

APA Style Citation Guide 7th Edition
- APA 7th Style Manual
- Books and eBooks
- Films, YouTube & More
- Government Sources
- Open Educational Resources
- AI or ChatGPT
- Social Media
- Art, Clip Art or Photos
- Authors: Missing or Anonymous
- Missing Reference Information
- Direct Quotes
- Reference Page Format
- Abstract and Keywords
- Annotated Bibliography
- Style and Grammar Guidlines
- Paper Formatting Tips
- Sample Paper
- APA 7th Style Chart
- Abbreviations
- Bias Free Language
- Capitalization
- DOIs and URLs
Literature Review
- Paraphrasing
- Preferred Spelling
- Quotation Marks
- APA 7th Tutorials
- APA 7th for Business
- APA 7th for Nursing
- Journal Accounting Reporting Standards (JARS)
- Presentations
- Dissertation & Thesis Resources
- Research Methods & Analysis Resources
- Statistics & Analysis Resources
- Publishing Resources
- CRAAP Criteria and Video
- Peer Review
- Zotero Reference Manager
- Literature Review via APA Style.org
"a narrative summary and evaluation of the findings or theories within a literature base. Also known as 'narrative literature review'. "
- Key takeaways from the Psi Chi webinar So You Need to Write a Literature Review via APA Style.org
Examples of Literature Reviews
- Financial socialization: A decade in review (2021)
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the development of anxiety disorders - a literature review (2021)
- << Previous: Italics
- Next: Paraphrasing >>
- Last Updated: Aug 19, 2024 2:23 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ggc.edu/apastyle_7th

Citation Styles
- Chicago Style
- Annotated Bibliographies
What is a Lit Review?
How to write a lit review.
- Video Introduction to Lit Reviews
Main Objectives
Examples of lit reviews, additional resources.
- Zotero (Citation Management)
What is a literature review?
- Either a complete piece of writing unto itself or a section of a larger piece of writing like a book or article
- A thorough and critical look at the information and perspectives that other experts and scholars have written about a specific topic
- A way to give historical perspective on an issue and show how other researchers have addressed a problem
- An analysis of sources based on your own perspective on the topic
- Based on the most pertinent and significant research conducted in the field, both new and old

- A descriptive list or collection of summaries of other research without synthesis or analysis
- An annotated bibliography
- A literary review (a brief, critical discussion about the merits and weaknesses of a literary work such as a play, novel or a book of poems)
- Exhaustive; the objective is not to list as many relevant books, articles, reports as possible
- To convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic
- To explain what the strengths and weaknesses of that knowledge and those ideas might be
- To learn how others have defined and measured key concepts
- To keep the writer/reader up to date with current developments and historical trends in a particular field or discipline
- To establish context for the argument explored in the rest of a paper
- To provide evidence that may be used to support your own findings
- To demonstrate your understanding and your ability to critically evaluate research in the field
- To suggest previously unused or underused methodologies, designs, and quantitative and qualitative strategies
- To identify gaps in previous studies and flawed methodologies and/or theoretical approaches in order to avoid replication of mistakes
- To help the researcher avoid repetition of earlier research
- To suggest unexplored populations
- To determine whether past studies agree or disagree and identify strengths and weaknesses on both sides of a controversy in the literature

- Choose a topic that is interesting to you; this makes the research and writing process more enjoyable and rewarding.
- For a literature review, you'll also want to make sure that the topic you choose is one that other researchers have explored before so that you'll be able to find plenty of relevant sources to review.

- Your research doesn't need to be exhaustive. Pay careful attention to bibliographies. Focus on the most frequently cited literature about your topic and literature from the best known scholars in your field. Ask yourself: "Does this source make a significant contribution to the understanding of my topic?"
- Reading other literature reviews from your field may help you get ideas for themes to look for in your research. You can usually find some of these through the library databases by adding literature review as a keyword in your search.
- Start with the most recent publications and work backwards. This way, you ensure you have the most current information, and it becomes easier to identify the most seminal earlier sources by reviewing the material that current researchers are citing.
The organization of your lit review should be determined based on what you'd like to highlight from your research. Here are a few suggestions:
- Chronology : Discuss literature in chronological order of its writing/publication to demonstrate a change in trends over time or to detail a history of controversy in the field or of developments in the understanding of your topic.
- Theme: Group your sources by subject or theme to show the variety of angles from which your topic has been studied. This works well if, for example, your goal is to identify an angle or subtopic that has so far been overlooked by researchers.
- Methodology: Grouping your sources by methodology (for example, dividing the literature into qualitative vs. quantitative studies or grouping sources according to the populations studied) is useful for illustrating an overlooked population, an unused or underused methodology, or a flawed experimental technique.

- Be selective. Highlight only the most important and relevant points from a source in your review.
- Use quotes sparingly. Short quotes can help to emphasize a point, but thorough analysis of language from each source is generally unnecessary in a literature review.
- Synthesize your sources. Your goal is not to make a list of summaries of each source but to show how the sources relate to one another and to your own work.
- Make sure that your own voice and perspective remains front and center. Don't rely too heavily on summary or paraphrasing. For each source, draw a conclusion about how it relates to your own work or to the other literature on your topic.
- Be objective. When you identify a disagreement in the literature, be sure to represent both sides. Don't exclude a source simply on the basis that it does not support your own research hypothesis.
- At the end of your lit review, make suggestions for future research. What subjects, populations, methodologies, or theoretical lenses warrant further exploration? What common flaws or biases did you identify that could be corrected in future studies?

- Double check that you've correctly cited each of the sources you've used in the citation style requested by your professor (APA, MLA, etc.) and that your lit review is formatted according to the guidelines for that style.
Your literature review should:
- Be focused on and organized around your topic.
- Synthesize your research into a summary of what is and is not known about your topic.
- Identify any gaps or areas of controversy in the literature related to your topic.
- Suggest questions that require further research.
- Have your voice and perspective at the forefront rather than merely summarizing others' work.
- Cyberbullying: How Physical Intimidation Influences the Way People are Bullied
- Use of Propofol and Emergence Agitation in Children
- Eternity and Immortality in Spinoza's 'Ethics'
- Literature Review Tutorials and Samples - Wilson Library at University of La Verne
- Literature Reviews: Introduction - University Library at Georgia State
- Literature Reviews - The Writing Center at UNC Chapel Hill
- Writing a Literature Review - Boston College Libraries
- Write a Literature Review - University Library at UC Santa Cruz
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Zotero (Citation Management) >>
- Last Updated: Aug 28, 2024 12:27 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.elac.edu/Citation
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

Literature Review: A Self-Guided Tutorial for NUR 288
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Peer-Review
- Reading the Literature
- Developing Research Questions
- 2. Review discipline styles
- Super Searching
- Finding the Full Text
- Citation Searching
- Evaluating online information
- When to stop searching
- How to cite your sources following APA
- In-Text Citations
- Keeping track of your references
- Annotating Articles Tip
- 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- How to review the literature
- Using a synthesis matrix
- 7. Write literature review
APA Overview
For a quick overview of how to cite your sources following APA Style, watch the video APA Style.
Watch the APA 7th Edition Overview 00:03:02
Source: American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
- Owl Excelsior Lab
APA Citation Style Overview
Start by Downloading the APA 7th Edition Reference Quick Guide to help you visualize how you cite your references.
The Quick Guide is missing on how to cite a webpage. A webpage will never be the home page of the URL. It is part of a greater whole that is the website. When the author and site name are the same, omit the site name from the source element. Provide the most specific date possible. Include a retrieval date only when the content is designed to change over time and the page is not archived.
Author, A. A. (Year, Month Day). Title of page or section. Site Name. URL
National Nurses United. (n.d.). National Nurses United response to COVID-19. https://www.nationalnursesunited.org/covid-19
The Quick Guide is missing how to cite Web supplemental materials.
- Report: Corporate/government, group author, retrieved on online:
- If a report, series, or issue number is given, provide this in parentheses after the title. Describe less common forms of reports in square brackets after the title like the example below. If the report number is available, and the report needs a special description, place the parentheses before the brackets in the reference entry.
Name of Group. (Year, Month Day). Title of report (Report number, if available) [Description, if needed]. Publisher Name (omit if the same name as group author). DOI or URL
National Institute of Health. (2019, May). Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd/index.shtml
- APA 7th ed. Reference Guide APA guide
- APA Documentation Style 7th edtion WCC Writing Center 2023
- << Previous: 4. Manage your references
- Next: In-Text Citations >>
- Last Updated: Aug 24, 2024 2:45 PM
- URL: https://libguides.wccnet.edu/literature_review
Boatwright Memorial Library
- Chicago/Turabian
- AP (Associated Press)
- APSA (Political Science)
- ASA & AAA (Soc/Ant)
- ACS (Chemistry)
- Harvard Style
- SBL (Society of Biblical Literature)
- EndNote Web
- Help Resources
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Literature Reviews
- Citation exercises This link opens in a new window
What is a Literature Review?
The literature review is a written explanation by you, the author, of the research already done on the topic, question or issue at hand. What do we know (or not know) about this issue/topic/question?
- A literature review provides a thorough background of the topic by giving your reader a guided overview of major findings and current gaps in what is known so far about the topic.
- The literature review is not a list (like an annotated bibliography) -- it is a narrative helping your reader understand the topic and where you will "stand" in the debate between scholars regarding the interpretation of meaning and understanding why things happen. Your literature review helps your reader start to see the "camps" or "sides" within a debate, plus who studies the topic and their arguments.
- A good literature review should help the reader sense how you will answer your research question and should highlight the preceding arguments and evidence you think are most helpful in moving the topic forward.
- The purpose of the literature review is to dive into the existing debates on the topic to learn about the various schools of thought and arguments, using your research question as an anchor. If you find something that doesn't help answer your question, you don't have to read (or include) it. That's the power of the question format: it helps you filter what to read and include in your literature review, and what to ignore.
How Do I Start?
Essentially you will need to:
- Identify and evaluate relevant literature (books, journal articles, etc.) on your topic/question.
- Figure out how to classify what you've gathered. You could do this by schools of thought, different answers to a question, the authors' disciplinary approaches, the research methods used, or many other ways.
- Use those groupings to craft a narrative, or story, about the relevant literature on this topic.
- Remember to cite your sources properly!
- Research: Getting Started Visit this guide to learn more about finding and evaluating resources.
- Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources (IUPUI Writing Center) An in-depth guide on organizing and synthesizing what you've read into a literature review.
- Guide to Using a Synthesis Matrix (NCSU Writing and Speaking Tutorial Service) Overview of using a tool called a Synthesis Matrix to organize your literature review.
- Synthesis Matrix Template (VCU Libraries) A word document from VCU Libraries that will help you create your own Synthesis Matrix.
Literature Reviews: Overview
This video from NCSU Libraries gives a helpful overview of literature reviews. Even though it says it's "for graduate students," the principles are the same for undergraduate students too!
Literature Review Examples
Reading a Scholarly Article
- Reading a Scholarly Article or Literature Review Highlights sections of a scholarly article to identify structure of a literature review.
- Anatomy of a Scholarly Article (NCSU Libraries) Interactive tutorial that describes parts of a scholarly article typical of a Sciences or Social Sciences research article.
- Evaluating Information | Reading a Scholarly Article (Brown University Library) Provides examples and tips across disciplines for reading academic articles.
- Reading Academic Articles for Research [LIBRE Project] Gabriel Winer & Elizabeth Wadell (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative (OERI))
Additional Tutorials and Resources
- UR Writer's Web: Using Sources Guidance from the UR Writing Center on how to effectively use sources in your writing (which is what you're doing in your literature review!).
- Write a Literature Review (VCU Libraries) "Lit Reviews 101" with links to helpful tools and resources, including powerpoint slides from a literature review workshop.
- Literature Reviews (UNC Writing Center) Overview of the literature review process, including examples of different ways to organize a lit review.
- “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review.” Pautasso, Marco. “Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review.” PLOS Computational Biology, vol. 9, no. 7, July 2013, p. e1003149.
- Writing the Literature Review Part I (University of Maryland University College) Video that explains more about what a literature review is and is not. Run time: 5:21.
- Writing the Literature Review Part II (University of Maryland University College) Video about organizing your sources and the writing process. Run time: 7:40.
- Writing a Literature Review (OWL @ Purdue)
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliographies
- Next: Citation exercises >>
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Credit: Getty
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
WENTING ZHAO: Be focused and avoid jargon
Assistant professor of chemical and biomedical engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
When I was a research student, review writing improved my understanding of the history of my field. I also learnt about unmet challenges in the field that triggered ideas.
For example, while writing my first review 1 as a PhD student, I was frustrated by how poorly we understood how cells actively sense, interact with and adapt to nanoparticles used in drug delivery. This experience motivated me to study how the surface properties of nanoparticles can be modified to enhance biological sensing. When I transitioned to my postdoctoral research, this question led me to discover the role of cell-membrane curvature, which led to publications and my current research focus. I wouldn’t have started in this area without writing that review.

Collection: Careers toolkit
A common problem for students writing their first reviews is being overly ambitious. When I wrote mine, I imagined producing a comprehensive summary of every single type of nanomaterial used in biological applications. It ended up becoming a colossal piece of work, with too many papers discussed and without a clear way to categorize them. We published the work in the end, but decided to limit the discussion strictly to nanoparticles for biological sensing, rather than covering how different nanomaterials are used in biology.
My advice to students is to accept that a review is unlike a textbook: it should offer a more focused discussion, and it’s OK to skip some topics so that you do not distract your readers. Students should also consider editorial deadlines, especially for invited reviews: make sure that the review’s scope is not so extensive that it delays the writing.
A good review should also avoid jargon and explain the basic concepts for someone who is new to the field. Although I trained as an engineer, I’m interested in biology, and my research is about developing nanomaterials to manipulate proteins at the cell membrane and how this can affect ageing and cancer. As an ‘outsider’, the reviews that I find most useful for these biological topics are those that speak to me in accessible scientific language.

Bozhi Tian likes to get a variety of perspectives into a review. Credit: Aleksander Prominski
BOZHI TIAN: Have a process and develop your style
Associate professor of chemistry, University of Chicago, Illinois.
In my lab, we start by asking: what is the purpose of this review? My reasons for writing one can include the chance to contribute insights to the scientific community and identify opportunities for my research. I also see review writing as a way to train early-career researchers in soft skills such as project management and leadership. This is especially true for lead authors, because they will learn to work with their co-authors to integrate the various sections into a piece with smooth transitions and no overlaps.
After we have identified the need and purpose of a review article, I will form a team from the researchers in my lab. I try to include students with different areas of expertise, because it is useful to get a variety of perspectives. For example, in the review ‘An atlas of nano-enabled neural interfaces’ 2 , we had authors with backgrounds in biophysics, neuroengineering, neurobiology and materials sciences focusing on different sections of the review.
After this, I will discuss an outline with my team. We go through multiple iterations to make sure that we have scanned the literature sufficiently and do not repeat discussions that have appeared in other reviews. It is also important that the outline is not decided by me alone: students often have fresh ideas that they can bring to the table. Once this is done, we proceed with the writing.
I often remind my students to imagine themselves as ‘artists of science’ and encourage them to develop how they write and present information. Adding more words isn’t always the best way: for example, I enjoy using tables to summarize research progress and suggest future research trajectories. I’ve also considered including short videos in our review papers to highlight key aspects of the work. I think this can increase readership and accessibility because these videos can be easily shared on social-media platforms.
ANKITA ANIRBAN: Timeliness and figures make a huge difference
Editor, Nature Reviews Physics .
One of my roles as a journal editor is to evaluate proposals for reviews. The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic.
It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the most interesting reviews instead provide a discussion about disagreements in the field.

Careers Collection: Publishing
Scientists often centre the story of their primary research papers around their figures — but when it comes to reviews, figures often take a secondary role. In my opinion, review figures are more important than most people think. One of my favourite review-style articles 3 presents a plot bringing together data from multiple research papers (many of which directly contradict each other). This is then used to identify broad trends and suggest underlying mechanisms that could explain all of the different conclusions.
An important role of a review article is to introduce researchers to a field. For this, schematic figures can be useful to illustrate the science being discussed, in much the same way as the first slide of a talk should. That is why, at Nature Reviews, we have in-house illustrators to assist authors. However, simplicity is key, and even without support from professional illustrators, researchers can still make use of many free drawing tools to enhance the value of their review figures.

Yoojin Choi recommends that researchers be open to critiques when writing reviews. Credit: Yoojin Choi
YOOJIN CHOI: Stay updated and be open to suggestions
Research assistant professor, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Daejeon.
I started writing the review ‘Biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells and bacteriophages’ 4 as a PhD student in 2018. It took me one year to write the first draft because I was working on the review alongside my PhD research and mostly on my own, with support from my adviser. It took a further year to complete the processes of peer review, revision and publication. During this time, many new papers and even competing reviews were published. To provide the most up-to-date and original review, I had to stay abreast of the literature. In my case, I made use of Google Scholar, which I set to send me daily updates of relevant literature based on key words.
Through my review-writing process, I also learnt to be more open to critiques to enhance the value and increase the readership of my work. Initially, my review was focused only on using microbial cells such as bacteria to produce nanomaterials, which was the subject of my PhD research. Bacteria such as these are known as biofactories: that is, organisms that produce biological material which can be modified to produce useful materials, such as magnetic nanoparticles for drug-delivery purposes.
Synchronized editing: the future of collaborative writing
However, when the first peer-review report came back, all three reviewers suggested expanding the review to cover another type of biofactory: bacteriophages. These are essentially viruses that infect bacteria, and they can also produce nanomaterials.
The feedback eventually led me to include a discussion of the differences between the various biofactories (bacteriophages, bacteria, fungi and microalgae) and their advantages and disadvantages. This turned out to be a great addition because it made the review more comprehensive.
Writing the review also led me to an idea about using nanomaterial-modified microorganisms to produce chemicals, which I’m still researching now.
PAULA MARTIN-GONZALEZ: Make good use of technology
PhD student, University of Cambridge, UK.
Just before the coronavirus lockdown, my PhD adviser and I decided to write a literature review discussing the integration of medical imaging with genomics to improve ovarian cancer management.
As I was researching the review, I noticed a trend in which some papers were consistently being cited by many other papers in the field. It was clear to me that those papers must be important, but as a new member of the field of integrated cancer biology, it was difficult to immediately find and read all of these ‘seminal papers’.
That was when I decided to code a small application to make my literature research more efficient. Using my code, users can enter a query, such as ‘ovarian cancer, computer tomography, radiomics’, and the application searches for all relevant literature archived in databases such as PubMed that feature these key words.
The code then identifies the relevant papers and creates a citation graph of all the references cited in the results of the search. The software highlights papers that have many citation relationships with other papers in the search, and could therefore be called seminal papers.
My code has substantially improved how I organize papers and has informed me of key publications and discoveries in my research field: something that would have taken more time and experience in the field otherwise. After I shared my code on GitHub, I received feedback that it can be daunting for researchers who are not used to coding. Consequently, I am hoping to build a more user-friendly interface in a form of a web page, akin to PubMed or Google Scholar, where users can simply input their queries to generate citation graphs.
Tools and techniques
Most reference managers on the market offer similar capabilities when it comes to providing a Microsoft Word plug-in and producing different citation styles. But depending on your working preferences, some might be more suitable than others.
Reference managers
Attribute | EndNote | Mendeley | Zotero | Paperpile |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Cost | A one-time cost of around US$340 but comes with discounts for academics; around $150 for students | Free version available | Free version available | Low and comes with academic discounts |
Level of user support | Extensive user tutorials available; dedicated help desk | Extensive user tutorials available; global network of 5,000 volunteers to advise users | Forum discussions to troubleshoot | Forum discussions to troubleshoot |
Desktop version available for offline use? | Available | Available | Available | Unavailable |
Document storage on cloud | Up to 2 GB (free version) | Up to 2 GB (free version) | Up to 300 MB (free version) | Storage linked to Google Drive |
Compatible with Google Docs? | No | No | Yes | Yes |
Supports collaborative working? | No group working | References can be shared or edited by a maximum of three other users (or more in the paid-for version) | No limit on the number of users | No limit on the number of users |
Here is a comparison of the more popular collaborative writing tools, but there are other options, including Fidus Writer, Manuscript.io, Authorea and Stencila.
Collaborative writing tools
Attribute | Manubot | Overleaf | Google Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
Cost | Free, open source | $15–30 per month, comes with academic discounts | Free, comes with a Google account |
Writing language | Type and write in Markdown* | Type and format in LaTex* | Standard word processor |
Can be used with a mobile device? | No | No | Yes |
References | Bibliographies are built using DOIs, circumventing reference managers | Citation styles can be imported from reference managers | Possible but requires additional referencing tools in a plug-in, such as Paperpile |
*Markdown and LaTex are code-based formatting languages favoured by physicists, mathematicians and computer scientists who code on a regular basis, and less popular in other disciplines such as biology and chemistry.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Tales of a migratory marine biologist
Career Feature 28 AUG 24

Nail your tech-industry interviews with these six techniques
Career Column 28 AUG 24

How to harness AI’s potential in research — responsibly and ethically
Career Feature 23 AUG 24
Binning out-of-date chemicals? Somebody think about the carbon!
Correspondence 27 AUG 24

No more hunting for replication studies: crowdsourced database makes them easy to find
Nature Index 27 AUG 24

Partners in drug discovery: how to collaborate with non-governmental organizations

Exclusive: the papers that most heavily cite retracted studies
News 28 AUG 24

Chain retraction: how to stop bad science propagating through the literature
Comment 28 AUG 24
Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Researcher/Associate Researcher
Xiaoliang Sunney XIE’s Group is recruiting researchers specializing in Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Beijing, China
Changping Laboratory
Supervisory Bioinformatics Specialist CTG Program Head
The National Library of Medicine (NLM) is a global leader in biomedical informatics and computational health data science and the world’s largest b...
Bethesda, Maryland (US)
National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information
Post Doctoral Research Scientist
Post-Doctoral Research Scientist Position in Human Transplant Immunology at the Columbia Center for Translational Immunology in New York, NY
New York City, New York (US)
Columbia Center for Translational Immunoogy
Postdoctoral Associate- Neuromodulation and Computational Psychiatry
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Postdoctoral Fellow
Modeling Autism Spectrum Disorders using genetically modified human stem cell-derived brain organoids and mouse models.
Weill Cornell Medical College
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Perspect Med Educ
- v.7(2); 2018 Apr

Writing an effective literature review
Lorelei lingard.
Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, Health Sciences Addition, Western University, London, Ontario Canada
In the Writer’s Craft section we offer simple tips to improve your writing in one of three areas: Energy, Clarity and Persuasiveness. Each entry focuses on a key writing feature or strategy, illustrates how it commonly goes wrong, teaches the grammatical underpinnings necessary to understand it and offers suggestions to wield it effectively. We encourage readers to share comments on or suggestions for this section on Twitter, using the hashtag: #how’syourwriting?
This Writer’s Craft instalment is the second in a two-part series that offers strategies for effectively presenting the literature review section of a research manuscript. This piece argues that citation is not just a technical practice but also a rhetorical one, and offers writers an expanded vocabulary for using citation to maximal effect.
Many writers think of citation as the formal system we use to avoid plagiarism and acknowledge others’ work. But citation is a much more nuanced practice than this. Not only does citation allow us to represent the source of knowledge, but it also allows us to position ourselves in relation to that knowledge, and to place that knowledge in relation to other knowledge . In short, citation is how we artfully tell the story of what the field knows, how it came to that knowledge, and where we stand in relation to it as we write the literature review section to frame our own work. Seen this way, citation is a sophisticated task, requiring in-depth knowledge of the literature in a domain.
Citation is more than just referencing; it is how we represent the social construction of knowledge in a field. A citation strategy is any indication in the text about the source and nature of knowledge. Consider the following passage, in which all citation strategies are italicized:
Despite years of effort to teach and enforce positive professional norms and standards, many reports of challenges to medical professionalism continue to appear, both in the medical and education literature and, often in reaction, in the lay press . 1,2,3,4,5 Examples of professional lapses dot the health care landscape: regulations are thwarted, records are falsified, patients are ignored, colleagues are berated. 2,4,6 The medical profession has articulated its sense of what professionalism is in a number of important position statements . 7,8 These statements tend to be built upon abstracted principles and values, such as the taxonomy presented in the American Board of Internal Medicine’s (ABIM’s) Project Professionalism : altruism, accountability, excellence, duty, honour, integrity, and respect for others. 7 (From Ginsburg et al., The anatomy of a professional lapse [ 1 ])
In this passage, citation as referencing (in the form of Vancouver format superscript numbers) is used to acknowledge the source of knowledge. There are more than just references in this passage, however. Citation strategies also include statements that characterize the density of that knowledge (‘many reports’), its temporal patterns (‘continue to appear’), its diverse origins (‘both in the medical and education literature’), its social nature (‘often in reaction’), and its social import (‘important position statements’). Citation does more than just acknowledge the source of something you’ve read. It is how you represent the social nature of knowledge as coming from somewhere, being debated and developed, and having impact on the world [ 2 ]. If we remove all these citation strategies, the passage sounds at best like common sense or, at worst, like unsubstantiated personal opinion:
Despite years of effort to teach and enforce positive professional norms and standards, challenges to medical professionalism continue. Examples of professional lapses dot the health care landscape: regulations are thwarted, records are falsified, patients are ignored, colleagues are berated. Professionalism is a set of principles and values: altruism, accountability, excellence, duty, honour, integrity, and respect for others.
But perhaps you’ve been told that your literature review should be ‘objective’—that you should simply present what is known without taking a stance on it. This is largely untrue, for two reasons. The first involves the distinction between summary and critical summary. A summary is a neutral description of material, but a good literature review contains very little pure summary because, as we review, we must also judge the quality, source and reliability of the knowledge claims we are presenting [ 3 ]. To do this, we engage in critical summary, not only summarizing existing knowledge but offering a stance on it.
The second reason is that, even when we’re aiming for simple summary, a completely neutral presentation of knowledge claims is very difficult to achieve. We take a stance in ways we hardly even notice. Consider how the verb in each of these statements adds a flavour of stance to what is otherwise a summary of a knowledge claim in the field:
Anderson describes how the assessment is overly time-consuming for use in the Emergency Department. Anderson discovered that the assessment was overly time-consuming for use in the Emergency Department. Anderson claims that the assessment is overly time-consuming for use in the Emergency Department.
The first verb, ‘describes’, is neutral: it is not possible to ascertain the writer’s stance on the knowledge Anderson has contributed to the field. The second verb, ‘discovered’, expresses an affiliation or positive stance in the writer, while the third verb, ‘claims’, distances the writer from Anderson’s work. Even these brief summary sentences contain a flavour of critical summary. This is not a flaw; in fact, it is an important method of portraying existing knowledge as a conversation in which the writer is positioning herself and her work. But it should be done consciously and strategically. Tab. 1 offers examples to help writers think about how the verbs in their literature review position them in relation to existing knowledge in the field. Meaning is subject to context and these examples should only be taken as a guide: e. g., ‘suggests’ can be used to signal neutrality or distancing.
Verbs to position the writer in relation to the literature being reviewed
| Neutral about the knowledge | Affiliating with the knowledge | Distancing from the knowledge | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| comments explains indicates notes describes | observes remarks states finds | discovers reveals realizes understands | addresses argues recognizes identifies | assumes claims contends argues | hopes believes |
Most of us have favourite verbs that we default to almost unconsciously when we are writing—reports, argues, describes, studies, explains, asserts—but these verbs are not interchangeable. They each inscribe a slightly different stance towards the knowledge—not only the writer’s stance, but also the stance of the researcher who created the knowledge. It is critical to get the original stance right in your critical summary. Nothing irritates me more than seeing my stance mispresented in someone else’s literature review. For example, if I wrote a paragraph offering tentative reflections on a new idea, I don’t want to see that summarized in someone’s literature review as ‘Lingard argues’, when more accurate would be ‘Lingard suggests’ or ‘Lingard explored’.
Writers need to extend their library of citation verbs to allow themselves to accurately and persuasively position knowledge claims published by authors in their field. You can find many online resources to help extend your vocabulary: Tab. 2 , adapted from one such online source [ 4 ], provides some suggestions. Tables like these should be thought of as tools, not rules—keep in mind that words have flexible meanings depending on context and purpose. This is why one word, such as suggest or conclude , can appear in more than one list.
Verbs to represent the nature and strength of an author’s contributions to the literature
| Verbs to report what an author DID | Verbs to report what an author SAID | Verbs to report an author’s OPINION | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| analyse, assess, , discover, describe, demonstrate, examine, explore, establish, find, identify, inquire, prove, observe, study, show | Weaker | Stronger | Weaker | Stronger |
| comment, describe, note, remark, add, offer, | affirm, emphasize, stress, maintain, stipulate, explain, , identify, insist | accept, believe, consider, think, , suspect, speculate | argue, assert, claim, contend, deny, recommend, reject, advocate, maintain | |
Knowledge is a social construction and it accumulates as researchers debate, extend and refine one another’s contributions. To avoid your literature review reading like a laundry list of disconnected ‘facts’, reporting verbs are an important resource. Tab. 3 offers a selection of verbs organized to reflect different relationships among authors in the field of knowledge being reviewed.
Verbs to express relations among authors in the field
| Depicting similar positions | Depicting contrasting positions | Depicting relating/responding positions |
|---|---|---|
| Taylor Jackson’s claim that … | Taylor Jackson’s claim that … | Taylor to Jackson’s claim that … |
| affirms, agrees, confirms, concurs, aligns, shares, echoes, supports, verifies, concedes, accepts | argues, disagrees, questions, dismisses, refuses, rejects, challenges contradicts, criticizes, opposes, counters, disputes | extends, elaborates, refines, builds on, reconsiders, draws upon, advances, repositions, addresses |
Finally, although we have focused on citation verbs in this article, adverbs (e. g., similarly, consequently) and prepositional phrases (e. g., by contrast, in addition) are also important for expressing similar, contrasting or responding relations among knowledge claims and their authors in the field being reviewed.
In summary, an effective literature review not only summarizes existing knowledge, it also critically presents that knowledge to depict an evolving conversation and understanding in a particular domain of study. As writers we need to know when we are summarizing and when we are critically summarizing—summary alone makes for a literature review that reads like a laundry list of undigested ‘facts-in-the-world’. Finally, writers need to attend to the subtle power of citation verbs to position themselves and the authors they are citing in relation to the knowledge being reviewed. Broadening our catalogue of ‘go-to’ verbs is an important step in enlivening and strengthening our writing.
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Mark Goldszmidt for his feedback on an early version of this manuscript.
PhD, is director of the Centre for Education Research & Innovation at Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, and professor for the Department of Medicine at Western University in London, Ontario, Canada.
New change to library operations
All Main Library and Weaver Library doors lock 15 minutes before closing.
Conduct a literature review
What is a literature review.
A literature review is a summary of the published work in a field of study. This can be a section of a larger paper or article, or can be the focus of an entire paper. Literature reviews show that you have examined the breadth of knowledge and can justify your thesis or research questions. They are also valuable tools for other researchers who need to find a summary of that field of knowledge.
Unlike an annotated bibliography, which is a list of sources with short descriptions, a literature review synthesizes sources into a summary that has a thesis or statement of purpose—stated or implied—at its core.
How do I write a literature review?
Step 1: define your research scope.
- What is the specific research question that your literature review helps to define?
- Are there a maximum or minimum number of sources that your review should include?
Ask us if you have questions about refining your topic, search methods, writing tips, or citation management.
Step 2: Identify the literature
Start by searching broadly. Literature for your review will typically be acquired through scholarly books, journal articles, and/or dissertations. Develop an understanding of what is out there, what terms are accurate and helpful, etc., and keep track of all of it with citation management tools . If you need help figuring out key terms and where to search, ask us .
Use citation searching to track how scholars interact with, and build upon, previous research:
- Mine the references cited section of each relevant source for additional key sources
- Use Google Scholar or Scopus to find other sources that have cited a particular work
Step 3: Critically analyze the literature
Key to your literature review is a critical analysis of the literature collected around your topic. The analysis will explore relationships, major themes, and any critical gaps in the research expressed in the work. Read and summarize each source with an eye toward analyzing authority, currency, coverage, methodology, and relationship to other works. The University of Toronto's Writing Center provides a comprehensive list of questions you can use to analyze your sources.
Step 4: Categorize your resources
Divide the available resources that pertain to your research into categories reflecting their roles in addressing your research question. Possible ways to categorize resources include organization by:
- methodology
- theoretical/philosophical approach
Regardless of the division, each category should be accompanied by thorough discussions and explanations of strengths and weaknesses, value to the overall survey, and comparisons with similar sources. You may have enough resources when:
- You've used multiple databases and other resources (web portals, repositories, etc.) to get a variety of perspectives on the research topic.
- The same citations are showing up in a variety of databases.
Additional resources
Undergraduate student resources.
- Literature Review Handout (University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill)
- Learn how to write a review of literature (University of Wisconsin-Madison)
Graduate student and faculty resources
- Information Research Strategies (University of Arizona)
- Literature Reviews: An Overview for Graduate Students (NC State University)
- Oliver, P. (2012). Succeeding with Your Literature Review: A Handbook for Students [ebook]
- Machi, L. A. & McEvoy, B. T. (2016). The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success [ebook]
- Graustein, J. S. (2012). How to Write an Exceptional Thesis or Dissertation: A Step-by-Step Guide from Proposal to Successful Defense [ebook]
- Thomas, R. M. & Brubaker, D. L. (2008). Theses and Dissertations: A Guide to Planning, Research, and Writing
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.

Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jun 20, 2024 9:08 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE: Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2024 11:05 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Researching and writing for Economics students
4 literature review and citations/references.

Figure 4.1: Literature reviews and references
Your may have done a literature survey as part of your proposal. This will be incorporated into your dissertation, not left as separate stand-alone. Most economics papers include a literature review section, which may be a separate section, or incorporated into the paper’s introduction. (See organising for a standard format.)
Some disambiguation:
A ‘Literature survey’ paper: Some academic papers are called ‘literature surveys’. These try to summarise and discuss the existing work that has been done on a particular topic, and can be very useful. See, for example, works in The Journal of Economic Perspectives, the Journal of Economic Literature, the “Handbook of [XXX] Economics”
Many student projects and undergraduate dissertations are mainly literature surveys.
4.1 What is the point of a literature survey?
Your literature review should explain:
what has been done already to address your topic and related questions, putting your work in perspective, and
what techniques others have used, what are their strengths and weaknesses, and how might they be relevant tools for your own analysis.

Figure 4.2: Take notes on this as you read, and write them up.
4.2 What previous work is relevant?
Focus on literature that is relevant to your topic only.
But do not focus only on articles about your exact topic ! For example, if your paper is about the relative price of cars in the UK, you might cite papers (i) about the global automobile market, (ii) about the theory and evidence on competition in markets with similar features and (iii) using econometric techniques such as “hedonic regression” to estimate “price premia” in other markets and in other countries.
Consider: If you were Colchester a doctor and wanted to know whether a medicine would be effective for your patients, would you only consider medical studies that ran tests on Colchester residents, or would you consider more general national and international investigations?
4.3 What are “good” economics journal articles?
You should aim to read and cite peer-reviewed articles in reputable economics journals. (Journals in other fields such as Finance, Marketing and Political Science may also be useful.) These papers have a certain credibility as they have been checked by several referees and one or more editors before being published. (In fact, the publication process in Economics is extremely lengthy and difficult.)
Which journals are “reputable”? Economists spend a lot of time thinking about how to rank and compare journals (there are so many papers written about this topic that they someone could start a “Journal of Ranking Economics Journals”. For example, “ REPEC ” has one ranking, and SCIMAGO/SCOPUS has another one. You may want to focus on journals ranked in the top 100 or top 200 of these rankings. If you find it very interesting and relevant paper published somewhere that is ranked below this, is okay to cite it, but you may want to be a bit more skeptical of its findings.
Any journal you find on JSTOR is respectable, and if you look in the back of your textbooks, there will be references to articles in journals, most of which are decent.
You may also find unpublished “working papers”; these may also be useful as references. However, it is more difficult to evaluate the credibility of these, as they have not been through a process of peer review. However, if the author has published well and has a good reputation, it might be more likely that these are worth reading and citing.
Unpublished “working papers”
You may also find unpublished “working papers” or ‘mimeos’; these may also be useful as references. In fact, the publication process in Economics is so slow (six years from first working paper to publication is not uncommon) that not consulting working papers often means not being current.
However, it is more difficult to evaluate the credibility of this ‘grey literature’, as they have not been through a process of peer review. However, if the author has published well and has a good reputation, it might be more likely that these are worth reading and citing. Some working paper series are vetted, such as NBER; in terms of credibility, these might be seen as something in between a working paper and a publication.
Which of the following are “peer-reviewed articles in reputable economics journals”? Which of the following may be appropriate to cite in your literature review and in your final project? 8
Klein, G, J. (2011) “Cartel Destabilization and Leniency Programs – Empirical Evidence.” ZEW - Centre for European Economic Research Discussion Paper No. 10-107
Spencer, B. and Brander, J.A. (1983) “International R&D Rivalry and Industrial Strategy”, Review of Economic Studies Vol. 50, 707-722
Troisi, Jordan D., Andrew N. Christopher, and Pam Marek. “Materialism and money spending disposition as predictors of economic and personality variables.” North American Journal of Psychology 8.3 (2006): 421.
The Economist,. ‘Good, Bad And Ugly’. Web. 11 Apr. 2015. [accessed on…]
Mecaj, Arjola, and María Isabel González Bravo. “CSR Actions and Financial Distress: Do Firms Change Their CSR Behavior When Signals of Financial Distress Are Identified?.” Modern Economy 2014 (2014).
Universities, U. K. “Creating Prosperity: the role of higher education in driving the UK’s creative economy.” London Universities UK (2010).
4.4 How to find and access articles
You should be able to find and access all the relevant articles online. Leafing through bound volumes and photocopying should not be neededs. (Having been a student in the late 90’s and 2000’s, I wish I could get those hours back.)

Figure 4.3: The old way!
Good online tools include Jstor (jstor.org) and Google Scholar (scholar.google.co.uk). Your university should have access to Jstor, and Google is accessible to all (although the linked articles may require special access). You will usually have the ‘most access’ when logged into your university or library computing system.If you cannot access a paper, you may want to consult a reference librarian.
It is also ok, if you cannot access the journal article itself, to use the last working paper version (on Google scholar find this in the tab that says “all X versions”, where X is some number, and look for a PDF). However, authors do not always put up the most polished versions, although they should do to promote open-access. As a very last resort, you can e-mail the author and ask him or her to send you the paper.
When looking for references, try to find ones published in respected refereed economics journals (see above ).
4.5 Good starting points: Survey article, course notes, and textbooks
A “survey article” is a good place to start; this is a paper that is largely a categorization and discussion of previous work on a particular topic. You can often find such papers in journals such as
- the Journal of Economic Perspectives,
- the Journal of Economic Surveys,
- and the Journal of Economic Literature.
These will be useful as a “catalog” of papers to read and considers citing. They are also typically very readable and offer a decent introduction to the issue or the field.
It is also helpful to consult module (course) notes and syllabi from the relevant field. Do not only limit yourself to the ones at your own university; many of universities make their course materials publicly accessible online. These will not only typically contain reading lists with well-respected and useful references, they may also contain slides and other material that will help you better understand your topic and the relevant issues.
However, be careful not to take material from course notes without properly citing it. (Better yet, try to find the original paper that the course notes are referring to.)
Textbooks serve as another extremely useful jumping off point. Look through your own textbooks and other textbooks in the right fields. Textbooks draw from, and cite a range of relevant articles and papers. (You may also want to go back to textbooks when you are finding the articles you are reading too difficult. Textbooks may present a simpler version of the material presented in an article, and explain the concepts better.)
4.6 Backwards and forwards with references
When you find a useful paper, look for its “family.” You may want to go back to earlier, more fundamental references, by looking at the articles that this paper cited. See what is listed as “keywords” (these are usually given at the top of the paper), and “JEL codes”. Check what papers this paper cites, and check what other papers cited this paper. On Google scholar you can follow this with a link “Cited by…” below the listed article. “Related articles” is also a useful link.
4.7 Citations
Keep track of all references and citations
You may find it helpful to use software to help you manage your citations
A storage “database” of citations (e.g., Jabref, Zotero, Endnote, Mendeley); these interface well with Google Scholar and Jstor
An automatic “insert citation” and “insert bibliography” in your word processing software
Use a tool like Endnote to manage and insert the bibliographies, or use a bibliography manager software such as Zotero or Jabref,
Further discussion: Citation management tools
List of works cited
Put your list of references in alphabetical order by author’s last name (surname).
Include all articles and works that you cite in your paper; do not include any that you don’t cite.
Avoiding plagiarism and academic offenses**
Here is a definition of plagiarism
The main point is that you need to cite everything that is not your own work. Furthermore, be clear to distinguish what is your own work and your own language and what is from somewhere/someone else.
Why cite? Not just to give credit to others but to make it clear that the remaining uncited content is your own.
Here are some basic rules:
(Rephrased from University of Essex material, as seen in Department of Economics, EC100 Economics for Business Handbook 2017-18, https://www1.essex.ac.uk/economics/documents/EC100-Booklet_2017.pdf accessed on 20 July 2019, pp. 15-16)
Do not submit anything that is not your own work.
Never copy from friends.
Do not copy your own work or previously submitted work. (Caveat: If you are submitting a draft or a ‘literature review and project plan’ at an earlier stage, this can be incorporated into your final submission.
Don’t copy text directly into your work, unless:
- you put all passages in quotation marks: beginning with ’ and ending with ’, or clearly offset from the main text
- you cite the source of this text.
It is not sufficient merely to add a citation for the source of copied material following the copied material (typically the end of a paragraph). You must include the copied material in quotation marks. … Ignorance … is no defence.’ (ibid, pp. 15 )
(‘Ibid’ means ‘same as the previous citation’.)
Your university may use sophisticated plagiarism-detection software. Markers may also report if the paper looks suspect
Before final submission, they may ask you to go over your draft and sign that you understand the contents and you have demonstrated that the work is your own.
Not being in touch with your supervisor may put you under suspicion.
Your university may give a Viva Voce oral exam if your work is under suspicion. It is a cool-sounding word but probably something you want to avoid.
Your university may store your work in its our database, and can pursue disciplinary action, even after you have graduated.
Penalties may be severe, including failure with no opportunity to retake the module (course). You may even risk your degree!
Comprehension questions; answers in footnotes
True or false: “If you do not directly quote a paper you do not need to cite it” 9
You should read and cite a paper (choose all that are correct)… 10
- If it motivates ‘why your question is interesting’ and how it can be modeled economically
- Only if it asks the same question as your paper
- Only if it is dealing with the same country/industry/etc as you are addressing
- If it has any connection to your topic, question, or related matters
- If it answers a similar question as your paper
- If it uses and discusses techniques that inform those you are using
4.8 How to write about previous authors’ analysis and findings
Use the right terminology.
“Johnson et al. (2000) provide an analytical framework that sheds substantial doubt on that belief. When trying to obtain a correlation between institutional efficiency and wealth per capita, they are left with largely inconclusive results.”
They are not trying to “obtain a correlation”; they are trying to measure the relationship and test hypotheses.
“Findings”: Critically examine sources
Don’t take everything that is in print (or written online) as gospel truth. Be skeptical and carefully evaluate the arguments and evidence presented. Try to really survey what has been written, to consider the range of opinions and the preponderance of the evidence. You also need to be careful to distinguish between “real research” and propaganda or press releases.
The returns to higher education in Atlantis are extremely high. For the majority of Atlanian students a university degree has increased their lifetime income by over 50%, as reported in the “Benefits of Higher Education” report put out by the Association of Atlantian Universities (2016).
But don’t be harsh without explanation:
Smith (2014) found a return to education in Atlantis exceeding 50%. This result is unlikely to be true because the study was not a very good one.
“Findings:” “They Proved”
A theoretical economic model can not really prove anything about the real world; they typically rely on strong simplifying assumptions.
Through their economic model, they prove that as long as elites have incentives to invest in de facto power, through lobbying or corruption for example, they will invest as much as possible in order to gain favourable conditions in the future for their businesses.
In their two period model, which assumes \[details of key assumptions here\] , they find that when an elite Agent has an incentive to invest in de facto power, he invests a strictly positive amount, up to the point where marginal benefit equals marginal cost”
Empirical work does not “prove” anything (nor does it claim to).
It relies on statistical inference under specific assumptions, and an intuitive sense that evidence from one situation is likely to apply to other situations.
“As Smith et al (1999) proved using data from the 1910-1920 Scandanavian stock exchange, equity prices always increase in response to reductions in corporate tax rates.”
“Smith et al (199) estimated a VAR regression for a dynamic CAP model using data from the 1910-1920 Scandanavian stock exchange. They found a strongly statistically significant negative coefficient on corporate tax rates. This suggests that such taxes may have a negative effect on publicly traded securities. However, as their data was from a limited period with several simultaneous changes in policy, and their results are not robust to \[something here\] , further evidence is needed on this question.”
Use the language of classical 11 statistics:
Hypothesis testing, statistical significance, robustness checks, magnitudes of effects, confidence intervals.
Note that generalisation outside the data depends on an intuitive sense that evidence from one situation is likely to apply to other situations.
“Findings”: How do you (or the cited paper) claim to identify a causal relationship?
This policy was explained by Smith and Johnson (2002) in their research on subsidies and redistribution in higher education. Their results showed that people with higher degree have higher salaries and so pay higher taxes. Thus subsidizing higher education leads to a large social gain.
The results the student discusses seem to show an association between higher degrees and higher salaries. The student seems to imply that the education itself led to higher salaries. This has not been shown by the cited paper. Perhaps people who were able to get into higher education would earn higher salaries anyway. There are ways economists used to try to identify a “causal effect” (by the way, this widely used term is redundant as all effects must have a cause), but a mere association between two variables is not enough
As inflation was systematically lower during periods of recession, we see that too low a level of inflation increases unemployment.
Economists have long debated the nature of this “Phillips curve” relationship. There is much work trying to determine whether the association (to the extent it exists) is a causal one. We could not rule out reverse causality, or third factor that might cause changes in both variables.
4.9 …Stating empirical results
Don’t write: “I accept the null hypothesis.”
Do write: “The results fail to reject the null hypothesis, in spite of a large sample size and an estimate with small standard errors” (if this is the case)
Note: The question of what to infer from acceptance/rejection of null hypotheses is a complex difficult one in Classical (as opposed to Bayesian) statistics. This difficulty is in part philosophical: classical hypothesis testing is deductive , while inference is necessarily inductive.
4.10 What to report
You need to read this paper more clearly; it is not clear what they conclude nor what their evidence is.
4.11 Organising your literature review
A common marking comment:
These papers seem to be discussed in random order – you need some structure organising these papers thematically, by finding, by technique, or chronologically perhaps.
How should you organise it? In what order?
Thematically (usually better)
By method, by theoretical framework, by results or assumptions, by field
Chronologically (perhaps within themes)
Exercise: Compare how the literature review section is organized in papers you are reading.

Figure 4.4: Organising a set of references
Q: What sort of structure am I using in the above outline?
It may also be helpful to make a ‘table’ of the relevant literature, as in the figure below. This will help you get a sense of the methods and results, and how the papers relate, and how to assess the evidence. You may end up putting this in the actual paper.

Figure 4.5: Organisational table from Reinstein and Riener, 2012b
4.12 What if you have trouble reading and understanding a paper?
Consult a survey paper, textbook, or lecture notes that discuss this paper and this topic
Try to find an easier related paper
Ask your supervisor for help; if he or she can
Try to understand what you can; do not try to “fake it”
4.13 Some literature survey do’s and don’ts
Do not cite irrelevant literature.
Do not merely list all the papers you could find.
Discuss them, and their relevance to your paper.
What are their strengths and weaknesses? What techniques do they use, and what assumptions do they rely on? How do they relate to each other?
Use correct citation formats.
Try to find original sources (don’t just cite a web link).
Don’t just cut and paste from other sources. And make sure to attribute every source and every quote. Be clear: which part of your paper is your own work and what is cited from others? The penalties for plagiarism can be severe!
- Critically examine the sources, arguments, and methods
4.14 Comprehension questions: literature review
How to discuss empirical results: “Causal” estimation, e.g., with Instrumental Variables
Which is the best way to state it? 12
“As I prove in table 2, more lawyers lead to slower growth (as demonstrated by the regression analysis evidence).”
“Table 2 provides evidence that a high share of lawyers in a city’s population leads to slower growth.”
3.“Table 2 shows that a high share of lawyers in a city’s population is correlated with slower growth.”
Which is better? 13
- “However, when a set of observable determinants of city growth (such as Census Region growth) are accounted for, the estimate of this effect becomes less precise.”
- “In the correct regression I control for all determinants of city growth and find that there is no effect of lawyers on growth”
Stating empirical results: descriptive
“Using the US data from 1850-1950, I find that inflation is lower during periods of recession. This is statistically significant in a t-test [or whatever test] at the 99% level, and the difference is economically meaningful. This is consistent with the theory of …, which predicts that lower inflation increases unemployment. However, other explanations are possible, including reverse causality, and unmeasured covarying lags and trends.”
“I find a significantly lower level of inflation during periods of recession, and the difference is economically meaningful. This relationship is statistically significant and the data is accurately measured. Thus I find that inflation increases unemployment.”
Some tips on writing a good paper– relevant to literature reviews
- Answer the question
- Provide clear structure and signposting
- Demonstrate an ability for critical analysis
- Refer to your sources
- Produce a coherent, clear argument
- Take time to proofread for style and expresssion
- Source “Assignment Writing Skills EBS 3rd year 2012”"
Answer: only b is a ‘peer reviewed article in a reputable economics journal’. All of these might be useful to cite, however. ↩
False. You need to cite any content and ideas that are not your own. ↩
Answers: 1, 5, and 6. Note that 2 and 3 are too narrow criteria, and 4 is too broad. ↩
or Bayesian if you like ↩
The second one; if this is really causal evidence. ↩
The first one. There is no ‘correct regression’. It is also not really correct in classical statistics to ‘find no effect’. ↩
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
How to Cite Sources | Citation Generator & Quick Guide
Citing your sources is essential in academic writing . Whenever you quote or paraphrase a source (such as a book, article, or webpage), you have to include a citation crediting the original author.
Failing to properly cite your sources counts as plagiarism , since you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
The most commonly used citation styles are APA and MLA. The free Scribbr Citation Generator is the quickest way to cite sources in these styles. Simply enter the URL, DOI, or title, and we’ll generate an accurate, correctly formatted citation.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you need to cite sources, which citation style should you use, in-text citations, reference lists and bibliographies.
Scribbr Citation Generator
Other useful citation tools
Citation examples and full guides, frequently asked questions about citing sources.
Citations are required in all types of academic texts. They are needed for several reasons:
- To avoid plagiarism by indicating when you’re taking information from another source
- To give proper credit to the author of that source
- To allow the reader to consult your sources for themselves
A citation is needed whenever you integrate a source into your writing. This usually means quoting or paraphrasing:
- To quote a source , copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks .
- To paraphrase a source , put the text into your own words. It’s important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don’t want to do this manually.
Citations are needed whether you quote or paraphrase, and whatever type of source you use. As well as citing scholarly sources like books and journal articles, don’t forget to include citations for any other sources you use for ideas, examples, or evidence. That includes websites, YouTube videos , and lectures .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Usually, your institution (or the journal you’re submitting to) will require you to follow a specific citation style, so check your guidelines or ask your instructor.
In some cases, you may have to choose a citation style for yourself. Make sure to pick one style and use it consistently:
- APA Style is widely used in the social sciences and beyond.
- MLA style is common in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography , common in the humanities
- Chicago author-date , used in the (social) sciences
- There are many other citation styles for different disciplines.
If in doubt, check with your instructor or read other papers from your field of study to see what style they follow.
In most styles, your citations consist of:
- Brief in-text citations at the relevant points in the text
- A reference list or bibliography containing full information on all the sources you’ve cited
In-text citations most commonly take the form of parenthetical citations featuring the last name of the source’s author and its year of publication (aka author-date citations).
An alternative to this type of in-text citation is the system used in numerical citation styles , where a number is inserted into the text, corresponding to an entry in a numbered reference list.
There are also note citation styles , where you place your citations in either footnotes or endnotes . Since they’re not embedded in the text itself, these citations can provide more detail and sometimes aren’t accompanied by a full reference list or bibliography.
| (London: John Murray, 1859), 510. |
A reference list (aka “Bibliography” or “Works Cited,” depending on the style) is where you provide full information on each of the sources you’ve cited in the text. It appears at the end of your paper, usually with a hanging indent applied to each entry.
The information included in reference entries is broadly similar, whatever citation style you’re using. For each source, you’ll typically include the:
- Author name
- Publication date
- Container (e.g., the book an essay was published in, the journal an article appeared in)
- Location (e.g., a URL or DOI , or sometimes a physical location)
The exact information included varies depending on the source type and the citation style. The order in which the information appears, and how you format it (e.g., capitalization, use of italics) also varies.
Most commonly, the entries in your reference list are alphabetized by author name. This allows the reader to easily find the relevant entry based on the author name in your in-text citation.
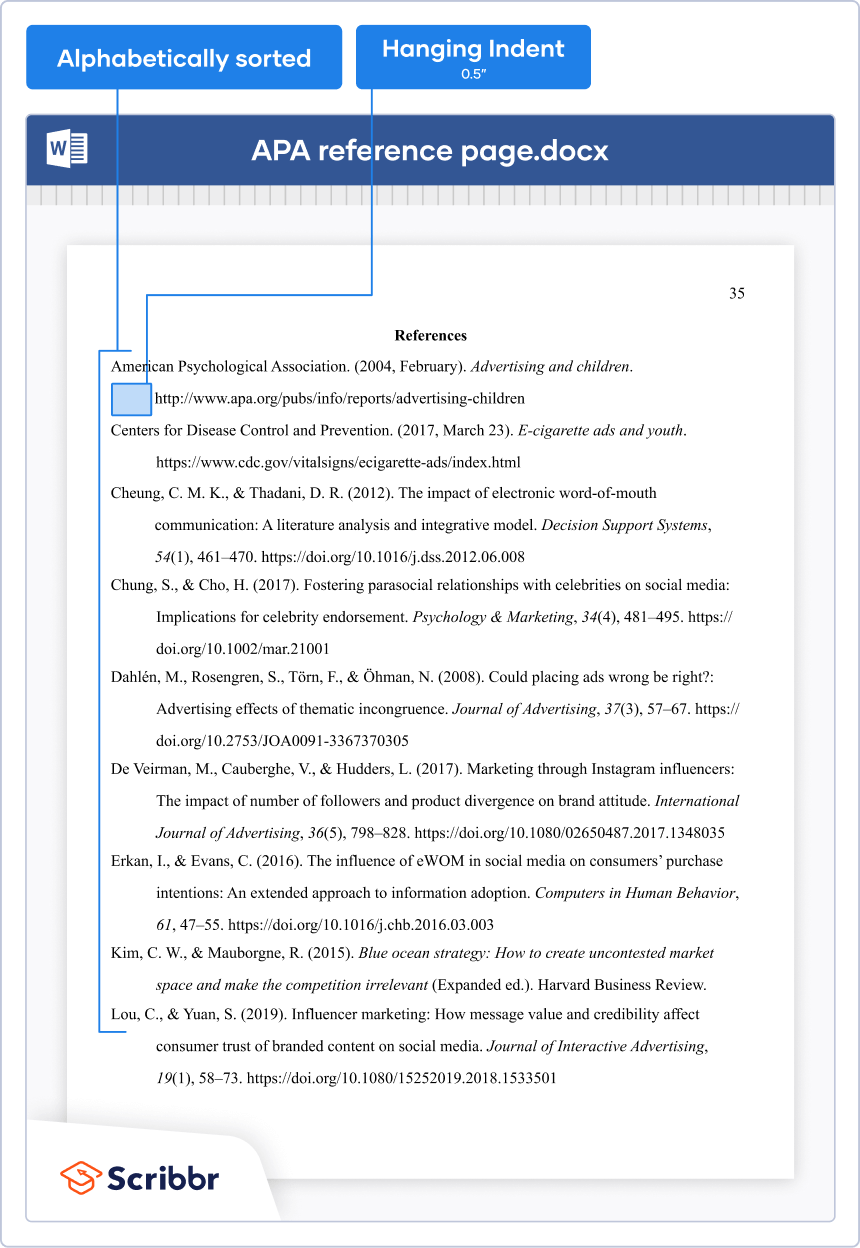
In numerical citation styles, the entries in your reference list are numbered, usually based on the order in which you cite them. The reader finds the right entry based on the number that appears in the text.
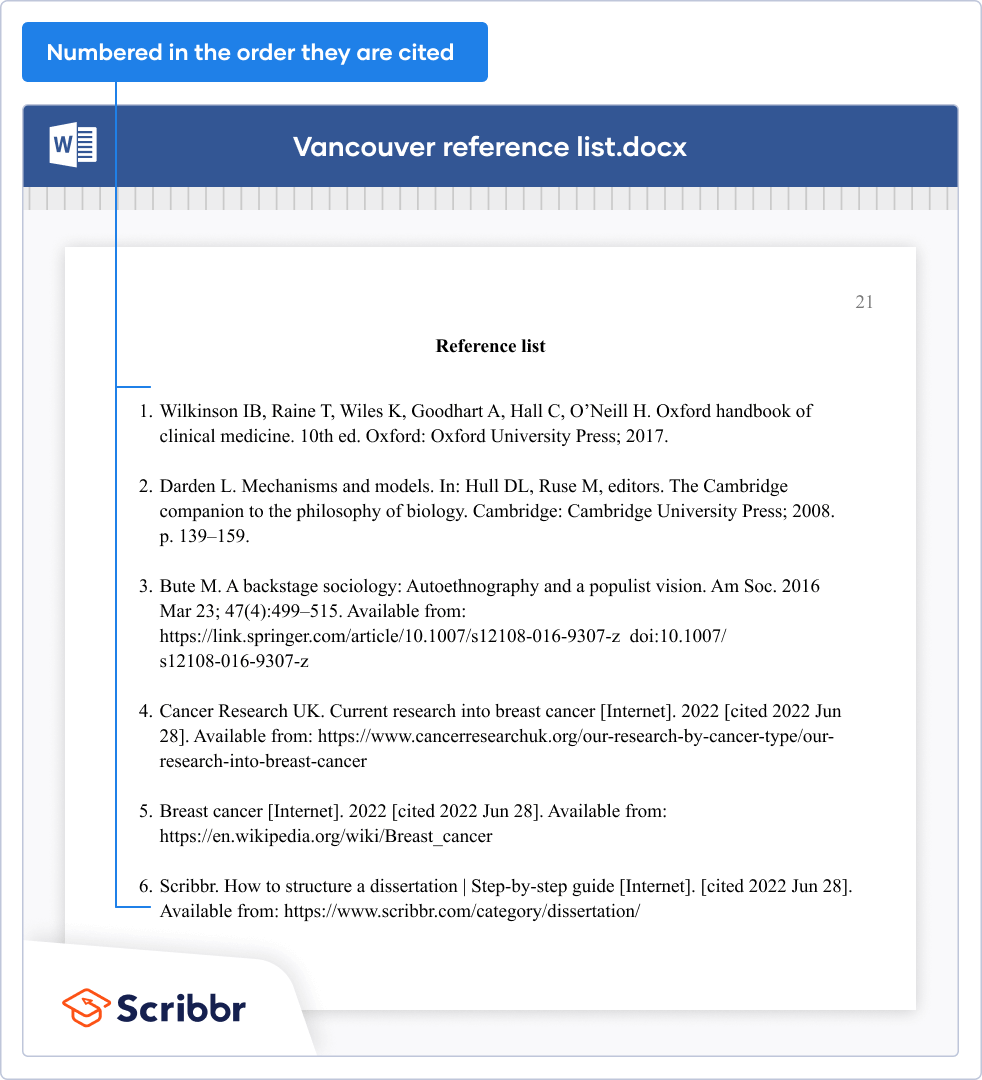
Because each style has many small differences regarding things like italicization, capitalization , and punctuation , it can be difficult to get every detail right. Using a citation generator can save you a lot of time and effort.
Scribbr offers citation generators for both APA and MLA style. Both are quick, easy to use, and 100% free, with no ads and no registration required.
Just input a URL or DOI or add the source details manually, and the generator will automatically produce an in-text citation and reference entry in the correct format. You can save your reference list as you go and download it when you’re done, and even add annotations for an annotated bibliography .
Once you’ve prepared your citations, you might still be unsure if they’re correct and if you’ve used them appropriately in your text. This is where Scribbr’s other citation tools and services may come in handy:
Plagiarism Checker
Citation Checker
Citation Editing
Plagiarism means passing off someone else’s words or ideas as your own. It’s a serious offense in academia. Universities use plagiarism checking software to scan your paper and identify any similarities to other texts.
When you’re dealing with a lot of sources, it’s easy to make mistakes that could constitute accidental plagiarism. For example, you might forget to add a citation after a quote, or paraphrase a source in a way that’s too close to the original text.
Using a plagiarism checker yourself before you submit your work can help you spot these mistakes before they get you in trouble. Based on the results, you can add any missing citations and rephrase your text where necessary.
Try out the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker for free, or check out our detailed comparison of the best plagiarism checkers available online.
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
Scribbr’s Citation Checker is a unique AI-powered tool that automatically detects stylistic errors and inconsistencies in your in-text citations. It also suggests a correction for every mistake.
Currently available for APA Style, this is the fastest and easiest way to make sure you’ve formatted your citations correctly. You can try out the tool for free below.
If you need extra help with your reference list, we also offer a more in-depth Citation Editing Service.
Our experts cross-check your in-text citations and reference entries, make sure you’ve included the correct information for each source, and improve the formatting of your reference page.
If you want to handle your citations yourself, Scribbr’s free Knowledge Base provides clear, accurate guidance on every aspect of citation. You can see citation examples for a variety of common source types below:
And you can check out our comprehensive guides to the most popular citation styles:
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles
- APA vs. MLA | The Key Differences in Format & Citation
- The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples
More interesting articles
- Citation examples for common sources types
- Et Al. | Meaning & Use in APA, MLA & Chicago
- Hanging Indent | Word & Google Docs Instructions
- How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Journal Article | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Lecture | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Newspaper Article | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Wikipedia Article | APA, MLA & Chicago
- How to Cite a YouTube Video | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite an Image | Photographs, Figures, Diagrams
- How to Cite an Interview | APA, MLA & Chicago Style
- Parenthetical Citation | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- What Are Endnotes? | Guide with Examples
- What Are Footnotes? | Guide with Word Instructions
- What Does Ibid. Mean? | Definition & Examples
- What is a DOI? | Finding and Using Digital Object Identifiers
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Literature Review
- Academic Integrity
- Using Sources and AI
- Academic Writing
- From Research to Writing
- GSD Writing Services
- Grants and Fellowships
- Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
- Theses and Dissertations
- Last Updated: Aug 20, 2024 4:05 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy

Literature Review: Citation Styles & Plagiarism
- Literature Review
- Purpose of a Literature Review
- Work in Progress
- Compiling & Writing
- Books, Articles, & Web Pages
- Types of Literature Reviews
- Departmental Differences
- Citation Styles & Plagiarism
- Know the Difference! Systematic Review vs. Literature Review
Citation Styles
What is a citation?
A citation is a reference to a source used in your research. It is how you give credit to the author for their creative and intellectual works that you referenced as support for your research. Generally, citations should include author’s name, date, publisher information, journal information and/or DOI (Digital Object Identifier).
What are citation styles?
Citation styles are the formal way that citation information is formatted. It dictates what information is included, how it is ordered as well as punctuation and other formatting. There are many different styles and each mandate order of appearance of information (such as publication date, title, and page numbers following the author name etc), conventions of punctuation, use of italics (and underlining for emphasis) that are particular to their style.
How do I choose a citation style?
There are many different ways of citing resources from your research. The citation style sometimes depends on the academic discipline involved and sometimes depends on the publisher/ place of publishing. For example:
- APA (American Psychological Association) is used by Education, Psychology, and some Sciences
- ACS (American Chemical Society) is often used in Chemistry and some of the physical sciences
- MLA (Modern Language Association) style is used by the Humanities
- Chicago & Turabian (two styles very similar in formatting) are generally used by Business, History, and the Fine Arts
REMEMBER : Ultimately your professor will decide which citation style will be used, remember to consult with your professor to determine what is required in your assignment.
- USC Upstate Citation Styles LibGuide
- Chicago / Turabian Style Guide USC Upstate
- USC Upstate LibGuide: MLA 8th Edition LibGuide
- USC Upstate LibGuide: APA 7th Ed. Style Guide
The Library has created a Plagiarism Prevention LibGuide that can help you to avoid accidental plagiarism mistakes. Remember you could be expelled or suspended if found guilty of plagiarism.
Many ways to Plagiarize
All of the following are considered plagiarism:
- Turning in someone’s work as your own.
- Failing to put a quotation in quotation marks.
- Copying words or ideas from someone else without giving credit.
- Giving incorrect information about the source of the quotation.
- Changing words but copying the sentence structure of a source without giving credit.
- Using a previous assignment or essay as a new assignment.
- 10 Most common types of Plagiarism
- Types of Plagiarism & Academic Cheating
- The Most Common and Serious Types of Research Plagiarism
- << Previous: Departmental Differences
- Next: Know the Difference! Systematic Review vs. Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 27, 2024 11:14 AM
- URL: https://uscupstate.libguides.com/Literature_Review
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 4. Manage Your References
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
Manage your references
Why do i have to cite my sources, citation styles, major citation styles - official and credible guidance.
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- 6. Synthesize
- 7. Write a Literature Review
Citation Management Tools
Citation managers help you collect, organize, cite, and share research. Click on the links below for guidance on using these tools.

Learning Opportunities
For help learning these tools, contact an expert listed on the tool's guide or sign up for one of our workshops:
- Sign up for UO Libraries workshops here!

As p art of your lit review, you'll need to provide a list of references -- your professors want to know where you found your information.
Your professor will also require that you use a specific format ("style") for citing your references, such as one of these:
- APA (American Psychological Association)
- Chicago Manual of Style
- MLA (Modern Language Association)
University Library provides an online guide to help you cite your sources correctly in multiple styles.
| Citations are important because: They help establish the credibility of your own research. They connect your work to the work of other scholars. It is one way that scholars enter into a dialogue with each other. It is a way to honor and acknowledge the work of others who have made your own research possible. |
Citation styles
In academic writing, there are many different formats for citing the sources you use in your research. Here are a few of the most common, and their related disciplines.
Accessibility note: Below is a chart with two columns for format and discipline.






COMMENTS
"a narrative summary and evaluation of the findings or theories within a literature base. Also known as 'narrative literature review'. Key takeaways from the Psi Chi webinar So You Need to Write a Literature Review via APA Style.org
Step 4: Write. Be selective. Highlight only the most important and relevant points from a source in your review. Use quotes sparingly. Short quotes can help to emphasize a point, but thorough analysis of language from each source is generally unnecessary in a literature review. Synthesize your sources.
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Start by Downloading the APA 7th Edition Reference Quick Guide to help you visualize how you cite your references.. The Quick Guide is missing on how to cite a webpage. A webpage will never be the home page of the URL. It is part of a greater whole that is the website.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply: be thorough, use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and. look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
A good literature review should help the reader sense how you will answer your research question and should highlight the preceding arguments and evidence you think are most helpful in moving the topic forward. The purpose of the literature review is to dive into the existing debates on the topic to learn about the various schools of thought ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
An APA style paper is organized in the author-date style. This means you cite the author's name and year of publication within the text with an in-text citation. You also include the page number, if appropriate. You then include the full information of that source in a reference list at the end of your paper.
Seen this way, citation is a sophisticated task, requiring in-depth knowledge of the literature in a domain. Citation is more than just referencing; it is how we represent the social construction of knowledge in a field. A citation strategy is any indication in the text about the source and nature of knowledge.
Step 2: Identify the literature. Start by searching broadly. Literature for your review will typically be acquired through scholarly books, journal articles, and/or dissertations. Develop an understanding of what is out there, what terms are accurate and helpful, etc., and keep track of all of it with citation management tools.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. ... Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help. Review the literature. Some questions to help you analyze the research:
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
Figure 4.1: Literature reviews and references. Your may have done a literature survey as part of your proposal. This will be incorporated into your dissertation, not left as separate stand-alone. Most economics papers include a literature review section, which may be a separate section, or incorporated into the paper's introduction.
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It's important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don't want to do this manually.
Write and Cite. This guide offers information on writing resources, citation style guides, and academic writing expectations and best practices, as well as information on resources related to copyright, fair use, permissions, and open access. This page is not currently available due to visibility settings. Last Updated: Aug 20, 2024 4:05 PM.
Citation styles are the formal way that citation information is formatted. It dictates what information is included, how it is ordered as well as punctuation and other formatting. There are many different styles and each mandate order of appearance of information (such as publication date, title, and page numbers following the author name etc ...
As p art of your lit review, you'll need to provide a list of references -- your professors want to know where you found your information. Your professor will also require that you use a specific format ("style") for citing your references, such as one of these:
A stable link is a web address that will consistently point to a specific information source such as an ebook, an article, a record in the catalog, a video, or a database. A stable link may also be called a permalink, document URL, persistent URL, or durable URL depending on the resource. You may also use a DOI (digital object identifier) found in many databases.
When to cite: You must cite the source for any information or ideas that are not your own. All quoted material must be correctly identified. What to cite: You must cite materials in any format - books, journals, newspapers, reports, theses/dissertations, video/audio recordings, conference proceedings, government documents, legal cases, web ...
Literature Cited Section. This is the last section of the paper. Here you should provide an alphabetical listing of all the published work you cited in the text of the paper. This does not mean every article you found in your research; only include the works you actually cited in the text of your paper. A standard format is used both to cite ...
Plagiarism is "the deliberate or reckless representation of another's words, thoughts, or ideas as one's own without attribution in connection with submission of academic work, whether graded or otherwise" (University of North Carolina 2009). The best way to avoid plagiarizing on your paper is to cite your sources using one of the many citations style used in academia.