Selecting a Research Topic: Overview
- Refine your topic
- Background information & facts
- Writing help
Here are some resources to refer to when selecting a topic and preparing to write a paper:
- MIT Writing and Communication Center "Providing free professional advice about all types of writing and speaking to all members of the MIT community."
- Search Our Collections Find books about writing. Search by subject for: english language grammar; report writing handbooks; technical writing handbooks
- Blue Book of Grammar and Punctuation Online version of the book that provides examples and tips on grammar, punctuation, capitalization, and other writing rules.
- Select a topic
Choosing an interesting research topic is your first challenge. Here are some tips:
- Choose a topic that you are interested in! The research process is more relevant if you care about your topic.
- If your topic is too broad, you will find too much information and not be able to focus.
- Background reading can help you choose and limit the scope of your topic.
- Review the guidelines on topic selection outlined in your assignment. Ask your professor or TA for suggestions.
- Refer to lecture notes and required texts to refresh your knowledge of the course and assignment.
- Talk about research ideas with a friend. S/he may be able to help focus your topic by discussing issues that didn't occur to you at first.
- WHY did you choose the topic? What interests you about it? Do you have an opinion about the issues involved?
- WHO are the information providers on this topic? Who might publish information about it? Who is affected by the topic? Do you know of organizations or institutions affiliated with the topic?
- WHAT are the major questions for this topic? Is there a debate about the topic? Are there a range of issues and viewpoints to consider?
- WHERE is your topic important: at the local, national or international level? Are there specific places affected by the topic?
- WHEN is/was your topic important? Is it a current event or an historical issue? Do you want to compare your topic by time periods?

Table of contents
- Broaden your topic
- Information Navigator home
- Sources for facts - general
- Sources for facts - specific subjects
Start here for help
Ask Us Ask a question, make an appointment, give feedback, or visit us.
- Next: Refine your topic >>
- Last Updated: Jul 30, 2021 2:50 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mit.edu/select-topic
- Writing Center
Beginner’s Guide to Research
Click here to download a .pdf copy of our Beginner’s Guide to Research !
Last updated : July 18, 2024
Consider keeping a printed copy to have when writing and revising your resume! If you have any additional questions, make an appointment or email us at [email protected] !
Most professors will require the use of academic (AKA peer-reviewed) sources for student writing. This is because these sources, written for academic audiences of specific fields, are helpful for developing your argument on many topics of interest in the academic realm, from history to biology. While popular sources like news articles also often discuss topics of interest within academic fields, peer-reviewed sources offer a depth of research and expertise that you cannot find in popular sources. Therefore, knowing how to (1) identify popular vs. academic sources, (2) differentiate between primary and secondary sources, and (3) find academic sources is a vital step in writing research. Below are definitions of the two ways scholars categorize types of sources based on when they were created (i.e. time and place) and how (i.e. methodology):
Popular vs. academic sources:
- Popular sources are publicly accessible periodicals–newspapers, magazines, and blogs–such as The Washington Post or The New Yorker . These sources are most often written for non-academic audiences, but can be helpful for finding general information and a variety of opinions on your topic.
- Academic sources , known also as peer reviewed or scholarly articles, are those that have undergone peer review before being published. Typically, these articles are written for other scholars in the field and are published in academic journals, like Feminist Studies or The American Journal of Psychology . Literature reviews, research projects, case studies, and notes from the field are common examples.
Primary vs. secondary sources:
- Primary sources are articles written by people directly involved in what they were writing about, including: News reports and photographs, diaries and novels, films and videos, speeches and autobiographies, as well as original research and statistics.
- Secondary sources , on the other hand, are second hand accounts written about a topic based on primary sources. Whether a journal article or other academic publication is considered a secondary source depends on how you use it.
How to Find Academic Sources
Finding appropriate academic sources from the hundreds of different journal publications can be daunting. Therefore, it is important to find databases –digital collections of articles–relevant to your topic to narrow your search. Albertson’s Library has access to several different databases, which can be located by clicking the “Articles and Databases” tab on the website’s homepage, and navigating to “Databases A-Z” to refine your search. Popular databases include: Academic Search Premier and Proquest Central (non-specific databases which include a wide variety of articles), JSTOR (humanities and social sciences, from literature to history), Web of Science (formal sciences and natural sciences such as biology and chemistry), and Google Scholar (a web search engine that searches scholarly literature and academic sources). If you are unable to access articles from other databases, make sure you’re signed in to Alberton’s Library through Boise State!
Performing a Database Search
Databases include many different types of sources besides academic journals, however, including book reviews and other periodicals. Using the search bar , you can limit search results to those containing specific keywords or phrases like “writing center” or “transfer theory.” Utilizing keywords in your search–names of key concepts, authors, or ideas–rather than questions is the most effective way to find articles in databases. When searching for a specific work by title, placing the title in quotation marks will ensure your search includes only results in that specific word order. In the example below, search terms including the author (“Virginia Woolf”) and subject (“feminism”) are entered into the popular database EBSCOhost:
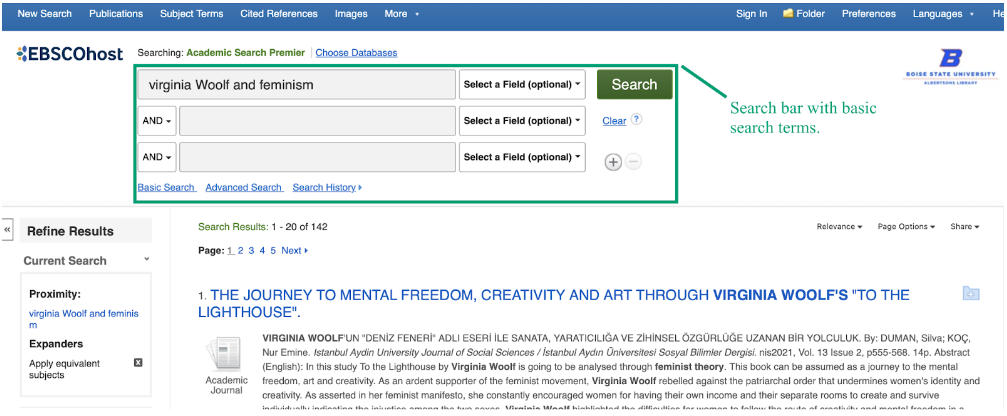
Refining Your Search Results
Many databases have a bar on the left of the screen where you can further refine your results. For example, if you are only interested in finding complete scholarly articles, or peer-reviewed ones, you can toggle these different options to further limit your search. These options are located under the “Refine Results” bar in EBSCOhost, divided into different sections, with a display of currently selected search filters and filter options to refine your search based on your specific needs, as seen in the figure below:
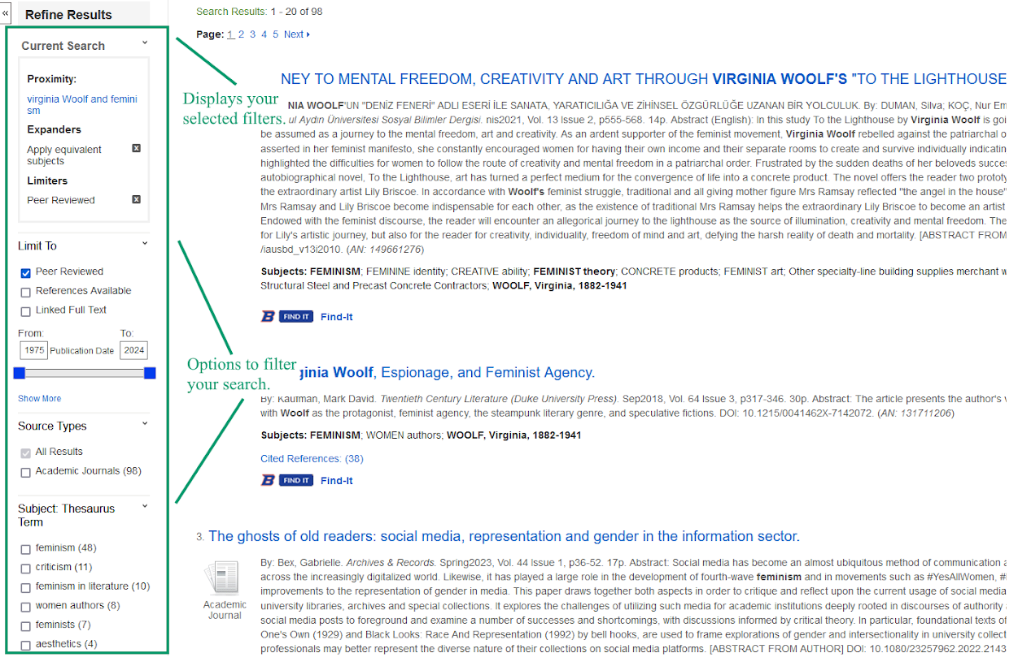
Search results can also be limited by subject : If you search “Romeo and Juliet” on Academic Search Premier to find literary analysis articles for your English class, you’ll find a lot of other sources that include this search term, such as ones about theater production or ballets based on Shakespeare’s play. However, if you’re writing a literary paper on the text of the play itself, you might limit your search results to “fiction” to see only articles that discuss the play within the field of literature. Alternatively, for a theater class discussing the play, you might limit your search results to “drama.”
The Writing Center

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- Health Topics
- Brochures and Fact Sheets
- Help for Mental Illnesses
- Clinical Trials
Children and Mental Health: Is This Just a Stage?

- Download PDF
- Order a free hardcopy
All children are sad, anxious, irritable, or aggressive at times, and many find it occasionally challenging to sit still, pay attention, or interact with others. In most cases, these are just typical developmental phases. However, such behaviors may also indicate a more serious problem in some children.
What mental disorders can affect children?
Many mental disorders can begin in childhood. Examples include anxiety disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression and other mood disorders, eating disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Early treatment can help children manage their symptoms and support their social and emotional well-being. Many adults reflect on how mental disorders affected their childhood and wish they had received help sooner.
What are the signs of mental health conditions in children?
Distinguishing between challenging behaviors and emotions that are a part of normal development and those that may be cause for concern can be hard. Consider seeking help if your child’s behavior or emotions last for weeks or longer, cause distress for your child or your family, or interfere with your child’s functioning at school, at home, or with friends. If your child’s behavior is unsafe, or if your child talks about wanting to hurt themselves or someone else, seek help immediately . Learn more about warning signs .
When might children benefit from an evaluation?
|
|
Get Immediate Help
If you, your child, or someone you know is struggling or having thoughts of suicide, call or text the 988 Suicide & Crisis Lifeline at 988 or chat at 988lifeline.org . In life-threatening situations, call 911 .
Where should I start if I’m concerned about my child’s mental health?
Being proactive and aware of your child’s mental health is an important first step. If you have concerns about your child’s mental health, start by talking with others who frequently interact with your child. For example, ask their teacher about your child’s behavior in school, at daycare, or on the playground.
You can talk with your child’s pediatrician or health care provider and describe your child's behavior and what you have observed and learned from talking with others. You can also ask the health care provider for a referral to a mental health professional with experience and expertise in evaluating and treating children. Learn about ways to get help and how to find a health care provider or access treatment.
How is children’s mental health assessed?
An evaluation by a mental health professional can help understand and clarify your child's emotions, behavior, and current situation. Based on this information, the mental health professional can decide if your child would benefit from an intervention and what intervention might work best.
A comprehensive evaluation of a child’s mental health usually involves:
- A parent interview to discuss the child’s developmental history, temperament, relationships with friends and family, medical history, interests, abilities, and any prior treatment
- Information gathering from the child’s school, such as standardized test scores and reports on behavior, capabilities, and difficulties
- If needed, an interview with the child for testing and behavioral observations
Asking questions and providing information to your child’s health care provider can improve your child’s care. Talking with the health care provider builds trust and leads to better results, quality, safety, and satisfaction with care.
Here are some questions you can ask when meeting with prospective treatment providers.
- Do you use treatment approaches that are supported by research?
- Do you involve parents in the treatment? If so, how are parents involved?
- Will there be “homework” between sessions?
- How will progress be evaluated?
- How soon can we expect to see progress?
- How long should treatment last?
Find tips for talking with a health care provider to improve your child’s care and get the most out of your visit.
How are childhood mental health disorders treated?
The mental health professional will review the evaluation results to help determine if a child’s emotions and behavior are related to changes or stresses at home or school or if they may indicate a disorder for which they would recommend treatment.
There are several treatment options the mental health professional may recommend.
- Parent involvement in the treatment
- Teaching the child skills to practice at home or school (between-session “homework assignments”)
- Measures of progress (such as rating scales and improvements on “homework assignments”) that are tracked over time
- Medications , which will depend on the diagnosis and may include antidepressants, stimulants, mood stabilizers, or other medications. Medications are often used in combination with psychotherapy. If multiple health care providers or specialists are involved, treatment information should be shared and coordinated between providers to achieve the best results.
- Family counseling , which includes family members to help them understand how a child’s challenges may affect relationships with parents and siblings.
- Support for parents , such as individual or group sessions that include training and the opportunity to talk with other parents. Parental support can provide new strategies for helping a child manage difficult emotions and behavior in a positive way. The therapist can also coach parents on how to work with schools to receive classroom accommodations.
Learn more about treatment options for specific disorders.

How can the school support my child’s mental health?
Children who have behavioral or emotional challenges that interfere with success in school may benefit from plans or accommodations provided under laws that prevent discrimination against children with disabilities. Your child’s health care providers can help you communicate with the school.
A first step may be to ask the school whether accommodations such as an individualized education program (IEP) are appropriate for your child. Accommodations might include providing a child with a tape recorder for taking notes, allowing more time for tests, or adjusting seating in the classroom to reduce distraction.
The U.S. Department of Education offers information and resources on what schools can and, in some cases, must provide for children who would benefit from accommodations and how parents can request evaluation and services for their child.
- The Office for Civil Rights provides information on federal laws that prohibit discrimination based on disability in public programs, such as schools.
- The Center for Parent Information and Resources lists Parent Training and Information Centers and Community Parent Resource Centers in each state
Many organizations listed in the More information and resources section also offer information on working with schools and more general information on disorders affecting children.
More information and resources
Information on specific disorders is available on NIMH's Mental Health Information webpage .
The following organizations and agencies have information on symptoms, treatments, and support for childhood mental disorders. Some offer guidance for working with schools and finding mental health professionals. Participating in support groups can provide an avenue for connecting with other parents dealing with similar issues.
Note: This resource list is provided for informational purposes only. It is not comprehensive and does not constitute an endorsement by NIMH.
- American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Facts For Families Guide
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America
- Association for Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Children’s Mental Health
- Child Mind Institute
- Mental Health America
- National Alliance on Mental Illness
- National Federation of Families
- Society of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, Effective Child Therapy
- StopBullying.gov
What research is being done on disorders affecting children?
NIMH conducts and supports research to help find new and improved ways to diagnose and treat mental disorders that occur in childhood. This research includes studies of risk factors—including genetics, experience, and the environment—which may provide clues to how these disorders develop and how to identify them early.
NIMH also supports efforts to develop and test new interventions, including behavioral, psychotherapeutic, and medication treatments, and ways to improve existing treatments and make them more available in communities, doctor's offices, and schools. Researchers are also exploring whether the benefits of treatment in childhood last into adolescence and adulthood.
What are clinical trials and why are they important?
Children are not little adults, yet they are often given medications and treatments that have been tested only in adults. Research shows that, compared to adults, children respond differently to medications and treatments, both physically and mentally. The way to get the best treatments for children is through research designed specifically for them.
Clinical trials are research studies that look at ways to prevent, detect, or treat diseases and conditions. These studies help show whether a treatment is safe and effective in people. Some people join clinical trials to help doctors and researchers learn more about a disease and improve health care. Other people, such as those with health conditions, join to try treatments that aren’t widely available.
NIMH supports clinical trials across the United States. Talk to a health care provider about clinical trials and whether one is right for your child. Learn more about participating in clinical trials .
For more information
Learn more about mental health disorders and topics . For information about various health topics, visit the National Library of Medicine’s MedlinePlus .
The information in this publication is in the public domain and may be reused or copied without permission. However, you may not reuse or copy images. Please cite the National Institute of Mental Health as the source. Read our copyright policy to learn more about our guidelines for reusing NIMH content.
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health NIH Publication No. 24-MH-8085 Revised 2024
- Environment
- Science & Technology
- Business & Industry
- Health & Public Welfare
- Topics (CFR Indexing Terms)
- Public Inspection
- Presidential Documents
- Document Search
- Advanced Document Search
- Public Inspection Search
- Reader Aids Home
- Office of the Federal Register Announcements
- Using FederalRegister.Gov
- Understanding the Federal Register
- Recent Site Updates
- Federal Register & CFR Statistics
- Videos & Tutorials
- Developer Resources
- Government Policy and OFR Procedures
- Congressional Review
- My Clipboard
- My Comments
- My Subscriptions
- Sign In / Sign Up
- Site Feedback
- Search the Federal Register
The Federal Register
The daily journal of the united states government.
- Legal Status
This site displays a prototype of a “Web 2.0” version of the daily Federal Register. It is not an official legal edition of the Federal Register, and does not replace the official print version or the official electronic version on GPO’s govinfo.gov.
The documents posted on this site are XML renditions of published Federal Register documents. Each document posted on the site includes a link to the corresponding official PDF file on govinfo.gov. This prototype edition of the daily Federal Register on FederalRegister.gov will remain an unofficial informational resource until the Administrative Committee of the Federal Register (ACFR) issues a regulation granting it official legal status. For complete information about, and access to, our official publications and services, go to About the Federal Register on NARA's archives.gov.
The OFR/GPO partnership is committed to presenting accurate and reliable regulatory information on FederalRegister.gov with the objective of establishing the XML-based Federal Register as an ACFR-sanctioned publication in the future. While every effort has been made to ensure that the material on FederalRegister.gov is accurately displayed, consistent with the official SGML-based PDF version on govinfo.gov, those relying on it for legal research should verify their results against an official edition of the Federal Register. Until the ACFR grants it official status, the XML rendition of the daily Federal Register on FederalRegister.gov does not provide legal notice to the public or judicial notice to the courts.
Group Registration of Updates to a News Website
A Rule by the Copyright Office, Library of Congress on 07/22/2024
Document Details
Information about this document as published in the Federal Register .
Published Document
This document has been published in the Federal Register . Use the PDF linked in the document sidebar for the official electronic format.
Enhanced Content - Table of Contents
This table of contents is a navigational tool, processed from the headings within the legal text of Federal Register documents. This repetition of headings to form internal navigation links has no substantive legal effect.
FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT:
Supplementary information:, i. background, ii. final rule, a. eligibility requirements, 1. works that may be included in the group, i. constitutional challenge, ii. news website limitation, iii. website limitation, 2. scope of collective work, 3. one-month limitation, 4. authorship, ownership, and work made for hire requirements, 5. subjects of inquiry, i. permitted additional title information, ii. permitted archived urls, b. filing fee, c. deposit requirements, 1. “home page” requirement, i. timing of deposit capture, ii. “complete copy”, 2. site maps, 3. additional deposit suggestions, 4. other comments, e. application requirements, f. conclusion, list of subjects, 37 cfr part 201, 37 cfr part 202, final regulations, part 201—general provisions, part 202—preregistration and registration of claims to copyright, enhanced content - submit public comment.
- This feature is not available for this document.
Enhanced Content - Read Public Comments
Enhanced content - sharing.
- Email this document to a friend
Enhanced Content - Document Print View
- Print this document
Enhanced Content - Document Tools
These tools are designed to help you understand the official document better and aid in comparing the online edition to the print edition.
These markup elements allow the user to see how the document follows the Document Drafting Handbook that agencies use to create their documents. These can be useful for better understanding how a document is structured but are not part of the published document itself.
Enhanced Content - Developer Tools
This document is available in the following developer friendly formats:.
- JSON: Normalized attributes and metadata
- XML: Original full text XML
- MODS: Government Publishing Office metadata
More information and documentation can be found in our developer tools pages .
Official Content
- View printed version (PDF)
This PDF is the current document as it appeared on Public Inspection on 07/19/2024 at 8:45 am. It was viewed 0 times while on Public Inspection.
If you are using public inspection listings for legal research, you should verify the contents of the documents against a final, official edition of the Federal Register. Only official editions of the Federal Register provide legal notice of publication to the public and judicial notice to the courts under 44 U.S.C. 1503 & 1507 . Learn more here .
U.S. Copyright Office, Library of Congress.
Final rule.
The U.S. Copyright Office is creating a new group registration for frequently updated news websites. This option will enable online news publishers to register a group of updates to a news website as a collective work with a deposit composed of identifying material representing sufficient portions of the work, rather than the complete contents of the website. The final rule is nearly identical to the provisions set forth in the January 2024 notice of proposed rulemaking, with one modification in response to public comments and one to reflect a technical change in the process for submitting these claims.
Effective July 22, 2024.
Rhea Efthimiadis, Assistant to the General Counsel, by email at [email protected] or by telephone at 202-707-8350.
The Copyright Act authorizes the Register of Copyrights to specify by regulation the administrative classes of works for the purpose of registration and the deposit required for each class. [ 1 ] In addition, Congress gave the Register the discretion to allow registration of groups of related works with one application and one filing fee. [ 2 ] This procedure is known as “group registration.” [ 3 ] Pursuant to this authority, the Register has issued several regulations permitting group registrations for certain types of works, including newspapers, newsletters and serials, unpublished works, unpublished and published photographs, contributions to periodicals, secure test items, works on an album of music, short online literary works, and database updates. [ 4 ]
This rulemaking expands the available group registration options because of several factors specifically impacting news websites. Along with receiving requests from online publishers, the Office observed the increase in news content offered online and the dynamic nature of such material. [ 5 ] It also reviewed stakeholder comments in prior proceedings that discussed the challenges associated with registering online news content, including those submitted in response to its 2022 Copyright Protections for Press Publishers report. [ 6 ] Finally, the Office acknowledged the deposit challenges associated with websites, particularly news websites, in its 2011 publication titled Priorities and Special Projects of the United States Copyright Office (October 2011-October 2013) . [ 7 ]
On January 3, 2024, the Office published a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (“NPRM”) to establish a new group registration option for frequently updated news websites. [ 8 ] The proposed rule would allow an applicant to register a news website as a collective work (including any individual component works it fully owns, such as literary works, photographs, and/or graphics) [ 9 ] with a deposit composed of identifying material, rather than the complete contents of the website. The proposed rule would also allow registration of the news website and any updates published within one calendar month, if the deposit evidences a sufficiently creative selection, coordination, or arrangement within each collective work to constitute a copyrightable compilation. [ 10 ] Each Start Printed Page 58992 collective work must have been created as a work made for hire, with the same person or entity named as both the author and copyright claimant. The proposed rule stated that applicants would be required to submit their claims through the online copyright registration system, using the application currently in use for a group of newspaper issues. [ 11 ]
The Office received twenty comments in response to the NPRM. [ 12 ] All but one [ 13 ] supported the Office's proposal to create the new group registration option, though the majority requested various modifications. Two commenters, however, expressly conditioned their support on substantive changes to the rule, which would substantially change its scope. [ 14 ] In general, commenters were interested in expanding eligibility for this option to a greater number of works and changing the deposit requirement. Proposals included revising the definition of “news website,” removing the work made for hire and author/claimant requirements, increasing the time limitation for updates to the news website, clarifying the “home page” deposit requirement, and asking the Office to confirm the scope of remedies for copyright infringement of a collective work. [ 15 ] Finally, one commenter encouraged the Office to “identify opportunities for improvement” and to remain “adaptive to technological changes.” [ 16 ]
Having reviewed and carefully considered each of the comments, the Office now issues a final rule that is nearly identical to the proposed rule, with one modification reflecting concerns raised by some commenters regarding the “home page” deposit requirement and one modification concerning the application form for this option. These modifications are discussed in more detail below. With respect to requests that we received to expand the scope of the rule, the Office will closely monitor how the new group option performs, including the number and complexity of the claims submitted, the amount of time needed to examine these claims, and the modest filing fee for this option. The Office remains open to revisiting these issues in the future based on this rule's performance.
In the NPRM, the Office proposed to limit this group registration option to updates to a “news website,” defined as “a website that is designed to be a primary source of written information on current events, either local, national, or international in scope, that contains a broad range of news on all subjects and activities and is not limited to any specific subject matter.” As described in the NPRM, the proposed rule stems from the rapid development and predominance of news websites over print newspapers, [ 17 ] and requests from news publishers for a feasible way to register “newspaper websites” that are “updated frequently.” [ 18 ] Thus, the proposed rule is an extension of the existing group newspaper option that has been available for decades. [ 19 ] Consistent with the Compendium of U.S. Copyright Office Practices, the proposed rule defines a “website” as “a web page or set of interconnected web pages that are accessed using a uniform resource locator (“URL”) organized under a particular domain name.” A number of commenters encouraged the Office to expand the type of works eligible under the rule and recommended revisions to both definitions.
Before turning to the requests to expand the rule, the Office addresses the argument made by a small number of commenters that the proposed group registration option would violate the First Amendment by limiting the option to a particular type of work. In a joint comment, NWU, NPPA, and NASW stated that restricting the option to “news” websites constitutes “[c]ontent-based discrimination,” which they considered “[c]onstitutionally suspect and subject to strict scrutiny” that the rule “cannot meet.” [ 20 ] In support of this argument, they cited Arkansas Writers Project v. Ragland, 481 U.S. 221 (1987), which reviewed a state sales tax scheme that taxed general interest magazines, but exempted newspapers and religious, professional trade, and sports journals. Because Arkansas “advanced no compelling justification for selective, content-based taxation of certain magazines,” the Supreme Court held the tax scheme invalid under the First Amendment. [ 21 ] Analogizing the tax scheme in Arkansas Writers Project to the proposed registration option, NWU, NPPA, and NASW argued that the exclusion of any web content that does not meet the “news website” definition is unconstitutional. [ 22 ]
Aligned with NWU, NPPA, and NASW, another commenter, Gordon Firemark, contended that, by limiting the group option to updates to news websites, the proposed rule “excludes other types of content from [its] benefits” and denies content creators “relief from the burdens of the current system.” [ 23 ] He argued that recent Supreme Court precedent concerning trademark registration requires a content-neutral approach. [ 24 ]
The Office disagrees with these arguments. It is correct that the Supreme Court has held that content-based laws—laws restricting or compelling Start Printed Page 58993 speech based on its communicative content—are presumptively unconstitutional, [ 25 ] and subject to strict scrutiny, under which the government must show that the law is the “least restrictive means” of advancing a “compelling” governmental interest. [ 26 ] A regulation can be content-based “on its face,” if its text applies to speech based on the subject matter, topic, or viewpoint of that speech. It can also be content-based if it has a discriminatory purpose that “cannot be justified without reference to the content of the regulated speech” or was “adopted by the government because of disagreement with the message” conveyed. [ 27 ] However, a regulation that places “a differential burden on speakers is insufficient by itself to raise First Amendment concerns.” [ 28 ] The tax scheme in Arkansas Writers Project was found to violate these principles by being directed at particular subjects, thus targeting a small group within the press. [ 29 ] That is not the case here.
The Office's proposed group registration option is not analogous to the unconstitutional tax statute in Arkansas Writers Project for multiple reasons. First, the option does not restrict or compel speech based on its communicative content. Nor does it favor or disfavor particular topics or subjects, or exclude a small group of the press. [ 30 ] Instead the option is available for updates to news websites that contain a broad range of topics regardless of the content of the speech involved.
Second, the registration option is viewpoint neutral and operates not as a restriction on speech, but as a condition for qualifying for one of many options available to register copyrights, including online websites and other publications. The Standard Application is available to any type of author for any type of work within the statutory categories. [ 31 ] Group registration options are discretionary accommodations offered by the Office in a number of areas. Currently, the Office administers ten group options covering unpublished works, short online literary works, works on an album of music, serials, newspapers, newsletters, contributions to periodicals, published and unpublished photographs, automated databases, and secure test items. [ 32 ] For online publications, group serials and group newsletters are other registration options for publications that fall outside of the “newspaper” or “news website” definitions.
The Supreme Court's recent ruling in a case involving trademark regulations supports the Office's view. There the Court reviewed a rule of the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”) barring the registration of trademarks that use the names of particular living individuals without their written consent. [ 33 ] The Court held that this bar, though content-based, is viewpoint neutral and does not violate the First Amendment. [ 34 ] The Court noted that while its precedents “distinguish between content-based and content-neutral regulations of speech,” [ 35 ] they further distinguish “a particularly `egregious form of content discrimination'—viewpoint discrimination,” which targets not merely a subject matter, “but particular views taken by speakers on a subject.” [ 36 ] The Court identified “[s]everal features of trademark [law]” that “counsel against a per se rule of applying heightened scrutiny to viewpoint-neutral, but content-based trademark regulations.” Most notably, it found that “trademark rights have always coexisted with the First Amendment, despite the fact that trademark protection necessarily requires content-based distinctions.” [ 37 ] Accordingly, the Court held that USPTO's “content-based, but viewpoint-neutral, trademark restriction [ ] is compatible with the First Amendment.” [ 38 ]
Similarly, copyright registration, and the broad administrative classification authority Congress granted to the Register, necessarily requires content-based distinctions. Indeed, since its passage in 1976, the Copyright Act has authorized the Register “to specify by regulation the administrative classes into which works are to be placed for purposes of deposit and registration” and to permit “ for particular classes, the deposit of identifying material instead of copies or phonorecords, the deposit of only one copy or phonorecord where two would normally be required, or a single registration for a group of related works.” [ 39 ] Like the USPTO's name bar, these administrative distinctions are not based on the particular views taken by authors and have always coexisted with the First Amendment. The addition of an administrative classification for this new group registration option, which adopts near-identical criteria for determining “news” content to that of the existing group option for newspapers, is “a matter of policy and discretion” [ 40 ] fully compatible with the First Amendment.
Further, unlike the viewpoint-based trademark provisions held unconstitutional for barring registration of scandalous or disparaging marks, [ 41 ] the Office's viewpoint-neutral administrative classification does not bar registration for non-news content or websites. Quite the opposite: to increase participation in the registration system, the Office has created several group options for the registration of works that are published online. [ 42 ] The Standard Application also remains available to any type of author for any type of work within the statutory categories. This rule does not prevent anyone's ability to register non-news works.
Multiple commenters urged the Office to expand the rule's definition of “news website” by removing the condition that the website must contain news on all subjects and activities. [ 43 ] In encouraging Start Printed Page 58994 the Office “not to exclude . . . specialized websites,” the ABA-IPL noted that the “proposed rule may provide especially meaningful benefit to smaller news websites—including those that focus on certain `specific subject matter.' ” [ 44 ] HBP argued that “websites, like HBR.org, that focus on a particular area of news . . . still face the same registration problems afflicting all news websites.” [ 45 ] The Authors Guild also expressed concern that the rule would exclude more specialized news publications, such as those that focus on political news. It argued that “these publications clearly qualify as news websites under any ordinary understanding of that term.” [ 46 ] Relatedly, commenters claimed that content restrictions “put[ ] examiners in an untenable position of deciding what is or is not `news.' ” [ 47 ] Finally, four commenters asked the Office to abandon the “news website” definition and extend the group option “to any periodically-produced content distributed through the internet.” [ 48 ]
After considering this request and in the interest of implementing this final rule as quickly as possible, the Office declines to revise the definition at this time. As an extension of the newspaper group option, the “news website” definition is modeled on the Office's longstanding regulation defining a “newspaper” as a publication that is “mainly designed to be a primary source of written information on current events, either local, national, or international in scope,” that “contains a broad range of news on all subjects and activities and is not limited to any specific subject matter.” [ 49 ] This definition is very broad and it is intended to “make any newspaper eligible for a group registration.” [ 50 ] It is also intended to distinguish a “newspaper” from a “newsletter,” which is defined elsewhere in the regulations as a publication that contains “news or information that is chiefly of interest to a special group, such as trade and professional associations, colleges, schools, or churches.” [ 51 ]
Under this definition, newspapers are aimed at any member of the general public who may be interested in newsworthy information or events that are reported on a given day. [ 52 ] By applying a similar definition to websites, the final rule recognizes that “news websites” are also intended to have universal appeal.
This definition would encompass news websites that cover current events and provide information on diverse topics, including some political websites like those identified in the Authors Guild's comment. [ 53 ] Although these sites focus primarily on issues involving politics and events with political implications, they do not limit their coverage to a particular subject matter nor are they directed at narrow or discrete groups of readers. [ 54 ]
The Office also disagrees with commenters that the “news website” eligibility requirement places a burden on examiners. Indeed, the definitions for “news website” and “newspaper” are similar, in part, to enable consistent application of both rules. Examiners are accustomed to assessing eligibility based on this definition.
However, if the definition proves too rigid or unworkable, the Office is willing to revisit this issue based on its experience in administering this rule. Importantly, however, this new group option is not intended to extend to the websites of all serials or newsletters, which in print or ePrint form have the benefit of separate group registration options. [ 55 ]
The Office received requests to expand the rule beyond websites. Commenters recommended that the proposed rule be amended to include mobile applications (“apps”) in the definition of “website.” [ 56 ] They argued that “[m]any news publishers encourage users to access content on an app rather than a website.” [ 57 ]
The Office declines to amend the definition. It considers an app to be “a computer program that is used directly or indirectly in a computer or handheld electronic device.” [ 58 ] The Office has a procedure for registering the underlying code that operates the app. [ 59 ] To the extent that news publishers seek to register the works published on the app, a registration for a newspaper or a news website would protect those works if they contain the same content.
AIPLA encouraged the Office to revise the definition of “website” to clarify that a website is not limited to content accessed using a single domain name. [ 60 ] It explained that “web pages are composed of various elements, like text, images, and videos” that “might be hosted on a different server than the one hosting the main web page for reasons such as efficiency, speed, and cost.” [ 61 ] The Office appreciates this distinction but declines to revise the definition. To qualify for this option, each collective work in the group must be published under one particular domain name. For registration purposes, the Office does not assess eligibility based on where component digital works may be stored. The Office believes the “particular web page” requirement is necessary to prevent applicants from using the option to register collective works published under different domain names on the same application, which would make it difficult to identify the website that is covered by the registration. Therefore, the final rule retains the definition proposed in the NPRM.
The proposed rule provides that claims registered under this option will be limited to the collective work authorship based on the selection, coordination, and/or arrangement of the individual component works, and that all parts of the collective work will constitute one work for purposes of 17 U.S.C. 504(c)(1) . [ 62 ] Additionally, the Start Printed Page 58995 Office made clear that the registration will also cover the individual contributions contained within the collective work if they are fully owned by the copyright claimant and were first published in that work.
NPR asked the Office to confirm that “the scope of the collective work will explicitly include all copyrightable contributions made by the claimant, not just textual works.” [ 63 ] As noted above, a “news website” is defined as “a website that is designed to be a primary source of written information.” [ 64 ] If the collective work contains individual contributions that are fully owned by the copyright claimant and were first published in the work, then the registration will cover those contributions, so long as they are copyrightable subject matter. However, a component work “that is perceptible to the user only by downloading or separately purchasing that particular work is not considered part of the website for registration purposes and must be registered separately.” [ 65 ] Additionally, any “externally linked content [ i.e., content residing on another website] is not considered part of the website's content for registration purposes.” [ 66 ]
HBP recommended that the Office permit applicants to disclaim content that is licensed and not owned by the applicant. As with group newspapers, the Office does not see the need for a limitation of claim for news websites, because the proposed rule expressly states that “[e]ach update to the website must be [an original] collective work.” A registration issued by the Office pursuant to this rule will only cover the new contributions owned by the copyright claimant. Consistent with any collective work registration, any articles, photos, or other contributions included in the collective work that were previously published, previously registered, owned by another party, or in the public domain are automatically excluded from the claim. As a practical matter, therefore, a disclaimer to expressly exclude material in the application is unnecessary.
Port. Prerogative Club asked the Office to “[c]larify whether updates to numerical information, such as prices, volumes, retweets, or other metrics, qualify as registrable under the rule, and whether the Office has changed its policy on the registrability of short phrases and headlines.” The Office states that its longstanding regulation denying protection for words and short phrases has not changed. [ 67 ] Regarding “prices, volumes, retweets, or other metrics,” it is unclear whether the commenter is referring to individual works of authorship, or whether these items appear in a compilation. Individual numbers and short phrases are not copyrightable. However, a copyrightable compilation of these items may be registrable.
The proposed rule permits an applicant to include updates published on the same website within the same calendar month. Three commenters urged the Office to remove the limitation, arguing that it is too “onerous.” [ 68 ] NPR recommended that the Office allow for the option to cover “three months, or six months, or a calendar year” to “reduce registration costs.” [ 69 ] Noting that “attorneys' fees and statutory damages can be awarded as long as copyright is registered within three months of first publication,” NWU, NPPA, and NASW requested that the rule be amended to allow registration of updates published “during any specified three-month period.” [ 70 ]
At this time, given administrative capabilities, the Office cannot expand the option to cover more than one month of updates. As the NPRM explained, to deliver the option promptly, and to minimize development time, the Office is adapting the existing group application for newspapers, which is used to register up to one month of newspaper issues and contains technical validations that prevent applicants from entering publication dates that are more than one month apart. Changing the limit would require additional modifications to the application and delay implementation of the final rule. Further, the Office seeks an appropriate balance between the interests of copyright owners and the administrative burden to the Office. Based on the modest fee set for this option, some limit on the number of works included in each claim is necessary. The Office will reassess whether the limit can be increased after it has gained sufficient experience administering the rule.
Under the proposed rule, to be eligible for the option, each collective work in the group must have been created as a work made for hire, with the same person or entity named as the author and copyright claimant. Multiple commenters questioned this requirement. [ 71 ] The Authors Guild argued that the work made for hire requirement “arbitrarily and unfairly confines the benefit of the rule to corporate entities even where other creators are producing substantially the same type of content.” [ 72 ] While they recognized that this requirement reflects practical and technical limitations, NMA and AIPLA noted that “there does not seem to be a fundamental reason for such a limitation in principle, and in many business cases, the work may be fully owned by the publisher, or obtained via assignment or operation of law.” [ 73 ]
The Office acknowledges that the work made for hire requirement may not reflect every business case of ownership. However, this requirement streamlines the registration procedures, which, as noted above, will adapt the existing group application option for newspapers. Under that option, the same person or entity must be named as the author and copyright claimant, and each issue must be a work made for hire. The Office retains the same requirements for the news websites option to minimize the need for additional development time that would otherwise be required. Start Printed Page 58996
Additionally, under general Copyright Office practice, if the author and claimant are not the same person, the applicant is statutorily required to provide a transfer statement explaining how the claimant acquired all of the rights initially belonging to the author. [ 74 ] If an applicant names a third party as the copyright claimant, but fails to provide a transfer statement, then the Office must correspond to determine whether the claimant actually owns all of the exclusive rights in the works, which delays the registration decision. The corresponding additional time and costs that the Office would incur are inconsistent with the reduced fee for examination of multiple collective works.
Moreover, imposing a work made for hire limitation is consistent with the goal of this rulemaking, which is to address obstacles to registering online news content produced by news publishers, who often also publish newspapers. Based on its experience with the existing group newspaper registrations, the Office expects that this requirement will produce an optimal public record, while reducing the administrative burden that these claims impose. The final rule accordingly retains the work made for hire requirement. Applicants who do not qualify for the option may still register their works individually using the Standard Application.
The Office invited public comments on whether it should give applicants the opportunity to provide additional information, such as individual article or photograph titles, as part of this group registration option. Commenters expressed support for the implementation of an opportunity to include granular information concerning individual component works at the applicant's discretion. [ 75 ] The Authors Guild noted that “in the event an individual article is the subject of a later infringement action, the applicant may need to rely on its own recordkeeping to establish that the article was on the website during the period covered by the registration.” [ 76 ] It concluded, “[t]he listing of individual titles or other information on the application may provide additional evidence relevant to that showing.” [ 77 ] The Office agrees and will provide instructions on its website explaining how applicants may submit additional information regarding component works on an optional basis. [ 78 ]
The Office also invited public comments on the availability and effectiveness of technological solutions for saving or archiving websites that could assist or supplement news websites' recordkeeping efforts while also informing the public of the contents of the website and/or any updates registered. The Office suggested that applicants may provide in the “Note to Office” field additional information regarding the contents of the work, such as archived URLs that capture the complete content of each collective work submitted for registration. The Copyright Alliance expressed support for this suggestion, provided that doing so is voluntary. [ 79 ] Therefore the Office encourages applicants to submit archived URLs in the “Note to Office” field on a voluntary basis.
The NPRM provided that the filing fee for this option will be $95, the same fee that currently applies to a claim in a group of newspapers. It noted that the Office believes it is reasonable to charge the same fee as for the group newspaper option, given the similarities in expected workflow associated with examining these claims. The NMA expressed support for this modest fee, describing it as “reasonable and unarbitrary.” [ 80 ] The final rule establishes this fee.
The NPRM proposed that for each collective work submitted under this group registration option, applicants must “submit a deposit that is sufficient to identify some of the updates that were made to the website.” [ 81 ] The Office specified that “applicants will need to submit separate PDF files that each contain a complete copy of the home page for the site. Each PDF must show how the home page appeared at a specific point during each day of the calendar month when new updates were published on the site.” [ 82 ] Additionally, the NPRM required that each deposit demonstrate “that the home page contains a sufficient degree of selection, coordination, and/or arrangement to be registered as a collective work.” [ 83 ] Several commenters requested that the Office consider different deposit requirements, though commenters varied on the specific changes they requested or discussed deposits generally. The Office addresses each suggested change below.
After considering NMA's request to resolve a purported ambiguity in the proposed rule regarding the time of day for daily deposits of home pages, the Office is clarifying the time period for capturing deposits. [ 84 ] The language within section (m)(6)(i) requiring “[e]ach PDF [to] show how the home page appeared at a specific point during each day of the calendar month” does not require applicants to capture PDFs of home pages at the same exact time every day. [ 85 ] Instead, PDFs of home pages must show how the home page appeared at some point during each day, in addition to satisfying other applicable deposit requirements.
Three commenters specifically requested that the Office expand the identifying material it will accept to encompass more than “a complete copy of the home page for the site.” [ 86 ] The NAB stated that “the Office should amend the deposit requirements proposed in § 202.4(m)(6)(i) to allow for the submission of a copy of identifying material in lieu of a complete copy of the home page.” [ 87 ] It explained that “many news websites utilize an `infinite scroll' feature that automatically and continuously loads more content as users scroll down the web page” making Start Printed Page 58997 it “technologically impossible for an applicant to satisfy the deposit requirement of providing a PDF of the home page in its entirety.” [ 88 ] Copyright Alliance echoed this sentiment stating “a user is able to continuously reveal additional content on the web page without having to leave the page to view the content on a separate web page. For such web pages, it is not possible to capture an `entire copy' of the page since the user can endlessly reveal the contents of the page.” [ 89 ] Similarly, NMA noted that, due to the difficulties posed by “extensive or close-to-infinite scroll,” the Office should clarify that an applicant could meet the deposit requirement “as long as [the PDF] captures the masthead, URL identifier, and a defined minimum amount of the homepage (which in most cases will encompass all of it), including representative updates from the previous deposit copy.” [ 90 ]
After considering these comments, the Office concludes that the requested modification to the proposed rule is reasonable and supports the overall goal of this group registration option. Accordingly, the final rule includes an alternative to the “complete copy of the home page” requirement where submitting a complete copy is not feasible due to the size or continuous nature of the home page. In such circumstances, applicants may “submit the first 25 pages of the home page that demonstrates updates from the previous deposit copy.” This portion of the rule is designed to decrease the burden on applicants that wish to utilize this group registration option, but are unable to satisfy the “complete copy” deposit requirement. The Office believes that this modification will facilitate registration, while also ensuring that the deposit provided is sufficient to identify the work and the copyrightable authorship covered by the registration. Applicants utilizing this provision are advised that any deposit should only include updates within the time period covered by the application. In the event that an applicant includes updates outside the time period, they would be considered previously published material, and would not be covered by the registration. Additionally, as stated in the NPRM, if a copyright owner is required to prove to a court or an alleged infringer “the specific contents of a website at any particular point in time, it will need to preserve and maintain its own copy of the site and rely on its own recordkeeping to provide such proof.” [ 91 ]
NWU, NPPA, and NASW disagreed that a home page would constitute sufficient identifying material for registration. [ 92 ] They asserted that “requiring deposit of PDFs of images of the home page is disconnected from the reality that updates aren't necessarily visible on the `home page' of a website.” [ 93 ] While “[u]pdates appear on the home pages of some—but far from all—newspaper publishers' websites,” the home pages of other websites, such as self-published or references websites, are “mostly or entirely static,” with updates occurring on other “inside” pages that are not indexed or referenced on the home page. [ 94 ] Instead, NWU, NPPA, and NASW suggested that the Office accept a “sitemap page or set of sitemap pages,” “as the way to indicate which pages of a site have most recently been added or modified, and when.” [ 95 ] Sitemaps, they alleged, “are structured, standardized, machine-readable, and human-readable” and “all updates in a given period can be identified by a single sitemap or set of sitemaps,” which the Office could “use[ ] immediately.” [ 96 ]
The Office declines to permit applicants to submit a sitemap page or a set of sitemap pages as identifying material for several reasons. First, it is not clear that sitemaps themselves provide information that would allow an examiner to determine whether each collective work within the group application contains sufficient creative selection, coordination, or arrangement. [ 97 ] Second, sitemaps do not satisfy the public notice function that deposits serve, as they do not display the work requested for registration and are not sufficient to identify the updates made to the websites. [ 98 ] As explained in the NPRM, any deposit requirement must “satisfy the public notice function of capturing, and making available for public inspection, a deposit that should be sufficient to identify” the work covered by the application. [ 99 ] Lastly, accepting sitemap deposits would likely not aid in efficiency as suggested. [ 100 ] If an examiner receives a sitemap, they would likely need to correspond with the applicant to determine what exactly the application covers. For these reasons, the Office declines to modify the final rule to include sitemaps.
Commenters also suggested that the Office accept deposits comprised of annotated Portable Document Formats (“PDFs”) [ 101 ] or PDF deposits of apps. [ 102 ] Specifically, one commenter encouraged the Office to consider accepting annotated PDFs of a single web page, where “[a]nnotations could circle content that is not included in registration, such as licensed content as compared to original news organization content” or “content already registered.” [ 103 ] Other commenters, including Copyright Alliance, NMA, and the Authors Guild, proposed that the Office should accept PDFs that “contain a complete copy of the home page of . . . mobile application[s]. ” [ 104 ] Start Printed Page 58998 They discussed the ease with which applicants could submit app PDFs [ 105 ] and how PDFs address record-keeping concerns and “concerns over whether the collective works stem from the same source.” [ 106 ] Copyright Alliance and NMA also suggested that the absence of a uniform resource locator (“URL”) from app PDFs, a requirement of the proposed rule, is immaterial because apps “generally prominently feature the logo or other visible identifier of the publication in question” and news content on an app is “organized and contained,” similar to a website. [ 107 ] NMA further recommended that because the USPTO has “long accepted” app screenshots for trademark specimens, subject to certain requirements, the Office should adopt similar standards. [ 108 ]
The Office declines to permit parties to submit annotated PDFs of a single web page. As discussed above, each update will be registered as a collective work. For that reason, there is no need to identify component works that are not owned by the claimant or component works that have been previously registered, because as a general rule, a registration for a collective work does not cover this type of preexisting material.
The Office also declines to accept PDF deposits of apps to represent a news website. Initially, it is unclear whether the selection, coordination, and/or arrangement of material encompassed within the PDFs would be identical to the selection, coordination, and/or arrangement of a website's home page, regardless of whether the same content is present on both. [ 109 ] Further, the Office continues to believe that the rule's deposit regulations offer flexibility, while still satisfying the public notice function of deposits. The regulation will permit applicants to submit a complete copy of the website's home page, and when that is not feasible due to the size or continuous nature of the home page, applicants may submit the first 25 pages of the home page demonstrating updates from the previous deposit copy.
Commenters made additional suggestions and remarks on the proposed rule's deposit requirements and the Office's deposit requirements generally. With respect to the Office's modernization efforts, ABA-IPL suggested that the Office consider generally expanding the “format of deposit copies accepted” and regularly reviewing and updating registration regulations. [ 110 ] ABA-IPL stated that the Office should accept deposits in .xml format for regularly updated news content, such as content covered under the proposed rule, “as [.xml] and similar formats are widely used in digital content creation and management.” [ 111 ] The University of Michigan Library (“UM-Library”) expressed concerns with the proposed regulations regarding fixation and preservation. [ 112 ] They asserted that the proposed deposit requirements are not “sufficiently fixed for copyright purposes” and that if deposit “materials are not collected and preserved—even as facsimiles or through emulation—then as a practical matter there will be a huge gap in the possibilities for research, scholarship, and understanding.”
The Office is sympathetic to commenters' desires to expand the file formats accepted for deposit purposes generally, including regularly updated news content. As stated above and in the NPRM, the current registration system only accepts certain file types. [ 113 ] The Office anticipates revisiting its acceptable file formats in connection with ongoing improvements to its technology systems. Until then, the Office continues to actively engage in research about the suitability of other file formats. [ 114 ]
The Office appreciates the fixation and preservation concerns about the proposed deposit requirements, codified in the final rule. It continues to believe, however, that the deposit requirements are sufficient. As stated above and in the NPRM, the Copyright Act imbues the Register with broad authority to accept identifying material in lieu of complete copies or phonorecords [ 115 ] where such copies or phonorecords are “bulky, unwieldly, easily broken, or otherwise impractical to [serve] . . . as records identifying the work[s] registered.” [ 116 ] This provision, and its legislative history, give the Register flexibility in determining the deposit requirements when identifying material is involved, and the Office has used this authority in the past. Within this rulemaking, the Office believes the proposed deposit requirements are appropriate, and less burdensome than general deposit requirements for websites. [ 117 ] As the Office discussed in the NPRM, the proposed deposit requirements satisfy the public notice function and still require that deposits sufficiently “identify some of the updates” made to the website. [ 118 ] Any fixation concerns may be alleviated by the fact that the proposed regulations are merely registration deposit requirements. They do not relieve a registrant from complying with other legal obligations, such as the obligation to maintain and preserve copies of a website, including its content, in the context of an infringement claim. [ 119 ]
The NPRM explained that the Office planned to use one of its existing group registration application forms to process these claims. Specifically, it said applicants would be required to submit their claims through the current electronic registration system using the application designated for a group of newspaper issues. None of the commenters objected to this proposal.
After consulting with the Library of Congress's Office of the Chief Information Officer, the Office determined that it would be feasible to create a separate application for news website claims that will be cloned from the corresponding application that is used for group newspaper claims. This should simplify the registration process for both applicants and Office staff by preventing potential confusion between claims involving newspaper issues and claims involving updates to a news website. The cloned application will include the same technical specifications and system validations that appear in the group newspaper Start Printed Page 58999 form. The final rule has been modified to reflect this change. Information and instructions on how to submit these claims will be provided in the application itself and on a dedicated page on the Office's website.
Based on requests from affected parties for the expeditious implementation of the rule [ 120 ] and the absence of arguments supporting a delay, the Office finds that good cause exists to issue these regulations as a final rule with an immediate effective date. Commenters have presented a record supporting “the demonstrable urgency of the conditions [the rule is] designed to correct.” [ 121 ] Finally, the registration option authorized by the final rule will be available to registrants at or near the rule's publication date.
- General provisions
- Copyright claims, preregistration and registration
For the reasons set forth in the preamble, the Copyright Office amends 37 CFR parts 201 and 202 as follows:
1. The authority citation for part 201 continues to read as follows:
Authority: 17 U.S.C. 702 .
Section 201.10 also issued under 17 U.S.C. 304 .
2. In § 201.3, amend table 1 to paragraph (c) by redesignating paragraphs (c)(12) through (c)(29) as (c)(13) through (c)(30), respectively, and adding a new paragraph (c)(12) to read as follows:
Table 1 to Paragraph ( c )
3. The authority citation for part 202 continues to read as follows:
Authority: 17 U.S.C. 408(f) , 702 .
4. Amend § 202.4 by adding paragraph (m) and revising paragraph (r) to read as follows:
(m) Group registration of updates to a news website. Pursuant to the authority granted by 17 U.S.C. 408(c)(1) , the Register of Copyrights has determined that a group of updates to a news website may be registered with one application, the required deposit, and the filing fee required by § 201.3 of this chapter, with each update being registered as a collective work, if the following conditions are met:
(1) Definitions. For the purposes of this paragraph (m):
(i) News website means a website that is designed to be a primary source of written information on current events, either local, national, or international in scope, that contains a broad range of news on all subjects and activities and is not limited to any specific subject matter.
(ii) Website means a web page or set of interconnected web pages that are accessed using a uniform resource locator (“URL”) organized under a particular domain name.
(2) Requirements for collective works. Each update to the website must be a collective work, and the claim must be limited to the collective work.
(3) Author and claimant. Each collective work in the group must be a work made for hire, and the author and claimant for each collective work must be the same person or organization.
(4) Updates must be from one news website; time period covered. Each collective work in the group must be published on the same news website under the same URL, and they must be published within the same calendar month. The applicant must identify the earliest and latest date that the collective works were published.
(5) Application. The applicant must complete and submit the online application designated for a group of updates to a news website. The application may be submitted by any of the parties listed in § 202.3(c)(1).
(6) Deposit. (i) For each collective work within the group, the applicant must submit identifying material from the news website. For these purposes “ identifying material ” shall mean separate Portable Document Format (PDF) files that each contain a complete copy of the home page of the website. In case a complete copy is technically unfeasible due to the size or continuous nature of the home page, the applicant may submit the first 25 pages of the home page that demonstrates updates from the previous deposit copy. Each PDF must show how the home page appeared at a specific point during each day of the calendar month when new updates were published on the website.
(ii) The identifying material must demonstrate that the home page contains sufficient selection, coordination, and arrangement authorship to be registered as a collective work If the home page does not demonstrate sufficient compilation authorship, the deposit should include as many additional pages as necessary to demonstrate that the updates to the news website can be registered as a collective work.
(iii) The identifying material must be submitted through the electronic registration system, and all of the Start Printed Page 59000 identifying material that was published on a particular date must be contained in the same electronic file. The files must be submitted in PDF format, they must be assembled in an orderly form, and each file must be uploaded to the electronic registration system as an individual electronic file ( i.e., not .zip files). The file size for each uploaded file must not exceed 500 megabytes, but files may be compressed to comply with this requirement.
(7) Special relief. In an exceptional case, the Copyright Office may waive the online filing requirement set forth in paragraph (m)(5) of this section or may grant special relief from the deposit requirement under § 202.20(d) of this chapter, subject to such conditions as the Associate Register of Copyrights and Director of the Office of Registration Policy and Practice may impose on the applicant.
(r) The scope of a group registration. When the Office issues a group registration under paragraph (d), (e), or (f) of this section, the registration covers each issue in the group and each issue is registered as a separate work or a separate collective work (as the case may be). When the Office issues a group registration under paragraphs (c), (g), (h), (i), (j), (k), or (o) of this section, the registration covers each work in the group and each work is registered as a separate work. When the Office issues a group registration under paragraph (m) of this section, the registration covers each update in the group, and each update is registered as a separate collective work. For purposes of registration, the group as a whole is not considered a compilation, a collective work, or a derivative work under section 101, 103(b), or 504(c)(1) of title 17 of the United States Code.
Shira Perlmutter,
Register of Copyrights and Director of the U.S. Copyright Office.
Approved by:
Carla D. Hayden,
Librarian of Congress.
1. 17 U.S.C. 408(c)(1) .
2. Id.
3. See generally 37 CFR 202.3(b)(5) , 202.4 .
4. Id. at 202.3(b)(5), 202.4(c)-(k), (o).
5. See 89 FR 311 , 311-12 (Jan. 3, 2024).
6. U.S. Copyright Office, Copyright Protection for Press Publishers (June 2022), https://copyright.gov/policy/publishersprotections/202206-Publishers-Protections-Study.pdf .
7. See 89 FR 311 , 312 .
8. Id. at 311. The final rule defines a “news website” as “a website that is designed to be a primary source of written information on current events, either local, national, or international in scope, that contains a broad range of news on all subjects and activities and is not limited to any specific subject matter.” 37 CFR 202.4(m)(1)(i) .
9. Because the Office will not examine each component work within the collective work, the copyright claimant bears the burden of proving that it owns the individual component works claimed in the submission.
10. A “collective work” is a type of compilation. See 17 U.S.C. 101 . A “compilation” is “a work formed by the collection and assembling of preexisting materials or of data that are selected, coordinated, or arranged in such a way that the resulting work as a whole constitutes an original work of authorship.” Id.
11. As noted in the NPRM, “in appropriate circumstances, the Office may waive the online filing requirement, subject to the conditions the Associate Register of Copyrights and Director of the Office of Registration Policy and Practice may impose.” 89 FR 311 , 316 n.55.
12. The Office also received a letter from several organizations reflecting their collective support for finalizing the rulemaking in a timely manner and in-line edits to the Office's proposed regulatory language. Letter from Ass'n of Am. Publishers et al. to Suzanne Wilson, Gen. Counsel and Assoc. Register of Copyrights (Apr. 4, 2024), https://www.copyright.gov/rulemaking/newswebsite/Association-of-American-Publishers-et-al%E2%80%93Letter-to-Copyright-Office.pdf .
13. See Am. Ass'n of Independent Music, Ass'n of Am. Publishers, Inc, and Recording Industry Ass'n of Am., Inc. (“A2IM, AAP, & RIAA”) Comment at 2 (“Commenters express no position on the primary focus of the NPRM—whether the Office should create a new group registration option for frequently updated news websites—or on the details of how such an option should be implemented.”).
14. See generally Nat'l Writers Union, Nat'l Press Photographers Ass'n, Nat'l Ass'n of Sci. Writers (“NWU, NPPA, & NASW”) Comment; Gordon Firemark 2 Comment.
15. A handful of commenters also proposed that the Office should adopt the NPRM immediately, as an interim rule. See, e.g., Copyright All. Comment at 11; Nat'l Pub. Radio (“NPR”) Comment at 3-5; News Media All. (“NMA”) Comment at 2.
16. Am. Bar Ass'n Section of Intell. Prop. L. (“ABA-IPL”) Comment at 4.
17. 89 FR at 311-12 (noting that “[m]ore than eight in ten Americans get news from digital devices, and, as of 2021, more than half prefer digital platforms to access news”).
18. Id. (citing Newspaper Association of America Comments at 12-18, Submitted in Response to July 15, 2009 Notice of Proposed Rulemaking, Mandatory Deposit of Published Electronic Works Available Only Online, U.S. Copyright Office Dkt. No. 2009-3 (Aug. 31, 2009) (emphasis omitted), https://www.copyright.gov/rulemaking/online-only/comments/naa.pdf ).
19. 37 CFR 202.4(e) . The Office's definition of newspapers is based on the Library of Congress's collection policy definition. Library of Congress, Collections Policy Statements: Newspapers—United States 1 (Sept. 2023), https://www.loc.gov/acq/devpol/neu.pdf .
20. NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 12-13; Gordon Firemark 2 Comment (asserting that “the proposed regulation is not Content Neutral, as required under the First Amendment”).
21. Arkansas Writers Project, 481 U.S. at 234.
22. NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 12-13.
23. Gordon Firemark 2 Comment.
24. Id. (citing Iancu v. Brunetti, 139 S. Ct. 2294 (2019), and Matal v. Tam, 582 U.S. 218 (2017)).
25. Reed v. Town of Gilbert, 576 U.S. 155, 163 (2015).
26. Sable Commc'ns of Cal. v. FCC, 492 U.S. 115, 126 (1989).
27. Reed, 576 U.S. at 164 (internal quotes omitted).
28. Leathers v. Medlock, 499 U.S. 439, 452-53 (1991) (citing Mabee v. White Plains Publ'g Co., 327 U.S. 178 (1946), and Oklahoma Press Publ'g Co. v. Walling, 327 U.S. 186 (1946)).
29. Arkansas Writers Project, 481 U.S. at 229 (finding the tax scheme impermissibly targets a small group of the press because “the magazine exemption means that only a few Arkansas magazines pay any sales tax”).
30. Arkansas Writers Project, 481 U.S. at 229-30.
31. 37 CFR 202.3(b)(2)(i)(A) .
32. See generally id. at 202.4.
33. Vidal v. Elster, No. 22-704, slip op. at 1 (2024).
34. Id.
35. Id. at 4 (2024) (quoting National Institute of Family and Life Advocates v. Becerra, 585 U.S. 755, 766 (2018)).
36. Id. (2024) (quoting Rosenberger v. Rector and Visitors of Univ. of Va., 515 U. S. 819, 829 (1995)).
37. Id. at 6.
38. Id. at 12.
39. 17 U.S.C. 408(c)(1) (emphasis added).
40. Leathers, 499 U.S. at 452 (quoting Regan v. Taxation with Representation, 461 U.S. 540, 549 (1983)).
41. See Gordon Firemark 2 Comment (citing Iancu v. Brunetti, 139 S. Ct. 2294 (2019), and Matal v. Tam, 582 U.S. 218 (2017)).
42. See, e.g., 85 FR 37341 , 37345 (June 22, 2020) (final rule for group registration of short online literary works); 83 FR 61546 , 61546-48 (Nov. 30, 2018) (final rule for group registration of newsletters and serials); 82 FR 29410 , 29410-11 (June 29, 2017) (final rule for group registration of contributions to periodicals).
43. See ABA-IPL Comment at 2; Am. Intell. Prop. L. Ass'n (“AIPLA”) Comment at 1 (“We encourage the Office to reconsider [the definition of `news website'] and clarify the final clause—`not limited to any specific subject matter'—which could be construed as excluding news websites with an industry-specific focus ( e.g., wired.com), and thus unnecessarily limiting access to this group registration option.”); Copyright All. Comment at 4 (“We urge deletion of the phrase `. . . on all subjects and activities and is not limited to any specific subject matter' in the proposed rule . . . .”); Harvard Bus. Publ'g (“HBP”) Comment; Nat'l Ass'n of Broad. (“NAB”) Comment at 3; NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 12-13; NMA Comment at 8; The Authors Guild Comment at 2; see also Letter from Ass'n of Am. Publishers et al. to Suzanne Wilson, Gen. Counsel and Assoc. Register of Copyrights (Apr. 4, 2024).
44. ABA-IPL Comment at 2.
45. HBP Comment.
46. The Authors Guild Comment at 1-2.
47. John Murphy Comment; The Authors Guild Comment at 2 (arguing that “making eligibility determinations based on the substantive content of the materials submitted for registration . . . goes well beyond the Office's ordinary examination process”).
48. Gordon Firemark 1 Comment; see NWU, NPPA, & NASW at 12-13; Brenda Ulrich Comment; John Murphy Comment.
49. 37 CFR 202.4(e)(1) .
50. 82 FR 51369 , 51371 (Nov. 6, 2017).
51. 37 CFR 202.4(f)(1)(i) .
52. Id. at 202.4(e)(1) (“Newspapers are intended either for the general public or for a particular ethnic, cultural, or national group”).
53. The Authors Guild Comment at 1-2.
54. Cf. 37 CFR 202.4(f)(1)(i) (designed for newsletters that “contain news or information that is chiefly of interest to a special group”).
55. Group registration of serials provides a registration option for serial issues within a three-month period that meet the eligibility requirements for that option. Id. at 202.4(d)(1). Group registration of newsletters provides an option for registering a group of newsletters published within a one-month period. Id. at 202.4(f)(1).
56. Copyright All. Comment at 6; NAB Comment at 4; NMA Comment at 10.
57. The Authors Guild Comment at 2; Copyright All. Comment at 6; NAB Comment at 4.
58. U.S. Copyright Office, Compendium of U.S. Copyright Office Practices sec. 722 (3d ed. 2021) (“ Compendium (Third) ”).
59. Id.
60. AIPLA Comment at 1-2.
61. Id.
62. In the NPRM, the Office also noted that when a website is registered as a compilation, the statute provides that the copyright owner may seek only one award of statutory damages for infringement of the compilation as a whole—rather than a separate award for each individual work that appears on the website—even if the defendant infringed all of the works covered by the registration. 17 U.S.C. 504(c)(1) (“For the purposes of this subsection, all the parts of a compilation or derivative work constitute one work.”). Some commenters urged the Office to acknowledge and adopt the “ `independent economic value' test to determine when copyrighted material constitutes a separate `work' for the purpose of determining eligibility for statutory damages.” A2IM, AAP, & RIAA Comment at 2-3; Copyright All. Comment at 8; NAB Comment at 6-8. Acknowledging that the NPRM correctly states “that the group registration option will extend to individual works that make up the collective work if they are fully owned by the applicant,” NMA asked the Office to confirm that its statement “do[es] not reflect a substantive opinion on eligibility for statutory damages.” NMA Comment at 11-12. The Office stands by its restatement of section 504(c)(1) and declines to address the matter further in this rulemaking. See H.R. Rep. No. 94-1476, at 162 (1976), reprinted in 1976 U.S.C.C.A.N. 5659, 5770 (“Subsection (c)(1) makes clear, however, that, although they are regarded as independent works for other purposes, `all the parts of a compilation or derivative work constitute one work' for this purpose.”).
63. NPR Comment at 7.
64. 37 CFR 202.4(m)(1)(i) (emphasis added).
65. Compendium (Third) sec. 1002.2.
66. Id.
67. See 37 CFR 202.1(a) .
68. John Murphy Comment; see NPR Comment at 5 (“[T]he office should further relax the frequency”); NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 16-17.
69. NPR Comment at 5.
70. NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 16.
71. The Authors Guild Comment at 3; NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 11; NMA Comment at 11; AIPLA Comment at 2; Letter from Ass'n of Am. Publishers et al. to Suzanne Wilson, Gen. Counsel and Assoc. Register of Copyrights (Apr. 4, 2024).
72. The Authors Guild Comment at 3; NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 11.
73. NMA Comment at 11; AIPLA Comment at 2 (“[W]e see no clear policy reason to disfavor registration of copyrights acquired through other means ( e.g., by assignment).”).
74. Compendium (Third) sec. 620.4.
75. ABA-IPL Comment at 3; AIPLA Comment at 2; Copyright All. Comment at 6-7; NAB Comment at 5; NMA Comment at 7; The Authors Guild Comment at 4.
76. The Authors Guild Comment at 4.
77. Id.
78. Note, however, the Office will not certify the accuracy of such additional information based on the identifying material deposited.
79. Copyright All. Comment at 7.
80. NMA Comment at 7.
81. 89 FR at 316.
82. Id.
83. Id.
84. NMA Comment at 11.
85. 37 CFR 202.4(m)(6)(i) (emphasis added); see also 89 FR at 316 (“Each PDF must show how the home page appeared at a specific point during each day of the calendar month when new updates were published on the site.”).
86. Copyright Alliance Comment at 10-11; NAB Comment at 4-5; NMA Comment at 11. See also Letter from Ass'n of Am. Publishers et al. to Suzanne Wilson, Gen. Counsel and Assoc. Register of Copyrights at App. at 2 (Apr. 4, 2024) (proposing regulatory language altering the deposit requirement when “a complete copy is technically unfeasible or unreadable due to the size or continuous nature of the home page”); Nexstar Media Group Inc. Comment (stating that Nexstar “would like to see even more modification of the requirements for article submission, so that each local television station or other news site would not be required to have dedicated staff purely for depositing copyrighted materials, which may be updated several times per day”).
87. NAB Comment at 5.
88. Id.
89. Copyright All. Comment at 10-11.
90. NMA Comment at 11.
91. 89 FR at 316.
92. NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 17-20.
93. Id.
94. Id.
95. Id.; see also id. at 20 (proposing “submission of `a file or set of files linked from a master file listing in structured form the text files on the site added or modified during the time period covered by the application, including the URL and the date each file was added to the site or most recently modified' ”).
96. Id. at 17, 20. NWU, NPPA, and NASW asserted that “the `sitemap.xml' standard has been widely accepted and adopted by website publishers, web publishing platforms, and developers of content management systems (CMSs).” Id. at 17-18.
97. See 17 U.S.C. 410(a) ; Compendium (Third) sec. 204.3 (“[D]eposit copy(ies) should be clear and should contain all the authorship that the applicant intends to register.”). This finding is bolstered by the examples cited in NWU, NPPA, and NASW's comment, which do not provide any information that would allow the examiner to determine any copyrightability of the collective work. See NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 18 nn.19-22; id. at 19 nn.23-26.
98. See H.R. Rep. No. 94-1476, at 153 (1976), reprinted in 1976 U.S.C.C.A.N. 5659, 5769 (“As a general rule the deposit of more than a tear sheet or similar fraction of a collective work is needed to identify the contribution properly and to show the form in which it was published.”).
99. 89 FR at 316.
100. See NWU, NPPA, & NASW Comment at 20 (suggesting that sitemaps “could be used immediately in manual Copyright Office work flow but would also lend themselves to efficiencies through automated parsing”).
101. Erik Gottlieb Comment.
102. Copyright All. Comment at 6; NMA Comment at 10; The Authors Guild Comment at 2. See also Letter from Ass'n of Am. Publishers et al. to Suzanne Wilson, Gen. Counsel and Assoc. Register of Copyrights at 1 & App. at 2 (Apr. 4, 2024) (proposing the Office “include[e] mobile app content in the scope of the rule”). The Office also received a comment from Port. Prerogative Club, suggesting that the Office “evaluate whether native [version control systems (“VCS”)] files would satisfy [the Office's] internal requirements for deposit copies.” Port. Prerogative Club Comment at 2. The Office currently does not accept this file format, but will revisit file formats as part of its ongoing work in developing the Enterprise Copyright System.
103. Erik Gottlieb Comment.
104. NMA Comment at App. at 16 (proposing regulatory language). See Copyright All. Comment at 6; NMA Comment at 10; The Authors Guild Comment at 2. See also Letter from Ass'n of Am. Publishers et al. to Suzanne Wilson, Gen. Counsel and Assoc. Register of Copyrights at 1 & App. at 2 (Apr. 4, 2024) (proposing the Office “includ[e] mobile app content in the scope of the rule”).
105. Copyright All. Comment at 6; The Authors Guild Comment at 2.
106. Copyright All. Comment at 6.
107. Id. (noting that “news content on an app is already organized and contained in an interconnected and uniform ecosystem, much like a website”); NMA Comment at 10 (stating that app screenshots serve the same “identifying function as URLs”).
108. NMA Comment at 10.
109. See 89 FR at 313 (“[T]he organization and arrangement show in a PDF package may vary depending on whether it depicts the website as it would appear on a desktop computer, a mobile phone or other electronic device.”). But cf. ABA-IPL Comment at 4 (“The Section is aware of no substantive difference between what is published at a URL and what is published on an app.”).
110. ABA-IPL Comment at 4-5.
111. Id. at 4.
112. UM-Library Comment at 1-2.
113. 89 FR at 313; see also eCO Acceptable File Types, U.S. Copyright Office, https://www.copyright.gov/eco/help-file-types.html (last visited July 5, 2024) (listing acceptable file formats).
114. For example, the Office is researching the web archive file format (“WARC”) that is utilized by the Library of Congress' Web Archiving Team. Research has shown that there are many publicly available options for adapting websites in the WARC format, including through internet browser extensions.
115. 17 U.S.C. 408(c)(1) ; see also 89 FR at 311 (discussing identifying material).
116. H.R. Rep. No. 94-1496, at 154 (1976), reprinted in 1976 U.S.C.C.A.N. 5659, 5770.
117. See 89 FR at 313, 316 (discussing how depositing complete copies of websites poses difficulties for applicants and the Office).
118. Id. at 316.
119. Id.
120. See Letter from Ass'n of Am. Publishers et al. to Suzanne Wilson, Gen. Counsel and Assoc. Register of Copyrights (Apr. 4, 2024); Copyright All. Comment at 11.
121. H.R. Rep. No. 79-1980, at 260 (1946). See 5 U.S.C. 553(d) (30-day notice not required where agency finds good cause).
[ FR Doc. 2024-15880 Filed 7-19-24; 8:45 am]
BILLING CODE 1410-30-P
- Executive Orders
Reader Aids
Information.
- About This Site
- Accessibility
- No Fear Act
- Continuity Information
How to choose research topic?
- Kerala Journal of Psychiatry 33(1)

- Manipal Academy of Higher Education

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Samir Kumar Praharaj

- Steven R Cummings
- Warren S. Browner
- Deborah Grady
- Stephen B. Hulley

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract. Selection of a research topic is a challenge for students and professionals alike. This paper addresses those challenges by presenting some strategies based on existing body of knowledge ...
Microsoft Word - topic.doc. DEVELOPING A RESEARCH TOPIC. Every good research project has a well-defined topic. Selecting and developing a topic is an ongoing process by which you define and refine your ideas. You can then focus your research strategies to find relevant and appropriate information. Before you begin the research process, be sure ...
1. Research Topic Selection - A beginner' s guide. Muhammad Jamaluddin Thaheem, PhD. Senior Lecturer in Construction Management, School of Architecture and Built Environm ent. Deakin ...
Selecting a Research Topic publishing academic research (2010). We provide a framework based on the work of Kuhn in his popular work The Structure of Scientific Revolutions (1962). We also provide points on how to prepare for and select research as a doctoral student. The remainder of this manuscript is format-
Choosing a Research Topic. library.whatcom.edu 360.383.3300. Choosing a Research Topic. Consider several questions to begin gathering information. Start with a broad topic. Do some brainstorming. You can ask yourself questions like: • What am I interested in?
In general, this includes all functions of business. The main areas include marketing, finance, human resources and strategy. Those of you on courses based on specific areas of business, e.g. a BA (Hons) in Marketing, will undoubtedly select a topic that is relevant to marketing. This might include.
Selecting a Suitable Topic T he selection of an appropriate topic is the first major challenge in conducting research. In many academic settings, this task is simplified by working with a faculty mentor who is already familiar with an inter-esting area of study and may even have defined one or more researchable questions.
Break down your research topic into smaller components and observe what categories and subdivisions emerge. Consider the causes and implications of change as well as emerging trends if your research topic is subject to change, such as a politician's career or crime statistics. Place your topic within the perspectives and methods of inquiry ...
PDF | This article provides an explanation of the process for selecting a research topic. The article uses Kuhn's classic work on scientific revolutions... | Find, read and cite all the research ...
Abstract This article provides an explanation of the process for selecting a research topic. The article uses Kuhn's classic work on scientific revolutions to delineate the steps in developing theoretical research within an area. The paper
The Best Topics. Generally speaking, the best choices for research topics have one or more of the following characteristics: Currency (the topic is currently being discussed widely by professionals in the field) Controversy or dispute (the topic lends itself easily to debate or can be argued from a pro and con perspective)
Select a topic. Choosing an interesting research topic is your first challenge. Here are some tips: Choose a topic that you are interested in! The research process is more relevant if you care about your topic. Narrow your topic to something manageable. If your topic is too broad, you will find too much information and not be able to focus.
research paper. You could write a whole book on that topic! "Depictions of Advertising in American Literature of the 1950s" is a more manageable topic to start with. Be flexible Understand that choosing a research topic is a cyclical process. No topic should be set in stone. Be prepared to change your topic as you search for information, read
Abstract. This article provides an explanation of the process for selecting a research topic. The article uses Kuhn's classic work on scientific revolutions to delineate the steps in developing theoretical research within an area. The paper provides methods for preparing to develop a research topic, steps for approaching a research problem ...
Each class or instructor will likely require a different format or style of research project. Use the steps below to guide you through the process of selecting a research topic. Step 1: Brainstorm for ideas Choose a topic that interests you. Use the following questions to help generate topic ideas.
PDF | On Feb 1, 2012, Junaid A Bhatti and others published Selecting a research topic | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
The "Heilmeier Catechism" (Use Google/Bing) Things to Consider. • What do you feel passionate about? • What are your strengths? • Collaboration. • Join a productive group where more senior students mentor new students • Selecting your own problem vs. having a problem handed to you. • Ask other students about faculty - what are ...
Selecting a Research Topic . Chapter Objectives. After completing this chapter, you should be able to: define the term topic and give an example of a topic conceptualized at two levels of specificity name two practical criteria in selecting your own research topic list at least three different kinds of sources of research ideas
Therefore, colleagues should make every effort to explain clearly their approach in selecting their research topic in the manuscript.7 Lastly, colleagues should not hesitate to seek help from those with experience in research methods to strengthen their approach of research topic selection.16 References 1. Ejaz K, Shamim MS, Hussain SA.
Beginner's Guide to Research. Most professors will require the use of academic (AKA peer-reviewed) sources for student writing. This is because these sources, written for academic audiences of specific fields, are helpful for developing your argument on many topics of interest in the academic realm, from history to biology.
beliefs. To prepare oneself for research, especially for identifying a research topic, students. need to have their own ontology, develop the ir own viewpoint, dig holes in the existing. theories ...
You must research, write, edit, format, and proofread your work while keeping your audience and purpose in mind. Sometimes, you may need to generate new content from existing sources, update your content to suit different contexts, organize your content more clearly, or transform your content into different formats or languages.
This fact sheet presents information on children's mental health including assessing your child's behavior, when to seek help, first steps for parents, treatment options, and factors to consider when choosing a mental health professional. It also provides guidance on how to work with your child's school, a list of resources, and information about clinical trials.
Criteria to select a good research topic. June 2019. June 2019. Authors: Syed Yousaf Gilani. University of Lahore. Content uploaded by Syed Yousaf Gilani. Author content. Content may be subject to ...
A regulation can be content-based "on its face," if its text applies to speech based on the subject matter, topic, or viewpoint of that speech. It can also be content-based if it has a discriminatory purpose that "cannot be justified without reference to the content of the regulated speech" or was "adopted by the government because of ...
research is choosing the research topic. Without a good research question, th e. outcome of any research is questionable and. will not have any impact whatsoever. It is. fairly common practice to ...