Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- Permissions
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Project intake
- Resource planning
- Product launches
- View all uses arrow-right icon

- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Leadership |
- 7 important steps in the decision makin ...

7 important steps in the decision making process

The decision making process is a method of gathering information, assessing alternatives, and making a final choice with the goal of making the best decision possible. In this article, we detail the step-by-step process on how to make a good decision and explain different decision making methodologies.
We make decisions every day. Take the bus to work or call a car? Chocolate or vanilla ice cream? Whole milk or two percent?
There's an entire process that goes into making those tiny decisions, and while these are simple, easy choices, how do we end up making more challenging decisions?
At work, decisions aren't as simple as choosing what kind of milk you want in your latte in the morning. That’s why understanding the decision making process is so important.
What is the decision making process?
The decision making process is the method of gathering information, assessing alternatives, and, ultimately, making a final choice.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

The 7 steps of the decision making process
Step 1: identify the decision that needs to be made.
When you're identifying the decision, ask yourself a few questions:
What is the problem that needs to be solved?
What is the goal you plan to achieve by implementing this decision?
How will you measure success?
These questions are all common goal setting techniques that will ultimately help you come up with possible solutions. When the problem is clearly defined, you then have more information to come up with the best decision to solve the problem.
Step 2: Gather relevant information
Gathering information related to the decision being made is an important step to making an informed decision. Does your team have any historical data as it relates to this issue? Has anybody attempted to solve this problem before?
It's also important to look for information outside of your team or company. Effective decision making requires information from many different sources. Find external resources, whether it’s doing market research, working with a consultant, or talking with colleagues at a different company who have relevant experience. Gathering information helps your team identify different solutions to your problem.
Step 3: Identify alternative solutions
This step requires you to look for many different solutions for the problem at hand. Finding more than one possible alternative is important when it comes to business decision-making, because different stakeholders may have different needs depending on their role. For example, if a company is looking for a work management tool, the design team may have different needs than a development team. Choosing only one solution right off the bat might not be the right course of action.
Step 4: Weigh the evidence
This is when you take all of the different solutions you’ve come up with and analyze how they would address your initial problem. Your team begins identifying the pros and cons of each option, and eliminating alternatives from those choices.
There are a few common ways your team can analyze and weigh the evidence of options:
Pros and cons list
SWOT analysis
Decision matrix
Step 5: Choose among the alternatives
The next step is to make your final decision. Consider all of the information you've collected and how this decision may affect each stakeholder.
Sometimes the right decision is not one of the alternatives, but a blend of a few different alternatives. Effective decision-making involves creative problem solving and thinking out of the box, so don't limit you or your teams to clear-cut options.
One of the key values at Asana is to reject false tradeoffs. Choosing just one decision can mean losing benefits in others. If you can, try and find options that go beyond just the alternatives presented.
Step 6: Take action
Once the final decision maker gives the green light, it's time to put the solution into action. Take the time to create an implementation plan so that your team is on the same page for next steps. Then it’s time to put your plan into action and monitor progress to determine whether or not this decision was a good one.
Step 7: Review your decision and its impact (both good and bad)
Once you’ve made a decision, you can monitor the success metrics you outlined in step 1. This is how you determine whether or not this solution meets your team's criteria of success.
Here are a few questions to consider when reviewing your decision:
Did it solve the problem your team identified in step 1?
Did this decision impact your team in a positive or negative way?
Which stakeholders benefited from this decision? Which stakeholders were impacted negatively?
If this solution was not the best alternative, your team might benefit from using an iterative form of project management. This enables your team to quickly adapt to changes, and make the best decisions with the resources they have.
Types of decision making models
While most decision making models revolve around the same seven steps, here are a few different methodologies to help you make a good decision.
Rational decision making models
This type of decision making model is the most common type that you'll see. It's logical and sequential. The seven steps listed above are an example of the rational decision making model.
When your decision has a big impact on your team and you need to maximize outcomes, this is the type of decision making process you should use. It requires you to consider a wide range of viewpoints with little bias so you can make the best decision possible.
Intuitive decision making models
This type of decision making model is dictated not by information or data, but by gut instincts. This form of decision making requires previous experience and pattern recognition to form strong instincts.
This type of decision making is often made by decision makers who have a lot of experience with similar kinds of problems. They have already had proven success with the solution they're looking to implement.
Creative decision making model
The creative decision making model involves collecting information and insights about a problem and coming up with potential ideas for a solution, similar to the rational decision making model.
The difference here is that instead of identifying the pros and cons of each alternative, the decision maker enters a period in which they try not to actively think about the solution at all. The goal is to have their subconscious take over and lead them to the right decision, similar to the intuitive decision making model.
This situation is best used in an iterative process so that teams can test their solutions and adapt as things change.
Track key decisions with a work management tool
Tracking key decisions can be challenging when not documented correctly. Learn more about how a work management tool like Asana can help your team track key decisions, collaborate with teammates, and stay on top of progress all in one place.
Related resources

How to give and take constructive criticism

Data-driven decision making: A step-by-step guide

Listening to understand: How to practice active listening (with examples)

How executives and individual contributors differ when it comes to AI

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)

Team Dynamics: Problem-Solving and Decision Making
- Teamwork and Team Leadership Table of Contents
- Fostering Communication & Promoting Cooperation
- Problem-Solving and Decision Making
- Handling Conflict
- Dealing with Power and Influence
1. Overview
- Different stages of team development call for different problem solving methods
- Problem solving requires the use of a systematic process
- The appropriate decision making method is determined by the amount of time available for the decision and the impact of the decision
- Effective decision making requires the use of smart techniques
2. Problem Solving in Team Development Stages

3. General Problem Solving Steps
- Defining the problem : phrase problem as probing questions to encourage explorative thinking; make explicit goal statement
- Establish criteria for evaluating the solution : identify characteristics of a satisfactory solution; distinguish requirements from desires
- Analyzing the problem : discover the root cause and extent of the problem
- Considering alternate solutions : brainstorm to generate many ideas before judging any of them
- Evaluate alternate solutions : use ranking-weighting matrix; check for issues/disagreement
- Deciding on a solution : choose best answer to the problem from among all possible solutions
- Develop action plan : make team assignments with milestones(don’t underestimate time)
- Implementing the action plan : check for consistency with requirements identified in step 2
- Following up on the solution : check up on the implementation and make necessary adjustments
- Evaluate outcomes and process : review performance, process, and personal aspects of the solution

4. Decision Making Method Based on Time and Impact

5. Smart Decision Making is Enabled By. . .
- Modeling an open mind and asking for candid opinions
- What elements would you choose to change?
- What changes would you make to solve …?
- Aligning rewards to team successes to ensure that individuals share what they know
- Ensuring that team members are aware of relevant roles and unique information required for team success
- Charging some team members to assume a position that opposes the team’s preference
- Creating an alternate team that attempts to find errors and weaknesses in the solution
- Using successive rounds of blind voting interspersed with discussions
6. Additional Readings
- Hartnett, T. (n.d). Consensus decision making. Retrieved from http://www.consensusdecisionmaking.org/
- UMass|Dartmouth (n.d.) 7 steps to effective decision making . Retrieved from https://www.umassd.edu/media/u massdartmouth/fycm/decision_ma king_process.pdf
- Sunstein, C.R. (2014). Making dumb groups smarter. Harvard Business Review, 92(12), 90-98.
- << Previous: Fostering Communication & Promoting Cooperation
- Next: Handling Conflict >>

- Last Updated: Jul 15, 2024 1:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.himmelfarb.gwu.edu/teamdynamics

- Himmelfarb Intranet
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- GW is committed to digital accessibility. If you experience a barrier that affects your ability to access content on this page, let us know via the Accessibility Feedback Form .
- Himmelfarb Health Sciences Library
- 2300 Eye St., NW, Washington, DC 20037
- Phone: (202) 994-2962
- [email protected]
- https://himmelfarb.gwu.edu
Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.
StrategyPunk
Introduction.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. At the end of the blog post, you can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates .
Step 1: Define the Problem
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Step 4: Workplan
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure everyone's perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Communicate
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template, multi-chapter growth strategy framework (free template), lidl swot analysis: free ppt template and in-depth insights.
Discover Lidl's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats with our free PowerPoint template. This in-depth SWOT analysis provides valuable insights to help you understand Lidl's market position and strategic direction.
Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Pestle analysis: decoding reddit's landscape (free ppt).
BUS403: Negotiations and Conflict Management
Problem-Solving and Decision-Making in Groups
This text summarizes common characteristics of problems and the five steps in group problem-solving. The reading describes brainstorming and discussions that should occur before group decision-making, compares and contrasts decision-making techniques, and explores various influences on decision-making. The section "Getting Competent" emphasizes the need for leaders and managers to delegate tasks and responsibilities as they identify specialized skills among their teams and employees.
Group Problem-Solving Process

Group problem-solving can be a confusing puzzle unless it is approached systematically.
There are several variations of similar problem-solving models based on American scholar John Dewey's reflective thinking process. As you read through the steps in the process, think about how you can apply what we learned regarding the general and specific elements of problems. Some of the following steps are straightforward, and they are things we would logically do when faced with a problem.
However, taking a deliberate and systematic approach to problem-solving has been shown to benefit group functioning and performance. A deliberate approach is especially beneficial for groups that do not have an established history of working together and will only be able to meet occasionally.
Although a group should attend to each step of the process, group leaders or other group members who facilitate problem-solving should be cautious not to dogmatically follow each element of the process or force a group along. Such a lack of flexibility could limit group member input and negatively affect cohesion and climate.
Step 1: Define the Problem
Define the problem by considering the three elements shared by every problem: the current undesirable situation, the goal or more desirable situation, and obstacles. At this stage, group members share what they know about the current situation, without proposing solutions or evaluating the information.
Here are some good questions to ask during this stage: What is the current difficulty? How did we come to know that the difficulty exists? Who/what is involved? Why is it meaningful/urgent/important? What have the effects been so far? What, if any, elements of the difficulty require clarification?
At the end of this stage, the group should be able to compose a single sentence that summarizes the problem called a problem statement . Avoid wording in the problem statement or question that hints at potential solutions. A small group formed to investigate ethical violations of city officials could use the following problem statement: "Our state does not currently have a mechanism for citizens to report suspected ethical violations by city officials".
Step 2: Analyze the Problem
During this step a group should analyze the problem and the group's relationship to the problem. Whereas the first step involved exploring the "what" related to the problem, this step focuses on the "why." At this stage, group members can discuss the potential causes of the difficulty. Group members may also want to begin setting an agenda or timeline for the group's problem-solving process, looking forward to the other steps.
To fully analyze the problem, the group can discuss the five common problem variables discussed before. Here are two examples of questions that the group formed to address ethics violations might ask: Why doesn't our city have an ethics reporting mechanism? Do cities of similar size have such a mechanism? Once the problem has been analyzed, the group can pose a problem question that will guide the group as it generates possible solutions. "How can citizens report suspected ethical violations of city officials and how will such reports be processed and addressed?" As you can see, the problem question is more complex than the problem statement, since the group has moved on to more in-depth discussion of the problem during step 2.
Step 3: Generate Possible Solutions
During this step, group members generate possible solutions to the problem. Again, solutions should not be evaluated at this point, only proposed and clarified. The question should be, "What could we do to address this problem?" not "What should we do to address it?" It is perfectly OK for a group member to question another person's idea by asking something like "What do you mean?" or "Could you explain your reasoning more?"
Discussions at this stage may reveal a need to return to previous steps to better define or more fully analyze a problem. Since many problems are multifaceted, group members must generate solutions for each part of the problem separately, ensuring multiple solutions for each part. Stopping the solution-generating process prematurely can lead to groupthink. For the problem question previously posed, the group would need to generate solutions for all three parts of the problem included in the question.
Possible solutions for the first part of the problem (how can citizens report ethical violations?) may include an "online reporting system, email, in-person, anonymously, on-the-record," and so on.
Possible solutions for the second part of the problem (how will reports be processed?) may include "daily by a newly appointed ethics officer, weekly by a nonpartisan nongovernment employee," and so on. Possible solutions for the third part of the problem (how will reports be addressed?) may include "by a newly appointed ethics commission, by the accused's supervisor, by the city manager," and so on.
Step 4: Evaluate Solutions
During this step, solutions can be critically evaluated based on their credibility, completeness, and worth. Once the potential solutions have been narrowed based on more obvious differences in relevance and/or merit, the group should analyze each solution based on its potential effects – especially negative effects. Groups that are required to report the rationale for their decision or whose decisions may be subject to public scrutiny would be wise to make a set list of criteria for evaluating each solution. Additionally, solutions can be evaluated based on how well they fit with the group's charge and the group's abilities.
To do this, group members may ask, "Does this solution live up to the original purpose or mission of the group?" "Can the solution be implemented with our current resources and connections?" and "How will this solution be supported, funded, enforced, and assessed?" Secondary tensions and substantive conflict, two concepts discussed earlier, emerge during this step of problem-solving, and group members will need to employ effective critical thinking and listening skills. Decision-making is part of the larger problem-solving process, and it plays a prominent role in this step. While there are several fairly similar models for problem-solving, there are many varied decision-making techniques that groups can use.
For example, to narrow the proposed solutions, group members may decide by majority vote, by weighing the pros and cons, or by discussing them until a consensus is reached. There are also more complex decision-making models like the "six hats method," which we will discuss later. Once the final decision is reached, the group leader or facilitator should confirm that the group is in agreement. It may be beneficial to let the group break for a while or even to delay the final decision until a later meeting to allow people time to evaluate it outside of the group context.
Step 5: Implement and Assess the Solution
Implementing the solution requires some advanced planning, and it should not be rushed unless the group is operating under strict time restraints or delay may lead to some kind of harm. Although some solutions can be implemented immediately, others may take days, months, or years. As was noted earlier, it may be beneficial for groups to poll those affected by the solution to their opinion or even to do a pilot test to observe the solution's effectiveness and how people react to it.
Before implementation, groups should also determine how and when they would assess the solution's effectiveness by asking, "How will we know if the solution is working?" Since solution assessment will vary based on whether or not the group is disbanded, groups should also consider the following questions: If the group disbands after implementation, who will be responsible for assessing the solution? If the solution fails, will the same group reconvene or will a new group be formed?

Once a solution has been reached and the group has the "green light" to implement it, it should proceed deliberately and cautiously, making sure to consider possible consequences and address them as needed. Certain elements of the solution may need to be delegated to various people inside and outside the group. Group members may also be assigned to implement a particular part of the solution based on their role in the decision-making or because it connects to their expertise. Likewise, group members may be tasked with publicizing the solution or "selling" it to a particular group of stakeholders. Last, the group should consider its future. In some cases, the group will get to decide if it will stay together and continue working on other tasks or if it will disband. In other cases, outside forces determine the group's fate.
Getting Competent
Giving a group presentation requires that individual group members and the group solve many problems and make many decisions. Although having more people involved in a presentation increases logistical difficulties and has the potential to create more conflict, a well-prepared and well-delivered group presentation can be more engaging and effective than a typical presentation.
The main problems facing a group giving a presentation are (1) dividing responsibilities, (2) coordinating schedules and time management, and (3) working out the logistics of the presentation delivery.
Regarding dividing responsibilities, assigning individual work at the first meeting and then trying to fit it all together before the presentation (which is what many college students do when faced with a group project) is not the recommended method. Integrating content and visual aids created by several different people into a seamless final product takes time and effort, and the person "stuck" with this job at the end usually ends up developing some resentment toward his or her group members.
While it is OK for group members to work independently outside of group meetings, spend time working together to help set up some standards for content and formatting expectations that will help make later integration of work easier. Taking the time to complete one part of the presentation together can help set those standards for later individual work.
Discuss the roles various group members will play openly to avoid role confusion. There could be one point person for keeping track of the group's progress and schedule, one point person for communication, one point person for content integration, one point person for visual aids, and so on. Each person shouldn't do all that work on his or her own but help focus the group's attention on his or her specific area during group meetings.
Scheduling group meetings is one of the most challenging problems groups face, given people's busy lives. From the beginning, it should be communicated that the group needs to spend considerable time in face-to-face meetings. Group members should know they may have to sacrifice occasionally to attend. Especially important is the commitment to scheduling time to rehearse the presentation. Consider creating a contract of group guidelines that includes expectations for meeting attendance to increase group members' commitment.
Group presentations require members to navigate many logistics of their presentation. While it may be easier for a group to assign each member to create a five-minute segment and then transition from one person to the next, this is not the most engaging method. Creating a master presentation and assigning individual speakers creates a more fluid and dynamic presentation. It allows everyone to become familiar with the content, which can help if a person does not show up to present and during the question-and-answer section.
Once the presentation's content is complete, figure out introductions, transitions, visual aids, and the use of time and space. In terms of introductions, figure out if one person will introduce all the speakers at the beginning, if speakers will introduce themselves at the beginning, or if introductions will occur as the presentation progresses. In terms of transitions, make sure each person has included in his or her speaking notes when presentation duties switch from one person to the next.
Visual aids can potentially cause hiccups in a group presentation if they aren't fluidly integrated. Practicing visual aids and having one person control them may help prevent this. Know how long your presentation is and know how you're going to use the space. Presenters should know how long the whole presentation should be and how long each segment should be so that everyone can share the responsibility of keeping time. Also consider the size and layout of the presentation space. You don't want presenters huddled in a corner until it's their turn to speak or trapped behind furniture when their turn comes around.
Of the three main problems facing group presenters, which do you think is the most challenging and why?
- Why do you think people tasked with a group presentation (especially students) prefer to divide the parts and have members work on them independently before coming back together and integrating each part?
- What problems emerge from this method? In what ways might developing a master presentation and then assigning parts to different speakers be better than the more divided method? What are the drawbacks to the master presentation method?
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The 5 steps of the solving problem process
August 17, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Whether you run a business, manage a team, or work in an industry where change is the norm, it may feel like something is always going wrong. Thankfully, becoming proficient in the problem solving process can alleviate a great deal of the stress that business issues can create.
Understanding the right way to solve problems not only takes the guesswork out of how to deal with difficult, unexpected, or complex situations, it can lead to more effective long-term solutions.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Understanding the problem solving process
When something isn’t working, it’s important to understand what’s at the root of the problem so you can fix it and prevent it from happening again. That’s why resolving difficult or complex issues works best when you apply proven business problem solving tools and techniques – from soft skills, to software.
The problem solving process typically includes:
- Pinpointing what’s broken by gathering data and consulting with team members.
- Figuring out why it’s not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem.
- Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution.
While skills like active listening, collaboration, and leadership play an important role in problem solving, tools like visual mapping software make it easier to define and share problem solving objectives, play out various solutions, and even put the best fit to work.
Before you can take your first step toward solving a problem, you need to have a clear idea of what the issue is and the outcome you want to achieve by resolving it.
For example, if your company currently manufactures 50 widgets a day, but you’ve started processing orders for 75 widgets a day, you could simply say you have a production deficit.
However, the problem solving process will prove far more valuable if you define the start and end point by clarifying that production is running short by 25 widgets a day, and you need to increase daily production by 50%.
Once you know where you’re at and where you need to end up, these five steps will take you from Point A to Point B:
- Figure out what’s causing the problem . You may need to gather knowledge and evaluate input from different documents, departments, and personnel to isolate the factors that are contributing to your problem. Knowledge visualization software like MindManager can help.
- Come up with a few viable solutions . Since hitting on exactly the right solution – right away – can be tough, brainstorming with your team and mapping out various scenarios is the best way to move forward. If your first strategy doesn’t pan out, you’ll have others on tap you can turn to.
- Choose the best option . Decision-making skills, and software that lets you lay out process relationships, priorities, and criteria, are invaluable for selecting the most promising solution. Whether it’s you or someone higher up making that choice, it should include weighing costs, time commitments, and any implementation hurdles.
- Put your chosen solution to work . Before implementing your fix of choice, you should make key personnel aware of changes that might affect their daily workflow, and set up benchmarks that will make it easy to see if your solution is working.
- Evaluate your outcome . Now comes the moment of truth: did the solution you implemented solve your problem? Do your benchmarks show you achieved the outcome you wanted? If so, congratulations! If not, you’ll need to tweak your solution to meet your problem solving goal.
In practice, you might not hit a home-run with every solution you execute. But the beauty of a repeatable process like problem solving is that you can carry out steps 4 and 5 again by drawing from the brainstorm options you documented during step 2.
Examples of problem solving scenarios
The best way to get a sense of how the problem solving process works before you try it for yourself is to work through some simple scenarios.
Here are three examples of how you can apply business problem solving techniques to common workplace challenges.
Scenario #1: Manufacturing
Building on our original manufacturing example, you determine that your company is consistently short producing 25 widgets a day and needs to increase daily production by 50%.
Since you’d like to gather data and input from both your manufacturing and sales order departments, you schedule a brainstorming session to discover the root cause of the shortage.
After examining four key production areas – machines, materials, methods, and management – you determine the cause of the problem: the material used to manufacture your widgets can only be fed into your equipment once the machinery warms up to a specific temperature for the day.
Your team comes up with three possible solutions.
- Leave your machinery running 24 hours so it’s always at temperature.
- Invest in equipment that heats up faster.
- Find an alternate material for your widgets.
After weighing the expense of the first two solutions, and conducting some online research, you decide that switching to a comparable but less expensive material that can be worked at a lower temperature is your best option.
You implement your plan, monitor your widget quality and output over the following week, and declare your solution a success when daily production increases by 100%.
Scenario #2: Service Delivery
Business training is booming and you’ve had to onboard new staff over the past month. Now you learn that several clients have expressed concern about the quality of your recent training sessions.
After speaking with both clients and staff, you discover there are actually two distinct factors contributing to your quality problem:
- The additional conference room you’ve leased to accommodate your expanding training sessions has terrible acoustics
- The AV equipment you’ve purchased to accommodate your expanding workforce is on back-order – and your new hires have been making do without
You could look for a new conference room or re-schedule upcoming training sessions until after your new equipment arrives. But your team collaboratively determines that the best way to mitigate both issues at once is by temporarily renting the high-quality sound and visual system they need.
Using benchmarks that include several weeks of feedback from session attendees, and random session spot-checks you conduct personally, you conclude the solution has worked.
Scenario #3: Marketing
You’ve invested heavily in product marketing, but still can’t meet your sales goals. Specifically, you missed your revenue target by 30% last year and would like to meet that same target this year.
After collecting and examining reams of information from your sales and accounting departments, you sit down with your marketing team to figure out what’s hindering your success in the marketplace.
Determining that your product isn’t competitively priced, you map out two viable solutions.
- Hire a third-party specialist to conduct a detailed market analysis.
- Drop the price of your product to undercut competitors.
Since you’re in a hurry for results, you decide to immediately reduce the price of your product and market it accordingly.
When revenue figures for the following quarter show sales have declined even further – and marketing surveys show potential customers are doubting the quality of your product – you revert back to your original pricing, revisit your problem solving process, and implement the market analysis solution instead.
With the valuable information you gain, you finally arrive at just the right product price for your target market and sales begin to pick up. Although you miss your revenue target again this year, you meet it by the second quarter of the following year.
Kickstart your collaborative brainstorming sessions and try MindManager for free today !
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager

- Management Consulting
- IT Services – ERP
- IT Services – Business Dashboard
- IT Services – Robotic Process Automation
- Employee Skill Development
- Training & Certification programs
- Programs to enhance placement offers
- Success stories
5 Phases of Problem-Solving using the Six Sigma DMAIC approach
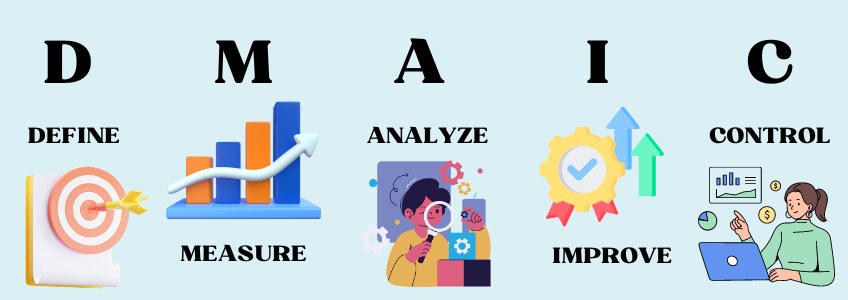
In the world of continuous improvement, the Six Sigma DMAIC methodology stands out as a powerful tool for problem-solving and process optimization.
|| 10 minutes read ||
Overview of the problem and the approach taken
In this blog, we delve into how a team of professionals tackled a daunting $65 million issue using DMAIC – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve and Control. By leveraging tools such as Pareto analysis, fishbone diagrams, 5 Whys, Gemba walks, and SCAMPER brainstorming sessions, the team was able to identify root causes, generate innovative solutions, and implement sustainable changes.
Join us on this step-by-step guide to see how DMAIC, combined with teamwork and strategic planning, can lead to successful problem resolution and long-term results.
1. Define: Identifying the problem and setting goals
In the Define phase of DMAIC, the first crucial step is to identify the problem at hand. By defining the problem statement and setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals, the team can align their efforts toward a common objective. It is essential to gather relevant data, engage stakeholders, and establish a baseline for current performance.
Through effective communication and collaboration, the team can ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the issue and the desired outcome.
Stay tuned to learn, how a well-defined problem statement lays the foundation for the success of the DMAIC process.
2. Measure: Collecting data and analyzing the current state
In the Measure phase of DMAIC, the focus shifts to collecting relevant data and analyzing the current state of affairs. This step involves identifying key metrics, establishing data collection methods, and ensuring data accuracy and reliability. By analyzing the gathered information, the team can gain valuable insights into the root causes of the problem and quantify the extent of the issue. Through rigorous data analysis and interpretation, the team can uncover patterns and trends that will guide future improvement efforts.
Stay tuned to discover how data-driven decision-making plays a crucial role in solving the 65-million-dollar problem using the DMAIC methodology.
3. Analyze: Identifying root causes and potential solutions
In the Analyze phase of DMAIC, the focus shifts towards identifying the root causes of the problem and exploring potential solutions. This stage involves conducting a thorough analysis of the collected data to pinpoint underlying issues that contribute to the $65 million problem. By utilizing various tools and techniques such as root cause analysis, fishbone diagrams, and statistical analysis, the team can delve deeper into the factors influencing the problem.
Through this meticulous process, the team can gain a comprehensive understanding of the issues at hand, paving the way for informed decision-making and targeted action plans.
Stay tuned to uncover, how the Analyze phase propels us closer to resolving the multi-million-dollar challenge.
4. Improve: Implementing changes and measuring results
In the Improve phase of DMAIC, the focus is on implementing solutions identified during the Analyze phase to address the root causes of the $65 million problem.
This stage involves developing and executing action plans aimed at improving processes and eliminating inefficiencies. By carefully monitoring and measuring the outcomes of these changes, the team can determine their effectiveness in tackling the problem. Continuous evaluation and adjustment of strategies are key elements of this phase to ensure sustainable improvements.
Stay engaged as we dive into how the Improve phase plays a pivotal role in transforming our approach to resolving this high-stakes challenge.
5. Control: Monitoring progress and sustaining improvements
In the final phase of DMAIC, Control, the emphasis shifts towards monitoring the progress of implemented solutions to ensure sustained improvements in addressing the $65 million problem. This stage involves establishing control measures and mechanisms to track key performance indicators and verify that the desired outcomes are being achieved consistently.
By setting up regular reviews and audits, the team can identify any deviations or issues early on, enabling prompt corrective action. Maintaining open communication channels and documenting procedures are essential in upholding the gains achieved during the Improve phase.
Join us as we explore how effective control measures solidify the success of DMAIC in resolving complex challenges.
Results and Lessons learned from using DMAIC

After implementing DMAIC in addressing the $65 million problem, the results were profound. By following the structured approach of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, the team successfully identified root causes, developed effective solutions, and ensured sustained improvements. The financial impact of saving $65 million is significant, showcasing the power of DMAIC in problem-solving.
Key lessons learned from this case study include the importance of data-driven decision-making, collaboration among team members from diverse backgrounds, and the value of maintaining a systematic and structured approach throughout the problem-solving process.
Stay tuned to gain further insights into how DMAIC can be leveraged to overcome complex challenges effectively.
Conclusion and final thoughts
In conclusion, the case study highlighting the successful resolution of a $65 million problem through DMAIC reinforces the effectiveness of this structured problem-solving methodology. The disciplined approach of Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control proved invaluable in achieving significant cost savings and sustainable improvements. Emphasizing data-driven decision- making, cross-functional collaboration, and systematic problem-solving methods were key takeaways.
As organizations face increasingly complex challenges, leveraging DMAIC can provide a systematic framework for driving positive change and delivering tangible results. By adhering to the principles of DMAIC, businesses can enhance their problem-solving capabilities and achieve long-term success.
If you are interested to achieve similar success stories, write to us!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to our Blogs

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The final stage of the problem-solving process during which decision makers evaluate the implementation is called the _____ stage., _____ decisions deal with unusual or exceptional situations and, in many cases, these decisions are difficult to quantify., In general, computerized decision support systems can either optimize or ...
a process that goes beyond decision making to include the implementation stage. a stage of problem solving in which a solution is put into effect. a decision made using a rule, procedure, or quantitative method. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like decision-making phase, intelligence phase, design stage and more.
A process that goes beyond decision making to include the implementation stage. A stage of problem solving n which a solution is put into effect. The final stage of the problem solving process, in which decision makers evaluate the implementation. A decision made using a rule, procedure, or quantative method.
Question: In the stage of the problem-solving process, decision makers evaluate the implementation to determine whether the anticipated results were achieved and to modify the process in light of new information.A implementationmonitoringC designD intelligence
Question: In the q, stage of the problem-solving process, decision makers evaluate the implementation to determine whether the anticipated results were achieved and to modify the process in light of new information.A implementationB monitoringC designD intelligence
Problem-solving is an important part of planning and decision-making. The process has much in common with the decision-making process, and in the case of complex decisions, can form part of the process itself. We face and solve problems every day, in a variety of guises and of differing complexity. Some, such as the resolution of a serious ...
In other situations, the process can drag on for weeks or even months. The entire decision‐making process is dependent upon the right information being available to the right people at the right times. The decision‐making process involves the following steps: 1.Define the problem. 2.Identify limiting factors. 3.Develop potential alternatives.
Step 3: Identify alternative solutions. This step requires you to look for many different solutions for the problem at hand. Finding more than one possible alternative is important when it comes to business decision-making, because different stakeholders may have different needs depending on their role.
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
the final stage of the problem-solving process in which decision makers evaluate the implementation; can include feedback and adjustment. Decision Tree Analysis. a decision-making technique that diagrams major decisions and possible outcomes from these decisions. Programmed Decision.
The Problem-Definition Process encourages you to define and understand the problem that you're trying to solve, in detail. It also helps you confirm that solving the problem contributes towards your organization's objectives. This stops you spending time, energy, and resources on unimportant problems, or on initiatives that don't align with ...
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Different stages of team development call for different problem solving methods; Problem solving requires the use of a systematic process; The appropriate decision making method is determined by the amount of time available for the decision and the impact of the decision; Effective decision making requires the use of smart techniques
Step 1: Define the Problem. The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable. One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions.
Step 1: Define the Problem. Define the problem by considering the three elements shared by every problem: the current undesirable situation, the goal or more desirable situation, and obstacles. At this stage, group members share what they know about the current situation, without proposing solutions or evaluating the information.
first part of problem solving, including three stages: intelligence, design, and choice. ... process that goes beyond decision making to include the implementation stage. ... decision makers evaluate the implementation to determine whether the anticipated results were achieved and to modify the implementation if needed. programmed decision ...
a process that goes beyond decision making to include the implementation and monitoring stages. implementation stage. a stage of problem solving in which a solution is put into effect. monitoring stage. the final stage of the problems-sovling process, in which decision makers evaluate the implementation. programmed decision. a decision made ...
The problem solving process typically includes: Pinpointing what's broken by gathering data and consulting with team members. Figuring out why it's not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem. Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution. While skills like active listening ...
Step 2: Analyze the Problem. During this step a group should analyze the problem and the group's relationship to the problem. Whereas the first step involved exploring the "what" related to the problem, this step focuses on the "why.". At this stage, group members can discuss the potential causes of the difficulty.
1. Define: Identifying the problem and setting goals In the Define phase of DMAIC, the first crucial step is to identify the problem at hand. By defining the problem statement and setting specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals, the team can align their efforts toward a common objective. It is essential to gather relevant data, engage stakeholders, and ...
Business; Operations Management; Operations Management questions and answers; stage of the problem-solving process, decision makers evaluate the implementation to determine whether the anticipated res ere achieved and to modify the process in light of new information.A implementationB monitoringC designD intelligence
A. One characteristic of a structured problem is that _____. a. it is straightforward, requiring known facts and relationships c. the data might be difficult to manipulate or obtain. b. the relationships among the pieces of data are not always clear d. the decision maker might not know the information requirements of the decision in advance. B.