- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax

12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.

7 Key Components of a Precise Business Plan (2024)
Learn the art of entrepreneurship with a business plan. Dive into executive summaries, discover templates, and understand what to include for a strategic edge.

Hadar Peretz
7 minute read

Short answer
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a strategic document outlining a company's vision, objectives, market analysis, marketing and sales strategies, organizational structure, and financial projections to guide its growth.
Innovation in Planning: The Untold Ingredient to Business Success
In the turbulent landscape of entrepreneurship, where over 20% of small ventures falter in their early days , this blog post sheds light on the importance of a well-structured business plan.
It delves into the specifics of an executive summary, steps, what to include, and innovation in business planning , guiding businesses to thrive rather than become failure statistics.
3 Main Purposes of a Business Plan
Embarking on the entrepreneurial journey without a business plan is like sailing in turbulent waters without a map.
A business plan serves three pivotal roles that steer the helm of a startup toward the shores of success.
1) Navigation Tool: Direction for Your Business
A business plan is your business’s North Star, providing direction and ensuring you stay on course amidst the storm of uncertainties.
Let’s take the example of “Bean There Coffee Shop,” a start-up that envisioned being a community hub. Their business plan outlined their mission, target market, competition analysis, and financial forecasts.
This helped them navigate the competition and establish a loyal customer base by providing a cozy ambiance that encouraged customer interaction.
2) Attraction for Investments: Encouraging Potential Investors
Your business plan is your passport to the realm of investors. Bean There Coffee Shop required a modern interior to reflect its brand's personality.
The detailed business plan showcased their unique selling proposition to investors, who were enticed by the predicted ROI and agreed to fund the renovations.
3) Measurement of Success: Evaluating Progress and Growth
A business plan sets a baseline to measure progress. Bean There Coffee Shop sets quarterly targets for customer retention and revenue in its business plan.
By comparing actual performance with the plan, they gauged their success and identified areas for improvement.
6 Key Elements of a Business Plan
Drafting a business plan might seem daunting initially, but breaking it down into core components makes it manageable and effective.
It’s about telling your business’s story in a compelling way to garner support and guide your actions.
1) Executive Summary
The executive summary is your business narrative condensed into a snapshot. For instance, the executive summary of Bean There Coffee Shop encapsulated its vision, mission, the experience it aimed to provide, and financial aspirations succinctly, giving readers an essence of what to expect in the subsequent sections.
For more information on executive summary design, delve into the design aspects of an executive summary. To glean insights on crafting a compelling and visually appealing executive summary for your startup venture.
2) Company Description
Delve into the what and why of your business. Bean There Coffee Shop described its longing to foster community interactions, reflecting its ethos in its service and interior design , resonating with the locals and creating a clientele.
3) Market Analysis
Understanding your market landscape is crucial. Analyze your competitors, the preferences of your target audience, and market trends.
For Bean There Coffee Shop, studying coffee consumption trends and identifying a locale lacking a community-centric cafe was a game-changer.
4) Organization and Management
Outline your business structure and team. Investors want to know who steers the ship.
At Bean There Coffee Shop, the experienced baristas and a seasoned manager showcased a competent team, instilling confidence in potential investors.
5) Product Line
Describe your offerings. Bean There Coffee Shop highlighted its organic coffee and locally sourced pastries, striking a chord with environmentally conscious consumers.
6) Marketing and Sales
How you plan to lure customers and keep them coming back is vital. Bean There Coffee Shop’s loyalty programs and community events were a hit, creating a buzz and building a loyal customer base.
What is a Business Plan in Entrepreneurship?
In the realm of entrepreneurship, a business plan goes beyond being just a document—it is a vibrant testament to your business vision and the roadmap illustrating how you aim to overcome challenges and achieve your objectives.
It's like the script of your entrepreneurial saga waiting to unfold.
A Framework for Strategy
A business plan embodies the strategy and operations of your entrepreneurial endeavor. Here's a simplified breakdown of what it may encompass:
Market Analysis: A thorough exploration of the market including size, demographics, and consumer behaviors.
Competitor Analysis: A detailed examination of competitors, their strengths, weaknesses, and market position.
Marketing Strategy: Tactics and channels you plan to use to promote your business.
Financial Projections: Anticipated income, expenses, and profitability over a certain period.
Risk Management
Venturing into entrepreneurship is akin to navigating turbulent waters, where risks are inevitable. A business plan aids in:
Identifying Potential Risks: Whether it's market fluctuation or operational challenges, a business plan helps in foreseeing possible hurdles.
Devising Contingency Plans: Strategies to mitigate identified risks, ensuring the business stays on the right track.
For instance, a cafe's business plan might highlight the risk of decreased foot traffic during winter months and propose hosting indoor events or offering seasonal promotions to maintain revenue.
Communication with Stakeholders
A business plan serves as a conduit between entrepreneurs and stakeholders, articulating the business vision, goals, and strategies.
When seeking investments for expansion, a well-drafted business plan can effectively communicate the growth potential and return on investment to investors, facilitating the funding process.
7 Steps of a Business Plan
Creating a business plan is a blend of art and science, distilled into seven systematic steps to ensure your entrepreneurial venture is on a trajectory toward success.
1) Research, Research, and Research
Before you set pen to paper, immerse yourself in thorough research about your industry, market, and competition. This step lays the groundwork for informed decision-making as you progress through subsequent stages of business planning.
Industry Insights: Delve into current industry trends, challenges, and opportunities to gain a comprehensive understanding.
Market Dynamics: Explore market demographics, customer preferences, and purchasing behaviors to tailor your business approach.
Competitor Analysis: Assess the strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning of competitors to identify your business’s unique selling proposition.
2) Defining Your Business Objectives
Having clear objectives is crucial. Whether it's capturing market share, hitting revenue targets, or achieving expansion goals, defining these objectives paves the way for a focused strategy.
Establishing well-defined objectives also serves as a yardstick for measuring your business’s performance over time.
3) Company Description
Articulate the ethos, offerings, and unique value proposition of your business.
Providing a compelling company description helps stakeholders, including potential investors and employees, to grasp your business's mission and the problems it aims to solve
4) Market Analysis
Delve into market trends, customer behavior, and competition analysis to tailor your strategies.
A robust market analysis provides the data necessary to target your audience effectively and position your business for success in a competitive landscape.
5) Organization and Management
Detail your organizational structure, key team members, and their expertise.
Illustrating a solid organizational structure demonstrates your business’s capacity to execute its strategies and achieve its objectives.
6) Service or Product Line
Describe your products or services, highlighting the benefits to customers. Detailing the attributes and advantages of your offerings allows stakeholders to understand the value your business brings to the market.
7. Marketing and Sales
Illustrate your marketing and sales strategy to attract and retain customers.
Outlining clear strategies for marketing and sales is crucial for driving business growth and achieving your financial objectives.
Market Positioning: Define how your products or services will be positioned in the market and how you intend to differentiate your offerings from competitors.
Promotional Strategies: Outline the various promotional tactics you will employ, such as social media marketing, search engine optimization, and paid advertising.
Sales Process: Describe the steps of your sales process from lead generation to closing sales, and identify the metrics you will use to measure sales effectiveness.
Customer Retention: Highlight the strategies for customer retention such as loyalty programs, excellent customer service, and regular engagement to keep customers coming back.
Pricing Strategy: Determine the pricing strategy that will be most effective for your market, considering factors like cost, competition, and perceived value.
Time to Master Your Business Pitch
Now that you have a robust business plan, it’s time to translate it into a compelling business pitch.
The mastery of your pitch lies in knowing your audience, presenting data compellingly, and choosing the right format for resonance.
Understanding Audience Expectations
Understanding your audience is pivotal. Tailoring your pitch to meet the expectations of investors, potential partners, or customers enhances its effectiveness significantly.
Here’s our CEO, Itai Amoza, discussing the key elements that make a presentation engaging:

Emphasizing Data Visualization for a Better Appeal
Visual presentation of data, through graphs or charts, can make complex information easily digestible.
Using the right data visualization tools can effectively narrate the story of your venture compellingly.
PDF (conservative) vs. Interactive
Choosing between a traditional PDF or interactive presentations like those on Storydoc or PowerPoint can significantly impact the engagement level of your audience.
Interactive formats allow for dynamic presentations with embedded videos and other multimedia elements making your pitch more engaging and memorable.

Consider Business Plan One-pager
Creating a one-page business plan rather than a multi-page business plan involves summarizing your business's essential aspects concisely.
This includes your value proposition, company overview, market analysis, the problem and solution, marketing strategy, financial projections, and a call to action for potential investors or partners.
Ready to Narrate Your Story? Begin with This Business Plan Template
Ah, the exhilarating journey of a startup. It's like crafting a story, with characters, plots, and a dash of suspense on what the next chapter brings.
Now, before you get swept away in this narrative, remember, that every good story needs a structured outline, and in the startup world, that outline is your business plan.
Pick a business plan one-pager template:
Create story from scratch

I am a Marketing Specialist at Storydoc, I research, analyze and write on our core topics of business presentations, sales, and fundraising. I love talking to clients about their successes and failures so I can get a rounded understanding of their world.

Found this post useful?
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Get notified as more awesome content goes live.
(No spam, no ads, opt-out whenever)
You've just joined an elite group of people that make the top performing 1% of sales and marketing collateral.
Create your best presentation to date
Try Storydoc interactive presentation maker for 14 days free (keep any presentation you make forever!)
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

The 10 Key Components of a Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1 million entrepreneurs and business owners write business plans. These plans have been used to raise funding and grow countless businesses.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
From working with all these businesses, we know what the 10 elements in any great business plan. Providing a comprehensive assessment of each of these components is critical in attracting lenders, angel investors, venture capitalists or other equity investors.
Get started with a title page that includes your company name, logo and contact information, since interested readers must have a simple way to find and reach out to you. After that be sure to include the 10 parts of a business plan documented below.
What are the 10 Key Components of a Business Plan?
The 10 sections or elements of a business plan that you must include are as follows:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a succinct synopsis of the business plan, and highlights the key points raised within. It often includes the company’s mission statement and description of the products and services. It’s recommended by me and many experts including the Small Business Administration to write the executive summary last.
The executive summary must communicate to the prospective investor the size and scope of the market opportunity, the venture’s business and profitability model, and how the resources/skills/strategic positioning of the company’s management team make it uniquely qualified to execute the business plan. The executive summary must be compelling, easy-to-read, and no longer than 2-4 pages.
2. Company Analysis
This business plan section provides a strategic overview of the business and describes how the company is organized, what products and services it offers/will offer, and goes into further detail on the business’ unique qualifications in serving its target markets. As any good business plan template will point out, your company analysis should also give a snapshot of the company’s achievements to date, since the best indicator of future success are past accomplishments.
3. Industry or Market Analysis
This section evaluates the playing field in which the company will be competing, and includes well-structured answers to key market research questions such as the following:
- What are the sizes of the target market segments?
- What are the trends for the industry as a whole?
- With what other industries do your services compete?
To conduct this market research, do research online and leverage trade associations that often have the information you need.
4. Analysis of Customers
The customer analysis business plan section assesses the customer segment(s) that the company serves. In this section, the company must convey the needs of its target customers. It must then show how its products and services satisfy these needs to an extent that the customer will pay for them.
The following are examples of customer segments: moms, engaged couples, schools, online retailers, teens, baby boomers, business owners, etc.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of business you operate as different segments often have different needs. Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. With regards to psychographic variables, discuss whether your customers have any unique lifestyles, interests, opinions, attitudes and/or values that will help you market to them more effectively.
5. Analysis of Competition
All capable business plan writers discuss the competitive landscape of your business. This element of your plan must identify your direct and indirect competitors, assesses their strengths and weaknesses and delineate your company’s competitive advantages. It’s a crucial business plan section.
Direct competitors are those that provide the same product or service to the same customer. Indirect competitors are those who provide similar products or services. For example, the direct competitors to a pizza shop are other local pizza shops. Indirect competitors are other food options like supermarkets, delis, other restaurants, etc.
The first five components of your business plan provide an overview of the business opportunity and market research to support it. The remaining five business plan sections focus mainly on strategy, primarily the marketing, operational, financial and management strategies that your firm will employ.
6. Marketing, Sales & Product Plan
The marketing and sales plan component of your business plan details your strategy for penetrating the target markets. Key elements include the following:
- A description of the company’s desired strategic positioning
- Detailed descriptions of the company’s product and service offerings and potential product extensions
- Descriptions of the company’s desired image and branding strategy
- Descriptions of the company’s promotional strategies
- An overview of the company’s pricing strategies
- A description of current and potential strategic marketing partnerships/ alliances
7. Operations Strategy, Design and Development Plans
These sections detail the internal strategies for building the venture from concept to reality, and include answers to the following questions:
- What functions will be required to run the business?
- What milestones must be reached before the venture can be launched?
- How will quality be controlled?
8. Management Team
The management team section demonstrates that the company has the required human resources to be successful. The business plan must answer questions including:
- Who are the key management personnel and what are their backgrounds?
- What management additions will be required to make the business a success?
- Who are the other investors and/or shareholders, if any?
- Who comprises the Board of Directors and/or Board of Advisors?
- Who are the professional advisors (e.g., lawyer, accounting firm)?
9. Financial Plan
The financial plan involves the development of the company’s revenue and profitability model. These financial statements detail how you generate income and get paid from customers,. The financial plan includes detailed explanations of the key assumptions used in building the business plan model, sensitivity analysis on key revenue and cost variables, and description of comparable valuations for existing companies with similar business models.
One of the key purposes of your business plan is to determine the amount of capital the firm needs. The financial plan does this along with assessing the proposed use of these funds (e.g., equipment, working capital, labor expenses, insurance costs, etc.) and the expected future earnings. It includes Projected Income Statements, Balance Sheets (showing assets, liabilities and equity) and Cash Flow Statements, broken out quarterly for the first two years, and annually for years 1-5.
Importantly, all of the assumptions and projections in the financial plan must flow from and be supported by the descriptions and explanations offered in the other sections of the plan. The financial plan is where the entrepreneur communicates how he/she plans to “monetize” the overall vision for the new venture. Note that in addition to traditional debt and equity sources of startup and growth funding that require a business plan (bank loans, angel investors, venture capitalists, friends and family), you will probably also use other capital sources, such as credit cards and business credit, in growing your company.
10. Appendix
The appendix is used to support the rest of the business plan. Every business plan should have a full set of financial projections in the appendix, with the summary of these financials in the executive summary and the financial plan. Other documentation that could appear in the appendix includes technical drawings, partnership and/or customer letters, expanded competitor reviews and/or customer lists.
Find additional business plan help articles here.
Expertly and comprehensively discussing these components in their business plan helps entrepreneurs to better understand their business opportunity and assists them in convincing investors that the opportunity may be right for them too.
In addition to ensuring you included the proper elements of a business plan when developing your plan always think about why you are uniquely qualified to succeed in your business. For example, is your team’s expertise something that’s unique and can ensure your success? Or is it marketing partnerships you have executed? Importantly, if you don’t have any unique success factors, think about what you can add to make your company unique. Doing so can dramatically improve your success. Also, whether you write it on a word processor or use business plan software , remember to update your plan at least annually. After several years, you should have several business plans you can review to see what worked and what didn’t. This should prove helpful as you create future plans for your company’s growth.
Download The 10 Key Components of a Business Plan Here
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies that have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customers Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Canvas Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Business consultants
Entrepreneurs and Small Business
Accelerators and Incubators
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Stratrgic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
10 Essential Components of a Business Plan and How to Write Them

Business Plan Template
Ayush Jalan
- January 4, 2024
12 Min Read
A business plan is an essential document for any business, whether it’s a startup or an established enterprise. It’s the first thing any interested investor will ask for if they like your business idea and want to partner with you.
That’s why it’s important to pay attention when writing your business plan and the components inside it. An incomplete business plan can give the impression that you’re unqualified—discouraging investors and lenders.
A good business plan reduces ambiguity and communicates all essential details such as your financials, market analysis, competitive analysis, and a timeline for implementation of the plan. In this article, we’ll discuss the 10 important business plan components.
10 Important Business Plan Components
A comprehensive and well-thought-out business plan acts as a roadmap that guides you in making sound decisions and taking the right actions at the right times. Here are its key components and what to include in them.
1. Executive summary
The executive summary is one of the most important parts of a business plan. It’s the first thing potential investors will read and should therefore provide a clear overview of your business and its goals.
In other words, it helps the reader get a better idea of what to expect from your company. So, when writing an executive summary of your business, don’t forget to mention your mission and vision statement.
Mission statement
A mission statement is a brief statement that outlines your objectives and what you want to achieve. It acts as a guiding principle that informs decisions and provides a clear direction for the organization to follow.
For instance, Google’s mission is to “organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” It’s short, inspiring, and immediately communicates what the company does.
A mission statement should be realistic, and hint towards a goal that is achievable in a reasonable amount of time with the resources you currently have or are going to acquire in the near future.
Vision statement
While a mission statement is more actionable and has an immediate effect on the daily activities of the company, a vision statement is more aspirational and has a much broader scope.
In other words, it highlights where the company aims to go in the future and the positive change it hopes to make in the world within its lifetime.
2. Company description
The second component of your business plan is the company description. Here, you provide a brief overview of your company, its products or services, and its history. You can also add any notable achievements if they are significant enough for an investor to know.
A company overview offers a quick bird’s-eye view of things such as your business model , operational capabilities, financials, business philosophy, size of the team, code of conduct, and short-term and long-term objectives.
Products and services
The products and services part of your company description explains what your business offers to its customers, how it’s delivered, and the costs involved in acquiring new customers and executing a sale.
Company History
Company history is the timeline of events that took place in your business from its origin to the present day. It includes a brief profile of the founder(s) and their background, the date the company was founded, any notable achievements and milestones, and other similar facts and details.
If you’re a startup, you’ll probably not have much of a history to write about. In that case, you can share stories of the challenges your startup faced during its inception and how your team overcame them.
3. Market analysis

The market analysis section of your business plan provides an in-depth analysis of the industry, target market, and competition. It should underline the risks and opportunities associated with your industry, and also comment on the attributes of your target customer.
Demographics and segmentation
Understanding the demographics of your customers plays a big role in how well you’re able to identify their traits and serve them.
By dividing your target audience into smaller and more manageable groups, you can tailor your services and products to better meet their needs.
You can use demographics such as age, gender, income, location, ethnicity, and education level to better understand the preferences and behaviors of each segment, and use that data to create more effective marketing strategies.
Target market and size
Understanding your target market lies at the core of all your marketing endeavors. After all, if you don’t have a clear idea of who you’re serving, you won’t be able to serve well no matter how big your budget is.
For instance, Starbucks’ primary target market includes working professionals and office workers. The company has positioned itself such that many of its customers start their day with its coffee.
Estimating the market size helps you know how much scope there is to scale your business in the future. In other words, you’re trying to determine how much potential revenue exists in this market and if it’s worth the investment.
Market need
The next step is to figure out the market need, i.e., the prevalent pain points that people in that market experience. The easiest way to find these pain points is to read the negative reviews people leave on Amazon for products that are similar to yours.
The better your product solves those pain points, the better your chances of capturing that market. In addition, since your product is solving a problem that your rivals can’t, you can also charge a premium price.
To better identify the needs of your target customers, it helps to take into account things such as local cultural values, industry trends, buying habits, tastes and preferences, price elasticity, and more.
4. Product Summary
The product summary section of your business plan goes into detail about the features and benefits that your products and services offer, and how they differ from your competitors. It also outlines the manufacturing process, pricing, cost of production, inventory, packaging, and capital requirements.
5. Competitive analysis
Unless you’ve discovered an untapped market, you’re probably going to face serious competition and it’s only going to increase as you scale your business later down the line.
This is where the competitive analysis section helps; it gives an overview of the competitive landscape, introduces your immediate rivals, and highlights the current dominant companies and their market share.
In such an environment, it helps to have certain competitive advantages against your rivals so you can stand out in the market. Simply put, a competitive advantage is the additional value you can provide to your customers that your rivals can’t—perhaps via unique product features, excellent customer service, or more.

Want to Perform Competitive Analysis for Your Business?
Discover your competition’s secrets effortlessly with our user-friendly and Free Competitor Analysis Generator!
6. Marketing and sales plan

The marketing and sales plan is one of the most important business plan components. It explains how you plan to penetrate the market, position your brand in the minds of the buyers, build brand loyalty, increase sales, and remain competitive in an ever-changing business environment.
Unique selling proposition
A unique selling proposition (USP) conveys how your products and services differ from those of your competitors, and the added value those differences provide.
A strong USP will stand out in a competitive market and make potential customers more likely to switch to your brand—essentially capturing the market share of your rivals.
Marketing Plan
Your product might be unique, but if people don’t even know that it exists, it won’t sell. That’s where marketing comes in.
A marketing plan outlines strategies for reaching your target market and achieving sales goals. It also outlines the budget required for advertising and promotion.
You may also include data on the target market, target demographics, objectives, strategies, a timeline, budget, and the metrics considered for evaluating success.
Sales and distribution plan
Once people are made aware of your product, the next step is to ensure it reaches them. This means having a competent sales and distribution plan and a strong supply chain.
Lay out strategies for reaching potential customers, such as online marketing, lead generation, retail distribution channels, or direct sales.
Your goal here is to minimize sales costs and address the risks involved with the distribution of your product. If you’re selling ice cream, for example, you would have to account for the costs of refrigeration and cold storage.
Pricing strategy
Pricing is a very sensitive yet important part of any business. When creating a pricing strategy , you need to consider factors such as market demand, cost of production, competitor prices, disposable income of target customers, and profitability goals.
Some businesses have a small profit margin but sell large volumes of their product, while others sell fewer units but with a massive markup. You will have to decide for yourself which approach you want to follow.
Before setting your marketing plans into action, you need a budget for them. This means writing down how much money you’ll need, how it will be used, and the potential return you are estimating on this investment.
A budget should be flexible, meaning that it should be open to changes as the market shifts and customer behavior evolves. The goal here is to make sure that the company is making the best use of its resources by minimizing the wastage of funds.
7. Operations plan
The operations plan section of your business plan provides an overview of how the business is run and its day-to-day operations. This section is especially important for manufacturing businesses.
It includes a description of your business structure, the roles and responsibilities of each team member, the resources needed, and the procedures you will use to ensure the smooth functioning of your business. The goal here is to maximize output whilst minimizing the wastage of raw material or human labor.
8. Management team
At the core of any successful business lies a dedicated, qualified, and experienced management team overlooking key business activities.
This section provides an overview of the key members of your management team including their credentials, professional background, role and responsibilities, experience, and qualifications.
A lot of investors give special attention to this section as it helps them ascertain the competence and work ethic of the members involved.
Organizational structure
An organizational structure defines the roles, responsibilities, decision-making processes, and authority of each individual or department in an organization.
Having a clear organizational structure improves communication, increases efficiency, promotes collaboration, and makes it easier to delegate tasks. Startups usually have a flatter organizational hierarchy whereas established businesses have a more traditional structure of power and authority.
9. Financial Plan
Financials are usually the least fun thing to talk about, but they are important nonetheless as they provide an overview of your current financial position, capital requirements, projections, and plans for repayment of any loans.
Your financial plan should also include an analysis of your startup costs, operating costs, administration costs, and sources of revenue.
Funding requirements
Once an investor has read through your business plan, it’s time to request funding. Investors will want to see an accurate and detailed breakdown of the funds required and an explanation of why the requested funds are necessary for the operation and expansion of your business.
10. Appendix
The appendix is the last section of your business plan and it includes additional supporting documents such as resumes of key team members, market research documents, financial statements, and legal documents.
In other words, anything important or relevant that couldn’t fit in any of the former sections of your business plan goes in the appendix.
Write a Business Plan Worth Reading
Starting a business is never easy, but it’s a little less overwhelming if you have a well-made business plan. It helps you better navigate the industry, reduce risk, stay competitive, and make the best use of your time and money.
Remember, since every business is unique, every business plan is unique too, and must be regularly updated to keep up with changing industry trends. Also, it’s very likely that interested investors will give you feedback, so make sure to implement their recommendations as well.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.

About the Author

Ayush is a writer with an academic background in business and marketing. Being a tech-enthusiast, he likes to keep a sharp eye on the latest tech gadgets and innovations. When he's not working, you can find him writing poetry, gaming, playing the ukulele, catching up with friends, and indulging in creative philosophies.
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates
We earn commissions if you shop through the links below. Read more
8 Components of a Business Plan
Back to Business Plans
Written by: Carolyn Young
Carolyn Young is a business writer who focuses on entrepreneurial concepts and the business formation. She has over 25 years of experience in business roles, and has authored several entrepreneurship textbooks.
Edited by: David Lepeska
David has been writing and learning about business, finance and globalization for a quarter-century, starting with a small New York consulting firm in the 1990s.
Published on February 19, 2023 Updated on February 27, 2024

A key part of the business startup process is putting together a business plan , particularly if you’d like to raise capital. It’s not going to be easy, but it’s absolutely essential, and an invaluable learning tool.
Creating a business plan early helps you think through every aspect of your business, from operations and financing to growth and vision. In the end, the knowledge you’ll gain could be the difference between success and failure.
But what exactly does a business plan consist of? There are eight essential components, all of which are detailed in this handy guide.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary opens your business plan , but it’s the section you’ll write last. It summarizes the key points and highlights the most important aspects of your plan. Often investors and lenders will only read the executive summary; if it doesn’t capture their interest they’ll stop reading, so it’s important to make it as compelling as possible.
The components touched upon should include:
- The business opportunity – what problem are you solving in the market?
- Your idea, meaning the product or service you’re planning to offer, and why it solves the problem in the market better than other solutions.
- The history of the business so far – what have you done to this point? When you’re just getting started, this may be nothing more than coming up with the idea, choosing a business name , and forming a business entity.
- A summary of the industry, market size, your target customers, and the competition.
- A strong statement about how your company is going to stand out in the market – what will be your competitive advantage?
- A list of specific goals that you plan to achieve in the short term, such as developing your product, launching a marketing campaign, or hiring a key person.
- A summary of your financial plan including cost and sales projections and a break-even analysis.
- A summary of your management team, their roles, and the relevant experience that they have to serve in those roles.
- Your “ask”, if applicable, meaning what you’re requesting from the investor or lender. You’ll include the amount you’d like and how it will be spent, such as “We are seeking $50,000 in seed funding to develop our beta product”.
Remember that if you’re seeking capital, the executive summary could make or break your venture. Take your time and make sure it illustrates how your business is unique in the market and why you’ll succeed.
The executive summary should be no more than two pages long, so it’s important to capture the reader’s interest from the start.
- 2. Company Description/Overview
In this section, you’ll detail your full company history, such as how you came up with the idea for your business and any milestones or achievements.
You’ll also include your mission and vision statements. A mission statement explains what you’d like your business to achieve, its driving force, while a vision statement lays out your long-term plan in terms of growth.
A mission statement might be “Our company aims to make life easier for business owners with intuitive payroll software”, while a vision statement could be “Our objective is to become the go-to comprehensive HR software provider for companies around the globe.”
In this section, you’ll want to list your objectives – specific short-term goals. Examples might include “complete initial product development by ‘date’” or “hire two qualified sales people” or “launch the first version of the product”.
It’s best to divide this section into subsections – company history, mission and vision, and objectives.
3. Products/Services Offered
Here you’ll go into detail about what you’re offering, how it solves a problem in the market, and how it’s unique. Don’t be afraid to share information that is proprietary – investors and lenders are not out to steal your ideas.
Also specify how your product is developed or sourced. Are you manufacturing it or does it require technical development? Are you purchasing a product from a manufacturer or wholesaler?
You’ll also want to specify how you’ll sell your product or service. Will it be a subscription service or a one time purchase? What is your target pricing? On what channels do you plan to sell your product or service, such as online or by direct sales in a store?
Basically, you’re describing what you’re going to sell and how you’ll make money.
- 4. Market Analysis
The market analysis is where you’re going to spend most of your time because it involves a lot of research. You should divide it into four sections.
Industry analysis
You’ll want to find out exactly what’s happening in your industry, such as its growth rate, market size, and any specific trends that are occurring. Where is the industry predicted to be in 10 years? Cite your sources where you can by providing links.
Then describe your company’s place in the market. Is your product going to fit a certain niche? Is there a sub-industry your company will fit within? How will you keep up with industry changes?
Competitor analysis
Now you’ll dig into your competition. Detail your main competitors and how they differentiate themselves in the market. For example, one competitor may advertise convenience while another may tout superior quality. Also highlight your competitors’ weaknesses.
Next, describe how you’ll stand out. Detail your competitive advantages and how you’ll sustain them. This section is extremely important and will be a focus for investors and lenders.
Target market analysis
Here you’ll describe your target market and whether it’s different from your competitors’. For example, maybe you have a younger demographic in mind?
You’ll need to know more about your target market than demographics, though. You’ll want to explain the needs and wants of your ideal customers, how your offering solves their problem, and why they will choose your company.
You should also lay out where you’ll find them, where to place your marketing and where to sell your products. Learning this kind of detail requires going to the source – your potential customers. You can do online surveys or even in-person focus groups.
Your goal will be to uncover as much about these people as possible. When you start selling, you’ll want to keep learning about your customers. You may end up selling to a different target market than you originally thought, which could lead to a marketing shift.
SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and it’s one of the more common and helpful business planning tools.
First describe all the specific strengths of your company, such as the quality of your product or some unique feature, such as the experience of your management team. Talk about the elements that will make your company successful.
Next, acknowledge and explore possible weaknesses. You can’t say “none”, because no company is perfect, especially at the start. Maybe you lack funds or face a massive competitor. Whatever it is, detail how you will surmount this hurdle.
Next, talk about the opportunities your company has in the market. Perhaps you’re going to target an underserved segment, or have a technology plan that will help you surge past the competition.
Finally, examine potential threats. It could be a competitor that might try to replicate your product or rapidly advancing technology in your industry. Again, discuss your plans to handle such threats if they come to pass.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategies
Now it’s time to explain how you’re going to find potential customers and convert them into paying customers.
Marketing and advertising plan
When you did your target market analysis, you should have learned a lot about your potential customers, including where to find them. This should help you determine where to advertise.
Maybe you found that your target customers favor TikTok over Instagram and decided to spend more marketing dollars on TikTok. Detail all the marketing channels you plan to use and why.
Your target market analysis should also have given you information about what kind of message will resonate with your target customers. You should understand their needs and wants and how your product solves their problem, then convey that in your marketing.
Start by creating a value proposition, which should be no more than two sentences long and answer the following questions:
- What are you offering
- Whose problem does it solve
- What problem does it solve
- What benefits does it provide
- How is it better than competitor products
An example might be “Payroll software that will handle all the payroll needs of small business owners, making life easier for less.”
Whatever your value proposition, it should be at the heart of all of your marketing.
Sales strategy and tactics
Your sales strategy is a vision to persuade customers to buy, including where you’ll sell and how. For example, you may plan to sell only on your own website, or you may sell from both a physical location and online. On the other hand, you may have a sales team that will make direct sales calls to potential customers, which is more common in business-to-business sales.
Sales tactics are more about how you’re going to get them to buy after they reach your sales channel. Even when selling online, you need something on your site that’s going to get them to go from a site visitor to a paying customer.
By the same token, if you’re going to have a sales team making direct sales, what message are they going to deliver that will entice a sale? It’s best for sales tactics to focus on the customer’s pain point and what value you’re bringing to the table, rather than being aggressively promotional about the greatness of your product and your business.
Pricing strategy
Pricing is not an exact science and should depend on several factors. First, consider how you want your product or service to be perceived in the market. If your differentiator is to be the lowest price, position your company as the “discount” option. Think Walmart, and price your products lower than the competition.
If, on the other hand, you want to be the Mercedes of the market, then you’ll position your product as the luxury option. Of course you’ll have to back this up with superior quality, but being the luxury option allows you to command higher prices.
You can, of course, fall somewhere in the middle, but the point is that pricing is a matter of perception. How you position your product in the market compared to the competition is a big factor in determining your price.
Of course, you’ll have to consider your costs, as well as competitor prices. Obviously, your prices must cover your costs and allow you to make a good profit margin.
Whatever pricing strategy you choose, you’ll justify it in this section of your plan.
- 6. Operations and Management
This section is the real nuts and bolts of your business – how it operates on a day-to-day basis and who is operating it. Again, this section should be divided into subsections.
Operational plan
Your plan of operations should be specific , detailed and mainly logistical. Who will be doing what on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis? How will the business be managed and how will quality be assured? Be sure to detail your suppliers and how and when you’ll order raw materials.
This should also include the roles that will be filled and the various processes that will be part of everyday business operations . Just consider all the critical functions that must be handled for your business to be able to operate on an ongoing basis.
Technology plan
If your product involves technical development, you’ll describe your tech development plan with specific goals and milestones. The plan will also include how many people will be working on this development, and what needs to be done for goals to be met.
If your company is not a technology company, you’ll describe what technologies you plan to use to run your business or make your business more efficient. It could be process automation software, payroll software, or just laptops and tablets for your staff.
Management and organizational structure
Now you’ll describe who’s running the show. It may be just you when you’re starting out, so you’ll detail what your role will be and summarize your background. You’ll also go into detail about any managers that you plan to hire and when that will occur.
Essentially, you’re explaining your management structure and detailing why your strategy will enable smooth and efficient operations.
Ideally, at some point, you’ll have an organizational structure that is a hierarchy of your staff. Describe what you envision your organizational structure to be.
Personnel plan
Detail who you’ve hired or plan to hire and for which roles. For example, you might have a developer, two sales people, and one customer service representative.
Describe each role and what qualifications are needed to perform those roles.
- 7. Financial Plan
Now, you’ll enter the dreaded world of finance. Many entrepreneurs struggle with this part, so you might want to engage a financial professional to help you. A financial plan has five key elements.
Startup Costs
Detail in a spreadsheet every cost you’ll incur before you open your doors. This should determine how much capital you’ll need to launch your business.
Financial projections
Creating financial projections, like many facets of business, is not an exact science. If your company has no history, financial projections can only be an educated guess.
First, come up with realistic sales projections. How much do you expect to sell each month? Lay out at least three years of sales projections, detailing monthly sales growth for the first year, then annually thereafter.
Calculate your monthly costs, keeping in mind that some costs will grow along with sales.
Once you have your numbers projected and calculated, use them to create these three key financial statements:
- Profit and Loss Statement , also known as an income statement. This shows projected revenue and lists all costs, which are then deducted to show net profit or loss.
- Cash Flow Statement. This shows how much cash you have on hand at any given time. It will have a starting balance, projections of cash coming in, and cash going out, which will be used to calculate cash on hand at the end of the reporting period.
- Balance Sheet. This shows the net worth of the business, which is the assets of the business minus debts. Assets include equipment, cash, accounts receivables, inventory, and more. Debts include outstanding loan balances and accounts payable.
You’ll need monthly projected versions of each statement for the first year, then annual projections for the following two years.
Break-even analysis
The break-even point for your business is when costs and revenue are equal. Most startups operate at a loss for a period of time before they break even and start to make a profit. Your break-even analysis will project when your break-even point will occur, and will be informed by your profit and loss statement.
Funding requirements and sources
Lay out the funding you’ll need, when, and where you’ll get it. You’ll also explain what those funds will be used for at various points. If you’re in a high growth industry that can attract investors, you’ll likely need various rounds of funding to launch and grow.
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
KPIs measure your company’s performance and can determine success. Many entrepreneurs only focus on the bottom line, but measuring specific KPIs helps find areas of improvement. Every business has certain crucial metrics.
If you sell only online, one of your key metrics might be your visitor conversion rate. You might do an analysis to learn why just one out of ten site visitors makes a purchase.
Perhaps the purchase process is too complicated or your product descriptions are vague. The point is, learning why your conversion rate is low gives you a chance to improve it and boost sales.
8. Appendices
In the appendices, you can attach documents such as manager resumes or any other documents that support your business plan.
As you can see, a business plan has many components, so it’s not an afternoon project. It will likely take you several weeks and a great deal of work to complete. Unless you’re a finance guru, you may also want some help from a financial professional.
Keep in mind that for a small business owner, there may be no better learning experience than writing a detailed and compelling business plan. It shouldn’t be viewed as a hassle, but as an opportunity!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Executive Summary
- Products/Services Offered
- Marketing and Sales Strategies
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Featured resources.
Crafting the Perfect Business Plan: A Deep Dive with Upmetrics’ Vinay Kevadiya
Carolyn Young
Published on October 13, 2023
In the first segment of our conversation with Vinay Kevadiya, the visionary behind Upmetrics, we explored the platform’s origins and itsunique ...

LivePlan Software Review
Published on September 15, 2023
When you’re starting a business, a business plan is essential whether you’re going to obtain financing or not. Creating a business plan helpsyou ...

What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix?
Published on September 13, 2023
Launching a business involves countless tasks, and one of the crucial early hurdles is writing a business plan. Many entrepreneurs who aren’tlooki ...
No thanks, I don't want to stay up to date on industry trends and news.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

- Frequently Asked Questions
- Business Credit Cards
- Talk to Us 1-800-496-1056

8 Things You Need in a Business Plan
The Harvard Business Review says a good business plan is super important for entrepreneurs. It’s like a guide for them in the tricky world of business. The plan has different parts, and each part is like a piece of the puzzle for success.

For example, there’s the short and powerful Executive Summary that tells the most important things about the business. Then, there’s the smart Market Analysis that helps you understand what customers want.
All of these parts work together to make a strong plan. So, let’s take a closer look at these important pieces that help turn business dreams into successful reality.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a detailed document that explains how a business works and what it aims to achieve. It outlines the business’s goals, strategies , and resources. It’s like a roadmap for the business, helping it stay on course and navigate challenges.
The plan typically includes sections about the business’s description , market research , marketing and sales strategies, operations, management, and financial projections .
Entrepreneurs use it to clarify their vision, secure funding, and measure progress. It’s a crucial tool for anyone starting or running a business, helping them make informed decisions and work toward success.
Need assistance in writing a business plan?
Contact our award-winning business plan writers now!
Eight Key Components of Business Plans
Crafting a business plan is akin to laying the foundation for a grand architectural masterpiece. It’s your roadmap to success, a strategic blueprint that breathes life into your entrepreneurial dreams. Allow me to take you on a journey through the essential components of this vital document.
- Executive Summary
- Business Description
- Market Analysis
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Operations Plan
- Management and Organization
- Financial Plan
1. Executive Summary
Picture this as the dazzling opening act of your business plan, where you showcase your vision, mission, and why your venture is destined for greatness. It’s a compelling glimpse into the heart and soul of your business.
It’s like a short summary of your business, including what it does and what makes it special.
- Advice: Keep it concise and engaging. Think of it as a teaser that makes people want to read more. Highlight what makes your business unique.
2. Business Description
Here, we dive deep into the DNA of your business. You’ll spill the beans on what you do, your industry, your history, and your grand plans for the future. It’s a snapshot that captures the essence of your business.
This part explains your business in detail, like what it sells, the industry it’s in, and its history.
- Advice: Be clear about what your business does and why it matters. Describe your industry and explain how your business fits into it.
Free Example Business Plans
Explore our free business plan samples now!
3. Market Analysis
This section is where we turn detective. We unearth market trends, study customer behaviors, and dissect your competitors. It’s a treasure trove of insights that helps you navigate the marketplace.
Here, you look at the market your business is in. You study things like customer behavior and what other businesses are doing.
- Advice: Research thoroughly. Understand your customers’ needs and your competition. Show that you know your market inside and out.

4. Marketing and Sales Strategy
Imagine this as the stage where you reveal your magic tricks. Here, you outline how you’ll entice and retain your customers. It’s where the art of attracting and selling meets strategy.
This section talks about how you’ll get customers and sell your products or services.
- Advice: Outline your plan for attracting customers and selling your products or services. Focus on how you’ll reach your target audience and convince them to buy from you.
5. Operations Plan
Ever wondered how the show runs backstage? This is where you spill the beans. From location to logistics, it’s the nitty-gritty of daily operations. It’s the backbone that keeps your business standing tall.
It’s about how your business will work day-to-day, like where you’ll be located and how you’ll make your products.
Advice: Detail how your business will operate day-to-day. Discuss your location, equipment, suppliers, and how you’ll ensure quality.
6. Management and Organization
Introducing the cast and crew of your business. Who’s in charge? What’s their expertise? It’s where you showcase your dream team and the hierarchy that keeps everything in check.
This part introduces the people running the business and how it’s organized.
- Advice: Introduce your team and their qualifications. Explain who’s in charge and how your business is structured.
7. Financial Plan
This section is your crystal ball into the future. It predicts your financial performance, balances your books, and forecasts cash flows. Investors love it, and you will too.
It’s like a prediction of how much money your business will make and spend in the future.
Advice: Be realistic with your financial projections. Include income, expenses, and cash flow predictions. Show how you’ll make a profit.
8. Appendix
This is your secret stash. All those extra documents, licenses, contracts, and accolades find their home here. It’s the vault of credibility that adds weight to your plan.
This is where you put extra documents like licenses, contracts, and other important stuff.
- Advice: Use this section for supporting documents. Include licenses, contracts, and anything that adds credibility to your plan.
Hire our professional business plan writing consultants now!
Remember, your business plan isn’t set in stone. It’s a living, breathing document that evolves with your journey. It’s your guiding star, your go-to reference, and your pitch to investors, all rolled into one.
With a well-crafted business plan, you’re equipped to clarify your vision, rally support from investors, and steer your venture to success. So, let’s get started on your masterpiece!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

- Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI
- Business Operations
- Cloud Computing
- Data Center
- Data Management
- Emerging Technology
- Enterprise Applications
- IT Leadership
- Digital Transformation
- IT Strategy
- IT Management
- Diversity and Inclusion
- IT Operations
- Project Management
- Software Development
- Vendors and Providers
- Enterprise Buyer’s Guides
- United States
- Middle East
- Italia (Italy)
- Netherlands
- United Kingdom
- New Zealand
- Data Analytics & AI
- Newsletters
- Foundry Careers
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Copyright Notice
- Member Preferences
- About AdChoices
- Your California Privacy Rights
Our Network
- Computerworld
- Network World
6 essential elements of a good business plan
Entrepreneurs, executives and venture capitalists discuss how to craft a business plan that will impress investors and be a good road map for your company..

Whether you are just starting out and need startup investment or are looking to expand your business and raise capital, a business plan is a must. Indeed, a business plan is not only essential if you want to get people to invest in your idea, it can help you articulate what it is you hope to accomplish with your business – your mission, goal(s) and values – and plot the company’s growth trajectory.
However, to be successful, a business plan cannot just be a bulleted list of an entrepreneur’s thoughts and musings, hopes and dreams. It needs to be a serious business document with the following six elements.
1. Executive summary
“An executive summary is the ‘elevator pitch’ of your business plan,” explains David Mercer, founder, SME Pals , a blog dedicated to helping entrepreneurs. “More often than not, landing a new investor relies on hooking them with a great elevator pitch. Without grabbing their attention, your business plan, no matter how well researched and presented, may not stand out enough.”
The executive summary should, in brief, describe the “problem you are going to solve, and why that problem needs to be solved right now,” by you, says Peter Arvai, CEO, Prezi presentation software. “If you aren’t able to communicate that deeper purpose to others, you will have a very hard time convincing investors to fund your idea and people to join your team.”
Tip: Write the Executive Summary last, after you’ve done all your research and put everything down on paper.
[ Related: 12 tips for creating a must-read business blog ]
2. Description and bios of your leadership/executive team
“The entrepreneur should clearly demonstrate what they are bringing to this venture – the idea, the technical ability or the passion,” says Hossein Rahnama, founder & CEO, Flybits . “Investors want to understand how you will execute using your personal strength.”
You should also “talk about the leadership team,” says Andrew Witkin, CEO, StickerYou . “If the leadership team has a previous track record of building and delivering businesses, this should be highlighted. Business plans serve multiple purposes, but one of them is to build trust, and the team is as important as the product to potential investors and partners.”
“Investors bet on jockeys, not horses, and knowing about who will execute on an idea is key to an investor making an investment decision,” says Richard J. Foster, president, Foster Management & Holdings. “Very frequently I’ll see multiple companies with the same idea, but the one to invest in is the one with the team who has the experience and the credentials to succeed. Having the best idea with the wrong team is a recipe for failure, but proving that your team is the [right] one to execute [your idea] can make all of the difference.”
3. Description of your product(s) or service(s)
“When developing a business plan, it’s crucial to clearly [explain] the need your product or service is trying to address,” says Elena Filimonova, senior vice president, global marketing and strategy, CGS . “Your business plan should highlight how the product or service will address the need, what is unique about your offering and why it would be difficult to replicate. To do this, you should outline key differentiators, features and why the product or service is something that stands out in the market.”
[ Related: 11 ways to build your online brand ]
4. Market/competitive analysis
“Every business plan should have a section that defines the target sales market – who you are selling to,” says Victor Clarke, owner, Clarke Inc. “This is the part that requires considerable research into areas such as industry sales data related to the service or product you are selling and trends within the industry. You should look at competitors and see who they are targeting, look at your current customer base and create a profile of an ideal customer or client for your product.”
“For a business plan to be effective and attractive to investors and partners, you must be able to provide tangible data and information that supports the notion that your demographic is strong and growing, and that market trends support the continued need for your service or product offering,” says Brock Murray, cofounder & COO, seoplus+ .
[ Related: 7 attributes of a successful CMO in the digital age ]
“Sequoia Capital has a great framework that every business plan should use: separate your Total Addressable Market (everyone who conceivably needs your product category), Serviceable Addressable Market (everyone who needs your specific product or service, limited by factors like where you can do business) and Serviceable Obtainable Market (the portion of the market you can realistically capture),” says Christopher S. Penn, vice president, Marketing Technology, SHIFT Communications . “For example, lots of companies say everyone is a customer, and while that may be a TAM, if the company has only one salesperson, their SOM is significantly smaller. VCs and investors especially want to understand what’s realistically obtainable, and splitting out your addressable markets… shows them you’re not just presenting pipe dreams.”
Also be sure to “include a competitive analysis section,” says Bryan Robertson, founder & chief revenue officer, Mindyra . “Every business has competition, so it’s a good idea to research companies in your industry who are fighting for the same customers. You should include specific details about their strengths and weaknesses. This forces you to become very familiar with your market. It also encourages you to think of ways to differentiate your business [from] the competition.”
5. Financials (how much cash you need and when you’ll pay it back)
“Make sure that the plan goes into exacting detail about how much startup capital will be needed, where it will come from and how it will be paid back,” says Bruce Stetar, executive director, Graduate Business Programs, SNHU . “Equal importance should be given to how you [plan to] pay back capital as how you acquire it. Investors want to know when they will see a return. Failing to plan adequately for capital acquisition and payback is one of the chief reasons that new businesses fail.”
“Whether you’re hoping to receive funding to build a brick-and-mortar shop or a technology venture, you must have your numbers straight,” says Erica Swallow, founder & CEO, Southern Swallow . “For tech entrepreneurs, I’m a big fan of the startup financial model template developed by startup investor David Teten, in collaboration with a couple of colleagues. Based in a nearly fully-automated Excel worksheet, it enables early-stage entrepreneurs to map out their financial plan, without being too overwhelming. It’s the best startup financial model I’ve encountered over the past five years.”
6. Marketing plan
“It is critical to have a plan [for] how you are going to spend your marketing budget,” says Deborah Sweeney, CEO, MyCorporation . “Assess different options (paid search, salespeople, flyers, [social media], etc.) and the associated ROI with each.”
“The plan should cover both sales and advertising strategies and costs,” says Stetar, as well as customer acquisition costs. “Be conservative here since you will look good if your over achieve but it will cost you investor confidence if you under achieve.”
A successful business plan is one is easy to read and follow
You need to make your business plan easy to read and follow. “There’s nothing more daunting than to receive an all-text business plan, 30 pages in length,” says Swallow. “Keep your potential investors engaged by including product and user photos, team headshots, colorful headings, financial graphs, charts, tables, anything to make reading more of a pleasure. Even bullet points help.”
Indeed, “don’t underestimate the importance of visuals,” says Arvai. “Researchers have found that presentations using visual aids are, on average, 43 percent more persuasive than those without.”
Finally, before you go public with your plan, “have trusted mentors and expert peers look over it [and give you] their feedback,” says Sam Lundin, CEO, Vimbly . “Having [someone] review your business plan [before you present it to investors] is crucial.”
Related content
Cios not entirely sold on generative ai copilots, persán embraces industry 5.0 to manage organizational assets, oracle to invest $8 billion in japan through 2034, 4 tips for championing contact center innovation from an award-winning customer experience leader, from our editors straight to your inbox, show me more, generative ai and cio.com: helping you get the smart answers you need.

Certinia bakes AI into its latest professional services updates

10 famous AI disasters

CIO Leadership Live UK with The Zensory Co-founders

CIO Leadership Live Australia with Scott Andrews, Chief Operating Officer, Idea Science

Eaton CIO Katrina Redmond on optimizing AI and digital services

Propelix lets companies easily build their own generative AI chatbots

3 Leadership Tips: Graeme Bryce, CTO, Holibob

What Are the Basic Components of a Business Plan?
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Elements of Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Main Steps in Business Planning
Four types of information in a business plan, what is the meaning of business finance.
- What Do Business Documents Include?
- 6 Types of Business Plans
Writing a business plan is a serious and exciting endeavor. Whether you're launching a new business or making changes to a company you already own, a business plan is where your hopes and dreams connect with the real world, like rubber on asphalt, propelling you toward the realization of those dreams.
Business plans can be complex documents – the product of a great deal of research and analysis covering every facet of your business. So before you get started, take a few minutes to review the major components, which you can use as a roadmap.
Six Key Components of Business Plans
The specific details of a business plan vary widely among industries and individual businesses; however, the majority of business plans contain six key components.
- Executive Summary: This one-page summary of your business plan includes the most important information and a table of contents that identifies where additional information can be found in the rest of the document.
- Mission, Goals, and Objectives: This component describes why you started the business, your long-term goals and the key short-term objectives you identified to work toward those goals.
- Background Information: This section describes the history of your industry, its current state and its future, as well as your company's place in the industry. If there are problems in your chosen industry, address them and list your solutions.
- Organization Description: This covers your company's planned business structure, key team members, including the management team, and your risk management strategies.
- Marketing Plan: This details everything about getting your products and services to customers, including identifying your target customers, where they live and other demographics. It also describes how you will promote your brand and products or services and the distribution channels you plan to use to get your products to your customers.
- Financial Plan: This documents your financial resources, estimated costs and estimated revenue, and it identifies any additional capital you may need. It should include a balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and a budget.
Writing a Business Plan
Where you begin depends on you. If you have a background in finance, the financial plan may be the best place to start, while a marketer might start with the marketing plan. If you're not sure where to start, begin with a draft of the executive summary and begin writing down the questions you need to research and answer.
As Penn State University Extension advises, a SWOT analysis helps you identify what you need to research. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. Examining each of these will reveal the risks you need to address and the opportunities you will want to capitalize on.
After completing your work, you can write a new executive summary based on your finished business plan. Note that an executive summary should always be finished last. It often serves as an independent document, called an executive summary business plan, which you can use to entice investors or attract business partners to your company.
Business Planning Is a Verb
Writing a business plan is a journey that may take you exactly where you anticipated or to a brand new realm with new opportunities you hadn't thought of before. So keep an open mind, and whenever you stumble across a new question, make a point of researching it.
Each component of your business plan depends on the others. While researching marketing, for example, you may realize that digital ads are more expensive in your industry than you realized. This not only affects your financial plan, it could also affect the types of products you sell and how you present them to customers. This, in turn, could affect your company's mission, goals and objectives. Instead of selling something like low-cost costume jewelry, this could direct you toward luxury watches and accessories.
As Purdue University explains, starting a business plan is one of the first things you should do before launching a company. Because it will influence your business decisions, you should ideally begin with a solid plan and keep planning as your business grows and evolves.
- Purdue University: The Elements of a Business Plan
- Penn State University Extension: Developing a Business Plan
A published author and professional speaker, David Weedmark has advised businesses on technology, media and marketing for more than 20 years. He has taught computer science at Algonquin College, has started three successful businesses, and has written hundreds of articles for newspapers and magazines and online publications including About.com, Re/Max and American Express.
Related Articles
What are the key elements of a business plan, what is an executive summary business plan, the breakdown of a marketing plan, what are the main purposes of a business plan, a high-level marketing plan, the importance of business plans, what to avoid in writing a business plan, final summary for a marketing plan, how to write a comprehensive business plan, most popular.
- 1 What Are the Key Elements of a Business Plan?
- 2 What Is an Executive Summary Business Plan?
- 3 The Breakdown of a Marketing Plan
- 4 What Are the Main Purposes of a Business Plan?

6 Key Elements of a Business Plan

As an entrepreneur starting a business, or even planning a scale-up, a business plan is a very important part of the process. This strategic tool helps define your short and long-term goals while providing a blueprint for your next steps.
Most business plans are developed during the first stages of a start-up, but that’s not to say that they aren’t important when you enter the growing phase of your business.
Your business plan is not a 'set it & forget it' document. As your venture develops and grows, revisiting your plan will be crucial to measuring your success and to continue supporting your journey during a new set of challenges.

What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that defines the goals of your business and how they will be achieved. It is an essential resource that provides strategic direction for your business.
When putting your business plan together you should ensure that you address these 6 key areas:
- Your executive summary
- The vision statement and goal overview of your business
- Target audience and competitor research
- Your products and services
- Business structure and operations
- Your financial plan
#1 The Executive Summary
Your executive summary briefly outlines the main points of your business plan and provides a glimpse of what your company does and how it operates.
It should include your mission statement which is a short description (1-2 sentences) describing your company, its purpose, and its values.
Remembering to keep your executive summary clear and concise, think about:
- Why you’re in business
- What services and products you offer
- Who your customers are
- How you’re different from your competitors
- What role you and your team will have
- What your goals are and how you’ll reach them
- Key relationships and how they will be maintained
Don’t be afraid to brainstorm with others connected to your business. This could be individuals directly involved such as employees, investors, or business partners.
Another option is discussing your executive summary and mission statement with those who play an external support role in your business such as your advisor or accountant.
Not only will they have knowledge of your venture, but they also have strategic planning experience. This will help reveal the strengths and weaknesses in your statement, as well as identify things you may have missed.
#2 Vision Statement and Goal Overview
You should have a section of your business plan dedicated to the future aspirations of your business. Your vision statement will articulate what you want to achieve and in turn provide a common direction for the entire team.
It’s important to keep your goals S.M.A.R.T (specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, time-based).
Five questions to ask about your goals:
- Are they clear and specific?
- How will the goals be evaluated?
- Is the goal 100% achievable?
- How will the goal improve the business?
- Do your goals have due dates?
#3 Target Audience and Competitor Research
In order to sell your product or service, you need to define your target audience. A target audience is a group of people you have identified as potential customers.
To help determine your target audience you will generally look at demographic traits such as:
You’ll then look at your product or service and the specific problem it solves. This, combined with the demographic data will help you fine tune the details surrounding your defined audience.
Defining your target audience will help you plan and execute your marketing strategy in the most efficient and effective way.
Once you've identified who you're selling to, research your market and identify your competitors. Evaluate how they promote their product or service as this will give you a better understanding of the overall market, allow you to identify any gaps, and help you develop or improve your business's strategy.
SWOT Analysis
As an additional project, it would be a good idea to perform and SWOT analysis and include this in your business plan. This detailed list of your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats will give you further perspective of both your business and your competitors.
#4 Products and Services
This section of your business plan will describe what your business offers to its consumers.
Although descriptions of each product or service is needed, don’t over complicate it. Keep wording easy to understand and ensure you’re including how your product or service differs from the competition.
If you own or have applied for any of the following, you should also include these in this section:
#5 business structure and operations.
The business structure you choose will have significant implications on the tax you pay and your liability.
There are four main types of business structures in the UK:
- Sole Trader - business is run and owned by one individual
- Partnership - business is owned and managed by two or more parties
- Limited Liability Partnership - business structure where liabilities are limited to the amount each individual has invested in the business
- Limited Company - business is separate from the individual and run as its own legal entity
Operations include the physical necessities required to run your business, businesses typically engage in these activities on a daily basis and they are essential to providing the highest quality product or service.
Four key areas of business operations you should address:
- Process - systems and procedures you will have in place
- Location - where you will do business (bricks and mortar/online)
- Team - who will be doing the work
- Equipment - the tools you will use
#6 Financial plan
A financial plan is not just where all the numbers come in, it’s the moment where you start turning your ideas into a reality.
In your financial plan, you’ll want to consider:
- Start-up or expansion costs
- Various business expenses
- Funding requirements
- Financial projections
A good plan of action would be to sit down and create a list that outlines what costs will be associated with your business.
For those revisiting their business plan and making adjustments during a phase of growth, these may be familiar things like lease fees, but at a higher amount. It could also be completely new costs or funding needs that are required to expand the business.
If you’re in the start-up stage, you will have to build your list from scratch as you won’t have the same historical financial information as an established business.
This is a list of some of the common businesses expenses to help you get started:
- Marketing, sales and advertising costs
- Office supplies
- Lease payments
- Licenses and permits
- Staff and employment
- Professional fees
The importance of the expert second opinion
Whether you’re in the start-up or growth stage, a business plan will play an important role in the success of your venture.
Bringing an expert on board will help build a solid foundation and uncover challenges you may face moving forward.
Working with your accountant will:
- Provide a second opinion backed by experience
- Offer constructive feedback on the key areas of your business plan
- Give you advice on the legal structure of your business and the financial implications of each
- Help make important decisions and offer other beneficial elements you may want to consider
Working with DSA Prospect
The DSA team have worked with clients across all industries, helping them get their business off the ground and prepare for the challenges ahead.
We have a wealth of knowledge that can help you develop a business plan that will guide you through your business journey, as well as a dedicated team here to support your individual needs and vision.
Title: How to write a business plan: 6 key components to a good plan

Disclaimer: The information shared on the DSA Prospect website and social media accounts (inclusive of all content, blogs, communications, graphics, guides and resources) is meant to provide helpful insight and discussion on various business and accounting related topics. It contains only general information that is subject to legal and regulatory change and is not to be used as an alternative to legal or professional advice. DSA Prospect Limited accepts no responsibility for any actions you take, or do not take, based on the information we provide and we always recommend that you speak with qualified professionals where necessary before making any decisions.
- Starting a Business
Our Top Picks
- Best Small Business Loans
- Best Business Internet Service
- Best Online Payroll Service
- Best Business Phone Systems
Our In-Depth Reviews
- OnPay Payroll Review
- ADP Payroll Review
- Ooma Office Review
- RingCentral Review
Explore More
- Business Solutions
- Entrepreneurship
- Franchising
- Best Accounting Software
- Best Merchant Services Providers
- Best Credit Card Processors
- Best Mobile Credit Card Processors
- Clover Review
- Merchant One Review
- QuickBooks Online Review
- Xero Accounting Review
- Financial Solutions
Human Resources
- Best Human Resources Outsourcing Services
- Best Time and Attendance Software
- Best PEO Services
- Best Business Employee Retirement Plans
- Bambee Review
- Rippling HR Software Review
- TriNet Review
- Gusto Payroll Review
- HR Solutions
Marketing and Sales
- Best Text Message Marketing Services
- Best CRM Software
- Best Email Marketing Services
- Best Website Builders
- Textedly Review
- Salesforce Review
- EZ Texting Review
- Textline Review
- Business Intelligence
- Marketing Solutions
- Marketing Strategy
- Public Relations
- Social Media
- Best GPS Fleet Management Software
- Best POS Systems
- Best Employee Monitoring Software
- Best Document Management Software
- Verizon Connect Fleet GPS Review
- Zoom Review
- Samsara Review
- Zoho CRM Review
- Technology Solutions
Business Basics
- 4 Simple Steps to Valuing Your Small Business
- How to Write a Business Growth Plan
- 12 Business Skills You Need to Master
- How to Start a One-Person Business
- FreshBooks vs. QuickBooks Comparison
- Salesforce CRM vs. Zoho CRM
- RingCentral vs. Zoom Comparison
- 10 Ways to Generate More Sales Leads
6 Elements of a Successful Financial Plan for a Small Business

Table of Contents
Many small businesses lack a full financial plan, even though evidence shows that it is essential to the long-term success and growth of any business.
For example, a study in the New England Journal of Entrepreneurship found that entrepreneurs with a business plan are more successful than those without one. If you’re not sure how to get started, read on to learn the six key elements of a successful small business financial plan.
What is a business financial plan, and why is it important?
A business financial plan is an overview of a business’s financial situation and a forward-looking projection for growth. A business financial plan typically has six parts: sales forecasting, expense outlay, a statement of financial position, a cash flow projection, a break-even analysis and an operations plan.
A good financial plan helps you manage cash flow and accounts for months when revenue might be lower than expected. It also helps you budget for daily and monthly expenses and plan for taxes each year.
Importantly, a financial plan helps you focus on the long-term growth of your business. That way, you don’t get so caught up in the day-to-day activities that you lose sight of your goals. Focusing on the long-term vision helps you prioritize your financial resources.
Financial plans should be created annually at the beginning of the fiscal year as a collaboration of finance, HR, sales and operations leaders.
The 6 components of a successful financial plan for business
1. sales forecasting.
You should have an estimate of your sales revenue for every month, quarter and year. Identifying any patterns in your sales cycles helps you better understand your business, and this knowledge is invaluable as you plan marketing initiatives and growth strategies .
For instance, a seasonal business can aim to improve sales in the off-season to eventually become a year-round venture. Another business might become better prepared by understanding how upticks and downturns in business relate to factors such as the weather or the economy.
Sales forecasting is also the foundation for setting company growth goals. For instance, you could aim to improve your sales by 10 percent over each previous period.
2. Expense outlay
A full expense plan includes regular expenses, expected future expenses and associated expenses. Regular expenses are the current ongoing costs of your business, including operational costs such as rent, utilities and payroll.
Regular expenses relate to standard business activities that occur each year, such as conference attendance, advertising and marketing, and the office holiday party. It’s a good idea to distinguish essential expenses from expenses that can be reduced or eliminated if needed.
Expected future expenses are known future costs, such as tax rate increases, minimum wage increases or maintenance needs. Generally, a part of the budget should also be allocated to unexpected future expenses, such as damage to your business caused by fire, flood or other unexpected disasters. Planning for future expenses ensures your business is financially prepared via budget reduction, increases in sales or financial assistance.
Associated expenses are the estimated costs of various initiatives, such as acquiring and training new hires, opening a new store or expanding delivery to a new territory. An accurate estimate of associated expenses helps you properly manage growth and prevents your business from exceeding your cost capabilities.
As with expected future expenses, understanding how much capital is required to accomplish various growth goals helps you make the right decision about financing options.
3. Statement of financial position (assets and liabilities)
Assets and liabilities are the foundation of your business’s balance sheet and the primary determinants of your business’s net worth. Tracking both allows you to maximize your business’s potential value.
Small businesses frequently undervalue their assets (such as machinery, property or inventory) and fail to properly account for outstanding bills. Your balance sheet offers a more complete view of your business’s health than a profit-and-loss statement or a cash flow report.
A profit-and-loss statement shows how the business performed over a specific time period, while a balance sheet shows the financial position of the business on any given day.
4. Cash flow projection
You should be able to predict your cash flow on a monthly, quarterly and annual basis. Projecting cash flow for the full year allows you to get ahead of any financial struggles or challenges.
It can also help you identify a cash flow problem before it hurts your business. You can set the most appropriate payment terms, such as how much you charge upfront or how many days after invoicing you expect payment .
A cash flow projection gives you a clear look at how much money is expected to be left at the end of each month so you can plan a possible expansion or other investments. It also helps you budget, such as by spending less one month for the anticipated cash needs of another month.
5. Break-even analysis
A break-even analysis evaluates fixed costs relative to the profit earned by each additional unit you produce and sell. This analysis is essential to understanding your business’s revenue and potential costs versus profits of expansion or growth of your output.
Having your expenses fully fleshed out, as described above, makes your break-even analysis more accurate and useful. A break-even analysis is also the best way to determine your pricing.
In addition, a break-even analysis can tell you how many units you need to sell at various prices to cover your costs. You should aim to set a price that gives you a comfortable margin over your expenses while allowing your business to remain competitive.
6. Operations plan
To run your business as efficiently as possible, craft a detailed overview of your operational needs. Understanding what roles are required for you to operate your business at various volumes of output, how much output or work each employee can handle, and the costs of each stage of your supply chain will aid you in making informed decisions for your business’s growth and efficiency.
It’s important to tightly control expenses, such as payroll or supply chain costs, relative to growth. An operations plan can also make it easier to determine if there is room to optimize your operations or supply chain via automation, new technology or superior supply chain vendors.
For this reason, it is imperative for a business owner to conduct due diligence and become knowledgeable about merchant services before acquiring an account. Once the owner signs a contract, it cannot be changed, unless the business owner breaks the contract and acquires a new account with a new merchant services provider.
Tips on writing a business financial plan
Business owners should create a financial plan annually to ensure they have a clear and accurate picture of their business’s finances and a realistic view for future growth or expansion. A financial plan helps the business’s leaders make informed decisions about purchases, debt, hiring, expense control and overall operations for the year ahead.
A business financial plan is essential if a business owner is looking to sell their business, attract investors or enter a partnership with another business. Here are some tips for writing a business financial plan.
Review the previous year’s plan.
It’s a good idea to compare the previous year’s plan against actual performance and finances to see how accurate the previous plan and forecast were. That way, you can address any discrepancies or overlooked elements in next year’s plan.
Collaborate with other departments.
A business owner or other individual charged with creating the business financial plan should collaborate with the finance department, human resources department, sales team , operations leader, and those in charge of machinery, vehicles or other significant business tools.
Each division should provide the necessary data about projections, value and expenses. All of these elements come together to create a comprehensive financial picture of the business.
Use available resources.
The Small Business Administration (SBA) and SCORE, the SBA’s nonprofit partner, are two excellent resources for learning about financial plans. Both can teach you the elements of a comprehensive plan and how best to work with the different departments in your business to collect the necessary information. Many websites, including business.com , and service providers, such as Intuit, offer advice on this matter.
If you have questions or encounter challenges while creating your business financial plan, seek advice from your accountant or other small business owners in your network. Your city or state has a small business office that you can contact for help.
Several small business organizations offer free financial plan templates for small business owners. You can find templates for the financial plan components listed here via SCORE .
Business financial plan templates
Many business organizations offer free information that small business owners can use to create their financial plan. For example, the SBA’s Learning Platform offers a course on how to create a business plan. It also offers worksheets and templates to help you get started. You can seek additional help and more personalized service from your local office.
SCORE is the largest volunteer network of business mentors. It began as a group of retired executives (SCORE stands for “Service Corps of Retired Executives”) but has expanded to include business owners and executives from many industries. Advice is free and available online, and there are SBA district offices in every U.S. state. In addition to participating in group or at-home learning, you can be paired with a mentor for individualized help.
SCORE offers templates and tips for creating a small business financial plan. SCORE is an excellent resource because it addresses different levels of experience and offers individualized help.
Other templates can be found in Microsoft Office’s template library, QuickBooks’ online resources, Shopify’s blog and other places. You can also ask your accountant for guidance, since many accountants provide financial planning services in addition to their usual tax services.
Diana Wertz contributed to the writing and research in this article.

Get Weekly 5-Minute Business Advice
B. newsletter is your digest of bite-sized news, thought & brand leadership, and entertainment. All in one email.
Our mission is to help you take your team, your business and your career to the next level. Whether you're here for product recommendations, research or career advice, we're happy you're here!
Protect your data
This site uses cookies and related technologies for site operation, and analytics as described in our Privacy Policy . You may choose to consent to our use of these technologies, reject non-essential technologies, or further manage your preferences.
- Career Advice
- 6 Key Components of a...
6 Key Components of a Business Strategy and How Knowing Them can Help you to Succeed at Work
8 min read · Updated on February 12, 2023

Business strategy jobs are in high demand. Do you know how to put together a stellar strategy that will help your company to reach its goals?
Benjamin Franklin said, “By failing to plan, you are planning to fail.” One of the factors that goes into building and growing a successful business centers around strategic focus and making plans for each operational aspect. Any knowledge that you possess that helps you to identify business opportunities, mitigate operational risks, and execute profitability initiatives will go a long way toward helping you to land a job to build strategies for companies.
Of the utmost importance is your ability to demonstrate knowledge of a basic business strategy. In this article, we'll discuss the 6 key components of a business strategy and how knowing them can help you to succeed at work.
What is a business strategy?
Every business has goals - big goals and small goals. The main objective could be to penetrate international markets, create a new product, or challenge the status quo to disrupt existing industries. It doesn't matter what the objective is; a great business strategy is necessary to define how to get stuff done. Think of it as a master plan geared toward the achievement of goals.
Business strategies, sometimes called company strategies, contain these six components:
Vision and objectives
Core values.
SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats)
Tactics and operational delivery
Resources and resource allocation
Measurement and analysis
It's critical to understand that there is a monumental difference between tactics and strategy. Simply speaking, tactics are actions and strategy is planning. It can be easy to get bogged down in the tactics, but those actions only support short-term goals. To ensure that you're leading your team toward long-term goals, you need to build a business strategy.
The beginning of your business strategy is the place to define your goal or goals. The vision gives you the direction, and the objectives detail the goals. As you think about the overall purpose of your business strategy, consider what steps you'll have to take to achieve the end result. Each objective that is fulfilled should take your organization one step closer to the goal or vision.
The values of your organization are powerful, in that they guide how the people within the company work together to achieve goals. Aligning core values with business strategy is imperative, if for no other reason than to demonstrate how employees should engage in the activities and objectives that have been set.
On top of that, core values help company leaders to identify potential staff members (or job seekers) that will work best for a given assignment. Identifying top talent and putting the right people in the right job will make measuring success much easier.
SWOT analysis
All business strategies must include an assessment of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT). Not only does this analysis show what factors exist that will guide success, but it also shows potential issues that could pop up. Knowing these things in advance will help you and your team to successfully navigate problems and could even pave the way for solving them before they arise.
Strengths are things your company excels at and how these qualities affect business operations. Strengths can be internal and external and include everything from your team having an innovative mindset to the company having a solid financial standing.
Weaknesses indicate areas for improvement. Weaknesses are demonstrated through low customer satisfaction, outdated equipment, and high debt levels.
Opportunities define what changes need to take place that can positively affect the company and the plan. Perhaps your business is in an area of expanding industry, or there have been recent government support programs put into place. All of these present possibilities of things your company can take advantage of, to propel the success of your business strategy.
Threats indicate risk. They are often external and can include things like supply chain issues or new regulations that could put up roadblocks.
In the spirit of getting things done, tactics are the things that most executives like to focus on. They want to know where things are, who is doing the things that need to be done, and how much it will cost. This section of the business strategy is important for showing how resources will be allocated.
Resource and resource allocation
Once you know how the resources need to be allocated, it's time to assign, issue, or administer them. Resources encompass everything from people to equipment and budgets to time. As time progresses, you may need to adapt this section to include more or less resources. When resources are properly allocated, you improve efficiency, save time/labor hours, increase workplace harmony, and achieve higher employee retention rates.
Resource allocation happens in stages . There's early stage allocation, which happens when the strategy is being put into place. As the business plan progresses, you reach the growth stage. At this point, you start setting new goals and start working on new business strategies, which means that you have to allocate more resources (or the same resources differently). Finally, there's end-stage resource allocation. At the end of the execution of a business strategy, resource needs change and need to be re-evaluated.
A great business strategy is moot if there's no way to measure success. Performance measurement, performance metrics, and performance indicators are prominent keywords in most job descriptions for business strategy jobs. Evaluating how the company is performing - whether goals are being achieved or not - allows you to make course corrections when necessary to keep things on track.
Business strategy examples
It's one thing to know the components of a business strategy and be able to talk about them during an interview; it's something else entirely to actually put a company strategy together. Let's dive into a couple of business strategy examples.
Example 1:
Build a loyal client base: The goal is to not only acquire new customers, but also to increase client retention to at least 80%. It's necessary to shift to a customer-first approach and fine-tune associates' client-facing relationship-building skills. Product and service delivery needs to improve, and the market needs to be continually monitored to guarantee that we're offering the best prices.
This strategy will work because it sets a goal (an objective) and addresses a core value of the business (customer-first approach). Then, it talks about SWOT by identifying that staff skills, product delivery, and pricing need to be improved. The tactics behind making this business strategy successful involve improving relationship-building skills and giving the customer the best product at the right price. It's certainly capable of being measured through the use of things like Net Promoter Scores and client surveys.
- Improve revenue by 50%: The goal is to increase sales by getting new products to market and pivoting from an in-person shop to include online shopping. Expanding technological capabilities and hiring a tech team will be imperative to the success of this plan. By expanding our product offerings to clients who don't have physical access to the store, we will experience a rapid increase in profitability.
This strategy's goal is apparent and extremely easy to measure. The strategist who built this plan also realizes that one of the company's weaknesses is a lack of technical personnel and it is immediately addressed. This example could technically be broken into two. One could define what the company will do to get new products to the market and the second could detail how they will address adding e-commerce capabilities.
Stay adaptable and flexible
These business strategy examples identify a course of action to improve business results surrounding a particular objective. In the end, you do have to remember that a business strategy isn't carved into stone. It's a roadmap with curves and turns that will have to be navigated along the way.
Sometimes, it must be adjusted or adapted to fit new circumstances or events. If there's one thing that's true, it's that everything changes. Often those changes are outside of your control - you can, however, control how you respond to the changes.
Are you ready for a business strategist job?
You already know about performance measurement being a skill that employers seek from new business strategists. Adaptability and flexibility are also great skills to possess. Your business strategist job is right around the corner, but your resume must show the necessary skills.
Upload your current resume and let TopResume's team of professional resume writers give it a free review . You'll find out what you're doing right and what can be improved .
Recommended reading:
How to Help Your New Business Survive Its First Year
How Does Money Come in During a Career Change?
10 Best Jobs for People with Economics Degrees
Related Articles:
Don't “Snowplow” Your Kids' Job Search — Set Them Up for Success Instead
What Kind of Job Candidate Are You?
Why December is the Best Time of Year to Look for a Job
See how your resume stacks up.
Career Advice Newsletter
Our experts gather the best career & resume tips weekly. Delivered weekly, always free.
Thanks! Career advice is on its way.
Share this article:
Let's stay in touch.
Subscribe today to get job tips and career advice that will come in handy.
Your information is secure. Please read our privacy policy for more information.
Become an Implementer | Implementer Directory | Log In

The EOS MODEL ®
The eos model provides a visual illustration of the six key components™ of any business that must be managed and strengthened to be a great business. this model applies to big and small businesses alike, in any industry..
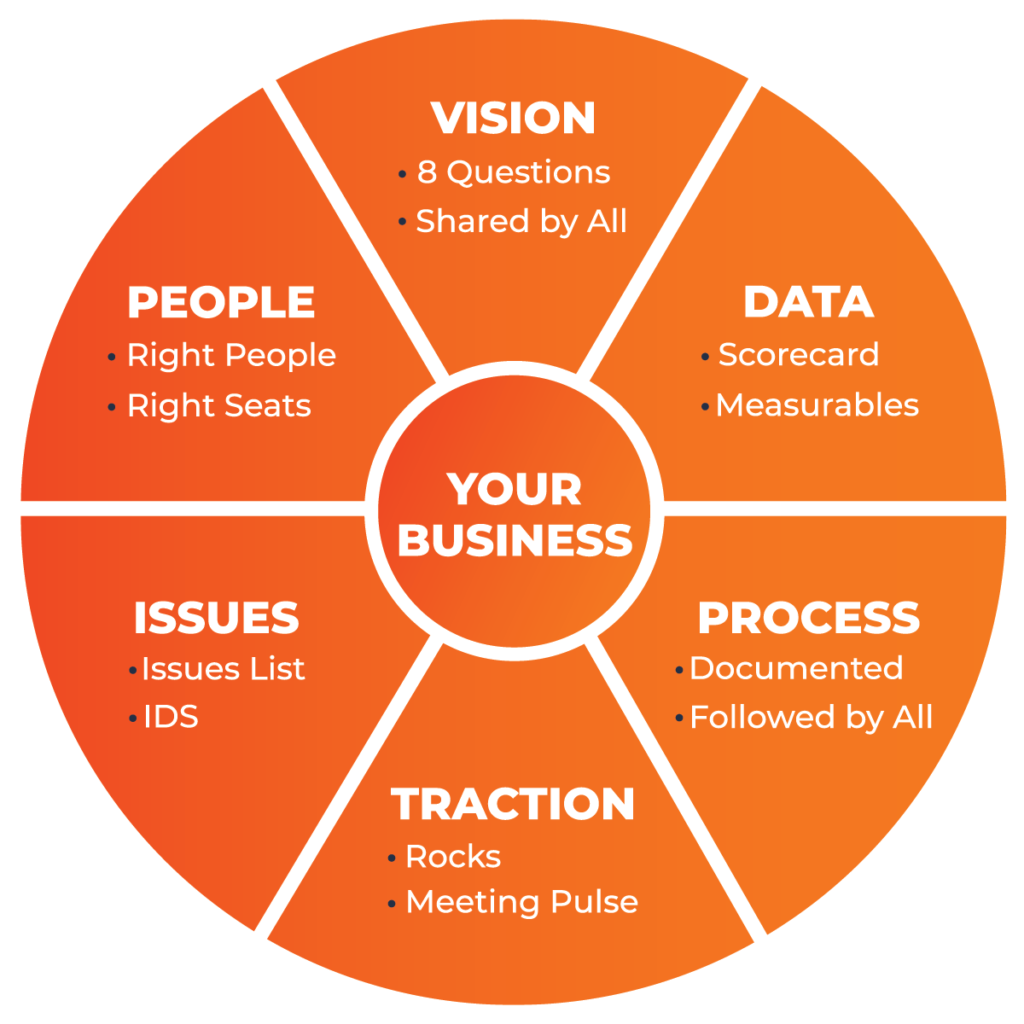
The Six Key Components of Any Business
Strengthening this component means getting everyone in the organization 100% on the same page with where you’re going and how you’re going to get there.
Simply put, we can’t do it without great people. This means surrounding yourself with great people, top to bottom, because you can’t achieve a great vision without a great team.
This means cutting through all the feelings, personalities, opinions, and egos and boiling your organization down to a handful of objective numbers that give you an absolute pulse on where things are.
With the Vision, People, and Data Components strong, you start to create a lucid, transparent, open and honest organization where everything becomes more visible and you start to “smoke out all the issues,” which leads to…
Strengthening this component means becoming great at solving problems throughout the organization – setting them up, knocking them down, and making them go away forever.
This is the secret ingredient in your organization. This means “systemizing” your business by identifying and documenting the core processes that define the way to run your business. You'll need to get everyone on the same page with what the essential procedural steps are, and then get everyone to follow them to create consistency and scalability in your organization.
This means bringing discipline and accountability into the organization – becoming great at execution – taking the vision down to the ground and making it real.
How strong is your organization?
Understand your performance in each of the six key components of your business..
Learn More About EOS ®
The EOS Process®

The EOS Toolbox™
Get Started
Get matched today, 90 minutes that will transform your business forever.
Tired of hitting ceilings? Your EOS Implementer has the sledge hammer. We’ll help you break through your toughest problems and transform your business.
Fill out the form to schedule a quick call with one of our EOS Implementer Match Specialists
Our Match Specialist will pair you with an EOS Implementer for a free 90 Minute Meeting in-person or virtually
Get a crystal clear picture of what EOS can do for you and your business.
YOUR PRIVACY CHOICES
- Cookie Policy
- Media & Promotion Guidelines
- 1-877-367-1877 (USA)
- +1-248-278-8220 (Worldwide)
- EOS Toolbox™
- EOS Model ®
- EOS Process ®
- EOS ONE™ SOFTWARE
- EOS Implementer Directory
- Self-Implementation
- Rocket Fuel Univ.
- Integrator™ Directory
- EOS Franchising
- EOS Conference
- Org. Checkup™
- Book a Speaker
- History & Team
©2024 EOS WORLDWIDE ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Client portal, organizational checkup, search the eos worldwide blog, change location, find awesome listings near you.

The Ultimate Guide To Starting Your Own PC Building Business

Are you passionate about computers and looking to turn that passion into a profitable venture? Starting your own PC building business might just be the perfect fit for you. A PC building business entails designing, assembling, and selling custom-built personal computers.
To ensure its success you, of course, need to have a great understanding of the PC building business.
But to stand out in the PC market, which is estimated at $204.07 billion in 2024, you’ll require more than just technical prowess. You also need a deep understanding of the PC building market, a good business plan, an effective marketing strategy, and a strong brand among other strategies.
This comprehensive article will walk you through all the key steps while providing great tips on how to start a PC building business successfully. Let’s get started!
1. Conduct market research and identify the niche
Before diving headfirst into starting your custom PC business, it’s crucial to conduct thorough market research to understand the landscape and identify your niche.
Start by researching the demand for custom-built PCs in your niche market. Identify the types of customers who are interested in custom PCs. Are they gamers, content creators, professionals, or businesses? Also, analyze market demand and industry trends, like the popularity of certain components, gaming genres, or emerging technologies like VR or AI.
Then dive deep into understanding your target customers’ specific needs and preferences. What are they looking for in a custom PC? Is it high-performance gaming rigs, silent workstations, compact HTPCs, or something else entirely?
It’s also equally important that you understand the competitive landscape. So ensure you research existing custom PC builders. Identify their strengths, weaknesses, pricing strategies, and target demographics. Look for gaps or underserved segments in the market where you can differentiate your business and carve out a niche for yourself.
Then armed with that information, define your unique selling proposition (USP)—which helps you stand out from your competition. See how MAINGEAR mainly highlights their rear-side cable connectors.

Your USP could be your superior craftsmanship, personalized customer service, exclusive partnerships with component manufacturers, or innovative customization options.
2. Craft a comprehensive business plan
We can’t discuss how to start a PC building business without covering creating a great business plan since it serves as the roadmap for your building journey. Here are some of the key details you must include in your comprehensive business plan as a custom PC builder:
- Executive summary : Provide the key highlights of your business plan, including your goals, target market, USP, and financial projections.
- Product and service offerings : Outline the products and services you plan to offer, including the types of custom PCs, customization options, additional services (e.g., overclocking, system optimization, warranty support), and pricing strategies.
- Marketing strategy : Develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business and attract a loyal customer base. This may include online marketing tactics such as SEO, social media advertising, email campaigns, content marketing, as well as offline strategies like networking events and word-of-mouth referrals.
- Financial projections : Create detailed financial projections for your PC building business, including startup costs, operating expenses, revenue forecasts, and profit margins.
- Operational plan : Define the day-to-day operations of your business, including inventory management, order fulfillment, customer service, and post-sale support.
- Risk assessment and contingency plans : Identify potential risks and challenges that may affect your business, such as supply chain disruptions, changes in market conditions, or competitive threats. Then include contingency plans and mitigation strategies to minimize risks and ensure business continuity.
With a comprehensive business plan, you can demonstrate your readiness to investors, lenders, and other stakeholders. Additionally, it will guide your decisions, helping you confidently navigate any challenges you face.
3. Register your business
With your business plan in hand, it’s time to make things official by registering your business. This is essential when starting any sort of business, whether it’s an online business like a call center business or an offline business like a cleaning business .
Start by choosing a suitable business name and structure, whether a sole proprietorship, partnership, or LLC. Each structure has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of liability, taxation, and regulatory requirements, so choose wisely based on your specific circumstances.
Next, register your PC building business with the appropriate government authorities. The registration processes will vary based on your location and chosen business structure. So check with your local business registration office for guidance on the registration process in your area.
However, the process will typically involve filing registration forms, paying registration fees, and obtaining necessary licenses or permits to operate legally.
Additionally, consider trademarking your business name, logo, or any unique product designs or inventions to protect your intellectual property.
4. Source quality components and forge partnerships with suppliers
You’ll need to source a wide range of components to build high-quality custom computers tailored to your customers’ needs. Some of these components include RAM modules, solid-state drives (SSDs), hard disk drives (HDDs), central processing units (CPUs), graphics cards, motherboards, and cooling solutions.
To ensure you source quality components start by researching reputable component suppliers and distributors. Look for suppliers with a track record of reliability, quality, and customer satisfaction. Then consider factors like product selection, pricing, delivery times, return policies, and customer service.
You can use a platform like PC Builder to easily find the right supplier. Additionally, the platform offers building guides and gives feedback on the most compatible components for your PC.

While it’s tempting to prioritize price when sourcing components, quality should always be your top priority. Invest in high-quality components from trusted brands to ensure great performance, reliability, and product longevity, customer satisfaction.
A poorly built PC device will only lead to poor system performance and slow processing, which affects tasks like gaming, video editing, and web browsing. In fact, even the fastest web hosting platform cannot compensate for a poorly built PC device.
Over time, build strong relationships with your component suppliers by making repeat orders, communicating regularly, and providing feedback. Establishing a good relationship with your suppliers can lead to better pricing, priority access, and personalized support, which will give you a competitive advantage.
However, it’s also key to know when to diversify your supplier base to mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions, shortages, or quality issues.
5. Build your brand and market your services
Once your products are ready for the market, it’s time to focus on building brand awareness and visibility.
Start by creating a professional website showcasing your services, portfolio of past builds, and customer testimonials.
Your website should be visually appealing, easy to navigate, and optimized for search engines to attract organic traffic and generate leads. Additionally, include helpful resources to show your customers how your products work or how well they work. For instance, you can record screen activities to prove your device is high-performing.
Digital Storm is a great example of an exceptional PC building business website. See how they use a clean design, images, product videos, consistent brand colors, and customer testimonials, among other design elements to capture potential customers’ attention.

You can also use guest blog posts , social media platforms, online forums, and key industry events to spread the word about your business and engage with potential customers. Besides sharing valuable content, consider offering special promotions or hosting giveaways, as shown below, to incentivize purchases and encourage repeat business.

Additionally, you can collaborate with tech influencers , bloggers, YouTubers, and streamers in the gaming and tech community to reach a wider audience and gain credibility.
6. Provide exceptional customer service and support
Providing exceptional customer service and support can set you apart from the competition. In fact, research shows that 80% of customers believe the experience a company provides is just as important as its products and services.
So how do you provide exceptional customer service and support? Here are a few effective ways:
- Expert recommendations : Offer expert recommendations and guidance to help customers make informed decisions about their custom PCs. Use your technical expertise to suggest the most suitable components, configurations, and customization options based on their needs. This will ensure they get the best value for their investment.
- Transparent communication : Keep your customers informed and updated throughout the PC building process. Provide regular updates on the status, any delays or issues encountered, and estimated completion times. Additionally, be transparent about pricing, component availability, and potential limitations to manage customer expectations effectively.
- Quality assurance : Conduct thorough quality assurance checks on each PC build to ensure that it meets the highest standards of performance, reliability, and aesthetics. This also enables you to address any issues or defects promptly before delivering the system to the customer.
- Post-sale support : Provide comprehensive post-sale support to assist customers with setup, installation, troubleshooting, and optimizing their custom PCs. You should also offer clear instructions, documentation, and tutorials on your website to guide customers through common tasks and issues they may encounter with their new systems.
- Warranty services : Reassure your customers they are making the right investment by offering generous warranties. Clearly communicate warranty terms and conditions, including coverage periods, repair or replacement policies, and any exclusions or limitations, to ensure transparency and accountability.
- Responsive communicatio n: Respond promptly to customer inquiries, feedback, and support requests through various channels, including phone, email, live chat, and social media. Quick responses demonstrate your commitment to customer satisfaction, which helps you easily earn their trust.
- Continuous improvement : Continuously seek customer feedback to identify areas for improvement and opportunities to enhance your custom PC building services. Then actively implement the changes to match customer expectations in the future.
Keep in mind, happy customers are more likely to return for future purchases, recommend your business to others, and contribute to your long-term success and growth.
Starting your own PC building business can be a rewarding and lucrative endeavor. While it’s not an easy task, like with any venture, it is not impossible.
By following our steps on how to start a PC building business, you can easily turn your dream of owning a successful PC building enterprise into a reality.
Start by conducting market research and identifying a niche. Then craft a business plan, register your business, source quality components, forge supplier partnerships, build your brand, market your services, and provide great customer service and support.
Above all stay adaptable, stay curious, and stay connected to keep building great PC products for your customers. Best of luck!
About the author
Nicholas Prins
I'm the founder of Launch Space. We work with global companies helping them scale lead generation through SEO and content marketing. Head over to the homepage to find out more.

How to Launch a Cafe Business

How to Start a Cleaning Business
Guest Post Guidelines
Business Blog Content Marketing Blog Entrepreneurship Blog General Blog
Software Review Software Comparison Lifetime Software Deals
I worked on cruises for 3 years. Here are 6 things I'd never do on board.
- I used to work on cruises. After many days at sea, there are things I'd never do on a cruise .
- I never wear my room key around my neck and try to avoid misnaming the ship.
- I never buy the drink package or pay for meal upgrades in the main dining room.

I've sailed around the world as a cruise-ship employee , and now I enjoy cruising as a passenger.
I love the salty sea air, waking up in a new country, and lazy days by the pool, but a week at sea could get more complicated this year with cruises predicted to be in high demand .
While fighting a little harder to secure a prime seat on the pool deck, you may as well also avoid some rookie mistakes.
Here are six things I'd never do on a cruise after working on them for three years.
Pay for upgrades in the main dining room
Typically, main dining room meals are included in the cost of a cruise. But in recent years, it's become common for cruise lines to charge guests extra if they want to upgrade to "supplementary" items like lobster or certain steaks.
I know $12 may not seem like much for a steak or lobster tail at dinner, but the cost of the cruise is supposed to include your food.
So, even though I enjoy lobster, I stick with the items without the upcharges.
Buy the drink package
I enjoy a piña colada by the pool or a Manhattan while listening to a jazz set after dinner. Even so, it doesn't make sense for me to pay in advance for 12 to 15 cocktails a day.
I've done the math on typical unlimited drink packages , and the cost simply isn't worth it for me.
This is especially true with a port-heavy itinerary. If I've gone ashore to explore all day, that means I'm not sidled up to the bar slurping down alcoholic slushies.
Related stories
I prefer to buy as I go and take advantage of happy hour and other drink specials that are available on certain cruise lines. I also check the beverage policy in advance and bring on my own wine, if allowed.
Touch shared contact surfaces with my fingers
Fellow guests will never see me touching the elevator buttons with my fingertips. Knuckles and elbows do the trick.
Some cruise lines are better than others at wiping down commonly touched surfaces, but I don't take any chances. I avoid touching things others frequently touch, and I wash my hands frequently.
This strategy has worked for me, as I have never contracted norovirus, even when it was running rampant on a ship I was on. It's quite contagious and can linger on your fingertips even after using hand sanitizer . I'd definitely rather be safe than sorry.
Wear my room key around my neck
I never walk around the ship with my room key around my neck, and I especially never do this when on land.
There are two reasons for this. First, I see many passengers using the room keys dangling from their necks to flaunt their cruise loyalty status . It just looks pretentious.
The sophisticated cruisers with the highest status, with the most days at sea, never show off their fancy room keys.
That's because they know the more important reason — safety. In port, that room key bouncing off your chest looks like an invitation to be robbed. It screams, "I have money! Come and take it from me."
Misname the ship
English is a funny language that has its quirks. Naming conventions make that even more complicated.
Ships have proper names, and so do not require a definite article. For example, "Tomorrow I am embarking on Discovery Princess," or "I enjoyed scenic cruising on MS Westerdam."
If you want to look like a savvy sailor, learn to drop the "the!"
Plan my port-day itinerary so tight that I may not make it back to the ship on time
Oh, the recurring nightmares I've had about not making it back to the ship on time during a port day.
I've never missed a sail away, but I have cut it too close at times and have had to run down a pier or two. Just recently, as a passenger, my taxi driver got lost returning our group to the port at night.
When I realized how late we were going to be, I forked over $8 per minute to be connected with the ship. I pleaded with them to wait for us. It was a sprint through the port to get back on and we received quite a scolding from the first officer.
That time, we got lucky. In the future, I'll be giving myself more time than I think I need to make it back.
- Main content
Southern California city council gives a key approval for Disneyland expansion plan
ANAHEIM, Calif. — Visitors to Disney’s California parks could one day walk through the snow-covered hamlet of Arendelle from “Frozen” or the bustling, critter-filled metropolis of “Zootopia” under a park expansion plan approved by the Anaheim City Council.
Disney would spend at least $1.9 billion over the next decade to transform its 490-acre (488-hectare) campus in densely-populated Southern California. It would be the biggest expansion of Disney’s Southern California theme parks in decades, aiming to create more immersive experiences for guests. Disney would also be required to spend tens of millions of dollars on street improvements, affordable housing and other infrastructure in the city.
The council unanimously approved the project early Wednesday at the end of an hourslong meeting that began Tuesday evening. A second council vote for final approval of Disney’s plan is required in May.
The plan wouldn’t expand Disney’s footprint in tourism-dependent Anaheim but would help it add rides and entertainment by letting the company relocate parking to a new multi-story structure and redevelop the massive lot, as well as make other changes to how it uses its properties.
Disneyland, Disney California Adventure and the Downtown Disney shopping area are surrounded by freeways and residential areas in the city 30 miles (48 kilometers) southeast of Los Angeles, so the company sees the plan as vital to creating to continue to create sizable new attractions.
“We are thrilled that the City of Anaheim has agreed to work together on this legacy project,” Disneyland Resort President Ken Potrock said in a statement, adding the company awaits the final vote in May. “We look forward to our bright future together!”
A significant share of public testimony to the city council focused on Disney’s plans to buy a public street near the theme park and turn it into a pedestrian walkway and its intention to add a crosswalk on another neighboring street.
Resident Cassandra Taylor said she looks forward to the new rides the expansion will bring but is concerned about Disney’s plans to privatize a city street, adding she first heard of the idea last month in a newspaper article even though she had attended two informational presentations.
“They might have a pedestrian walkway planned now, but once it is theirs, they could just as easily remove it,” Taylor said. “It will be theirs and theirs entirely. Voters will have no say in its future use.”
Over the last two decades, Disney investments have included Cars Land, Pixar Pier, Star Wars Galaxy’s Edge and Avengers Campus in Southern California. The company has not committed to which stories it plans to feature given that the new development will take years.
It’s the first time Disney has sought a major change to its California theme parks since the 1990s, when the company obtained approvals to turn Disneyland, its original theme park dubbed “the happiest place on Earth” and built in 1955, into a resort hub. It later built the Disney California Adventure theme park and the Downtown Disney shopping and entertainment area.
Disneyland was the second-most visited theme park in the world in 2022 with 16.8 million people coming through the gates, according to a report by the Themed Entertainment Association and AECOM.
Anaheim is Orange County’s most populous city and home to 345,000 people, a major league baseball team and a national hockey league team. Hotel revenue typically makes up about half of the city’s revenue and is expected to climb to $236 million this year, according to city estimates.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom welcomed the vote as a way to create more jobs in the state of 39 million people.
“We look forward to cultivating more Disney magic and building opportunities for all as this investment drives billions of dollars in revenue for our state and local communities,” Newsom said in a statement.
For Anaheim, the plan would translate directly into much-needed cash for police, fire, libraries and other community services, said Mike Lyster, a city spokesman.
“Whenever Disney invests in Anaheim, we see city revenue grow and our economy expand,” Lyster said. “This is a milestone vote for our city.”

- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- March Madness
- AP Top 25 Poll
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Southern California city council gives a key approval for Disneyland expansion plan
FILE - Visitors pass through Disneyland in Anaheim, Calif., April 30, 2021. (AP Photo/Jae C. Hong, File)
- Copy Link copied
ANAHEIM, Calif. (AP) — Visitors to Disney’s California parks could one day walk through the snow-covered hamlet of Arendelle from “Frozen” or the bustling, critter-filled metropolis of “Zootopia” under a park expansion plan approved by the Anaheim City Council.
Disney would spend at least $1.9 billion over the next decade to transform its 490-acre (488-hectare) campus in densely-populated Southern California. It would be the biggest expansion of Disney’s Southern California theme parks in decades, aiming to create more immersive experiences for guests. Disney would also be required to spend tens of millions of dollars on street improvements, affordable housing and other infrastructure in the city.
The council unanimously approved the project early Wednesday at the end of an hourslong meeting that began Tuesday evening. A second council vote for final approval of Disney’s plan is required in May.
The plan wouldn’t expand Disney’s footprint in tourism-dependent Anaheim but would help it add rides and entertainment by letting the company relocate parking to a new multi-story structure and redevelop the massive lot, as well as make other changes to how it uses its properties.
Disneyland, Disney California Adventure and the Downtown Disney shopping area are surrounded by freeways and residential areas in the city 30 miles (48 kilometers) southeast of Los Angeles, so the company sees the plan as vital to creating to continue to create sizable new attractions.
“We are thrilled that the City of Anaheim has agreed to work together on this legacy project,” Disneyland Resort President Ken Potrock said in a statement, adding the company awaits the final vote in May. “We look forward to our bright future together!”
A significant share of public testimony to the city council focused on Disney’s plans to buy a public street near the theme park and turn it into a pedestrian walkway and its intention to add a crosswalk on another neighboring street.
Resident Cassandra Taylor said she looks forward to the new rides the expansion will bring but is concerned about Disney’s plans to privatize a city street, adding she first heard of the idea last month in a newspaper article even though she had attended two informational presentations.
“They might have a pedestrian walkway planned now, but once it is theirs, they could just as easily remove it,” Taylor said. “It will be theirs and theirs entirely. Voters will have no say in its future use.”
Over the last two decades, Disney investments have included Cars Land, Pixar Pier, Star Wars Galaxy’s Edge and Avengers Campus in Southern California. The company has not committed to which stories it plans to feature given that the new development will take years.
It’s the first time Disney has sought a major change to its California theme parks since the 1990s, when the company obtained approvals to turn Disneyland, its original theme park dubbed “the happiest place on Earth” and built in 1955, into a resort hub. It later built the Disney California Adventure theme park and the Downtown Disney shopping and entertainment area.
Disneyland was the second-most visited theme park in the world in 2022 with 16.8 million people coming through the gates, according to a report by the Themed Entertainment Association and AECOM.
Anaheim is Orange County’s most populous city and home to 345,000 people, a major league baseball team and a national hockey league team. Hotel revenue typically makes up about half of the city’s revenue and is expected to climb to $236 million this year, according to city estimates.
California Gov. Gavin Newsom welcomed the vote as a way to create more jobs in the state of 39 million people.
“We look forward to cultivating more Disney magic and building opportunities for all as this investment drives billions of dollars in revenue for our state and local communities,” Newsom said in a statement.
For Anaheim, the plan would translate directly into much-needed cash for police, fire, libraries and other community services, said Mike Lyster, a city spokesman.
“Whenever Disney invests in Anaheim, we see city revenue grow and our economy expand,” Lyster said. “This is a milestone vote for our city.”
2024 federal budget's key takeaways: Housing and carbon rebates, students and sin taxes
Budget sees nearly $53b in new spending over the next 5 years.

What's in the new federal budget?
Social sharing.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland today tabled a 400-page-plus budget her government is pitching as a balm for anxious millennials and Generation Z.
The budget proposes $52.9 billion in new spending over five years, including $8.5 billion in new spending for housing. To offset some of that new spending, Ottawa is pitching policy changes to bring in new revenue.
Here are some of the notable funding initiatives and legislative commitments in budget 2024.
Ottawa unloading unused offices to meet housing targets
One of the biggest pillars of the budget is its housing commitments. Before releasing the budget, the government laid out what it's calling Canada's Housing Plan — a pledge to "unlock" nearly 3.9 million homes by 2031.

The government says two million of those would be net new homes and it believes it can contribute to more than half of them.
It plans to do that by:
- Converting underused federal offices into homes. The budget promises $1.1 billion over ten years to transform 50 per cent of the federal office portfolio into housing.
- Building homes on Canada Post properties. The government says the 1,700-plus Canada Post offices across the country can be used to build new homes while maintaining postal services. The federal government says it's assessing six Canada Post properties in Quebec, Alberta and British Columbia for development potential "as a start."
- Rethinking National Defence properties. The government is promising to look at redeveloping properties and buildings on National Defence lands for military and civilian use.
- Building apartments. Ottawa is pledging a $15 billion top-up to the Apartment Construction Loan Program, which says it will build 30,000 new homes across Canada.
Taxing vacant land?
As part of its push on housing, the federal government also says it's looking at vacant land that could be used to build homes.
It's not yet committing to new measures but the budget says the government will consider introducing a new tax on residentially zoned vacant land.
- Freeland's new federal budget hikes taxes on the rich to cover billions in new spending
- Are you renting with no plans to buy? Here's what the federal budget has for you
The government said it plans to launch consultations on the measure later this year.
Help for students
There's also something in the budget for students hunting for housing.

The government says it will update the formula used by the Canada Student Financial Assistance Program to calculate housing costs when determining financial need, to better reflect the cost of housing in the current climate.
The government estimates this could deliver more aid for rent to approximately 79,000 students each year, at an estimated cost of $154.6 million over five years.
- Updated Federal budget's funding boost for defence spread out over multiple years
- Liberals pledge $9B in new money for Indigenous communities in 2024 budget
The government is also promising to extend increased student grants and interest-free loans, at an estimated total cost of $1.1 billion this year.
Increase in taxes on capital gains
To help cover some of its multi-billion dollar commitments, the government is proposing a tax hike on capital gains — the profit individuals make when assets like stocks and second properties are sold.
The government is proposing an increase in the taxable portion of capital gains, up from the current 50 per cent to two thirds for annual capital gains over $250,000.
New investment to lead 'housing revolution in Canada,' Freeland says
Freeland said the change would impact the wealthiest 0.1 per cent.
There's still some protection for small businesses. There's been a lifetime capital gains exemption which allows Canadians to exempt up to $1,016,836 in capital gains tax-free on the sale of small business shares and farming and fishing property. This June the tax-free limit will be increased to $1.25 million and will continue to be indexed to inflation thereafter, according to the budget.
The federal government estimates this could bring in more than $19 billion over five years, although some analysts are not convinced.
Disability benefit amounts to $200 per month
Parliament last year passed the Canada Disability Benefit Act, which promised to send a direct benefit to low-income, working-age people with disabilities.
Budget 2024 proposes funding of $6.1 billion over six years, beginning this fiscal year, and $1.4 billion per year ongoing, for a new Canada Disability Benefit.
Advocates had been hoping for something along the lines of $1,000 per month per person . They'll be disappointed.
According to the budget document, the maximum benefit will amount to $2,400 per year for low income individuals with disabilities between the ages of 18 and 64 — about $200 a month.
- Federal government plans to lease public lands for construction through new housing strategy
- Alberta premier says she's prepared to take Ottawa to court over housing deals
The government said it plans for the Canada Disability Benefit Act to come into force in June 2024 and for payments to start in July 2025.
Carbon rebate for small businesses coming
The federal government has heard an earful from small business advocates who accuse it of reneging on a promise to return a portion of carbon pricing revenues to small businesses to mitigate the tax's economic costs.
- What's behind the carbon tax, and does it work?
- Federal government scales back carbon tax rebates for small businesses
The budget proposes to return fuel charge proceeds from 2019-20 through 2023-24 to an estimated 600,000 businesses with 499 or fewer employees through a new refundable tax credit.
The government said this would deliver $2.5 billion directly to Canada's small- and medium-sized businesses.
Darts and vape pods will cost more
Pitching it as a measure to cut the number of people smoking and vaping, the Liberals are promising to raise revenues on tobacco and smoking products.
- Just Asking wants to know: What questions do you have about quitting smoking or vaping? Do you think sin taxes will encourage smoking cessation? Fill out the details on this form and send us your questions ahead of our show on April 20.
Starting Wednesday, the total tobacco excise duty will be $5.49 per carton. The government estimates this could increase federal revenue by $1.36 billion over five years starting in 2024-25.

The budget also proposes to increase the vaping excise duty rates by 12 per cent effective July 1. That means an increase of 12 to 24 cents per pod, depending on where you live.
- 'Stay the hell away from our kids': Health minister vows to restrict nicotine pouches — but how?
Ottawa hopes this increase in sin taxes will bring in $310 million over five years, starting in 2024-25.
More money for CBC
Heritage Minister Pascale St-Onge has mused about redefining the role of the public broadcaster before the next federal election . But before that happens, CBC/Radio-Canada is getting a top-up this year.

The budget promises $42 million more in 2024-25 for CBC/Radio-Canada for "news and entertainment programming." CBC/Radio-Canada received about $1.3 billion in total federal funding last year.
The government says it's doing this to ensure that Canadians across the country, including rural, remote, Indigenous and minority language communities, have access to independent journalism and entertainment.
Last year, the CBC announced a financial shortfall, cut 141 employees and eliminated 205 vacant positions. In a statement issued Tuesday, CBC spokesperson Leon Mar said the new funding means the corporation can balance its budget "without significant additional reductions this year."
Boost for Canada's spy agency

As the government takes heat over how it has handled the threat of foreign election interference, it's promising more money to bolster its spy service.
The Canadian Security Intelligence Service is in line to receive $655.7 million over eight years, starting this fiscal year, to enhance its intelligence capabilities and its presence in Toronto.
- CSIS chief defends his spies' work after PM casts doubt on reliability of agency's reports
- Trudeau says it's his job to question CSIS intelligence, call out 'contradictions'
The budget also promises to guarantee up to $5 billion in loans for Indigenous communities to participate in natural resource development and energy projects in their territories.
These loans would be provided by financial institutions or other lenders and guaranteed by the federal government, meaning Indigenous borrowers who opt in could benefit from lower interest rates, the budget says.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Catharine Tunney is a reporter with CBC's Parliament Hill bureau, where she covers national security and the RCMP. She worked previously for CBC in Nova Scotia. You can reach her at [email protected]
- Follow Cat on Twitter
Add some “good” to your morning and evening.
Your weekly guide to what you need to know about federal politics and the minority Liberal government. Get the latest news and sharp analysis delivered to your inbox every Sunday morning.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Thames Water has six weeks to agree survival plan with Ofwat
While the company believes it has cash to last 15 months, it will have to move fast to stave off insolvency
- Analysis: Thames Water is everyone’s problem and time is running out to fix it
Thames Water has just six weeks to convince its regulator that it has a viable survival plan for its business, the Guardian can reveal.
While the company believes it has enough cash to survive for about 15 months, insiders and investors fear that it must move quickly to strike a deal with its watchdog to stave off insolvency.
The UK’s largest water monopoly must present a new turnaround strategy and business plan before 23 May – Ofwat’s final board meeting before it issues a verdict on how much water companies will be allowed to charge consumers.
Thames, which has 16 million customers across London and the Thames valley, has been thrown into crisis after its shareholders last month pulled the plug on a plan to inject £500m into the business , amid a deepening battle with the watchdog.
This has forced Thames’s holding company, Kemble Water Finance, to admit it will not be able to repay a £190m loan due by the end of April.
Thames holds cash reserves which should fund its operations for 15 months without a substantial increase in bills, but investors, including bondholders in the operating company, are understood to believe it may struggle to meet debt obligations if a deal is not struck by May.
Ofwat is understood to be sceptical that Thames’s current business plan for the next two years or its longer turnaround plan – aimed at revamping its management and infrastructure – are viable or fair on consumers.
Sources have claimed that Ofwat is concerned about bills rising without there being a clear strategy to overhaul how the business is managed, since this would risk the burden of poor business decisions being pushed on to customers.
Thames’s operating company, which is ringfenced by the regulator so it can continue even if Kemble collapses, is labouring under debts of almost £15bn, making it Britain’s most indebted water company. It was privatised in 1989 with no debt .
Investors in Thames backed out of providing £500m of emergency funding in March, after the regulator refused the company’s demands for a 40% increase in bills.
Investors, which include UK university pension scheme USS, Canadian investor Omers and China’s sovereign wealth fund, said Ofwat’s current position – to limit bill increases, levy fines and restrict payment of dividends – rendered the company “uninvestible” .
Ofwat reviews water companies’ business plans and holds a price review in order to set the amount the utility firms can raise their bills over the next five-year period.
Despite its rejection of Thames’s plan, it is understood that bills are still expected to rise by as much as 35%, on average, over the next five years .
after newsletter promotion
Thames’s owners are running out of time because the regulator must issue its so-called draft determination on bill increases for each regional monopoly company in June. Those plans will govern how much water investors can earn and how much they must invest over the next five years.
If Thames and Ofwat cannot agree on a new financial plan and a fresh strategy for how to run the company by then, it will ramp up the likelihood of nationalisation.
Bondholders in the operating company have said they may be forced to write down their investment. A likely knock-on effect would be to increase borrowing costs for Thames, and bring forward possible nationalisation of the company via a so-called special administration.
Lenders to Thames argue that forcing them to incur losses on their debts would also drive up the cost of borrowing for all UK water companies, and potentially other utilities such as gas and electricity.
An Ofwat spokesperson said: “We do not comment on speculation. Ofwat is continuing to work on draft determinations that will be published in June.
“We will continue to monitor Thames Water as it seeks to turn around its performance for customers and the environment.”
Thames Water declined to comment on the record. Its board in March agreed a turnaround plan that it believes is “well under way” .
- Thames Water
- Water industry
- Water bills

Thames Water to add to debt mountain in bid for survival

Australia’s Macquarie among lenders to Thames Water’s parent company

Thames Water parent tells creditors it has defaulted on debt

Today in Focus Profits over pipes: who should own our water?

Thames Water funding crisis: the key players in the row over its future

Chinese lenders key as Thames Water’s owner seeks time to pay debts

Thames Water owner bond slumps to record lows amid uncertainty over firm

Thames Water hires restructuring advisers amid fears of collapse

What now for Thames Water as investors turn off the taps?

One in three UK water workers verbally abused amid sewage fury, GMB finds
Most viewed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For a thorough explanation of how to write a business plan, refer to Shopify's guide. 12 components of a business plan. Business plans vary depending on the product or service. Some entrepreneurs choose to use diagrams and charts, while others rely on text alone. Regardless of how you go about it, good business plans tend to include the ...
Please re-read my previous post for more details on how to build a team for your startup in a way that will most appeal to investors. 5. Cash Requirements. Sales and marketing investment will ...
Above all, the numbers should help answer why your business can do it better. 4. Competitive Analysis. A good business plan will present a clear comparison of your business vs your direct and indirect competitors. This is where you prove your knowledge of the industry by breaking down their strengths and weaknesses.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
6 Key Elements of a Business Plan. Drafting a business plan might seem daunting initially, but breaking it down into core components makes it manageable and effective. It's about telling your business's story in a compelling way to garner support and guide your actions. 1) Executive Summary.
13 Key Business Plan Components. We've built a comprehensive guide to the major parts of a business plan for you. From elements like the executive summary to product descriptions, traction, and financials, we'll guide you on all of the key sections you should include in your business plan. December 14th, 2022 | By: The Startups Team | Tags ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
According to Investopida.com and Nerd Wallet, most business plan templates include seven elements: an executive summary, company description, products and services, market analysis, marketing strategy, financials, and budget. You will also want to include an appendix that contains data supporting the main sections.
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
The 10 sections or elements of a business plan that you must include are as follows: 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary provides a succinct synopsis of the business plan, and highlights the key points raised within. It often includes the company's mission statement and description of the products and services.
Here are its key components and what to include in them. 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is one of the most important parts of a business plan. It's the first thing potential investors will read and should therefore provide a clear overview of your business and its goals.
There are eight essential components, all of which are detailed in this handy guide. 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary opens your business plan, but it's the section you'll write last. It summarizes the key points and highlights the most important aspects of your plan.
It's like a roadmap for the business, helping it stay on course and navigate challenges. The plan typically includes sections about the business's description, market research, marketing and sales strategies, operations, management, and financial projections. Entrepreneurs use it to clarify their vision, secure funding, and measure progress.
It needs to be a serious business document with the following six elements. 1. Executive summary. "An executive summary is the 'elevator pitch' of your business plan," explains David ...
1. Executive summary. This short section introduces the business plan as a whole to the people who will be reading it, including investors, lenders, or other members of your team. Start with a sentence or two about your business, development goals, and why it will succeed. If you are seeking funding, summarise the basics of the financial plan. 2.
Six Key Components of Business Plans The specific details of a business plan vary widely among industries and individual businesses; however, the majority of business plans contain six key components.
The first five components of a business plan provide an overview of the business opportunity and market research to support it. The remaining five components of the plan focus mainly on strategy, primarily the marketing, operational, financial and management strategies that that firm will employ. This article details these elements.
When putting your business plan together you should ensure that you address these 6 key areas: Your executive summary. The vision statement and goal overview of your business. Target audience and competitor research. Your products and services. Business structure and operations. Your financial plan.
A business financial plan typically has six parts: sales forecasting, expense outlay, a statement of financial position, a cash flow projection, a break-even analysis and an operations plan. A good financial plan helps you manage cash flow and accounts for months when revenue might be lower than expected. It also helps you budget for daily and ...
In this article, we'll discuss the 6 key components of a business strategy and how knowing them can help you to succeed at work. ... As the business plan progresses, you reach the growth stage. At this point, you start setting new goals and start working on new business strategies, which means that you have to allocate more resources (or the ...
Traction®. This means bringing discipline and accountability into the organization - becoming great at execution - taking the vision down to the ground and making it real. To the degree you focus on strengthening these Six Components as leaders and managers, everything will fall into place. That will move your business into the top 5 percent.
Here are the top six key components for building a killer strategic plan for your business. 1. Assess Industry, Competitor & Customer Trends. The first step of any strategic planning starts with ...
2. Craft a comprehensive business plan. We can't discuss how to start a PC building business without covering creating a great business plan since it serves as the roadmap for your building journey. Here are some of the key details you must include in your comprehensive business plan as a custom PC builder:
Wear my room key around my neck. I never walk around the ship with my room key around my neck, and I especially never do this when on land. There are two reasons for this. First, I see many ...
The plan wouldn't expand Disney's footprint in tourism-dependent Anaheim but would help it add rides and entertainment by letting the company relocate parking to a new multi-story structure ...
SANTA ANA, Calif. (AP) — Visitors to Disney's California parks could one day walk through the snow-covered hamlet of Arendelle from "Frozen" or the bustling, critter-filled metropolis of "Zootopia" under a park expansion plan approved by the Anaheim City Council. Disney would spend at least $1.9 billion over the next decade to ...
The government estimates this could increase federal revenue by $1.36 billion over five years starting in 2024-25. A man exhales vapor while using a vape pen in Vancouver on Nov. 24, 2020. (Ben ...
Thames Water has just six weeks to convince its regulator that it has a viable survival plan for its business, the Guardian can reveal. While the company believes it has enough cash to survive for ...
Within the tax district are 2.9 million square feet of retail space, 1,000 companies employing 32,000 people, 5.6 million square feet of office space, four Fortune 1000 headquarters and 6,200 ...