- Bankruptcy Basics
- Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
- Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy
- Debt Collectors and Consumer Rights
- Divorce and Bankruptcy
- Going to Court
- Property & Exemptions
- Student Loans
- Taxes and Bankruptcy
- Wage Garnishment

Understanding the Assignment of Mortgages: What You Need To Know
3 minute read • Upsolve is a nonprofit that helps you get out of debt with education and free debt relief tools, like our bankruptcy filing tool. Think TurboTax for bankruptcy. Get free education, customer support, and community. Featured in Forbes 4x and funded by institutions like Harvard University so we'll never ask you for a credit card. Explore our free tool
A mortgage is a legally binding agreement between a home buyer and a lender that dictates a borrower's ability to pay off a loan. Every mortgage has an interest rate, a term length, and specific fees attached to it.

Written by Attorney Todd Carney . Updated November 26, 2021
If you’re like most people who want to purchase a home, you’ll start by going to a bank or other lender to get a mortgage loan. Though you can choose your lender, after the mortgage loan is processed, your mortgage may be transferred to a different mortgage servicer . A transfer is also called an assignment of the mortgage.
No matter what it’s called, this change of hands may also change who you’re supposed to make your house payments to and how the foreclosure process works if you default on your loan. That’s why if you’re a homeowner, it’s important to know how this process works. This article will provide an in-depth look at what an assignment of a mortgage entails and what impact it can have on homeownership.
Assignment of Mortgage – The Basics
When your original lender transfers your mortgage account and their interests in it to a new lender, that’s called an assignment of mortgage. To do this, your lender must use an assignment of mortgage document. This document ensures the loan is legally transferred to the new owner. It’s common for mortgage lenders to sell the mortgages to other lenders. Most lenders assign the mortgages they originate to other lenders or mortgage buyers.
Home Loan Documents
When you get a loan for a home or real estate, there will usually be two mortgage documents. The first is a mortgage or, less commonly, a deed of trust . The other is a promissory note. The mortgage or deed of trust will state that the mortgaged property provides the security interest for the loan. This basically means that your home is serving as collateral for the loan. It also gives the loan servicer the right to foreclose if you don’t make your monthly payments. The promissory note provides proof of the debt and your promise to pay it.
When a lender assigns your mortgage, your interests as the mortgagor are given to another mortgagee or servicer. Mortgages and deeds of trust are usually recorded in the county recorder’s office. This office also keeps a record of any transfers. When a mortgage is transferred so is the promissory note. The note will be endorsed or signed over to the loan’s new owner. In some situations, a note will be endorsed in blank, which turns it into a bearer instrument. This means whoever holds the note is the presumed owner.
Using MERS To Track Transfers
Banks have collectively established the Mortgage Electronic Registration System , Inc. (MERS), which keeps track of who owns which loans. With MERS, lenders are no longer required to do a separate assignment every time a loan is transferred. That’s because MERS keeps track of the transfers. It’s crucial for MERS to maintain a record of assignments and endorsements because these land records can tell who actually owns the debt and has a legal right to start the foreclosure process.
Upsolve Member Experiences
Assignment of Mortgage Requirements and Effects
The assignment of mortgage needs to include the following:
The original information regarding the mortgage. Alternatively, it can include the county recorder office’s identification numbers.
The borrower’s name.
The mortgage loan’s original amount.
The date of the mortgage and when it was recorded.
Usually, there will also need to be a legal description of the real property the mortgage secures, but this is determined by state law and differs by state.
Notice Requirements
The original lender doesn’t need to provide notice to or get permission from the homeowner prior to assigning the mortgage. But the new lender (sometimes called the assignee) has to send the homeowner some form of notice of the loan assignment. The document will typically provide a disclaimer about who the new lender is, the lender’s contact information, and information about how to make your mortgage payment. You should make sure you have this information so you can avoid foreclosure.
Mortgage Terms
When an assignment occurs your loan is transferred, but the initial terms of your mortgage will stay the same. This means you’ll have the same interest rate, overall loan amount, monthly payment, and payment due date. If there are changes or adjustments to the escrow account, the new lender must do them under the terms of the original escrow agreement. The new lender can make some changes if you request them and the lender approves. For example, you may request your new lender to provide more payment methods.
Taxes and Insurance
If you have an escrow account and your mortgage is transferred, you may be worried about making sure your property taxes and homeowners insurance get paid. Though you can always verify the information, the original loan servicer is responsible for giving your local tax authority the new loan servicer’s address for tax billing purposes. The original lender is required to do this after the assignment is recorded. The servicer will also reach out to your property insurance company for this reason.
If you’ve received notice that your mortgage loan has been assigned, it’s a good idea to reach out to your loan servicer and verify this information. Verifying that all your mortgage information is correct, that you know who to contact if you have questions about your mortgage, and that you know how to make payments to the new servicer will help you avoid being scammed or making payments incorrectly.
Let's Summarize…
In a mortgage assignment, your original lender or servicer transfers your mortgage account to another loan servicer. When this occurs, the original mortgagee or lender’s interests go to the next lender. Even if your mortgage gets transferred or assigned, your mortgage’s terms should remain the same. Your interest rate, loan amount, monthly payment, and payment schedule shouldn’t change.
Your original lender isn’t required to notify you or get your permission prior to assigning your mortgage. But you should receive correspondence from the new lender after the assignment. It’s important to verify any change in assignment with your original loan servicer before you make your next mortgage payment, so you don’t fall victim to a scam.
Attorney Todd Carney
Attorney Todd Carney is a writer and graduate of Harvard Law School. While in law school, Todd worked in a clinic that helped pro-bono clients file for bankruptcy. Todd also studied several aspects of how the law impacts consumers. Todd has written over 40 articles for sites such... read more about Attorney Todd Carney
Continue reading and learning!

It's easy to get debt help
Choose one of the options below to get assistance with your debt:
Considering Bankruptcy?
Our free tool has helped 13,990+ families file bankruptcy on their own. We're funded by Harvard University and will never ask you for a credit card or payment.
Private Attorney
Get a free evaluation from an independent law firm.
Learning Center
Research and understand your options with our articles and guides.
Already an Upsolve user?
Bankruptcy Basics ➜
- What Is Bankruptcy?
- Every Type of Bankruptcy Explained
- How To File Bankruptcy for Free: A 10-Step Guide
- Can I File for Bankruptcy Online?
Chapter 7 Bankruptcy ➜
- What Are the Pros and Cons of Filing Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
- What Is Chapter 7 Bankruptcy & When Should I File?
- Chapter 7 Means Test Calculator
Wage Garnishment ➜
- How To Stop Wage Garnishment Immediately
Property & Exemptions ➜
- What Are Bankruptcy Exemptions?
- Chapter 7 Bankruptcy: What Can You Keep?
- Yes! You Can Get a Mortgage After Bankruptcy
- How Long After Filing Bankruptcy Can I Buy a House?
- Can I Keep My Car If I File Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
- Can I Buy a Car After Bankruptcy?
- Should I File for Bankruptcy for Credit Card Debt?
- How Much Debt Do I Need To File for Chapter 7 Bankruptcy?
- Can I Get Rid of my Medical Bills in Bankruptcy?
Student Loans ➜
- Can You File Bankruptcy on Student Loans?
- Can I Discharge Private Student Loans in Bankruptcy?
- Navigating Financial Aid During and After Bankruptcy: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Filing Bankruptcy to Deal With Your Student Loan Debt? Here Are 3 Things You Should Know!
Debt Collectors and Consumer Rights ➜
- 3 Steps To Take if a Debt Collector Sues You
- How To Deal With Debt Collectors (When You Can’t Pay)
Taxes and Bankruptcy ➜
- What Happens to My IRS Tax Debt if I File Bankruptcy?
- What Happens to Your Tax Refund in Bankruptcy
Chapter 13 Bankruptcy ➜
- Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 13 Bankruptcy: What’s the Difference?
- Why is Chapter 13 Probably A Bad Idea?
- How To File Chapter 13 Bankruptcy: A Step-by-Step Guide
- What Happens When a Chapter 13 Case Is Dismissed?
Going to Court ➜
- Do You Have to Go To Court to File Bankruptcy?
- Telephonic Hearings in Bankruptcy Court
Divorce and Bankruptcy ➜
- How to File Bankruptcy After a Divorce
- Chapter 13 and Divorce
Chapter 11 Bankruptcy ➜
- Chapter 7 vs. Chapter 11 Bankruptcy
- Reorganizing Your Debt? Chapter 11 or Chapter 13 Bankruptcy Can Help!
State Guides ➜
- Connecticut
- District Of Columbia
- Massachusetts
- Mississippi
- New Hampshire
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- West Virginia

Upsolve is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit that started in 2016. Our mission is to help low-income families resolve their debt and fix their credit using free software tools. Our team includes debt experts and engineers who care deeply about making the financial system accessible to everyone. We have world-class funders that include the U.S. government, former Google CEO Eric Schmidt, and leading foundations.
To learn more, read why we started Upsolve in 2016, our reviews from past users, and our press coverage from places like the New York Times and Wall Street Journal.
Difference Between Assignment and Transfer
The difference between assignment and transfer is that assign means it's legal to transfer property or a legal right from one person to another. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
The difference between assignment and transfer is that assign means it's legal to transfer property or a legal right from one person to another, while transfer means it's legal to arrange for something to be controlled by or officially belong to another person.
When used as verbs, assign means to set apart or designate something for a purpose while transfer means to pass or move from one person, place, or thing to someone or someplace else. When used as nouns, assign means the assignee and transfer is the act of removing or conveying something from one person, thing, or place to another. Transfer generally refers to titles whereas assignment is used with obligations and rights.
Definitions of Assignment and Transfer
- Assignment: Assignment is used in real estate law and contracts law. It covers the transfer of rights held by the assignor to the assignee.
- Transfer: To remove or convey from one person or place to someone or somewhere else.
Distinction Between Assignment and Transfer
When distinguishing between assignment and transfer, take licenses, for example. Licenses are contracts that don't allow legal action for infringement. They fall under state law. Therefore, state law will decide whether the license is an obligation or right that can be transferred or assigned legally.
One way to distinguish this example is that an individual contract under an agreement cannot be assigned, like entitlement to grant back royalties . In addition, the contract cannot be transferred. You need to break it down and figure out what the actual issue is — the parties' intent. An additional distinction is when the contract holder is an entity and the business owners want to transfer a portion or all of their stock. This can be seen as an implied transfer of the whole contract. However, it would not likely be an assignment of the rights covered under this agreement.
Difference Between Assign and License
The key difference between assign and license is that with a license, the person who grants permission, known as the licensor, keeps an interest in the product being licensed . In an assignment, the assignor will transfer his or her rights to the product or property being assigned.
Another difference is that assignments must be in writing and a license can be executed without being written. Consider, for example, intellectual property such as patents. Patents can be licensed verbally in some instances, but assignments for patents must be in writing and filed with the United States Patent and Trademark Office .
Assignments grant the assignee full ownership of a product or property. Therefore, an assignment will typically cost more to acquire than a license.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there ever situations in which a license can be transferred but is not assignable?
- Yes, in the case of allowing an assignment to one of your affiliates, the assignor would still be liable for the performance of the agreement under general assignment law. In this situation, you would not typically permit a transfer, because in a transfer, the person transferring would not maintain any obligations related to performance. Don't rely solely on this general understanding, but still expressly detail your agreement on what a licensee can legally do.
How will transfer and assignment rights affect someone's ability to sublicense?
- In theory, if a licensee has the authority to assign license rights to someone else, you could argue that it also provides the right to sublicense it. The issue here is that with a sublicense, the person sublicensing it keeps a license right, therefore effectively creating two licensees. With an assignment, only one right is assigned, and the assignee is the one who has possession of the license. With well-drafted licenses, the right to sublicense is not typically implied, as the licensor is the one who reserves all rights that are not expressly granted.
What is the effect of poorly drafted licenses?
- A poorly drafted license could result in giving someone implied rights to also sublicense. An example is a software license that allows a licensee to access the software without clarifying any restrictions or clearly defining the word “use.” This means that, depending on what this software is supposed to do, someone could think the term “use” means the licensee has permission to grant a sublicense as part of their usage rights.
If you need help understanding the difference between assignment and transfer, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel only accepts the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Assignment Law
- Assignment and Novation Agreement: What You Need to Know
- Legal Assignment
- Assignment Legal Definition
- Assignment Of Contracts
- Assignment of Rights and Obligations Under a Contract
- Partial Assignment of Contract
- Assignment of Rights Example
- What Is the Definition of Assigns
- Transfer of Intellectual Property

Buying and Selling Real Estate Notes
Not as Simple as One Might Think by David J. Willis J.D., LL.M.
Introduction
Investors often buy and sell real estate lien notes, either singly or in a package, a transaction that is customarily effected by a Sale & Assignment of Notes and Liens . This transfer instrument is referred to in this article simply as an assignment.
The idea of buying or selling a note seems simple until one delves into it. Is the assignment to be made “as is” with all faults that may exist in the note and the lien instrument? Will there be representations and warranties made by the parties and, if so, how extensive? How long will they last? Will recourse provisions apply if the note goes into default, and if so what is the recourse mechanism? Will indemnities be included? The closer one looks the more questions arise.
Our focus in this article is on the final assignment instrument signed by the parties at closing of the transfer rather than preliminary agreements that may come before closing.
The Assignment Process
In the case of real estate lien notes, a completed assignment involves not just a transfer of a note but the liens securing payment as well, which is why the assignment instrument is referred to as an assignment of note and liens. Two liens may be involved: the vendor’s lien retained in the deed from the seller to the borrower and the lien granted by a deed of trust.
One must distinguish between an absolute assignment of a note (a permanent transfers to a new owner and holder) versus a collateral assignment (made to a lender as collateral for a loan). Notes may be assigned in either way.
This discussion addresses absolute assignments. Steps in the process are usually: (1) an initial letter of intent or preliminary contract phase when basic terms are agreed to—similar to an earnest money contract for real estate—with “outs” for the prospective buyer; (2) a due-diligence or inspection period when a prospective buyer studies and evaluates the note (or package of notes) along with the lien instrument(s) and supporting documentation; (3) a cure period for objections, if any, raised by the buyer; (4) a closing document negotiation phase in which the terms of the final assignment instrument are hammered out and agreed to; and (5) a closing where a final sale and assignment of note and liens is executed, the purchase price paid, and the original note and loan file are delivered to the buyer-assignee.
BUSINESS & COMMERCE CODE
Negotiable instruments.
A properly written and endorsed real estate lien note is a negotiable instrument for purposes of Business & Commerce Code Section 3.201 et seq. Specific requirements of negotiability are listed in Section 3.104:
Bus. & Com. Code Sec. 3.104(a). NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENT. Except as provided in Subsections (c) and (d), “negotiable instrument” means an unconditional promise or order to pay a fixed amount of money, with or without interest or other charges described in the promise or order, if it:
(1) is payable to bearer or to order at the time it is issued or first comes into possession of a holder;
(2) is payable on demand or at a definite time; and
(3) does not state any other undertaking or instruction by the person promising or ordering payment to do any act in addition to the payment of money, but the promise or order may contain: (A) an undertaking or power to give, maintain, or protect collateral to secure payment; (B) an authorization or power to the holder to confess judgment or realize on or dispose of collateral; or (C) a waiver of the benefit of any law intended for the advantage or protection of an obligor.
A real estate note that does not qualify as a negotiable instrument may still be valid and enforceable, and it may still be sold and assigned, but common law rules relating to the assignment of contracts will apply—the negotiable instrument rules of the Business & Commerce Code will not.
The resale value of a note that is non-negotiable is likely to be discounted.
Statutory Warranties
Business & Commerce Code Section 3.416 provides minimal warranties for notes that are negotiable instruments. These are automatically in place unless the assignment instrument disclaims them:
Bus. & Com. Code Sec. 3.416(a). TRANSFER WARRANTIES. A person who transfers an instrument for consideration warrants to the transferee and, if the transfer is by indorsement, to any subsequent transferee that:
(1) the warrantor is a person entitled to enforce the instrument;
(2) all signatures on the instrument are authentic and authorized;
(3) the instrument has not been altered;
(4) the instrument is not subject to a defense or claim in recoupment of any party that can be asserted against the warrantor;
(5) the warrantor has no knowledge of any insolvency proceeding commenced with respect to the maker. . . .
Unless contradicted or disclaimed in the assignment, these statutory warranties co-exist with contractual representations and warranties of the parties (discussed below).
DUE DILIGENCE BY BUYER-ASSIGNEE
Are the note and lien valid.
Determining the validity and enforceability of a real estate note and the lien(s) securing it is the core due-diligence task of any prospective buyer—who should obtain the whole loan file not just a copy of the note itself. A complete file will include (at least) the note; a copy of a recorded deed of trust; a copy of a recorded deed into the name of the property owner (the borrower); and a payment history. Even if only copies are being reviewed, the original note should exist and be available for inspection.
For a note to be valid, there must be consideration extended—money that is actually loaned. Hughes v. Belman , 239 S.W.2d 717, 720 (Tex.App.—Austin 1951, writ ref’d n.r.e.); and Bus. & Com. Code Sec. 3.303.
Generally, a note offered for sale should:
(1) be correct as to all material information including clearly identifying borrower and lender as well as the security property; (2) recite an unconditional promise to pay a sum-certain debt (and the numerical portion must match the written portion); (3) contain authentic signatures of all debtors and be dated; (4) provide clear terms of repayment; (5) be secured by a valid, recorded, and unreleased deed of trust; (6) contain the signature of both spouses if the property is homestead; (7) not contain any provisions that are illegal such as requiring usurious interest; (8) not be in default (monetary of technical) or the subject of any dispute with the borrower; (9) not be in litigation or bankruptcy whether existing, threatened, or anticipated; (10) not be the subject of any interest or claim by third parties; and (11) not have been previously sold or transferred in whole or in part.
This is a partial list. Sensible note purchasers will also want to perform minimal due diligence as to the value and condition of the security property since such factors may influence future note payment and performance. Does the property exist? Is it owner-occupied or occupied by renters? Is it in a state of good repair or is it underwater as a result of a recent flood?
If the parties to the note are registered entities (LLCs, corporations, or limited partnerships) it is important to verify that they are in good standing with the Secretary of State and the Texas Comptroller. If not, they do not have the legal capacity to do business, whether it is selling or buying notes or anything else.
All of the foregoing factors affect the quality of the note or notes being considered—and quality affects price.
The importance of thorough due diligence cannot be over-emphasized. A prospective buyer should engage an experienced attorney to assist in determining the validity and enforceability of the loan documents before substantial funds are committed.
Even when a note is being transferred entirely “as is” a prospective buyer-assignee should insist on an adequate due diligence/inspection period before closing.
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES
Beyond statutory minimum warranties.
A well-drafted assignment may (and should) go beyond minimum statutory warranties to include contractual representations and warranties by the parties. It is possible for the assignment to include extensive reps and warranties, limited reps and warranties, or no reps and warranties at all—in which case the assignment is made “as is” and almost always without recourse. These terms should be expressly stated in the assignment instrument.
The goal of the seller-assignor is to minimize ongoing liability by limiting the number of reps and warranties. The buyer-assignee will instead prefer a longer list of assurances concerning note quality and completeness of the loan file.
Core representations and warranties of the seller-assignor include assurances that the note and lien(s) contain correct information and are legally valid and enforceable; that they are secured by a lawful vendor’s lien retained in a recorded general or special warranty deed plus a valid first-lien recorded deed of trust against the security property; that payments are current and there is no threat of monetary or technical default; that no adverse litigation is pending or threatened; and that the assignor is the sole owner and holder of the debt with power to transfer the note and liens.
There may be many more seller reps and warranties that a careful buyer will want to include. An example: if the seller-assignor was the original payee on a real estate note, and the note arose from seller financing, the buyer-assignee should want a specific warranty that the SAFE Act and Dodd Frank were fully complied with in the course of the original transaction.
There is the question of how long reps and warranties will survive closing (if at all)—30 days? 90 days? Forever?
Obtaining adequate reps and warranties from the seller-assignor does not substitute for thorough due diligence by a prospective buyer-assignee.
OTHER CLAUSES IN THE ASSIGNMENT
Assignments made “as is”.
What if the transaction is entirely “as is,” with no reps and warranties? There is certainly a market for this although the sales price of the note(s) will be discounted as a result. The key element in the assignment (for the seller-assignor) will be an effective “as is” clause similar to ones found in earnest money contracts and warranty deeds. Drafting these clauses can be tricky. Simplistic, one-liner “as is” clauses will not suffice since the seller-assignor needs not only to disclaim assurances regarding the note being transferred but also any reps or warranties concerning the condition and value of the security property.
Disclosure by the Seller-Assignor
Notwithstanding that an assignment is being made and accepted “as is,” a buyer should seek to obtain an agreement by the seller to make full disclosure of material facts. A sample clause might be: Assignor covenants and agrees to fully disclose to Assignee, prior to expiration of the inspection period, any and all material facts, conditions, and circumstances pertaining to the note(s), the lien(s), and the security property that could reasonably be expected to affect the Assignee’s decision to buy or not buy, even if this assignment is agreed to be “as is,”in present condition with all faults and without recourse.
Recourse by the Buyer-Assignee
Notes are sold with or without recourse by the buyer-assignee against the seller-assignor. Recourse comes in three varieties: none, full, or limited.
No recourse means what it says: if the borrower defaults then the buyer-assignee is stuck with a non-performing note (a near-worthless asset) and is solely responsible for pursuing the debtor and foreclosing on the security property.
Full recourse means that the buyer-assignee gets to give the note back to the seller-assignor if the debtor defaults. One of two things generally happen: (1) the buyer-assignee gets a credit or refund or (2) the buyer-assignee can substitute another note that is current and performing. There are other variations.
Limited recourse is, contractually speaking, all over the place. There are as many different provisions for limited recourse as there are creative attorneys to write them. Limited recourse provisions may state that there will be some sharing of effort and expense in collection or foreclosure, possibly with a reckoning after foreclosure sale of the security property. Remedies may be different when a batch of notes is involved: for example, if 100 notes are sold, the assignment might provide that the first 10 problematic notes will be full recourse, but the remaining 90 will not. In either case, there may be a hard limit on the total monetary amount of recourse available against the seller-assignor.
The availability of recourse—whether none, full, or limited—may also be contained within a specific time period. The availability of recourse is seldom indefinite.
Indemnity Provisions
If possible, the seller-assignor will want an indemnity clause holding him harmless against issues that may later arise in connection with the legality, enforceability, or collectability of the note. As with sellers of anything, the goal is no comebacks after closing.
Note buyers, on the other hand, resist not only taking the heat for defects in what they are purchasing but also paying the cost of defending against lawsuits arising from those defects. As with so many issues in real estate it comes down to quality and price. A seller-assignor may be able to get an indemnity provision included but it may be costly when it comes to the assignment sales price.
Indemnity provisions, although important, may be overrated since they are not self-executing. After all, the terms of an assignment can do nothing to prevent a borrower from suing both the seller-assignor and the buyer-assignee at some later time, resulting in inescapable up-front defense costs. One party to the assignment is left with a claim against the other based on the indemnity provision, often resulting in a second lawsuit.
As is the case with many other types of contracts, it is often beneficial to include a mandatory mediation clause in the assignment.
Drafting Considerations Generally
An assignment of note and lien(s) should be a comprehensive document. (If it is one page or less, something is amiss.) All obligations should be express. Nothing should be implied. No one should be allowed to assume anything or rely on anything unless expressly stated in writing. Oral statements should be disclaimed. A poorly-written assignment that involves unwritten assumptions and reliance on oral statements can easily form the basis for future litigation.
The foregoing discussion is by no means intended to be an exhaustive list of possible provisions that can be included in an assignment of note and liens. (Such documents can easily run 10 to 20 pages.) It merely hits the highlights.
CLOSING OF THE ASSIGNMENT
Endorsement and delivery of the note.
The note itself should be marked or stamped appropriately and the endorsement (or indorsement as it is referred to in the Business & Commerce Code) signed by the seller-assignor. The endorsement should include wording appropriate to the circumstances such as “payable to assignee without representations, warranties, or recourse” and would include the effective date.
Where does one place the endorsement? “For an instrument to be negotiable, indorsements must be written on the instrument or on a paper so firmly affixed thereto as to become a part thereof [sometimes called an allonge ]. An allonge is a piece of paper annexed to a negotiable instrument or promissory note, on which to write endorsements for which there is no room on the instrument itself.” Failure to properly endorse a note when it is transferred may impair its negotiability, resulting in the recipient being a mere transferee rather than having the superior status of a holder in due course [see Bus. & Com. Code Sec. 3.302].” Federal Fin. Co. v. Delgado, 1 S.W.3d 181, 185-86 (Tex.App.—Corpus Christi 1999, no pet.).
The original note(s) should be delivered to the buyer-assignee at closing.
Execution and Recording of the Assignment
Both the seller-assignor and the buyer-assignee should sign the assignment in order to indicate mutual assent to its terms and conditions. A properly-drafted assignment is not merely a unilateral transfer but represents a complex contract between the parties. The assigning party’s signature is not enough.
It is usually advisable for the buyer-assignee to record the assignment in the real property records of the county where the security property is located, so the assignment should be prepared in recordable form.
INVESTOR STRATEGIES
Notes are financial assets and their acquisition can be a part of an investor’s long-term buy-and-hold strategy. Like rents, a portfolio of mixed-age performing notes can produce a stream of income; however, unlike real property, there is no underlying equity that appreciates over time. In fact, the value of note assets depreciates so a stable portfolio requires continual replenishment. As notes age and mature new notes must be acquired in their stead if the income stream is to be maintained.
It is, of course, possible to acquire notes for other reasons. One aggressive strategy is to buy a secured note in default with the specific intention of foreclosing on the security property. A long-term hold is not the objective; acquiring the property is the objective. This scenario contemplates more of an “as is” approach to the note since its price is likely to be heavily discounted. In such cases, thorough due diligence is necessary in order to ensure that both the note and deed of trust are valid and enforceable with no obvious defenses available to the debtor.
Information in this article is provided for general informational and educational purposes only and is not offered as legal advice upon which anyone may rely. The law changes. No attorney-client relationship is created by the offering of this article. This firm does not represent you unless and until it is expressly retained in writing to do so. Legal counsel relating to your individual needs and circumstances is advisable before taking any action that has legal consequences. Consult your tax advisor as well.
Copyright © 2023 by David J. Willis. All rights reserved. Mr. Willis is board certified in both residential and commercial real estate law by the Texas Board of Legal Specialization. More information is available at his website, www.LoneStarLandLaw.com .
Share this entry
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit
- Share by Mail

Consumer Notices:
State Bar of Texas Notice to Clients TREC Consumer Protection Notice TREC Information about Brokerage Services (IABS) Policies Applicable to All Cases and Clients Policies Regarding Copying of Website Content
Office Meeting Address:
Lucid Suites at the Galleria 5718 Westheimer, Suite 1000 (Westheimer at Bering Drive) Houston, TX 77057
Hours: 8 am – 6pm M-F Phone: 713-621-3100 Fax: 832-201-5321 Contact Us Vacation Schedule
© 2024 David J. Willis – LoneStarLandLaw.com
Design and Marketing – Advanced Web Site Publishing


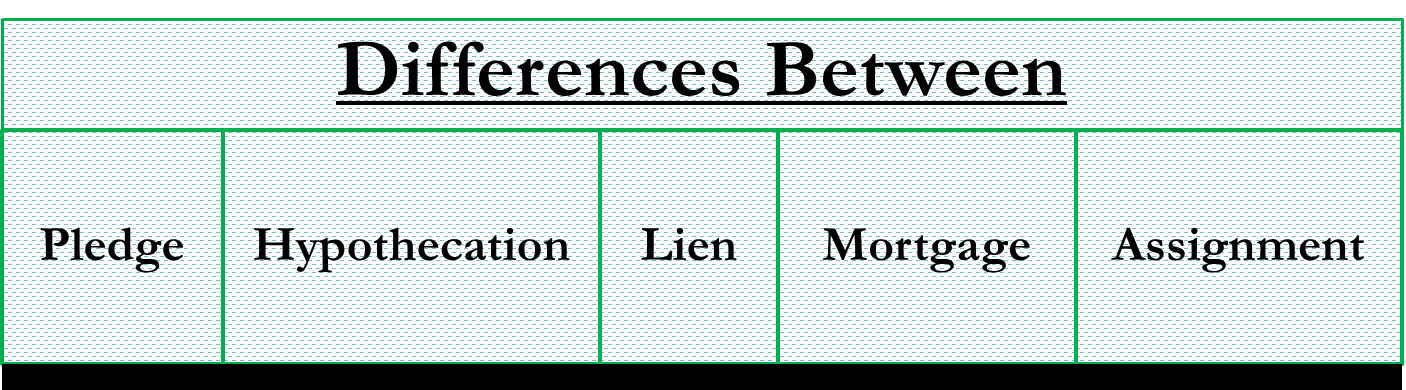
Pledge vs Hypothecation vs Lien vs Mortgage vs Assignment
The difference between pledge, hypothecation, lien, mortgage, and assignment lies in the security charge that can be created on any asset held by a lender against the money lent (usually called the collateral). The type of asset charge defines whether the agreement can be classified as a pledge, lien, or mortgage. Let us see in detail the difference between pledge vs hypothecation vs lien vs mortgage vs assignment.
There are several types of security interests that can be adopted by banks or lenders depending upon the collateral involved and the circumstances. Different forms of creating charges on assets are as follows:
Hypothecation
Short summary table.
Pledge is commonly used for goods or securities such as gold, stocks, certificates, etc. The lender (pledgee) holds the actual possession of such securities until the borrower (pledger) has the borrowed amount with him. Once the borrowed amount has been returned, the securities are returned as well. If the pledger defaults on the loan amount, the pledgee can sell off the goods pledged to him as security in order to recover the principal and the interest amount. In this case risk of lending comparatively reduces because possession of assets is with the lender.
Hypothecation is usually when the charge is on movable assets rather than having a charge on fixed assets. However, hypothecation is different from pledges in the sense that the possession of such movable security stays with the borrower. Hence, in the event of default, the lender is first required to take possession / seize such property or asset in order to recover the principal and interest. An example of hypothecation is vehicle financing, where the lender has the asset that has been hypothecated against the loan with a bank. If the borrower defaults, the bank then takes possession of the vehicle after sufficient notice to recover the money.
Also Read: Hypothecation
Under a lien, the lender gets the right to hold up a property or machinery used as collateral against funds borrowed. However, unless the contract states otherwise, the lender doesn’t have the right to sell the property or the asset if the borrower defaults on the loan. Examples of lien include rent receivable, unpaid fees, etc. It is a right given to the creditor to retain/possess the security until the loan amount g. Since possession is with the creditor, it is the strongest form of security. Lien can be on both movable and immovable property. But generally, lending companies choose to have mortgages on immovable property and lien on movable security like shares, gold, deposits, etc.
Under a mortgage , the legal ownership of the asset can be transferred to the lender if the borrower defaults on the loan amount. However, the borrower continues to remain in possession of the property. A mortgage is usually used for immovable assets (example: house, land, building, or any property which is permanently fixed to the earth or attached to the land). Home loans classify as mortgages.
An assignment is another type of charge on current assets or fixed assets. Under assignment, the charge is created on the assets held in the books. It is another mode of providing security against borrowing. Examples of assignments include life insurance policies, books of debts, receivables, etc., which the bank can finance. For example – A bank can finance against the book debts. The borrower assigns the book debts to the bank in such a case.
To get an idea about the difference between pledge vs hypothecation vs lien vs mortgage vs assignment, refer to the table below.
| Basis | Pledge | Hypothecation | Lien | Mortgage | Assignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collateral | Goods or securities such as gold, stocks, certificates, etc | Movable assets | Property or machinery | Immovable assets | Current assets or fixed assets |
| Examples | Gold, stocks, certificates, etc. | Vehicle financing | Rent receivable, unpaid fees, etc | House, land, building, | Life insurance policies, books of debts, receivables, etc. |
Quiz on Pledge vs Hypothecation vs Lien vs Mortgage vs Assignment
Let’s take a quick test on the topic you have read here.
Your answer:
Correct answer:
SHARE YOUR RESULTS
Your Answers
RELATED POSTS
- Mortgage Vs. Hypothecation – Similarities and Differences
- Secured Loans
- Secured Personal Loans – Meaning, Features, Benefits and Drawbacks
- Recourse vs Non-Recourse Loan/Debt
- Floating Lien – Meaning, Importance and More
- Restrictive Debt Covenants on Term Loan Agreement

Sanjay Bulaki Borad
MBA-Finance, CMA, CS, Insolvency Professional, B'Com
Sanjay Borad, Founder of eFinanceManagement, is a Management Consultant with 7 years of MNC experience and 11 years in Consultancy. He caters to clients with turnovers from 200 Million to 12,000 Million, including listed entities, and has vast industry experience in over 20 sectors. Additionally, he serves as a visiting faculty for Finance and Costing in MBA Colleges and CA, CMA Coaching Classes.
5 thoughts on “Pledge vs Hypothecation vs Lien vs Mortgage vs Assignment”
Really simple and so easy to refer .Especially good for nonfinance people who aims to move to general top management .
Thanks for sharing. I really like your explanations.
Tysm sir it helps me easily to understand n differentiate between all type of securities
Really great way illustration. It helped me a lot.
I love the concept; so very easy to understand.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign me up for the newsletter!
Unauthorized Request
Unauthorized activity detected.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Lien?
How liens work, types of lien, the bottom line.
- Corporate Finance
- Corporate Debt
Lien: Main Types of Claims Against an Asset
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
A lien is a claim or legal right against assets that are typically used as collateral to satisfy a debt.
A creditor or a legal judgment could establish a lien. A lien serves to guarantee an underlying obligation, such as the repayment of a loan. If the underlying obligation is not satisfied, the creditor may be able to seize the asset that is the subject of the lien.
There are many types of lien that are used to secure assets.
Key Takeaways
- A lien is a claim or legal right against assets that are usually used as collateral to satisfy a debt.
- The creditor may be able to seize the asset that is the subject of the lien.
- Bank, real estate, and tax are three types of lien.
- If a contract on a property is not paid, the lender has a legal right to seize and sell the property.
- Various types of lien can be established, including by a creditor, legal judgment, or tax authority.
Dennis Madamba / Investopedia
A lien provides a creditor with the legal right to seize and sell the collateral property or asset of a borrower who fails to meet the obligations of a loan or contract. The owner cannot sell the property that is the subject of a lien without the consent of the lien holder. A floating lien refers to a lien on inventory or other unfixed property.
Liens can be voluntary or consensual, such as a lien on a property for a loan. However, involuntary or statutory liens exist whereby a creditor seeks legal action for nonpayment. As a result, a lien is placed on assets, including property and bank accounts.
Some liens are filed with the government to let the public know that the lienholder has an interest on the asset or property. A lien’s public record tells anyone interested in purchasing the asset or collateral that the lien must be released before the asset can be sold.
There are many types of lien and lien holder. Liens can be put in place by financial institutions, governments, and small businesses. Below are some of the most common liens.
A lien is often granted when an individual takes out a loan from a bank to purchase an asset . For example, if an individual purchases a vehicle, the seller would be paid using the borrowed funds from the bank. In turn, the bank would be granted a lien on the vehicle. If the borrower does not repay the loan, the bank may execute the lien , seize the vehicle, and sell it to repay the loan.
If the borrower does repay the loan in full, the lien holder (the bank) then releases the lien, and the individual owns the car free and clear of any liens.
Judgment Lien
A judgment lien is a lien placed on assets by the courts, which is usually a result of a lawsuit. A judgment lien could help a defendant get paid back in a nonpayment case by liquidating the accused’s assets.
Mechanic’s Lien
A mechanic’s lien can be attached to real property if the owner fails to pay a contractor for services rendered. If the debtor never pays, the contractor could go to court and get a judgment against the nonpaying party whereby property or assets can be auctioned off to pay the lien holder. Many service providers have the option to place a lien to secure payment, including construction companies and dry cleaners.
Real Estate Lien
A real estate lien is a legal right to seize and sell real estate property if a contract is not fulfilled. Some real estate liens are automatically put in place, such as in the case of a mortgage lien. When a party borrows money from a bank to purchase their home, the bank places a lien on the house until the mortgage is paid off.
However, some real estate liens are due to nonpayment to a creditor or financial institution and, as a result, are involuntary and nonconsensual liens.
There are also several statutory liens, meaning liens created by law instead of those created by a contract. These liens are very common in the field of taxation, where laws often allow tax authorities to put liens on the property of delinquent taxpayers. For example, municipalities can use liens to recover unpaid property taxes .
In the United States, if a taxpayer becomes delinquent and does not demonstrate any indication of paying owed taxes, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) may place a legal claim against a taxpayer’s property, including the taxpayer’s home, vehicle, and bank accounts. A notice of federal tax lien notifies creditors of the government’s claim and can lead to a sheriff’s sale . A sheriff’s sale is a public auction whereby assets are repossessed and sold, and the generated funds are used to repay a debt to a creditor, bank, or the IRS.
A tax lien also affects the taxpayer’s ability to sell existing assets and obtain credit. The only way to release a federal tax lien is to fully pay the tax owed or reach a settlement with the IRS. The IRS has the authority to seize the assets of a taxpayer who ignores a tax lien. Typically, the IRS uses liens for delinquent taxes as a last resort, following all other options being exhausted, such as collection, installment repayment plans, and settlement.
What Is a Lien on My House?
When you buy a house using a mortgage, the lender has a legal right to seize your property if you don’t pay the mortgage. Your house is basically the collateral for the mortgage loan, and when you borrow money to buy it, a mortgage lien is put on your house until you pay off your mortgage.
What Does a Lien Mean?
A lien is simply the legal right of a lender to sell your property (a house or a car, for example) if don’t meet your contractual obligations on the loan you took out to purchase it.
How Do I Get Rid of a Lien?
You can get rid of a lien on your property, car, or other asset by paying off your loan in full.
A lien is a claim or legal right against assets that are normally used as collateral to satisfy a debt. That lien could be established by a creditor, legal judgment, or tax authority, and it serves to guarantee an underlying obligation, such as the repayment of a loan. If that doesn’t happen, the creditor could then seize the asset that is the subject of the lien.
Internal Revenue Service. “ Understanding a Federal Tax Lien .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/manatlaptop-ec509e96dc2045af99d32dffee715c0f.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
Lien Assignment Process and Procedure
The lien assignment process almost always begins with the owner’s mortgage lender (i.e. bank) commencing a foreclosure on its first deed of trust. Prior to the bank proceeding to foreclosure sale, it must submit a bid to the Public Trustee’s office. At that time, investors review the bank’s bid and determine if they would be interested in paying off the bank in exchange for acquiring the property. This is usually about the same time that investors obtain title work on the property and contact the association, its management company or our office to inquire about the potential purchase of the association’s lien. Most investors realize that even if no recorded lien exists, the association still may have an assignable lien by operation of Colorado Common Interest Ownership Act.
Assuming the investor gets in touch with our office (whether directly or following a referral from the manager or association), our firm will contact the board or management company for an updated ledger on the property. We then review the ledger and add in any time that may have been written off because of a bankruptcy and additional attorney fees that are not yet reflected on the ledger. We use this information to formulate a lien sale price. In some instances we will attempt to sell the lien for more than the total amount owed, but we always assign the lien for at least payment in full through the current month. Following an agreement with an investor to purchase the lien, our office processes the lien sale through the execution of a lien assignment document. This document sets forth the legal rights and obligations between the investor and the association and allows the investor to acquire property through a redemption process.
If the lien is sold, the association receives payment in full (or occasionally, more than payment in full) and the investor receives all rights associated with the association’s lien. The investor takes the completed lien assignment to the Public Trustee and files what is known as an Intent to Redeem. This document tells the Public Trustee that the investor has purchased the association’s lien and corresponding right to redeem at the Public Trustee’s sale. The investor then tenders payment to the Public Trustee for all amounts owed to the foreclosing lender. This process is known as redemption.
Following a successful redemption, the investor will take title to the property and will be issued a Public Trustee’s Deed. This Deed confirms that the investor now owns the property. It is important to remember that the Public Trustee’s Deed is sometimes issued several weeks after the investor actually takes legal title to a property. Technically, legal title transfers once all applicable redemption periods expire. Associations should contact our office if there are any questions about the actual date that a title transferred to an investor.
Usually, investors that acquire association liens through the lien assignment process are interested in rehabilitating the property and reselling it relatively quickly. However, during the time the investor owns the property, he or she is subject to all the same covenants as any other owner, including the obligation to pay assessments.
Keep In Touch
Sign up for our Newsletter and Blog today.
I'm Ready to Gain Some Altitude
Schedule a Consultation
If you’re looking for legal consultation, schedule one today .
- Received a document?

Assignment of Mechanics Lien: What Contractors Need To Know

727 articles
Because a lien claim is an asset, most states allow you to assign the claim to another person or entity. In other words: You can transfer or sell your right to a mechanics lien claim from one party (the assignor) to another party (the assignee). In that case, the party who receives the right to the claim has the right to collect on the lien.
You may know why you should file a mechanics lien , but you should also consider whether your state provides the right to assign a mechanics lien—and what to consider if “assignment of lien” is on your radar.
Table of Contents
Are mechanics lien rights always assignable?
Lien rights are not always assignable, and it typically comes down to state law to determine if you’re able to assign your mechanics lien rights.
Since a lien claim is an asset, most states will allow it to be assigned. There are, however, a few states that do not authorize the assignment of a mechanics lien claim.
If you are not allowed to assign your mechanics lien claim and you try to do so, you may cause some serious problems to the claim. Not only may your claim face invalidation, but you may also get yourself into legal trouble with the other party for assigning a claim you had no right to assign.
Why would you assign a mechanics lien claim?
Choosing to assign your mechanics lien rights means you’ll enter into a negotiation. The buyer will offer you some amount of money (which will be less than the full value of the claim) to obtain the full value of your rights. You’ll need to evaluate the offer and decide if the amount is high enough for you to walk away from the claim.
Since a mechanics lien claim requires foreclosure and legal effort to collect, usually liens are assigned for a fraction of their worth. If you want to sell your lien claims, be prepared to take a significant discount. The benefit, of course, is that you will be paid now—without a potentially lengthy legal fight.
Follow proper procedure when assigning a mechanics lien
While most states allow claim assignment, there are usually some procedures that must be followed to effect the assignment.
Vincent Pallaci of the New York Mechanic’s Construction Payment Blog just posted an article about assignment requirement in New York: “ Assigning a mechanic’s lien in New York? Make sure you record your assignment .”
This article does a great job of highlighting on very important step that assignors and assignees must take when executing an assignment: Recording the assignment.
This is an example of just one procedure in one state. If you decide to assign your mechanics lien claim (or to buy a mechanics lien claim) make sure you consult with a construction attorney to do it right.
Scott Wolfe Jr
View Profile
About the author
Recommended for you
Can construction managers file mechanics liens.
Construction managers used to be rare finds on construction projects. In today’s market, however, construction managers are commonplace. Construction management...
Can a Contractor File a Lien Without a Written Contract?
Whether you need a written contract to be eligible for a mechanics lien depends on the state where you're located....
Filing a Lien on a Project with Multiple Properties
Mechanics liens can be the last line of defense standing between a construction participant and nonpayment. But with all of...
Rejected Mechanics Liens: Lack of Supporting Documentation
At Levelset, we file hundreds of mechanics lien documents a month, all across the United States. The documents are sent...
Can You File A Mechanics Lien for Cleaning Services?
When cleaning services, janitorial services, or other similar services struggle with getting paid on a job, can they file a...
What You Need To Know About Liening An Apartment Complex
Last week, I read an Associated Press article commenting on the economy’s effects on the home building market: As fewer...
The Complications of Signing A Mechanics Lien
The act of signing a mechanics lien is more complex than it would seem. The danger of getting it wrong...
Mechanics Lien Or Bond Rights When Working On University Construction Project
While some construction projects are clearly state, federal or private, the waters are muddy in other instances. For example, when...
An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know keyboard_arrow_down
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Jump to main content

Transferring ownership/ Assignments FAQs
Assignment Center has replaced the Electronic Patent Application System (EPAS) and Electronic Trademark Assignment System (ETAS). Assignment Center makes it easier to transfer ownership or change the name on your patent or trademark registration.
See our how-to guides on using Assignment Center for patents and trademarks . If you have questions, email [email protected] or call customer service at 800-972-6382.
Show all FAQs
- Browse FAQs
Transferring Ownership / Assignments
- Transferring Ownership / Assignments, Procedures
The Assignment Recordation Branch in the Public Records Division processes and records assignment documents for both patent and trademark properties.
Essentially the rules:
(1) specify the minimum information about the transaction that must be submitted;
(2) require submitters to submit this information of a separate cover sheet; and
(3) specify that submissions must be legible and of such quality to permit processing; and
(4) pay the proper recording fee.
The rules permit submission of true copies of assignment-related documents; original documents are not required nor desired, as they will not be returned.
You may contact the Assignment Center customer service desk at 571-272-3350 from 8:30 a.m. to 5 pm ET Mondays through Fridays, except on federal holidays. You may e-mail questions about electronic filing to [email protected] .
Payment may be made by use of a check, credit card, money order or USPTO deposit account if submitting documents in paper. Trademark assignments submitted electronically may be paid by credit card, USPTO deposit account or electronic fund transfer (EFT). The USPTO accepts VISA, MASTERCARD, AMERICAN EXPRESS and DISCOVER credit cards.
>> see How to Pay Fees for a current fee schedule and for more about fee payments
No. All documents that meet the minimum requirement in 37 CFR 3 are processed and recorded. Persons buying or selling properties should be sure that there is an accurate chain of title in place before submitting recordation requests.
No, these forms are not mandatory. However, the USPTO strongly encourages their use. Completing the forms in their entirety ensures that all the required information for recordation has been sent to the office. The forms are available in PDF-fillable format on the USPTO Forms page , thus making them quick and easy to prepare.
When these forms are received in the USPTO, they are scanned along with the supporting documentation. The bibliographic data from the cover sheet is then entered into the PTAS system and the documents are processed.
Additional information about this page
- Find a Lawyer
- Ask a Lawyer
- Research the Law
- Law Schools
- Laws & Regs
- Newsletters
- Justia Connect
- Pro Membership
- Basic Membership
- Justia Lawyer Directory
- Platinum Placements
- Gold Placements
- Justia Elevate
- Justia Amplify
- PPC Management
- Google Business Profile
- Social Media
- Justia Onward Blog
2006 Alabama Code - Section 35-11-233 — Assignment of lien; transfer of lien on real property to other security.
Disclaimer: These codes may not be the most recent version. Alabama may have more current or accurate information. We make no warranties or guarantees about the accuracy, completeness, or adequacy of the information contained on this site or the information linked to on the state site. Please check official sources.
Get free summaries of new opinions delivered to your inbox!
- Bankruptcy Lawyers
- Business Lawyers
- Criminal Lawyers
- Employment Lawyers
- Estate Planning Lawyers
- Family Lawyers
- Personal Injury Lawyers
- Estate Planning
- Personal Injury
- Business Formation
- Business Operations
- Intellectual Property
- International Trade
- Real Estate
- Financial Aid
- Course Outlines
- Law Journals
- US Constitution
- Regulations
- Supreme Court
- Circuit Courts
- District Courts
- Dockets & Filings
- State Constitutions
- State Codes
- State Case Law
- Legal Blogs
- Business Forms
- Product Recalls
- Justia Connect Membership
- Justia Premium Placements
- Justia Elevate (SEO, Websites)
- Justia Amplify (PPC, GBP)
- Testimonials

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Banks often sell and buy mortgages from each other. An "assignment" is the document that is the legal record of this transfer from one mortgagee to another. In a typical transaction, when the mortgagee sells the debt to another bank, an assignment is recorded, and the promissory note is endorsed (signed over) to the new bank.
When your original lender transfers your mortgage account and their interests in it to a new lender, that's called an assignment of mortgage. To do this, your lender must use an assignment of mortgage document. This document ensures the loan is legally transferred to the new owner. It's common for mortgage lenders to sell the mortgages to ...
The difference between assignment and transfer is that assign means it's legal to transfer property or a legal right from one person to another, while transfer means it's legal to arrange for something to be controlled by or officially belong to another person. When used as verbs, assign means to set apart or designate something for a purpose ...
Define Transfer of Lien. means an absolute assignment of note and liens (including, without limitation, all mortgages and any other security for each of the Assigned Loans) or other similar document transferring a lien or security interest, executed by Borrower or any Guarantor to Administrative Agent, for the benefit of the Lenders, in form agreed to by Borrower and Administrative Agent ...
In the case of real estate lien notes, a completed assignment involves not just a transfer of a note but the liens securing payment as well, which is why the assignment instrument is referred to as an assignment of note and liens. Two liens may be involved: the vendor's lien retained in the deed from the seller to the borrower and the lien ...
Mortgages are assigned using a document called an assignment of mortgage. This legally transfers the original lender's interest in the loan to the new company. After doing this, the original lender will no longer receive the payments of principal and interest. However, by assigning the loan the mortgage company will free up capital.
The difference between pledge, hypothecation, lien, mortgage, and assignment lies in the security charge that can be created on any asset held by a lender against the money lent (usually called the collateral). The type of asset charge defines whether the agreement can be classified as a pledge, lien, or mortgage. Let us see in detail the ...
Every transfer of a mortgage loan, whether an "absolute" transfer or a limited assignment as "collateral" for another loan, starts with the transfer of the borrower's promissory note from the existing lender to an assignee. Some ancient cases suggest that the holder of a promissory note can . in . some circumstances transfer it with
The previous owner will transfer the rights associated with a security instrument (a mortgage or deed of trust) to the investor who purchased the loan using an assignment. Because mortgages and deeds of trust are usually recorded in county records shortly after closing, any subsequent assignment of the security instrument should also be recorded.
An "assignment" is the document that's the legal record of the mortgage transfer from one entity to another. If you're a homeowner facing foreclosure and the lender sold your loan to a new owner but didn't complete a proper assignment of mortgage, you might be able to challenge the foreclosure in court .
A mortgage assignment occurs when the holder of a mortgage transfers the mortgage to another person or entity. Assignments are generally freely permitted in most modern mortgage agreements.
ASSIGNMENT OF LIEN. The Assignor must be listed as secured party on the application for title or on the current certificate of title. The Assignor must complete section A and list the name and address of the Assignee in section B. The assignment must be submitted with the current certificate of title. Fees: $1 plus $12 filing fee.
Lien: A lien is a legal right granted by the owner of property, by a law or otherwise acquired by a creditor. A lien serves to guarantee an underlying obligation, such as the repayment of a loan ...
Posted September 17, 2011. Tweet. The lien assignment process almost always begins with the owner's mortgage lender (i.e. bank) commencing a foreclosure on its first deed of trust. Prior to the bank proceeding to foreclosure sale, it must submit a bid to the Public Trustee's office. At that time, investors review the bank's bid and ...
Assignment of Mechanics Lien: What Contractors Need To Know. Because a lien claim is an asset, most states allow you to assign the claim to another person or entity. In other words: You can transfer or sell your right to a mechanics lien claim from one party (the assignor) to another party (the assignee). In that case, the party who receives ...
Assignment Center makes it easier to transfer ownership or change the name on your patent or trademark registration. See our how-to guides on using Assignment Center for patents and trademarks. If you have questions, email [email protected] or call customer service at 800-972-6382. Show all FAQs. Browse FAQs.
2006 Alabama Code - Section 35-11-233 — Assignment of lien; transfer of lien on real property to other security. (a) Any claim for which a lien is provided in this division may be assigned; and the assignee shall thereby be invested with all the rights of the original holder of the lien, and be entitled to all his remedies to enforce them.
Examples of Assignment of Lien in a sentence. On May 5, 2009, an Assignment of Lien ("Assignment") was executed by an Agent of JPMC, as purchaser of loans and other assets of WaMu from the FDIC, and he recorded the Assignment in the real property records of Dallas County, Texas.. The municipality will execute, and return to the County, an Assignment of Lien naming "Cook County, Illinois ...
ASSIGNMENT OF LIEN Form 78-007-17-8-1-000 Rev(09/17) The lien shown in favor of the undersigned Assignor on the attached Certificate of Title. ... The undersigned assignee confirms transfer of the lien described above and hereby makes application for a new Certificate of Title subject to the following named liens and none other: FIRST LIEN .
Difference between a charge, lien, and pledge Section 100 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882 defines a charge "Where immoveable property of one person is by act of parties or operation of law made security for the payment of money to another; and the transaction does not amount to a mortgage, the latter person is said to have a charge on the property; and all the provisions hereinbefore ...
Assignment Note Lien Form. Do you need an Assignment Note Lien Form? This agreement serves to assign a lender's interest in promissory note, secured by collateral, to a third party. This document is used when the third party purchases the note rights from the lender, or otherwise pays off the lender in exchange for the right to collect all ...
Related to Assignment, Transfer and Lien. Assignment; Transfer Neither this Agreement nor any of the rights, interests or obligations hereunder or under the Option shall be assigned or transferred by any of the parties hereto (whether by operation of law or otherwise) without the prior written consent of the other party, except that Grantee may assign this Agreement to a wholly owned ...
Open the file in the editor. Enter the required information in the blank fields using Text, Check, and Cross tools. Follow the document navigation not to miss any mandatory fields in the template. Circle some of the critical details and add a URL to it if needed. Use the Highlight or Line tools to point out the most important facts.