Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods

What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics


What to Include in a Case Study: Layout, Content & Visuals
Learn what info to include in a business case study and how to structure it for maximum conversion, and see real-life examples and templates.

Dominika Krukowska
9 minute read

Short answer
What to include in a case study?
A successful case study should include the following elements:
- Introduction (what was the problem and how it was solved in 1-2 sentences)
- Client overview
- The problem or challenge
- How they solved their problem (with your solution)
- Customer quotes and testimonials
For a case study to work all critical components must be in place.
Case studies can be gold mines for conversions, but extracting that gold isn't as straightforward as it seems.
What goes into a case study that tells a compelling story and draws your prospects down the conversion funnel?
There are some critical elements that you must include in your case study if you hope to generate conversions.
Yes, you read that right— making a partial case study could very well mean leaving money on the table.
In this post, I’ll share with you the secrets to creating a case study that’ll turn it from ‘blah’ to ‘bingo’.
You’ll learn what you must include in your case study to convert readers into buyers.
Let’s go!
What to include in your case study structure?
Crafting your case study is like writing a gripping novel, filled with characters, conflicts, and resolutions. Each component of your case study serves a unique purpose in narrating the story of how your product or service helps your clients conquer their challenges.
Here are the main chapters of your case study structure:
1. Introduction
Think of the introduction as your story's opening scene. It's your first impression, your initial hook, the gateway to the world you're about to unfold. Here, you aim to spark curiosity and give your reader a taste of the journey ahead.
How to create an introduction slide:
Include a video —this will get 32% more people to interact with your case study .
Create an opening line that instantly hooks your reader —think surprising statistics, bold statements, or intriguing questions.
Introduce the central theme of your case study —what's the big challenge or opportunity at play?
Connect with the reader's pain points to foster engagement right from the start.
Here’s an example of an introduction slide that hooks attention:

2. Company overview
Here, you introduce your main hero—your client. You want to provide a clear and relatable backdrop that helps your audience understand who your client is, what they do, and what stakes are at play for them.
How to create a company overview slide:
Offer key details about the client's business —what's their industry? What's their market position?
Highlight the client's aspirations and values —this helps to humanize the company and build emotional connection.
Make sure to relate the company's context back to your reader. How does this company's situation reflect the challenges or opportunities your reader might face?
Here’s an example of a company overview slide:

3. The problem or challenge
This is the conflict that propels your story. It's the mountain your client needs to climb, the dragon they must slay. Without a significant problem or challenge, there's no tension, and without tension, there's no story and no engagement.
How to create a problem slide:
Clearly articulate the problem or challenge. Make it tangible and relatable.
Explore the implications of this problem. What's at stake for the client if it goes unresolved?
Aim to evoke emotion here. The more your reader feels the weight of the problem, the more invested they'll be in the solution.
Here’s an example of a problem slide:

4. Your solution
Enter the trusted guide and confidant—your product or service. This is the pivotal moment where your client's fortunes begin to turn. Show how your offering comes into play, lighting the way toward resolution.
How to create a solution slide:
Detail how your solution addresses the client's problem. Show how the features of your product or service connect to the challenges at hand.
Walk your reader through the implementation process. Offer insights into the collaborative efforts and innovative approaches that made the difference.
Don’t shy away from any obstacles or setbacks that occurred during the solution phase. Showing how you overcame these can actually make your story more credible and relatable.
Here’s an example of a solution slide:

This is the climax of your story, where all the tension that's been built up finally gets released. You need to demonstrate the transformation that occurred as a result of your solution.
How to create a results slide:
Show, don't tell. Use numbers, stats, and graphs to make your results concrete and impactful.
Discuss not just quantitative, but also qualitative results. How did your solution affect the client's morale, their customer satisfaction, their market reputation? Give detailed examples set in short anecdotes as experienced by a person (not an organization).
A side-by-side comparison of the 'before' and 'after' can be a powerful visual aid to highlight your impact.
Here’s an example of a results slide:

6. Customer quotes/testimonials
Nothing reinforces a story better than having the hero vouch for its authenticity. Direct quotes from your client add depth, credibility, and emotional resonance to your case study.
How to create a testimonials slide:
Select quotes that reinforce the narrative of your case study.
The more genuine and heartfelt, the better. Authenticity speaks volumes.
Consider sprinkling testimonials throughout the case study rather than bunching them together to keep the reader engaged.
Here’s an example of a testimonials slide:

7. Next steps
Your story doesn’t end when the problem is solved. This is where you guide your reader toward the future, inspiring them to take action based on the journey they've just been through.
How to create a next steps slide:
Provide clear and compelling calls-to-action. What do you want the reader to do next? Download a whitepaper? Request a demo? Sign up and try your solution? Make it a small concession, not a big ask. The next reasonable action they can take to establish the relationship a tiny bit further.
Make it simple for readers to take the next step. Include links, contact information, or even embed your calendar into the case study.
Here’s an example of a next steps slide:

What storytelling elements to include in a case study?
Compelling storytelling is an art, and when applied to business case studies, it can turn a rather dry piece of data into a riveting tale of success.
It's a chance to illustrate your value proposition in the real world, giving prospective clients a peek at what they could experience when they choose to work with you.
Here are some storytelling elements to include in your case study:
1. A clear storyline
Start with the basics: Who is your customer? What was their challenge? How did your product or service solve their problem? And, what was the outcome?
This forms the narrative arc of your case study, providing a backbone for your story. Ensure it’s a seamless narrative, taking the reader along a journey of transformation.
Here’s our recommended presentation storyline:
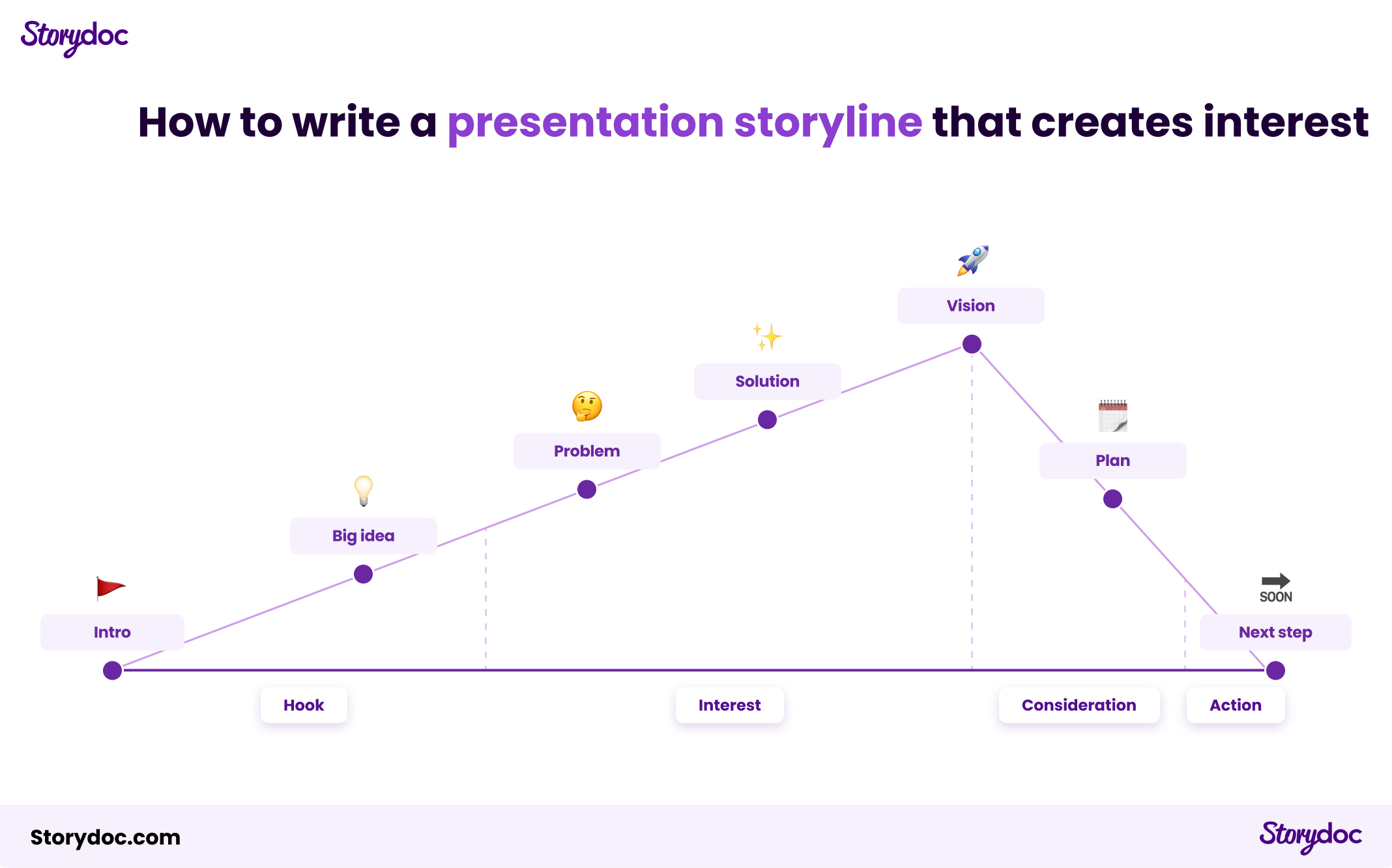
2. Concrete outcomes
Data provides the meat of your case study. Numbers, percentages, and concrete results serve as proof that your solution works.
It's one thing to claim that your product or service is effective, but showcasing the results achieved by a real customer through hard data adds credence to your assertions.
3. Visuals that support and expand on the text
Just as a picture is worth a thousand words, well-placed visuals in your case study can make the message clearer and more compelling.
Graphs, charts, and infographics can help break down complex data, making it easier for the audience to digest. Furthermore, they break up long blocks of text, making your case study more engaging.
4. Interactive elements
In a world where scrolling has become second nature, your case study needs to be more than a static document.
Incorporating interactive elements like tabs to click through benefits, live data calculators, or sliders with case studies and customer testimonials invites your audience to engage with your content actively.
Our research showed that decks with interactive elements got scrolled to the bottom 41% more often and had a 21% longer average reading time than non-interactive ones.
Making interactive case studies sounds complicated but it’s actually very easy if you do it with our AI case study creator . You can send it to prospects directly from Storydoc or embed it as part of your website.
By making your reader an active participant in the story, you boost their engagement and increase the chances of them reading your content through to the end.
Benefits of including interactive elements in your case study presentation
More decks read in full
Longer average reading time
5. Testimonials and quotes directly from customers
Customer testimonials and direct quotes inject a sense of authenticity and credibility into your case study.
They bring a human touch to your narrative and foster trust in potential clients.
It's no longer just your voice touting the effectiveness of your solution; it's the voice of a satisfied customer who has personally experienced the benefits of your product or service.
6. Clear call to action
Finally, after painting a vivid picture of your product or service in action, you need to tell your audience what to do next.
A clear CTA—whether it’s to learn more, book a demo, or sign up—makes the next step evident for your audience.
Our data reveals that decks with a clear next step had a conversion rate 27% higher than those that ended with a generic "thank you."
Make the next step simple, straightforward, and compelling, so your reader knows precisely what to do to start their own success story with you.
What not to include in your case study?
While we've covered the essentials to include in your case study, it's equally important to identify elements that could distract from your message, decrease trust, or even confuse your audience.
Here's what you should avoid including in your case study:
1. Unverified claims / data
Every claim you make and every piece of data you share in your case study must be true and easy to check.
Trust is crucial in a case study, and even one bit of wrong information can damage trust and hurt your image.
So, make sure all your facts, figures, and results are correct, and always get the right permissions to share them.
2. Confidential or sensitive information
When writing a case study, it's crucial to remember that privacy matters. Even though it's exciting to share all the details, you need to protect your client's private information.
Always get clear permission before using any client data and remember to hide any information that could identify specific individuals.
This careful approach shows your respect for privacy and builds trust with your audience, making your case study not just engaging, but also responsible and professional.
3. Technical jargon
A case study should be easy for everyone to understand, so avoid using industry-specific language. Even if you know the jargon, your audience might not.
Keeping your language simple and clear will help more people understand your case study. Too much technical language can confuse readers and distract from the story you're trying to tell.
4. Salesy language
While a case study is designed to show prospective clients how valuable your offer is, it's important not to sound too pushy.
A case study should tell a story, not sound like a sales pitch. Keep your language helpful and interesting. The success story should be enough to sell itself.
Create your best case study yet from ready-made templates
Now that you're equipped with all the essentials of crafting a compelling case study, it's time to bring your narrative to life.
Don’t work hard if you can work easy and get better results.
Interactive case study templates are your shortcut to creating engaging and informative case studies. They provide a clear path for your narrative, intuitive ways to present your data, and an engaging space for sharing customer testimonials.
Grab a template, and let your story do the talking!

Hi, I'm Dominika, Content Specialist at Storydoc. As a creative professional with experience in fashion, I'm here to show you how to amplify your brand message through the power of storytelling and eye-catching visuals.

Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
Create your best case study to date
Try Storydoc interactive case study creator for 14 days free (keep any presentation you make forever!)
- Content Writing Services
- Get in Touch
9 Components of a Case Study You Absolutely Need to Include
SaaS case studies help you educate prospects on the value of your products and the results your customers have achieved. To make your case study creation process easier, it’s crucial to follow a format. In this post, learn the 9 components of a case study you need to include in order to provide the social proof your prospects are looking for.
This is the first post in a 9-part series on how to write a B2B case study .
Must-have components of a case study
1. a compelling executive summary.
One of the most important components of a case study is a powerful executive summary . It lets your reader know what they’re getting into, and how they might relate to and benefit from what they’ll learn. Firstly, it needs to introduce your customer and their challenges. Secondly, it should highlight how your B2B SaaS company helped deliver the right solution. And be sure to include a preview of the results your customer saw from your products.

2. Outline your customer’s challenges
Illustrating the obstacles your customer faced that prompted them to seek out a B2B SaaS solution is one of the most crucial components of a case study. For example, maybe their business processes were a drain on time, resources or budgets—or all of the above. This section is an ideal spot to use a customer quote and let them share their story in their words. Remember to paint your customer in a positive light. And focus on how they wanted to improve their business, and avoid overly negative language.

3. Lead your reader along your customer’s journey
Help your reader picture themselves in your customer’s shoes. Lay out the steps your customer took to try to solve their problem, including an overview of the other products they investigated before they decided on yours. But be mindful not to toot your own horn—you’re simply recapping the facts.
4. The moment of discovery
The core elements of a case study wouldn’t be complete without a section on how your customer decided on your specific B2B SaaS solution. First, provide insight into which of their business requirements it met. Then include any other reasons the partnership was a good fit—perhaps your companies shared similar organizational values. This is an area where case study testimonials make for powerful storytelling . They allow you to set your case study up to dive into how you and your product solved your customer’s challenges.

5. Spend some time on the solution
In the “solution” component of your case study, you get to pitch your products without the fear of sounding like a used car salesman. Remember, you didn’t rush in and save the day—this is about your customer’s goals and how your solution helped them reach their objectives. As a result, you simply need to outline the products your customer purchased and the benefits they provided.

6. Walk your reader through the implementation
Change can be daunting, especially when it comes to the unknown, so it’s crucial that you give your reader a clear sense of how the implementation process went for your customer. For example, if problems arose, don’t be afraid to be transparent about them, but tie the storyline back to how you and your customer overcame the challenges. This is one of the most important components of a case study, and is an opportunity to let your customer service shine.
7. Celebrate your customer’s results
77% of SaaS companies include metrics in at least 50% of their case studies . Metrics are where you can show off the data—hard numbers like revenue gains and time saved that illustrate the return on investment your customer gained from your solution. Showcase how well your products solved the customer’s problems. Find out what to do if you don’t have case study metrics to work with.

8. Close the loop with a call to action
Using the right components of a case study so far has helped keep your reader’s attention until the end of the piece, creating an important opportunity for you to guide them to the next step you want them to take. You can accomplish this by including a clear call to action (CTA) that speaks directly to them at the end of your B2B SaaS case study. See these case study CTA examples to learn how to make your calls to action stand out.

9. Don’t get too caught up in using the perfect format
A lot of experts will tell you that your content needs to include all of the components of a case study and follow a structured formula. But don’t stress over this.
A creative story doesn’t lock itself into anything too prescriptive. And you don’t have to chunk your content into specific modules like some ’90s business plan. The most interesting and compelling stories take a creative approach to case study layout , and they play with perspective.
9 components of a case study: did you include them all?
Now that you know the 9 parts of a case study, take a look back through your own case studies. Have you included each of the components?
And last, but certainly not least, have you squeezed every last ounce of value from your case studies? Here are 8 ways to fully leverage your case studies for maximum results.
Get help writing your case studies
Partnering with a SaaS content marketing agency like Uplift Content allows you to produce a consistent flow of high-quality marketing and sales collateral that generates and nurtures leads—and closes sales faster. Check out our case study writing services .

As the founder of Uplift Content, Emily leads her team in creating done-for-you case studies, ebooks and blog posts for high-growth SaaS companies like ClickUp, Calendly and WalkMe. Connect with Emily on Linkedin
Sign up for the Content Huddle newsletter
Learn from Emily’s 17 years of aha moments, mistakes, observations, and insights—and find out how you can apply these lessons to your own marketing efforts.
You can unsubscribe any time. Visit our Terms of Use for information on our privacy practices.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Designing and Conducting Case Studies
This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of records, and collections of writing samples. Starting with a definition of the case study, the guide moves to a brief history of this research method. Using several well documented case studies, the guide then looks at applications and methods including data collection and analysis. A discussion of ways to handle validity, reliability, and generalizability follows, with special attention to case studies as they are applied to composition studies. Finally, this guide examines the strengths and weaknesses of case studies.
Definition and Overview
Case study refers to the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including the accounts of subjects themselves. A form of qualitative descriptive research, the case study looks intensely at an individual or small participant pool, drawing conclusions only about that participant or group and only in that specific context. Researchers do not focus on the discovery of a universal, generalizable truth, nor do they typically look for cause-effect relationships; instead, emphasis is placed on exploration and description.
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. This type of comprehensive understanding is arrived at through a process known as thick description, which involves an in-depth description of the entity being evaluated, the circumstances under which it is used, the characteristics of the people involved in it, and the nature of the community in which it is located. Thick description also involves interpreting the meaning of demographic and descriptive data such as cultural norms and mores, community values, ingrained attitudes, and motives.
Unlike quantitative methods of research, like the survey, which focus on the questions of who, what, where, how much, and how many, and archival analysis, which often situates the participant in some form of historical context, case studies are the preferred strategy when how or why questions are asked. Likewise, they are the preferred method when the researcher has little control over the events, and when there is a contemporary focus within a real life context. In addition, unlike more specifically directed experiments, case studies require a problem that seeks a holistic understanding of the event or situation in question using inductive logic--reasoning from specific to more general terms.
In scholarly circles, case studies are frequently discussed within the context of qualitative research and naturalistic inquiry. Case studies are often referred to interchangeably with ethnography, field study, and participant observation. The underlying philosophical assumptions in the case are similar to these types of qualitative research because each takes place in a natural setting (such as a classroom, neighborhood, or private home), and strives for a more holistic interpretation of the event or situation under study.
Unlike more statistically-based studies which search for quantifiable data, the goal of a case study is to offer new variables and questions for further research. F.H. Giddings, a sociologist in the early part of the century, compares statistical methods to the case study on the basis that the former are concerned with the distribution of a particular trait, or a small number of traits, in a population, whereas the case study is concerned with the whole variety of traits to be found in a particular instance" (Hammersley 95).
Case studies are not a new form of research; naturalistic inquiry was the primary research tool until the development of the scientific method. The fields of sociology and anthropology are credited with the primary shaping of the concept as we know it today. However, case study research has drawn from a number of other areas as well: the clinical methods of doctors; the casework technique being developed by social workers; the methods of historians and anthropologists, plus the qualitative descriptions provided by quantitative researchers like LePlay; and, in the case of Robert Park, the techniques of newspaper reporters and novelists.
Park was an ex-newspaper reporter and editor who became very influential in developing sociological case studies at the University of Chicago in the 1920s. As a newspaper professional he coined the term "scientific" or "depth" reporting: the description of local events in a way that pointed to major social trends. Park viewed the sociologist as "merely a more accurate, responsible, and scientific reporter." Park stressed the variety and value of human experience. He believed that sociology sought to arrive at natural, but fluid, laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society. These laws weren't static laws of the kind sought by many positivists and natural law theorists, but rather, they were laws of becoming--with a constant possibility of change. Park encouraged students to get out of the library, to quit looking at papers and books, and to view the constant experiment of human experience. He writes, "Go and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesque. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seats of your pants dirty in real research."
But over the years, case studies have drawn their share of criticism. In fact, the method had its detractors from the start. In the 1920s, the debate between pro-qualitative and pro-quantitative became quite heated. Case studies, when compared to statistics, were considered by many to be unscientific. From the 1930's on, the rise of positivism had a growing influence on quantitative methods in sociology. People wanted static, generalizable laws in science. The sociological positivists were looking for stable laws of social phenomena. They criticized case study research because it failed to provide evidence of inter subjective agreement. Also, they condemned it because of the few number of cases studied and that the under-standardized character of their descriptions made generalization impossible. By the 1950s, quantitative methods, in the form of survey research, had become the dominant sociological approach and case study had become a minority practice.
Educational Applications
The 1950's marked the dawning of a new era in case study research, namely that of the utilization of the case study as a teaching method. "Instituted at Harvard Business School in the 1950s as a primary method of teaching, cases have since been used in classrooms and lecture halls alike, either as part of a course of study or as the main focus of the course to which other teaching material is added" (Armisted 1984). The basic purpose of instituting the case method as a teaching strategy was "to transfer much of the responsibility for learning from the teacher on to the student, whose role, as a result, shifts away from passive absorption toward active construction" (Boehrer 1990). Through careful examination and discussion of various cases, "students learn to identify actual problems, to recognize key players and their agendas, and to become aware of those aspects of the situation that contribute to the problem" (Merseth 1991). In addition, students are encouraged to "generate their own analysis of the problems under consideration, to develop their own solutions, and to practically apply their own knowledge of theory to these problems" (Boyce 1993). Along the way, students also develop "the power to analyze and to master a tangled circumstance by identifying and delineating important factors; the ability to utilize ideas, to test them against facts, and to throw them into fresh combinations" (Merseth 1991).
In addition to the practical application and testing of scholarly knowledge, case discussions can also help students prepare for real-world problems, situations and crises by providing an approximation of various professional environments (i.e. classroom, board room, courtroom, or hospital). Thus, through the examination of specific cases, students are given the opportunity to work out their own professional issues through the trials, tribulations, experiences, and research findings of others. An obvious advantage to this mode of instruction is that it allows students the exposure to settings and contexts that they might not otherwise experience. For example, a student interested in studying the effects of poverty on minority secondary student's grade point averages and S.A.T. scores could access and analyze information from schools as geographically diverse as Los Angeles, New York City, Miami, and New Mexico without ever having to leave the classroom.
The case study method also incorporates the idea that students can learn from one another "by engaging with each other and with each other's ideas, by asserting something and then having it questioned, challenged and thrown back at them so that they can reflect on what they hear, and then refine what they say" (Boehrer 1990). In summary, students can direct their own learning by formulating questions and taking responsibility for the study.
Types and Design Concerns
Researchers use multiple methods and approaches to conduct case studies.
Types of Case Studies
Under the more generalized category of case study exist several subdivisions, each of which is custom selected for use depending upon the goals and/or objectives of the investigator. These types of case study include the following:
Illustrative Case Studies These are primarily descriptive studies. They typically utilize one or two instances of an event to show what a situation is like. Illustrative case studies serve primarily to make the unfamiliar familiar and to give readers a common language about the topic in question.
Exploratory (or pilot) Case Studies These are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. Their basic function is to help identify questions and select types of measurement prior to the main investigation. The primary pitfall of this type of study is that initial findings may seem convincing enough to be released prematurely as conclusions.
Cumulative Case Studies These serve to aggregate information from several sites collected at different times. The idea behind these studies is the collection of past studies will allow for greater generalization without additional cost or time being expended on new, possibly repetitive studies.
Critical Instance Case Studies These examine one or more sites for either the purpose of examining a situation of unique interest with little to no interest in generalizability, or to call into question or challenge a highly generalized or universal assertion. This method is useful for answering cause and effect questions.
Identifying a Theoretical Perspective
Much of the case study's design is inherently determined for researchers, depending on the field from which they are working. In composition studies, researchers are typically working from a qualitative, descriptive standpoint. In contrast, physicists will approach their research from a more quantitative perspective. Still, in designing the study, researchers need to make explicit the questions to be explored and the theoretical perspective from which they will approach the case. The three most commonly adopted theories are listed below:
Individual Theories These focus primarily on the individual development, cognitive behavior, personality, learning and disability, and interpersonal interactions of a particular subject.
Organizational Theories These focus on bureaucracies, institutions, organizational structure and functions, or excellence in organizational performance.
Social Theories These focus on urban development, group behavior, cultural institutions, or marketplace functions.
Two examples of case studies are used consistently throughout this chapter. The first, a study produced by Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988), looks at a first year graduate student's initiation into an academic writing program. The study uses participant-observer and linguistic data collecting techniques to assess the student's knowledge of appropriate discourse conventions. Using the pseudonym Nate to refer to the subject, the study sought to illuminate the particular experience rather than to generalize about the experience of fledgling academic writers collectively.
For example, in Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman's (1988) study we are told that the researchers are interested in disciplinary communities. In the first paragraph, they ask what constitutes membership in a disciplinary community and how achieving membership might affect a writer's understanding and production of texts. In the third paragraph they state that researchers must negotiate their claims "within the context of his sub specialty's accepted knowledge and methodology." In the next paragraph they ask, "How is literacy acquired? What is the process through which novices gain community membership? And what factors either aid or hinder students learning the requisite linguistic behaviors?" This introductory section ends with a paragraph in which the study's authors claim that during the course of the study, the subject, Nate, successfully makes the transition from "skilled novice" to become an initiated member of the academic discourse community and that his texts exhibit linguistic changes which indicate this transition. In the next section the authors make explicit the sociolinguistic theoretical and methodological assumptions on which the study is based (1988). Thus the reader has a good understanding of the authors' theoretical background and purpose in conducting the study even before it is explicitly stated on the fourth page of the study. "Our purpose was to examine the effects of the educational context on one graduate student's production of texts as he wrote in different courses and for different faculty members over the academic year 1984-85." The goal of the study then, was to explore the idea that writers must be initiated into a writing community, and that this initiation will change the way one writes.
The second example is Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of a group of twelfth graders. In this study, Emig seeks to answer the question of what happens to the self as a result educational stimuli in terms of academic writing. The case study used methods such as protocol analysis, tape-recorded interviews, and discourse analysis.
In the case of Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of eight twelfth graders, four specific hypotheses were made:
- Twelfth grade writers engage in two modes of composing: reflexive and extensive.
- These differences can be ascertained and characterized through having the writers compose aloud their composition process.
- A set of implied stylistic principles governs the writing process.
- For twelfth grade writers, extensive writing occurs chiefly as a school-sponsored activity, or reflexive, as a self-sponsored activity.
In this study, the chief distinction is between the two dominant modes of composing among older, secondary school students. The distinctions are:
- The reflexive mode, which focuses on the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- The extensive mode, which focuses on conveying a message.
Emig also outlines the specific questions which guided the research in the opening pages of her Review of Literature , preceding the report.
Designing a Case Study
After considering the different sub categories of case study and identifying a theoretical perspective, researchers can begin to design their study. Research design is the string of logic that ultimately links the data to be collected and the conclusions to be drawn to the initial questions of the study. Typically, research designs deal with at least four problems:
- What questions to study
- What data are relevant
- What data to collect
- How to analyze that data
In other words, a research design is basically a blueprint for getting from the beginning to the end of a study. The beginning is an initial set of questions to be answered, and the end is some set of conclusions about those questions.
Because case studies are conducted on topics as diverse as Anglo-Saxon Literature (Thrane 1986) and AIDS prevention (Van Vugt 1994), it is virtually impossible to outline any strict or universal method or design for conducting the case study. However, Robert K. Yin (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design:
- A study's questions.
- A study's propositions (if any).
- A study's units of analysis.
- The logic that links the data to the propositions.
- The criteria for interpreting the findings.
In addition to these five basic components, Yin also stresses the importance of clearly articulating one's theoretical perspective, determining the goals of the study, selecting one's subject(s), selecting the appropriate method(s) of collecting data, and providing some considerations to the composition of the final report.
Conducting Case Studies
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of approaches and methods. These approaches, methods, and related issues are discussed in depth in this section.
Method: Single or Multi-modal?
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of methods. Some common methods include interviews , protocol analyses, field studies, and participant-observations. Emig (1971) chose to use several methods of data collection. Her sources included conversations with the students, protocol analysis, discrete observations of actual composition, writing samples from each student, and school records (Lauer and Asher 1988).
Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) collected data by observing classrooms, conducting faculty and student interviews, collecting self reports from the subject, and by looking at the subject's written work.
A study that was criticized for using a single method model was done by Flower and Hayes (1984). In this study that explores the ways in which writers use different forms of knowing to create space, the authors used only protocol analysis to gather data. The study came under heavy fire because of their decision to use only one method.
Participant Selection
Case studies can use one participant, or a small group of participants. However, it is important that the participant pool remain relatively small. The participants can represent a diverse cross section of society, but this isn't necessary.
For example, the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study looked at just one participant, Nate. By contrast, in Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composition process of twelfth graders, eight participants were selected representing a diverse cross section of the community, with volunteers from an all-white upper-middle-class suburban school, an all-black inner-city school, a racially mixed lower-middle-class school, an economically and racially mixed school, and a university school.
Often, a brief "case history" is done on the participants of the study in order to provide researchers with a clearer understanding of their participants, as well as some insight as to how their own personal histories might affect the outcome of the study. For instance, in Emig's study, the investigator had access to the school records of five of the participants, and to standardized test scores for the remaining three. Also made available to the researcher was the information that three of the eight students were selected as NCTE Achievement Award winners. These personal histories can be useful in later stages of the study when data are being analyzed and conclusions drawn.
Data Collection
There are six types of data collected in case studies:
- Archival records.
- Interviews.
- Direct observation.
- Participant observation.
In the field of composition research, these six sources might be:
- A writer's drafts.
- School records of student writers.
- Transcripts of interviews with a writer.
- Transcripts of conversations between writers (and protocols).
- Videotapes and notes from direct field observations.
- Hard copies of a writer's work on computer.
Depending on whether researchers have chosen to use a single or multi-modal approach for the case study, they may choose to collect data from one or any combination of these sources.
Protocols, that is, transcriptions of participants talking aloud about what they are doing as they do it, have been particularly common in composition case studies. For example, in Emig's (1971) study, the students were asked, in four different sessions, to give oral autobiographies of their writing experiences and to compose aloud three themes in the presence of a tape recorder and the investigator.
In some studies, only one method of data collection is conducted. For example, the Flower and Hayes (1981) report on the cognitive process theory of writing depends on protocol analysis alone. However, using multiple sources of evidence to increase the reliability and validity of the data can be advantageous.
Case studies are likely to be much more convincing and accurate if they are based on several different sources of information, following a corroborating mode. This conclusion is echoed among many composition researchers. For example, in her study of predrafting processes of high and low-apprehensive writers, Cynthia Selfe (1985) argues that because "methods of indirect observation provide only an incomplete reflection of the complex set of processes involved in composing, a combination of several such methods should be used to gather data in any one study." Thus, in this study, Selfe collected her data from protocols, observations of students role playing their writing processes, audio taped interviews with the students, and videotaped observations of the students in the process of composing.
It can be said then, that cross checking data from multiple sources can help provide a multidimensional profile of composing activities in a particular setting. Sharan Merriam (1985) suggests "checking, verifying, testing, probing, and confirming collected data as you go, arguing that this process will follow in a funnel-like design resulting in less data gathering in later phases of the study along with a congruent increase in analysis checking, verifying, and confirming."
It is important to note that in case studies, as in any qualitative descriptive research, while researchers begin their studies with one or several questions driving the inquiry (which influence the key factors the researcher will be looking for during data collection), a researcher may find new key factors emerging during data collection. These might be unexpected patterns or linguistic features which become evident only during the course of the research. While not bearing directly on the researcher's guiding questions, these variables may become the basis for new questions asked at the end of the report, thus linking to the possibility of further research.
Data Analysis
As the information is collected, researchers strive to make sense of their data. Generally, researchers interpret their data in one of two ways: holistically or through coding. Holistic analysis does not attempt to break the evidence into parts, but rather to draw conclusions based on the text as a whole. Flower and Hayes (1981), for example, make inferences from entire sections of their students' protocols, rather than searching through the transcripts to look for isolatable characteristics.
However, composition researchers commonly interpret their data by coding, that is by systematically searching data to identify and/or categorize specific observable actions or characteristics. These observable actions then become the key variables in the study. Sharan Merriam (1988) suggests seven analytic frameworks for the organization and presentation of data:
- The role of participants.
- The network analysis of formal and informal exchanges among groups.
- Historical.
- Thematical.
- Ritual and symbolism.
- Critical incidents that challenge or reinforce fundamental beliefs, practices, and values.
There are two purposes of these frameworks: to look for patterns among the data and to look for patterns that give meaning to the case study.
As stated above, while most researchers begin their case studies expecting to look for particular observable characteristics, it is not unusual for key variables to emerge during data collection. Typical variables coded in case studies of writers include pauses writers make in the production of a text, the use of specific linguistic units (such as nouns or verbs), and writing processes (planning, drafting, revising, and editing). In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, researchers coded the participant's texts for use of connectives, discourse demonstratives, average sentence length, off-register words, use of the first person pronoun, and the ratio of definite articles to indefinite articles.
Since coding is inherently subjective, more than one coder is usually employed. In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, three rhetoricians were employed to code the participant's texts for off-register phrases. The researchers established the agreement among the coders before concluding that the participant used fewer off-register words as the graduate program progressed.
Composing the Case Study Report
In the many forms it can take, "a case study is generically a story; it presents the concrete narrative detail of actual, or at least realistic events, it has a plot, exposition, characters, and sometimes even dialogue" (Boehrer 1990). Generally, case study reports are extensively descriptive, with "the most problematic issue often referred to as being the determination of the right combination of description and analysis" (1990). Typically, authors address each step of the research process, and attempt to give the reader as much context as possible for the decisions made in the research design and for the conclusions drawn.
This contextualization usually includes a detailed explanation of the researchers' theoretical positions, of how those theories drove the inquiry or led to the guiding research questions, of the participants' backgrounds, of the processes of data collection, of the training and limitations of the coders, along with a strong attempt to make connections between the data and the conclusions evident.
Although the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study does not, case study reports often include the reactions of the participants to the study or to the researchers' conclusions. Because case studies tend to be exploratory, most end with implications for further study. Here researchers may identify significant variables that emerged during the research and suggest studies related to these, or the authors may suggest further general questions that their case study generated.
For example, Emig's (1971) study concludes with a section dedicated solely to the topic of implications for further research, in which she suggests several means by which this particular study could have been improved, as well as questions and ideas raised by this study which other researchers might like to address, such as: is there a correlation between a certain personality and a certain composing process profile (e.g. is there a positive correlation between ego strength and persistence in revising)?
Also included in Emig's study is a section dedicated to implications for teaching, which outlines the pedagogical ramifications of the study's findings for teachers currently involved in high school writing programs.
Sharan Merriam (1985) also offers several suggestions for alternative presentations of data:
- Prepare specialized condensations for appropriate groups.
- Replace narrative sections with a series of answers to open-ended questions.
- Present "skimmer's" summaries at beginning of each section.
- Incorporate headlines that encapsulate information from text.
- Prepare analytic summaries with supporting data appendixes.
- Present data in colorful and/or unique graphic representations.
Issues of Validity and Reliability
Once key variables have been identified, they can be analyzed. Reliability becomes a key concern at this stage, and many case study researchers go to great lengths to ensure that their interpretations of the data will be both reliable and valid. Because issues of validity and reliability are an important part of any study in the social sciences, it is important to identify some ways of dealing with results.
Multi-modal case study researchers often balance the results of their coding with data from interviews or writer's reflections upon their own work. Consequently, the researchers' conclusions become highly contextualized. For example, in a case study which looked at the time spent in different stages of the writing process, Berkenkotter concluded that her participant, Donald Murray, spent more time planning his essays than in other writing stages. The report of this case study is followed by Murray's reply, wherein he agrees with some of Berkenkotter's conclusions and disagrees with others.
As is the case with other research methodologies, issues of external validity, construct validity, and reliability need to be carefully considered.
Commentary on Case Studies
Researchers often debate the relative merits of particular methods, among them case study. In this section, we comment on two key issues. To read the commentaries, choose any of the items below:
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
Most case study advocates point out that case studies produce much more detailed information than what is available through a statistical analysis. Advocates will also hold that while statistical methods might be able to deal with situations where behavior is homogeneous and routine, case studies are needed to deal with creativity, innovation, and context. Detractors argue that case studies are difficult to generalize because of inherent subjectivity and because they are based on qualitative subjective data, generalizable only to a particular context.
Flexibility
The case study approach is a comparatively flexible method of scientific research. Because its project designs seem to emphasize exploration rather than prescription or prediction, researchers are comparatively freer to discover and address issues as they arise in their experiments. In addition, the looser format of case studies allows researchers to begin with broad questions and narrow their focus as their experiment progresses rather than attempt to predict every possible outcome before the experiment is conducted.
Emphasis on Context
By seeking to understand as much as possible about a single subject or small group of subjects, case studies specialize in "deep data," or "thick description"--information based on particular contexts that can give research results a more human face. This emphasis can help bridge the gap between abstract research and concrete practice by allowing researchers to compare their firsthand observations with the quantitative results obtained through other methods of research.
Inherent Subjectivity
"The case study has long been stereotyped as the weak sibling among social science methods," and is often criticized as being too subjective and even pseudo-scientific. Likewise, "investigators who do case studies are often regarded as having deviated from their academic disciplines, and their investigations as having insufficient precision (that is, quantification), objectivity and rigor" (Yin 1989). Opponents cite opportunities for subjectivity in the implementation, presentation, and evaluation of case study research. The approach relies on personal interpretation of data and inferences. Results may not be generalizable, are difficult to test for validity, and rarely offer a problem-solving prescription. Simply put, relying on one or a few subjects as a basis for cognitive extrapolations runs the risk of inferring too much from what might be circumstance.
High Investment
Case studies can involve learning more about the subjects being tested than most researchers would care to know--their educational background, emotional background, perceptions of themselves and their surroundings, their likes, dislikes, and so on. Because of its emphasis on "deep data," the case study is out of reach for many large-scale research projects which look at a subject pool in the tens of thousands. A budget request of $10,000 to examine 200 subjects sounds more efficient than a similar request to examine four subjects.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers conducting case studies should consider certain ethical issues. For example, many educational case studies are often financed by people who have, either directly or indirectly, power over both those being studied and those conducting the investigation (1985). This conflict of interests can hinder the credibility of the study.
The personal integrity, sensitivity, and possible prejudices and/or biases of the investigators need to be taken into consideration as well. Personal biases can creep into how the research is conducted, alternative research methods used, and the preparation of surveys and questionnaires.
A common complaint in case study research is that investigators change direction during the course of the study unaware that their original research design was inadequate for the revised investigation. Thus, the researchers leave unknown gaps and biases in the study. To avoid this, researchers should report preliminary findings so that the likelihood of bias will be reduced.
Concerns about Reliability, Validity, and Generalizability
Merriam (1985) offers several suggestions for how case study researchers might actively combat the popular attacks on the validity, reliability, and generalizability of case studies:
- Prolong the Processes of Data Gathering on Site: This will help to insure the accuracy of the findings by providing the researcher with more concrete information upon which to formulate interpretations.
- Employ the Process of "Triangulation": Use a variety of data sources as opposed to relying solely upon one avenue of observation. One example of such a data check would be what McClintock, Brannon, and Maynard (1985) refer to as a "case cluster method," that is, when a single unit within a larger case is randomly sampled, and that data treated quantitatively." For instance, in Emig's (1971) study, the case cluster method was employed, singling out the productivity of a single student named Lynn. This cluster profile included an advanced case history of the subject, specific examination and analysis of individual compositions and protocols, and extensive interview sessions. The seven remaining students were then compared with the case of Lynn, to ascertain if there are any shared, or unique dimensions to the composing process engaged in by these eight students.
- Conduct Member Checks: Initiate and maintain an active corroboration on the interpretation of data between the researcher and those who provided the data. In other words, talk to your subjects.
- Collect Referential Materials: Complement the file of materials from the actual site with additional document support. For example, Emig (1971) supports her initial propositions with historical accounts by writers such as T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and D.H. Lawrence. Emig also cites examples of theoretical research done with regards to the creative process, as well as examples of empirical research dealing with the writing of adolescents. Specific attention is then given to the four stages description of the composing process delineated by Helmoltz, Wallas, and Cowley, as it serves as the focal point in this study.
- Engage in Peer Consultation: Prior to composing the final draft of the report, researchers should consult with colleagues in order to establish validity through pooled judgment.
Although little can be done to combat challenges concerning the generalizability of case studies, "most writers suggest that qualitative research should be judged as credible and confirmable as opposed to valid and reliable" (Merriam 1985). Likewise, it has been argued that "rather than transplanting statistical, quantitative notions of generalizability and thus finding qualitative research inadequate, it makes more sense to develop an understanding of generalization that is congruent with the basic characteristics of qualitative inquiry" (1985). After all, criticizing the case study method for being ungeneralizable is comparable to criticizing a washing machine for not being able to tell the correct time. In other words, it is unjust to criticize a method for not being able to do something which it was never originally designed to do in the first place.
Annotated Bibliography
Armisted, C. (1984). How Useful are Case Studies. Training and Development Journal, 38 (2), 75-77.
This article looks at eight types of case studies, offers pros and cons of using case studies in the classroom, and gives suggestions for successfully writing and using case studies.
Bardovi-Harlig, K. (1997). Beyond Methods: Components of Second Language Teacher Education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
A compilation of various research essays which address issues of language teacher education. Essays included are: "Non-native reading research and theory" by Lee, "The case for Psycholinguistics" by VanPatten, and "Assessment and Second Language Teaching" by Gradman and Reed.
Bartlett, L. (1989). A Question of Good Judgment; Interpretation Theory and Qualitative Enquiry Address. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco.
Bartlett selected "quasi-historical" methodology, which focuses on the "truth" found in case records, as one that will provide "good judgments" in educational inquiry. He argues that although the method is not comprehensive, it can try to connect theory with practice.
Baydere, S. et. al. (1993). Multimedia conferencing as a tool for collaborative writing: a case study in Computer Supported Collaborative Writing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
The case study by Baydere et. al. is just one of the many essays in this book found in the series "Computer Supported Cooperative Work." Denley, Witefield and May explore similar issues in their essay, "A case study in task analysis for the design of a collaborative document production system."
Berkenkotter, C., Huckin, T., N., & Ackerman J. (1988). Conventions, Conversations, and the Writer: Case Study of a Student in a Rhetoric Ph.D. Program. Research in the Teaching of English, 22, 9-44.
The authors focused on how the writing of their subject, Nate or Ackerman, changed as he became more acquainted or familiar with his field's discourse community.
Berninger, V., W., and Gans, B., M. (1986). Language Profiles in Nonspeaking Individuals of Normal Intelligence with Severe Cerebral Palsy. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 2, 45-50.
Argues that generalizations about language abilities in patients with severe cerebral palsy (CP) should be avoided. Standardized tests of different levels of processing oral language, of processing written language, and of producing written language were administered to 3 male participants (aged 9, 16, and 40 yrs).
Bockman, J., R., and Couture, B. (1984). The Case Method in Technical Communication: Theory and Models. Texas: Association of Teachers of Technical Writing.
Examines the study and teaching of technical writing, communication of technical information, and the case method in terms of those applications.
Boehrer, J. (1990). Teaching With Cases: Learning to Question. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 42 41-57.
This article discusses the origins of the case method, looks at the question of what is a case, gives ideas about learning in case teaching, the purposes it can serve in the classroom, the ground rules for the case discussion, including the role of the question, and new directions for case teaching.
Bowman, W. R. (1993). Evaluating JTPA Programs for Economically Disadvantaged Adults: A Case Study of Utah and General Findings . Washington: National Commission for Employment Policy.
"To encourage state-level evaluations of JTPA, the Commission and the State of Utah co-sponsored this report on the effectiveness of JTPA Title II programs for adults in Utah. The technique used is non-experimental and the comparison group was selected from registrants with Utah's Employment Security. In a step-by-step approach, the report documents how non-experimental techniques can be applied and several specific technical issues can be addressed."
Boyce, A. (1993) The Case Study Approach for Pedagogists. Annual Meeting of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance. (Address). Washington DC.
This paper addresses how case studies 1) bridge the gap between teaching theory and application, 2) enable students to analyze problems and develop solutions for situations that will be encountered in the real world of teaching, and 3) helps students to evaluate the feasibility of alternatives and to understand the ramifications of a particular course of action.
Carson, J. (1993) The Case Study: Ideal Home of WAC Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication. (Address). San Diego.
"Increasingly, one of the most pressing questions for WAC advocates is how to keep [WAC] programs going in the face of numerous difficulties. Case histories offer the best chance for fashioning rhetorical arguments to keep WAC programs going because they offer the opportunity to provide a coherent narrative that contextualizes all documents and data, including what is generally considered scientific data. A case study of the WAC program, . . . at Robert Morris College in Pittsburgh demonstrates the advantages of this research method. Such studies are ideal homes for both naturalistic and positivistic data as well as both quantitative and qualitative information."
---. (1991). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication. 32. 365-87.
No abstract available.
Cromer, R. (1994) A Case Study of Dissociations Between Language and Cognition. Constraints on Language Acquisition: Studies of Atypical Children . Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 141-153.
Crossley, M. (1983) Case Study in Comparative and International Education: An Approach to Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap. Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the Australian Comparative and International Education Society. Hamilton, NZ.
Case study research, as presented here, helps bridge the theory-practice gap in comparative and international research studies of education because it focuses on the practical, day-to-day context rather than on the national arena. The paper asserts that the case study method can be valuable at all levels of research, formation, and verification of theories in education.
Daillak, R., H., and Alkin, M., C. (1982). Qualitative Studies in Context: Reflections on the CSE Studies of Evaluation Use . California: EDRS
The report shows how the Center of the Study of Evaluation (CSE) applied qualitative techniques to a study of evaluation information use in local, Los Angeles schools. It critiques the effectiveness and the limitations of using case study, evaluation, field study, and user interview survey methodologies.
Davey, L. (1991). The Application of Case Study Evaluations. ERIC/TM Digest.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method.
Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions.
DeVoss, G. (1981). Ethics in Fieldwork Research. RIE 27p. (ERIC)
This article examines four of the ethical problems that can happen when conducting case study research: acquiring permission to do research, knowing when to stop digging, the pitfalls of doing collaborative research, and preserving the integrity of the participants.
Driscoll, A. (1985). Case Study of a Research Intervention: the University of Utah’s Collaborative Approach . San Francisco: Far West Library for Educational Research Development.
Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education, Denver, CO, March 1985. Offers information of in-service training, specifically case studies application.
Ellram, L. M. (1996). The Use of the Case Study Method in Logistics Research. Journal of Business Logistics, 17, 2, 93.
This article discusses the increased use of case study in business research, and the lack of understanding of when and how to use case study methodology in business.
Emig, J. (1971) The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Urbana: NTCE.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process.
Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
This book discusses the nature, characteristics, and basic methodological issues of the case study as a research method.
Feldman, H., Holland, A., & Keefe, K. (1989) Language Abilities after Left Hemisphere Brain Injury: A Case Study of Twins. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 9, 32-47.
"Describes the language abilities of 2 twin pairs in which 1 twin (the experimental) suffered brain injury to the left cerebral hemisphere around the time of birth and1 twin (the control) did not. One pair of twins was initially assessed at age 23 mo. and the other at about 30 mo.; they were subsequently evaluated in their homes 3 times at about 6-mo intervals."
Fidel, R. (1984). The Case Study Method: A Case Study. Library and Information Science Research, 6.
The article describes the use of case study methodology to systematically develop a model of online searching behavior in which study design is flexible, subject manner determines data gathering and analyses, and procedures adapt to the study's progressive change.
Flower, L., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). Images, Plans and Prose: The Representation of Meaning in Writing. Written Communication, 1, 120-160.
Explores the ways in which writers actually use different forms of knowing to create prose.
Frey, L. R. (1992). Interpreting Communication Research: A Case Study Approach Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
The book discusses research methodologies in the Communication field. It focuses on how case studies bridge the gap between communication research, theory, and practice.
Gilbert, V. K. (1981). The Case Study as a Research Methodology: Difficulties and Advantages of Integrating the Positivistic, Phenomenological and Grounded Theory Approaches . The Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for the Study of Educational Administration. (Address) Halifax, NS, Can.
This study on an innovative secondary school in England shows how a "low-profile" participant-observer case study was crucial to the initial observation, the testing of hypotheses, the interpretive approach, and the grounded theory.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381.
This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
Glennan, S. L., Sharp-Bittner, M. A. & Tullos, D. C. (1991). Augmentative and Alternative Communication Training with a Nonspeaking Adult: Lessons from MH. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 7, 240-7.
"A response-guided case study documented changes in a nonspeaking 36-yr-old man's ability to communicate using 3 trained augmentative communication modes. . . . Data were collected in videotaped interaction sessions between the nonspeaking adult and a series of adult speaking."
Graves, D. (1981). An Examination of the Writing Processes of Seven Year Old Children. Research in the Teaching of English, 15, 113-134.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case Study Methods . Newbury Park: Sage. .
"In a most economical fashion, Hamel provides a practical guide for producing theoretically sharp and empirically sound sociological case studies. A central idea put forth by Hamel is that case studies must "locate the global in the local" thus making the careful selection of the research site the most critical decision in the analytic process."
Karthigesu, R. (1986, July). Television as a Tool for Nation-Building in the Third World: A Post-Colonial Pattern, Using Malaysia as a Case-Study. International Television Studies Conference. (Address). London, 10-12.
"The extent to which Television Malaysia, as a national mass media organization, has been able to play a role in nation building in the post-colonial period is . . . studied in two parts: how the choice of a model of nation building determines the character of the organization; and how the character of the organization influences the output of the organization."
Kenny, R. (1984). Making the Case for the Case Study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 16, (1), 37-51.
The article looks at how and why the case study is justified as a viable and valuable approach to educational research and program evaluation.
Knirk, F. (1991). Case Materials: Research and Practice. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 4 (1 ), 73-81.
The article addresses the effectiveness of case studies, subject areas where case studies are commonly used, recent examples of their use, and case study design considerations.
Klos, D. (1976). Students as Case Writers. Teaching of Psychology, 3.2, 63-66.
This article reviews a course in which students gather data for an original case study of another person. The task requires the students to design the study, collect the data, write the narrative, and interpret the findings.
Leftwich, A. (1981). The Politics of Case Study: Problems of Innovation in University Education. Higher Education Review, 13.2, 38-64.
The article discusses the use of case studies as a teaching method. Emphasis is on the instructional materials, interdisciplinarity, and the complex relationships within the university that help or hinder the method.
Mabrito, M. (1991, Oct.). Electronic Mail as a Vehicle for Peer Response: Conversations of High and Low Apprehensive Writers. Written Communication, 509-32.
McCarthy, S., J. (1955). The Influence of Classroom Discourse on Student Texts: The Case of Ella . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
A look at how students of color become marginalized within traditional classroom discourse. The essay follows the struggles of one black student: Ella.
Matsuhashi, A., ed. (1987). Writing in Real Time: Modeling Production Processes Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Investigates how writers plan to produce discourse for different purposes to report, to generalize, and to persuade, as well as how writers plan for sentence level units of language. To learn about planning, an observational measure of pause time was used" (ERIC).
Merriam, S. B. (1985). The Case Study in Educational Research: A Review of Selected Literature. Journal of Educational Thought, 19.3, 204-17.
The article examines the characteristics of, philosophical assumptions underlying the case study, the mechanics of conducting a case study, and the concerns about the reliability, validity, and generalizability of the method.
---. (1988). Case Study Research in Education: A Qualitative Approach San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Merry, S. E., & Milner, N. eds. (1993). The Possibility of Popular Justice: A Case Study of Community Mediation in the United States . Ann Arbor: U of Michigan.
". . . this volume presents a case study of one experiment in popular justice, the San Francisco Community Boards. This program has made an explicit claim to create an alternative justice, or new justice, in the midst of a society ordered by state law. The contributors to this volume explore the history and experience of the program and compare it to other versions of popular justice in the United States, Europe, and the Third World."
Merseth, K. K. (1991). The Case for Cases in Teacher Education. RIE. 42p. (ERIC).
This monograph argues that the case method of instruction offers unique potential for revitalizing the field of teacher education.
Michaels, S. (1987). Text and Context: A New Approach to the Study of Classroom Writing. Discourse Processes, 10, 321-346.
"This paper argues for and illustrates an approach to the study of writing that integrates ethnographic analysis of classroom interaction with linguistic analysis of written texts and teacher/student conversational exchanges. The approach is illustrated through a case study of writing in a single sixth grade classroom during a single writing assignment."
Milburn, G. (1995). Deciphering a Code or Unraveling a Riddle: A Case Study in the Application of a Humanistic Metaphor to the Reporting of Social Studies Teaching. Theory and Research in Education, 13.
This citation serves as an example of how case studies document learning procedures in a senior-level economics course.
Milley, J. E. (1979). An Investigation of Case Study as an Approach to Program Evaluation. 19th Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research. (Address). San Diego.
The case study method merged a narrative report focusing on the evaluator as participant-observer with document review, interview, content analysis, attitude questionnaire survey, and sociogram analysis. Milley argues that case study program evaluation has great potential for widespread use.
Minnis, J. R. (1985, Sept.). Ethnography, Case Study, Grounded Theory, and Distance Education Research. Distance Education, 6.2.
This article describes and defines the strengths and weaknesses of ethnography, case study, and grounded theory.
Nunan, D. (1992). Collaborative language learning and teaching . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Included in this series of essays is Peter Sturman’s "Team Teaching: a case study from Japan" and David Nunan’s own "Toward a collaborative approach to curriculum development: a case study."
Nystrand, M., ed. (1982). What Writers Know: The Language, Process, and Structure of Written Discourse . New York: Academic Press.
Owenby, P. H. (1992). Making Case Studies Come Alive. Training, 29, (1), 43-46. (ERIC)
This article provides tips for writing more effective case studies.
---. (1981). Pausing and Planning: The Tempo of Writer Discourse Production. Research in the Teaching of English, 15 (2),113-34.
Perl, S. (1979). The Composing Processes of Unskilled College Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 13, 317-336.
"Summarizes a study of five unskilled college writers, focusing especially on one of the five, and discusses the findings in light of current pedagogical practice and research design."
Pilcher J. and A. Coffey. eds. (1996). Gender and Qualitative Research . Brookfield: Aldershot, Hants, England.
This book provides a series of essays which look at gender identity research, qualitative research and applications of case study to questions of gendered pedagogy.
Pirie, B. S. (1993). The Case of Morty: A Four Year Study. Gifted Education International, 9 (2), 105-109.
This case study describes a boy from kindergarten through third grade with above average intelligence but difficulty in learning to read, write, and spell.
Popkewitz, T. (1993). Changing Patterns of Power: Social Regulation and Teacher Education Reform. Albany: SUNY Press.
Popkewitz edits this series of essays that address case studies on educational change and the training of teachers. The essays vary in terms of discipline and scope. Also, several authors include case studies of educational practices in countries other than the United States.
---. (1984). The Predrafting Processes of Four High- and Four Low Apprehensive Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 18, (1), 45-64.
Rasmussen, P. (1985, March) A Case Study on the Evaluation of Research at the Technical University of Denmark. International Journal of Institutional Management in Higher Education, 9 (1).
This is an example of a case study methodology used to evaluate the chemistry and chemical engineering departments at the University of Denmark.
Roth, K. J. (1986). Curriculum Materials, Teacher Talk, and Student Learning: Case Studies in Fifth-Grade Science Teaching . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
Roth offers case studies on elementary teachers, elementary school teaching, science studies and teaching, and verbal learning.
Selfe, C. L. (1985). An Apprehensive Writer Composes. When a Writer Can't Write: Studies in Writer's Block and Other Composing-Process Problems . (pp. 83-95). Ed. Mike Rose. NMY: Guilford.
Smith-Lewis, M., R. and Ford, A. (1987). A User's Perspective on Augmentative Communication. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 3, 12-7.
"During a series of in-depth interviews, a 25-yr-old woman with cerebral palsy who utilized augmentative communication reflected on the effectiveness of the devices designed for her during her school career."
St. Pierre, R., G. (1980, April). Follow Through: A Case Study in Metaevaluation Research . 64th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. (Address).
The three approaches to metaevaluation are evaluation of primary evaluations, integrative meta-analysis with combined primary evaluation results, and re-analysis of the raw data from a primary evaluation.
Stahler, T., M. (1996, Feb.) Early Field Experiences: A Model That Worked. ERIC.
"This case study of a field and theory class examines a model designed to provide meaningful field experiences for preservice teachers while remaining consistent with the instructor's beliefs about the role of teacher education in preparing teachers for the classroom."
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
This book examines case study research in education and case study methodology.
Stiegelbauer, S. (1984) Community, Context, and Co-curriculum: Situational Factors Influencing School Improvements in a Study of High Schools. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Discussion of several case studies: one looking at high school environments, another examining educational innovations.
Stolovitch, H. (1990). Case Study Method. Performance And Instruction, 29, (9), 35-37.
This article describes the case study method as a form of simulation and presents guidelines for their use in professional training situations.
Thaller, E. (1994). Bibliography for the Case Method: Using Case Studies in Teacher Education. RIE. 37 p.
This bibliography presents approximately 450 citations on the use of case studies in teacher education from 1921-1993.
Thrane, T. (1986). On Delimiting the Senses of Near-Synonyms in Historical Semantics: A Case Study of Adjectives of 'Moral Sufficiency' in the Old English Andreas. Linguistics Across Historical and Geographical Boundaries: In Honor of Jacek Fisiak on the Occasion of his Fiftieth Birthday . Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
United Nations. (1975). Food and Agriculture Organization. Report on the FAO/UNFPA Seminar on Methodology, Research and Country: Case Studies on Population, Employment and Productivity . Rome: United Nations.
This example case study shows how the methodology can be used in a demographic and psychographic evaluation. At the same time, it discusses the formation and instigation of the case study methodology itself.
Van Vugt, J. P., ed. (1994). Aids Prevention and Services: Community Based Research . Westport: Bergin and Garvey.
"This volume has been five years in the making. In the process, some of the policy applications called for have met with limited success, such as free needle exchange programs in a limited number of American cities, providing condoms to prison inmates, and advertisements that depict same-sex couples. Rather than dating our chapters that deal with such subjects, such policy applications are verifications of the type of research demonstrated here. Furthermore, they indicate the critical need to continue community based research in the various communities threatened by acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (AIDS) . . . "
Welch, W., ed. (1981, May). Case Study Methodology in Educational Evaluation. Proceedings of the Minnesota Evaluation Conference. Minnesota. (Address).
The four papers in these proceedings provide a comprehensive picture of the rationale, methodology, strengths, and limitations of case studies.
Williams, G. (1987). The Case Method: An Approach to Teaching and Learning in Educational Administration. RIE, 31p.
This paper examines the viability of the case method as a teaching and learning strategy in instructional systems geared toward the training of personnel of the administration of various aspects of educational systems.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Advancing Rigorous Methodologies: A Review of 'Towards Rigor in Reviews of Multivocal Literatures.' Review of Educational Research, 61, (3).
"R. T. Ogawa and B. Malen's article does not meet its own recommended standards for rigorous testing and presentation of its own conclusions. Use of the exploratory case study to analyze multivocal literatures is not supported, and the claim of grounded theory to analyze multivocal literatures may be stronger."
---. (1989). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. London: Sage Publications Inc.
This book discusses in great detail, the entire design process of the case study, including entire chapters on collecting evidence, analyzing evidence, composing the case study report, and designing single and multiple case studies.
Related Links
Consider the following list of related Web sites for more information on the topic of case study research. Note: although many of the links cover the general category of qualitative research, all have sections that address issues of case studies.
- Sage Publications on Qualitative Methodology: Search here for a comprehensive list of new books being published about "Qualitative Methodology" http://www.sagepub.co.uk/
- The International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education: An on-line journal "to enhance the theory and practice of qualitative research in education." On-line submissions are welcome. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/tf/09518398.html
- Qualitative Research Resources on the Internet: From syllabi to home pages to bibliographies. All links relate somehow to qualitative research. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/qualres.html
Becker, Bronwyn, Patrick Dawson, Karen Devine, Carla Hannum, Steve Hill, Jon Leydens, Debbie Matuskevich, Carol Traver, & Mike Palmquist. (2005). Case Studies. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=60
All You Wanted to Know About How to Write a Case Study

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: ' WHAT IS A CREDIBLE SOURCES ?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

- Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references.
- In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research.
- Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world.
- Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case.
- At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself.
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
What Is A Case Study?
How to cite a case study in apa, how to write a case study, related articles.
.webp)
At SmartBug Media ® , we do it all. We’re with you at every stage of the customer lifecycle.
- Meet the Team
- SmartBug Culture
- News & Media
- Inbound Marketing

We’re Hiring!
Join our award-winning team of whip-smart marketers.
Client Success
- Case Studies
- Digital Designs
- Email Strategy
- Web Designs
- Testimonials
- View All Projects
- Senior Living
- Manufacturing
Recent Case Studies
How email marketing increased aov by 25%, how we used a digital overlay at an in-person event to increase mqls.
- Marketing Hub
- Service Hub
- Operations Hub
- Content Hub
- Commerce Hub

More Partners
Explore more of our top-tier partnerships.

- Marketing Strategy
- Sales & Marketing Alignment
- Reporting & Attribution
- Demand Generation
- Public Relations
Content Type
- Assessments
- View All Resources
- Senior Care
Recent Resources
Cmo marketing dashboard, utilizing hubspot service hub to maximize your full customer lifecycle.

The 7 Essential Elements of a Great Case Study

March 24, 2023
By Mike Wolfe
Research shows that 93 percent of consumers say online reviews will affect shopping choices . Online reviews certainly help tell a part of your organization’s story, but when you want to offer a bigger picture and really show off what you can do, there’s nothing like a case study.
A great case study can help assure your audience that you’re more than capable of helping them with their problems because you’ve been there and done that for similar organizations. Ever looked at an organization’s website and checked out their case studies or testimonials before filling out a form or giving them a call?
These are great pieces of collateral that can have an immediate impact on the audience you connect with and can be used in a number of ways throughout the course of your marketing and sales efforts.
When you are looking to put together your next case study (or revamp some of your older ones), take these essential elements into consideration.
1. Common Problem or Challenge
Start with clearly defined issues..
When your audience takes the time to read your case study, they likely do so because they want to see that you resolved a problem or challenge they’re facing. Before writing a case study, consider some common problems or challenges your personas are experiencing and start there.
2. Explanation of Resolution
Describe the problems, but really showcase your solutions..
Your customer came to you with a problem or need for you to solve—and you knocked it out of the park! Don’t sell yourself short when it comes to describing how you resolved the customer’s problems. Highlight the ways your product or service was the perfect fit for your customer so potential customers can start connecting the dots on how you can help them too.
3. Compelling Story
Tell the story of your customers’ experience..
Problems and solutions are important to cover, but don’t forget to make your case study relatable to your audience. Telling the story from the perspective of the customer and describing how they felt and what they experienced throughout the process helps your audience put themselves in your customer’s shoes.

4. Customer Quotes
Give your customer a voice..
Take your storytelling to the next level by using real customer quotes that support your case study. The best quotes will draw a clear connection between the customer’s good experience and your product or service, offering an intimate look at how your business helped them succeed. Be sure to choose quotes that perfectly illustrate the results you achieved for your customer, and make sure they accurately reflect the customer’s opinion.
5. Successful Outcome
Let’s see some results.
You’ve got the beginning of the story (why you and the customer met) and the middle of the story (how you worked to help them). Now, in order for this to have a happy ending for both your customers and your audience, you need the results to bring it home.
The key here is to be as specific as possible with your outcomes. Let those results shine and give your audience a glimpse into what they can potentially see from partnering with your organization.
6. Visual Aids
Engage readers visually..
Visual aids help bring a tangible element to the case study, making it more memorable and engaging for readers. Case studies that include visual elements such as photos, diagrams, infographics, or videos can often be more persuasive and effective than those that don’t. Visual aids can also help make complex topics more easily understandable, and they often create a stronger emotional connection with potential customers.
7. Descriptive Name
Cap it off with a great title..
When writing a marketing case study, it is important to include an effective title that accurately describes the content. A catchy and well-crafted title can help draw readers in and entice them to learn more about the journey your customer went through. Good titles are concise yet descriptive, so readers can quickly understand what the case study is about and why it is important.
Ready to Write Your Amazing New Case Study?
Here are a few quick tips to get you started:
- Interview your customer about their experience. Ask questions that will help you tell the full story from their point of view, such as:
- What was the customer looking to solve when partnering with you?
- What did the customer need that you were able to provide?
- What has their experience been with your product or service?
- Show their results and give a brief overview of how your tools, strategies, and/or recommendations were impactful.
- Use bullet points to emphasize key findings within the story and grab some quotes from your conversation with the customer to highlight.
- Create some calls to action for the sidebars or footers of your related blog content.
Once created, there are many great places to showcase your next case study. Link to it from your sales collateral or event materials (including your booths and product sheets). Have the resources to use video in your customer conversations? Send these videos out through your social channels to help your audience put a face and a voice to the results you can bring them.
One final piece of advice: Look at metrics about how your audience is primarily viewing content, and capitalize on those options for your next great case study. Best of luck!
This post was originally published in May 2016 and has been updated since.

Easily craft compelling customer interviews & provide leads with the information they need to make an informed decision.
Case Study Questions Template

About the author
Mike Wolfe is an Inbound Marketing Strategist at SmartBug Media helping clients find success through inbound marketing. Read more articles by Mike Wolfe .
Subscribe to get our new blogs delivered right to your inbox
Other insights you might like.

Content Marketing
Writing Awesome ChatGPT Prompts for Marketing: The Pro Writer’s Guide

Driving Sales One Resource at a Time: The Importance of Sales Enablement Content

Inbound Copywriting: What Great Authors Can Teach Us

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: Apr 2, 2024 6:35 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools

February 9, 2024
Can't find what you're looking for?
Case Study Mastery: Examples & Step-by-Step Templates
Master case study: Uncover key strategies to conduct & present findings that influence decisions charachters.
What's Inside?
Understanding and sharing success stories in the business management world is crucial for grasping the growth journey of a business.
In this article, we will delve into the concept of a business management case study, exploring its definition, benefits, limitations, step-by-step process, types, and essential elements.
What is a Case Study?
A case study research is a detailed analysis of a particular subject, often a real-world situation or scenario, to draw insights and conclusions. It serves as a valuable tool for learning from successful strategies, identifying challenges, and making informed decisions.

Key Characteristics of a Case Study:
Specific Focus: Case studies concentrate on a particular subject, narrowing down the scope to delve deeply into specific aspects.
Real-world Context: Unlike theoretical studies, case studies are grounded in the real world. They often involve the examination of actual events, circumstances, or challenges.
Comprehensive Exploration: Case studies involve a thorough investigation of multiple facets of the chosen subject. This may include collecting and analyzing data, conducting interviews, and reviewing relevant documents.

Contextualization: Each case study is set within a context, providing background information to help readers or viewers understand the circumstances surrounding the case.
Problem-Solving Orientation: While exploring the intricacies of a case, case studies often aim to identify problems, challenges, or opportunities. They can be used as tools for problem-solving and decision-making.
In-depth Analysis: The analysis in a case study goes beyond surface-level observations. It involves a detailed examination of factors contributing to the situation, allowing for a nuanced understanding.
Presentation of Findings: A case study concludes with the presentation of findings, insights, and conclusions. Leveraging a visually compelling presentation plays a vital role for a case study to speak out.

Why You Should Write a Case Study?
Writing a case study offers several compelling reasons for individuals and businesses alike:
Demonstrate Success: A case study allows you to showcase your achievements and successes. It provides tangible evidence of your capabilities, helping build trust and credibility with potential clients, customers, or collaborators.

Educate and Inform: Use case studies to share valuable insights, lessons learned, and best practices. By documenting your experiences, you contribute to the collective knowledge within your industry, positioning yourself as an authority and resource.
Problem-Solving Showcase: If your case study revolves around overcoming challenges, it highlights your problem-solving abilities. This can be particularly impactful in industries where complex issues require innovative solutions.
Engage Your Audience: Well-crafted case studies are engaging and resonate with your audience. They tell a story, making information more relatable and memorable. This storytelling aspect can captivate readers and enhance their understanding of your work.

Build Brand Awareness: Case studies provide an opportunity to promote your brand in a context that goes beyond traditional marketing. Through real-world examples, you can reinforce your brand message and values.
Attract New Opportunities: A compelling case study can attract new opportunities, whether it be clients, partnerships , or collaborations. It serves as a powerful marketing tool, showcasing your expertise and capabilities to a wider audience.
Validate Your Methods: For businesses, case studies serve as a validation of their methods and strategies. Employing a robust case study methodology is a way to demonstrate the effectiveness of your products, services, or approaches to potential clients or customers through a thorough research process.
Internal Learning: Writing a case study requires reflection on your processes and approach case outcomes. This internal learning process can contribute to continuous improvement within your organization , fostering a culture of innovation and adaptability.

SEO Benefits: Case studies can be optimized for search engines, contributing to your online visibility. Including relevant keywords and internal links in your case studies can improve your website's SEO , attracting more organic traffic.
Differentiation: In competitive industries, a well crafted case study sets you apart from the competition. It allows you to highlight what makes your approach unique and why clients or customers should choose your products or services.
Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies

Benefits of Case Studies:
- Evident Success Stories: Case studies serve as tangible evidence of a business's success, allowing them to showcase real-world achievements and build credibility with potential clients or customers.
- Effective Marketing Tool: They function as powerful marketing tools by providing in depth insights into a business's capabilities , differentiating it from competitors, and influencing the decision making process of potential clients.
- Client Relationship Building: Through detailed case studies, businesses can strengthen relationships with existing clients by demonstrating their commitment, problem solving abilities, and delivering measurable results.
- Versatile Content: Case studies offer versatile content that can be repurposed across various marketing channels, including websites, social media, presentations, and promotional materials.
- Educational Value: Businesses can use case studies to educate their target audience about their industry, innovative solutions, and best practices, positioning themselves as thought leaders.
Limitations of Case Studies:
- Resource Intensive: Creating comprehensive case studies demands significant resources, including time, effort, and potential costs, making them resource-intensive for businesses.
- Limited Generalization: Findings from a specific case study may not be universally applicable, limiting their generalizability to other scenarios or industries.
- Potential Bias: There is a risk of bias in the selection and presentation of information, as businesses may be inclined to emphasize positive outcomes and downplay challenges.
- Confidentiality Concerns: Businesses may face challenges in sharing detailed information, especially if it involves sensitive data or strategies, raising concerns about confidentiality.
- Difficulty in Replication: The unique circumstances of a case study may make it challenging to replicate the same success in different contexts, limiting the broader applicability of the insights gained.
How to Conduct a Case Analysis: Step-by-step
1. define the objective:.
- Clearly outline the purpose of the case study. What do you aim to achieve or understand through this analysis?

2. Select the Case:
- Identify a relevant and specific case that aligns with your objective. For an important case study this could be a real-world situation, event, or phenomenon.
3. Background Research:
- Gather background information about the case. This may include historical context, key players involved, and any existing literature on the subject.


4. Identify Key Issues or Questions:
- Formulate specific research questions or highlight key issues you want to address through the case study.
5. Choose the Research Method:
- Decide on the case study method or approach for data collection. A case study research method could involve qualitative methods such as interviews, observations, or document analysis.
6. Develop Data Collection Plan:
- Outline a detailed plan for collecting data. Specify sources, methods, and tools you will use to gather relevant information.

7. Data Collection:
- Execute the data collection plan. Conduct interviews , observe events, and analyze documents to accumulate necessary data.
8. Data Analysis:
- Apply appropriate analytical techniques to interpret the gathered data. This may involve coding, categorizing, and identifying patterns or themes.
9. Construct the Case Study Narrative:
- Organize the findings into a coherent and structured narrative. Develop sections that cover the introduction, background, analysis, and conclusion.

10. Draw Conclusions:
- Based on your analysis, after you conduct case study , draw conclusions that address the research questions or objectives. Consider the implications of your findings.
11. Peer Review or Feedback:
- Seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or peers to ensure the validity and reliability of your case study.
12. Finalize the Case Study:
- Incorporate feedback and make necessary revisions. Finalize the case study, ensuring clarity, coherence, and adherence to ethical guidelines.
13. Document and Share:
- Prepare the case study for publication or presentation and take advantage of Decktopus AI, a user-friendly and efficient presentation generator powered by AI. Easily convert your case study insights into a visually compelling deck.
- Decktopus ensures your case studies are presented in a format that engages your audience, making your narratives more impactful and memorable. Explore the benefits of Decktopus AI to elevate your case study presentations effortlessly.
What are the Components of a Case Study
The format of a case study typically comprises several key components to present information in a structured and comprehensive manner. While variations may exist based on the context and purpose, a standard case study format often includes the following elements:
1. Introduction:
Provide a brief overview of the case and set the stage for the reader. Outline the main objectives and establish the context of the study.

2. Background:
Present relevant background information about the subject of the case. This may include the history, industry context, or any pertinent details necessary for understanding the situation.

3. Problem Statement or Objectives:
Clearly state the problem or the main objectives of the case study. Define the issues or challenges that the study aims to address.

4. Analysis:
Dive into the analysis of the case. This section often comprises multiple sub-sections, each exploring different aspects such as market conditions, internal factors, external influences, etc.

5. Solution or Action:
Propose solutions or actions to address the identified problems. Detail the steps taken or recommended strategies based on the analysis.

6. Results:
Present the outcomes of the solutions or actions taken. Include any measurable results, impacts, or changes observed.

7. Conclusion:
Summarize the key points, outcomes, and lessons learned. Revisit the problem statement and emphasize the significance of the study, highlighting how the research design shaped the results.

Types of Case Studies
Case study examples, 1. marketing case study template.

The Marketing Case Study Template is tailored for marketers, highlighting successful marketing strategies . Uncover the methods employed, target audience engagement, and measurable outcomes.
Ideal for marketing professionals seeking insights into effective campaign executions. With Decktopus AI , spending your precious time perpetually recreating your product's presentation has become an ancient practice.
Along with our collection of case-study templates, with our one-click platform, you can easily create beautiful presentations for yourself or your clients.
Also check out: creative marketing case study template .
2. Sales Case Study Template

The Sales Case Study Template is designed for salespeople to present and discuss case studies in sales meetings. With its professional look and engaging layout, your clients will be impressed with the level of detail you put into your analysis.
This professionally designed template is easy to use and easy to customize, making it the perfect way to show off your small business expertise.
So whether you're looking to wow potential clients or just need a little more confidence in your sales meetings, our client case study template will help you make an impact.
Also check-out: case study template for sales teams .
3. Design Case Study Example: UI Case Study Template

The UI Case Study Template is specifically designed for UI designers, making it easy to discuss your design process and findings. Present your design case studies like a pro with our target-spesific case study templates. With our design case study template , you'll be able to showcase your work in a clear, professional manner.
Looking to create a stunning case study presentation for your next client meeting? Look no further than our case study templates! Our professional and easy-to-use templates are perfect for designers of all experience levels, and will help you showcase your work in a clear and concise way.
Also check out: Art Case Study Template .
Explore More Case Study Templates

Discover a vast collection of case study templates from various fields, including marketing, sales, and design, in our dedicated Case Study Examples Blog. Gain insights into diverse business scenarios and find inspiration for your own projects.
Case Study Presentation Creation with Decktopus AI
Streamlining the creation of engaging visual case studies has never been easier than with Decktopus AI . This innovative platform offers a seamless experiencensimply write your input, and Decktopus takes care of the rest, ensuring that your templates not only boast a polished visual appeal but also integrate relevant and impactful content effortlessly.
Discover how easy it is to create engaging case study templates using Decktopus AI . Our platform ensures your templates look great and contain relevant content. With the help of our AI assistant, you not only get support during presentations but also receive tips, facilitate Q&A, and increase overall engagement.
Explore the unique storytelling format that Decktopus offers, making your case studies more relatable. For a step-by-guide on how to easily create a visually stunning case study with Decktopus, see our case study examples blog.

This approach allows you to present information in a narrative style, connecting better with your audience. Find practical tips for smoother case study presentations, from effective storytelling to engaging your audience. Improve your presentation experience with Decktopus AI , where simplicity meets interactivity and storytelling for effective communication.
It features, practical design, mobilizing easy principles of marketing ecosystem platform design. Making it by far the easiest thing to use in your daily practice of mobilizing marketing ecosystems through platform strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
1) what is a marketing case study.
A marketing case study is a concise analysis of a business's marketing strategy, showcasing its objectives, challenges, tactics, and outcomes. It offers practical insights into real-world marketing applications, serving as a valuable learning tool for understanding successful practices and lessons learned in achieving specific marketing goals.
2) What is a case study?
A case study, or case report, is a concise examination of a specific subject, often real-world situations or problems, providing detailed insights and analysis for learning or decision-making purposes.
3) How should you write a case study?
To create an impactful case study, define objectives, choose a relevant case, gather key information, and use Decktopus for a polished presentation. Employ data analysis, construct a clear narrative, and offer actionable recommendations.
Validate findings and consider broader implications. Decktopus streamlines this process, providing a user-friendly platform for creating compelling case study presentations effortlessly.

Don't waste your time designing your presentations by yourself!
Type your content and let our platform design your presentations automatically. No more wasting time for your presentations. Use hundreds of presentation templates to impress your audience. This is the only tool you need to prepare presentations. Try our Presentation Builder today >>
Don’t waste your time by trying to make a website for all your content
Place your content links and let our platform design your bio link automatically. No more wasting time for your social content distribution. Use hundreds of presentation biolink to impress your audience. This is the only tool you need to prepare good-looking bio links. Try our Bio Link Builder today >>
Do You Want To Create a Presentation?
Latest Articles

April 5, 2024
Top Sell Sheet Examples to Boost Your Sales Impact in 2024
Discover impactful sales sheet examples demonstrating effective design and content presentation techniques across various industries.
.jpg)
How to Craft an Effective Business Growth Strategy: Unveiling the Blueprint for Success
Discover proven ways and strategies to grow your business with our comprehensive guide on crafting an effective business strategy for sustainable growth.

20+ Sales Promos Examples with Proven Tactics and Ideas for Attracting More Customers Through Promotions
Uncover top sales promotions! Get + examples of cashback, discounts, and coupons to draw more customers & increase promos.
Sign up for our newsletter to stay up-to-date on the latest news and tips from Decktopus.
Let’s create a form here to get visitors’ email addresses.
Ready to dive in? Start your free trial today.
- Ask a Librarian
- Case Study Research
- What is a Case Study?
- Finding a Case Study
Related Guides
- Abstracts - A Guide to Writing by David Woolard Last Updated May 15, 2023 323 views this year
- Annotated Bibliography by Clara Volker Last Updated Jan 16, 2024 1607 views this year
- Literature Reviews by Clara Volker Last Updated Oct 25, 2023 2686 views this year
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research by Suzanne Eichler Last Updated Nov 16, 2023 165 views this year
- The Research Paper Process by Clara Volker Last Updated Nov 16, 2023 1606 views this year
- SAGE Research Methods by Kristen Davis Last Updated Oct 25, 2023 286 views this year
What is a case study?
A case study is a type of research method. In case studies, the unit of analysis is a case . The case typically provides a detailed account of a situation that usually focuses on a conflict or complexity that one might encounter in the workplace.
- Case studies help explain the process by which a unit (a person, department, business, organization, industry, country, etc.) deals with the issue or problem confronting it, and offers possible solutions that can be applied to other units facing similar situations.
- The information presented in case studies is usually qualitative in nature - gathered through methods such as interview, observation, and document collection.
- There are different types of case study, including intrinsic, instrumental, naturalistic, and pragmatic.
This research guide will assist you in finding individual case studies, as well as providing information on designing case studies. If you need assistance locating information, please Ask a Librarian .
- Next: Case Study Research >>
- Last Updated: Nov 2, 2023 2:39 PM
- URL: https://guides.erau.edu/case-studies
Hunt Library
Mori Hosseini Student Union 1 Aerospace Boulevard Daytona Beach, FL 32114
Phone: 386-226-6595 Toll-Free: 800-678-9428
Maps and Parking
- Report a Problem
- Suggest a Purchase
Library Information
- Departments and Staff
- Library Collections
- Library Facilities
- Library Newsletter
- Hunt Library Employment
University Initiatives
- Scholarly Commons
- Data Commons
- University Archives
- Open and Affordable Textbooks
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 21, Issue 1
- What is a case study?
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- Roberta Heale 1 ,
- Alison Twycross 2
- 1 School of Nursing , Laurentian University , Sudbury , Ontario , Canada
- 2 School of Health and Social Care , London South Bank University , London , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Roberta Heale, School of Nursing, Laurentian University, Sudbury, ON P3E2C6, Canada; rheale{at}laurentian.ca
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2017-102845
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
What is it?
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research. 1 However, very simply… ‘a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units’. 1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a single individual, group, community or some other unit in which the researcher examines in-depth data relating to several variables. 2
Often there are several similar cases to consider such as educational or social service programmes that are delivered from a number of locations. Although similar, they are complex and have unique features. In these circumstances, the evaluation of several, similar cases will provide a better answer to a research question than if only one case is examined, hence the multiple-case study. Stake asserts that the cases are grouped and viewed as one entity, called the quintain . 6 ‘We study what is similar and different about the cases to understand the quintain better’. 6
The steps when using case study methodology are the same as for other types of research. 6 The first step is defining the single case or identifying a group of similar cases that can then be incorporated into a multiple-case study. A search to determine what is known about the case(s) is typically conducted. This may include a review of the literature, grey literature, media, reports and more, which serves to establish a basic understanding of the cases and informs the development of research questions. Data in case studies are often, but not exclusively, qualitative in nature. In multiple-case studies, analysis within cases and across cases is conducted. Themes arise from the analyses and assertions about the cases as a whole, or the quintain, emerge. 6
Benefits and limitations of case studies
If a researcher wants to study a specific phenomenon arising from a particular entity, then a single-case study is warranted and will allow for a in-depth understanding of the single phenomenon and, as discussed above, would involve collecting several different types of data. This is illustrated in example 1 below.
Using a multiple-case research study allows for a more in-depth understanding of the cases as a unit, through comparison of similarities and differences of the individual cases embedded within the quintain. Evidence arising from multiple-case studies is often stronger and more reliable than from single-case research. Multiple-case studies allow for more comprehensive exploration of research questions and theory development. 6
Despite the advantages of case studies, there are limitations. The sheer volume of data is difficult to organise and data analysis and integration strategies need to be carefully thought through. There is also sometimes a temptation to veer away from the research focus. 2 Reporting of findings from multiple-case research studies is also challenging at times, 1 particularly in relation to the word limits for some journal papers.
Examples of case studies
Example 1: nurses’ paediatric pain management practices.
One of the authors of this paper (AT) has used a case study approach to explore nurses’ paediatric pain management practices. This involved collecting several datasets:
Observational data to gain a picture about actual pain management practices.
Questionnaire data about nurses’ knowledge about paediatric pain management practices and how well they felt they managed pain in children.
Questionnaire data about how critical nurses perceived pain management tasks to be.
These datasets were analysed separately and then compared 7–9 and demonstrated that nurses’ level of theoretical did not impact on the quality of their pain management practices. 7 Nor did individual nurse’s perceptions of how critical a task was effect the likelihood of them carrying out this task in practice. 8 There was also a difference in self-reported and observed practices 9 ; actual (observed) practices did not confirm to best practice guidelines, whereas self-reported practices tended to.
Example 2: quality of care for complex patients at Nurse Practitioner-Led Clinics (NPLCs)
The other author of this paper (RH) has conducted a multiple-case study to determine the quality of care for patients with complex clinical presentations in NPLCs in Ontario, Canada. 10 Five NPLCs served as individual cases that, together, represented the quatrain. Three types of data were collected including:
Review of documentation related to the NPLC model (media, annual reports, research articles, grey literature and regulatory legislation).
Interviews with nurse practitioners (NPs) practising at the five NPLCs to determine their perceptions of the impact of the NPLC model on the quality of care provided to patients with multimorbidity.
Chart audits conducted at the five NPLCs to determine the extent to which evidence-based guidelines were followed for patients with diabetes and at least one other chronic condition.
The three sources of data collected from the five NPLCs were analysed and themes arose related to the quality of care for complex patients at NPLCs. The multiple-case study confirmed that nurse practitioners are the primary care providers at the NPLCs, and this positively impacts the quality of care for patients with multimorbidity. Healthcare policy, such as lack of an increase in salary for NPs for 10 years, has resulted in issues in recruitment and retention of NPs at NPLCs. This, along with insufficient resources in the communities where NPLCs are located and high patient vulnerability at NPLCs, have a negative impact on the quality of care. 10
These examples illustrate how collecting data about a single case or multiple cases helps us to better understand the phenomenon in question. Case study methodology serves to provide a framework for evaluation and analysis of complex issues. It shines a light on the holistic nature of nursing practice and offers a perspective that informs improved patient care.
- Gustafsson J
- Calanzaro M
- Sandelowski M
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Designing process evaluations using case study to explore the context of complex interventions evaluated in trials
Aileen grant.
1 School of Nursing, Midwifery and Paramedic Practice, Robert Gordon University, Garthdee Road, Aberdeen, AB10 7QB UK
Carol Bugge
2 Faculty of Health Sciences and Sport, University of Stirling, Pathfoot Building, Stirling, FK9 4LA UK
3 Department of Surgery and Cancer, Imperial College London, Charing Cross Campus, London, W6 8RP UK
Associated Data
No data and materials were used.
Process evaluations are an important component of an effectiveness evaluation as they focus on understanding the relationship between interventions and context to explain how and why interventions work or fail, and whether they can be transferred to other settings and populations. However, historically, context has not been sufficiently explored and reported resulting in the poor uptake of trial results. Therefore, suitable methodologies are needed to guide the investigation of context. Case study is one appropriate methodology, but there is little guidance about what case study design can offer the study of context in trials. We address this gap in the literature by presenting a number of important considerations for process evaluation using a case study design.
In this paper, we define context, the relationship between complex interventions and context, and describe case study design methodology. A well-designed process evaluation using case study should consider the following core components: the purpose; definition of the intervention; the trial design, the case, the theories or logic models underpinning the intervention, the sampling approach and the conceptual or theoretical framework. We describe each of these in detail and highlight with examples from recently published process evaluations.
Conclusions
There are a number of approaches to process evaluation design in the literature; however, there is a paucity of research on what case study design can offer process evaluations. We argue that case study is one of the best research designs to underpin process evaluations, to capture the dynamic and complex relationship between intervention and context during implementation. We provide a comprehensive overview of the issues for process evaluation design to consider when using a case study design.
Trial registration
DQIP - ClinicalTrials.gov number, {"type":"clinical-trial","attrs":{"text":"NCT01425502","term_id":"NCT01425502"}} NCT01425502 - OPAL - ISRCTN57746448
Contribution to the literature
- We illustrate how case study methodology can explore the complex, dynamic and uncertain relationship between context and interventions within trials.
- We depict different case study designs and illustrate there is not one formula and that design needs to be tailored to the context and trial design.
- Case study can support comparisons between intervention and control arms and between cases within arms to uncover and explain differences in detail.
- We argue that case study can illustrate how components have evolved and been redefined through implementation.
- Key issues for consideration in case study design within process evaluations are presented and illustrated with examples.
Process evaluations are an important component of an effectiveness evaluation as they focus on understanding the relationship between interventions and context to explain how and why interventions work or fail and whether they can be transferred to other settings and populations. However, historically, not all trials have had a process evaluation component, nor have they sufficiently reported aspects of context, resulting in poor uptake of trial findings [ 1 ]. Considerations of context are often absent from published process evaluations, with few studies acknowledging, taking account of or describing context during implementation, or assessing the impact of context on implementation [ 2 , 3 ]. At present, evidence from trials is not being used in a timely manner [ 4 , 5 ], and this can negatively impact on patient benefit and experience [ 6 ]. It takes on average 17 years for knowledge from research to be implemented into practice [ 7 ]. Suitable methodologies are therefore needed that allow for context to be exposed; one appropriate methodological approach is case study [ 8 , 9 ].
In 2015, the Medical Research Council (MRC) published guidance for process evaluations [ 10 ]. This was a key milestone in legitimising as well as providing tools, methods and a framework for conducting process evaluations. Nevertheless, as with all guidance, there is a need for reflection, challenge and refinement. There have been a number of critiques of the MRC guidance, including that interventions should be considered as events in systems [ 11 – 14 ]; a need for better use, critique and development of theories [ 15 – 17 ]; and a need for more guidance on integrating qualitative and quantitative data [ 18 , 19 ]. Although the MRC process evaluation guidance does consider appropriate qualitative and quantitative methods, it does not mention case study design and what it can offer the study of context in trials.
The case study methodology is ideally suited to real-world, sustainable intervention development and evaluation because it can explore and examine contemporary complex phenomena, in depth, in numerous contexts and using multiple sources of data [ 8 ]. Case study design can capture the complexity of the case, the relationship between the intervention and the context and how the intervention worked (or not) [ 8 ]. There are a number of textbooks on a case study within the social science fields [ 8 , 9 , 20 ], but there are no case study textbooks and a paucity of useful texts on how to design, conduct and report case study within the health arena. Few examples exist within the trial design and evaluation literature [ 3 , 21 ]. Therefore, guidance to enable well-designed process evaluations using case study methodology is required.
We aim to address the gap in the literature by presenting a number of important considerations for process evaluation using a case study design. First, we define the context and describe the relationship between complex health interventions and context.
What is context?
While there is growing recognition that context interacts with the intervention to impact on the intervention’s effectiveness [ 22 ], context is still poorly defined and conceptualised. There are a number of different definitions in the literature, but as Bate et al. explained ‘almost universally, we find context to be an overworked word in everyday dialogue but a massively understudied and misunderstood concept’ [ 23 ]. Ovretveit defines context as ‘everything the intervention is not’ [ 24 ]. This last definition is used by the MRC framework for process evaluations [ 25 ]; however; the problem with this definition is that it is highly dependent on how the intervention is defined. We have found Pfadenhauer et al.’s definition useful:
Context is conceptualised as a set of characteristics and circumstances that consist of active and unique factors that surround the implementation. As such it is not a backdrop for implementation but interacts, influences, modifies and facilitates or constrains the intervention and its implementation. Context is usually considered in relation to an intervention or object, with which it actively interacts. A boundary between the concepts of context and setting is discernible: setting refers to the physical, specific location in which the intervention is put into practice. Context is much more versatile, embracing not only the setting but also roles, interactions and relationships [ 22 ].
Traditionally, context has been conceptualised in terms of barriers and facilitators, but what is a barrier in one context may be a facilitator in another, so it is the relationship and dynamics between the intervention and context which are the most important [ 26 ]. There is a need for empirical research to really understand how different contextual factors relate to each other and to the intervention. At present, research studies often list common contextual factors, but without a depth of meaning and understanding, such as government or health board policies, organisational structures, professional and patient attitudes, behaviours and beliefs [ 27 ]. The case study methodology is well placed to understand the relationship between context and intervention where these boundaries may not be clearly evident. It offers a means of unpicking the contextual conditions which are pertinent to effective implementation.
The relationship between complex health interventions and context
Health interventions are generally made up of a number of different components and are considered complex due to the influence of context on their implementation and outcomes [ 3 , 28 ]. Complex interventions are often reliant on the engagement of practitioners and patients, so their attitudes, behaviours, beliefs and cultures influence whether and how an intervention is effective or not. Interventions are context-sensitive; they interact with the environment in which they are implemented. In fact, many argue that interventions are a product of their context, and indeed, outcomes are likely to be a product of the intervention and its context [ 3 , 29 ]. Within a trial, there is also the influence of the research context too—so the observed outcome could be due to the intervention alone, elements of the context within which the intervention is being delivered, elements of the research process or a combination of all three. Therefore, it can be difficult and unhelpful to separate the intervention from the context within which it was evaluated because the intervention and context are likely to have evolved together over time. As a result, the same intervention can look and behave differently in different contexts, so it is important this is known, understood and reported [ 3 ]. Finally, the intervention context is dynamic; the people, organisations and systems change over time, [ 3 ] which requires practitioners and patients to respond, and they may do this by adapting the intervention or contextual factors. So, to enable researchers to replicate successful interventions, or to explain why the intervention was not successful, it is not enough to describe the components of the intervention, they need to be described by their relationship to their context and resources [ 3 , 28 ].
What is a case study?
Case study methodology aims to provide an in-depth, holistic, balanced, detailed and complete picture of complex contemporary phenomena in its natural context [ 8 , 9 , 20 ]. In this case, the phenomena are the implementation of complex interventions in a trial. Case study methodology takes the view that the phenomena can be more than the sum of their parts and have to be understood as a whole [ 30 ]. It is differentiated from a clinical case study by its analytical focus [ 20 ].
The methodology is particularly useful when linked to trials because some of the features of the design naturally fill the gaps in knowledge generated by trials. Given the methodological focus on understanding phenomena in the round, case study methodology is typified by the use of multiple sources of data, which are more commonly qualitatively guided [ 31 ]. The case study methodology is not epistemologically specific, like realist evaluation, and can be used with different epistemologies [ 32 ], and with different theories, such as Normalisation Process Theory (which explores how staff work together to implement a new intervention) or the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research (which provides a menu of constructs associated with effective implementation) [ 33 – 35 ]. Realist evaluation can be used to explore the relationship between context, mechanism and outcome, but case study differs from realist evaluation by its focus on a holistic and in-depth understanding of the relationship between an intervention and the contemporary context in which it was implemented [ 36 ]. Case study enables researchers to choose epistemologies and theories which suit the nature of the enquiry and their theoretical preferences.
Designing a process evaluation using case study
An important part of any study is the research design. Due to their varied philosophical positions, the seminal authors in the field of case study have different epistemic views as to how a case study should be conducted [ 8 , 9 ]. Stake takes an interpretative approach (interested in how people make sense of their world), and Yin has more positivistic leanings, arguing for objectivity, validity and generalisability [ 8 , 9 ].
Regardless of the philosophical background, a well-designed process evaluation using case study should consider the following core components: the purpose; the definition of the intervention, the trial design, the case, and the theories or logic models underpinning the intervention; the sampling approach; and the conceptual or theoretical framework [ 8 , 9 , 20 , 31 , 33 ]. We now discuss these critical components in turn, with reference to two process evaluations that used case study design, the DQIP and OPAL studies [ 21 , 37 – 41 ].
The purpose of a process evaluation is to evaluate and explain the relationship between the intervention and its components, to context and outcome. It can help inform judgements about validity (by exploring the intervention components and their relationship with one another (construct validity), the connections between intervention and outcomes (internal validity) and the relationship between intervention and context (external validity)). It can also distinguish between implementation failure (where the intervention is poorly delivered) and intervention failure (intervention design is flawed) [ 42 , 43 ]. By using a case study to explicitly understand the relationship between context and the intervention during implementation, the process evaluation can explain the intervention effects and the potential generalisability and optimisation into routine practice [ 44 ].
The DQIP process evaluation aimed to qualitatively explore how patients and GP practices responded to an intervention designed to reduce high-risk prescribing of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or antiplatelet agents (see Table 1 ) and quantitatively examine how change in high-risk prescribing was associated with practice characteristics and implementation processes. The OPAL process evaluation (see Table 2 ) aimed to quantitatively understand the factors which influenced the effectiveness of a pelvic floor muscle training intervention for women with urinary incontinence and qualitatively explore the participants’ experiences of treatment and adherence.
Data-driven Quality Improvement in Primary Care (DQIP)
Optimising Pelvic Floor Exercises to Achieve Long-term benefits (OPAL)
Defining the intervention and exploring the theories or assumptions underpinning the intervention design
Process evaluations should also explore the utility of the theories or assumptions underpinning intervention design [ 49 ]. Not all theories underpinning interventions are based on a formal theory, but they based on assumptions as to how the intervention is expected to work. These can be depicted as a logic model or theory of change [ 25 ]. To capture how the intervention and context evolve requires the intervention and its expected mechanisms to be clearly defined at the outset [ 50 ]. Hawe and colleagues recommend defining interventions by function (what processes make the intervention work) rather than form (what is delivered) [ 51 ]. However, in some cases, it may be useful to know if some of the components are redundant in certain contexts or if there is a synergistic effect between all the intervention components.
The DQIP trial delivered two interventions, one intervention was delivered to professionals with high fidelity and then professionals delivered the other intervention to patients by form rather than function allowing adaptations to the local context as appropriate. The assumptions underpinning intervention delivery were prespecified in a logic model published in the process evaluation protocol [ 52 ].
Case study is well placed to challenge or reinforce the theoretical assumptions or redefine these based on the relationship between the intervention and context. Yin advocates the use of theoretical propositions; these direct attention to specific aspects of the study for investigation [ 8 ] can be based on the underlying assumptions and tested during the course of the process evaluation. In case studies, using an epistemic position more aligned with Yin can enable research questions to be designed, which seek to expose patterns of unanticipated as well as expected relationships [ 9 ]. The OPAL trial was more closely aligned with Yin, where the research team predefined some of their theoretical assumptions, based on how the intervention was expected to work. The relevant parts of the data analysis then drew on data to support or refute the theoretical propositions. This was particularly useful for the trial as the prespecified theoretical propositions linked to the mechanisms of action on which the intervention was anticipated to have an effect (or not).
Tailoring to the trial design
Process evaluations need to be tailored to the trial, the intervention and the outcomes being measured [ 45 ]. For example, in a stepped wedge design (where the intervention is delivered in a phased manner), researchers should try to ensure process data are captured at relevant time points or in a two-arm or multiple arm trial, ensure data is collected from the control group(s) as well as the intervention group(s). In the DQIP trial, a stepped wedge trial, at least one process evaluation case, was sampled per cohort. Trials often continue to measure outcomes after delivery of the intervention has ceased, so researchers should also consider capturing ‘follow-up’ data on contextual factors, which may continue to influence the outcome measure. The OPAL trial had two active treatment arms so collected process data from both arms. In addition, as the trial was interested in long-term adherence, the trial and the process evaluation collected data from participants for 2 years after the intervention was initially delivered, providing 24 months follow-up data, in line with the primary outcome for the trial.
Defining the case
Case studies can include single or multiple cases in their design. Single case studies usually sample typical or unique cases, their advantage being the depth and richness that can be achieved over a long period of time. The advantages of multiple case study design are that cases can be compared to generate a greater depth of analysis. Multiple case study sampling may be carried out in order to test for replication or contradiction [ 8 ]. Given that trials are often conducted over a number of sites, a multiple case study design is more sensible for process evaluations, as there is likely to be variation in implementation between sites. Case definition may occur at a variety of levels but is most appropriate if it reflects the trial design. For example, a case in an individual patient level trial is likely to be defined as a person/patient (e.g. a woman with urinary incontinence—OPAL trial) whereas in a cluster trial, a case is like to be a cluster, such as an organisation (e.g. a general practice—DQIP trial). Of course, the process evaluation could explore cases with less distinct boundaries, such as communities or relationships; however, the clarity with which these cases are defined is important, in order to scope the nature of the data that will be generated.
Carefully sampled cases are critical to a good case study as sampling helps inform the quality of the inferences that can be made from the data [ 53 ]. In both qualitative and quantitative research, how and how many participants to sample must be decided when planning the study. Quantitative sampling techniques generally aim to achieve a random sample. Qualitative research generally uses purposive samples to achieve data saturation, occurring when the incoming data produces little or no new information to address the research questions. The term data saturation has evolved from theoretical saturation in conventional grounded theory studies; however, its relevance to other types of studies is contentious as the term saturation seems to be widely used but poorly justified [ 54 ]. Empirical evidence suggests that for in-depth interview studies, saturation occurs at 12 interviews for thematic saturation, but typically more would be needed for a heterogenous sample higher degrees of saturation [ 55 , 56 ]. Both DQIP and OPAL case studies were huge with OPAL designed to interview each of the 40 individual cases four times and DQIP designed to interview the lead DQIP general practitioner (GP) twice (to capture change over time), another GP and the practice manager from each of the 10 organisational cases. Despite the plethora of mixed methods research textbooks, there is very little about sampling as discussions typically link to method (e.g. interviews) rather than paradigm (e.g. case study).
Purposive sampling can improve the generalisability of the process evaluation by sampling for greater contextual diversity. The typical or average case is often not the richest source of information. Outliers can often reveal more important insights, because they may reflect the implementation of the intervention using different processes. Cases can be selected from a number of criteria, which are not mutually exclusive, to enable a rich and detailed picture to be built across sites [ 53 ]. To avoid the Hawthorne effect, it is recommended that process evaluations sample from both intervention and control sites, which enables comparison and explanation. There is always a trade-off between breadth and depth in sampling, so it is important to note that often quantity does not mean quality and that carefully sampled cases can provide powerful illustrative examples of how the intervention worked in practice, the relationship between the intervention and context and how and why they evolved together. The qualitative components of both DQIP and OPAL process evaluations aimed for maximum variation sampling. Please see Table 1 for further information on how DQIP’s sampling frame was important for providing contextual information on processes influencing effective implementation of the intervention.
Conceptual and theoretical framework
A conceptual or theoretical framework helps to frame data collection and analysis [ 57 ]. Theories can also underpin propositions, which can be tested in the process evaluation. Process evaluations produce intervention-dependent knowledge, and theories help make the research findings more generalizable by providing a common language [ 16 ]. There are a number of mid-range theories which have been designed to be used with process evaluation [ 34 , 35 , 58 ]. The choice of the appropriate conceptual or theoretical framework is, however, dependent on the philosophical and professional background of the research. The two examples within this paper used our own framework for the design of process evaluations, which proposes a number of candidate processes which can be explored, for example, recruitment, delivery, response, maintenance and context [ 45 ]. This framework was published before the MRC guidance on process evaluations, and both the DQIP and OPAL process evaluations were designed before the MRC guidance was published. The DQIP process evaluation explored all candidates in the framework whereas the OPAL process evaluation selected four candidates, illustrating that process evaluations can be selective in what they explore based on the purpose, research questions and resources. Furthermore, as Kislov and colleagues argue, we also have a responsibility to critique the theoretical framework underpinning the evaluation and refine theories to advance knowledge [ 59 ].
Data collection
An important consideration is what data to collect or measure and when. Case study methodology supports a range of data collection methods, both qualitative and quantitative, to best answer the research questions. As the aim of the case study is to gain an in-depth understanding of phenomena in context, methods are more commonly qualitative or mixed method in nature. Qualitative methods such as interviews, focus groups and observation offer rich descriptions of the setting, delivery of the intervention in each site and arm, how the intervention was perceived by the professionals delivering the intervention and the patients receiving the intervention. Quantitative methods can measure recruitment, fidelity and dose and establish which characteristics are associated with adoption, delivery and effectiveness. To ensure an understanding of the complexity of the relationship between the intervention and context, the case study should rely on multiple sources of data and triangulate these to confirm and corroborate the findings [ 8 ]. Process evaluations might consider using routine data collected in the trial across all sites and additional qualitative data across carefully sampled sites for a more nuanced picture within reasonable resource constraints. Mixed methods allow researchers to ask more complex questions and collect richer data than can be collected by one method alone [ 60 ]. The use of multiple sources of data allows data triangulation, which increases a study’s internal validity but also provides a more in-depth and holistic depiction of the case [ 20 ]. For example, in the DQIP process evaluation, the quantitative component used routinely collected data from all sites participating in the trial and purposively sampled cases for a more in-depth qualitative exploration [ 21 , 38 , 39 ].
The timing of data collection is crucial to study design, especially within a process evaluation where data collection can potentially influence the trial outcome. Process evaluations are generally in parallel or retrospective to the trial. The advantage of a retrospective design is that the evaluation itself is less likely to influence the trial outcome. However, the disadvantages include recall bias, lack of sensitivity to nuances and an inability to iteratively explore the relationship between intervention and outcome as it develops. To capture the dynamic relationship between intervention and context, the process evaluation needs to be parallel and longitudinal to the trial. Longitudinal methodological design is rare, but it is needed to capture the dynamic nature of implementation [ 40 ]. How the intervention is delivered is likely to change over time as it interacts with context. For example, as professionals deliver the intervention, they become more familiar with it, and it becomes more embedded into systems. The OPAL process evaluation was a longitudinal, mixed methods process evaluation where the quantitative component had been predefined and built into trial data collection systems. Data collection in both the qualitative and quantitative components mirrored the trial data collection points, which were longitudinal to capture adherence and contextual changes over time.
There is a lot of attention in the recent literature towards a systems approach to understanding interventions in context, which suggests interventions are ‘events within systems’ [ 61 , 62 ]. This framing highlights the dynamic nature of context, suggesting that interventions are an attempt to change systems dynamics. This conceptualisation would suggest that the study design should collect contextual data before and after implementation to assess the effect of the intervention on the context and vice versa.
Data analysis
Designing a rigorous analysis plan is particularly important for multiple case studies, where researchers must decide whether their approach to analysis is case or variable based. Case-based analysis is the most common, and analytic strategies must be clearly articulated for within and across case analysis. A multiple case study design can consist of multiple cases, where each case is analysed at the case level, or of multiple embedded cases, where data from all the cases are pulled together for analysis at some level. For example, OPAL analysis was at the case level, but all the cases for the intervention and control arms were pulled together at the arm level for more in-depth analysis and comparison. For Yin, analytical strategies rely on theoretical propositions, but for Stake, analysis works from the data to develop theory. In OPAL and DQIP, case summaries were written to summarise the cases and detail within-case analysis. Each of the studies structured these differently based on the phenomena of interest and the analytic technique. DQIP applied an approach more akin to Stake [ 9 ], with the cases summarised around inductive themes whereas OPAL applied a Yin [ 8 ] type approach using theoretical propositions around which the case summaries were structured. As the data for each case had been collected through longitudinal interviews, the case summaries were able to capture changes over time. It is beyond the scope of this paper to discuss different analytic techniques; however, to ensure the holistic examination of the intervention(s) in context, it is important to clearly articulate and demonstrate how data is integrated and synthesised [ 31 ].
There are a number of approaches to process evaluation design in the literature; however, there is a paucity of research on what case study design can offer process evaluations. We argue that case study is one of the best research designs to underpin process evaluations, to capture the dynamic and complex relationship between intervention and context during implementation [ 38 ]. Case study can enable comparisons within and across intervention and control arms and enable the evolving relationship between intervention and context to be captured holistically rather than considering processes in isolation. Utilising a longitudinal design can enable the dynamic relationship between context and intervention to be captured in real time. This information is fundamental to holistically explaining what intervention was implemented, understanding how and why the intervention worked or not and informing the transferability of the intervention into routine clinical practice.
Case study designs are not prescriptive, but process evaluations using case study should consider the purpose, trial design, the theories or assumptions underpinning the intervention, and the conceptual and theoretical frameworks informing the evaluation. We have discussed each of these considerations in turn, providing a comprehensive overview of issues for process evaluations using a case study design. There is no single or best way to conduct a process evaluation or a case study, but researchers need to make informed choices about the process evaluation design. Although this paper focuses on process evaluations, we recognise that case study design could also be useful during intervention development and feasibility trials. Elements of this paper are also applicable to other study designs involving trials.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Professor Shaun Treweek for the discussions about context in trials.
Abbreviations
Authors’ contributions.
AG, CB and MW conceptualised the study. AG wrote the paper. CB and MW commented on the drafts. All authors have approved the final manuscript.
No funding was received for this work.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethics approval and consent to participate is not appropriate as no participants were included.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication is not required as no participants were included.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Aileen Grant, Email: [email protected] .
Carol Bugge, Email: [email protected] .
Mary Wells, Email: [email protected] .

GOOGLE UX DESIGN PROFESSIONAL CERTIFICATE
Course 6 – responsive web design in adobe xd, week 6: document design work and search for jobs, coursera study guide, table of content, test your knowledge on handing off designs, test your knowledge on portfolio case studies, weekly challenge 6: document design work and search for jobs.
With your responsive website designs complete, you’ll be ready to share your work with others. To start, you’ll learn how to prepare and handoff designs to engineers, who will build the final product. You’ll also add a case study to your professional UX portfolio featuring your responsive website designs. Then, you’ll pivot to focus on your big picture goal: getting a job as a UX designer. You’ll learn tips and tricks to scan job postings, and you’ll create a compelling resume that highlights your new UX skills.
Learning Objectives
- Annotate and document designs for hand off to engineers
- Explain the benefits and parts of a portfolio case study
- Add a case study with website designs to a portfolio
- [Optional] Summarize the professional goals and interests that motivate job searches and explore job opportunities
- [Optional] Highlight key words and requirements from example job descriptions
- [Optional] Draft a resume to highlight UX design accomplishments
1. When building websites, what type of team members are crucial in building the UX team’s vision? Select all that apply.
- Program manager
- Data scientist
- Back-end (CORRECT)
- Front-end (CORRECT)
Correct: Back-end developers write code for the website’s architecture and data storage or retrieval, which is based on the UX sitemap and functionality. They play a crucial role in making a website possible. Fast load times are a result of good back-end development! UX designers also work with front-end developers. They create websites by writing code for all the user-facing interfaces.
Correct: Also known as web developers, front-end developers work with UX designers to create websites by writing code for all the user-facing interfaces. In other words, they create the functionality that users interact with on a website. UX designers also work with back-end developers. They write code for the website’s architecture and data storage or retrieval, which is based on the UX sitemap and functionality.
2. Fill in the blank: Designers provide mockups, prototypes, and ____ so the engineering team can begin the coding process.
- research reports
- case studies
- specifications (CORRECT)
Correct: Designers provide mockups, prototypes, and specifications, so the engineering team can begin the coding process.
3. How does a designer determine when their designs are final before sending them off to the engineering team?
- As long as design specifications have been finalized, then it’s ready to be delivered to the engineering team.
- If the designs are true representations of the intended user experience, assets are finalized, and users are able to interact with the designs without external guidance, then it’s ready for the engineering team. (CORRECT)
- If the design passes usability studies and participants seem mostly satisfied with the design, then it’s ready to be delivered to the engineering team.
- As long as assets have been finalized and the designer believes the product looks good, then it’s ready for the engineering team.
Correct: Are the designs a true representation of the intended user experience? Have placeholder texts, icons, and images been replaced with finalized assets? Are users able to interact with a design without external guidance? If you can answer “yes” to all three, then the designs are ready.
1. What are the typical components of a case study? Select all that apply.
- Usability study participant profiles
- Outcome of the project (CORRECT)
- Project goal and objectives (CORRECT)
- Designer’s role in the project (CORRECT)
- Process the team followed (CORRECT)
Correct: A project’s goal and objectives, the designer’s role, the team’s process, and the project’s outcome are typically included in a case study.
2. Fill in the blank: You complete a case study on your latest design project and add it to your portfolio. You should present your case study in a clear and _____ way to tell recruiters what they need to know as quickly and efficiently as possible.
- Concise (CORRECT)
Correct: Your case study should be clear and concise so recruiters can quickly assess your design knowledge and skills.
3. Fill in the blank: Sharing case studies in your portfolio is important because case studies are a visual demonstration of your _____. Select all that apply.
- interests and hobbies
- design knowledge (CORRECT)
- ability to see an idea through from start to finish, despite challenges (CORRECT)
- willingness to collaborate with a team (CORRECT)
Correct: Case studies are a visual demonstration of your design knowledge, willingness to collaborate with a team, and ability to see an idea through from start to finish. Demonstrating your design knowledge in a case study allows recruiters to determine how well you would fit in a potential UX role.
Correct: Case studies are a visual demonstration of your design knowledge, willingness to collaborate with a team, and ability to see an idea through from start to finish. Demonstrating your ability to progress throughout an entire project shows recruiters you can see an idea through from beginning to end.
Correct: Case studies are a visual demonstration of your design knowledge, willingness to collaborate with a team, and ability to see an idea through from start to finish. Demonstrating your willingness to collaborate with a team is a characteristic recruiters would like to see in a case study.
4. You complete a design project for a photo sharing app and want to create a case study for your portfolio. What should you include in the case study to show recruiters you would be a strong candidate for a UX design role? Select all that apply.
- Rough drafts of every idea
- Disagreements with team members
- Explanation of learnings from the design process (CORRECT)
- Sketches, wireframes, and final polished designs (CORRECT)
Correct: Your case study should include a explanations of what you learned so recruiters can understand your thought process and approach to design. It should also include samples of your best sketches, wireframes, and final polished designs to showcase your design knowledge and skills.
Correct: Your case study should include samples of your best sketches, wireframes, and final polished designs to showcase your design knowledge and skills. It should also include explanations of what you learned, so recruiters can understand your thought process and approach to design.
1. A design team completes their high-fidelity prototype of a responsive website. Before they hand off designs to the engineering team, they need to confirm that the designs are final. What questions should they answer before handing off the designs? Select all that apply.
- Have the engineers written code for the website’s architecture and data storage?
- Are the designs a true representation of the intended user experience? (CORRECT)
- Have placeholder text, icons, and imagery been replaced with finalized assets? (CORRECT)
- Are users able to interact with and interpret the designs without external guidance? (CORRECT)
Correct: This is a key question the team needs to answer before handing off designs to engineers. If the team can answer “yes” to this question, it’s one indication that the designs are complete.
2. What is the difference between a back-end developer and a front-end developer?
- A back-end developer writes code based on UX designer specifications; a front-end developer writes code based on the UX sitemap and functionality.
- A back-end developer writes code based on the UX sitemap and functionality; a front-end developer writes code based on UX designer specifications. (CORRECT)
- A back-end developer writes code for user interactions; a front-end developer writes code for website architecture.
- A back-end developer writes code to enhance website accessibility; a front-end developer writes code to streamline information architecture.
Correct: A front-end developer, or web developer, writes code for all the user-facing interfaces based on UX designer specifications. A back-end developer writes code for the website’s architecture and data storage or retrieval, based on the UX sitemap and functionality.
3. When you want to share a prototype with developers in Adobe XD, what file format should you use?
- Development (CORRECT)
- Presentation
- Design Review
- User Testing
Correct: Development allows you to share your prototype specifically with developers; Design Review shares a document that allows you to receive feedback on your design or prototype.
4. Imagine a designer finishes their prototype in Adobe XD. They want to share it with developers. Should the designer set permissions so that anyone with a link can access the prototype?
- Yes. It’s best to allow anyone with a link to access the documents, so designers and developers can seamlessly collaborate.
- No. It’s best practice to share documents with password protection. That way, designers maintain control over who can view the prototype.
- Sometimes. It depends on the sensitivity of the material. (CORRECT)
5. A designer wraps up a final prototype of a language learning app in Adobe XD, and wants to share their work with the development team. Before they publish the prototype on the cloud, they name the file: LanguageApp-Version-Final. Does this file name reflect best practices?
- Yes. A file name should include the project name and version. (CORRECT)
- No. A file name must include the date, the author, and the version number.
- Maybe. A file name can reflect the designer’s preferences, which vary designer to designer.
Correct: The file name reflects best practices, as it clearly indicates to developers what the designer is sending.
6. Imagine a designer finishes a client project and wants to write a case study. They draft a case study that describes their role in the project, the goal of the project, and the target user. They also add sketches and wireframes, and their polished designs. What critical components are missing from the case study? Select all that apply.
- The designer’s thoughts on how the design could be improved
- The research conducted and research findings (CORRECT)
- The key challenges or constraints the designer faced (CORRECT)
- The designer’s learnings during the design process (CORRECT)
Correct: The research conducted and its findings are a critical component of the case study. The case study should also include a description of what the designer learned, and the challenges and constraints they encountered.
Correct: The key challenges or constraints is a critical component of the case study. The case study should also include a description of the designer’s learnings, and the research conducted and its findings.
Correct: What the designer learns during the process is a critical component of the case study. The case study should also include the challenges and constraints, as well as a description of the research conducted and its findings.
7. Imagine that you finish your prototype in Adobe XD and want to share it with developers. What is the first step to sharing your document?
- In the upper-right corner, click the Link tab.
- Then, under the Cloud Settings panel, name your file.
- In the menu bar, open Share Settings.
- Then, using the Link tab, rename and upload your file.
- In the upper-left corner, click the Share tab.
- Then, under the Link Settings panel, name your file. (CORRECT)
- In the menu bar, open Link Settings.
- Then, using the Share tab, rename and upload your file.
Correct: To share your prototype you first need to publish it to the cloud. Under the Link Settings panel, you should first name your project clearly so the developers know what you’re sending.
8. Fill in the blank: In Adobe XD, you can customize the level of security on a document under _____.
- Create Link
- Update Link
- Link Access (CORRECT)
Correct: You can customize the level of security on the document under Link Access. Select the option that is best suited to the sensitivity of the material you are sharing.
9. What is true of a good case study? Select all that apply.
- Quick to compile
- Applies standard template
- Easy to skim (CORRECT)
- Visually appealing (CORRECT)
Correct: A good case study should be easy to skim. If it’s text-heavy or the overall look is too busy, people are more likely to skip over important details.
Correct: A good case study is visually appealing because it can instantly capture attention, especially for those who’d prefer to skim graphics and visual components than text.
10. When a recruiter or hiring manager considers you for a job, they’ll expect to find case studies in your portfolio.
- True (CORRECT)
Correct: A case study is an important component of every designer’s portfolio. It serves to demonstrate your design knowledge and skills, how you collaborate, and your ability to carry ideas to completion.
11. What are some key elements that make up an entry-level UX resume? Select all that apply.
- General awards
- Portfolio link (CORRECT)
- Technical skills and design knowledge (CORRECT)
- Course summary of UX-related courses (CORRECT)
Correct: A portfolio link is essential to include in a UX resume because it is the main focus when recruiters evaluate potential candidates.
Correct: Hard skills like technical knowledge of design-related tools should be highlighted in a UX resume.
Correct: UX-related education or courses in a resume demonstrates the depth of design knowledge a UX design candidate has.
12. Why are case studies important components in a design portfolio? Select all that apply.
- They demonstrate your ability to work through a project quickly.
- They demonstrate your design knowledge. (CORRECT)
- They demonstrate your willingness to collaborate with a team. (CORRECT)
- They demonstrate your ability to see an idea from start to finish. (CORRECT)
Correct: Case studies are important in a portfolio because they are visual demonstrations of your design knowledge.
Correct: Case studies are important in a portfolio because they demonstrate how well you work within a team.
Correct: Case studies are important in a portfolio because they demonstrate your ability to complete a design project from start to finish, despite challenges along the way.
13. What role do developers play in creating a usable product?
- They make stable the preliminary code that UX designers compile
- They make interactive the low-fi mockups that UX designers hand off
- They make accessible the feature updates that UX researchers recommend
- They make functional the designs and features that UX designers create (CORRECT)
Correct: It takes designers, researchers, and developers to create a functional and usable product. Developers take UX designers’ work and make the designs and features functional.
14. Fill in the blank: In Adobe XD, you can choose the type of file you want to share with viewers under _____.
- View Settings (CORRECT)
- Link Settings
- Link Access
Correct: Under View Settings, you can choose the type of file you’d like to share with viewers.
15. If you share highly sensitive material in Adobe XD, what type of access permission should you select?
- Anyone With The Link
- Only User Testing
- Only Invited People
- Anyone With Password (CORRECT)
Correct: You can customize the level of security on the document you share. Anyone With The Link permissions are best for sensitive materials.
16. What are the components of a case study?
- Project budget and timeline, the designer’s project tasks, the makeup of the team followed, and stakeholder feedback
- Project background and research, the design team’s budget, the process user testing followed, and product manager feedback
- Project goal and objectives, the designer’s role in the project, the process the team followed, and project outcome (CORRECT)
- Project pitch deck and summary, the design team’s objective, the project burndown chart, and beta test feedback
Correct: Project goal and objectives, the designer’s role in the project, the process the team followed, and the project outcome are all components that should be included in a case study.Correct: Project goal and objectives, the designer’s role in the project, the process the team followed, and the project outcome are all components that should be included in a case study.
17. Fill in the blank: A case study can serve as a visible representation of your design knowledge, your willingness to collaborate, and your ability to _____.
- manage complex projects within a tight deadline
- see an idea through from start to finish, despite challenges (CORRECT)
- arrive at optimal design solutions, despite competing objectives
- supervise front- and back-end developers while they write code
Correct: A case study can serve as a visible representation of your design knowledge, your willingness to collaborate, and your ability to see an idea through from start to finish, despite challenges.
18. Imagine a designer sends their portfolio to a recruiter for a potential job opportunity. One of the designer’s case studies discusses how the designer worked with a diverse team for a complex project. Which case study component is this an example of?
- Design processes followed
- Project outcome
- Project goal and objectives
Correct: This case study component is an example of the designer’s role in the project because it discusses how the designer worked within a project team.
19. Fill in the blank: Case studies are the major components of a portfolio because they are a _____.
- view of a design challenge
- reflection of how a company implements a design system
- visual demonstration of your design knowledge (CORRECT)
- representation of a company’s design goals
Correct: Case studies are important because they demonstrate your design knowledge throughout a project.
20. Which team member writes code for the website’s architecture and data storage?
- Back-end developer (CORRECT)
- UX designer
- UX engineer
- Front-end developer
Correct: Back-end developers write code for the website’s architecture and data storage or retrieval, based on the UX sitemap and functionality.
21. Fill in the blank: A case study needs to tell recruiters what they need to know _____.
- with short descriptions, rather than images
- while highlighting key industry trends
- as quickly and efficiently as possible (CORRECT)
- in a simple, animated deck or video
22. A designer should have multiple resume versions that are tailored to specific jobs they apply to.
Correct: Multiple versions of a designer’s resume should be ideal because they can target specific jobs by incorporating key terms listed in the desired job description.
23. What components typically make up a case study? Select all that apply.
- Designer’s resume
Correct: It is important to explain the project’s outcome in a case study. This helps recruiters understand the designer’s process from beginning to end.
Correct: It is important to include project goals and objectives in a case study. These help recruiters understand a designer’s design process.
Correct: In a case study, it is important to explain a designer’s role in their project. This helps recruiters understand how the designer contributed to the project.
24. A designer finds a job that she is interested in, but needs to create a resume quickly before the upcoming job application deadline. What tool can she use to create a solid resume with all the necessary elements?
- A template from a word processing program (CORRECT)
Correct: Using a template is the fastest way to create a resume because it already includes all of the necessary elements a designer needs to include.
25. What type of developers write code for all the user-facing interfaces based on the UX designer’s specifications?
Correct: Front-end developers, or web developers, help to create the functionality for users as they interact with an app or website.
26. Which of the following specialist roles focuses on designing a product’s experience and function?
- Motion designers
- Visual designers
- Interaction designers (CORRECT)
- UI designers
Correct: Interaction designers focus on designing a product’s experience and function by examining how to connect the user’s needs and the business goals with what’s feasible to build.
27. Which of the following elements make up a basic resume’s structure? Select all that apply.
- Education (CORRECT)
- Contact information (CORRECT)
- Skills (CORRECT)
Correct: Education, including the completion of this certificate program, is included in a resume. Resumes should also include contact information and relevant skills.
Correct: Resumes should include the candidate’s contact information for recruiters and employers to get in touch with them. They should also include education information and relevant skills.
Correct: Relevant skills, such as the skills gained through this program, should be included in a resume. They should also include education and contact information.
28. It’s important to include keywords and key phrases in your resume.
Correct: Hiring managers often skim for keywords that are also listed on the job description of the role they’re trying to fill. Sometimes there are resume scanners that search for keywords, so if your application doesn’t include enough keywords, it may get filtered out before reaching a manager.
29. What can you do with a job description to make it easier for hiring managers and software to notice your resume or portfolio?
- Copy and paste the description verbatim
- Study the requirements
- Match key phrases and keywords (CORRECT)
- Add it to a cover letter
Correct: To make it easier for hiring managers and software to notice your resume or portfolio, match key phrases and keywords from the job description.
30. Should you only include case studies from your work as a professional UX designer in your design portfolio?
- Yes. Case studies should present designs that you have completed for companies or clients in your professional work.
- No. You should include case studies that represent your best design work. Case studies do not necessarily need to present work from projects with clients and companies. (CORRECT)
- Maybe. Case studies should present designs that you have completed for companies or clients in your professional work, but only if these projects went as planned.
31. Imagine a recruiter has requested that you share your portfolio for consideration in a newly created role. You want to include some case studies from past projects but need to finalize them before adding them to the portfolio. What should you consider to ensure the case studies are well presented?
- Case studies should be detailed and extensive.
- Case studies should include just your polished designs.
- Case studies should be visually appealing and easy to skim. (CORRECT)
- Case studies should include every aspect of the design project.
32. A design team completes their high-fidelity prototype of a responsive website. They confirm that the designs represent the expected user experience. What else must they confirm before handing off designs to the engineering team? Select all that apply.
- The design includes finalized assets rather than placeholders. (CORRECT)
- The users can interact with and interpret designs without guidance. (CORRECT)
- The back-end developers have a clear roadmap for creating the user-facing interface.
- The front-end developers have a clear roadmap for creating the website’s architecture.
Correct: The design needs to confirm the designs are complete. The design must represent the intended user experience and include finalized assets. Beyond that, users should be able to interact with the designs without guidance.
Correct: The design team needs to confirm the designs are complete. The design must represent the intended user experience and include finalized assets. Beyond that, users should be able to interact with the designs without guidance.
33. Which team member writes code for the user-facing interfaces?
- Back-end developer
- Front-end developer (CORRECT)
Correct: Front-end developers work with specifications provided by UX designers. They help to create the functionality that users will be interacting with on an app or website.
34. A designer wraps up a final prototype of a storm tracking app in Adobe XD and wants to share their work with the development team. Before they publish the prototype on the cloud, they name the file. Which of the following example file names reflects best practices?
- App-To-Test-2021
- StormApp-To-Test
- StormApp-Version-Final (CORRECT)
- App-For-Review
Correct: This includes the project name and version, which clearly indicates to the developers what the designer is sending.
35. Fill in the blank: A _____ typically includes a project’s goal and objectives, a designer’s role in the project, the process the design team followed, and the project outcome.
- design portfolio
- hi-fi prototype
- project summary
- case study (CORRECT)
Correct: A case study typically includes the project goal and objectives, your role in the project, the process your team followed, and the outcome of the project.
36. Imagine a designer finishes a client project and wants to write a case study. They draft a case study that highlights their sketches, wireframes, and polished designs. Should they also include a description of the project and its goals?
- Yes. This is critical information. They should also include information about the target user, research conducted, and learnings during the design process. (CORRECT)
- No. This is unnecessary information. The case study should focus on the designer’s product, including the sketches, wireframes, and polished designs.
- Sometimes. This can be helpful information to provide context. Studies should only include detailed descriptions when they compliment the designs.
Correct: The case study should include details about the project, including descriptions of the research, the project and its goals, the designer’s role, and lessons learned.
37. What is a case study?
- Portfolio containing the final design products
- Summarized presentation of a design project (CORRECT)
- Interactive prototype of a draft design product
- Description of a project’s goals and objectives
38. What should a designer include in the file name when sharing content with a developer?
- Design budget and deadline
- File type and project name
- Development start and end dates
- Project name and version (CORRECT)
Correct: It’s important to include the project name and version, which clearly indicates to the developers what the designer is sending.
39. Imagine a designer is applying for a job at a new design firm. They want to highlight their ability to collaborate with a team. How can they convey this to the firm’s recruiter?
- Prepare interview responses that highlight your practiced collaboration skills
- Share a portfolio with a case study, which demonstrates your willingness to collaborate (CORRECT)
- Ask former colleagues to submit reference letters to the firm’s recruiter
- Submit a cover letter without a resume, and write about your collaboration skills
Correct: A case study can serve as a visible representation of your design knowledge, your willingness to collaborate, and your ability to see ideas through.
40. When applying for UX design jobs, it is important to include which of the following materials in your application? Select all that apply.
- Portfolio (CORRECT)
- Resume (CORRECT)
- Case studies (CORRECT)
Correct: A portfolio is important to include in job applications. Recruiters and hiring managers review this material during the application process.
Correct: A resume is important to include in job applications. Recruiters and hiring managers review this material during the application process.
Correct: Case studies are important to include in job applications. Recruiters and hiring managers review this material during the application process.
41. Fill in the blank: When creating a case study, critical pieces include the designer’s role in the project, the goal of the project, and the sketches and wireframes. Most importantly, the case study should include _____.
- key challenges encountered
- what the designer learned during the design process (CORRECT)
- the designer’s design experience
- the designer’s final product
Subscribe to our site
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Enter your email address
Quiztudy Top Courses
Popular in coursera.
- Google Advanced Data Analytics
- Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate
- Meta Marketing Analytics Professional Certificate
- Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate
- Google UX Design Professional Certificate
- Meta Social Media Marketing Professional Certificate
- Google Project Management Professional Certificate
- Meta Front-End Developer Professional Certificate
Liking our content? Then, don’t forget to ad us to your BOOKMARKS so you can find us easily!

Liking our Study Guides, Subscribe Now!!!
Get hired - read our latest posts, the latest's study guides in the market for you to accelerate your progress, and achieve your goals.

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Writing a Case Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Reading Research Effectively
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Bibliography
The term case study refers to both a method of analysis and a specific research design for examining a problem, both of which are used in most circumstances to generalize across populations. This tab focuses on the latter--how to design and organize a research paper in the social sciences that analyzes a specific case.
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or among more than two subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in this writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a single case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- Does the case represent an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- Does the case provide important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- Does the case challenge and offer a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in practice. A case may offer you an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to the study a case in order to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- Does the case provide an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings in order to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- Does the case offer a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for exploratory research that points to a need for further examination of the research problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of Uganda. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a particular village can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community throughout rural regions of east Africa. The case could also point to the need for scholars to apply feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation.
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work. In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What was I studying? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why was this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the research problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would include summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to study the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in the context of explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular subject of analysis to study and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that frames your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; c) what were the consequences of the event.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experience he or she has had that provides an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of his/her experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using him or her as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, cultural, economic, political, etc.], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, why study Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research reveals Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks from overseas reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should be linked to the findings from the literature review. Be sure to cite any prior studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for investigating the research problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is more common to combine a description of the findings with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps to support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings It is important to remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations for the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and needs for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) restate the main argument supported by the findings from the analysis of your case; 2) clearly state the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in and your professor's preferences, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented applied to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were on social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood differently than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis.
Case Studies . Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical (context-dependent) knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Reviewing Collected Essays
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jan 17, 2023 10:50 AM
- URL: https://libguides.pointloma.edu/ResearchPaper

COMMENTS
To have the most success, including the following eight essential components of a case study is imperative. I've also included some questions to help guide your interview with your customer. 1. Start with a Compelling Title and Summary. As with any story, you should include an eye-catching headline.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Here's what you should avoid including in your case study: 1. Unverified claims / data. Every claim you make and every piece of data you share in your case study must be true and easy to check. Trust is crucial in a case study, and even one bit of wrong information can damage trust and hurt your image.
Definition, Elements and 15 Examples. Case studies help expose individuals to previous problems and what it took to revise them. They're useful in training new employees or showing potential clients what an agency is capable of. However, they require a specific structure to be effective.
1. A compelling executive summary. One of the most important components of a case study is a powerful executive summary. It lets your reader know what they're getting into, and how they might relate to and benefit from what they'll learn. Firstly, it needs to introduce your customer and their challenges.
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case ...
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. ... (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design: A study's questions. A study's propositions (if any). A study's units of analysis. The logic that links the data to the ...
Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you're researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences. Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
Case studies that include visual elements such as photos, diagrams, infographics, or videos can often be more persuasive and effective than those that don't. Visual aids can also help make complex topics more easily understandable, and they often create a stronger emotional connection with potential customers. 7. Descriptive Name.
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the Components of a Case Study. The format of a case study typically comprises several key components to present information in a structured and comprehensive manner. While variations may exist based on the context and purpose, a standard case study format often includes the following elements: 1. Introduction:
The case typically provides a detailed account of a situation that usually focuses on a conflict or complexity that one might encounter in the workplace. Case studies help explain the process by which a unit (a person, department, business, organization, industry, country, etc.) deals with the issue or problem confronting it, and offers ...
Case study research is typically extensive; it draws on multiple methods of data collection and involves multiple data sources. The researcher begins by identifying a specific case or set of cases to be studied. Each case is an entity that is described within certain parameters, such as a specific time frame, place, event, and process.
Usually, the case studies conducted in business and management disciplines assume the interpretive paradigm. The objective of authors' case studies was to understand the process of value cocreation. This has been done while visiting the context, interviewing actors involved in the process, making notes of meetings/projects, and finally ...
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
Case study is a research methodology, typically seen in social and life sciences. There is no one definition of case study research.1 However, very simply… 'a case study can be defined as an intensive study about a person, a group of people or a unit, which is aimed to generalize over several units'.1 A case study has also been described as an intensive, systematic investigation of a ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Case studies can include single or multiple cases in their design. Single case studies usually sample typical or unique cases, their advantage being the depth and richness that can be achieved over a long period of time. The advantages of multiple case study design are that cases can be compared to generate a greater depth of analysis.
What components typically make up a case study? Select all that apply. Designer's role in the project Outcome of the project Project goal and objectives. Imagine a recruiter has requested that you share your portfolio for consideration in a newly created role. You want to include some case studies from past projects but need to finalize them ...
Process the team followed (CORRECT) Correct: A project's goal and objectives, the designer's role, the team's process, and the project's outcome are typically included in a case study. 2. Fill in the blank: You complete a case study on your latest design project and add it to your portfolio.
A case study paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or among more than two subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm. ...
Click here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ What components typically make up a case study? Select all that apply. a. Designer's role in the project b…