Essay Papers Writing Online
Various formats for writing essays – tips and guidelines.

Welcome to the comprehensive guide that will enhance your understanding of various essay writing formats. Crafting a well-structured and organized essay is a crucial skill for students and professionals alike. Different types of essays require adherence to specific formatting guidelines to effectively communicate ideas and arguments.
Whether you are writing a persuasive essay, analytical essay, narrative essay, or any other type, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the key elements of each format. By mastering the nuances of essay writing formats, you will be able to express your thoughts clearly, logically, and persuasively, captivating your readers and achieving your communication goals.
Through this comprehensive guide, you will learn about the essential components of various essay formats, including thesis statements, introductions, body paragraphs, supporting evidence, and conclusions. By understanding the specific requirements of each format, you can tailor your writing style to meet the expectations of your audience and effectively convey your message.

The Complete Essay Format Guide
Understanding the proper essay format is essential for writing effective essays. Whether you are a student or a professional writer, knowing how to structure your essays can greatly impact the clarity and coherence of your writing. In this guide, we will walk you through the essential elements of essay formats and provide tips on how to structure your essays effectively.
1. Introduction
- The introduction is the first paragraph of your essay and should provide a brief overview of the topic you will be discussing.
- It should also include a thesis statement, which explains the main argument or point of your essay.
2. Body Paragraphs
- The body of your essay should consist of several paragraphs that develop and support your thesis statement.
- Each paragraph should focus on a single idea or point and include evidence or examples to support it.
3. Conclusion
- The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay and should summarize your main points and restate your thesis.
- It should also provide a closing thought or reflection on the topic you have discussed.
4. Formatting
- Essays should be double-spaced and formatted with a clear font, such as Times New Roman, in 12-point size.
- Margins should be set to one inch on all sides of the page.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your essays are well-structured and easy to read. Remember to revise and edit your essays carefully to ensure that they are well-written and coherent.
Understanding Essay Structure Basics
When it comes to writing an essay, understanding the basic structure is essential. A typical essay consists of three main parts: an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each of these sections serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall coherence of the essay.
- Introduction: This is where you introduce the topic of your essay and provide some background information. The introduction should also include a thesis statement, which is the main idea or argument that you will be discussing in the essay.
- Body Paragraphs: The body of the essay consists of several paragraphs that develop and support the thesis statement. Each paragraph should focus on a single point or idea and provide evidence and examples to support it.
- Conclusion: The conclusion brings the essay to a close by restating the thesis statement and summarizing the main points of the essay. It is also a good place to discuss the broader implications of your argument or suggest areas for further research.
By following this basic structure, you can ensure that your essay is well-organized and easy for readers to follow. Remember to use transitions between paragraphs to help connect your ideas and create a smooth flow of information throughout the essay.
Types of Essay Formats
When it comes to writing essays, there are several different formats that you may encounter. Each format has its own unique structure and requirements. Here are some of the most common types of essay formats:
- Argumentative Essay: This type of essay presents a claim or argument and supports it with evidence and reasoning.
- Descriptive Essay: Descriptive essays focus on describing a person, place, object, or event in detail.
- Narrative Essay: Narrative essays tell a story and often include personal experiences or anecdotes.
- Expository Essay: Expository essays aim to explain and inform the reader about a specific topic.
- Persuasive Essay: Persuasive essays are similar to argumentative essays but focus more on convincing the reader to adopt a particular point of view.
- Compare and Contrast Essay: This type of essay analyzes the similarities and differences between two or more subjects.
- Cause and Effect Essay: Cause and effect essays explore the reasons behind a particular phenomenon and its outcomes.
It’s important to understand the requirements of each essay format and tailor your writing style accordingly to effectively convey your ideas and arguments.
Exploring Common Essay Styles

When it comes to writing essays, there are several common styles that you may encounter. Understanding the different types of essays can help you determine the best approach for your writing task. Here are some of the most common essay styles that you may come across:
1. Narrative Essays: These essays tell a story or recount an event. They often include personal anecdotes and can be quite engaging for the reader.
2. Descriptive Essays: In a descriptive essay, the writer paints a vivid picture of a person, place, object, or event. These essays appeal to the reader’s senses and emotions.
3. Expository Essays: Expository essays provide information, explain a topic, or analyze a concept. They are typically objective and present facts or opinions in a logical manner.
4. Persuasive Essays: Persuasive essays are meant to convince the reader of a particular point of view or argument. They often use evidence and reasoning to support a specific position.
5. Argumentative Essays: Similar to persuasive essays, argumentative essays present a claim or thesis and support it with evidence and analysis. However, argumentative essays also address counterarguments and refute opposing viewpoints.
By familiarizing yourself with these common essay styles, you can better tailor your writing to meet the requirements of your assignment and effectively communicate your ideas to your audience.
Comparing Argumentative and Narrative Essays
When it comes to essay writing, two common types of essays are argumentative and narrative essays. While they both aim to convey a message or argument, they differ in their purpose and structure.
- Argumentative Essays: Argumentative essays are designed to persuade the reader to adopt a particular point of view or take a specific action. These essays present a clear thesis statement and provide evidence to support the argument. They often involve research and logical reasoning to make a compelling case.
- Narrative Essays: Narrative essays, on the other hand, focus on telling a story or recounting an experience. They are often more personal and emotional, using descriptive language to engage the reader. Narrative essays may not have a thesis statement but instead focus on engaging the reader through vivid storytelling.
While argumentative essays rely on facts and evidence to support a specific viewpoint, narrative essays rely on personal experiences and storytelling to draw the reader in. It’s essential to understand the differences between these two essay formats to effectively convey your message and engage your audience.
Elements of a Well-Formatted Essay
Introduction : The introduction sets the stage for your essay, providing an overview of the topic and presenting the thesis statement.
Body Paragraphs : The body of the essay presents your arguments and evidence in support of the thesis statement. Each paragraph should focus on a single idea and provide clear evidence to support it.
Transitions : Transitions help to smoothly move from one idea to the next, connecting paragraphs and ensuring the essay flows logically.
Conclusion : The conclusion restates the thesis statement and summarizes the main points of the essay. It may also provide insights or recommendations based on the arguments presented.
Citations : Proper citations are essential in academic writing to give credit to the sources used and avoid plagiarism. Use the appropriate citation style required by your instructor.
Formatting : Pay attention to formatting elements such as font size, margins, spacing, and referencing style. Consistent formatting enhances readability and professionalism of your essay.
Key Components for a Strong Essay
When crafting a strong essay, there are several key components that you should consider to ensure that your writing is clear, coherent, and effective. These key components include:
1. A clear and concise thesis statement that presents the main argument or point of your essay.
2. Well-developed paragraphs that support and expand upon your thesis statement with relevant evidence and analysis.
3. Smooth transitions between paragraphs and ideas to guide the reader through your essay and maintain coherence.
4. Proper organization and structure, including an introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion that effectively communicate your ideas.
5. Attention to detail, including grammar, punctuation, and spelling to ensure that your writing is polished and professional.
By incorporating these key components into your essay writing, you can create a strong and compelling piece that effectively conveys your message to your audience.
Choosing the Right Format for Your Essay
When it comes to writing an essay, choosing the right format is crucial for effectively communicating your ideas and arguments. There are several different essay formats to choose from, each with its own unique structure and guidelines. Here are some tips to help you select the best format for your essay:
1. Consider your audience: Think about who will be reading your essay and what format would be most appropriate for them. For example, a formal academic essay might require a more structured format, while a personal essay could be more freeform.
2. Determine your purpose: Consider the purpose of your essay and choose a format that will best suit your goals. If you’re trying to persuade your reader, a persuasive essay format might be most effective. If you’re analyzing a topic, an analytical essay format could be more suitable.
3. Follow guidelines: If you’re writing an essay for a class or publication, make sure to follow any specific guidelines provided. This could include requirements for formatting, citation style, and overall structure.
4. Experiment and revise: Don’t be afraid to experiment with different formats to see what works best for your essay. Once you’ve written a draft, revise and refine your work to ensure that the format enhances your message.
By taking these factors into account, you can choose the right format for your essay and ensure that your ideas are conveyed effectively to your readers.
Considerations for Selecting Essay Styles
When selecting an essay style, consider the purpose of your essay. Are you trying to persuade, inform, or analyze? The style you choose should align with your overall goal and message.
Think about your target audience. Are you writing for a scholarly audience, a general audience, or a specific group of readers? The style of your essay should be tailored to resonate with your intended readers.
Consider the requirements of your assignment. Does your instructor specify a particular style or format to follow? Make sure to adhere to any guidelines provided to ensure you meet the expectations of the assignment.
Reflect on your own writing strengths and weaknesses. Are you more comfortable with a formal, structured style, or do you excel in a more creative, narrative format? Choose a style that plays to your strengths as a writer.
Lastly, consider the conventions of the discipline or field you are writing in. Different subjects may have specific expectations for essay styles, so make sure to research and understand the norms of your field.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, tips and techniques for crafting compelling narrative essays.

Learn the Standard Essay Format: MLA, APA, Chicago Styles

Being able to write an essay is a vital part of any student's education. However, it's not just about linearly listing ideas. A lot of institutions will require a certain format that your paper must follow; prime examples would be one of a basic essay format like MLA, the APA, and the Chicago formats. This article will explain the differences between the MLA format, the APA format, and the Chicago format. The application of these could range from high school to college essays, and they stand as the standard of college essay formatting. EssayPro — dissertation services , that will help to make a difference!
What is an Essay Format: Structure
Be it an academic, informative or a specific extended essay - structure is essential. For example, the IB extended essay has very strict requirements that are followed by an assigned academic style of writing (primarily MLA, APA, or Chicago):
- Abstract: comprised of 3 paragraphs, totaling about 300 words, with 100 words in each.
- ~ Paragraph 1: must include a research question, thesis, and outline of the essay’s importance.
- ~ Paragraph 2: Key resources, scope and limits of research, etc.
- ~ Paragraph 3: Conclusion that you’ve already reached in your essay.
- Table of Contents (with page numbers)
- ~ Research question
- ~ Introduction
- ~ Arguments
- ~ Sub-headings
- ~ Conclusion
- ~ Works cited (bibliography)
- Introduction
- ~ The research question is required
- Bibliography (Works Cited)
This outline format for an extended essay is a great example to follow when writing a research essay, and sustaining a proper research essay format - especially if it is based on the MLA guidelines. It is vital to remember that the student must keep track of their resources to apply them to each step outlined above easily. And check out some tips on how to write an essay introduction .
Lost in the Labyrinth of Essay Formatting?
Navigate the complexities of essay structures with ease. Let our experts guide your paper to the format it deserves!
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format
To write an essay in MLA format, one must follow a basic set of guidelines and instructions. This is a step by step from our business essay writing service
- Font : 12pt Times New Roman
- ~ Double spaced everywhere
- ~ No extra spaces, especially between paragraphs
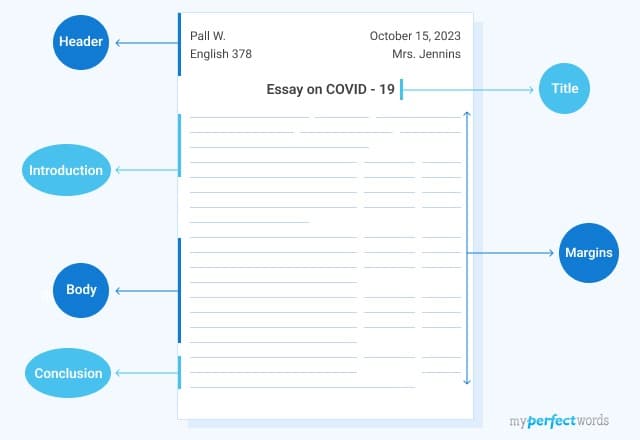
- Heading : Example of the heading on the first page of the essay (upper left corner)
- ~ Your name (John Smith)
- ~ Teacher’s / Professor’s name (Margot Robbie)
- ~ The class (Depends on course/class)
- ~ Date (20 April 2017)
- Margins : One-inch margin on the top, bottom, left and right.
- Page Numbers : Last name and page number must be put on every page of the essay as a “header”. Otherwise, it would go in place of the text.
- Title : There needs to be a proper essay title format, centered and above the first line of the essay of the same font and size as the essay itself.
- Indentation : Just press tab (1/2 inch, just in case)
- Align : Align to the left-hand side, and make sure it is aligned evenly.

It’s important to remember that the essay format of MLA is usually used in humanities, which differs from other types of academic writing that we’ll go into detail later. For now, feast your eyes upon an MLA format essay example:
Essay in MLA Format Example
Mla format digital technology and health, mla vs. apa.
Before we move on to the APA essay format, it is important to distinguish the two types of formatting. Let’s go through the similarities first:
- The formatting styles are similar: spacing, citation, indentation.
- All of the information that is used within the essay must be present within the works cited page (in APA, that’s called a reference page)
- Both use the parenthetical citations within the body of the paper, usually to show a certain quote or calculation.
- Citations are listed alphabetically on the works cited / reference page.
What you need to know about the differences is not extensive, thankfully:
- MLA style is mostly used in humanities, while APA style is focused more on social sciences. The list of sources has a different name (works cited - MLA / references - APA)
- Works cited differ on the way they display the name of the original content (MLA -> Yorke, Thom / APA -> Yorke T.)
- When using an in-text citation, and the author’s name is listed within the sentence, place the page number found at the end: “Yorke believes that Creep was Radiohead’s worst song. (4).” APA, on the other hand, requires that a year is to be inserted: “According to Yorke (2013), Creep was a mess.”
Alright, let’s carry over to the APA style specifics.
Order an Essay Now & and We Will Cite and Format It For Free :
How to write an essay in apa format.
The APA scheme is one of the most common college essay formats, so being familiar with its requirements is crucial. In a basic APA format structure, we can apply a similar list of guidelines as we did in the MLA section:
- Spacing : Double-space that bad boy.
- Margins : One Inch margins on all sides.
- Page Numbers : Insert a header at the top left of every page that includes a shortened title of your essay, below 50 characters including punctuation. Slap a number in there too (top right corner).
- Title Page : Title of the paper, author’s name, institutional affiliation. Additional information may be required, such as course title, instructor name and date.
- Headings: All headings should be written in bold and titlecase. Different heading levels have different additional criteria to apply.
You can also ask us to write or rewrite essay in APA format if you find it difficult or don't have time.
Note that some teachers and professors may request deviations from some of the characteristics that the APA format originally requires, such as those listed above.

Note that some teachers and professors maybe have deviations to some of the characteristics that the APA format originally requires, such as those listed above.
If you think: 'I want someone write a research paper for me ', you can do it at Essaypro.
Essay in APA Format Example
Apa format chronobiology, chicago style.
The usage of Chicago style is prevalent in academic writing that focuses on the source of origin. This means that precise citations and footnotes are key to a successful paper.
Chicago Style Essay Format
The same bullet point structure can be applied to the Chicago essay format.
- ~ Chicago style title page is all about spacing.
- ~ Down the page should be the title, with regular text. If longer than one line, double-spaced.
- ~ Next, in the very middle, center your full name.
- ~ Down the page - course number, instructor’s name and the date in separate double-spaced lines.
- Margins : Use one-inch margins apart from the right side.
- ~ Double spaced everywhere.
- ~ No extra spaces, especially between paragraphs.
- Font : Times New Roman is the best choice (12pt)
- Page Numbers
- ~ Last name, page number in the heading of every page on the top right
- ~ Do not number the title page. The first page of the text should start with a 2.
- Footnotes : The Chicago format requires footnotes on paraphrased or quoted passages.
- Bibliography : The bibliography is very similar to that of MLA. Gather the proper information and input it into a specialized citation site.

Tips for Writing an Academic Paper
There isn’t one proper way of writing a paper, but there are solid guidelines to sustain a consistent workflow. Be it a college application essay, a research paper, informative essay, etc. There is a standard essay format that you should follow. For easier access, the following outline will be divided into steps:
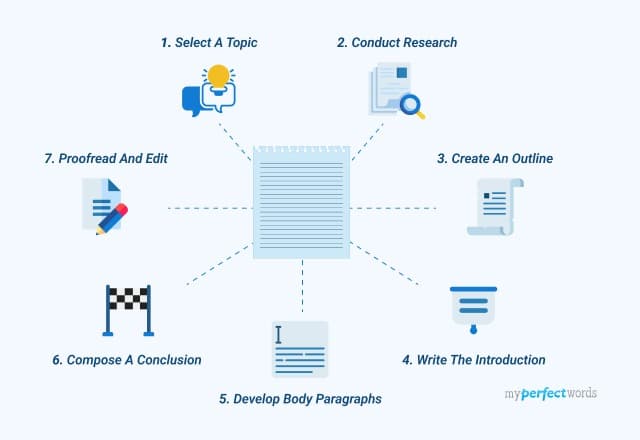
Choose a Good Topic
A lot of students struggle with picking a good topic for their essays. The topic you choose should be specific enough so you can explore it in its entirety and hit your word limit if that’s a variable you worry about. With a good topic that should not be a problem. On the other hand, it should not be so broad that some resources would outweigh the information you could squeeze into one paper. Don’t be too specific, or you will find that there is a shortage of information, but don’t be too broad or you will feel overwhelmed. Don’t hesitate to ask your instructor for help with your essay writing.
Start Research as Soon as Possible
Before you even begin writing, make sure that you are acquainted with the information that you are working with. Find compelling arguments and counterpoints, trivia, facts, etc. The sky is the limit when it comes to gathering information.
Pick out Specific, Compelling Resources
When you feel acquainted with the subject, you should be able to have a basic conversation on the matter. Pick out resources that have been bookmarked, saved or are very informative and start extracting information. You will need all you can get to put into the citations at the end of your paper. Stash books, websites, articles and have them ready to cite. See if you can subtract or expand your scope of research.
Create an Outline
Always have a plan. This might be the most important phase of the process. If you have a strong essay outline and you have a particular goal in mind, it’ll be easy to refer to it when you might get stuck somewhere in the middle of the paper. And since you have direct links from the research you’ve done beforehand, the progress is guaranteed to be swift. Having a list of keywords, if applicable, will surely boost the informational scope. With keywords specific to the subject matter of each section, it should be much easier to identify its direction and possible informational criteria.
Write a Draft
Before you jot anything down into the body of your essay, make sure that the outline has enough information to back up whatever statement you choose to explore. Do not be afraid of letting creativity into your paper (within reason, of course) and explore the possibilities. Start with a standard 5 paragraph structure, and the content will come with time.
Ask for a Peer Review of Your Academic Paper
Before you know it, the draft is done, and it’s ready to be sent out for peer review. Ask a classmate, a relative or even a specialist if they are willing to contribute. Get as much feedback as you possibly can and work on it.
Final Draft
Before handing in the final draft, go over it at least one more time, focusing on smaller mistakes like grammar and punctuation. Make sure that what you wrote follows proper essay structure. Learn more about argumentative essay structure on our blog. If you need a second pair of eyes, get help from our service.
Read also our movie review example and try to determine the format in which it is written.
Want Your Essay to Stand Out in Structure and Style?
Don't let poor formatting dim your ideas. Our professional writers are here to give your paper the polished look it needs!
What Is Essay Format?
How to format a college essay, how to write an essay in mla format, related articles.
.webp)
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Format an Essay
Last Updated: April 11, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Carrie Adkins, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Aly Rusciano . Carrie Adkins is the cofounder of NursingClio, an open access, peer-reviewed, collaborative blog that connects historical scholarship to current issues in gender and medicine. She completed her PhD in American History at the University of Oregon in 2013. While completing her PhD, she earned numerous competitive research grants, teaching fellowships, and writing awards. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 86,557 times.
You’re opening your laptop to write an essay, knowing exactly what you want to write, but then it hits you—you don’t know how to format it! Using the correct format when writing an essay can help your paper look polished and professional while earning you full credit. There are 3 common essay formats—MLA, APA, and Chicago Style—and we’ll teach you the basics of properly formatting each in this article. So, before you shut your laptop in frustration, take a deep breath and keep reading because soon you’ll be formatting like a pro.
Setting Up Your Document

- If you can’t find information on the style guide you should be following, talk to your instructor after class to discuss the assignment or send them a quick email with your questions.
- If your instructor lets you pick the format of your essay, opt for the style that matches your course or degree best: MLA is best for English and humanities; APA is typically for education, psychology, and sciences; Chicago Style is common for business, history, and fine arts.

- Most word processors default to 1 inch (2.5 cm) margins.

- Do not change the font size, style, or color throughout your essay.

- Change the spacing on Google Docs by clicking on Format , and then selecting “Line spacing.”
- Click on Layout in Microsoft Word, and then click the arrow at the bottom left of the “paragraph” section.

- Using the page number function will create consecutive numbering.
- When using Chicago Style, don’t include a page number on your title page. The first page after the title page should be numbered starting at 2. [4] X Research source
- In APA format, a running heading may be required in the left-hand header. This is a maximum of 50 characters that’s the full or abbreviated version of your essay’s title. [5] X Research source

- For APA formatting, place the title in bold at the center of the page 3 to 4 lines down from the top. Insert one double-spaced line under the title and type your name. Under your name, in separate centered lines, type out the name of your school, course, instructor, and assignment due date. [6] X Research source
- For Chicago Style, set your cursor ⅓ of the way down the page, then type your title. In the very center of your page, put your name. Move your cursor ⅔ down the page, then write your course number, followed by your instructor’s name and paper due date on separate, double-spaced lines. [7] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- Double-space the heading like the rest of your paper.
Writing the Essay Body

- Use standard capitalization rules for your title.
- Do not underline, italicize, or put quotation marks around your title, unless you include other titles of referred texts.

- A good hook might include a quote, statistic, or rhetorical question.
- For example, you might write, “Every day in the United States, accidents caused by distracted drivers kill 9 people and injure more than 1,000 others.”

- "Action must be taken to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving, including enacting laws against texting while driving, educating the public about the risks, and giving strong punishments to offenders."
- "Although passing and enforcing new laws can be challenging, the best way to reduce accidents caused by distracted driving is to enact a law against texting, educate the public about the new law, and levy strong penalties."

- Use transitions between paragraphs so your paper flows well. For example, say, “In addition to,” “Similarly,” or “On the other hand.” [12] X Research source

- A statement of impact might be, "Every day that distracted driving goes unaddressed, another 9 families must plan a funeral."
- A call to action might read, “Fewer distracted driving accidents are possible, but only if every driver keeps their focus on the road.”
Using References

- In MLA format, citations should include the author’s last name and the page number where you found the information. If the author's name appears in the sentence, use just the page number. [14] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- For APA format, include the author’s last name and the publication year. If the author’s name appears in the sentence, use just the year. [15] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- If you don’t use parenthetical or internal citations, your instructor may accuse you of plagiarizing.

- At the bottom of the page, include the source’s information from your bibliography page next to the footnote number. [16] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Each footnote should be numbered consecutively.

- If you’re using MLA format , this page will be titled “Works Cited.”
- In APA and Chicago Style, title the page “References.”

- If you have more than one work from the same author, list alphabetically following the title name for MLA and by earliest to latest publication year for APA and Chicago Style.
- Double-space the references page like the rest of your paper.
- Use a hanging indent of 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) if your citations are longer than one line. Press Tab to indent any lines after the first. [17] X Research source
- Citations should include (when applicable) the author(s)’s name(s), title of the work, publication date and/or year, and page numbers.
- Sites like Grammarly , EasyBib , and MyBib can help generate citations if you get stuck.
Formatting Resources

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://www.une.edu.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0010/392149/WE_Formatting-your-essay.pdf
- ↑ https://content.nroc.org/DevelopmentalEnglish/unit10/Foundations/formatting-a-college-essay-mla-style.html
- ↑ https://camosun.libguides.com/Chicago-17thEd/titlePage
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/page-header
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/title-page
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/chicago_manual_17th_edition/cmos_formatting_and_style_guide/general_format.html
- ↑ https://www.uvu.edu/writingcenter/docs/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://www.deanza.edu/faculty/cruzmayra/basicessayformat.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/apa_style/apa_formatting_and_style_guide/in_text_citations_the_basics.html
- ↑ https://library.menloschool.org/chicago
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Maansi Richard
May 8, 2019
Did this article help you?
Jan 7, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Essay Writing Guide
Essay Format
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
10 min read
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
Learn How to Write An Essay in Simple Steps
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 500+ Essay Topics for Students
Explore Different Types of Essays, their Purpose, and Sub-types
Learn How to Create a Perfect Essay Outline
How to Start an Essay- A Step-by-Step Guide
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
20+ Hook Examples to Grab Reader’s Attention
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
How to Make an Essay Longer: 14 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay - A Detailed Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
Are you having trouble making your essay look just right? Lots of students find formatting tricky, so you're not alone.
This guide is here to help you figure out how to format your essay. We've got examples of essays in APA, MLA, Chicago, and other styles to make it easier for you to learn.
So, keep reading – we've got you covered!
- 1. What is an Essay Format?
- 2. How To Format Essay in MLA Style
- 3. How to Format Essay in APA
- 4. How to Format Essay in Chicago Style
- 5. Formatting In-Text Citations: APA, MLA, and Chicago Styles
- 6. How to Determine What Format to Follow
What is an Essay Format?
An essay format refers to a set of guidelines that decides how the elements of your paper should be arranged. No matter what type of essay you’re writing, formatting is an essential step in the essay writing process.
The format guidelines cover the essay structure, title, citations, and the basic outline of the essay.
When formatting a paper, there are certain things that you need to pay attention to. These include the structure of an essay, title page, works cited page, and citation styles .
Here is a basic essay format template:
How To Format Essay in MLA Style
Formatting an essay in MLA style is a common requirement in many academic settings, particularly in the humanities.
MLA provides guidelines for various aspects of your essay, from font and margins to citations and bibliography. Here’s an essay format MLA you can use as a reference:
MLA Essay Format Template
- Title Page: MLA does not typically require a separate title page. Instead, place your title at the top of the first page, centered, and do not use bold, italics, or underline for the title. Below the title, include your name, the instructor's name, the course name and number, and the due date, each on a separate line, left-aligned.
- Header and Page Numbers: Create a header with your last name and page number in the upper right corner of every page, half an inch from the top, and flush with the right margin. For example: Smith 1.
- Margins and Spacing: Set all margins to 1 inch, and use double-spacing throughout the essay.
- Font and Size: Use a legible font like Times New Roman or Arial, size 12.
- Indentation: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches, which can be done automatically using the "Tab" key.
- Paragraphs: Leave only one space after periods or other punctuation marks within sentences.
- Title: Place the title of your essay (centered) at the top of the first page. Do not use bold, italics, or underlining for the title. Capitalize major words.
- Citations: MLA uses in-text citations to acknowledge sources. When quoting or paraphrasing, include the author's last name and the page number (e.g., Smith 45).
- Works Cited Page: At the end of your essay, include a separate page titled "Works Cited." List all sources alphabetically by the author's last name. Follow the specific MLA citation style for different types of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.).
Sample MLA Essay

How to Format Essay in APA
Formatting an essay in APA style is commonly used in the social sciences and psychology.
APA provides a set of guidelines for various elements of your essay, including formatting, citations, and references. Here’s how to format essay in apa:
APA Essay Format Template
- Title Page: The title page in APA includes: Title of the Essay (centered, bold, and in title case) Your Name (centered) Institutional Affiliation (centered) Running head: [Shortened Title] (flush left, in uppercase) Page Number (flush right)
- Header and Page Numbers: Create a header with the title of your essay in all capital letters, followed by a colon and a shortened version of the title (up to 50 characters), in the upper left corner of every page. The page number should be in the upper right corner.
- Font and Size: Use a clear and readable font like Times New Roman or Arial, size 12.
- Paragraphs: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches. Use a hanging indent for references on the reference page.
- Citations: Use in-text citations to acknowledge sources. Include the author's last name and the publication year (e.g., Smith, 2023) when quoting or paraphrasing.
- Title: Use bold and title case for the title of your essay on the title page. On subsequent pages, use a shortened version of the title (in uppercase) as the header.
- References Page: At the end of your essay, create a separate page titled "References." List all sources alphabetically by the author's last name. Follow the specific APA citation style for different types of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.).
Sample APA Essay

How to Format Essay in Chicago Style
Formatting an essay in Chicago style, often used in history and some other humanities disciplines, requires specific guidelines for citations and formatting. Here are the guidelines to format your essay in Chicago style:
Chicago Essay Format Template
- Title Page: The title page in Chicago style includes: Title of the Essay (centered, in headline-style capitalization) Your Name (centered) Course Name and Number (centered) Instructor's Name (centered) Date (centered)
- Margins and Spacing: Set all margins to 1 inch. Use double-spacing throughout the essay.
- Page Numbers: Number pages in the upper right corner of each page, beginning with the first page of the main text (usually page 1). Page numbers should be in Arabic numerals (1, 2, 3, etc.).
- Paragraphs: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches. Use a block paragraph style with no extra space between paragraphs.
- Citations: In Chicago style, you have two citation options: footnotes and endnotes. In your text, place a superscript number (e.g., ^1) at the end of the sentence containing the cited information. Corresponding footnotes or endnotes should provide full citation details.
- Title: Use headline-style capitalization for the title of your essay (e.g., "The History of Ancient Civilizations").
- Bibliography: At the end of your essay, include a separate page titled "Bibliography." List all sources alphabetically by the author's last name. Follow the specific Chicago citation style for different types of sources (books, articles, websites, etc.).
Sample Chicago Essay

Formatting In-Text Citations: APA, MLA, and Chicago Styles
An in-text citation is a brief reference within the body of your essay or research paper that indicates the source of information you have incorporated into your writing.
Each of the formatting style have a unique way for adding in-text citations:
In APA style, remember to include the author's last name, the publication date, and the page number (if applicable) within parentheses.
Example: "The impact of climate change on biodiversity is a growing concern (Smith, 2020, p. 27)."
In MLA style, provide the author's last name and the page number without any punctuation between them.
Example: "The impact of climate change on biodiversity is a growing concern (Jones 42)."
Chicago Style Format
The Chicago Manual of Style offers two distinct options for in-text citations:
- Author-Date Style: In this approach, you place your citations within parentheses directly within the text. This style involves citing the author's last name and the publication date within the body of your text. Example: (Smith 2021) or "According to Smith (2021),..."
- Notes and Bibliography Style: This style utilizes numbered footnotes or endnotes to provide citations. Instead of placing citations within the text, you include a superscript number at the end of the relevant sentence, which corresponds to a full citation located in a footnote at the bottom of the page (or endnotes at the end of the document). Example: Johnson argues that "the data is unconvincing."¹ Nevertheless, Smith contends that the study makes "a compelling case" for this plan of action.²
Each of these Chicago citation styles has its unique advantages and is chosen based on the requirements of the assignment or the preferences of the writer.
How to Determine What Format to Follow
Selecting the appropriate citation format for your academic writing is essential to ensure that your work meets the expected standards. To make an informed decision, consider the following factors:
Subject and Discipline
- APA Style: Primarily used in the social sciences, such as psychology, sociology, and education. It is also common in business and nursing disciplines.
- MLA Style: Commonly employed in humanities disciplines, including literature, languages, and cultural studies. It's widely used for papers related to literature and the arts.
- Chicago Style: Used in history, some social sciences, and certain humanities disciplines. Chicago offers both author-date and notes and bibliography styles, making it versatile for various subjects.
Professor's Instructions
Always adhere to your professor's specific instructions regarding citation style and writing convention . Professors may have preferences or requirements based on the nature of the course or assignment.
For instance, an English professor might prefer MLA for literary analysis, while a psychology professor may opt for APA to encourage familiarity with research norms. However, when formatting styles are not specified by the instructor, you can follow whatever is appropriate for your subject.
Institutional Guidelines
Your educational institution may have established guidelines or standards for citation formats.
Check your institution's style guide or consult with academic advisors to ensure compliance with their specific requirements.
By considering the subject matter, your professor's preferences, and your institution's guidelines, you can confidently choose the appropriate citation style to enhance the clarity and professionalism of your academic writing.
Now that you've gained a solid understanding of the basics for three major formatting styles, you're well-prepared to tackle your essay formatting with confidence.
Whether you're crafting an essay, a research paper, or any academic document, these formatting principles will help you present your ideas professionally.
If you find yourself in a time crunch, our expert writers are here to help you tackle your academic challenges in no time.
With our custom essay writing service , you get reliable help with any type of assignment, even with tight deadlines. Our writers are sure to deliver you 100% original papers that meet your requirements.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, the 3 popular essay formats: which should you use.
General Education

Not sure which path your essay should follow? Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it’s an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we’ll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
For each, we’ll do a high-level overview of what your essay’s structure and references should look like, then we include a comparison chart with nitty-gritty details for each style, such as which font you should use for each and whether they’re a proponent of the Oxford comma. We also include information on why essay formatting is important and what you should do if you’re not sure which style to use.
Why Is Your Essay Format Important?
Does it really matter which font size you use or exactly how you cite a source in your paper? It can! Style formats were developed as a way to standardize how pieces of writing and their works cited lists should look.
Why is this necessary? Imagine you’re a teacher, researcher, or publisher who reviews dozens of papers a week. If the papers didn’t follow the same formatting rules, you could waste a lot of time trying to figure out which sources were used, if certain information is a direct quote or paraphrased, even who the paper’s author is. Having essay formatting rules to follow makes things easier for everyone involved. Writers can follow a set of guidelines without trying to decide for themselves which formatting choices are best, and readers don’t need to go hunting for the information they’re trying to find.
Next, we’ll discuss the three most common style formats for essays.
MLA Essay Format
MLA style was designed by the Modern Language Association, and it has become the most popular college essay format for students writing papers for class. It was originally developed for students and researchers in the literature and language fields to have a standardized way of formatting their papers, but it is now used by people in all disciplines, particularly humanities. MLA is often the style teachers prefer their students to use because it has simple, clear rules to follow without extraneous inclusions often not needed for school papers. For example, unlike APA or Chicago styles, MLA doesn’t require a title page for a paper, only a header in the upper left-hand corner of the page.
MLA style doesn’t have any specific requirements for how to write your essay, but an MLA format essay will typically follow the standard essay format of an introduction (ending with a thesis statement), several body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
One of the nice things about creating your works cited for MLA is that all references are structured the same way, regardless of whether they’re a book, newspaper, etc. It’s the only essay format style that makes citing references this easy! Here is a guide on how to cite any source in MLA format. When typing up your works cited, here are a few MLA format essay rules to keep in mind:
- The works cited page should be the last paper of your paper.
- This page should still be double-spaced and include the running header of your last name and page number.
- It should begin with “Works Cited” at the top of the page, centered.
- Your works cited should be organized in alphabetical order, based on the first word of the citation.
APA Essay Format
APA stands for the American Psychological Association. This format type is most often used for research papers, specifically those in behavioral sciences (such as psychology and neuroscience) and social sciences (ranging from archeology to economics). Because APA is often used for more research-focused papers, they have a more specific format to follow compared to, say, MLA style.
All APA style papers begin with a title page, which contains the title of the paper (in capital letters), your name, and your institutional affiliation (if you’re a student, then this is simply the name of the school you attend). The APA recommends the title of your paper not be longer than 12 words.
After your title page, your paper begins with an abstract. The abstract is a single paragraph, typically between 150 to 250 words, that sums up your research. It should include the topic you’re researching, research questions, methods, results, analysis, and a conclusion that touches on the significance of the research. Many people find it easier to write the abstract last, after completing the paper.
After the abstract comes the paper itself. APA essay format recommends papers be short, direct, and make their point clearly and concisely. This isn’t the time to use flowery language or extraneous descriptions. Your paper should include all the sections mentioned in the abstract, each expanded upon.
Following the paper is the list of references used. Unlike MLA style, in APA essay format, every source type is referenced differently. So the rules for referencing a book are different from those for referencing a journal article are different from those referencing an interview. Here’s a guide for how to reference different source types in APA format . Your references should begin on a new page that says “REFERENCES” at the top, centered. The references should be listed in alphabetical order.

Chicago Essay Format
Chicago style (sometimes referred to as “Turabian style”) was developed by the University of Chicago Press and is typically the least-used by students of the three major essay style formats. The Chicago Manual of Style (currently on its 17th edition) contains within its 1000+ pages every rule you need to know for this style. This is a very comprehensive style, with a rule for everything. It’s most often used in history-related fields, although many people refer to The Chicago Manual of Style for help with a tricky citation or essay format question. Many book authors use this style as well.
Like APA, Chicago style begins with a title page, and it has very specific format rules for doing this which are laid out in the chart below. After the title page may come an abstract, depending on whether you’re writing a research paper or not. Then comes the essay itself. The essay can either follow the introduction → body → conclusion format of MLA or the different sections included in the APA section. Again, this depends on whether you’re writing a paper on research you conducted or not.
Unlike MLA or APA, Chicago style typically uses footnotes or endnotes instead of in-text or parenthetical citations. You’ll place the superscript number at the end of the sentence (for a footnote) or end of the page (for an endnote), then have an abbreviated source reference at the bottom of the page. The sources will then be fully referenced at the end of the paper, in the order of their footnote/endnote numbers. The reference page should be titled “Bibliography” if you used footnotes/endnotes or “References” if you used parenthetical author/date in-text citations.
Comparison Chart
Below is a chart comparing different formatting rules for APA, Chicago, and MLA styles.
How Should You Format Your Essay If Your Teacher Hasn’t Specified a Format?
What if your teacher hasn’t specified which essay format they want you to use? The easiest way to solve this problem is simply to ask your teacher which essay format they prefer. However, if you can’t get ahold of them or they don’t have a preference, we recommend following MLA format. It’s the most commonly-used essay style for students writing papers that aren’t based on their own research, and its formatting rules are general enough that a teacher of any subject shouldn’t have a problem with an MLA format essay. The fact that this style has one of the simplest sets of rules for citing sources is an added bonus!

What's Next?
Thinking about taking an AP English class? Read our guide on AP English classes to learn whether you should take AP English Language or AP English Literature (or both!)
Compound sentences are an importance sentence type to know. Read our guide on compound sentences for everything you need to know about compound, complex, and compound-complex sentences.
Need ideas for a research paper topic? Our guide to research paper topics has over 100 topics in ten categories so you can be sure to find the perfect topic for you.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
How to Format an Essay: Different Styles and Examples
%20(1).webp)
Samuel Gorbold
Crafting essays is a big part of school, and it's not just about putting ideas in order. Schools often want essays in a certain way, like using MLA, APA, or Chicago styles. Each essay format has its own way of doing things, like how you set up your title page, the spacing you use, and even how you write your name. It might seem like a lot, but it's just about making your essay look neat and organized.
You might use these formats from high school all the way to college, so getting the hang of them early on is a good idea. They're kind of like the toolkit you need for presenting your ideas in a way that everyone can understand. But don't worry; in this article, our expert essay writers will break down every detail for you!

What is an Essay Format?
An essay format is the blueprint that shapes the presentation of your ideas. While it provides a framework, creativity and individual style can still shine through in your piece. When stuck with wondering how to write an academic essay , it is a tool to organize your thoughts effectively and ensure your message is conveyed with clarity and impact. Here's a breakdown of essential elements in different formats of writing:
Title page:
- Includes the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date.
- Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution.
- A concise summary of your essay.
- Highlights the main objectives, methods, results, and conclusions of your study.
- Usually, it's a brief overview, typically around 150 to 250 words.
Table of contents:
- An organized list of the main sections and subsections in your essay.
- Includes page numbers for quick reference.
- Helps readers navigate through the document easily.
Introduction:
- Provides background information on the topic.
- States the research question or thesis.
- Outlines the scope and purpose of the study.
Literature review:
- Surveys existing study and scholarly articles relevant to your topic.
- Demonstrates your understanding of the current state of knowledge in the field.
- Identifies gaps or areas where your research contributes.
Methodology:
- Describes the study design, methods, and procedures used in your study.
- Allows others to replicate your research.
- Clarifies the rationale behind your chosen methods.
Research question or hypothesis:
- Clearly states the question or hypothesis your research aims to address.
- Guides the reader in understanding the purpose of your study.
- Presents the findings of your study.
- Often includes data, statistics, graphs, or tables.
- Focuses on objective reporting without interpretation.
Discussion:
- Analyzes and interprets the results in the context of the research question.
- Discusses the implications and significance of the findings.
- Compares results with existing literature.
Conclusion:
- Summarizes the key points of your study.
- Restates the thesis and its significance.
- Offers suggestions for future study.
References or works cited:
- Lists all sources cited in your essay.
- Follows a specific citation format (e.g., APA, MLA).
Appendices:
- Includes supplementary materials, such as raw data, surveys, or additional details.
- Items that are too extensive for the main body but are essential for understanding your study.
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format?
The MLA format is commonly employed in humanities, setting it apart from other academic writing styles. When tackling an essay in MLA format, it's crucial to follow a set of clear guidelines:
- Opt for 12pt Times New Roman for uniformity.
- Maintain consistent double spacing throughout the essay.
- Steer clear of additional spaces, particularly between paragraphs.
- Position the heading in the upper left corner of the initial page.
- Include essential details: your name (e.g., Leah Brown), the teacher's/professor's name (e.g., Josh Parker), the class (depending on the course/class), and the date (e.g., 14 May 2018).
- Set one-inch margins on all sides—top, bottom, left, and right.
Page numbers:
- Ensure your last name and page number appear as a header on every page.
- Center the essay title above the essay's first line.
- Keep it in the same font and size as the rest of the essay.
Indentation:
- Utilize the tab key for consistent indentation (1/2 inch).
- Align text to the left-hand side evenly for a neat appearance.
Essay in MLA Format Example
The Impact of Technology on Modern Society
The rapid advancement of technology has become a defining characteristic of the 21st century. This essay explores the profound impact of technology on various aspects of modern society, including communication, education, and the workplace (Smith 1).
Body Paragraphs:
Technology has revolutionized the way we communicate. With the rise of smartphones and social media platforms, individuals can connect instantly, transcending geographical boundaries. This ease of communication has both positive and negative implications, influencing the dynamics of personal relationships and societal interactions (Jones 45).
In the realm of education, technology has transformed traditional learning methods. Online courses and digital resources provide accessibility to a wealth of information. However, the digital divide remains a challenge, highlighting disparities in access to educational opportunities (Brown 112).
The integration of technology in the workplace has streamlined processes, enhancing efficiency. Remote work has become more prevalent, allowing for flexibility and global collaboration (Miller 78).
In conclusion, the adoption of technology has reshaped various facets of modern society. Understanding its implications on communication, education, and the workplace is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by the digital age (Smith 2).
Works Cited
Brown, A. "The Digital Divide in Education." Journal of Educational Technology , vol. 30, no. 2, 2019, pp. 112–130.
Jones, R. Social Media, and Society: An Analysis. Academic Press, 2020.
Miller, C. "Technology and Workplace Efficiency." Journal of Business Technology, vol. 45, no. 3, 2018, pp. 76–89.
Smith, J. "The Digital Revolution." Modern Tech Review , vol. 15, no. 1, 2017, pp. 1–15.
How to Write an Essay in APA Format?
Familiarizing yourself with the APA format is essential, as it is commonly used in college essays. The basic APA format includes guidelines similar to those of other essay formats:
- Font: Use 12pt Times New Roman.
- Spacing: Double-space the entire document.
- Margins: Maintain one-inch margins on all sides.
- Page Numbers: Insert a header at the top left of each page with a shortened name (below 50 characters) and a page number at the top right.
- Title Page: Include the title, author's name, institutional affiliation, and additional details like course name, instructor name, and date.
Headings: Bold and title case for all headings. Different levels of headings have specific additional criteria.
Example of Essay in APA Format
The Impact of Social Media on Interpersonal Relationships
The ubiquitous presence of social media has fundamentally altered the landscape of interpersonal relationships in contemporary society. This essay delves into the multifaceted impact of social media on personal connections, exploring both positive and negative aspects.
Social media facilitates seamless communication and connection across geographical boundaries. Individuals can stay in touch, share experiences, and build relationships, fostering a sense of global community (Johnson, 2018).
However, the constant exposure to curated online personas may contribute to feelings of inadequacy and societal comparison (Smith & Davis, 2019). The pursuit of perfection, often portrayed on social media, can strain real-life relationships.
The abbreviated nature of online communication, characterized by emojis and short messages, has altered traditional communication styles. While it enhances efficiency, it may also lead to misunderstandings and misinterpretations (Jones, 2020).
In conclusion, the impact of social media on interpersonal relationships is complex, with both positive and negative consequences. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for individuals navigating the evolving landscape of personal connections in the digital age.
References:
Johnson, A. (2018). The Global Village: Social Connectedness in the Digital Era. Journal of Communication, 42(3), 127-140.
Smith, R., & Davis, L. (2019). Social Media and Self-Esteem: A Comparative Analysis. Journal of Collective Psychology, 55(2), 201-215.
Jones, M. (2020). Shaping Communication: The Impact of Emojis on Online Interaction. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Collective Networking, 33(4), 432-445.
MLA vs. APA
Before delving into the nuances of the APA essay format, it's essential to distinguish between the two formatting styles. Let's first explore their similarities:
%20(1).webp)
- Both APA and MLA formatting styles share commonalities in terms of spacing, citation, and indentation.
- All information used within the essay must be properly represented in the works cited page (referred to as the reference page in APA).
- Both styles make use of parenthetical citations within the body of the essay, typically to highlight specific quotes or calculations.
- Citations are organized alphabetically on the works cited/reference page.
Now, let's briefly touch on the key differences:
- MLA style is primarily used in humanities, while APA format is more geared towards the social sciences.
- The list of sources assumes different names—MLA employs 'works cited,' while APA uses 'references.'
- Works cited entries differ in how they display the name of the original content (MLA format: Last name, First name / APA format: Last name, First initial).
Regarding in-text citations where the author's name is integrated into the sentence, there's a distinction in how page numbers and years are handled:
- In MLA format, the page number is placed at the end of the sentence, for instance: "Smith argues that 'Nature' is a profound work (25)."
- In APA format, the publication year is included, as in: "According to Smith (2015), 'Nature' remains a timeless masterpiece."
Chicago Style
Chicago format is a common way of writing in academics, especially when it comes to giving credit to your sources. This means being careful about citing your references and using footnotes. These details are vital for a good essay because they show where your information comes from and make your work more trustworthy.
In Chicago, using footnotes or endnotes is a special part of the writing. These notes give extra information or references, making your essay more informative.
Using the Chicago format might seem a bit detailed, but it shows that you take your study seriously. Whether you're a student or a researcher, getting the hang of this format makes your piece more accurate and respected in academic circles.
Chicago Style Essay Format
The Chicago essay format follows the following structure:
- The title page focuses on spacing.
- Place the title down the page in regular text, double-spaced if longer than one line.
- Center your full name in the middle of the page.
- List the course number, instructor's name, and date on separate double-spaced lines.
- Maintain one-inch margins, except for the right side.
- Double space throughout, avoiding extra spaces, especially between paragraphs.
- Use Times New Roman font (12pt).
- Include your last name and page number in the heading on the top right of every page.
- Exclude numbering on the title page; the text begins numbering from page 2.
- The Chicago format requires footnotes for paraphrased or quoted passages.
Bibliography:
- Similar to MLA, the Chicago bibliography gathers proper information and is input into a specialized citation site.
Tips for Academic Paper Writing
Crafting an essay doesn't have a one-size-fits-all approach, but there are practical guidelines to ensure a smooth writing process. Whether you're tackling a college application essay, a research paper, or an informative piece, embracing a standard essay format is crucial. To simplify things, let's break down the following outline into manageable steps for your convenience.
.webp)
Select an Engaging Topic
Selecting a topic while working on your essay writing format is your ticket to an engaging paper. Think about what genuinely interests you or sparks your curiosity. It could be a subject you've always wanted to explore or a current issue that caught your attention. The key is to pick something that makes you want to dive into the research.
Begin Research Early
Getting a head start on your study is like giving yourself a time advantage. Delve into books, articles, and credible online sources to gather information. By beginning early, you not only avoid the last-minute rush but also give yourself time to absorb and understand the material. Early research lays the foundation for a well-informed and well-structured essay.
Choose Relevant and Interesting Sources
Opt for sources that not only provide information but also captivate your interest. Look for articles, books, and studies that are reliable and directly related to your chosen topic. It's like assembling a team of experts to support your essay—each source should contribute valuable insights to make your work more robust.
Develop an Outline
An outline acts as the skeleton of your paper, providing a framework for your thoughts. So, how to make an outline for an essay , you may wonder. First of all, begin by jotting down the main points you want to cover and organizing them logically.
Then, break down your main points into subtopics, creating a hierarchy that reflects the flow of your ideas. This step-by-step format structure not only helps you maintain focus but also ensures that your paper unfolds in a clear and organized manner.
Consider each section of your outline as a building block, contributing to the overall strength of your paper. It's a tool that allows you to see the big picture while providing a roadmap for the detailed content you'll add in each section. This systematic approach makes the writing process more manageable and results in a well-organized and coherent final product.
Craft an Initial Draft
Don't aim for perfection on the first try; think of your initial draft as a rough sketch. Get your thoughts on paper without worrying too much about perfect sentences or flawless format. This is your chance to explore ideas freely and lay the foundation for your polished final draft.
Seek Peer Feedback for Your Essay
Don't be a lone explorer in the writing process. Share your draft with a peer or a friend who can offer fresh perspectives. They can provide valuable feedback on areas that may need improvement or clarification. It's like having a second set of eyes to ensure your ideas are clear and your essay resonates with your audience.
Polish and Complete the Final Draft
Now is the time to polish your work until it shines. Review your preliminary draft with a critical eye. Focus on refining your language, ensuring clarity, and checking for any overlooked errors. It's like putting the finishing touches on a masterpiece. Take the opportunity to make your final draft a polished and well-crafted representation of your ideas.
.png)
- Plagiarism Report
- Unlimited Revisions
- 24/7 Support
Exploring Article Writing Formats: Examples and Best Practices
Are you tired of staring at a blank document, desperately trying to come up with the perfect article format for your next piece? Well, worry no more! Whether you're a seasoned writer or just starting out, understanding the art of article writing formats can greatly enhance your ability to engage readers effectively. From traditional news articles to feature stories and opinion pieces, this article will serve as your guide to exploring different writing formats.
We'll dive into examples and bestpractices, equipping you with the necessary tools to captivate your audience and leave a lasting impact. So, grab your pen and paper (or keyboard and mouse) because it's time to unravel the secrets of article writing!
Understanding Article Writing Formats
What is an article writing format.
Start for free
An article writing format is a structured framework that helps writers organize their thoughts and ideas. It typically includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction provides background information and grabs the reader's attention. The body paragraphs present relevant information, facts, and arguments to support the article's main idea.
Finally, the conclusion summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement. Examples of article writing formats include feature articles, news articles, opinion pieces, and blog posts . Following a specific format ensures that articles are coherent, easy to read, and effectively communicate the intended message to the target audience.
Importance of Choosing the Right Format
Choosing the right format is crucial for an article as it determines how well your content is received by the readers. A clear and well-organized format helps to convey your message effectively and enhances the readability of the article. Different formats suit different types of content, whether it's a news article, a how-to guide, or an opinion piece.
Proper formatting involves using headings, subheadings, bullet points, and paragraphs to break up the text and make it easier to skim and digest. A well-structured article not only improves readability but also increases the chances of attracting and retaining readers, ultimately leading to a more successful piece of writing.
Benefits of Using Different Article Writing Formats
There are several benefits to using different article writing formats. These formats provide a structured framework that helps to organize ideas and improve readability. Some advantages include:
- Variety : Different formats offer versatility, allowing writers to cater to various audiences and topics.
- Engagement : Unique formats, such as lists or how-tos, can capture readers' attention and keep them engaged .
- Easy navigation : Well-structured formats with headings and subheadings make it easier for readers to navigate and find the information they need.
- SEO optimization : Certain formats, like the "question and answer" or "FAQ" style, can boost search engine optimization by targeting specific keywords .
- Visual appeal : Breaking content into short paragraphs, utilizing bullets or numbering, creates visual appeal and improves overall readability.
Incorporating different article writing formats adds diversity, keeps readers interested, and enhances the overall quality of the content.
Common Article Writing Formats
News article format.
- Headline : The title should be catchy, concise, and accurately reflect the article's content.
- Lead : The first paragraph should grab readers' attention with a captivating summary of the main story.
- Introduction : Provide background information, context, and a brief overview of the topic.
- Body : Present facts, quotations, and supporting evidence in logical paragraphs. Each paragraph should cover one main point.
- Attribution : Always attribute information to its source, whether it's a person, study, or organization.
- Balance : Present multiple perspectives on controversial topics to maintain objectivity and fairness.
- Subheadings : Use subheadings to break up the article into sections, making it easier for readers to skim and understand the main points.
- Language : Use clear, concise, and jargon-free language to ensure clarity for a diverse audience .
- Conclusion : Summarize key points, provide potential implications or future developments, and end on a strong note.
- Citations : Include a list of references and sources used to support the information presented.
- Formatting : Use paragraphs that are 2-3 sentences long, incorporate bullet or numbered points when appropriate, and include relevant visual elements such as images or graphs to enhance the article's presentation.
- Length : Aim for around 500-800 words, though it can vary depending on the depth and complexity of the topic.
Remember, following a clear news article format helps readers easily navigate the information while maintaining credibility and professionalism.
Structure and Components
The structure and components of an article play a crucial role in delivering information effectively. A typical article consists of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction hooks the reader and provides a brief overview of the topic. The body paragraphs delve deeper into the subject, presenting evidence, examples, and arguments. Transition words help maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs.
Finally, the conclusion wraps up the main points, leaving the reader with a lasting impression.
Additionally, headers and subheadings help organize the strategic content and make it easier to navigate. Including visuals and bullet points can further enhance the readability of an article.
Examples of News Article Writing Formats
News articles come in different formats, depending on the context and purpose. The Inverted Pyramid is a common style used in news writing, where the most important information is presented at the beginning, followed by supporting details. Another popular format is the Feature Story, which dives into a topic in more depth, often incorporating personal stories or perspectives.
On the other hand, the Listicle format presents information in a list format, breaking down the subject into easily digestible chunks. Lastly, the Q&A format allows for direct question-and-answer format, allowing readers to quickly find relevant information. Each format serves its own purpose and caters to different reader preferences.
Best Practices for News Articles
When writing news articles, it's crucial to adhere to best practices to ensure accuracy and engage readers.
First, start with a strong headline that grabs attention. Keep paragraphs short and concise, with the most important information upfront. Use simple language and avoid jargon. Include quotes from reliable sources to add credibility. Fact-check all information thoroughly and attribute sources when necessary. Use clear subheadings and bullet points to enhance readability.
Finally, end with a strong conclusion that summarizes the main points.
Feature Article Format
Feature articles typically follow a specific format to engage readers and convey information effectively. They usually begin with a captivating introduction that hooks the reader and presents the main topic. The article then dives into the body, where the writer delves deeper into the subject matter, providing evidence, examples, and expert opinions. Each paragraph should focus on one key idea and flow logically into the next.
To maintain reader interest, the writer may employ storytelling techniques, including anecdotes or personal experiences, to make the article relatable.
Finally, a compelling conclusion wraps up the piece by summarizing the main points and leaving the reader with a lasting impression.
The structure and components of an article are critical for effective communication. Here's what you need to know:
- Introduction : Capture the reader's attention and provide a clear thesis statement or objective.
- Body : Present main ideas in a logical order, providing supporting evidence, examples, and analysis.
- Conclusion : Summarize key points, reinforce the main argument, and leave a lasting impression.
- Headings and subheadings : Use these to organize different sections and make the article more readable.
- Imagery : Include relevant visuals like images, charts, or graphs to enhance understanding.
- Format : Use an appropriate font, size, and line spacing, and follow any specific guidelines from the publisher.
Remember, a well-structured article with engaging components is more likely to captivate readers and effectively convey your message.
Examples of Feature Article Writing Formats
There are several formats that can be used for feature article writing. One popular format is the narrative style, where the article tells a story and engages the reader emotionally. Another format is the descriptive style, which provides vivid details and paints a picture in the reader's mind. The informative style focuses on providing facts, statistics, and expert opinions. The persuasive style aims to convince the reader of a certain viewpoint or opinion.
Lastly, the interview style involvesconducting interviews with relevant individuals and incorporating their quotes into the article. These different formats can be used depending on the topic and target audience of the feature article.
Best Practices for Feature Articles
When writing feature articles, it's important to grab the reader's attention right from the start. Begin with a compelling and catchy headline that piques their curiosity. Use clear and concise language throughout the article to keep readers engaged. Break up the content into short paragraphs to make it easier to read. Incorporate vivid descriptions and anecdotes to make the article more vivid and relatable. Use quotes and expert opinions to add credibility.
Finally, end the article with a strong conclusion that leaves readers with a lasting impression.
Opinion Article Format
Opinion articles require a specific format to effectively convey your viewpoint. Start with a strong introduction that grabs the reader's attention. Present your opinion in a clear and concise manner, supporting it with relevant evidence. Use short and focused paragraphs to enhance readability. Support your arguments with examples, statistics, or expert opinions. Acknowledge and counter opposing viewpoints to strengthen your argument further.
Conclude your article by summarizing your main points and leaving the reader with a thought-provoking statement. By following this format, your opinion article becomes more persuasive and engaging to readers.
The structure of an article typically consists of an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction grabs readers' attention and provides a brief overview. The body contains the main information, presented in paragraphs with subheadings. Each paragraph focuses on a specific point or idea, supported by evidence or examples. Transition words help maintain coherence and flow between paragraphs. The conclusion summarizes the main points and may offer a call to action or final thoughts.
Additionally, articles can include components like a headline, subheadings, images, and citations to enhance readability and credibility.
Examples of Opinion Article Writing Formats
Opinion articles come in different formats depending on the writer's style and the intended audience. One popular format is the argumentative essay, which presents a clear thesis supported by evidence and logical reasoning. Another format is the personal reflection, where the writer shares their own experiences and thoughts on a particular issue. Satire and humor can also be used to convey opinions, adding an entertaining twist to the article.
Regardless of the format chosen, an opinion articleshould always engage readers and provoke thought, aiming to influence or challenge existing perspectives.
Best Practices for Opinion Articles
- Clear and compelling introduction : Start with a concise yet attention-grabbing opening sentence that sets the tone and captures the reader's interest. In case you are unable to write compelling words for the opening sentence, then use a paraphrase tool to automatically make it appealing to read.
- Strong thesis statement : Clearly state your opinion in a concise manner and highlight the main argument that you will be presenting throughout the article.
- Support arguments with evidence : Back up your opinion with relevant facts, examples, and research to strengthen your argument and persuade readers.
- Engage with counterarguments : Anticipate and address opposing viewpoints with counterarguments that demonstrate a understanding of the topic and add credibility to your opinion.
- Organize your thoughts : Break your article into sections or paragraphs to ensure logical flow and coherence, making it easier for readers to follow your reasoning.
- Use persuasive language : Employ rhetorical techniques like emotional appeal, logic, and storytelling to captivate readers and make your opinion resonate with them.
- Create a compelling conclusion : Summarize your main points, restate your thesis, and leave readers with a thought-provoking or memorable concluding statement.
- Edit and proofread : Review your article for grammatical errors, clarity, and coherence.
Ensure your writing is concise, coherent, and free from spelling or punctuation mistakes.
Remember, these best practices are guidelines for writing opinion articles; feel free to adapt and adjust them to suit your unique writing style and the topic at hand.
Article Writing Format Examples for Various Industries
Technology industry.
The technology industry is a fast-paced and ever-evolving sector that is continuously driving innovation. With new advancements in fields such as artificial intelligence , cloud computing, and the internet of things, technology companies are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. This industry plays a crucial role in shaping how we live, work, and communicate in today's digital world.
From smartphones to smart homes, technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, transforming industries and revolutionizing the way we do things. With trends like remote work and virtual reality on the rise, and the burgeoning field of flutter app development , the technology industry shows no signs of slowing down.
Health and Wellness Industry
The Health and Wellness industry is booming. People are becoming increasingly conscious about their well-being and are investing in products and services that promote a healthy lifestyle. From gym memberships and fitness classes to organic food and supplements, there is a wide range of offerings in the market. With the rise of social media and influencers, wellness trends have gained significant traction and have become mainstream.
This industry caters to those looking to improve their physicaland mental health, offering solutions for stress relief, weight loss, and mindfulness practices. With the increasing demand for healthier options, the Health and Wellness industry shows no sign of slowing down anytime soon.
Fashion and Beauty Industry
The fashion and beauty industry is a thriving global market . It encompasses clothing, cosmetics, and accessories, driving trends and influencing consumers worldwide. Its rapid growth is fueled by constant change, innovation, and the insatiable desire for self-expression. The industry plays a significant role in shaping cultural norms and personal identities. Its impact extends beyond aesthetics, as it creates job opportunities and generates substantial revenue.
However, the industry also faces criticism for promoting unrealistic beauty standards and unsustainable production practices. Despite its flaws, the fashion and beauty industry remains a powerful force in shaping society's perception of style and appearance.
Best Practices for Writing an Article in Any Format
Research and outline.
- To write a well-structured and informative article, it is crucial to conduct thorough research on the chosen topic. This helps you gather relevant information and develop a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
- Start by exploring reputable sources such as books, academic journals, reliable websites, or expert interviews. Ensure that the information obtained is up-to-date and accurate.
- After gathering the necessary data, creating an outline provides a clear structure for your article. Divide your information into logical sections or headings to ensure a coherent flow of ideas.
- The outline serves as a roadmap, guiding you throughout the writing process and helping you maintain focus on your main points. It also enables you to prioritize information and maintain a logical progression.
- With thorough research and a well-organized outline, you can write an engaging and well-structured article that conveys your message effectively.
Clear and Organized Structure
Clear and organized structure is crucial when it comes to writing articles. Readers appreciate a well-organized piece that flows smoothly. To achieve this, start with an introduction that grabs attention and clearly states the main idea. Break up the article into paragraphs with clear subheadings for each section, ensuring a logical flow between them. Use bullet points or numbered lists to present information concisely.
Remember to maintain coherence by linking ideas and providing smooth transitions.
Additionally, a strong conclusion that summarizes the key points is essential. Summarizing your content to make a lasting conclusion can be tricky and can’t be handled by everyone. The easiest way to do this is to use smart AI tools like a conclusion generator . These tools are specifically trained to generate compelling conclusions of any given text or article. So let such smart tool handle the job because a weakly drafted conclusion can mar the impression you generated by writing a impressing blog post. By presenting your content in a clear and organized manner, you ensure that readers can easily understand and navigate through your article.
Use Relevant Examples
When writing an article, using relevant examples is key. This helps to illustrate and support your points, making them more relatable and understandable for readers. For instance, if you're writing an article about the benefits of exercise, you can provide examples of successful athletes or include personal anecdotes of individuals who have experienced positive changes in their health through regular exercise.
By incorporating these real-life examples, you offer concrete evidence and make your article more engaging. Remember, relevant examples not only help to clarify your ideas but also make your writing more persuasive and captivating.
Use Proper Formatting and Style
Proper formatting and style are crucial in article writing. Use short, concise paragraphs to enhance readability. Break up the text with subheadings to give your article structure. Utilize bullet points or numbered lists for easy digestion of information. Make sure to use appropriate font sizes and styles to create an appealing visual experience for readers.
Additionally, pay attention to grammar, spelling, and punctuation to maintain a professional tone. Consistency in formatting and style will make your article more engaging and accessible to a broader audience.
Edit and Proofread
Edit and Proofread: Once you've finished writing your article, take some time to edit and proofread it. Read through your work and make sure your ideas flow logically. Check for any grammatical or spelling errors. Consider the overall structure and organization of the article. Are the paragraphs concise and focused? Is the tone appropriate for your target audience? Trim any unnecessary words or sentences to make your writing more impactful. Using tools like FineVoice TTS to read your work could help you spot the flaws more easily.
Finally, ask someone else to read your article and provide feedback. A fresh set of eyes can catch mistakes or suggest improvements that you might have missed.
Over to you
In this informative article, we delve into the world of article writing formats and share some practical examples and best practices. We explore various formats, such as listicles, how-to guides, news articles, and opinion pieces, highlighting their unique features and purposes. By breaking down lengthy paragraphs, we ensure easy-to-read content. This article is written in a conversational style, making it relatable for readers.
The aim is to provide valuable insights and guidelines that can help writers craft engaging and effective articles.
Trying to devise a structure for your essay can be one of the most difficult parts of the writing process. Making a detailed outline before you begin writing is a good way to make sure your ideas come across in a clear and logical order. A good outline will also save you time in the revision process, reducing the possibility that your ideas will need to be rearranged once you've written them.
The First Steps
Before you can begin outlining, you need to have a sense of what you will argue in the essay. From your analysis and close readings of primary and/or secondary sources you should have notes, ideas, and possible quotes to cite as evidence. Let's say you are writing about the 1999 Republican Primary and you want to prove that each candidate's financial resources were the most important element in the race. At this point, your notes probably lack much coherent order. Most likely, your ideas are still in the order in which they occurred to you; your notes and possible quotes probably still adhere to the chronology of the sources you've examined. Your goal is to rearrange your ideas, notes, and quotes—the raw material of your essay—into an order that best supports your argument, not the arguments you've read in other people's works. To do this, you have to group your notes into categories and then arrange these categories in a logical order.
Generalizing
The first step is to look over each individual piece of information that you've written and assign it to a general category. Ask yourself, "If I were to file this in a database, what would I file it under?" If, using the example of the Republican Primary, you wrote down an observation about John McCain's views on health care, you might list it under the general category of "Health care policy." As you go through your notes, try to reuse categories whenever possible. Your goal is to reduce your notes to no more than a page of category listings.
Now examine your category headings. Do any seem repetitive? Do any go together? "McCain's expenditure on ads" and "Bush's expenditure on ads," while not exactly repetitive, could easily combine into a more general category like "Candidates' expenditures on ads." Also, keep an eye out for categories that no longer seem to relate to your argument. Individual pieces of information that at first seemed important can begin to appear irrelevant when grouped into a general category.
Now it's time to generalize again. Examine all your categories and look for common themes. Go through each category and ask yourself, "If I were to place this piece of information in a file cabinet, what would I label that cabinet?" Again, try to reuse labels as often as possible: "Health Care," "Foreign Policy," and "Immigration" can all be contained under "Policy Initiatives." Make these larger categories as general as possible so that there are no more than three or four for a 7-10 page paper.
With your notes grouped into generalized categories, the process of ordering them should be easier. To begin, look at your most general categories. With your thesis in mind, try to find a way that the labels might be arranged in a sentence or two that supports your argument. Let's say your thesis is that financial resources played the most important role in the 1999 Republican Primary. Your four most general categories are "Policy Initiatives," "Financial Resources," "Voters' Concerns," and "Voters' Loyalty." You might come up with the following sentence: ÒAlthough McCain's policy initiatives were closest to the voters' concerns, Bush's financial resources won the voters' loyalty.Ó This sentence should reveal the order of your most general categories. You will begin with an examination of McCain's and Bush's views on important issues and compare them to the voters' top concerns. Then you'll look at both candidates' financial resources and show how Bush could win voters' loyalty through effective use of his resources, despite his less popular policy ideas.
With your most general categories in order, you now must order the smaller categories. To do so, arrange each smaller category into a sentence or two that will support the more general sentence you've just devised. Under the category of "Financial Resources," for instance, you might have the smaller categories of "Ad Expenditure," "Campaign Contributions" and "Fundraising." A sentence that supports your general argument might read: "Bush's early emphasis on fundraising led to greater campaign contributions, allowing him to have a greater ad expenditure than McCain."
The final step of the outlining process is to repeat this procedure on the smallest level, with the original notes that you took for your essay. To order what probably was an unwieldy and disorganized set of information at the beginning of this process, you need now only think of a sentence or two to support your general argument. Under the category "Fundraising," for example, you might have quotes about each candidate's estimation of its importance, statistics about the amount of time each candidate spent fundraising, and an idea about how the importance of fundraising never can be overestimated. Sentences to support your general argument might read: "No candidate has ever raised too much money [your idea]. While both McCain and Bush acknowledged the importance of fundraising [your quotes], the numbers clearly point to Bush as the superior fundraiser [your statistics]." The arrangement of your ideas, quotes, and statistics now should come naturally.
Putting It All Together
With these sentences, you have essentially constructed an outline for your essay. The most general ideas, which you organized in your first sentence, constitute the essay's sections. They follow the order in which you placed them in your sentence. The order of the smaller categories within each larger category (determined by your secondary sentences) indicates the order of the paragraphs within each section. Finally, your last set of sentences about your specific notes should show the order of the sentences within each paragraph. An outline for the essay about the 1999 Republican Primary (showing only the sections worked out here) would look something like this:
I. POLICY INITIATIVES
II. VOTERS' CONCERNS
III. FINANCIAL RESOURCES
A. Fundraising
a. Original Idea
b. McCain Quote/Bush Quote
c. McCain Statistics/Bush Statistics
B. Campaign Contributions
C. Ad Expenditure
IV. VOTERS' LOYALTY
Copyright 2000, David Kornhaber, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
The Complete Guide to Article Writing Format
Mastering the art of article writing can propel your career, establish you as an expert in your field, and drive traffic to your website or blog. Understanding how to structure and format an engaging article is critical for professional growth and capturing readers’ attention. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the essentials of article writing format, step-by-step instructions for crafting compelling content, various types of articles, best practices for formatting an article to capture leads, and much more. Read on to elevate your skills and learn how to create stunning articles that captivate audiences.
What is the Article Writing Format?

An article writing format is a structured template that guides writers to effectively communicate their ideas through clear organization, logical development, and coherent presentation. Adhering to a well-structured manner ensures that the author’s thoughts are easily understood by readers while maintaining consistency across different components such as headings, subheadings, introduction, body text, images or infographics, and conclusion.
What is the format for article writing?
The standard format for composing an article entails six primary elements:
- Heading : A captivating title sums up the topic or expresses a unique angle.
- Introduction : An engaging opening paragraph hooks readers by introducing the subject matter while sparking curiosity.
- Body : Well-structured paragraphs are subdivided into subsections or bullet points that clearly explain each point with concise language.
- Subheadings : These break up long stretches of text into manageable sections or highlight main ideas for easy scanning.
- Images and Infographics : Visual aids complement written content by further illustrating your points or presenting complex data in simplified form.
- Conclusion : A summary reiterating key highlights without repeating exact phrases used earlier – often ending with a call-to-action to provoke reader response.
Objectives of Article Writing

The article writing process involves various objectives to effectively communicate with your target audience. A well-crafted article serves multiple purposes, making it essential to content creation. By understanding the primary objectives of article writing, you can ensure that your content effectively meets its intended goals.
Inform and Educate
One of the key objectives of article writing is to inform and educate readers about a particular topic or subject matter. Incorporate accurate, up-to-date information backed by reliable sources into your content to achieve this goal. Providing information clearly and concisely helps maintain reader interest and enhances comprehension.
Engage the Reader
Engaging your reader is crucial to retaining their attention throughout the whole article. Utilize an active voice and conversational tone to create compelling content while maintaining professionalism. Incorporating personal anecdotes and real-life examples can make complex topics more relatable and accessible to readers.
Establish Authority and Expertise
Establishing yourself as an authoritative figure in your niche is another important objective of good article writing. To do so:
- Conduct thorough research
- Reference reputable sources
- Showcase industry expertise through insightful analysis
Expertise adds credibility to your content, encouraging readers to trust your opinions on relevant subjects.
Persuade Your Audience
When persuading readers to adopt a specific viewpoint, presenting solid arguments supported by credible evidence is vital. Employ persuasive techniques such as addressing counterarguments or providing data-driven insights to bolster your position convincingly.
Encourage Action
Some articles are written to influence readers towards taking action – whether it entails subscribing to an email newsletter, purchasing, or supporting a cause. Using persuasive language or offering incentives, such as exclusive benefits from acting promptly, can be helpful strategies for driving desired actions.
Four Types of Article Writing

An effective content creator should have a solid understanding of the four major types of article writing. Each type has its purpose, style, and intended audience. By mastering all these formats, you’ll be able to engage different readers effectively and convey your message precisely. This section explores the characteristics of expository, persuasive, narrative, and descriptive writing styles.
Expository Article Writing
Expository writing is an informative approach that educates readers about a specific topic or concept without expressing personal views or opinions. It requires extensive research and factual accuracy to present information clearly and concisely objectively. Some common examples of this article writing format include:
- How-to guides
- Product reviews
- News articles
When creating expository articles, consider the following elements:
- Develop a clear thesis statement or central idea.
- Use logical organization with headings and subheadings .
- Include credible sources and evidence to support claims.
- Keep your language precise, neutral, and easy to understand.
Persuasive Article Writing
In contrast to expository writing’s objective nature, persuasive writing articles aim to convince readers to adopt a particular viewpoint or take specific actions based on provided arguments. This article’s writing format often relies on emotional reasoning and rhetoric while incorporating strong evidence from reliable sources. Common examples of an argumentative article include opinion pieces, editorials, and product recommendations.
To craft compelling, persuasive content:
- Clearly state your position or argument.
- Provide well-reasoned points supported by facts or expert opinions.
- Address counterarguments respectfully while showing their weaknesses.
- Employ persuasive language techniques such as analogies or rhetorical questions.
Narrative Article Writing
Narrative articles focus on storytelling by sharing personal experiences or fictional tales for readers’ entertainment or enlightenment purposes. These stories typically follow chronological order with engaging characters and vivid descriptions; however, narrative-style business case studies or product testimonials can also be powerful marketing tools. Some examples are personal essays, anecdotes, and travelogues.
Tips for successful narrative writing:
- Utilize a robust and engaging hook to capture your audience’s attention.
- Develop relatable characters and realistic dialogue.
- Use descriptive language to paint a visual image for your audience.
- Follow a clear story arc with a beginning, middle, and end.
Descriptive Article Writing
Descriptive articles offer detailed descriptions of people, places, objects, or events to engage readers emotionally and create vivid mental images. Article writers often use sensory details (sight, hearing, smell, taste, touch) and figurative language (similes and metaphors) to bring the subject to life in this article’s writing format. Common instances include food reviews, travel experiences, and event reports.
To excel in descriptive writing:
- Choose a specific aspect or experience you want to convey.
- Use rich sensory information to evoke emotions or reactions.
- Employ figurative language strategically—don’t overdo it!
- Strive for an immersive experience by showing rather than telling.
Understanding these four article writing formats will allow you to craft compelling content tailored for each purpose and audience type successfully. Familiarize yourself with the unique characteristics of expository, persuasive, narrative, and descriptive styles to elevate your article-writing skills considerably.
The Article Writing Format

Understanding the article writing format is essential to producing high-quality, engaging content. An effective article-written format will help guide your readers through your ideas logically and clearly. This section will discuss the key components of a well-written article: Heading, Introduction, Body, and Conclusion.
An attention-grabbing heading is critical for drawing readers in. Make sure it accurately reflects the content of an article while keeping it concise and intriguing. Here are some tips you can follow:
- Use powerful vocabulary words that evoke emotion or curiosity
- Keep it short (ideally between 5-10 words)
- Avoid clickbait but make sure it generates interest
- Frame it as a question or use numbers if relevant (e.g., “5 Steps to Improve Your Sleep”)
Experiment with different formats to find what works best for your target audience when writing headings.
- Introduction
The introductory paragraph sets the stage for what readers should expect from your article. It aims to hook them into reading further by providing a glimpse of the value they’ll get by continuing. To achieve this, adhere to these guidelines:
- Start with an interesting fact or statistic that demonstrates the significance of your topic.
- Establish context and relevance by addressing why this topic matters to your readers.
- Give a brief overview of what you’ll discuss without diving too deep.
- End with a thought-provoking statement or question that encourages people to read on.
Remember that a strong introduction entices readers while setting expectations for the rest of the article.
The body comprises the bulk of your article content and forms the heart of its substance. In this section, elaborate on points introduced in earlier sections, supporting them with evidence such as research, anecdotal examples, clear statements, or expert quotes when necessary.
To write effectively in the body:
- Break down your main ideas into digestible subheadings to guide the reader.
- Be descriptive but concise – avoid excessive jargon and focus on conveying your key message.
- Use logical transitions between paragraphs or subsections to ensure a coherent flow of ideas.
- Utilize bullet points or numbered lists when presenting multiple concepts.
- Incorporate multimedia elements, such as images or graphics, to support and engage.
Organizing the body effectively ensures readers can easily understand and retain your present information.
Subheadings
Subheadings play a crucial role in enhancing the readability and organization of an article. They break up large chunks of text, making it easier for readers to consume the content and maintain their interest. Subheadings act as guideposts that lead the reader from one important component or topic to another, quickly conveying the essence of each section.
When incorporating subheadings into your article, consider the following tips:
- Make them informative: A good subheading should provide a snapshot of the section’s content. It should be concise yet descriptive enough to give the reader an idea of the topic that will be covered.
- Keep them consistent: Subheadings should maintain a consistent format throughout the article. This can involve using a similar font style, size, or emphasis. Consistency makes it easy for readers to recognize and navigate through different sections.
- Use SEO-friendly keywords: Including relevant keywords in your subheadings can improve the SEO (Search Engine Optimization) of your article, making it more discoverable by search engines. This strategy makes your content more likely to appear in users’ search results when they’re looking for information on your topic.
- Space them appropriately: Breaking up your content into logical sections helps improve readability. Avoid cramming too many subheadings close together or leaving large gaps between sections. A well-spaced article ensures a smooth reading experience and helps readers find the specific information they need.
- Keep paragraphs short -Ideally, paragraphs should not exceed three to five sentences in length. Focusing on one central idea per paragraph can help you create a clear and organized structure throughout your article.
Images and Infographics
Visual elements like images and infographics greatly enhance an article by providing visual appeal, enhancing understanding, and supporting the content. They can break up the lengthy text, making the content more digestible and engaging for readers.
- Use high-quality images: High-resolution images not only look professional, but they also convey your message more effectively. Ensure that the images you use are sharp, clear, and well-composed. Always credit the source of the image or make sure you have the appropriate permissions to use it.
- Relevance is key: Images and infographics should be directly related to the content they accompany. They should support the points being made and help clarify or elaborate on the information presented in the text. Avoid using irrelevant or generic images just for the sake of visual appeal.
- Opt for original visuals: Create or commission original images and infographics whenever possible. This not only adds a unique touch to your article but also helps set your content apart from others on similar topics.
- Use captions and descriptions: Including captions and descriptions with your images and infographics provides additional context and ensures that readers understand their relevance to the content. This can also improve the accessibility of your article for individuals who use screen readers or have visual impairments.
- Optimize for SEO: By including relevant keywords in the file names, alt text, and captions of your images and infographics, you can boost the overall SEO of your article. This helps search engines better understand the content and context of your visuals, making your content more discoverable.
A well-crafted conclusion is a closing statement that reaffirms your article’s main point(s). It reinforces what has been learned and provides direction for readers who want to explore further or take action related to your topic. Follow these tips to write a good and logical ending:
- Summarize key points made throughout the article without introducing new information.
- Highlight implications, real-world applications, or future trends relating to your subject matter.
- Invite feedback or discussion, or urge readers to consider the following steps (e.g., following a call-to-action).
- Claim your mastery by crafting an end with a thought-provoking question or inspiring quote that leaves an impact.
By effectively crafting the final paragraph, you’ll leave your audience feeling satisfied and enriched by their reading experience while wanting more from you in future articles. Ultimately, mastering this article writing format empowers you to consistently create high–quality content–benefitting you and those who read it.
Step By Step Guide for Writing an Article

To write good articles, it’s crucial to follow a systematic approach that covers all aspects of the topic. This section discusses a step-by-step guide to use as a blueprint when writing good articles .
Step 1: Identify your target audience
Before diving into the writing process, it’s essential to determine who your target audience is. Your readers’ preferences and interests will significantly influence the content of your article and its tone. To identify them:
- Define demographic characteristics such as age, gender, location, and occupation.
- Determine their needs, aspirations, confusions, or problems they are facing.
- Assess their level of expertise in your chosen topic; are they beginners or experts?
Understanding your target audience helps customize the article format and ensure the content resonates with them.
1. Remember who you’re speaking to. Understand their passions, pains, and what keeps them up at night. Once this picture becomes clear:
- Shape your content’s tone to match their preferences – heavy jargon for professionals versus simpler terms for beginners.
- Provide answers or solutions tailored specifically for them. This attentiveness ensures your articles resonate deeply and foster loyalty from those who find sanctuary in your words.
2. Readers often approach articles with clear intentions – seeking answers, learning skills, or simply finding entertainment. Your mission is thus twofold: discern these intents accurately, then craft content that aligns perfectly with their quests:
- Research keywords they use when searching online.
- Deliver content formats meeting those searched criteria—from how-to guides to thought pieces.
Aligning with search intent satisfies readers and signals search engines that your content is valuable. This leads us to our next point gracefully.
Step 2: Select an appropriate topic and an attractive heading
Next, pick one topic relevant to your niche or industry and develop an attention-grabbing headline that will pique readers’ curiosity. A captivating heading encourages potential visitors to click on your link and read through the entire piece.
Some tips for selecting topics and creating headlines:
- Address current trends or industry developments,
- Tackle issues faced by your target audience,
- Pose thought-provoking questions,
- Use numbers in listicles (e.g., “10 Tips for __”),
- Implement power words such as ‘How-to,’ ‘Ultimate Guide,’ ‘Secrets,’ etc.

Step 3: Conduct thorough research
Once you’ve chosen your topic, invest time in researching. It not only raises credibility but also helps provide well-rounded, relevant information to a larger audience of readers. As you gather data:
- Seek reliable sources like academic articles, government publications, books by renowned authors, or interviews with subject-matter experts.
- Maintain organized notes with valuable findings, including statistics, case studies, or expert opinions.
- Cross-check data to ensure its authenticity and relevance.
Step 4: Write an article outline
Creating an outline serves as the backbone of a good article, ultimately contributing to a clear and coherent content structure. Divide the piece into logical sections like:
- Main body (subheadings)
You can further break down each section into smaller sub-sections or bullet points to make it more digestible for readers.
Step 5: Write and proofread
With your research and outline in place, begin writing using a conversational tone while keeping it professional and informative. Keep in mind the following considerations:
- Use active voice and simple sentences
- Create engaging, relatable content for your target audience
- Utilize appropriate transition phrases between ideas
- Incorporate relevant keywords throughout the article
After completing your rough draft, set aside some time before revisiting it with fresh eyes to proofread. Correct any grammatical mistakes, unclear sentences, or inconsistencies.
Use AI Tools to speed up the process
Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools can significantly help streamline the writing process. Some popular AI writing assistants include Grammarly, Hemingway Editor, INK, or Copy.ai , which offer features like grammar checks, readability score improvements, or even generating content ideas.
Step 6: Add images and infographics
Lastly, enhance your article by incorporating relevant visuals such as photos, illustrations, or infographics to aid comprehension or break up text-heavy portions. Ensure they are high-quality images, and remember to credit sources.
1. Include Relevant and High-Quality Visuals
We live in a highly visual society where images can communicate complex ideas swiftly and memorably. Enhance reader engagement by integrating visuals such as:
- Crisp photographs
- Informative charts
- Vibrant infographics
High-quality visuals serve as waypoints on the journey through your text, keeping audiences anchored and immersed.
Step 7: Optimize for SEO
Optimizing for SEO means more than sprinkling keywords throughout your text. It’s about making sure those seeking what you’ve written find it effortlessly amid the vast ocean of online information. Here lies an opportunity:
- Employ relevant keywords naturally within headings and body paragraphs.
- Anchor texts should flow smoothly with internal links , leading readers deeper into related topics on your site.
By weaving SEO strategies through each paragraph, you enhance discoverability without sacrificing quality storytelling, a balance worthy of pursuit.
Article Writing Rules – Rules for Writing Good Articles
Following basic article writing rules is essential to create compelling and high-quality articles. These rules make the process easier and ensure your content is engaging, informative, and valuable to your readers. Let’s delve into these crucial guidelines that can elevate your article-writing skills.
Use Appropriate Keywords
Naturally integrating relevant keywords helps improve your article’s visibility, search engine rankings, and engagement rates. Be sure to use 3-5 of the appropriate keywords per section without compromising the quality of your content or forcing yourself to use them unnaturally.
Be Clear and Concise
Simplicity works wonders in the world of article writing. Keep sentences short and precise with a maximum of 15 words each since shorter sentences are easier for readers to read, understand, and absorb.
Maintain Coherence
Ensure that consecutive blocks of text don’t begin with the exact phrases or words to maintain coherence throughout the entire article. Each section should expand on the content covered previously while avoiding unnecessary repetition.
Stay Focused on Your Topic
Stay focused on your chosen subject matter by providing substantial information relevant to the topic at hand—straying too far from it may leave readers confused and disinterested.
Utilize Proper Formatting
Applying appropriate formatting techniques enhances readability by breaking down large chunks of text into smaller sections using headings, subheadings, bullet points, ordered lists, etc., making it enjoyable for readers.
Apply Logical Transitional Phrases
Using logical transitional phrases between ideas significantly improves readability as they connect related thoughts smoothly instead of relying solely on conjunctions like ‘and’ or ‘but.’
Fact-Check Your Content
Validate data through reliable sources like studies or research; this practice eliminates errors and boosts your content’s credibility.
Edit and Proofread
Ensure grammatical accuracy and clarity by thoroughly editing and proofreading your work, eliminating potential distractions for your readers in the form of errors or inconsistencies. Seeking feedback from a fellow article writer, editor, or reader can be incredibly valuable for enhancing the quality of your content.
By effectively applying these rules to your article writing process, you’ll notice increased engagement while providing the readers with the information they desire in a clear and user-friendly manner. Remember that practice makes perfect, so keep refining your skills to craft exceptional articles that captivate readers’ attention and sustain their interest throughout.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Article Writing

Even experienced writers can fall into common pitfalls that stall their articles from reaching their full potential. Let’s explore some frequent mistakes so you can steer clear of them.
Lack of Clarity or Coherence in Writing
Have you ever read a passage several times and still felt lost? A lack of clarity can leave readers confused and disengaged. To ensure that your thoughts flow seamlessly:
- Keep sentences short and sweet.
- Use subheadings to break up the text and organize thoughts.
- Transition smoothly between ideas with phrases like “Additionally” or “Another aspect to consider.”
Remember, article writing for websites should guide your reader through the topic like a knowledgeable friend leading the way in uncharted territory.
Poor Grammar and Spelling Errors
Nothing diminishes credibility quicker than grammar blunders or typos. They’re like little bumps on the road – each one jarring your reader from the experience.
- Utilize tools like Grammarly to catch sneaky errors.
- Never rely solely on spellcheck. Read aloud to see awkward phrasing.
- If feasible, have someone else review your work – fresh eyes find new mistakes.
Your command over language demonstrates professionalism and respect towards your audience. Don’t let simple slip-ups undercut your message.
Overuse or Misuse of Keywords
Keywords help people find your articles, but cramming them in willy-nilly makes for stilted reading. Keyword stuffing is a passe SEO tactic that today’s savvy algorithms easily spot as manipulative.
- Use keywords naturally within the context.
- Aim for keyword variations and synonyms to maintain readability.
- Concentrate on creating valuable content first; let keywords serve as subtle signposts rather than glaring billboards.
For website article writing, balance is key: enough keywords to be found by search engines but not so many that readers lose interest.
Insufficient or Inaccurate Research
In this digital age, everyone’s an expert…until they’re not. Ensure every fact you state could stand up in court if need be:
- Cross-check information against reputable sources.
- Cite statistics from authoritative studies (and link back where possible).
- Stay updated with recent data – because today’s fact might be tomorrow’s fiction.
Invest time in research – it reinforces your authority and trustworthiness as a writer much more than unfounded assertions ever could.
Lack of Originality or Unique Perspective
Lastly, don’t just rehash what’s out there. Offer something new:
- Fuse personal experience with external knowledge – it adds authenticity.
- Engage with controversial viewpoints (respectfully) to stimulate discussion.
- Present solutions, not just problems – be helpful, insightful, and inspirational.
Originality will set you apart from the informational echo chamber that often inundates web searches. Stand out by being distinctly YOU when engaging in article writing for website topics – it’s about adding value through unique insight as much as imparting wisdom through words.
How Should an Article Be Written?
The article writing process varies based on available resources and the chosen approach. To create compelling content, you have several options: hiring a freelancer, engaging an agency, or utilizing AI writing tools . Each method has its advantages and drawbacks. Let’s examine each option in detail.
Freelancer Article Writers
Hiring a freelancer is often the go-to choice for businesses seeking to outsource their article-writing tasks . By choosing this route, you gain access to various benefits:
- Expertise: Freelance writers possess diverse skill sets to tackle multiple topics in different formats.
- Flexibility: Working with a freelancer enables flexibility regarding deadlines and communication.
- Cost Savings: Hiring freelancers may result in cost savings compared to engaging with an agency.
However, possible challenges include inconsistency in quality and uncertainties surrounding accountability.
When considering freelance writers for your articles, keep these guidelines in mind:
- Review their portfolio, focusing on relevant samples;
- Check online reviews or seek recommendations;
- Communicate your expectations regarding format, tone, and style;
- Discuss project timelines and payment terms.
Collaborating with an agency can provide access to comprehensive expertise while maintaining consistent results. Agencies typically offer teams of writers, editors, and graphic designers who work together cohesively on your projects.
Benefits of working with an agency include:
- Consistency: A professional agency ensures overall consistency across all content produced.
- Scalability: An agency can handle large-scale projects more efficiently than individual freelancers.
- Streamlined Communication: Agencies usually assign a dedicated project manager for efficient communication.
On the downside, agencies tend to be more expensive than freelancers.
To find the right fit when exploring agency options:
- Research reputable agencies within your niche;
- Evaluate their offerings by verifying case studies or reviews;
- Discuss project scope, schedule, and budget before signing agreements.
- AI Article Writer
Artificial Intelligence (AI) writing tools like SEOwind have emerged as innovative solutions for content creation. These programs rely on advanced algorithms to generate articles at a faster pace. However, the degree of human involvement is still crucial for maintaining quality and effectiveness.
Some advantages of AI writing tools include the following:
- Efficiency: AI-powered tools can generate articles swiftly, which may save time compared to manual writing.
- Content Ideas Generation: They can provide content suggestions based on your chosen keywords or topics.
- Proofreading and Editing: Many AI tools also assist in improving readability by identifying grammar errors and suggesting sentence structure improvements.
There are limitations when relying solely on AI-generated content , such as a potential lack of creativity, knowing the specifics of your domain or company, and problems with factual data.
To successfully leverage AI writing tools:
- Research reliable options that address your specific needs;
- Use them alongside human input, striking a balance between automation and human touch;
- Ensure thorough editing before publishing any AI-generated article .
Each method – freelancer, agency, or AI writing tool – has its strengths when creating articles that follow the ideal format. The key is understanding your requirements while ensuring your chosen approach complements your goals regarding quality, efficiency, and budget constraints in article production.
How Can I Start Writing Articles?

Starting to write articles may seem overwhelming, but with a step-by-step approach and understanding of the article writing format, you can successfully begin your journey. Here are some essential steps to consider when starting:
Define Your Interests and Expertise
Before delving into article writing, recognize your interests and areas of expertise. This will guide you in choosing relevant topics that align with your passion and knowledge.
Identify a Target Audience
Knowing your audience is crucial for any content creation. Understand your target readership’s demographics, preferences, needs, and language style.
Choose Article Writing Topics Wisely
Pick engaging topics based on current trends or issues your target audience faces. Conduct keyword research to identify popular search phrases related to the subject matter.
Learn Article Writing Fundamentals
Familiarize yourself with the components of an article writing format, such as heading, introduction, body, and conclusion. Study sample articles related to your niche to understand how professionals structure their work.
Plan Your Content
Create an outline before beginning the actual writing process. This will help you organize thoughts effectively while covering all necessary points within the content.
Write Regularly
Refining your skills takes time and practice; make it a priority to write consistently (daily or at least several times per week). Ensure you maintain focus on quality over quantity during this learning phase.
Edit Thoroughly
Reviewing your work is essential when crafting high-quality articles; eliminate errors or redundancy within sentences to ensure conciseness and clarity in communication.
Seek Feedback
Ask friends, family members, or colleagues for honest feedback regarding writing style, flow, tone, and accuracy — constructive criticism contributes to writing growth.
Expand into Different Formats
Experimentation allows improvement; explore different article formats, such as persuasive or descriptive writing, to strengthen your versatility in content creation.
Learn from Others
Study articles by other writers within your niche to observe their techniques and styles. Analyzing their approach empowers you to develop your unique voice over time.
Starting a career in article writing begins with self-awareness and an understanding of the target audience’s needs. Building a solid foundation in the essentials of article writing format, followed by consistent practice, leads to growth and success in this field. Embrace feedback and continuously challenge yourself by exploring various formats, styles, and niches within written communication.
Grow Your Article Writing with a Focused Niche

Choosing a focused niche is essential in honing your article writing skills, building credibility within your industry, and positioning yourself as an authority. A narrow niche will enable you to create specialized content that appeals to your target audience and meets their unique needs.
Benefits of Selecting a Specific Niche
- Expertise: A concentrated focus allows you to deepen your understanding of the subject matter and build expertise – vital components for creating high-quality articles.
- Targeted content: You can craft content tailored to your intended audience’s challenges and aspirations by zeroing in on a particular area.
- Establish authority and credibility: Writing informative articles on topics related to your niche over time will help position you as an authoritative voice.
- Audience loyalty: Readers searching for information about a specific topic are more likely to return for additional insights from writers who consistently provide valuable content in their area of interest.
- Higher relevance for SEO : Focusing on a specific type of content or set of keywords improves search engine optimization (SEO) performance because search engines find ranking pages containing relevant, authoritative information easier.
To succeed in growing your article writing by concentrating on one area, consider these strategies:
Identifying Your Niche
Selecting a suitable niche requires careful assessment of both personal interests and market demands. Aligning these two factors ensures sustained motivation while creating ample opportunities for professional growth.
- Evaluate personal passions: Choose a subject that genuinely fascinates or excites you since this will reflect positively on the quality and tone of your articles.
- Discover areas where readers need answers: Identify niches with insufficient high-quality content or new developments driving demand for updated resources.
- Assess competition: Research how other writers fare in potential niches by analyzing the format, quality, and reader engagement of existing articles.
Staying Updated in Your Niche
Once you have selected your niche, you must stay informed about new technical developments and trends within the industry. This will enable you to:
- Produce articles that are up-to-date and relevant,
- Address the ever-changing needs of your target readers,
- Offer insights based on recent research and findings.
To remain current, tap into resources such as:
- Industry news websites or reputable blogs,
- Research publications from authoritative sources,
- Online communities or social media groups related to your niche.
Adapting Article Writing Format for Your Niche
An effective article writing format resonates with your specific audience by addressing their unique concerns and interests. To tailor your article format for maximum effectiveness within your chosen niche:
- Understand your audience: Identify the content preferences, knowledge level, and reading habits of people interested in your niche.
- Customize headings: Use headings that reflect your target readers’ challenges or offer potential solutions specific to their context.
- Adjust tone and vocabulary: Write using an appropriate tone of voice (professional or conversational) while incorporating industry-specific jargon where necessary to enhance credibility.
- Create captivating introductions: Design introductions that grab attention with compelling hooks tied specifically to questions and concerns within the domain.
- Structure articles for easy scanning: Utilize subheadings, bullet points, numbered lists, and text formatting techniques such as boldface or italics to improve readability.
How Do I Know It’s a Good Niche?
Selecting the right niche is critical for successful article writing. A good niche is one that not only piques your interest but also has a substantial demand and audience. To determine if a specific niche is worth pursuing, consider the following factors:
Interest and Passion
First and foremost, check whether you have a genuine interest in the niche. Writing about something you are passionate about will make producing engaging and informative content easier. Having expertise in the subject matter also provides an added advantage.
Available Audience
A strong market presence with an existing audience indicates a potentially profitable niche. Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner or Ubersuggest to identify search volume trends on related topics within the chosen niche.
Competition
Analyze your competition before committing to any specific topic. Suppose there’s low competition for a particular keyword set or subtopic. In that case, it may be wise to pursue it further to position yourself as an authoritative source of information.
- High competition: Beware of overcrowded subjects where standing out from other writers might prove challenging.
- Moderate competition: Optimal scenario – there’s enough interest surrounding the topic, yet room exists to establish your voice as an expert.
- Low competition: Assess if low demand or limited content quality is causing fewer people to write about this subject; high-quality articles might still attract readership.
Monetization Potential
If generating income through article writing is part of your goals, assess the monetization potential for your chosen niche. Consider options such as affiliate marketing programs, sponsored posts, advertising revenue, or even creating eBooks based on your articles.
Evergreen Content Possibilities
Lastly, evaluate if your selected niche lends itself well to producing evergreen content – timeless information that remains relevant regardless of when it was published. Establishing evergreen content ensures steady traffic flow over time without constantly needing updates or relying solely on trending topics.
Considering these factors, you can ascertain if your chosen niche will lead to profitable and engaging article-writing experiences. As your expertise grows within a specific niche, generating fresh content and captivating readers will become increasingly effortless, allowing you to leverage your skills for greater success.
What is the Best Article Writing Format to Capture Leads?

Capturing leads through effective article writing has become essential in reaching your target audience and driving conversions. Creating quality content that resonates with readers in various formats helps showcase your expertise, fostering credibility and trust. To determine the best format for efficiently capturing leads using articles, consider incorporating these key elements:
Attention-Grabbing Headline
An enticing headline works as a hook that can grab the reader’s attention and pique their interest before they even start reading your content. Make sure to use powerful words that resonate with your target audience and ensure it demonstrates the value they would receive by reading the article.
Introduction with Strong Value Proposition
The introduction to the perfect article should be engaging and provide a quick overview of what the reader can expect from the article. A solid value proposition is often indispensable in establishing why this piece will benefit them or solve their problem.
Include Infographics, Images, and Videos
Visual aid helps break up long walls of text and adds depth to your content while making it more appealing to readers. Including relevant infographics, images, or videos within an article enriches user experience leading to better engagement rates.
Easy-to-Digest Content Format
Consider employing one of these formats for better comprehension:
- Bullet points: They allow easy scanning.
- Subheadings: Allow breaking complex topics into smaller sections.
- Short paragraphs: Simplify structure while maintaining readability.
Remember to keep sentences short (up to 15 words) for better readability.
Call-to-Action (CTA)
Including a strong call-to-action at strategic points throughout the article encourages readers to download resources such as e-books or sign up for newsletters–thus capturing leads effectively.
Overall, choosing an article writing format highly depends on understanding which method resonates most with your target audience and the type of content produced. Experimenting with several approaches lets you ascertain which format yields better lead-capture results while consistently delivering value through compelling and informative content.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Article Writing
The journey of writing articles is filled with questions. Let’s tackle a few pressing queries to help you navigate the art of article writing.
What is the Ideal Length for an Article?
Ah, the age-old question: “How long should my article be?” There isn’t a one-size-fits-all answer. It depends largely on your audience, topic complexity, and publication venue. However, a rule of thumb suggests:
- Short-form articles typically range from 500 to 800 words and are superb for online platforms where readers seek quick insights.
- Medium-length articles, hovering around 1,200 to 1,500 words, hit a sweet spot by providing enough space to delve deeper without over-testing readers’ attention spans.
- Long-form pieces stretch beyond 2,000 words and suit topics requiring comprehensive coverage or detailed storytelling.
Assessing what you aim to achieve with what an article in writing is helps solidify this decision. Remember engagement metrics because reader retention can drop if content feels needlessly drawn out.
Can I Use References or Citations in My Articles?
Absolutely! Referencing authoritative sources underpins your credibility and enriches your work by demonstrating thorough research. When you’re mulling over how to write articles for publication, consider these citation tips:
- Choose reliable sources such as scholarly journals or recognized experts in the field.
- Following the recommended citation style to bolster professionalism – APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian are common picks.
- Include citations when stating facts or figures that aren’t common knowledge.
Incorporating references demonstrates due diligence and respect towards intellectual property rights, a sign of meticulous writing articles ethos.
How Can I Make My Articles Stand Out from Others?
Every writer desires their prose to pop off the page—or screen—as uniquely compelling. Achieving standout status hinges on the following:
- Offering fresh perspectives: Bring something new to the table—uncommon insights, novel angles, or untold stories can distinguish your piece from others cluttering cyberspace.
- Engaging narrative: Storytelling isn’t just for fiction writers. Weaving anecdotes or creating vivid scenarios makes any topic more relatable and memorable.
- Voice authenticity: Your voice is as distinct as your fingerprints. Don’t be afraid to let your personality shine through while addressing an article in writing—readers gravitate toward authenticity.
Alongside exceptional content quality goes impeccable presentation—sleek formatting and crisp visuals if applicable—and applying solid SEO practices heightens visibility. Take care not only about what you say but how you say it. That’s how lasting impressions are made daily amidst the crowded cacophony of content.
Remember that these FAQs reflect just a fraction of considerations central to crafting successful articles. Dive into each phase with curiosity and caution for the best results!
Kate Kandefer
Entrepreneur passionate about scaling SaaS companies on a global B2B stage. My expertise in AI, SEO, and Content Marketing is my toolkit for driving tangible results. I'm a hands-on executor guided by results, deeply passionate about marketing, and skilled at aligning business objectives with people's needs and motivations. With a pragmatic mindset. My approach is all about clarity, efficiency, and open dialogue.
Table of Contents
- 1 What is the Article Writing Format?
- 2 Objectives of Article Writing
- 3 Four Types of Article Writing
- 4 The Article Writing Format
- 5 Step By Step Guide for Writing an Article
- 6 Article Writing Rules – Rules for Writing Good Articles
- 7 Common Mistakes to Avoid in Article Writing
- 8 How Should an Article Be Written?
- 9 How Can I Start Writing Articles?
- 10 Grow Your Article Writing with a Focused Niche
- 11 How Do I Know It’s a Good Niche?
- 12 What is the Best Article Writing Format to Capture Leads?
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Article Writing
Related Posts

- Does Google Penalize AI Content – All You Should Know
- 15+ AI Best Practices: AI Content Guide for Creators

Why AI Content Repurposing is Your New Best Friend
- #100Posts30DaysChallenge
- Affiliate program
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Latest Posts
- Does AI Content Rank in Google?
- Grow Your Agency – Proven Tactics to Scale Fast
- SEOwind vs MarketMuse vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Marketmuse vs Clearscope
- SEOwind vs Clearscope vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Surfer SEO vs Clearscope
- SEOwind vs Surfer SEO vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Jasper AI vs Frase
- SEOwind vs Rytr vs Jasper
- SEOwind vs Writesonic vs Rytr
- SEOwind vs Writesonic vs Copy.ai
© 2024 SEOwind.
- Content Brief Generator
- CyborgMethod Bootcamp
- Human vs AI Experiment
Privacy Overview
[CyborgMethod™ Bootcamp] Got a small team and want to boost organic leads? Learn How.
How to Write a Formal Essay: Format, Rules, & Example
If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!

Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide you through the process. This article will:
- explain what a formal essay is;
- show how to write it step by step;
- provide you with an essay sample.
👔 Formal Essay Definition
- ✅ How to Write
- ✍️ Writing Rules
- 🖥️ Essay Format
- 📑 Sample Paper
🔍 References
A formal essay is a well-structured piece of writing with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. This type of essay often includes cited research, uses an academic tone, and is written in 3rd person. While writing a formal essay, it’s necessary to back up your arguments with factual evidence.
What Is an Informal Essay vs. Formal Essay?
Essays come in two formats: formal and informal (also known as personal .) They differ in terms of style and context. You can choose one of the formats depending on the situation and the type of paper you need to write.
Don’t know how to tell the difference between them? Well, here are some key characteristics of these essay types:
As you can see, these types of writing are almost total opposites. Informal essays are only reserved for creative assignments, which means that most of the papers you write need to be formal.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Our article on creative essays can help you write an informal paper. But how do you craft a perfect formal essay? Keep reading to find out.
✅ How to Write a Formal Essay
Traditionally, a formal essay it’s composed of 3 sections: an introduction, 3 or more body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Let’s examine each part in detail.
Formal Essay Introduction
The introduction is what your essay starts with. Its primary goal is to catch the reader’s attention with a hook, briefly introduce the topic, and lead toward the thesis statement located at the end of the first paragraph.
Here is what you might want to keep in mind while writing the introduction:
If you want some more inspiration for your introduction, check out our article on hooks in writing .
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Now on to the thesis statement : the key idea of your essay. When working on it, keep in mind that it should answer the central question in your topic and reflect your essay’s overall structure. your essay’s overall structure.
Suppose your topic is related to the teaching methods involving poetry. In that case, the thesis statement can be like this:
Teaching methods that involve reading and writing poetry in elementary school are beneficial for children as they enhance their capacity for empathy, develop creativity, and help with self-realization.
Formal Essay Body
The next part of an essay is the main body paragraphs. They support the thesis statement with well-developed arguments and explore the topic in-depth. Each body paragraph starts with a topic sentence stating its main point. The length of a paragraph can vary, but the best option is to have between 4 and 7 sentences.
To make the text flow easily, you may use transitional words. Here are some examples:
- after all,
- for instance,
- on the one/other hand,
- initially,
- as a result.
How to Write a Formal Essay Conclusion
Lastly, every essay needs closure. A good conclusion summarizes the essay’s main ideas, includes a paraphrased thesis, and encourages the readers to think more about the topic.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
The structure of a conclusion may change slightly depending on the subject. For instance, it can suggest some solutions to a problem, express an opinion, or give a recommendation. It’s important to remember that the conclusion is a part that emphasizes your essay’s most important points and doesn’t introduce new information.
If you’re curious about writing each essay part, check out our article on 5-paragraph essays .
✍️ Formal Writing Rules
Just like choosing the proper attire to wear to a formal event, we need to use the right words while writing a formal essay. Here are some suggestions that can help you maintain a formal tone in your paper:
Dos of formal writing
- Pay attention to your vocabulary. The words you will use in a formal essay will likely have a nuanced meaning. Make sure you know exactly what the terms mean, and do your best to sound precise.
- Use punctuation correctly. Here are some of the things to watch out for: Avoid exclamation marks; Use dashes for insertions; Use colons with enumerations; If you’re unsure of whether to use a punctuation mark or not, rewrite the sentence in a way that doesn’t require it.
- Use varied sentence structure. In formal writing, there is always a danger of sounding monotonous. Avoid repeating sentence structures to make your essay more readable.
- Provide references. It’s essential to cite every idea that you borrow. Try to paraphrase quotations from your sources: it will help you avoid plagiarism.
Don’ts of formal writing
- Avoid using pronouns. With words such as “I,” “me,” “we,” or “us,” an essay becomes wordy. It also makes the author seem less sure of their ideas. If you want to use personal pronouns, try substituting them with words like “the reader,” “viewers,” or “one.”
- Avoid using slang expressions and nonstandard diction. Slang words in a formal essay will make it less appealing to the readers. If you want to be taken seriously, it’s best to avoid those expressions and use proper Standard English.
- Avoid informal tone. When you write a formal essay, incorporate the language and the expressions you would use while delivering a speech, not the words you use when you casually talk to friends. A formal tone suggests that the author is serious about the topic and respects the audience.
- Avoid passive voice. Passive verbs are hard to read, and they are wordy. Use active voice to sound more straightforward and concise.
Contractions in Formal Writing
A contraction is usually a combination of two words into one, such as “don’t,” “isn’t,” “can’t,” and “wouldn’t.” When you work on a formal essay, it’s essential to be careful about contractions. It’s inappropriate to use them in academic writing, so it’s best to stick to the full variant.
However, there are exceptions to this rule. For instance, when working with direct quotations, it’s essential to reproduce words exactly as they are used in the original. To learn more about it, be sure to check out the University of North Florida’s article on in-text citations .
What to Use Instead of “You” in an Essay
Another common mistake students make is using the “you” and “yours” pronouns to address the readers. This mistake can make the essay overly informal and lead to misinterpretations of the text.
How do you fix it? Our advice is to replace 2nd-person pronouns with the following words:
- individuals,
You can find more formal writing tips in this informative video from Smrt English:
🖥️ Formal Essay Format
Now that we’ve discussed formal essay writing in detail, it’s time to look at the formatting. A formal essay is usually written in MLA or APA formats. If you’re asked to write a paper in one of these formats, you may find the guidelines below helpful:
📑 Formal Essay Example
Here is an excellent sample of a formal essay that uses all the guidelines mentioned in this article. It will help you to produce a perfect paper of your own:
For more information, check out Purdue OWL’s resources on various formatting styles .
Formal Essay Topics
- Stress management techniques
- The effects of coffee
- Negative effects of technology on children
- Causes and outcomes of organizational conflicts in sports
- Different types of friends
- Same-sex marriages in the United States
- Are early marriages harmful or beneficial?
- How do nutrition and hydration improve athletes’ performance?
- Is polygamy morally acceptable?
- Different features of sports business
- What characterizes friendship in the age of media ?
- Positive and negative effects of tourism on environment in the Caribbean
- How does society treat single parents ?
- How does the uninvolved parenting style affect child’s future well-being?
- The role of family relationships in Odyssey
- Financial concepts in sport finance
- Main features of a strong marriage
- The importance of media coverage for sport teams
- Reasons why students choose to get internship
- The role of stadiums in the sports industry
- The multiracial family: the Carters case analysis
- Characteristics of children’s sports
- Crucial factors affecting health fitness
- How is technology used in hotel management ?
- Structure and operational context of Four Seasons
- What are the main qualities of a true friend?
- Different websites that promote rental properties
- The imperative aspects of tourism
- Importance of hotel training
- What factors determine adolescents’ adjustment after they experience parental divorce ?
- How does tobacco use affect the human body?
- The importance of language and world view for communication
- What makes a combination of reinforcement and punishment in parenting efficient?
- The scientific approach of sports economics
- How does divorce affect children?
- Living on-campus vs. living off-campus when attending university: a comparison
- How does the New Moves program promote a healthy lifestyle?
- How to be an effective counselor
- Various types of restaurants in Ireland
- Carolina Dog’s characteristics
- Comparison of Monzameon’s The Love Suicides at Amijima and Tartuffe by Moliere
- Comparing homosexual and heterosexual families
- How is family presented in Everyday Use by Alice Walker ?
- In what ways can Anaerobic Threshold be assessed?
- Is bad parenting a healthcare problem?
- Why student-athletes should benefit from sports
- Mind-body awareness and its health benefits
- Can punishment boost academic performance?
- Techniques to teach students swimming
- Issues faced by the sports licensing field
Thanks for reading through this guide! We hope that you found it helpful and now have a better idea of how to write an excellent formal essay. Don’t hesitate to share our article with a friend who may need it. Good luck!
Further reading:
- How to Write a Critical Thinking Essay: Examples & Outline
- What Is a Discourse Analysis Essay: Example & Guide
- How to Write a Narrative Essay Outline: Template & Examples
- How to Write a Précis: Definition, Guide, & Examples
❓ Formal Essay FAQs
It’s best not to use pronouns such as “I,” “my,” “we,” “our,” etc., in a formal essay since it give the paper an informal tone and the text becomes wordy. It also makes the writer seem less sure about their ideas.
It’s better to avoid using parentheses and dashes in formal academic writing. If the information you want to include in the essay is important enough, it should be a part of the sentence. Otherwise, you can simply omit it.
The formal and informal essays differ in style and context. While a formal essay is a piece of well-structured writing that tries to convince the reader by providing arguments, an informal essay has no set structure. It reflects the author’s personal thoughts or opinions.
Starting your sentence with “because” in formal writing is not the best idea. The word “because” is a subordinate conjunction, which means it’s used to join the main clause to a subordinate clause, not to start a sentence.
It’s best to avoid using 1st- and 2nd-person pronouns, slang expressions, nonstandard diction, and contractions in a formal essay. They are primarily used in daily speech and are considered inappropriate in academic writing.
- Point of View in Academic Writing: St. Louis Community College
- Components of a Good Essay: University of Evansville
- Introductions & Conclusions: University of Arizona Global Campus
- How to Improve Your Academic Writing: University of York
- Nine Basic Ways to Improve Your Style in Academic Writing: University of California, Berkeley
- Academic Writing Style: Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: University of Southern California
- Formal and Informal Style: Northern Illinois University
- Formal Writing: Davenport University: LibGuides
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Rhetorical analysis is never a simple task. This essay type requires you to analyze rhetorical devices in a text and review them from different perspectives. Such an assignment can be a part of an AP Lang exam or a college home task. Either way, you will need a solid outline...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

A critical analysis essay is an academic paper that requires a thorough examination of theoretical concepts and ideas. It includes a comparison of facts, differentiation between evidence and argument, and identification of biases. Crafting a good paper can be a daunting experience, but it will be much easier if you...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
![essay writing article format Critical Writing: Examples & Brilliant Tips [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/fingers-note-report-journalist-filling-284x153.jpg)
Any critique is nothing more than critical analysis, and the word “analysis” does not have a negative meaning. Critical writing relies on objective evaluations of or a response to an author’s creation. As such, they can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves. To write a critique, you...

If you are assigned to write a rhetorical analysis essay, you have one significant advantage. You can choose a text from an almost infinite number of resources. The most important thing is that you analyze the statement addressed to an audience. The task of a rhetorical analysis essay is to...

Any literary analysis is a challenging task since literature includes many elements that can be interpreted differently. However, a stylistic analysis of all the figurative language the poets use may seem even harder. You may never realize what the author actually meant and how to comment on it! While analyzing...

As a student, you may be asked to write a book review. Unlike an argumentative essay, a book review is an opportunity to convey the central theme of a story while offering a new perspective on the author’s ideas. Knowing how to create a well-organized and coherent review, however, is...

The difference between an argumentative and persuasive essay isn’t always clear. If you’re struggling with either style for your next assignment, don’t worry. The following will clarify everything you need to know so you can write with confidence. First, we define the primary objectives of argumentative vs. persuasive writing. We...

Article Writing

Different writing compositions are used to inform various target audiences. They can be find in almost any source, which includes print media and online sources. With the advancement of modern technology, such sources have become more easier to access by the day. The word article can be used to refer to a brief written composition which is often found among other compositions typically included in different publications (e.g. newspaper , magazines, online, etc). An article can tackle about different topics, depending on the writer, and is usually intended for a target audience.
What Is Article Writing? Article writing is a process of creating written pieces of content, paragraphs to reach a broad audience through different platforms. These platforms include newspapers, magazines, journals, and other publishing mediums. The goal is to engage readers by sharing information, stories, or opinions in a written format. This type of writing is common in various media outlets, making it an essential way to communicate and connect with people.
Writers present information in various ways, such as in an informative writing or argumentative writing form. Basis of information written on articles may vary. Such facts may be gathered from different sources, such as eyewitness accounts, one on one interviews, and online, among others.

Download Sample Article Writing Bundle
Article Writing Format
An article will have an Introduction, Body Paragraphs and Conclusion . The introduction Briefly explains the topic and makes user strict to the content. The body paragraphs explains the subject in detail with evidence, examples, stats, arguments. The conclusion summarizes the important points to give overview to the reader.
1. Introduction
The introduction in article writing is the first section that sets the stage for the entire article. It serves to grab the reader’s attention and give them a reason to keep reading. This part typically includes:
Hook : Start with an interesting fact, question, or statement to grab attention. Background Information : Provide context or background related to the topic. Thesis Statement : Clearly state the main idea or purpose of the article.
2. Body Paragraph
In article writing, a body paragraph is a key section where the main ideas and arguments are developed. Each body paragraph typically follows this structure
Subheadings : Organize the content with relevant subheadings. Main Points : Discuss each main point in separate paragraphs. Supporting Information : Provide evidence, examples, and details. Clarity and Flow : Use simple language and smooth transitions.
3. Conclusion
The conclusion in article writing is the final section where the writer wraps up the discussion. It serves several key purposes:
Summary : Recap the main arguments or points. Final Thoughts : Conclude with a compelling closing statement or call to action.
Article Samples on Various Topics
Environment article samples.
- Water Conservation
- Need to Save Water
- Global Warming and Climate Change
- Deforestation
- Environment and Nature
Society and Culture Article Samples
- Importance of Education
- Teacher’s Day
- US Independence Day
- Discrimination
- Homelessness
- Women Empowerment
- Child Labor
- Globalization
Technology and Innovation Article Samples
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) – The Future of Technology
- Machine Learning
- Robotics and Automachines Manufacturing
- Wearable Technology and Its Health Applications
- 3D Printing Innovations and Applications
- Nano-technology: Advancements and Future Prospects
- Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency
- 5G Network Expansion and Its Impacts
- The Future of Electric and Autonomous Vehicles
- Cybersecurity: Protecting Our Digital World
- Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Education
- Big Data Analytics and Its Role in Business Decision Making
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Home Innovations
Health and Lifestyle Article Samples
- Health is Wealth
- Healthy Eating
- Impact of Social Media on Teenagers
- The Importance of Physical Fitness in Student Life
- Mental Health
Education Article Samples
- The Evaluation of Online Learning and its Impacts
- The Role of Technology in Modern Education
- Road Safety
Articles Writing Examples & Templates in PDF and DOC
Newspaper article writing example.

Creative Article Writing for School

Technical Article Writing Example

Short Article Writing Example

Medical Article Sample Writing Example

Sample Article Writing Example

Free SEO Article Writing Example

Persuasive Article Travel Example

Importance of Article Writing
Articles deliver information effectively, like other persuasive writing compositions. Which explains why article writing is an important skill which needs to be developed. The process of article writing, as compared to writing other compositions can be tricky.
For example, a news article needs to be written without carrying any biased opinion from the writer. Article writing requires the writer to gather accurate information from reliable sources of information. You may also see essay writing examples
Basically, article writing helps the writer develop both the writing and data gathering writing skills—which in turn develops his/her communication skills. At the end of the day, article writing, or writing in general, helps in improving an individual’s communication skills in general.
Types of Article Writing
Article writing is a versatile form of writing used in various contexts, including journalism, blogging, academic writing, and more. Here are some examples of different types of articles:
1. News Article
News articles report current events and provide facts and information about newsworthy topics. They typically follow the “inverted pyramid” structure, with the most important information presented at the beginning.
Example : “COVID-19 Vaccination Drive Reaches Milestone with 1 Billion Doses Administered Worldwide”
2. Feature Article
Feature articles offer in-depth coverage of a particular topic, often with a more narrative or storytelling approach. They provide background, analysis, and context, going beyond the surface details.
Example : “The Hidden Wonders of the Amazon Rainforest: A Journey into Biodiversity and Conservation Efforts”
3. Opinion or Editorial Article
Opinion articles express the author’s viewpoint on a particular issue. They are often persuasive in nature and present arguments or personal perspectives.
Example : “Why We Should Prioritize Renewable Energy Sources for a Sustainable Future”
4. How-To Article
How-to articles provide step-by-step instructions on how to perform a specific task, solve a problem, or achieve a goal.
Example : “How to Start Your Own Vegetable Garden: A Beginner’s Guide”
5. Review Article
Review articles assess and provide an opinion on a product, service, book, movie, or any subject of interest. They often include an evaluation of the item’s pros and cons.
Example : “Film Review: ‘The Trial of the Chicago 7’ – A Riveting Dive into 1960s Political Turmoil”
6. Academic or Research Article
Academic articles are scholarly publications that present research findings or discuss academic topics. They often follow specific formats and are published in academic journals.
Example : “The Impact of Climate Change on Coral Reefs: A Comprehensive Ecological Study”
7. Blog Post
Blog articles cover a wide range of topics and are typically written in a conversational, engaging style. They are commonly found on personal blogs, corporate blogs, and news websites.
Example : “10 Tips for Effective Time Management in a Remote Work Environment”
8. Travel Article
Travel articles describe and share experiences about specific travel destinations, providing insights, tips, and recommendations for travelers.
Example : “Exploring the Rich History and Culture of Rome: A Traveler’s Guide”
9. Technical or Instructional Article
Technical articles focus on complex or specialized subjects and are often used in industries like technology, science, or engineering. They explain technical concepts or processes.
Example: “A Comprehensive Guide to Data Encryption Algorithms for Cybersecurity Professionals”
10. Entertainment or Lifestyle Article
These articles cover topics related to entertainment, lifestyle, and popular culture, including celebrity news, fashion, food, and more.
Example: “10 Must-Watch Movies for Film Buffs this Summer”
How Do I Write a Good Article? – Step by Step Guide
Understand your audience and purpose.
- Identify Your Readers : Understand who your audience is – their interests, level of understanding, and what they are looking for in an article.
- Define Your Purpose : Clearly state your objective. Are you informing, persuading, or entertaining?
Choose a Compelling Topic
Select a topic that resonates with your audience. It should be relevant, timely, and offer a fresh perspective.
Research and Gather Information
- Source Credible Information : Use reliable sources to gather facts, statistics, and other pertinent data.
- Organize Your Research : Group similar information together for coherence.
Create an Outline
An outline helps in organizing thoughts and ensuring a logical flow. It typically includes:
- Introduction
- Body Paragraphs – Sub Headings (H2), Child Headings (H3)
Write the Article
- Introduction : Start with a hook – a fact, question, or statement that grabs attention. Briefly outline what the article will cover.
- Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph should focus on a single idea, supported by facts, examples, and explanations.
- Transitions : Use smooth transitions to maintain flow and coherence.
- Conclusion : Summarize the main points and leave the reader with something to think about.
Starting an Article
What is written at the beginning of an article? At the beginning of an article, you typically find an introduction. This part is crucial because it aims to grab the reader’s attention. It usually starts with something interesting like a surprising fact, a question, or a short story related to the topic. The introduction also gives a brief idea of what the article is about and sets the tone for the rest of the content.
Crafting a well-written article requires planning, research, and a keen understanding of your audience. By following this format, you can create articles that are not only informative and engaging but also resonate with your readers.
What is the Easiest way to write an Article? To write an effective article, first choose a topic that aligns with your interests and knowledge. Clearly determine your article’s purpose, such as informing or persuading. Conduct thorough research from reliable sources to support your content. Plan your article with a structured outline. Begin with an engaging introduction that includes a clear thesis statement. In the body, develop focused paragraphs, each addressing a single point, supported by evidence like facts or statistics. Write using clear, simple language for better understanding. Ensure your paragraphs smoothly transition to maintain flow. Conclude by summarizing the main points and restating the central message.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Article Writing
- Ignoring the Audience : Not tailoring the content to the interests and understanding of your target readers.
- Lack of Clear Purpose : Not having a clear goal or message in your article.
- Poor Structure : Failing to organize the article in a logical, coherent manner.
- Overcomplicating Language : Using complex words or sentences that confuse readers.
- Repetitive Content : Repeating the same ideas or examples.
- Inadequate Research : Not backing up your points with accurate and reliable information.
- Plagiarism : Copying someone else’s work without giving credit.
- Ignoring SEO Principles : Not including relevant keywords for online articles, which helps in search engine ranking.
- Skipping Proofreading : Not checking for spelling, grammar, or punctuation errors.
- Neglecting a Strong Conclusion : Failing to summarize the main points or ending the article abruptly.
Avoiding these common mistakes can significantly improve the quality and effectiveness of your article writing.
Do’s and Don’ts of Article Writing
Quick overview on how to write an article – tips & tricks.
Discover key tips for writing an engaging article: select a relevant topic, conduct thorough research, create a clear structure, and write with simplicity for an impactful, reader-friendly piece.
- Understand Your Audience: Tailor to audience interests and knowledge.
- Choose a Clear, Relevant Topic: Focus on specific, timely topics.
- Organize Your Ideas: Structure with clear outline and logical flow.
- Engaging Introduction: Start with an interesting hook; set tone.
- Strong Body Content: Maintain one idea per paragraph; use subheadings.
- Concise and Clear Language: Use simple language and active voice.
- Incorporate Research and Examples: Back points with research; cite sources.
- SEO Optimization: Include relevant keywords; write concise meta descriptions.
- Edit and Proofread: Review for errors; seek feedback.
- Effective Conclusion: Summarize key points; end impactfully.
- Stay Consistent: Write regularly; learn from feedback.
What Is An Article?
An article is a written piece that informs, educates, entertains, or persuades readers about a specific subject. It can take various forms, including news reports, opinion pieces, how-to guides, or in-depth features. Articles are published in newspapers, magazines, websites, and academic journals, offering information, analysis, and commentary to a wide audience.
What Makes a Strong Article?
A strong article is well-researched, clearly written, engaging, and informative. It should have a compelling introduction, a coherent structure, and a conclusive ending.
Are Articles Hard to Write?
Writing articles can be challenging but rewarding. It requires research, planning, and the ability to clearly convey ideas to your audience.
How Does an Article Look Like?
An article typically has a clear title, an engaging introduction, body paragraphs with headings, and a summarizing conclusion. It’s structured logically to guide the reader.
How many words should there be in an article?
The word count for an article can vary widely, typically ranging from 500 to 2000 words, depending on the topic, audience, and publication requirements.
Mastering article writing involves understanding your audience, choosing engaging topics, structuring your content logically, and using clear language. Remember to research thoroughly, use SEO strategies, and edit meticulously. By following these guidelines and tips, you can craft compelling articles that captivate and inform your readers, enhancing your writing skills in the process.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Medical Article Sample Writing Example
Sample Article Writing Example
SEO Article Writing Example
Steps of Article Writing
Article Writing Format: Suppose you have some opinions regarding a topic and you want to tell people about it. How will you do so? You can tell the opinions to persons near you. But what if you want to tell not only those people but, say, the world? How will you do so? You will write those opinions, isn’t it?
Many a time you have seen some writers or people write their problems and suggestions in some newspapers, magazines, and journals or in their blogs. They are writing their opinions and beliefs in the form of an article. In this section, we will get ourselves familiar with article writing and the article writing format.
An article is a piece of writing written for a large audience. The main motive behind writing an article is that it should be published in either newspapers or magazines or journals so as to make some difference to the world.

It may be the topics of interest of the writer or it may be related to some current issues. The topic can either be serious or not-so-serious; Same goes for its tone and language.
Browse more Topics under Article Writing
- Definition, Essential Elements of Article Writing
Objectives of Article Writing
An article is written with the following objectives
- It brings out the topics or the matter of interest in the limelight
- The article provides information on the topics
- It offers suggestions and pieces of advice
- It influences the readers and urges them to think
- The article discusses various stories, persons, locations, rising-issues, and technical developments
The Format of Article Writing
An article must be organized in a proper way so as to draw the attention of the readers. The basic outline for an article writing format is
- Heading / Title
- A line having the writer’s name
- Body (the main part of the article, 2 – 3 paragraphs)
- Conclusion (Ending paragraph of the article with the opinion or recommendation, anticipation or an appeal)

Steps for Article Writing Format
Think of the topic you want to write the article about. Only after you’ve decided your topic you can go ahead and undertake the further steps in the process one by one:
- Target Audience: Identify the concerning reading group
- Purpose: Find the objective or aim of writing the article
- Collect & Select: Gather as such information as possible. Also, identify the details that are most significant
- Organize: Arrange the information and the facts in a logical way
Once you’ve taken care of all the Above steps you move forward to the final step- Writing.
- While writing an article, always use proper grammar , spelling , and proper punctuations
- Use vocabulary skill
- Keep the introduction of the topic catching, interesting, and short
- Discuss the opinion and the matter in an organized and descriptive manner
Common Mistakes in the Article Writing Format
Now that you know the steps of article writing and the article writing format, the occurrence of mistakes becomes obvious. Some of the common mistakes are:
- Not using facts or quotes or similar cases
- The language should not be too formal
- The article must be in easy language for better understanding
- The title of the article must be catchy and clearly understandable
- No use of paragraphs
- Expressing personal views is fine but the author must never talk about himself/herself
Points to Keep in Mind for the Article Writing Format
- The topics of the articles should be unique and relevant
- The article has to get attention
- It has to be interesting
- It has to be easy to read
- The reader is identified
- Find the main goal of writing an article. The goal can be anything from providing information, entertainment, and advice or for comparing, etc.
- The title must be eye-catching, clear, and interesting
- The introduction or the starting paragraph must be highly attentive. Use your vocabulary skills or try to use some interrogative words for the start
- Use clear statements and make assertions
- Avoid repetition and over the top logic and reasons
- Use the style of paragraph writing and write the contents uniquely and unambiguously
- Avoid using the points which interest you only and not for the general public
- Write a good and logical ending
Solved Example on Steps of Article Writing
Problem: Classify the following into Do’s and Don’ts in article writing.
- Write very lengthy articles
- Add the writer’s name
- The title should be lengthy and clear
- The heading of the article should be short, clear and informative
- Only the introduction and the conclusion should be attractive and attention seeking
- Target the audience
- One can advise, suggest and give the solutions to a problem in any paragraph other than the starting one
- The language and the style of writing should be according to the concerning readers
- There must be only three paragraphs in an article – introduction, middle one, and conclusion
- Use proper punctuations
- Use any tense , person, voice, as many abbreviations , and self-made words while writing an article
Customize your course in 30 seconds
- IBPS RRB Exam 2023 - Free Course
- Current Affairs
- General Knowledge
- SSC CGL Pre.Yrs.Papers
- SSC CGL Practice Papers
- SBI Clerk PYQ
- IBPS PO PYQ
- IBPS Clerk PYQ
- SBI PO Practice Paper
- What is Article Writing? Objective, Format, Samples & Tips
- Email Writing - Format and Samples
- English Essay Writing Tips, Examples, Format
- Difference between Paper and Article for Scientific Writings
- Which specific tag is used to represent the article in HTML ?
- Article Writing Format: Objective and Steps
- How to write articles in HTML document ?
- 4 Key Benefits of Writing Technical Articles
- How to Write JavaScript Articles on GeeksforGeeks ?
- Tips for Writing a Research Paper
- What is Content Writing? 10 Best Tips for Great Content Writing
- 5 Content Writing Tools to Improve your Content Writing Skills
- A Guide to Writing an Essay for Job Interviews
- How to Write DSA Articles on GeeksforGeeks?
- Difference between Technical Writing and General Writing
- Difference between Academic Writing and General Writing
- Content Writing 101 | A Beginner's Guide for Content Writer
- How to Start Blog Writing in 2024 [Updated]
- How to Write a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
- Difference between Academic Writing and Non Academic Writing
- Pilot Salary in India 2024
- List of Best Courses After 10th With High Salary In 2024
- List of Government Jobs After 12th (High Salary Jobs), Eligibility, Vacancy
- Doctor Salary In India 2024 (per Month): Freshers & Experienced
- 10 Best NDA Coaching in India in 2024: Check Fees, Duration, Location
- Best IAS Coaching Centres in India
- Top Colleges in Delhi University (DU) Based on NIRF Ranking 2023
- BCA 1st Semester Syllabus (2023)
- Geeksforgeeks Cheatsheets - All Coding Cheat Sheets Collections
- 10 Best Paramedical Courses With High Salary 2024
What is Article Writing? Objective, Format, Samples & Tips
Do you have some good opinions, ideas and suggestions which you want to share to the readers across the globe? If you want so then article writing is one of the ways through which you can share your thoughts and voice all around the world. There are various types of techniques of article writing. Here you will learn some of them.
This post will serve as step-by-step instructions on how to develop an article writing. In addition, we’ll share advice on how to write popular articles that people want to read.
Table of Content
Article Writing: What is it?
Article writing: objectives, article writing: format, article writing: a step-by-step guide, tips & techniques for article writing, common mistakes in the article writing, faqs- article writing.
An article is a piece of writing that serves to clarify, present ideas, or discuss a subject systematically. You’ll find stories in newspapers, magazines, blogs, websites, and other publications.
Publications intending to persuade or enlighten the public play an important role in today’s society, and articles are no exception. An article’s structure and style may change depending on the topic or author. However, the ideal article would engage readers, challenge their thinking, and motivate them while providing useful information.
The following goals should guide the writing of any given article:
- The objective is to highlight the central idea or theme.
- The report has to cover all the bases.
- Recommendations or suggestions to the readers are required.
- To be considered, the piece must have the potential to move and provoke its audience.
- The essay should include a variety of subjects, such as historical figures, geographical locations, new threats, and technological developments.
Articles often have the following components:
- Heading / Title
- Body (the main part of the article, 3-4 paragraphs)
- Conclusion (Ending paragraph of the article with the opinion or recommendation, anticipation or an appeal)
Heading You want it to be memorable but must also be relevant to the reader’s query. The ideal length of a heading is merely 5 or 6 words. Think imaginatively & impress the audience or readers with this one line & enhance their anxiety to continue reading your post. Byline What it refers to is the author of the piece. The answer is typically included in the inquiry. If prompted, only have your name and contact information. Body The article’s body receives the bulk of the assignment’s marks. The article’s body should have at least three to four paragraphs. Conclusion In the final paragraph of your article, leave your readers with a positive impression of the piece by appealing to their emotions. Students from CBSE and other boards would study this format and use it while writing articles, as doing so will get them higher scores and attract more readers.
After you’re familiar with the structure, there are seven easy steps to creating an article.
Step 1: Determine your core theme and goals
Choosing a topic is the first step in article writing. Avoid broad generalisations by focusing. Write down your material’s objectives. Configure your article. A theme will make writing your post easier. After choosing a topic, stick to it.
Step 2: Audience-target
After you’ve decided on a central theme, you need to identify your audience. Consider what you hope readers will take away from your piece. Which details from your content are essential for them to grasp? And establish your writing approach.
Step 3: Research and gather
Research previous works after settling on a primary theme and audience. Look for stuff on the web that shares your preferred tone and style. Once you start writing the post, you’ll want to ensure you have some support. Gain knowledge and prove your points. Opinion pieces require cited research and published works as supporting evidence. Writing becomes more natural when you use bullet points and emphasise important terms. And remember, you must always reference your sources.
Step 4: Outline and rough sketch your topic
Make a preliminary draught as you gather information and ideas from your investigation. Outlining your topics is a great method to get your thoughts down on paper. Please write down your reviews and divide them up into paragraphs. Jot down everything that comes to mind. At this stage, your focus should be less on grammar, punctuation, and analysis. Put your thoughts and hands to work. Create your article by injecting ideas. You can strengthen your post by using bullet points and keywords.
Step 5: Revise your paper
Editing your work after writing a rough draft is the following step in any article writing tutorial. Always use proper grammar and punctuation. Check for typos and see how smoothly your writing flows. To keep your readers engaged, you need to have something to say. Find the right wording for your intended readers.
Step 6: Please proofread your work
All article writing guides recommend editing and proofreading. Put only some of your faith in your editing abilities. Your tone and impression of your readers are determined by how carefully you proofread. Use this opportunity to check for any remaining errors and work towards a more fluid reading experience.
Step 7: Include photos and infographics
Article writing tips end with adding relevant visuals like infographics and photos. Your audience will welcome the break. Visual content is more engaging and easier to understand in today’s fast-paced corporate world. Insert valuable photos throughout your content.
The following is a comprehensive approach that will help you quickly and easily compose a high-quality article:
- If you want to write an essay about a topic, you should ask yourself if you know enough about it to do justice to the subject.
- The second thing to consider is the article’s purpose.
- The next thing to think about is who you’re writing the article for since if you don’t know who you’re writing for, you won’t be able to write in a way that would convince them to read it.
- Proper spelling, grammar, punctuation, and sentence structure are essential since the piece can only sell itself with these.
- Use search terms to draw in many viewers.
- Keep the paragraphs and the essay as a whole consistent.
- Always verify your facts and figures before publishing, no matter the article genre.
- Make sure the title and description are brief yet descriptive.
- Editing and proofreading are necessary steps before publication.
Errors are more likely to occur now you are familiar with the procedure and structure of writing articles. Several typical errors include the following:
- Not citing references, quotations, or comparable cases
- It is not necessary to use excessively formal language.
- For easier comprehension, the article needs to be written in simple terms.
- The article’s title ought to be intriguing and easily comprehensible.
- The absence of paragraphs
- It’s acceptable to voice personal opinions, but the writer should never discuss themselves.
Articles have a structure that includes headings for the introduction, body, and conclusion and a list of sources at the end. Articles can have several functions: informing, convincing, entertaining, and educating the reader. You may write content that connects with your readers if you take the time to learn the conventions of article writing and why you’re writing in the first place.
Q.1 Can I write a good article?
You can write an excellent article if you have thorough knowledge of the subject matter, command of the language, and the ability to maintain the piece’s simplicity and interest throughout.
Q.2 What is the format of an article?
The article needs a heading or title that clearly explains its topic and a description. Depending on how much content there is to cover on the subject, the article’s body can be divided into three to five paragraphs. Subheadings are allowed, and bullet points should be used whenever practical. Make sure your conclusion satisfies readers and your introduction entices them to read the entire piece.
Q.3 What is the significance of article writing?
This is the true motivation behind the writing and analysis of articles. Composing articles is regarded as significant since it allows one to provide information to a global audience and allows readers to connect the content of the articles with their own experiences and opinions.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- GFG Academy
- SSC/Banking

Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
2. Determine your purpose: Consider the purpose of your essay and choose a format that will best suit your goals. If you're trying to persuade your reader, a persuasive essay format might be most effective. If you're analyzing a topic, an analytical essay format could be more suitable. 3.
To write an essay in MLA format, start by setting your document to double-spacing, 1-inch margins, and a readable font such as Times New Roman, size 12. Include a header with your last name and page number in the upper right-hand corner of each page. Create a title page with your name, instructor's name, course title, and date (unless specified ...
2. Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches (1.3 cm) for all styles. Whether you're writing in MLA, APA, or Chicago Style, always use a 0.5 in (1.3 cm) indent. This signals to the reader that a new paragraph is beginning. The easiest way to indent your essay is to press the tab key. 3.
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Harvard College Writing Center 5 Asking Analytical Questions When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates. In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills. Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence ...
The page number should be in the upper right corner. Margins and Spacing: Set all margins to 1 inch, and use double-spacing throughout the essay. Font and Size: Use a clear and readable font like Times New Roman or Arial, size 12. Paragraphs: Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
Formatting an essay may not be as interesting as choosing a topic to write about or carefully crafting elegant sentences, but it's an extremely important part of creating a high-quality paper. In this article, we'll explain essay formatting rules for three of the most popular essay styles: MLA, APA, and Chicago.
Here's a breakdown of essential elements in different formats of writing: Title page: Includes the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date. Follow any specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or institution. Abstract: A concise summary of your essay.
Finally, the conclusion summarizes the key points and provides a closing statement. Examples of article writing formats include feature articles, news articles, opinion pieces, and blog posts. Following a specific format ensures that articles are coherent, easy to read, and effectively communicate the intended message to the target audience.
Making a detailed outline before you begin writing is a good way to make sure your ideas come across in a clear and logical order. A good outline will also save you time in the revision process, reducing the possibility that your ideas will need to be rearranged once you've written them. The First Steps. Before you can begin outlining, you need ...
Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline. Writing: Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion. Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.
An article writing format is a structured template that guides writers to effectively communicate their ideas through clear organization, logical development, and coherent presentation. Adhering to a well-structured manner ensures that the author's thoughts are easily understood by readers while maintaining consistency across different components such as headings, subheadings, introduction ...
This article provides an overview of writing for publication in peer-reviewed journals. While the main focus is on writing a research article, it also provides guidance on factors influencing journal selection, including journal scope, intended audience for the findings, open access requirements, and journal citation metrics.
Title. Write your name, the instructor's name, your class, and the date in the upper left corner of the 1st page. Make the title centered and place it after the heading information in the same font as the rest of your paper. Create a separate title page. Make your title centered and written in boldface.
"Writing" is usually understood as the expression of thought. This book redefines "writing" as the thought process itself. Writing is not what you do with thought. Writing is thinking. Better living through interpretation: that's the promise of academic writing, which is a foundational course in most schools because it's a
Article writing is a process of creating written pieces of content, paragraphs to reach a broad audience through different platforms. These platforms include newspapers, magazines, journals, and other publishing mediums. The goal is to engage readers by sharing information, stories, or opinions in a written format.
Start by applying these MLA format guidelines to your document: Times New Roman 12. 1″ page margins. Double line spacing. ½" indent for new paragraphs. Title case capitalization for headings. For accurate citations, you can use our free MLA Citation Generator. Download Word template Open Google Docs template.
The basic outline for an article writing format is. Heading / Title; A line having the writer's name; Body (the main part of the article, 2 - 3 paragraphs) Conclusion (Ending paragraph of the article with the opinion or recommendation, anticipation or an appeal) Steps for Article Writing Format. Think of the topic you want to write the ...
Article Writing: Format. Articles often have the following components: Heading / Title; By Line; Body (the main part of the article, 3-4 paragraphs) ... The following is a comprehensive approach that will help you quickly and easily compose a high-quality article: If you want to write an essay about a topic, you should ask yourself if you know ...