problem was encountered for the first time;
- Where is a problem was noted;
- Assessment criticality of the defect.
Step 3 (D3) – Definition urgent measures.
This step explains the content of the problem and localizes it. Immediately after receiving information about the defect must be entered urgent measures to prevent the transfer of products into operation, in which may occur this or a similar defect. Based on initial investigation, it is necessary to determine the location of all products (parties) that could potentially be affected by the same issue and identify them. The report should include, if possible, the part numbers (batches) and the date of manufacture of potentially defective products.
Step 4 (D4) – Definition causes of this defect.
This step consists of a defect analysis and establishing the root causes of the problem. The corresponding part is also contained in the report 8D method, annexes may be added for clarification. It is necessary to give a detailed description of the cause of the defects, which allows you to understand why they happen. Then describe the root cause, indicating how it affects the mechanism of the defect. All phenomena originating from this the root causes and leading to the defect should be listed in the explanation. It is necessary to prove that the identified cause leads to established defect, for this purpose various methods are used (brain assault, affinity chart, multi-vote, Ishikawa diagram, “5-Why” analysis, method 5W+1H, bounce tree analysis (FTA), scattering (scattering) diagram, Pareto diagram, control charts, a method for analyzing the types and consequences of potential defects (FMEA)).
5 Step (D5) – Formulation and verification of corrective Action.
In this discipline, all possible corrective actions are identified, aimed at eliminating the root cause of the problem. Corrective executors the actions and schedule should be indicated in this part of the report. Also recommended, that an explanation of each corrective action regarding Root cause. Sometimes setting the best corrective actions for addressing the root cause requires preliminary assessments and studies. This is called “verification of corrective actions”. These steps are followed by being carried out in cases where the scope of work is very large, and the price of an error, expressed in money and time, too great. Verification is also possible corrective actions in practice to prove their effectiveness and exclude undesirable side effects.
6 Step(D6) – Implement corrective actions and track their impact.
Activities that have been audited and have received a positive result should be implemented. This section should the completion dates and executors of corrective actions are listed, and data showing that corrective actions do lead to eliminating the root causes. Any shortcomings in the effectiveness of corrective actions should be eliminated to improve them. In conclusion, there should be urgent events that have been cancelled.
Step 7 (D7) – Preventive actions to prevent recurrence of defects.
This step should not be confused with Fixing the cause of a specific problem. Problem prevention includes identification products or delivery kits that are equally exposed to the action problems identified by the consumer, even if they have not been identified in this situation. in the report you should specify all the warning actions and their executors and dates of implementation. An important aspect of this step is standardization and implementation of corrective actions that may affect similar products in the future. If necessary, activities should be introduced in training. At this stage, it is necessary to answer the questions: how it could arise defect, why it was not possible to prevent the defect, how the defect will be prevented in future, whether it is necessary to transfer the problem to other processes, nodes, depots.
Step 8(D8) – Performance Evaluation Group 8D.
The final step of the 8D process is to inspire the team with leadership. for a job well done. The condition for completion is that the reason problems have been clarify and prove, measures to eliminate as before them introduction. And after were tested for their effectiveness and were introduced measures to prevent the recurrence of the defect. At this point, the report should approve.
Related Posts
Six sigma does not equal total customer satisfaction, quality control circle [qcc] : basic guide, entrepreneurship: navigating challenges and cultivating success, 7s management, enterprises quality management innovation, pre-control charts | pre-control limits | narrow-limit gauging, cost control in production | efficiency and optimization, lean: kanban tools, lean manufacturing optimises enterprise production.
How to Solve Any Problem with the Eight Disciplines (8D)
What’s the best way to solve product and process-related problems? According to Ford Motor Company’s Team Orientated Problem Solving program (TOPS) , you need to take an 8-D perspective. It’s not as complicated as it may sound. The 8Ds or disciplines, target three basic aims: identify the problem, correct it, and make sure it doesn’t happen again.
Since the eight disciplines were first defined, the philosophy has been adjusted with the addition of a “0” discipline , so we’re really looking at nine steps or disciplines to guide you on your path to problem-solving success. Don’t be deterred by the word “discipline,” the process outlined in the eight (or nine) disciplines provides a straightforward template for problem-solving, and you don’t need any special training to follow it.
D0: Prepare For Problem Solving
Nobody likes putting out fires, but preparedness can avert disaster. The D0 step is the added discipline that gives us a total of nine, and it was tacked on after the eight disciplines had already been formulated.
The need for this additional step will be apparent to anyone who has faced a potential business disaster. Panicking isn’t a solution, and since the kind of problems we address with 8D methodology aren’t predictable, its good to be prepared for the unexpected and be ready to face it with a cool head. Knowing how you’ll respond in emergencies helps you to act faster.
What is Tallyfy?
Tallyfy helps you document and automate tasks between co-workers and clients
Once you’ve taken this vital step, you can begin working on any problems that arise without losing your cool.
D1: You Need the Right Team
You need inside information from the people best-acquainted with the process or product that proved to be dysfunctional. It’s important that they understand what role they’ll play in fixing the problem. You should let them know that you’re not looking to pin blame on someone – you’re a project team working on solving the problem.
To complete all eight disciplines, you need a committed and knowledgeable team composed of members who are as eager to solve the problem and prevent its recurrence as you are. Communication is key. When things go wrong, those with the most intimate knowledge of the product or process are waiting for the ax to fall. They will feel responsible for the problem, but that works in your favor when you allow them an opportunity to be part of the solution.
D2: Define What the Problem Is
Knowing what the problem you’re working on might seem obvious – but it usually isn’t. To avoid miscommunication between your team, you need to clearly define what the problem (and the definition should cover all the bases). Just saying “A component is faulty,” for example, isn’t a clear enough definition. To get all the details you need to effectively define a problem, you need to use the 5W2H approach. In a nutshell, you need to figure out…
- Who is directly affected by the problem? Is it your customers? Is it a problem that was picked up internally?
- What is the problem? Pinpoint it as finely as you can. A customer who has a customer service or technical complaint might have one or more reasons to be unhappy. Exactly what was it that didn’t work?
- When was the problem first picked up?
- Where did it happen? Your problem-solving approach is a bit like a game of Cluedo. Defining the problem means you need to know the location as well as the person, the particulars of the problem, and its timing.
- Why did it happen? Your team may have more than one explanation as to why the problem happened. Record all the possible reasons they can think of.
- How did it happen? Circumstances are important too. This piece of information is vital because it might point towards an overlooked scenario that you’ll need to take into account in future.
- How many / much ? Quantification forms the basis of measurement . It will also help you to determine how effective your problem-solving efforts have been once you’ve implemented solutions.
D3: What Interim Measures Can You take to Contain or Limit the Consequences of the Problem?
Letting a potentially problematic system run or producing potentially defective products will only amplify the problem you’re trying to solve. Interim measures could be as drastic as stopping production. This, however, is sometimes mandatory. It’s better to delay shipment rather than ship a defective product.
Damage control is not a permanent solution, but at least it ensures that you’ve limited the negative effects the problem has on your customers and your business. Allowing work to continue as normal when you know that there’s a problem isn’t an option you can risk.
While you and your team search for solutions, you need to know that further harm to your business reputation isn’t happening. Decide on the right strategy to temporarily curtail the issue and implement it as soon as possible and move on to D4 .
D4: What Caused the Problem?
Identifying the root cause of a problem can be trickier than it seems on the surface. There’ll usually be a chain of events leading up to an issue, and solving the problem requires you to track the chain of events that led up to it all the way back to the single set of circumstances that triggered it.
For example, a clothing manufacturer discovers that the seams of its jackets are coming apart. It would be easy to blame the person who was in charge of the stitching, but perhaps the machine was faulty, and its just possible that the machine was faulty because of the type of cotton that was fed into it, and the wrong cotton was fed into it because there was a mix-up in the stores, but the stores only made their error because the supplier didn’t label packages properly.
Use the 6m method to help you track problems to their source:
- Man or Manpower : If it seems that human error is to blame, what caused the mistake? Was the operator aware of what is required? Did he or she have sufficient training to meet the requirements of the job? What if he or she wasn’t physically up to the task?
- Machine : If you thought that working with machines was any easier, think again. There is a multitude of reasons why machines might fail. Is the right equipment being used? Was the equipment correctly calibrated? Has the machine been adequately maintained so that it is in good working order?
- Materials : As any manufacturer will know, you can’t make good quality products out of poor materials. But were the right materials being used? Did they have the right physical or chemical properties?
- Method : your staff could be well-trained, your machines well-maintained, and your materials of a suitable standard, but if the methods used aren’t up to scratch, you aren’t going to get the desired results.
- Measurement : If you ever added a tablespoon of salt to a recipe that required a teaspoon, you’ll know that using the correct, standard measurements are necessary if you want to get good results.
- Environment : The workplace environment: temperature, humidity, light, and cleanliness can also be to blame when problems arise.
Other than the 6m method, you could also try using the 5 Whys analysis. It’s a problem-solving methodology that helps you find the rootcausee of an issue by asking “why” enough times.
D5: Decide on Appropriate Corrective Action
Now that you and your team are confident that you’ve pinpointed the cause of the problem you encountered, it’s time to start working on the determination of solutions. This could involve generating a list of possible actions and thinning it down to the ones you think likely to be the most effective. Your aim is to remove the cause of the problem, and that could entail anything from a simple intervention to a multi-faceted improvement plan.
Whatever solutions you choose, you need to be sure that the measures you implement will continue being implemented in the long-term. This may involve setting up a system of checks and balances, additional quality control measures, or extra steps to be incorporated into standard workflows.
D6: Act and Confirm that Your Action Corrected the Problem
Having come this far with the eight disciplines approach to problem-solving, you might feel that it’s time to celebrate success, but you still need to wait a little longer. This is only the fifth of the eight disciplines, so although you’ve come a long way, your job isn’t done yet. Implementing the sixth discipline (corrective action) is even more important than deciding what ought to be done.
Communicate with affected employees so that they can understand the importance of any changes that are likely to affect them, why you’re making these changes, and what problem you’re working to eliminate. But even once they’re doing everything according to the new methods you’ve devised with your team, you still need to be sure that you’ve correctly identified and dealt with the gremlin that’s the cause of your woes.
That means careful monitoring of the “what” that started you on your problem-solving journey. Have you eliminated the problem? Keep tabs on your outputs in the long-term to be sure that you have.
D7: Prevent the Recurrence of the Problem and Entrench New Standards
So far, you and your team have hit the spot. You’ve identified why things went wrong, and you’ve successfully introduced changes that address the root cause of the problem that set you all to work. But you haven’t reached the final step just yet. By introducing new methods, you’ve effectively introduced a new standard, and you want that standard to be upheld. Your company’s reputation depends on it.
The work you’ve done has shown that you need to make changes to the way your company does things. You’ve implemented the modifications you and your team thought necessary with success. But these changes need to be incorporated into long-term business processes so that they become second-nature. There will certainly be changes to policies, procedures , and workflows even if they’re as simple as adding a new quality-control step to a process.
The Change management process can be tough, even if you’re only improving or changing a single process . Be sure everyone’s on the same page and follow up. To make this step easier, you can try either documenting your new processes or adopting workflow management software .
Workflow software can help enforce any changes you make to the new process – rather than having to manually explain the change to the employee, you can simply let the software do it for you.
D8: Eight Disciplines Reached. Celebrate Success With your Team
Without your problem-solving team, you would never have come this far or been this successful. By putting your heads together, you have permanently resolved a knotty problem. That’s reason to celebrate, and it’s also time to thank each team member for his or her contributions to the process. Each of them deserves recognition, and that recognition should be formal and organization-wide.
It’s also time to renew you and your team’s commitment to continuous improvement a commitment no organization should be without. Giving thanks where they are due will encourage future efforts, both within your team and across the organization. Who doesn’t want to be a hero? The eight disciplines approach to problem-solving depends on your team, and they deserve the recognition you give them.

Auto-document and track workflows with other people in real-time
FlashLearners
Education And Career Blog
8D Problem-Solving Process: How To Apply The 8 Disciplines
Modified On Nov 7, 2023
Industries ranging from health care and manufacturing to retail often rely on strategic methods for addressing issues. One of the most common is the 8D problem-solving method, which involves identifying the root of the problem and developing preventative measures. Implementing this measure can help teams collaborate in a way that increases efficiency, reduces costs and improves customer satisfaction.
In this article, we explain 8D problem-solving, how to apply the eight disciplines and discuss the benefits and applications of this process.
PAGE CONTENTS
What is 8D problem-solving?
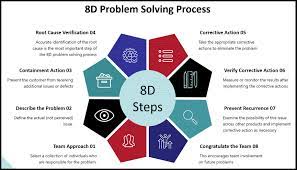
8D problem-solving is an approach that quality engineers and manufacturers use to identify and address challenges throughout a project. 8D refers to the eight different disciplines, or steps, that the process entails. Note that since its inception, the 8D problem-solving method has added a stage for planning at the beginning of the process.
While the 8D problem-solving method first gained popularity in the automotive industry, industries ranging from health care and manufacturing to finance, government and retail implement it today. 8D works by finding the root cause of a problem and conducting a statistical analysis. Then, it implements interim solutions that can alleviate some of the negative effects of the problem while a team continues searching for and implementing permanent corrective actions.
How to use 8D problem-solving
Here’s how to use 8D problem-solving:
1. D0: Prepare and plan
Before starting the 8D process, evaluate the problem you’re trying to solve. Collect information about the different effects of the problem and the most severe issues that may result from the problem. Keep a checklist of these issues to better work to resolve them, including by deciding what resources you may need. Consider seeking feedback from others involved to ensure a well-informed and rational approach. During the 8D process, try to protect the customer from any ongoing negative effects associated with the problem until you’re able to solve it.
2. D1: Form a team
Create a team of people familiar with the various products and processes. Choose people who also have the time and skills in the necessary areas to solve the problem and implement corrective actions. Some of the different actions that comprise this step in the 8D problem-solving process include:
Naming team members and setting up the team
Appointing a team leader
Developing and sharing team guidelines
Going over team goals and priorities
Arranging team-building exercises, if needed
3. D2: Describe the problem
Identify the problem in clear, quantifiable terms by identifying the who, what, where, when, why, how and how many (5W2H) of the problem. Then, clearly describe the problem. Actions for this step include:
Developing a problem statement
Deciding if the problem is caused by a change in something already there or if it’s a new problem
Developing a project plan with goals and objectives
Creating a diagram to pinpoint possible causes
Marking a flowchart of the process, including various steps as related to the problem description
4. D3: Develop interim containment actions
Define and implement actions that can contain the problem within the business and isolate it from any customer. Containing the problem is a temporary solution while the team develops permanent corrective or preventive actions to solve the problem. After defining and implementing an interim containment action, the team also checks with the customer to see if the action has been effective.
5. D4: Define and verify root causes and escape points
Look for causes that may explain why the problem happened. Test each potential root cause against the problem description and related test data. Try to find where the first indications of a problem arose and identify why your team didn’t notice it. This point is called the escape point. Those using the 8D model can consider all potential root causes before verifying or dismissing them. Some people may use the five whys and cause-and-effect diagrams to test the various causes of the problem they’ve identified.
6. D5: Choose and verify permanent corrective actions (PCAs) for the problem
Choose the most likely solution to remove the root cause of the problem, then come up with the most likely solution to the issues with the escape point. Double-check to ensure that both these solutions have a good chance of correcting the problem for the customer without any negative outcomes or unwanted effects.
7. D6: Implement and validate permanent corrective actions
The next step is to plan, define and implement the ideal permanent corrective actions, or CAs, to remove any root causes and escape points. Once you implement these corrective actions, you can remove any interim containment actions. Observe the results over a long period and verify the success of the new solutions by seeing how they affect the customer. Consider identifying the negative effects of these newly implemented solutions.
8. D7: Prevent recurrence
Modify the management systems, operation systems, methods and procedures to ensure that this problem is less likely to happen again. Look for opportunities to improve these systems and procedures to eliminate the current problem you’ve been working to resolve. Additionally, you can look for ways to improve your methods to stop similar problems from developing later.
9. D8: Recognize team and individual contribution
The final step in the 8D process is to review the problem-solving project and the group’s work. Document everything and save all notes, lessons, research and test data. Then, openly acknowledge your appreciation for the team’s collaborative efforts while also recognizing the contributions of team members.
Why apply 8D problem-solving?
8D problem-solving offers many benefits. It can help:
Focus on collaboration and cooperation rather than relying solely on individual contribution
Allow team members to become familiar with an efficient and successful method of problem-solving
Allow the project team to learn from earlier problems or errors
Improve knowledge of problem-solving techniques and tools so that team members can more easily address other problems that they may encounter
Encourage open communication around problematic situations, which can increase teamwork overall
Keep management informed about problems that affect the business so that they can address problems more quickly and effectively
Encourage company-wide improvements
When to apply 8D problem-solving
You might use the 8D problem-solving method in situations such as:
Someone discovers that there are concerns about safety or regulations.
Customers express concerns about a product’s functionality.
Tests and usage reveal above-average failure rates.
Reports reveal high levels of waste, scraps and manufacturing defects.
Product testing reveals high numbers of failed tests or poor performance.
I hope you find this article helpful.

About Chinedu
Based in Nigeria's Enugu, I'm a student crafting captivating tales as a writer and igniting sparks as a Motivational Speaker.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
8D Manufacturing Report: Your Guide to Effective Problem Solving
- Written by Brecht Plasschaert
- Compliance , Lean Manufacturing
- Updated on January 10, 2024
- Published on August 16, 2022
Manufacturing companies are the backbone of any economy. They produce goods for local or international markets, employ people, and keep their customers happy.
That’s why manufacturers often use 8D reports to identify and solve problems before they impact their production and business to ensure the quality of produced goods. The methodology was developed by Toyota Motors Manufacturing (TMM) in Japan in the 1960s to help the company achieve better performance.
For companies who want to compete with other manufacturers around the world, it’s essential to identify and track root causes of non-conformities or problems in a production environment. This helps them achieve a high level of product efficiency and quality, which translates into lower costs and higher profits.
In this article we cover the ins and outs of 8D reporting, how to use it, and the advantages it may offer to your workforce.
Download our 8D template as well to make your problem-solving process simpler.
The 8D method structure
The 8D problem-solving method is a systematic approach to problem solving that emphasizes team participation. This method generally covers:
- Identifying the Problem — You must first identify what is wrong with the process or operation.
- Determining Causes — After identifying a problem, you will have to determine its root cause(s). This may not be easy, but it’s imperative if you want to fix your processes and prevent future problems from arising again.
- Developing Corrective Action — Once you’ve identified the causes of your problems and analyzed all possible solutions, it’s time to develop corrective actions. Create a plan for how each possible solution would work (i.e., “if we use this part instead,” or “if we add these people,” etc.). You’ll also need metrics and checkpoints throughout this process to ensure that everything is working as intended.
The 8 disciplines
The eight disciplines (8D) follow a logical sequence of eight steps. It’s one of the most common methods used in manufacturing because it’s a structured approach, but it can also be applied to other industries.
D1: Create a team When using 8D, it is important to have a cross-functional team with individuals from different disciplines to assist you cover more territory. There should be two subgroups for the team members:
- Core members: people who are more data-driven and typical product, process, and data experts.
- Subject Matter Experts (SME): members who may contribute to brainstorming, research, and process observation. Bring in fresh SMEs without hesitation to assist with any step of the process.
These team members have to be equipped with the knowledge necessary to identify the issue and implement solutions.
D2: Describe the problem
The problem description is a narrative that describes the issue in detail and should be understood across the team members. It explains how the issue happened, what impact it had on your business, and why you need to fix it. The problem description should include:
- The underlying causes of your problem (the root cause). Why did this happen?
- What’s the impact of this issue? How much money are you losing because of this? What other problems does it cause within your company?
- How will fixing these underlying causes help solve or prevent future issues related to this one?
Here are some techniques and tools to identify and formulate the problems:
- 5 Why’s formulation
- Affinity Diagram
- Fishbone Diagram
- Is / Is Not method
D3: Develop a containment plan
Once you have identified, isolated, and controlled your manufacturing process problems, it’s time to create a plan for containment. You need clear descriptions so that everyone understands what they’re supposed to do in order to solve this issue. Be aware, an Interim Containment Action (ICA) is a temporary plan and should only be replaced with the Permanent Corrective Action (PCA) after completing 8D.
D4: Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Escape Point
You might find yourself wandering down several rabbit holes before reaching this point. Be patient and methodical as you work through each step in your investigation process. This process should always be guided by facts rather than assumptions or guesses about what could be going wrong behind closed doors at your company’s factories overseas!
Review your results, then talk with your team about potential causes of the issue. Each probable root cause is mapped to the issue statement and any associated test results as part of the root cause analysis. Be cautious to rule out all probable reasons; hazy brainstorming and careless analysis might lead you to miss important details.
Some methods during this step include:
- Comparative Analysis
- Development of Root Cause Theories
- Verification of Root Cause Theories
- Review Process Flow Diagrams
- Determine Escape Points, the closest point in the process where root cause could be found
In addition to determining the underlying causes, attempt to remember when and why you first discovered the issue in the process. This is called an escape point, and there can be more than one.
D5: Formulate Permanent Corrective Actions (PCA)
Corrective actions should be based on the root cause analysis. The first step in formulating corrective actions is to determine the root cause of the failure mode. To do this, you will need to analyze all of your data and identify which potential factors contributed to the problem. Once you have determined what caused the failure, you can then come up with ways of preventing similar failures from occurring in the future.
For example, if an assembly line stops due to an electrical issue with one machine, it would not make sense to fix just one machine; rather, you should look at all machines on that line and make sure they have proper electrical connections so that they are able to function properly.
So when something goes wrong, you will have a plan for fixing it before it causes even bigger problems down the road. There are several steps involved in creating an effective corrective action plan:
- Plan out how long it will take before implementing any changes that can help fix whatever issue has arisen;
- Create an actionable plan detailing exactly what needs changing;
- Check in at regular intervals on progress made toward completing this project so that no one gets forgotten along its path until completion (this includes monitoring by both parties involved)
- If necessary take appropriate steps like adding more resources or reallocating existing ones when delays arise from unforeseen factors such as weather conditions etc .”
D6: Implement and Validate the Permanent Corrective Action
Interim measures are temporary solutions to a problem. They can be used to prevent further damage or to allow time for a permanent solution to be implemented. Interim measures can also be used to reduce the impact of the problem until it is solved.
When you have identified an issue in your business, create an action plan that includes interim measures as well as final goals and expectations. If there is some sort of delay in implementing these interim measures, report back on progress at least monthly so management stays up-to-date on what is happening within your department and company at large.
Some activities during the 6D step include:
- Creating a project plan
- Share the plan with relevant parties.
- Use metrics to verify progress
D7: Monitoring of corrective measures
Monitoring is a key part of the 8D method. Monitoring is a way to check if a corrective action is working, or if it needs to be changed or completed. It’s also a way to check if the root cause has been addressed, and if your company has learned anything new from the incident that could help prevent future errors.
Your team needs to retain and document the shared knowledge that was gained while identifying, resolving, and preventing this problem. It’s important to review existing documents or procedures and update them accordingly to improve future outcomes.
Activities you need to keep in mind during this step are:
- Reviewing comparable products and procedures to avoid other problems.
- Creating or updating work instructions and procedures.
- Capturing new industry standards and procedures.
- Confirming the most recent failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA).
- Confirming the revision of control plans.
D8: Recognize team and individual efforts
Giving feedback to ensure a good outcome is crucial for any team to flourish. Recognize the efforts and labor that each person has put into what they have brought to the process at this moment.
The tasks in this stage consist of:
- Archive 8D for later use.
- Keep track of your learnings to enhance your problem-solving techniques.
- Comparisons of the before and after
- Celebration and acknowledgement of the group
How to Write an 8D report for your company when you have a product defect or a problem to solve?
An 8D report is a tool for managing a problem. It consists of eight columns and four rows:
- The first row, called the title row, lists each column’s name.
- Define the Problem
- Determine Causes
- Develop Solutions
- Verify Solutions
- Control Risks
- Document Your Improvements and Lessons Learned (optional)
- Closeout (optional).
- 1a through 7a include action steps related to 1 through 7 above;
- 6b includes an optional section that can be used if it becomes necessary to document lessons learned from this process at some later time (e.g., after you implement Solution 3b).
8D Report Pros and Cons for manufacturers
8d report advantages:.
More awareness of the root cause (s)
It improves your quality control processes by identifying the potential causes of nonconformance at each stage of production and prioritizes corrective action steps based on their risk level, priority, impact, probability, etc., thus ensuring that you address the system issues first before they result in incurring costs due to rework/scrap or adverse customer response or regulatory intervention.
Enhanced quality control strategies and plans.
8D enables you to reduce lead times by identifying where bottlenecks are occurring within a process so that resource allocation can be adjusted accordingly in order to improve throughput while maintaining quality standards (i.e., having sufficient workers available at all stages). This can also help with preventing employee burnout by covering more shifts so there is less overtime required from employees who might otherwise be tired from working too many hours without breaks when there is high demand for their services during peak times (like Christmas shopping season).
Avoid future problems
The 8D report can help your manufacturing company avoid costly mistakes, as you can see exactly where problems may occur and take action to prevent them.
Team-based approach
An 8D report gives you an opportunity to check if everything is running smoothly and confirm that everyone understands their tasks and responsibilities. With this information at hand, it’s easier to make improvements based on what works best or needs improvement in different areas of your business. In addition, it’s easy to access historical data on procedures and products.
Better communication flows
Finally, It also allows for better communication flows between teams responsible for different processes in the manufacturing process and reduces the amount of time spent investigating issues that aren’t really problems.
8D report Cons:
Extensive training
There aren’t many cons to applying 8D problem solving techniques. The most important one is that it will require that people who take part in problem-solving activities obtain the right training and instructions on how 8D operates.
They will also need to comprehend other closely linked concepts related to 8D issue solving methodologies. Examples of these may be pareto charts , process maps, fishbone diagrams, and more.
Lack in flexibility
In addition, an 8D report is not a good tool when there are several problems at once or when an issue in the manufacturing process needs immediate attention.
Dedicated budget
An 8D report also has requirements that smaller enterprises with fewer resources can find complicated and costly. For example: you need to have a dedicated budget to provide extensive training so your team has the right knowledge to do the job right.
Technology to Assist in 8D Reporting for manufacturers
There are a number of software solutions available to help companies implement 8D programs and manage their Supplier Quality Management (SQM) efforts.
Why should you digitize your 8D processes?
Automating the 8D report process will ensure that all problems are captured and reported consistently, with no one falling through the cracks.
It facilitates collaboration across teams and departments. All stakeholders will have access to information on the status of every problem as it progresses through its lifecycle, so they can respond quickly if an issue arises or make suggestions for how best to resolve it. This saves time and allows everyone involved in a particular issue to feel more connected with one another than they otherwise would be able to do without this kind of technology at their disposal.
8D Solutions
8D reporting is a powerful tool for monitoring progress and identifying issues in manufacturing. This can help you improve your processes, reduce cost, and increase profits. With the help of technology, you can easily keep track of your 8D reports. Here are some solutions to assist manufacturers with this process:
A program like SAP or Oracle ERP allows you to integrate 8D reporting into your system. This way, all information is in one place and updated automatically.
A no-code software tool like Azumuta allows you to integrate 8D reporting into your system. This way, all information is in one place and updated automatically. Easily capture data with your phone or tablet , while offline from the field at any time! Create an 8D report right away and distribute it to your stakeholders and coworkers and track corrective actions to team members through a single app.
With real-time data, companies can improve communication among team members, improve problem solving skills for individuals on the team (including managers), and develop new solutions for existing issues based on past experience with similar problems at other locations or companies.
Microsoft Office
If you don’t want to invest in new software at this time but still want an easy way to manage your project issues and progress, consider using an online database like Excel for managing risks, defects, quality assurance methods, etc. This will allow you to access information from anywhere with a laptop or mobile device. This way is rather tedious though and important information can be lost.
Digitize your 8D Processes
As you can see, there are many benefits to using a software for 8D reporting. While it may seem like a lot of work initially, once you get the hang of it, it will be easy to maintain and manage your 8D records. The most important thing is to start now! Make sure that your company gets started on an 8D reporting software today so that your team can begin documenting problems as soon as possible!
See how our platform can help streamline data collection, increase productivity, and increase quality assurance with a demo of Azumuta.
Don't forget to share this post!
In this article.
Recent Blog Updates
How to Apply Lean Principles in High-Mix, Low-Volume Manufacturing?
High-mix, low-volume manufacturing produces a diverse range of products in small quantities. Facing challenges in supply chain and workforce training, how could manufacturers optimize production with lean principles?
Training in Heavy & Light Industries: What’s the Difference?
What are the differences in frontline employee training for heavy industry vs light industry? Learn about the differences, with examples.
Azumuta Had a Blast at Hannover Messe 2024!
Azumuta recently took part in Hannover Messe 2024, the most important international event and hot spot for industrial transformation. Here’s what we learned at the event.
Heavy Industry vs Light Industry: What’s the Difference?
In this article, we will do a heavy industry vs light industry comparison. We will analyze their definitions, characteristics, and industry examples.
What Is Heavy Industry?
Learn more about heavy industry: its definition, examples, and the common characteristics of heavy industrial manufacturing.
Azumuta Is Now Compatible With BarTender!
Azumuta is now compatible with BarTender- the professional batch label design & printing software. See how you can benefit from this plug-and-play integration!
What Is Light Industry?
What is light industry? Check out its definition, characteristics, and examples of light industry sectors.
How to Prepare Your Team for an IATF 16949 Certification?
Know more about IATF internal auditor training. See which materials are needed, how to create an IATF audit checklist, assess their expertise, and standardize the improvements that you’ve made.
Take advantage of your time, International Six Sigma Inc. offers both Instructor-led Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training . Enroll Today!

8D Process: Its Importance and Advantages
The 8Ds — also known as the 8 Disciplines — Problem Solving Process is a team-oriented methodology that is mainly used to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems.
The methodology focuses on the origin of a problem by determining the root cause and establishes a permanent corrective and preventive action accordingly. It is an 8 tier process with integrated basic problem-solving tools.
This article will help you looks at 8D best practices how it can be helpful for manufacturers to better understand tools and techniques to address nonconformances and reduce risk.
History of 8D Problem Solving Process
There was a dire need for a team-oriented problem-solving strategy based on the use of statistical methods of data analysis. Ford Motors during World War II were manufacturing war vehicles in bulk. To ease up the assembly lines and the entire management in general, the executives of Powertrain Organization wanted a methodology where teams could work on recurring problems.
In 1986, the assignment was given to develop a manual and a course that will teach a new approach to solving tough engineering design and manufacturing defects. The manual for this methodology was documented and defined in “Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS)”, published in 1987.
The manual and courses were led at World Headquarters in Dearborn, Michigan. Subsequent changes and revisions were made based on the feedback from pilot sessions. The materials were extensive and the 8D titles were mere chapter headings for the steps in the process. Ford also refer to their current variant of the 8D process as G8D (Global 8D)
Use of 8D Process in Military
The US Government recognized the full caliber of the 8D process. During World War II, they standardized a process as Military Standard 1520 “Corrective Action and Disposition System for Non-confirming Materials”
Their 8D process was used to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems, whilst the methodology was useful in product and process improvement. It established a permanent corrective action based on a statistical analysis of the problem. It also focused on the origin of the problem by determining the root cause.
The 8D approach
The 8D model establishes a permanent corrective action based on statics and data of the problem. It focuses on the origin of the problem by determining its root causes. The earlier 8D models comprised of eight stages, the model got changed as time progressed. It was later expanded by an initial planning stage.
The stages (or Disciplines) are as follow:
D0 — Plan adequately
Proper planning and preparation is of utmost necessity before taking any action. So, before forming a team for the project, you’ll need to consider the following:
- Problem description
- Timeframe of the task
- Amount of resources
D1 — Establish your team
Create a diverse team with extensive portfolios. Make sure they have enough experience so that they can lead to the best quality inputs and complete solutions. For teams to function smoothly, define clear roles and responsibilities.
D2 — Describe the problem
The 8D methodology focuses on describing a problem objectively, capturing every vital information. During the analysis, a loop of 5W1H (why, what, who, where, when, and how) should be applied to develop a clear problem description.
D3 — Contain the problem
Projects that are big and take days to run a single task on them require a temporary problem containment plan to minimize the impact of a problem until a permanent solution is found. On developing the plan based on hypothetical cases, the resources for addressing the main problem can be released.
D4 — Identify the root cause
When the problem is temporarily contained, you can work on identifying the root cause of the nonconformance. You can use the 5W1H framework to understand the problem in-depth, or the Fishbone diagrams to categorize visually, or Pareto Charts to identify the vital causes.
D5 — Identify corrective actions
Once the root cause is recognized, the team can start brainstorming permanent corrections to identify the best long-term solution. Brainstorming with the team along with taking help from tools like affinity diagrams can help in organizing ideas.
D6 — Implement and validate corrective actions
Once a solution is identified, the management needs to implement and verify the corrective action. The PDCA (plan-do-check-act) approach is beneficial in this stage to do small-scale testing. To successfully implement a permanent change, a project plan should incorporate:
- Project plan development for implementation
- Communication of the plan with stakeholders
- Validating improvements using measurements
D7 — Implement preventive actions
A complete solution always provides no reoccurrence of problems. Even if you have created a complete solution, you should still work on preventive measures (after all, better today than tomorrow!).
In this stage, teams must consider actions that include updating audit process questions and verifying corrective actions periodically to reduce risk in processes. Teams can utilize the Poka-Yoke/Error Proofing methodologies to run tests to find defects.
D8 — Recognize team and individual efforts
At the end of the day, everyone wants their work to be recognized. Don’t be shy about that. Celebrate the team’s success and congratulate individuals for their work contribution. Doing such will facilitate motion and employee engagement while helping the organization to improve quality control.
Six Sigma tools that synergize with 8D
8D has become one of the leading frameworks for process improvement. It is robust and can mix easily with other prominent methodologies such as Six Sigma.
The following are improvement tools often used in Six Sigma processes. Learn how the addition of 8D can improve the process even further.
DMAIC – Lean Six Sigma
The DMAIC process is a data-driven cycle for process improvement. It is designed for businesses to identify flaws, errors, defects, or inefficiencies in a process.
Learn more on DMAIC and the process here .
In terms of combining 8D:
- One can use DMAIC to identify the root cause as in step D4
- One can implement the same technique to better understand prospects for corrective actions in steps D5 & D6
FMEA – Failure Mode & Effects Analysis
FMEA helps in understanding the potential for problems and making preemptive preparations to avoid them. This methodology is used majorly by Risk Management teams.
FMEA & 8D:
- 8D can use information gathered during an FMEA process to identify potential problems and the root causes.
- The information gathered during the FMEA process can be reused to feed into representational diagrams like Ishikawa (Fishbone) diagram.
- 8D brainstorming data can be used for new design processes. This allows the FMEA to take actual failures into account, thus producing effective results.
- Database from previous FMEA can be used as a benchmark for root causes of the problem to inform on 8D process development.
Pareto Charts
Pareto charts are majorly used to analyze data on the frequency of problems/causes in a process. It helps in understanding the impact of different variations of input and outputs via data and graphical representation.
- In relation to 8D, Pareto charts help in prioritizing which root cause to target based on which will have the greatest impact on the improvement process.
The 5 Whys is a deductive reasoning technique that asks “Why?” five times. The logic here is to ask the same question (WHY?) over and over again, making the reasoning process dig deeper into the complexity of a problem from a single point of focus.
When someone reaches the “5th Why?”, they should have something that has a high likelihood of being a root cause.
Benefits of 8D Problem Solving
8D focuses on teamwork. The framework’s philosophy is to encourage teams as a whole and individually. It’s a pragmatic methodology, i.e. a fact-based problem-solving process.
One of the main strengths of 8D is its focus on teamwork. 8D philosophy encourages the idea that teams, as a whole, are more powerful than the sum of the individual qualities of each team member.
Here are a few of the benefits that you can expect from the 8D problem-solving process:
- Institutes a structured and consistent problem-solving approach within an organization
- Enables individuals to become more effective at problem-solving
- Encourages team-based approach
- Helps ensure customers receive a timely and effective response to any concern
- Supports the requirements of quality management systems for corrective action, problem-solving, and continual improvement
- Helps in avoiding future problems by solving them in the present time
- Reduces Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ) by using the lessons learned in process improvement actions
- Assists organizations to comply with the customer-specific requirement for management concerns
SixSigma.com offers both Live Virtual classes as well as Online Self-Paced training. Most option includes access to the same great Master Black Belt instructors that teach our World Class in-person sessions. Sign-up today!
Comments are disabled for this post.
At home or workplace, we have you covered
Training Options
More than 500 locations
Classroom Training
Learn anytime, anywhere
Online Training
Live instructor-led training
Webinar Training
Customized training programs
On-site Training
Accelerated training programs
Blended Training
For streamlined business plans
Operational Excellence
Exclusive consulting services
Consulting Services
Fully customized programs
Group/Corporate Training
International six sigma inc. accreditation & affiliations.

Email: [email protected] Toll Free in the US: (866) 409-1363
Courses / Training
Login and registration
- Forgot Username?
- Forgot Password?
8D method (8 disciplines)
Origins of the 8d method, steps of the 8d method.
D1: Form a team
- Objective : Assemble a cross-functional team with the necessary skills to solve the problem.
- Select members based on their technical expertise, process knowledge, and problem-solving ability.
- Appoint a team leader responsible for oversight and coordination.
D2: Describe the problem
- Objective : Clearly understand the problem using factual data.
- Gather and document data and facts.
- Conduct a preliminary analysis to identify some probable major causes and detail the problem. Tools like "5W2H" (what, who, where, when, how, and why) can be used for this purpose.
- Ensure the problem is well-defined so everyone understands the same thing.
D3: Implement urgent actions (if necessary)
- Objective : Provide an urgent, likely temporary, solution to prevent the problem from spreading.
- Identify and implement temporary measures to contain the problem based on the preliminary analysis conducted in the previous step.
- Inform relevant parties about these actions.
D4: Identify and verify root causes
- Objective : Discover the true cause of the problem to avoid only treating the symptoms.
- Use analysis tools such as the 5 Whys, Ishikawa diagram (fishbone diagram), or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
- Validate the root cause by ensuring that eliminating it makes the problem disappear.
D5: Developp permanent actions
- Objective : Develop solutions to eliminate the root cause.
- Brainstorm to identify potential solutions.
- Select the best solution based on costs, available resources, and potential impacts.
- Test the chosen solution to ensure its effectiveness.
D6: Implement permanent actions
- Objective : Implement the long-term solution to permanently eliminate the problem.
- Deploy the solution on a large scale.
- Train relevant parties and update the necessary documentation.
D7: Prevent recurrence
- Objective : Ensure the problem will not reoccur in the future.
- Review and modify processes, standards, or systems to prevent a recurrence of the problem.
- Regularly monitor to verify that the corrective actions remain effective.
- Update any relevant documentation, be it manuals, standards, or specifications to reflect the changes made.
D8: Congratulate the team
- Objective : Recognize the team's efforts and reinforce a problem-solving culture.
- Celebrate successes.
- Share lessons learned with the entire organization.
- Encourage a culture of continuous improvement.
Pros and cons of the 8D method
The 8D method is widely used for problem-solving, especially in the automotive industry. However, like any approach, it has its advantages and disadvantages compared to other popular methods like DMAIC, A3, or PDCA. Here's an overview of the pros and cons of the 8D method compared to these methods.
Advantages of the 8D method :
Explicit emergency action : The 8D method includes a dedicated step (D3) for implementing emergency actions to immediately contain the issue. This allows for a quick response to at least partially address the problem, which none of the other three methods specify as explicitly.
Emphasis on team recognition : Step D8, focused on team recognition, emphasizes the importance of team dynamics and motivation, which can boost morale and encourage active participation in the future. Although recognizing individuals is also often part of other methods, it's not as explicitly defined in them.
Disadvantages of the 8D method :
Less emphasis on data analysis : Unlike DMAIC, which heavily emphasizes data analysis, the 8D method might sometimes not delve as deeply into quantitative analysis, possibly leading to less optimal solutions in some situations.
Structural rigidity : The linear structure of 8D, though providing clarity, can sometimes feel rigid. But this is also the case with the DMAIC and A3 methods (though the former has only 5 steps instead of 8, and the latter is less specified). The PDCA, with its cyclical nature, is noticeably more flexible allowing for a smoother iteration.
Possibly perceived as too action-oriented : The emphasis on emergency and corrective actions can sometimes overshadow the need for deep thinking and thorough analysis, especially if teams feel pressured to quickly solve issues.
Less suited for broader or systemic problems : While 8D is excellent for specific issues, methods like DMAIC or A3 might be better suited to tackle more complex or systemic problems that require deeper analysis.
8D: a method for addressing urgent, low-complexity problems?
- As time and resources are limited, that's always less to dedicate to researching the root causes of problems. Thus, if the problem is complex, we're less likely to implement the right methods to durably solve the problem.
- Since actions are taken in step D3, there's a risk that one might settle for them, at least initially... before realizing the problem isn't solved.
- Moreover, as actions are put into place in step D3, there's a risk that it might be more challenging to successfully implement other actions with the individuals who have to carry them out (classic phenomenon of staff mobilization, resistance to change, credibility of management in implementing successive actions...).
When you subscribe to the blog, we will send you an e-mail when there are new updates on the site so you wouldn't miss them.
Related Posts
A3 is a principle, not a problem-solving method !!
The pdca cycle or deming wheel: how and why to use it, the 5 whys method: how and when to use it, 5w2h or 5w1h methods: how and when to use them, ishikawa diagram and root cause analysis, comparison of problem-solving methods and techniques, continuous improvement process : a challenge for significant benefits, dmaic process: a methodology to implement six sigma, what is an operational audit of the organisation, improvement and innovation excellence.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The 8D problem solving model establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the problem and focuses on the origin of the problem by determining its root causes. Although it originally comprised eight stages, or disciplines, the eight disciplines system was later augmented by an initial planning stage.
The 8D problem solving process is a detailed, team oriented approach to solving critical problems in the production process. The goals of this method are to find the root cause of a problem, develop containment actions to protect customers and take corrective action to prevent similar problems in the future. The strength of the 8D process lies ...
8D Problem Solving is a systematic and structured approach used to solve business related problems. It names has been given by the fact there are 8 steps or 8 disciplines that are followed to identify, correct and eliminate recurring problems. 8D Problem Solving is regarded as robust methodology that has proven its worth across multiple ...
But issues can still pop up, angering customers and jacking costs while hurting a company's image. This is where the 8D corrective action problem-solving method earns its stripes. It was developed by Ford in the 80s and has since spread widely across manufacturing, healthcare, aerospace, and more. The 8D approach is a methodical process ...
The Ford Motor Company® developed the 8D (8 Disciplines) Problem Solving Process, and published it in their 1987 manual, "Team Oriented Problem Solving (TOPS)." In the mid-90s, Ford added an additional discipline, D0: Plan. The process is now Ford's global standard, and is called Global 8D. Ford created the 8D Process to help teams deal with ...
Eight Disciplines (8D) is a problem-solving methodology designed to address, correct, and eliminate recurring problems impacting business operations, manufacturing, and product development. Developed by Ford Motor Company in the 1980s, the 8D method has since been widely adopted across various industries as a comprehensive quality and process ...
By embracing quality management principles like ISO 9001, the 8D approach transformed from a 'military-specific' solution to a universally applicable method for problem-solving. This was a pivotal moment in its history, paving the way for the methodology's future evolutions and its adoption across diverse sectors.
D1: Form a Team. The first step in the 8D Problem-Solving Methodology is to form a cross-functional team. A well-assembled team is the backbone of any successful problem-solving initiative. While it may be tempting to rush through this step, investing time and effort here can pay dividends later.
Eight Disciplines Methodology (8D) is a method or model developed at Ford Motor Company used to approach and to resolve problems, typically employed by quality engineers or other professionals. Focused on product and process improvement, its purpose is to identify, correct, and eliminate recurring problems. It establishes a permanent corrective action based on statistical analysis of the ...
The eight disciplines (8D) method is a problem-solving approach that identifies, corrects, and eliminates recurring problems. By determining the root causes of a problem, managers can use this method to establish a permanent corrective action and prevent recurring issues. First introduced by Ford, the 8D method offers a consistent way of ...
There are different problem-solving tools that are shown in the problem - solving pyramid depending on time/complexity and the percentage of problems. 5 Why Figure 1: problem-solving pyramid 8D is one of these systematic methods used to tackle and solve problems. The primary aims of the 8D methodology are to identify the root cause, correct and
8D is a problem-solving methodology, useful for finding a short term fix and permanent solution to your product or process problems. It provides structure to the problem-solving process.8D methodology gives a hollistic approach to problem-solving. It covers containment till prevention of problem recurrence. Moreover, this tool can be used as a ...
8D (sometimes Global 8D or G8D) stands for eight disciplines, and is a problem solving methodology. It's basically a process for understanding and preventing problems. Much like how risk management seeks to take a proactive, preventative stance, 8D aims to gain insight into the root causes of why the problems happen, so they won't happen again.
Eight Disciplines ( 8D Method) - 8 Disciplines Process, which can be translated as the Eight-Step Process of Responding to a Quality Problem. This method aims to treat defects quickly and consistently and to prevent such problems by preventing them. It boosts customer satisfaction and, despite the possible high costs at first, reduces costs ...
According to Ford Motor Company's Team Orientated Problem Solving program (TOPS), you need to take an 8-D perspective. It's not as complicated as it may sound. The 8Ds or disciplines, target three basic aims: identify the problem, correct it, and make sure it doesn't happen again. Since the eight disciplines were first defined, the ...
D1: Form a team. Create a team of people familiar with the various products and processes. Choose people who also have the time and skills in the necessary areas to solve the problem and implement corrective actions. Some of the different actions that comprise this step in the 8D problem-solving process include: 3.
The 8D problem-solving method is a systematic approach to problem solving that emphasizes team participation. This method generally covers: Identifying the Problem — You must first identify what is wrong with the process or operation. Determining Causes — After identifying a problem, you will have to determine its root cause(s).
What is 8D Problem Solving. 8D problem solving is a structured and systematic approach to solving complex problems that require cross-functional collaboration and root cause analysis. It was developed by Ford Motor Company in the late 1980s as a way to address customer complaints and improve product quality.
This approach offers businesses a systematic and practical procedure to improve their efficiency and adopt corrective measures when necessary. The problem-solving method follows these steps: 1. D0: preparing a plan. The process starts with preparing a plan and evaluating the problem the organisation wants to solve.
Here are a few of the benefits that you can expect from the 8D problem-solving process: Institutes a structured and consistent problem-solving approach within an organization. Enables individuals to become more effective at problem-solving. Encourages team-based approach.
The 8D method is widely used for problem-solving, especially in the automotive industry. However, like any approach, it has its advantages and disadvantages compared to other popular methods like DMAIC, A3, or PDCA. Here's an overview of the pros and cons of the 8D method compared to these methods. Advantages of the 8D method:
When to use 8D problem solving -. How to apply eight disciplines of (8D) problem-solving -. D0 - Prepare and plan for 8D -. D1-Grab a team. D2-Understand the problem. D3-Take containment action. D4- Find the Root cause. D5- Choose permanent corrective action. D6- Implement and validate corrective action.
8-d concern (responsible for its resolution and follow-up). should include their title and phone # for reference and date 8-d was opened. problem description: it is extremely important that assignee of the 8-d or team fully understand precisely what the specific problem is. the best way is to physically look at the example "hands-on".