- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
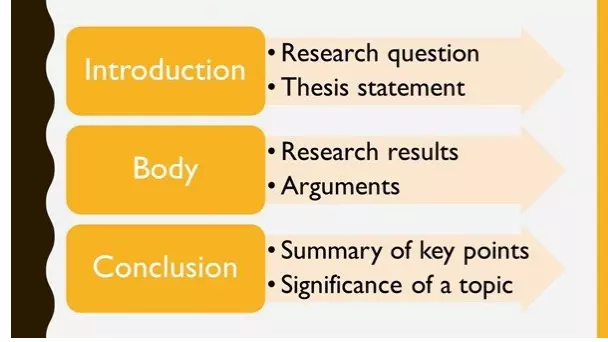
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- Learning Tips
- Exam Guides
- School Life
How Many Paragraphs in an Essay, Research Paper or in Pages
- by Joseph Kenas
- January 18, 2024

For many students, deciding the number of paragraphs to be included in their research papers can be a big challenge.
Various factors determine the number of paragraphs in a research paper as we shall discuss later in this article. However, before exploring that, it is important to have an informed estimate on the number of paragraphs that should be contained in a research paper.
How Many Paragraphs in an Essay or Research Paper?
As aforementioned, various factors can determine the number of paragraphs in a research paper. However, to have an informed estimate, we have to consider the structure of a typical research paper.
The number of paragraphs in an essay or paper depends on its length in terms of pages. For instance, there should be 3 paragraphs in a 1-page essay or 5 paragraphs for a 2-page one. This includes an introduction paragraph, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Essays longer than that have more paragraphs depending on the length and the instructions from your faculty.
Longer research papers have many paragraphs compared to short essays. A typical research paper contains an introduction, literature review section, methodology section, findings and discussions section, and finally the conclusion.
For college or undergraduate research papers, your introduction and the conclusion should be made of a single paragraph each. Therefore, the introduction and the conclusion will account for 2 paragraphs in your research paper.
Now, the literature review should review credible and recent sources that relate to your research topic.
You are required to identify at least 3 sources and review them within the literature review section while making sure that you relate them to your research topic.
Therefore, if we assume that the review of each source will take 1 paragraph, then you are supposed to have a minimum of 3 paragraphs within the literature review.
When it comes to the methodology section, you are supposed to present the different strategies you will use to gather your research data.
Methods of data collection include but are not limited to experiments, interviews, sampling, questionnaires, observation, and so on. Here, you should be clear and succinct concerning the methods of data collection so that the reader can understand.
Furthermore, you should provide the population of the study, the variables of the methodologies, and other important research information.
You should also connect the methodologies to the research hypothesis or main claim. As such, the methodology section will take about 2 paragraphs for a college-level research paper.
The findings and discussion section should contain more paragraphs compared to the rest of the sections. This is because you are discussing the findings of your research and relating them to your topic and original claims. This section should not be less than 4 paragraphs in length.
Therefore, if we add the 2 paragraphs for the introduction and the conclusion, 3 paragraphs for the literature review, 2 paragraphs for the methodology, and 4 paragraphs for the findings and discussions, you will have a total of 11 paragraphs.
Depending on the content you will be writing, a research paper will have between 10 and 12 paragraphs.
You should note that this is for a short research paper. A research paper may be more than 20 pages and therefore the number of paragraphs will increase.
However, the basic structure of a research paper should act as a guideline. The number of paragraphs provided above is a minimum.
Factors Determining the Number of Paragraphs in a Paper
1. professor’s instructions.
The professor’s instructions are key in determining the number of paragraphs in a research paper. They may be very specific in terms of their number due to the research paper structure they give you.
They may provide the basic or typical essay structure and specify the number of paragraphs required for each section.
2. The Length of the Paper
This is an obvious determinant of the number of paragraphs in a research paper. If the research paper tackles a complex topic, it will be longer.
Check out our word to pages converter tool that can help you know the number of pages so that you can monitor the length of your paper.
A longer research paper will have more paragraphs while shorter research papers will have fewer paragraphs.
If your professor or instructor requires you to submit a long research paper, let’s say 15 pages and more, the paper will have more paragraphs.
3. The Size of the Paragraphs
The size of the paragraph is also a determinant of the number of paragraphs in a research paper. It should be noted that body paragraphs contain individual claims that are supported with evidence within a single paragraph.

If you have a claim that needs further elaboration and more supporting evidence, you may be forced to write a longer paragraph that may consume more space within a page.
Therefore, if the size of your paragraphs is larger, your research paper will contain fewer paragraphs because they are consuming more space within the paper.
However, if the size of the paragraphs is smaller, then there will be more paragraphs in your search paper.
4. Personal Preference
At times, your professor may give you the freedom to come up with your research paper. This will include the number of pages, the structure, the number of paragraphs, and even the topic.
In this case, you will craft your research paper based on your preference. You may decide to include more paragraphs that contain more claims to support your argument or even fewer paragraphs.
You may decide to write larger or smaller paragraphs depending on the content you are including in your paragraphs. In the end, you may have more or fewer paragraphs.
5. Formatting Style
As aforementioned, there is a basic or typical formatting style for college-level research papers. When following such a formatting style, then a research paper will have a minimum of 12 paragraphs.

However, some research paper formats will require you to include more paragraphs in the form of the abstract.
Background of study that comes after the introduction, data analysis that comes after the research methodology, and limitations plus the future scope of your research.
This will add more paragraphs to your research paper.
6. Number of Graphics in the Essay
Some research papers will require you to represent your data in a graphical format so that your readers can easily understand the data. Good research papers should contain a few graphics.
You should remember that graphics are not part of the text hence they are not part of a paragraph. Be mindful that everything counts. Even spaces do count as characters when you are writing an essay or a paper.
Though this is the case, they still occupy some space within the research paper. As such, the more the graphics in the paper, the lesser the paragraphs, and vice versa.
FAQs on Paragraphs in an Essay
How many paragraphs are in an essay.
To respond to this question, it should be noted that an essay is less complex compared to a research paper because it tackles simpler topics and doesn’t require too much research. An essay does not need to be divided into sections like in research papers. As such, they have fewer paragraphs compared to research papers.
Typically, an essay will contain 1 paragraph for the introduction, 3 paragraphs for the body, and 1 paragraph for the conclusion, making the total number of paragraphs to be 5. However, depending on the topic, the number of body paragraphs may increase.
How many sentences are in a paragraph?
A paragraph should have between 4 and 6 complete sentences. However, the number of sentences in a paragraph is determined by the length of an individual sentence within the paragraph. The longer it is, the fewer the sentences will be, and vice versa.
How many paragraphs are 10 pages double-spaced?
When calculating this, it is assumed that a double-spaced page should contain 3 paragraphs. Therefore, if there are 10 pages, there will be a total of 30 paragraphs in the paper.
How many sentences is a paragraph in college?
A college-level paragraph should contain adequate details to support individual claims. As such, it should contain more, well-constructed sentences. When this is considered, such a paragraph should have a minimum of 5 sentences to adequately discuss and support a claim.

Joseph is a freelance journalist and a part-time writer with a particular interest in the gig economy. He writes about schooling, college life, and changing trends in education. When not writing, Joseph is hiking or playing chess.
How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How Many Paragraphs Should an Essay Have?

- 6-minute read
- 19th May 2023
You have an essay to write. You’ve researched the topic and crafted a strong thesis statement . Now it’s time to open the laptop and start tapping away on the keyboard. You know the required word count, but you’re unsure of one thing: How many paragraphs should you have in the essay? Gee, it would’ve been nice if your professor had specified that, huh?
No worries, friend, because in this post, we’ll provide a guide to how many paragraphs an essay should have . Generally, the number of paragraphs will depend on how many words and how many supporting details you need (more on that later). We’ll also explore the concept of paragraphs if you’re wondering what they’re all about. And remember, paragraphs serve a purpose. You can’t submit an essay without using them!
What Is a Paragraph?
You likely know what a paragraph is, but can you define it properly in plain English? Don’t feel bad if that question made you shake your head. Off the top of our heads, many of us can’t explain what a paragraph is .
A paragraph comprises at least five sentences about a particular topic. A paragraph must begin with a well-crafted topic sentence , which is then followed by ideas that support that sentence. To move the essay forward, the paragraph should flow well, and the sentences should be relevant.
Why Are Paragraphs Important?
Paragraphs expand on points you make about a topic, painting a vivid picture for the reader. Paragraphs break down information into chunks, which are easier to read than one giant, uninterrupted body of text. If your essay doesn’t use paragraphs, it likely won’t earn a good grade!
How Many Paragraphs Are in an Essay?
As mentioned, the number of paragraphs will depend on the word count and the quantity of supporting ideas required. However, if you have to write at least 1,000 words, you should aim for at least five paragraphs. Every essay should have an introduction and a conclusion. The reader needs to get a basic introduction to the topic and understand your thesis statement. They must also see key takeaway points at the end of the essay.
As a rule, a five-paragraph essay would look like this:
- Introduction (with thesis statement)
- Main idea 1 (with supporting details)
- Main idea 2 (with supporting details)
- Main idea 3 (with supporting details)
Your supporting details should include material (such as quotations or facts) from credible sources when writing the main idea paragraphs.
If you think your essay could benefit from having more than five paragraphs, add them! Just make sure they’re relevant to the topic.
Professors don’t care so much about the number of paragraphs; they want you to satisfy the minimum word requirement. Assignment rubrics rarely state the number of required paragraphs. It will be up to you to decide how many to write, and we urge you to research the assigned topic before writing the essay. Your main ideas from the research will generate most of the paragraphs.
When Should I Start a New Paragraph?
Surprisingly, some students aren’t aware that they should break up some of the paragraphs in their essays . You need to start new paragraphs to keep your reader engaged.
As well as starting a new paragraph after the introduction and another for the conclusion, you should do so when you’re introducing a new idea or presenting contrasting information.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Starting a paragraph often involves using transitional words or phrases to signal to the reader that you’re presenting a new idea. Failing to use these cues may cause confusion for the reader and undermine your essay’s coherence.
Let’s consider examples of transitional words and phrases in action in a conclusion. Note that the essay is about too much mobile device screen time and that transitional words and phrases can occur later in a paragraph too:
Thanks to “In conclusion” and “Additionally,” the reader clearly knows that they are now in the conclusion stage. They can also follow the logic and development of the essay more easily.
How Do I Know Whether I Have Enough Paragraphs?
While no magic number exists for how many paragraphs you need, you should know when you have enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. It helps if you can answer yes to the following questions:
- Does my essay have both an introduction and a conclusion?
- Have I provided enough main ideas with supporting details, including quotes and cited information?
- Does my essay develop the thesis statement?
- Does my essay adequately inform the reader about the topic?
- Have I provided at least one takeaway for the reader?
Conclusion
Professors aren’t necessarily looking for a specific number of paragraphs in an essay; it’s the word count that matters. You should see the word count as a guide for a suitable number of paragraphs. As a rule, five paragraphs should suffice for a 1,000-word essay. As long as you have an introduction and a conclusion and provide enough supporting details for the main ideas in your body paragraphs, you should be good to go.
Remember to start a new paragraph when introducing new ideas or presenting contrasting information. Your reader needs to be able to follow the essay throughout, and a single, unbroken block of text would be difficult to read. Transitional words and phrases help start new paragraphs, so don’t forget to use them!
As with any writing, we always recommend proofreading your essay after you’ve finished it. This step will help to detect typos, extra spacing, and grammatical errors. A second pair of eyes is always useful, so we recommend asking our proofreading experts to review your essay . They’ll correct your grammar, ensure perfect spelling, and offer suggestions to improve your essay. You can even submit a 500-word document for free!
1. What is a paragraph and what is its purpose?
A paragraph is a group of sentences that expand on a single idea. The purpose of a paragraph is to introduce an idea and then develop it with supporting details.
2. What are the benefits of paragraphs?
Paragraphs make your essay easy to read by providing structure and flow. They let you transition from one idea to another. New paragraphs allow you to tell your reader that you’ve covered one point and are moving on to the next.
3. How many paragraphs does a typical essay have?
An essay of at least 1,000 words usually has five paragraphs. It’s best to use the required word count as a guide to the number of paragraphs you’ll need.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Paragraph Development
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A paragraph is a group of related sentences that support one main idea. In general, paragraphs consist of three parts: the topic sentence, body sentences, and the concluding or the bridge sentence to the next paragraph or section. Paragraphs show where the subdivisions of a research paper begin and end and, thus, help the reader see the organization of the essay and grasp its main points.
Arnaudet, Martin L. and Mary Ellen Barrett. Paragraph Development: A Guide for Students of English . 2nd edition. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall Regents, 1990.
Importance of Constructing Good Paragraphs
Paragraphs are the building blocks of papers . Without well-written paragraphs that flow logically from one idea to the next and that inform and help support in some meaningful way the central research problem being investigated, your paper will not be viewed as credible and, well, you'll probably receive a poor grade.
Here are some suggestions for troubleshooting common problems associated with developing paragraphs:
1. The paragraph has no controlling idea . Imagine each paragraph as having three general layers of text. The core content is in the middle. It includes all the evidence you need to make the point. However, this evidence needs to be introduced by a topic sentence in some way or your readers don't know what to do with all the evidence you have given them. Therefore, the beginning of the paragraph explains the controlling idea of the paragraph. The last part of the paragraph tells the reader how the paragraph relates to the broader argument and often provides a transition to the next idea. Once you have mastered the use of topic sentences, you may decide that the topic sentence for a particular paragraph really should not be the first sentence of the paragraph. This is fine—the topic sentence can actually go at the beginning, middle, or end of a paragraph; what's important is that it is there to inform readers what the main idea of the paragraph is and how it relates back to the broader thesis of your paper.
2. The paragraph has more than one controlling idea . This is the most common reason why a paragraph is too long. If a paragraph is more than a page long, it likely contains more than one controlling idea. In this case, consider eliminating sentences that relate to the second idea, with the thought that maybe they don't really inform and help support the central research problem, or split the paragraph into two or more paragraphs, each with only one controlling idea.
3. Transitions are needed within the paragraph . You are probably familiar with the idea that transitions may be needed between paragraphs or sections in a paper. Sometimes they are also helpful within the body of a single paragraph. Within a paragraph, transitions are often single words or short phrases that help to establish relationships between ideas and to create a logical progression of those ideas in a paragraph. This is especially true within paragraphs that discuss multiple examples or discuss complex ideas, issues, or concepts.
Arnaudet, Martin L. and Mary Ellen Barrett. Paragraph Development: A Guide for Students of English . 2nd edition. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall Regents, 1990; Paragraph Development: Importance of Constructing Good Paragraphs. AP English Literature and Composition. Edublogs, 2012; Paragraphing. Centre for Applied Linguistics. University of Warwick.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Structure
Most paragraphs in an essay parallel the general three-part structure of each section of a research paper and, by extension, the overall research paper, with an introduction, a body that includes facts and analysis, and a conclusion. You can see this structure in paragraphs whether they are narrating, describing, comparing, contrasting, or analyzing information. Each part of the paragraph plays an important role in communicating the meaning you intend to covey to the reader.
Introduction : the first section of a paragraph; should include the topic sentence and any other sentences at the beginning of the paragraph that give background information or provide a transition.
Body : follows the introduction; discusses the controlling idea, using facts, arguments, analysis, examples, and other information.
Conclusion : the final section; summarizes the connections between the information discussed in the body of the paragraph and the paragraph’s controlling idea. For long paragraphs, you may also want to include a bridge sentence that introduces the next paragraph or section of the paper. In some instances, the bridge sentence can be written in the form of a question. However, use this rhetorical device sparingly, otherwise, ending a lot of paragraphs with a question to lead into the next paragraph sounds cumbersome.
NOTE: This general structure does not imply that you should not be creative in your writing. Arranging where each element goes in a paragraph can make a paper more engaging for the reader. However, do not be too creative in experimenting with the narrative flow of paragraphs. To do so may distract from the main arguments of your research and weaken the quality of your academic writing.
II. Development and Organization
Before you can begin to determine what the composition of a particular paragraph will be, you must consider what is the most important idea that you are trying to convey to your reader. This is the "controlling idea," or the thesis statement from which you compose the remainder of the paragraph. In other words, your paragraphs should remind your reader that there is a recurrent relationship between your controlling idea and the information in each paragraph. The research problem functions like a seed from which your paper, and your ideas, will grow. The whole process of paragraph development is an organic one—a natural progression from a seed idea to a full-blown research study where there are direct, familial relationships in the paper between all of your controlling ideas and the paragraphs which derive from them. The decision about what to put into your paragraphs begins with brainstorming about how you want to pursue the research problem . There are many techniques for brainstorming but, whichever one you choose, this stage of paragraph development cannot be skipped because it lays a foundation for developing a set of paragraphs [representing a section of your paper] that describes a specific element of your overall analysis. Each section is described further in this writing guide. Given these factors, every paragraph in a paper should be :
- Unified —All of the sentences in a single paragraph should be related to a single controlling idea [often expressed in the topic sentence of the paragraph].
- Clearly related to the research problem —The sentences should all refer to the central idea, or the thesis, of the paper.
- Coherent —The sentences should be arranged in a logical manner and should follow a definite plan for development.
- Well-developed —Every idea discussed in the paragraph should be adequately explained and supported through evidence and details that work together to explain the paragraph's controlling idea.
There are many different ways you can organize a paragraph . However, the organization you choose will depend on the controlling idea of the paragraph. Ways to organize a paragraph in academic writing include:
- Narrative : Tell a story. Go chronologically, from start to finish.
- Descriptive : Provide specific details about what something looks or feels like. Organize spatially, in order of appearance, or by topic.
- Process : Explain step by step how something works. Perhaps follow a sequence—first, second, third.
- Classification : Separate into groups or explain the various parts of a topic.
- Illustrative : Give examples and explain how those examples prove your point.
Arnaudet, Martin L. and Mary Ellen Barrett. Paragraph Development: A Guide for Students of English . 2nd edition. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall Regents, 1990; On Paragraphs. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Organization: General Guidelines for Paragraphing. The Reading/Writing Center. Hunter College; The Paragraph. The Writing Center. Pasadena City College; Paragraph Structure. Effective Writing Center. University of Maryland; Paragraphs. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; Paragraphs. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Paragraphs. University Writing Center. Texas A&M University; Paragraphs and Topic Sentences. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Weissberg, Robert C. “Given and New: Paragraph Development Models from Scientific English.” TESOL Quarterly 18 (September 1984): 485-500.
Writing Tip
Coherence of Ideas is What Matters, Not Length!
Do not think of developing paragraphs in terms of their length. Length and appearance do not determine whether a part in your paper is a paragraph. It is the unity and coherence of ideas represented in a sentence or among sentences that constitutes to a good paragraph.
Bahl, Vik. Paragraph Development. English 127 Research Writing syllabus. Green River Community College.
- << Previous: Making an Outline
- Next: Research Process Video Series >>
- Last Updated: May 1, 2024 9:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

What this handout is about
This handout will help you understand how paragraphs are formed, how to develop stronger paragraphs, and how to completely and clearly express your ideas.
What is a paragraph?
Paragraphs are the building blocks of papers. Many students define paragraphs in terms of length: a paragraph is a group of at least five sentences, a paragraph is half a page long, etc. In reality, though, the unity and coherence of ideas among sentences is what constitutes a paragraph. A paragraph is defined as “a group of sentences or a single sentence that forms a unit” (Lunsford and Connors 116). Length and appearance do not determine whether a section in a paper is a paragraph. For instance, in some styles of writing, particularly journalistic styles, a paragraph can be just one sentence long. Ultimately, a paragraph is a sentence or group of sentences that support one main idea. In this handout, we will refer to this as the “controlling idea,” because it controls what happens in the rest of the paragraph.
How do I decide what to put in a paragraph?
Before you can begin to determine what the composition of a particular paragraph will be, you must first decide on an argument and a working thesis statement for your paper. What is the most important idea that you are trying to convey to your reader? The information in each paragraph must be related to that idea. In other words, your paragraphs should remind your reader that there is a recurrent relationship between your thesis and the information in each paragraph. A working thesis functions like a seed from which your paper, and your ideas, will grow. The whole process is an organic one—a natural progression from a seed to a full-blown paper where there are direct, familial relationships between all of the ideas in the paper.
The decision about what to put into your paragraphs begins with the germination of a seed of ideas; this “germination process” is better known as brainstorming . There are many techniques for brainstorming; whichever one you choose, this stage of paragraph development cannot be skipped. Building paragraphs can be like building a skyscraper: there must be a well-planned foundation that supports what you are building. Any cracks, inconsistencies, or other corruptions of the foundation can cause your whole paper to crumble.
So, let’s suppose that you have done some brainstorming to develop your thesis. What else should you keep in mind as you begin to create paragraphs? Every paragraph in a paper should be :
- Unified : All of the sentences in a single paragraph should be related to a single controlling idea (often expressed in the topic sentence of the paragraph).
- Clearly related to the thesis : The sentences should all refer to the central idea, or thesis, of the paper (Rosen and Behrens 119).
- Coherent : The sentences should be arranged in a logical manner and should follow a definite plan for development (Rosen and Behrens 119).
- Well-developed : Every idea discussed in the paragraph should be adequately explained and supported through evidence and details that work together to explain the paragraph’s controlling idea (Rosen and Behrens 119).
How do I organize a paragraph?
There are many different ways to organize a paragraph. The organization you choose will depend on the controlling idea of the paragraph. Below are a few possibilities for organization, with links to brief examples:
- Narration : Tell a story. Go chronologically, from start to finish. ( See an example. )
- Description : Provide specific details about what something looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels like. Organize spatially, in order of appearance, or by topic. ( See an example. )
- Process : Explain how something works, step by step. Perhaps follow a sequence—first, second, third. ( See an example. )
- Classification : Separate into groups or explain the various parts of a topic. ( See an example. )
- Illustration : Give examples and explain how those examples support your point. (See an example in the 5-step process below.)
Illustration paragraph: a 5-step example
From the list above, let’s choose “illustration” as our rhetorical purpose. We’ll walk through a 5-step process for building a paragraph that illustrates a point in an argument. For each step there is an explanation and example. Our example paragraph will be about human misconceptions of piranhas.

Step 1. Decide on a controlling idea and create a topic sentence
Paragraph development begins with the formulation of the controlling idea. This idea directs the paragraph’s development. Often, the controlling idea of a paragraph will appear in the form of a topic sentence. In some cases, you may need more than one sentence to express a paragraph’s controlling idea.
Controlling idea and topic sentence — Despite the fact that piranhas are relatively harmless, many people continue to believe the pervasive myth that piranhas are dangerous to humans.
Step 2. Elaborate on the controlling idea
Paragraph development continues with an elaboration on the controlling idea, perhaps with an explanation, implication, or statement about significance. Our example offers a possible explanation for the pervasiveness of the myth.
Elaboration — This impression of piranhas is exacerbated by their mischaracterization in popular media.
Step 3. Give an example (or multiple examples)
Paragraph development progresses with an example (or more) that illustrates the claims made in the previous sentences.
Example — For example, the promotional poster for the 1978 horror film Piranha features an oversized piranha poised to bite the leg of an unsuspecting woman.
Step 4. Explain the example(s)
The next movement in paragraph development is an explanation of each example and its relevance to the topic sentence. The explanation should demonstrate the value of the example as evidence to support the major claim, or focus, in your paragraph.
Continue the pattern of giving examples and explaining them until all points/examples that the writer deems necessary have been made and explained. NONE of your examples should be left unexplained. You might be able to explain the relationship between the example and the topic sentence in the same sentence which introduced the example. More often, however, you will need to explain that relationship in a separate sentence.
Explanation for example — Such a terrifying representation easily captures the imagination and promotes unnecessary fear.
Notice that the example and explanation steps of this 5-step process (steps 3 and 4) can be repeated as needed. The idea is that you continue to use this pattern until you have completely developed the main idea of the paragraph.
Step 5. Complete the paragraph’s idea or transition into the next paragraph
The final movement in paragraph development involves tying up the loose ends of the paragraph. At this point, you can remind your reader about the relevance of the information to the larger paper, or you can make a concluding point for this example. You might, however, simply transition to the next paragraph.
Sentences for completing a paragraph — While the trope of the man-eating piranhas lends excitement to the adventure stories, it bears little resemblance to the real-life piranha. By paying more attention to fact than fiction, humans may finally be able to let go of this inaccurate belief.
Finished paragraph
Despite the fact that piranhas are relatively harmless, many people continue to believe the pervasive myth that piranhas are dangerous to humans. This impression of piranhas is exacerbated by their mischaracterization in popular media. For example, the promotional poster for the 1978 horror film Piranha features an oversized piranha poised to bite the leg of an unsuspecting woman. Such a terrifying representation easily captures the imagination and promotes unnecessary fear. While the trope of the man-eating piranhas lends excitement to the adventure stories, it bears little resemblance to the real-life piranha. By paying more attention to fact than fiction, humans may finally be able to let go of this inaccurate belief.
Troubleshooting paragraphs
Problem: the paragraph has no topic sentence.
Imagine each paragraph as a sandwich. The real content of the sandwich—the meat or other filling—is in the middle. It includes all the evidence you need to make the point. But it gets kind of messy to eat a sandwich without any bread. Your readers don’t know what to do with all the evidence you’ve given them. So, the top slice of bread (the first sentence of the paragraph) explains the topic (or controlling idea) of the paragraph. And, the bottom slice (the last sentence of the paragraph) tells the reader how the paragraph relates to the broader argument. In the original and revised paragraphs below, notice how a topic sentence expressing the controlling idea tells the reader the point of all the evidence.
Original paragraph
Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. If the fish are well-fed, they won’t bite humans.
Revised paragraph
Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, for the most part, entirely harmless. Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. If the fish are well-fed, they won’t bite humans.
Once you have mastered the use of topic sentences, you may decide that the topic sentence for a particular paragraph really shouldn’t be the first sentence of the paragraph. This is fine—the topic sentence can actually go at the beginning, middle, or end of a paragraph; what’s important is that it is in there somewhere so that readers know what the main idea of the paragraph is and how it relates back to the thesis of your paper. Suppose that we wanted to start the piranha paragraph with a transition sentence—something that reminds the reader of what happened in the previous paragraph—rather than with the topic sentence. Let’s suppose that the previous paragraph was about all kinds of animals that people are afraid of, like sharks, snakes, and spiders. Our paragraph might look like this (the topic sentence is bold):
Like sharks, snakes, and spiders, piranhas are widely feared. Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, for the most part, entirely harmless . Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. If the fish are well-fed, they won’t bite humans.
Problem: the paragraph has more than one controlling idea
If a paragraph has more than one main idea, consider eliminating sentences that relate to the second idea, or split the paragraph into two or more paragraphs, each with only one main idea. Watch our short video on reverse outlining to learn a quick way to test whether your paragraphs are unified. In the following paragraph, the final two sentences branch off into a different topic; so, the revised paragraph eliminates them and concludes with a sentence that reminds the reader of the paragraph’s main idea.
Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, for the most part, entirely harmless. Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ first instinct is to flee, not attack. Their fear of humans makes sense. Far more piranhas are eaten by people than people are eaten by piranhas. A number of South American groups eat piranhas. They fry or grill the fish and then serve them with coconut milk or tucupi, a sauce made from fermented manioc juices.
Problem: transitions are needed within the paragraph
You are probably familiar with the idea that transitions may be needed between paragraphs or sections in a paper (see our handout on transitions ). Sometimes they are also helpful within the body of a single paragraph. Within a paragraph, transitions are often single words or short phrases that help to establish relationships between ideas and to create a logical progression of those ideas in a paragraph. This is especially likely to be true within paragraphs that discuss multiple examples. Let’s take a look at a version of our piranha paragraph that uses transitions to orient the reader:
Although most people consider piranhas to be quite dangerous, they are, except in two main situations, entirely harmless. Piranhas rarely feed on large animals; they eat smaller fish and aquatic plants. When confronted with humans, piranhas’ instinct is to flee, not attack. But there are two situations in which a piranha bite is likely. The first is when a frightened piranha is lifted out of the water—for example, if it has been caught in a fishing net. The second is when the water level in pools where piranhas are living falls too low. A large number of fish may be trapped in a single pool, and if they are hungry, they may attack anything that enters the water.
In this example, you can see how the phrases “the first” and “the second” help the reader follow the organization of the ideas in the paragraph.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Lunsford, Andrea. 2008. The St. Martin’s Handbook: Annotated Instructor’s Edition , 6th ed. New York: St. Martin’s.
Rosen, Leonard J., and Laurence Behrens. 2003. The Allyn & Bacon Handbook , 5th ed. New York: Longman.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7. Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

How Many Paragraphs in a Research Paper: Steps on How to Write

Paragraphs In Research Paper
A research paper is an essay where after exploring a particular topic thoroughly, you can write a detailed essay about it.
In as much as you are allowed to use your thoughts, opinions, ideas, and knowledge, you must also include information from sources, books, journals, internet sites, and interviews in your research.

Therefore, at least 80% of the research paper should be written in your own words. Paragraphs must be detailed and arranged in order to maintain the flow of the essay, with each explaining a new point or contribution.
How Many Body Paragraphs Should a Research Paper Have?
The number of body paragraphs in a research paper depends on the length of the research paper. Some instructors usually hand out a specific length for research papers.

With each paragraph containing five to six sentences, each page should have three paragraphs.
Therefore, a three-page research paper should have nine paragraphs, and a ten-page research paper should have at least 30 paragraphs.
However, some research papers may require longer paragraphs where two paragraphs are enough for every page. As such, a three-page essay and a ten-page essay should have six and twenty paragraphs, respectively.
The paragraphs should always be proportional to your paper length, with shorter paragraphs in short research papers and longer paragraphs in long research paragraphs.
Types of Paragraphs in a Research Paper
1. introduction paragraph.
This is the paragraph where you set up the topic of the paper and the way you are approaching it to the reader. First, you have to introduce the topic. You have to tell the reader what you are writing about using a hooking sentence.
This sentence should grab the attention of the reader and convey the relevance of your topic. Secondly, you have to describe the background of the topic. This usually depends on the approach you are using in your paper and is mostly used in argumentative research.
It is where you review previous research and reveal how yours will fit in.
Thirdly is establishing your research problem. After showing how your research fits in, show the problems it addresses too.
Fourthly, you will have to specify the objectives of your paper. This is what you intend to find out and express in your paper.
Fifthly, you will have to include a brief overview of your paper. In a paper that uses the standard methods of research writing, it is not necessary, but if the structure is not predictable, it is important to describe it for the reader.
The last sentence in the introduction is always the thesis statement. It reveals everything the paper is all about.

2. Body Paragraphs
Arranging ideas and points in body paragraphs is a challenge for many students.
Each paragraph should always cover a different point. If two paragraphs have to explain the same thing, make sure that the approach taken in both is different.
To write a body paragraph, you will first start with a topic sentence to establish the main point of the paragraph. Reading the topic sentence in every body paragraph should provide the reader with the main points of your research.
The next task is unpacking the topic sentence. This is where you explain and discuss the individual parts of the topic sentence. After that, you give evidence to support your data. This is done by providing arguments, data, facts, figures, and quotations from credible sources .
Next, you will have to analyze the evidence. Never leave the evidence hanging. Instead, link it to the ideas you are trying to prove. Also, you will have to prove the objective by tying the body paragraph with the main topic of the research.
Finally, provide a transition to link your body paragraph to the next. The connection should be clear to maintain the flow of the paper.
3. Conclusion Paragraphs
This is the paragraph where you wrap up your thoughts and ideas and leave the reader with an impression.
The first thing to do when writing a conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem. Paraphrase the research problem to make sure it is not identical to the one in the essay introduction.
Next, you will have to sum up the paper. Summarize what you addressed in the body of the essay and provide the conclusions they lead to. Generally, you have to summarize your overall findings.
After that, you discuss the implications. After formulating the summary of your findings, it is necessary to consider the implications of the broader research.
This is by providing the takeaways from your paper which are either practical or theoretical. For example, you can provide a reasonable call for action or suggest a research topic that is not covered in your paper.
How Many Paragraphs for Each of the Above Types?
Introduction paragraph.
A research paper’s introduction paragraphs depend on the length of the paper. If you are writing a five-page page essay, then the introduction should not take more than half of a page.

Therefore, one or two paragraphs are enough for such a paper. However, when writing a longer essay, the introduction paragraphs should be more in order to introduce everything you will talk about in the essay.
There is always an approximation that the introduction should be 10 percent of the total word count.
If you are writing an 1800-word research paper, then the introduction should be at least 180 words which translates to two introduction paragraphs.
Body Paragraphs
The shortest research paper usually has five paragraphs. Therefore, you are supposed to have three body paragraphs and one each for the introduction and conclusion.
However, this varies depending on the length of the research paper. For example, an 1800-word research paper should at least have 16 body paragraphs.
Research papers should have one or two paragraphs that summarize everything that has been written in the paper. Making it too long may lead to repetition.
However, for longer essays, more paragraphs can be required to summarize the key findings and their significance. One can also use the 10% rule. A conclusion with 10% of the total word count is proportional to the essay length.
To add to that, professional empirical research articles usually have conclusions that range from five to six paragraphs.
On the other hand, novice and student research papers usually have two to three conclusion paragraphs.
How Long Should a Paragraph Be in a Research Paper?
The introduction paragraph of an essay should at least have five or six sentences that build up to the thesis statement at the end.

The first sentence should introduce the topic. The second should provide background information. The third should show the problem being addressed. The fourth should provide the objectives.
Lastly, the fifth should provide the overview, and the thesis statement should come last.
The body paragraphs of an essay should have six to seven sentences. These should contain sentences that introduce the main topic of the paragraph and unpack it.
Further sentences should provide evidence of the topic. Additionally, other sentences should analyze the evidence and prove the objective of the research paper. The last sentence should be a link to the body paragraph of the next
Lastly, the conclusion paragraphs should have five to six sentences. The average number of words should be between 75 to 85 words.
These paragraphs should not only be long enough to summarise your research paper but also short enough to avoid repetition of what is already written in the paper.
The sentences in the conclusion should be brief and straight to the point because there is nothing new that should be introduced. Every sentence should reflect the main idea of the essay.

James Lotta
Related posts.

what Respondus Records
Does Respondus Record you, Sound or Screen? Is it Safe?
writing Single-spaced Essay
Single Spaced Essay in Word: What it is, Meaning and Format

Comparing Thesis and a Claim
Is a Thesis the same as a Claim: How to Write Each
Paragraph Length: Data from 9,830 Research Papers
I analyzed a random sample of 9,830 full-text research papers, uploaded to PubMed Central between the years 2016 and 2021, to answer the question:
How long should a paragraph be in a research paper?
I used the BioC API to download the data (see the References section below).
Paragraph length
Our sample of 9,830 research articles had 325,500 paragraphs. The following table summarizes the length of these paragraphs::
From these data we can conclude that:
- The median paragraph length is 4 sentences (or 109 words), and most paragraphs are between 2 and 6 sentences (or 65 and 167 words).
- A paragraph can be just one sentence long. In fact, 13% (n=42,349) of all paragraphs in our sample were 1 sentence long.
- 90% of paragraphs were between 19 and 286 words (1 and 11 sentences). So, a paragraph shorter than 19 words can be considered too short; and a paragraph longer than 286 words (or 11 sentences) can be considered too long.
Paragraph length in each section of the research paper
A research paper is usually divided into 4 sections: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. The following table shows the median paragraph length for each of these sections:
The Discussion section has slightly longer paragraphs than other sections with a median of 5 sentences and 131 words.
Paragraph length in different types of studies
The data suggests that paragraph length did not differ for different study designs. Review papers (systematic reviews and meta-analyses) had almost the same paragraph length (median=103 words) as original research papers (median=110 words).
- Comeau DC, Wei CH, Islamaj Doğan R, and Lu Z. PMC text mining subset in BioC: about 3 million full text articles and growing, Bioinformatics , btz070, 2019.
Further reading
- Can a Research Title Be a Question? Real-World Examples
- How Long Should a Research Paper Be? Data from 61,519 Examples
- How Many References to Cite? Based on 96,685 Research Papers
- How Old Should References Be? Based on 3,823,919 Examples
How Many Paragraphs Are There In An Essay?
- How Many Paragraphs?
- Five-Paragraph Essay
- Types Of Five-Paragraph Essays
- Best Practices For Five-Paragraph Essays
- Three-Paragraph Essay
- Types Of Three-Paragraph Essays
- Best Practices For Three-Paragraph Essays
So you need to write an essay. You’ve picked out your topic, determined your thesis, and now you’re ready to put pen to paper (or fingertips to keyboard) to start writing your epic piece. Before you get rolling, there’s only one thing left to decide: how many paragraphs does this essay actually need?
Unless you’re working under a strict assignment, essays can come in all shapes and sizes. Choosing the right format can help you present your ideas in the clearest way possible and make your writing process even easier. Here are the most common formats to consider and what to know before you decide which one to choose.
How many paragraphs are in an essay?
There’s no hard and fast rule for deciding how many paragraphs an essay should have, but it’s important to know that a single paragraph is generally not considered an essay. Standard essays have a designated introduction and conclusion, along with supporting details. This means that even a short essay will still have about three paragraphs, and many have more.
Things to consider before you write an essay
Before you can decide how to divide the information, you need to consider a few things:
- What type of essay are you writing?
- How many supporting details do you need to share?
- Do you have enough information to write a three- to five-sentence paragraph for each supporting detail?
- Do you have a required word count?
- What will be the clearest format for the reader?
There are a lot of different kinds of essays you might be assigned. Generally, multi-paragraph essays are used to compare and contrast things, in persuasive writing, as a form of narrative writing, and for informative or researched essays. Most of these essays end up fitting nicely into one of two main categories:
The five-paragraph essay
Arguably the most common essay format is the standard five-paragraph essay. This essay devotes a paragraph each to the introduction, conclusion, and three different supporting details. Let’s break down what each of those sections includes.
Parts of a standard five-paragraph essay
1. Introduction
This part of the essay includes your thesis statement , introduces your reader to your topic or point of view, and lays out the main ideas of your following three body paragraphs. Generally, this paragraph is brief and intended to grab your reader’s attention.
2. Body paragraphs
A five-paragraph essay includes three body paragraphs. Each of these paragraphs should focus on one supporting detail that aligns with your thesis. They will begin with a topic sentence and share the relevant research, quotes, and anecdotes you’ve gathered.
3. Conclusion
The conclusion to a five-paragraph essay will restate your thesis, sum up your supporting details, and present the reader with one final takeaway from reading your piece.
Wondering what goes into nailing each of these categories? Here’s a sample five-paragraph essay outline and some examples to help you get started.
Which kinds of essays work best with five paragraphs?
Five-paragraph essays are best used to convey complex and detailed topics that require extra information, like:
Comparison essays
A five-paragraph essay allows you to devote one paragraph to each item you’re comparing, as well as include one paragraph on the similarities between the two things.
Argumentative essays
In the five-paragraph format, there is ample space to explore multiple sides of an argument and include plenty of supporting facts and research.
Informative essays
Complex topics are broken down in simple and intuitive ways when the information is spread across multiple paragraphs.
Make Your Writing Shine!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Best practices for writing a five-paragraph essay
If you’re considering a five-paragraph format for your essay, remember:
- These essays must have a clear thesis and conclusion.
- Each body paragraph should contain a strong and complete supporting detail.
- Transition words are necessary to help the flow of the essay.
- These essays usually involve research.
- This is among the most organized ways to present complex topics.
The three-paragraph essay
Three-paragraph essays are shorter and more simplified than the standard five-paragraph essay. Typically, these essays include a conclusion, introduction, and only one body paragraph. This single body paragraph might focus on one supporting detail or it may include a comprehensive summary of a lot of supporting information.
Parts of a standard three-paragraph essay
The introduction to a three-paragraph essay typically includes a hook or attention-grabbing first sentence , followed by a summary of your supporting details and then your thesis. The thesis statement helps lead into the rest of your essay.
Refresh your memory on the different types of thesis statements to get your essay started!
2. Body paragraph
This is the one and only body paragraph in a three-paragraph essay, so it needs to be clear, concise, and as detailed as possible within the space constraints. The body paragraph should include a topic sentence, as well as any details or facts that underscore your thesis. It may focus on one element of your supporting argument or sum up several in brief, clear sentences that relate to the topic sentence.
3. Conclusion
Much like in a five-paragraph essay, your conclusion is the place to restate your thesis, summarize the points you made in the body paragraph, and leave your reader with a final takeaway or call to action.
Which kinds of essays work best with three paragraphs?
For less complex topics, the three-paragraph essay provides enough space to thoughtfully explain a topic and provide additional information.
Narrative essays
Personal essays that don’t necessarily need multiple paragraphs of supporting information work well in this format.
For emerging writers, one body paragraph provides ample space to compare and contrast two items or ideas. Single sentences can be devoted to each comparison or similarity.
Best practices for writing a three-paragraph essay
If you’re considering a three-paragraph format for your essay, remember:
- Even short essays still need a clear thesis.
- Organize your body paragraph so your ideas are presented clearly.
- The introduction and conclusion should each be a separate paragraph.
- This format provides excellent practice for new writers.
- One body paragraph still leaves room for strong supporting information.
Avoid confusing sentences and write with clarity with these tips.

Ways To Say
Synonym of the day

How Many Paragraphs in an Essay?

As a rule, you’ll write your essay in three main parts. First, you’ll introduce your topic to your reader. Next, you will have body text in which you discuss the topic in more detail, and finally, you’ll have a conclusion that tells your reader what you were able to see after looking into the facts or thinking through the topic.
In its simplest form, an essay can consist of three paragraphs with one paragraph being devoted to each section. Proponents of the five paragraph essay say that the body text should consist of three paragraphs, but in reality, it’s fine to write more or fewer paragraphs in this section.
Guessing How Many Paragraphs Before You Begin
This is a rule of thumb, which means it won’t always work quite that way, but it’s handy all the same. In academic work, your paragraphs are likely to be a bit longer than most of the ones you see in this blog post. On average, there are usually 100 to 200 words in a paragraph . So if you’d like a guesstimate, you can assume that a 1,000-word essay will have between five and ten paragraphs.
What Points Do You Have to Cover?
Another, less limiting and more accurate way to work out how many paragraphs you need to cover your topic is to look at the main points you have to cover in the body text. A paragraph contains all the ideas that support or explain a single concept.
When you are planning your essay, you will think of or research the main elements that are needed in the body text. It would be safe to assume you need at least one paragraph for each of these. Of course, if there is a lot of information to cover in order to explore each area, you may need more.
For example, if you are writing an essay on childhood development and exposure to technology, you will want to look into the physical, psychological and cognitive developmental effects of tech on kids. When you research this topic, you will find that there are contrasting points of view and researchers have identified several physical, developmental, and psychological effects of technology use in children.
Assuming five psychological effects have been identified, you can assume you’ll need to write five paragraphs if you are going to write a relatively in-depth essay. But if both those who say technology is bad for kids and those who say it can be good have done a great deal of work on the sub-topic, you might want to make that ten paragraphs so that you can cover both sides of the argument and look into how earlier authors reached their conclusions.
Of course, if you have been set a relatively short word limit , you may not be able to go in-depth at all, in which case a paragraph for each of the main sub-topics (psychology, physical development, and cognitive development) will likely be adequate.
Essay Content Is More Important Than the Number of Paragraphs
Ultimately, your essay will be evaluated on the information you present, not on the number of paragraphs in the essay. Early in your academic life, teachers and lecturers may give you both a structure for your essay and a guideline on how long each part of the essay should be. I have seen essay instructions say how many marks are allocated for each section, and my trick is to take the total word count and allocate a percentage of words to each section based on the percentage of marks you can get for it. After all, if the teacher is allocating 80 marks for content in total and you can see 50% of the mark relates to a certain part of the essay, then 50% of your essay’s words should be devoted to that section.
Sometimes, you’ll just be given a topic and told to air your opinion. This gives you more freedom, but it’s a tad more difficult. The research will show you how many angles you should look at, and it’ll help you to find information that both supports and contradicts your point of view. To make a strong argument, you need to look at both supporting and contradictory information.
To avoid getting tangled up in one aspect of the discussion, you’ll have to decide how long it should be. If it’s the most important aspect informing your conclusion, you can spend a little more time (and words) on that particular point. It could run into several paragraphs rather than just one or two.
Always Remember the Purpose of Paragraphs
Paragraphs structure information into sub-topics, and they make your work easier to read and understand thanks to the structure they provide. With careful advance planning, you’ll be able to work out more or less how many paragraphs you need to complete your essay.
How many paragraphs is…
For those looking for a general rule-of-thumb, below are some estimates on the number of paragraphs there would be in an essay of different lengths based on an average length of 150 words per paragraph. Of course, the number of paragraphs for your essay will depend on many different factors. You can use the following information for a general reference, but don’t take these numbers as literal. .
Basic Essay Word to Paragraphs Conversions
- A 100 word essay is 3 paragraph. (minimum for an essay)
- A 200 word essay is 3 paragraphs. (minimum for an essay)
- A 250 word essay is 3 paragraphs. (minimum for an essay)
- A 300 word essay is 3 paragraphs. (minimum for an essay)
- A 400 word essay is 3 paragraphs. (minimum for an essay)
- A 500 word essay is 3 to 4 paragraphs.
- A 600 word essay is 4 paragraphs.
- A 700 word essay is 4 to 5 paragraphs.
- A 750 word essay is 5 paragraphs.
- A 800 word essay is 5 to 6 paragraphs.
- A 900 word essay is 6 paragraphs.
- A 1,000 word essay is 6 to 7 paragraphs.
- A 1,250 word essay is 8 to 9 paragraphs.
- A 1,500 word essay is 10 paragraphs.
- A 1,750 word essay is 11 to 12 paragraphs.
- A 2,000 word essay is 13 to 14 paragraphs.
- A 2,500 word essay is 16 to 17 paragraphs.
- A 3,000 word essay is 20 paragraphs.
- A 4,000 word essay is 26 to 27 paragraphs.
- A 5,000 word essay is 33 to 34 paragraphs.
- A 6,000 word essay is 40 paragraphs.
- A 7,000 word essay is 46 to 37 paragraphs.
- A 7,500 word essay is 50 paragraphs.
- A 8,000 word essay is 53 to 54 paragraphs.
- A 9,000 word essay is 60 paragraphs.
- A 10,000 word essay is 66 to 67 paragraphs.
I don’t understand, How can a 100, 200, 300 and 400 word essay all have 3 paragraphs if a paragraph is 100 to 200 words long? A 100 word essay should be 1 paragraph or 1/2 a paragraph, not 3 paragraphs. Can someone explain this too me?
A sentence is an idea. A paragraph is a group of ideas that relate to one another. That’s the most important point. The second most important one is remembering that your text consists of introduction, body, conclusion with at LEAST one paragraph for each. While teachers like 100 to 200 word paragraphs, you can’t always apply that. Call it a guideline rather than a rule!
the general rule is that 3 paragraphs are minimum for an essay. So, no matter how short your essay is, you should still need 3 paragraphs. If you are really for some reason writing a 100 word essay, then you should have one short sentence for both your introduction and conclusion.
I was always taught an essay has five paragraphs by my teachers. Did they lie to me? If an essay only needs three paragraphs, why would my teachers tell me that they should have five?
I think the five paragraphs for an essay is more of a rule-of-thumb number that is easy to teach students when they are first learning to write. Your teacher was just trying to make sure you understood how to write, not give you a rule you had to always obey.
I think five paragraphs is a good number to shoot for when writing, but it isn’t a hard-fast rule you need to hit every time. Each essay is different and require more or less paragraphs depending on the information you need to provide in the writing.
yes and no.. i would say a good on as 4 paragraph. Intro, 2 body P, and a conclusion.
My teachers always taught by eight paragraph essays, but five-paragraph essays normally lie precedent to the more advanced or larger essays.
I was taught essays should be 7 paragraphs long, not 5. My teacher said 3 central paragraphs never gives enough detail to the topic, so we should write 5. It makes sense to me and that is how I’ve always done it.
What you’re taught is often a general rule to shoot for, not a rule set in concrete. That’s the case with this. Your teacher felt that 7 paragraphs was a good number for the essays you wrote for her, but it doesn’t always have to be that way. it’s a general rule, not a concrete one.
How many sentences if we don’t know how many sentences we need to write?
The average paragraph contains 5-6 sentences. If you’re feeling a little extra, paragraphs can be 7-10 sentences.
It also depends on whether or not you are bringing outside information into the paragraph as well. Using quotes makes a paragraph longer than not doing so.
I think the length of a paper depends mainly on the instructions given by the instructor. Secondly, I would decide a paper length on the basis of the grading rubric.
I already knew an essay has three paragraphs
Inilividual project: follow all steps and develop a paragraph of your choice and write all expository essay with not less than 500 words of the povoloped paragraph?
On average for a five-paragraph essay, I write around 1,000-1300 words. For an eight paragraph essay, I write around 2,000-2,600 words on the document. Keep in mind your quotes too, you should have one quote per paragraph (expected) or two (recommended). It really is up to the person though, I have a buddy who writes considerably less than I do, but is able to get his point across. It is really up to the person.
Student A: Sir, do we have to write a long essay?
How will I determine my word count for 1300 to 1500 maximum words in the academic writing?
Popular Posts
- The Top 10 Most Difficult-to-Spot Writing Mistakes
- 4 Simple Tips for Great Writing
- Avoiding Wordiness: 330 Examples & What to Use Instead
- The Oxford Comma: The Splice of Life
- Who vs. Whom
- Affect vs. Effect
- How to Take Notes: The 10-Step Guide to Note-Taking (Infographic)
- CMOS vs. AP – Recent Changes & Comparison (Updated 1. Nov. 2021)
- The Daily Word Counts of 19 Famous Writers
- The Ideal Length of Everything You Write Online ( Infographic)
Recent Comments
- Trilby on Avoiding Wordiness: 330 Examples & What to Use Instead
- Trilby on Words Everyone Seems to Hate
- Julie Retallack on Words Everyone Seems to Hate
- Cat on Who vs. Whom
- Cat on The Oxford Comma: The Splice of Life
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.
How Long Should A Research Paper Be?

You must have known what research looks like. It has a particular structure that should be followed at any cost since it is the criteria for writing a research paper . Several questions come into the mind of students such as how to write a research paper, how long should a research paper be, etc.
That’s why we have brought a series of research writing and addressing different questions related to it. This blog aims to answer queries about the duration your research should ideally take, including insights on how to write an 8-page paper effectively. Although it depends upon the guidelines given by your teacher, there is also a standard length of research writing. Let’s dive in and learn everything about the ideal word count of any research.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is an essay that is based on your investigational work you have completed or will complete on just one or many specific topics of a specific discipline. Research or investigation essays are lengthy depending on the scope and extensive nature of the topic.
It’s just an analysis of the topic from your own perspective. A student or a reader present facts and their theories in front of the audience to inform them about the specific subject matter. If you dont know how long is a research paper, here we will take you on a deeper tour to help you understand these essays thoroughly.
What is the Standard Length of a Research Paper?
Discussing the standard length of a paper, it’s important to note that it varies depending on the specific instructions given to each student and the structural requirements related to their chosen finance research topics . It is never a fixed one for all types of papers yet, there are some conditions and possibilities because of which the word count varies.
Research that has a thesis statement only requires 2 to 3 arguments to be proved and will be summed up in 500 to 700 words. After providing the introduction and a little background on the research, you can directly shift to mentioning the arguments and claims so you may prove the statement and complete the research.
Some research requires detailed analysis and interpretation of the findings. This kind of paper has several stages such as introduction, background, thesis statement, objective, research questions, literature review, research methodology, data collection, discussion, findings, conclusion, and bibliography. Such research easily crosses 5000 words because it is important to discuss everything about the topic.
So it entirely depends upon the structure you are following to write the research. It could be as long as just 500 words, or 5000 words, and even more. It all varies therefore you must be prepared for writing a paper no matter how long it should be.
How long is introduction in research paper?
Many students wonder how long should an introduction be in a research paper? The simple answer to this query is as short as possible that justify the requirements and employ all the methods that are necessary for coveying your message.
Typically, a standard length of introductory paragraph is 300-500 words. If your topic needs more than the standard word count than always ask for suggestion from your professor on first priority. We hope now you know how long should an introduction be for a research paper.
Why Considering Length of a Research Paper is Important
Identifying the length of research is important because of so many reasons. You might have never realized the significance of considering how long a paper should be, so here we go with some of the vital reasons.
1. Going Extra May Ruin Your Research
You cannot write more than is required in research. If you are doing so then you are automatically ignoring the quality measures of writing a paper. If you are writing more than words than is required then there are chances you are going to submit a poor quality research work.
2. Sticking to the Guidelines is Important
When your guidelines have mentioned 1000 words maximum and you are submitting research of 2000 words, you already know what wrong you have done. If you are not sticking to the guidelines it will result in deduction of marks, fall in grades, and repetition of the class course.
3. Having a Balance is Good
It is necessary to keep a balance between the word count of all the headings. Without this much-needed balance, you might end up submitting a poor paper that has a longer introduction, and a shorter explanation of the findings. That’s why attaining a balance is important in your research word count.
4. Delivering Quality Research is the Criteria
When you are delivering quality content, you will be appreciated no matter what. If you consider the length of your research, you are one step forward in delivering quality research work to your teacher.
How Long Should a Research Paper Be?
This question is valid and one of the frequently asked questions by the students of high school and college. It is also important to know before you start working on your paper. Don’t forget to read the instructions provided by your teacher, however, we have more suggestions for you regarding the length of the research.
1. It All Depends On Your Teacher First
Your teacher indeed decides what should be the ideal length of your research. They have given some guidelines to you and you need to follow them. The teachers always know the best and they will suggest to you how long your essay should be.
Some teachers have kept a certain word limit for the paper while others provide you complete freedom to write as long as you want. It is necessary to figure out what’s best for your research. In high schools, a standard length of any research is a maximum of 7 to 8 pages while the minimum should be 5 pages.
2. Check How Much Length is Required to Justify Your Statement
Sometimes it is based on the thesis for research paper . From the part of the abstract to the conclusion, there must be a balance between the word count of every heading. It is your responsibility as a writer to track the word count when you are trying to justify your thesis by giving several arguments and claims.
If you have decided how many arguments it will take to prove your thesis, then you have already finalized the length of your research. All you have to do is prepare everything in advance and see if you are proving your point within 5 or 8 pages.
3. It Shouldn’t Miss Any Point
A researcher must be discussing all the standard details that could justify the purpose of writing the paper. It must have all the headings properly discussed. Since all the points must be 100% clear in the research, deciding on a word limit in the very beginning could be a little hard.
But it is not impossible to identify by making an outline and checking how many pages will be covered in writing about a certain topic. All you have to do is take care that no point is missing in the research. Cutting the research short and trying to discuss facts to the exact point won’t help unless you are entirely explaining every aspect as required.
How Long a Research Paper Should be in Words?
You have learned something about the ideal length of research. When it comes to the word count, the criterion is a bit different. For example, if you need a Ph.D. research paper help , you must know the word count, typically between 70,000 to 80,000 words. As you suggest a specific word count for every heading, it is easier to guess how many words are required to summarize every title.
1. Assign Word Count To Each Heading
It is easier to assign a specific word count to every heading and then see what’s the total word length of the paper. For instance, you have to decide how many words will be used to cover your introduction section. A literature review is a second longer part after the discussion in every research so it is necessary to make an outline in advance and see what is the ideal length of every heading.
By giving a suggested word count to each heading you will make a clear pathway to follow during the complete research. It will be automatically easier for you to see how many words will be written to explain everything in your research thoroughly.
There are several sections in research that require certain word counts. Let’s see what word count is usually subjected to every heading.
An abstract for a research paper is the first main part that summarizes the research from the beginning to the conclusion. It contains the thesis, methodology, findings, and conclusion. So to explain the complete research in a few sentences, roughly 100 to 200 words will be required. So you may keep in mind the word count for an abstract is a maximum of 200 words.
● Introduction
An introduction is also a major part of the research and it is easily covered within 300 words maximum. Nothing else is required to explain terminologies or theories in this section. However, there are many opinion on this topic and each have different answers. That’s the prime reason students spend day and night on google looking for answers on their questions such as how long should introduction be for research paper. In short, 300 to 500 words are more than enough to state your thoughts in an into section and persuade your readers.
● Literature Review
The literature review is the second-longest section in any research. It contains a reference to the past research done in a similar field by other researchers. Every research must have 5 to 8 or even more past papers discussed in it. Therefore the ideal word count for this section is 500 to 1000 words.
● Methodology
The methodology section also has subcategories in which you have to explain the method of research, data collection, population, research implications, research Instrument, etc. It will take around 300 to 400 words and 100 words extra if you are discussing a theoretical framework too.
● Discussion and Interpretation
This is the longest part of any research since you have to explain all the findings and tell your readers how successfully you have managed to prove your thesis. This part is as long as 500 to 1000 or even 1500 words depending upon the results and the explanation required.
● Conclusion
A conclusion is a not so lengthy part of the paper. It is usually done within only 100 or 150 words maximum. It is that simple and thus it doesn’t need so many words to finish the argument and put a full stop.
2. Form a Paper Outline
Forming a paper outline in advance will also help you in understanding how many words you may need to cover every heading. This is one of the best ideas for assigning a particular word count to every heading of the paper.
As you’ll create a paper outline, you will get an instant idea of how many words you have to write in total to complete the research. Following this strategy will surely help you won’t be puzzled later during the writing process.
3. Ask Your Instructor
It is always a good idea to ask your teacher or instructor before following any word count technique. They have assigned you a paper so they can provide you with a better guideline to write your paper. It is the easiest method of identifying the word count of your research as it’s something recommended by an expert. Your job will become much easier and simpler by just seeking advice from your teacher.
How Long a Research Paper Should be for Middle School?
A middle school student is just starting with the research work and they are at the initial stages of learning how to conduct research. To understand how long a paper should be for middle school, you need to do some work.
1. Seek Expert Help
It is always better to seek help from an expert to decide the word limit of your essay when you’re a high school student. It could be your teacher or any senior student who will help you and guide how many pages you should write for your research. It is suggested to write 4 to 5 pages when you are a middle school student in writing a paper.
2. Do Research
It is always important to do some research and find out what’s best for your paper. Google is always open to helping students in learning new things without any limit. You can open the Google search engine, write down your query in the search bar and click on it.
Next, you will have everything to read and understand how a paper for middle school will work. By doing so you will automatically get an in-depth idea of crafting research for the initial level project.
After analyzing everything you can easily guess what should be the length of any research written by a middle school student. In pages, it is suggested to write 3 to 5 pages, but in words, it is recommended to write 400 to 500 words only. You can also hire a professional paper writing service to aid you in the process.
As it’s a new thing for the students to perform, they might get nervous easily. That’s why starting slow and taking baby steps towards learning research writing will help a lot.
How long Should a Research Paper be for High School?
High school is a different stage than middle school. You are mature, better at studies, and even more creative than before. This stage comes with its challenges and one of them is writing the research. If you are a new high school student we bet you don’t know much about paper writing at this level.
When a high school student writes a research paper, it’s usually written within 500 to 1000 words. It could be more than this word count or just 5 to 6 pages. The teacher’s instructions do matter a lot in this aspect and without them, you can’t understand the criteria of research writing. It takes a lot of research, consultation, and creativity to write a paper that stands out. The competition is even tougher in high schools so you know how tough it can get to write a research paper fast .
Your research will decide if you are going to pass the school or not. Many students stay stuck in a class because they are incapable of submitting a brilliant research paper. Most of the time it’s because they don’t know the standard guidelines for writing a paper.
They usually end up ignoring the pattern, writing incorrect information, or exceeding or limiting the length assigned for the research. So it’s better to keep in mind what is the better approach for research writing and how a high school student can learn to write it.
How Long Should a Research Paper be for College?
Have you ever thought about how long your research should be when you have finally reached college? It is the final stage of your education and writing research in this phase will require a lot of preparation. In college, you have to write the longest research papers because it is the standard of a paper written by a college student.
So how exactly long should research be for college? It starts with roughly 3000 words and goes up to 15000 words. 15000 words is a lot but students who are working on their thesis need a lot of details to justify and complete their research. Without doing this they are not getting passed at any cost so now you know why it is so important.
Different sections of the paper require their particular word count. It is sometimes difficult to identify but your teachers will always be there to guide you. Sometimes students are given the entire freedom to keep their essay length on their own. It helps them understand how easily they can prove their thesis either in a few or a lot of pages.
For newcomers in college unsure about the ideal length for research papers, utilizing Google is a great option to delve deeper into the nuances of research writing. It’s particularly helpful in exploring various guidelines related to history research topics . A lot of content is already published on the web which teaches the students almost everything they need.
We hope you know how long is a research paper, no matter if you are writing one for your middle school, high school, or college. All of them have different requirements and basic criteria that should be followed. We also hope this blog has helped you learn everything about deciding the word count or overall length of your research.
Our comment section is always open for your discussion and feedback. If you want to get in touch with us or discuss the topic more, just leave a comment in the given box. We would love to hear from our readers and see what they have in their minds after reading our blog.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
The number of paragraphs in an essay or paper depends on its length in terms of pages. For instance, there should be 3 paragraphs in a 1-page essay or 5 paragraphs for a 2-page one. This includes an introduction paragraph, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Essays longer than that have more paragraphs depending on the length and the instructions from your faculty.
Step 2: Develop a structure and outline. With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it's time to move on to planning your actual research paper. It might sound obvious, but it's really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper.
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
As a rule, five paragraphs should suffice for a 1,000-word essay. As long as you have an introduction and a conclusion and provide enough supporting details for the main ideas in your body paragraphs, you should be good to go. Remember to start a new paragraph when introducing new ideas or presenting contrasting information.
Given these factors, every paragraph in a paper should be: Unified—All of the sentences in a single paragraph should be related to a single controlling idea [often expressed in the topic sentence of the paragraph]. Clearly related to the research problem—The sentences should all refer to the central idea, or the thesis, of the paper.
Most paragraphs have four components: • Topic sentence • Evidence • Analysis • Transition Topic sentence The topic sentence is usually the first in the paragraph. As the name implies, it tells the reader your main point, and should connect to the thesis stated in your introduction. Subsequent sentences in the
Essay length guidelines. Type of essay. Average word count range. Essay content. High school essay. 300-1000 words. In high school you are often asked to write a 5-paragraph essay, composed of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. College admission essay. 200-650 words.
Table of contents. Step 1: Identify the paragraph's purpose. Step 2: Show why the paragraph is relevant. Step 3: Give evidence. Step 4: Explain or interpret the evidence. Step 5: Conclude the paragraph. Step 6: Read through the whole paragraph. When to start a new paragraph.
Paragraphs are the building blocks of papers. Many students define paragraphs in terms of length: a paragraph is a group of at least five sentences, a paragraph is half a page long, etc. In reality, though, the unity and coherence of ideas among sentences is what constitutes a paragraph. A paragraph is defined as "a group of sentences or a ...
Conclusion. Research papers should have one or two paragraphs that summarize everything that has been written in the paper. Making it too long may lead to repetition. However, for longer essays, more paragraphs can be required to summarize the key findings and their significance. One can also use the 10% rule.
1- The median length of a research paper is 4,133 words (equivalent to 166 sentences or 34 paragraphs), excluding the abstract and references, with 90% of papers being between 2,023 and 8,284 words. 2- A typical article is divided in the following way: Introduction section: 14.6% of the total word count.
Our sample of 9,830 research articles had 325,500 paragraphs. The following table summarizes the length of these paragraphs:: From these data we can conclude that: The median paragraph length is 4 sentences (or 109 words), and most paragraphs are between 2 and 6 sentences (or 65 and 167 words). A paragraph can be just one sentence long.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
You got the assignment, started brainstorming, and now it's time to write ... how long should your essay be? Learn about how many paragraphs are in an essay.
1 Answer to this question. Answer: There is no universal expectation or convention regarding the number of paragraphs in the Introduction. The purpose of the introduction is generally to explain to the reader the reasons why the study was conducted—the background of previous research, why such a study is needed, any gaps in knowledge or clear ...
A 1,750 word essay is 11 to 12 paragraphs. A 2,000 word essay is 13 to 14 paragraphs. A 2,500 word essay is 16 to 17 paragraphs. A 3,000 word essay is 20 paragraphs. A 4,000 word essay is 26 to 27 paragraphs. A 5,000 word essay is 33 to 34 paragraphs. A 6,000 word essay is 40 paragraphs.
Typically, a standard length of introductory paragraph is 300-500 words. If your topic needs more than the standard word count than always ask for suggestion from your professor on first priority. We hope now you know how long should an introduction be for a research paper. ... When a high school student writes a research paper, it's usually ...
For the exact word or page count, you would need to know the word count set by the journal. Say the journal limit is 6K words, spreading this across the different sections (from introduction to discussion), you may arrive at a count of about 750-1000 words for the introduction (depending on your topic, of course), and therefore, at a background ...