Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption

How to conduct a feasibility study: Template and examples

Opportunities are everywhere. Some opportunities are small and don’t require many resources. Others are massive and need further analysis and evaluation.

One of your key responsibilities as a product manager is to evaluate the potential success of those opportunities before investing significant money, time, and resources. A feasibility study, also known as a feasibility assessment or feasibility analysis, is a critical tool that can help product managers determine whether a product idea or opportunity is viable, feasible, and profitable.
So, what is a feasibility analysis? Why should product managers use it? And how do you conduct one?
What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study is a systematic analysis and evaluation of a product opportunity’s potential to succeed. It aims to determine whether a proposed opportunity is financially and technically viable, operationally feasible, and commercially profitable.
A feasibility study typically includes an assessment of a wide range of factors, including the technical requirements of the product, resources needed to develop and launch the product, the potential market gap and demand, the competitive landscape, and economic and financial viability.
Based on the analysis’s findings, the product manager and their product team can decide whether to proceed with the product opportunity, modify its scope, or pursue another opportunity and solve a different problem.
Conducting a feasibility study helps PMs ensure that resources are invested in opportunities that have a high likelihood of success and align with the overall objectives and goals of the product strategy .
What are feasibility analyses used for?
Feasibility studies are particularly useful when introducing entirely new products or verticals. Product managers can use the results of a feasibility study to:
- Assess the technical feasibility of a product opportunity — Evaluate whether the proposed product idea or opportunity can be developed with the available technology, tools, resources, and expertise
- Determine a project’s financial viability — By analyzing the costs of development, manufacturing, and distribution, a feasibility study helps you determine whether your product is financially viable and can generate a positive return on investment (ROI)
- Evaluate customer demand and the competitive landscape — Assessing the potential market size, target audience, and competitive landscape for the product opportunity can inform decisions about the overall product positioning, marketing strategies, and pricing
- Identify potential risks and challenges — Identify potential obstacles or challenges that could impact the success of the identified opportunity, such as regulatory hurdles, operational and legal issues, and technical limitations
- Refine the product concept — The insights gained from a feasibility study can help you refine the product’s concept, make necessary modifications to the scope, and ultimately create a better product that is more likely to succeed in the market and meet users’ expectations
How to conduct a feasibility study
The activities involved in conducting a feasibility study differ from one organization to another. Also, the threshold, expectations, and deliverables change from role to role.
For a general set of guidelines to help you get started, here are some basic steps to conduct and report a feasibility study for major product opportunities or features.
1. Clearly define the opportunity
Imagine your user base is facing a significant problem that your product doesn’t solve. This is an opportunity. Define the opportunity clearly, support it with data, talk to your stakeholders to understand the opportunity space, and use it to define the objective.
2. Define the objective and scope
Each opportunity should be coupled with a business objective and should align with your product strategy.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Determine and clearly communicate the business goals and objectives of the opportunity. Align those objectives with company leaders to make sure everyone is on the same page. Lastly, define the scope of what you plan to build.
3. Conduct market and user research
Now that you have everyone on the same page and the objective and scope of the opportunity clearly defined, gather data and insights on the target market.
Include elements like the total addressable market (TAM) , growth potential, competitors’ insights, and deep insight into users’ problems and preferences collected through techniques like interviews, surveys, observation studies, contextual inquiries, and focus groups.
4. Analyze technical feasibility
Suppose your market and user research have validated the problem you are trying to solve. The next step should be to, alongside your engineers, assess the technical resources and expertise needed to launch the product to the market.
Dig deeper into the proposed solution and try to comprehend the technical limitations and estimated time required for the product to be in your users’ hands.
5. Assess financial viability
If your company hasa product pricing team, work closely with them to determine the willingness to pay (WTP) and devise a monetization strategy for the new feature.
Conduct a comprehensive financial analysis, including the total cost of development, revenue streams, and the expected return on investment (ROI) based on the agreed-upon monetization strategy.
6. Evaluate potential risks
Now that you have almost a complete picture, identify the risks associated with building and launching the opportunity. Risks may include things like regulatory hurdles, technical limitations, and any operational risks.
7. Decide, prepare, and share
Based on the steps above, you should end up with a report that can help you decide whether to pursue the opportunity or not. Either way, prepare your findings, including any recommended modifications to the product scope, and present your final findings and recommendations to your stakeholders.
Make sure to prepare an executive summary for your C-suite; they will be the most critical stakeholders and the decision-makers at the end of the meeting.
Feasibility study example
Imagine you’re a product manager at a digital software company that specializes in building project management tools.
Your team has identified a potential opportunity to expand the product offering by developing a new AI-based feature that can automatically prioritize tasks for users based on their deadlines, workload, and importance.
To assess the viability of this opportunity, you can conduct a feasibility study. Here’s how you might approach it according to the process described above:
- Clearly define the opportunity — In this case, the opportunity is the development of an AI-based task prioritization feature within the existing project management software
- Define the objective and scope — The business objective is to increase user productivity and satisfaction by providing an intelligent task prioritization system. The scope includes the integration of the AI-based feature within the existing software, as well as any necessary training for users to understand and use the feature effectively
- Conduct market and user research — Investigate the demand for AI-driven task prioritization among your target audience. Collect data on competitors who may already be offering similar features and determine the unique selling points of your proposed solution. Conduct user research through interviews, surveys, and focus groups to understand users’ pain points regarding task prioritization and gauge their interest in the proposed feature
- Analyze technical feasibility — Collaborate with your engineering team to assess the technical requirements and challenges of developing the AI-based feature. Determine whether your team has the necessary expertise to implement the feature and estimate the time and resources required for its development
- Assess financial viability — Work with your pricing team to estimate the costs associated with developing, launching, and maintaining the AI-based feature. Analyze the potential revenue streams and calculate the expected ROI based on various pricing models and user adoption rates
- Evaluate potential risks — Identify any risks associated with the development and implementation of the AI-based feature, such as data privacy concerns, potential biases in the AI algorithm, or the impact on the existing product’s performance
- Decide, prepare, and share — Based on your analysis, determine whether the AI-based task prioritization feature is a viable opportunity for your company. Prepare a comprehensive report detailing your findings and recommendations, including any necessary modifications to the product scope or implementation plan. Present your findings to your stakeholders and be prepared to discuss and defend your recommendations
Feasibility study template
The following feasibility study template is designed to help you evaluate the feasibility of a product opportunity and provide a comprehensive report to inform decision-making and guide the development process.
Remember that each study will be unique to your product and market, so you may need to adjust the template to fit your specific needs.
- Briefly describe the product opportunity or feature you’re evaluating
- Explain the problem it aims to solve or the value it will bring to users
- Define the business goals and objectives for the opportunity
- Outline the scope of the product or feature, including any key components or functionality
- Summarize the findings from your market research, including data on the target market, competitors, and unique selling points
- Highlight insights from user research, such as user pain points, preferences, and potential adoption rates
- Detail the technical requirements and challenges for developing the product or feature
- Estimate the resources and expertise needed for implementation, including any necessary software, hardware, or skills
- Provide an overview of the costs associated with the development, launch, and maintenance of the product or feature
- Outline potential revenue streams and calculate the expected ROI based on various pricing models and user adoption rates
- Identify any potential risks or challenges associated with the development, implementation, or market adoption of the product or feature
- Discuss how these risks could impact the success of the opportunity and any potential mitigation strategies
- Based on your analysis, recommend whether to proceed with the opportunity, modify the scope, or explore other alternatives
- Provide a rationale for your recommendation, supported by data and insights from your research
- Summarize the key findings and recommendations from your feasibility study in a concise, easily digestible format for your stakeholders
Overcoming stakeholder management challenges
The ultimate challenge that faces most product managers when conducting a feasibility study is managing stakeholders .
Stakeholders may interfere with your analysis, jumping to conclude that your proposed product or feature won’t work and deeming it a waste of resources. They may even try to prioritize your backlog for you.
Here are some tips to help you deal with even the most difficult stakeholders during a feasibility study:
- Use hard data to make your point — Never defend your opinion based on your assumptions. Always show them data and evidence based on your user research and market analysis
- Learn to say no — You are the voice of customers, and you know their issues and how to monetize them. Don’t be afraid to say no and defend your team’s work as a product manager
- Build stakeholder buy-in early on — Engage stakeholders from the beginning of the feasibility study process by involving them in discussions and seeking their input. This helps create a sense of ownership and ensures that their concerns and insights are considered throughout the study
- Provide regular updates and maintain transparency — Keep stakeholders informed about the progress of the feasibility study by providing regular updates and sharing key findings. This transparency can help build trust, foster collaboration, and prevent misunderstandings or misaligned expectations
- Leverage stakeholder expertise — Recognize and utilize the unique expertise and knowledge that stakeholders bring to the table. By involving them in specific aspects of the feasibility study where their skills and experience can add value, you can strengthen the study’s outcomes and foster a more collaborative working relationship
Final thoughts
A feasibility study is a critical tool to use right after you identify a significant opportunity. It helps you evaluate the potential success of the opportunity, analyze and identify potential challenges, gaps, and risks in the opportunity, and provides a data-driven approach in the market insights to make an informed decision.
By conducting a feasibility study, product teams can determine whether a product idea is profitable, viable, feasible, and thus worth investing resources into. It is a crucial step in the product development process and when considering investments in significant initiatives such as launching a completely new product or vertical.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

Mastering customer surveys: Design, execution, and analysis
A customer survey is a structured research tool that product people use to gather insights about their customers.

Leader Spotlight: Growing the omnichannel market, with Christine Kuei
Christine Kuei, Director of Product Management at Forever 21, shares her experience growing and optimizing omnichannel experiences.

Decoding marketing jargon: A glossary of terms
The world of product marketing is always evolving. Even for experts, it can be hard to keep up with the latest concepts, terms, and jargon.
Leader Spotlight: Bettering learning velocity, with Jonas O. Klink
Jonas talks about his team’s initiatives to “better the learning velocity” — taking an initial idea through hypothesis-driven development to build customer-centric, scalable solutions.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- How to use a feasibility study in proje ...
How to use a feasibility study in project management

It can be exciting to run a large, complex project that has a huge potential impact on your organization. On the one hand, you’re driving real change. On the other, failure is intimidating.
What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study—sometimes called a feasibility analysis or feasibility report—is a way to evaluate whether or not a project plan could be successful. A feasibility study evaluates the practicality of your project plan in order to judge whether or not you’re able to move forward with the project.
It does so by answering two questions:
Does our team have the required tools or resources to complete this project?
Will there be a high enough return on investment to make the project worth pursuing?
Feasibility studies are important for projects that represent significant investments for your business. Projects that also have a large potential impact on your presence in the market may also require a feasibility study.
As the project manager , you may not be directly responsible for driving the feasibility study, but it’s important to know what these studies are. By understanding the different elements that go into a feasibility study, you can better support the team driving the feasibility study and ensure the best outcome for your project.
When should you conduct a feasibility study
A feasibility study should be conducted after the project has been pitched but before any work has actually started. The study is part of the project planning process. In fact, it’s often done in conjunction with a SWOT analysis or project risk assessment , depending on the specific project.
Feasibility studies help:
Confirm market opportunities before committing to a project
Narrow your business alternatives
Create documentation about the benefits and detriments of your proposed initiative
Provide more information before making a go/no go decision
You likely don’t need a feasibility study if:
You already know the project is feasible
You’ve run a similar project in the past
Your competitors are succeeding with a similar initiative in market
The project is small, straightforward, and has minimal long-term business impact
Your team ran a similar feasibility study within the past three years
One thing to keep in mind is that a feasibility study is not a project pitch. During a project pitch, you’re evaluating whether or not the project is a good idea for your company, and whether the goals of the project are in line with your overall strategic plan. Typically, once you’ve established that the project is a good idea, you’d then run a feasibility study to confirm the project is possible with the tools and resources you have at your disposal.
Feasibility study vs. project charter
A project charter is a relatively informal document to pitch your project to stakeholders. Think of the charter like an elevator pitch of your project objectives, scope, and responsibilities. Typically, your project sponsor or executive stakeholders reviews the charter before ratifying the project.
A feasibility study should be implemented after the project charter has been ratified. This isn’t a document to pitch whether or not the project is in line with your team’s goals—rather, it’s a way to ensure the project is something you and your team can accomplish.
Feasibility study vs. business case
A business case is a more formalized version of the project charter. While you’d typically create a project charter for small or straightforward initiatives, you should create a business case if you are pitching a large, complex initiative that will make a major impact on the business. This longer, more formal document will also include financial information, and typically involves more senior stakeholders.
After your business case is approved by relevant stakeholders, you’d then run a feasibility study to make sure the work is doable. If you find it isn’t, you might return to your executive stakeholders and request more resources, tools, or time in order to ensure your business case is feasible.
Feasibility study vs. business plan
A business plan is a formal document of your organization’s goals. You typically write a business plan when founding your company, or when your business is going through a significant shift. Your business plan informs a lot of other business decisions, including your three to five year strategic plan .
As you implement your business and strategic plan, you’ll invest in individual projects. A feasibility study is a way to evaluate the practicality of any given individual project or initiative.
4 elements of a feasibility analysis
There are four main elements that go into a feasibility study: technical feasibility, financial feasibility, market feasibility (or market fit), and operational feasibility. You may also see these referred to as the four types of feasibility studies, though most feasibility studies actually include a review of all four elements.
Technical feasibility
A technical feasibility study reviews the technical resources available for your project. This study determines if you have the right equipment, enough equipment, and the right technical knowledge to complete your project objectives . For example, if your project plan proposes creating 50,000 products per month, but you can only produce 30,000 products per month in your factories, this project isn’t technically feasible.
Financial feasibility
Financial feasibility describes whether or not your project is fiscally viable. A financial feasibility report includes a cost/benefit analysis of the project. It also forecasts an expected return on investment (ROI), as well as outlines any financial risks. The goal at the end of the financial feasibility study is to understand the economic benefits the project will drive.
Market feasibility
The market feasibility study is an evaluation of how your team expects the project’s deliverables to perform in the market. This part of the report includes a market analysis, market competition breakdown, and sales projections.
Operational feasibility
An operational feasibility study evaluates whether or not your organization is able to complete this project. This includes staffing requirements, organizational structure, and any applicable legal requirements. At the end of the operational feasibility study, your team will have a sense of whether or not you have the resources, skills, and competencies to complete this work.
Feasibility study checklist
Most feasibility studies are structured in a similar way. These documents serve as an assessment of the practicality of a proposed business idea. Creating a clear feasibility study helps project stakeholders during the decision making process.
A feasibility study contains:
An executive summary describing the project’s overall viability
A description of the product or service being developed during this project
Any technical considerations , including technology, equipment, or staffing
The market survey , including a study of the current market and the marketing strategy
The operational feasibility study , evaluating whether or not your team’s current organizational structure can support this initiative
The project timeline
Financial projections based on your financial feasibility report
6 steps to conduct a feasibility study
You likely won’t be conducting the feasibility study yourself, but you will probably be called on to provide insight and information. To conduct a feasibility study, hire a trained consultant or, if you have an in-house project management office (PMO) , ask if they take on this type of work. In general, here are the steps they’ll take to complete this work:
1. Run a preliminary analysis
Creating a feasibility study is a time-intensive process. Before diving into the feasibility study, it’s important to evaluate the project for any obvious and insurmountable roadblocks. For example, if the project requires significantly more budget than your organization has available, you likely won’t be able to complete it. Similarly, if the project deliverables need to be live and in market by a certain date, but they won’t be available for several months after the fact, the project likely isn’t feasible either. These types of large-scale obstacles make a feasibility study unnecessary, because it’s clear the project is not viable.
2. Evaluate financial feasibility
Think of the financial feasibility study as the projected income statement for the project. This part of the feasibility study clarifies the expected project income and outlines what your organization needs to invest—in terms of time and money—in order to hit the project objectives.
During the financial feasibility study, take into account whether or not the project will impact your business's cash flow. Depending on the complexity of the initiative, your internal PMO or external consultant may want to work with your financial team to run a cost-benefit analysis of the project.
3. Run a market assessment
The market assessment, or market feasibility study, is a chance to identify the demand in the market. This study offers a sense of expected revenue for the project, and any potential market risks you could run into.
The market assessment, more than any other part of the feasibility study, is a chance to evaluate whether or not there’s an opportunity in the market. During this study, it’s critical to evaluate your competitor’s positions and analyze demographics to get a sense of how the project will do.
4. Consider technical and operational feasibility
Even if the financials are looking good and the market is ready, this initiative may not be something your organization can support. To evaluate operational feasibility, consider any staffing or equipment requirements this project needs. What organizational resources—including time, money, and skills—are necessary in order for this project to succeed?
Depending on the project, it may also be necessary to consider the legal impact of the initiative. For example, if the project involves developing a new patent for your product, you will need to involve your legal team and incorporate that requirement into the project plan.
5. Review project points of vulnerability
At this stage, your internal PMO team or external consultant have looked at all four elements of your feasibility study—financials, market analysis, technical feasibility, and operational feasibility. Before running their recommendations by you and your stakeholders, they will review and analyze the data for any inconsistencies. This includes ensuring the income statement is in line with your market analysis. Similarly, now that they’ve run a technical feasibility study, are any liabilities too big of a red flag? (If so, create a contingency plan !)
Depending on the complexity of your project, there won’t always be a clear answer. A feasibility analysis doesn’t provide a black and white decision for a complex problem. Rather, it helps you come to the table with the right questions—and answers—so you can make the best decision for your project and for your team.
6. Propose a decision
The final step of the feasibility study is an executive summary touching on the main points and proposing a solution.
Depending on the complexity and scope of the project, your internal PMO or external consultant may share the feasibility study with stakeholders or present it to the group in order to field any questions live. Either way, with the study in hand, your team now has the information you need to make an informed decision.
Achieve project success with Asana
Done with your feasibility study? You’re ready to run a project! Set your project up for success by tracking your progress in a work management tool , like Asana. From the small stuff to the big picture, Asana organizes work so teams know what to do, why it matters, and how to get it done.
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

10 Feasibility study and business plan differences you should know
by Naiyer Jawaid | Nov 8, 2021 | Development , Real Estate | 5 comments

Feasibility study and business plan differences are subtle. In this post we will discuss 10 differences will help you to evaluate and differentiate between a feasibility study and a business plan.
Do you know what is a feasibility report? Do you know what is a business plan? Can you easily differentiate between a feasibility report and a business plan?
It’s easy! Just read out through the article and it will all be easy.
Let’s start by learning about a feasibility report:
A feasibility study is a formal document that assist in the identification and investigation of a proposed project. We can identify the project's weaknesses and strengths with the support of a feasibility study report, which saves us time and energy. We can determine whether the suggested idea will be lucrative and practicable in the future.
Before investing in a project, it is critical to determine if the project will be beneficial in the long run. The organization also needs to know how much the project will cost. Overall, a feasibility analysis indicates whether the firm should invest or continue with the project.

You should also like to read When to do feasibility study?
Now let us learn about business plan:
A business plan is a formal document that contains the goals/ objective of the business, the time in which the goal will be completed and the strategies that can be adopted to reach the specific goal.
A business plan is a necessary document for every new firm to have in place before it can begin operations. Writing a credible business plan is typically a requirement for banks and venture capital companies before contemplating granting funding to new enterprises.
It is not a smart idea to operate without a business strategy. In fact, very few businesses can survive for long without one. There are many more advantages to developing and keeping to a strong business plan, such as the ability to think through ideas without investing too much money and, eventually, losing money. Business plans are used by start-ups to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
A feasibility study is used to assess if a business or a concept is viable. After the business opportunity has been identified, the business strategy is produced. “A feasibility study is carried out with the goal of determining the workability and profitability of a company venture. A feasibility study is conducted before any money is committed in a new business endeavour to see whether it is worth the time, effort, and resources.

Similarities between a Feasibility study and a business plan
It's essential to analyse the similarities between a feasibility study and a business plan because they're both implemented altogether in same ways to help you build a lucrative company. The following are some of the similarities between the two documents:
Time: Both the reports are completed before the business begins and can be repeated afterwards to decide the next stages for new concepts.
Input: Both Feasibility report and the Business plan include input from a variety of people or departments with a variety of talents.
Format: Both report formats incorporate other documents that are gathered in order to create the report.
Components: Examining the target market, market circumstances, and financial expenses are some of the topics examined.
Use: Both may be displayed to potential investors and can assist the organization's management in making choices.
Organizations uses a business plan and a feasibility study as analytical and decision-making tools.
Although the three tools can be used in conjunction with one another in decision-making processes, they each have their own strengths and weaknesses, and they appear to target and address separate processes.
You might also like to read How to write a feasibility study report?

Now let us evaluate the difference between feasibility report and a business report-
- A feasibility study is conducted to determine the viability and profitability of a business endeavour. A feasibility study is conducted before any money is committed in a new business endeavour to see whether it is worth the time, effort, and resources.
A business plan, on the other hand, is created only when it has been determined that a business opportunity exists and that the endeavour is about to begin.
- A feasibility report is the first step and after that a business plan is made to be implemented, without feasibility report a business plan cannot be made.
- A feasibility study contains computations, research, and projected financial forecasts for a company possibility. A business plan, on the other hand, is mostly comprised of tactics and strategies to be applied to establish and expand the company.
- A feasibility study is concerned with the viability of a business concept, but a business plan is concerned with the development and sustainability of a company.
- A feasibility report informs the entrepreneur about the profit potential of a company concept or opportunity, whereas a business plan assists the entrepreneur in raising the necessary start-up cash from investors.
- Key components of a feasibility study and a business plan
- A business plan does not include the description of the sales methods used, such as distribution agreements, strategic alliances, and the amount of involvement with partners, as well as the payment terms, warranties, and other customer support.
But a feasibility report includes all the sales methods, strategies, alliances to payment and customer support.
- Feasibility report contains:
- Assists in cost estimation, describe the production site, required inputs, and sourcing region.
- Physical description of the factory, including machine, capacity, warehouse, and supply chain, is necessary.
- Indicate if the area used for production is rented or owned. This will have an impact on the financial forecast.
- Information regarding the manufacturer's capacity, order details, price, and so on, if manufacturing is outsourced. To aid in cost estimation, describe the production site, needed inputs, and sourcing location.
- A physical description of the factory, including machine, capacity, warehouse, and supply chain, is necessary.
But a business plan does not contain anything related to production and operations, but a business plan contains all the information related to management.
- A poorly written business plan – poor projections, strategies, analysis, business model, and environmental factors, among other things – can be easily adjusted during business operations, but this cannot be said of a feasibility study because an incorrect conclusion in a feasibility study can be costly — it could mean launching a venture with little chance of survival or approving a proposal that wastes the company's human and financial resources.
- A business plan presume that a company will prosper and lays out the procedures needed to get there. Those in charge of conducting a feasibility study should not have any predetermined notions regarding the likelihood of success. They must maintain as much objectivity as possible. They do research and allow the facts to lead to the study's conclusion. If the study concludes that the idea is viable, some of the findings, such as market size predictions, may be incorporated in the company's business plan.
You should also read What is land development feasibility study?
These 10 differences will help you to evaluate and differentiate between a feasibility study and a business plan.
Feasibility study may appear to be like the business plan in many respects. "A feasibility study may easily be transformed to a business plan” but it is crucial to remember that the feasibility study is completed prior to the endeavor. The business plan should be thought of in terms of growth and sustainability, whereas the feasibility study should be thought of in terms of concept viability.
This is all you need to know and understand about feasibility study and business plan.
Get ready to apply your knowledge in the real words with lots of success.
You might also like to explore below external contents on feasibility study :
- What Is a Feasibility Study? – Types & Benefits
- Best 8 Property Management Software
- FEASIBILITY STUDIES & BUSINESS PLANS
Hope you enjoyed this post on feasibility study , let me know what you think in the comment section below.
Are you someone involved with real estate feasibility?
We are excited to launch the next generation of real estate feasibility software to help you manage your development projects with ease.
Register now for a free trail license!
This is a very good piece of writing. When you have a concept for a company but want to be sure it’s a good idea, you do a feasibility study.
It was very helpful. Thank you so much!
Appropriately timed! A company’s future operations are laid out in great detail in the company’s business plan. Once you’ve done your feasibility study, you’ll know whether or not the proposal has merit. The next step is to lay out your goals, whether financial and otherwise, as well as the strategies you want to use to attain them and the organisational structure you envision.
Prior to the company opening, both are undertaken, and may be repeated again in the future to identify the next steps on new ideas that may arise.
Great Content.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Follow Us On
Latest Posts

Get your ultimate guide to feasibility study for FREE!

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is a Feasibility Study?
A Feasibility Study measures if a project is legally and financially viable. Read more about its importance, types of Feasibility Studies, and how to carry one out. Knowing everything related to it guarantees that the project will be a success and that you are in line with the rules and regulations. Let's read the blog to learn further.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- CGPM (Certified Global Project Manager) Course
- CDSPM (Certified Digital Services Project Manager) Course
- PgM (Programme Management) Course
- Project Management Office Fundamentals Certification Course
- Project Management for Non-Project Managers Course

An effective Feasibility Study is crucial in achieving a goal or decision-making in Project Management and business. It serves as a single and integrated examination to approve a project, startup, or investment by determining if it can be implemented, if it will succeed and if it will be sustainable to operate the project, the startup or the investment.
In addition, this powerful tool is fundamental in that it offers decision-makers beneficial insights. It enables them to make the right decisions, spend resources appropriately, and if necessary, control the risks that exist. All these are important for desirable outcomes in any projects.
Thus, it is crucial to learn about this important approach and take your Project Management game to the next level. In this blog, you will understand what Feasibility Study does, its focus, its benefits as well as steps to conduct it.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding a Feasibility Study
2) Importance of a Feasibility Study
3) Types of Feasibility Studies
4) What is included in a Feasibility Study Report?
5) Examples of a Feasibility Study
6) 7 Steps to do a Feasibility Study
7) Conclusion
Understanding a Feasibility Study
A Feasibility Study is the systematic evaluation of an idea that uses objective analysis to determine whether it is realistic and can be successful. The focus is on whether all requirements can actually run the project successfully. This work also involves researching the obstacles that may happen throughout the process.
In the project, Project Managers are required to know is that there is a right team, capital or budget, and that there is the right technology. They must also see whether the project yields the returns they want given that they are prepared to contribute to the initiative.
To do this, they must look at how much money the project could get compared with how much money it could cost to operate it. This enables them to compute if the project costs are higher than its positive cash flows. Additionally, they must examine risks associated with the investment and determine if the potential reward is solid enough.
To make it clear, a Feasibility Study is the homework that managers must do in order to get a good understanding of a project idea and see if it’s worth implementing.

Importance of a Feasibility Study
A Feasibility Study is really important as it is the tool for organisations to ensure they are making the right decisions before they dedicate time, money or resources to any project. It can actually reveal innovative ideas that might completely change the whole plan! It's better to discover these things before the project is started than to learn about the problem as the project progresses. Here are some important reasons why doing a Feasibility Study is a good idea:
a) Its purpose is the efficiency of the project team.
b) It's just another chance to look at it from a different angle.
c) Also, it may acquire the necessary data to determine whether to actualise the project.
d) It acts as an organiser by eliminating diverse approaches to the project plan.
e) It makes it easier for me to justify the cost.
f) It increases the probability of success by double-checking numerous items.
g) It tells the Project Manager whether to go on with the project.
Types of Feasibility Studies
Feasibility Studies are of the greatest importance in the decision-making process when it comes to projects, businesses, and investments. They are mostly structured assessments that are focused on various aspects of a project`s Feasibility.
There are several types of Feasibility Studies, each aimed at something particular, and together, they provide a complete assessment of the project's worthiness. Let's delve into five distinct types of Feasibility Studies:
Pre-Feasibility Study
First of all, preliminary research is crucial before you dig deep with a Feasibility Study. Pre-feasibility study is carried out by decision-makers and experts who aim to present different project ideas or approaches to shed light on any glaring problems. This initial evaluation of all fundamental aspects such as technical, financial, operational, or other areas helps effectively highlight any outright issues like flaws. The feasibility examination is done, and the project proposal it finds favourable is moved to the next level, which is the comprehensive feasibility study.
Technical Feasibility Study
A technical Feasibility Study aims to verify whether the organisation is eligible to use its technical in-house resources and expertise to perform successfully. This assessment involves scrutinising various aspects, including:
a) Production capacity: Does the company have the resource base to produce that number of products and services for the customers?
b) Facility needs: Do today’s facilities fulfil the standards required, or will new facilities be constructed?
c) Raw materials and supply chain: Are there enough purchases, and have the organisation maintained a supply chain?
d) Regulatory compliance: Does the project follow the relevant guidelines and bear the appropriate certifications to meet the requirements and the industry standards?
Economic Feasibility Study
It is a financial Feasibility Study that primarily examines the project's financial viability. The economic feasibility study typically involves several steps:
a) Determining capital requirements: Calculation of funding collection, overhead, and other capital.
b) Cost breakdown: Determining and listing all the project costs including the purchase of materials, hardware, labour, and overheard costs are too.
c) Funding sources: Trying out a variety of possible solutions like banks, stakes, or grants.
d) Revenue projection: By using prediction tools such as a cost-benefit analysis or business forecasting to get the level of income, return on investment and profit margin.
e) Financial analysis: Projecting the performance of the project based on means that are related to a financial analysis and are characterised by the utilisation of such things as cash flow statements, balance sheets and financial projections.
Learn the tools and methods to manage projects by signing up for our Introduction to Project Management Certification Course now!
Legal Feasibility Study
Legal Feasibility is a type of analysis that seeks to confirm that a project follows all the relevant laws and regulations. Key considerations include:
a) Regulatory compliance: Briefing the whole project team about all required laws and regulations that the project has to comply with.
b) Business structure: Assessing the legal systems (e.g., LLCs vs. corporations) that would best protect liability, governance, and minimising taxation, if any.
Market Feasibility Study
The market feasibility first considers the project's issues and whether it succeeds in the market. This study involves analysing various factors such as:
a) Industry overview: Concerning this field we should first evaluate its current state in terms of a relevant growth trends, competitive environment, and supply availability.
b) SWOT analysis: Highlighting the project's inner force, suitable action, sectoral opportunities and threats for its effective positioning.
c) Market research: Acquiring B2B market research data on consumer sentiment including market trends, pricing dynamics it necessary to analyse the market response.
d) Target market analysis: The definition of the target audience, the buyer personas creation, the market segments evaluation to define my project according to end-users desires.
Acquire the skills and methods necessary to deliver projects effectively by signing up for our Project Management Masterclass now!
What is included in a Feasibility Study Report?
You should make a Feasibility Study Report before starting a business. This way you can analyse if your business idea is really viable and will bring you success. When you conduct this study, you would have to consider lots of factors such as if the people are going to buy your product or service, how much competition is out there, if the company can afford it and so on.
The study must include things like how much technology and resources you need and how much you can hope to earn from your investment. The results of this study are put together in a report, which usually includes these sections:
Executive Summary
It takes a broad summary of what the study resulted in. Since this is the introduction section of the paper, it is advisable to use simple and clear language. It includes specifying the following:
a) Specifications of the item or service: In this section, you mention what specific services your business stands for and how they will satisfy the needs of potential customers.
b) Considerations for the future of technology: This paragraph describes how technological innovation influences how your business operates in the years to come.
c) The marketplace for goods and services: You stand before a mirror and make an evaluation of the competition. You think of the unique aspect that will set you apart from the rest.
1) Approach to marketing:
The section of the plan describes all the marketing activities you will apply and what will persuade people to come and shop with you.
2) Organisation/staffing:
Here, you say who will be made a part of the company structure and what it will look like. Schedule: The outline for the dates of which various parts are a part of your business when you are throwing it out.
a) The financial forecasts: From here, it all moves about the money as you forecast whether for you & your business & the good, you make the profit.
b) Recommendations based on research: Eventually, you suggest something about which your feasibility study found that should be acted upon, such as implementing the business idea or making improvements first.
Examples of a Feasibility Study
Feasibility Studies help decide if big ideas can work. Here are two examples:
University Science Building Upgrade
a) A university wanted to upgrade its old science building from the 1970s. They thought it was outdated and needed a change.
b) They looked at different options and how much they would cost. Some people worried about the project being too expensive or causing issues in the community.
c) The study also checked what technology the new building would need, how it would help students, and if it would attract more students.
d) They looked at the money side too, like how they would pay for it and if they would make more money from having more students.
e) The study showed that the project could work, so they went ahead with the upgrade.
High-Speed Rail Project
a) The Washington State Department of Transportation wanted to see if they could build a fast train connecting Vancouver, Seattle, and Portland.
b) They first figured out how to make decisions about the project in the future.
c) They talked to lots of people and groups to make sure everyone was okay with the plan. They formed a team to come up with ideas on how to talk to people about the project.
d) They also looked at how to pay for it. They thought it would cost between $24 billion to $42 billion. They would get money from the government and maybe from loans and investors too.
e) The study showed that the train could bring lots of good things like better jobs and less traffic.
f) They started looking into this in 2016 and finished the study in 2020. They then shared the report with the government.
7 Steps to do a Feasibility Study
1) do a preliminary analysis and define the scope of the study.
Before going through a feasibility study, it is wise that you do just one small check now. The time and resources involved in feasibility studies may be burdensome; hence, it is imperative to determine if it is worth it as early as possible.
Through this form, one is able to establish whether the study holds awarding potential and who else should be involved on a higher level. You further this stage by answering questions like what you might win, what pitfalls you will face, and what you need for the success of the project.
2) Prepare a projected income statement
First, while doing a Feasibility Study, you should obtain the income statement projection. In this, the statement calculates earnings and expenditures in subsequent one-year amounts. It is made up of the sum of what you will surely get and the cost you will need to cover.
Smaller businesses tend to need marketing strategies to grow into bigger companies. These facts are extremely important because they help business owners make smart decisions regarding the stage of the business.
3) Carry out market research
Market research or, naturally, it will be of no use when developing the Feasibility Study. Primarily, it operates to ascertain the viability of the project. This point tells you time, which gives you knowledge of the current market state: who your customers are, who your competitors are, how big the market is, and how many of it you could have. One way of doing this market research is by asking people questions, referring to experts, and checking very broad social media and other public info to find out what's going on.
4) Organisation and operations plan
Once you've figured out how the market behaves and the scope of your organisation, you can draft the setup of your plan. The detailed work plan for the project will provide the answer to how it will work in a practical form. It tests three aspects of your project, like whether it can be run, whether it is cost-effective, whether it complies with the law, and whether the technology fits.
This is to help you comprehend everything you can do and what you may require getting this project going, for example, the equipment, the materials to start the project, additional costs, and if you need to hire or train people. If you need to, you may make that change if the information you have brought is enough.
5) Calculate and prepare the initial balance of expected revenue and expenses
In this step, you must be expert in handling things from the financial part. You’ll make estimates on how much you may initially spend starting up your project, and then how much your project could make and spend based on that estimate. Among the many issues involved are such as the amount of money you are receiving from your customers, money you owe to others and assets that you own.
Fixed costs, such as variable costs that will change based on the number of goods you produce, and equipment costs also need to be factored in money you may borrow or pay for land and service other companies. Keeping this in mind, you should also consider scenarios where your business may not succeed and how much risk are you willing to take. These calculations save a lot of time and effort and can be used to answer the most difficult questions of feasibility.
6) Review and analyse all data
After going through all the steps, it's crucial to do a thorough review and analysis. This helps ensure that everything is in order and there's nothing that needs adjusting. Take a moment to carefully look back at your work, including the income statement, and compare it with your expenses and debts. Ask yourself: does everything still seem realistic?
This is also the perfect opportunity to consider any risks that might come up and create contingency plans to handle them. By doing this, you'll be better prepared for any unexpected challenges that may arise.
7) Make a go/No-go decision
Now, it's time to decide if the project can actually work. This might seem simple, but all the work you've done so far leads up to this moment of decision-making. Before making the final call, there are a few more things to think about. First, consider if the project is worth the time, effort, and money you'll be putting into it. Is the commitment worth it?
Secondly, think about whether the project fits with what your organisation wants to achieve in the long run. Does it align with the organisation’s strategic goals and future plans? These factors are essential to consider before making your decision.
Attain the skills to become a stellar Project Manager by signing up for our Project Management Courses | Training & Certifications now!
Conclusion
You are now more familiar with how a well-executed Feasibility Study is a cornerstone of informed decision-making in Project Management and business ventures. It acts as a critical guide, helping organisations assess the practicality and viability of their initiatives, ultimately minimising risks and increasing the likelihood of success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Employers value skills like analysis, problem-solving, attention to detail, and communication in Feasibility Study specialists. They need to be good at crunching numbers, finding solutions, and explaining complex ideas clearly.
Many industries need expertise in feasibility studies, like construction, healthcare, tech, and more. It helps decide if projects are doable.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Project Management Courses , including Introduction to Project Management Certification Course and Project Management Masterclass. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Project Resource Management .
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Project Management Skills, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills in Project Management, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 12th Apr 2024
Fri 17th May 2024
Fri 21st Jun 2024
Fri 19th Jul 2024
Fri 16th Aug 2024
Fri 13th Sep 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 8th Nov 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel & Certification Course
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Filter by Keywords
Project Management
Mastering project viability: 7-step guide to a flawless feasibility study.
Sarah Burner
ClickUp Contributor
December 30, 2023
Coming up with a groundbreaking project idea that could skyrocket your company’s success is thrilling! But before diving headfirst into making it a reality, it’s crucial to pause and assess its feasibility . Can this project really succeed? Do you have the necessary tools and resources? Will the results be worth the investment?
Enter feasibility study—the key to answering these critical questions and shaping the destiny of your project.
In this article, we’re delving deep into the world of feasibility studies. We’ll equip you with everything you need to know about conducting a feasibility study and determining whether your project has what it takes to flourish. 🌷
What is a Feasibility Study?
What are the benefits of a feasibility study, types of feasibility studies, step 1: do the preliminary analysis, step 2: make a project scope outline, step 3: prepare a projected income statement, step 4: perform market research, step 5: create an opening-day balance sheet, step 6: review and analyze all data, step 7: reach a go or no-go decision.
A feasibility study examines if a proposed project is doable and evaluates its chances of success. While doing this study, you should pinpoint project goals , delve into market research , and outline the necessary resources and budget for successful project execution.
After the study, the decision-making executives or investors determine whether the project should get the green light based on the feasibility analysis. ✅
The importance of a feasibility study lies in the following:
- Establishing whether a company, team, or organization can fulfill its promises within a reasonable timeframe
- Stopping a company from taking on risky projects
- Providing details on the company’s operations, potential challenges, competitors, and funding sources, along with their allocation
A feasibility study evaluates if your project or product is viable and has the potential to succeed. The main benefits of having a feasibility study report include:
- Risk assessment: It helps identify potential risks and challenges that may arise during project implementation so you can mitigate them in due time
- Cost evaluation: It aids in determining if the project is financially viable and if the potential ROI justifies the expenses
- Resource allocation: It assists in determining the necessary resources —human, financial, and technological—required for the project, helping in effective resource allocation and management
- Market analysis: Feasibility studies help you understand the demand, competition, and potential customer base through market research, shaping the product to fit market needs
- Decision-making: The insights gained from a feasibility study help stakeholders make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project, modify it, or abandon it altogether
- Legal and regulatory compliance: It helps ensure that the project complies with laws and regulations, minimizing potential legal issues in the future
Conducting various feasibility studies allows you to evaluate your project from diverse angles and perspectives. Feasibility studies can be broadly categorized into several types based on the focus of the assessment:
- Technical feasibility: Evaluates if the proposed project can be implemented from a technical standpoint. It assesses the availability of technology, expertise, and infrastructure required
- Economic feasibility: Analyzes the cost-effectiveness of the project. It estimates potential costs, returns on investment , and the overall financial viability
- Legal feasibility: Examines legal aspects like compliance with laws, regulations, permits, and any potential legal hurdles
- Operational feasibility: Evaluates if the project can meet the organization’s needs and to what extent
- Scheduling feasibility: Digs into the project’s timeframe , assessing if it can be completed within a reasonable and acceptable time
- Market feasibility: Focuses on understanding the market demand, competition, and potential customers suitable for the project’s products or services
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study in 7 Easy Steps
For a successful feasibility study, following the correct steps and ensuring every aspect is thoroughly analyzed is vital. We’re here to guide you through seven simple steps to assess feasibility , ensuring your project is fully prepared for its long-anticipated launch. Let’s take a look!
Running a full feasibility study can eat up time and technical resources. Instead of diving straight into the assessment, try dipping your toes in first by doing a preliminary analysis. Think of it like a test before the big test. 🤓
Here are four simple steps for this initial check :
- Start by laying out what you want from this project and why it matters to your team or business
- Look for similar projects out there and see if they’ve been successful
- Figure out what sets your idea apart—maybe it’s your team, the location, or the technology you use
- Determine the risks by listing out the things that could go wrong
Once you’ve done this check, you’ll better understand whether it’s worth digging deeper into the project’s feasibility.
To gather and easily share all this information, you can rely on ClickUp —a one-stop shop for all your business and project needs!
ClickUp Docs feature is excellent for collecting information in a single document so everything is accessible to all your team members. You can write, edit, leave comments, and collaborate in Docs in real-time.
Need to assign tasks or tag teammates? You can do it in Docs with ease! Plus, you can jazz up your documents with tables and subsections to ensure all data is presented in a structured manner. 🎺
You can also effortlessly create dedicated subpages for each preliminary analysis stage, ensuring streamlined organization of all data. On top of this, you can create easily shareable links and manage permissions efficiently for your team members and stakeholders.
If starting a feasibility report from scratch seems daunting, leverage the ClickUp Project Outline Template ! It breaks things down into steps so you don’t miss a beat. 🥁
It has separate pages for:
- Project timeline
- Budget and investments
- Constraints and assumptions
Like all ClickUp Docs, the template is fully customizable , so feel free to rename pages or create new ones to match your feasibility analysis needs.
To determine your project’s impact, you have to nail down what the project is all about. That means getting a clear idea of its goals, tasks, costs, and deadlines . Plus, you’ll have to identify everyone involved, from stakeholders to clients and customers.
When it’s brainstorming time , nothing beats a good old whiteboard. It’s your canvas for creativity, color-coded organization, and ensuring everyone’s on the same page. But if you’re operating with remote or hybrid teams , the ClickUp Project Scope Whiteboard Template is the perfect solution! ✨
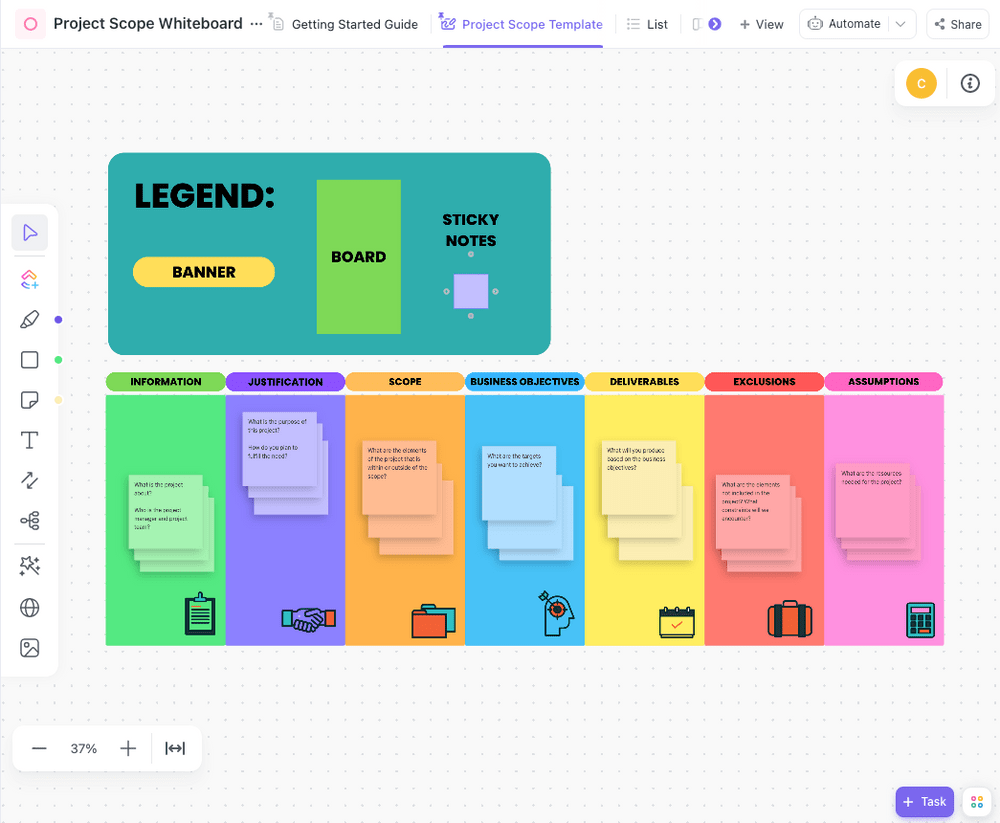
This template has all the benefits of a physical whiteboard but goes the extra mile with additional features, making it a more versatile tool. It includes seven components—information, justification, scope, business objectives, deliverables, exclusions, and assumptions.
You have the freedom to customize it by:
- Adding or removing sticky notes
- Including text, links, files, photos, and drawings
- Sharing it for seamless collaboration 🤝
This ClickUp Whiteboard is a great starting point for organizing your project and brainstorming its key elements. Plus, you can personalize it by adding, erasing, or renaming elements as needed.
Crafting a projected income statement is like looking into your business’s crystal ball for the upcoming year. It tells you all about the estimated revenue and expenses, serving as a vital tool for informed business decisions. Factors shaping this statement include:
- Services provided
- Service fees
- Service volume
- Revenue adjustments
Create a personalized income statement effortlessly with the ClickUp General Ledger Template ! Think of this handy tool as your financial assistant. It easily manages your income statement and your company’s entire financial records, staying on as a powerful sidekick even after your project passes the feasibility analysis! 💪
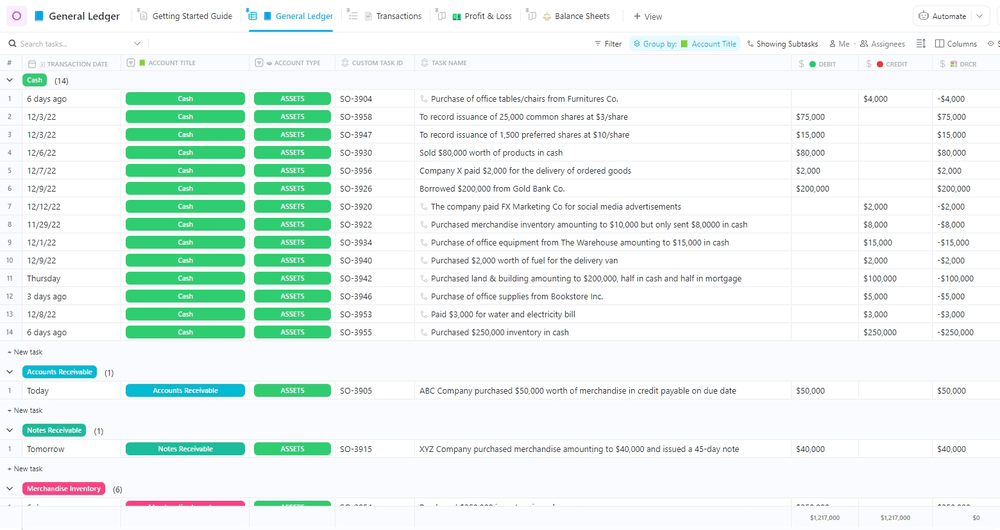
This template comes with Custom Fields tailor-made to capture every nitty-gritty transaction detail, including transaction dates, receipts, and entry numbers.
After recording transactions, leverage the document’s four main views to generate diverse financial statements:
- Profit & Loss Board view : Provides a financial scoreboard and helps you visualize revenues, expenses, and profits from recorded transactions. It lets you easily track and reclassify items by dragging them across the board
- Balance Sheets Board view : Maps out your assets, liabilities, and equity in one neat ClickUp Dashboard , making sure your financial ship stays on course
- General Ledger and Transaction List views : Allows day-to-day transaction tracking grouped by account title or other parameters
With the template’s comprehensive financial overview, every detail will be accounted for. This gives you the confidence to make accurate financial decisions and successfully navigate the feasibility analysis for your project.
Market research is crucial for understanding what your potential customers want and need , helping you understand whether there’s a market for your product or service. It also lets you size up your competition and determine the best way to position your business for success. 🎉
There are different ways to do market research; one popular method is sending a market survey. ClickUp AI makes creating market research surveys a breeze! Take advantage of its quick, generative power to craft surveys tailored to your brand and audience in the blink of an eye.
All you need to do is ask the right questions and target the desired audience. Then, leave it to the AI assistant to generate significant trends , preferences, and opinions that will shape your business decisions .
Speaking of AI, you can also conduct speedy market research with the ClickUp ChatGPT Prompts For Market Research And Analysis Template ! This handy tool offers hundreds of AI prompts to generate content useful for analyzing market trends and preferences.

Let’s say you need information on the latest industry trends for your marketing strategy. Try the prompt: Can you provide a report on market trends and predictions for [insert name] industry to inform our business strategy? And you’ll get the results you were looking for in a jiff! ⚡
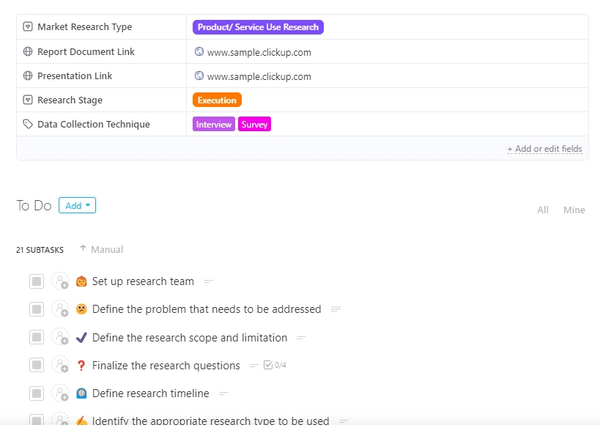
To make sure you cover all the steps in your research and nothing slips through the cracks, leverage the ClickUp Market Research Template as your personal task list .
This Task template guides you through the intricacies of research, encompassing your methodology, data collection methods, and the invaluable findings acquired from existing or prospective customers using Custom Fields.
Within this template, every task is accompanied by a subtask list, enabling you to closely monitor each research step. These tasks include critical actions like defining research scopes and assembling a proficient research team. 🕵🏼♂️
Assignees can easily oversee the progress of each subtask by employing Custom Statuses like Open, Under Review, or Closed, streamlining the monitoring process.
One of the smartest ways to collect all your assets, liabilities, and equity is by starting with an opening-day balance sheet. It’s like a snapshot of where your company stands regarding finances and assets when you’re launching a new project or business venture.
First, input all the assets you’ll need to run your operations smoothly. This includes cash for day-to-day expenses, inventory, equipment, property—all the essentials. Next, list liabilities like loans and leases and how much you’ll need to invest. It may take time, but having these details puts you on the right financial track.
Want to skip the hassle of crafting your balance sheet? The ClickUp Balance Sheet Sample Template has your back! It comes loaded with ready-made tables and fields you can tweak with your financial specifics, and voila—your balance sheet is good to go! 👌
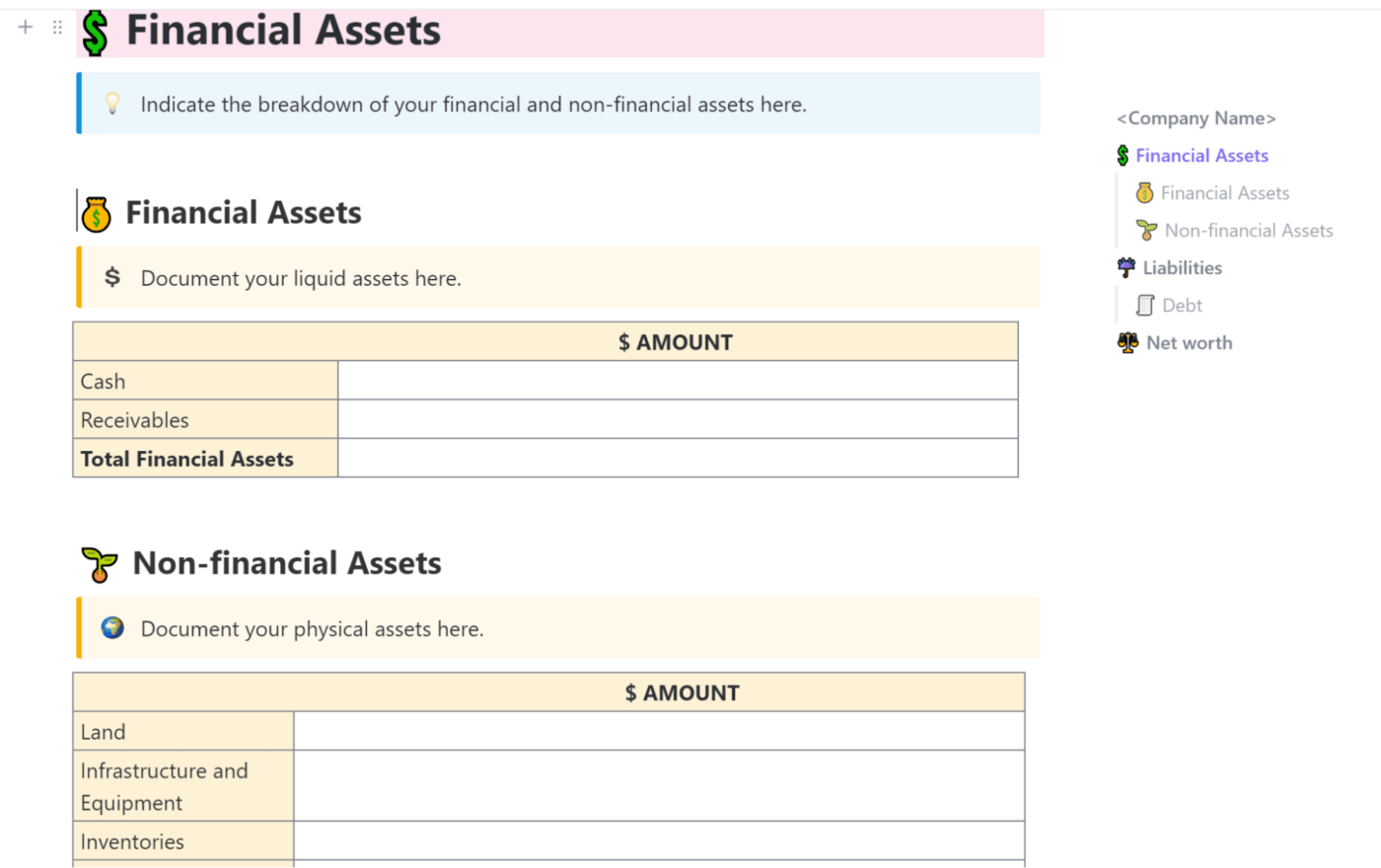
This Doc template comes with dedicated tables for:
- Financial assets
- Non-financial assets
- Liabilities
Feel free to add more rows and columns to fit your business needs and share the document with the whole team for an easy financial rundown.
Now, take a breather and reflect on your plan again. Checking and analyzing things ensures everything’s on track and there’s no need for further customization.
Cross-check the data against its original sources and flag any inconsistencies . The whole point of a feasibility study is to help you make better decisions, so the data you collect needs to back up those choices.
You should review the feasibility study by considering both the upsides and downsides of the project. When it comes to the finances, leave no stone unturned—document all the assumptions.
During this stage, it’s crucial to pinpoint potential risks and have mitigation strategies to tackle them. This can make or break your project feasibility—if the risks involved are worth the reward, your project may get the green light. Otherwise, you may want to reconsider your business idea.
Visualize your project’s risk landscape using the ClickUp Risk Analysis Whiteboard Template ! Pinpoint the probability and severity of each risk from your feasibility study by placing sticky notes on the color-coded Whiteboard map.
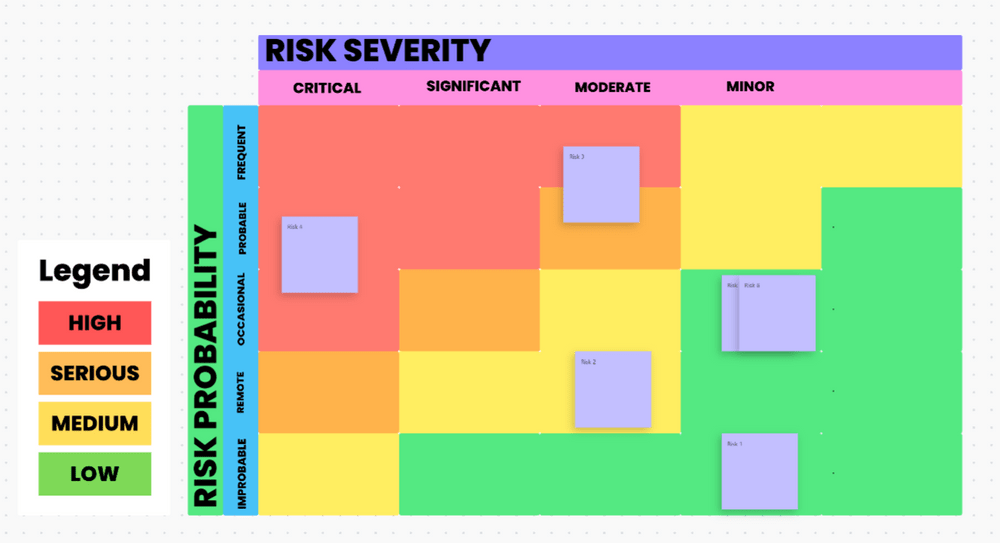
When the probability and severity of a potential risk rank as High or Serious, it might signal a need to rethink your approach or brainstorm solutions with your team. Conversely, if most risks fall into the Medium/Low category , your project stands a better chance of getting the thumbs-up. 👍
Congrats, you’ve reached the exciting moment of deciding whether the project will get the green light!
Before taking the plunge, it’s up to relevant clients or stakeholders to decide whether the project is worth their time, effort, and money and if it syncs up with the organization’s big-picture goals. 🖼️
To wrap up and pitch your feasibility study, grab the ClickUp Feasibility Study Executive Summary Template . Leverage its pre-designed layout to provide:
- Project Overview
- Focused Issue
- Proposed Solution
Then, dive into the Project Highlights —impress the stakeholders by summarizing crucial findings like market analysis and project strengths and rely on charts and graphs for that visual punch. 👊
Use the provided tables to note resources, timelines, and other success strategies. Finally, don’t forget the financial forecast —charts and graphs also come in handy here, as they will paint a more vivid picture of the project’s value for money.

Presenting all this information in a slick, structured way will help stakeholders wrap their heads around your idea, making their decision-making journey much smoother.
Conduct a Feasibility Study Effortlessly with ClickUp
Running a comprehensive feasibility study doesn’t happen in a flash. But navigating it becomes much more relaxed when you stick to the seven key steps we’ve laid out and use the appropriate project management tools.
For a seamless journey through your analysis objectives, sign up for a free ClickUp account today ! This powerful tool not only aids in every step of the feasibility study but also serves as an all-in-one project management wizard !
Once your project gets the green light, you’ll love using ClickUp’s treasure trove of project management tools , a library of 1,000+ templates , and numerous collaboration tools to stay on top of your project like a pro! 😎
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
11.3 Conducting a Feasibility Analysis
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the purpose of a feasibility analysis
- Describe and develop the parts of a feasibility analysis
- Understand how to apply feasibility outcomes to a new venture
As the name suggests, a feasibility analysis is designed to assess whether your entrepreneurial endeavor is, in fact, feasible or possible. By evaluating your management team, assessing the market for your concept, estimating financial viability, and identifying potential pitfalls, you can make an informed choice about the achievability of your entrepreneurial endeavor. A feasibility analysis is largely numbers driven and can be far more in depth than a business plan (discussed in The Business Plan ). It ultimately tests the viability of an idea, a project, or a new business. A feasibility study may become the basis for the business plan, which outlines the action steps necessary to take a proposal from ideation to realization. A feasibility study allows a business to address where and how it will operate, its competition, possible hurdles, and the funding needed to begin. The business plan then provides a framework that sets out a map for following through and executing on the entrepreneurial vision.
Organizational Feasibility Analysis
Organizational feasibility aims to assess the prowess of management and sufficiency of resources to bring a product or idea to market Figure 11.12 . The company should evaluate the ability of its management team on areas of interest and execution. Typical measures of management prowess include assessing the founders’ passion for the business idea along with industry expertise, educational background, and professional experience. Founders should be honest in their self-assessment of ranking these areas.
Resource sufficiency pertains to nonfinancial resources that the venture will need to move forward successfully and aims to assess whether an entrepreneur has a sufficient amount of such resources. The organization should critically rank its abilities in six to twelve types of such critical nonfinancial resources, such as availability of office space, quality of the labor pool, possibility of obtaining intellectual property protections (if applicable), willingness of high-quality employees to join the company, and likelihood of forming favorable strategic partnerships. If the analysis reveals that critical resources are lacking, the venture may not be possible as currently planned. 46
Financial Feasibility Analysis
A financial analysis seeks to project revenue and expenses (forecasts come later in the full business plan); project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections Figure 11.13 .
The financial analysis may typically include these items:
- A twelve-month profit and loss projection
- A three- or four-year profit-and-loss projection
- A cash-flow projection
- A projected balance sheet
- A breakeven calculation
The financial analysis should estimate the sales or revenue that you expect the business to generate. A number of different formulas and methods are available for calculating sales estimates. You can use industry or association data to estimate the sales of your potential new business. You can search for similar businesses in similar locations to gauge how your business might perform compared with similar performances by competitors. One commonly used equation for a sales model multiplies the number of target customers by the average revenue per customer to establish a sales projection:
Another critical part of planning for new business owners is to understand the breakeven point , which is the level of operations that results in exactly enough revenue to cover costs (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for an in-depth discussion on calculating breakeven points and the breakdown of cost types). It yields neither a profit nor a loss. To calculate the breakeven point, you must first understand the two types of costs: fixed and variable. Fixed costs are expenses that do not vary based on the amount of sales. Rent is one example, but most of a business’s other costs operate in this manner as well. While some costs vary from month to month, costs are described as variable only if they will increase if the company sells even one more item. Costs such as insurance, wages, and office supplies are typically considered fixed costs. Variable costs fluctuate with the level of sales revenue and include items such as raw materials, purchases to be sold, and direct labor. With this information, you can calculate your breakeven point—the sales level at which your business has neither a profit nor a loss. 47 Projections should be more than just numbers: include an explanation of the underlying assumptions used to estimate the venture’s income and expenses.
Projected cash flow outlines preliminary expenses, operating expenses, and reserves—in essence, how much you need before starting your company. You want to determine when you expect to receive cash and when you have to write a check for expenses. Your cash flow is designed to show if your working capital is adequate. A balance sheet shows assets and liabilities, necessary for reporting and financial management. When liabilities are subtracted from assets, the remainder is owners’ equity. The financial concepts and statements introduced here are discussed fully in Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting .
Market Feasibility Analysis
A market analysis enables you to define competitors and quantify target customers and/or users in the market within your chosen industry by analyzing the overall interest in the product or service within the industry by its target market Figure 11.14 . You can define a market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. This information allows you to better position your company in competing for market share. After you’ve determined the overall size of the market, you can define your target market, which leads to a total available market (TAM) , that is, the number of potential users within your business’s sphere of influence. This market can be segmented by geography, customer attributes, or product-oriented segments. From the TAM, you can further distill the portion of that target market that will be attracted to your business. This market segment is known as a serviceable available market (SAM) .
Projecting market share can be a subjective estimate, based not only on an analysis of the market but also on pricing, promotional, and distribution strategies. As is the case for revenue, you will have a number of different forecasts and tools available at your disposal. Other items you may include in a market analysis are a complete competitive review, historical market performance, changes to supply and demand, and projected growth in demand over time.
Are You Ready?
You’ve been hired by a leading hotel chain to determine the market and financial potential for the development of a mixed-use property that will include a full-service hotel in downtown Orlando, located at 425 East Central Boulevard, in Orlando, Florida. The specific address is important so you can pinpoint existing competitors and overall suitability of the site. Using the information given, conduct a market analysis that can be part of a larger feasibility study.
Work It Out
Location feasibility.
You’re considering opening a boutique clothing store in downtown Atlanta. You’ve read news reports about how downtown Atlanta and the city itself are growing and undergoing changes from previous decades. With new development taking place there, you’re not sure whether such a venture is viable. Outline what steps you would need to take to conduct a feasibility study to determine whether downtown Atlanta is the right location for your planned clothing store.
Applying Feasibility Outcomes
After conducting a feasibility analysis, you must determine whether to proceed with the venture. One technique that is commonly used in project management is known as a go-or-no-go decision . This tool allows a team to decide if criteria have been met to move forward on a project. Criteria on which to base a decision are established and tracked over time. You can develop criteria for each section of the feasibility analysis to determine whether to proceed and evaluate those criteria as either “go” or “no go,” using that assessment to make a final determination of the overall concept feasibility. Determine whether you are comfortable proceeding with the present management team, whether you can “go” forward with existing nonfinancial resources, whether the projected financial outlook is worth proceeding, and make a determination on the market and industry. If satisfied that enough “go” criteria are met, you would likely then proceed to developing your strategy in the form of a business plan.
What Can You Do?
Love beyond walls.
When Terence Lester saw a homeless man living behind an abandoned, dilapidated building, he asked the man if he could take him to a shelter. The man scoffed, replying that Lester should sleep in a shelter. So he did—and he saw the problem through the homeless man’s perspective. The shelter was crowded and smelly. You couldn’t get much sleep, because others would try to steal your meager belongings. The dilapidated building provided isolation away from others, but quiet and security in its own way that the shelter could not. This experience led Lester to voluntarily live as a homeless person for a few weeks. His journey led him to create Love Beyond Walls (www.lovebeyondwalls.org), an organization that aids the homeless, among other causes. Lester didn’t conduct a formal feasibility study, but he did so informally by walking in his intended customers’ shoes—literally. A feasibility study of homelessness in a particular area could yield surprising findings that might lead to social entrepreneurial pursuits.
- What is a social cause you think could benefit from a formal feasibility study around a potential entrepreneurial solution?
- 46 Ulrich Kaiser. “A primer in Entrepreneurship – Chapter 3 Feasibility analysis” University of Zurich Institute for Strategy and Business Economics . n.d. https://docplayer.net/7775267-A-primer-in-entrepreneurship-chapter-3-feasibility-analysis.html
- 47 In a preliminary financial model and business plan, startup costs should be allocated, as they are intended for one-time investments in development; pre-launch costs and other necessary expenses will not carry over once the product/solution has launched.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-3-conducting-a-feasibility-analysis
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Feasibility Study?
Understanding a feasibility study, how to conduct a feasibility study.
- Feasibility Study FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Feasibility Study
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
A feasibility study is a detailed analysis that considers all of the critical aspects of a proposed project in order to determine the likelihood of it succeeding.
Success in business may be defined primarily by return on investment , meaning that the project will generate enough profit to justify the investment. However, many other important factors may be identified on the plus or minus side, such as community reaction and environmental impact.
Although feasibility studies can help project managers determine the risk and return of pursuing a plan of action, several steps should be considered before moving forward.

Key Takeaways
- A company may conduct a feasibility study when it's considering launching a new business, adding a new product line, or acquiring a rival.
- A feasibility study assesses the potential for success of the proposed plan or project by defining its expected costs and projected benefits in detail.
- It's a good idea to have a contingency plan on hand in case the original project is found to be infeasible.
Investopedia / Lara Antal
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a proposed plan or project. A feasibility study analyzes the viability of a project to determine whether the project or venture is likely to succeed. The study is also designed to identify potential issues and problems that could arise while pursuing the project.
As part of the feasibility study, project managers must determine whether they have enough of the right people, financial resources, and technology. The study must also determine the return on investment, whether this is measured as a financial gain or a benefit to society, as in the case of a nonprofit project.
The feasibility study might include a cash flow analysis, measuring the level of cash generated from revenue versus the project's operating costs . A risk assessment must also be completed to determine whether the return is enough to offset the risk of undergoing the venture.
When doing a feasibility study, it’s always good to have a contingency plan that is ready to test as a viable alternative if the first plan fails.
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
There are several benefits to feasibility studies, including helping project managers discern the pros and cons of undertaking a project before investing a significant amount of time and capital into it.
Feasibility studies can also provide a company's management team with crucial information that could prevent them from entering into a risky business venture.
Such studies help companies determine how they will grow. They will know more about how they will operate, what the potential obstacles are, who the competition is, and what the market is.
Feasibility studies also help convince investors and bankers that investing in a particular project or business is a wise choice.
The exact format of a feasibility study will depend on the type of organization that requires it. However, the same factors will be involved even if their weighting varies.
Preliminary Analysis
Although each project can have unique goals and needs, there are some best practices for conducting any feasibility study:
- Conduct a preliminary analysis, which involves getting feedback about the new concept from the appropriate stakeholders
- Analyze and ask questions about the data obtained in the early phase of the study to make sure that it's solid
- Conduct a market survey or market research to identify the market demand and opportunity for pursuing the project or business
- Write an organizational, operational, or business plan, including identifying the amount of labor needed, at what cost, and for how long
- Prepare a projected income statement, which includes revenue, operating costs, and profit
- Prepare an opening day balance sheet
- Identify obstacles and any potential vulnerabilities, as well as how to deal with them
- Make an initial "go" or "no-go" decision about moving ahead with the plan
Suggested Components
Once the initial due diligence has been completed, the real work begins. Components that are typically found in a feasibility study include the following:
- Executive summary : Formulate a narrative describing details of the project, product, service, plan, or business.
- Technological considerations : Ask what will it take. Do you have it? If not, can you get it? What will it cost?
- Existing marketplace : Examine the local and broader markets for the product, service, plan, or business.
- Marketing strategy : Describe it in detail.
- Required staffing : What are the human capital needs for this project? Draw up an organizational chart.
- Schedule and timeline : Include significant interim markers for the project's completion date.
- Project financials .
- Findings and recommendations : Break down into subsets of technology, marketing, organization, and financials.
Examples of a Feasibility Study
Below are two examples of a feasibility study. The first involves expansion plans for a university. The second is a real-world example conducted by the Washington State Department of Transportation with private contributions from Microsoft Inc.
A University Science Building
Officials at a university were concerned that the science building—built in the 1970s—was outdated. Considering the technological and scientific advances of the last 20 years, they wanted to explore the cost and benefits of upgrading and expanding the building. A feasibility study was conducted.
In the preliminary analysis, school officials explored several options, weighing the benefits and costs of expanding and updating the science building. Some school officials had concerns about the project, including the cost and possible community opposition. The new science building would be much larger, and the community board had earlier rejected similar proposals. The feasibility study would need to address these concerns and any potential legal or zoning issues.
The feasibility study also explored the technological needs of the new science facility, the benefits to the students, and the long-term viability of the college. A modernized science facility would expand the school's scientific research capabilities, improve its curriculum, and attract new students.
Financial projections showed the cost and scope of the project and how the school planned to raise the needed funds, which included issuing a bond to investors and tapping into the school's endowment . The projections also showed how the expanded facility would allow more students to be enrolled in the science programs, increasing revenue from tuition and fees.
The feasibility study demonstrated that the project was viable, paving the way to enacting the modernization and expansion plans of the science building.
Without conducting a feasibility study, the school administrators would never have known whether its expansion plans were viable.
A High-Speed Rail Project
The Washington State Department of Transportation decided to conduct a feasibility study on a proposal to construct a high-speed rail that would connect Vancouver, British Columbia, Seattle, Washington, and Portland, Oregon. The goal was to create an environmentally responsible transportation system to enhance the competitiveness and future prosperity of the Pacific Northwest.
The preliminary analysis outlined a governance framework for future decision-making. The study involved researching the most effective governance framework by interviewing experts and stakeholders, reviewing governance structures, and learning from existing high-speed rail projects in North America. As a result, governing and coordinating entities were developed to oversee and follow the project if it was approved by the state legislature.
A strategic engagement plan involved an equitable approach with the public, elected officials, federal agencies, business leaders, advocacy groups, and indigenous communities. The engagement plan was designed to be flexible, considering the size and scope of the project and how many cities and towns would be involved. A team of the executive committee members was formed and met to discuss strategies, lessons learned from previous projects and met with experts to create an outreach framework.
The financial component of the feasibility study outlined the strategy for securing the project's funding, which explored obtaining funds from federal, state, and private investments. The project's cost was estimated to be between $24 billion to $42 billion. The revenue generated from the high-speed rail system was estimated to be between $160 million and $250 million.
The report bifurcated the money sources between funding and financing. Funding referred to grants, appropriations from the local or state government, and revenue. Financing referred to bonds issued by the government, loans from financial institutions, and equity investments, which are essentially loans against future revenue that needs to be paid back with interest.
The sources for the capital needed were to vary as the project moved forward. In the early stages, most of the funding would come from the government, and as the project developed, funding would come from private contributions and financing measures. Private contributors included Microsoft Inc., which donated more than $570,000 to the project.
The benefits outlined in the feasibility report show that the region would experience enhanced interconnectivity, allowing for better management of the population and increasing regional economic growth by $355 billion. The new transportation system would provide people with access to better jobs and more affordable housing. The high-speed rail system would also relieve congested areas from automobile traffic.
The timeline for the study began in 2016 when an agreement was reached with British Columbia to work together on a new technology corridor that included high-speed rail transportation. The feasibility report was submitted to the Washington State land Legislature in December 2020.
What Is the Main Objective of a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is designed to help decision-makers determine whether or not a proposed project or investment is likely to be successful. It identifies both the known costs and the expected benefits.
In business, "successful" means that the financial return exceeds the cost. In a nonprofit, success may be measured in other ways. A project's benefit to the community it serves may be worth the cost.
What Are the Steps in a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study starts with a preliminary analysis. Stakeholders are interviewed, market research is conducted, and a business plan is prepared. All of this information is analyzed to make an initial "go" or "no-go" decision.
If it's a go, the real study can begin. This includes listing the technological considerations, studying the marketplace, describing the marketing strategy, and outlining the necessary human capital, project schedule, and financing requirements.
Who Conducts a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study may be conducted by a team of the organization's senior managers. If they lack the expertise or time to do the work internally it may be outsourced to a consultant.
What Are the 4 Types of Feasibility?
The study considers the feasibility of four aspects of a project:
Technical: A list of the hardware and software needed, and the skilled labor required to make them work.
Financial: An estimate of the cost of the overall project and its expected return.
Market: An analysis of the market for the product or service, the industry, competition, consumer demand, sales forecasts, and growth projections
Organizational: An outline of the business structure and the management team that will be needed.
Feasibility studies help project managers determine the viability of a project or business venture by identifying the factors that can lead to its success. The study also shows the potential return on investment and any risks to the success of the venture.
A feasibility study contains a detailed analysis of what's needed to complete the proposed project. The report may include a description of the new product or venture, a market analysis, the technology and labor needed, as well as the sources of financing and capital. The report will also include financial projections, the likelihood of success, and ultimately, a go-or-no-go decision.
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Ultra-High-Speed Rail Study ."
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Cascadia Ultra High Speed Ground Transportation Framework for the Future ."
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Ultra-High-Speed Rail Study: Outcomes ."
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Ultra-High-Speed Ground Transportation Business Case Analysis ." Page ii.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1084171152-8445a490b5894f0a9bb588dbfc2ac22d.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Starting a Business | What is
What Is a Feasibility Study for Small Business?
Published July 17, 2020
Published Jul 17, 2020
WRITTEN BY: Blake Stockton
This article is part of a larger series on Starting a Business .
A feasibility study for small business is an in-depth research and financial analysis that recommends if one should pursue a business idea or product. The study contains estimates of items such as income, costs, obstacles, and technical challenges. Typically, a feasibility study for a small business costs a minimum of $5,000. However, they can cost up to $100,000 for businesses that have a multimillion dollar startup budget.
Throughout this article, we discuss what a feasibility study is and how it differs from a business plan, so that you can decide whether or not you really need one for your business.
How the Feasibility Study Works
Usually, businesses conduct feasibility studies to determine if their idea or product is worth pursuing. It’s one of the more complicated and costly ways to test a business idea.
Depending on the idea’s complexity and scope, a study can take weeks or months to prepare. With the help of templates or programs, business owners can conduct feasibility studies on their own. However, because of the in-depth research and complicated financial projections, they often hire an expert to create the study.
Feasibility studies do not determine the final decision but present all the evidence and make a strong recommendation on whether or not it’s best to move forward. The entrepreneur, stakeholders, and/or other authorities decide whether to go ahead with the business idea or product, using the study as a guide.
Who Should Get a Feasibility Study?
Small business entrepreneurs use a feasibility study to prevent the costly mistake of launching an unsuccessful business, product, or project. You can use a study to help make strategic decisions, such as determining whether you should:
- Start a new business
- Open a new store or factory
- Change product lineup or approach
- Expand to a new area or market
- Acquire another company
- Make a significant investment in new technology
- Enter an already crowded or competitive market segment
- Invest personal capital into a project
Feasibility Study vs Business Plan
A feasibility study often comes before the business plan, because the information and data uncovered in the study are included in the business plan. Plus, if the feasibility gives a recommendation not to move forward, you may want to rethink your business idea or product altogether before creating a plan.
What Should Be in a Feasibility Study?
Depending on the project or business, you will use each of the aspects below to a certain degree. The feasibility study’s organization may vary depending on its focus—you may have a section for each of these topics:
- Executive Summary: This summarizes the project and business. The ultimate conclusions are outlined here. It should be about a page long.
- Demand: A marketing analysis determines the need for your product or business in the industry you want to sell. Even if you have a brick-and-mortar business, you should consider online aspects as well.
- Technical issues: What tool, hardware, or software do you need to create your business or product? Will you create the tech, buy it, or rent it? This section also includes the facilities, including layout, shelving, offices, and manufacturing space.
- Logistics issues: This piece outlines vendors, pricing schedules, exclusive agreements, and franchised product contracts. It may include getting supplies and delivering finished products or working online elements like an ecommerce site. Location issues can be placed here.
- Legal concerns: Do you need permits? Are there regulations or prohibitions to consider? What about environmental, historical, or legacy issues to negotiate?
- Marketing strategy: This section will define the target market as specific as possible: How you will meet their needs, and how you will target them?
- Required staffing: How many employees will you need? What are their qualifications? What is the typical salary in your area? You can include a sample organizational chart along with a corresponding discussion of who among your current employees may change jobs to fill new positions.
- Scheduling: This section includes milestones for financials as well as physical projects and a timeline for completion.
- Financials: In addition to anticipated expenses and potential profits, this section will include an opening day balance sheet that lists total assets and liabilities on your business’s first day. This financial data gives you an indication of your return on investment (ROI).
- ROI: If you don’t see a return on investment, it makes no sense to start or expand your business. A feasibility study estimates when you’ll earn profits and what or how much they may be.
- Analysis: You will see discussions answering questions like: Does it seem realistic? Are the sources strong? Are there outlying data points to consider? Also, analyze potential risks: What are the worst-case scenarios, and how likely are they?
- Recommendations: This gives a go or no-go recommendation and breaks down specific suggestions based on the main elements. If the project is not feasible, it may offer alternatives.
Cost of a Feasibility Study
A feasibility study for small business takes an average of 60 to 90 days to complete and may cost anywhere from $5,000 to $10,000. As a general rule of thumb, a feasibility study will cost 1% of the business’s total cost to open or a product’s cost to build. So if you’re requesting a feasibility study for a complicated business with millions in startup costs, be prepared to spend more than $10,000.
The cost is also determined by the study’s depth, the tools needed to conduct it—survey software, focus groups, and lawyers—and the scope of the project. For example, a study to determine if a business should bring manufacturing back to the US from overseas will cost more than a study on whether to open a restaurant.
Here are costs for various feasibility study projects:
Who Provides Feasibility Studies?
You may find it challenging to find a firm that only produces feasibility studies. Often, a market research firm will provide feasibility studies in addition to other services. For example, Drive Research in Syracuse, New York, offers a host of market research services, including feasibility studies .
There are also business plan writing companies that specialize in feasibility studies. Wise Business Plans provides a study with in-depth market research and industry analysis.
If you’d like to connect one-on-one and choose your own independent market researcher for a feasibility study, you could look to the freelancer platform Upwork . You can find several market research experts and analysts that may be interested in tackling your specific project. Upwork is an excellent platform to find market researchers, because you can review a freelancer’s past work to see if they’d be a good fit.
Tips and Best Practices to Follow When Purchasing a Feasibility Study
- Conduct a preliminary analysis first: Before paying thousands of dollars for a feasibility study, do a minor check to ensure there are no insurmountable technical, legal, or financial obstacles to the business idea or product.
- Involve stakeholders: Before, during, and after the study, keep people relevant to the business in the loop. Get their input, suggestions, and feedback.
- Review research: Review the feasibility study data and see if you come to a similar conclusion as the research analyst. You may also want to pay for a second expert’s opinion on the final determination.
- Assess your current company or situation: Before making any decision on a business idea or product, consider your own strengths, weaknesses, and financial situation in the final decision to move forward or not.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for a Feasibility Study
Is it better to hire out for a feasibility study.
Most likely, yes. Feasibility studies typically contain in-depth expert data analysis and financial projections. Hiring out the work will ensure you get an objective evaluation of the project and its potential downfalls and successes. It’s human nature to bias our own ideas, and a third party can avoid.
How much should I invest in a feasibility study?
For a simpler study on a business idea or product, expect to pay anywhere from $5,000 to $10,000. The general rule of thumb is that a feasibility study will cost 1% of the expected project budget or business’s cost to build.
Should feasibility studies include solutions as well as pointing out obstacles?
Yes, the more information the study provides, the better it will aid in the decision-making process. Feasibility studies should provide an objective determination because of the time and expense involved.
Can my feasibility study become my business plan?
Many times, yes. With some changes in focus and scope, a feasibility study can be re-imagined into a business plan. However, be sure it meets the purpose, which outlines the strategic and tactical steps needed to make the business work.
Bottom Line
Feasibility studies can cost thousands of dollars, but they can save you millions you may lose from making a poor business decision. They examine a new business or product idea by researching the endeavor’s technological, financial, and operational aspects. The study analyzes the data and offers a recommendation on if you should move ahead with your project or idea and how to maximize its success.
About the Author

Find Blake On LinkedIn Twitter
Blake Stockton
Blake Stockton is a staff writer at Fit Small Business focusing on how to start brick-and-mortar and online businesses. He is a frequent guest lecturer at several undergraduate business and MBA classes at University of North Florida . Prior to joining Fit Small Business, Blake consulted with over 700 small biz owners and assisted with starting and growing their businesses.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
What Is a Feasibility Study? How to Conduct One for Your Project

Table of Contents
What is a feasibility study, what’s the importance of a feasibility study, what is included in a feasibility study report, types of feasibility study.
- 7 Steps To Do a Feasibility Study
Feasibility Study Examples
Why is a feasibility study so important in project management? For one, the feasibility study or feasibility analysis is the foundation upon which your project plan resides. That’s because the feasibility analysis determines the viability of your project. Now that you know the importance, read on to learn what you need to know about feasibility studies.
A feasibility study is simply an assessment of the practicality of a proposed project plan or method. This is done by analyzing technical, economic, legal, operational and time feasibility factors. Just as the name implies, you’re asking, “Is this feasible?” For example, do you have or can you create the technology that accomplishes what you propose? Do you have the people, tools and resources necessary? And, will the project get you the ROI you expect?

Get your free
Feasibility study template
Use this free Feasibility Study Template for Word to manage your projects better.
A project feasibility study should be done during the project management life cycle after the business case has been completed. So, that’s the “what” and the “when” but how about the “why?” Why is it important to conduct a feasibility study?
An effective feasibility study points a project in the right direction by helping decision-makers have a holistic view of the potential benefits, disadvantages, barriers and constraints that could affect its outcome. The main purpose of a feasibility study is to determine whether the project can be not only viable but also beneficial from a technical, financial, legal and market standpoint.
The findings of your project feasibility study are compiled in a feasibility report that usually includes the following elements.
- Executive summary
- Description of product/service
- Technology considerations
- Product/service marketplace
- Marketing strategy
- Organization/staffing
- Financial projections
- Findings and recommendations
Free Feasibility Study Template
Use this free feasibility study template for Word to begin your own feasibility study. It has all the fundamental sections for you to get started, and it’s flexible enough to adapt to your specific needs. Download yours today.
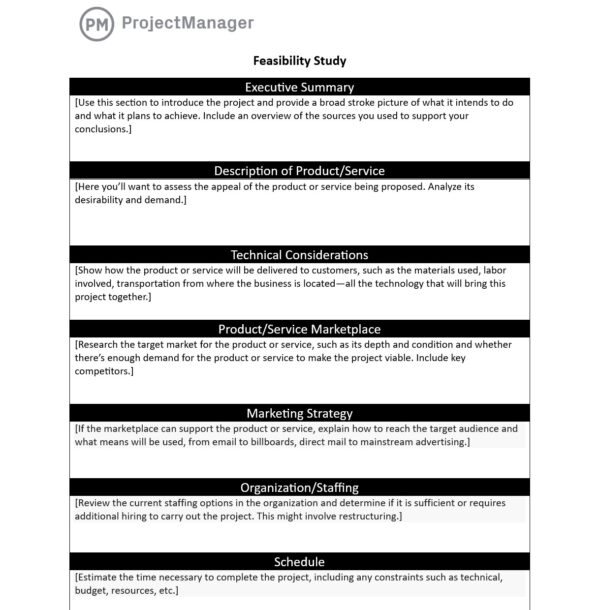
There are many things to consider when determining project feasibility, and there are different types of feasibility studies you might conduct to assess your project from different perspectives.
Pre-Feasibility Study
A pre-feasibility study, as its name suggests, it’s a process that’s undertaken before the feasibility study. It involves decision-makers and subject matter experts who will prioritize different project ideas or approaches to quickly determine whether the project has fundamental technical, financial, operational or any other evident flaws. If the project proposal is sound, a proper feasibility study will follow.
Technical Feasibility Study
A technical feasibility study consists in determining if your organization has the technical resources and expertise to meet the project requirements . A technical study focuses on assessing whether your organization has the necessary capabilities that are needed to execute a project, such as the production capacity, facility needs, raw materials, supply chain and other inputs. In addition to these production inputs, you should also consider other factors such as regulatory compliance requirements or standards for your products or services.
Economic Feasibility Study
Also called financial feasibility study, this type of study allows you to determine whether a project is financially feasible. Economic feasibility studies require the following steps:
- Before you can start your project, you’ll need to determine the seed capital, working capital and any other capital requirements, such as contingency capital. To do this, you’ll need to estimate what types of resources will be needed for the execution of your project, such as raw materials, equipment and labor.
- Once you’ve determined what project resources are needed, you should use a cost breakdown structure to identify all your project costs.
- Identify potential sources of funding such as loans or investments from angel investors or venture capitalists.
- Estimate the expected revenue, profit margin and return on investment of your project by conducting a cost-benefit analysis , or by using business forecasting techniques such as linear programming to estimate different future outcomes under different levels of production, demand and sales.
- Estimate your project’s break-even point.
- Conduct a financial benchmark analysis with industrial averages and specific competitors in your industry.
- Use pro forma cash flow statements, financial statements, balance sheets and other financial projection documents.
Legal Feasibility Study
Your project must meet legal requirements including laws and regulations that apply to all activities and deliverables in your project scope . In addition, think about the most favorable legal structure for your organization and its investors. Each business legal structure has advantages and disadvantages when it comes to liability for business owners, such as limited liability companies (LLCs) or corporations, which reduce the liability for each business partner.
Market Feasibility Study
A market feasibility study determines whether your project has the potential to succeed in the market. To do so, you’ll need to analyze the following factors:
- Industry overview: Assess your industry, such as year-over-year growth, identify key direct and indirect competitors, availability of supplies and any other trends that might affect the future of the industry and your project.
- SWOT analysis: A SWOT analysis allows organizations to determine how competitive an organization can be by examining its strengths, weaknesses and the opportunities and threats of the market. Strengths are the operational capabilities or competitive advantages that allow an organization to outperform its competitors such as lower costs, faster production or intellectual property. Weaknesses are areas where your business might be outperformed by competitors. Opportunities are external, such as an underserved market, an increased demand for your products or favorable economic conditions. Threats are also external factors that might affect your ability to do well in the market such as new competitors, substitute products and new technologies.
- Market research: The main purpose of market research is to determine whether it’s possible for your organization to enter the market or if there are barriers to entry or constraints that might affect your ability to compete. Consider variables such as pricing, your unique value proposition, customer demand, new technologies, market trends and any other factors that affect how your business will serve your customers. Use market research techniques to identify your target market, create buyer personas, assess the competitiveness of your niche and gauge customer demand, among other things.
7 Steps to Do a Feasibility Study
If you’re ready to do your own feasibility study, follow these 7 steps. You can use this free feasibility study template to help you get started.
1. Conduct a Preliminary Analysis
Begin by outlining your project plan . You should focus on an unserved need, a market where the demand is greater than the supply and whether the product or service has a distinct advantage. Then, determine if the feasibility factors are too high to clear (i.e. too expensive, unable to effectively market, etc.).
2. Prepare a Projected Income Statement
This step requires working backward. Start with what you expect the income from the project to be and then what project funding is needed to achieve that goal. This is the foundation of an income statement. Factor in what services are required and how much they’ll cost and any adjustments to revenues, such as reimbursements, etc.
Related: Free Project Management Templates
3. Conduct a Market Survey or Perform Market Research
This step is key to the success of your feasibility study, so make your market analysis as thorough as possible. It’s so important that if your organization doesn’t have the resources to do a proper one, then it is advantageous to hire an outside firm to do so.
Market research will give you the clearest picture of the revenues and return on investment you can realistically expect from the project. Some things to consider are the geographic influence on the market, demographics, analyzing competitors, the value of the market and what your share will be and if the market is open to expansion (that is, in response to your offer).
4. Plan Business Organization and Operations
Once the groundwork of the previous steps has been laid, it’s time to set up the organization and operations of the planned project to meet its technical, operational, economic and legal feasibility factors. This isn’t a superficial, broad-stroke endeavor. It should be thorough and include start-up costs, fixed investments and operating costs.
These costs address things such as equipment, merchandising methods, real estate, personnel, supply availability, overhead, etc.
5. Prepare an Opening Day Balance Sheet
This includes an estimate of the assets and liabilities, one that should be as accurate as possible. To do this, create a list that includes items, sources, costs and available financing. Liabilities to consider are such things as leasing or purchasing land, buildings and equipment, financing for assets and accounts receivables.
6. Review and Analyze All Data
All of these steps are important, but the review and analysis are especially important to ensure that everything is as it should be and that nothing requires changing or tweaking. Take a moment to look over your work one last time.
Reexamine your previous steps, such as the income statement, and compare them with your expenses and liabilities. Is it still realistic? This is also the time to think about risk and come up with any contingency plans .
7. Make a Go/No-Go Decision
You’re now at the point to make a decision about whether or not the project is feasible. That sounds simple, but all the previous steps lead to this decision-making moment. A couple of other things to consider before making that binary choice are whether the commitment is worth the time, effort and money and whether it aligns with the organization’s strategic goals and long-term aspirations.
Here are some simple feasibility study examples so you have a better idea of what a feasibility study is used for in different industries.
Construction Feasibility Study
For this construction feasibility study example, let’s imagine a large construction company that’s interested in starting a new project in the near future to generate profits.
- Pre-Feasibility Study: The first step is to conduct a preliminary feasibility study. It can be as simple as a meeting where decision-makers will prioritize projects and discuss different project ideas to determine which poses a bigger financial benefit for the organization.
- Technical Feasibility Study: Now it’s time to estimate what resources are needed to execute the construction project, such as raw materials, equipment and labor. If there’s work that can’t be executed by the company with its current resources, a subcontractor will be hired to fill the gap.
- Economic Feasibility Study: Once the construction project management team has established what materials, equipment and labor are needed, they can estimate costs. Cost estimators use information from past projects, construction drawings and documents such as a bill of quantities to come up with an accurate cost estimate. Then, based on this estimate, a profit margin and financial forecasts will be analyzed to determine if there’s economic feasibility.
- Legal Feasibility Study: Now the company needs to identify all potential regulations, building codes and laws that might affect the project. They’ll need to ask for approval from the local government so that they can begin the construction project .
- Market Feasibility Study: Market feasibility will be determined depending on the nature of the project. For this feasibility example, let’s assume a residential construction project will be built. To gauge market potential, they’ll need to analyze variables such as the average income of the households in the city, crime rate, population density and any trends in state migration.
Manufacturing Feasibility Study
Another industry that uses feasibility studies is manufacturing. It’s a test run of the steps in the manufacturing production cycle to ensure the process is designed properly. Let’s take a look at what a manufacturing feasibility study example would look like.
- Feasibility Study: The first step is to look at various ideas and decide which is the best one to pursue. You don’t want to get started and have to stop. That’s a waste of time, money and effort. Look at what you intend to manufacture, does it fill an unserved need, is the market able to support competition and can you manufacture a quality product on time and within your budget?
- Financial Feasibility Study: Find out if your estimated income from the sale of this product is going to cover your costs, both direct and indirect costs. Work backward from the income you expect to make and the expenses you’ll spend for labor, materials and production to determine if the manufacturing of this product is financially feasible.
- Market Feasibility Study: You’ve already determined that there’s a need that’s not being served, but now it’s time to dig deeper to get realistic projections of revenue. You’ll want to define your target demographic, analyze the competitive landscape, determine the total market volume and what your market share will be and estimate what market expansion opportunities there are.
- Technical Feasibility Study: This is where you’ll explore the production , such as what resources you’ll need to produce your product. These findings will inform your financial feasibility study as well as labor, material, equipment, etc., costs have to be within your budget. You’ll also figure out the processes you’ll use to produce and deliver your product to the market, including warehousing and retail distribution.
There could be other feasibility studies you’ll have to make depending on the product and the market, but these are the essential ones that all manufacturers have to look at before they can make an educated decision as to whether to go forward or abandon the idea.
Best Practices for a Feasibility Study
- Use project management software like ProjectManager to organize your data and work efficiently and effectively
- Use templates or any data and technology that gives you leverage
- Involve the appropriate stakeholders to get their feedback
- Use market research to further your data collection
- Do your homework and ask questions to make sure your data is solid
If your project is feasible, then the real work begins. ProjectManager helps you plan more efficiently. Our online Gantt chart organizes tasks, sets deadlines, adds priority and links dependent tasks to avoid delays. But unlike other Gantt software, we calculate the critical path for you and set a baseline to measure project variance once you move into the execution phase.
Watch a Video on Feasibility Studies
There are many steps and aspects to a project feasibility study. If you want yours to be accurate and forecast correctly whether your project is doable, then you need to have a clear understanding of all its moving parts.
Jennifer Bridges, PMP, is an expert on all aspects of project management and leads this free training video to help you get a firm handle on the subject.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference!

Pro tip: When completing a feasibility study, it’s always good to have a contingency plan that you test to make sure it’s a viable alternative.
ProjectManager Improves Your Feasibility Study
A feasibility study is a project, so get yourself a project management software that can help you execute it. ProjectManager is an award-winning software that can help you manage your feasibility study through every phase.
Once you have a plan for your feasibility study, upload that task list to our software and all your work is populated in our online Gantt chart. Now you can assign tasks to team members, add costs, create timelines, collect all the market research and attach notes at the task level. This gives people a plan to work off of, and a collaborative platform to collect ideas and comments.
If you decide to implement the project, you already have it started in our software, which can now help you monitor and report on its progress. Try it for yourself with this free 30-day trial.
Transcription
Today we’re talking about How to Conduct A Feasibility Study, but first of all, I want to start with clarifying what a feasibility study is.
Feasibility Analysis Definition
Basically, it’s an assessment of the practicality of a proposed plan or method. Basically, we’ll want to want to know, is this feasible. Some of the questions that may generate this or we can hear people asking are, “Do we have or can we create the technology to do this? Do we have the people resource who can produce this and will we get our ROI, our Return On Investment?”
When to Do a Feasibility Study
So when do we do the feasibility study? So it’s done during a project lifecycle and it’s done after the business case because the business case outlines what we’re proposing. Is it a product or service that we’re proposing?
So why do we do this? The reason we do this is that we need to determine the factors that will make the business opportunity a success.
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study
Well, let’s talk about a few steps that we do in order to conduct the feasibility study.
Well, first of all, we conduct a preliminary analysis of what all’s involved in the business case and what we’re analyzing and what we’re trying to determine is feasible.
Then we prepare a projected income statement. We need to know what are the income streams, how are we gonna make money on this. Where’s the revenue coming from? We also need to conduct a market survey.
We need to know, is this a demand? Is there a market for this? Are customers willing to use this product or use this service?
The fourth one is to plan the business organization and operations. What is the structure, what kind of resources do we need? What kind of staffing requirements do we have?
We also want to prepare an opening day balance sheet. What are the…how again, what are the expenses, what’s the revenue and to ensure that being able to determine if we’re gonna make our ROI.
So we want to review and analyze all of the data that we have and with that, we’re going to determine, we’re going to make a go, no-go decision. Meaning, are we going to do this project or this business opportunity or not.
Well, here are some of the best practices to use during your feasibility study.
One is to use templates, tools and surveys that exist today. The great news is, data is becoming more and more prevalent. There are all kinds of technologies. There are groups that they do nothing but research. Things that we can leverage today.
We want to involve the appropriate stakeholders to ensure that input is being considered from the different people involved.
We also want to use again the market research to ensure we’re bringing in good, reliable data.
Do your homework, meaning act like is if this is your project, if it’s your money. So do your homework and do it well and make sure you give credible data.
What Is a Feasibility Report?
So ultimately in the end what we’re doing is, we’re producing and we’re providing a feasibility report. So in that report, think of this is like a template.
So what you’re gonna do is give it an executive summary of the business opportunity that you’re evaluating and the description of the product or the service.
You want to look at different technology considerations. Is it technology that you’re going to use? Are you going to build the technology?
What kind of product and service marketplace and being able again, to identify the specific market you’re going to be targeting? Also, what is the marketing strategy you’re going to use to target the marketplace?
And also what’s the organizational structure? What are the staffing requirements? What people do you need to deliver the product or service and even support it?
So also we want to know the schedule to be able to have the milestones to ensure that as we’re building things, that as we’re spending money that we’re beginning to bring in income to pay and knowing when we’re going to start recuperating some of the funding. Again, which also ties into the financial projections.
Ultimately in this report, you’re going to provide the findings and the recommendations.
Again, we’ll probably talk about technology. Are you going to build it? Are you going to buy it? What are the marketing strategies for the specific marketplace organization? You may have some recommendations for whether you’re going to insource the staff, maybe you are going to outsource some staff and what that looks like and also financial recommendation.
If you’ve been looking for an all-in-one tool that can help with your feasibility study, consider ProjectManager. We offer five project views and countless features that make it seamless to plan projects, organize tasks and stay connected with your team. See what our software can do for you by taking this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
Business Plan Vs. Feasibilty Study
by Brian Hill
Published on 1 Jan 2021
Business plans and feasibility studies are analysis and decision-making tools used by companies. Feasibility studies are used to determine whether a proposed action has a high enough probability of success that it should be undertaken. Business plans are blueprints for implementing actions that have already been deemed feasible by the company's management.
Many Decisions vs. One
Business plans map out the direction a company intends to take to reach its revenue and profit objectives in the future. They are a compilation of numerous decisions made by the management team about how the company should be run. Feasibility studies are designed to provide guidance for one decision. Feasibility studies are often done to decide whether to start the business or not -- whether the likelihood of success is high enough to make the financial risk worthwhile. They can also be used to make decisions about whether to launch a new product in an existing company, or enter a new market -- any activity where there is a question about whether the company should take the action or not. Feasibility studies are sometimes termed cost/benefit analyses because the projected costs of the project are compared to the expected benefits to yield a conclusion.
Although the content and emphasis of business plans vary by company and industry, all plans have many elements in common. They describe the products or services the company intends to sell, why customers need these products or services, the target customers, how the company intends to reach them through its marketing strategy, the background and capabilities of the management team, and risk factors the company may face. They also contain information on projected revenue and profit. Plans contain these specific elements because many times they will be read by investors or other people outside the company, and these individuals want to see very specific information in a plan. Feasibility studies may have some or many of the same elements of a business plan, including a description of the human resources required and financial projections, but all the information leads to a conclusion or recommendation.
Differences
A business plan assumes a business is going to succeed and presents the steps necessary to achieve success. Those in charge of conducting a feasibility study should not have a preconceived view about whether success will be attained. They must be as objective as possible. They conduct research and let the facts lead to the ultimate opinion given in the study. If the study's conclusion is that the project is viable, some of the research done may be included in the company's business plan, such as projections of the size of the market.
Both business plans and feasibility studies attempt to predict future outcomes using assumptions about what is likely to happen in the business environment -- the economy and the company's competition. But this environment is always changing and the assumptions a company uses in its projections of revenue or profit may prove to be incorrect. Companies find that some of the strategies in their plan do not work to the degree the business owner expected, and have to be adjusted. In the case of a feasibility study, an incorrect conclusion can be especially costly -- it could mean launching a venture that has very little chance of surviving or approving a project that wastes the company's human and financial resources.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.1.4: Conducting a Feasibility Analysis
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 73815
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the purpose of a feasibility analysis
- Describe and develop the parts of a feasibility analysis
- Understand how to apply feasibility outcomes to a new venture
As the name suggests, a feasibility analysis is designed to assess whether your entrepreneurial endeavor is, in fact, feasible or possible. By evaluating your management team, assessing the market for your concept, estimating financial viability, and identifying potential pitfalls, you can make an informed choice about the achievability of your entrepreneurial endeavor. A feasibility analysis is largely numbers-driven and can be far more in-depth than a business plan. It ultimately tests the viability of an idea, a project, or a new business. A feasibility study may become the basis for the business plan, which outlines the action steps necessary to take a proposal from ideation to realization. A feasibility study allows a business to address where and how it will operate, its competition, possible hurdles, and the funding needed to begin. The business plan then provides a framework that sets out a map for following through and executing the entrepreneurial vision.
Organizational Feasibility Analysis
Organizational feasibility aims to assess the prowess of management and sufficiency of resources to bring a product or idea to market Figure 5.1.4.1. The company should evaluate the ability of its management team on areas of interest and execution. Typical measures of management prowess include assessing the founders’ passion for the business idea along with industry expertise, educational background, and professional experience. Founders should be honest in their self-assessment of ranking these areas.

Resource sufficiency pertains to nonfinancial resources that the venture will need to move forward successfully and aims to assess whether an entrepreneur has a sufficient amount of such resources. The organization should critically rank its abilities in six to twelve types of such critical nonfinancial resources, such as availability of office space, quality of the labor pool, possibility of obtaining intellectual property protections (if applicable), willingness of high-quality employees to join the company, and likelihood of forming favorable strategic partnerships. If the analysis reveals that critical resources are lacking, the venture may not be possible as currently planned.
Financial Feasibility Analysis
A financial analysis seeks to project revenue and expenses (forecasts come later in the full business plan); project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections Figure 5.1.4.2.

The financial analysis may typically include these items:
- A twelve-month profit and loss projection
- A three- or four-year profit-and-loss projection
- A cash-flow projection
- A projected balance sheet
- A breakeven calculation
The financial analysis should estimate the sales or revenue that you expect the business to generate. A number of different formulas and methods are available for calculating sales estimates. You can use industry or association data to estimate the sales of your potential new business. You can search for similar businesses in similar locations to gauge how your business might perform compared with similar performances by competitors. One commonly used equation for a sales model multiplies the number of target customers by the average revenue per customer to establish a sales projection:
T × A = ST × A = S
Target(ed) Customers/Users × Average Revenue per Customer = Sales Projection
Another critical part of planning for new business owners is to understand the breakeven point , which is the level of operations that results in exactly enough revenue to cover costs. It yields neither a profit nor a loss. To calculate the breakeven point, you must first understand the two types of costs: fixed and variable. Fixed costs are expenses that do not vary based on the amount of sales. Rent is one example, but most of a business’s other costs operate in this manner as well. While some costs vary from month to month, costs are described as variable only if they will increase if the company sells even one more item. Costs such as insurance, wages, and office supplies are typically considered fixed costs. Variable costs fluctuate with the level of sales revenue and include items such as raw materials, purchases to be sold, and direct labor. With this information, you can calculate your breakeven point—the sales level at which your business has neither a profit nor a loss. Projections should be more than just numbers: include an explanation of the underlying assumptions used to estimate the venture’s income and expenses.
Projected cash flow outlines preliminary expenses, operating expenses, and reserves—in essence, how much you need before starting your company. You want to determine when you expect to receive cash and when you have to write a check for expenses. Your cash flow is designed to show if your working capital is adequate. A balance sheet shows assets and liabilities, necessary for reporting and financial management. When liabilities are subtracted from assets, the remainder is owners’ equity.
Market Feasibility Analysis
A market analysis enables you to define competitors and quantify target customers and/or users in the market within your chosen industry by analyzing the overall interest in the product or service within the industry by its target market Figure 5.1.4.3. You can define a market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. This information allows you to better position your company in competing for market share. After you’ve determined the overall size of the market, you can define your target market, which leads to a total available market (TAM) , that is, the number of potential users within your business’s sphere of influence. This market can be segmented by geography, customer attributes, or product-oriented segments. From the TAM, you can further distill the portion of that target market that will be attracted to your business. This market segment is known as a serviceable available market (SAM) .

Projecting market share can be a subjective estimate, based not only on an analysis of the market but also on pricing, promotional, and distribution strategies. As is the case for revenue, you will have a number of different forecasts and tools available at your disposal. Other items you may include in a market analysis are a complete competitive review, historical market performance, changes to supply and demand, and projected growth in demand over time.
ARE YOU READY?
You’ve been hired by a leading hotel chain to determine the market and financial potential for the development of a mixed-use property that will include a full-service hotel in downtown Orlando, located at 425 East Central Boulevard, in Orlando, Florida. The specific address is important so you can pinpoint existing competitors and overall suitability of the site. Using the information given, conduct a market analysis that can be part of a larger feasibility study.
WORK IT OUT
Location Feasibility

You’re considering opening a boutique clothing store in downtown Atlanta. You’ve read news reports about how downtown Atlanta and the city itself are growing and undergoing changes from previous decades. With new development taking place there, you’re not sure whether such a venture is viable. Outline what steps you would need to take to conduct a feasibility study to determine whether downtown Atlanta is the right location for your planned clothing store.
Applying Feasibility Outcomes
After conducting a feasibility analysis, you must determine whether to proceed with the venture. One technique that is commonly used in project management is known as a go-or-no-go decision . This tool allows a team to decide if criteria have been met to move forward on a project. Criteria on which to base a decision are established and tracked over time. You can develop criteria for each section of the feasibility analysis to determine whether to proceed and evaluate those criteria as either “go” or “no go,” using that assessment to make a final determination of the overall concept feasibility. Determine whether you are comfortable proceeding with the present management team, whether you can “go” forward with existing nonfinancial resources, whether the projected financial outlook is worth proceeding, and make a determination on the market and industry. If satisfied that enough “go” criteria are met, you would likely then proceed to developing your strategy in the form of a business plan.
WHAT CAN YOU DO?
Love Beyond Walls
When Terence Lester saw a homeless man living behind an abandoned, dilapidated building, he asked the man if he could take him to a shelter. The man scoffed, replying that Lester should sleep in a shelter. So he did—and he saw the problem through the homeless man’s perspective. The shelter was crowded and smelly. You couldn’t get much sleep, because others would try to steal your meager belongings. The dilapidated building provided isolation away from others, but quiet and security in its own way that the shelter could not. This experience led Lester to voluntarily live as a homeless person for a few weeks. His journey led him to create Love Beyond Walls (www.lovebeyondwalls.org), an organization that aids the homeless, among other causes. Lester didn’t conduct a formal feasibility study, but he did so informally by walking in his intended customers’ shoes—literally. A feasibility study of homelessness in a particular area could yield surprising findings that might lead to social entrepreneurial pursuits.
- What is a social cause you think could benefit from a formal feasibility study around a potential entrepreneurial solution?

- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Commercial Law
- Organisational Behaviour
- Human Resource Management
- Entrepreneurship
Interview Preparation
- Interview Preparation For Software Developers
- Must Coding Questions - Company-wise
- Must Do Coding Questions - Topic-wise
- Company-wise Practice Problems
- Company Preparation
- Competitive Programming
- Software Design-Patterns
- Company-wise Interview Experience
- Experienced - Interview Experiences
- Internship - Interview Experiences
Practice @Geeksforgeeks
- Problem of the Day
- Topic-wise Practice
- Difficulty Level - School
- Difficulty Level - Basic
- Difficulty Level - Easy
- Difficulty Level - Medium
- Difficulty Level - Hard
- Leaderboard !!
- Explore More...
Data Structures
- Linked List
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- Advance Data Structures
- All Data Structures
- Analysis of Algorithms
- Searching Algorithms
- Sorting Algorithms
- Pattern Searching
- Geometric Algorithms
- Mathematical Algorithms
- Randomized Algorithms
- Greedy Algorithms
- Dynamic Programming
- Divide & Conquer
- Backtracking
- Branch & Bound
- All Algorithms
Programming Languages
Web technologies.
- Tailwind CSS
- Web Browser
- File Formats
Computer Science Subjects
- Operating Systems
- Computer Network
- Computer Organization & Architecture
- Compiler Design
- Digital Elec. & Logic Design
- Software Engineering
- Engineering Mathematics
Data Science & ML
- Complete Data Science Course
- Data Science Tutorial
- Machine Learning Tutorial
- Deep Learning Tutorial
- NLP Tutorial
- Machine Learning Projects
- Data Analysis Tutorial
Tutorial Library
- Python Tutorial
- Django Tutorial
- Pandas Tutorial
- Kivy Tutorial
- Tkinter Tutorial
- OpenCV Tutorial
- Selenium Tutorial
- GATE CS Notes
- Gate Corner
- Previous Year GATE Papers
- Last Minute Notes (LMNs)
- Important Topic For GATE CS
- GATE Course
- Previous Year Paper: CS exams
- Git Tutorial
- AWS Tutorial
- Docker Tutorial
- Kubernetes Tutorial
- Microsoft Azure Tutorial
QUIZ Section
- Python Quiz
- JavaScript Quiz
- Data Structures Quiz
- Algorithms Quiz
- Topic-wise MCQs
School Content
- CBSE Notes 2023-24
- CBSE Class 8 Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Notes
- School Programming
- English Grammar
- Top 100 Puzzles
- Mathematical Riddles
Difference between Feasibility Study and Business Plan
Feasibility Study and Business Plan are essential tools in the business development process. They serve different purposes and are conducted at different stages. A feasibility study helps determine the viability of a business idea; whereas, a business plan provides a detailed roadmap for executing that idea and achieving business goals.
What is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a comprehensive assessment conducted at the early stages of a business idea or project to evaluate its potential viability and identify potential risks and challenges. The primary purpose of a feasibility study is to determine whether the proposed business venture is feasible and worth pursuing further.
Features of the Feasibility Study are:
- Market Analysis: Feasibility Study evaluates the target market , including its size, growth potential, demographics, and competition. This involves researching customer needs, preferences, and behavior to assess demand for the proposed product or service .
- Technical Feasibility: A feasibility study assesses the technical requirements and capabilities needed to develop and deliver the product or service. This may involve evaluating technology, equipment, facilities, and expertise required for production or implementation.
- Financial Feasibility: A feasibility study conducts financial analysis to estimate the costs involved in starting and operating the business, as well as potential revenue and profitability. This includes preparing financial projections, such as income statements , cash flow statements , and Return on Investment (ROI) calculations.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, strategies, operations, and financial projections of a business. It serves as a roadmap for the organization’s future direction and provides a detailed blueprint for how the business will be structured, managed, and operated.
Features of a Business Plan are:
- Executive Summary: A business plan gives a brief overview of the business concept, objectives, products or services offered, target market, competitive advantage, and financial projections.
- Company Description: It gives detailed information about the business, including its history, mission statement, vision, values, legal structure, location, and ownership.
- Market Analysis: A business plan is formed after analyzing the target market, including its size, growth potential, demographics, buying behavior , market trends, and competition. This section also outlines the business’s market positioning and competitive strategy.
Feasibility Study and Business Plan – FAQs
When should a feasibility study be conducted.
A feasibility study is typically conducted at the early stages of developing a business idea or project, before significant resources are invested. It helps entrepreneurs and stakeholders make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the venture.
Who conducts a feasibility study?
Feasibility Studies are often conducted by entrepreneurs, business owners, project managers, consultants, or other professionals with expertise in the relevant industry or field. They may also involve collaboration with specialists such as market researchers, engineers, financial analysts, and legal advisors.
When should a business plan be developed?
A business plan is typically developed after a feasibility study has been conducted and the decision to move forward with the business venture has been made. It provides a detailed blueprint for executing the business idea and achieving its objectives.
Who uses a business plan?
Business plans are used by entrepreneurs, startups, existing businesses, investors, lenders, partners, employees, and other stakeholders interested in understanding the organization’s goals, strategies, operations, and financial prospects.
What are the benefits of conducting a feasibility study?
Benefits of conducting a feasibility study include minimizing risks, identifying potential challenges and opportunities, validating assumptions, attracting investors or lenders, guiding decision-making , and increasing the likelihood of success for the proposed business venture.
Please Login to comment...
- Commerce - Difference Between
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- Otter AI vs Dragon Speech Recognition: Which is the best AI Transcription Tool?
- Google Messages To Let You Send Multiple Photos
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

The Latest Industry News & Insights
#e2 #l1 #eb5 #sba #investor #financial #franchise #hemp #startup
The Benefits of an Outside Review of Your Business Concept: The Case for a Pre-Feasibility Study
- Advisory , Business Plans , Commercial
- 01 Dec, 2020
Pre-feasibility studies (PFS) can be a vital part of business and strategic planning processes. Yet, they are not discussed or formally produced as often as business plans. Despite the lack of notoriety, feasibility studies play a very important role in ensuring you are pursuing an idea that is likely to lead to success.
A pre-feasibility study is an internal study that examines the viability of an idea. This includes for individual projects as well as full business plans. The study will ensure the project/business idea is advantageous economically, as well as technically and legally sound.
Sometimes pre-feasibility studies look at several options to narrow down potential ideas, especially when it comes to projects. There are those that view pre-feasibility studies as narrowing down several ideas and refer to it as a feasibility study only when it is concentrated on thoroughly investigating the most viable idea(s). However, these terms are typically used interchangeably.
Upon reading the definition, a feasibility study may seem indistinguishable from a business plan but the expected outcome, way they are approached, and resulting document varies significantly. Gary Wright, a management specialist from Iowa State University, explains it this way, “The feasibility study provides an investigating function. It addresses the question of ‘Is this a viable business venture?’ The business plan provides a planning function. The business plan outlines the actions needed to take the proposal from idea to reality.”
In order to illustrate what the final outcome may look like, Joorney’s pre-feasibility studies include the following sections:
- Executive Summary
- Service Description
- Competitors Analysis
- Projected Financials with Indicative Investment Required, IRR, NPV
- Risks and Mitigating Actions
- Market Survey with a Focus on Supply & Demand
- Sales and Marketing Strategy
- Operational Plan
- SWOT Analysis

Often times pre-feasibility studies are done internally, but that doesn’t need to be the case. It is wise to work with outside advisors or business consultants, like Joorney’s, to get a truly objective view of your business idea or development project. We collaborate with our clients to fully evaluate their ideas and produce a final document that thoroughly lays out the results from the study, organized into the sections referred to above.
As it relates to a business plan, conducting a pre-feasibility study, especially one done in conjunction with an outside firm, will strengthen the plan and make a stronger case to potential investors or lenders. It not only shows that you have done your due diligence but that outside, objective business experts have also confirmed the validity of your plan. Through a proper feasibility analysis, it becomes easier to understand and support how much funding is needed and how it will be spent which lays the groundwork for explaining why a capital infusion is required.
Although the pre-feasibility study and business plan are different, you will be able to use a great deal of the research from the PFS to build the foundation of your business plan. This is particularly evident in the market research and financial sections. Both processes and documents stand on their own merits but are even more useful when paired with the other.

Joorney at the 2024 Small Business Expo – Miami

Webinar Recap — Pathways towards the EB2-NIW for Information Technology (IT) and Energy Sector Professionals

Pathways towards the EB2-NIW for Information Technology (IT) and Energy Sector Professionals

Marketing Success for Immigration Lawyers: Expert Tips fo...

Webinar Recap — Pathways towards the EB2-NIW for Informat...

Pathways towards the EB2-NIW for Information Technology (...

Joorney at the 45th Annual AILA South Florida Immigration...

Joorney at the 2024 AILA Investors and Entrepreneurs Conf...

Webinar Recap: If You Don’t See RFEs Then You’re Not Doin...

If You Don’t See RFEs, You’re Not Doing EB2-NIWs – ...
In the press:.

- Immigration
- Testimonials
- Start-up Advisory
- M&A Advisory
- Pro Bono Work
- Premium Market Research
- Joorney Digital
- Partner Program
- Joorney Blog
- Ask the Joorney Expert
We Offer Services. Built On Trust
1-844 (566-7639) CALL US

Miami 1688 Meridian Ave Ste 700 Miami Beach, FL 33139
Canada 1200 McGill College Avenue Suite 1100, Montreal, QC, H3B4G7
France 11 rue de Rouvray 92200 Neuilly sur Seine
Serbia Bulevar Kralja Aleksandra 28 Floor 2, 11000 Belgrade
Australia Unit A1 / 35-39 Bourke Road, Alexandria NSW 2015
Immigration | Commercial | Start-Up Advisory | M&A Advisory |
Copyright © 2024 Joorney. All rights reserved. | Privacy Policy
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Email Address *
- Country Code *
- Phone Number *
- How did you hear about us? * How did you hear about us? (Required) Immigration Attorney Friend Google Ads Google Search Webinar Tradeshow French Founders AILA FACC Consultant Real Estate Agent Accountant/CPA Business Broker LinkedIn Facebook BBB Other
- What is the attorney's name?
- What is the tradeshows name?
- What is the consultant name?
- What is the real estate agent name?
- What is the accountant/CPA name?
- What is the business broker name?
- Company Name
- Do you have a website? (Optional) Do you have a website? (Optional) Yes, I do. No, I don't.
- What is your website address? (Optional)
- Would you like help building a website for your business? (Optional) Would you like help building a website for your business? (Optional) Yes, please! No, thank you.
- When would you expect to need to start these services? (Optional) How soon would you like to be contacted about building a website? (Optional) ASAP! Once I start my business plan. After my business plan is finalized. After my visa is approved. I'll reach out when I'm ready.
- Other Industry
- How Do you Prefer To Be Contacted? * How Do you Prefer To Be Contacted? (Required) Phone Zoom Whatsapp Skype Wechat
- What Language Do You Prefer To Speak? (Optional) What Language Do You Prefer To Speak? (Optional) English Spanish Portuguese French Chinese Russian Other
- Other Language
- I am....(Required) * I am....(Required) Applying For A Visa An Immigration Attorney A Start-Up An Established Business An M&A Firm A Business Broker Other
- Select A Business Stage (Optional) Select A Business Stage (Optional) Idea Pre-revenue Post-revenue I'm not sure
- What Is Your Average Deal Size (Optional) What Is Your Average Deal Size (Optional) Under $1M $1-10M $10-20M Over $20M
- What Service Are You Interested In? - ALL (Required) * What Service Are You Interested In? (Required) Immigration Business Plan SBA/Bank Loan Business Plan Franchise Business Plan Grant Business Plan Landlord Deck Market Research Marketing & Sales Plan Financial Model Investor Business Plan Pitch Deck Feasibility Study Idea Selection Capital Raise Strategic Business Plan Debt Financing Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) Executive Summary Teaser Other
- What Service Are You Interested In? - Startup (Required) * What Service Are You Interested In? (Required) SBA/Bank Loan Business Plan Grant Business Plan Market Research Marketing & Sales Plan Financial Model Investor Business Plan Pitch Deck Feasibility Study Idea Selection Capital Raise Strategic Business Plan Debt Financing Executive Summary Teaser
- What Service Are You Interested In? - M&A Advisor & Business Broker (Required) * What Service Are You Interested In? (Required) Confidential Information Memorandum (CIM) Executive Summary Teaser
- What Service Are You Interested In? - Established Business What Service Are You Interested In? (Required) SBA/Bank Loan Business Plan Franchise Business Plan Grant Business Plan Landlord Deck Market Research Marketing & Sales Plan Financial Model Investor Business Plan Pitch Deck Feasibility Study Idea Selection Capital Raise Strategic Business Plan Debt Financing Executive Summary Teaser
- Other Service
- Visa Type? * What Immigration Business Plan Visa Type Do You Need? (Required) E2 L1 EB2 NIW EB5 Direct EB-5 Regional Center H1B O1 EB1A EB1C Canada I am not sure
- Are you the Visa Applicant? Are you the Visa Applicant? (Optional) Yes, I am the visa applicant No, I'm not the visa applicant
- What is your relationship to the visa applicant? What is your relationship to the visa applicant? (Optional) Family Friend Attorney Other
- Other relationship
- Is this a New Application, RFE, Renewal or Denial? Is this a New Application, RFE, Renewal or Denial? (Optional) New Visa Application RFE Renewal Denial I don't know
- Do you have a deadline? * Do you have a visa application deadline? (Optional) Yes, I have a deadline No, I don't have a deadline
- By When? MM slash DD slash YYYY
- Details/Notes?
- Google Re-Captcaha
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

- E2 Visa Business Plan
- Pitch Decks
- Market Research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For a general set of guidelines to help you get started, here are some basic steps to conduct and report a feasibility study for major product opportunities or features. 1. Clearly define the opportunity. Imagine your user base is facing a significant problem that your product doesn't solve. This is an opportunity.
The technical feasibility study assesses the practicality of implementing your project from a technical standpoint. It involves evaluating the project's design, technical requirements, technological feasibility, resource availability, and risk analysis. Let's delve into each aspect in more detail.
Feasibility study vs. business plan. A business plan is a formal document of your organization's goals. You typically write a business plan when founding your company, or when your business is going through a significant shift. Your business plan informs a lot of other business decisions, including your three to five year strategic plan.
Social objectives. For example, a sample of business goals and objectives for a business plan for a bakery could be: To increase its annual revenue by 20% in the next year. To reduce its production costs by 10% in the next six months. To launch a new product line of gluten-free cakes in the next quarter.
The business plan should be thought of in terms of growth and sustainability, whereas the feasibility study should be thought of in terms of concept viability. This is all you need to know and understand about feasibility study and business plan. Get ready to apply your knowledge in the real words with lots of success.
Here are the key differences between a feasibility study and a business plan: Differences in Purpose. Feasibility Study: Feasibility studies are conducted in the early stages of project development or business planning. Their primary purpose is to determine whether a proposed project or business idea is viable and should be pursued.
Assess the legal and financial considerations of the project, such as zoning laws and license requirements. A feasibility study projects the success or failure of a potential business idea. The ...
An effective Feasibility Study is crucial in achieving a goal or decision-making in Project Management and business. It serves as a single and integrated examination to approve a project, startup, or investment by determining if it can be implemented, if it will succeed and if it will be sustainable to operate the project, the startup or the investment.
Step 1: Do the preliminary analysis. Running a full feasibility study can eat up time and technical resources. Instead of diving straight into the assessment, try dipping your toes in first by doing a preliminary analysis. Think of it like a test before the big test. 🤓.
Financial Feasibility Analysis. A financial analysis seeks to project revenue and expenses (forecasts come later in the full business plan); project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections Figure 11.13. Figure 11.3.2 11.3. 2: An analysis of financial feasibility focuses on expenses, cash flow ...
A feasibility study may become the basis for the business plan, which outlines the action steps necessary to take a proposal from ideation to realization. A feasibility study allows a business to address where and how it will operate, its competition, possible hurdles, and the funding needed to begin.
Feasibility Study: A feasibility study is an analysis of how successfully a project can be completed, accounting for factors that affect it such as economic, technological, legal and scheduling ...
A feasibility study for small business is an in-depth research and financial analysis that recommends if one should pursue a business idea or product. The study contains estimates of items such as income, costs, obstacles, and technical challenges. Typically, a feasibility study for a small business costs a minimum of $5,000.
A feasibility study is an essential tool for any business looking to launch a new venture or product. It provides valuable insights that can help entrepreneurs and investors determine whether their idea has the potential to be successful. By conducting a thorough analysis of the market, competition, and financials of the proposed venture, a ...
3. Conduct a Market Survey or Perform Market Research. This step is key to the success of your feasibility study, so make your market analysis as thorough as possible. It's so important that if your organization doesn't have the resources to do a proper one, then it is advantageous to hire an outside firm to do so.
Sale. Feasibility Studies: An Architect's Guide. Farrall, Peter (Author) English (Publication Language) 128 Pages - 02/01/2023 (Publication Date) - RIBA Publishing (Publisher) −$3.99 $28.96. Buy on Amazon. Technical requirements are another critical aspect considered in a feasibility study.
Feasibilty Study. Business plans and feasibility studies are analysis and decision-making tools used by companies. Feasibility studies are used to determine whether a proposed action has a high enough probability of success that it should be undertaken. Business plans are blueprints for implementing actions that have already been deemed ...
2. Never make a decision to proceed with a feasibility study or accept a feasibility study on negative reactions; for example, out of resentment or envy toward middlemen, money lenders, etc. 3. For group action, a few reliable and loyal persons are superior to a larger number of doubtful persons. 4.
A feasibility analysis is largely numbers-driven and can be far more in-depth than a business plan. It ultimately tests the viability of an idea, a project, or a new business. A feasibility study may become the basis for the business plan, which outlines the action steps necessary to take a proposal from ideation to realization.
The outcome of the feasibility study helps selection of a defined project which meets the stated project objectives, together with a broad plan of implementation. If the feasibility study shows that the objectives of the owner are best met through the ideas generated then the project is moved to further stage to deliver intended objectives of ...
A feasibility study is an analysis of whether a business idea is practical and viable, while a business plan outlines the strategy and operations of a business in detail. Essentially, a feasibility study is a precursor to a business plan, helping to determine whether the business idea is worth pursuing before investing time and resources into developing a full plan.
Meaning. A feasibility study is conducted at the early stages of a business idea to assess its viability and determine whether it is feasible to pursue further. A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, strategies, operations, and financial projections of an existing or proposed business. Focus.
As it relates to a business plan, conducting a pre-feasibility study, especially one done in conjunction with an outside firm, will strengthen the plan and make a stronger case to potential investors or lenders. It not only shows that you have done your due diligence but that outside, objective business experts have also confirmed the validity ...
It presents a conceptual vision for the future only, with long-range goals and objectives in regards to land use and road improvements. Note: The proposed road improvements shown in the plan are conceptual as well and subject to further study, political support, environmental & feasibility analysis, and engineering.