How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.

Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Federal vs. private parent student loans.
Erika Giovanetti May 9, 2024

14 Colleges With Great Food Options
Sarah Wood May 8, 2024

Colleges With Religious Affiliations
Anayat Durrani May 8, 2024

Protests Threaten Campus Graduations
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 6, 2024

Protesting on Campus: What to Know
Sarah Wood May 6, 2024

Lawmakers Ramp Up Response to Unrest
Aneeta Mathur-Ashton May 3, 2024

University Commencements Must Go On
Eric J. Gertler May 3, 2024

Where Astronauts Went to College
Cole Claybourn May 3, 2024

College Admitted Student Days
Jarek Rutz May 3, 2024

Universities, the Police and Protests
John J. Sloan III May 2, 2024

- History Classics
- Your Profile
- Find History on Facebook (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Twitter (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on YouTube (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on Instagram (Opens in a new window)
- Find History on TikTok (Opens in a new window)
- This Day In History
- History Podcasts
- History Vault
COVID-19 Pandemic
By: History.com Editors
Updated: March 11, 2024 | Original: April 25, 2023
The outbreak of the infectious respiratory disease known as COVID-19 triggered one of the deadliest pandemics in modern history. COVID-19 claimed nearly 7 million lives worldwide. In the United States, deaths from COVID-19 exceeded 1.1 million, nearly twice the American death toll from the 1918 flu pandemic . The COVID-19 pandemic also took a heavy toll economically, politically and psychologically, revealing deep divisions in the way that Americans viewed the role of government in a public health crisis, particularly vaccine mandates. While the United States downgraded its “national emergency” status over the pandemic on May 11, 2023, the full effects of the COVID-19 pandemic will reverberate for decades.
A New Virus Breaks Out in Wuhan, China
In December 2019, the China office of the World Health Organization (WHO) received news of an isolated outbreak of a pneumonia-like virus in the city of Wuhan. The virus caused high fevers and shortness of breath, and the cases seemed connected to the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan, which was closed by an emergency order on January 1, 2020.
After testing samples of the unknown virus, the WHO identified it as a novel type of coronavirus similar to the deadly SARS virus that swept through Asia from 2002-2004. The WHO named this new strain SARS-CoV-2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2). The first Chinese victim of SARS-CoV-2 died on January 11, 2020.
Where, exactly, the novel virus originated has been hotly debated. There are two leading theories. One is that the virus jumped from animals to humans, possibly carried by infected animals sold at the Wuhan market in late 2019. A second theory claims the virus escaped from the Wuhan Institute of Virology, a research lab that was studying coronaviruses. U.S. intelligence agencies maintain that both origin stories are “plausible.”
The First COVID-19 Cases in America
The WHO hoped that the virus outbreak would be contained to Wuhan, but by mid-January 2020, infections were reported in Thailand, Japan and Korea, all from people who had traveled to China.
On January 18, 2020, a 35-year-old man checked into an urgent care center near Seattle, Washington. He had just returned from Wuhan and was experiencing a fever, nausea and vomiting. On January 21, he was identified as the first American infected with SARS-CoV-2.
In reality, dozens of Americans had contracted SARS-CoV-2 weeks earlier, but doctors didn’t think to test for a new type of virus. One of those unknowingly infected patients died on February 6, 2020, but her death wasn’t confirmed as the first American casualty until April 21.
On February 11, 2020, the WHO released a new name for the disease causing the deadly outbreak: Coronavirus Disease 2019 or COVID-19. By mid-March 2020, all 50 U.S. states had reported at least one positive case of COVID-19, and nearly all of the new infections were caused by “community spread,” not by people who contracted the disease while traveling abroad.
At the same time, COVID-19 had spread to 114 countries worldwide, killing more than 4,000 people and infecting hundreds of thousands more. On March 11, the WHO made it official and declared COVID-19 a pandemic.
The World Shuts Down
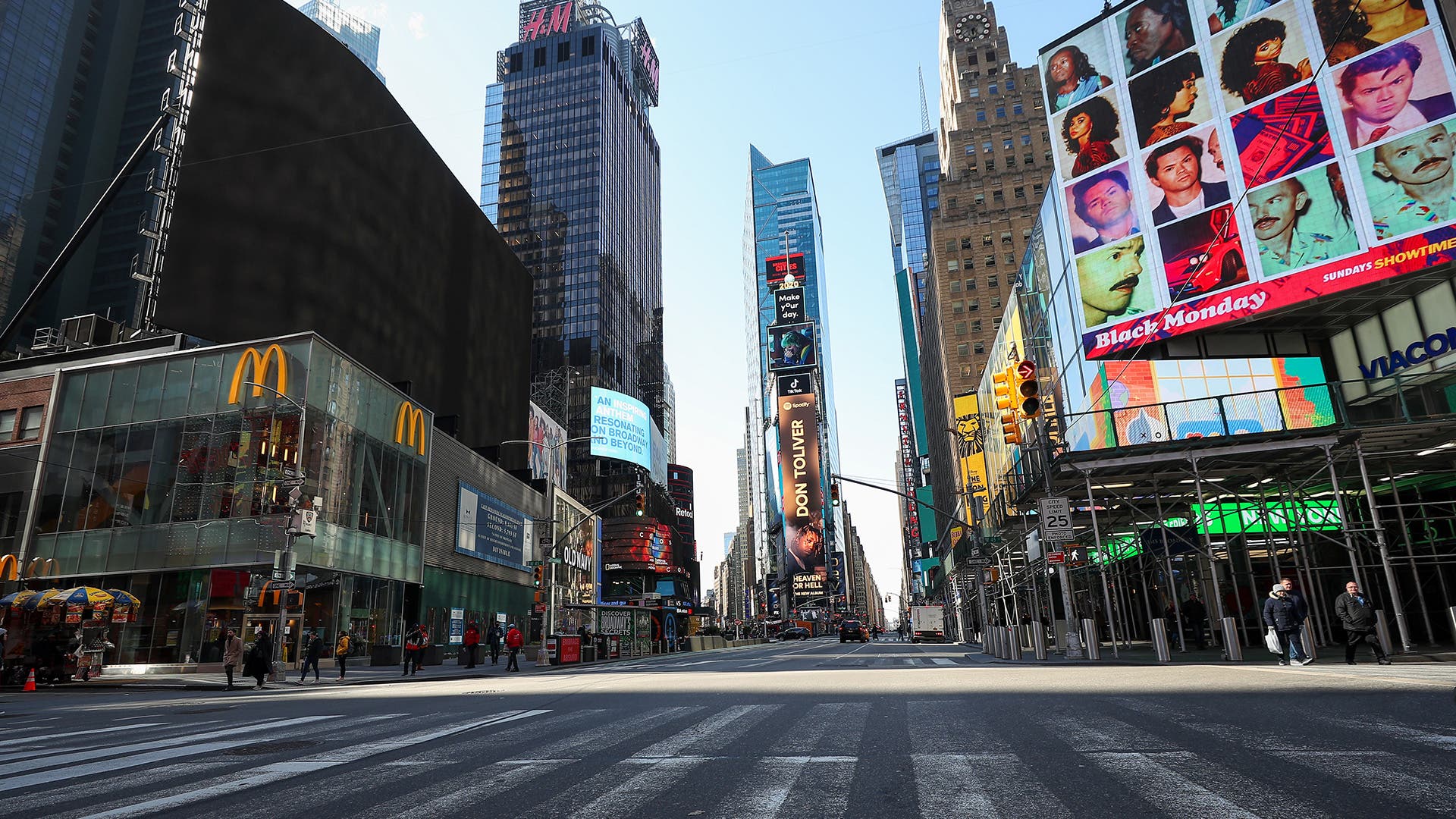

Pandemics are expected in a globally interconnected world, so emergency plans were in place. In the United States, health officials at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) set in motion a national response plan developed for flu pandemics.
State by state and city by city, government officials took emergency measures to encourage “ social distancing ,” one of the many new terms that became part of the COVID-19 vocabulary. Travel was restricted. Schools and churches were closed. With the exception of “essential workers,” all offices and businesses were shuttered. By early April 2020, more than 316 million Americans were under a shelter-in-place or stay-at-home order.
With more than 1,000 deaths and nearly 100,000 cases, it was clear by April 2020 that COVID-19 was highly contagious and virulent. What wasn’t clear, even to public health officials, was how individuals could best protect themselves from COVID-19. In the early weeks of the outbreak, the CDC discouraged people from buying face masks, because officials feared a shortage of masks for doctors and hospital workers.
By April 2020, the CDC revised its recommendations, encouraging people to wear masks in public, to socially distance and to wash hands frequently. President Donald Trump undercut the CDC recommendations by emphasizing that masking was voluntary and vowing not to wear a mask himself. This was just the beginning of the political divisions that hobbled the COVID-19 response in America.
Global Financial Markets Collapse
In the early months of the COVID-19 pandemic, with billions of people worldwide out of work, stuck at home, and fretting over shortages of essential items like toilet paper , global financial markets went into a tailspin.
In the United States, share prices on the New York Stock Exchange plummeted so quickly that the exchange had to shut down trading three separate times. The Dow Jones Industrial Average eventually lost 37 percent of its value, and the S&P 500 was down 34 percent.
Business closures and stay-at-home orders gutted the U.S. economy. The unemployment rate skyrocketed, particularly in the service sector (restaurant and other retail workers). By May 2020, the U.S. unemployment rate reached 14.7 percent, the highest jobless rate since the Great Depression .
All across America, households felt the pinch of lost jobs and lower wages. Food insecurity reached a peak by December 2020 with 30 million American adults—a full 14 percent—reporting that their families didn’t get enough to eat in the past week.
The economic effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, like its health effects, weren’t experienced equally. Black, Hispanic and Native Americans suffered from unemployment and food insecurity at significantly higher rates than white Americans.
Congress tried to avoid a complete economic collapse by authorizing a series of COVID-19 relief packages in 2020 and 2021, which included direct stimulus checks for all American families.
The Race for a Vaccine
A new vaccine typically takes 10 to 15 years to develop and test, but the world couldn’t wait that long for a COVID-19 vaccine. The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) under the Trump administration launched “ Operation Warp Speed ,” a public-private partnership which provided billions of dollars in upfront funding to pharmaceutical companies to rapidly develop vaccines and conduct clinical trials.
The first clinical trial for a COVID-19 vaccine was announced on March 16, 2020, only days after the WHO officially classified COVID-19 as a pandemic. The vaccines developed by Moderna and Pfizer were the first ever to employ messenger RNA, a breakthrough technology. After large-scale clinical trials, both vaccines were found to be greater than 95 percent effective against infection with COVID-19.
A nurse from New York officially became the first American to receive a COVID-19 vaccine on December 14, 2020. Ten days later, more than 1 million vaccines had been administered, starting with healthcare workers and elderly residents of nursing homes. As the months rolled on, vaccine availability was expanded to all American adults, and then to teenagers and all school-age children.
By the end of the pandemic in early 2023, more than 670 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines had been administered in the United States at a rate of 203 doses per 100 people. Approximately 80 percent of the U.S. population received at least one COVID-19 shot, but vaccination rates were markedly lower among Black, Hispanic and Native Americans.
COVID-19 Deaths Heaviest Among Elderly and People of Color
In America, the COVID-19 pandemic impacted everyone’s lives, but those who died from the disease were far more likely to be older and people of color.
Of the more than 1.1 million COVID deaths in the United States, 75 percent were individuals who were 65 or older. A full 93 percent of American COVID-19 victims were 50 or older. Throughout the emergence of COVID-19 variants and the vaccine rollouts, older Americans remained the most at-risk for being hospitalized and ultimately dying from the disease.
Black, Hispanic and Native Americans were also at a statistically higher risk of developing life-threatening COVID-19 systems and succumbing to the disease. For example, Black and Hispanic Americans were twice as likely to be hospitalized from COVID-19 than white Americans. The COVID-19 pandemic shined light on the health disparities between racial and ethnic groups driven by systemic racism and lower access to healthcare.
Mental health also worsened during the COVID-19 pandemic. The anxiety of contracting the disease, and the stresses of being unemployed or confined at home, led to unprecedented numbers of Americans reporting feelings of depression and suicidal ideation.
A Time of Social & Political Upheaval
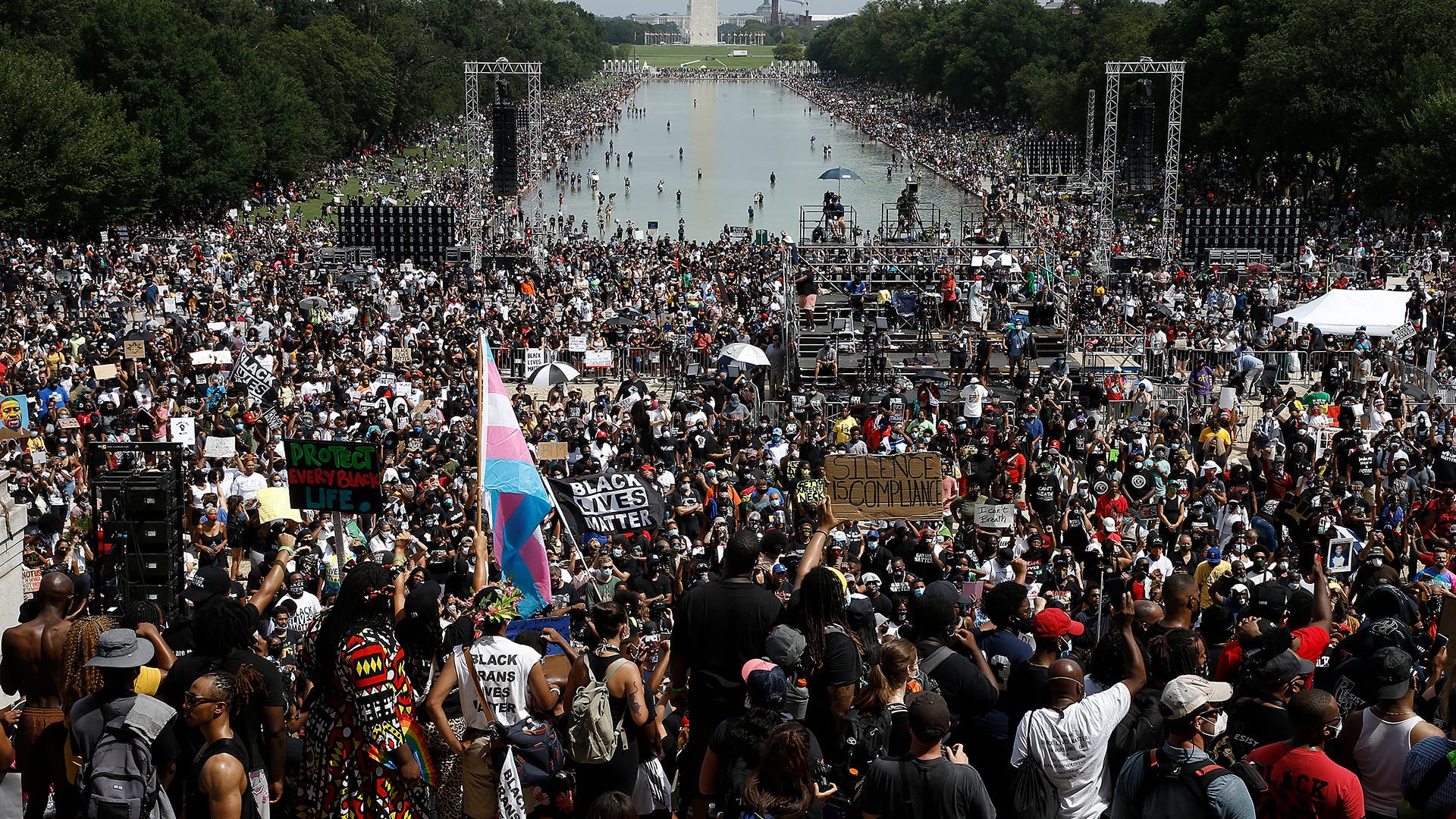

In the United States, the three long years of the COVID-19 pandemic paralleled a time of heightened political contention and social upheaval.
When George Floyd was killed by Minneapolis police on May 25, 2020, it sparked nationwide protests against police brutality and energized the Black Lives Matter movement. Because so many Americans were out of work or home from school due to COVID-19 shutdowns, unprecedented numbers of people from all walks of life took to the streets to demand reforms.
Instead of banding together to slow the spread of the disease, Americans became sharply divided along political lines in their opinions of masking requirements, vaccines and social distancing.
By March 2024, in signs that the pandemic was waning, the CDC issued new guidelines for people who were recovering from COVID-19. The agency said those infected with the virus no longer needed to remain isolated for five days after symptoms. And on March 10, 2024, the Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center stopped collecting data for its highly referenced COVID-19 dashboard.
Still, an estimated 17 percent of U.S. adults reported having experienced symptoms of long COVID, according to the Household Pulse Survey. The medical community is still working to understand the causes behind long COVID, which can afflict a patient for weeks, months or even years.

HISTORY Vault
Stream thousands of hours of acclaimed series, probing documentaries and captivating specials commercial-free in HISTORY Vault
“CDC Museum COVID Timeline.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . “Coronavirus: Timeline.” U.S. Department of Defense . “COVID-19 and Related Vaccine Development and Research.” Mayo Clinic . “COVID-19 Cases and Deaths by Race/Ethnicity: Current Data and Changes Over Time.” Kaiser Family Foundation . “Number of COVID-19 Deaths in the U.S. by Age.” Statista . “The Pandemic Deepened Fault Lines in American Society.” Scientific American . “Tracking the COVID-19 Economy’s Effects on Food, Housing, and Employment Hardships.” Center on Budget and Policy Priorities . “U.S. Confirmed Country’s First Case of COVID-19 3 Years Ago.” CNN .

Sign up for Inside History
Get HISTORY’s most fascinating stories delivered to your inbox three times a week.
By submitting your information, you agree to receive emails from HISTORY and A+E Networks. You can opt out at any time. You must be 16 years or older and a resident of the United States.
More details : Privacy Notice | Terms of Use | Contact Us
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 76, Issue 2
- COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on social relationships and health
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1512-4471 Emily Long 1 ,
- Susan Patterson 1 ,
- Karen Maxwell 1 ,
- Carolyn Blake 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7342-4566 Raquel Bosó Pérez 1 ,
- Ruth Lewis 1 ,
- Mark McCann 1 ,
- Julie Riddell 1 ,
- Kathryn Skivington 1 ,
- Rachel Wilson-Lowe 1 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4409-6601 Kirstin R Mitchell 2
- 1 MRC/CSO Social and Public Health Sciences Unit , University of Glasgow , Glasgow , UK
- 2 MRC/CSO Social and Public Health Sciences Unit, Institute of Health & Wellbeing , University of Glasgow , Glasgow , UK
- Correspondence to Dr Emily Long, MRC/CSO Social and Public Health Sciences Unit, University of Glasgow, Glasgow G3 7HR, UK; emily.long{at}glasgow.ac.uk
This essay examines key aspects of social relationships that were disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. It focuses explicitly on relational mechanisms of health and brings together theory and emerging evidence on the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic to make recommendations for future public health policy and recovery. We first provide an overview of the pandemic in the UK context, outlining the nature of the public health response. We then introduce four distinct domains of social relationships: social networks, social support, social interaction and intimacy, highlighting the mechanisms through which the pandemic and associated public health response drastically altered social interactions in each domain. Throughout the essay, the lens of health inequalities, and perspective of relationships as interconnecting elements in a broader system, is used to explore the varying impact of these disruptions. The essay concludes by providing recommendations for longer term recovery ensuring that the social relational cost of COVID-19 is adequately considered in efforts to rebuild.
- inequalities
Data availability statement
Data sharing not applicable as no data sets generated and/or analysed for this study. Data sharing not applicable as no data sets generated or analysed for this essay.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 Unported (CC BY 4.0) license, which permits others to copy, redistribute, remix, transform and build upon this work for any purpose, provided the original work is properly cited, a link to the licence is given, and indication of whether changes were made. See: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/jech-2021-216690
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Infectious disease pandemics, including SARS and COVID-19, demand intrapersonal behaviour change and present highly complex challenges for public health. 1 A pandemic of an airborne infection, spread easily through social contact, assails human relationships by drastically altering the ways through which humans interact. In this essay, we draw on theories of social relationships to examine specific ways in which relational mechanisms key to health and well-being were disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Relational mechanisms refer to the processes between people that lead to change in health outcomes.
At the time of writing, the future surrounding COVID-19 was uncertain. Vaccine programmes were being rolled out in countries that could afford them, but new and more contagious variants of the virus were also being discovered. The recovery journey looked long, with continued disruption to social relationships. The social cost of COVID-19 was only just beginning to emerge, but the mental health impact was already considerable, 2 3 and the inequality of the health burden stark. 4 Knowledge of the epidemiology of COVID-19 accrued rapidly, but evidence of the most effective policy responses remained uncertain.
The initial response to COVID-19 in the UK was reactive and aimed at reducing mortality, with little time to consider the social implications, including for interpersonal and community relationships. The terminology of ‘social distancing’ quickly became entrenched both in public and policy discourse. This equation of physical distance with social distance was regrettable, since only physical proximity causes viral transmission, whereas many forms of social proximity (eg, conversations while walking outdoors) are minimal risk, and are crucial to maintaining relationships supportive of health and well-being.
The aim of this essay is to explore four key relational mechanisms that were impacted by the pandemic and associated restrictions: social networks, social support, social interaction and intimacy. We use relational theories and emerging research on the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic response to make three key recommendations: one regarding public health responses; and two regarding social recovery. Our understanding of these mechanisms stems from a ‘systems’ perspective which casts social relationships as interdependent elements within a connected whole. 5
Social networks
Social networks characterise the individuals and social connections that compose a system (such as a workplace, community or society). Social relationships range from spouses and partners, to coworkers, friends and acquaintances. They vary across many dimensions, including, for example, frequency of contact and emotional closeness. Social networks can be understood both in terms of the individuals and relationships that compose the network, as well as the overall network structure (eg, how many of your friends know each other).
Social networks show a tendency towards homophily, or a phenomenon of associating with individuals who are similar to self. 6 This is particularly true for ‘core’ network ties (eg, close friends), while more distant, sometimes called ‘weak’ ties tend to show more diversity. During the height of COVID-19 restrictions, face-to-face interactions were often reduced to core network members, such as partners, family members or, potentially, live-in roommates; some ‘weak’ ties were lost, and interactions became more limited to those closest. Given that peripheral, weaker social ties provide a diversity of resources, opinions and support, 7 COVID-19 likely resulted in networks that were smaller and more homogenous.
Such changes were not inevitable nor necessarily enduring, since social networks are also adaptive and responsive to change, in that a disruption to usual ways of interacting can be replaced by new ways of engaging (eg, Zoom). Yet, important inequalities exist, wherein networks and individual relationships within networks are not equally able to adapt to such changes. For example, individuals with a large number of newly established relationships (eg, university students) may have struggled to transfer these relationships online, resulting in lost contacts and a heightened risk of social isolation. This is consistent with research suggesting that young adults were the most likely to report a worsening of relationships during COVID-19, whereas older adults were the least likely to report a change. 8
Lastly, social connections give rise to emergent properties of social systems, 9 where a community-level phenomenon develops that cannot be attributed to any one member or portion of the network. For example, local area-based networks emerged due to geographic restrictions (eg, stay-at-home orders), resulting in increases in neighbourly support and local volunteering. 10 In fact, research suggests that relationships with neighbours displayed the largest net gain in ratings of relationship quality compared with a range of relationship types (eg, partner, colleague, friend). 8 Much of this was built from spontaneous individual interactions within local communities, which together contributed to the ‘community spirit’ that many experienced. 11 COVID-19 restrictions thus impacted the personal social networks and the structure of the larger networks within the society.
Social support
Social support, referring to the psychological and material resources provided through social interaction, is a critical mechanism through which social relationships benefit health. In fact, social support has been shown to be one of the most important resilience factors in the aftermath of stressful events. 12 In the context of COVID-19, the usual ways in which individuals interact and obtain social support have been severely disrupted.
One such disruption has been to opportunities for spontaneous social interactions. For example, conversations with colleagues in a break room offer an opportunity for socialising beyond one’s core social network, and these peripheral conversations can provide a form of social support. 13 14 A chance conversation may lead to advice helpful to coping with situations or seeking formal help. Thus, the absence of these spontaneous interactions may mean the reduction of indirect support-seeking opportunities. While direct support-seeking behaviour is more effective at eliciting support, it also requires significantly more effort and may be perceived as forceful and burdensome. 15 The shift to homeworking and closure of community venues reduced the number of opportunities for these spontaneous interactions to occur, and has, second, focused them locally. Consequently, individuals whose core networks are located elsewhere, or who live in communities where spontaneous interaction is less likely, have less opportunity to benefit from spontaneous in-person supportive interactions.
However, alongside this disruption, new opportunities to interact and obtain social support have arisen. The surge in community social support during the initial lockdown mirrored that often seen in response to adverse events (eg, natural disasters 16 ). COVID-19 restrictions that confined individuals to their local area also compelled them to focus their in-person efforts locally. Commentators on the initial lockdown in the UK remarked on extraordinary acts of generosity between individuals who belonged to the same community but were unknown to each other. However, research on adverse events also tells us that such community support is not necessarily maintained in the longer term. 16
Meanwhile, online forms of social support are not bound by geography, thus enabling interactions and social support to be received from a wider network of people. Formal online social support spaces (eg, support groups) existed well before COVID-19, but have vastly increased since. While online interactions can increase perceived social support, it is unclear whether remote communication technologies provide an effective substitute from in-person interaction during periods of social distancing. 17 18 It makes intuitive sense that the usefulness of online social support will vary by the type of support offered, degree of social interaction and ‘online communication skills’ of those taking part. Youth workers, for instance, have struggled to keep vulnerable youth engaged in online youth clubs, 19 despite others finding a positive association between amount of digital technology used by individuals during lockdown and perceived social support. 20 Other research has found that more frequent face-to-face contact and phone/video contact both related to lower levels of depression during the time period of March to August 2020, but the negative effect of a lack of contact was greater for those with higher levels of usual sociability. 21 Relatedly, important inequalities in social support exist, such that individuals who occupy more socially disadvantaged positions in society (eg, low socioeconomic status, older people) tend to have less access to social support, 22 potentially exacerbated by COVID-19.
Social and interactional norms
Interactional norms are key relational mechanisms which build trust, belonging and identity within and across groups in a system. Individuals in groups and societies apply meaning by ‘approving, arranging and redefining’ symbols of interaction. 23 A handshake, for instance, is a powerful symbol of trust and equality. Depending on context, not shaking hands may symbolise a failure to extend friendship, or a failure to reach agreement. The norms governing these symbols represent shared values and identity; and mutual understanding of these symbols enables individuals to achieve orderly interactions, establish supportive relationship accountability and connect socially. 24 25
Physical distancing measures to contain the spread of COVID-19 radically altered these norms of interaction, particularly those used to convey trust, affinity, empathy and respect (eg, hugging, physical comforting). 26 As epidemic waves rose and fell, the work to negotiate these norms required intense cognitive effort; previously taken-for-granted interactions were re-examined, factoring in current restriction levels, own and (assumed) others’ vulnerability and tolerance of risk. This created awkwardness, and uncertainty, for example, around how to bring closure to an in-person interaction or convey warmth. The instability in scripted ways of interacting created particular strain for individuals who already struggled to encode and decode interactions with others (eg, those who are deaf or have autism spectrum disorder); difficulties often intensified by mask wearing. 27
Large social gatherings—for example, weddings, school assemblies, sporting events—also present key opportunities for affirming and assimilating interactional norms, building cohesion and shared identity and facilitating cooperation across social groups. 28 Online ‘equivalents’ do not easily support ‘social-bonding’ activities such as singing and dancing, and rarely enable chance/spontaneous one-on-one conversations with peripheral/weaker network ties (see the Social networks section) which can help strengthen bonds across a larger network. The loss of large gatherings to celebrate rites of passage (eg, bar mitzvah, weddings) has additional relational costs since these events are performed by and for communities to reinforce belonging, and to assist in transitioning to new phases of life. 29 The loss of interaction with diverse others via community and large group gatherings also reduces intergroup contact, which may then tend towards more prejudiced outgroup attitudes. While online interaction can go some way to mimicking these interaction norms, there are key differences. A sense of anonymity, and lack of in-person emotional cues, tends to support norms of polarisation and aggression in expressing differences of opinion online. And while online platforms have potential to provide intergroup contact, the tendency of much social media to form homogeneous ‘echo chambers’ can serve to further reduce intergroup contact. 30 31
Intimacy relates to the feeling of emotional connection and closeness with other human beings. Emotional connection, through romantic, friendship or familial relationships, fulfils a basic human need 32 and strongly benefits health, including reduced stress levels, improved mental health, lowered blood pressure and reduced risk of heart disease. 32 33 Intimacy can be fostered through familiarity, feeling understood and feeling accepted by close others. 34
Intimacy via companionship and closeness is fundamental to mental well-being. Positively, the COVID-19 pandemic has offered opportunities for individuals to (re)connect and (re)strengthen close relationships within their household via quality time together, following closure of many usual external social activities. Research suggests that the first full UK lockdown period led to a net gain in the quality of steady relationships at a population level, 35 but amplified existing inequalities in relationship quality. 35 36 For some in single-person households, the absence of a companion became more conspicuous, leading to feelings of loneliness and lower mental well-being. 37 38 Additional pandemic-related relational strain 39 40 resulted, for some, in the initiation or intensification of domestic abuse. 41 42
Physical touch is another key aspect of intimacy, a fundamental human need crucial in maintaining and developing intimacy within close relationships. 34 Restrictions on social interactions severely restricted the number and range of people with whom physical affection was possible. The reduction in opportunity to give and receive affectionate physical touch was not experienced equally. Many of those living alone found themselves completely without physical contact for extended periods. The deprivation of physical touch is evidenced to take a heavy emotional toll. 43 Even in future, once physical expressions of affection can resume, new levels of anxiety over germs may introduce hesitancy into previously fluent blending of physical and verbal intimate social connections. 44
The pandemic also led to shifts in practices and norms around sexual relationship building and maintenance, as individuals adapted and sought alternative ways of enacting sexual intimacy. This too is important, given that intimate sexual activity has known benefits for health. 45 46 Given that social restrictions hinged on reducing household mixing, possibilities for partnered sexual activity were primarily guided by living arrangements. While those in cohabiting relationships could potentially continue as before, those who were single or in non-cohabiting relationships generally had restricted opportunities to maintain their sexual relationships. Pornography consumption and digital partners were reported to increase since lockdown. 47 However, online interactions are qualitatively different from in-person interactions and do not provide the same opportunities for physical intimacy.
Recommendations and conclusions
In the sections above we have outlined the ways in which COVID-19 has impacted social relationships, showing how relational mechanisms key to health have been undermined. While some of the damage might well self-repair after the pandemic, there are opportunities inherent in deliberative efforts to build back in ways that facilitate greater resilience in social and community relationships. We conclude by making three recommendations: one regarding public health responses to the pandemic; and two regarding social recovery.
Recommendation 1: explicitly count the relational cost of public health policies to control the pandemic
Effective handling of a pandemic recognises that social, economic and health concerns are intricately interwoven. It is clear that future research and policy attention must focus on the social consequences. As described above, policies which restrict physical mixing across households carry heavy and unequal relational costs. These include for individuals (eg, loss of intimate touch), dyads (eg, loss of warmth, comfort), networks (eg, restricted access to support) and communities (eg, loss of cohesion and identity). Such costs—and their unequal impact—should not be ignored in short-term efforts to control an epidemic. Some public health responses—restrictions on international holiday travel and highly efficient test and trace systems—have relatively small relational costs and should be prioritised. At a national level, an earlier move to proportionate restrictions, and investment in effective test and trace systems, may help prevent escalation of spread to the point where a national lockdown or tight restrictions became an inevitability. Where policies with relational costs are unavoidable, close attention should be paid to the unequal relational impact for those whose personal circumstances differ from normative assumptions of two adult families. This includes consideration of whether expectations are fair (eg, for those who live alone), whether restrictions on social events are equitable across age group, religious/ethnic groupings and social class, and also to ensure that the language promoted by such policies (eg, households; families) is not exclusionary. 48 49 Forethought to unequal impacts on social relationships should thus be integral to the work of epidemic preparedness teams.
Recommendation 2: intelligently balance online and offline ways of relating
A key ingredient for well-being is ‘getting together’ in a physical sense. This is fundamental to a human need for intimate touch, physical comfort, reinforcing interactional norms and providing practical support. Emerging evidence suggests that online ways of relating cannot simply replace physical interactions. But online interaction has many benefits and for some it offers connections that did not exist previously. In particular, online platforms provide new forms of support for those unable to access offline services because of mobility issues (eg, older people) or because they are geographically isolated from their support community (eg, lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer (LGBTQ) youth). Ultimately, multiple forms of online and offline social interactions are required to meet the needs of varying groups of people (eg, LGBTQ, older people). Future research and practice should aim to establish ways of using offline and online support in complementary and even synergistic ways, rather than veering between them as social restrictions expand and contract. Intelligent balancing of online and offline ways of relating also pertains to future policies on home and flexible working. A decision to switch to wholesale or obligatory homeworking should consider the risk to relational ‘group properties’ of the workplace community and their impact on employees’ well-being, focusing in particular on unequal impacts (eg, new vs established employees). Intelligent blending of online and in-person working is required to achieve flexibility while also nurturing supportive networks at work. Intelligent balance also implies strategies to build digital literacy and minimise digital exclusion, as well as coproducing solutions with intended beneficiaries.
Recommendation 3: build stronger and sustainable localised communities
In balancing offline and online ways of interacting, there is opportunity to capitalise on the potential for more localised, coherent communities due to scaled-down travel, homeworking and local focus that will ideally continue after restrictions end. There are potential economic benefits after the pandemic, such as increased trade as home workers use local resources (eg, coffee shops), but also relational benefits from stronger relationships around the orbit of the home and neighbourhood. Experience from previous crises shows that community volunteer efforts generated early on will wane over time in the absence of deliberate work to maintain them. Adequately funded partnerships between local government, third sector and community groups are required to sustain community assets that began as a direct response to the pandemic. Such partnerships could work to secure green spaces and indoor (non-commercial) meeting spaces that promote community interaction. Green spaces in particular provide a triple benefit in encouraging physical activity and mental health, as well as facilitating social bonding. 50 In building local communities, small community networks—that allow for diversity and break down ingroup/outgroup views—may be more helpful than the concept of ‘support bubbles’, which are exclusionary and less sustainable in the longer term. Rigorously designed intervention and evaluation—taking a systems approach—will be crucial in ensuring scale-up and sustainability.
The dramatic change to social interaction necessitated by efforts to control the spread of COVID-19 created stark challenges but also opportunities. Our essay highlights opportunities for learning, both to ensure the equity and humanity of physical restrictions, and to sustain the salutogenic effects of social relationships going forward. The starting point for capitalising on this learning is recognition of the disruption to relational mechanisms as a key part of the socioeconomic and health impact of the pandemic. In recovery planning, a general rule is that what is good for decreasing health inequalities (such as expanding social protection and public services and pursuing green inclusive growth strategies) 4 will also benefit relationships and safeguard relational mechanisms for future generations. Putting this into action will require political will.
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not required.
- Office for National Statistics (ONS)
- Ford T , et al
- Riordan R ,
- Ford J , et al
- Glonti K , et al
- McPherson JM ,
- Smith-Lovin L
- Granovetter MS
- Fancourt D et al
- Stadtfeld C
- Office for Civil Society
- Cook J et al
- Rodriguez-Llanes JM ,
- Guha-Sapir D
- Patulny R et al
- Granovetter M
- Winkeler M ,
- Filipp S-H ,
- Kaniasty K ,
- de Terte I ,
- Guilaran J , et al
- Wright KB ,
- Martin J et al
- Gabbiadini A ,
- Baldissarri C ,
- Durante F , et al
- Sommerlad A ,
- Marston L ,
- Huntley J , et al
- Turner RJ ,
- Bicchieri C
- Brennan G et al
- Watson-Jones RE ,
- Amichai-Hamburger Y ,
- McKenna KYA
- Page-Gould E ,
- Aron A , et al
- Pietromonaco PR ,
- Timmerman GM
- Bradbury-Jones C ,
- Mikocka-Walus A ,
- Klas A , et al
- Marshall L ,
- Steptoe A ,
- Stanley SM ,
- Campbell AM
- ↵ (ONS), O.f.N.S., Domestic abuse during the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, England and Wales . Available: https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/crimeandjustice/articles/domesticabuseduringthecoronaviruscovid19pandemicenglandandwales/november2020
- Rosenberg M ,
- Hensel D , et al
- Banerjee D ,
- Bruner DW , et al
- Bavel JJV ,
- Baicker K ,
- Boggio PS , et al
- van Barneveld K ,
- Quinlan M ,
- Kriesler P , et al
- Mitchell R ,
- de Vries S , et al
Twitter @karenmaxSPHSU, @Mark_McCann, @Rwilsonlowe, @KMitchinGlasgow
Contributors EL and KM led on the manuscript conceptualisation, review and editing. SP, KM, CB, RBP, RL, MM, JR, KS and RW-L contributed to drafting and revising the article. All authors assisted in revising the final draft.
Funding The research reported in this publication was supported by the Medical Research Council (MC_UU_00022/1, MC_UU_00022/3) and the Chief Scientist Office (SPHSU11, SPHSU14). EL is also supported by MRC Skills Development Fellowship Award (MR/S015078/1). KS and MM are also supported by a Medical Research Council Strategic Award (MC_PC_13027).
Competing interests None declared.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
Writing about COVID-19 in a college admission essay
by: Venkates Swaminathan | Updated: September 14, 2020
Print article

For students applying to college using the CommonApp, there are several different places where students and counselors can address the pandemic’s impact. The different sections have differing goals. You must understand how to use each section for its appropriate use.
The CommonApp COVID-19 question
First, the CommonApp this year has an additional question specifically about COVID-19 :
Community disruptions such as COVID-19 and natural disasters can have deep and long-lasting impacts. If you need it, this space is yours to describe those impacts. Colleges care about the effects on your health and well-being, safety, family circumstances, future plans, and education, including access to reliable technology and quiet study spaces. Please use this space to describe how these events have impacted you.
This question seeks to understand the adversity that students may have had to face due to the pandemic, the move to online education, or the shelter-in-place rules. You don’t have to answer this question if the impact on you wasn’t particularly severe. Some examples of things students should discuss include:
- The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic.
- The candidate had to deal with personal or family issues, such as abusive living situations or other safety concerns
- The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges.
- Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams.
Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions office has a blog about this section. He recommends students ask themselves several questions as they go about answering this section:
- Are my experiences different from others’?
- Are there noticeable changes on my transcript?
- Am I aware of my privilege?
- Am I specific? Am I explaining rather than complaining?
- Is this information being included elsewhere on my application?
If you do answer this section, be brief and to-the-point.
Counselor recommendations and school profiles
Second, counselors will, in their counselor forms and school profiles on the CommonApp, address how the school handled the pandemic and how it might have affected students, specifically as it relates to:
- Grading scales and policies
- Graduation requirements
- Instructional methods
- Schedules and course offerings
- Testing requirements
- Your academic calendar
- Other extenuating circumstances
Students don’t have to mention these matters in their application unless something unusual happened.
Writing about COVID-19 in your main essay
Write about your experiences during the pandemic in your main college essay if your experience is personal, relevant, and the most important thing to discuss in your college admission essay. That you had to stay home and study online isn’t sufficient, as millions of other students faced the same situation. But sometimes, it can be appropriate and helpful to write about something related to the pandemic in your essay. For example:
- One student developed a website for a local comic book store. The store might not have survived without the ability for people to order comic books online. The student had a long-standing relationship with the store, and it was an institution that created a community for students who otherwise felt left out.
- One student started a YouTube channel to help other students with academic subjects he was very familiar with and began tutoring others.
- Some students used their extra time that was the result of the stay-at-home orders to take online courses pursuing topics they are genuinely interested in or developing new interests, like a foreign language or music.
Experiences like this can be good topics for the CommonApp essay as long as they reflect something genuinely important about the student. For many students whose lives have been shaped by this pandemic, it can be a critical part of their college application.
Want more? Read 6 ways to improve a college essay , What the &%$! should I write about in my college essay , and Just how important is a college admissions essay? .
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How our schools are (and aren't) addressing race

The truth about homework in America

What should I write my college essay about?
What the #%@!& should I write about in my college essay?
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
- Patient Care & Health Information
- Diseases & Conditions
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
COVID-19, also called coronavirus disease 2019, is an illness caused by a virus. The virus is called severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, or more commonly, SARS-CoV-2. It started spreading at the end of 2019 and became a pandemic disease in 2020.
- Coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses. These viruses cause illnesses such as the common cold, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
The virus that causes COVID-19 spreads most commonly through the air in tiny droplets of fluid between people in close contact. Many people with COVID-19 have no symptoms or mild illness. But for older adults and people with certain medical conditions, COVID-19 can lead to the need for care in the hospital or death.
Staying up to date on your COVID-19 vaccine helps prevent serious illness, the need for hospital care due to COVID-19 and death from COVID-19 . Other ways that may help prevent the spread of this coronavirus includes good indoor air flow, physical distancing, wearing a mask in the right setting and good hygiene.
Medicine can limit the seriousness of the viral infection. Most people recover without long-term effects, but some people have symptoms that continue for months.
Products & Services
- A Book: Endemic - A Post-Pandemic Playbook
- A Book: Future Care
- Begin Exploring Women's Health Solutions at Mayo Clinic Store
Typical COVID-19 symptoms often show up 2 to 14 days after contact with the virus.
Symptoms can include:
- Shortness of breath.
- Loss of taste or smell.
- Extreme tiredness, called fatigue.
- Digestive symptoms such as upset stomach, vomiting or loose stools, called diarrhea.
- Pain, such as headaches and body or muscle aches.
- Fever or chills.
- Cold-like symptoms such as congestion, runny nose or sore throat.
People may only have a few symptoms or none. People who have no symptoms but test positive for COVID-19 are called asymptomatic. For example, many children who test positive don't have symptoms of COVID-19 illness. People who go on to have symptoms are considered presymptomatic. Both groups can still spread COVID-19 to others.
Some people may have symptoms that get worse about 7 to 14 days after symptoms start.
Most people with COVID-19 have mild to moderate symptoms. But COVID-19 can cause serious medical complications and lead to death. Older adults or people who already have medical conditions are at greater risk of serious illness.
COVID-19 may be a mild, moderate, severe or critical illness.
- In broad terms, mild COVID-19 doesn't affect the ability of the lungs to get oxygen to the body.
- In moderate COVID-19 illness, the lungs also work properly but there are signs that the infection is deep in the lungs.
- Severe COVID-19 means that the lungs don't work correctly, and the person needs oxygen and other medical help in the hospital.
- Critical COVID-19 illness means the lung and breathing system, called the respiratory system, has failed and there is damage throughout the body.
Rarely, people who catch the coronavirus can develop a group of symptoms linked to inflamed organs or tissues. The illness is called multisystem inflammatory syndrome. When children have this illness, it is called multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, shortened to MIS -C. In adults, the name is MIS -A.
When to see a doctor
Contact a healthcare professional if you test positive for COVID-19 . If you have symptoms and need to test for COVID-19 , or you've been exposed to someone with COVID-19 , a healthcare professional can help.
People who are at high risk of serious illness may get medicine to block the spread of the COVID-19 virus in the body. Or your healthcare team may plan regular checks to monitor your health.
Get emergency help right away for any of these symptoms:
- Can't catch your breath or have problems breathing.
- Skin, lips or nail beds that are pale, gray or blue.
- New confusion.
- Trouble staying awake or waking up.
- Chest pain or pressure that is constant.
This list doesn't include every emergency symptom. If you or a person you're taking care of has symptoms that worry you, get help. Let the healthcare team know about a positive test for COVID-19 or symptoms of the illness.

More Information
- COVID-19 vs. flu: Similarities and differences
- COVID-19, cold, allergies and the flu
- Unusual symptoms of coronavirus
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Review/update the information highlighted below and resubmit the form.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
Error Email field is required
Error Include a valid email address
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Thank you for subscribing!
You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Sorry something went wrong with your subscription
Please, try again in a couple of minutes
COVID-19 is caused by infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, also called SARS-CoV-2.
The coronavirus spreads mainly from person to person, even from someone who is infected but has no symptoms. When people with COVID-19 cough, sneeze, breathe, sing or talk, their breath may be infected with the COVID-19 virus.
The coronavirus carried by a person's breath can land directly on the face of a nearby person, after a sneeze or cough, for example. The droplets or particles the infected person breathes out could possibly be breathed in by other people if they are close together or in areas with low air flow. And a person may touch a surface that has respiratory droplets and then touch their face with hands that have the coronavirus on them.
It's possible to get COVID-19 more than once.
- Over time, the body's defense against the COVID-19 virus can fade.
- A person may be exposed to so much of the virus that it breaks through their immune defense.
- As a virus infects a group of people, the virus copies itself. During this process, the genetic code can randomly change in each copy. The changes are called mutations. If the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 changes in ways that make previous infections or vaccination less effective at preventing infection, people can get sick again.
The virus that causes COVID-19 can infect some pets. Cats, dogs, hamsters and ferrets have caught this coronavirus and had symptoms. It's rare for a person to get COVID-19 from a pet.
Risk factors
The main risk factors for COVID-19 are:
- If someone you live with has COVID-19 .
- If you spend time in places with poor air flow and a higher number of people when the virus is spreading.
- If you spend more than 30 minutes in close contact with someone who has COVID-19 .
Many factors affect your risk of catching the virus that causes COVID-19 . How long you are in contact, if the space has good air flow and your activities all affect the risk. Also, if you or others wear masks, if someone has COVID-19 symptoms and how close you are affects your risk. Close contact includes sitting and talking next to one another, for example, or sharing a car or bedroom.
It seems to be rare for people to catch the virus that causes COVID-19 from an infected surface. While the virus is shed in waste, called stool, COVID-19 infection from places such as a public bathroom is not common.
Serious COVID-19 illness risk factors
Some people are at a higher risk of serious COVID-19 illness than others. This includes people age 65 and older as well as babies younger than 6 months. Those age groups have the highest risk of needing hospital care for COVID-19 .
Not every risk factor for serious COVID-19 illness is known. People of all ages who have no other medical issues have needed hospital care for COVID-19 .
Known risk factors for serious illness include people who have not gotten a COVID-19 vaccine. Serious illness also is a higher risk for people who have:
- Sickle cell disease or thalassemia.
- Serious heart diseases and possibly high blood pressure.
- Chronic kidney, liver or lung diseases.
People with dementia or Alzheimer's also are at higher risk, as are people with brain and nervous system conditions such as stroke. Smoking increases the risk of serious COVID-19 illness. And people with a body mass index in the overweight category or obese category may have a higher risk as well.
Other medical conditions that may raise the risk of serious illness from COVID-19 include:
- Cancer or a history of cancer.
- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
- Weakened immune system from solid organ transplants or bone marrow transplants, some medicines, or HIV .
This list is not complete. Factors linked to a health issue may raise the risk of serious COVID-19 illness too. Examples are a medical condition where people live in a group home, or lack of access to medical care. Also, people with more than one health issue, or people of older age who also have health issues have a higher chance of severe illness.
Related information
- COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? - Related information COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
Complications
Complications of COVID-19 include long-term loss of taste and smell, skin rashes, and sores. The illness can cause trouble breathing or pneumonia. Medical issues a person already manages may get worse.
Complications of severe COVID-19 illness can include:
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome, when the body's organs do not get enough oxygen.
- Shock caused by the infection or heart problems.
- Overreaction of the immune system, called the inflammatory response.
- Blood clots.
- Kidney injury.
Post-COVID-19 syndrome
After a COVID-19 infection, some people report that symptoms continue for months, or they develop new symptoms. This syndrome has often been called long COVID, or post- COVID-19 . You might hear it called long haul COVID-19 , post-COVID conditions or PASC. That's short for post-acute sequelae of SARS -CoV-2.
Other infections, such as the flu and polio, can lead to long-term illness. But the virus that causes COVID-19 has only been studied since it began to spread in 2019. So, research into the specific effects of long-term COVID-19 symptoms continues.
Researchers do think that post- COVID-19 syndrome can happen after an illness of any severity.
Getting a COVID-19 vaccine may help prevent post- COVID-19 syndrome.
- Long-term effects of COVID-19
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends a COVID-19 vaccine for everyone age 6 months and older. The COVID-19 vaccine can lower the risk of death or serious illness caused by COVID-19.
The COVID-19 vaccines available in the United States are:
2023-2024 Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. This vaccine is available for people age 6 months and older.
Among people with a typical immune system:
- Children age 6 months up to age 4 years are up to date after three doses of a Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
- People age 5 and older are up to date after one Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
- For people who have not had a 2023-2024 COVID-19 vaccination, the CDC recommends getting an additional shot of that updated vaccine.
2023-2024 Moderna COVID-19 vaccine. This vaccine is available for people age 6 months and older.
- Children ages 6 months up to age 4 are up to date if they've had two doses of a Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.
- People age 5 and older are up to date with one Moderna COVID-19 vaccine.
2023-2024 Novavax COVID-19 vaccine. This vaccine is available for people age 12 years and older.
- People age 12 years and older are up to date if they've had two doses of a Novavax COVID-19 vaccine.
In general, people age 5 and older with typical immune systems can get any vaccine approved or authorized for their age. They usually don't need to get the same vaccine each time.
Some people should get all their vaccine doses from the same vaccine maker, including:
- Children ages 6 months to 4 years.
- People age 5 years and older with weakened immune systems.
- People age 12 and older who have had one shot of the Novavax vaccine should get the second Novavax shot in the two-dose series.
Talk to your healthcare professional if you have any questions about the vaccines for you or your child. Your healthcare team can help you if:
- The vaccine you or your child got earlier isn't available.
- You don't know which vaccine you or your child received.
- You or your child started a vaccine series but couldn't finish it due to side effects.
People with weakened immune systems
Your healthcare team may suggest added doses of COVID-19 vaccine if you have a moderately or seriously weakened immune system. The FDA has also authorized the monoclonal antibody pemivibart (Pemgarda) to prevent COVID-19 in some people with weakened immune systems.
Control the spread of infection
In addition to vaccination, there are other ways to stop the spread of the virus that causes COVID-19 .
If you are at a higher risk of serious illness, talk to your healthcare professional about how best to protect yourself. Know what to do if you get sick so you can quickly start treatment.
If you feel ill or have COVID-19 , stay home and away from others, including pets, if possible. Avoid sharing household items such as dishes or towels if you're sick.
In general, make it a habit to:
- Test for COVID-19 . If you have symptoms of COVID-19 test for the infection. Or test five days after you came in contact with the virus.
- Help from afar. Avoid close contact with anyone who is sick or has symptoms, if possible.
- Wash your hands. Wash your hands well and often with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. Or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol.
- Cover your coughs and sneezes. Cough or sneeze into a tissue or your elbow. Then wash your hands.
- Clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces. For example, clean doorknobs, light switches, electronics and counters regularly.
Try to spread out in crowded public areas, especially in places with poor airflow. This is important if you have a higher risk of serious illness.
The CDC recommends that people wear a mask in indoor public spaces if you're in an area with a high number of people with COVID-19 in the hospital. They suggest wearing the most protective mask possible that you'll wear regularly, that fits well and is comfortable.
- COVID-19 vaccines: Get the facts - Related information COVID-19 vaccines: Get the facts
- Comparing the differences between COVID-19 vaccines - Related information Comparing the differences between COVID-19 vaccines
- Different types of COVID-19 vaccines: How they work - Related information Different types of COVID-19 vaccines: How they work
- Debunking COVID-19 myths - Related information Debunking COVID-19 myths
Travel and COVID-19
Travel brings people together from areas where illnesses may be at higher levels. Masks can help slow the spread of respiratory diseases in general, including COVID-19 . Masks help the most in places with low air flow and where you are in close contact with other people. Also, masks can help if the places you travel to or through have a high level of illness.
Masking is especially important if you or a companion have a high risk of serious illness from COVID-19 .
- COVID-19 travel advice
- COVID-19 vaccines
- COVID-19 vaccines for kids: What you need to know
- Debunking coronavirus myths
- Different COVID-19 vaccines
- Fight coronavirus (COVID-19) transmission at home
- Herd immunity and coronavirus
- How well do face masks protect against COVID-19?
- Safe outdoor activities during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Safety tips for attending school during COVID-19
- COVID-19 and vitamin D
- COVID-19: How can I protect myself?
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How dirty are common surfaces?
- Mayo Clinic Minute: You're washing your hands all wrong
- Goldman L, et al., eds. COVID-19: Epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, community prevention, and prognosis. In: Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Elsevier; 2024. https://www.clinicalkey.com. Accessed Dec. 17, 2023.
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines. National Institutes of Health. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed Dec. 18, 2023.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Testing, symptoms. Mayo Clinic; Nov. 2, 2023.
- Symptoms of COVID-19. Centers for Disease Control and Preventions. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html. Accessed Dec. 20, 2023.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Outpatient management. Mayo Clinic; Oct. 10, 2023.
- Morris SB, et al. Case series of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in adults associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection — United Kingdom and United States, March-August 2020. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2020;69:1450. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6940e1external icon.
- COVID-19 testing: What you need to know. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/testing.html. Accessed Dec. 20, 2023.
- SARS-CoV-2 in animals. American Veterinary Medical Association. https://www.avma.org/resources-tools/one-health/covid-19/sars-cov-2-animals-including-pets. Accessed Jan. 17, 2024.
- Understanding exposure risk. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/your-health/risks-exposure.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- People with certain medical conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-with-medical-conditions.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Factors that affect your risk of getting very sick from COVID-19. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/your-health/risks-getting-very-sick.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Regan JJ, et al. Use of Updated COVID-19 Vaccines 2023-2024 Formula for Persons Aged ≥6 Months: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices—United States, September 2023. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 2023; 72:1140–1146. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm7242e1.
- Long COVID or post-COVID conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Stay up to date with your vaccines. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/stay-up-to-date.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Interim clinical considerations for use of COVID-19 vaccines currently approved or authorized in the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/covid-19-vaccines-us.html#CoV-19-vaccination. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Use and care of masks. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/about-face-coverings.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- How to protect yourself and others. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/prevent-getting-sick/prevention.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- People who are immunocompromised. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-who-are-immunocompromised.html. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- Masking during travel. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/page/masks. Accessed Jan. 10, 2024.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Testing. Mayo Clinic. 2023.
- COVID-19 test basics. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/covid-19-test-basics. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- At-home COVID-19 antigen tests — Take steps to reduce your risk of false negative results: FDA safety communication. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/safety-communications/home-covid-19-antigen-tests-take-steps-reduce-your-risk-false-negative-results-fda-safety. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- Interim clinical considerations for COVID-19 treatment in outpatients. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-care/outpatient-treatment-overview.html. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- Know your treatment options for COVID-19. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/know-your-treatment-options-covid-19. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID:19 Drug regimens and other treatment options. Mayo Clinic. 2023.
- Preventing spread of respiratory viruses when you're sick. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/prevention/precautions-when-sick.html. Accessed March 5, 2024.
- AskMayoExpert. COVID-19: Quarantine and isolation. Mayo Clinic. 2023.
- COVID-19 resource and information guide. National Alliance on Mental Illness. https://www.nami.org/Support-Education/NAMI-HelpLine/COVID-19-Information-and-Resources/COVID-19-Resource-and-Information-Guide. Accessed Jan. 11, 2024.
- COVID-19 overview and infection prevention and control priorities in non-U.S. healthcare settings. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/non-us-settings/overview/index.html. Accessed Jan. 16, 2024.
- Kim AY, et al. COVID-19: Management in hospitalized adults. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/search. Accessed Jan. 17, 2024.
- O'Horo JC, et al. Outcomes of COVID-19 with the Mayo Clinic Model of Care and Research. Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 2021; doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.12.006.
- At-home OTC COVID-19 diagnostic tests. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/home-otc-covid-19-diagnostic-tests. Accessed Jan. 22, 2024.
- Emergency use authorizations for drugs and non-vaccine biological products. U.S. Food and Drug Association. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/emergency-preparedness-drugs/emergency-use-authorizations-drugs-and-non-vaccine-biological-products. Accessed March 25, 2024.
- Coronavirus infection by race
- COVID-19 and pets
- COVID-19 and your mental health
- COVID-19 drugs: Are there any that work?
- COVID-19 in babies and children
- COVID-19 variant
- COVID-19: Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms?
- How do COVID-19 antibody tests differ from diagnostic tests?
- Is hydroxychloroquine a treatment for COVID-19?
- Pregnancy and COVID-19
- Sex and COVID-19
- Treating COVID-19 at home
Associated Procedures
- Convalescent plasma therapy
- COVID-19 antibody testing
- COVID-19 tests
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
News from Mayo Clinic
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Who should get the latest COVID-19 vaccine? Nov. 21, 2023, 01:30 p.m. CDT
- Can you get COVID-19 and the flu at the same time? A Mayo Clinic expert weighs in Oct. 16, 2023, 04:30 p.m. CDT
- At-home COVID-19 tests: A Mayo Clinic expert answers questions on expiration dates and the new variants Sept. 18, 2023, 04:00 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic expert answers questions about the new COVID-19 vaccine Sept. 13, 2023, 04:15 p.m. CDT
- Study identifies risk factors for long-haul COVID disease in adults Sept. 13, 2023, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- Mayo researchers find vaccine may reduce severity of long-haul COVID symptoms Aug. 23, 2023, 04:34 p.m. CDT
- Corticosteroids lower the likelihood of in-hospital mortality from COVID-19 Aug. 04, 2023, 03:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 vaccine administration simplified April 21, 2023, 07:00 p.m. CDT
- Science Saturday: COVID-19 -- the pandemic that's forever changed laboratory testing April 15, 2023, 11:00 a.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic expert talks about the new omicron variant April 13, 2023, 02:13 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic to ease universal face mask requirement April 04, 2023, 03:05 p.m. CDT
- 'Deaths of Despair' contribute to 17% rise in Minnesota's death rate during COVID-19 pandemic March 13, 2023, 12:00 p.m. CDT
- Rising cases of COVID-19 variant, XBB.1.5 Jan. 09, 2023, 05:15 p.m. CDT
- Bivalent COVID-19 booster approved for children 6 months and older Dec. 09, 2022, 09:33 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Minute: How to self-care at home when you have COVID-19 Dec. 06, 2022, 05:00 p.m. CDT
- Halloween safety tips from a Mayo Clinic infectious diseases expert Oct. 27, 2022, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19, RSV and flu--season of respiratory infections Oct. 26, 2022, 04:30 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 bivalent booster vaccines for kids 5-11 approved, Mayo Clinic awaits supply Oct. 13, 2022, 04:54 p.m. CDT
- Questions answered about the COVID-19 bivalent booster vaccines Oct. 12, 2022, 03:30 p.m. CDT
- Will the COVID-19 booster be like an annual flu shot? Sept. 12, 2022, 04:30 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Who needs back-to-school COVID-19 vaccinations and boosters? Sept. 04, 2022, 11:00 a.m. CDT
- Q&A podcast: Updated COVID-19 boosters target omicron variants Sept. 02, 2022, 12:30 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Minute: Back-to-school COVID-19 vaccinations for kids Aug. 15, 2022, 03:15 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic research shows bebtelovimab to be a reliable option for treating COVID-19 in era of BA.2, other subvariants Aug. 15, 2022, 02:09 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: New variants of COVID-19 Aug. 04, 2022, 12:30 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 variant BA.5 is dominant strain; BA.2.75 is being monitored July 28, 2022, 02:30 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic researchers pinpoint genetic variations that might sway course of COVID-19 July 25, 2022, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: BA.5 omicron variant fueling latest COVID-19 surge July 15, 2022, 12:00 p.m. CDT
- What you need to know about the BA.5 omicron variant July 14, 2022, 06:41 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: The importance of COVID-19 vaccines for children under 5 July 06, 2022, 01:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 vaccination for kids age 5 and younger starting the week of July 4 at most Mayo sites July 01, 2022, 04:00 p.m. CDT
- Patients treated with monoclonal antibodies during COVID-19 delta surge had low rates of severe disease, Mayo Clinic study finds June 27, 2022, 03:00 p.m. CDT
- Long COVID and the digestive system: Mayo Clinic expert describes common symptoms June 21, 2022, 02:43 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: COVID-19 update June 17, 2022, 01:08 p.m. CDT
- Study finds few COVID-19 patients get rebound symptoms after Paxlovid treatment June 14, 2022, 10:06 a.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Minute: What to expect with COVID-19 vaccinations for youngest kids June 08, 2022, 04:35 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: Community leaders are key to reaching people underrepresented in research May 26, 2022, 02:00 p.m. CDT
- COVID-19 booster vaccinations extended to kids 5-11 May 20, 2022, 06:10 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic expert shares tips for navigating a return to work with long COVID May 19, 2022, 02:08 p.m. CDT
- Mayo Clinic Q&A podcast: COVID-19 update May 17, 2022, 01:14 p.m. CDT
- Symptoms & causes
- Diagnosis & treatment
- Doctors & departments
- COVID-19 vaccines: Get the facts
- How well do face masks protect against coronavirus?
- Post-COVID Recovery
News on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Learn the latest medical news about COVID-19 on Mayo Clinic News Network.
Your gift holds great power – donate today!
Make your tax-deductible gift and be a part of the cutting-edge research and care that's changing medicine.
Special Issue: COVID-19
This essay was published as part of a Special Issue on Misinformation and COVID-19, guest-edited by Dr. Meghan McGinty (Director of Emergency Management, NYC Health + Hospitals) and Nat Gyenes (Director, Meedan Digital Health Lab).
Peer Reviewed
The causes and consequences of COVID-19 misperceptions: Understanding the role of news and social media
Article metrics.
CrossRef Citations
Altmetric Score
PDF Downloads
We investigate the relationship between media consumption, misinformation, and important attitudes and behaviours during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We find that comparatively more misinformation circulates on Twitter, while news media tends to reinforce public health recommendations like social distancing. We find that exposure to social media is associated with misperceptions regarding basic facts about COVID-19 while the inverse is true for news media. These misperceptions are in turn associated with lower compliance with social distancing measures. We thus draw a clear link from misinformation circulating on social media, notably Twitter, to behaviours and attitudes that potentially magnify the scale and lethality of COVID-19.
Department of Political Science, McGill University, Canada
Munk School of Global Affairs and Public Policy, University of Toronto, Canada
Max Bell School of Public Policy, McGill University, Canada
School of Computer Science, McGill University, Canada
Department of Languages, Literatures, and Cultures, McGill University, Canada
Computer Science Program, McGill University, Canada

Research Questions
- How prevalent is misinformation surrounding COVID-19 on Twitter, and how does this compare to Canadian news media?
- Does the type of media one is exposed to influence social distancing behaviours and beliefs about COVID-19?
- Is there a link between COVID-19 misinformation and perceptions of the pandemic’s severity and compliance with social distancing recommendations?
Essay Summary
- We evaluate the presence of misinformation and public health recommendations regarding COVID-19 in a massive corpus of tweets as well as all articles published on nineteen Canadian news sites. Using these data, we show that preventative measures are more encouraged and covered on traditional news media, while misinformation appears more frequently on Twitter.
- To evaluate the impact of this greater level of misinformation, we conducted a nationally representative survey that included questions about common misperceptions regarding COVID-19, risk perceptions, social distancing compliance, and exposure to traditional news and social media. We find that being exposed to news media is associated with fewer misperceptions and more social distancing compliance while conversely, social media exposure is associated with more misperceptions and less social distancing compliance.
- Misperceptions regarding the virus are in turn associated with less compliance with social distancing measures, even when controlling for a broad range of other attitudes and characteristics.
- Association between social media exposure and social distancing non-compliance is eliminated when accounting for effect of misperceptions, providing evidence that social media is associated with non-compliance through increasing misperceptions about the virus.
Implications
The COVID-19 pandemic has been accompanied by a so-called “infodemic”—a global spread of misinformation that poses a serious problem for public health. Infodemics are concerning because the spread of false or misleading information has the capacity to change transmission patterns (Kim et al., 2019) and consequently the scale and lethality of a pandemic. This information can be shared by any media, but there is reason to be particularly concerned about the role that social media, such as Facebook and Twitter, play in incidentally boosting misperceptions. These platforms are increasingly relied upon as primary sources of news (Mitchell et al., 2016) and misinformation has been heavily documented on them (Garrett, 2019; Vicario et al., 2016). Scholars have found medical and health misinformation on the platforms, including that related to vaccines (Radzikowski et al., 2016) and other virus epidemics such as Ebola (Fung et al., 2016) and Zika (Sharma et al., 2017).
However, misinformation content typically makes up a low percentage of overall discussion of a topic (e.g. Fung et al., 2016) and mere exposure to misinformation does not guarantee belief in that misinformation. More research is thus needed to understand the extent and consequences of misinformation surrounding COVID-19 on social media. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Twitter, Facebook and other platforms have engaged in efforts to combat misinformation but they have continued to receive widespread criticism that misinformation is still appearing on prominent pages and groups (Kouzy et al., 2020; NewsGuard, 2020). The extent to which misinformation continues to circulate on these platforms and influence people’s attitudes and behaviours is still very much an open question.
Here, we draw on three data sets and a sequential mixed method approach to better understand the consequences of online misinformation for important behaviours and attitudes. First, we collected nearly 2.5 million tweets explicitly referring to COVID-19 in the Canadian context. Second, we collected just over 9 thousand articles from nineteen Canadian English-language news sites from the same time period. We coded both of these media sets for misinformation and public health recommendations. Third, we conducted a nationally representative survey that included questions related to media consumption habits, COVID-19 perceptions and misperceptions, and social distancing compliance. As our outcome variables are continuous, we use Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) regression to identify relationships between news and social media exposure, misperceptions, compliance with social distancing measures, and risk perceptions. We use these data to illustrate: 1) the relative prevalence of misinformation on Twitter; and 2) a powerful association between social media usage and misperceptions, on the one hand, and social distancing non-compliance on the other.
Misinformation and compliance with social distancing
We first compare the presence of misinformation on Twitter with that on news media and find, consistent with the other country cases (Chadwick & Vaccari, 2019; Vicario et al., 2016), comparatively higher levels of misinformation circulating on the social media platform. We also found that recommendations for safe practices during the pandemic (e.g. washing hands, social distancing) appeared much more frequently in the Canadian news media. These findings are in line with literature examining fake news which finds a large difference in information quality across media (Al-Rawi, 2019; Guess & Nyhan, 2018).
Spending time in a media environment that contains misinformation is likely to change attitudes and behaviours. Even if users are not nested in networks that propagate misinformation, they are likely to be incidentally exposed to information from a variety of perspectives (Feezell, 2018; Fletcher & Nielsen, 2018; Weeks et al., 2017). Even a highly curated social media feed is thus still likely to contain misinformation. As cumulative exposure to misinformation increases, users are likely to experience a reinforcement effect whereby familiarity leads to stronger belief (Dechêne et al., 2010).
To evaluate this empirically, we conducted a national survey that included questions on information consumption habits and a battery of COVID-19 misperceptions that could be the result of exposure to misinformation. We find that those who self-report exposure to the misinformation-rich social media environment do tend to have more misperceptions regarding COVID-19. These findings are consistent with others that link exposure to misinformation and misperceptions (Garrett et al., 2016; Jamieson & Albarracín, 2020). Social media users also self-report less compliance with social distancing.
Misperceptions are most meaningful when they impact behaviors in dangerous ways. During a pandemic, misperceptions can be fatal. In this case, we find that misperceptions are associated with reduced COVID-19 risk perceptions and with lower compliance with social distancing measures. We continue to find strong effects after controlling for socio-economic characteristics as well as scientific literacy. After accounting for the effect of misperceptions on social distancing non-compliance, social media usage no longer has a significant association with non-compliance, providing evidence that social media may lead to less social distancing compliance through its effect on COVID-19 misperceptions.
While some social media companies have made efforts to suppress misinformation on their platforms, there continues to be a high level of misinformation relative to news media. Highly polarized political environments and media ecosystems can lead to the spread of misinformation, such as in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic (Allcott et al., 2020; Motta et al., 2020). But even in healthy media ecosystems with less partisan news (Owen et al., 2020), social media can continue to facilitate the spread of misinformation. There is a real danger that without concerted efforts to reduce the amount of misinformation shared on social media, the large-scale social efforts required to combat COVID-19 will be undermined.
We contribute to a growing base of evidence that misinformation circulating on social media poses public health risks and join others in calling for social media companies to put greater focus on flattening the curve of misinformation (Donovan, 2020). These findings also provide governments with stronger evidence that the misinformation circulating on social media can be directly linked to misperceptions and public health risks. Such evidence is essential for them to chart an effective policy course. Finally, the methods and approach developed in this paper can be fruitfully applied to study other waves of misinformation and the research community can build upon the link clearly drawn between misinformation exposure, misperceptions, and downstream attitudes and behaviours.
We found use of social media platforms broadly contributes to misperceptions but were unable to precise the overall level of misinformation circulating on non-Twitter social media. Data access for researchers to platforms such as Facebook, YouTube, and Instagram is limited and virtually non-existent for SnapChat, WhatsApp, and WeChat. Cross-platform content comparisons are an important ingredient for a rich understand of the social media environment and these social media companies must better open their platforms to research in the public interest.
Finding 1: Misinformation about COVID-19 is circulated more on Twitter as compared to traditional media.
We find large differences between the quality of information shared about COVID-19 on traditional news and Twitter. Figure 1 shows the percentage of COVID-19 related content that contains information linked to a particular theme. The plot reports the prevalence of information on both social and news media for: 1) three specific pieces of misinformation; 2) a general set of content that describes the pandemic itself as a conspiracy or a hoax; and 3) advice about hygiene and social distancing during the pandemic. We differentiate content that shared misinformation (red in the plot) from content that debunked misinformation (green in the plot).
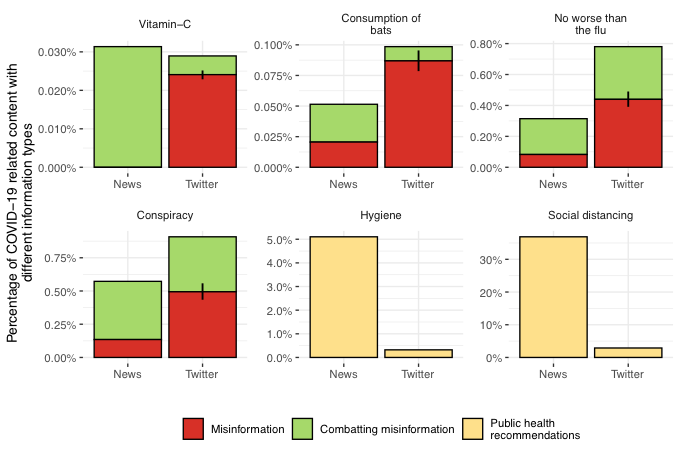
There are large differences between the levels of misinformation on Twitter and news media. Misinformation was comparatively more common on Twitter across all four categories, while debunking was relatively more common in traditional news. Meanwhile, advice on hygiene and social distancing appeared much more frequently in news media. Note that higher percentages are to be expected for longer format news articles since we rely on keyword searches for identification. This makes the misinformation findings even starker – despite much higher average word counts, far fewer news articles propagate misinformation.
Finding 2: There is a strong association between social media exposure and misperceptions about COVID-19. The inverse is true for exposure to traditional news.
Among our survey respondents we find a corresponding strong association between social media exposure and misperceptions about COVID-19. These results are plotted in Figure 2, with controls included for both socioeconomic characteristics and demographics. Moving from no social media exposure to its maximum is expected to increase one’s misperceptions of COVID-19 by 0.22 on the 0-1 scale and decreased self-reported social distancing compliance by 0.12 on that same scale.
This result stands in stark contrast with the observed relationship between traditional news exposure and our outcome measures. Traditional news exposure is positively associated with correct perceptions regarding COVID-19. Moving from no news exposure to its highest level is expected to reduce misperceptions by 0.12 on the 0-1 scale and to increase social distancing compliance by 0.28 on that same scale. The effects are plotted in Figure 2. Social media usage appears to be correlated with COVID-19 misperceptions, suggesting these misperceptions are partially a result of misinformation on social media. The same cannot be said of traditional news exposure.
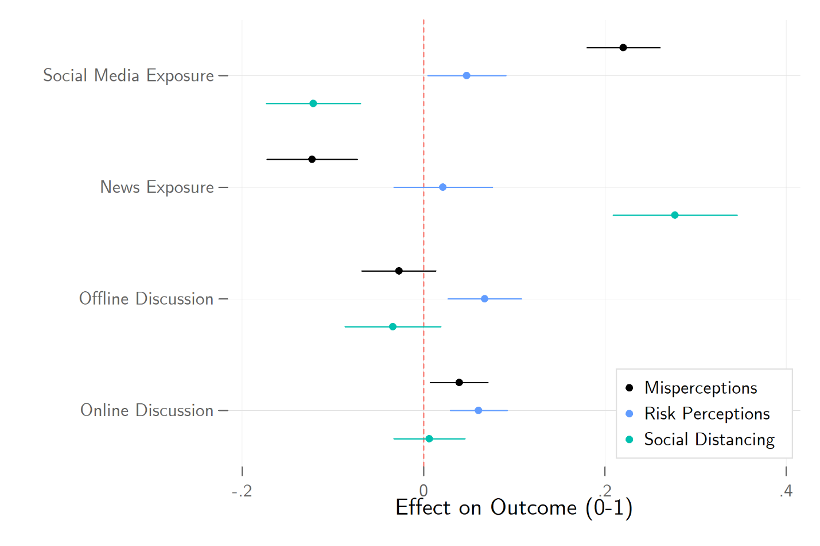
Finding 3: Misperceptions about the pandemic are associated with lower levels of risk perceptions and social distancing compliance.
COVID-19 misperceptions are also powerfully associated with lower levels of social distancing compliance. Moving from the lowest level of COVID-19 misperceptions to its maximum is associated with a reduction of one’s social distancing by 0.39 on the 0-1 scale. The previously observed relationship between social media exposure and misperceptions disappears, suggestive of a mediated relationship. That is, social media exposure increases misperceptions, which in turn reduces social distancing compliance. Misperceptions is also weakly associated with lower COVID-19 risk perceptions. Estimates from our models using COVID-19 concern as the outcome can be found in the left panel of Figure 3, while social distancing can be found in the right panel.
Finally, we also see that the relationship between misinformation and both social distancing compliance and COVID-19 concern hold when including controls for science literacy and a number of fundamental predispositions that are likely associated with both misperceptions and following the advice of scientific experts, such as anti-intellectualism, pseudoscientific beliefs, and left-right ideology. These estimates can similarly be found in Figure 3.
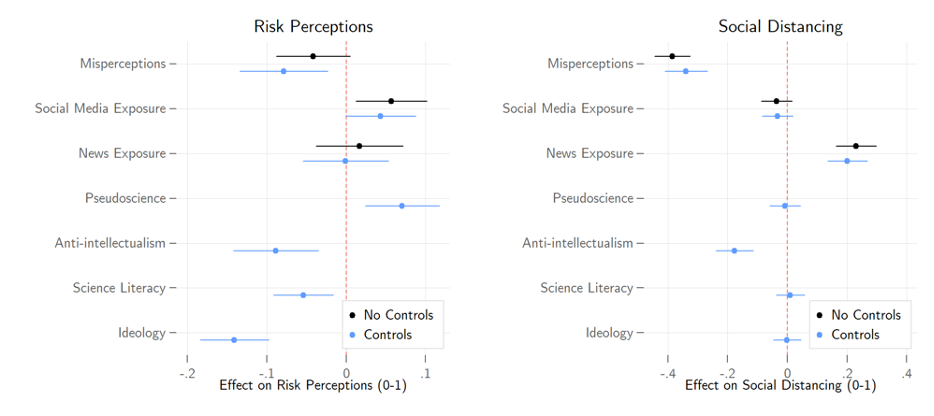
Canadian Twitter and news data were collected from March 26 th to April 6 th , 2020. We collected all English-language tweets from a set of 620,000 users that have been determined to be likely Canadians. For inclusion, a given user must self-identify as Canadian-based, follow a large number of Canadian political elite accounts, or frequently use Canadian-specific hashtags. News media was collected from nineteen prominent Canadian news sites with active RSS feeds. These tweets and news articles were searched for “covid” or “coronavirus”, leaving a sample of 2.25 million tweets and 8,857 news articles.
Of the COVID-19 related content, we searched for terms associated with four instances of misinformation that circulated during the COVID-19 pandemic: that COVID-19 was no more serious than the flu, that vitamin C or other supplements will prevent contraction of the virus, that the initial animal-to-human transfer of the virus was the direct result of eating bats, or that COVID-19 was a hoax or conspiracy. Given that we used keyword searches to identify content, we manually reviewed a random sample of 500 tweets from each instance of misinformation. Each tweet was coded as one of four categories: propagating misinformation, combatting misinformation, content with the relevant keywords but unrelated to misinformation, or content that refers to the misinformation but does not offer comment.
We then calculated the overall level of misinformation for that instance on Twitter by multiplying the overall volume of tweets by the proportion of hand-coded content where misinformation was identified. Each news article that included relevant keywords was similarly coded. The volume of the news mentioning these terms was sufficiently low that all news articles were hand coded. To identify health recommendations, we used a similar keyword search for terms associated with particular recommendations: 1) social distancing including staying at home, staying at least 6 feet or 2 meters away and avoiding gatherings; and 2) washing hands and not touching any part of your face. 1 Further details on the media collection strategy and hand-coding schema are available in the supporting materials.
For survey data, we used a sample of nearly 2,500 Canadian citizens 18 years or older drawn from a probability-based online national panel fielded from April 2-6, 2020. Quotas we set on age, gender, region, and language to ensure sample representativeness, and data was further weighted within region by gender and age based on the 2016 Canadian census.
We measure levels of COVID-19 misperceptions by asking respondents to rate the truthfulness of a series of nine false claims, such as the coronavirus being no worse than the seasonal flu or that it can be warded off with Vitamin C. Each was asked on a scale from definitely false (0) to definitely true (5). We use Cronbach’s Alpha as an indicator of scale reliability. Cronbach’s Alpha ranges from 0-1, with scores above 0.8 indicating the reliability is “good.” These items score 0.88, so we can safely construct a 0-1 scale of misperceptions from them.
We evaluate COVID-19 risk perceptions with a pair of questions asking respondents how serious of a threat they believe the pandemic to be for themselves and for Canadians, respectively. Each question was asked on a scale from not at all (0) to very (4). We construct a continuous index with these items.
We quantify social distancing by asking respondents to indicate which of a series of behaviours they had undertaken in response to the pandemic, such as working from home or avoiding in-person contact with friends, family, and acquaintances. We use principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce the number of dimensions in these data while minimizing information loss. The analysis revealed 2 distinct dimensions in our questions. One dimension includes factors strongly determined by occupation, such as working from home and switching to online meetings. The other dimension contains more inclusive behaviours such as avoiding contact, travel, and crowded places. We generate predictions from the PCA for this latter dimension to use in our analyses. The factor loadings can be found in Table A1 of the supporting materials.
We gauge news and social media consumption by asking respondents to identify news outlets and social media platforms they have used over the past week for political news. The list of news outlets included 17 organizations such as mainstream sources like CBC and Global, and partisan outlets like Rebel Media and National Observer. The list of social media platforms included 10 options such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, and Instagram. We sum the total number of outlets/platforms respondents report using and take the log to adjust for extreme values. We measure offline political discussion with an index based on questions asking how often respondents have discussed politics with family, friends, and acquaintances over the past week. Descriptions of our primary variables can be found in Table A2 of the supporting materials.
We evaluate our hypotheses using a standard design that evaluates the association between our explanatory and outcome variables controlling for other observable factors we measured. In practice, randomly assigning social media exposure is impractical, while randomly assigning misinformation is unethical. This approach allows us to describe these relationships, though we cannot make definite claims to causality.
We hypothesize that social media exposure is associated with misinformation on COVID-19. Figure 2 presents the coefficients of models predicting the effects of news exposure, social media exposure, and political discussion on COVID-19 misinformation, risk perceptions, and social distancing. Socio-economic and demographic control estimates are not displayed. Full estimation results can be found in the Table A3 of the supporting materials.
We further hypothesize that COVID-19 misinformation is associated with lower COVID-19 risk perceptions and less social distancing compliance. Figure 3 presents the coefficients for models predicting the effects of misinformation, news exposure, and social media exposure on severity perceptions and social distancing. We show models with and without controls for science literacy and other predispositions. Full estimation results can be found in the Table A4 of the supporting materials.
Limitations and robustness
A study such as this comes with clear limitations. First, we have evaluated information coming from only a section of the overall media ecosystem and during a specific time-period. The level of misinformation differs across platforms and online news sites and a more granular investigation into these dynamics would be valuable. Our analysis suggests that similar dynamics exist across social media platforms, however. In the supplementary materials we show that associations between misperceptions and social media usage are even higher for other social media platforms, suggesting that our analysis of Twitter content may underrepresent the prevalence of misinformation on social media writ large. As noted above, existing limitations on data access make such cross-platform research difficult.
Second, our data is drawn from a single country and language case study and other countries may have different media environments and levels of misinformation circulating on social media. We anticipate the underlying dynamics found in this paper to hold across these contexts, however. Those who consume information from platforms where misinformation is more prevalent will have greater misperceptions and that these misperceptions will be linked to lower compliance with social distancing and lower risk perceptions. Third, an ecological problem is present wherein we do not link survey respondents directly to their social media consumption (and evaluation of the misinformation they are exposed to) and lack the ability to randomly assign social media exposure to make a strong causal argument. We cannot and do not make a causal argument here but argue instead that there is strong evidence for a misinformation to misperceptions to lower social distancing compliance link.
- / Fake News
- / Mainstream Media
- / Public Health
- / Social Media
Cite this Essay
Bridgman, A., Merkley, E., Loewen, P. J., Owen, T., Ruths, D., Teichmann, L., & Zhilin, O. (2020). The causes and consequences of COVID-19 misperceptions: Understanding the role of news and social media. Harvard Kennedy School (HKS) Misinformation Review . https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-028
Bibliography
Allcott, H., Boxell, L., Conway, J. C., Gentzkow, M., Thaler, M., & Yang, D. Y. (2020). Polarization and Public Health: Partisan Differences in Social Distancing during the Coronavirus Pandemic (Working Paper No. 26946; Working Paper Series). National Bureau of Economic Research. https://doi.org/10.3386/w26946
Al-Rawi, A. (2019). Gatekeeping Fake News Discourses on Mainstream Media Versus Social Media. Social Science Computer Review , 37 (6), 687–704. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894439318795849
Chadwick, A., & Vaccari, C. (2019). News sharing on UK social media: Misinformation, disinformation, and correction [Report]. Loughborough University. https://repository.lboro.ac.uk/articles/News_sharing_on_UK_social_media_misinformation_disinformation_and_correction/9471269
Dechêne, A., Stahl, C., Hansen, J., & Wänke, M. (2010). The Truth About the Truth: A Meta-Analytic Review of the Truth Effect. Personality and Social Psychology Review , 14 (2), 238–257. https://doi.org/10.1177/1088868309352251
Donovan, J. (2020). Social-media companies must flatten the curve of misinformation. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-01107-z
Feezell, J. T. (2018). Agenda Setting through Social Media: The Importance of Incidental News Exposure and Social Filtering in the Digital Era. Political Research Quarterly , 71 (2), 482–494. https://doi.org/10.1177/1065912917744895
Fletcher, R., & Nielsen, R. K. (2018). Are people incidentally exposed to news on social media? A comparative analysis. New Media & Society , 20 (7), 2450–2468. https://doi.org/10.1177/1461444817724170
Fung, I. C.-H., Fu, K.-W., Chan, C.-H., Chan, B. S. B., Cheung, C.-N., Abraham, T., & Tse, Z. T. H. (2016). Social Media’s Initial Reaction to Information and Misinformation on Ebola, August 2014: Facts and Rumors. Public Health Reports , 131 (3), 461–473. https://doi.org/10.1177/003335491613100312
Garrett, R. K. (2019). Social media’s contribution to political misperceptions in U.S. Presidential elections. PLoS ONE , 14 (3). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213500
Garrett, R. K., Weeks, B. E., & Neo, R. L. (2016). Driving a Wedge Between Evidence and Beliefs: How Online Ideological News Exposure Promotes Political Misperceptions. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , 21 (5), 331–348. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12164
Guess, A., & Nyhan, B. (2018). Selective Exposure to Misinformation: Evidence from the consumption of fake news during the 2016 U.S. presidential campaign. European Research Council , 49.
Jamieson, K. H., & Albarracín, D. (2020). The Relation between Media Consumption and Misinformation at the Outset of the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic in the US. Harvard Kennedy School Misinformation Review , 2 . https://doi.org/10.37016/mr-2020-012
Kim, L., Fast, S. M., & Markuzon, N. (2019). Incorporating media data into a model of infectious disease transmission. PLOS ONE , 14 (2), e0197646. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0197646
Kouzy, R., Abi Jaoude, J., Kraitem, A., El Alam, M. B., Karam, B., Adib, E., Zarka, J., Traboulsi, C., Akl, E. W., & Baddour, K. (2020). Coronavirus Goes Viral: Quantifying the COVID-19 Misinformation Epidemic on Twitter. Cureus , 12 (3). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7255
Mitchell, A., Gottfried, J., Barthel, M., & Shearer, E. (2016, July 7). The Modern News Consumer. Pew Research Center’s Journalism Project . https://www.journalism.org/2016/07/07/the-modern-news-consumer/
Motta, M., Stecula, D., & Farhart, C. E. (2020). How Right-Leaning Media Coverage of COVID-19 Facilitated the Spread of Misinformation in the Early Stages of the Pandemic [Preprint]. SocArXiv. https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/a8r3p
NewsGuard. (2020). Superspreaders . https://www.newsguardtech.com/superspreaders/
Owen, T., Loewen, P., Ruths, D., Bridgman, A., Gorwa, R., MacLellan, S., Merkley, E., & Zhilin, O. (2020). Lessons in Resilience: Canada’s Digital Media Ecosystem and the 2019 Election . Public Policy Forum. https://ppforum.ca/articles/lessons-in-resilience-canadas-digital-media-ecosystem-and-the-2019-election/
Radzikowski, J., Stefanidis, A., Jacobsen, K. H., Croitoru, A., Crooks, A., & Delamater, P. L. (2016). The Measles Vaccination Narrative in Twitter: A Quantitative Analysis. JMIR Public Health and Surveillance , 2 (1), e1. https://doi.org/10.2196/publichealth.5059
Sharma, M., Yadav, K., Yadav, N., & Ferdinand, K. C. (2017). Zika virus pandemic—Analysis of Facebook as a social media health information platform. American Journal of Infection Control , 45 (3), 301–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajic.2016.08.022
Shin, J., Jian, L., Driscoll, K., & Bar, F. (2018). The diffusion of misinformation on social media: Temporal pattern, message, and source. Computers in Human Behavior , 83 , 278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.02.008
Vicario, M. D., Bessi, A., Zollo, F., Petroni, F., Scala, A., Caldarelli, G., Stanley, H. E., & Quattrociocchi, W. (2016). The spreading of misinformation online. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 113 (3), 554–559. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1517441113
Weeks, B. E., Lane, D. S., Kim, D. H., Lee, S. S., & Kwak, N. (2017). Incidental Exposure, Selective Exposure, and Political Information Sharing: Integrating Online Exposure Patterns and Expression on Social Media. Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication , 22 (6), 363–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcc4.12199
The project was funded through the Department of Canadian Heritage’s Digital Citizens Initiative.
Competing Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The research protocol was approved by the institutional review board at University of Toronto. Human subjects gave informed consent before participating and were debriefed at the end of the study.
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided that the original author and source are properly credited.
Data Availability
All materials needed to replicate this study are available via the Harvard Dataverse: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/5QS2XP .
What to Know About the ‘FLiRT’ Variants of COVID-19

T he COVID-19 lull in the U.S. may soon come to an end, as a new family of SARS-CoV-2 variants—nicknamed “FLiRT” variants—begins to spread nationwide.
These variants are distant Omicron relatives that spun out from JN.1, the variant behind the surge in cases this past winter . They’ve been dubbed “FLiRT” variants based on the technical names for their mutations, one of which includes the letters “F” and “L,” and another of which includes the letters “R” and “T.”
Within the FLiRT family, one variant in particular has risen to prominence: KP.2, which accounted for about 25% of new sequenced cases during the two weeks ending Apr. 27, according to data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Other FLiRT variants, including KP.1.1, have not become as widespread in the U.S. yet.
Researchers are still learning about the FLiRT variants, and many questions remain about how quickly they’ll spread, whether they’ll cause disease that’s more or less severe than what we’ve seen previously, and how well vaccines will stand up to them. Here’s what we know so far.
Is another COVID-19 wave coming?
Despite KP.2's rise in the U.S., it’s too soon to tell whether the FLiRT family will be responsible for a major surge in cases, says Dr. Eric Topol, executive vice president at Scripps Research, who wrote about the FLiRT variants in a recent edition of his newsletter . For now, the amount of SARS-CoV-2 virus in U.S. wastewater remains “minimal,” according to the CDC , and hospitalizations and deaths have also continued to decline steadily since their recent peaks in January. At the global level , case counts rose from early to mid-April, but remain far lower than they were a few months ago.
KP.2 and its relatives will likely cause an uptick in cases, but “my hunch is it won’t be a big wave,” Topol says. “It might be a ‘wavelet.’” That’s because people who were recently infected by the JN.1 variant seem to have some protection against reinfection, Topol says, and the virus hasn’t mutated enough to become wildly different from previous strains. A recent study from researchers in Japan, which was posted online before being peer-reviewed, also found that KP.2 is less infectious than JN.1.
Do vaccines protect against KP.2 and other FLiRT variants?
Vaccines still provide good protection against COVID-19-related hospitalization and death. But two preliminary studies—the one from Japan and another from researchers in China , which was also posted online before being peer-reviewed—suggest the FLiRT variants may be better at dodging immune protection from vaccines than JN.1 was.
“That isn’t good,” Topol says, especially since many people who got the most recent booster—roughly 30% of adults in the U.S. — got it last fall, meaning their protection has begun to wane.
In an Apr. 26 statement , the World Health Organization recommended basing future vaccine formulations on the JN.1 lineage, since it seems the virus will continue to evolve from that variant. The most recent booster was based on an older strain, XBB.1.5.
How can I stay safe from new COVID-19 variants?
The virus continues to evolve, but public-health advice remains the same: stay up-to-date on vaccines, test before gatherings, stay home when you're ill, and consider masking and avoiding crowded indoor areas, especially when lots of COVID-19 is going around.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- What Student Photojournalists Saw at the Campus Protests
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Why Maternity Care Is Underpaid
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Scientists Are Finding Out Just How Toxic Your Stuff Is
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Jamie Ducharme at [email protected]
Featured Clinical Reviews
- Screening for Atrial Fibrillation: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement JAMA Recommendation Statement January 25, 2022
- Evaluating the Patient With a Pulmonary Nodule: A Review JAMA Review January 18, 2022
Select Your Interests
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
- Download PDF
- Share X Facebook Email LinkedIn
- Permissions
National Academies Report: COVID-19 Vaccines Don’t Cause Many Potential Harms
The COVID-19 vaccines made by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna do not cause such conditions as female infertility, myocardial infarction, Bell palsy, or Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults, according to a report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine that reviewed evidence for potential harms for 19 conditions associated with these vaccines. There was not enough evidence involving children to draw conclusions about possible harms.
The committee did conclude that there is evidence that these vaccines can cause myocarditis, although the group emphasized cases linked with vaccines are rare. The report follows a recent study published by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention showing no association between COVID-19 vaccination and sudden cardiac death among healthy young people.
The committee’s evidence also suggests that the Janssen vaccine may cause Guillain-Barré syndrome and thrombosis with thrombocytopenia syndrome. More broadly, the committee concluded that vaccinations in general might cause certain shoulder injuries from the injection itself.
The results of the report, which analyzed studies conducted soon after vaccines were available, represent a “snapshot in time,” and might not fully reflect the real-world use of the vaccines, author George Isham, MD, said in a statement . The report was sponsored by the Health Resources and Services Administration, a branch of the US Department of Health and Human Services.
Published Online: May 10, 2024. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.7724
See More About
Harris E. National Academies Report: COVID-19 Vaccines Don’t Cause Many Potential Harms. JAMA. Published online May 10, 2024. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.7724
Manage citations:
© 2024
Artificial Intelligence Resource Center
Cardiology in JAMA : Read the Latest
Browse and subscribe to JAMA Network podcasts!
Others Also Liked
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
Advertisement
Supported by
AstraZeneca Is Withdrawing Its Covid Vaccine Worldwide, Citing Low Demand
The shot is no longer being manufactured or supplied, and it is no longer authorized for use in Europe.
- Share full article

By Rebecca Robbins
AstraZeneca has started to pull its Covid-19 vaccine from global markets because of low demand, the pharmaceutical giant said. The decision closes the chapter on a shot that was widely used in the early stages of vaccination drives in many parts of the world before being supplanted by rivals that were better suited to take on an evolving virus.
The move was not related to any concerns about the shot’s side effects, the company said.
Since the vaccine was approved in Britain in December 2020, over three billion doses have been supplied globally. But in the past few years, demand has plummeted as other manufacturers have released shots tailored to newer variants and countries have opted to use those. AstraZeneca’s shot, which was developed with Oxford University, is no longer being manufactured or supplied.
The company said it had decided to voluntarily withdraw all licenses to market its Covid vaccine. That process began months ago, and very few active licenses remain, the company said. The Telegraph in Britain earlier reported the decision on Tuesday.
In March, AstraZeneca requested that the vaccine be withdrawn from most European countries. The European Commission approved the move, which went into effect this week.
Sheena Cruickshank, an immunologist at the University of Manchester, said the company’s decision to pull the shot was “not a surprise.” Unlike other manufacturers, AstraZeneca did not update its shot to target emerging virus variants because it used a vaccine technology, known as a viral vector, that was less amenable to such changes.
“There was just a recognition that it wasn’t going to be a vaccine that could continue to evolve for what we need now, and that it wasn’t really useful now because the SARS-CoV-2 virus has changed too much,” Dr. Cruickshank said.
In clinical trials, AstraZeneca’s shot did not perform as well in preventing Covid as Pfizer’s and Moderna’s shots did in their own studies, but AstraZeneca’s still proved highly effective in preventing serious illness and death from the virus.
Concerns about a link between AstraZeneca’s shot and an extremely rare but serious blood clotting disorder contributed to less demand for the vaccine. Its product information was updated in April 2021 to include risks about the potential side effect. AstraZeneca’s vaccine was cheaper and easier to transport and store than its competitors. It became the predominant vaccine used in developing countries for much of 2021, when shots from Pfizer and Moderna were mostly going to wealthy nations.
Kim Blomley, an AstraZeneca spokesman, said the company was “incredibly proud” of the vaccine’s role in ending the coronavirus pandemic.
The vaccine was distributed in more than 170 countries, and most of its doses were administered in 2021. It was never administered in the United States outside clinical trials.
Rebecca Robbins is a reporter covering the pharmaceutical industry. She has been reporting on health and medicine since 2015. More about Rebecca Robbins
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

AstraZeneca withdraws Covid-19 vaccine worldwide, citing surplus of newer vaccines
Pharmaceutical company says newer shots led to decline in demand for AstraZeneca vaccine, which is no longer being manufactured or supplied
AstraZeneca has begun the worldwide withdrawal of its Covid-19 vaccine due to a “surplus of available updated vaccines” that target new variants of the virus.
The announcement follows the pharmaceutical company in March voluntarily withdrawing its European Union marketing authorisation , which is the approval to market a medicine in member states.
On 7 May, the European Medicines Agency issued a notice that the vaccine is no longer authorised for use .
In a statement, AstraZeneca said the decision was made because there is now a variety of newer vaccines available that have been adapted to target Covid-19 variants. This had led to a decline in demand for the AstraZeneca vaccine, which is no longer being manufactured or supplied.
“According to independent estimates, over 6.5 million lives were saved in the first year of use alone and over 3bn doses were supplied globally,” the statement said.
“Our efforts have been recognised by governments around the world and are widely regarded as being a critical component of ending the global pandemic. We will now work with regulators and our partners to align on a clear path forward to conclude this chapter and significant contribution to the Covid-19 pandemic.”
Other countries have already stopped supplying the vaccine. It has not been available for use in Australia since March 2023, though its use was already being phased out from June 2021 due to the widespread availability of newer vaccines.
AstraZeneca changed the name of its Covid vaccine to Vaxzevria in 2021. The vaccine was authorised for use in those aged 18 and older, delivered as two injections, usually into the muscle of the upper arm, about three month apart. It was also used by some countries as a booster shot.
Vaxzevria is made up of another virus of the adenovirus family modified to contain the gene for making a protein from SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19. The vaccine does not contain the virus itself and cannot cause the virus.
Although the vaccine was found to be safe and effective overall, it carried the risk of a rare but serious side-effect, known as thrombosis with thrombocytopenia, or TTS. The rare syndrome occurred in about two to three people per 100,000 who were vaccinated with the Vaxzevria vaccine.
The chair of epidemiology at Deakin University in Australia, Prof Catherine Bennett, said the vaccine had played a pivotal part in the worldwide fight against the virus, particularly in the early days of the pandemic when limited vaccines were available.
“It has saved millions of lives and that should not be forgotten,” she said.
“It was a really important part of the initial global response. However, it targeted the initial ancestral variants. We’ve now moved into a vaccine chain where we have products available that are chasing the variants that are emerging.
“There’s also a shift in the risk calculus as well, given populations are much more protected and, even though of course Covid still causes deaths, we are overall less vulnerable to the disease.”
The latest Covid-19 vaccine advice issued by the World Health Organisation in April advised that formulations of Covid-19 vaccines should target the JN.1 lineage of the virus, which is displacing existing XBB lineage variants.
- AstraZeneca
- Coronavirus
- Infectious diseases
- Pharmaceuticals industry
Most viewed
More From Forbes
The dramatically rising toll of alcohol abuse.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
The toll of alcohol abuse is rising dramatically.
In the United States, the leading preventable cause of death is tobacco and second is poor diet and physical inactivity. Care to guess what comes in third? You can’t be faulted if you guessed opioids such as illicit fentanyl, given all the media attention it gets. But no, it’s something much more accessible, advertised directly to the consumer and having a negative impact across all socioeconomic groups: Alcohol, and specifically the problem of alcohol abuse which is dramatically worsening recently.
From 1999 to 2017, the number of alcohol-related deaths in the U.S. doubled, to more than 70,000 a year. These numbers got much worse at the height of the Covid-19 pandemic. According to the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, alcohol-related deaths soared , reaching 178,000 in 2020 and 2021. Comprehensive federal datasets have yet to be released for 2022 and 2023.
In a study published in 2020 in the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers showed that significant increases in mortality started emerging in the mid 2010s across all racial and ethnic groups. But the steepest rate of acceleration of alcohol-induced deaths occurred among younger, white individuals, especially women. Authors noted that the large increases among younger age groups presaged “substantial future increases in alcohol-related disease.” In light of more recent figures which suggest an intensifying problem, it appears that the researchers’ warning provided more than four years ago was prescient.
What could be compounding the problem of youth drinking are the ways in which advertisers depict alcohol consumption. They emphasize its social acceptability—even its supposed link to social success—and this especially applies when commercials direct their messages at a comparatively young demographic.
The data demonstrate that the marketing works. Researchers publishing in the Journal of Public Health Research found a strong association between the youth-appeal of marketing content of televised alcohol advertisements and the brand-specific consumption of both underage youth and adults.
The Best Mattress For Couples, Regardless Of Your Sleep Styles
Wwe smackdown results winners and grades on may 10 2024, the 8 best trampolines with insights from an industry expert.
Critics of certain commercials that are aimed at a younger demographic, like a beer ad which aired in 2019 promoting “Coors Light. The Official Beer of Saturday Morning,” suggest the companies that sponsor the advertising are going too far.
The negative health effects of alcohol are usually because of excessive drinking over long periods of time. Here, the leading causes of alcohol-attributable deaths are liver and cardiovascular diseases, seven types of cancer—including liver, throat, mouth, esophagus and stomach—as well as alcohol use disorder. NIAAA defines the latter as a “medical condition characterized by an impaired ability to stop or control alcohol use despite adverse social, occupational, or health consequences.” This can encompass alcohol abuse, dependence, addiction and the colloquial term, alcoholism.
But consuming a large amount of alcohol in a short period of time can also be deadly, as it may lead to alcohol poisoning or other dangers like motor vehicle accidents. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that 17% of U.S. adults binge drink. Moreover, in 2021 alcohol-impaired driving fatalities accounted for 13,384 (roughly a third) of all motor vehicular deaths. And 40% of violent crimes such as assault, homicide and domestic abuse, were committed by people who had high blood alcohol content at the time of their arrest.
The rise in alcohol abuse certainly isn’t limited to the U.S. In the United Kingdom, for instance, The Guardian reported last month that heavier drinking during the Covid-19 pandemic led to 2,500 more deaths from alcohol in 2022 than in 2019, a 33% jump.
While alcohol can be a toxic, carcinogenic drug, it’s also enjoyed by many people in moderation and often as an accompaniment—a lubricant of sorts—in a variety of social settings. Research psychologists have found that drinking moderate amounts of alcohol in a group setting “boosts people’s emotions and enhances social bonding.”
In addition, there may be physical gains associated with consumption of small amounts of alcohol. The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and others, like WebMD, still tout certain cardiovascular health benefits related to moderate intake of alcohol.
Nevertheless, other health entities, such as the Mayo Clinic, appear to be taking a different stance lately. The hospital group now says that “drinking alcohol in any amount carries a health risk,” though it qualifies the statement by suggesting that “while the risk is low for moderate intake, the risk increases as the amount you drink goes up.”
And a STAT News article published this month indicates that “alcohol isn’t healthy after all.” The publication asks whether the new dietary guidelines, set by the U.S. Departments of Agriculture and Health and Human Services and scheduled to be released in 2025, will be shaped more by health or (alcohol) industry interests? It’s suggested that changes in guidance are likely if the experts who draft the recommendations take into account the evidence of alcohol-related harms, including “heightened risks of certain cancers, chronic diseases, and injuries.”
While prevention is important, treatment is equally vital. Research published by The Lancet shows that early, preventive strategies in primary care can be effective, and a variety of interventions are available to treat alcohol dependence.
However, access to quality care for alcohol misuse and alcohol-associated diseases is often lacking. Additionally, there may be a stigma attached to seeking help for something as socially acceptable and easily accessible as alcohol.
Public health specialists have therefore asserted that it’s time for a national dialogue about substance misuse of all drugs, legal and illegal, and that this discussion should include alcohol. In this context, experts suggest that efforts need to be centered around research on alcoholism, addiction and abuse, as well as ways to improve access to therapy for alcohol use disorders, possible curbs on advertising and targeted awareness and education campaigns.
However, alcohol abuse and misuse is not (yet) considered a public health emergency. Without declaring it as such, sufficient funding for a concerted nationwide policy is not forthcoming, which means the federal government hasn’t prioritized an alcohol policy in the same way it has done for illicit drugs, or prescription opioids for that matter. Perhaps the latest alarming figures on the rising toll of alcohol abuse will help trigger more urgency.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
New COVID-19 FLiRT strain detected in Arizona. Here's what you need to know

A new set of COVID-19 subvariants has been significantly increasing in prevalence but the strains, known as FLiRT, are not expected to cause more serious illness than prior versions of the virus.
David Engelthaler, who leads the infectious-diseases division of the Arizona-based Translational Genomics Research Institute, says the FLiRT strains of the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes COVID-19 are "definitely the latest sequel to omicron."
People at high risk should still be on alert, but FLiRT does not appear to pose a higher threat than other strains of the COVID-19 virus, he said.
There have been a "couple of instances of FLiRT variants" detected in Arizona but it's difficult to have a good gauge on how much is here because sequencing of the virus strains has significantly declined from the levels of sequencing that happened during the pandemic, Engelthaler said.
"We do know it's here. We've seen it and that's not a surprise," Engelthaler said of the FLiRT strains. "It is likely showing up in every state."
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention is tracking the KP.2 and KP.1.1 strains of the COVID-19 virus, which are sometimes referred to as FLiRT, officials told The Arizona Republic in an email. KP.2 is right now the dominant COVID-19 variant in the U.S., but laboratory testing data indicate low levels of transmission of the virus at the moment, a CDC spokesperson wrote.
"That means that while KP.2 is proportionally the most predominant variant, it is not causing an increase in infections as transmission of SARS-CoV-2 is low," the spokesperson wrote. "Based on current data there are no indicators that KP.2 would cause more severe illness than other strains. CDC will continue to monitor community transmission of the virus and how vaccines perform against this strain."
Will FLiRT will cause a summer surge of COVID-19?
There is not enough evidence to say whether FLiRT strains will cause a summer COVID-19 surge, Engelthaler said.
The latest estimates from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention say that the FLiRT subvariant KP.2 was 25% of the strains in circulation across the U.S. for the two-week period ending April 27, up from 11% from the prior two-week period ending April 13.
KP.1.1, another of the FLiRT strains, went from 3% of the estimated strains in circulation to 7.5% in the reporting period ending April 27, CDC data shows.
"Clearly it's becoming the more common set of variants that are out there now but it doesn't mean that we are really seeing increases in cases," Engelthaler said. "In fact, when you look at the numbers pretty much everywhere it looks like it is trending down. So this is just the most efficient version."
Similarly, Dr. Eric Topol, a cardiologist and executive vice president at Scripps Research who writes a popular newsletter about the latest COVID-19 research, on April 18 predicted that there could be a "wavelet but not a significant new wave of infections as a result of the FLiRT variants over the next couple of months."
Topol believes it will take a much bigger challenge to our immune response than what the FLiRT subvariants are showing to cause a big new wave, but "we can't necessarily count on that optimistic perspective" and "time will tell."
Why is it significant that FLiRT is related to the omicron variant?
Like other strains of the COVID-19 virus, the FLiRT versions are descendants of the omicron subvariant. Omicron subvariants have the same characteristics: They seem to spread easily and evade antibodies built up from vaccinations and previous infections which is why new subvariants keep emerging.
"It's a couple of variants that are additional subvariants of the original omicron," Engelthaler said of FLiRT. "This will likely spread around a little easier but right now we're not seeing any indications that it's causing a real uptick. It's possible we see that, but I don't know that that risk is very high."
FLiRT earned its nickname because of mutations in the spike protein on the COVID-19 virus, one where an F amino acid turned into an L and one where an R turned into a T.
"Pretty much every infection in the world and every form of this virus we see is all omicron, just different variants of omicron," Engelthaler said.
"It is possible that there are some that are circulating out in some animals. ... It could be a different version, a non-omicron version and that might be cause for concern and that is why we are continuing to test animals and watching this out in the environment, as well as seeing what is still spreading between humans."
Why is the COVID-19 virus still circulating?
The COVID-19 virus has settled into an evolutionary strategy, Engelthaler explained. The virus is making minor tweaks in the spike protein just enough to get away from the antibodies people have built up from the previous versions, he said, and that way it can survive and move around.
"This is still the same omicron virus. By and large for most people, it could be a nasty cold. Some people could still have a serious outcome from it, but those are the people that we know are the highest risk," Engelthaler said. "And if they haven't had a previous infection or vaccination or a recent one, they would be at higher risk."
Engelthaler compared the subvariants of omicron to the "Fast & Furious" action film franchise.
"Every six months it feels like there's a new sequel coming out. There's a bit of hype around it and it is a little bit different from the last one," Engelthaler said. "But in the end you really can't tell the difference between them and this is pretty much how this virus is going to keep moving around."
Reach health-care reporter Stephanie Innes at [email protected] or at 480-313-3775. Follow her on X, formerly known as Twitter, @stephanieinnes .
A deadly coronavirus has resurfaced in Saudi Arabia, killing at least one patient
First detected in 2012, mers has about a 36% fatality rate and is similar to the virus that causes covid-19, by matthew rozsa.
On Wednesday, May 8, the World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed an April outbreak of a coronavirus similar to SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19. Four new infections of a coronavirus known as Middle East respiratory syndrome ( MERS-CoV ) have been reported in Saudi Arabia , according to health officials in that country. At least one of those cases resulted in death.
Because at least two of the MERS-CoV infections involved human-to-human transmission, some researchers are concerned that the outbreak could cause a new pandemic. Despite these fears, the WHO still assesses the overall risk posed by MERS to be "moderate" both regionally and globally. That is in part because three of the four confirmed cases were all limited to a single hospital in the Saudi Arabian capital of Riyadh. The last infection occurred in the city of Taif and involved a patient who had contact with camels. That infection is not believed to be directly connected to the other three.
"The three cases are epidemiologically linked to exposures in a health-care facility in Riyadh, although investigations are ongoing to verify this and understand the route of transmission," the WHO said.
In the one case that became a fatality, the WHO reports that the patient was a 56-year-old male schoolteacher who reported a cough, runny nose, fever and body aches on March 29. He was admitted to an emergency room at a Riyadh hospital on April 4, and two days later was transferred to the Intensive Care Unit isolation and intubated. He had preexisting health conditions that may have contributed to his death, including high blood pressure and chronic renal failure requiring hemodialysis. It is unclear how he was initially exposed to MERS-CoV.
MERS first came to light in 2012, and since then has been responsible for about 940 deaths out of 2,500 cases, giving it a pretty high fatality rate of 36%. There is currently no vaccine for this virus.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Coronavirus may have originated in bats or pangolins. The first known cases of COVID-19 were in Wuhan, China. Learn more about its origin, causes, and transmission here.
The coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) is a highly transmittable and pathogenic viral infection caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which emerged in Wuhan, China and spread around the world. Genomic analysis revealed that SARS-CoV-2 is phylogenetically related to severe acute respiratory syndrome-like (SARS ...
Yet well into the fourth year of the Covid-19 pandemic, intense political and scientific debates about its origins continue. The two major hypotheses are a natural zoonotic spillover, most likely ...
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays. Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic. The global impact of COVID-19, the disease ...
On February 11, 2020, the WHO released a new name for the disease causing the deadly outbreak: Coronavirus Disease 2019 or COVID-19. By mid-March 2020, all 50 U.S. states had reported at least one ...
The ongoing spread of COVID-19 has been fueled by the emergence of variants in evolving lineages of SARS-CoV-2. Such variants generally carry mutations that strengthen characteristics such as the virus's ability to infect individuals (including individuals who are vaccinated and who previously had COVID-19), to cause severe disease, and to potentially escape certain treatments.
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Most people infected with the virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory illness and recover without requiring special treatment. However, some will become seriously ill and require medical attention. Older people and those with underlying medical ...
This essay examines key aspects of social relationships that were disrupted by the COVID-19 pandemic. It focuses explicitly on relational mechanisms of health and brings together theory and emerging evidence on the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic to make recommendations for future public health policy and recovery. We first provide an overview of the pandemic in the UK context, outlining the ...
The student or a family member had COVID-19 or suffered other illnesses due to confinement during the pandemic. The student suffered from a lack of internet access and other online learning challenges. Students who dealt with problems registering for or taking standardized tests and AP exams. Jeff Schiffman of the Tulane University admissions ...
Horrific history. Looking back, the COVID-19 pandemic stands as arguably the most disruptive event of the 21st century, surpassing wars, the September 11, 2001, terrorist attacks, the effects of climate change, and the Great Recession. It has killed more than seven million people to date and reshaped the world economy, public health, education ...
The most widespread coronavirus to date was discovered in Wuhan, China in November 2019, and the disease it causes is named coronavirus disease (COVID‐19). The disease is a class of epidemics with human‐to‐human transmission caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) (Kumar et al., 2021 ; Li et al., 2021 ...
But the virus that causes COVID-19 has only been studied since it began to spread in 2019. So, research into the specific effects of long-term COVID-19 symptoms continues. Researchers do think that post-COVID-19 syndrome can happen after an illness of any severity. Getting a COVID-19 vaccine may help prevent post-COVID-19 syndrome.
COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. COVID-19 can cause mild to severe respiratory illness, including death. The best preventive measures include getting vaccinated, wearing a mask during times of high transmission, staying 6 feet apart, washing hands often and avoiding sick people. Contents Overview Symptoms and Causes Diagnosis and ...
We investigate the relationship between media consumption, misinformation, and important attitudes and behaviours during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. We find that comparatively more misinformation circulates on Twitter, while news media tends to reinforce public health recommendations like social distancing. We find that exposure to social media is associated with ...
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a dramatic loss of human life worldwide and presents an unprecedented challenge to public health, food systems and the world of work. The economic and social disruption caused by the pandemic is devastating: tens of millions of people are at risk of falling into extreme poverty, while the number of ...
1. Introduction. The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to unprecedented changes in people's daily lives, with implications for mental health and well-being [1-4], both at the level of a given country's population, and when considering specific vulnerable groups [5-7].In order to mitigate the untoward impact of the pandemic (including lockdown) and support mental health ...
The Covid-19 essay was introduced so universities could gain a better understanding of how their applicants have had their lives and education disrupted due to the pandemic. You'll want to give ...
The COVID-19 pandemic is among the deadliest infectious diseases to have emerged in recent history. As with all past pandemics, the specific mechanism of its emergence in humans remains unknown. ... In 2016, yet another novel bat-origin coronavirus, an α-coronavirus, emerged in China to cause a novel epizootic disease in pigs, termed swine ...
From lifestyle changes to better eating habits, people are using this time to get healthier in many areas. Since the pandemic started, nearly two-thirds of the survey's participants (62%) say ...
100 Words Essay on Covid 19. COVID-19 or Corona Virus is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in 2019. It is similar to other coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, but it is more contagious and has caused more severe respiratory illness in people who have been infected. The novel coronavirus became a global pandemic in a very ...
The COVID-19 lull in the U.S. may soon come to an end, as a new family of SARS-CoV-2 variants—nicknamed "FLiRT" variants—begins to spread nationwide. These variants are distant Omicron ...
The COVID-19 vaccines made by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna do not cause such conditions as female infertility, myocardial infarction, Bell palsy, or Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults, according to a report by the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine that reviewed evidence for potential harms for 19 conditions associated with these vaccines.
A novel coronavirus (CoV) named '2019-nCoV' or '2019 novel coronavirus' or 'COVID-19' by the World Health Organization (WHO) is in charge of the current outbreak of pneumonia that began at the beginning of December 2019 near in Wuhan City, Hubei Province, China [1-4]. COVID-19 is a pathogenic virus. From the phylogenetic analysis ...
The F.D.A. is monitoring reports of tinnitus, but "at this time, the available evidence does not suggest a causal association with the Covid-19 vaccines," the agency said in a statement.
AstraZeneca has started to pull its Covid-19 vaccine from global markets because of low demand, the pharmaceutical giant said. The decision closes the chapter on a shot that was widely used in the ...
Vaxzevria is made up of another virus of the adenovirus family modified to contain the gene for making a protein from SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes Covid-19. The vaccine does not contain the ...
From 1999 to 2017, the number of alcohol-related deaths in the U.S. doubled, to more than 70,000 a year. These numbers got much worse at the height of the Covid-19 pandemic.
A new set of COVID-19 subvariants has been significantly increasing in prevalence but the strains, known as FLiRT, are not expected to cause more serious illness than prior versions of the virus.
COVID-19 (Coronavirus) has affected day to day life and is slowing down the global economy. This pandemic has affected thousands of peoples, who are either sick or are being killed due to the spread of this disease. The most common symptoms of this viral infection are fever, cold, cough, bone pain and breathing problems, and ultimately leading ...
A deadly coronavirus has resurfaced in Saudi Arabia, killing at least one patient First detected in 2012, MERS has about a 36% fatality rate and is similar to the virus that causes COVID-19