Remarkable Recovery: Samsung Crisis Management Case Study
Have you ever wondered how a global tech giant like Samsung managed to navigate a major crisis and bounce back stronger?
In the world of corporate governance, effective crisis management can be the difference between irreparable damage to a company’s reputation and a successful recovery.
In this blog post, we delve into a Samsung crisis management case study to learn about exploding batteries to the intricate strategies employed to restore trust.
Samsung’s journey offers valuable insights into the intricacies of crisis management in the digital age.
Join us as we explore the key lessons learned and best practices from this high-stakes situation, shedding light on the remarkable recovery efforts that propelled Samsung forward.
Let’s learn about sailing through tough times through Samsung crisis management case study
Background of Samsung History and growth of Samsung as a global conglomerate
Samsung, founded in 1938 by Lee Byung-chul, started as a small trading company in South Korea. Over the years, it steadily expanded into various industries, such as textiles, insurance, and retail.
In the 1960s, Samsung ventured into electronics, marking the beginning of its transformation into a global conglomerate.
With a focus on technological innovation and a commitment to quality, Samsung rapidly gained recognition for its consumer electronics products, including televisions and appliances.
Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Samsung significantly diversified its business portfolio, entering the semiconductor, telecommunications, and shipbuilding industries.
This diversification strategy helped Samsung become a key player in multiple sectors, solidifying its position as a global leader. Notably, Samsung’s semiconductor division became one of the largest chip manufacturers in the world, supplying components to various electronic devices worldwide.
Samsung’s ascent continued in the 2000s, driven by its successful expansion into the mobile phone market. The introduction of the Galaxy series, powered by the Android operating system, catapulted Samsung to the forefront of the smartphone industry.
The company’s innovative designs, cutting-edge features, and aggressive marketing campaigns contributed to its rise as a major competitor to Apple’s iPhone.
With its global reach, Samsung has consistently ranked among the world’s largest technology companies, epitomizing South Korea’s economic prowess and technological advancements.
Samsung has also been considered one the best companies that successfully managed and implemented change initiatives.
Overview of Samsung’s position in the technology industry
In the consumer electronics segment, Samsung has established itself as a dominant force. Its diverse product lineup encompasses televisions, smartphones, tablets, wearables, home appliances, and audio devices.
The Galaxy series of smartphones, in particular, has enjoyed immense popularity and has emerged as a fierce competitor to other industry giants. Samsung’s televisions are also highly regarded for their cutting-edge display technologies, such as QLED and MicroLED.
The company’s advancements in semiconductor technology have contributed to faster computing speeds, increased storage capacities, and improved energy efficiency.
Samsung’s influence extends beyond consumer electronics and semiconductors. The company is actively involved in telecommunications infrastructure, including the development of 5G networks and the production of network equipment.
Samsung has also made notable strides in the realm of software solutions, including its own mobile operating system, Tizen, and various software platforms for smart devices.
Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Crisis
The Note 7 battery issue marked a significant crisis for Samsung, leading to a widespread recall of the flagship smartphone and causing considerable damage to the company’s reputation.
The crisis began in September 2016 when reports emerged of Note 7 devices catching fire or exploding due to faulty batteries. These incidents raised concerns about consumer safety and triggered a wave of negative publicity for Samsung.
Upon receiving initial reports of battery-related incidents, Samsung initially responded by issuing a voluntary recall of the Note 7 in September 2016. The company acknowledged the problem and expressed its commitment to addressing the issue promptly and effectively.
Samsung attributed the battery malfunctions to a manufacturing defect, specifically a flaw in the design that caused a short circuit.
To ensure customer safety, Samsung advised Note 7 owners to power down their devices and refrain from using them. The company swiftly implemented measures to exchange the affected devices, offering customers the option to either replace their Note 7 with a new unit or receive a refund.
Samsung also collaborated with mobile network operators and retail partners to facilitate the recall process.
In its initial response, Samsung took steps to communicate with customers and the public about the issue. The company published official statements expressing regret for the inconvenience caused and assuring customers of its commitment to resolving the problem. Samsung emphasized its dedication to quality and safety, promising to conduct thorough investigations and implement necessary improvements to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Media coverage and public perception during the crisis
During the Note 7 crisis, media coverage played a significant role in shaping public perception and amplifying the negative impact on Samsung’s brand.
The crisis received extensive coverage from both traditional media outlets and online platforms, leading to widespread awareness and public scrutiny. Here’s an overview of media coverage and its influence on public perception:
- News Outlets: Major news organizations across the globe reported on the Note 7 battery issue, highlighting incidents, the recall, and subsequent developments. Television news segments, newspapers, and online news articles extensively covered the crisis , emphasizing the potential safety risks and consumer concerns. The constant media attention contributed to the widespread dissemination of information and increased public awareness of the issue.
- Online Platforms and Social Media: Social media platforms played a pivotal role in the crisis, enabling the rapid spread of information and user-generated content. Users took to platforms such as Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube to share their experiences, express concerns, and criticize Samsung’s handling of the situation. Viral videos, photos, and personal accounts of Note 7 incidents gained traction, further fueling negative sentiment and influencing public perception.
- Expert Analysis and Opinions: Alongside news coverage, experts and industry analysts provided their insights and opinions on the crisis. Their assessments of Samsung’s response, the potential causes of the battery issue, and the implications for the company’s brand reputation contributed to the overall narrative. Expert opinions had the power to sway public perception and shape the understanding of the crisis.
- Consumer Forums and Discussion Platforms: Online forums and discussion boards dedicated to technology and consumer experiences became hubs for discussions surrounding the Note 7 crisis. Consumers shared their frustrations, exchanged information, and warned others about potential risks. These platforms served as gathering places for individuals affected by the crisis and amplified the negative sentiment surrounding Samsung’s brand.
Financial implications and losses incurred by Samsung
The Note 7 crisis had significant financial implications for Samsung, resulting in substantial losses for the company. Here are some of the key financial impacts experienced by Samsung as a result of the crisis:
- Recall and Replacement Costs: The recall and replacement process incurred significant costs for Samsung. The expenses involved in collecting and replacing over 2 million of Note 7 devices, including logistics, shipping, and refurbishment, were substantial. The costs also encompassed the testing and certification of replacement devices to ensure their safety. The total recall cost was estimated at $5.3 billion.
- Decline in Sales and Market Share: The crisis had a detrimental impact on Samsung’s sales and market share in the smartphone industry. As consumer confidence in the Note 7 and Samsung’s brand reputation declined, potential buyers shifted their preferences to alternative smartphone options. The decline in sales of the Note 7, coupled with the negative impact on the perception of other Samsung products, led to a loss of market share for the company.
- Stock Price Decline: The Note 7 crisis had an immediate impact on Samsung’s stock price. News of the battery issue, recalls, and subsequent negative media coverage led to a decline in Samsung’s stock value. Samsung shares fell approximately to 7 percent right after 2 months of the crisis.

Crisis Management Strategy Employed by Samsung
Following are the key aspects of Samsung Galaxy Note 7 crisis management strategy:
Immediate actions taken by Samsung to address the crisis
In the face of the Note 7 crisis, Samsung swiftly implemented a range of immediate actions to address the situation and mitigate the impact on consumers and the company’s brand reputation. Here are some of the key actions taken by Samsung:
- Voluntary Recall: As soon as reports of battery issues emerged, Samsung initiated a voluntary recall of the Note 7. This proactive step demonstrated the company’s commitment to consumer safety and willingness to take responsibility for the problem.
- Temporary Production Halt: To address the root cause of the battery issue, Samsung temporarily halted production of the Note 7. This decision aimed to prevent further distribution of potentially defective devices and allow for thorough investigations and corrective measures.
- Transparent Communication: Samsung made efforts to communicate openly and transparently about the crisis. The company issued official statements and press releases acknowledging the problem, expressing regret for the inconvenience caused, and reassuring customers of its commitment to resolving the issue. Transparent communication was crucial in maintaining trust and providing timely updates to affected consumers.
- Collaboration with Authorities: Samsung collaborated closely with regulatory authorities and industry experts to investigate the battery issue comprehensively. By engaging external expertise, the company aimed to identify the root cause and develop effective solutions. This collaboration demonstrated Samsung’s commitment to finding the best possible resolution.
- Customer Support and Safety Guidelines: Samsung provided clear instructions to consumers regarding the use of Note 7 devices, emphasizing the importance of safety. The company advised customers to power down their devices, participate in the recall, and utilize alternative devices in the interim. This approach prioritized customer safety and aimed to prevent further incidents.
- Increased Battery Testing and Safety Measures: Samsung implemented enhanced battery testing procedures and stringent safety measures to prevent similar incidents in the future. The company adopted more rigorous quality control processes, including additional safety certifications and testing standards, to ensure the highest levels of product safety.
Communication strategies employed by Samsung
Samsung employed various communication strategies to address the Note 7 crisis and manage the impact on its brand reputation. Effective communication was crucial in maintaining transparency, addressing consumer concerns, and rebuilding trust. Here are some of the communication strategies employed by Samsung:
- Official Statements and Press Releases: Samsung issued official statements and press releases to provide updates on the progress of the recall, investigations, and corrective actions. These statements expressed remorse for the inconvenience caused and reiterated the company’s commitment to customer safety. Clear and concise communication helped keep customers informed and reassured them that Samsung was actively working to resolve the issue.
- Direct Customer Communication: Samsung directly communicated with customers to provide instructions and updates on the recall process. The company utilized various channels such as email, SMS messages, and notifications through its official website and smartphone apps. This direct communication ensured that customers received important information and guidance regarding the recall and replacement program.
- Social Media Engagement: Samsung actively engaged with customers and the public on social media platforms, including Twitter, Facebook, and YouTube. The company responded to customer queries, addressed concerns, and provided updates on the progress of the recall. By engaging in two-way communication, Samsung demonstrated its willingness to listen, respond, and provide assistance to affected customers.
- Collaboration with Industry Experts: Samsung collaborated with industry experts, battery manufacturers, and regulatory authorities to investigate the root cause of the battery issue. This collaboration was communicated to the public, showcasing Samsung’s commitment to finding solutions and ensuring that the necessary expertise was involved in resolving the crisis.
- Advertisements and Marketing Campaigns: Samsung launched advertising and marketing campaigns focused on rebuilding trust and emphasizing its commitment to quality and safety. These campaigns highlighted Samsung’s dedication to addressing the issue and regaining consumer confidence. Advertisements often emphasized the company’s rigorous testing procedures and quality control measures to assure customers of the safety of its products.
- CEO Apology: Samsung’s CEO issued a public apology, taking personal responsibility for the crisis and expressing regret for the inconvenience and concern caused to customers. The CEO’s apology aimed to convey sincerity, empathy, and a commitment to rectifying the situation, while also reinforcing the company’s accountability and determination to regain trust. The apology was published on a full page in 03 major US newspapers – the Wall Street Journal, The Washington Post and The New York Times.
Collaborations with regulatory authorities and industry experts
Samsung worked closely with government agencies and regulatory bodies in various countries where incidents related to the Note 7 were reported. The company shared information, conducted investigations, and cooperated with authorities to ensure compliance with safety regulations and guidelines. Collaboration with government agencies helped align efforts to address the crisis and establish industry-wide safety standards.
In the United States, Samsung collaborated with the CPSC, an independent federal agency responsible for ensuring the safety of consumer products. Samsung worked together with the CPSC to investigate the battery issue and coordinate the recall process. This collaboration ensured that the recall efforts followed established safety protocols and provided consumers with accurate information.
Samsung collaborated with battery manufacturers to investigate the specific manufacturing defects that caused the battery issue. The company worked closely with these partners to analyze the battery designs, manufacturing processes, and quality control measures. By involving battery manufacturers in the investigation, Samsung aimed to identify the root cause and implement corrective actions to prevent similar issues in the future.
Samsung engaged independent testing labs to conduct thorough assessments of the Note 7 batteries and verify the effectiveness of corrective measures. These labs specialized in battery testing and certification, providing expertise and unbiased evaluation of the battery performance and safety. Collaboration with independent testing labs helped validate Samsung’s efforts to address the battery issue and instill confidence in the effectiveness of the solutions.
Post-Crisis Recovery and Rebuilding
Samsung implemented more stringent quality control measures across its product development and manufacturing processes. This included enhanced battery testing protocols, increased inspections, and stricter quality assurance standards. By demonstrating a commitment to producing reliable and safe products, Samsung aimed to rebuild customer trust.
Extended Warranty and Customer Support: Samsung extended warranty periods for existing and new devices, including the Note 7, to provide customers with added assurance. The company also enhanced its customer support services, ensuring that customers could easily access assistance, product information, and technical support. These initiatives aimed to demonstrate Samsung’s commitment to customer satisfaction and support.
Launch of subsequent product lines and their impact on brand perception
Following the Note 7 crisis, Samsung launched subsequent product lines, including flagship smartphones like the Galaxy S8 and subsequent iterations. These launches played a crucial role in shaping brand perception and rebuilding trust. Key factors that influenced brand perception and the recovery process include:
- Emphasis on Safety and Quality: Samsung placed a strong emphasis on safety and quality in its subsequent product launches. The company implemented rigorous testing procedures and introduced new safety features to ensure the reliability and safety of its devices. By highlighting these improvements, Samsung aimed to regain customer trust and reassure them of its commitment to producing high-quality products.
- Positive User Experience: Samsung focused on delivering positive user experiences with its new product lines. This included improvements in design, performance, and functionality to enhance customer satisfaction. By providing users with exceptional products, Samsung aimed to rebuild its reputation and generate positive word-of-mouth, contributing to brand recovery.
- Brand Messaging and Marketing: Samsung’s marketing efforts during subsequent product launches were carefully crafted to reinforce positive brand associations and regain customer trust. The company emphasized innovation, customer-centricity, and the commitment to quality and safety. Marketing campaigns highlighted features, benefits, and technological advancements to create a positive brand image and overcome the negative perceptions associated with the Note 7 crisis.
Final Words
Samsung’s handling of the Note 7 crisis serves as a case study in crisis management. Despite the significant financial and reputational setbacks, the company took proactive steps to address the crisis, regain customer trust, and prevent similar incidents in the future.
The Samsung crisis management case study highlights the importance of swift and transparent communication, customer-centric actions, and continuous improvement in product safety and quality. By effectively addressing the crisis, Samsung was able to navigate the challenging situation and rebuild its brand, reaffirming its position as a leading global technology company.
Overall, the Samsung crisis management case study provides valuable insights into how a company can recover from a major setback, restore customer trust, and strengthen its position in the market through strategic actions and a relentless commitment to customer satisfaction and product excellence.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

Nudge Theory in Change Management

Why Neuroscience of Change Management is Important?

Emotional Reactions to Change in the Workplace

Samsung Electronics—A Detailed Case Study

Devashish Shrivastava
Samsung is a South Korean electronic gadget manufacturer in Samsung Town, Seoul. Samsung Electronics was established by Lee Byung-Chul in 1938 as an exchanging organization.
We all know this information about Samsung. Don't we? But what we don't know? Do you know how much Samsung has grown in these years? What are the Future Plans of Samsung? How much Samsung invested in its R&D? What difficulties did the company face coming all this way? What is the history behind this multinational conglomerate?
Don't worry we got you covered. We have penned down a detailed Case Study on Samsung Electronics. Let's find out in this thoroughly studied Samsung case study.
Let's start the detailed case study from here.
Samsung entered the electronics industry in the late 1960s and the development and shipbuilding ventures in the mid-1970. Following Lee's demise in 1987, Samsung was divided into five business groups - Samsung Group, Shinsegae Group, CJ Group, Hansol Group and Joongang Group.
Some of the notable Samsung industrial subsidiaries include Samsung Electronics, Samsung Heavy Industries Samsung Engineering, and Samsung C&T (separately the world's 13th and 36th biggest development companies). Other notable subsidiaries include Samsung Life Insurance, Samsung Everland, and Cheil Worldwide.
Samsung has a powerful influence on South Korea's monetary advancement, legislative issues, media, and culture. Samsung has played a significant role behind the "Miracle on the Han River". Its subsidiary organizations produce around a fifth of South Korea's complete exports. Samsung's revenue was equivalent to 17% of South Korea's $1,082 billion GDP.
History of Samsung Electronics Samsung's Business Strategy Samsung Rides High In India Business Growth in India Future Plans of Samsung FAQ's
History of Samsung Electronics

1938 (Inception of Samsung)-
- In 1938, Lee Byung-Chul (1910–1987) of a huge landowning family in the Uiryeong region moved to nearby city Daegu and established Samsung Sanghoe.
- Samsung began as a little exchanging organization with forty representatives situated in Su-dong. It managed dried fish, privately developed staple goods and noodles. The organization succeeded and Lee moved its head office to Seoul in 1947.
- When the Korean War broke out, Lee had to leave Seoul. He began a sugar processing plant in Busan named Cheil Jedang. In 1954, Lee founded Cheil Mojik. It was the biggest woollen factory in the country.
- Samsung broadened into a wide range of territories. Lee wanted to build Samsung as a pioneer in a wide scope of enterprises.
- In 1947, Cho Hong-Jai, the Hyosung gathering's organizer, put resources into another organization called Samsung Mulsan Gongsa or the Samsung Trading Corporation with Samsung's founder Lee Byung-Chul. The exchanging firm developed into the present-day Samsung C&T Corporation .
- After few years in business, Cho and Lee got separated due to the differences in the management style. In 1980, Samsung acquired the Gumi-based Hanguk Jeonja Tongsin and entered the telecommunications market . During the initial days, it sold switchboards.
1987 (Demise of Lee Byung-Chul)-
- After Lee's demise in 1987, the Samsung Group was divided into four business gatherings—Samsung Group, Shinsegae Group, CJ Group, and the Hansol Group.
- One Hansol Group agent stated, "Just individuals uninformed of the laws overseeing the business world could think something so ridiculous," while also adding, "When Hansol got separated from the Samsung Group in 1991, it cut off all installment assurances and offer holding ties with Samsung subsidiaries."
- One Hansol Group source attested, "Hansol, Shinsegae, and CJ have been under autonomous administration since their particular divisions from the Samsung Group."
- One Shinsegae retail chain official executive stated, "Shinsegae has no installment certifications related to the Samsung Group." In 1982, it constructed a TV get-together plant in Portugal, a plant in New York in 1984, a plant in Tokyo in 1985 and an office in England in 1996.
2000 (Samsung in 20th Century)
- In 2000, Samsung opened a development center in Warsaw, Poland. It started with set-top-box technology before moving to TV and cell phones. The cell phone stage was created with accomplices and formally propelled with the first Samsung Solstice line of gadgets and different subordinates in 2008. It later emerged into the Samsung Galaxy line of gadgets that is Notes, Edge, and other models.
- In 2010, Samsung declared a ten-year development system based on five businesses. One of these organizations was to be centered around bio-pharmaceuticals in which ₩2,100 billion was invested.
- In the first quarter of 2012, Samsung Electronics turned into the world's biggest cell phone creator by unit deals, surpassing Nokia which had been the market chief since 1998.
- In 2015, Samsung was granted U.S. patents as compared to other organizations like IBM , Google , Sony, Microsoft , and Apple. Samsung got 7,679 utility licenses before 11 December 2015.
- On 2 August 2016, Samsung Electronics revealed the Galaxy Note7 smartphone, which went on sale on 19 August 2016. At the beginning of September 2016, it halted its selling of smartphones due to some problems with the smartphones. Samsung suspended the selling of the smartphones and recalled its units for inspection.
- This happened after certain units of the telephones had batteries with a deformity that made them produce extreme warmth, prompting flames and blasts. Samsung replaced the reviewed units of the telephones with a new version. It was later found that the new version of the Galaxy Note 7 also had the same battery deformity.
- Samsung recalled all Galaxy Note7 cell phones worldwide on 10 October 2016 and permanently ended its production on the same day.
Samsung's Business Strategy
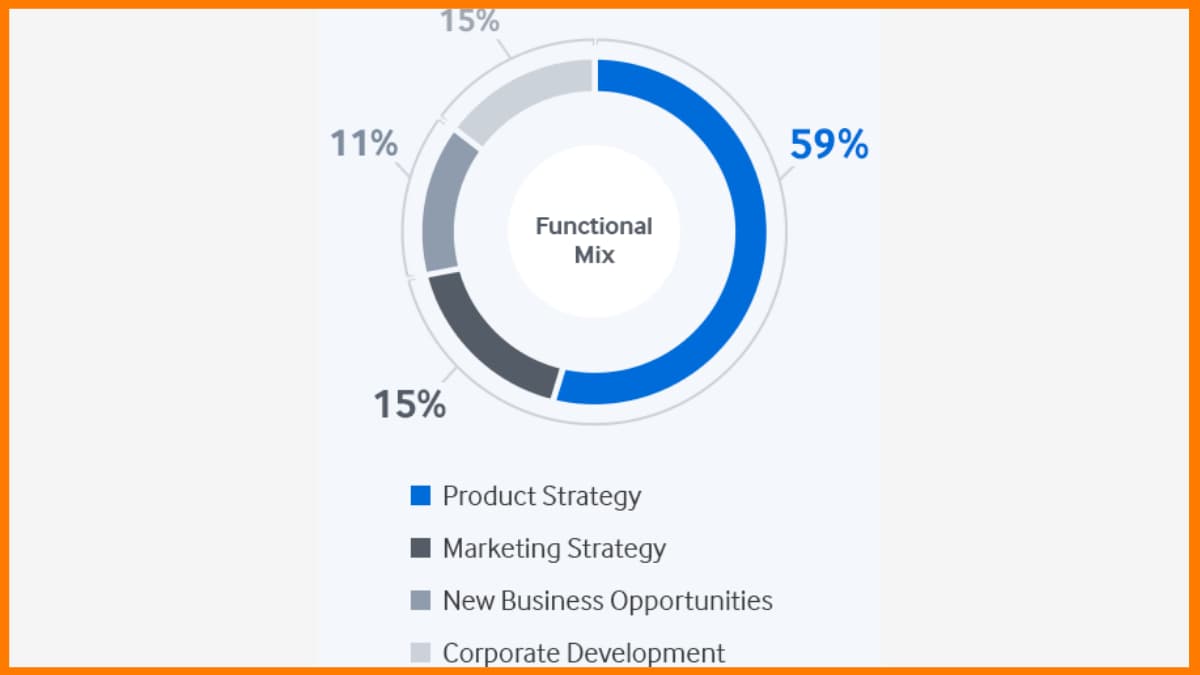
Great business strategies have been applied by Samsung over the years. Not very far back, Samsung wasn't as famous as now. Samsung has now advanced so much that it is the principal contender of Apple Inc. Samsung is the biggest tech business by income and the seventh most significant brand today. The showcasing procedure it applied encouraged Samsung electronics to turn into an industry driving innovation organization.
The Samsung marketing strategy was one of the best systems at any point because it helped a cost-driven organization to change its structure and become a power producer. Due to the consistently changing tastes of purchasers in the innovation business, organizations needed to pursue the pace and offer dynamic and advancing devices to their clients. In this way, Samsung additionally needed to change to pick up the high ground available, and the new Samsung showcasing methodology was the way to advancement.
Some of the business strategies of Samsung Electronics are listed below:
Promotional Mix Of Samsung
Samsung has arrived at fantastic statures with its cell phones which helped the brand to turn into an image of value and unwavering quality for its purchasers.
Samsung Marketing Mix Pricing Strategy and Samsung Advertising Methodology are the two estimating techniques used by the organization. Other than its items, Samsung is celebrated for its customer support . However, item variety is the most dominant part of the promoting blend of Samsung.
- Skimming Price
Like Apple , Samsung uses skimming costs to pick up the high ground over its rivals. For example, Galaxy S6 and S6 Edge are the brand's new results of Samsung conveying the trademark "Next is Now" and guaranteeing that they are the best smartphone maker at any point made.
What will happen when different contenders will dispatch a cell phone with indistinguishable highlights? Straightforward. Samsung will bring down the cost and effectively steal the customers from its competitors.
- Focused Pricing
Samsung experiences issues in increasing an edge over its rivals with different items. Doubtlessly, Samsung is a credible brand. However, regarding home appliances, it can't be in any way, shape, or form outperform LG In the cameras segment and other home appliance units. Also, Samsung cannot compete with Canon and Nikon.
For Samsung to withstand this savage challenge, it's crucial to utilize aggressive valuing of its products. Moreover, Samsung is neither a newbie underway nor non-inventive. For the most part, it is often the first company to be innovative with its products and present a change among its competitors.
- Putting in Samsung Marketing Strategy
Samsung uses divert advertising strategies. Retailers who present the innovation chain will undoubtedly incorporate Samsung in their rundown on account of the firm being a world-celebrated brand. Samsung can likewise fill in as an option for the purchasers. The circulation is a convincing piece of the Samsung promoting methodology.
In specific urban communities, Samsung has an agreement with a solitary dissemination organization that circulates the items all through the city. For example, Mumbai is an incredible case where Samsung conveys its products through a solitary organization.
Samsung Rides High In India

The greatest leader by far in the smartphone business is Samsung Electronics, the world's greatest cell phone and TV producer.
Samsung is India's greatest, versatile brand. It is the developer of Reliance Jio's 4G LTE system — the greatest and busiest information system on the planet.
Discernments, advertise wars, openings, rivalry — now and then from conventional remote adversaries, from nearby upstarts, and emerging Chinese brands trouble Samsung.
Be that as it may, every time Samsung has had the option to fight off the dangers and hold its ground. It has been leading the market in the TV fragment for more than 12 years and in the versatile business for a long time after it toppled Nokia in 2012.
Riding The Smartphone Wave
As indicated by some statistical surveying firms following cell phone shipments, Chinese firm Xiaomi is creeping nearer — or has even surpassed Samsung after December 2017 quarter.
While for the entire year 2017, Samsung was No. 1 in the cell phone space, IDC information indicated Xiaomi drove the last quarter with 26.8% piece of the overall industry. Samsung was at 24.2%. Different players, for example, Vivo, Lenovo, and Oppo stayed at 6.5, 5.6, and 4.9%, separately.
Warsi, who has been working with Samsung for as far back as 12 years and has as of late been advanced as Global Vice President, is unflinching, "These difficulties offer us the chance to work more earnestly for our customers and with our accomplices.
Furthermore, shoppers love marks that emphasis on them," he says. "Samsung is India's No. 1 cell phone organization crosswise over sections — premium, mid and reasonable. That is what makes a difference."
Statistical surveying firm GfK tracks disconnected offers of handsets — which make up around 70% of the market — in which Xiaomi is attempting to make advances.
Samsung had a 42% worth piece of the overall industry in the general cell phone showcase in the nation in 2019 and 55% in the superior fragment as indicated by GfK. An industry official who would not like to be named says that India must be Samsung's greatest market by large volumes.
The thought currently is to become the cell phone business which gets more worth. As indicated by reports, Samsung India's incomes from cell phone deals in 2018-19 remained at an astounding INR 34,300 crore. That is over $5.5 billion and development of 27%. Samsung's nearest adversaries are talking about incomes of $1 billion in India, going up to $2 billion.
Samsung is the world's largest manufacturer of consumer electronics by revenue. As of 2019, Samsung Electronics is the world's second-largest technology company by revenue, and its market capitalization stood at US$301.65 billion, the 18th largest in the world.
Shopper Is At The Center

Samsung is a worldwide advancement powerhouse that leads the patterns. It profoundly put resources in India — 22 years of connections in the exchange, and tremendous interests in neighborhood R&D . It has around 10,000 architects working in research offices in India and is perhaps the greatest scout from the IITs.
"Samsung has a solid brand picture in India, as it has been available in various customer electronic portions with quality items for quite a while now. The brand is trusted because of its long history in the nation, dish India nearness, and a vigorous after deals support for buyers," says Shobhit Srivastava, explore expert at Counterpoint Research.
Indeed, even an item fizzle of the size of the Galaxy Note7 in September 2016 couldn't affect Samsung. While the organization was fast enough to get back to every one of the units that had been sold and cease the gadget totally, Samsung's activities and ensuing effective dispatches of leads like Galaxy S8, Note8, the Galaxy S9 and S9+, which were propelled in February, rescued the harm and raised the profile of the brand as a dependable organization. "They rushed to concede their error and that helped them interface with the perceiving clients of today far superior," says Koshy.
Make For India
Samsung's system 'Make for India', which resounds with the administration's ' Make in India ' activity, was conceived in the late spring of 2015. Samsung India's new President and CEO, H.C. Hong, had recently moved in from Latin America and was looked with the prompt tough assignment of fighting a firm challenge from two nearby versatile organizations that is Micromax and Intex.
Samsung's customer hardware business containing TVs, fridges, and other advanced machines were additionally confronting challenges from Sony and LG.
Around a similar time, the legislature of India propelled its 'Make in India' activity. "In this way, Mr. Hong revealed to us we have been doing Make in India effectively for two decades. What we should concentrate on widely to remain on top of things is Make for India (MFI)," says Dipesh Shah, Managing Director of Samsung R&D Institute in Bengaluru, the greatest R&D community for Samsung outside Korea.
Truth be told, the R&D focuses in India contribute intensely to the improvement of worldwide items, for example, Samsung's lead cell phones (Galaxy S9 and S9+). While different organizations focused on propelling their worldwide items in India, Samsung went about rethinking items for the nation at its R&D focuses.
India is significant for Samsung, thinking of the nation as the second biggest cell phone showcase on the planet today, and it is possibly the greatest undiscovered market for some advanced apparatuses. The entrance of iceboxes, clothes washers, microwaves, and forced air systems are appallingly low because of components like the accessibility of continuous power, social conduct, way of life, and earnings.
Business Growth in India

Samsung India crossed the INR 50,000 crore deals achievement in 2017 according to the simply distributed organization filings with the Registrar of Companies (RoC), uniting its situation as the nation's biggest unadulterated play purchaser products MNC. The Korean mammoth's all-out salary, including turnover and other pay, developed by 15.5% to INR 55,511.9 crore in FY 2017 from INR 48,053 crore in the earlier year regardless of Chinese organizations making genuine advances into the Indian cell phone advertise.
Samsung's cell phone business developed deals at 26.7% to INR 34,261 crore, while the home apparatus business developed by 12% to INR 6,395.6 crore. The organization's TV business stayed dormant at INR 4,481.2 crore even though Samsung held the market initiative.
The organization's net benefit developed at a quicker pace of 38% to INR 4,156.2 crore which industry examiners credited to more concentrate on premium models crosswise over cell phones and customer hardware having higher edges.
Samsung, in its filings, said the 'Make for India' activity, through which a large portion of the items was planned and created given the Indian customer's needs, has been an enormous achievement and a major factor behind the development.
All the units at Samsung India improved their gross productivity with the TV business dramatically increasing it and the home machine business nearly trebling it. The cell phone business was the biggest supporter of gross benefit having developed by 44% in FY17 at INR 5,005.9 crore.
Future Plans of Samsung

Samsung has arranged a new venture of around INR 2,500 crore to transform its India tasks into a center for parts business, two senior industry administrators said. The ventures could be increased further, they included. The Korean organization has set up two new parts fabricating substances in India—Samsung Display Co and Samsung SDI India—for the generation of cell phones and batteries.
Independently, Samsung's funding arm—Samsung Venture Investment Corp—has set up activities in India to support new companies in gadgets equipment and programming organizations. The segment organizations will supply items to both Samsung India and other cell phone merchants who as of now source parts from Samsung's abroad tasks.
Samsung sees a big opportunity for segment business considering the administration's push on 'Make in India' where expense on imported cell phone segments and purchaser hardware is going up, the administrators said.
Samsung is likewise pitching to the administration for fare impetuses so it can even fare segments from India. Samsung Display has just marked an update of comprehension with the Uttar Pradesh government for an INR 1,500 crore plant for assembling telephone show to be operational by one year from now April. The plant will come up in Noida, the administrators said.
Samsung SDI India has plans to set up an assembling unit in India for lithium-particle batteries after the organization was drifted a month ago, according to its administrative filings with the Registrar of Companies (RoC).
As per the administrators, Samsung SDI has plans to contribute another INR 900-1,000 crore and will settle the plans after counseling with the Center post general races. These speculations come after it introduced the world's biggest cell phone fabricating unit in India a year ago at an all-out cost of INR 4,915 crore. It is expected to be completed in 2020.
That's all for now. Share your learnings and findings. What did you learn from this article? Which information surprised or amused you the most? Feel free to reach us and share your feedback. We would love to hear from you. Do comment us in the comments section below. Happy Reading.
Who is the owner of Samsung Electronics?
Samsung Group is the owner of Samsung Electronics.
Who is the Founder of Samsung?
Samsung Electronics was established by Lee Byung-Chul (1910–1987) in 1938 as an exchanging organization.
Who is the current CEO of Samsung?
Kim, Ki Nam, Kim, Hyun Suk and Koh, Dong Jin are the current CEO of multinational conglomerate Samsung.
What does Samsung Electronics make?
Samsung Electronics produces smartphones, TV sets, laptops, solid-state drives, digital cinemas screens, etc.
Is Samsung a Chinese company?
Samsung is a South Korean electronic gadget manufacturer in Samsung Town, Seoul.
What is Samsung's strategy?
- Promotional Mix of Samsung
How large is Samsung Electronics?
Samsung is the world's largest manufacturer of consumer electronics by revenue. Samsung Electronics is the world's second-largest technology company by revenue, and its market capitalization stood at US$ 301.65 billion, the 18th largest in the world.
What are the future plans of Samsung Company?
Samsung has arranged a new venture of around INR 2,500 crore to transform its India tasks into a center for parts business, two senior industry administrators said.
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
Best Strategies for Content Optimization Straight from Marketing and SEO Gurus!
Considering the increasing competition among websites to rank, it is essential to employ effective optimization strategies. With approximately 99,000 search queries processed by Google every second, totaling about 8.5 billion searches daily, this becomes even more important. At StartupTalky, we've reached out to Marketing and SEO experts for
How Are Experts Adapting to Recent Google Algorithm Updates? Learn Their Strategies Now!
Since the release of Google Search in 1997, the company has dominated the search engine market. As of January 2024, it holds a massive 95.32% share of the global mobile search engine market. Understanding and adapting to Google's algorithm updates are extremely important for SEO success. In tune with
How to Create a Standout CV: A Step-by-Step Guide from Formatting to Submission
This article has been contributed by Nirupama VG, Founder & MD, Ad Astra Consultants Private Limited. In today's competitive job market, a carefully created curriculum vitae (CV) can determine whether or not you land an interview. Your resume is your promotional tool, highlighting your abilities, background, and credentials for prospective employers.
Maximizing Efficiency: 8 Best Productivity Gadgets for Entrepreneurs
According to technology experts, productivity gadgets are devices or innovations that help individuals complete tasks more efficiently and effectively. These devices frequently use technology to automate operations, organize information, or simplify complex activities, eliminating distractions while increasing output. These devices come in various forms, from hardware to software programs, each

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Samsung’s Generic Competitive Strategy & Growth Strategies

Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies set business goals for technological innovation as a critical factor in developing competitive advantages. Headquartered in Korea, the conglomerate competes with technology-intensive firms, such as Apple , Google (Alphabet) , Microsoft , Sony , and Intel , which create strong competitive forces, as determined through a Five Forces analysis of Samsung. The industry environment imposes aggressive competitive behavior that typically involves rapid technological innovation for product differentiation, as seen in the evolution of smartphones available in the global market. To effectively compete, Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and growth strategies must involve investment in technological innovation. The resulting competitive advantages enable the company to keep its competitive position as one of the best performers in the semiconductors, consumer electronics, and home appliances industries. Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive strategies for growth are suited to the current business environment and the strategic positioning of the multinational organization’s operations.
The generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies of Samsung Group permeate its entire organization, influencing the strategic choices and implementations of its divisions and subsidiaries. The Group’s unitary leadership is responsible for the corporate strategic direction and competitive advantages of the conglomerate and its technology-focused subsidiaries. Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies are observable in product design, marketing strategies, and the business organizational development direction of subsidiaries.
Samsung’s Generic Competitive Strategy (Porter Model)
Samsung applies broad differentiation as its generic competitive strategy. Based on Michael E. Porter’s competitive strategy model, the strategic objective of broad differentiation is to maintain competitive advantage by providing unique (or differentiated) products targeting a wide market, which in this case is industry-wide, involving practically every person or group that buys smartphones, laptops, and other equipment. To achieve Samsung’s strategic plans for growth and expansion in the global market, this generic competitive strategy requires the application of product development as a main intensive growth strategy to compete with other technology firms.
Samsung’s investments in product development are a strategic implication of differentiation as its generic competitive strategy. For example, the company invests in technological innovation to support the competitive advantage of its products in the consumer electronics market. Another implication of this generic competitive strategy is Samsung’s marketing mix (4Ps) and related strategies that promote products as unique or different alternatives to the majority of competitors. This marketing approach and technological innovation sustain the corporation’s competitive advantages and value chain effectiveness in satisfying customers’ needs in consumer electronics, computing technology, and home appliances.
Other generic competitive strategies, such as cost leadership, differentiation focus, and cost focus, are also applied in Samsung’s operations, but to a limited extent. Cost focus leads to the company’s being the best-cost provider in some segments of the semiconductor and electronic components markets. The limited application of cost focus still comes with innovation standards that reflect Samsung’s main generic competitive strategy of broad differentiation. These generic strategies align with the company’s intensive growth strategies to succeed in sustaining the technology firm’s competitive advantages.
Samsung’s Intensive Growth Strategies (Ansoff Matrix)
Market Penetration (Primary) . Samsung’s revenue growth depends on market penetration as the primary intensive strategy. In Igor Ansoff’s matrix, the strategic objective of market penetration is to grow the technology business by increasing its revenues from the sale of current products in current markets, such as the European Union’s consumer electronics market, where the corporation already has operations. Competitive advantages and business strengths identified in the SWOT analysis of Samsung combat negative forces from competition in these markets. As an intensive growth strategy, market penetration depends on the effectiveness of the generic competitive strategy of broad differentiation, in terms of how the company creates technologically innovative products that are differentiated enough to attract target customers in current or existing markets.
Product Development (Secondary) . Considering the emphasis of product superiority in Samsung’s corporate mission and vision statements , product development is a major intensive growth strategy of the enterprise. A strategic objective of product development in this case is to grow the business through new products, such as new electronic gadgets. Also, this intensive strategy grows Samsung’s operations through iterative innovation, which leads to improved versions or variants of existing products. For example, the company regularly rolls out new smartphone models, similar to what competitors are doing in their product development strategy. The implementation of product development as an intensive growth strategy is based on Samsung’s generic competitive strategy of differentiation, which requires product development for uniqueness that differentiates the business from the competition. Economies of scope based on the conglomerate’s various subsidiaries support product development and competitive advantage by providing technological expertise and material inputs from the subsidiaries. Samsung’s organizational culture (work culture) affects human-resource support for operational effectiveness, value chain efficiencies, supply chain management, and other business activities that fulfill the strategic objectives of product development.
Market Development . The global scale of Samsung’s operations makes market development a minor intensive strategy for business growth. Market development’s strategic objective is to enter new markets using the company’s existing products, such as introducing new Galaxy tablets in Latin American markets after these products’ introduction in the United States. As an intensive growth strategy, market development’s success depends on product value and competitive advantage, which in this case comes with Samsung’s generic strategy of differentiation via technological innovation. For example, effective innovation for cutting-edge technological design makes the corporation’s products more competitive when rolled out in target markets. With this intensive growth strategy, introducing products to new markets may come with changes in the geographical units of Samsung’s organizational structure (company structure) .
Diversification . Samsung’s diversified business operations maintain multiple revenue channels and spread risk across industries and markets. This intensive growth strategy’s implementation is infrequent in the technology conglomerate, considering regulatory hurdles and other barriers. With the strategic objective of establishing new profitable businesses, the diversification strategy grows Samsung typically through acquisitions of smaller firms, such as Harman International Industries. The minor role designation of this intensive growth strategy limits the risks of establishing new business operations. In implementing diversification, the generic competitive strategy of differentiation is also applied for competitiveness and strategic alignment among Samsung subsidiaries’ business operations.
Some Considerations – Samsung’s Generic Competitive Strategy & Intensive Growth Strategies
Samsung’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies direct the organization’s growth and development. Differentiation plays a major role in building the company’s competitive advantage, although other generic competitive strategies, such as cost leadership and focus strategies, also support the technology enterprise and its competitiveness. Samsung’s operations management strategies and administration must align with the differentiation generic competitive strategy and the intensive growth strategies to support business growth while competing with aggressive multinational companies.
- López, D., & Oliver, M. (2023). Integrating innovation into business strategy: Perspectives from innovation managers. Sustainability, 15 (8), 6503.
- Samsung – Brand Identity .
- Samsung R&D Center .
- Samsung Catalyst Fund .
- Taherdoost, H. (2023). An overview of trends in information systems: Emerging technologies that transform the information technology industry. Cloud Computing and Data Science , 1-16.
- U.S. Department of Commerce – International Trade Administration – Software and Information Technology Industry .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The Globe: The Paradox of Samsung’s Rise
- Tarun Khanna,
- Jaeyong Song,
- Kyungmook Lee
Samsung’s unlikely success in mixing Western best practices with an essentially Japanese business system holds powerful lessons for today’s emerging giants.
Reprint: R1107N
Twenty years ago, few people would have predicted that Samsung could become a world leader in R&D, marketing, and design. Fewer still would have predicted success given the path it has taken: grafting Western business practices onto its essentially Japanese model.
Like today’s emerging giants, Samsung faced a paradox: The tightly integrated business system that worked in its home market could not secure its future in global markets. So into an organization focused on continuous process improvement, Samsung introduced a focus on innovation. Into a homogeneous workforce, it introduced outsiders who could not speak the language and were unfamiliar with the company’s culture. Into a Confucian tradition of reverence for elders, it introduced merit pay and promotion, putting some young people in positions of authority over their elders.
Chairman Lee Kun-Hee recognized at the outset the challenges of opening up Samsung’s culture to new ideas. He changed only what needed to be changed, ensured that people understood the new practices, and never flagged in his commitment to the effort.
As today’s emerging giants face the challenge of moving beyond their home markets, they have much to learn from the pathbreaking experience of South Korea’s Samsung Group, arguably the most successful globalizer of the previous generation.
- Tarun Khanna is the Jorge Paulo Lemann Professor at Harvard Business School, the director of Harvard’s Lakshmi Mittal South Asia Institute, and the author of Trust: Creating the Foundation for Entrepreneurship in Developing Countries (Berrett-Koehler, 2018).
- JS Jaeyong Song ( [email protected] ) and
- KL Kyungmook Lee ( [email protected] ) are professors at Seoul National University in South Korea.
Partner Center
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Business Analysis » Case Study: Samsung’s Innovation Strategy
Case Study: Samsung’s Innovation Strategy
The success of Samsung has been widely acknowledged in the last decade. Samsung, the world’s largest television producer and second largest mobile phone manufacturer, is also the largest firm of flash memory maker. Furthermore, Samsung was ranked by Fast Company Magazine to be third most innovative company in the consumer electronics. The company grew from a local industrial leader into a worldwide consumer electronics brand, with up to 261,000 employees, 14 public listed companies, 470 offices and facilities in 67 countries. Samsung was ranked as 11th world’s most innovative companies. It is one of the two Korean companies in the Top 20 companies. While Sony, the Japan’s biggest consumer electronics, was ranked as 10th, only one position above Samsung. This has brought questions among management gurus how this growing company could drive innovation to create success within a short time and remain innovative despite the difficulties of internationalization . In addition, it could overcome many well-built rivals from Japan and Europe.

Shared vision and top management commitment are the important component leading to create innovative atmosphere . In creating such organization, if leaders are not committed in their actions, innovation couldn’t be systematic in a company. Top executive’s role modelling is one of the main differences between innovative and non-innovative organizations. Moreover, employees should realize a company’s goals to align with their innovative effort. Samsung’s new management beliefs applied in the late 1990’s is “we will devote our human resources and technology to create superior products and services, thereby contributing to a better global society.” This shows the company’s strong willpower to contribute to the worldwide people’s prosperity in the 21st century. This message encourages every employee in the firm to innovate with the clear goal of being global superior producer.
Appropriate Structure
The innovative organization tends to have characteristics of organic structures with open and dynamics systems. At first, the reduction of organizational layer and downsizing are concerned as cost control . An increase in use of information technologies, such as email, internal blog, shared data repository, also leads to the need of eliminating middle management. The possible consequences for this are faster responsiveness to market, higher competitiveness, more flexibility, and reducing processes between divisions. This leads to flatter organisation that is not only the change of organisational structure but also the change of decision-making process . In order to avoid delays and support for rapid innovation, decisions should be delegated to the innovation team. The approval of top management is only needed at the checkpoints or gates of the innovation process. Furthermore, Innovation is not suitable with multi-level hierarchy as the new idea and radical innovation must pass through many approvals with high possibility of ideas being rejected. Moreover, this will discourage strong leaders, who try to overcome its cumbersome, but the slow-response organisation will eventually obstruct their abilities. For example, in 1989, Samsung had 3-7 steps for project approval. This took up 24 days for the proposal to go through 7 approvals to arrive final decision step from the president. On the contrary, proposal in 1995 needed maximum of 3 approvals decided on the same day. This change of the important process leads to speed of running business. Furthermore, the proposal form in 1995 is in English, this signified an attempt for globalization .
Key Individuals
With the goal of creating innovation in the company, Samsung needs the world-class human resources from both technical and business backgrounds. Its branding strategy is not only to create a brand that people trust and admire, but also to be a company that they desire to join. To foster this breakthrough R&D, Samsung set up worldwide objectives to catch the attention of the smartest people from around the world, and retain them. These people will be trained and implanted Korean and Samsung culture through one week of intensive Korean daily conversation class, one week of Orientation about company’s history, philosophy, and culture, and develop general management skills delivered by senior Samsung executives. The recruitment of world’s smartest innovators, inventors and designers are fundamental to the company’s success in creating the future technology.
Besides having the best people for the development of innovative capabilities, Samsung has a tool to identify the key players, such as Project leader, promoters, idea champions, or gatekeeper, in the organization. Experiential education programs that are enjoyable, innovative and effective have performed this identification task. For example in the Samsung Semiconductor unit, 90 managers were organised into groups and assigned to build up new equipment through the use of Lego blocks. The tool was just simple Lego blocks, but the equipment created in this experiment had to be functional. This activity, which required both creativity and teamwork, provided managers comprehension of the role each member played in team. Who is promoter, supporter, idea generator, and critical thinker are identified.
Effective Team-working
Currently, team-working increasingly reflects a deeper recognition that this method of working offers greater economic benefits. Cross-functional teams is an effective tool to bring in different knowledge sets needed for solving production problems, creating new businesses , or develop new strategies. Work as a team needs more participation, higher commitment, sharing knowledge and self-management . This is more organic and flexible approach that helps to initiate innovation implanting across organisational and national boundaries. For example, Automakers from USA and Japan collectively worked on the development of new car model. Committing to consumer trends, Samsung set up a group of about 30 businessmen called CNB (Create New Businesses) who had to discover long-term social and technological fashions and imagine new products, which fulfill promising demands. Samsung has harvested the fruits from its team-working and strong commitment to innovation , transforming low-quality producer to become a brand that create stylish mobile phone. In 2010, its sales of mobile phones were ranked as number one in the US market.
Long-term Commitment to Education
Invest in people is another key initiative needed to emphasize in the development of innovative organisation. Army without essential weapons cannot deliver its full potential. Those needed weapons are knowledge, which has to be developed by best practice training. Companies, such as Hewlett Packard, and Samsung, have committed in training and development programs to help spread innovation capability all over the organisation. Besides internal training programs, offering scholarship, postgraduate study opportunities and international work placement for its staff in 120 offices across 57 countries provide Samsung linkage with renowned universities, also bringing in knowledge and collaboration to the organisation. The by-product from doing so is incentives that help to attract and retain of the best and brightest inventor and businessperson from the global industry.
Extensive Communication
Communication is one of the factors causing failure in investing in ideas that go wrong since the beginning. These are those ideas that do not align with the company’s need. Communication within company about its strategy and customer demands is needed for the clear innovation pathways of researchers. Idea generated from either internal or external organisation must go through many steps of modification before adopting into a company. These steps become troubles for the huge companies. In the case of Samsung, idea management has been introduced to manage ideas from thinkers and distribute them all over the company. They will be evaluated by colleagues, supervisors, or assigned review staffs who add views, opinions and knowledge. In addition to internal communication, networking between firms is also key component in the creation of innovation . The network organisation is a group of several independent companies, which perform different tasks and contract one another. For example, one firm in the network focus on research and product design, another manufactures it, and a third does distribution. This approach gains a wide acceptance as it has strong rationale including rapid change of business environment , the cumbersome of large-size companies, importance of speed and flexibility. Moreover, partners’ collaboration helps to blend and complement different core competency in creating better innovation. Samsung has utilized this concept by building a team, called TechnoValley, undertaking only planning and marketing of product. Other partners in the network took care of technology, production, distribution, and promotion.
High Involvement in Innovation
Building a visionary company requires 1 percent vision and 99 percent alignment. In order to build a sustainable innovation culture, staffs have to practice innovation in everything they do. Practicing to tackle small challenge will make them ready for a bigger challenge. Samsung manager plays an important role in supporting this culture of practicing innovation by encouraging the innovation process and not pushing employees to short circuit the solution process.
External Forces
External forces shapes Samsung to become technology leaders. Previously, closed innovation was the model that Samsung Electronics followed. They invested in the best people and centralized their R&D unit. Today, Samsung cannot depend only on internal innovations, which may create the advanced operating system for mobile phone but not attractive one. Samsung open innovation center established to create striking design and user-friendly interface of Samsung mobile phone. It successfully engaged customers and suppliers in the innovation process at the early stage. Being based in Korea with large group of young technology-concerned consumers provides Samsung an innovative edge in consumer electronics including mobile phones. The replacement rate for mobile phones in Korea is estimated at 6-18 months, thanks to young Koreans who swiftly adapt new technology. Therefore, these trendy people have participated in testing and giving feedback, which provide significant information about customers’ desire. Korea, therefore, becomes an invaluable testing location for innovations prior to the companies unveil them on the world stage.
Creative Climate
Public reward for those who distinguish themselves as mains actor in innovation culture and who promote the value of innovation is the powerful tool to expand innovative thinking throughout the enterprise. There are many examples of escalating the visibility of innovation success, such as the company innovation award, inventor hall of fame. This illustrates the commitment a company have on its innovation and inspire employees by making them proud of their success. Idea management through the use of IT have increased the rate of product and process improvement, as contributions of ideas are traceable. It open up the communication all over the company and promote culture of sharing and creativity. Ideas are developed and talked widely not only in vertical but in horizontal fashion leading to innovative atmosphere. After the introduction of knowledge management solution in Samsung Electronics, there was a change in organizational climate. Employees have been become confident to be more suggestive, trustful, responsive to change, and eager to innovate. Forum and blog postings are the place for knowledge sharing where an automatic rewarding system is executed. The profitability of the products launched, have been chosen as the innovation performance indicators.
Learning Organization
Sharing knowledge and skill of employees brings about innovative performance. Samsung has identified two main challenges in the creation of learning organisation that are knowledge discovery and knowledge sharing. In the past, problems occurred due to lack of knowledge management, for example, lost of valuable knowledge from poor management, or repeating the same failures. To tackle such problems, organizational mechanisms and technological solutions to facilitate the innovation process in Samsung have been introduced. Firstly, Samsung Brainstorming Hours has been arranged to capture and spread ideas in any step of innovation process from idea generation to conversion and commercialization. This is not applied only in the new product development process, but also solving complex problems or business improvement. Two hours weekly meeting for cross-functional team in the room with tall windows, wireless connection, big-screen TV, snacks and drinks is designed to foster innovation process. This comfortable surroundings helps innovation workers to socialise with each other and share ideas. Secondly, company-wide simple but powerful blog has been introduced to encourage knowledge sharing and discovery. The blog helps employees understand and discuss ideas so as to extend previous knowledge continuously. Thirdly, knowledge warehouses have been built to have codifiable critical knowledge stored and accessible throughout Samsung Company. The “Lessons Learned System with Alert function” has been used to manage this knowledge and share it. For storing lesson learned, project managers has been trained about how and what knowledge to collect and given the project management manuals including many useful procedures such as how to write a closing report, how to create and store a project model, how to perform an After Action Review. In order to control overwhelming information, Alerts system notifies employees of newly stored knowledge that might be of interest and useful to their work.
Samsung has successfully transformed from local low quality manufacturer to a brand that produce admirable and stylish consumer electronics. Company performance has proven that Samsung has come to the right direction in last decade. The achievement of becoming innovative organisation started from the declaration to be the global leader in the industry in late 1990s. After the re-configuration and adopting team-working practice, Samsung organisation has been altered to be flexible and organic, leading to ability to develop innovative capability. In addition to the recruitment of the best people into the organization , Samsung has an experimental education tool to identify the key individuals, such as project leader, promoters, or gatekeeper, so as to blend different roles in creating innovation . These people are working under the well-designed knowledge management system and trustful and suggestive communication with the support of supervisors, fostering creative climate. Rewards system for innovative contributor, organisational mechanism and technological solutions has brought about the knowledge discovery and sharing throughout the company, creating learning organisation that sustains Samsung innovation competency.
Related posts:
- Case Study: iPod, Apple’s Best Innovation
- Case Study of Dyson: Competitive Advantage through Innovation
- Case Study: Business Model Innovation and Customer-Driven Innovation at Dell
- Case Study: Kellogg’s Business Strategy
- Case Study: Business Strategy of Sony Corporation
- Case Study of Apple: Competitive Advantage Through Innovation
- Case Study of Apple: Strategic Enablers and Barriers to Innovation
- Case Study of Jack Welch: Leadership that Creates Innovation
- Case Study: Disney’s Diversification Strategy
- Case Study: Ryanair Business Strategy Analysis
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Apple v. Samsung patent trial recap: How it all turned out (FAQ)
The tech companies battled in a San Jose, Calif., court over patents. CNET breaks down what happened during the monthlong trial.

The latest round in the Apple v. Samsung patent-infringement battle is finally over -- well at least until it's appealed.
A jury on Friday handed back a mixed verdict in the Apple v. Samsung patent-infringement case, determining that both companies were guilty in some aspects but not guilty in others.
The trial included about 52 hours of testimony, three hours of opening arguments, and four hours of closings. It covered everything from the invention of the technology at issue in the case to what damages should total. Apple argued throughout the trial that its case was about Samsung, not Google, and that Samsung copied Apple out of desperation. Samsung, meanwhile, argued that Apple's suit was about hurting competition and Android.
CNET details what exactly happened:
What was this trial about?
For the latest case, Apple filed suit against Samsung on February 8, 2012, accusing it of infringing several patents. Samsung then filed counterclaims against Apple. In Apple's original suit, the company said Samsung "has systematically copied Apple's innovative technology and products, features, and designs, and has deluged markets with infringing devices in an effort to usurp market share from Apple." Judge Lucy Koh ordered for the trial to start March 31.
Apple v. Samsung 2014: The infringing devices (pictures)

The whole spat started when Apple filed suit against Samsung in April 2011, accusing its rival of copying the look and feel of its iPhones and iPads. Samsung countersued, and the case went to trial in August 2012. A nine-person jury sided with Apple on a majority of its patent infringement claims against Samsung. It a warded Apple $1.05 billion in damages, much less than the $2.75 billion sought by the Cupertino, Calif., company. Samsung, which asked for $421 million in its countersuit, didn't get anything.
However, US District Court Judge Lucy Koh in March 2013 ordered a new trial to recalculate some of the damages in the case, striking $450.5 million off the original judgment against Samsung. A jury in November awarded Apple an additional $290.5 million in damages, bringing the total damages to $930 million.
What did the companies argue this time around?
Apple argued, as it had in the past, that it took on a lot of work and risk to develop the first iPhone and iPad. Samsung, meanwhile, argued that Apple was trying to hurt competition by targeting it for litigation. It also claims that Apple infringed some of its patents. "Without the ability to enforce its intellectual property rights ... Samsung would not be able to sustain the extensive commitment to research and development that has enabled it to lead the way into numerous improvements across a broad range of technologies," the company said in a court document in April 2012.
What patents were involved?
There were seven patents at issue in the latest case -- five held by Apple and two by Samsung. Apple accused Samsung of infringing US patents Nos. 5,946,647; 6,847,959; 7,761,414; 8,046,721; and 8,074,172. All relate to software features, such as quick links for '647, universal search for '959, background syncing for '414, slide-to-unlock for '721, and automatic word correction for '172. Overall, Apple argued that the patents enable ease of use and make a user interface more engaging.
Samsung, meanwhile, had accused Apple of infringing US patents Nos. 6,226,449 and 5,579,239. The '449 patent, which Samsung purchased from Hitachi, involves camera and folder organization functionality. The '239 patent, which Samsung also acquired, covers video transmission functionality, and the Korean company accused Apple's FaceTime of infringing the technology.
What patents were found to be infringed?
The jury found all of Samsung's accused gadgets infringed Apple's '647 "quick links" patent but that none infringed the '959 "universal search" patent or the '414 "background sync" patent. Results were mixed for the '721 "slide to unlock" patent, with some Samsung devices, such as the Galaxy Nexus, found to infringe, and others found not to. Judge Koh, in a pretrial judgement, had already ruled that Samsung infringed the '172 "automatic word correction" patent, and the jury simply calculated damages.
What gadgets were found to infringe?
The Samsung Admire, Galaxy Nexus, Galaxy Note, Galaxy S2, Galaxy S2 Epic 4G Touch, Galaxy S2 Skyrocket, and Stratosphere infringed Apple's '172 patent. Those device -- as well as the Galaxy Note 2, Galaxy S3, and Galaxy Tab 2 (10.1) -- also infringed Apple's '647 patent. The Samsung Admire, Galaxy Nexus, and Stratosphere were found to infringe Apple's 721 patent.
Apple's iPhone 4, iPhone 4S, iPhone 5, iPod Touch (fifth generation, 2012), and iPod Touch (fourth generation, 2011) were found to infringe Samsung's '449 patent.
To see what patents each Samsung device is accused of infringing (denoted by an X), and what patents the jury ultimately decided Samsung did violate (denoted by an asterisked X*), refer to the chart below.
Samsung devices accused by Apple
Outlined below are the Apple devices the jury deemed guilty of patent violation.
Apple devices accused by Samsung
How long did the trial last?
The case kicked off March 31 with jury selection and wrapped up May 5. Court was in session Mondays, Tuesdays, and Fridays throughout the month of April, with the companies granted a total of 52 hours of testimony, three hours of opening arguments, and four hours of closings. The jury started its deliberations late in the day April 29. It reached a verdict at the end of the day May 2, but Judge Koh recalled the jury May 5 to recalculate one of the damages figures.
What did the jury miscalculate?
It had awarded Apple no damages for one version of the Galaxy S2, but Apple believed it should be awarded some money for Samsung's infringement of the '172 patent. The jury had granted Apple $4.02 million for the Galaxy S2 Epic 4G Touch and $5.8 million for the Galaxy S2 Skyrocket. After reconsidering the figures, the jury shuffled around damages awarded to each of the Galaxy S2 models but didn't change the total. The jury foreman, Tom Dunham, said it was a "clerical error."
That's tricky. Both companies were found guilty of infringing some of each other's patents and ordered to pay damages. Ultimately, it wasn't a clear-cut win for either company, but the verdict also wasn't the overwhelming defeat Samsung faced in 2012. By awarding Apple less than 10 percent of the damages it wanted, the jury of mostly tech novices, which deliberated for three full days after a four-week trial, sent a much different message than the prior trial that netted Apple nearly $1 billion. Samsung surely feels relieved by the outcome, though it still was deemed a copycat in some respects. And Apple, which was vindicated in some of its accusations, probably believes Samsung's punishment is too light.
How much money was involved?
The jury ordered Samsung to pay $119.6 million for infringing three of Apple's five patents, much less than the $2.2 billion the iPhone maker had demanded. At the same time, Apple was ordered to pay Samsung $158,400 for infringing one of the Korean company's two patents. Samsung had asked for $6.2 million in damages, and it had argued that if it had infringed all of Apple's patents, it only owed $38.4 million.
While the companies asked for damages, the case was about more than money. What's really at stake is the market for mobile devices. Apple now gets two-thirds of its sales from the iPhone and iPad; South Korea-based Samsung is the world's largest maker of smartphones; and both want to keep dominating the market.
How did the companies react to the verdict?
Apple said Friday, following the verdict:
"Today's ruling reinforces what courts around the world have already found: that Samsung willfully stole our ideas and copied our products. We are fighting to defend the hard work that goes into beloved products like the iPhone, which our employees devote their lives to designing and delivering for our customers."
Samsung said Monday, following the jury recalculation:
"We agree with the jury's decision to reject Apple's grossly exaggerated damages claim. Although we are disappointed by the finding of infringement, we are vindicated that for the second time in the US, Apple has been found to infringe Samsung's patents. It is our long history of innovation and commitment to consumer choice, that has driven us to become the leader in the mobile industry today."
What role did Google play in all of this?
Samsung argued during the trial that most features Apple said infringed were part of Android, Google's mobile operating system that powers Samsung's devices. All patents except one, called "slide to unlock," are built into Android, the Korean company said, and it accused Apple of attacking Android . Apple argued that the patent infringement trial had nothing to do with Android .
It came out during the trial, however, that Google was helping Samsung with its defense for two patents, '414 for background syncing and '959 for universal search. Those patents wielded by Apple directly target features of Android that Google developed, including the Google search box and Gmail. The other patents target features that can be tweaked by handset makers or by the Android open source community.
The jury determined that Samsung had not infringed the '414 and '959 patents but that it did infringe Apple's three other patents.
The jury said Google didn't factor into its decision for infringement or damages, but it believed Apple and Google needed to battle directly instead of involve handset makers such as Samsung.
"I guess if you really feel that Google is something that's the cause behind this, as I think everybody observed, then don't beat around the bush," said jury foreman Tom Dunham, a retired IBM software executive. "The fact is Apple has [intellectual property] they believe in. So does Samsung. So does Google. Let the courts decide, but a more direct approach might be something to think about."
Why doesn't Apple sue Google?
Suing Google wouldn't get Apple far since Google doesn't make its own phones or tablets and gives away its operating system for free. Instead, Apple has sued companies that sell physical devices using Android, a rival to Apple's iOS mobile operating system. In particular, Apple believes Samsung has followed a strategy to copy its products and then undercut Apple's pricing.
For Apple, it's easier to point fingers at the handset makers who generate revenue and profit off of Android phones, rather than Google, which only indirectly generates revenue through mobile advertising and services. It's also easier to display an iPhone next to a Galaxy device and show the similarities and describe how the iPhone predated other rival smartphones. Work had started on Android before the iPhone launched, making it harder to persuade a jury that Google was a copycat.
Overall, the lawsuits are part of a broader effort by Apple to halt the momentum of Android, which has long surpassed iOS as the dominant mobile operating system. Apple isn't just looking for damages; it wants the phones barred from sale. Legal experts say Apple could deal more damage and potentially reap a higher reward going after multiple handset manufacturers than by just striking at Google.
"It is much more effective to sue the device makers as their incremental margin per device is low relative to the benefit that Google gets from having access to your eyeballs," said Chris Marlett, CEO of MDB Capital Group, an investment bank that maintain an intellectual property database. "Ultimately if the device companies can't make a good margin on the phones, they will go out of the phone business. This ends up being a much more effective route to hurting Android."
What witnesses did each side present?
The trial contained testimony by numerous technical and damages experts, as well as people who invented the technology at issue in the case.
The first day of arguments featured testimony by Phil Schiller , Apple's head of marketing. Other witnesses who have testified for Apple include Greg Christie, an Apple engineer who invented the slide-to-unlock iPhone feature; Thomas Deniau, a France-based Apple engineer who helped develop the company's quick link technology; and Justin Denison, chief strategy officer of Samsung Telecommunications America. Denison's testimony came via a deposition video.
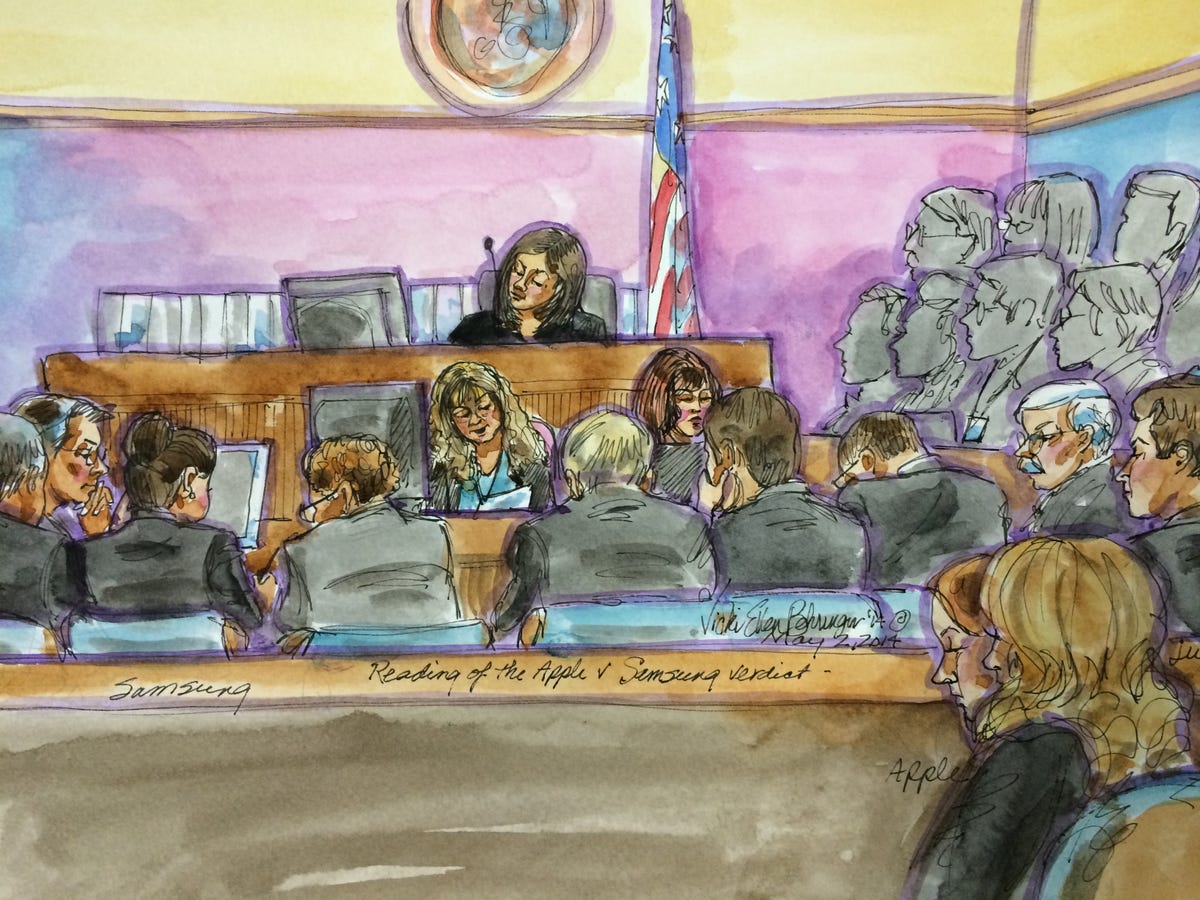

The crux of Apple's case came with two expert witnesses, John Hauser, the Kirin professor of marketing at the MIT Sloan School of Management, and Christopher Vellturo, an economist and principal at consultancy Quantitative Economic Solutions. Hauser conducted a conjoint study that determined Apple's patented features made Samsung's devices more appealing, while Vellturo determined the amount of damages Apple should be due for Samsung's infringement: $2.191 billion.
Samsung, which launched its defense April 11 after Apple rested its case, called several Google engineers to the stand to testify about the early days of Android and technology they created before Apple received its patents. Hiroshi Lockheimer, Google vice president of engineering for Android, said his company never copied iPhone features for Android. Other Google Android engineers, Bjorn Bringert and Dianne Hackborn, also testified about features of the operating system.
High-ranking Samsung executives, including former Samsung Telecommunications America CEO Dale Sohn and STA Chief Marketing Officer Todd Pendleton, also took the stand during the monthlong trial. The two executives testified about Samsung's marketing push for the Galaxy S2 and other devices, saying a shift in the Korean company's sales and marketing efforts -- not copying Apple -- boosted its position in the smartphone market.
The latter half of the trial largely featured experts hired by Samsung to dispute the validity of Apple's patents and to argue that Samsung didn't infringe. David Reibstein, chaired professor of marketing at the University of Pennsylvania's Wharton School of Business, refuted Apple expert Hauser's testimony from earlier in the trial. Judith Chevalier, a professor of economics and finance at the Yale University School of Management who was hired by Samsung, said her analysis determined that a reasonable royalty for Samsung's assumed infringement would be $1.75 per device, or $38.4 million overall . Apple had argued it deserved $40 per device for infringement as well as lost profits for a total of $2.191 billion.
After presenting its defense, Samsung on April 21 launched its own infringement suit against Apple. Dan Schonfeld, a professor of computer science at the University of Illinois at Chicago, testified that Apple infringed the '239 patent in its iPhone through the use of FaceTime and a feature for attaching video to messages and mail. And Ken Parulski, another expert who was part of the Kodak team that developed the world's first color digital camera, testified that Apple infringed another Samsung patent for organizing video and photos in folders.
James Storer, a professor of computer science at Brandeis University hired by Apple as an expert witness, then testified April 22 that Apple didn't infringe Samsung's patents. The company then called witnesses such as Apple engineers Tim Millet and Roberto Garcia to testify about the creation of technology used in iPhones and iPads. Millet serves as senior director of platform architecture at Apple, helping create the processors that power iOS devices. Garcia, meanwhile talked about the creation of the FaceTime technology that had been accused of infringing a Samsung patent.
How did the jury reach its decision?
The jury foreman, Tom Dunham, said the jurors simply looked at the evidence that was presented. While Google popped up time and again, that didn't impact jurors' opinions. They declined to specify which testimony or witnesses swayed their opinions.
What was the most influential evidence for the jury?
The jury said it was most influenced by information that Google was helping Samsung mount and fund its defense.
What does the verdict mean for consumers?
Ultimately for consumers, the verdict means little. It's highly unlikely that US District Court Judge Koh, who has been overseeing the battle in federal court in San Jose, Calif., for the past three years, will issue a sales ban on gadgets from either company. And Apple and Samsung already have workarounds or have changed features in the devices to avoid any more patent violations.
Buyers likely also won't see any difference in device pricing or features. But what they may see are less innovative products if litigation keeps taking attention away from product design and development.
What's next?
Appeals galore. Samsung's lead attorney, John Quinn, already said Samsung will appeal. "In post-trial motions and on appeal, we will ask the judge and the federal circuit to cut the 6 [percent] verdict to 0, which is where it should end," he said. And Apple likely will file appeals of its own. The companies could appeal the case as far as the US Supreme Court.
There also could be fresh suits in the future, particularly since Apple had so much success with its '647 patent. All Samsung devices in the case were found to infringe that patent for automatically detecting data in messages that can be clicked, such as phone numbers.
Corrected last name of MDB Capital Group on May 9.
Mobile Guides
- Best iPhone
- Best Galaxy S24 Deals
- Best iPhone Deals
- Samsung Galaxy S24 Review
- Best Android Phones
- Best Samsung Galaxy Phone
- Pixel 8 Pro Review
- iPhone 15 Pro/Pro Max Review
- Best iPhone 15 Deals
- Best Foldable Phones
- Galaxy Z Fold 5 Review
- OnePlus Open Review
- Best Galaxy Z Flip Deals
- Best Wireless Earbuds
- Best Noise Canceling Headphones
- Best Headphones
- Best Over Ear Headphones
- Best Wireless Earbuds and Headphones for Making Calls
- Best Headphones for Work at Home
- Best Noise Canceling Wireless Earbuds
- Best Sounding Wireless Earbuds
- Best Cheap Wireless Earbuds
- Best Wireless Headphones
- Best iPhone 15 Cases
- Best iPhone 14 Cases
- Best Power Bank for iPhone
- Best Airpods Pro Accessories
- Best Magsafe iPhone Accessories
- Best Speakerphone
- Best Wireless Car Charger and Mount
- Best iPhone Fast Charger
- Best Portable Chargers and Power Banks for Android
- Apple Watch Series 8 vs Series 7
- Best Apple Watch Bands
- Best Android Smartwatch
- Apple Watch Ultra Review
- Best Smartwatch
- Best Prepaid Phone Plans
- Best Cheap Phone Plans
- Best Unlimited Data Plans
- Best Phone Plans
- Best Phone Plan Deals
- Best Senior Phone Plans
- Best Family Phone Plans
- Best Travel Phone Plans
- Best Verizon Plans
Table of Contents
Digital presence of samsung, digital marketing campaigns of samsung , marketing mix of samsung, swot analysis, results of samsung marketing strategy, conclusion , how samsung marketing strategy solidifies its brand value.

The global electronics powerhouse– Samsung began its journey as a low-tier manufacturing brand. A strong Samsung marketing strategy revolutionized its stance in the market, making it the No.1 smartphone producer worldwide. The tech giant ranks 4th in Forbes' list of the World's Largest Tech Companies. A perfect blend of digital marketing and innovation has established Samsung as a unique, high-quality brand worthy of customer loyalty.
Become a Certified Marketing Expert in 8 Months
Samsung's adept use of social currency has contributed to its success in digital marketing. Expanding its social media presence, Samsung provides customers and brand loyalists several chances to share their experiences with those in their circle.

Samsung YouTube Channel
To connect with the various segments of the population their products target, Samsung has social profiles on all of the major social networks, including
- Facebook: 162M
- Twitter: 12.5M
- YouTube: 6.24M
- Instagram: 4.5M
Samsung Facebook Page with 162 Million Likes
Moreover, Samsung has several profiles on each platform. For instance, Instagram has Samsung, Samsung India, Samsung UK, Samsung UA, Samsung Mobile and more.
The company adheres to the best digital marketing practices like SEO and quality content creation that solves customer problems.
Being a community-oriented brand that impacts audiences worldwide, Samsung introduces various marketing campaigns. The promising Samsung marketing strategy focuses on leveraging the power of exceptional marketing campaigns to promote its products and appeal to the audience.
Social media ads, sponsorships, and online advertising strengthened the brand. Some exceptional Samsung marketing campaigns are as follows:
- #YouMake Campaigns: It brings up a global marketing platform for consumers to take the lead with device customization. It brings a better way of personalization via customized control enabled by SmartThings IoT solutions. The #YouMake campaign offers continuous services and virtual benefits, encouraging customer participation by utilizing the best metaverse platforms.
- Growing Up: Another commercial on YouTube that made people reconsider their options. The company directly targeted its main competitor–Apple, and the video took the internet by storm.
Product, Price, Place, and Promotion–the 4Ps of the marketing mix constitute an integrated marketing model. Samsung’s marketing mix plan gives insights into the company’s success secret.
1. Product Mix
Delivering excellent results in recent years, Samsung products are well-known for their services and quick support. Samsung’s marketing mix in its product line is one of its major strong points. The products fall into the following categories:
- Mobile phones
- Televisions – LEDs, Plasma TV, LCDs, SMART TV, HDTV
- Refrigerators
- Air Conditioners
- Washing Machine
- IT – Printers, laptops, and accessories
2. Price Mix
Price mix is one of the strongest points in the Samsung marketing strategy. It offers two pricing schemes to satisfy its clients. The corporation adopts a price skimming tactic whenever it releases a new smartphone with the latest technology. Moreover, it reduces the price of that product when the competitors launch identical products.
3. Promotion Mix
Samsung attracts customers via advertising while employing the best tactics to push products through sales promotions.
The company employs several marketing vehicles both during the festive season and outside of it. It grants numerous discounts and incentives to business partners, encouraging them to sell Samsung products above the competition.
4. Place Mix
Samsung service dealers are responsible for corporate sales. Its selling point is its distribution. They distribute their goods via a single distribution business. They then distribute them to other locations.
SWOT analysis is one of the best ways to dive deeper into the Samsung marketing technique. It provides insights into Samsung’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats concerning its marketing competitiveness.
Samsung’s Strengths
- It has held a strong position in the smartphone manufacturing industry for years. Climbing the ladder, Samsung ranks first on the world’s best smartphone manufacturers list.
- Significant investments in the innovative research and development sector have helped Samsung generate a diverse product offering compared to its competitors.
- Its transition to a customer-centric management system has brought about revolutionary changes.
- Its consistent efforts for sustainable development, such as the adoption of eco-packaging for TVs, give it the upper hand.
- Samsung leads the development of advanced technologies like AI, 5G, automotive and robotics.
- Lastly, it is rapidly expanding commercial marketing in India and China.
Samsung’s Weakness
- Despite expanding its operations in Asia, the company relies heavily on American markets.
- Samsung’s defective items, such as the Samsung Galaxy A20e and a malfunctioning foldable phone.
Samsung’s Opportunities
- Samsung can achieve tremendous development in the smartphone industry by setting the standard with innovative goods like foldable phones.
- As the world adopts 5G, Samsung has the know-how to capitalize on the opportunity.
- The company can hire exceptionally skilled professionals using its brand image.
Samsung’s Threats
- Samsung’s entanglement in controversies can jeopardize its business, such as the lawsuit filed by Apple for patent infringement.
- Xiaomi, Apple, and Huawei stand as major threats and technological competitors who can outsmart Samsung.
Samsung’s revamped marketing programs and competitive strategy implementation have significantly contributed to its huge success over the years.
Performing continuous market research, adding new features, serving customer pain points and employing special efforts to reduce costs, Samsung has paved the way for its success from the very beginning.
Its global value increased by more than 200% in a short span ranging from 2003 to 2008.
Samsung took over Sony–one of the most valuable consumer-electronics brands worldwide. Consequently, Samsung’s sales reached $119 billion by 2009. When the company introduced Samsung Galaxy and leveraged the power of digital platforms for promotions and marketing, its revenue grew to $218 billion in 2018.
Today, Samsung stands 5th on Interbrand’s list of Best Global Brands with a brand value of USD 74.6 billion. It has witnessed a 20% increase in comparison to the last year.
Sparking creativity worldwide, Samsung is the most profitable tech company. The robust Samsung marketing strategy has made it one of the most valuable brands today. Its smart digital marketing tactics set an excellent example of how to revamp your online business as a digital marketer.
Want to know more about Digital Marketing? Enroll on Simplilearn’s Digital Marketing Specialist Program and upskill yourself digitally.
Our Digital Marketing Courses Duration And Fees
Digital Marketing Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Recommended Reads
Digital Marketing Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Digital Marketing Specialist
A Case Study on Netflix Marketing Strategy
12 Powerful Instagram Marketing Strategies To Follow in 2021
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
A Case Study on Apple Marketing Strategy
What is Digital Marketing and How Does It Work?
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Post graduate program in digital marketing.
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Harvard Business School →
- Faculty & Research →
- June 2005 (Revised February 2009)
- HBS Case Collection
Samsung Electronics
- Format: Print
- | Pages: 26
More from the Authors
- Faculty Research
Global Strategic Management
- April 2013 (Revised November 2013)
Microsoft in Korea
The unfairness trap: a key missing factor in the economic theory of discrimination.
- Global Strategic Management By: Jordan I. Siegel
- Microsoft in Korea By: Jordan I. Siegel and Lynn Pyun
- The Unfairness Trap: A Key Missing Factor in the Economic Theory of Discrimination By: Jordan I. Siegel, Naomi Kodama and Hanna Halaburda

Lesson Learned: Samsung vs. Apple (2011) Patent Lawsuit Case Study

Introduction
In 2011, the world watched as two technology giants, Samsung and Apple, engaged in a high-stakes legal battle over patent infringement . The dispute, which centered around similarities between Samsung's Galaxy tablets and Apple's iPad, resulted in a lengthy court battle and significant financial penalties for both companies.
The Samsung vs. Apple case study serves as a cautionary tale for businesses looking to expand into Europe. With global e-commerce on the rise and software companies seeking to expand their reach internationally, it's more important than ever to understand the complexities of global trademark laws and to protect intellectual property when operating in Europe.
In this article, we'll explore the background of the Samsung vs. Apple lawsuit, examine the trademark laws at the heart of the case, and discuss the lessons that businesses can learn from this high-profile dispute.
Background on the Samsung vs. Apple Patent Lawsuit
Facts of the case.
- The Samsung vs. Apple lawsuit began in April 2011 when Apple filed a lawsuit against Samsung, alleging that Samsung's Galaxy tablets infringed on the design of the iPad.
- Specifically, Apple claimed that Samsung's tablets copied the look and feel of the iPad, including the device's rectangular shape, rounded edges, and minimalist design.
- Samsung countered by filing its own lawsuit, accusing Apple of infringing on several of its patents related to wireless technology.
- The legal battle played out in courts around the world, with both companies seeking injunctions against each other and pursuing damages for alleged patent infringement.
- In August 2012, a jury in the United States ruled in favor of Apple, awarding the company $1.05 billion in damages.
- Samsung appealed the decision, and the case continued to work its way through the courts for years.
- Ultimately, Samsung agreed to pay Apple $548 million in damages, though the two companies continued to engage in legal disputes over other patent-related issues.
The Samsung vs. Apple lawsuit was a watershed moment in the tech industry, highlighting the importance of protecting intellectual property in an increasingly global marketplace. As we'll see in the next section, the patent laws at the heart of this case are crucial for businesses looking to operate in Europe.
- Madrid Protocol Trademark Filing Basics
Lessons learned from the Samsung vs. Apple case study
The Samsung vs. Apple patent lawsuit is a prime example of the importance of protecting intellectual property and understanding global trademark laws when doing business in Europe. The following are key lessons that businesses can learn from this case study:
Importance of conducting thorough patent searches before entering a new market
Samsung's failure to conduct a thorough patent search before launching their Galaxy tablet in the European market resulted in the infringement of Apple's design patent. This mistake led to costly legal battles, negative publicity, and loss of revenue. To avoid similar mistakes, businesses should conduct comprehensive research on existing patents and trademarks in the countries they plan to operate in before launching their products.
Need for businesses to have a solid understanding of the intellectual property laws in the countries where they operate
Intellectual property laws vary from country to country, and businesses should be aware of the specific laws and regulations in the countries where they plan to operate. In the Samsung vs. Apple case, the dispute centered around design patents, which are unique to the US legal system. This case underscores the importance of businesses having a solid understanding of the intellectual property laws in the countries where they operate to avoid costly legal battles and protect their intellectual property. Samsung argued that their design was different from Apple's, but the court ruled in Apple's favor, highlighting the importance of understanding local intellectual property laws.
Value of proactive measures, such as patent registration, to protect intellectual property
Patent registration can offer legal protection and prevent competitors from copying a business's intellectual property. This is especially important for businesses that operate in multiple countries, where laws can vary widely. By taking proactive measures to protect their intellectual property, businesses can avoid costly legal battles and protect their reputation. In the Samsung vs. Apple case, Apple was able to successfully argue that Samsung's products infringed on their design patents because Apple had registered those patents with the US Patent and Trademark Office. This highlights the value of proactive measures to protect intellectual property.
Consequences of not protecting intellectual property, including costly legal battles and damage to a company's reputation
The Samsung vs. Apple case study is a prime example of the consequences of not protecting intellectual property. Samsung's failure to conduct a thorough patent search and to register their design led to a lengthy legal battle that damaged the company's reputation and cost them millions of dollars in legal fees and lost revenue. Businesses that fail to protect their intellectual property risk losing their competitive advantage and facing similar consequences.
Patent Laws in Europe
European patent law is regulated by the European Patent Convention (EPC), which was established in 1973. The EPC provides a unified system for the grant of patents in Europe through a centralized European Patent Office (EPO). The EPC is an international treaty ratified by its member states and governs the grant of European patents.
In Europe, patents are territorial, meaning that the protection they offer only applies in the country or countries where they have been granted. However, the European Patent Convention provides a streamlined process for granting patents that can be enforced in multiple European countries.
The process for obtaining a European patent begins with filing an application with the EPO. The application must meet specific requirements, including a detailed description of the invention and its intended use, and must be filed in one of the three official languages of the EPO: English, French, or German. The application is then examined to determine if it meets the requirements for patentability under the EPC.
If the application is successful, the EPO will grant a European patent, which provides protection in the designated European countries. Once granted, the patent owner is responsible for enforcing their patent rights in each country where protection is sought. This can involve litigation in multiple jurisdictions and requires a thorough understanding of the patent laws and procedures in each country.
- International Industrial Design Patent Portfolio
- What Is The Priority Of Patent Application?
Implications for cross-border e-commerce company owners
The lessons learned from the Samsung vs. Apple case study also have important implications for cross-border e-commerce company owners operating in Europe. Here are some key takeaways for these businesses:

Explanation of how the Samsung vs. Apple case study can apply to e-commerce businesses operating in Europe
E-commerce businesses that operate in Europe must comply with local intellectual property laws and regulations. Failure to do so can result in legal consequences and damage to the business's reputation. The Samsung vs. Apple case highlights the importance of protecting intellectual property and understanding local laws, even for businesses that primarily operate online.
Importance of understanding trademark laws and registering patents in order to protect the brand and products
Patent registration can offer legal protection and prevent competitors from using similar names or logos. E-commerce businesses should register their trademarks in all countries where they operate to prevent others from copying their brand and products.
Discussion of potential risks for businesses that fail to take these measures
E-commerce businesses that fail to protect their intellectual property risk facing legal battles, negative publicity, and loss of revenue. These consequences can have a significant impact on a business's success and growth potential. It is essential for e-commerce businesses to take proactive measures to protect their intellectual property and ensure compliance with local laws and regulations.
The Samsung vs. Apple case study provides valuable lessons for businesses operating in Europe. By conducting thorough patent searches, understanding local intellectual property laws, and taking proactive measures to protect their intellectual property, businesses can avoid costly legal battles and protect their reputation. Cross-border e-commerce businesses must also be aware of local laws and regulations and take steps to protect their trademarks and products to avoid potential risks.
Implications for software companies looking to expand internationally
As the world becomes increasingly connected and software plays an even larger role in our daily lives, software companies are looking to expand their reach beyond their domestic markets. However, expanding into new markets requires careful consideration of the intellectual property laws and regulations in the target countries. The Samsung vs. Apple case study can serve as a valuable lesson for software companies looking to expand internationally.
Secure Your Intellectual Property
Firstly, securing intellectual property rights is crucial. This includes patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Software companies should conduct thorough research and analysis to determine whether their intellectual property is eligible for protection in the target country, and then take the necessary steps to secure it. In some cases, companies may need to adapt their products or services to comply with local laws and regulations.
Understand the Legal Landscape
Secondly, understanding the legal landscape in the target country is equally important. Software companies should work with legal professionals who have expertise in the target country's intellectual property laws and regulations. This can help companies navigate the complexities of the legal system, avoid potential legal pitfalls, and protect their intellectual property from infringement. There are companies that specialize in patent infringement analysis , such as Flatfee.com, among others.
Enforcing the Measures
Lastly, failing to take these measures can have serious consequences, including lawsuits and loss of market share. The Samsung vs. Apple case study illustrates the risks of not protecting intellectual property and the importance of taking proactive measures to avoid costly legal battles and reputational damage.
- What Are the Differences between Patents and Trademarks?
- Can I File a Patent in Another Country?
Implications for Intellectual Property Managers and Heads of Legal of international businesses expanding in Europe
For Intellectual Property Managers and Heads of Legal of international businesses expanding in Europe, the Samsung vs. Apple case study highlights the importance of advising clients on the need to protect their intellectual property when entering new markets.
Work With Legal Professionals
Legal professionals should work closely with their clients to develop a comprehensive intellectual property strategy that takes into account the legal and regulatory landscape in the target country. This includes conducting thorough patent searches and patent registration to protect intellectual property from infringement.
Moreover, legal professionals should advise their clients on the potential risks of failing to protect their intellectual property, including costly legal battles and damage to their reputation. By taking proactive measures to protect their intellectual property, businesses can avoid these risks and ensure that they are well-positioned to succeed in the global marketplace.
Protect Intellectual Property
This case serves as a valuable lesson for businesses expanding into Europe. By understanding the importance of protecting their intellectual property, conducting thorough research and analysis, and working with legal professionals who have expertise in the target country's intellectual property laws and regulations, businesses can avoid costly legal battles and reputational damage and position themselves for success in the global marketplace.
Conclusion
The Samsung vs. Apple trademark lawsuit case study highlights the importance of understanding global trademark laws and protecting intellectual property when doing business in Europe.
By examining the background, details, and implications of the case study, businesses can learn valuable lessons about the importance of conducting thorough patent searches before entering a new market, having a solid understanding of intellectual property laws, and patent registration to protect intellectual property.
For cross-border e-commerce company owners, it is crucial to understand trademark laws and register trademarks to protect their brand and products. Failure to do so can result in legal battles and damage to a company's reputation.
Similarly, for software companies looking to expand internationally, it is essential to secure intellectual property rights and understand the legal landscape in the target country. Failure to take these measures can lead to lawsuits and loss of market share.
For Intellectual Property Managers and Heads of Legal of international businesses expanding in Europe, it is critical to advise clients on the need to protect intellectual property and the potential consequences of failing to do so.
Best practices for managing intellectual property in a global marketplace include conducting thorough patent searches, registering trademarks and patents, and understanding the legal landscape in each country where a business operates.
In conclusion, businesses must take proactive steps to protect their intellectual property when operating in Europe. The Samsung vs. Apple case study serves as a valuable lesson, emphasizing the importance of understanding global patent laws and intellectual property rights.
By learning from this case study, businesses can take the necessary measures to protect their intellectual property and avoid costly legal battles and damage to their reputation.
- “Apple and Samsung settle seven-year-long patent fight over copying the iPhone.” https://www.theverge.com/2018/6/27/17510908/apple-samsung-settle-patent-battle-over-copying-iphone
- “Apple Inc. v. Samsung Elecs. Co.” https://casetext.com/case/apple-inc-v-samsung-elecs-co
- “Apple vs. Samsung: the complete timeline.” https://www.theverge.com/apple/2011/11/2/2533472/apple-vs-samsung
- “Apple v. Samsung: The patent trial of the century.” https://www.wsj.com/articles/SB10000872396390443295404577543221814648592
- “Intellectual property.” https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/industry/strategy/intellectual-property_en
- “The European market potential for software development services.” https://www.cbi.eu/market-information/outsourcing-itobpo/software-development-services/market-potential
- “Software intellectual property: What it is and how to protect it.” https://cpl.thalesgroup.com/software-monetization/protecting-software-intellectual-property#:~:text=It%20gives%20the%20owner%20the,elements%20in%20the%20user%20interface .
- “Retaining protection in the UK for EU intellectual property rights.” https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/retaining-protection-in-the-uk-for-eu-intellectual-property-rights
- "The protection of intellectual property." by https://www.eesc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/files/factsheet_-_the_protection_of_intellectual_property_0.pdf
Author’s Bio: Ning Zhang
Obtained Doctor of Law (JD) at Georgetown University. Ning Zhang is an M&A and corporate attorney with 10 years of experience. She has advised clients on complex cross-border transactions in the U.S. and Hong Kong. Notable work includes advising on a licensing deal between U.S. and Chinese pharmaceutical companies. She has worked in multiple global offices, focusing on U.S.-China investments and business operations.

ATTORNEY ADVERTISEMENT: Attorneys advertised on this site are independent attorneys. See the attorney in your area who's responsible for this advertisement. Flatfee is not an “attorney referral service” or a law firm. The information you provide to Flatfee is not protected by attorney-client privilege.
- web_stories Remote Operations
- volunteer_activism Services
- shopping_cart 0 Cart
- SMB Technology
- Mobile Productivity
- Mobile Security
- Computing & Monitors
- Memory & Storage
- Digital Signage
- Trending Tech
- Hospitality
- Manufacturing
- Transportation
- Food & Beverage
- Live Events & Sports
- Spectaculars & DOOH
- Gaming & Esports
- White Papers
- Infographics
- Assessments & Calculators
Case Studies
- About Samsung Insights
- Our Experts
Subscribe to Insights
Get the latest insights from Samsung delivered right to your inbox.
See our Privacy Policy
Samsung Business Insights
All Case Studies

Houston Astros up the score at Minute Maid Park with state-of-the-art Samsung displays
The Houston Astros recently upgraded with a state-of-the-art Samsung LED scoreboard and video displays at Minute Maid Park to enhance fan experience and engagement.

Millard Public Schools level up their technology game with Samsung digital displays
At Millard Public Schools in Omaha, Nebraska, Samsung displays with ScorevisionLE (SVLE) software amplify the middle school experience, in both competitive programming and fan engagement.

The Wall powers collaborative design at Lucid Motors
While reviewing new designs, the design team at Lucid Motors benefits from the high-definition image quality and color resolution on Samsung’s The Wall.

Hilton Waikiki Beach welcomes and wows guests with The Wall
Located above the main lobby bar, Samsung’s The Wall in the Hilton Waikiki enhances the experience for both guests and locals. Hospitality TVs in guest rooms and other Samsung displays throughout the property elevate the property.

Buona Beef selects Samsung Kiosk for its digital transformation
Buona Beef, a renowned Chicago brand, added Samsung Kiosks to their locations to increase sales and efficiency of service.

West Sayville Fire Department leads the way with interactive displays
Samsung digital signage throughout the West Sayville Fire Department improves operations, communications, and productivity for all its members.

Miami high school’s connected campus elevates education and engagement
College preparatory Christopher Columbus High School recently outfitted their campus with Samsung display technology to create a connected campus. Interactive whiteboards in the classroom promote effective, collaborative learning, while digital signage throughout the campus streamline communication for all.

The Wall brings digital excellence to Syracuse University
The S.I. Newhouse School of Public Communications at Syracuse University installed Samsung's The Wall to provide a wow factor to current and prospective students.

Stevens Institute of Technology gets on board with interactive boards
Stevens Institute of Technology in Hoboken, NJ uses Samsung interactive whiteboards throughout classrooms and meeting rooms for hybrid classrooms and in-person collaboration.

The Wall brings design at the Hyundai America Technical Center to life
The Wall's MicroLED technology gives designers at Hyundai America Technical Center true to life renditions of their design.
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, samsung electronics: analyzing qualitative complaint data.
Publication date: 20 January 2017
Teaching notes
“Samsung Electronics had experienced a series of quality-related problems, including the recall of one of its LCD TV models. Unfortunately for quality director Kevin Sarni, there was no single root cause behind these problems: Samsung's supply chain management, product design, and testing/quality assurance functions all played a role.
Sarni regularly worked with quantitative data from Samsung's customer complaint database, but recently he had been shown comments about Samsung products posted on the website ConsumerAffairs.com . The number and emotional tone of the website postings concerned him; he worried these kinds of complaints might touch off a social media—fueled public relations firestorm that would make his job more difficult.
He wanted to analyze this feedback, but had no experience with qualitative data. An internal Six Sigma Black Belt consultant suggested he start by creating an affinity diagram and use that to create a Pareto chart to determine which issues to address first. Once Sarni completed the unfamiliar diagrams he had still another task ahead of him: examining the results to see if they justified taking short—term action to address the quality problems raised in the complaints.”
Organize and analyze qualitative data using affinity diagrams
Identify priorities using Pareto charts
The case reinforces the importance of approaching problem solving in a methodical and data-driven manner and demonstrates the power of visual (vs. table-driven) tools.
- Business Process Improvement
- Crisis Management
- Customer Relationship Management
- Customer Service
- Manufacturing
- Operations Management
- Organizational Effectiveness
- Total Quality
- Customer Satisfaction
Boepple, J. (2017), "Samsung Electronics: Analyzing Qualitative Complaint Data", . https://doi.org/10.1108/case.kellogg.2016.000291
Kellogg School of Management
Copyright © 2013, The Kellogg School of Management at Northwestern University
You do not currently have access to these teaching notes. Teaching notes are available for teaching faculty at subscribing institutions. Teaching notes accompany case studies with suggested learning objectives, classroom methods and potential assignment questions. They support dynamic classroom discussion to help develop student's analytical skills.
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

- Pre-Recorded Courses
- Free SEO Tools

Samsung’s Digital Marketing Strategies: Detailed Case Study
- February 4, 2023

Table of Contents
Before we look into Samsung’s digital marketing strategies, A recent study revealed that Samsung is all set to lead the worldwide smartphone market in 2022 with yearly shipments of 272 million devices. 272 MILLION! Samsung inculcated innovation each step of the way and used smart branding to position itself in the market. Wondering how it happened?
One of the ways Samsung is so innovative – with multiple product announcements one after the other – is that it is substantially involved in its employees; it seeks out special talent wherever it can find it and has looked at digital marketing as a major opportunity to brand all their existing and new products.
Let’s find out how they used digital platforms to increase awareness and maintain their brand image.
About Samsung
Back in 1970, Samsung’s electronics division began by producing low-cost TV sets under the Sanyo brand, but through time, it evolved into an innovative firm that has been a pioneer in manufacturing huge flat-screen displays, plasma TVs, and cutting-edge smartphones.
However, until the mid-1990s, they competed mostly by developing technical components and low-cost manufactured goods for larger brands such as Dell, Hewlett Packard, and General Electric . They were also selling other low-cost consumer products under the Samsung brand, including TVs and microwave ovens, through cheap retailers such as Walmart.
The low-cost-driven competitive strategy served them well until the Asian market meltdown in 1997. At the time, the market for memory chips and other components provided by Samsung to electronics manufacturers was experiencing greater competition, resulting in surplus capacity, while sales of Samsung branded products were also declining.
Despite these facts, the company’s CEO, Yun Jong-Yong , stated that Samsung could make goods that were as good as Sony’s, but because of the brand’s low-end image, their TVs would be relegated to the rear of stores.
Why Should Marketers Study Samsung’s Digital Marketing Strategies ?
Samsung has managed to gain the market share (and love) of millions of people around the world. Samsung’s key principles include “people, excellence, change, honesty, and co-prosperity.” Samsung has a very rich culture in all of its facilities across the world, with similar and comparable practices. This is due to the fact that they all operate under the same values as previously discussed. Their marketing strategies played a huge role in boosting their sales and gaining recognition online.
The ‘adventurous’ branding
The goal of brand films is to introduce your audience to your values, visions, and, ultimately, the heart of your brand. Visuals, music, and stories may help you communicate your brand in ways that no other media can.
Remembering the outdoor-focused ad campaigns for a long time, Samsung has been side-reflecting an adventurous concept as a brand image for a long time. In their 2013 marketing film, shown below, we witness 18 risky places in Scandinavia filmed at -31 degrees Celsius with helicopter shots, husky dog sledges, and snowmobiles. Samsung is using the film to market their new Heat Pump, N-Series, specifically for Scandinavia, but it has also been exhibited at exhibits and trade events across the world.
Out-of-the-Box Marketing
We are all aware that Samsung’s product price strategy is neither A-class or competitive in general. That is where the brand must establish other auxiliary activities in order to make their products and service their technologies in an engaging way. So, basically, they need to think outside the box.
This was their “TV when it’s on. Art when its off” campaign
Above, Samsung’s “Galleried” spot makes picture frames cool again. Regardless of the quality of the artworks, Samsung’s problem is with picture frames – and their enigma. During a day at the museum, art lovers are astounded to see how the valuable artworks inside the frames mysteriously vanish. A swarm of anxious people stare at empty frames where paintings formerly hung. The employees are concerned, but there is an explanation: TV When it’s turned on. When the Lights Go Out.
Clever, funny, strategic: Apple vs Samsung
Before the iPhone X’s release date, Samsung released a new commercial that is totally aimed at criticising Apple. Samsung always comes up with innovative ways to mock apple, but this time, it elevated its concept to a different level. ‘Growing Up,’ created by Wieden + Kennedy Portland, relates to everything from storage space to water resistance — and, of course, the never-ending line-ups, which is the funniest part.
The commercial began in 2007, with the launching of the first-generation iPhone. Erik, the hero, of course, purchases the goods, while his girlfriend Lauren owns a Samsung by 2013. Eric began to experience storage troubles even when using an older version of iOS.
Then, in 2013, when the screen sizes and water resistance are compared, the results are disgraceful. He hence shifts to Samsung, and according to the commercial, he finally “grows up”
Samsung’s digital marketing strategies
Samsung’s marketing communication mix includes a variety of channels such as print and media advertising, sales promotion, events and experiences, and public relations. Samsung Electronics employs these channels in an integrated fashion. We have discussed the digital aspect of their marketing strategies below.
Samsung’s social media marketing strategies
They are continuously working to maintain their popularity, and they must work really hard in order to do so. When it comes to social media marketing, they use Instagram, Facebook and YouTube to help them in generating good earnings as well as making a big influence on users and followers.
Samsung’s Instagram marketing strategies
Samsung India’s Instagram page (@ samsungindia ) has an engagement rate of 0.05% with an average of 2,137 likes and 15 comments on each post.

Samsung uses Instagram as a way to communicate with its audience and establish a one-on-one relationships. Most of their posts are product-based, talking about the various features of the particular product.
#WeOwnTheNight
Off late, Samsung has posted a series of posts highlighting the
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Samsung India (@samsungindia)
Samsung’s Facebook marketing strategies
When you access Samsung’s Facebook page, you will discover that it has over 16 million fans and that its cover image clearly indicates the latest planned Samsung announcements or products.

Scrolling down will take you to the posts that Samsung has published on this fan page. No one is permitted to post on Samsung’s Facebook page. Customers, on the other hand, can comment on their blogs and provide feedback.
They post on a regular basis and typically receive a large number of comments on each of their postings.

Samsung’s Twitter marketing strategies
Samsung not only rules through its Facebook page, but it also has a sizable fan base on Twitter. The frequency of posts on this site is extremely high.

The engagement rate of Twitter is 0.10% and they receive an average of 12,077 likes and 3,472 retweets on each of their posts.

Samsung’s SEO strategies
Samsung Customer Care Department has evolved naturally in SEO, and it now has a small but powerful in-house staff overseeing SEO, SEM, and content. Because the SEO team is in charge of the internal search platform, its major purpose is to translate what consumers search for into genuine meaning and intent.
Their constant SEO efforts have ensured that they get a steady increase in their website rankings and keywords. They receive a YOY increase in organic traffic of 4% . Their keyword ranking position, too, has increased by 12% YOY .
Let’s study their SEO strategies in detail
Website overview
With a worldwide brand in such a competitive field, Samsung has taken a broad view of the entire customer journey across several departments, from mobile devices to home appliances, to achieve the greatest potential improvement in online performance.
They have been more effective at improving ranks and generating sales by taking a step back to study user behaviour and purpose and then optimising on-site SEO.
Samsung has an almost perfect website with a high domain authority of 93 . The rest of their statistics too are extremely high and rated ‘amazing’ by Ubersuggest.
They have over 6,666,167 organic keywords , 102,927,027 organic monthly traffic and 96,177,850 backlinks .

www.samsung.com
The top 5 organic keywords include
- Samsung
- Samsung galaxy s21 ultra
- Samsung galaxy
- Samsung galaxy s9

Samsung’s Top Digital Marketing Campaigns
#indiareadyaction.
Samsung India launched #IndiaReadyAction, a statewide digital campaign encouraging Gen Z and millennials to defy prejudices about India by filming and sharing films of Real India via their smartphones. The month-long campaign #IndiaReadyAction will encourage Gen Z and young millennials in India to contribute up to 60-second movies showcasing their vision of Real India, which will break any prejudices about the country that may exist around the globe.
The campaign was launched through a video :
Sports partnerships
Samsung sponsored the Olympic Winter Games in 1998 and will formally support Olympic Games and Olympic movements for the following eight years, which will only help Samsung’s global reputation. From 1998 through 2010, Samsung was the official sponsor of the telecommunications equipment category.
Sponsors of the English Premier League club Chelsea FC, the Premier League is well-known around the world and draws a large number of fans from all around the world. In 2008, Samsung also inked a six-year collaboration agreement with Mexican football team Club Deportivo Guadalajara, providing plasma and LCD screens for the team’s new stadium Estadio Chivas, indirectly promoting the brand.
They continued to sponsor different sports teams around the world in the following decades. In India, they have brand ambassadors for every product category.
Aamir Khan is the brand ambassador for mobile phones, Priyanka Chopra is the brand ambassador for home appliances, and Olympic Gold Medalist Abhinav Bindra is the brand ambassador for consumer electronics.

Aamir Khan has appeared in a number of commercials, including Next Is What, Wave, and the Galaxy series. He is renowned in the industry as Mr Perfect, and they are exploiting this to demonstrate that their mobile phones are perfect. Also, because Samsung is an Olympic sponsor, the image of Abhinav Bindra, the first Indian individual gold medalist, was used.
Another campaign that illustrates Samsung’s usage of social and online communities to sell new goods is #OverToYou.
Samsung provided 12 notable bloggers, athletes, and YouTubers with Galaxy S4s so they could produce content and share it with their audience.
These 12 people were exhibiting the potential of the new technology by utilising the S4 to create a unique, thrilling video. The videos were obviously shareable, giving Samsung some extra visibility outside of its typical marketing platforms.

Digital line
Another ad aimed at Apple fanboys, this time by generating a digital queue in anticipation of the Galaxy S4’s introduction in New Zealand.
Samsung’s own followers may join the queue online 12 days before the phone was released by posting details of the S4’s new features as they were revealed each day on their Facebook or Twitter accounts.
The more their friends retweeted, commented on, “loved,” and shared the content, the higher they climbed the queue. It’s simply highly incentivized word-of-mouth marketing that also pokes fun at the company’s main competitor.
Conclusion
As can be seen, Samsung has joined the realm of online marketing to promote its products and brand. Do you wish to develop your own strategy?
Do you wish to raise the profile of your company? Enrolling in digital marketing courses online is the right solution.
Enrol in Digital Scholar’s online digital marketing course to strengthen the digital marketing techniques of your company. This course is designed for anyone who wants to learn everything they can about digital marketing and how to use it in their own business. To discover more about them, go to www.digitalscholar.in
What do you find most appealing about Samsung’s campaigns? Please share your thoughts in the comments section below!
Written By Digital Scholar
Digital Scholar is a premier agency-styled digital marketing institute in India. Which offers an online digital marketing course and a free digital marketing course worldwide to elevate their digital skills and become industry experts. Digital Scholar is headed by Sorav Jain and co-founder Rishi Jain, who are pioneers in the field of digital marketing. Digital Scholar’s blogs touch upon numerous aspects of digital marketing and help you get intensive ideas of different domains of digital marketing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts

Facebook vs Instagram: Which Is Better To Invest Money in 2024

SEO KPIs to Track: 9 Critical SEO Metrics in 2024

10 Best SEO Competitor Analysis Tools To Improve Your Traffic in 2024 [Free & Paid]

What are 404 Errors: Impact on SEO Ranking and How to Fix?
Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study
Introduction, conclusions.
In August 2016, several Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Smartphones were reported to explode. The manufacturer called upon its engineers hurriedly to diagnose the source of the problem. The initial report pointed to a fault in batteries procured from one of the suppliers. This led to a recall of these smartphones and continued shipping of the same mobile device with batteries from a different supplier [1]. However, the issue surfaced again with reports of the new replacements also exploding, prompting the company to halt the entire Samsung Galaxy Note 7 production. The failure, subsequent recall, and the complete halt of the Galaxy Note 7 production have had social and legal ramifications.
This Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Failure case study aims to analyze the issue, its history, and the aftermath, including the crisis management and the discovered reasons behind the battery explosion.
Smartphones have very advanced computing capabilities, such as high-definition cameras, media players, sensors, GPS navigation units, accelerometers, and gyroscopes, among other features. For most Smartphones, an Android operating system is used. The features need to be supported by stable memory, batteries with the correct power output, an efficient power system, and a good shell to operate efficiently. The risk of failure of Smartphones is mainly in the memory access violation and mobile phone hardware such as the batteries and the shell [2]. Overall, studies on the failure of Smartphones have pointed to two major types of failures, i.e., accidental or malfunction of the software or Android. For this report, the focus is on the hardware or software malfunction.
Samsung Galaxy Note 7 Failure
The explosion of the Samsung Galaxy Note 7 resulted in the recall of the phones [1]. The phones that were overheating were analyzed to establish the causes of the explosion. The techniques employed for the analysis were Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA). This entails a critical analysis of the entire lifecycle of a product. It analyzes the specifications of the design, operation, and maintenance by establishing the system functions, identification of the failure modes in the system, and functions which then determine the effects and possible causes [3]. The analysis covers both the software and hardware functionalities.
The FMEA is used by engineers in the design stages of a product or post-analysis in the case of issues arising. The initial FMEA conducted after the failure was hardware FMEA. This is a straightforward analysis guided by the understanding that mechanical, electronic, and electrical failures happen due to some issues, such as unanticipated stress, overload, and faulty wiring. The analysis by the engineers concluded that lithium-ion batteries from one of the suppliers had a fault. Part of the battery’s inside was coiled incorrectly, causing stress to the battery.
By performing critical risk analysis, the possible malfunction of software or hardware can be established before the product is launched into the market. The critical failure modes can be ascertained by calculating the Risk Priority Numbers (RPN) through brainstorming [2]. This helps to establish the potential areas of failure and the possible degree of damage. As a result, mitigation measures are taken before the product is released to ensure that the risk is contained.
It is thus paramount that Samsung should have carried out a thorough risk analysis for all the hardware and software from the suppliers before launching the product. Also, after the recall, the analysis was hurriedly carried out; hence, the conclusion that the failure was from a battery procured from a particular manufacturer was theorized rather than being scientifically proven with quantifiable data.
Discussion on Samsung Note 7 Failure
The failure of Samsung’s Galaxy Note 7 has had enormous financial implications. It is estimated that it may lead to a revenue loss of over $ 5 billion. Even though the company could easily deal with the loss of income, the failure has great social and legal ramifications. For instance, the failure has already attracted class-action lawsuits against the company, which touch on how the recall and replacement were carried out.
Also, there is a high likelihood of lawsuits that relate to the damages and injuries caused by the explosions. These lawsuits will affect the consumer perception of Samsung’s Smartphones. For example, the Google search for ‘Samsung Explosion’ spiked in August and September despite the recall being only for Galaxy Note 7. The failure has also had social implications for Samsung phone users. Some airlines in the U.S. do not allow passengers to use any Samsung phone onboard their planes.
The failure of any product leads to unintended consequences for the manufacturer and the consumers. Even though investigations are still ongoing to establish the exact cause of the Samsung Note 7 explosions, Samsung’s engineers need to give more care to the materials used to develop the software and hardware of its Smartphones. Also, there should be a critical risk analysis in which an RPN for each possible failure mode is calculated before a product is released to the market. This will ensure that parameters with high-risk factors are properly investigated, and risk reduction measures are taken in advance.
- B. Chen and C. Sang-Hun, “Why Samsung Abandoned Its Galaxy Note 7 Flagship Phone”, The New YorK Times, 2016.
- K. Krishnakanth and P. Kavipriya, “Android application development for environment monitoring using Smartphones”, International journal of Mobile Network Communications & Telematics, vol . 3, no. 3, pp. 41-45, 2013.
- S. Malek, R. Roshandel, D. Kilgore and I. Elhag, “Improving the reliability of mobile software systems through continuous analysis and proactive reconfiguration,” Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Software Engineering-Companion Volume. ICSE-Companion 2009. Vancouver, BC, Canada, pp. 275-278, 2009.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, October 9). Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/
"Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." IvyPanda , 9 Oct. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study'. 9 October.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." October 9, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
1. IvyPanda . "Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." October 9, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Samsung Note 7 Failure Case Study." October 9, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/failure-analysis-samsung-galaxy-note-7/.
- Exploding of Samsung Galaxy Note 7: A Case Study
- Samsung Galaxy SIII Product Features
- Benchmarking Description on Apple iphone 4s vs. BlackBerry, Android and Samsung Galaxy
- Short Message Service (Center) Technologies
- Outcomes of the Phone Usage While Driving
- Steering Wheel and Smartphone: A Deadly Combination
- International Students and Mobile Services in Australia
- Wireless Communication and the Trends in This Industry
Samsung Galaxy A15 5G review: Best Android phone under $200
If you buy through a BGR link, we may earn an affiliate commission, helping support our expert product labs.
Samsung Galaxy A15 5G
The Samsung Galaxy A15 5G isn’t perfect, but it is cheap, and ultimately, makes a serious case for itself at $200 or less.
Great battery life
- Nice-looking display
- Long updates roadmap
- Inexpensive
Plastic build
- Camera is only fine
Samsung is arguably the most important manufacturer of Android phones, building some of the most powerful and most desirable models out there. But the company also happens to make some of the best phones for the money — largely through the Galaxy A series . Currently, the cheapest model in the Galaxy A series is the Samsung Galaxy A15 5G (not to be confused with the previous-generation, non-5G mode).
Samsung Galaxy A15 5G specs
What i liked, solid display.
Samsung is known for building excellent displays into its phones, and despite being one of Samsung’s cheapest phones, the Galaxy A15 5G does indeed have a nice-looking screen for the price. The 6.5-inch display is a Super AMOLED screen , and it has a 1080p resolution — but more importantly, it has a 90Hz refresh rate. It’s not as fast as most higher-end phones with a 120Hz screen, but it still feels relatively fluid and responsive.

The screen gets quite bright, too. It easily gets bright enough for use even in direct sunlight, and most of the time, you probably won’t crank it up to full brightness.
Tech. Entertainment. Science. Your inbox.
Sign up for the most interesting tech & entertainment news out there.
By signing up, I agree to the Terms of Use and have reviewed the Privacy Notice.
Is this the highest-end screen out there? No, but it sure could be for $200 or less.
The phone has a 5,000mAh battery, and that relatively large battery is able to deliver an excellent battery life. In fact, I found the device was easily able to last a full day of use, and well into a second day, even with relatively heavy use. Of course, if you game for hours on end or something, you may find that you have to charge before the end of the day. But the majority of people will easily get a day of use from the Galaxy A15 5G.

Excellent update promises
The Galaxy A15 5G comes with Android 14, with Samsung’s One UI 6.0 over the top. The software itself is fine — One UI has never been my favorite, however those that like it will find it to work just the same on this phone as on any other Samsung device.
Performance is good for the price
Under the hood, the Samsung Galaxy A15 5G is powered by a MediaTek Dimensity 6100+, coupled with between 4GB and 8GB of RAM. The phone’s performance doesn’t really compare with more expensive phones, but it’s not bad for the price.
What I didn’t like
Camera could be better.

The camera on the Galaxy A15 5G isn’t bad, but it certainly could be better. The phone comes with a triple camera array, made up of a 50-megapixel main camera, a 5-megapixel ultrawide camera, and a 2-megapixel macro camera.
The ultrawide camera is fine, but really nothing to write home about. Edges are pretty distorted, and the colors are a little washed out.
The overall design of the Samsung Galaxy A15 5G isn’t bad — it has an edge-to-edge display, with a relatively minimalistic look. And, I like the blue color on the model I’m reviewing.

However, the build quality leaves a little to be desired. To be clear, it’s not terrible — but it’s not the most premium-feeling device and much of that comes down to the largely plastic body.
Conclusions
The competition.
In the $200 price range, there aren’t a ton of great alternatives to the Samsung Galaxy A15 5G, and ultimately, the Galaxy A15 5G is the way to go for most people. However, if you’re looking for a longer battery life and slightly better performance, it may be worth going for a device like the Motorola Moto G Power instead.
Should I buy the Samsung Galaxy A15 5G?
This article talks about:.
Christian de Looper is based in sunny Santa Cruz, California. He has been expertly reviewing tech products for more than 8 years, and brings experience in deep technical analysis of consumer electronics devices to BGR's reviews channel.
- Google Pixel 8a review: A better buy than the pricier Pixel 8
- Infinix Note 40 Pro+ review: Note quite there
More Reviews

Ecovacs DEEBOT T30S Combo Review

Narwal Freo X Ultra review: 6 things I love, and 2 big problems

XGIMI HORIZON Ultra 4K projector review: The home-sized movie theater I always wanted

Samsung Galaxy Tab A9+ review: Cutting the right corners
Latest news.

Prepare to drop $22,000 off your paycheck if you want to stay working hybrid

The ultra-thin iPhone 17 Slim may turn out to be a bigger deal than we all think

tvOS 18: Release date, features, Apple TV compatibility, more

Leak claims iPhone 16 Pro Max will once again have exclusive camera features
Sign up for the most interesting tech & entertainment news out there.
- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- Partner Content
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
- Pro Kabaddi League
Study on Covaxin should revise statement on conclusions for clarity
It likely overstates actual risks associated with the vaccine and conflates common illnesses with vaccine-related adverse effects.
)
Dr. Meenu Singh and Dr. Indar Sherawat
AstraZeneca admits its Covishield vaccine may lead to rare side effect
Astrazeneca admits covishield has rare side effect: is concern warranted, after covishield, new study 'finds' side effects in covaxin recipients, covaxin has 'excellent record', says bharat biotech after study cites risks, why covishield vaccine case doesn't qualify for medical negligence in india, india must create 115 mn jobs by 2030 as more people enter workforce: study, india-eu fta: will the marriage reconcile, fiscal prudent odisha faces many challenges on socioeconomic front, intellectual property and competition law: two sides of the same coin, dmrc vs damepl: sc broadens scope of court intervention in arbitral awards.
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: May 21 2024 | 3:55 PM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Tata Power Share Price
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- Budget 2024 Lok Sabha Election 2024 IPL 2024 Pro Kabaddi League IPL Points Table 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In conclusion, Samsung is a huge and a powerful empire that covers many sectors. ... Purpose/Research questionThe paper provides an empirical research of the Samsung case. In particular, we study ...
The Samsung crisis management case study highlights the importance of swift and transparent communication, customer-centric actions, and continuous improvement in product safety and quality. By effectively addressing the crisis, Samsung was able to navigate the challenging situation and rebuild its brand, reaffirming its position as a leading ...
Let's start the detailed case study from here. Samsung entered the electronics industry in the late 1960s and the development and shipbuilding ventures in the mid-1970. Following Lee's demise in 1987, Samsung was divided into five business groups - Samsung Group, Shinsegae Group, CJ Group, Hansol Group and Joongang Group.
Other generic competitive strategies, such as cost leadership, differentiation focus, and cost focus, are also applied in Samsung's operations, but to a limited extent. Cost focus leads to the company's being the best-cost provider in some segments of the semiconductor and electronic components markets. The limited application of cost focus ...
This case study describes how Samsung Electronics transformed into a world-class company and the strategic challenges it faces as it looks to sustain its success in both developed and emerging markets. It has been 20 years since Lee Kun-Hee announced the New Management initiative that played a crucial role in transforming Samsung from a second-tier
by. Tarun Khanna, Jaeyong Song, and. Kyungmook Lee. From the Magazine (July-August 2011) Summary. Twenty years ago, few people would have predicted that Samsung could become a world leader in R ...
Case Study: Samsung's Innovation Strategy. June 16, 2011 Abey Francis. The success of Samsung has been widely acknowledged in the last decade. Samsung, the world's largest television producer and second largest mobile phone manufacturer, is also the largest firm of flash memory maker. Furthermore, Samsung was ranked by Fast Company Magazine ...
A nine-person jury sided with Apple on a majority of its patent infringement claims against Samsung. It a warded Apple $1.05 billion in damages, much less than the $2.75 billion sought by the ...
Executive Summary This study evaluates the corporate strategy of Samsung Electronics, a multinational company, with operations in 80 counties, and a global market leader in several business ...
Consequently, Samsung's sales reached $119 billion by 2009. When the company introduced Samsung Galaxy and leveraged the power of digital platforms for promotions and marketing, its revenue grew to $218 billion in 2018. Today, Samsung stands 5th on Interbrand's list of Best Global Brands with a brand value of USD 74.6 billion.
In this case, students assess whether Samsung Electronics has been able to achieve such a dual advantage, and if so, how this was possible. Moreover, Samsung Electronics' long-held competitive advantage is under renewed attack. Students also can assess how Samsung should respond to large-scale Chinese entry into its industry.
Facts of the Case. The Samsung vs. Apple lawsuit began in April 2011 when Apple filed a lawsuit against Samsung, alleging that Samsung's Galaxy tablets infringed on the design of the iPad. Specifically, Apple claimed that Samsung's tablets copied the look and feel of the iPad, including the device's rectangular shape, rounded edges, and ...
The Wall brings design at the Hyundai America Technical Center to life. 1-10 of 105 Results. 1 2 3 … 11. In-depth case studies of Samsung business technology deployments.
For two days in late May 2012, Apple CEO Tim Cook and Samsung CEO Gee-Sung Choi met with a judge in the U.S. District Court of Northern California in an attempt to reach a settlement in a high-profile U.S. patent case, a sobering example of negotiation in business.
The case study provides detailed information on how Samsung implemented Six Sigma and its positive impact on the company's operations and business performance. Read this report to gain insights into how Six Sigma can be effectively used to improve a company's supply chain. We will write a custom essay on your topic. 809 writers online.
After analyzing the case, students should be able to: Organize and analyze qualitative data using affinity diagrams. Identify priorities using Pareto charts. The case reinforces the importance of approaching problem solving in a methodical and data-driven manner and demonstrates the power of visual (vs. table-driven) tools.
The main vision of Samsung is to inspire the world with their innovative technologies, the wide. range of innovative products and the state- of -the-art designs that are meant to make the lives ...
The purpose of this paper is to present a case study of Apple v. Samsung. The case study is offered in a different light, in which the application and understanding of big data analytics is hypothetically applied. A comprehensive review of existing research on the case will be included in the proceeding sections.
Digital line. Conclusion. Before we look into Samsung's digital marketing strategies, A recent study revealed that Samsung is all set to lead the worldwide smartphone market in 2022 with yearly shipments of 272 million devices. 272 MILLION! Samsung inculcated innovation each step of the way and used smart branding to position itself in the ...
Case law also plays a crucial role in shaping the legal landscape for businesses and innovators. Landmark cases, such as Apple Inc. v. Samsung Electronics Co., highlight the complexities of IP law ...
Discussion on Samsung Note 7 Failure. The failure of Samsung's Galaxy Note 7 has had enormous financial implications. It is estimated that it may lead to a revenue loss of over $ 5 billion. Even though the company could easily deal with the loss of income, the failure has great social and legal ramifications.
9/13/2016. 100% (7) View full document. Conclusion Samsung is the main brand for mobile phones with its high-end specifications. The users are average consumers and companies. The main competitor is Apple; however Samsung gives the competitive attention through mobile features. Many customers are loyal to Samsung mobile phones and will continue ...
UX case studies must be kept short, and, when considering the length of your beginning, process and conclusion sections, it's the beginning and the conclusion sections that should be the shortest of all. In some case studies, you can keep the ending to two or three short phrases. Other, longer case studies about more complex projects may ...
The business covers electronics, finance, machinery, and chemistry (Samsung, 2019). The Samsung Group was founded in 1938 by Lee Byung-Chull (Samsung, 2019). Each of its Samsung industries is a family business and is managed by other members of the family. In the early 1990s, Lee Byung-Chull was dissatisfied with the company's product quality ...
This study investigates potential financing and management strategies that the Energy Corporation, a Chinese renewable energy company, could adopt in order to expand its green development projects. While China has made significant advancements in renewable energy, its heavy reliance on fossil fuels necessitates a shift towards a more sustainable energy system. To analyze the factors driving ...
Introduction In this digital era, access to premium content on platforms like YouTube has become increasingly popular. With the release of YouTube Premium APK 19.20.33, users now have the opportunity to enjoy an ad-free experience and unlocked premium features. This article serves as your comprehens...
Conclusions. The Samsung Galaxy A15 5G is a great phone for the price. It offers solid performance, a great display, and a promise of years of software updates. It's far from perfect, and if you ...
It was also found that product quality contributed 51.6% to purchasing decisions while 48.4% was determined by other variables not included in this study. Prices of Samsung Products Offered in ...
The case is the only one of Trump's four indictments expected to come to trial and a conclusion before Election Day, even if the charges of falsifying financial records related to a hush-money payment made to a porn actor do not match the gravity of the indictments accusing Trump of trying to thwart the peaceful transfer of power in 2020 ...
The conclusions of the study by Kaur and colleagues, 2024 seem to be superfluous and likely to raise undue concern among the general public. The absence of a control group as one of the major shortcomings of the study by Kaur and colleagues. ... Hence, in this case, the authors should have been more cautious in using the term causality and ...