GKT101: General Knowledge for Teachers – Math

Independent and Dependent Events
Watch this lecture series to see more various examples of calculating probabilities of independent and dependent events. When the outcome of one event depends on the outcome of another, the events are considered dependent. Complete the interactive exercises
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
- Probability
Independent events
Here you will learn about independent events, including what independent events are and how to calculate the probability of independent events occurring.
Students will first learn about independent events as part of statistics and probability in 7 th grade and continue to learn about them in high school.
What are independent events?
Independent events are events whose probability of occurrence is not affected by other events.
For example, if you roll a die twice, the outcome of the first roll and second roll have no effect on each other – they are independent. The chances of rolling a 1, \; 2, \; 3, \; 4, \; 5 or 6 are the same on each roll, as shown in the table.
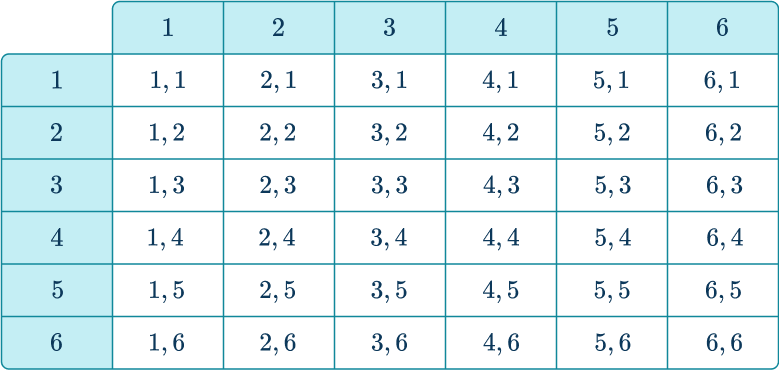
If two events are independent then P(A \text { and } B)=P(A) \times P(B).
This is called the multiplication rule.
Let’s look at an example.
If you are rolling a dice twice, we can find the probability of getting two sixes.
The probability of getting a 6 is \cfrac{1}{6}.
So the probability of getting a 6 and a 6 is \cfrac{1}{6} \times\cfrac{1}{6} = \cfrac{1}{36}.

Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 7 th grade math and 5 th grade math?
- Grade 7 – Statistics and Probability (7.SP.C.8) Find probabilities of compound events using organized lists, tables, tree diagrams, and simulation.
- Statistics and Probability – Conditional Probability and the rules of Probability (HS.S.CP.A.2) Understand that two events A and B are independent if the probability of A and B occurring together is the product of their probabilities, and use this characterization to determine if they are independent.
![homework practice independent and dependent events [FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Probability-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Probability Worksheet (Grade 7 to 12)
Use this quiz to check your grade 7 to 12 students’ understanding of probability. 15+ questions with answers covering a range of 7th to 12th grade probability topics to identify areas of strength and support!
How to calculate the probability of independent events
In order to calculate the probability of independent events:
Confirm that the events are independent.
Identify the probabilities of the events.
Multiply the probabilities.
Independent event examples
Example 1: identifying independent events.
Look at the events below. Which are examples of independent events?
- Rolling a die and getting a 6 and tossing a coin and getting a head.
- Tossing two coins and getting two heads.
- Choosing a green marble from a bag containing blue and yellow marbles and then choosing another green marble from the same bag.
- A student in Mr. Lopez’s class has brown hair and shoe size 6.
The definition of independence is that the events have no effect on each other.
When you roll a die and toss a coin, the outcome of one does not affect the outcome of the other therefore, the events are independent.
When you toss two coins, the outcome of one coin toss does not affect the other therefore, the events are independent.
When you choose a marble from a bag, you are changing the number of marbles in the bag, and therefore, the outcome of choosing the first marble will have an effect on the outcome of the second drawing for the second marble.
For example, if you choose a green marble the first time, the probability of choosing a green marble the second time will decrease. Therefore, these are dependent events.
The color of someone’s hair does not affect the size of their feet therefore, the events are independent.
Example 2: probability of two independent events
The probability that Tom forgets his homework is 0.3. The probability that Noah forgets his homework is 0.1. The events are independent. Calculate the probability that both Tom and Noah forget their homework on the same day.
You are told in the question that the events are independent.
The first event is that Tom forgets his homework. The probability that Tom forgets his homework is 0.3.
The second event is that Noah forgets his homework. The probability that Noah forgets his homework is 0.1.
The probability that Tom and Noah both forget their homework is
0.3 \times 0.1 = 0.03.
Example 3: probability of three independent events
Rachel tosses three fair coins. Find the probability that all three coins land on tails.
The outcome for each coin is not affected by the other coins therefore, the events are independent.
Since the coins are fair, for each coin, the probability that it lands on tails is \cfrac{1}{2}.
The probability of getting three tails is \cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{1}{2} = \cfrac{1}{8}.
Example 4: using a tree diagram
Niamh plays a game of ping pong on Saturday and a game of badminton on Sunday. The different outcomes are represented on the tree diagram below.
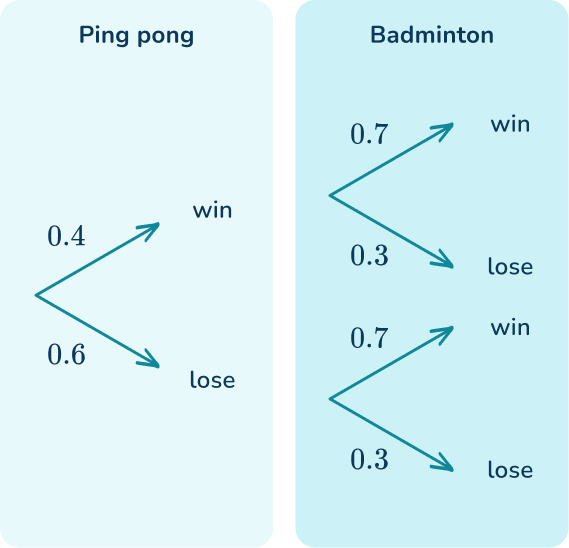
Calculate the probability that Niamh wins both games.
The outcome of one game does not affect the outcome of the other game therefore, the events are independent.
The probability that Niamh wins ping pong is 0.4 and the probability that Niamh wins badminton is 0.7.
The probability that Niamh wins ping pong and badminton is 0.4 \times 0.7=0.28.
Example 5: finding the probability of individual events
Zainab has two bags of mixed candy. She picks one candy from each bag. The probability that Zainab picks a lollipop from the first bag is \cfrac{1}{6} and the probability that she picks a lollipop from both bags is \cfrac{1}{15}. What is the probability that she picks a lollipop from the second bag?
The type of candy that is picked from one bag has no effect on the candy picked from the other bag therefore, the events are independent.
The probability that Zainab picks a lollipop from the first bag is \cfrac{1}{6} and the probability that she picks a lollipop from both bags is \cfrac{1}{15}.
If you call the probability of picking a lollipop from the second bag P(L) then \cfrac{1}{6} \times \text{P(L)}=\cfrac{1}{15}.
Solving this:
Example 6: finding the probability of individual events
Rosie flips a biased coin twice. The probability that Rosie gets two heads is 0.64. Find the probability that Rosie gets a head on a single coin flip.
The results of the first coin flip will not affect the second coin flip, so the events are independent.
Here, you only know that the probability that Rosie gets two heads is 0.64.
If you call the probability that Rosie gets a head P(H) then,
P(H) \times P(H)=0.64
The probability of getting a head on a single coin flip is 0.8.
Teaching tips for independent events
- Let students experience independent events in the classroom, but using examples that involve dice, coins, cards, marbles and other commonly found objects.
- Have students explore the sample spaces of independent events before introducing the rule. Many students will figure out the multiplication rule without being told. And even if they don’t, they will have more than one strategy to utilize when solving.
Easy mistakes to make
- Multiplying or dividing fractions incorrectly To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators and multiply the denominators. To divide fractions, find the reciprocal of the second fraction and multiply.
- Adding probabilities instead of multiplying them For independent events P(A \text { and } B)=P(A) \times P(B). For mutually exclusive events P(A \text { or } B)=P(A) + P(B).
Related probability lessons
- Probability notation
- How to find probability
- How to calculate probability
- Probability formula
- Mutually exclusive events
- Probability scale
- Conditional probability
- Venn diagram
Practice independent events questions
1. Identify the pair of events that are not independent.
Rolling two dice and each landing on 6.

Rain falling on 20 th December 2020 and 20 th December 2021.
Flipping a coin and landing on tails and picking a king from a deck of cards.
Picking one card from a deck of cards and then a second card and getting an ace both times.

If you choose one card from a deck of cards, you are changing the number of cards left and therefore the probabilities of each outcome for the next draw.
Picking the first card followed by a second card from a deck of cards are not independent events.
2. Events A and B are shown below.
Event A – rolling a die and landing on an even number.
Event B – picking a diamond from a deck of cards.
Felicity rolls a die and picks a card from a deck of cards. Find the probability of both events A and B occurring.
The events are independent, because one outcome does not affect the other.
The probability of a die landing on an even number is \cfrac{1}{2}.
The probability of picking a diamond from a deck of cards is \cfrac{1}{4}.
The probability of events A and B both occurring is \cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{1}{4} = \cfrac{1}{8}.
3. The probability that my train is late on any given day is 0.3. Find the probability that my train is late three days in a row.
The probability that the train is late on any one day is 0.3.
The probability that the train is late on day 1 and day 2 and day 3 is 0.3 \times 0.3 \times 0.3 = 0.027.
4. Sam has different options for her lunch. The probabilities of her choosing the different options are shown below.
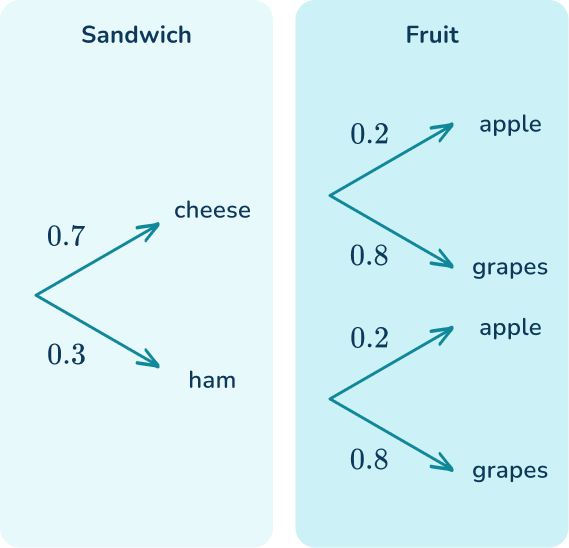
Find the probability that Sam chooses a cheese sandwich and grapes.
The probability that Sam chooses a cheese sandwich is 0.7 and the probability that Sam chooses grapes is 0.8.
The probability that Sam chooses a cheese sandwich and grapes is 0.7 \times 0.8=0.56.
5. Sheila and Pete are playing darts. The probability that Sheila hits a bullseye is 0.1 and the probability that they both hit a bullseye is 0.02. Find the probability that Pete hits a bullseye.
If you call the probability that Pete hits a bullseye P(P) then
6. Marwa rolls a biased die twice. The probability that she gets two sixes is \cfrac{4}{25}.
Find the probability that Marwa rolls a six on any one roll.
If you call the probability of rolling a six P(6) then
Independent events FAQs
The sample space is the set of all possible outcomes in a probability experiment.
This is conditional probability and there are various theorems and formulas for calculating, depending on the circumstances.
The next lessons are
- Compound events
- Probability distribution
- Units of measurement
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs .
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!

Privacy Overview
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Statistics
Course: ap®︎/college statistics > unit 7, conditional probability and independence.
- Conditional probability with Bayes' Theorem
- Conditional probability using two-way tables
- Calculate conditional probability
- Conditional probability tree diagram example
- Tree diagrams and conditional probability
Example 1: Income and universities
| Annual income | University A | University B | TOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under $20,000 | | | |
| $20,000 to 39,999 | | | |
| $40,000 and over | | | |
| | | |
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
- a proper fraction, like 1 / 2 or 6 / 10
- (Choice A) Yes A Yes
- (Choice B) No B No
Example 2: Income and universities (continued)
What if the probabilities are close, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Lesson Independent and Dependent Events
Independent and Dependent Events Worksheets
The independent and dependent events worksheets will help students memorize and capture real-life situations faster. Want to improve your grasp on probability? The Independent and dependent Events Worksheets are the best resource for students. Students will hone their memorization skills and grasping skills with the help of ve diagrams and fractions .
Benefits of Independent and Dependent Events Worksheets
These handy and fun worksheets will introduce students to basic mathematical logic and teach them the process of independent events as well. With the help of the guide provided in the worksheets, students can solve their doubts and go onto complex topics.
Read More:- Topic-wise Math Worksheets
Download Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet PDFs
Students can download the pdf format of worksheets to practice some fun and exciting questions for free.
| Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet - 1 |
|
| Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet - 2 |
|
| Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet - 3 |
|
| Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet - 4 |
|
Dependent Events
Analysis: The probability that the first card is a queen is 4 out of 52. However, if the first card is not replaced, then the second card is chosen from only 51 cards. Accordingly, the probability that the second card is a jack given that the first card is a queen is 4 out of 51.
Conclusion: The outcome of choosing the first card has affected the outcome of choosing the second card, making these events dependent.
Definition: Two events are dependent if the outcome or occurrence of the first affects the outcome or occurrence of the second so that the probability is changed.
Now that we have accounted for the fact that there is no replacement, we can find the probability of the dependent events in Experiment 1 by multiplying the probabilities of each event.
Probabilities:
| P(queen on first pick) | = | |||||||
| 52 | ||||||||
| P(jack on 2nd pick given queen on 1st pick) | = | |||||||
| 51 | ||||||||
| P(queen and jack) | = | = | = | |||||
| 52 | 51 | 2652 | 663 | |||||
Experiment 1 involved two compound, dependent events. The probability of choosing a jack on the second pick given that a queen was chosen on the first pick is called a conditional probability .
The conditional probability of an event B in relationship to an event A is the probability that event B occurs given that event A has already occurred. The notation for conditional probability is P(B|A) [pronounced as The probability of event B given A ].
The notation used above does not mean that B is divided by A. It means the probability of event B given that event A has already occurred . To find the probability of the two dependent events, we use a modified version of Multiplication Rule 1 , which was presented in the last lesson.
Multiplication Rule 2: When two events, A and B, are dependent, the probability of both occurring is:
P(A and B) = P(A) · P(B|A)
Let’s look at some experiments in which we can apply this rule.
Probabilities P(Girl 1 and Girl 2) = P(Girl 1) and P(Girl 2|Girl 1)
| = | ||||
| 30 | 29 | |||
| = | ||||
| 870 | ||||
| = | ||||
| 145 | ||||
Probabilities: P(3 defectives) =
| = | = | |||||||
| 20 | 19 | 18 | 6840 | 1140 |
Probabilities: P(10 and 9 and 8 and 7) =
| = | = | |||||||||
| 52 | 51 | 50 | 49 | 6,497,400 | 812,175 |
Probabilities: P(3 aces) =
| = | = | |||||||
| 52 | 51 | 50 | 132,600 | 5,525 |
Summary: Two events are dependent if the outcome or occurrence of the first affects the outcome or occurrence of the second so that the probability is changed. The conditional probability of an event B in relationship to an event A is the probability that event B occurs given that event A has already occurred. The notation for conditional probability is P(B|A). When two events, A and B, are dependent, the probability of both occurring is: P(A and B) = P(A) · P(B|A)
Directions: Read each question below. Select your answer by clicking on its button. Feedback to your answer is provided in the RESULTS BOX. If you make a mistake, choose a different button.
|
RESULTS BOX: |
- Skills by Standard
- Skills by Grade
- Skills by Category
Go to profile
- Assignments
- Assessments
- Report Cards
- Our Teachers
Remove ads and gain access to the arcade and premium games!
Unlock harder levels by getting an average of 80% or higher.
Earn up to 5 stars for each level The more questions you answer correctly, the more stars you'll unlock!
Each game has 10 questions. Green box means correct. Yellow box means incorrect.
Need some help or instruction on how to do this skill?
Want a paper copy? Print a generated PDF for this skill.
Share MathGames with your students, and track their progress.
See how you scored compared to other students from around the world.
Learn Math Together.
Grade 7 - Statistics & Probability
Standard 7.SP.C.8a - Calculte the probability of independent and dependent events.
Included Skills:
Understand that, just as with simple events, the probability of a compound event is the fraction of outcomes in the sample space for which the compound event occurs.
If you notice any problems, please let us know .

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
- Inspiration
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Formative Assessment: Everything You Need to Know
How to replace a macbook pro battery, writing and differentiated instruction: everything you need to know, improving language proficiency and scientific literacy in learners, how to teach spelling: everything you need to know, product review of ticktalk 5, product review of the grid duffle backpack, product review of naturopathica’s active body bundle, the benefits of differentiated instruction: everything you need to know, teaching children inferential thinking: everything you need to know, activities to teach students to identify independent and dependent events.

As a teacher, it is essential to help your students understand the concepts of independent and dependent events. Independent events are those that are not influenced by other events, whereas dependent events are those that are affected by the outcome of another event. This concept is crucial in probability, and it is important that students understand it thoroughly. Here are some activities that you can use to help teach students to identify independent and dependent events.
1. Probability Darts Game
This activity involves using a dartboard and individual darts with different probabilities written on them. The students are divided into groups, and they take turns throwing their darts at the board. Before each throw, the students predict which number they will hit. The teacher then discusses whether the events are independent or dependent. For instance, if a student aims for a section that is already occupied by another dart, the outcome of that throw is dependent on the previous throw. If the student aims for an open section, then the event is independent.
2. The Probability Walk
This activity involves assigning probabilities to different outcomes of an experiment. The teacher takes the students for a walk and conducts a probability experiment at each stop. For example, at one stop, the teacher may flip a coin, and the students predict whether it lands on heads or tails. At another stop, the teacher may ask the students to predict the color of the next car that passes by. After each experiment, the teacher discusses whether the events are independent or dependent.
3. The Game of Rock-Paper-Scissors
This game is a classic probability activity that can be used to teach students about independent and dependent events. The students pair up and play several rounds of rock-paper-scissors. The teacher then asks the students to determine whether the outcome of each round is independent or dependent. For instance, if a student wins a round, their next move may be influenced by their previous success, making the events dependent.
4. Probability Bubbles
This activity involves filling a bowl with water and soap bubbles. The students blow bubbles and predict which bubble will burst first. The teacher then asks the students to determine whether the events are independent or dependent. For example, if one student blows a large bubble that pops, it may cause smaller bubbles to pop as well, making the events dependent.
5. The Game of Heads or Tails
This game requires a coin and a partner. One student flips the coin and calls out heads or tails. The other student predicts whether the coin lands on the called side. The teacher then discusses whether the events are independent or dependent. If one student gets several correct answers in a row, the outcome of the next flip may be influenced by their previous successes or failures, making the events dependent.
In conclusion, these activities are a great way to help students understand independent and dependent events. By using real-life scenarios and games, you can make the lessons more interactive, fun, and engaging. With practice, students will be able to identify independent and dependent events confidently, which will help them in their future probability studies.
Activities to Teach Students to Identify Independent ...
Activities to teach students to identify linear ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.

15 Nature Webcams for Science Learning at a Distance

15 Spooky and Educational Halloween Videos for Kids

15 Cool Ways To Use Plastic Easter Eggs for Learning

9 Templates for Responding to Tricky Parent Emails

8 Ways to Get Middle School Students to Care About Their Grades

7 Ways Audiobooks Benefit Students Who Struggle with Reading
- Notifications 0

- Add Friend ($5)

As a registered member you can:
- View all solutions for free
- Request more in-depth explanations for free
- Ask our tutors any math-related question for free
- Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free
- Grade 7 McGraw Hill Glencoe - Answer Keys
|
| ||
| P(tails and 3) | ||

Explanation:
P(heads and odd)
Cards labeled 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are in a stack. A card is drawn and not replaced. Then, a second card is drawn at random. Find the probability of drawing two even numbers.
Building on the Essential Question Explain the difference between independent events and dependent events.
- Type below:
Yes, email page to my online tutor. ( if you didn't add a tutor yet, you can add one here )
Thank you for doing your homework!
Submit Your Question

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
you got your answer. 13+13+13+13=52. Probability of drawing a spade=13/52. Simplify 13/52=1/4. 1/4 x 1/4 = 1/16. Using the letters in the word FABRIC, find the number of permutations that can be formed using 2 letters at a time. Show your work or explain how you got your. answer. 6 letters in the word FABRIC.
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Probability of Independent Score (__/__) and Dependent Events Worksheet Practice Directions: Solve the following problems on probability of independent and dependent events. Round decimals to the nearest tenths. Make sure to bubble in your answers below on each page so that you can check your work. Show all of your work! 2 What is the ...
dependent. The 232 members of the freshman class all vote by secret ballot for the class representative to the Student Senate. independent. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like selecting members for a team, tossing a penny, rolling a die, then tossing a dime, deciding the order in which to complete your homework ...
The events are independent. P (red then blue) = P (red) • P (blue) = 3/12 • 5/12 = 15/144 = 5/48. When you toss a coin, the probability of getting a head is 1 out of 2 or ½. If you toss the coin again, the probability of getting a head is still 1 out of 2 or ½. If you toss a coin 10 times and get a head each time, you may think that your ...
Independent and Dependent Events. Watch this lecture series to see more various examples of calculating probabilities of independent and dependent events. When the outcome of one event depends on the outcome of another, the events are considered dependent. Complete the interactive exercises.
Terms in this set (5) Independent Events. The outcome of one event does not affect the outcome of the second event. Probability of Independent Events. If A and B are independent events, then P (A and B) = P (A) × P (B) Dependent Events. if the occurrence of an event does affect how another event occurs. Conditional Probability.
Flipping a coin and landing on tails and picking a king from a deck of cards. Picking one card from a deck of cards and then a second card and getting an ace both times. 2. Events A A and B B are shown below. Event A A - rolling a die and landing on an even number. Event B B - picking a diamond from a deck of cards.
What is conditional probability and how does it relate to independence? Learn how to use formulas and tables to calculate conditional probabilities and check if two events are independent. Khan Academy is a free online learning platform that covers various topics in math, science, and more.
1,2,3,4,5,6 = 1,3,5 = 3 out of 6, or 3/6, which can be reduced to 1/2. Dependent Event: One event affects outcome of second event. Example: Pick a flower from a garden. Then pick another flower from the same garden. Picking the first flower affects the possible outcomes of picking the second flower. Independent Event: When an outcome of one ...
Download Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet PDFs. Students can download the pdf format of worksheets to practice some fun and exciting questions for free. Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet - 1. Download PDF. Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet - 2. Download PDF. Independent and Dependent Events Worksheet - 3. Download PDF.
Homework and Practice 10-5 Probability of Independent and Dependent Events Decide if each set of events is independent or dependent. Explain your answer. 1. Cora tosses a number cube. Then she spins a spinner. 2. Kevin chooses a book for a book report from a list of titles. Hiroshi chooses a book for a book report from the remaining titles. 3.
If the two events are independent, find the probabilities: P P ( Jane will make both connections) P P (Jane will make at least one connection) For a three-child family, let the events E E, F F, and G G be as follows. E E: The family has at least one boy. F F: The family has children of both sexes.
Experiment 1 involved two compound, dependent events. The probability of choosing a jack on the second pick given that a queen was chosen on the first pick is called a conditional probability.. The conditional probability of an event B in relationship to an event A is the probability that event B occurs given that event A has already occurred.The notation for conditional probability is P(B|A ...
Grade 7 - Statistics & Probability. Standard 7.SP.C.8a - Calculte the probability of independent and dependent events. Included Skills: Understand that, just as with simple events, the probability of a compound event is the fraction of outcomes in the sample space for which the compound event occurs. If you notice any problems, please let us know.
When two events A and B are dependent, P(A, then B) = P(A) x P(B following A) 4. There are 4 oranges, 7 bananas, and 5 apples in a fruit basket. Tony selects a piece of fruit and then Terrance selects a piece of fruit. a. Find the probability that 2 apples are chosen. P(first piece is an apple) = P(second piece is an apple) = P(2 apples) = b.
Example 1: One of the most common carnival games is rolling dice. The objective is to roll the dice and land on a specific number. For this example, the player must roll a 5. Sounds simple to do ...
Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free; ... Independent and Dependent Events. Please share this page with your friends on FaceBook. Independent Practice. A number cube is rolled and a marble is selected at random from the bag below. Find each probability. Show your work. ... Math Practice 101 ...
Lesson 7 Homework Practice Independent and Dependent Events The two spinners at the right are spun. Find each probability. 1. P(4 and C) 2. P(1 and A) 3. P(even and C) 4. P(odd and A) 5. P(greater than 3 and B) 6. P(less than 5 and B) GAMES There are 10 yellow, 6 green, 9 orange, and 5 red cards in a stack of cards turned facedown.
Lesson 7 Homework Practice Independent and Dependent Events - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
sec. SmartScore. out of 100. IXL's SmartScore is a dynamic measure of progress towards mastery, rather than a percentage grade. It tracks your skill level as you tackle progressively more difficult questions. Consistently answer questions correctly to reach excellence (90), or conquer the Challenge Zone to achieve mastery (100)!
3. The Game of Rock-Paper-Scissors. This game is a classic probability activity that can be used to teach students about independent and dependent events. The students pair up and play several rounds of rock-paper-scissors. The teacher then asks the students to determine whether the outcome of each round is independent or dependent.
Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free; ... Guided Practice. A penny is tossed and a number cube is rolled. Find each probability. ... Building on the Essential Question Explain the difference between independent events and dependent events. Type below: (show solution) Yes, email page to my online tutor. ...