

Literature reviews
- Introduction
Why write a literature review?
What is a literature review, how do i get started, searching for sources.
- Undertaking your literature review
- Developing your literature review
- Writing systematic reviews
Useful links for literature reviews
- Study Advice Helping students to achieve study success with guides, video tutorials, seminars and one-to-one advice sessions.
- Doing your literature review (video) Watch this brief video tutorial for more on the topic.
- Doing your literature review (transcript) Read along while watching the video tutorial.
- Literature searching guide A guide to finding articles, books and other materials on your subject
- Doing your literature search video - University of Reading Brief video on literature searching from our Academic Liaison Librarians.
- Royal Literary Fund: Writing a Literature Review A guide to writing literature reviews from the Royal Literary Fund
- What it means to be a critical student A brief and very useful video tutorial from the University of Leicester.
- Reading and notemaking LibGuide Expert guidance on managing your reading and making effective notes.
- Dissertations and major projects LibGuide Expert guidance on planning, researching and writing dissertations and major projects.
Before getting started on sourcing and reviewing the background literature for a research project, it is important to understand the role that a literature review plays in the research process, and how it can be helpful later on for placing your own findings in context. Knowing the job that a literature review does means you can be more targeted and systematic in your literature searching. The guidance on this page will explain what you need to know about the purpose of a literature review and how to begin scoping your search.
New discoveries don't materialise out of nowhere; they build upon the findings of previous experiments and investigations. A literature review shows how the investigation you are conducting fits with what has gone before and puts it into context.
If you are doing a thesis, dissertation, or a long report it is likely that you will need to include a literature review. If you are doing a lab write-up or a shorter report, some background reading may be required to give context to your work, but this is usually included as an analysis in the introduction and discussion sections.
A literature review is a select analysis of existing research which is relevant to your topic, showing how it relates to your investigation. It explains and justifies how your investigation may help answer some of the questions or gaps in this area of research.
A literature review is not a straightforward summary of everything you have read on the topic and it is not a chronological description of what was discovered in your field.
A longer literature review may have headings to help group the relevant research into themes or topics. This gives a focus to your analysis, as you can group similar studies together and compare and contrast their approaches, any weaknesses or strengths in their methods, and their findings.
One common way to approach a literature review is to start out broad and then become more specific . Think of it as an inverted triangle:

- First briefly explain the broad issues related to your investigation; you don't need to write much about this, just demonstrate that you are aware of the breadth of your subject.
- Then narrow your focus to deal with the studies that overlap with your research.
- Finally, hone in on any research which is directly related to your specific investigation. Proportionally you spend most time discussing those studies which have most direct relevance to your research.

- What research has already been done on this topic?
- What are the sub-areas of the topic you need to explore?
- What other research (perhaps not directly on the topic) might be relevant to your investigation?
- How do these sub-topics and other research overlap with your investigation?
Note down all your initial thoughts on the topic. You can use a spidergram or list to help you identify the areas you want to investigate further. It is important to do this before you start reading so that you don't waste time on unfocussed and irrelevant reading.
It's easy to think that the best way to search for texts is to use the Internet - to 'Google it'. There are useful online tools that you may use, like Google Scholar. However, for most literature reviews you will need to focus on academically authoritative texts like academic books, journals, research reports, government publications. Searching Google will give you thousands of hits, few of them authoritative, and you will waste time sorting through them.
A better idea is to use databases. These are available through the Library in paper and electronic (usually online) forms.
Use journal articles: They normally have the most up-to-date research and you will be expected to refer to them in your literature review. The Library has a guide on finding journal articles.
The Library also has an Academic Liaison Librarian for each subject and guides to finding information in your subject.
You may find review articles that survey developments in your field. These are very useful for identifying relevant sources - but do go back to the original texts and develop your own critical analysis if possible.
Another good way to find sources is to look at the reference lists in articles or books already identified as relevant to your topic. You will be expected to prioritise recent research, but it's also important to acknowledge the standard texts in your field. An easy way to identify these is to check reference lists to see which texts are frequently cited.
- Finding journal articles A guide from the Library about how to find articles for your research.
- Literature searching Includes tips on planning and conducting an effective search for literature using techniques such as search operators (AND/OR), truncation and wildcards.
- Doing your literature search - University of Reading Short video tutorial on literature searching from the Library.
- Subject guides Guides to specialist resources in subjects studied at the University.
- Keeping up-to-date (Library) Library guide to keeping up to date with new publications in your subject.
- Contact your Academic Liaison Librarian
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Undertaking your literature review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 10:25 AM
- URL: https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/literaturereview
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Literature review

How to write a literature review in 6 steps
How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.

How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]
How do you write a systematic literature review? What types of systematic literature reviews exist and where do you use them? Learn everything you need to know about a systematic literature review in this guide

What is a literature review? [with examples]
Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.
The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window
What Will You Do Differently?
Please help your librarians by filling out this two-minute survey of today's class session..
Professor, this one's for you .
Introduction
Literature reviews take time. here is some general information to know before you start. .
- VIDEO -- This video is a great overview of the entire process. (2020; North Carolina State University Libraries) --The transcript is included --This is for everyone; ignore the mention of "graduate students" --9.5 minutes, and every second is important
- OVERVIEW -- Read this page from Purdue's OWL. It's not long, and gives some tips to fill in what you just learned from the video.
- NOT A RESEARCH ARTICLE -- A literature review follows a different style, format, and structure from a research article.
Steps to Completing a Literature Review

- Next: Find >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade, paperpal’s new ai research finder empowers authors to....
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
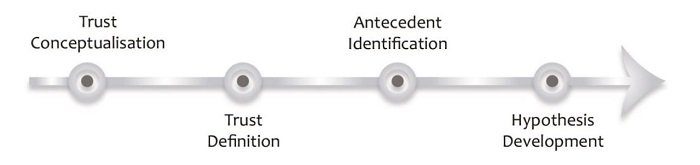
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Getting Started on Your Literature Review
Here you can find a short guide and a few suggestions for higher degree research candidates on how to get started on a literature review.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an examination of the research that has been conducted in a particular field of study.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
- To demonstrate your scholarly ability to identify relevant information and to outline existing knowledge.
- To identify the ‘gap’ in the research that your work is attempting to address, positioning your work in the context of previous research and creating a space for your work.
- To evaluate and synthesise the information in line with the concepts that you have set yourself for the research.
- To produce a rationale or justification for your study.
Getting Started
- Identify your research question(s). This is essential in helping you direct and frame your reading.
- Identify and locate appropriate information. Generate some keywords and undertake topic searches.
- Contact the Library at UNSW and book a Research Consultation with the UNSW library ( this can be done online here )
However, remember that the literature review needs to relate to and explain your research question. Although there may seem to be hundreds of sources of information that appear pertinent, once you have your question you will be able to refine and narrow down the scope of your reading.
- Take notes of not only the information that you read, but also your thoughts about this information. This will help you draw your ideas together when you start writing.
- File and store your readings and notes. Use an effective method that lets you retrieve information quickly and easily.
- Plan, organise and write critically about the literature that you have located. You will need to establish which literature is most pertinent to your review and be able to synthesise and critique the relevant materials. Don’t underestimate the planning stage. Having a sense of the overall organisation of your literature review may help expedite the process.

How could I write my literature review?
When writing your literature review, it is important to keep in mind that it will only be completed when your thesis is almost completed, because new research is always being produced and published. At some stage you will have to be satisfied with what you have and leave it at that; however, throughout your thesis you will be continually adding to your review and will probably rewrite it a number of times.
It is invaluable to read the literature reviews in other theses. These will provide possible structural models for your own literature review. The UNSW library has many theses available on-line, so it is easy to locate examples of current theses in your area of research. Check out the UNSW library website and UNSWorks. Another useful strategy is to examine how literature reviews are undertaken in journal articles, although these are generally much shorter.
It is important that your literature review has a logical and coherent structure, and that this structure is clearly apparent to the reader. It is a good idea to let your readers know exactly how the review is organised. Although the suggestions (below) are commonly used in structuring the literature in a review, these methods are by no means the only ways of organising material. Remember that that the way you choose to organise your review will largely depend upon the type of information that you have gathered. Also remember that some literature reviews use a combination of structural approaches.
Possible ways of structuring a literature review
Chronological organisation.
The discussion of the research /articles is ordered according to an historical or developmental context.
The 'Classic' studies organisation
A discussion or outline of the major writings regarded as significant in your area of study. (Remember that in nearly all research there are 'benchmark' studies or articles that should be acknowledged).
Topical or thematic organisation
The research is divided into sections representing the categories or conceptual subjects for your topic. The discussion is organised into these categories or subjects.
Inverted pyramid organisatio n
The literature review begins with a discussion of the related literature from a broad perspective. It then deals with more and more specific or localised studies which focus increasingly on the specific question at hand.
Discussing and evaluating the literature
Critically examine the literature.
The literature review needs to critically examine the texts that relate to your research question, rather than to just list what you have located. Therefore, you must link the literature to your research question, demonstrating how it supports or extends the topic or the existing knowledge in the area.
You should also highlight the strengths, weaknesses and omissions of the literature, providing a critique of the research. Hence, the language used in a literature review is often evaluative and demonstrates your perspectives of the literature in relation to your question.
Make your 'voice' clear
Your 'voice', that is, your perspective, position or standpoint, should be clearly identifiable in the literature review, as in the thesis as a whole. However, in the literature review because you are writing about other people's work it is easy for your own 'voice' to be lost. The literature review then reads like a mixture of different tones and arguments.
It is important that, firstly, your theoretical position is clearly and strongly stated and that your critical evaluations are an integral part of this. Secondly, it is important that your language indicates your own or other writers' attitudes to the question or issue. Some ways of using language to do this are outlined in the Text Sample on the next page.
See next: Sample review text
Postgrad research.
- Academic skills support
- Thesis proposals
- Sample literature review
Scholarly Resources 4 Students | scite.ai 21 May 2024
Discover your Library: Main Library 21 May 2024
- UConn Library
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide
- Introduction
Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide — Introduction
- Getting Started
- How to Pick a Topic
- Strategies to Find Sources
- Evaluating Sources & Lit. Reviews
- Tips for Writing Literature Reviews
- Writing Literature Review: Useful Sites
- Citation Resources
- Other Academic Writings
What are Literature Reviews?
So, what is a literature review? "A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries." Taylor, D. The literature review: A few tips on conducting it . University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
Goals of Literature Reviews
What are the goals of creating a Literature Review? A literature could be written to accomplish different aims:
- To develop a theory or evaluate an existing theory
- To summarize the historical or existing state of a research topic
- Identify a problem in a field of research
Baumeister, R. F., & Leary, M. R. (1997). Writing narrative literature reviews . Review of General Psychology , 1 (3), 311-320.
What kinds of sources require a Literature Review?
- A research paper assigned in a course
- A thesis or dissertation
- A grant proposal
- An article intended for publication in a journal
All these instances require you to collect what has been written about your research topic so that you can demonstrate how your own research sheds new light on the topic.
Types of Literature Reviews
What kinds of literature reviews are written?
Narrative review: The purpose of this type of review is to describe the current state of the research on a specific topic/research and to offer a critical analysis of the literature reviewed. Studies are grouped by research/theoretical categories, and themes and trends, strengths and weakness, and gaps are identified. The review ends with a conclusion section which summarizes the findings regarding the state of the research of the specific study, the gaps identify and if applicable, explains how the author's research will address gaps identify in the review and expand the knowledge on the topic reviewed.
- Example : Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398
Systematic review : "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139). Nelson, L. K. (2013). Research in Communication Sciences and Disorders . Plural Publishing.
- Example : The effect of leave policies on increasing fertility: a systematic review: 10.1057/s41599-022-01270-w
Meta-analysis : "Meta-analysis is a method of reviewing research findings in a quantitative fashion by transforming the data from individual studies into what is called an effect size and then pooling and analyzing this information. The basic goal in meta-analysis is to explain why different outcomes have occurred in different studies." (p. 197). Roberts, M. C., & Ilardi, S. S. (2003). Handbook of Research Methods in Clinical Psychology . Blackwell Publishing.
- Example : Employment Instability and Fertility in Europe: A Meta-Analysis: 10.1215/00703370-9164737
Meta-synthesis : "Qualitative meta-synthesis is a type of qualitative study that uses as data the findings from other qualitative studies linked by the same or related topic." (p.312). Zimmer, L. (2006). Qualitative meta-synthesis: A question of dialoguing with texts . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 53 (3), 311-318.
- Example : Women’s perspectives on career successes and barriers: A qualitative meta-synthesis: 10.1177/05390184221113735
Literature Reviews in the Health Sciences
- UConn Health subject guide on systematic reviews Explanation of the different review types used in health sciences literature as well as tools to help you find the right review type
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: How to Pick a Topic >>
- Last Updated: Sep 21, 2022 2:16 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/literaturereview
How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)
The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader’s guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide step-by-step guidance on how to craft your own, along with examples.
Why you need an introduction for a literature review
When you need an introduction for a literature review, what to include in a literature review introduction, examples of literature review introductions, steps to write your own literature review introduction.
A literature review is a comprehensive examination of the international academic literature concerning a particular topic. It involves summarizing published works, theories, and concepts while also highlighting gaps and offering critical reflections.
In academic writing , the introduction for a literature review is an indispensable component. Effective academic writing requires proper paragraph structuring to guide your reader through your argumentation. This includes providing an introduction to your literature review.
It is imperative to remember that you should never start sharing your findings abruptly. Even if there isn’t a dedicated introduction section .
Instead, you should always offer some form of introduction to orient the reader and clarify what they can expect.
There are three main scenarios in which you need an introduction for a literature review:
- Academic literature review papers: When your literature review constitutes the entirety of an academic review paper, a more substantial introduction is necessary. This introduction should resemble the standard introduction found in regular academic papers.
- Literature review section in an academic paper or essay: While this section tends to be brief, it’s important to precede the detailed literature review with a few introductory sentences. This helps orient the reader before delving into the literature itself.
- Literature review chapter or section in your thesis/dissertation: Every thesis and dissertation includes a literature review component, which also requires a concise introduction to set the stage for the subsequent review.
You may also like: How to write a fantastic thesis introduction (+15 examples)
It is crucial to customize the content and depth of your literature review introduction according to the specific format of your academic work.
In practical terms, this implies, for instance, that the introduction in an academic literature review paper, especially one derived from a systematic literature review , is quite comprehensive. Particularly compared to the rather brief one or two introductory sentences that are often found at the beginning of a literature review section in a standard academic paper. The introduction to the literature review chapter in a thesis or dissertation again adheres to different standards.
Here’s a structured breakdown based on length and the necessary information:
Academic literature review paper
The introduction of an academic literature review paper, which does not rely on empirical data, often necessitates a more extensive introduction than the brief literature review introductions typically found in empirical papers. It should encompass:
- The research problem: Clearly articulate the problem or question that your literature review aims to address.
- The research gap: Highlight the existing gaps, limitations, or unresolved aspects within the current body of literature related to the research problem.
- The research relevance: Explain why the chosen research problem and its subsequent investigation through a literature review are significant and relevant in your academic field.
- The literature review method: If applicable, describe the methodology employed in your literature review, especially if it is a systematic review or follows a specific research framework.
- The main findings or insights of the literature review: Summarize the key discoveries, insights, or trends that have emerged from your comprehensive review of the literature.
- The main argument of the literature review: Conclude the introduction by outlining the primary argument or statement that your literature review will substantiate, linking it to the research problem and relevance you’ve established.
- Preview of the literature review’s structure: Offer a glimpse into the organization of the literature review paper, acting as a guide for the reader. This overview outlines the subsequent sections of the paper and provides an understanding of what to anticipate.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will provide a clear and structured overview of what readers can expect in your literature review paper.
Regular literature review section in an academic article or essay
Most academic articles or essays incorporate regular literature review sections, often placed after the introduction. These sections serve to establish a scholarly basis for the research or discussion within the paper.
In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction. It should encompass:
- An introduction to the topic: When delving into the academic literature on a specific topic, it’s important to provide a smooth transition that aids the reader in comprehending why certain aspects will be discussed within your literature review.
- The core argument: While literature review sections primarily synthesize the work of other scholars, they should consistently connect to your central argument. This central argument serves as the crux of your message or the key takeaway you want your readers to retain. By positioning it at the outset of the literature review section and systematically substantiating it with evidence, you not only enhance reader comprehension but also elevate overall readability. This primary argument can typically be distilled into 1-2 succinct sentences.
In some cases, you might include:
- Methodology: Details about the methodology used, but only if your literature review employed a specialized method. If your approach involved a broader overview without a systematic methodology, you can omit this section, thereby conserving word count.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will effectively integrate your literature review into the broader context of your academic paper or essay. This will, in turn, assist your reader in seamlessly following your overarching line of argumentation.
Introduction to a literature review chapter in thesis or dissertation
The literature review typically constitutes a distinct chapter within a thesis or dissertation. Often, it is Chapter 2 of a thesis or dissertation.
Some students choose to incorporate a brief introductory section at the beginning of each chapter, including the literature review chapter. Alternatively, others opt to seamlessly integrate the introduction into the initial sentences of the literature review itself. Both approaches are acceptable, provided that you incorporate the following elements:
- Purpose of the literature review and its relevance to the thesis/dissertation research: Explain the broader objectives of the literature review within the context of your research and how it contributes to your thesis or dissertation. Essentially, you’re telling the reader why this literature review is important and how it fits into the larger scope of your academic work.
- Primary argument: Succinctly communicate what you aim to prove, explain, or explore through the review of existing literature. This statement helps guide the reader’s understanding of the review’s purpose and what to expect from it.
- Preview of the literature review’s content: Provide a brief overview of the topics or themes that your literature review will cover. It’s like a roadmap for the reader, outlining the main areas of focus within the review. This preview can help the reader anticipate the structure and organization of your literature review.
- Methodology: If your literature review involved a specific research method, such as a systematic review or meta-analysis, you should briefly describe that methodology. However, this is not always necessary, especially if your literature review is more of a narrative synthesis without a distinct research method.
By addressing these elements, your introduction will empower your literature review to play a pivotal role in your thesis or dissertation research. It will accomplish this by integrating your research into the broader academic literature and providing a solid theoretical foundation for your work.
Comprehending the art of crafting your own literature review introduction becomes significantly more accessible when you have concrete examples to examine. Here, you will find several examples that meet, or in most cases, adhere to the criteria described earlier.
Example 1: An effective introduction for an academic literature review paper
To begin, let’s delve into the introduction of an academic literature review paper. We will examine the paper “How does culture influence innovation? A systematic literature review”, which was published in 2018 in the journal Management Decision.

The entire introduction spans 611 words and is divided into five paragraphs. In this introduction, the authors accomplish the following:
- In the first paragraph, the authors introduce the broader topic of the literature review, which focuses on innovation and its significance in the context of economic competition. They underscore the importance of this topic, highlighting its relevance for both researchers and policymakers.
- In the second paragraph, the authors narrow down their focus to emphasize the specific role of culture in relation to innovation.
- In the third paragraph, the authors identify research gaps, noting that existing studies are often fragmented and disconnected. They then emphasize the value of conducting a systematic literature review to enhance our understanding of the topic.
- In the fourth paragraph, the authors introduce their specific objectives and explain how their insights can benefit other researchers and business practitioners.
- In the fifth and final paragraph, the authors provide an overview of the paper’s organization and structure.
In summary, this introduction stands as a solid example. While the authors deviate from previewing their key findings (which is a common practice at least in the social sciences), they do effectively cover all the other previously mentioned points.
Example 2: An effective introduction to a literature review section in an academic paper
The second example represents a typical academic paper, encompassing not only a literature review section but also empirical data, a case study, and other elements. We will closely examine the introduction to the literature review section in the paper “The environmentalism of the subalterns: a case study of environmental activism in Eastern Kurdistan/Rojhelat”, which was published in 2021 in the journal Local Environment.
The paper begins with a general introduction and then proceeds to the literature review, designated by the authors as their conceptual framework. Of particular interest is the first paragraph of this conceptual framework, comprising 142 words across five sentences:
“ A peripheral and marginalised nationality within a multinational though-Persian dominated Iranian society, the Kurdish people of Iranian Kurdistan (a region referred by the Kurds as Rojhelat/Eastern Kurdi-stan) have since the early twentieth century been subject to multifaceted and systematic discriminatory and exclusionary state policy in Iran. This condition has left a population of 12–15 million Kurds in Iran suffering from structural inequalities, disenfranchisement and deprivation. Mismanagement of Kurdistan’s natural resources and the degradation of its natural environmental are among examples of this disenfranchisement. As asserted by Julian Agyeman (2005), structural inequalities that sustain the domination of political and economic elites often simultaneously result in environmental degradation, injustice and discrimination against subaltern communities. This study argues that the environmental struggle in Eastern Kurdistan can be asserted as a (sub)element of the Kurdish liberation movement in Iran. Conceptually this research is inspired by and has been conducted through the lens of ‘subalternity’ ” ( Hassaniyan, 2021, p. 931 ).
In this first paragraph, the author is doing the following:
- The author contextualises the research
- The author links the research focus to the international literature on structural inequalities
- The author clearly presents the argument of the research
- The author clarifies how the research is inspired by and uses the concept of ‘subalternity’.
Thus, the author successfully introduces the literature review, from which point onward it dives into the main concept (‘subalternity’) of the research, and reviews the literature on socio-economic justice and environmental degradation.
While introductions to a literature review section aren’t always required to offer the same level of study context detail as demonstrated here, this introduction serves as a commendable model for orienting the reader within the literature review. It effectively underscores the literature review’s significance within the context of the study being conducted.
Examples 3-5: Effective introductions to literature review chapters
The introduction to a literature review chapter can vary in length, depending largely on the overall length of the literature review chapter itself. For example, a master’s thesis typically features a more concise literature review, thus necessitating a shorter introduction. In contrast, a Ph.D. thesis, with its more extensive literature review, often includes a more detailed introduction.
Numerous universities offer online repositories where you can access theses and dissertations from previous years, serving as valuable sources of reference. Many of these repositories, however, may require you to log in through your university account. Nevertheless, a few open-access repositories are accessible to anyone, such as the one by the University of Manchester . It’s important to note though that copyright restrictions apply to these resources, just as they would with published papers.
Master’s thesis literature review introduction
The first example is “Benchmarking Asymmetrical Heating Models of Spider Pulsar Companions” by P. Sun, a master’s thesis completed at the University of Manchester on January 9, 2024. The author, P. Sun, introduces the literature review chapter very briefly but effectively:

PhD thesis literature review chapter introduction
The second example is Deep Learning on Semi-Structured Data and its Applications to Video-Game AI, Woof, W. (Author). 31 Dec 2020, a PhD thesis completed at the University of Manchester . In Chapter 2, the author offers a comprehensive introduction to the topic in four paragraphs, with the final paragraph serving as an overview of the chapter’s structure:
PhD thesis literature review introduction
The last example is the doctoral thesis Metacognitive strategies and beliefs: Child correlates and early experiences Chan, K. Y. M. (Author). 31 Dec 2020 . The author clearly conducted a systematic literature review, commencing the review section with a discussion of the methodology and approach employed in locating and analyzing the selected records.

Having absorbed all of this information, let’s recap the essential steps and offer a succinct guide on how to proceed with creating your literature review introduction:
- Contextualize your review : Begin by clearly identifying the academic context in which your literature review resides and determining the necessary information to include.
- Outline your structure : Develop a structured outline for your literature review, highlighting the essential information you plan to incorporate in your introduction.
- Literature review process : Conduct a rigorous literature review, reviewing and analyzing relevant sources.
- Summarize and abstract : After completing the review, synthesize the findings and abstract key insights, trends, and knowledge gaps from the literature.
- Craft the introduction : Write your literature review introduction with meticulous attention to the seamless integration of your review into the larger context of your work. Ensure that your introduction effectively elucidates your rationale for the chosen review topics and the underlying reasons guiding your selection.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
The best answers to "What are your plans for the future?"
10 tips for engaging your audience in academic writing, related articles.

10 key skills of successful master’s students

How to write effective cover letters for a paper submission

Dealing with failure as a PhD student

Reject decisions: Sample peer review comments and examples

Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
Home → Academic Writing → How to Start a Literature Review (Like a Pro)
How to Start a Literature Review (Like a Pro)
Jordan Kruszynski
- June 26, 2023

Ah, how to start a literature review – those words will be all too familiar to battle-hardened researchers, but to the rest of us, they may be a bit of a mystery.
Are you a student trying to get ahead of the game with your first literature review? Or are you a professional looking to learn more about literature reviews? If so, then this post is for you.
In this article, we’ll discuss how to start a literature review, the types of sources used in literature reviews, and the benefits of writing them. We’ll also outline the steps for preparing and writing your own literature review.
Read on and let the magic begin!
Literature Reviews – The Researcher’s Friend
A literature review is an essential part of any research project. It is a compilation of all the literature and research related to a particular topic. It is used to provide context and background for a research project. Literature reviews are important for two primary reasons. First, they provide a comprehensive and objective review of the existing literature on a topic. Second, they provide support for any conclusions or hypotheses that may be drawn from the research.
Literature reviews are used in many different fields, including business, education, and the sciences. They are used to provide an overview of a topic and to support the conclusions and hypotheses of a research project.
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical appraisal of existing research on a particular topic . It is a systematic and comprehensive review of all the published work in a particular field. The purpose of a literature review is to provide an overview of the existing research on a topic, to identify gaps in the literature, and to propose new directions for future research.
The literature review is an important part of the research process and should be conducted thoroughly and objectively. It should include a critical analysis of the existing literature, an evaluation of the research methods used, and an assessment of the quality of the evidence.
Types of Literature Review
There are several different types of literature reviews. They include narrative reviews, systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and scoping reviews.
- Narrative reviews are the most common type of literature review. They provide an overview of the existing literature on a topic. Narrative reviews typically include an introduction, a review of the literature, and a conclusion.
- Systematic reviews are more rigorous and comprehensive than narrative reviews. They involve rigorous and systematic searches of the literature and include a critical appraisal of the evidence. Systematic reviews are typically used in clinical research.
- Meta-analyses are reviews that combine the results of multiple studies to evaluate the overall effect of a particular treatment or intervention. Meta-analyses are more rigorous and comprehensive than narrative reviews and systematic reviews.
- Scoping reviews are used to identify the range of research on a particular topic. They are typically used to identify gaps in the literature and to propose new directions for future research.
Sourcing Pieces for Your Review
When conducting a literature review, it is important to use a variety of sources. These sources include journal articles, books, conference proceedings, dissertations, and other academic sources. It is also important to use a variety of search strategies to identify the most relevant and up-to-date sources.
Research papers will probably form the bulk of your literature review, and this is where Audemic can help – simply load any papers you want to use into the app, and you can organise them intuitively to make sourcing a breeze.
It is important to note that not all sources are created equal. Some sources may be more reliable than others. When evaluating sources for your literature review, it is important to consider their credibility, relevance, accuracy, and objectivity.
Benefits of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews are an essential part of any research project. They provide an overview of the existing literature on a topic and can be used to identify gaps in the literature, as well as propose new directions for future research. They also provide support for any conclusions or hypotheses that may be drawn from the research.
Literature reviews can also help researchers save time and money. By conducting a thorough and comprehensive review of the existing literature, researchers can avoid redundant research and save time and money.
How to Start a Literature Review
Now that you understand the purpose and benefits of a literature review, it’s time to learn how to start one. The first step in starting a literature review is to identify a topic. Once you have identified a topic, you can start searching for sources.
When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies, such as keyword searches, author searches, and database searches. It is also important to use a variety of sources, such as journal articles, books, conference proceedings, and dissertations.
Preparing for Your Literature Review
Once you have identified and located the sources for your literature review, it is time to start preparing. Before you begin writing, it is important to read and analyse each source. This will help you identify the key points of each source and understand how it contributes to the literature on your topic.
It is also important to organise your sources. This can be done by creating a spreadsheet or using a reference management software, such as Mendeley or Zotero. This will help you keep track of your sources and make it easier to cite them in your literature review.
Did somebody say Zotero? Audemic features Zotero integration, so you can not only organise your sources, but also listen to them when you need a change of pace. Nice, eh?
Searching for Sources for Your Review
Now that you have identified a topic and prepared your sources, it’s time to start searching for additional sources. When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies. These search strategies include keyword searches, author searches, database searches, and library catalogue searches.
It is also important to use a variety of sources. These sources include journal articles, books, conference proceedings, dissertations, and other academic sources. It is also important to consider the credibility, relevance, accuracy, and objectivity of each source.
Writing and Structuring Your Literature Review
Once you have identified and located the sources for your literature review, it is time to start writing. When writing your literature review, it is important to keep the structure and organisation in mind. Your literature review should include an introduction, a review of the literature, and a conclusion.
- When writing your introduction , it is important to provide context for your topic. This should include an explanation of the purpose of the literature review and a description of the research question.
- The review of the literature should provide an overview of the existing literature on the topic. It should include a summary of each source and an analysis of the evidence. It should also include an evaluation of the research methods used and an assessment of the quality of the evidence.
- Finally, the conclusion should summarise the key points of the literature review and provide recommendations for future research.
Final Thoughts
A literature review is an essential part of any research project, so it pays to master this critical academic skill. And with the guidance in this post, you should be well on your way to knowing how to start a literature review for yourself. By putting it into practice, you can unlock your writing potential and produce a thorough, engaging and comprehensive literature review.
So what are you waiting for? Search for those sources and get started! And why not use Audemic to speed up the review process and boost it into the cosmos!
Keep striving, researchers! ✨
Table of Contents
Related articles.

How to Publish a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
You’re in academia. You’re going steady. Your research is going well and you begin to wonder: ‘How exactly do I get a

Behind the Scenes: What Does a Research Assistant Do?
Have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes in a research lab? Does it involve acting out the whims of

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction: Hook, Line, and Sinker
Want to know how to write a research paper introduction that dazzles? Struggling to hook your reader in with your opening sentences?

Blog Podcast
Privacy policy Terms of service
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Discover more from Audemic: Access any academic research via audio
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Do a Literature Review
Last Updated: March 27, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Alexander Ruiz, M.Ed. . Alexander Ruiz is an Educational Consultant and the Educational Director of Link Educational Institute, a tutoring business based in Claremont, California that provides customizable educational plans, subject and test prep tutoring, and college application consulting. With over a decade and a half of experience in the education industry, Alexander coaches students to increase their self-awareness and emotional intelligence while achieving skills and the goal of achieving skills and higher education. He holds a BA in Psychology from Florida International University and an MA in Education from Georgia Southern University. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 320,850 times.
Some people might think of a literature review as reading a book and then giving it a thumbs up or thumbs down. Nope, not so. A literature review is a review of various pieces of literature on one topic, ranging from series of books to shorter pieces like pamphlets. Sometimes, the literary review is a part of a larger research paper. Its purpose is to prevent duplication of efforts, resolve conflicts, and point the way for further research.
Before Writing

- How many sources should you include? Does he/she want a specific number of each type? Do they have to be at least semi-current?
- In discussing your themes, are you just summarizing or critiquing? Some reviews require a thesis, some may not.
- Should you offer your opinion on your sources?
- Do you need to provide background information, such as definitions or histories, to aid in your audience's understanding?
- Is there a page or word requirement?

- Get current. If you are writing a review in the humanities, history, or social sciences, you can afford to be less concerned with timing (in fact, changing opinions throughout history may be an aspect of your paper). But if you are writing a literary review for the sciences, say, on treating diabetes, information from 5 years ago could already be obsolete. Sort through current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. [2] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- Read between the lines. You're not necessarily looking for explicit content. Is there an aspect of the field that is missing? Are your sources all prescribing to one specific theory? Do you see trends being revealed? This will help you structure your paper immensely, zeroing in on what will give your paper purpose.

- For example, "Current trends in [topic] are A, B, and C," or "The X Theory is assumed by most sources from 1985 on." Stating something like this begs a few questions, making your review more interesting and meaningful: How will trends change in the future? What if the assumed theories are wrong?
- Again, this is not new information. You are not analyzing the material and coming up with your own, fresh perspective on it. You are simply acting like a computer--noting patterns, holes, and assumptions all your sources are taking.

- What are the author's credentials? How are their arguments supported (narratives, statistics, historical findings, etc.)?
- Is the author's perspective unbiased and objective? Are they ignoring any data to make their points seem stronger?
- How persuasive are they? Do any of their points leave a bit to be desired?
- Does their work lead to a greater understanding of the subject? [5] X Research source
Constructing Your Paper

- Help the reader along by letting them know what kind of ride they're in for. If you are employing a thesis statement, place it toward the end of your introductory paragraph. At the end, your reader should be anticipating getting into the evidence and bulk of your paper.

- Arrange it chronologically. If you are dealing with varying opinions by era or changing trends over time, chronological organization may make the most sense.
- Arrange it by publication. This organizational method fares well if each publication has a different stance. If there is a natural progression (radical to conservative, for example) between the sources, this works swimmingly.
- Arrange it by trend. If you are noticing patterns in your sources, arranging them by the trends they suggest may be the most obvious structure. Certain sources may, together, suggest one pattern that shifts over time, region, or other variable.
- Arrange it thematically. This highly depends on your thesis statement and what sources you have chosen. If you are choosing a focus that is more abstract ("Colonialism is depicted as evil," for example), the subsections may be arranged on the different methods employed to put the theme across.

- You may make your conclusion suggestive. Where might the discussion proceed if someone else picked it up where you left off? What are the consequences of the patterns and holes in today's sources?

- However, use quotes sparingly. The survey nature of the literature review does not allow for in-depth discussion or detailed quotes from the text. [10] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source Some short ones are fine, sure, but all in all, it should be written by you.

- When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author’s information or opinions accurately and in your own words. [12] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source Then, relate it to the context of your review.
- Some professors may require that you evaluate the sources and conclude which pieces add the greatest contribution to the field. If yours is keen on this, determine your take in the introduction and string it throughout your paper.
Revising Your Work

- Does your instructor require APA formatting? What should your margins be? Headers, footers, footnotes, and page numbers? How do they want your name, headings, and subheadings? How do they want your works cited page?

- With everything said as clear as day, does it flow together? Do you transition well not only from paragraph to paragraph, but from sentence to sentence? Be sure your evidence lines up with the support and your arrangement of sources flows logically.
- Eliminate useless jargon or slang. You may have grown an entirely new vocabulary during this endeavor, but your professor has not. Write a paper that can be read by the masses. Don't make it overly esoteric.

- It's best to have someone else go over your work, too. You may have read it so many times you can no longer see you lapsed into Portuguese absent-mindedly. A different set of eyes can locate mistakes you may not have seen, ask questions you didn't realize were left unaddressed, or seek clarification on the foggier points.
Community Q&A
- Use correct citations. Your assignment will likely specify what kinds of formats you should use for citations within the text. Often, professors are looking for strict use of these formats as part of the grade. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Outline your literature review. It will help you order your thoughts into an organized presentation, making the paper ultimately easier to write. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid plagiarism. Using your own words will help you avoid plagiarism, which many academic departments take very seriously. Evidence of plagiarism can get students suspended or otherwise disciplined (this includes a failing paper). Make sure to correctly attribute any direct quotes. Thanks Helpful 14 Not Helpful 3
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://guides.lib.uoguelph.ca/c.php?g=130964&p=5000948
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/literature-reviews/
- ↑ https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
- ↑ https://library.concordia.ca/help/writing/literature-review.php
- ↑ http://guides.library.ucsc.edu/content.php?pid=364099&sid=2979684
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/conducting_research/writing_a_literature_review.html
- ↑ https://www.ed.ac.uk/institute-academic-development/study-hub/learning-resources/literature-review
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/editing-and-proofreading-techniques
- How to Conduct Academic Research
- How to Create a Successful Project (for School)
- How to Begin Writing a Research Paper
- How to Be More Analytical
- How to Find Primary Source Documents
- How to Complete a Project on Time
About This Article

To do a literature review, start by finding a variety of reliable sources that all relate to one topic or theme. Then, read through the sources and come up with a thesis statement for your paper. Once you have your thesis, explain how the sources you used back up your thesis in the body of your literature review. You can arrange the sources chronologically, by publication, or even thematically. For help writing an introduction and conclusion for a literature review, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Maryam Lawal
Nov 12, 2016
Did this article help you?

Jul 7, 2016
Galal Sheher
Oct 22, 2016
Alljey Gimpes
Jun 15, 2016
Jvert Smith
Oct 4, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Perspective
- Open access
- Published: 08 May 2024
Facing the storm: Developing corporate adaptation and resilience action plans amid climate uncertainty
- Katharina Hennes ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0001-1779-4877 1 ,
- David Bendig 1 &
- Andreas Löschel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3366-8053 2 , 3 , 4
npj Climate Action volume 3 , Article number: 37 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Climate sciences
Climate hazards disrupt global value chains and business operations, leading to €52 billion in losses for the European Union in 2022 alone. In response to this escalating crisis, there is a need for corporate climate adaptation and resilience strategies (henceforth: CCAR) to effectively integrate climate risk challenges into strategic planning. Despite this urgency, there is a shortfall of research synthesising the drivers, strategies, and outcomes of corporate adaptation and resilience. Our study addresses this gap by conducting a systematic literature review to elucidate the academic status quo. From an initial dataset of over 3000 publications, we narrowed the sample to 66 papers, which specifically focus on these topics in the private sector. Grounded in this comprehensive review and regulatory observations, we delineate a CCAR typology to define the key elements required for a corporate approach to physical climate risks. This typology is translated into an actionable business adaptation framework, offering a clear path to begin the adaptation journey. Our in-depth content analysis contributes to the existing literature by identifying two main themes and several gaps: Current research covers the drivers, detailing why companies embark on such initiatives. Another stream focuses on how companies adapt, examining strategies to overcome these climate risks. However, work on the effectiveness and outcomes thereof is scarce. Consequently, our study delineates six trajectories for future research, the outcomes of which can serve as catalysts for advancing future CCAR efforts.
Similar content being viewed by others
International bureaucrats’ attitudes toward global climate adaptation

The politics of climate risk assessment
Climate change and health: three grand challenges
Introduction.
The climate crisis and its physical risks have become a pressing issue for humanity—every tenth of a degree beyond the 1.5 °C target has the potential to dramatically alter the world as we know and understand it today through cascading physical climate risks 1 . Increasing in frequency and intensity 1 , these range from acute risks (e.g., floods, heat waves, wildfires) to chronic impacts (e.g., changing precipitation patterns, rising average temperatures) 2 . One of the very (financially) costly consequences is that human-made systems, such as global value chains, are substantially disrupted 3 . Beyond these physical impacts, the private sector faces liability 4 and transition risks 5 , 6 , for instance being sued for lack of climate initiatives or misleading reporting thereupon 4 , 7 . Thus, climate risks become relevant not only to the natural environment but also to our human systems, i.e., our economies, that are dependent on it 1 .
In today’s business reality, there are numerous examples of physical consequences building up to a systemic risk that threatens financial stability 6 , 8 , 9 . For instance, in 2021, Hurricane Ida caused losses of $65 billion in North America 10 . Only one year later, US companies were exposed to extreme droughts that built up to supply chain costs of $20 billion 11 —simultaneously, floods caused economic losses and reconstruction costs of over $31 billion to Pakistan’s economy 12 . These disruptions demonstrate the challenges that the private sector faces globally. Various weather extremes can strike in a relatively short timeframe, causing infrastructural damages, supply chain disconnections, wreaked production sites 3 , 13 , or surges in global raw material prices 14 —to name but a few. Following these incidents, it is common for businesses to shut down operations, at least temporarily, to accommodate repairs and rebuilds, if financially viable 15 , 16 .
Decarbonisation aims to tackle the root cause of climate change, but insufficient progress 17 leads to intensifying rather than declining feedback loops, requiring corporates to prepare for these challenges 18 . This is where corporate climate adaptation and resilience (henceforth: CCAR) comes in—it acknowledges the reality of a changing climate and focuses on adjusting to a world where some consequences are now inevitable and where requirements for corporate disclosure of physical risks are growing 4 . Despite this scientific clarity and emerging regulations, most corporates currently do not understand how to prepare for the acute extremes that we are already seeing today, nor how to adapt to the long-term chronic impacts 19 . This calls for a translation of scientific evidence and risk disclosure standards into the operationalisation of corporate adaptation 20 . To date, no such conversion has been conducted and there is limited research on the corporate level. This is noteworthy given the vital role businesses play in adaptive efforts 21 to maintain societal functioning amid surging climate crises. Consequently, it is crucial to identify what motivates globally operating businesses to engage in adaptation, how they do it, and the results of these efforts.
Although corporate climate adaptation and resilience have recently been addressed by some prominent publications 14 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 and regulations 26 , 27 , we still see three gaps. Firstly, even though existing research has broadly investigated overall climate risk impact, small businesses’ issues with infrastructure, agriculture, tourism, or the public sector’s role, a synthesis of CCAR knowledge that corporates can leverage has been largely overlooked. Secondly, the absence of a concise, universally applicable typology that defines the key elements of CCAR at the firm-level leaves too much room for interpretation or missteps and thus presents another gap. Lastly, from a practical lens, there is a lack of operationalisation of academic knowledge coupled with reporting insights into an actionable first-step adaptation guide. This could assist the private sector in informing its strategies, operations, and disclosure approaches. From a theoretical perspective, this would also serve as a basis for identifying areas requiring further research. In an effort to close these gaps and thereby answer manifold research calls 14 , 25 , we conduct a systematic literature review aiming to bring clarity to the following questions:
(i) What is and what is not known about CCAR from an academic perspective?
(ii) What defines CCAR for practice?
(iii) What adaptive steps can businesses take to enhance their climate resilience?
As our study’s foundation, the systematic literature review presents the latest adaptation and resilience insights, specifically focused on the private sector (i). Thoroughly evaluating existing academic knowledge at the firm-level, we contribute to the current literature by identifying what is known about corporate adaptation drivers, strategies, and outcomes. By incorporating observations on recent regulatory developments in climate risk disclosure, we enrich these academic findings and establish the foundation for our subsequent analyses to answer research questions (ii) and (iii). This synthesis enables us to delineate a CCAR typology at the firm-level, which defines the key elements required for a corporate approach to physical climate risk challenges. To the best of our knowledge, we are among the first to turn these theoretical contributions into practical firm-level guidance. More specifically, we translate the CCAR elements of the typology into an actionable business adaptation framework, thereby offering corporates a clear path to begin their adaptation journey. This is designed to bridge the gap between the current state of business and the identification, adaptation and eventual disclosure of climate risks. Lastly, we highlight central research blindspots. Going forward, topics like the measurement of CCAR outcomes or conducive regulatory incentives warrant further investigation (Box 1 elaborates on research pathways).
Building an academic foundation for CCAR
To compile the dataset of relevant articles, we followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) procedure 28 and began by (1) searching four central databases at the hand of 12 keywords (please refer to Fig. 1 or the Supplementary Methods 1 for further information on the selection of keywords.): EBSCO, Web of Science, Scopus, Science Direct. Between 2010 and 2022, a total of 3030 papers were published. As a second step, we (2) filtered via exclusion criteria (English language, peer-reviewed, Scimago Top 2000 rank), which left us with 983 articles. Lower-ranked journals were included to account for the fact that CCAR is a new topic of academic interest. Subsequently, we (3) systematically analysed all 983 articles’ abstracts to distill those that do indeed address sustainability in the private sector. Due to a multitude of unsuitable works (e.g., unrelated, small business, public sector or CSR focused, sustainability only as a side topic), we eliminated 860 papers.
The flow diagram, generated according to PRISMA, describes the process of the systematic literature review, including all steps from the identification of the initial sample to the analysis of the final sample. Each step details the number of articles that were included or excluded and the reasons for their inclusion or exclusion. The abbreviations have the following meaning: corp. corporate; bus. business.
This narrowed the dataset down to 123 articles for a detailed review of corporate adaptation. Lastly (4), we dropped 83 further papers that did not focus on firm-level analyses. This distilled a sample of 40 papers, which are all corporate-focused and specifically encompass adaptation drivers, levers, and outcomes. In light of recent regulatory changes regarding climate risks, we conducted a further search for important accounting and regulatory research articles that were not identified in our initial search. Specifically, we focused on articles relevant to the period between 01/2023 and 01/2024 using forward snowballing and cross-referencing techniques to review the dataset. Once we added these articles, our final sample increased to 66 papers (please refer to Supplementary Table 1 , which contains the full list). An in-depth analysis of all articles was performed by applying a review framework we developed to cover the breadth of potential CCAR topics (please refer to Supplementary Discussion 1 for limitations and Supplementary Methods 2 and 3 for details on the review framework). The review framework’s functionality was also tested with other business sustainability academics. Systematically extracting data from the final sample, we found manifold insights.
Research foci
For instance, the sample demonstrates geographical and topical patterns. As such, the CCAR literature originates from the Global North, offering a perspective mainly from the private sectors of highly developed nations. This trend is no surprise, considering that these regions wield sizeable global corporate influence and resources to devote to adaptation and resilience research 29 , 30 . This raises questions about the equitability of these efforts. It prompts consideration of the disparity between corporations with the financial means to pre-emptively adapt and well-functioning institutions surrounding them that provide regulatory support or guidance, versus those in developing countries that already face some of the most acute climate risks 1 . This also suggests that a key adaptation aspect of corporates’ global operations might be ignored, i.e., their suppliers and manufacturers at the start of the value chain.
Beyond geographical implications, our analysis displays a limited sectoral focus, as only half (45%) of the articles are industry-specific (percentages represent the relative emphasis of an adaptation aspect). Among these, over three quarters (36% overall) originate from two broader sectoral spectrums: (1) manufacturing and producing industries (18%), (2) management and finance (18%). All others contribute about two to three percent each. This is substantiated when examining business functions, as roughly a fourth of the papers display a concentration on organisations’ accounting & finance (27%). It is mirrored by production/operations (21%) and followed by other streams dedicated to management, administration, marketing and sales (15%) and sustainability (6%). Notably, about a third of the papers do not entail information regarding business functions (30%). Given these foci, we delineate a research tendency towards manufacturing, resource-intensive businesses and the management thereof, which points to the need for strategic planning in response to the high operational impact of these physical risks.
Review insights
Investigating adaptation to physical climate risks in the selected papers, two clear streams were detected: (1) Current CCAR literature provides considerable knowledge on antecedents, with the majority of the papers analysing the driving forces that lead corporates to engage in adaptation. (2) Another substantial body of work examines adaptation strategies, meaning what levers do corporates employ to overcome physical climate risks.
(1) A key conclusion from our analysis is that particularly a company’s value chain positioning, as well as its resulting climate risk exposure and managerial awareness thereof, are key predictors of its engagement in adaptation. Specifically, over two-thirds (71%) of the underlying literature elaborates on adaptation-inducing factors. As a corporate’s exposure to climate risks 31 , 32 has a measurable negative impact on revenue potential or performance indicators like sales 33 , 34 , 35 or stock market performance 36 , 37 , 38 , it plays a critical role in whether and how businesses adapt. The papers emphasise that action upon these risks can only be taken if there is managerial awareness thereof. Thus, internalities like key personnel’s (climate) risk perception 22 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 and general integration of risk management into corporate processes 24 , 31 , 44 are adaptation facilitators. Beyond these firm-internal factors, externalities are also acknowledged as crucial determinants, such as institutional pressures 45 , 46 , 47 like specific climate regulation 48 , 49 , disclosure requirements 50 , 51 or a company’s embeddedness and interdependencies within its business network 52 , 53 .
(2) In response to these drivers, corporates implement specific strategic or operational adaptation and resilience levers. Approximately half of the underlying papers (53%) showcase strategic initiatives like climate risk measurement and monitoring 24 , 31 , 44 , 54 , 55 , 56 or building cross-company adaptation networks 52 , 57 , 58 . They also highlight strategic compensation for business interruption or cash flow shortfalls due to physical hazards. Examples thereof are financial mechanisms such as weather 34 , 53 , 59 , 60 or climate change news 61 hedging. Adjusted leverage structures 62 , 63 , 64 , cash holdings 65 or loss provisions 66 also aim to mitigate these physical impacts. From a decision-making perspective, statistical approaches to incorporate adaptation considerations into pricing 67 , 68 and investment 69 are on the rise. Further operational dimensions (35%) can be adjustments to supply chains or production processes 57 , 70 in terms of, e.g., flexibilisation of inputs or logistics chains 15 , 71 , 72 , fortification of infrastructure 14 or even relocation thereof 59 , 73 . All of the above changes for long-term adaptation should, in theory, be mirrored by resilience levers that corporates employ to address sudden climate events. However, our analysis reveals that only a minor proportion of the literature (11%) touches upon acute disaster recovery measures like emergency response and disaster relief plans 16 , 24 , 48 . This limited acute resilience focus raises concerns, particularly given the ongoing occurrence of extreme weather events 1 . Failing to develop effective countermeasures exposes corporates to multiple risks like disrupted input logistics, damaged production sites and consequently financial losses 14 , 59 , 73 . Ultimately leading to bigger systemic impacts, this threatens the financial stability across a variety of sectors and economies 51 .
Regulatory and reporting influences
In recognition of these emerging global risks, regulators and standard-setters are increasingly demanding transparency in how companies assess and respond to them 74 . A variety of reporting standards have now emerged to facilitate this: voluntary ones companies choose to implement such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP); nationally adapted ones as in the state of California 75 based on, e.g., the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) or the Standards 1 and 2 of the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) 76 ; or legally mandated cross-country ones such as the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) 1 and 2. Amidst the need for comparability between various disclosures and expanding regulatory demands 77 , climate risk reporting standards are beginning to converge, as evidenced by the recent shift of TCFD monitoring responsibilities to the ISSB 78 . In this evolving regulatory landscape, disclosure is becoming increasingly pertinent to corporates. More specifically, various states have already initiated legislative processes (e.g., California 75 , EU 27 , New Zealand 79 , UK 26 ), or have announced to do so recently (e.g., US SEC 80 , 81 ). As these come into force, companies will be legally obliged to focus on the impact of physical risks on their financials or beyond, depending on, e.g., size or operational boundaries. In this respect, the EU’s ESRS, starting in 2024, stands out as one of the most advanced 76 in terms of an internationally agreed, legally binding reporting standard that investigates not only financial but also the impact materiality of physical climate risks 82 .
Creating transparency on the concept of climate adaptation for private sector organisations
Blending the systematic literature review with the regulatory insights presented above, we understand that distinct factors drive corporate adaptation, and, in response, organisations employ specific measures. Despite rising academic attention to CCAR due to noticeable climate extremes and increased concern from countries and regulators, there remains confusion in the public discourse about the nature of adaptation and resilience for businesses. This is not surprising, as, to date, the reporting suggestions can be imprecise 83 and there is no succinct definition of CCAR on the firm-level 14 , leaving considerable ambiguity. Consequently, we usually do not see corporates with a clearly defined action plan for both acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term) climate impacts yet 84 —generally speaking, there is limited clarity on where the private sector stands 85 . This uncertainty calls into question its comprehension of climate risk disclosure standards like TCFD or ESRS and the sincerity of its ambition and ability to tackle these impacts today and in the future 50 . Acknowledging the complexity of the adaptation action and regulation landscape underscores the need for a common CCAR understanding to accelerate its momentum.
To build this foundational understanding, it is essential to define a universally applicable typology as a frame of reference that outlines the fundamental elements of firms’ adaptation and resilience efforts. It is critical that these are clarified so that they are comprehensible to every firm before they begin to engage in or report on CCAR. Derived from our review and the key notions of climate risk regulation, we conceptualise a triad of overarching elements (Fig. 2 ). Convinced that these are integral to a comprehensive CCAR strategy, we propose the following: (1) Well-researched scientific knowledge and risk assessments present the basis of any climate-related strategy, i.e., ‘ Climate proficiency’ is key. On this base, (2) acute, short-term climate impacts must be urgently confronted, i.e., ‘Resilience to acute risks’ , while (3) chronic, long-term changes need to be prepared for, i.e., ‘ Adaptation to chronic risks’ . This triad stems from seeing a focus on time- and physical-risk-oriented movements in our systematic literature review—one toward short-term natural disasters and the other toward long-term adaptation planning.
Figure 2 outlines the three key elements that need to be incorporated into a strategy to address physical climate risks. For clarity in the following business adaptation framework (see Fig. 3 ), each component is distinctly colour-coded. In this context, the adjectives ‘short-term’ and ‘acute’ are used interchangeably. The same applies to ‘long-term’ and ‘chronic’.
Climate proficiency
‘ Climate proficiency’ presents the initial element of this holistic CCAR typology. It is grounded in our learning that managerial perception of climate change and a company’s exposure to its risks are significant determinants of adaptation 22 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 . Given the clear importance of awareness as a base, companies need to enable and upskill their staff 50 . Thus, this first element encompasses integrating climate science as key knowledge for a firm to be able to conduct thorough climate risk assessments. As such, scientific (climate) literacy implies an up-to-date understanding of current climate and regulatory developments. Spreading these insights develops managerial awareness and perception of this cause’s urgency. Any company aiming for high literacy should thus regularly monitor the latest science 50 , e.g., provided by the IPCC, to update its risk exposures according to changes in predictions 13 , 86 , 87 . Ultimately, this supports the process of identifying and quantifying acute and chronic impacts on a company’s operations along its value chain 3 , 31 , 56 , 88 .
Resilience to acute risks
Engaging in fast risk management today is especially relevant for short-term, unpredictable events like sudden hurricanes or wildfires 1 , 89 . Consequently, the second element of the CCAR typology is ’ Resilience to acute risks’ . It draws on the literature highlighting how climate risks affect business operations 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , and how embeddedness in networks and value chains 52 , 53 can assist in responding to these immediate shocks. As such, this second element encapsulates both the operational and value chain strength required to deal with sudden physical impacts. Operational resilience refers to the imperative to have a ready-to-implement plan to assure production continuity and maintain essential functions in the face of all types of extreme weather events 15 , 24 , 90 . As an enabler thereof, simultaneous value chain resilience is of the essence. This is equally critical, as reflected in the literature discussing modifications of the supply chain 15 , 71 , 72 . It suggests resilience measures such as supplier choice or transportation flexibility to withstand or recover from such short-term disruptions 52 .
Adaptation to chronic risks
Simultaneously, responses to chronic risks like rising temperatures or changes in precipitation need to be developed 1 . Thus, underpinned by the CCAR literature’s focus on long-term strategic 59 , 73 , financial 34 , 53 , 59 , 60 or company-internal adjustments 56 , 58 , 70 , 91 , 92 , 93 , 94 , the last element of this holistic CCAR typology is ‘ Adaptation to chronic risks’ . Based on identified future vulnerabilities, strategically adaptive measures can be delineated and planned accordingly. In line with the foreseeability of such chronic impacts, this element also links to the anticipated regulatory landscape for climate risks 95 . Currently under development and already mandatory in some countries, companies will soon be required to acknowledge the potential (non-)financial impacts on their business and disclose their corresponding risk mitigation strategies 74 . They therefore need to adjust internal reporting mechanisms 95 to take account of these new measurements 55 and to disclose them externally 47 .
Operationalising a practical business adaptation and resilience framework
Following this definition of the CCAR typology, we now turn to the question: How does a company operationalise these elements to navigate toward a climate-adapted and -resilient way of doing business? Grounded in our analyses, we answer this question by delineating a practical business adaptation framework. As such, it aims to bridge the gap between the private sector’s current and aspirational, climate-adapted state, which should be disclosed to regulatory bodies (Fig. 3 ). It is a practical tool that firms can leverage to get an overview on which first steps to take toward a thorough CCAR strategy. As a step-by-step process, the business adaptation framework operates through a question series and starts by building a baseline to review the status quo. Key actions for adaptation and resilience are identified. Ultimately, these form part of a publicly disclosed CCAR strategy that is integrated into a firm’s business strategy.
This figure presents a practical application of the CCAR typology elements (see Fig. 2 ), transforming them into actionable steps within the business adaptation framework. On the left side, pivotal questions corresponding to the three typology elements prompt strategic considerations for each operational step of the framework, which is illustrated on the right. The colour-coding establishes a visual link between each step of the framework and its respective element within the CCAR typology.
Step 1: Setting a CCAR foundation by identifying climate risks and their impact
Initially, the business adaptation framework directly links to the CCAR typology’s first element—‘ Climate proficiency’ . Its subdimensions ( scientific literacy and risk assessment ) present the starting point for identifying and categorising climate risks. These can be either physical (acute and chronic) or liability and transition-related consequences of physical risks 24 , 94 . Depending on the jurisdiction in which a company operates, it could use the global TCFD guidelines as a working basis for this first step—many countries and regional governments also provide useful local climate risk assessments. Having assessed which climate risks the business is exposed to along the value chain from procurement to sales 31 , 56 , 88 , these should be further analysed to rank them according to their likelihood of occurrence under different global warming scenarios. For instance, the Network for Greening the Financial System’s ‘Scenarios Portal’ could be leveraged for a global overview 96 . This prioritisation exercise should be carried out for varying timeframes 56 —i.e., what are the key climate risks today, in 10, 15 and 20 years’ time? Communicating these evaluations internally enables corporates to build the foundational knowledge, i.e., the scientific literacy and risk assessment , necessary to fully operationalise element 1.
Step 2: Building acute climate resilience operationally and along the supply chain
Having identified the base (where, how, and when climate risks are likely to occur), the business adaptation framework’s next step draws the connection to the second element ‘ Resilience to acute risks’ . Corporates increasingly realise that not all climate risks can be foreseen and mitigated pre-emptively, as some impacts happen suddenly and without warning. Referring to both subdimensions of element 2, companies must develop short-term resilience levers to have the capability to react immediately upon acute physical impact 15 , 97 . These levers aim at both their own operations as well as aspects up and down their supply chain. For instance, rapid response mechanisms could include establishing a climate disaster task force, implementing emergency operations plans, or even storing slack inventory 15 , 16 , 97 . Beyond that, companies could also investigate parametric vs. indemnity arrangements with their insurers to cover potential losses due to acute impacts 98 .
Step 3: Developing strategic adaptation initiatives for chronic impacts
As climate science clearly shows that long-term chronic impacts are coming, there is immense value for companies to be proactive in addressing these. While element 2 is about creating reactive, short-term measures to face acute risks, element 3 dives into proactive, long-term levers to address chronic impacts. Thus, the business adaptation framework’s third step focuses on developing adaptation actions that enable businesses to mitigate these. Firms need to think strategically and initiate such adaptation 14 , 40 early to implement countermeasures for foreseeable climate change impacts 91 . Operational tactics may include modified production processes, locations or fortification of infrastructure. From a more strategic perspective, corporates could explore new markets and products, or financially hedge chronic risks such as changed precipitation or temperature patterns with, e.g., weather derivatives 34 , 53 .
Step 4: Integrating CCAR with business strategy and disclosure requirements
The final step operationalises the last part of the CCAR typology’s third element by preparing the adaptation and resilience efforts for integration into the business strategy and disclosure to external stakeholders. In this step, corporates first translate the CCAR strategy into concrete initiatives and targets, covering both long-term adaptations and short-term reactivity. To implement these in the business strategy 92 , 99 , 100 , companies could set up cross-functional teams that hold responsibility for aligning stakeholders in the implementation of these levers and ensuring that they are considered in budgeting decisions. They also need to introduce climate risk assessments into routine business operations, aligning CCAR goals with business objectives. Ultimately, to evaluate the levers’ success, established evaluation processes should track both initiative progress and effectiveness using pre-defined key performance indicators. Leveraging the latter, companies can complement their existing disclosures by reporting on material climate risks and their plans to address them.
While this paper develops a CCAR typology and an operationalisation thereof as a practical business adaptation framework, our work also uncovers a noticeable shortfall of research probing the outcomes and performance of these initiatives, i.e., measuring CCAR success in terms of financial, market or societal benefits. Just a tenth of the reviewed literature delves into financial outcomes of adaptive actions (11%) 31 , 59 , 60 , 99 —even fewer studies investigate consequences such as keeping up the status quo (6%) 59 , 101 , reputation or even innovation opportunities (5% each) 88 , 102 , 103 , 104 . This limited outcome-oriented exploration underlines the scarcity of attention paid to actual CCAR measurement. Without robust measurement of a lever’s success, its long-term viability and efficacy remain unproven. Hence, it is unclear whether the strategic or operational levers hold when faced with increasing climate risks. As the stakes of maladapting are high, these knowledge gaps constitute essential areas for future investigation.
Intriguingly, the emphasis of CCAR research seems to be solely on nature-based risks, as a significant proportion of the papers analysed (79%) concentrate on physical impacts. In contrast, only a minority also dive into regulatory and liability (29%) or financial and transition risks (33%). Academics’ high focus on physical aspects is interesting considering that some businesses may perceive regulatory ones as the most critical 92 , 100 . It showcases a discrepancy between researchers and the private sector’s perception of the risks posed by the climate crisis. This misalignment could also be due to the so-called ‘tragedy of the horizon’, as companies and managers may have a shorter-term focus on what is most relevant 5 than academics. In line with their focus on physical risks, a number of tools have been developed to assess companies’ exposure to physical impacts 105 . Given the wide variation in the results of the assessments 105 , it is crucial to point out that the transition towards adaptation and resilience is a continuously evolving process for both academics and practitioners 14 , 106 —it is by no means static or a one-time event. As a testament to the topic’s dynamic nature 52 , 56 , evolving CCAR research could balance its focus with the private sector’s practical concerns. For example, to better understand CCAR and its effectiveness, future work could develop standardised measures of industry risk exposure and examine the outcomes of efforts to adapt to these risks. The exploration of regulatory incentives as a complement to existing disclosure standards may also prove conducive to this transition. We elaborate on these pathways in Box 1 to encourage future scholarly inquiries.
Box 1 Crucial research pathways for CCAR academics
1. Improve measurement of climate risk exposure across industries
Based on our review, we conclude that if existing research sets a focus, it is on manufacturing sectors 49 , 88 , 93 , 102 rather than physical climate risks. The extent of these risks’ impacts varies strongly depending on the assessment tool in question 105 . This is why their key takeaways should be taken cautiously when generalising to differing industries or when comparing one score 105 or rating 8 to another, as they use varying methodologies, input data and climate scenarios 74 . Thus, a globally agreed-upon and consistent methodology to measure these physical risks is needed. If this is not developed, policymakers and industry bodies may establish CCAR incentives of which the effectiveness would be limited or potentially even detrimental due to misleading industry- or risk-specific insights.
2. Build theorising on outcomes of CCAR initiatives
Currently, we do not know much about or measure whether corporates’ pilot adaptation and resilience levers prove to be successful when climate risks strike 13 , 86 . Only very few papers theorise and investigate how, e.g., financial hedging may lead to more stable financial outcomes for corporates 34 , 53 , 59 , 60 . However, this financial perspective is only one of many outcomes of adaptation and resilience initiatives. Others could be, e.g., potential for technological innovation 14 , cross-company partnerships 71 or cooperations with the public sector 14 . To assess these opportunities, theory is needed that dives into levers and their potential outcomes. Only then can we test this ‘black box’ and assess whether current assumptions about the effectiveness of initiatives are correct or need improvement.
3. Develop quantitative measurements to assess corporates’ extent of CCAR engagement
Building on the above, approaches to measuring CCAR implementation are currently limited with only a few approximations 87 , 107 , 108 . Ultimately, this makes it difficult to assess the progress and outcomes of firms’ adaptation. The definition of standardised performance indicators to capture the extent of corporate CCAR engagement is therefore crucial. Only when a measurement base is established will it be possible to highlight best practices and inform policymakers. Such a standardised perspective could be put forward by a consortium of regulatory bodies, overlooking a variety of climate risk disclosure approaches. This would also be useful for comparing future disclosures by firms which, given the current state of regulation, do not seem to have a clear method for doing so 84 . In light of these considerations, the role of company-internal accounting and reporting departments will become increasingly important in developing and/or reporting these standardised CCAR indicators 55 .
4. Assess opportunities of public-private partnerships
As the private sector faces complex changes, it might seek external support to tackle these. Cooperations like public-private partnerships have the potential to advance topics that surpass the capacity of any single actor 109 , 110 . As one of these topics, CCAR promises to be an interesting partnership area. Combining the strengths of public and private actors could create a robust platform for innovation and solutions, as exemplified by the Green Climate Fund 111 . An in-depth examination could look at how resources should be pooled to drive adaptation and what public incentives could kickstart CCAR initiatives. Diving into this will yield crucial insights for both policy and practice.
5. Encompass the Global South to develop a CCAR understanding across diverging regions
Predominantly stemming from the Global North, CCAR research does not provide a global picture. It is widely known that climate change disproportionally affects the Global South 1 ; their private sectors face different challenges than peers in the Global North. Among such hurdles, limited institutional or regulatory support can hinder this transition 112 , 113 . Current CCAR work in economics and management neglects to address these regions, limiting the development of geography-specific adaptation pathways. Cross-regional studies could solve this and provide an inclusive overview.
6. Expand the knowledge of climate risks’ true cost
An initial understanding of the overall economic costs of climate-related events has been developed 114 , 115 . Still, it is limited by a lack of precision on the sectoral level. Overlooking the specific cost and benefit implications for particular industries is dangerous, as the true cost of non-adaptation cannot be established 13 , 14 . Only this knowledge can adequately inform strategic decisions and help prioritise investments—both from a public and private sector lens. Addressing this, interdisciplinary research should involve economics and management, environmental, and risk science. Pilot case studies could explore these costs in-depth, ultimately enabling the development of effective CCAR strategies across sectors.
Our review of the most prominent business adaptation papers enabled us to develop a thorough understanding of the existing body of knowledge on corporate climate adaptation and resilience. We complemented this synthesis of the academic status quo with valuable regulatory insights to propose CCAR tools for corporates. Specifically, we contribute a firm-level typology of private sector adaptation and resilience to the academic discourse. It defines the crucial elements necessary for a corporate approach to physical climate risks. Exemplifying the urgency of addressing acute threats, planning for long-term chronic impacts, and the need for disclosure and integration across the organisation, this is particularly relevant for businesses looking to begin their adaptation journey. For a practical perspective, we operationalised this typology into concrete steps by introducing the business adaptation framework. As a demonstration of the CCAR typology, it is designed as a globally applicable, step-by-step process to kickstart companies seeking to improve their climate resilience or that will soon be subject to disclosure requirements. Complementing regulatory standards, our framework helps businesses take the first steps to systematically assess risks and strategise countermeasures; thereby aiming to set a precedent for climate-adapted businesses.
Integrating theoretical knowledge and practical CCAR implications, we facilitate a nuanced understanding of what state of climate adaptation and resilience corporates should strive for. To develop this further, the systematic literature review allowed us to identify blindspots where future academic work is required. Highlighting these gaps, we aim to direct research towards areas that will best support private sector adaptation endeavours. As the climate crisis accelerates, the ability of corporates to adapt will be critical. This research should serve as a stepping stone, equipping businesses with a better understanding of how to navigate the complexities that lie ahead.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
All articles included in this systematic literature review are available in the Supplementary Information. Further data that support the findings of this study will be made available upon reasonable request by the Corresponding Author.
IPCC. Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report . (eds. Lee, H. and Romero, J.), 35–115 (IPCC, 2023).
TCFD. Recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures. https://www.fsb-tcfd.org/recommendations/ (TCFD, 2023).
Fiedler, T. et al. Business risk and the emergence of climate analytics. Nat. Clim. Change 11 , 87–94 (2021).
Article Google Scholar
Rajavuori, M., Savaresi, A. & van Asselt, H. Mandatory due diligence laws and climate change litigation: bridging the corporate climate accountability gap? Regul. Gov. 17 , 944–953 (2023).
Carney, M. Breaking the Tragedy of the Horizon—Climate Change and Financial Stability (Speech given at Lloyd’s of London) , Bank of England. https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/-/media/boe/files/speech/2015/breaking-the-tragedy-of-the-horizon-climate-change-and-financial-stability.pdf (2015).
NGFS. A Call for Action—climate Change as A Source of Financial Risk . https://www.ngfs.net/sites/default/files/medias/documents/ngfs_first_comprehensive_report_-_17042019_0.pdf (NGFS, 2019).
Eskander, S., Fankhauser, S. & Setzer, J. Global lessons from climate change legislation and litigation. Environ. Energy Policy Econ. 2 , 44–82 (2021).
Klusak, P., Agarwala, M., Burke, M., Kraemer, M. & Mohaddes, K. Rising temperatures, falling ratings: the effect of climate change on sovereign creditworthiness. Manag. Sci. 69 , 7468–7491 (2023).
Monasterolo, I. Climate change and the financial system. Annu. Rev. Resourc. Econ. 12 , 299–320 (2020).
Munich Re NatCatSERVICE. Natural Catastrophes in 2021 . https://www.munichre.com/content/dam/munichre/mrwebsiteslaunches/natcat-2022/2021_Figures-of-the-year.pdf (Munich Re NatCatSERVICE, 2022).
World Economic Forum. Droughts are Creating New Supply Chain Problems. This Is What You Need to Know . https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2022/11/drought-trade-rivers-supply-chain/ (World Economic Forum, 2022).
The World Bank. Pakistan: Flood Damages and Economic Losses Over USD 30 billion and Reconstruction Needs Over USD 16 billion—New Assessment. https://www.worldbank.org/en/news/press-release/2022/10/28/pakistan-flood-damages-and-economic-losses-over-usd-30-billion-and-reconstruction-needs-over-usd-16-billion-new-assessme (The World Bank, 2022).
Dietz, S., Bowen, A., Dixon, C. & Gradwell, P. ‘Climate value at risk’ of global financial assets. Nat. Clim. Change 6 , 676–679 (2016).
Goldstein, A., Turner, W. R., Gladstone, J. & Hole, D. G. The private sector’s climate change risk and adaptation blind spots. Nat. Clim. Change 9 , 18–25 (2019).
Linnenluecke, M. & Griffiths, A. Beyond adaptation: resilience for business in light of climate change and weather extremes. Bus. Soc. 49 , 477–511 (2010).
McKnight, B. & Linnenluecke, M. K. Patterns of firm responses to different types of natural disasters. Bus. Soc. 58 , 813–840 (2019).
Sanderson, K. Net-zero pledges are growing—how serious are they? Nature News . https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-01976-0 (2023).
Doh, J. P., Tashman, P. & Benischke, M. H. Adapting to grand environmental challenges through collective entrepreneurship. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 33 , 450–468 (2019).
S&P Global. Adaptation Planning Is the next Step for Companies to Prepare for Climate Risk . https://www.spglobal.com/esg/insights/adaptation-planning-is-the-next-step-for-companies-to-prepare-for-climate-risk (S&P Global, 2023).
Lee, C.-C. et al. How does the research community contribute to corporate climate-related risk disclosures? The gap between ideals and reality. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 30 , 927–940 (2023).
Stoll, P. P., Pauw, W. P., Tohme, F. & Grüning, C. Mobilizing private adaptation finance: lessons learned from the Green Climate Fund. Clim. Change 167 , 1–19 (2021).
Krueger, P., Sautner, Z. & Starks, L. T. The importance of climate risks for institutional investors. Rev. Financ. Stud. 33 , 1067–1111 (2020).
Tashman, P. & Rivera, J. Ecological uncertainty, adaptation, and mitigation in the U.S. ski resort industry: managing resource dependence and institutional pressures. Strateg. Manag. J. 37 , 1507–1525 (2016).
Oetzel, J. & Oh, C. H. A storm is brewing: antecedents of disaster preparation in risk prone locations. Strateg. Manag. J. 42 , 1545–1570 (2021).
Berrang-Ford, L. et al. A systematic global stocktake of evidence on human adaptation to climate change. Nat. Clim. Change 11 , 989–1000 (2021).
UK Government. Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD)-Aligned Disclosure Application Guidance—Phase 1. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/tcfd-aligned-disclosure-application-guidance/task-force-on-climate-related-financial-disclosure-tcfd-aligned-disclosure-application-guidance (UK Government, 2023).
European Commission. The Commission adopts the European Sustainability Reporting Standards . https://finance.ec.europa.eu/news/commission-adopts-european-sustainability-reporting-standards-2023-07-31_en (European Commission, 2023).
Haddaway, N. R. et al. Eight problems with literature reviews and how to fix them. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 4 , 1582–1589 (2020).
European Commission. Economic Power Shifts. https://knowledge4policy.ec.europa.eu/foresight/topic/expanding-influence-east-south/power-shifts_en (European Commission, 2020).
The Economist. Can the West Win over the Rest of the World? https://www.economist.com/asia/2023/05/16/can-the-west-win-over-the-rest-of-the-world (The Economist, 2023).
Huang, H. H., Kerstein, J., Wang, C. & Wu, F. Firm climate risk, risk management, and bank loan financing. Strateg. Manag. J. 43 , 2849–2880 (2022).
Ben-Amar, W., Gomes, M., Khursheed, H. & Marsat, S. Climate change exposure and internal carbon pricing adoption. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 31 , 2854–2870 (2022).
Pankratz, N., Bauer, R. & Derwall, J. Climate change, firm performance, and investor surprises. Manag. Sci. 69 , 7352–7398 (2023).
Bertrand, J.-L., Brusset, X. & Fortin, M. Assessing and hedging the cost of unseasonal weather: case of the apparel sector. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 244 , 261–276 (2015).
Tran, B. R. Sellin’ in the rain: weather, climate, and retail sales. Manag. Sci. 69 , 7423–7447 (2023).
Sautner, Z., Van Lent, L., Vilkov, G. & Zhang, R. Pricing climate change exposure. Manag. Sci. 69 , 7540–7561 (2023).
Ardia, D., Bluteau, K., Boudt, K. & Inghelbrecht, K. Climate change concerns and the performance of green vs. brown stocks. Manag. Sci. 69 , 7607–7632 (2023).
Alok, S., Kumar, N. & Wermers, R. Do fund managers misestimate climatic disaster risk. Rev. Financ. Stud. 33 , 1146–1183 (2020).
Todaro, N. M., Testa, F., Daddi, T. & Iraldo, F. The influence of managers’ awareness of climate change, perceived climate risk exposure and risk tolerance on the adoption of corporate responses to climate change. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 30 , 1232–1248 (2021).
Griese, K.-M., Franz, M., Busch, J. N. & Isensee, C. Acceptance of climate adaptation measures for transport operations: conceptual and empirical overview. Transp. Res. D: Transp. Environ. 101 , 103068 (2021).
Kump, B. When do threats mobilize managers for organizational change toward sustainability? An environmental belief model. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 30 , 2713–2726 (2021).
Pinkse, J. & Gasbarro, F. Managing physical impacts of climate change: an attentional perspective on corporate adaptation. Bus. Soc. 58 , 333–368 (2019).
Haigh, N. & Griffiths, A. Surprise as a catalyst for including climatic change in the strategic environment. Bus. Soc. 51 , 89–120 (2012).
Ng, A. K. Y., Wang, T., Yang, Z., Li, K. X. & Jiang, C. How is business adapting to climate change impacts appropriately? Insight from the commercial port sector. J. Bus. Ethics 150 , 1029–1047 (2018).
Kim, J.-B., Wang, C. & Wu, F. The real effects of risk disclosures: evidence from climate change reporting in 10-Ks. Rev. Account. Stud. 28 , 2271–2318 (2023).
Daddi, T., Bleischwitz, R., Todaro, N. M., Gusmerotti, N. M. & De Giacomo, M. R. The influence of institutional pressures on climate mitigation and adaptation strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 244 , 118879 (2020).
Ilhan, E., Krueger, P., Sautner, Z. & Starks, L. T. Climate risk disclosure and institutional investors. Rev. Financ. Stud. 36 , 2617–2650 (2023).
Nyberg, D. & Wright, C. Performative and political: corporate constructions of climate change risk. Organization 23 , 617–638 (2016).
Dang, V. A., Gao, N. & Yu, T. Climate policy risk and corporate financial decisions: evidence from the NOx budget trading program. Manag. Sci. 69 , 7517–7539 (2022).
Andersson, F. N. G. & Arvidsson, S. Understanding, mapping and reporting of climate-related risks among listed firms in Sweden. Clim. Policy 23 , 945–958 (2023).
Chabot, M. & Bertrand, J.-L. Climate risks and financial stability: Evidence from the European financial system. J. Financ. Stab. 69 , 101190 (2023).
Canevari‐Luzardo, L. M., Berkhout, F. & Pelling, M. A relational view of climate adaptation in the private sector: how do value chain interactions shape business perceptions of climate risk and adaptive behaviours? Bus. Strateg. Environ. 29 , 432–444 (2020).
Brusset, X. & Bertrand, J.-L. Hedging weather risk and coordinating supply chains. J. Oper. Manag. 64 , 41–52 (2018).
Truong, C. & Trück, S. It’s not now or never: implications of investment timing and risk aversion on climate adaptation to extreme events. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 253 , 856–868 (2016).
Linnenluecke, M. K., Birt, J. & Griffiths, A. The role of accounting in supporting adaptation to climate change. Account . Account. Financ. 55 , 607–625 (2015).
Huiskamp, U., Brinke, B. & Kramer, G. J. The climate resilience cycle: Using scenario analysis to inform climate‐resilient business strategies. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 31 , 1763–1775 (2022).
Wieland, A., Stevenson, M., Melnyk, S. A., Davoudi, S. & Schultz, L. Thinking differently about supply chain resilience: what we can learn from social-ecological systems thinking. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 43 , 1–21 (2023).
Orsato, R. J., Ferraz de Campos, J. G. & Barakat, S. R. Social learning for anticipatory adaptation to climate change: evidence from a community of practice. Organ. Environ. 32 , 416–440 (2019).
Tang, C.-H. & Jang, S. Weather risk management in ski resorts: Financial hedging and geographical diversification. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 30 , 301–311 (2011).
Bertrand, J.-L., Brusset, X. & Chabot, M. Protecting franchise chains against weather risk: a design science approach. J. Bus. Res. 125 , 187–200 (2021).
Engle, R. F., Giglio, S., Kelly, B., Lee, H. & Stroebel, J. Hedging climate change news. Rev. Financ. Stud. 33 , 1184–1216 (2020).
Ginglinger, E. & Moreau, Q. Climate risk and capital structure. Manag. Sci. 69 , 7492–7516 (2023).
Li, Y. & Zhang, Z. Corporate climate risk exposure and capital structure: evidence from Chinese listed companies. Finance Res. Lett. 51 , 103488 (2023).
Zhou, Z. & Wu, K. Does climate risk exposure affect corporate leverage adjustment speed? International evidence. J. Clean. Prod. 389 , 136036 (2023).
Javadi, S., Masum, A. A., Aram, M. & Rao, R. P. Climate change and corporate cash holdings: Global evidence. Financ. Manag. 52 , 253–295 (2023).
Dal Maso, L., Kanagaretnam, K., Lobo, G. J. & Mazzi, F. Does disaster risk relate to banks' loan loss provisions? Eur. Account. Rev. 31 , 1–30 (2022).
Wang, T., Liu, B., Zhang, J. & Li, G. A real options-based decision-making model for infrastructure investment to prevent rainstorm disasters. Prod. Oper. Manag. 28 , 2699–2715 (2019).
Calabrese, R., Dombrowski, T., Mandel, A., Pace, R. K. & Zanin, L. Impacts of extreme weather events on mortgage risks and their evolution under climate change: a case study on Florida. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 314 , 377–392 (2024).
Truong, C., Trück, S. & Mathew, S. Managing risks from climate impacted hazards—the value of investment flexibility under uncertainty. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 269 , 132–145 (2018).
Day, E., Fankhauser, S., Kingsmill, N., Costa, H. & Mavrogianni, A. Upholding labour productivity under climate change: an assessment of adaptation options. Clim. Policy 19 , 367–385 (2019).
Dahlmann, F. & Roehrich, J. K. Sustainable supply chain management and partner engagement to manage climate change information. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 28 , 1632–1647 (2019).
Farahani, M. H., Dawande, M., Gurnani, H. & Janakiraman, G. Better to bend than to break: sharing supply risk using the supply-flexibility contract. Manuf. Serv. Oper. Manag. 23 , 1257–1274 (2021).
Linnenluecke, M. K., Stathakis, A. & Griffiths, A. Firm relocation as adaptive response to climate change and weather extremes. Glob. Environ. Change 21 , 123–133 (2011).
UNEP. The 2023 Climate Risk Landscape , United Nations. https://www.unepfi.org/themes/climate-change/2023-climate-risk-landscape/ (UNEP, 2023).
IAS Plus. California Adopts Legislation Requiring Climate Disclosures . https://www.iasplus.com/en/news/2023/10/california-climate-bills (IAS Plus, 2023).
Cooper, K. IFRS S1 & IFRS S2: a Global Baseline of Financial Sustainability Reporting? The Accountant Online. https://www.theaccountant-online.com/features/ifrs-s1-ifrs-s2-a-global-baseline-of-financial-sustainability-reporting/?cf-view (2023).
S&P Global. Key Sustainability Trends That Will Drive Decision-making in 2023 . https://www.spglobal.com/esg/insights/featured/special-editorial/key-sustainability-trends-that-will-drive-decision-making-in-2023 (S&P Global, 2023).
IFRS. IFRS Foundation to Assume TCFD Monitoring Duties as ISSB Standards Pave the Way for Global Sustainability Reporting . https://www.ifrs.org/news-and-events/news/2023/07/foundation-welcomes-tcfd-responsibilities-from-2024/ (IFRS, 2023).
New Zealand Government. Mandatory Climate-related Disclosures . https://environment.govt.nz/what-government-is-doing/areas-of-work/climate-change/mandatory-climate-related-financial-disclosures/ (New Zealand Government, 2023).
McKinsey & Company. Understanding the SEC’s Proposed Climate Risk Disclosure Rule . https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/strategy-and-corporate-finance/our-insights/understanding-the-secs-proposed-climate-risk-disclosure-rule (McKinsey & Company, 2022).
Greenstone, M., Leuz, C. & Breuer, P. Mandatory disclosure would reveal corporate carbon damages. Science 381 , 837–840 (2023).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Deloitte. Double Materiality—5 Challenging Key Aspects to Consider . https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/de/Documents/risk/Deloitte_Sustainability_Double_Materiality.pdf (Deloitte, 2023).
Kaplan, R. & Ramanna, K. Accounting for Climate Change . Harv. Bus. Rev . https://hbr.org/2021/11/accounting-for-climate-change (2021).
O’Sullivan, M., Law, O. & Price, R. The Green Shoots of TCFD Reporting , PWC. https://www.pwc.com/jg/en/services/assets/pdf/green-shoots-of-tcfd-reporting.pdf (2022).
Lord, G. Weathering the Storm of Reporting: Factoring Climate Change Into Audited Financial Statements , PWC. https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/services/audit-assurance/corporate-reporting/climate-risks-audit.html (2023).
Gambhir, A. et al. Near-term transition and longer-term physical climate risks of greenhouse gas emissions pathways. Nat. Clim. Change 12 , 88–96 (2022).
Ilhan, E., Sautner, Z. & Vilkov, G. Carbon tail risk. Rev. Financ. Stud. 34 , 1540–1571 (2020).
Reddy, S. M. W. et al. Finding solutions to water scarcity: Incorporating ecosystem service values into business planning at The Dow Chemical Company’s Freeport, TX facility. Ecosyst. Serv. 12 , 94–107 (2015).
Nyberg, D. & Wright, C. Climate-proofing management research. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 36 , 713–728 (2022).
Oh, C. H. & Oetzel, J. Multinational enterprises and natural disasters: Challenges and opportunities for IB research. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 53 , 231–254 (2022).
Herrmann, J. & Guenther, E. Exploring a scale of organizational barriers for enterprises’ climate change adaptation strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 160 , 38–49 (2017).
Sakhel, A. Corporate climate risk management: are European companies prepared? J. Clean. Prod. 165 , 103–118 (2017).
Nicolletti, M., Lutti, N., Souza, R. & Pagotto, L. Social and organizational learning in the adaptation to the process of climate change: the case of a Brazilian thermoplastic resins and petrochemical company. J. Clean. Prod. 226 , 748–758 (2019).
Beermann, M. Linking corporate climate adaptation strategies with resilience thinking. J. Clean. Prod. 19 , 836–842 (2011).
Christensen, H. B., Hail, L. & Leuz, C. Mandatory CSR and sustainability reporting: economic analysis and literature review. Rev. Account. Stud 26 , 1176–1248 (2021).
NGFS. Scenarios Portal . https://www.ngfs.net/ngfs-scenarios-portal/ (NGFS, 2023).
Linnenluecke, M. K., Griffiths, A. & Winn, M. Extreme weather events and the critical importance of anticipatory adaptation and organizational resilience in responding to impacts. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 21 , 17–32 (2012).
SwissRe. Comprehensive Guide to Parametric Insurance. https://corporatesolutions.swissre.com/dam/jcr:0cd24f12-ebfb-425a-ab42-0187c241bf4a/2023-01-corso-guide-of-parametric-insurance.pdf (SwissRe, 2023).
Ali, K., Nadeem, M., Pandey, R. & Bhabra, G. S. Do capital markets reward corporate climate change actions? Evidence from the cost of debt. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 32 , 3417–3431 (2023).
Kouloukoui, D., de Marinho, M. M. O., da Silva Gomes, S. M., Kiperstok, A. & Ednildo Andrade, A. Corporate climate risk management and the implementation of climate projects by the world’s largest emitters. J. Clean. Prod. 238 , 117935 (2019).
Rivera, J. & Clement, V. Business adaptation to climate change: American ski resorts and warmer temperatures. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 28 , 1285–1301 (2019).
Gasbarro, F., Rizzi, F. & Frey, M. Adaptation measures of energy and utility companies to cope with water scarcity induced by climate change. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 25 , 54–72 (2016).
Ozkan, A., Temiz, H. & Yildiz, Y. Climate risk, corporate social responsibility, and firm performance. Br. J. Manag. 34 , 1791–1810 (2023).
Hossain, A. T. & Masum, A.-A. Does corporate social responsibility help mitigate firm-level climate change risk? Finance Res. Lett. 47 , 102791 (2022).
Hain, L. I., Kölbel, J. F. & Leippold, M. Let’s get physical: comparing metrics of physical climate risk. Finance Res. Lett. 46 , 102406 (2022).
Tsalis, T. A. & Nikolaou, I. E. Assessing the effects of climate change regulations on the business community: a system dynamic approach. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 26 , 826–843 (2017).
Nagar, V. & Schoenfeld, J. Measuring weather exposure with annual reports. Rev. Account. Stud. 29 , 1–32 (2022).
Huynh, T. D. & Xia, Y. Climate change news risk and corporate bond. Returns. J. Financial Quant. Anal. 56 , 1985–2009 (2021).
Robin, S. & Schubert, T. Cooperation with public research institutions and success in innovation: evidence from France and Germany. Res. Policy 42 , 149–166 (2013).
Laplane, A. & Mazzucato, M. Socializing the risks and rewards of public investments: economic, policy, and legal issues. Res. Policy 49 , 100008 (2020).
Kalinowski, T. The green climate fund and private sector climate finance in the global south. Clim. Policy 24 , 1–16 (2023).
Google Scholar
Kivimaa, P. & Rogge, K. S. Interplay of policy experimentation and institutional change in sustainability transitions: the case of mobility as a service in Finland. Res. Policy 51 , 104412 (2022).
Lindberg, M. B., Markard, J. & Andersen, A. D. Policies, actors and sustainability transition pathways: a study of the EU’s energy policy mix. Res. Policy 48 , 103668 (2019).
European Environment Agency. Assessing the Costs and Benefits of Climate Change Adaptation . https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/assesing-the-costs-and-benefits-of (European Environment Agency, 2023).
European Environment Agency. Economic Losses from Climate-related Extremes in Europe . https://www.eea.europa.eu/ims/economic-losses-from-climate-related (European Environment Agency, 2023).
Download references
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Münster, Institute for Entrepreneurship, Münster, Germany
Katharina Hennes & David Bendig
Ruhr-University Bochum, School of Business and Economics, Bochum, Germany
Andreas Löschel
RWI—Leibniz Institute for Economic Research, Essen, Germany
Fraunhofer Center for International Management and Knowledge Economy IMW, Leipzig, Germany
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
K.H. conducted the analyses, developed the concepts and wrote the manuscript. D.B. and A.L. contributed with project administration, supervision and conceptual support. All authors approved the final version and assumed responsibility for the paper.
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Katharina Hennes , David Bendig or Andreas Löschel .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary analyses, reporting summary, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Hennes, K., Bendig, D. & Löschel, A. Facing the storm: Developing corporate adaptation and resilience action plans amid climate uncertainty. npj Clim. Action 3 , 37 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44168-024-00116-2
Download citation
Received : 07 December 2023
Accepted : 27 March 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s44168-024-00116-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: Anthropocene newsletter — what matters in anthropocene research, free to your inbox weekly.
Advertisement
Supported by
Three Lives Entwined by Tragedy — and a Love of Literature
In Monica Wood’s rich new novel, “How to Read a Book,” death, prison and poetry become the catalyst for new beginnings.
- Share full article

By Helen Simonson
Helen Simonson is the author of “Major Pettigrew’s Last Stand” and “The Summer Before the War.” Her latest novel, “The Hazelbourne Ladies Motorcycle and Flying Club ,” is out now.
- Barnes and Noble
- Books-A-Million
When you purchase an independently reviewed book through our site, we earn an affiliate commission.
HOW TO READ A BOOK, by Monica Wood
”How to Read a Book” might be the perfect pick to really light a fire under my book club, and yours. It’s a charming, openhearted novel, deceptively easy to read but layered with sharp observations, hard truths and rich ideas.
Set in Portland, Maine, the novel opens in a women’s prison book club full of caustic inmates whose spirited discussions reveal a thick vein of humor and a weary compassion. According to Violet, a young woman with a manslaughter conviction and a gift for wicked turns of phrase, the weekly meetings are the highlight of a prison life so dull that “every day: same, same, same. The boredom feels like lice and you itch all over.” She and her fellow members have insulted every book choice but, she admits, “sometimes a sparkling sentence can really rip you up.”
Violet’s voice is self-aware, with a haunting fragility beneath the tough talk. And just as we fall for her we also meet Frank, a bookstore handyman still stunned by the death of his wife in a drunk-driving accident — caused by Violet. So much for easy! Wadsworth Books, a warm and welcoming independent bookstore full of young people and foster cats, is also the favorite haunt of our third narrative voice: the book club’s leader, Harriet, a widowed English teacher who is struggling to find purpose. “Retired people were often thought to be lonely, but it wasn’t that. It was the feeling of uselessness, of being done with it all,” she reflects. Harriet cultivates her prison book club as if gardening, “exposing the women to the open air of literature, to the sunshine of fresh ideas.” When Violet is released from prison, Harriet bumps into her at the bookstore and must hustle her to safety as Frank suffers a full meltdown.
Even after these three lives are neatly entangled (and recounted in alternating chapters), the heart of the story remains Violet, who stumbles into a job as an assistant at a research lab dedicated to proving that African gray parrots don’t just talk but also think (at last, real talking animals!). As she makes her fresh start, with the help of Harriet and occasional acts of random kindness from strangers, Violet still has to face Frank and the tragedy she caused.
Harriet instructs us that “stories have a ‘meanwhile’ — an important thing that’s happening while the rest of the story moves along,” and so the many layers of “meanwhile” delicately accrue. The novel asks us to stop and consider: Which kinds of people deserve second chances? Are people their worst acts, or a lifetime of better days? Is it possible to stop judging fictional characters (or each other in this divided, angry world) long enough to see that we are all “fellow creatures”? Personally, I want to talk about the parrots whose powers of cognition did nothing to free them from their life sentences.
Another “meanwhile”: The story here also serves as a meditation on the power of books. While Edgar Lee Masters’s 1915 poetry collection “Spoon River Anthology” plays a prominent role, works from J.D. Salinger, F. Scott Fitzgerald and William Butler Yeats to Zadie Smith and Maya Angelou underpin and suffuse every chapter.
“Harriet had always considered Angelou a tad pious,” Wood notes — a pot-calling-kettle moment that made me chortle, as “How to Read a Book” nudges the conscience as much as it pulls at the heartstrings. But it is also generously seasoned with unexpected twists and a wonderful wit. It’s never saccharine. In book clubs and in life, sometimes you just need a break from the sense of gritty hopelessness. This novel is a reminder that goodness, and books, can still win in this world.
HOW TO READ A BOOK | By Monica Wood | Mariner Books | 288 pp. | $28
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
The complicated, generous life of Paul Auster, who died on April 30 , yielded a body of work of staggering scope and variety .
“Real Americans,” a new novel by Rachel Khong , follows three generations of Chinese Americans as they all fight for self-determination in their own way .
“The Chocolate War,” published 50 years ago, became one of the most challenged books in the United States. Its author, Robert Cormier, spent years fighting attempts to ban it .
Joan Didion’s distinctive prose and sharp eye were tuned to an outsider’s frequency, telling us about ourselves in essays that are almost reflexively skeptical. Here are her essential works .
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .
- Case report
- Open access
- Published: 02 May 2024
Nexplanonectomy—the surgical removal of an embolized implanted contraceptive device: a case report and review of the literature
- Edward K. Maybury ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0006-3750-3922 1 ,
- Zachary C. Affrin 2 ,
- Christian Popa 2 ,
- Max Fowler 2 ,
- Bryan D. Laliberte 2 &
- Sarah C. Clarke 3
Journal of Medical Case Reports volume 18 , Article number: 234 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
128 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Nexplanon implants are a common hormonal contraceptive modality. Though rare, these devices can embolize into the injured wall of the basilic vein, through the right heart, and finally wedge itself into a pulmonary artery. With adherence to the arterial wall over time, it becomes less amenable to endovascular retrieval. Patients may present with symptoms mimicking a pulmonary embolism, or without any symptoms at all. In asymptomatic cases, endovascular retrieval and/or surgery is required when patients wish to begin having children prior to biological inactivity. The current literature showed as little as nine case reports detailing lung tissue removal in the aim of reversing a patient’s implanted contraceptive device.
Case presentation
A 22-year-old asymptomatic active-duty Caucasian female presented for elective outpatient Nexplanon removal. The suspicion of possible implant migration arose when it was discovered to be non-palpable in her left arm. After plain film x-rays failed to localize the implant, a chest x-ray and follow-up Computed Tomography (CT) scan revealed that the Nexplanon had migrated to a distal branch of the left pulmonary artery. Due to the patient’s strong desires to begin having children, the decision was made for removal. Initial endovascular retrieval failed due to Nexplanon encapsulation within the arterial wall. Ultimately, the patient underwent a left video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) for exploration and left lower lobe basilar S7–9 segmentectomy, which successfully removed the Nexplanon.
Conclusions
Implanted contraceptive devices can rarely result in migration to the pulmonary vasculature. These radiopaque devices are detectable on imaging studies if patients and clinicians are unable to palpate them. An endovascular approach should be considered first to spare lung tissue and avoid chest-wall incisions, but can be complicated by encapsulation and adherence to adjacent tissue. A VATS procedure with single-lung ventilation via a double-lumen endotracheal tube allows surgeons to safely operate on an immobilized lung while anesthesiologists facilitate single-lung ventilation. This patient’s case details the uncommon phenomenon of Nexplanon migration, and the exceedingly rare treatment resolution of lung resection to remove an embolized device.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Patients elect to receive and remove implantable contraceptive devices at many different stages of life, and for a myriad of reasons. Some are young without comorbidities, while others can be older with many health conditions to consider. Nexplanon is an estrogen-free hormonal implant measuring 4 cm in length and designed to be inserted into the upper arm for constant gradual administration of etonogestrel over 3 years. They are meant to be detected by direct palpation to the arm, where they are placed. Rarely, they can embolize through a large vein and travel through the right atrium, then the right ventricle, and end up in the pulmonary vasculature. As the vascular diameter narrows, the device can wedge into a pulmonary artery, preventing blood supply similar in nature to a pulmonary embolism. When these devices migrate, a patient can become suddenly symptomatic, gradually symptomatic, or not symptomatic as all [ 1 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 11 , 14 ]. This varied presentation is a product of the ultimate end-location of the migrated device, and the patient’s overall health. Upon the discovery that a device has migrated, typically by failure to palpate the implant, imaging studies are employed, which reflects the actions taken in this case [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ]. Following Computed Tomography (CT) chest imaging, the device was confirmed to be located in the left lower lobe, highly suspicious of migration via the left upper extremity (LUE) basilic vein. Herein, we present a rare case of Nexplanonectomy via partial lung lobectomy in a young, healthy female.
Case description
A 22-year-old healthy active-duty Caucasian female presented to her primary care clinic for removal of her implanted Nexplanon device approximately 1 year after placement at another facility. Palpation of her upper arm yielded no appreciable rod. Subsequent imaging of the upper arm and chest was concerning for the presence of a foreign body in the left lung field. CT imaging of the chest revealed the Nexplanon implant to be located in her left lower lobe (Fig. 1 ). At no time did she express respiratory symptoms, pain, or decrease in physical stamina either at rest or while exercising. There was concern for a loss of perfusion and destruction of the parenchyma, however, previously reported asymptomatic cases like this one have safely left devices in situ per the patient’s wishes. This option would alleviate the need for surgery, but would also prevent her from bearing children. Though she had been asymptomatic, she expressed a strong desire to start a family imminently, and did not wish to leave the implant in place and wait for it to become hormonally inactive. Thus, the decision for removal was made and the patient was scheduled for an endovascular procedure.
CT chest showing embolized Nexplanon (thin white arrow)
The patient was taken to the interventional radiology suite, where she received a general anesthetic with endotracheal intubation. Interventional radiology attempted to remove the implant safely from the distal branch of the left pulmonary artery, via femoral vascular access. After numerous attempts there was a high suspicion that the Nexplanon had become encapsulated and was adhered to the wall of that artery, as the implant did not retract freely when snared (Figs. 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , Additional file 1 : Video S1, Additional file 2 : Video S2, Additional file 3 : Video S3). There was a concern for catastrophic bleeding should further attempts at endovascular removal be made. This new consideration led to the halting of this procedure and a discussion with the patient about how to proceed.
Interventional radiology image with contrast dye proximal to Nexplanon device (yellow arrow) series A
Interventional radiology image with contrast dye obstructed by Nexplanon device (yellow arrow) series A
Interventional radiology image with contrast dye obstructed by Nexplanon device (yellow arrow) series B
Interventional radiology image with contrast dye progressing through distal pulmonary arteries not obstructed by Nexplanon device (yellow arrow)
Interventional radiology image without contrast showing radiopaque Nexplanon device near the left heart border
Interventional radiology image with contrast showing the Nexplanon device obstructing contrast flow to distal arterial vessels
Thoracic surgery was consulted and the patient underwent a left VATS for exploration and left lower lobe basilar S7–9 segmentectomy (Fig. 8 ). General anesthesia with a double lumen endotracheal tube was used to simultaneously allow for adequate respiration and isolated left lung deflation. The S6 superior segment of the left lower lobe was spared with preoperative and postoperative fiberoptic bronchoscopy. The procedure was uncomplicated, and the patient was transferred to the surgical intensive care unit for recovery. On post-operative day 1, she was ambulating and her pain was well controlled. She was transferred to a floor unit on post-operative day 2. On post-operative day 3, her chest tube was discontinued and she was discharged. At her 28-week and 45-week follow-up, she had continuing chronic left flank pain as well as chest pain with deep inspiration. She complied with her pain medication regimen and continued to follow up as needed.
Segmentectomy with excised Nexplanon
Discussion and conclusions
The estimated incidence of Nexplanon migration into pulmonary vasculature is 3.17 per 100,000 implants (95% CI 1.37 to 6.24) [ 12 ]. Statistics from the National Survey of Family Growth estimated the percentage of women aged 15–49 who have ever used contraceptive implants to be 5.6 from 2015 to 2017 (SE 0.50, n = 5594), and 5.8 from 2017 to 2019 (SE 0.46, n = 6141) [ 9 ]. The above case is highly unusual, both with respect to the device migrating from brachial subcutaneous tissue to the vasculature of the lung, and the ultimate action needed for removal. Of the 55 reported cases of contraceptive device migration from the upper arm into the pulmonary vasculature, much can be gathered. The first consideration would be to attempt an endovascular retrieval, lessening the need for an open procedure. 21 of the 55 cases detail successful retrieval of the pulmonary embolized Nexplanon, without major complications. Of the 7 unsuccessful endovascular procedures, 5 moved forward with successful VATS, without major complications. The remaining 2 were left in situ. Of the total cases, 11 elected for successful VATS without an endovascular attempt. 13 cases did not move forward with any retrieval attempts, and left their devices in situ. 3 cases have unknown surgical considerations or outcomes. These findings can be seen in Tables 1 , 2 , 3 .
The impetus for suspicion of migration of a Nexplanon is varied. Some patients may be symptomatic, and exhibit presentation signs of pulmonary embolism in the event of an implant migration. Our patient was quite athletic, and as the Nexplanon had embolized to a distal branch of the left pulmonary artery, the loss of perfusion to that segment of the lung did not result in symptoms.
Following placement, patients are instructed on how to palpate for their Nexplanon device. They and their clinicians should be able to reliably relocate it at any time. Patients are also instructed to seek evaluation should they notice any irregularities with routine palpations. Despite the absence of guidelines pertaining to the work-up of a possibly embolized Nexplanon [ 4 ], these devices are radio-opaque and plain films of the arm and then the chest should be considered upon failure to palpate the device. Findings on a chest x-ray of possible pulmonary migration should be followed up by CT imaging to further characterize the location. A minimally invasive approach, such as endovascular retrieval should then be considered if the patient strongly desires implant removal, or if the patient is symptomatic because of the embolized device. Endovascular approaches have the benefit of sparing lung tissue and avoiding the pain of chest-wall incisions, but can be complicated by the Nexplanon’s tendency to encapsulate and adhere to adjacent tissue [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 6 , 12 , 13 ]. This encapsulation is by design and is meant to prevent a Nexplanon from leaving its primary placement site, but can be problematic if it occurs after the device has moved. As seen in this case, this encapsulation can occur at the wall of a vessel, and thus make the device adherent and not amenable to endovascular removal. There are only a handful of studies correlating the duration of time since implantation in relation to successful endovascular retrieval [ 1 , 3 , 6 , 12 ]. Utilizing patient history in regard to how long the implant has been in place is not a reliable measure to predict endovascular fibrosis and trapping. Our patient did not seek consultation until a desire for removal approximately 1 year following implantation. In asymptomatic patients, like ours, it is unclear whether the embolization occurred closer to the time of implantation or some time thereafter. In 38% of the reported cases, endovascular retrieval proved successful. In rare cases, such as this one, a VATS operation will be necessary after a failed endovascular procedure (11%). It is key that patients are aware of the potential need for two procedures when making the decision to remove an embolized Nexplanon.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during this case report and literature review are publicly available, as well as available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery
Computed tomography
Left upper extremity
Clermidy H, et al . Management of etonogestrel implant migration into the pulmonary artery. Contraception. 2022;113:62–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2022.03.017 . ( Epub 2022 Mar 26 ).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
KafiMallak F, et al . Migration of a subdermal contraceptive implant into a subsegmental pulmonary artery and etonogestrel serum concentration over time—a case report. Eur J Contracept Reprod Health Care. 2022;27(3):261–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/13625187.2022.2036977 . ( Epub 2022 Feb 17 ).
Article Google Scholar
Barlow-Evans R, et al . Migration of a Nexplanon contraceptive implant to the pulmonary artery. BMJ Case Rep. 2017;2017: bcr2017219259. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-219259 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hindy JR, Souaid T, Larus CT, Glanville J, Aboujaoude R. Nexplanon migration into a subsegmental branch of the pulmonary artery: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine. 2020;99(4): e18881. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000018881 .
Tricard J, Chermat A, Bertin F. Transparenchymal thoracoscopic retrieval of a contraceptive implant pulmonary embolism. JTCVS Tech. 2022;13:240–1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xjtc.2022.01.027 .
O’Brien A, O’Reilly MK, Sugrue G, Lawler L, Farrelly C. Subdermal contraceptive implant embolism to a pulmonary artery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;99(6):2254–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.12.017 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Heudes PM, LaigleQuerat V, Darnis E, Defrance C, Douane F, Frampas E. Migration of a contraceptive subcutaneous device into the pulmonary artery. Report of a case. Case Rep Womens Health. 2015;8:6–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crwh.2015.09.002 .
D’Journo XB, Vidal V, Agostini A. Intravascular pulmonary migration of a subdermal contraceptive implant. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;99(5):1828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2014.12.049 .
NSFG—listing C—key statistics from the National Survey of Family Growth. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 29 June 2022. www.cdc.gov/nchs/nsfg/key_statistics/c-keystat.htm#contraception .
Thomas PA, Di Stefano D, Couteau C, D’Journo XB. Contraceptive implant embolism into the pulmonary artery: thoracoscopic retrieval. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103(3):e271–2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.08.094 .
Choi JH, Kim HY, Lee SS, Cho S. Migration of a contraceptive subdermal device into the lung. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2017;60(3):314–7. https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2017.60.3.314 . ( Epub 2017 May 15 ).
Simon C, Maurier A, Gaboriau L, Vrignaud L, Dayani P, Vaillant T, Andrée Bos-Thompson M, Jonville-Bera AP. Incidence and characteristics of intravascular pulmonary migration of etonogestrel implants: a French nationwide study. Contraception. 2020;102(3):186–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.contraception.2020.05.006 . ( Epub 2020 May 14 ).
Cerato A, Luyckx M, Ghaye B. Migration of implanon contraceptive implant into the pulmonary artery. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2019;100(1):59–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2018.08.006 . ( Epub 2018 Sep 6 ).
Kew EP, Senanayake E, Djearaman M, Bishay E. Migration of contraceptive implant into the left pulmonary arterial system. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2017;25(7–8):537–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/0218492317716589 . ( Epub 2017 Jun 12 ).
Gao GT, Binder W. Embolization of a contraceptive implant into the pulmonary vasculature in an adolescent female. Am J Emerg Med. 2018;36(6):1122.e1-1122.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2018.03.004 . ( Epub 2018 Mar 3 ).
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
No grants or financial support was received for this case report.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Naval Medical Center San Diego, 34800 Bob Wilson Drive, San Diego, CA, 92134, USA
Edward K. Maybury
Department of Anesthesiology, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, MD, 20814, USA
Zachary C. Affrin, Christian Popa, Max Fowler & Bryan D. Laliberte
Darnall Medical Library, Walter Reed National Military Medical Center, Bethesda, MD, 20814, USA
Sarah C. Clarke
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Edward K. Maybury: this author was primarily responsible for drafting and editing the manuscript. This author also edited supplemental video and imaging files, constructed pertinent tables, and conducted the primary literature review. Zachary C. Affrin: this author was primarily responsible for drafting and editing the manuscript, as well as collecting pertinent documentation. Max Fowler: this author was responsible for drafting and editing the manuscript, as well as collecting supplemental imaging and video files. Bryan D. Laliberte: this author was responsible for drafting and editing the manuscript, as well as collecting supplemental imaging and video files. Christian Popa: this author provided reviews, recommendations, and supervision throughout the project. Sarah C. Clarke: this author provided thorough supplementary literature review references in conjunction with the Darnall Medical Library. All authors were involved in writing, editing, and reviewing the paper prior to submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Edward K. Maybury .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Written and verbal informed consent was obtained from the patient for participation in this case report. Ethics Committee approval not applicable for this case report.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Video S1. Nexplanon obstructing contrast flow (right side of screen).
Additional file 2: Video S2. Nexplanon obstructing contrast flow (alternate angle).
Additional file 3: Video S3. Nexplanon visible while contrast applied to a nearby uninvolved pulmonary artery.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Maybury, E.K., Affrin, Z.C., Popa, C. et al. Nexplanonectomy—the surgical removal of an embolized implanted contraceptive device: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Reports 18 , 234 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04547-7
Download citation
Received : 30 January 2024
Accepted : 05 April 2024
Published : 02 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-024-04547-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Implanted device migration
- Segmentectomy
- Single-lung ventilation
- Endovascular retrieval
- Contraceptive removal
Journal of Medical Case Reports
ISSN: 1752-1947
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A literature review shows how the investigation you are conducting fits with what has gone before and puts it into context. A literature review demonstrates to your reader that you are able to: Understand and critically analyse the background research. Select and source the information that is necessary to develop a context for your research.
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
Step One: Decide on your areas of research: Before you begin to search for articles or books, decide beforehand what areas you are going to research. Make sure that you only get articles and books in those areas, even if you come across fascinating books in other areas. A literature review I am currently working on, for example, explores ...
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
3. Evaluate and select literature. 4. Analyze the literature. 5. Plan the structure of your literature review. 6. Write your literature review. Other resources to help you write a successful literature review.
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
How to write a literature review in 6 steps. How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.
Steps to Completing a Literature Review. Conduct searches for relevant information. Critically review your sources. Create a synthesis matrix to find connections between resources, and ensure your sources relate to your main ideas. Use the synthesis matrix to organize your literature review. Integrate the individual main ideas to put together ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Option 1: Chronological (according to date) Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
Make sure you develop a good system that works for you and use it. 3. Don't write a laundry list of papers A literature review should be a synthesis of the papers you have read to tell a meaningful story about the literature, not a simple list of paraphrases of what each paper said. 4.
Don't know how to write a literature review or where to begin? This video will give you a quick run-through of the 5 steps you need to follow when writing a ...
The literature review needs to critically examine the texts that relate to your research question, rather than to just list what you have located. Therefore, you must link the literature to your research question, demonstrating how it supports or extends the topic or the existing knowledge in the area. You should also highlight the strengths ...
Example: Predictors and Outcomes of U.S. Quality Maternity Leave: A Review and Conceptual Framework: 10.1177/08948453211037398 ; Systematic review: "The authors of a systematic review use a specific procedure to search the research literature, select the studies to include in their review, and critically evaluate the studies they find." (p. 139).
The topic must at least be: interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary), an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and.
The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader's guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. ... Example 1: An effective introduction for an academic literature review paper. To begin, let ...
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way. ... Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later. If you ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. ... A convenient way to start your literature search can be to use published review articles or academic text books to learn the background to a subject. This might help ...
The first step in starting a literature review is to identify a topic. Once you have identified a topic, you can start searching for sources. When searching for sources, it is important to use a variety of search strategies, such as keyword searches, author searches, and database searches. It is also important to use a variety of sources, such ...
To do a literature review, start by finding a variety of reliable sources that all relate to one topic or theme. Then, read through the sources and come up with a thesis statement for your paper. Once you have your thesis, explain how the sources you used back up your thesis in the body of your literature review. You can arrange the sources ...
Your literature review should begin with a clear definition of its scope. This involves setting the boundaries of your research, such as the time frame, the educational levels, and the subjects ...
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
The flow diagram, generated according to PRISMA, describes the process of the systematic literature review, including all steps from the identification of the initial sample to the analysis of the ...
In other words, Biden threatening to cut off aid to the Jewish state if it takes measures against its enemies is a feature, rather than a bug, of his decades-old policy. Menachem Begin saw clearly ...
Set in Portland, Maine, the novel opens in a women's prison book club full of caustic inmates whose spirited discussions reveal a thick vein of humor and a weary compassion. According to Violet ...
Due to the patient's strong desires to begin having children, the decision was made for removal. Initial endovascular retrieval failed due to Nexplanon encapsulation within the arterial wall. ... and conducted the primary literature review. Zachary C. Affrin: this author was primarily responsible for drafting and editing the manuscript, as ...
The present study attempts, through an extensive review of the literature, to provide a holistic view and deeper knowledge of the most significant factors that influence university students' decisions to be self-employed or to start a business. A systematic review as well as a bibliometric analysis of the literature was implemented, using a ...