Published In: Brief

How to Write a Biography (Examples & Templates)
A biography is a written account of a person’s life that details their life in chronological order. Another person usually writes this detailed account, and it contains reports of their childhood, career, major life events, relationships, and social impact. It also details their relationships with their family, children, and life accomplishments.
The best way to find out more about a popular figure is through reading their biographies, so you need to make sure you get the correct information. Before writing a biography, you need to do a lot of research and interviews to represent a person’s life accurately.
Types of Biography
A biography is the story of someone’s life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest.
A biography aims to share a person’s story or highlight a part of their life.
There are different types of biographies, depending on the story. Some biographies are written true to the story, while some are written as fictional works. Biographies can give you true understanding of a person on an internal as well as external level along with a lot of life lessons.
Autobiography
An autobiography is different from a biography because it is written by the subject of the story, themselves. The author writes in the first-person narrative, and it flows step-by-step like a story of their life. Autobiographies contain personal accounts of the subject’s life, along with their perspectives and opinions on events in their life.
How To Write a Biography
Pick a subject.
Picking a subject is the first step in writing a biography. You can pick an already famous person or a relatively unknown person with a great life story. If you already have a few in mind, you can start by asking yourself some questions such as;
- What has the subject accomplished that makes them a good subject?
- Have they had an impact on society?
- Is the subject a celebrity or a well-known personality?
- Will the biography appeal to a wide audience?
Get Permission
When you pick a subject, the next thing to do is to get permission from them or their family or rights owners. Although, with some historical figures, there may not be any need for permission. Getting permission from your subject makes it easier for you to get stories to put into your book. You can get the chance to obtain additional personal stories and anecdotes that will make your book more interesting by doing so as well.
Do The Research
Research is the most important part of a biography’s process as the entire content of the book is dependent on it. Irrespective of what you know about the subject, you need to carry out as much research as possible to get the story’s facts precisely.
Biography research comes from various sources, depending on the book’s subject. Firsthand reports from family, friends, or personal accounts from the subjects are primary sources. They are usually the most accurate and reliable, and they are crucial for a biography. Secondary sources come from other sources like magazines or documentaries.
Pick a Format
Biographies come in various formats, with each of them having their pros and cons. A typical biography will start at the beginning, usually with the birth and childhood of the subject. Yet, if the biography’s theme involves a different event in their life, the author may want to explore the flashback option or one with concurrent events from different times.
Usually, biographies have a theme or a general life lesson at the center. The author’s role is to tell the subject’s story leading up to the major event.
Which-ever format you choose should place the theme at the center, with the other events detailing the journey.
Create a Timeline Of The Story
Since a biography takes place in chronological order, there needs to be a timeline of the events in the right order. The timeline should contain the key events in the subject’s life, in the order the author plans on revealing them. A great way to declutter the story and keep it interesting is to use flashbacks . This way, the author can introduce past events and explain later events excluding the element of monotony.
Add In Your Thoughts
The good thing about biographies is that you don’t have to stick to the hard facts only. As the author, you can share your opinions and emotions in writing. The author has the freedom to do this by commenting on a significant action by the subject in a manner that describes why they feel the subject may have done what they did.
The author can also include commentary on events depicted in the biography – how it was influenced society or its impact on the lives around them. Recounting these events through a different perspective can make the biography more relatable and interesting to read.
FAQ’s
Why is a biography template important.
A biography template has an outline that makes the writing easier for the author. Biography templates usually contain a sample timeline, format, and questions that provide more information about the subject. With a great biography template, you can cut your writing time in half and spend less time coming up with an outline.
How are biographies better in comparison to autobiographies
Since a different person writes biographies, they tend to be more objective and somewhat accurate than autobiographies. An autobiography tells things from the author’s perspective, so their views and perspective cloud it. Thus, a biography will likely tell a more factual story.
These are the important steps you need to take to help you write a great biography. Now, to make things easier for you, we have a free customizable autobiography and biography template that you can use to start your first book. Get the template and start writing today
What are some of the most important elements to keep in consideration while writing a biography?
Any author looking to write a biography must consider the factors below. They aren’t the only important factors, but a biography isn’t complete without them. • Date and place of their birth • Academic background • Professional expertise • Death, if deceased • Facts and anecdotes about the person • Main accomplishments • Detailed accounts of their child and adult life
Biographies tell the untold stories of some incredibly relevant people in the world. But biographies are not always strictly accurate. So, every biographer needs to follow the necessary steps to provide a biography with all the requirements.
Related Documents
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Write a Biography
Last Updated: May 28, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Stephanie Wong Ken, MFA . Stephanie Wong Ken is a writer based in Canada. Stephanie's writing has appeared in Joyland, Catapult, Pithead Chapel, Cosmonaut's Avenue, and other publications. She holds an MFA in Fiction and Creative Writing from Portland State University. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,867,565 times.
Writing a biography can be a fun challenge, where you are sharing the story of someone’s life with readers. You may need to write a biography for a class or decide to write one as a personal project. Once you have identified the subject of the biography, do your research so you know as much about them as possible. Then, dive into the writing of the biography and revising it until it is at its finest.
Researching Your Subject

- If the subject does not give you permission to write the biography, you may want to choose a different subject. If you decide to publish the biography without the subject’s permission, you may be susceptible to legal action by the subject.
- If the subject is no longer alive, you obviously do not need to ask permission to write about them.

- You may create research questions to help focus your research of the subject, such as, What do I find interesting about the subject? Why is this subject important to readers? What can I say that is new about the subject? What would I like to learn more about?

- For in person interviews, record them with a tape recorder or a voice recorder on your computer or phone.
- You may need to interview the subject and others several times to get the material you need.

- You may also want to visit areas where the subject made a major decision or breakthrough in their life. Being physically in the area can give you a sense of how the subject might have felt and help you write their experiences more effectively.

- When researching the time period ask yourself: What were the social norms of that time? What was going on economically and politically? How did the social and political climate affect the subject?

- You may also include historical events or moments that affected the subject on the timeline. For example, maybe there was a conflict or civil war that happened during the person’s life that affected their life.
Writing the Biography

- You may end up focusing on particular areas of the person’s life. If you do this, work through a particular period in the person’s life chronologically.

- For example, you may have a thesis statement about focusing on how the person impacted the civil rights movement in America in the 1970s. You can then make sure all your content relates back to this thesis.

- Flashbacks should feel as detailed and real as present day scenes. Use your research notes and interviews with the subject to get a good sense of their past for the flashbacks.
- For example, you may jump from the person’s death in the present to a flashback to their favorite childhood memory.

- For example, you may focus on the person’s accomplishments in the civil rights movement. You may write a whole section about their contributions and participation in major civil rights marches in their hometown.

- For example, you may notice that the person’s life is patterned with moments of adversity, where the person worked hard and fought against larger forces. You can then use the theme of overcoming adversity in the biography.

- For example, you may note how you see parallels in the person’s life during the civil rights movement with your own interests in social justice. You may also commend the person for their hard work and positive impact on society.
Polishing the Biography

- Revise the biography based on feedback from others. Do not be afraid to cut or edit down the biography to suit the needs of your readers.

- Having a biography riddled with spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors can turn off your readers and result in a poor grade if you are handing in the text for a class.

- If the biography is for a class, use MLA , APA , or Chicago Style citations based on the preferences of your instructor.
Biography Help

Community Q&A
- Be careful when publishing private or embarrassing information, especially if the person is not a celebrity. You may violate their "Right of Privacy" or equivalent. Thanks Helpful 31 Not Helpful 5
- Have the sources to back up your statements about the subject's life. Untruthful written statements can lead to litigation. If it is your opinion, be clear that it is such and not fact (although you can support your opinion with facts). Thanks Helpful 16 Not Helpful 15

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://grammar.yourdictionary.com/writing/how-to-write-a-biography.html
- ↑ https://au.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-bio
- ↑ https://www.writersdigest.com/writing-articles/3-tips-for-writing-successful-flashbacks
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-bio/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
- ↑ https://www.plagiarism.org/article/how-do-i-cite-sources
About This Article

Before you write a biography, gather as much information about the subject that you can from sources like newspaper articles, interviews, photos, existing biographies, and anything else you can find. Write the story of that person’s life, including as much supporting detail as you can, including information about the place and time where the person lived. Focus on major events and milestones in their life, including historical events, marriage, children, and events which would shape their path later in life. For tips from our reviewer on proofreading the biography and citing your sources, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Jan 24, 2021
Did this article help you?

Janis Hendrick
Oct 10, 2018
Teresa Bradley
Sep 15, 2020
Apr 18, 2016
Latanya Foster
Apr 26, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
How to Write a Biography in 8 Steps (The Non-Boring Way!)
Compelling biographies help us better connect with others while fostering empathy and understanding. Discover the steps to write one that captivates your audience!
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter
Have you ever been captivated by someone’s life story? From the ancient tales of great conquerors to the modern accounts of influential figures, biographies have enchanted readers and viewers for centuries.
The stories of real people’s lives not only entertain and educate but also provide a unique window into the human experience. In fact, according to research 1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8796048/ , human stories like biographies can help us better connect with others while fostering empathy and understanding.
In this article, let’s dive into how to write a compelling biography, from the research phase to delivery.
What Are the Key Elements of a Biography?
The key elements of a well-written biography bring characters to life. They include thorough research, relevant interviews, clear structure, captivating prose, compelling themes, and a balance between objectivity and empathy.
- Thorough research: Helps create an accurate portrayal of your subject
- Relevant interviews: Insights help provide a deeper understanding of your subject
- Clear structure: Helps you outline your ideas for a compelling narrative
- Captivating prose: Provides descriptive language to paint a picture of your subject
- Compelling themes: Showcases the motivations and desires behind your subject
- A balance between objectivity and empathy: Keeps biases in check and allows your subject to shine for who they are
As you develop your biography, remember that these stories hold an enduring appeal because they offer people an opportunity to explore the depths of the human psyche, unravel extraordinary accomplishments, and discover the vulnerabilities and triumphs of individuals who have left their mark on the world.
Here are the topics a biography typically covers:
- Early life and background : Provide context about the subject’s upbringing, family, and cultural influences.
- Achievements and milestones: Highlight notable accomplishments, contributions, and significant events throughout their life.
- Challenges and struggles: Explore the obstacles they faced, the lessons learned, and how they overcame adversity.
- Personal characteristics: Describe their personality traits, values, beliefs, and motivations that shaped their actions and decisions.
- Impact and legacy: Discuss the lasting influence and contributions of the subject, both during their lifetime and beyond.
Ready to start crafting your biography? Find greater success with this helpful goal-setting resource!
How To Set Better Goals Using Science
Do you set the same goals over and over again? If you’re not achieving your goals – it’s not your fault! Let me show you the science-based goal-setting framework to help you achieve your biggest goals.
Let’s look at the six key elements of a well-written biography more closely and the steps you can follow to develop your own.
How to Write a Biography in 8 Steps Using Key Elements
Choose your presentation format.
Presenting your biography can take on various forms, the most traditional being written form. The basis for this article assumes you’re writing a conventional biography; however, this foundation can also help you create a multimedia presentation or website as well.
Consider these various formats to present your biography:
- Traditional Written Biographies: This classic approach provides a comprehensive account of a person’s life through the written word. Traditional biographies can be published in print or ebooks , allowing readers to engage deeply with the subject’s story.
- Multimedia Presentations: In the digital age, multimedia presentations offer a dynamic way to present biographies. Incorporate audio, video, photographs, and interactive elements to enhance the audience’s experience.
- Online Platforms: Online platforms, such as blogs or dedicated biography websites, provide accessible avenues for sharing biographies. They allow for easy updates, reader engagement, and the incorporation of multimedia elements.
Choose your subject and conduct research
To create a vivid and accurate portrayal of a person’s life, conduct extensive research. Dive into archives, read letters, examine diaries, explore photographs, and immerse yourself in the historical and cultural context surrounding your subject. This will help you unearth the small details that breathe life into your biography.
Whether you’re writing a biography about a historical figure, contemporary icon, or everyday individual, you’ll want to consider the different factors to focus on. Here are some examples of three types of individuals and the kind of research that will be most helpful.
- Historical Figures: When writing about historical figures, immerse yourself in their era. Understand the social, political, and cultural forces that shaped their lives. I recommend visiting your local library and connecting with a research librarian for support. Otherwise, other tools for historical research include Google Scholar. Analyze primary sources and multiple perspectives to present a well-rounded account.
- Contemporary Icons: Biographies of modern icons offer a chance to delve into their ongoing impact. Conduct interviews or gather insights from their close associates to understand their present-day influence. Stay current with the latest developments, and be prepared to update your work as the subject’s story unfolds.
- Everyday Individuals: Biographies need not be reserved for the famous. Every day individuals possess stories that can be just as compelling. Uncover the extraordinary within the ordinary, highlighting the struggles, triumphs, and personal growth of individuals who might otherwise remain unsung.
- Yourself! Want to write a biography on yourself? Autobiographies are a great way to explore who you are. Get ready to do some serious self-reflection with the steps below.
Pro Tip: Compile your research digitally using helpful cloud filings systems like Google Drive , OneDrive , or Dropbox . Organize your files by category, including information about their youth, family, achievements, and life lessons. You may also choose to write down research references or collect paper clippings on note cards, categorizing your physical files of research along the way.
Develop compelling themes and motifs
Identify overarching themes or motifs that emerge from the subject’s life. These could be resilience, ambition, love, or societal change. Weave these elements into the narrative, highlighting their significance and impact on the person’s journey. Here are some examples:
- Overcoming Adversity: These biographies feature perseverance, resilience, and determination. Examples include Helen Keller, Nelson Mandela, and Malala Yousafzai.
- Pursuit of Excellence: These biographies highlight people who have worked tirelessly to achieve their goals. Examples include Steve Jobs, Serena Williams, and Michael Jordan.
- Quest for Knowledge: These biographies focus on the curiosity that led to significant contributions to our world. Examples include Albert Einstein, Marie Curie, and Charles Darwin.
- Personal Transformation: These biographies explore a change in beliefs, values, or priorities. Examples include Malcolm X, Oprah Winfrey, and Maya Angelou.
- Legacy and Impact: These biographies examine a body of work that made a lasting contribution to society. Examples include Martin Luther King Jr., Mother Teresa, and Mahatma Gandhi.
Conduct relevant interviews
Whenever possible, seek firsthand accounts from those who knew or interacted with the subject. Conduct interviews with family members, friends, colleagues, or experts in the field. Their insights and anecdotes can provide a deeper understanding of the person’s character and experiences.
When conducting interviews for a biography, consider the following tips to ensure a productive and insightful conversation:
- Familiarize yourself with the interviewee’s background and accomplishments.
- Develop a list of well-thought-out questions that cover key aspects of their lives and experiences, including questions about your subject’s youth, family, achievements, and life transitions or struggles.
- Begin the interview by establishing a comfortable and friendly atmosphere to put the interviewee at ease.
- Show genuine interest in their story and listen actively to their responses.
- Ask open-ended questions encouraging detailed and reflective responses.
- Avoid yes/no questions and ask for their insights, memories, and personal perspectives.
- Some topics you might consider for your questions include early life, achievements, challenges, motivations, values, relationships, lessons learned, and advice.
- Pay close attention to the interviewee’s answers, body language, and tone of voice.
- Ask follow-up questions to clarify or delve deeper into specific topics.
- Show empathy and understanding, creating a safe space for the interviewee to share personal or sensitive information.
- Remain flexible during the interview, allowing the conversation to flow naturally.
- Be prepared to deviate from your prepared questions if unexpected but relevant topics arise.
- Respect the interviewee’s boundaries and be mindful of any topics they may not wish to discuss.
- Take thorough and organized notes during the interview to capture important details.
- Consider recording the interview (with permission) to ensure accurate quotes and references.
- Ask for permission to follow up with additional questions or for clarification.
- Doing a biography on yourself? Ask yourself deep questions to harvest new stories and anecdotes.
Remember, the goal of the interview is to gather valuable information and personal perspectives that will contribute to the authenticity and depth of your biography. Approach the interview process with sensitivity, respect, and genuine curiosity about the interviewee’s life and experiences.
Develop a clear structure
Outline your biography, ensuring a logical and engaging narrative flow. Consider the chronological order, significant milestones, and turning points in the subject’s life. Organize your gathered information to capture the essence of their journey while maintaining a compelling rhythm throughout.
A good outline for a biography can vary depending on the specific subject and the desired structure of the narrative. However, here’s a general outline that can serve as a starting point:
A. Introduction
a) Hook or engaging opening to capture the reader’s attention
b) Background information (birthplace, date, family, etc.)
c) A brief overview of the subject’s significance or why they are worth exploring
B. Early Life and Background
a) Childhood and upbringing
b) Influences, such as family, education, or cultural factors
c) Formative experiences or events that shaped the subject’s character or interests
C. Major Achievements and Milestones
a) A chronological exploration of the subject’s notable accomplishments, contributions, or milestones
b) Focus on key moments or achievements that highlight their impact or significance.
c) Provide context and details to paint a vivid picture of their achievements
D. Challenges and Obstacles
a) Discussion of the challenges, setbacks, or adversities the subject encountered
b) How they overcame obstacles or grew through difficult experiences
c) Insights into their resilience, determination, or problem-solving abilities
E. Personal Life and Relationships
a) Exploration of the subject’s relationships, such as family, friends, or romantic partners
b) Insights into their personal joys, struggles, or transformative experiences
c) How their personal life intersected with their professional or public achievements
F. Legacy and Impact
a) Examination of the subject’s lasting influence, contributions, or impact on society
b) Discuss how their work or actions continue to resonate or shape the world today
c) Reflection on their legacy and the lessons we can learn from their life story
G. Conclusion
a) Summarize the key aspects of the subject’s life and their significance
b) Provide a final reflection or insight on their overall journey or impact
c) Leave the reader with a lasting impression or call to action
Pro Tip: Looking for help drafting an outline to get you started? Use free tools like ChatGPT to jumpstart your outline by putting in a prompt request like, “Write an outline for a biography about X, including any relevant details on the subject that should be included.”
Craft captivating prose
Employ descriptive language to transport readers into the subject’s world. Paint vivid portraits of their physical appearance, mannerisms, and surroundings. Use sensory details to evoke emotions and create a strong connection between the reader and the subject.
Here are some examples:
- “She was a force of nature, with a fierce determination and an unwavering commitment to justice.” (Ruth Bader Ginsburg)
- “His piercing blue eyes seemed to look right through you, and his voice had a commanding presence that demanded attention.” (Winston Churchill)
- “She moved with a grace and elegance that belied her inner strength and resilience.” (Audrey Hepburn)
- “His rugged features and piercing gaze made him a natural leading man, but it was his depth and vulnerability that set him apart.” (Marlon Brando)
- “She had a contagious energy and a magnetic personality that drew people to her like a moth to a flame.” (Princess Diana)
- “His quiet intensity and unwavering dedication to his craft made him one of the greatest artists of his time.” (Leonardo da Vinci)
Action Step: While writing descriptive prose takes some practice, it’s an art you can master with little creative writing skills. To help you write descriptive prose, practice closing your eyes and imagining your subject.
- What expression is on their face?
- How are they dressed?
- What does their body language express?
- How do they smell?
- How do they make you feel?
- How do they make others feel?
- What’s in their surroundings?
- What are they doing with their hands?
- What do you imagine they’re thinking about?
With questions like these, you’ll start to use descriptive language to bring your subject to life.
Build a balance of objectivity and empathy
Strive for an objective portrayal while infusing empathy and understanding into your writing. Remain aware of biases and preconceived notions, giving your subject the space to shine in their unique light.
To check yourself, filter your writing and interviewing with these tips:
- Verify Information: Cross-reference information from various sources to ensure accuracy. Use tools like Fact Check Explorer to fact-check claims, dates, and events to avoid errors or inaccuracies that could skew the narrative.
- Multiple Perspectives: Seek out different viewpoints on the subject. This includes interviewing or reaching out to people with significant interactions or relationships with the subject. Incorporating diverse perspectives can counterbalance biases and provide a broader understanding.
- Empathetic Listening: During interviews or conversations, practice active listening and empathize with the interviewee’s experiences and emotions. This allows you to understand the subject’s perspective and incorporate their insights and feelings into the narrative.
- Contextualize Emotions: When sharing the subject’s emotional experiences or personal struggles, provide sufficient context and background. This helps readers understand the motivations and circumstances behind their actions and allows for empathetic understanding without veering into excessive sentimentality.
- Credible Interpretation: While interpreting the subject’s thoughts, motives, or intentions, be clear about what is factual and what is speculative. Clearly distinguish between evidence-based information and your interpretations to maintain objectivity.
- Respect Boundaries: Be mindful of the subject’s privacy and any requests they may have regarding sensitive or personal information. Respecting their boundaries shows empathy and allows for a respectful portrayal while maintaining the necessary level of objectivity.
- Acknowledge Limitations: Recognize that achieving complete objectivity in a biography is challenging. Biases can inadvertently seep into the narrative. However, by being aware of your biases and consciously presenting a fair and balanced account, you can mitigate their influence.
Respect truth, privacy, and sensitivity
Remember, writing biographies carries ethical responsibilities. It’s important to maintain accuracy through credible research and gain consent while being sensitive to controversial or difficult topics. Here are some considerations:
- Accuracy: Maintain a commitment to truth and accuracy. Verify facts and corroborate information from multiple sources to ensure the reliability of your narrative. Cite your sources and be transparent about any uncertainties or gaps in knowledge.
- Privacy and Consent: Respect the privacy of living individuals mentioned in your biography. Seek consent when sharing personal details or sensitive information. Balance the subject’s right to privacy with the importance of honesty and transparency.
- Sensitivity: Approach sensitive or controversial topics with care and empathy. Consider the potential impact of your words on the subject’s loved ones or affected communities—present differing perspectives without sensationalism or bias.
Writing a Biography FAQs
The length of a biography can vary greatly, depending on the subject and the depth of exploration. Some biographies span a few hundred pages, while others extend to multiple volumes. Focus on capturing the subject’s life’s essence rather than strictly adhering to a predetermined length.
Some common mistakes to avoid when writing a biography include the following: Lack of thorough research or reliance on a single source. Inaccurate or misleading information. Excessive personal bias or projection onto the subject. Neglecting to verify facts or failing to cite sources. Poor organization or a disjointed narrative flow. Neglecting to balance objectivity with empathy. Overloading the biography with irrelevant details or digressions. Failing to respect privacy or ethical considerations.
While chronological order is commonly used in biographies, it is not required. Some biographers employ a thematic approach or explore specific periods or events in the subject’s life. Experiment with different structures to find the most engaging way to tell your subject’s story.
The purpose of writing a biography is to capture and share an individual’s life story. Biographies provide insights into a person’s experiences, achievements, and challenges, offering readers inspiration, knowledge, and understanding. They preserve the legacy of individuals, contribute to historical records, and celebrate the diversity of human lives.
When choosing a subject for your biography, consider someone who inspires you, interests you, or has significantly impacted society. It could be a historical figure, a contemporary icon, or even an everyday individual with a remarkable story. Choose a subject with sufficient available information, access to primary sources or interviews, and a narrative that resonates with you and potential readers.
Key elements to include in a biography are: Early life and background: Provide context about the subject’s upbringing, family, and cultural influences. Achievements and milestones: Highlight notable accomplishments, contributions, and significant events throughout their life. Challenges and struggles: Explore the obstacles they faced, the lessons learned, and how they overcame adversity. Personal characteristics: Describe their personality traits, values, beliefs, and motivations that shaped their actions and decisions. Impact and legacy: Discuss the lasting influence and contributions of the subject, both during their lifetime and beyond.
Including personal anecdotes can add depth and humanize the subject of your biography. However, be selective and ensure that the stories are relevant, contribute to understanding the person’s character or experiences, and align with the overall narrative. Balancing personal anecdotes with factual information is critical to maintaining accuracy and credibility.
Conducting research for a biography involves exploring a variety of sources. Start with primary sources such as personal papers, letters, journals, and interviews with the subject or people who knew them. Secondary sources such as books, articles, and academic papers provide additional context and perspectives. Online databases, archives, libraries, and museums are valuable resources for finding relevant information.
Consult a wide range of sources to ensure a comprehensive and accurate biography. Primary sources, such as personal documents, letters, diaries, and interviews, offer firsthand accounts and unique insights. Secondary sources provide broader context and analysis, including books, articles, scholarly works, and historical records. Remember to evaluate the credibility and reliability of your sources critically.
Organize the information in your biography logically and engagingly. Consider using a chronological structure, starting with the subject’s early life and progressing through significant events and milestones. Alternatively, adopt a thematic approach, grouping related information based on themes or significant aspects of their life. Use clear headings, subheadings, and transitions to guide readers through the narrative flow.
Writing Biographies Key Takeaways
In summary, take note of these ideas and tips before you start writing your biography:
- Biographies hold enduring appeal, offering a glimpse into the human experience across time.
- Thorough research, interviews, and captivating prose are essential for crafting compelling biographies.
- Ethical considerations, such as accuracy, privacy, and sensitivity, are crucial when writing about real people’s lives.
- Choose subjects that genuinely inspire and resonate with you.
- Immerse yourself in the subject’s world to understand their motivations and challenges.
- Develop strong research skills and utilize a wide range of sources.
- Craft a compelling narrative that engages readers from the very first page.
- Seek feedback from trusted sources to refine your writing and storytelling abilities.
- Continuously explore new biographies to broaden your understanding of different styles and approaches.
- Embrace the unique voice and perspective you bring to the storytelling process.
Writing a biography book? Check out this helpful article, How to Write a Book: 10 Questions to Ask Before You Start Writing !
Article sources
Popular guides, how to deal with difficult people at work.
Do you have a difficult boss? Colleague? Client? Learn how to transform your difficult relationship. I’ll show you my science-based approach to building a strong, productive relationship with even the most difficult people.
Related Articles
Science of People offers over 1000+ articles on people skills and nonverbal behavior.
Get our latest insights and advice delivered to your inbox.
It’s a privilege to be in your inbox. We promise only to send the good stuff.

How to Write a Short Bio: 5 Examples and Templates
By Status.net Editorial Team on June 16, 2023 — 12 minutes to read
- How to Write a Short Bio Part 1
- What to Include in a Short Professional Bio Part 2
- Example of a Formal Short Bio Part 3
- Example of a Casual Short Bio Part 4
- Examples of Well-Written Short Bios Part 5
- Short Bio: Best Templates Part 6
- Tips for Writing a Short Bio Part 7
- Optimizing Your Bio for Different Platforms Part 8
A short bio is a concise and informative summary of your professional background, accomplishments, and personal interests. It’s an opportunity for you to introduce yourself to others, whether it’s for networking, job applications, or social media profiles. By writing a short bio, you allow others to quickly understand your expertise, strengths, and personality.
As you write your short bio, consider your audience and tailor the content accordingly. You might want to have different versions of your bio for varying contexts, such as a professional conference, a job application, or a social media platform. Regardless of the situation, strive to be authentic and maintain a tone that reflects your personality while also adhering to professional standards.
Part 1 How to Write a Short Bio
When writing a short bio, first focus on being concise and relevant. A short bio should be approximately 4-6 sentences or about 150 words. Be sure to highlight your achievements, experience, and expertise with confidence and clarity.
To start, introduce yourself briefly, including your name, title, and current role or profession. Next, mention your most significant accomplishments in your field thus far. This can include awards, certifications, publications, or any other relevant milestones. Discuss your current work and projects, providing the reader with a snapshot of your professional life. Make sure to emphasize your unique strengths and specialties. Then, touch upon your education or any other credentials that showcase your expertise.
“Jeremiah Smith, an award-winning graphic designer, specializes in creating visually stunning websites and marketing materials for a diverse clientele. With over 10 years of experience, Jeremiah has led branding projects for major corporations and small businesses alike, receiving accolades for his innovative design solutions. Currently, he serves as the Creative Director at X Design Studio, where he is dedicated to helping clients grow their digital presence. Jeremiah holds a Bachelor of Fine Arts in Graphic Design from the prestigious Art Institute of Chicago.”
For a stronger impact, customize your short bio by tailoring it to the specific platform, audience, or purpose. By prioritizing information and emphasizing the most relevant points, you can create a brief, engaging bio that showcases your unique skills and accomplishments.
Part 2 What to Include in a Short Professional Bio
- Your job title and current role : Start by mentioning your current role and the industry you’re working in. This helps to establish your expertise and gives readers an immediate understanding of your professional focus.
- Career accomplishments and milestones : Highlight a few significant achievements in your career thus far. These can be successful projects, promotions, or awards you’ve received. Be specific about what you’ve accomplished and how it demonstrates your expertise.
- Skills and qualifications : Briefly mention the key skills and qualifications you possess that make you an expert in your field. This can include technical abilities, soft skills, certifications, or degrees.
- Interests and personal touch : Add a few personal details that showcase your interests and passions outside of work. This can humanize your professional persona and help you connect with readers on a more personal level. However, be careful not to share too much personal information.
- LinkedIn and networking opportunities : Include a link to your LinkedIn profile or other professional social media accounts. This provides readers with an opportunity to connect with you and discover more about your background.
To present this information effectively, write your short professional bio in the third person and maintain a confident, knowledgeable, and clear tone of voice. Keep the content concise and easy to understand by breaking it into paragraphs and using formatting elements such as bullet points and bold text when necessary.
Here is one more example of a well-crafted short professional bio:
“John Smith is a seasoned marketing manager with over 10 years of experience in the tech industry. He currently leads product marketing efforts at X Company, where he has successfully launched new products and significantly increased market share.
John holds a Bachelor’s degree in Business Administration and is certified in digital marketing. His expertise includes strategic planning, content creation, and driving brand awareness through innovative campaigns.
In his free time, John enjoys hiking, photography, and volunteering at the local animal shelter. Connect with him on LinkedIn to learn more about his professional experience and accomplishments.”
Taking Into Account Personal and Professional Aspects
Try to strike a balance between your personal and professional aspects:
- Make sure to mention any relevant professional accomplishments and skills that showcase your expertise in your field. If you are a student or a working professional, add details about your university, current position, or professional experiences that give readers an insight into your capabilities.
- Don’t forget to add a touch of personality to your bio. Including personal details, interests, and hobbies will make you more relatable and create a connection with your audience. However, try to keep these personal elements brief and relevant to your overall bio. For example, if you are writing a bio for a personal website or Twitter, you could mention that you are an avid painter or a dedicated volunteer at a local animal shelter.
When writing in the second person, use short paragraphs to make your bio easy to read and understand. For instance:
- Full name: Briefly mention your full name at the beginning of your bio.
- Professional skills: List your core skills and accomplishments in bullet points or a table format.
- Personal interests: Share some hobbies or interests related to your profession or that showcase your values.
- Personal goals or mission statement: Include a sentence or two about your professional philosophy and core values to give readers a sense of your personal brand.
Related: How to Write a Personal Mission Statement (20 Examples)
Be cautious with the contact information you provide, especially if your bio will be accessible to the public on your personal website or social media profiles. Make sure only the necessary details are included to avoid any privacy concerns.
In summary, your short bio should be a reflection of both your personal and professional self. Showcase your skills and accomplishments while adding personal touches to make it engaging and relatable. Keep the text concise, use appropriate formatting, and remember to maintain a confident, knowledgeable, neutral, and clear tone throughout your bio.
Related: What Are Your Values? How to Discover Your Values
Selecting the Tone for Your Short Bio
Selecting the right tone for your short bio is crucial to portraying yourself in the way you want to be perceived. Consider the context in which the bio will be read and choose a tone accordingly. There are two main tones you can adopt: formal and casual.
Part 3 Example of a Formal Short Bio
Formal Tone : If you’re writing a bio for a professional context, such as a job, conference, or publication, opt for a formal tone. This means using more sophisticated language, avoiding slang, and maintaining a professional vibe throughout the bio. To achieve this, write in complete sentences, utilize proper grammar and punctuation, and highlight your achievements and expertise. Be sure to remain confident and clear in your writing. Example: “Dr. Jane Doe is a renowned expert in the field of molecular biology, with over 15 years of research experience to her credit. As the recipient of several prestigious awards, Dr. Doe’s groundbreaking work has had a significant impact on the scientific community.”
Part 4 Example of a Casual Short Bio
Casual Tone : A casual tone works well for less formal situations, such as bios on personal websites, blogs, or social media profiles. Here, you can use more relaxed language and showcase your personality. However, it’s still important to sound knowledgeable and approachable. Feel free to use contractions, incorporate humor, and speak directly to your audience to create an engaging tone.
“Hey there! I’m John, a travel enthusiast who loves exploring new cultures and tasting exotic dishes. When I’m not backpacking across the globe, you can find me geeking out about the latest tech gadgets or sipping on a well-crafted cocktail.”
In both cases, whether formal or casual, always ensure that your voice is confident, neutral, and clear. Remember to keep it concise, avoid exaggeration or false claims, and maintain a second-person point of view.
Part 5 Examples of Well-Written Short Bios
Short bio example 1.
Jane Smith is a marketing expert with over 10 years of experience in helping brands elevate their online presence. With a passion for storytelling, Jane excels in creating content that engages and inspires. In her free time, she enjoys hiking, photography, and exploring her city’s local coffee shops. Connect with Jane on LinkedIn or follow her on Twitter @JaneSmith.
Short Bio Example 2
John Doe is an experienced software engineer with a knack for developing cutting-edge applications. Specializing in full-stack web development, John’s expertise lies in JavaScript, Python, and Node.js. When he’s not coding, John can be found playing the guitar, tutoring local students in programming, or cheering on his favorite esports team.
Part 6 Short Bio: Best Templates
Short bio template 1.
[Your Name] is a [industry or profession] expert with [number of years] of experience in [specific skills or areas of expertise]. [He/She/They] specializes in [technical skills or industry knowledge] and has a passion for [relevant interests]. In [his/her/their] free time, [your name] enjoys [hobbies or activities]. Connect with [your name] on [social media platforms] or through [his/her/their] website.
Short Bio Template 2
As a [occupation or field], [Your Name] incorporates [unique qualities or skills] to produce [specific type of work]. With a background in [relevant experience], [He/She/They] has been able to [achievement or accomplishment] through [personal path or passion]. When not [working or creating], [Your Name] spends [his/her/their] time [hobbies or activities], always seeking new inspiration.
[Your name] is a [profession or role] with a background in [relevant expertise or industry]. [He/She/They] earned a [degree] in [field] from [institution]. [Your name] has [number of years] experience in [profession/industry], providing [valuable service or skill]. Outside of work, [your name] enjoys [hobbies or personal interests]. Connect with [your name] on [social media platform] or visit [your website or portfolio].
Customize these examples and templates to fit your own unique skills, experiences, and personality. Using a second person point of view, focus on the key aspects you want your audience to know about. Be confident and transparent about your achievements and interests, and let your short bio speak for itself. Happy writing!
Part 7 Tips for Writing a Short Bio
- Know your target audience : Consider the people who will be reading your bio and focus on the information that will be most relevant to them. Tailor your bio to best serve their needs and expectations.
- Highlight your accomplishments : Share information on your achievements, awards, and notable experiences. This will give your audience an understanding of your expertise and success in your field.
- Include your goals and mission statement : Tell your audience what drives you and what you hope to achieve. This can help create a connection with the reader and showcase your dedication to your work.
- Maintain a professional tone : Write in a clear and concise manner, avoiding casual language and slang. A confident and knowledgeable tone will convey your competence in your field.
- Keep personal information to a minimum : While you may choose to mention some personal tidbits, be mindful of what you share. Focus on information that enhances your professional image, rather than oversharing personal details.
- Promote your brand and company : If you represent a business or have a personal brand, mention your company name and mission statement. This can help reinforce your brand identity and make a stronger impression on your audience.
- Prioritize transparency and authenticity : Be honest about your experience and qualifications. Avoid exaggerating or making false claims in order to maintain trust with your audience.
- Limit self-promotion : While it’s important to show off your accomplishments, be sure to keep the focus on meaningful information rather than excessive self-promotion. This will help engage readers and build credibility.
- Use formatting to enhance readability : Break up your bio into paragraphs, use bullet points for lists, and bold text for important details. This will make it easier for your audience to read and understand your bio.
- Include contact information : Provide a way for your audience to get in touch with you, whether it’s an email address, phone number, or a link to your website.
Part 8 Optimizing Your Bio for Different Platforms
On LinkedIn , focus on your professional achievements and skills. Use bullet points or a table to highlight your most significant accomplishments. Feel free to include any relevant certifications, courses, or awards. Remember that LinkedIn is a professional networking platform, so maintaining a professional tone is crucial.
For a resume , your bio should be concise and focus on summarizing your career history and specific expertise. Make it easy for potential employers to grasp your main strengths quickly. Use bold text to emphasize crucial information, such as your job title, years of experience, or industry-specific skills.
On a personal website , you have more freedom to express your personality and showcase unique aspects of your life. Consider adding anecdotes, hobbies, or personal achievements to give visitors a glimpse of who you are outside of your professional life. You can also touch on your professional capabilities but keep it concise.
For Twitter , keep in mind the character limit for bios and make every word count. Capture your profession or industry, and maybe add a touch of your personality or interests through emojis or hashtags. It’s common to see authors and celebrities mention their latest projects, books, or achievements here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the essential elements of a short bio.
A short bio should include:
- Your name and current role or profession.
- Brief background information including education and relevant work experience.
- Notable accomplishments or skills relevant to your profession.
- Personal interests or ambitions that showcase your personality.
- A call-to-action, such as directing readers to your portfolio or LinkedIn profile.
How can I create a compelling short professional bio?
To create a compelling short professional bio, follow these steps:
- Start strong with a clear and concise introduction.
- Focus on your most relevant qualifications and experience.
- Highlight key achievements and successes.
- Provide a personal touch that showcases your unique attributes.
- Keep it brief and easy to read, aiming for around 100-150 words.
What are some tips to make my short bio stand out?
- Use vivid language and strong, active verbs.
- Tailor your bio to your audience, emphasizing information that is most relevant to them.
- Share a unique or unexpected personal interest to pique interest.
- Edit and proofread your bio carefully, ensuring it is free of errors and reads smoothly.
How can I tailor my short bio to different contexts?
Adjust your short bio for different contexts by:
- Focusing on relevant skills, experience, or accomplishments for each specific audience.
- Adjusting the tone or language to suit the platform (e.g., more casual for a social media profile or more formal for a conference bio).
- Emphasizing specific personal interests or accomplishments that align with the context or audience.
- Updating your call-to-action as needed to direct readers to relevant content or profiles.
Related: 150+ Awesome Examples of Personal Values
- 20 Inspiring Examples: How to Write a Personal Mission Statement
- How to Live By Your Values
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Blog • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Jun 30, 2023
How to Write a Biography: A 7-Step Guide [+Template]
From time to time, nonfiction authors become so captivated by a particular figure from either the present or the past, that they feel compelled to write an entire book about their life. Whether casting them as heroes or villains, there is an interesting quality in their humanity that compels these authors to revisit their life paths and write their story.
However, portraying someone’s life on paper in a comprehensive and engaging way requires solid preparation. If you’re looking to write a biography yourself, in this post we’ll share a step-by-step blueprint that you can follow.
How to write a biography:
1. Seek permission when possible
2. research your subject thoroughly, 3. do interviews and visit locations, 4. organize your findings, 5. identify a central thesis, 6. write it using narrative elements, 7. get feedback and polish the text.

FREE RESOURCE
Biography Outline Template
Craft a satisfying story arc for your biography with our free template.
While you technically don’t need permission to write about public figures (or deceased ones), that doesn't guarantee their legal team won't pursue legal action against you. Author Kitty Kelley was sued by Frank Sinatra before she even started to write His Way , a biography that paints Ol Blue Eyes in a controversial light. (Kelley ended up winning the lawsuit, however).

Whenever feasible, advise the subject’s representatives of your intentions. If all goes according to plan, you’ll get a green light to proceed, or potentially an offer to collaborate. It's a matter of common sense; if someone were to write a book about you, you would likely want to know about it well prior to publication. So, make a sincere effort to reach out to their PR staff to negotiate an agreement or at least a mutual understanding of the scope of your project.
At the same time, make sure that you still retain editorial control over the project, and not end up writing a puff piece that treats its protagonist like a saint or hero. No biography can ever be entirely objective, but you should always strive for a portrayal that closely aligns with facts and reality.
If you can’t get an answer from your subject, or you’re asked not to proceed forward, you can still accept the potential repercussions and write an unauthorized biography . The “rebellious act” of publishing without consent indeed makes for great marketing, though it’ll likely bring more headaches with it too.
✋ Please note that, like other nonfiction books, if you intend to release your biography with a publishing house , you can put together a book proposal to send to them before you even write the book. If they like it enough, they might pay you an advance to write it.

Book Proposal Template
Craft a professional pitch for your nonfiction book with our handy template.
Once you’ve settled (or not) the permission part, it’s time to dive deep into your character’s story.
Deep and thorough research skills are the cornerstone of every biographer worth their salt. To paint a vivid and accurate portrait of someone's life, you’ll have to gather qualitative information from a wide range of reliable sources.
Start with the information already available, from books on your subject to archival documents, then collect new ones firsthand by interviewing people or traveling to locations.
Browse the web and library archives

Put your researcher hat on and start consuming any piece on your subject you can find, from their Wikipedia page to news articles, interviews, TV and radio appearances, YouTube videos, podcasts, books, magazines, and any other media outlets they may have been featured in.
Establish a system to orderly collect the information you find 一 even seemingly insignificant details can prove valuable during the writing process, so be sure to save them.
Depending on their era, you may find most of the information readily available online, or you may need to search through university libraries for older references.

For his landmark biography of Alexander Hamilton, Ron Chernow spent untold hours at Columbia University’s library , reading through the Hamilton family papers, visiting the New York Historical Society, as well as interviewing the archivist of the New York Stock Exchange, and so on. The research process took years, but it certainly paid off. Chernow discovered that Hamilton created the first five securities originally traded on Wall Street. This finding, among others, revealed his significant contributions to shaping the current American financial and political systems, a legacy previously often overshadowed by other founding fathers. Today Alexander Hamilton is one of the best-selling biographies of all time, and it has become a cultural phenomenon with its own dedicated musical.
Besides reading documents about your subject, research can help you understand the world that your subject lived in.
Try to understand their time and social environment
Many biographies show how their protagonists have had a profound impact on society through their philosophical, artistic, or scientific contributions. But at the same time, it’s worth it as a biographer to make an effort to understand how their societal and historical context influenced their life’s path and work.
An interesting example is Stephen Greenblatt’s Will in the World . Finding himself limited by a lack of verified detail surrounding William Shakespeare's personal life, Greenblatt, instead, employs literary interpretation and imaginative reenactments to transport readers back to the Elizabethan era. The result is a vivid (though speculative) depiction of the playwright's life, enriching our understanding of his world.

Many readers enjoy biographies that transport them to a time and place, so exploring a historical period through the lens of a character can be entertaining in its own right. The Diary of Samuel Pepys became a classic not because people were enthralled by his life as an administrator, but rather from his meticulous and vivid documentation of everyday existence during the Restoration period.
Once you’ve gotten your hands on as many secondary sources as you can find, you’ll want to go hunting for stories first-hand from people who are (or were) close to your subject.
With all the material you’ve been through, by now you should already have a pretty good picture of your protagonist. But you’ll surely have some curiosities and missing dots in their character development to figure out, which you can only get by interviewing primary sources.
Interview friends and associates
This part is more relevant if your subject is contemporary, and you can actually meet up or call with relatives, friends, colleagues, business partners, neighbors, or any other person related to them.
In writing the popular biography of Steve Jobs, Walter Isaacson interviewed more than one hundred people, including Jobs’s family, colleagues, former college mates, business rivals, and the man himself.
🔍 Read other biographies to get a sense of what makes a great one. Check out our list of the 30 best biographies of all time , or take our 30-second quiz below for tips on which one you should read next.
Which biography should you read next?
Discover the perfect biography for you. Takes 30 seconds!
When you conduct your interviews, make sure to record them with high quality audio you can revisit later. Then use tools like Otter.ai or Descript to transcribe them 一 it’ll save you countless hours.
You can approach the interview with a specific set of questions, or follow your curiosity blindly, trying to uncover revealing stories and anecdotes about your subject. Whatever your method, author and biography editor Tom Bromley suggests that every interviewer arrives prepared, "Show that you’ve done your work. This will help to put the interviewee at ease, and get their best answers.”
Bromley also places emphasis on the order in which you conduct interviews. “You may want to interview different members of the family or friends first, to get their perspective on something, and then go directly to the main interviewee. You'll be able to use that knowledge to ask sharper, more specific questions.”
Finally, consider how much time you have with each interviewee. If you only have a 30-minute phone call with an important person, make it count by asking directly the most pressing questions you have. And, if you find a reliable source who is also particularly willing to help, conduct several interviews and ask them, if appropriate, to write a foreword as part of the book’s front matter .
Sometimes an important part of the process is packing your bags, getting on a plane, and personally visiting significant places in your character’s journey.
Visit significant places in their life
A place, whether that’s a city, a rural house, or a bodhi tree, can carry a particular energy that you can only truly experience by being there. In putting the pieces together about someone’s life, it may be useful to go visit where they grew up, or where other significant events of their lives happened. It will be easier to imagine what they experienced, and better tell their story.
In researching The Lost City of Z , author David Grann embarked on a trek through the Amazon, retracing the steps of British explorer Percy Fawcett. This led Grann to develop new theories about the circumstances surrounding the explorer's disappearance.

Hopefully, you won’t have to deal with jaguars and anacondas to better understand your subject’s environment, but try to walk into their shoes as much as possible.
Once you’ve researched your character enough, it’s time to put together all the puzzle pieces you collected so far.
Take the bulk of notes, media, and other documents you’ve collected, and start to give them some order and structure. A simple way to do this is by creating a timeline.
Create a chronological timeline
It helps to organize your notes chronologically 一 from childhood to the senior years, line up the most significant events of your subject’s life, including dates, places, names and other relevant bits.
You should be able to divide their life into distinct periods, each with their unique events and significance. Based on that, you can start drafting an outline of the narrative you want to create.
Draft a story outline
Since a biography entails writing about a person’s entire life, it will have a beginning, a middle, and an end. You can pick where you want to end the story, depending on how consequential the last years of your subject were. But the nature of the work will give you a starting character arc to work with.
To outline the story then, you could turn to the popular Three-Act Structure , which divides the narrative in three main parts. In a nutshell, you’ll want to make sure to have the following:
- Act 1. Setup : Introduce the protagonist's background and the turning points that set them on a path to achieve a goal.
- Act 2. Confrontation : Describe the challenges they encounter, both internal and external, and how they rise to them. Then..
- Act 3. Resolution : Reach a climactic point in their story in which they succeed (or fail), showing how they (and the world around them) have changed as a result.
Only one question remains before you begin writing: what will be the main focus of your biography?
Think about why you’re so drawn to your subject to dedicate years of your life to recounting their own. What aspect of their life do you want to highlight? Is it their evil nature, artistic genius, or visionary mindset? And what evidence have you got to back that up? Find a central thesis or focus to weave as the main thread throughout your narrative.

Or find a unique angle
If you don’t have a particular theme to explore, finding a distinct angle on your subject’s story can also help you distinguish your work from other biographies or existing works on the same subject.
Plenty of biographies have been published about The Beatles 一 many of which have different focuses and approaches:
- Philip Norman's Shout is sometimes regarded as leaning more towards a pro-Lennon and anti-McCartney stance, offering insights into the band's inner dynamics.
- Ian McDonald's Revolution in the Head closely examines their music track by track, shifting the focus back to McCartney as a primary creative force.
- Craig Brown's One Two Three Four aims to capture their story through anecdotes, fan letters, diary entries, and interviews.
- Mark Lewisohn's monumental three-volume biography, Tune In , stands as a testament to over a decade of meticulous research, chronicling every intricate detail of the Beatles' journey.

Finally, consider that biographies are often more than recounting the life of a person. Similar to how Dickens’ Great Expectations is not solely about a boy named Pip (but an examination and critique of Britain’s fickle, unforgiving class system), a biography should strive to illuminate a broader truth — be it social, political, or human — beyond the immediate subject of the book.
Once you’ve identified your main focus or angle, it’s time to write a great story.

While biographies are often highly informative, they do not have to be dry and purely expository in nature . You can play with storytelling elements to make it an engaging read.
You could do that by thoroughly detailing the setting of the story , depicting the people involved in the story as fully-fledged characters , or using rising action and building to a climax when describing a particularly significant milestone of the subject’s life.
One common way to make a biography interesting to read is starting on a strong foot…
Hook the reader from the start
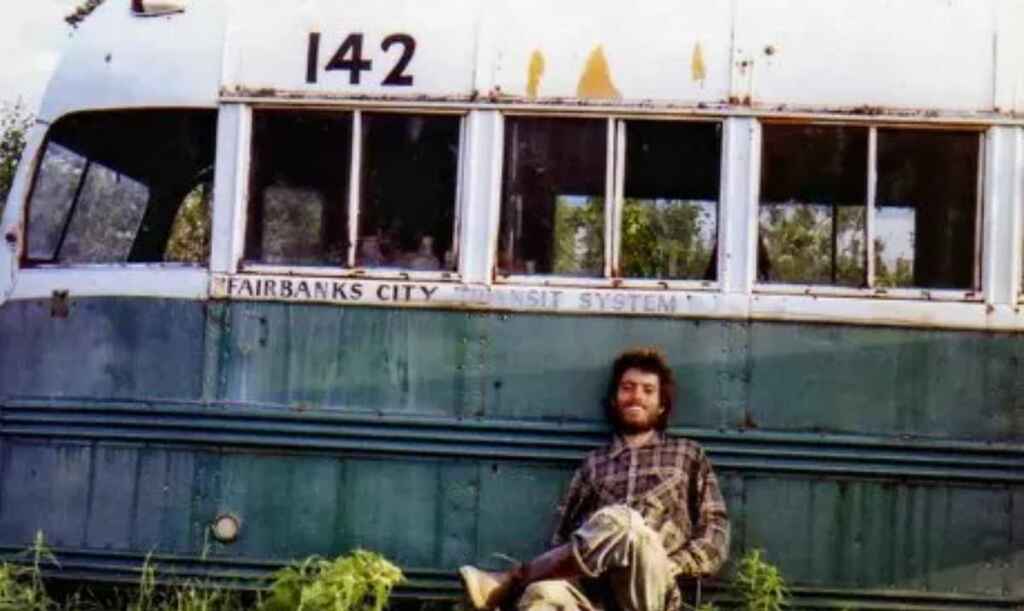
Just because you're honoring your character's whole life doesn't mean you have to begin when they said their first word. Starting from the middle or end of their life can be more captivating as it introduces conflicts and stakes that shaped their journey.
When he wrote about Christopher McCandless in Into the Wild , author Jon Krakauer didn’t open his subject’s childhood and abusive family environment. Instead, the book begins with McCandless hitchhiking his way into the wilderness, and subsequently being discovered dead in an abandoned bus. By starting in the middle of the action in medias res, Krakauer hooks the reader’s interest, before tracing back the causes and motivations that led McCandless to die alone in that bus in the first place.

You can bend the timeline to improve the reader’s reading experience throughout the rest of the story too…
Play with flashback
While biographies tend to follow a chronological narrative, you can use flashbacks to tell brief stories or anecdotes when appropriate. For example, if you were telling the story of footballer Lionel Messi, before the climax of winning the World Cup with Argentina, you could recall when he was just 13 years old, giving an interview to a local newspaper, expressing his lifelong dream of playing for the national team.
Used sparsely and intentionally, flashbacks can add more context to the story and keep the narrative interesting. Just like including dialogue does…
Reimagine conversations
Recreating conversations that your subject had with people around them is another effective way to color the story. Dialogue helps the reader imagine the story like a movie, providing a deeper sensory experience.

One thing is trying to articulate the root of Steve Jobs’ obsession with product design, another would be to quote his father , teaching him how to build a fence when he was young: “You've got to make the back of the fence just as good looking as the front of the fence. Even though nobody will see it, you will know. And that will show that you're dedicated to making something perfect.”
Unlike memoirs and autobiographies, in which the author tells the story from their personal viewpoint and enjoys greater freedom to recall conversations, biographies require a commitment to facts. So, when recreating dialogue, try to quote directly from reliable sources like personal diaries, emails, and text messages. You could also use your interview scripts as an alternative to dialogue. As Tom Bromley suggests, “If you talk with a good amount of people, you can try to tell the story from their perspective, interweaving different segments and quoting the interviewees directly.”

FREE COURSE
How to Write Believable Dialogue
Master the art of dialogue in 10 five-minute lessons.
These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you’ve finished your manuscript, it’s a good idea to ask for feedback.
If you’re going to publish your own biography, you’ll have to polish it to professional standards. After leaving your work to rest for a while, look at it with fresh eyes and edit your own manuscript eliminating passive voice, filler words, and redundant adverbs.

Then, have a professional editor give you a general assessment. They’ll look at the structure and shape of your manuscript and tell you which parts need to be expanded on or cut. As someone who edited and commissioned several biographies, Tom Bromley points out that a professional “will look at the sources used and assess whether they back up the points made, or if more are needed. They would also look for context, and whether or not more background information is needed for the reader to understand the story fully. And they might check your facts, too.”
In addition to structural editing, you may want to have someone copy-edit and proofread your work.

MEET EDITORS
Polish your book with expert help
Sign up, meet 1500+ experienced editors, and find your perfect match.
Importantly, make sure to include a bibliography with a list of all the interviews, documents, and sources used in the writing process. You’ll have to compile it according to a manual of style, but you can easily create one by using tools like EasyBib . Once the text is nicely polished and typeset in your writing applications , you can prepare for the publication process.
In conclusion, by mixing storytelling elements with diligent research, you’ll be able to breathe life into a powerful biography that immerses readers in another individual’s life experience. Whether that’ll spark inspiration or controversy, remember you could have an important role in shaping their legacy 一 and that’s something not to take lightly.
Continue reading
Recommended posts from the Reedsy Blog

450+ Powerful Adjectives to Describe a Person (With Examples)
Want a handy list to help you bring your characters to life? Discover words that describe physical attributes, dispositions, and emotions.

How to Plot a Novel Like a NYT Bestselling Author
Need to plot your novel? Follow these 7 steps from New York Times bestselling author Caroline Leavitt.

How to Write an Autobiography: The Story of Your Life
Want to write your autobiography but aren’t sure where to start? This step-by-step guide will take you from opening lines to publishing it for everyone to read.

What is the Climax of a Story? Examples & Tips
The climax is perhaps a story's most crucial moment, but many writers struggle to stick the landing. Let's see what makes for a great story climax.

What is Tone in Literature? Definition & Examples
We show you, with supporting examples, how tone in literature influences readers' emotions and perceptions of a text.

Writing Cozy Mysteries: 7 Essential Tips & Tropes
We show you how to write a compelling cozy mystery with advice from published authors and supporting examples from literature.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

We made a writing app for you
Yes, you! Write. Format. Export for ebook and print. 100% free, always.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
Become a Bestseller
Follow our 5-step publishing path.
Fundamentals of Fiction & Story
Bring your story to life with a proven plan.
Market Your Book
Learn how to sell more copies.
Edit Your Book
Get professional editing support.
Author Advantage Accelerator Nonfiction
Grow your business, authority, and income.
Author Advantage Accelerator Fiction
Become a full-time fiction author.
Author Accelerator Elite
Take the fast-track to publishing success.
Take the Quiz
Let us pair you with the right fit.
Free Copy of Published.
Book title generator, nonfiction outline template, writing software quiz, book royalties calculator.
Learn how to write your book
Learn how to edit your book
Learn how to self-publish your book
Learn how to sell more books
Learn how to grow your business
Learn about self-help books
Learn about nonfiction writing
Learn about fiction writing
How to Get An ISBN Number
A Beginner’s Guide to Self-Publishing
How Much Do Self-Published Authors Make on Amazon?
Book Template: 9 Free Layouts
How to Write a Book in 12 Steps
The 15 Best Book Writing Software Tools
How to Write a Biography: 11 Step Guide + Book Template

So you’d like to know how to write a biography. We can help with that! Learning how to write a biography doesn't have to be intimidating. In fact, it can be a lot of fun!
In this guide, we show you how to write a biography from the initial book idea all the way through to publishing your book , and we throw in a free template to help you on your way.
Ready to learn how to start a biography? Let’s jump right in.
Get Our 6″ x 9″ Pre-Formatted Book Template for Word or Mac
We will send you a Book Template for US Trade (standard paperback size).
How to Write a Biography in 11 Simple Steps
Here are the steps you need to take to learn how to write a biography:
1. Read other biographies
Austin Kleon, Author of Steal Like an Artist , says “the writer tries to master words. All of these pursuits involve the study of those who have come before and the effort to build upon their work in some way.”
In other words, if you want to learn how to write a biography, you need to read the best biographies written by other excellent authors!
In this case, it would behoove you to read several biographies – whether historical or celebrity biographies is up to you and your sub-genre.
A good author to start with? Walter Isaacson . He’s written highly acclaimed biographies on everyone from Abraham Lincoln and Steve Jobs to Leonardo Da Vinci and Elon Musk.
Once you've read some well-crafted biographies, you'll have a better idea of how to start a biography of your own.
2. Identify your subject
In order to learn how to start a biography, you need to choose who you’d like to write about – if you don’t already have someone in mind.
The most important factor will be, of course, your interest in the person you’re planning to write about. You’ll spend months (or even years) deep-diving into this person’s history, so you want to choose someone who you’re unlikely to tire of.
When learning how to write a biography, here are few factors to consider:
- How impactful has your potential subject’s life been? In other words, will people care to learn more about this person?
- How readily available is information about your potential subject? Biographies require extensive research, so it’s critical to choose someone who has enough information out there to dig into! Consider whether your subject has done interviews, written journals, has family or a partner willing to speak with you, and more.
- Are there already books written about your potential subject? Just because there’s an existing biography about the person you’re interested in doesn’t (necessarily) mean you can’t write another one. But if there are two or three biographies, you may want to reconsider. If you do choose to write about someone who has already been well-documented, be mindful about approaching the topic with a new angle or perspective. For instance, there are several biographies about George Washington, but author Alexis Coe wrote one about how Washington isn’t “quite the man we remember.” This brilliant iteration has over 12,000 ratings on Goodreads .
- Is there a market demand for a book about your potential subject? If you’re learning how to write a biography, you need to be mindful of whether folks will want to read it. Do some research to determine if readers will be receptive to a book about the person you’re interested in.
Related: Is a Biography a Primary Source?
3. Get permission to write about your subject
We’ll start by stating the obvious. It’s a good idea to get permission to write about your subject, even if you’re not legally required to. For one thing, it’s just good manners. Plus, you’re much more likely to get unfettered access to the information and sources you need to write your book.
But do you have to get permission? It depends.
In some cases, if your subject is considered a “public figure,” permission may not be required. The definition of a public figure varies depending on your jurisdiction, so you should always consult a lawyer before writing a biography.
If you do decide to proceed without permission, be mindful of how your book will be received and any legal issues that may arise. That's why we always recommend asking permission from your subject when learning how to write a biography.
Related : Difference Between A Memoir and Biography
4. Create an outline
The next step of learning how to write a biography is to outline your story. It’s critical to outline your biography before you begin writing it. Among other things, it helps ensure you cover every topic you’d like to and get the book in the correct chronological order. It also helps you identify themes that emerge as you organize your ideas.

Need help creating your outline? Learn how to do it (and take advantage of free templates!) in our guide to outlining a book .
5. Select a working title (using a title generator)
Now is the fun part of learning how to write a biography! It’s time to create a working title for your book. A working title is just what it sounds like: it’s a title that works – for now.
Of course, it’s helpful to have something to call the book as you’re working on it. And it encourages you to think about the message you’d like your book to convey. When your biography is complete, you can always do a little more research on how to write book titles for your specific sub-genre and update your working title accordingly.
Or, you can decide you still love your initial title and publish your book with that one!
We’ve made it easy for you to develop a working title – or multiple – using our book title generator .
Don't like it?
6. Write a rough draft
Okay, now it’s time to start writing your rough draft. Don’t be intimidated; just focus on getting something down on the page. As experts on all things writing and self-publishing, we’ve got a rough draft writing guide to help you get through this phase of writing a biography.
Remember to be as balanced and objective as possible when learning how to write a biography.
Make good use of your primary and secondary sources, and double-check all of your facts. You’ve got this!

7. Self-edit
There are several different types of editing that we recommend each manuscript undergo. But before you give your rough draft to anyone else to review, you should edit it yourself.
The first step to self-editing?
Take a break! It’s essential to give your mind some time to recuperate before you go over your work. And never self-edit as you go!
After you’ve completed your break, here are a few things to consider as you edit:
- Grammar. This one is self-explanatory and usually the easiest. You can use an AI editor to make a first pass and quickly catch obvious spelling errors. Depending on prompts and your experience with the tool, you can also use AI to catch some grammar and syntax issues as well.
- Content and structure . This is the time to make sure the bones of your piece are good. Make sure your content flows logically (and in chronological order), no important pieces of information are missing, and there isn’t redundant or unhelpful information.
- Clarity and consistency. Keep an eye out for any confusing copy and ensure your tone is uniform throughout the book.
- Try reading your draft aloud. You’d be surprised at how many errors, shifts in tone, or other things you’d like to change that you don’t notice while reading in your head. Go ahead and do a read-through of your draft out loud.
8. Work with an editor
Once you’ve created the best draft you can, it’s time to hire an editor. As we mentioned, there are multiple types of book editing, so you’ll need to choose the one(s) that are best for you and your project when learning how to write a biography.
For instance, you can work with a developmental editor who helps with big-picture stuff. Think book structure, organization, and overall storytelling. Or you might work with a line editor who focuses on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and the like.
There are also specialized copy editors, content editors, fact-checkers, and more.
It’s in your best interest to do a substantial amount of research before choosing an editor since they’ll have a large impact on your book. Many editors are open to doing a paid trial so you can see their work before you sign them on for the entire book.
9. Hire a book cover designer
Once you’ve worked with your editor(s) to finalize your book, it’s time to get your book ready to go out into the world. So the nest step in learning how to write a biography is to hire a book cover designer to create a cover that grabs readers’ attention (pssst: did you know that all SelfPublishing authors get done-for-you professional book design? Ask us about it !).
10. Get an ISBN
The next step in learning how to write a biography is getting an ISBN number for your book – or an International Standard Book Number. It’s a unique way to identify your book and is critical for ordering, inventory tracking, and more.
Bear in mind that each rendition of your book – regardless of when you publish them – will need their own ISBN numbers. So if you initially publish as a softcover and hardcover book and then decide to publish an ebook with the same exact content, you'll need 3 total ISBN numbers.
To get an ISBN, head to ISBN.org and follow the steps they provide. Or reference our guide right here for step-by-step instructions (complete with photos) on how to get an ISBN number for self-published books.
11. Create a launch plan
Now is the most exciting part of learning how to write a biography. It’s time to get your book out into the world! You’ll need to map out your plan, schedule events , finalize your pricing strategy, and more.
And you can't just launch your book in a single day. When you go through all the work of learning how to write a biography, you want your book to succeed – and that requires a strategic marketing plan. Luckily, we have an entire guide to launching a book to help you figure it out.

Get your free book template!
Learning how to write a biography can be challenging, but when you have a clear plan and guidance, the process is much easier. We've helped thousands of aspiring authors just like you write and self-publish their own books. We know what works – and how to become a successfully published author faster.
Take the first step today and down the book template below!
And, if you need additional help with learning how to write a biography, remember that we’re standing by to assist you. Just schedule a book consultation and one of our team members will help answer any of your questions about the writing or self-publishing process.

Elite Author T. Lynette Yankson Teaches Perseverance in Her Children’s Book About a True Story
Children's Book, Non-Fiction

Elite Author Peder Tellefsdal Is On a Mission to Rebrand the Church with His New Book
Non-Fiction

Elite Author Lisa Bray Reawakens the American Dream in Her Debut Business Book
Join the community.
Join 100,000 other aspiring authors who receive weekly emails from us to help them reach their author dreams. Get the latest product updates, company news, and special offers delivered right to your inbox.
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
The Best Short Professional Bios (Examples + Templates)
- Resume Tips
- Best Resume Writing Services
- Things To Avoid On A Resume
- Resume Paper To Use
- What To Include In A Resume
- How To Write A Bio
- How To Write A Personal Statement
- Lied on Your Resume?
- Avoid Age Discrimination
- Words and Phrases You Shouldn't Include in Your Resume
- How Many Skills Should You List On A Resume
- Send A Resume As A Pdf
- Resume Critique
- Make A Resume Stand Out
- Resume Spelling
- Resume Past Or Present Tense
- How To List Projects On A resume
- Best Resume Action Words
- How To Quantify Your Resume
- Resume Bullet Points
- Are Resume Writers Worth It
- How Many Jobs To List On Resume
Summary. To write a short bio you should first make an initial introduction introducing yourself in the first or first person. Your short bio should include your brand, your accomplishments, and your values and goals. Your short bio should be one to three short paragraphs or four to eight sentences long.
Knowing how to write a concise, informative, and interesting biography about yourself can help throughout various parts of the professional process. You can use your bio to capture the attention of potential employers or clients and convince them to choose to employ or work with you.
In this article, you’ll learn more about what goes into a short bio and how to write one, and you’ll also get to see some short bio templates and examples to help you get an idea of what yours should look like.
Key Takeaways
A short bio serves to introduce you, your achievements, and what you offer professionally to potential employers or clients.
It’s important to keep your bio brief so that readers stay engaged and will remember your main points.
You may need to adjust your bio for different audiences, as your clients may want to know different information than a recruiter would.
Talk about your skills and accomplishments in your bio, but don’t exaggerate them.
What Is a Short Bio?
How to write a short bio, what to include in a short professional bio, short bio examples, short bio templates, tips for writing a short bio, writing a short bio faq.
- Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs
A short bio serves as your introduction to the professional world. In terms of finding or expanding on your job, a bio will cover your:
Work history
Achievements
Any other relevant professional information
Think of it as a professional memoir that a hiring manager or consumer can read and understand quickly. It’s usually about one to three paragraphs depending on experience.
There’s an emphasis on being succinct when it comes to writing a professional bio. This is because a bio is supposed to be a preface to attract recruiter attention and incline them to reach out for more information. Many readers will get lost or bored with a lengthy bio.
Using a short bio can be helpful across very different industries, from marketing to accounting, from psychiatry to sales.
You’re probably familiar with providing short bios on social media websites and applications. While the information and skills you include in a professional bio may differ, the general formatting is similar.
There’s a lot of considerations to take into account when writing a short bio, and it can quickly become intimidating. Deciding what information is relevant and how to keep it near 140 characters is no small task.
If you’re having difficulty writing a short bio, follow the outline below to craft an introduction that engages your reader.
Make an initial introduction. You can’t jump right into everything you’ve done and what you want to do in the future before introducing yourself.
Your bio’s first sentence should begin with your full name in the third person or introduce yourself in the first person and continue to briefly outline your most notable skills and accomplishments. It’s a good place to state your current job and employer.
Go deeper with what motivates you. Once you’ve catchily illustrated who you are in your short bio, you can use the second sentence to describe your motivations for your work.
Stating what drives you to do the work you do is essential to employers and customers alike. Whether you work as a physician or fitness consultant , there’s a reason why this is your profession, and you should explain that in your short professional bio.
Describe your accomplishments. Your short bio is for detailing why you’re the ideal candidate to be trusted with handling an employer or consumer’s business. By describing your prior accomplishments, you let them know what you could offer as an employee and how you’ve succeeded in the past.
While you should avoid sounding braggy, the reader is looking for information about what your qualifications are , and your accomplishments generally measure these qualities.
Even though you could probably go on for ages about the details of your accomplishments, save that for an interview . In a short bio, only include the most impressive of your achievements to outline.
Accomplishments relevant to a short bio could include:
Impressive results on a project
Former promotions
Awards received in your field
Certifications received
Include contact information. The purpose of a short bio as either a business or a job seeker is to inspire the reader to reach out. Without contact information, this pursuit becomes futile. Make sure your short bio has some way to contact you at the end.
Relevant contact information may include:
Phone number
Professional networking profile
A short professional bio includes:
Your full name. You can choose to write your bio in the first person (I, me, my) or third person (he, she, they), but either way, you need to include your full name at some point. Branding doesn’t work so well without a brand name (i.e., you!)
Your brand. Of course, if you have an actual brand that you’re trying to market, you should include the brand name as well.
What you do. Summarize what you want the reader to know about what you do in one sentence — tricky, we know.
Your accomplishments. For a short bio, you can stick with just one major accomplishment from your professional life. Or, if you have a string of impressive achievements, try condensing all of them down to one sentence.
Your goals and values. Let the reader know what makes you tick — why do you do what you do and what do you hope to achieve with your work? People are compelled by a story more than anything else, so it’s important to get this part right.
Something personal (optional). If you have a quirky tidbit about yourself you’d like to include, go for it. Just make sure it doesn’t throw off te the tone of the rest of your bio.
Contact info (optional). If your bio is serving as a call-to-action to drum up business or get leads on job opportunities, it makes sense to include your contact information at the end of your bio. It’s not necessary if that information is available elsewhere on the page , though.
Entry-Level Job-Seeker Bio Example
Mitchell Morrison is an upcoming video producer and editor who believes in the art of visual organization. He is a recent graduate from the University of Washington and focused on post-production during his time studying there. He was introduced to the magical world of visual art production by watching his father work on editing commercials growing up and has been working towards his dream of becoming a video editor ever since. During his last year of college, Mitchell participated in a competitive internship with Digital Space Films. He was chosen out of 2,000 applicants based on his academic portfolio and personal statement essay. This internship was an incredible learning experience and resulted in three professional accreditations for music video editing. Mitchell currently lives in Seattle, Washington pursuing freelance opportunities and spending time with his Dog, Pikachu. To get into contact with Mitchell: MitchellMorrisonVideo.com/contact
Working Professional Website Bio Example
Lisa Kennedy is an experienced real estate professional. She knows how important a home is for long-term happiness and has invested her career in putting people in the house they’ve always dreamed of. Lisa was driven to pursue real estate from her passion for helping people during life-altering times, and a keen interest in high-end, luxury homes. She’s been working in the real estate industry for ten years and in that time has assisted over 3,500 people in finding homes. She was educated at the University of Los Angeles with a bachelor’s in business management. She’s worked for some of the most respectable Real Estate companies in Los Angeles and individually under her agency “Kennedy Homes.” Lisa has also been published in Real Estate Quarterly Magazine as the 2017 winner of the “Top Luxury Home Seller” award. Lisa loves the culture of Los Angeles and has been living there with her family of five since she graduated from college. She enjoys spending her free time exploring towns along the West Coast and swimming. If you’d like to get in touch with Lisa: Email: [email protected]
Professional Networking Profile Bio Example
Bianca Jones Marketing Manager Miami, FL The first step towards customer satisfaction is being reached by stellar product marketing, and that’s what I aim to provide. My professional experience as a product marketing manager has allowed me to assist many organizations in improving their sales margins and audience response to emerging products. I’ve brought dedication and positive results to the companies I’ve worked for because I am passionate about product perception, marketing, and business statistics. What drives a product to success interests and inspires me. I specialize in long-term growth strategies and audience outreach. In addition to eight years of experience in professional product marketing, I have also published two books on creating a career as a marketer called “What to Do After Your Bachelor’s” and “A Marketer’s How-To.” If you’re interested in learning more about how to market your business better, or just discuss more, feel free to contact me by email at [email protected].
Your first choice is whether you want your bio to be written in the third person or first person. These short bio templates show both options, and also include different ideas for what to include, and how. Feel free to pick and choose your favorite parts of each of the two.
[Full Name] is a [job title] who [believes/knows] in the power of [what you do]. [He/She/They] began their journey in [field] by [how you got started in the field], and now dreams of [what you hope to accomplish]. [His/Her/Their] biggest accomplishment to date has been [your biggest accomplishment]. [Full Name] lives in [where you live] and participates in [a hobby/interest]. To get in touch with [Full Name], call/email/message me on [how you’d like to be contacted].
I am a [job title] who helps [who you help] [what you help them do]. It’s my belief that [your unique perspective on the field]. In the past [# of years] years, I’ve [major accomplishment #1] through [how you accomplished it]. I have a passion for [your professional passion], but on the side, I also enjoy [personal passion]. Get in touch with me today at [contact info] — I look forward to talking with you about [what you want to talk to your readers about].
You have a firm grasp of the structure of a short bio and what to include. Now, you may need some tips for how to polish your short professional bio and make it stand out from the competition.
Be mindful of length. While you’re probably getting sick of hearing that your bio should be short, it’s good to keep in mind throughout the writing process. It’s easy to go off on a tangent while trying to include everything relevant or rationalize, making your bio too long.
Avoid this impulse. The point of a bio is that it’s limited. You want to intrigue the reader enough to inspire them to seek more information about you or your services.
Tailor your bio to your intended audience. Whether you’re using a short bio to attract a particular customer base or potential employer, tailoring it to fit their wants and needs is crucial. Consider your intended audience base and what they’re looking for in a candidate or service.
Be genuine. Your short bio should be an authentic representation of your traits, experience, and personality. People are repelled by what they interpret as stretching the truth. If you’re being received as disingenuous by the reader, they’ll probably move on.
Proofread. The only way to steer clear of errors in your short bio is by proofreading it. Imagine a hiring manager being completely interested in your bio.
They love what you have to say about yourself and find your prior experience enticing. That is, until they come across a mistake that clearly shows you didn’t do proofread or edit.
Include links to your portfolio, website, or networking profile. One way to circumvent the confining factor of keeping your bio short is by including links to more detailed sources.
This can be in the form of linking your portfolio or website to allow the reader to go deeper into your discussed skills if they please, without taking up more space in your bio.
Implement these links seamlessly into your bio by attaching them to anchor words that describe what clicking will lead them to.
Add some personality. You aren’t the only person who has an impressive list of accomplishments to put on a bio, so you’re going to need to find some additional ways to make an impression.
What should a short bio include?
A short bio should include your name, what you do, and your achievements. You should also include your company or product’s brand, if you have one, and your goals and motivations for doing what you do. This humanizes you and helps you stand out from the rest of the pack.
How long is a short bio?
A short bio is typically one to three paragraphs long. These should be short paragraphs though, as other experts say that between four and eight sentences is the ideal length for a short bio.
What makes a good bio?
A good bio is succinct and memorable. Readers don’t want to spend long reading about your professional and personal life, so go back and cut it down to the important parts multiple times after you draft it. You might be surprised at how little you actually need to include.
What should you avoid putting in a short bio?
You should avoid including anything negative or arrogate. It’s never a good idea to write anything negative about previous jobs or employers. Only include positive things in your professional short bio.
It’s important to include your achievements in a short bio, but there is a fine line between mentioning your achievements and bragging about them. Stick to the facts when talking about your accomplishments.
Fremont University – Building Your Professional Bio
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Sky Ariella is a professional freelance writer, originally from New York. She has been featured on websites and online magazines covering topics in career, travel, and lifestyle. She received her BA in psychology from Hunter College.
Don Pippin is an executive and HR leader for Fortune 50 and 500 companies and startups. In 2008, Don launched area|Talent with a focus on helping clients identify their brand. As a Certified Professional Resume Writer, Certified Digital Career Strategist, and Certified Personal Branding Strategist, Don guides clients through career transitions.
Recent Job Searches
- Registered Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Truck Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Call Center Representative Jobs Resume Location
- Customer Service Representative Jobs Resume
- Delivery Driver Jobs Resume Location
- Warehouse Worker Jobs Resume Location
- Account Executive Jobs Resume Location
- Sales Associate Jobs Resume Location
- Licensed Practical Nurse Jobs Resume Location
- Company Driver Jobs Resume
Related posts
How To Put Projects On A Resume (With Examples)
Creating A Medical CV (With Examples)

How Many Skills Should You List On A Resume?
How To Make A Resume In Word (With Examples)
- Career Advice >

- Learn How to Write a Biography: A Step-by-Step Guide.
- Self Publishing Guide
Human lives are intricate tapestries woven with experiences, emotions, challenges, and triumphs. Biographies and autobiographies serve as windows into these remarkable stories, offering insight into the lives of individuals who have left their mark on history or those who wish to chronicle their own journeys.
I n this guide, we will explore the art of writing biographies and autobiographies, delving into the nuances of both genres and providing valuable tips on how to craft compelling narratives.
Understanding Biography and Autobiography
- Biography: Exploring Lives Beyond the Surface A biography is a literary exploration that unveils the intricate layers of a person’s existence, transcending the mere listing of events. It provides a comprehensive account of an individual’s life, offering insights into their achievements, struggles, societal impact, and distinct qualities that define them. These narratives serve as windows into history, allowing readers to traverse time and understand the legacy left by remarkable individuals. Biographies are usually crafted by biographers, individuals skilled in research and storytelling. They undertake a meticulous journey of gathering information from diverse sources, such as historical records, interviews, letters, and secondary literature. The biographer’s role is to curate these fragments of information into a coherent narrative, painting a vivid portrait of the subject. This comprehensive approach lends credibility and depth to the portrayal, enriching the reader’s understanding of the subject’s contributions and character. Example: Consider the biography of Mahatma Gandhi. A biographer compiling his life story would explore not only his role in India’s fight for independence but also his principles of nonviolence, his experiments with truth, and his impact on the world’s political landscape. By presenting a holistic view of Gandhi’s life, the biography reveals the nuances of his personality, beliefs, and the larger context in which he operated.
- Autobiography: The Intimate Dialogue of Self-Discovery An autobiography is a narrative journey undertaken by the subject themselves—a profound sharing of one’s life experiences, emotions, and reflections. This genre provides readers with an intimate insight into the subject’s psyche, allowing them to witness their life’s trajectory through personal recollections. Autobiographies carry a unique authenticity, as they are composed from the vantage point of the person who lived those moments, providing a firsthand account of their journey. Autobiographies draw from the subject’s reservoir of memories, emotions, and introspections. This self-exploration leads to a narrative that is often more than a linear chronicle; it becomes a tapestry woven with the threads of emotions, thoughts, and personal revelations. By directly communicating with the reader, the autobiographer creates a powerful connection, allowing readers to step into their shoes and experience their story from within. Example: A notable example of an autobiography is “The Diary of a Young Girl” by Anne Frank. Written during her time in hiding during World War II, the book offers a candid portrayal of Anne’s life, fears, hopes, and dreams. Through her own words, readers gain a deep understanding of the challenges faced by Jews during the Holocaust, as well as the resilience and humanity that Anne exudes even in the face of adversity.
Writing a Biography:
Research: The Foundation of a Compelling Biography Thorough research is the cornerstone of a captivating biography. Delve into reputable sources like books, articles, interviews, and archives to gather a comprehensive view of your subject’s life. By immersing yourself in these materials, you gain insights into their experiences, motivations, and contributions. Scrutinise the historical context to understand the era’s impact on their journey. Successful research forms the bedrock of your biography, enabling you to present an accurate and nuanced portrayal that resonates with readers. It’s through meticulous research that you uncover the hidden stories and connect the dots, allowing the subject’s essence to shine through the pages.
Selecting a Focus: Defining the Narrative Scope Choosing a focal point is essential for a well-structured biography. Decide whether to cover the subject’s entire life or concentrate on specific periods or achievements. This decision shapes the narrative’s trajectory, preventing it from becoming overwhelming or disjointed. A focused approach allows you to delve deeply into pivotal moments, providing a more profound understanding of the subject’s journey. By clarifying the scope, you enable readers to follow a coherent storyline, making it easier for them to engage with the subject’s life in a meaningful way.
Structuring the Biography: Chronology and Themes The organisation of your biography greatly impacts its readability. Structure your work into logical sections or chapters, employing either a chronological or thematic arrangement. Begin with an engaging introduction that captures readers’ attention and provides essential context. A chronological structure follows the subject’s life in sequential order, offering a clear timeline of events. Alternatively, a thematic structure groups events by themes, allowing you to explore different facets of the subject’s life. A well-structured biography guides readers smoothly through the subject’s experiences, fostering a deeper connection and understanding.
Show, Don’t Tell: Evocative Storytelling Vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes breathe life into your biography. Rather than merely listing facts, employ descriptive language to recreate scenes and emotions, allowing readers to immerse themselves in the subject’s world. Use anecdotes to illustrate key moments, capturing the essence of the subject’s character and the impact of events on their journey. Integrating quotes from the subject, contemporaries, or relevant sources adds authenticity and depth. Through this technique, you transport readers into the subject’s experiences, enabling them to witness the moments that shaped their lives.
Balanced Perspective: Portraying Strengths and Flaws A balanced portrayal adds credibility and depth to your biography. While it’s tempting to focus solely on accomplishments, a well-rounded view includes the subject’s strengths and flaws. This authenticity humanises the subject, making it relatable and multidimensional. By acknowledging both successes and challenges, readers gain a more honest understanding of their journey. Balancing positives and negatives helps readers empathise with the subject, connecting them on a deeper level and offering a more genuine insight into their lives.
Engaging Emotions: Creating Emotional Resonance Emotions are a potent tool in biography writing. Delve into the subject’s feelings, struggles, and aspirations to create an emotional connection with readers. By tapping into their emotional experiences, you make the narrative relatable and engaging. Sharing personal challenges and triumphs allows readers to empathise and reflect on their own lives. This emotional resonance elevates the biography from a mere factual account to a compelling and moving story that lingers in readers’ minds, leaving a lasting impact.
Citing Sources: Ensuring Accuracy and Credibility Accurate information is vital in biography writing. Properly cite your sources to maintain credibility and integrity. Clear citations not only lend authority to your work but also provide readers with the opportunity to explore further if they desire. Accurate referencing safeguards against misinformation and ensures that your portrayal is based on reliable evidence. In addition to enhancing your credibility, thorough citations demonstrate your commitment to thorough research and ethical writing practises, contributing to the overall trustworthiness of your biography.

Complete Guide to Write a Biography. Start Writing Your Biography Now
Writing an Autobiography:
Reflecting on Significant Moments and Experiences Initiating an autobiography involves introspection into your life’s pivotal moments. Delve into memories that have influenced your journey, such as turning points, challenges, relationships, and achievements. Reflect on these experiences, dissecting their impact on your personal growth and development. By contemplating these key events, you gain insight into the narrative threads that weave your life story together. This reflective process sets the foundation for an authentic autobiography that resonates with readers on a profound level.
Developing Your Unique Voice and Tone Crafting an autobiography demands a consistent voice and tone that reflect your personality. Write in a way that feels true to you, capturing your unique perspective and emotions. Authenticity is key, as it allows readers to connect with your narrative on a personal level. Whether your tone is introspective, humorous, or contemplative, ensure it aligns with the essence of your experiences. By embracing your genuine voice, you create an autobiography that not only tells your story but also conveys the essence of who you are.
Structured Storytelling for Engagement While autobiographies can be more flexible in structure compared to biographies, organising your narrative into coherent sections or themes enhances its readability. By grouping related experiences together, you provide readers with a clearer understanding of the themes that have shaped your life. This structure helps maintain their engagement by guiding them through your journey in a logical and compelling manner. While allowing for creativity, a structured approach ensures that your autobiography remains focused and accessible.
Embracing honesty and authenticity Honesty is the bedrock of an impactful autobiography. Share not only your triumphs but also your mistakes and failures. Authenticity creates relatability, allowing readers to connect with your humanity and vulnerabilities. Your journey’s challenges and setbacks are just as integral to your story as your successes. By being candid about your experiences, you demonstrate resilience and growth, inspiring readers to reflect on their own paths. This level of authenticity fosters a deeper connection, making your autobiography a source of empathy and encouragement.
Adding Depth Through Reflection Incorporate reflection to imbue your autobiography with depth and meaning. Explore the lessons you’ve learned from your experiences and the transformations they’ve prompted. Delve into how these moments shaped your beliefs, values, and perspective on life. By offering insights gained from introspection, you provide readers with wisdom and a broader understanding of your journey. Reflection transforms your autobiography from a chronicle of events into a thoughtful exploration of personal growth and the profound impact of life’s moments.
Creating vivid details for immersion Immerse readers in your world by employing sensory details and vivid descriptions. Paint a picture with words, allowing readers to visualise the scenes and emotions you’re describing. By incorporating sensory elements like sights, sounds, smells, and feelings, you transport readers into the moments you’re recounting. This immersive experience draws them closer to your story, fostering a stronger connection. Vivid details not only make your autobiography more engaging but also enable readers to forge a deeper connection with your experiences and emotions.
In the realm of literature, biographies and autobiographies stand as powerful testaments to the diversity and richness of human existence. Whether you’re capturing the life of a historical figure or penning your own life story, the art of writing these genres involves meticulous research, introspection, and a keen understanding of human emotions.
Through carefully chosen words and evocative storytelling, biographers and autobiographers alike can craft narratives that resonate with readers and offer a deeper understanding of the human experience. So, whether you’re writing about the extraordinary or the everyday, embrace the challenge and privilege of narrating lives through the written word.
Publish your book with BlueRoseONE and become a bestselling author . Don’t let your dream of becoming an author fade away, grab the opportunity now and publish your book – be it fiction, non fiction, poetry or more.
- About The Author
- Latest Posts
Mansi Chauhan

You May Also Like

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

How to Write a Biography
Biographies are big business. Whether in book form or Hollywood biopics, the lives of the famous and sometimes not-so-famous fascinate us.
While it’s true that most biographies are about people who are in the public eye, sometimes the subject is less well-known. Primarily, though, famous or not, the person who is written about has led an incredible life.
In this article, we will explain biography writing in detail for teachers and students so they can create their own.
While your students will most likely have a basic understanding of a biography, it’s worth taking a little time before they put pen to paper to tease out a crystal-clear definition of one.

What Is a Biography?

A biography is an account of someone’s life written by someone else . While there is a genre known as a fictional biography, for the most part, biographies are, by definition, nonfiction.
Generally speaking, biographies provide an account of the subject’s life from the earliest days of childhood to the present day or, if the subject is deceased, their death.
The job of a biography is more than just to outline the bare facts of a person’s life.
Rather than just listing the basic details of their upbringing, hobbies, education, work, relationships, and death, a well-written biography should also paint a picture of the subject’s personality and experience of life.

Full Biographies
Teaching unit.
Teach your students everything they need to know about writing an AUTOBIOGRAPHY and a BIOGRAPHY.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ ( 26 reviews )
Features of a Biography
Before students begin writing a biography, they’ll need to have a firm grasp of the main features of a Biography. An excellent way to determine how well they understand these essential elements is to ask them to compile a checklist like the one-blow
Their checklists should contain the items below at a minimum. Be sure to help them fill in any gaps before moving on to the writing process.
The purpose of a biography is to provide an account of someone’s life.
Biography structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Open your biography with a strong hook to grab the reader’s attention
SEQUENCING: In most cases, biographies are written in chronological order unless you are a very competent writer consciously trying to break from this trend.
COVER: childhood, upbringing, education, influences, accomplishments, relationships, etc. – everything that helps the reader to understand the person.
CONCLUSION: Wrap your biography up with some details about what the subject is doing now if they are still alive. If they have passed away, make mention of what impact they have made and what their legacy is or will be.
BIOGRAPHY FEATURES
LANGUAGE Use descriptive and figurative language that will paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read. Use time connectives to link events.
PERSPECTIVE Biographies are written from the third person’s perspective.
DETAILS: Give specific details about people, places, events, times, dates, etc. Reflect on how events shaped the subject. You might want to include some relevant photographs with captions. A timeline may also be of use depending upon your subject and what you are trying to convey to your audience.
TENSE Written in the past tense (though ending may shift to the present/future tense)
THE PROCESS OF WRITING A BIOGRAPHY
Like any form of writing, you will find it simple if you have a plan and follow it through. These steps will ensure you cover the essential bases of writing a biography essay.
Firstly, select a subject that inspires you. Someone whose life story resonates with you and whose contribution to society intrigues you. The next step is to conduct thorough research. Engage in extensive reading, explore various sources, watch documentaries, and glean all available information to provide a comprehensive account of the person’s life.
Creating an outline is essential to organize your thoughts and information. The outline should include the person’s early life, education, career, achievements, and any other significant events or contributions. It serves as a map for the writing process, ensuring that all vital information is included.
Your biography should have an engaging introduction that captivates the reader’s attention and provides background information on the person you’re writing about. It should include a thesis statement summarising the biography’s main points.
Writing a biography in chronological order is crucial . You should begin with the person’s early life and move through their career and achievements. This approach clarifies how the person’s life unfolded and how they accomplished their goals.
A biography should be written in a narrative style , capturing the essence of the person’s life through vivid descriptions, anecdotes, and quotes. Avoid dry, factual writing and focus on creating a compelling narrative that engages the reader.
Adding personal insights and opinions can enhance the biography’s overall impact, providing a unique perspective on the person’s achievements, legacy, and impact on society.
Editing and proofreading are vital elements of the writing process. Thoroughly reviewing your biography ensures that the writing is clear, concise, and error-free. You can even request feedback from someone else to ensure that it is engaging and well-written.
Finally, including a bibliography at the end of your biography is essential. It gives credit to the sources that were used during research, such as books, articles, interviews, and websites.
Tips for Writing a Brilliant Biography
Biography writing tip #1: choose your subject wisely.
There are several points for students to reflect on when deciding on a subject for their biography. Let’s take a look at the most essential points to consider when deciding on the subject for a biography:
Interest: To produce a biography will require sustained writing from the student. That’s why students must choose their subject well. After all, a biography is an account of someone’s entire life to date. Students must ensure they choose a subject that will sustain their interest throughout the research, writing, and editing processes.
Merit: Closely related to the previous point, students must consider whether the subject merits the reader’s interest. Aside from pure labors of love, writing should be undertaken with the reader in mind. While producing a biography demands sustained writing from the author, it also demands sustained reading from the reader.
Therefore, students should ask themselves if their chosen subject has had a life worthy of the reader’s interest and the time they’d need to invest in reading their biography.
Information: Is there enough information available on the subject to fuel the writing of an entire biography? While it might be a tempting idea to write about a great-great-grandfather’s experience in the war. There would be enough interest there to sustain the author’s and the reader’s interest, but do you have enough access to information about their early childhood to do the subject justice in the form of a biography?
Biography Writing Tip #2: R esearch ! Research! Research!
While the chances are good that the student already knows quite a bit about the subject they’ve chosen. Chances are 100% that they’ll still need to undertake considerable research to write their biography.
As with many types of writing , research is an essential part of the planning process that shouldn’t be overlooked. If students wish to give as complete an account of their subject’s life as possible, they’ll need to put in the time at the research stage.
An effective way to approach the research process is to:
1. Compile a chronological timeline of the central facts, dates, and events of the subject’s life
2. Compile detailed descriptions of the following personal traits:
- Physical looks
- Character traits
- Values and beliefs
3. Compile some research questions based on different topics to provide a focus for the research:
- Childhood : Where and when were they born? Who were their parents? Who were the other family members? What education did they receive?
- Obstacles: What challenges did they have to overcome? How did these challenges shape them as individuals?
- Legacy: What impact did this person have on the world and/or the people around them?
- Dialogue & Quotes: Dialogue and quotations by and about the subject are a great way to bring color and life to a biography. Students should keep an eagle eye out for the gems that hide amid their sources.
As the student gets deeper into their research, new questions will arise that can further fuel the research process and help to shape the direction the biography will ultimately go in.
Likewise, during the research, themes will often begin to suggest themselves. Exploring these themes is essential to bring depth to biography, but we’ll discuss this later in this article.
Research Skills:
Researching for biography writing is an excellent way for students to hone their research skills in general. Developing good research skills is essential for future academic success. Students will have opportunities to learn how to:
- Gather relevant information
- Evaluate different information sources
- Select suitable information
- Organize information into a text.
Students will have access to print and online information sources, and, in some cases, they may also have access to people who knew or know the subject (e.g. biography of a family member).
These days, much of the research will likely take place online. It’s crucial, therefore, to provide your students with guidance on how to use the internet safely and evaluate online sources for reliability. This is the era of ‘ fake news ’ and misinformation after all!
COMPLETE TEACHING UNIT ON INTERNET RESEARCH SKILLS USING GOOGLE SEARCH

Teach your students ESSENTIAL SKILLS OF THE INFORMATION ERA to become expert DIGITAL RESEARCHERS.
⭐How to correctly ask questions to search engines on all devices.
⭐ How to filter and refine your results to find exactly what you want every time.
⭐ Essential Research and critical thinking skills for students.
⭐ Plagiarism, Citing and acknowledging other people’s work.
⭐ How to query, synthesize and record your findings logically.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip #3: Find Your Themes In Biography Writing
Though predominantly a nonfiction genre, the story still plays a significant role in good biography writing. The skills of characterization and plot structuring are transferable here. And, just like in fiction, exploring themes in a biographical work helps connect the personal to the universal. Of course, these shouldn’t be forced; this will make the work seem contrived, and the reader may lose faith in the truthfulness of the account. A biographer needs to gain and maintain the trust of the reader.
Fortunately, themes shouldn’t need to be forced. A life well-lived is full of meaning, and the themes the student writer is looking for will emerge effortlessly from the actions and events of the subject’s life. It’s just a case of learning how to spot them.
One way to identify the themes in a life is to look for recurring events or situations in a person’s life. These should be apparent from the research completed previously. The students should seek to identify these patterns that emerge in the subject’s life. For example, perhaps they’ve had to overcome various obstacles throughout different periods of their life. In that case, the theme of overcoming adversity is present and has been identified.
Usually, a biography has several themes running throughout, so be sure your students work to identify more than one theme in their subject’s life.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING Tip: #4 Put Something of Yourself into the Writing
While the defining feature of a biography is that it gives an account of a person’s life, students must understand that this is not all a biography does. Relating the facts and details of a subject’s life is not enough. The student biographer should not be afraid to share their thoughts and feelings with the reader throughout their account of their subject’s life.
The student can weave some of their personality into the fabric of the text by providing commentary and opinion as they relate the events of the person’s life and the wider social context at the time. Unlike the detached and objective approach we’d expect to find in a history textbook, in a biography, student-writers should communicate their enthusiasm for their subject in their writing.
This makes for a more intimate experience for the reader, as they get a sense of getting to know the author and the subject they are writing about.
Biography Examples For Students
- Year 5 Example
- Year 7 Example
- Year 9 Example
“The Rock ‘n’ Roll King: Elvis Presley”
Elvis Aaron Presley, born on January 8, 1935, was an amazing singer and actor known as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Even though he’s been dead for nearly 50 years, I can’t help but be fascinated by his incredible life!
Elvis grew up in Tupelo, Mississippi, in a tiny house with his parents and twin brother. His family didn’t have much money, but they shared a love for music. Little did they know Elvis would become a music legend!
When he was only 11 years old, Elvis got his first guitar. He taught himself to play and loved singing gospel songs. As he got older, he started combining different music styles like country, blues, and gospel to create a whole new sound – that’s Rock ‘n’ Roll!
In 1954, at the age of 19, Elvis recorded his first song, “That’s All Right.” People couldn’t believe how unique and exciting his music was. His famous hip-swinging dance moves also made him a sensation!
Elvis didn’t just rock the music scene; he also starred in movies like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.” But fame came with challenges. Despite facing ups and downs, Elvis kept spreading happiness through his music.

Tragically, Elvis passed away in 1977, but his music and charisma live on. Even today, people worldwide still enjoy his songs like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love.” Elvis Presley’s legacy as the King of Rock ‘n’ Roll will live forever.
Long Live the King: I wish I’d seen him.
Elvis Presley, the Rock ‘n’ Roll legend born on January 8, 1935, is a captivating figure that even a modern-day teen like me can’t help but admire. As I delve into his life, I wish I could have experienced the magic of his live performances.
Growing up in Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis faced challenges but found solace in music. At 11, he got his first guitar, a symbol of his journey into the world of sound. His fusion of gospel, country, and blues into Rock ‘n’ Roll became a cultural phenomenon.
The thought of being in the audience during his early performances, especially when he recorded “That’s All Right” at 19, sends shivers down my spine. Imagining the crowd’s uproar and feeling the revolutionary energy of that moment is a dream I wish I could have lived.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical prodigy; he was a dynamic performer. His dance moves, the embodiment of rebellion, and his roles in films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock” made him a true icon.
After watching him on YouTube, I can’t help but feel a little sad that I’ll never witness the King’s live performances. The idea of swaying to “Hound Dog” or being enchanted by “Can’t Help Falling in Love” in person is a missed opportunity. Elvis may have left us in 1977, but he was the king of rock n’ roll. Long live the King!
Elvis Presley: A Teen’s Take on the Rock ‘n’ Roll Icon”
Elvis Presley, born January 8, 1935, was a revolutionary force in the music world, earning his title as the “King of Rock ‘n’ Roll.” Exploring his life, even as a 16-year-old today, I’m captivated by the impact he made.
Hailing from Tupelo, Mississippi, Elvis grew up in humble beginnings, surrounded by the love of his parents and twin brother. It’s inspiring to think that, despite financial challenges, this young man would redefine the music scene.
At 11, Elvis got his first guitar, sparking a self-taught journey into music. His early gospel influences evolved into a unique fusion of country, blues, and gospel, creating the electrifying genre of Rock ‘n’ Roll. In 1954, at only 19, he recorded “That’s All Right,” marking the birth of a musical legend.
Elvis wasn’t just a musical innovator; he was a cultural phenomenon. His rebellious dance moves and magnetic stage presence challenged the norms. He transitioned seamlessly into acting, starring in iconic films like “Love Me Tender” and “Jailhouse Rock.”

However, fame came at a cost, and Elvis faced personal struggles. Despite the challenges, his music continued to resonate. Even now, classics like “Hound Dog” and “Can’t Help Falling in Love” transcend generations.
Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is undeniable. He was known for his unique voice, charismatic persona, and electrifying performances. He sold over one billion records worldwide, making him one of the best-selling solo artists in history. He received numerous awards throughout his career, including three Grammy Awards and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Elvis’s influence can still be seen in today’s music. Many contemporary artists, such as Bruno Mars, Lady Gaga, and Justin Timberlake, have cited Elvis as an inspiration. His music continues to be featured in movies, TV shows, and commercials.
Elvis left us in 1977, but his legacy lives on. I appreciate his breaking barriers and fearlessly embracing his artistic vision. Elvis Presley’s impact on music and culture is timeless, a testament to the enduring power of his artistry. His music has inspired generations and will continue to do so for many years to come.

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
BIOGRAPHY WRITING TEACHING IDEAS AND LESSONS
We have compiled a sequence of biography-related lessons or teaching ideas that you can follow as you please. They are straightforward enough for most students to follow without further instruction.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 1:
This session aims to give students a broader understanding of what makes a good biography.
Once your students have compiled a comprehensive checklist of the main features of a biography, allow them to use it to assess some biographies from your school library or on the internet using the feature checklist.
When students have assessed a selection of biographies, take some time as a class to discuss them. You can base the discussion around the following prompts:
- Which biographies covered all the criteria from their checklist?
- Which biographies didn’t?
- Which biography was the most readable in terms of structure?
- Which biography do you think was the least well-structured? How would you improve this?
Looking at how other writers have interpreted the form will help students internalize the necessary criteria before attempting to produce a biography. Once students have a clear understanding of the main features of the biography, they’re ready to begin work on writing a biography.
When the time does come to put pen to paper, be sure they’re armed with the following top tips to help ensure they’re as well prepared as possible.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 2:
This session aims to guide students through the process of selecting the perfect biography subject.
Instruct students to draw up a shortlist of three potential subjects for the biography they’ll write.
Using the three criteria mentioned in the writing guide (Interest, Merit, and Information), students award each potential subject a mark out of 5 for each of the criteria. In this manner, students can select the most suitable subject for their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 3:
This session aims to get students into the researching phase, then prioritise and organise events chronologically.
Students begin by making a timeline of their subject’s life, starting with their birth and ending with their death or the present day. If the student has yet to make a final decision on the subject of their biography, a family member will often serve well for this exercise as a practice exercise.
Students should research and gather the key events of the person’s life, covering each period of their life from when they were a baby, through childhood and adolescence, right up to adulthood and old age. They should then organize these onto a timeline. Students can include photographs with captions if they have them.
They can present these to the class when they have finished their timelines.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 4:
Instruct students to look over their timeline, notes, and other research. Challenge them to identify three patterns that repeat throughout the subject’s life and sort all the related events and incidents into specific categories.
Students should then label each category with a single word. This is the thematic concept or the broad general underlying idea. After that, students should write a sentence or two expressing what the subject’s life ‘says’ about that concept.
This is known as the thematic statement . With the thematic concepts and thematic statements identified, the student now has some substantial ideas to explore that will help bring more profound meaning and wider resonance to their biography.
BIOGRAPHY LESSON IDEA # 5:
Instruct students to write a short objective account of an event in their own life. They can write about anyone from their past. It needn’t be more than a couple of paragraphs, but the writing should be strictly factual, focusing only on the objective details of what happened.
Once they have completed this, it’s time to rewrite the paragraph, but they should include some opinion and personal commentary this time.
The student here aims to inject some color and personality into their writing, to transform a detached, factual account into a warm, engaging story.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING BIOGRAPHIES

Teach your students to write AMAZING BIOGRAPHIES & AUTOBIOGRAPHIES using proven RESEARCH SKILLS and WRITING STRATEGIES .
- Understand the purpose of both forms of biography.
- Explore the language and perspective of both.
- Prompts and Challenges to engage students in writing a biography.
- Dedicated lessons for both forms of biography.
- Biographical Projects can expand students’ understanding of reading and writing a biography.
- A COMPLETE 82-PAGE UNIT – NO PREPARATION REQUIRED.
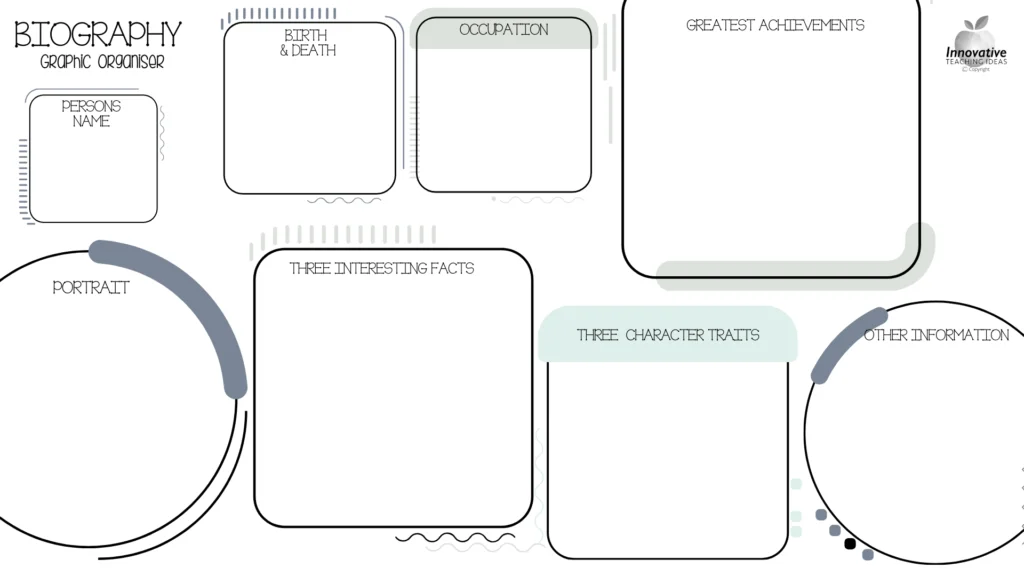
FREE Biography Writing Graphic Organizer
Use this valuable tool in the research and writing phases to keep your students on track and engaged.
WRITING CHECKLIST & RUBRIC BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
To Conclude
By this stage, your students should have an excellent technical overview of a biography’s essential elements.
They should be able to choose their subject in light of how interesting and worthy they are, as well as give consideration to the availability of information out there. They should be able to research effectively and identify emerging themes in their research notes. And finally, they should be able to bring some of their personality and uniqueness into their retelling of the life of another.
Remember that writing a biography is not only a great way to develop a student’s writing skills; it can be used in almost all curriculum areas. For example, to find out more about a historical figure in History, to investigate scientific contributions to Science, or to celebrate a hero from everyday life.
Biography is an excellent genre for students to develop their writing skills and to find inspiration in the lives of others in the world around them.
HOW TO WRITE A BIOGRAPHY TUTORIAL VIDEO

OTHER GREAT ARTICLES RELATED TO BIOGRAPHY WRITING

How to write an Autobiography

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Personal Narrative Writing Guide

How to Write a Biography in 8 Easy Steps
by Bennett R. Coles

This article will provide you with the basic building blocks required to write a biography starting from a blank page. Before we get into the nuts and bolts, let’s define what a biography is:
A biography is the full account of another person’s life (unlike an autobiography, which is the account of the author’s own life). For a biography to work, it must tell the story of an extraordinary or otherwise captivating life.
For this reason, most popular biographies center around famous people, be they politicians, artists, entrepreneurs, entertainers, or other well-known individuals. But this isn’t a must. Many biographies are also written about ordinary people who lived extraordinary lives outside the public spotlight.
Now, there are two main categories of biographies: authorized and unauthorized.
Authorized biographies are written with the explicit permission of the subject of the biography. The main advantage of authorized biographies is that they provide easy access to family members, friends and acquaintances — and even the subject themselves — during the very important research phase.
Unauthorized biographies, on the other hand, are written without the permission of the subject and therefore the authors usually have no access to their inner circle. As a result, authors must draw all of their information from sources that are at arms-length of the subject and therefore may be less reliable or truthful.
Let’s now begin to outline the process for creating a biography from the ground up.
Step 1: Choose the Biography’s Subject
The first thing you need to do is to choose the subject of your biography. In most cases this will be an obvious choice – that is, you’ll select someone you’ve been following and have admired for a long time.
You’ll already know their life story and will therefore know the aspects of their life that will be inspiring and compelling to your readers. In essence, you’ll be writing your biography for an audience of like-minded people who admire your subject as much as you do and who already have a deep thirst for any information about them.
Your subject might be a public figure, a politician, a business person, a scientist, an academic, or as stated in the introduction, an ordinary person who’s lived an extraordinary life. In every case, I advise that you seek their permission to write and publish the biography.
If granted, you’ll be able to gain immediate access to the subject and also family members and friends, who in many cases will provide you with exclusive details not published anywhere else.
Now, if you do get your subject’s permission, it’ll likely come accompanied with a first right of refusal for any information that they deem is not accurate as written and you’ll have to allow for the possibility of people changing their minds about certain aspects of your work as you go on.
You’ll just have to be flexible and accommodating, and sometimes this will be frustrating. But in the grand scheme of things, it’s a small price to pay for almost unlimited access to credible and in many cases unpublished information.
If you’re unsuccessful in obtaining your subject’s permission, you can still write an unauthorized biography, but there are some caveats you should be aware of:
- Stay away from writing unauthorized biographies about private persons (no matter how extraordinary their lives may be) because you’ll risk breaching privacy laws with serious legal consequences — in other words, those people may wish to remain private and will certainly not appreciate someone writing an unauthorized biography of their private lives.
- If you write about public figures, make sure you stick to publicly available information and that you don’t publish any private, sensitive or otherwise embarrassing information that is not in the public domain or that was illicitly obtained (e.g. through hacked or stolen information)
- If you choose to write a biography about some well-known figure in the public domain who you despise and you want to expose their “bad” side to the world, I advise that you consult with an attorney before you proceed, since you’ll be embarking on a journey potentially fraught with expensive litigation
Step 2: Study Popular Biographies
Before you proceed to the writing stage, you’ll be well-served to learn valuable lessons from those who’ve walked this path this before you, especially those who’ve found success in the marketplace.
Find 2-3 biographies about similar subjects to yours that have made it to the bestseller lists. For example, if you’ll be writing about a tech CEO, then find bestselling biographies of two or three other tech CEOs. Also, ensure that those biographies are of the same type as yours (i.e. authorized or unauthorized).
If cost is an object, get those books from the library but, if you can, purchase them instead so that you can make notations and underline text right on the page.
Next, read them twice cover-to-cover — first as a reader and then as a writer.
In your first reading pass, put on your audience hat and enjoy the read. Don’t pause to make notes yet so as not to disrupt the experience. In your second pass, however, make frequent stops to take notes about how the author uses literary devices, such as storytelling, hooks, descriptive techniques, and so on to drive their narrative.
If you read a story or passage that you deeply connect with, analyze it and try to figure out what it is about it that makes it work so effectively. Make note of the author’s literary choices, their use of language, the flow of the story, etc.
When you’re done with this initial genre research, you’ll be ready to start working on your biography!
Step 3: Choose Your Central Theme
Biographies are not unlike any other nonfiction book: you need to know who the target audience is before you write them (in this case it’ll be you and people like you). But just as importantly, you need to have a central theme that permeates the book.
In most cases, the central theme of your biography will be the aspect that has personally attracted you to your subject, such as:
- Their sense of urgency in enacting change in their personal lives and around them, which your readers will find inspiring
- Their wisdom and brilliance in their specific approach to life, business, etc., which will inform your readers about proven strategies that they’ll be able to use themselves
- Their prophetic power about certain world events, which could help readers make better choices about their investments, their choice of careers, etc.
- Or just their raw courage in the face of extreme adversity, a quality many people strive to achieve in their own lives
You always need to have a clear central theme your biography, an essence that goes beyond a strictly chronological account of someone life (which doesn’t make for a particularly engaging read).
Step 4: Research Your Subject
Now it’s time to begin your research about your subject and their lives.
There are two types of sources of information that you’ll need to rely on for your biography:
1) Primary sources, which originate from your subject and their close circle, and 2) Secondary sources, which originate from people at arm’s length to your subject. Here are some examples:
Primary sources:
- Anything publicly written or recorded by the subject
- Anything privately written or recorded by the subject (you’ll need their written consent to publish this information)
- Anything publicly written or recorded by direct witnesses to events that involved the subject
- Anything privately written or recorded by direct witnesses to events that involved the subject (again, you’ll need their permission to publish this information)
A Note on Privacy:
Whenever you publish information about a subject that’s not already in the public domain, particularly if the subject is not a public figure, you must ensure that you have their written permission to do so.
If you don’t and choose to publish anyway, you’re opening yourself to expensive litigation. People are entitled to their privacy and if you reveal unauthorized information that they deem to be embarrassing or injurious to their reputation in any way, expect them to seek financial damages through libel litigation and other legal remedies.
Secondary sources:
Writings or recordings by people who don’t know the subject personally and who haven’t directly witnessed events involving the subject. Examples are:
- Documentaries
- Magazine articles
- Online articles or recordings
A Note on Secondary Sources:
Before you use these sources, you’ll need to establish their credibility and the veracity of their accounts. Whenever you do refer to secondary sources in your biography, make sure to include the proper citations so that your readers can access the original information if they desire.
Also, make sure that you don’t infringe the copyright of your secondary sources by reproducing entire passages from their works, unless you obtain their written permission first (which usually carries a financial cost).
Step 5: Organize the Information
Once you’ve collected all the relevant information for your project, it’s time to put it into perspective by first creating a timeline for your subject’s life. You want to be able to see where it all fits chronologically so that you can begin to draw a through-line in relation to your biography’s central theme.
Your timeline will allow you to see the sequence of events that formed the character, ability or special circumstances that led your subject to live an extraordinary life. Also, this through-line will allow you to draw inspiration to choose specific time periods and past events should you wish to use flashbacks as a device in your narrative.
Once you’ve defined the proper chronology of events in your subject’s life, you can begin to draft a general outline for your biography, driven by your central theme. Begin by choosing the main milestones on your subject’s journey. These are the building blocks of your central theme. Then, break them down further into as many layers as necessary.
Finally, label your outline entries and, looking at your timeline, allocate your research materials throughout the outline by assigning them to the relevant label.
Step 6: Write Your Manuscript
You now have a fleshed-out timeline, an outline that aligns with your central theme, and lots of well-researched notes. In other words, you’re ready to begin the writing process ! But first, you’ll need to develop a clear writing routine.
When it comes to book writing , there’s no substitute for rubber to the road and this means that you’ll need to get into the habit of writing for a set amount of time every day. Like professional authors do, you’ll need to budget this time religiously and have clear boundaries.
Consistency is key, especially if you’ve never done a project like this before. What you don’t want to do is to write for 4-5 hours straight one day and then take a break for the next day or two.
How long should you write each day? I recommend between 2 and 3 hours but no longer than that — you don’t want to end up creatively spent by the end of a writing session.
Now, it’s critically important during this time that you have no disruptions such as phone calls, notifications from electronic devices, people walking in and asking you for help, etc.
So, enlist the help of those around you to keep you undisturbed, turn your smartphone and tablet to airplane mode, and mute the sound of your laptop.
Step 7: Hire a Professional Editor
When you complete the first draft of your manuscript, take a break to re-calibrate before you begin the re-writing process. Then revisit your manuscript from top to bottom as many times as necessary. This should take you a few weeks.
Keep in mind that the revision process is as creative as your original writing process but in a different way. While your initial writing is more like a stream of consciousness, the revision process is much more clinical and measured. What you’re looking for here is attention to detail, not the broad strokes.
But at some point, you’ll begin to experience diminishing returns for your efforts and here’s when you’ll need to hire the services of a professional editor. In fact, professional editors are paramount to the success of all authors, not just first-time authors but also those with long and illustrious careers.
No author worth their salt would dare publish an unedited book and neither should you. Your biography will be your calling card as an author and you never want to present a less than professional image. So, make sure you budget for a professional editor to take your diamond in the rough and make it shine!
Step 8: Hire a Professional Book and Cover Designer
Now that you have a fully edited manuscript, it’s time to focus on book design. Biographies need to not only be well-edited, but also to be well-produced. That means, they need to have a professional cover design that reflects your central theme, and a book interior as well-designed as your traditionally published competitors.
Don’t fall for the temptation to use free layout templates and book cover maker apps. As sharp as they may look on the surface, they’ll appear amateurish in comparison to what a professional can do and you don’t want to be judged by decision makers and gatekeepers on your path in a less-than-ideal light.
For example, some colors and visual patterns on your book cover may look great to you but won’t work in the market . The same goes for font styles, font sizes and font treatments. Leave this important work to the pros and you’ll never regret your decision.
Best of luck on the journey to your first biography!
If you enjoyed this article and are in the process of writing a nonfiction book, be sure to check out my free nonfiction success guide , drawn from years of experience editing books for bestselling authors (including a New York Times bestseller) and ghostwriting for CEOs and politicians. Simply click here to get instant access .
Leave me a comment below if you have any questions or a specific need that I can help you address – I operate an author services firm that specializes in helping entrepreneurs, professionals and business owners who want to publish books as a calling card for prospects, to establish their status as an expert or to just to generate additional leads for their businesses.
Here are some related posts I highly recommend:
How to write a compelling book in 12 steps: a must-read guide for nonfiction authors, what to look for in a top book self-publishing company, the 7 most effective book promotion ideas for nonfiction authors.

One response to “How to Write a Biography in 8 Easy Steps”
Very useful hints indeed
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Same Cascadia, New Management!
by Harry Wallett

The Inevitable Journey of Ghazanfar Iqbal: Expatriate, Entrepreneur, and Author

Publishing for Peace: Author Ben JS Maure Inspires Canadian Peacekeepers

Unleashing Literary Flames: Award-Winning Author TK Riggins Keeps Readers Coming Back for More with 7-Book Series
Get our free definitive guide to creating a nonfiction bestseller here.
How to Write an Interesting Biography
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A biography is a written account of the series of events that make up a person's life. Some of those events are going to be pretty boring, so you'll need to try to make your account as interesting as possible!
Every student will write a biography at some point, but the level of detail and sophistication will differ. A fourth grade biography will be much different from a middle school-level biography or a high school or college-level biography.
However, each biography will include the basic details. The first information you should gather in your research will include biographical details and facts. You must use a trustworthy resource to ensure that your information is accurate.
Using research note cards , collect the following data, carefully recording the source for each piece of information:
Including Basic Details
- Date and place of birth and death
- Family information
- Lifetime accomplishments
- Major events of life
- Effects/impact on society, historical significance
While this information is necessary to your project, these dry facts, on their own, don't really make a very good biography. Once you've found these basics, you'll want to dig a little deeper.
You choose a certain person because you think he or she is interesting, so you certainly don't want to burden your paper with an inventory of boring facts. Your goal is to impress your reader!
Start off with great first sentence . It's a good idea to begin with a really interesting statement, a little-known fact, or really intriguing event.
You should avoid starting out with a standard but boring line like:
"Meriwether Lewis was born in Virginia in 1774."
Instead, try starting with something like this:
"Late one afternoon in October, 1809, Meriwether Lewis arrived at a small log cabin nestled deep in the Tennessee Mountains. By sunrise on the following day, he was dead, having suffered gunshot wounds to the head and chest.
You'll have to make sure your beginning is motivating, but it should also be relevant. The next sentence or two should lead into your thesis statement , or main message of your biography.
"It was a tragic end to a life that had so deeply affected the course of history in the United States. Meriwether Lewis, a driven and often tormented soul, led an expedition of discovery that expanded a young nation's economic potential, increased its scientific understanding, and enhanced its worldwide reputation."
Now that you've created an impressive beginning , you'll want to continue the flow. Find more intriguing details about the man and his work, and weave them into the composition.
Examples of Interesting Details:
- Some people believed that Lewis and Clark would encounter elephants in the western wilderness, having misunderstood the wooly mammoth bones discovered in the United States.
- The expedition resulted in the discovery and description of 122 new animal species and subspecies.
- Lewis was a hypochondriac.
- His death is still an unsolved mystery, although it was ruled a suicide.
You can find interesting facts by consulting diverse sources.
Fill the body of your biography with material that gives insight into your subject's personality. For instance, in a biography about Meriwether Lewis, you would ask what traits or events motivated him to embark on such a monumental exercise.
Questions to Consider in Your Biography:
- Was there something in your subject's childhood that shaped his/her personality?
- Was there a personality trait that drove him/her to succeed or impeded his progress?
- What adjectives would you use to describe him/her?
- What were some turning points in this life?
- What was his/her impact on history?
Be sure to use transitional phrases and words to link your paragraphs and make your composition paragraphs flow . It is normal for good writers to re-arrange their sentences to create a better paper.
The final paragraph will summarize your main points and re-assert your main claim about your subject. It should point out your main points, re-name the person you're writing about, but it should not repeat specific examples.
As always, proofread your paper and check for errors. Create a bibliography and title page according to your teacher's instructions. Consult a style guide for proper documentation.
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
- How to Write a Personal Narrative
- 10 Steps to Writing a Successful Book Report
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
- Tips for Writing an Art History Paper
- How to Write a Great Book Report
- How to Write a Narrative Essay or Speech
- How to Help Your 4th Grader Write a Biography
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- How to Write a Research Paper That Earns an A
- How to Write a Film Review
- Overused and Tired Words
- How to Write a Great Essay for the TOEFL or TOEIC
- Assignment Biography: Student Criteria and Rubric for Writing
Business , Education
24 Biography Templates and Examples (Word | PDF | Google Docs)
Biographies serve as a fascinating lens into the lives of individuals, ranging from influential family members and historical figures to renowned personalities. Whether you’re a student, an aspiring writer, or someone captivated by the art of telling a life story , grasping the essential elements of a biography is vital. Writing a biography goes beyond compiling facts; it involves crafting a narrative that educates and inspires your readers. This guide provides you with practical steps, style advice, and, importantly, biography templates to assist you in structuring your work effectively. With these resources, you can start to create biographies that not only inform but also captivate your audience. Are you ready to capture the essence of a life story in words? Let’s delve into the fundamentals of crafting a compelling and memorable biography.
Biography Templates & Examples

Aesthetic Biography Template
An Aesthetic Biography Template is a carefully designed layout that allows individuals to present their personal and professional information in an organized and visually appealing manner. The template provided in the previous response offers a structured format for users to showcase their educational background, work experience, skills, and personal interests. This format is particularly useful for creating a compelling narrative of one's life and achievements, making it ideal for applications, personal websites, or professional profiles. The inclusion of sample data guides users on how to effectively fill out each section, ensuring clarity and coherence in presenting their unique story.

Short Biography Template
A Short Biography template is a structured format for summarizing an individual's personal, educational, and professional background. It offers a concise yet informative way to present one's achievements, skills, and experiences. The template provided above is designed to capture a wide range of details, from basic personal information to career highlights and skills. It is versatile and can be tailored to suit different situations, whether for a professional profile, a speaker introduction, or a personal website. The inclusion of sample data in the brackets makes it user-friendly, allowing for easy customization. This template serves as a useful starting point for anyone looking to create a clear and engaging biography.

Professional Biography Template
A Professional Bio Template is a structured format designed to aid individuals in crafting a succinct and engaging biography that highlights their career achievements, skills, and personal qualities. This template helps users efficiently organize and present their professional story, ensuring that key elements like career milestones, skills, and personal interests are effectively communicated. This assists in creating a compelling bio that resonates with various audiences, such as potential employers or networking contacts, enhancing their professional presence and impact.

Personal Biography Template
A personal biography template is a structured outline designed to guide individuals in documenting their life stories, achievements, and experiences. It provides a framework to organize personal details in a coherent and engaging manner. This template, created in our prior response, can assist users by simplifying the process of writing their biography. It offers a clear structure, ensuring that key aspects of one's life are highlighted effectively. This can be particularly useful for creating professional bios, personal introductions, or for preserving personal history.
You can explore more free biography templates and examples in the collection at Highfile . This resource offers a diverse range of templates suitable for various needs, whether for professional, personal, or academic purposes.

What Is a Biography?
A biography is an in-depth narrative of someone’s life, written by another person. It encompasses more than just basic facts like birthplace and education. A biography delves into the subject’s personal experiences, significant life events, and the influences that shaped their character and achievements. It’s not just a timeline of events; a biography weaves these details into a compelling story, offering insights into the individual’s motivations and impacts. The aim is to present a well-rounded portrait that is both informative and engaging, allowing readers to understand and empathize with the subject’s journey. A biography, in essence, is a vivid window into another person’s life experience, capturing their unique contributions and the essence of their existence.
Fun Fact: Did you know that one of the earliest biographies ever recorded was about an ancient Egyptian official named Ptahhotep around 2400 BC? This ancient biography was not written in a book but carved on the walls of his tomb, depicting his life and achievements. This highlights how the art of biography writing has been significant throughout human history, evolving from ancient carvings to modern digital formats!
Essential Elements of a Biography Template
Crafting a professional biography involves creating a concise yet comprehensive summary of your career objectives, current position, and notable achievements. This type of bio is ideally suited for professional networking platforms like LinkedIn or AngelList, where a more detailed and career-focused narrative is expected compared to the brief bios often seen on other social media sites.
Key Components to Include in Your Professional Biography:
- Your Name : Clearly state your full name at the beginning.
- Personal Brand or Company Affiliation : Mention your business or the brand you represent.
- Professional Tagline or Current Role : Include your current job title or a tagline that encapsulates your professional essence.
- Career Aspirations : Briefly outline your career goals or what you aim to achieve professionally.
- Unique Personal Fact : Share an interesting personal detail that sets you apart.
- Top Achievements : Highlight two or three significant accomplishments relevant to your professional trajectory.
While primarily professional in tone, don’t hesitate to weave in personal elements like a favorite book or hobby. This adds a human touch, making your bio more relatable and engaging. Remember, a well-rounded biography balances professional accomplishments with personal insights, creating a holistic view of you as both a professional and an individual.
How to Write a Biography
Writing a compelling biography requires a structured approach. Follow these steps to create an engaging and informative biography:
- Choose a Subject : Select a person whose life story is interesting and impactful. Consider whether their contributions or experiences have the potential to inspire or connect with your audience.
- Obtain Permission : If your subject is alive, obtaining their consent is crucial, as it involves discussing personal details. For deceased or public figures, ensure all information is factual to avoid legal issues.
- Conduct Thorough Research : Gather information from primary sources like interviews, letters, and personal accounts for an authentic portrayal. Complement these with secondary sources like documentaries and articles for additional context.
- Formulate a Thesis : In the opening section, clearly state what the reader will learn from the biography. This thesis sets the stage for the narrative to unfold.
- Organize Chronologically : Structure the biography in a timeline format, presenting events in the order they occurred. This helps in maintaining a clear narrative flow.
- Incorporate Flashbacks : Skillfully use flashbacks to provide context or highlight significant past events, enriching the narrative without overloading it with background details.
- Inject Personal Insight : While sticking to factual information, don’t shy away from adding your own perspective on the subject’s achievements and their societal impact. This adds depth and personal touch to the biography.
A good biography balances factual accuracy with narrative flair, bringing the subject’s story to life in a way that resonates with the readers.
Tips on Writing a Biography
Crafting a biography requires a blend of accuracy, creativity, and attention to detail. Here are some essential tips to guide you in writing an effective biography:
- Write in Third Person : Use the third person perspective for a professional and objective tone.
- Inject Humor Appropriately : While maintaining professionalism, subtle humor can make the biography more engaging and relatable.
- Be Mindful of Length : Keep an eye on the word count. A biography should be comprehensive yet concise enough to hold the reader’s interest.
- Narrate a Story, Not Just Facts : Instead of listing events, weave them into a compelling narrative to make the biography more interesting and readable.
- Include Relevant Links : Provide links to your work, projects, or publications to offer readers additional context and evidence of your achievements.
- Provide Contact Information : Make it easy for readers to reach you by including up-to-date contact details.
- Edit Thoroughly : Ensure your biography is free of errors and well-polished. Comprehensive editing enhances readability and professionalism.
- Keep it Concise : Aim for brevity while ensuring all critical information is included. A succinct biography is often more impactful and memorable.
Important Note: Before diving into our FAQs, it’s crucial to remember that while a biography aims to be factual and accurate, it also requires a respectful approach, especially when dealing with sensitive aspects of a person’s life. As a biographer, your responsibility extends beyond mere storytelling; it involves ethical considerations, such as respecting privacy and presenting information in a manner that is fair and considerate to the subject and their family. Keep this in mind as you explore the frequently asked questions and embark on your journey of writing a biography.
For online platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest, and Twitter, a three-sentence bio should be concise yet informative. It should briefly introduce you, focusing on key aspects: Your Name : Start with your full name. Your Current Role : Mention your profession or the role you’re known for. A Notable Achievement or Personal Touch : Include a significant accomplishment or a unique personal detail (like a hobby or goal). This format ensures your bio is succinct but covers essential details.
A personal biography is a brief narrative focusing on your professional life, used for job searches or on professional platforms like LinkedIn. It’s slightly more detailed than a social media bio and should include: Your Name Personal Brand or Company : If applicable. Professional Tagline or Current Role Two or Three Key Achievements : Choose the most relevant and impressive ones. While primarily professional, feel free to add a personal detail like a hobby or favorite book to give a glimpse of your personality.
In a work-related bio, focus on aspects directly relevant to your professional life. This might be more detailed, including your career journey, key skills, and notable projects or roles you’ve held. Personal anecdotes or interests can be included if they relate to your professional persona or add value to your professional story. Remember, the context dictates the bio’s content and tone. Tailor it to suit the platform and the audience you are addressing.
When choosing a subject, consider individuals whose life stories are not only interesting but also have the potential to inspire or educate others. Look for unique experiences, significant achievements, or challenges they’ve overcome. Public figures, historical personalities, or even unsung heroes in your community can make excellent subjects.
Begin with an engaging opening that captures the essence of your subject’s life. This could be a pivotal moment, a significant achievement, or an anecdote that reflects their character. Starting with something compelling draws readers in and sets the tone for the biography.
Effective research methods include conducting interviews with people who know the subject well, reviewing primary documents like letters or diaries, and consulting reputable secondary sources for historical context. Online archives, libraries, and specialized databases are also valuable resources.
To maintain objectivity, present facts without bias, and avoid letting personal opinions color the narrative. Acknowledge different perspectives on the subject’s life, especially in controversial or unclear aspects. Being fair and balanced is key to a trustworthy biography.
Yes, you can write a biography about a family member. However, it’s important to balance personal insights with objective storytelling. Ensure you have enough distance to present their story truthfully and respect their privacy and perspective.
Approach sensitive topics with care and respect. Verify the accuracy of such information and consider its relevance to the overall story. Be mindful of the impact this could have on the subject and their family, especially if they are still living.
The length of a biography depends on the depth of the subject’s life story and the intended audience. Some biographies are short, focusing on key events, while others are comprehensive, covering the subject’s life in detail. Tailor the length to suit the story’s complexity and readers’ expectations.
Final Thoughts
Crafting a biography requires a thoughtful blend of accuracy and creativity to captivate and engage your readers. By focusing on these essential elements and following the outlined steps, you can transform a simple life story into a compelling narrative that holds the reader’s interest from start to finish. Whether you’ve always wanted to write a biography or are just beginning to explore this genre, this guide provides a solid foundation to embark on your biographical writing journey. Remember, a well-written biography not only informs but also inspires, offering a deeper understanding of the subject’s life and legacy.
How did our templates helped you today?
Opps what went wrong, related posts.

23+ Business Travel Itinerary Templates

Restaurant Employee Evaluation Form

Peer Evaluation Form: Templates and Examples

Free Newspaper Templates

40 Free Event Program Templates

44 Open House Sign in Sheet Templates

22+ Free Packing Slip Templates

40+ Free Christmas Wish List Templates
Thank you for your feedback.

How to Write a Short Professional Bio
U.S. News & World Report
June 25, 2024, 8:00 PM
- Share This:
- share on facebook
- share on threads
- share on linkedin
- share on email
A professional bio can help you stand out from the crowd by showcasing who you are and what you strive for in your work. However, writing a professional biography for potential employers, clients, colleagues or networking is easier said than done. It can feel awkward to write about yourself and fluently express your contributions.
Here are essential elements for any professional bio:
— Your name and professional title
— What you do in your current position
— Your branding statement
— One to two outstanding professional accomplishments with measurable results
— One to two details to describe your personality
You may post your professional bio on your personal website, your personal blog, your company’s website, your professional portfolio, your LinkedIn “about” section, your Facebook business page or another social media site such as Instagram.
While the length of your bio will vary depending on where you aim to publish it, this outline of elements will help you create a complete bio. For example, if you post your bio in your “about” section on LinkedIn , you are limited to about 2,000 characters. Your website might include a lengthier bio, but a short professional bio works best on social media pages.
[ READ: Job Skills to List on Your Resume (And What to Exclude) ]
How to Start a Biography
You may know who you are professionally, but it can be hard to articulate this clearly and precisely, especially in writing. To start, outline what you want to include in your bio using the elements above. You can use your resume and other documents where you’ve tracked professional accomplishments to help you, but avoid copying and pasting.
You can also look up the professional bios of successful professionals whom you admire. What impresses you about their bios? Take note of the elements that stand out to you and use them as inspiration for your own bio.
To help you come across authentically, think about what you would say out loud to someone if they asked you about the items on the list above. For example, how would you explain your job or branding statement? Write it down. This can help you to “see” your voice on paper.
Generally, a professional bio should be written in third person , especially if it’s for a company website. However, there are exceptions. For example, your “about” section on LinkedIn should be written in first person.
Here are some additional details to include on your professional bio.
Your Name and Professional Title
Include your full name and your title. For example: John Doe, Marketing Director. If you don’t have a job, list your last job title or certifications .
What You Do in Your Current Position
This helps the reader understand if your experience would be a good fit for their organization. For example: John specializes in all forms of digital marketing, including social media marketing, online advertising and search engine optimization.
Your Branding Statement
A branding statement is a sentence or two that reflects your professional values and how you stand out from others in the industry. For example: John is diligent and adapts seamlessly to evolving processes and technologies. This allows him to provide the best service to his customers.
Outstanding Professional Accomplishments
Listing a few accomplishments allows readers to understand your level of expertise and how you positively contribute to your organization or industry. Examples could include how you helped your company save money, increased visibility or attained positive results for your clients.
Personal Details
Including a few personal details can help a reader connect with you on a more personal level. This may make them more likely to reach out to you. Examples could include hobbies, pets or interesting details about your background that you feel comfortable sharing.
[ See: Red Flag Phrases to Leave Off Your Resume. ]
How to Write a Bio for Work
If your company has asked you to write a professional bio for its website, make sure you include the requested elements. If you are unsure, ask your supervisor for additional information. Also, check your company’s “about” page and note what others have included in their bios. Try to follow the same format and order of information. Once you have finished your professional bio, ask someone you trust to proofread it for grammatical errors and clarity.
Sean McLoughlin, vice president of operations at the executive search firm HireMinds, recommends always writing your corporate bio with the company in mind. “If you have been with the company for a significant amount of time, your short professional bio should highlight achievements within the company. If you’re new to the organization, they should be written highlighting why you’re going to be successful in your new role,” he said in an email.
Professional Bio Examples
Here are a few examples of what a short professional bio could look like:
1. Physician Sample Bio
James Oliver is an empathetic family medicine physician leveraging 10-plus years of experience promoting health and improving the quality of patients through changes in research, medical education and patient care across organizations and the community. He’s known for his innovative, tactical thinking and authentic, influential leadership style. He’s also skilled in building the relationships, consensus and strategic partnerships needed to move large-scale and challenging initiatives forward.
2. Graphic Designer Sample Bio
Amy Lin is a freelance graphic designer known for her creative thinking and attention to detail. With over a decade of experience in the industry, Amy specializes in translating complex ideas into compelling visual narratives. She has a background in visual arts and has worked on diverse projects ranging from logo designs to website layouts. In her free time, Amy likes to find inspiration for her art in nature, travel, dance and music.
3. Software Engineer Sample Bio
Lucy Michaels is a senior software engineer at Meta who works closely with product and design teams to build innovative application experiences for the iOS platform. Her technical prowess spans from backend systems architecture to frontend user interface design, with a strong focus on optimizing performance and usability. She’s also well-versed in various programming languages and frameworks like C++, Ruby on Rails, Python and Java. On the weekends, Lucy enjoys going on hikes and training Muay Thai.
4. Human Resources Sample Bio
Michael Sanchez is a human resources professional with three years of experience in talent acquisition and HR operations. His empathetic approach and strong communication skills make him a go-to person for resolving issues and boosting team morale. He’s also played a key role in building high-performing teams and is known for his strong interpersonal skills and ability to create a supportive work environment. With him on board, you can expect a workplace where people feel valued and empowered to shine.
5. Sales Sample Bio
Sarah David is a tech sales specialist known for her talent in building strong client relationships and driving revenue growth. She has a solid background in the tech industry and excels at understanding customer needs and consistently exceeding quota each month. Outside of work, Sarah enjoys doing yoga and roller skating.
6. First-Person Sample Bio
Hi! My name is Tracy Jones. I’m a content marketing specialist passionate about helping brands connect authentically with their audiences through compelling storytelling and well-defined content strategies. Over the past six years, I’ve had the privilege of working with leading brands, including tech giants like Microsoft and startups like Airbnb, to help them create engaging blog posts and social media campaigns. In my free time, I enjoy learning Spanish and spending time with my three cats.
[ Read: How to Highlight Interpersonal Skills in Interviews and Resumes. ]
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing Your Professional Bio
— Being too generic. Always tailor your bio to reflect your unique skills and avoid using clichés or generic statements that don’t differentiate you from others in your field. “Nobody expects a generalist to solve their issues,” Sharon Rose Hayward, a women’s career coach and founder at Winning at Work, said in an email.
— Exaggerating or misrepresenting. Exaggerating your accomplishments or misrepresenting your achievements won’t do you any good and could damage your reputation. Be truthful when describing your skills and experiences.
— Not updating regularly. Don’t use outdated information that no longer reflects your current professional status and make sure to update your professional bio periodically.
— Committing grammar mistakes. A bio riddled with errors gives the impression that you’re careless and lack attention to detail. Always triple-check your professional bio before publishing, and consider asking a friend or colleague to proofread it.
— Using industry or location-specific abbreviations or acronyms. Industry jargon and location-specific abbreviations or acronyms likely mean nothing to your readers. “Leaving someone wanting to know more because they’re interested is different than creating confusion,” Hayward said.
— Making your bio too long. Laurie Cure, executive coach and CEO at Innovative Connections, a consulting company that provides organizational solutions, warns against writing a long bio. “Have you ever sat at a conference and spent the first five minutes of a session listening to the moderator read a two-page bio of how great someone is? It’s a bore. Always keep your bio short and sweet,” she said in an email.
Be Authentic
Focus on highlighting your unique strengths and showcasing your personality. “Your word choice and language will say a lot about who you are and how you want to be represented,” Cure said. “Your personality will show in how you describe yourself and your experiences, as well as what you choose to highlight.”
Don’t be afraid to embrace your individuality and emphasize what truly matters to you. Whether you choose to tell your story with a polished professional tone or a more conversational approach, always let your bio reflect your authentic self.
More from U.S. News
10 Communication Skills for Your Resume
How to Write an Objective for a Resume
15 Best Jobs for Remote Workers
How to Write a Short Professional Bio originally appeared on usnews.com
Update 06/26/24: This story was published at an earlier date and has been updated with new information.
Related News
Shares of Trump Media swing wildly after first US presidential debate, fall 10%

Chevron takeaways: Supreme Court ruling removes frequently used tool from federal regulators

Divided Supreme Court rules in major homelessness case that outdoor sleeping bans are OK
Recommended.

Where to celebrate the Fourth of July in the DC area

Fourth of July in DC means fun, fireworks and, of course, road closures

Police identify man killed in Fairfax County motorcycle crash
Related categories:.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Choose a voice. The first step in writing a short bio is deciding on a voice. For our purposes, choosing a voice involves deciding whether you are writing in the first or third person. Writing in the first person means using the words "I" and "me", and writing in the third person means using your name.
A biography is the story of someone's life as written by another writer. Most biographies of popular figures are written years, or even decades, after their deaths. Authors write biographies of popular figures due to either a lack of information on the subject or personal interest. A biography aims to share a person's story or highlight a ...
Whether you want to start writing a biography about a famous person, historical figure, or an influential family member, it's important to know all the elements that make a biography worth both writing and reading. Biographies are how we learn information about another human being's life. Whether you want to start writing a biography about ...
2. Introduce yourself… like a real person. This is one of the most important pieces of understanding how to write a personal biography. Always start with your name. When many people start learning how to write a bio, they skip this important part. People need to know who you are before they learn what you do.
1. Go for a chronological structure. Start chronologically from the subject's birth to their death or later life. Use the timeline of the person's life to structure the biography. Start with birth and childhood. Then, go into young adulthood and adulthood.
Conduct relevant interviews. Whenever possible, seek firsthand accounts from those who knew or interacted with the subject. Conduct interviews with family members, friends, colleagues, or experts in the field. Their insights and anecdotes can provide a deeper understanding of the person's character and experiences.
How to Write a Short Bio Part 1. What to Include in a Short Professional Bio Part 2. Example of a Formal Short Bio Part 3. Example of a Casual Short Bio Part 4. Examples of Well-Written Short Bios Part 5. Short Bio: Best Templates Part 6. Tips for Writing a Short Bio Part 7. Optimizing Your Bio for Different Platforms Part 8.
Facebook. These are just some of the story elements you can use to make your biography more compelling. Once you've finished your manuscript, it's a good idea to ask for feedback. 7. Get feedback and polish the text. If you're going to self-publish your biography, you'll have to polish it to professional standards.
How to Write a Biography in 11 Simple Steps. Here are the steps you need to take to learn how to write a biography: 1. Read other biographies. Austin Kleon, Author of Steal Like an Artist, says "the writer tries to master words. All of these pursuits involve the study of those who have come before and the effort to build upon their work in ...
A good writing routine can make the process smoother and more enjoyable. Choose a Writing Space: Find a quiet, comfortable place free of distractions. Set a Time: Write at the same time each day to build a habit. Prepare Mentally: Take a few minutes before writing to clear your mind and focus on the task ahead.
Your short bio should include your brand, your accomplishments, and your values and goals. Your short bio should be one to three short paragraphs or four to eight sentences long. Knowing how to write a concise, informative, and interesting biography about yourself can help throughout various parts of the professional process.
Wondering how to write a biography? We've constructed a simple step-by-step process for writing biographies. Use our tips & tricks to help you get started!
By acknowledging both successes and challenges, readers gain a more honest understanding of their journey. Balancing positives and negatives helps readers empathise with the subject, connecting them on a deeper level and offering a more genuine insight into their lives. Emotions are a potent tool in biography writing.
A biography is an account of someone's life written by someone else.While there is a genre known as a fictional biography, for the most part, biographies are, by definition, nonfiction. Generally speaking, biographies provide an account of the subject's life from the earliest days of childhood to the present day or, if the subject is deceased, their death.
The process of writing a biography can be easier with a map to follow. You can follow these steps to write a biography: 1. Research your subject. The first step to writing a great biography is to spend time conducting extensive research on the person you're writing about, their career, their family and other information about them.
Step 3: Choose Your Central Theme. Biographies are not unlike any other nonfiction book: you need to know who the target audience is before you write them (in this case it'll be you and people like you). But just as importantly, you need to have a central theme that permeates the book.
How to Write a Short Bio: 7 Things to Put in Your Bio. Whether for your company's website or your own personal use, it's important to know how to write a short bio about yourself and your personal accomplishments. These little blurbs help you stand out from the crowd by showing what makes you a unique and qualified addition to the workforce.
2. Get clear on the basicfacts of the person's life. Reading a few short articles—Wikipedia- or encyclopedia-style articles, obituaries, feature articles, or academic articles, for example—should help you to form a short profile of your subject. 3. Start digging a little deeper to learn more about the person and their life.
Start off with great first sentence. It's a good idea to begin with a really interesting statement, a little-known fact, or really intriguing event. You should avoid starting out with a standard but boring line like: "Meriwether Lewis was born in Virginia in 1774." Instead, try starting with something like this:
1. Choose the appropriate name and professional title. Writing a professional bio starts by choosing the right name and professional titles to use. Different names and titles can change depending on the purpose and audience of the bio. For example, some people choose to use a different first name in their bio instead of their given name.
When writing a biography, research effectively and gain the support of the publishing house. Write a biography with tips from an author in this free video on...
A personal biography template is a structured outline designed to guide individuals in documenting their life stories, achievements, and experiences. It provides a framework to organize personal details in a coherent and engaging manner. This template, created in our prior response, can assist users by simplifying the process of writing their ...
While the length of your bio will vary depending on where you aim to publish it, this outline of elements will help you create a complete bio. For example, if you post your bio in your "about ...