
Aligning human resources and business strategy
Reading time: about 7 min
You have to consider many factors when you create a go-to-market or business strategy. From brand messaging to product roadmaps to sales processes, effective business strategies also rely on the input of lots of people across many departments.
Few departments have a better bird’s-eye view of the entire organization than human resources. HR professionals can see both why a strategy exists and how it’s developed and implemented. Yet, too often, HR departments don’t have a seat at the strategy table. Let’s take a look at how HR can help shape business strategy and bring it to life.
Why HR should get involved with setting corporate strategy
Today, business moves faster than ever—it’s a platitude, but it’s still true. Technologies, industries, and consumers themselves continually evolve in a digitally-driven market, and companies continuously shift their strategic focus to keep pace.
This culture of change has a significant impact on people. Every business decision has a real-life impact, and HR departments are specially equipped to inform strategy and help employees navigate the resulting changes.
Consider these reasons why it’s so important for HR to align with business strategy:
- Move in lockstep with the rest of the company: Goals are always more achievable when there is universal buy-in and alignment across teams.
- Give HR initiatives a strategic focus: In today’s changing economy, there are countless ways to recruit, train, attract, invest in, and support employees. But it’s impossible to tackle every initiative all at once. Aligning with business strategy gives HR a strategic focus and helps prioritize goals.
- Secure the right talent: Good talent is always valuable, but companies may need to invest in different skill sets or roles at different times. Understanding the strategic goals of the business will help HR attract and retain the right talent at the right time.
What role human resources plays in strategic planning
So how does HR become part of the broader business decision-making process? How do HR departments move from a reactive, service-oriented function to a more executive-level, strategic one?
It starts with setting clear objectives for the department and strong values for the entire organization. Companies with documented values are less likely to ignore the real-life impact of any strategy shifts or big decisions. Consider these steps as you begin.
1. Align and set your HR goals
The main strategic role of HR is to create goals to help meet key business objectives. Goals may vary depending on the company’s strategic plan, but focusing on HR fundamentals is an excellent place to start. Here are some areas of HR most commonly affected by broader strategic business shifts.
Organizational structure
The way companies are organized largely depends on their current strategic objectives and growth stages. If a company is in a high-growth stage, it may have a sales-driven culture with more sales employees and sales executives in decision-making roles. Mature companies with a retention-focused strategy may hire more customer success roles.
See 7 types of organizational structures—along with pros and cons for each—to find one that fits your strategy.
Employee compensation
Maybe current business goals are more focused on employee retention or culture-building. Conversely, perhaps the company needs to cut costs. In either case, compensation structure may be an important consideration. When HR is aligned and informed on these goals, they can make strategic decisions to help the organization meet them.
Employee development
Depending on the business goals and immediate initiatives, it may be necessary to train employees on new skill sets. Some employees may resist additional roles and responsibilities, so the role of HR in these situations is to both evangelize additional training and ensure teams are developed to keep pace with shifting needs.
Performance reviews
Change management .
As a people-focused department, HR often has the best pulse on employee sentiment throughout the organization. HR departments can encourage employees to share their feedback on new business strategies or technology investments to ensure any changes or strategic shifts make sense from an operational perspective.
2. Formulate specific actions to hit those goals
Once you’ve aligned and set goals, it’s time to develop action plans to execute your HR strategic vision. Focus on developing and improving processes for recruiting, hiring, employee development, and performance reviews.
When you develop an action plan, you'll need to have a clear understanding of your organization’s current structure and identify any gaps or shortcomings in your processes. Where should you invest more in recruiting? If budgets are tight, what training or employee development programs could maximize the productivity and effectiveness of your existing talent? The ability to visualize where every player fits into the larger organization can help HR departments align employees to business strategy, maximize efficiency, and see data in context to drive better decisions. Org charts and related visuals can help HR departments optimize organizational structure at every level and make better decisions, such as:
- Assigning employees where their skills can make the most significant impact
- Making informed decisions about pay, equity, and performance
- Modeling current and future org structures to determine how best to scale your business

Does your organization needs to hire new talent to meet its strategic goals? See how to develop a staffing plan.
3. Track and measure performance
Historically, the role of HR has stayed in the “softer,” people-focused side of the business. However, people analytics are now the new HR, and HR departments are just as responsible for reporting on the performance of their initiatives as any other department.
With human resource alignment around data-driven goals, HR leaders can ensure that decision-making not only aligns with strategic business objectives but also helps drive those goals. HR leaders can analyze data from sales, marketing, and accounting to break down departmental silos and better align with overall business goals.
According to a Bersin by Deloitte study, data-driven HR teams are four times more likely to be respected by their business counterparts, which can result in more input in strategic decision-making. By combining departmental data and HR data and visualizing it all in a single workspace, HR departments can better align their decisions to business strategy. Consider the ways these types of people analytics can impact the broader business:
Employee analytics
Measure the performance of all the HR initiatives in terms of cost, time, performance, then use a dashboard to track recruiting times, onboarding speed, employee satisfaction, and employee salaries. This data-driven approach to people management helps HR departments evaluate pay disparities, track employee retention, identify trends, and see critical employee metrics that will provide quick insights for better decision-making.
All this gives you the chance to onboard new employees more efficiently, improve employee satisfaction, and reduce retention.
Talent analytics
Today, effective talent acquisition goes way beyond budget and headcount. HR departments can rely on algorithmic data to quickly sift through deep pools of qualified applicants to attract and retain top talent.
Today, effective talent acquisition goes way beyond budget and headcount. HR departments can rely on algorithmic data to quickly sift through deep pools of qualified applicants to attract and retain top talent. This allows you to identify and attract high-quality employees and improve your workforce planning.
Predictive analytics
Set up indicators to see when an employee is at risk of leaving the company. HR departments can use data to identify risk facts and predict employee churn and how this will affect the company. This leads to better retention and employee planning
Invest in better people planning
Modern human resources departments manage much more than hiring, onboarding, and benefits. Aligning HR with business strategy can boost employee satisfaction and performance, ensure teams are aligned to help the business achieve its strategic objectives and increase their influence and decision-making power across the organization.

Align teams, boost efficiency, and drive better decisions with Lucidchart.
About Lucidchart
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Related articles
4 steps to strategic human resource planning.
Many CEOs believe that their employees are the most important factor in their company’s economic success, so if you want to succeed, find and keep the best talent. Learn how to develop your strategic human resource plan.
What does HR actually do? 11 key responsibilities
Everyone knows that HR is an important department in your organization, but few employees know why. Read our in-depth description of what the HR department does (or what they should be doing) to meet the needs of employees.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
By registering, you agree to our Terms of Service and you acknowledge that you have read and understand our Privacy Policy .
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Human Resources 6 Steps to Create a Strategic HR Plan [With Templates]
6 Steps to Create a Strategic HR Plan [With Templates]
Written by: Jessie Strongitharm Aug 25, 2022

The backbone of any successful business is the people and processes behind it — that’s why creating a human resources (HR) plan is key. This strategic document drives your business forward by evaluating where your workforce is at, and comparing it to future needs.
Without an HR plan, organizations can suffer from issues that would have otherwise been avoided. From productivity pitfalls to costly employee turnover, there’s no shortage of risks you can sidestep if you do human resource planning in advance.
Not sure where to start? No worries. I’ve outlined six steps you can take to create an effective HR plan that ensures your organization is well-staffed and well-served. You’ll also find a variety of HR templates that you can customize in just a few clicks — no design expertise required.
Click to jump ahead:
What is human resource planning?
- Assess employees’ current skill levels
- Forecast your labor needs based on available information
- Revisit your organizational design
- Outline how you will manage, motivate and retain talent
- Align your workforce planning with your budget
- Establish KPIs for your human resource planning objectives
Human resource planning is the process of considering the current and future “people needs” of an organization.
This involves evaluating an organization’s workforce structure and protocols to ensure operational goals are met, productivity stays high and future demands for labor and talent can be fulfilled. Staying updated with industry trends using the LinkedIn People Directory can help achieve this.
The result of this process is the creation of an HR plan, which typically takes the form of a written document sometimes autogenerated using HR software . These documents tend to follow a similar structure to most strategic business plans and are created on an annual basis, by HR managers or company leaders.
Check out the template below for an example.
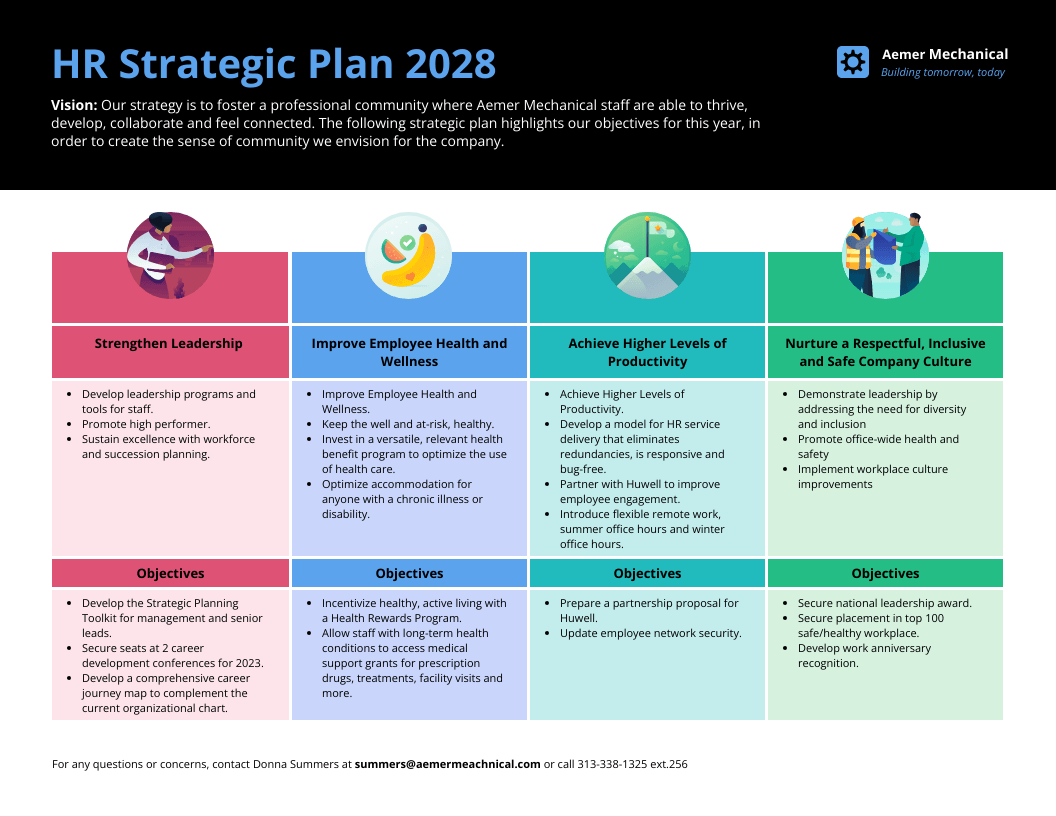
This eye-catching, one-page HR Strategic Plan Template offers a concise summary of your human resource planning efforts, so you can easily share info with colleagues.
Just swap out the text and visual assets for those of your choosing in Venngage’s editor , and you’re off to the races.
6 steps to create a strategic HR plan
Ready to create a strategic plan for the human resources that power your business? Here are six steps to help you succeed at the human resource planning process.
1. Assess current employees’ skill levels
The first step to creating a future-forward HR plan is to assess employees’ current skill sets, and compare them to your operational needs moving forward. This will help you identify gaps and inform any hiring of new employees.
Employees’ skill levels can be assessed by reviewing their work history, hard and soft skills and professional growth over time.
Using a matrix is a great way to understand where the skill gaps in your current workforce exist. Below is an example that describes the skills needed for different marketing roles.
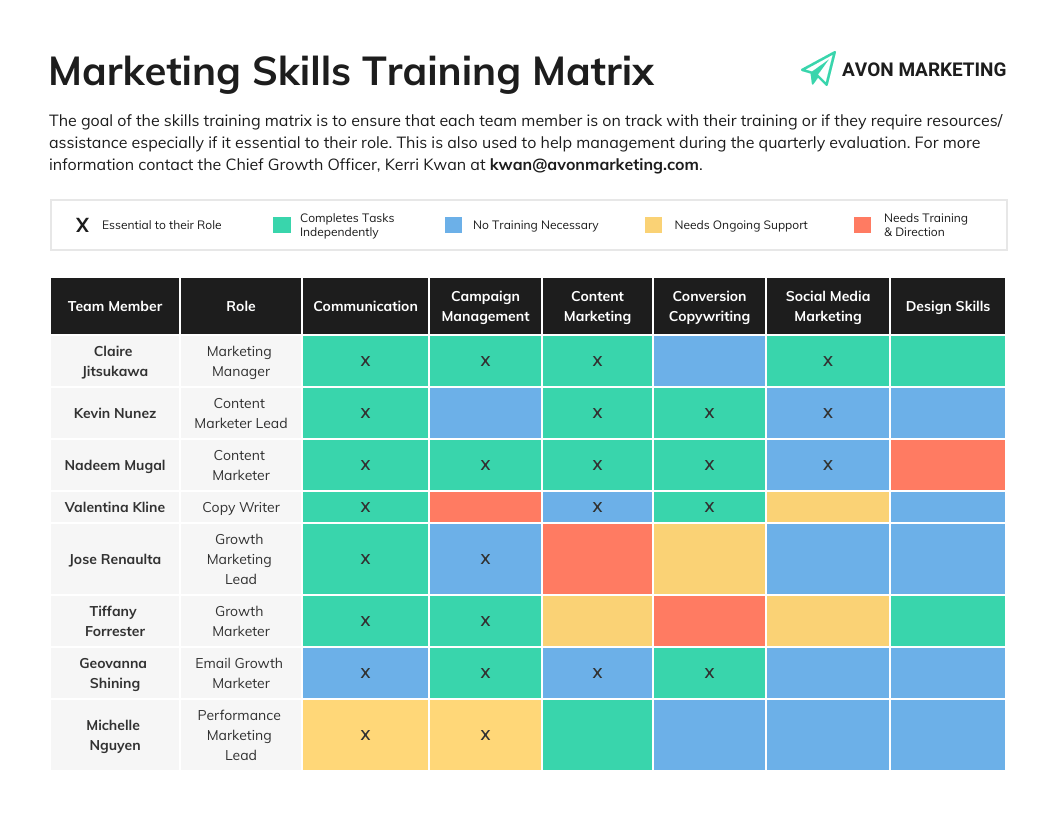
Don’t need it for marketing specifically? No worries — you can fully customize this template by swapping in your own text to examine any human resource gaps.
Another way to assess skills is by giving employees a questionnaire they can fill out. This Employee Competency Assessment Template does just that.

Based on the information collected, you’ll get a sense of what positions best suit each individual, and whether any upskilling or hiring is required.
2. Forecast your labor needs based on available information
Next in your strategic strategic HR management plan, you’ll want to consider the future. This involves accounting for any upcoming changes to your workforce, so operations can continue without error.
When forecasting labor needs, the following should be considered:
- Planned promotions
- Upcoming retirements
- Layoffs
- Personnel transfers
- Extended leaves of absence (i.e. maternity/paternity leave)
Beyond those, it’s a good idea to assess the impact of external conditions on your labor needs during your human resource planning. For example, new technological developments may decrease the amount of employees you require to operate your business.
3. Revisit your organizational design
Organizational design is the process of structuring the way a business operates so it can best achieve its goals. This is hugely important when it comes to your human resource planning process!
With a clear understanding of your organization’s strategic objectives in mind, reviewing your organizational design allows you to understand the staffing requirements you’ll need to succeed at them. This means taking into account your organizational structure and chains of command, as well as how work gets done and the way information flows.
From there, you’ll be able to see which departments need more team members so it can accomplish the organization’s objectives.
An easy way to get started is by using an organizational flow chart.

With its color coding and layout, even a new manager can quickly look at this chart to identify the people responsible for leading teams and making decisions.
And if there are any changes, it’s easy to to reflect them in the chart itself. All you need to do is customize the text and visual assets in Venngage’s Chart Maker as desired.
Not quite your style? There’s plenty of other organizational chart templates to choose from.

Here’s an organizational chart that’s perfect for small businesses that have limited employees. One quick look, and you’re good to go.
The bottom line is, no matter how big or small your business may be, you should always revisit your organizational design to optimize your workforce management and business operations.
Related: Types of Organizational Structure [+ Visualization Tips]
4. Outline how you will manage, motivate and retain talent
In this day and age, it’s a known fact that companies must provide more than just a paycheque to attract and retain talent, and encourage growth.
It’s true — studies have shown employees are more engaged in their work when they feel it is meaningful, fulfilling and slightly challenging. So your human resource plan should consider how to inspire such feelings, and what actions you can take to motivate employees to stay. (Hint: a strong HR training and development program is key.)
The talent management infographic template below is a great way to begin.

Using this process chart , you can detail the steps you’ll take to retain the talent you have. Reference it as needed in your human resource planning.
Another great way to keep staff motivated and geared towards their professional growth is by coming up with ideas for employee development . Facilitating a company culture that champions continuous learning guarantees your team will feel supported and challenged in all the right ways.
The two employee development plan templates below will help you do just that.

Though both templates are geared towards healthcare organizations, it’s easy to customize their content in Venngage to promote the continuous learning and development of employees in any industry.
As a result, your employees will be able to reach their full potential, while simultaneously supporting the long-term goals of your organization.
Related: 6 Employee Development Ideas for Efficient Training
5. Align your workforce planning with your budget
Let’s face it, human resources ain’t cheap.
Meaning, if you struggle at organizing and monitoring your HR budget, you’re bound to overspend on your initiatives —and no financially savvy business wants that.
That’s why I recommend including financial information in your HR planning process, so you can reference your budget and expenses as needed. This includes not only hiring and training costs but also the complexities of managing a global payroll for diverse teams.
Ensuring this allows you to stay within range as you work towards achieving your strategic goals for human capital . Plus, you don’t need to use one that contains walls of text and wack-loads numbers. Check out the clean and cheery option below — it’s as easy to fill out as it is to understand.

And if you’re looking to compare a forecasted budget to previous annual spending when strategizing your HR budget, the Budget Comparison Infographic Template below will help.

The bar graph is a great data visualization of annual expenses, organized by category. Just add (or import) any values to Venngage’s editor, swap out the text, and you’re ready to compare with ease.
Related: 10+ Expense Report Templates You Can Edit Easily
6. Establish KPIs for your human resource planning objectives
Measurable results are important when it comes to your HR planning processes, because they indicate whether your strategy is working or not.
Keeping those metrics in mind, your company can make adjustments and improve upon any future plans — AKA strategize for future success in business. That’s why your human resource plan should include info re: the specific key performance indicators (KPI) you’ll be measuring.
KPIs are established to help determine if HR strategies and plans are working. Much like those used for evaluating the performance of marketing or sales plan , KPIs for human resources are measurable results that indicate an organization’s success at achieving predetermined goals.
These may take the form of headcounts, turnover rates, demographic information, time to hire and employee satisfaction scores.
Here’s one employee satisfaction survey you can use to understand your workforce better.
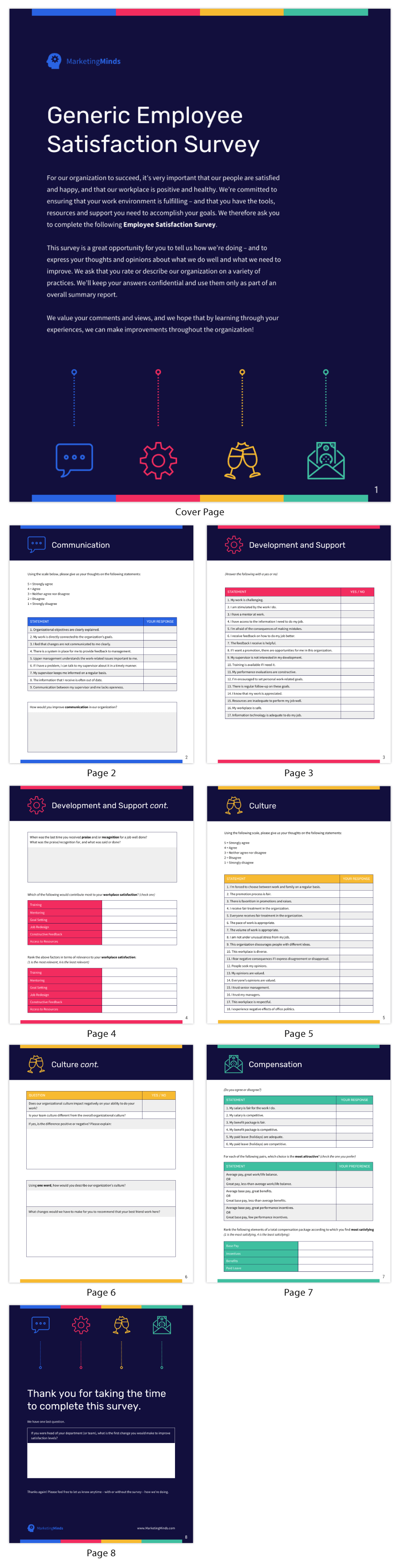
When you’re ready to organize those HR KPIs in a document, the recruiting template below is perfect for keeping tabs at a glance.

Related: 10+ Customizable HR Report Templates & Examples
How do I make an HR plan?
After you’ve collected the data you need, you’ll want to convey this info in an engaging, professional manner for easy referencing and sharing amongst colleagues. Given this, using Venngage is the best route to go.
Here are the simple steps to help you bring an actionable HR plan to life:
- Outline the information you would like to include in your strategic hr plan
- Pick the human resource planning templates that best suits your needs
- Customize the templates’ text and visual assets so they speak to your organization
- Apply your company’s brand guidelines with a few clicks using Venngage’s automated branding feature, My Brand Kit
- Download and share as desired
Note: sharing is available free-of-charge. However, the option to download your creations and access features like My Brand Kit and Team Collaboration are available with a Business plan .
FAQ about HR plans
How long should an hr plan be .
There are no hard and fast rules when it comes to the length of an HR plan. That being said, if you’re going to share it with colleagues, you probably don’t want to create a 20+ page document. One to five pages should suffice.
Try to be as concise as possible when relaying the facts, and use data visualizations wherever possible to save room.
Do I need an HR contingency plan?
In the same way creating an HR plan is a proactive move that helps your organization account for future needs, it’s a good idea to devise an HR contingency plan. This ensures there’s a back-up plan in place should your initiatives not go as expected.
For example, if you’ve identified that you need five new hires to keep up with consumer demand, but the talent pool is lacking, a contingency plan could house suggestions for restructuring your workforce to mitigate this.
In other words, it’s best-practice to hope for the best, but prepare for the worst.
Is an HR plan different from an employee development plan?
Yes. While an HR plan is a strategic document describing how an organization addresses its personnel-related needs at a high-level, an employee development plan outlines the processes needed to help an individual achieve their professional goals.
Even though the human resource planning process may involve outlining some employee development tactics, it is not unique to each employee as in the case of an employee development plan.
Make your HR planning processes effortless
You don’t need a crystal ball to feel confident about your people moving forward. With a solid HR plan and strategy in place, you’ll prime your workforce — and all business endeavors — to succeed in even the most competitive of markets.
Just remember this: human resources planning, and creating strategic business plans in general, doesn’t have to be exhausting.
With Venngage’s huge selection of professionally-designed templates and easy-to-use editor, all it takes is a few minutes to produce a polished document perfect for all your needs. Sign up for free today !
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
Human Resource Planning (HRP): A Step-By-Step Guide
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, having a plan in place for managing your human capital is key — and that’s where human resource planning (HRP) comes in. Human resource planning plays a critical role in making sure that your organization is well-equipped with the right talent at the right time.
Today, we’re walking through the intricacies of HRP so you can implement this practice in your organization.
What Is Human Resource Planning?
Human resource planning, or HRP, stands out as a strategic and methodical process designed to ensure that your organization fully leverages its human capital . It is not a one-time event but rather a continuous journey toward operational excellence and strategic alignment.
At its core, HRP aims to establish a seamless alignment between your employees and their respective roles, meticulously crafting a workforce that is both skilled and adequately sized to meet your organizational demands.
This proactive approach goes a long way in safeguarding your business against potential manpower shortages or surpluses, ensuring that you are well-prepared for the future.
Why Is HRP Important?
HRP is crucial for syncing your current workforce with your future needs. It entails a rigorous analysis of your existing staff, evaluating their skills, competencies, and performance.
This is where metrics come into play, providing a quantitative backbone to your workforce planning efforts. By leveraging data-driven insights, you can make informed decisions, ensuring that your team is not only talented but also aligned with your business objectives.
HRP doesn’t stop there, though — it’s a comprehensive approach that intertwines various facets of human resource management. Staffing, forecasting , performance management, and employee retention all fall under its umbrella. Each of these elements is crucial in building and maintaining a robust workforce.
In terms of staffing, HRP helps you decipher not just the number of employees you need, but also the types of skills and competencies they should possess. Forecasting, on the other hand, empowers your HR department to anticipate future demand, aligning your human resources with your company’s strategic direction.
Performance management is another vital cog in the HRP machine. It ensures that your employees are not just present but also productive and engaged. This, in turn, enhances employee retention, fostering a company culture that values growth, stability, and satisfaction.
HRP even plays a role in shaping your company culture . By aligning your human resources with your company’s needs and values, you create an environment where employees feel valued and aligned with the organization’s goals.
What Are the Advantages of Human Resource Planning?
At its core, human resource planning places the right talent in the right place at the right time, ensuring that your organization’s objectives align with your workforce’s capabilities. Now, let’s talk about the advantages of HRP and how it can lay the foundation for organizational success.
Ensures Effective Management of Current Employees
Strategic workforce alignment is at the heart of HRP. With effective human resource management, HR professionals can ensure that the current workforce is in sync with the company’s overarching goals.
This alignment can translate to better resource allocation, more informed decision-making, and enhanced overall performance.
Reveals Knowledge Gaps in the Workforce
The ever-evolving business landscape means organizations need to be adept at forecasting and adapting — and human resource planning plays a role here.
By examining current employees’ skill sets and comparing them with future needs, knowledge gaps can become more apparent. Addressing these gaps, whether through hiring new talent or upskilling existing employees, helps you ensure that your business stays competitive.
Balances HR Costs
Cost-effectiveness is crucial for the HR planning process. By anticipating future human resource needs, last-minute external recruitments — which often come with high costs — can be avoided.
Plus, recognizing surplus areas within your current workforce allows for internal reassignments to take place, cutting down on recruitment and onboarding expenses.
Keeps Companies Adaptable to Change
Change is constant, especially in today’s fast-paced business world, and human resource planning positions organizations to seamlessly navigate these changes.
From staying updated with industry trends to adapting to regulatory shifts, an HR department’s proactive planning ensures businesses remain resilient and agile. With Mosey , you can more effectively track, manage, and stay on top of changing regulations and requirements, making HR compliance a breeze.
Helps Secure Long-Term Growth
Another key component of HRP is succession planning. Identifying roles and preparing a talent pipeline ensures that your organization isn’t caught off-guard if leadership positions open up.
This planning not only opens the door to future leaders, but also ensures that institutional knowledge is retained, fueling your business’s long-term growth and stability.
Contributes to Organizational Goals
The nexus between human resource planning and organizational goals is undeniable. By streamlining the hiring process, ensuring employee satisfaction , and fostering employee retention, HRP contributes directly to the achievement of business objectives.
When employees see clear growth trajectories and development avenues, their commitment to the company’s vision intensifies, driving the organization closer to its goals.
What Are the Steps for Human Resource Planning?
HRP ensures that businesses are well-equipped, both in terms of the quantity and quality of their workforce, to meet their evolving goals and challenges. So, how can you actually navigate the intricacies of HRP? Here’s a step-by-step walkthrough of the essential phases that make up the human resource planning process.
Analyze Employee Skills and Performance
Human resource planning centers around an understanding of your company’s current workforce.
During this initial phase, the HR department dives into understanding the number of employees, their competencies, qualifications, positions, benefits, and performance levels. This skill inventory ensures that HR professionals have a clear picture of the strengths and areas for improvement in the present workforce.
Research Industry Trends and Forecasts
Effective human resource planning can also help you predict, and plan for, the future, so the next stage is to outline what your company will need in terms of human capital in the foreseeable future.
This forecasting phase requires the HR department to consider various factors, such as potential promotions, retirements, layoffs, and transfers. External conditions, like emerging technologies or industry shifts, can also have a significant impact on labor demand. Ensuring you stay ahead in terms of industry trends helps you align your staffing needs more effectively.
Conduct Demand Forecasting
Having a clear understanding of both the present workforce, potential employees, and future needs is vital to bridge the two through demand forecasting. This step in the HR planning process involves creating a gap analysis that points out discrepancies between the current workforce and future human resource demands.
This type of analysis leads to important questions like:
- Should current employees learn new skills?
- Is there a need for more managers?
- Are all employees fully utilizing their competencies in their present roles?
Answering these questions is key to crafting a strategic human resource plan that aligns with both the present and the future.
Determine Future Human Resource Needs
Once your demand forecasting has highlighted the shortages or surpluses in terms of competencies or number of employees, the next step is to determine the specific future human resource needs.
Whether it’s upskilling the current employees, succession planning for key roles, or identifying the need for new hires, this phase ensures that your business is poised for future growth without any HR hiccups.
Align HR Needs With Organizational Strategy
Human resource planning is intertwined with your broader business goals and strategies. Once your HR needs are identified, it’s important to make sure those needs align with your organizational goals.
This strategic planning phase ensures that every hiring process, training initiative, or retention effort contributes directly to your company’s overarching objectives.
Plan for Employee Development and Training
Once your future human resource needs are aligned with your company strategy, it’s time to implement plans for employee development. This might involve setting up training programs, workshops, or certifications to upskill current employees.
Ensuring your workforce is equipped with the right skills enhances employee satisfaction and retention and gives your business a competitive advantage.
Implement Plan for Forecasted HR Needs
The culmination of the human resource planning process is the implementation of your action plan. Taking cues from the gap analysis and strategic alignment, HR can now roll out a well-thought-out plan.
This could involve tweaking job descriptions, initiating new hiring processes, onboarding new employees, or even revisiting HR policies such as vacation, sick days, or overtime compensation. Collaboration with all departments is key here to ensure the successful execution of your plan, ensuring the HR strategies benefit the organization as a whole.
Support HRP Efforts With Mosey
From identifying when and where to open payroll accounts to managing workers’ compensation and paid family medical leave, Mosey simplifies the complex web of compliance and regulatory demands.
Why not explore how Mosey can streamline your HR processes and compliance management ? Our platform is designed to provide clarity, guidance, and ease, allowing you to focus on what matters most — nurturing and growing your most valuable asset, your employees. Try Mosey today .
Read more from Mosey:
- Compliance Automation: How It Works & Its Value
- Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC: Key Differences
- What Is a Foreign Corporation? FAQs Explained
- What Is a C Corporation (C Corp)?
- What Is Payroll? A Guide for Small Business Payroll
- What Is a Legal Entity? Definition & Examples
- What Is SUI? State Unemployment Insurance FAQs
Review your compliance risks, free.
Use our compliance checkup to learn more about what to do to be compliant in any state! It's free and takes less than five minutes.
Ready to get started?
Schedule a free consultation to see how Mosey transforms business compliance.
Mosey has everything you need to get compliant in all 50 states in one, easy to use, platform.
Filter by Keywords
People Management
Human resource planning (hrp): a guide for hr professionals.
March 21, 2024
Start using ClickUp today
- Manage all your work in one place
- Collaborate with your team
- Use ClickUp for FREE—forever
In the business world of sameness, your employees are your true differentiator.
And that’s where HR teams come in—meticulously planning every step of the employee lifecycle to ensure your business’ success. Whether you’re a seasoned HR professional or a new member of an HR team, brush up on the must-haves for optimal human resource planning (HPR).
What Is Human Resource Planning?
Understanding human resource planning, steps to effective human resource planning, the role of hrp in boosting organizational performance, challenges of human resource planning, utilizing technology in human resource planning, future trends in human resource planning.
Companies need to ensure their human resource goals match their business goals. Businesses use human resource planning to evaluate their current workforce and predict its alignment with future needs.
In this process, you and the rest of your HR team identify skill requirements and formulate recruitment, training, management, and succession planning. Meticulously planning for future needs enables companies to optimize staffing levels while staying prepared for upcoming challenges and opportunities.
Human resource planning is often the unsung hero in a company’s strategic framework—the behind-the-scenes MVP deserves a closer look.
HR planning must align human resources with the broader organizational strategy and business goals to be effective. To do this, the HR planning process must be comprehensive, accurately assessing current employees and forecasting future needs so that any gaps can be filled at the appropriate time.
Different roles of human resource planning
Because a strategic human resource plan aligns with organizational goals, it encompasses everything from workforce planning to employee retention. To fully appreciate the benefits of HR planning, let’s zoom in and see the different hats it wears in a company.
The most obvious role human resource planning plays is in determining how many employees are necessary for the company to operate. To do this, HRP must also rely heavily on performance management, where past reviews are assessed to understand the current workforce’s strengths and weaknesses. Employee self-evaluations can be helpful in this regard.
Next, human resource planning plays a critical role in gap analysis. It lets companies know when and where they lack specific skills, not only for the present but also for future needs. Through this gap analysis, a business can more effectively plan for training current employees and hiring new employees.
“Hard” vs. “soft” human resource planning

There are two approaches to HRP: “Hard” and “soft.”
In “hard” human resource planning, a quantitative approach is taken. The focus is on workforce capabilities and resource planning. Supply forecasting and skills inventory data is used to predict future workforce requirements.
The sole mission is getting that sweet alignment between human resources and the business’s needs.
“Soft” human resource planning flips the script, prioritizing the qualitative side of the process. It’s all about company culture, employee satisfaction, and fine-tuning those essential soft skills.
Soft HRP aims to create a supportive work environment that fosters employee retention while aligning with organizational objectives. It’s accomplished through employee training programs, building skilled employees from within who can meet the organization’s strategy.

To understand the process more deeply, let’s break down the key steps of human resource planning and unlock its secrets.
Analyzing organizational objectives and plans
The HR planning process must align with the overall business strategy for human resource planning to be effective. The organization must carefully lay out its long-term goals so the human resource department has a roadmap.
HR professionals must work closely with department leads to understand the business objectives comprehensively. Only through this collaboration can the human resource plan strategically align with where the company wants to go.
Evaluating the current state of the workforce and uncovering gaps
The current workforce status must be assessed in the second step of the HR planning process. This involves a detailed analysis of their skills, capabilities, and performance, vividly showing the team’s strengths and areas for improvement.
HR teams use tools like performance management systems to build a comprehensive skills inventory. Try conducting employee self-evaluations to get a broader picture of where gaps may be.
The next steps hinge on how effectively the current employees align with the present and future needs of the business.
Forecasting future HR requirements
Once the HR manager knows the company’s future goals and the workforce’s current state, they can begin forecasting future HR requirements. They’ll use the data to predict the need for new employees.
This is a complex process—changes to the business environment, company culture, and market trends must all be considered to forecast future demand accurately. As markets shift, the pool of available quality employees changes, too. Supply forecasting helps HR human resource planners factor this in and initiate the hiring process at an optimal time.
Developing and implementing a plan
Now that we understand the the gaps between current staffing and future needs, let’s move on to developing and implementing a strategic HR plan.
The HR team should create talent strategies for recruiting and retaining new hires while developing the skills of existing employees to keep pace with changing business needs. Creating detailed job descriptions, refining the hiring process, and planning for benefits administration are vital during this step.
Monitoring, reviewing, and reassessing the plan
The final step is more of an ongoing HRP process. The team must continually monitor and reassess the needs of the company.
HR software and analytics tools help track the effectiveness of human resource planning over time. Continuously monitoring employee performance and the impact of training programs ensures that strategic human resource management stays aligned with the changing business environment.
A company’s performance depends heavily on how well-staffed it is. It isn’t just about the number of employees on the payroll but how well those employees meet the organization’s needs. The human resource planning process is the best way to ensure that alignment.
Strategic human resource planning effectively identifies the number of employees required, their needed skills, and the optimal hiring times to maximize the chances of securing qualified individuals when they’re needed.
HR professionals identify gaps in the ability of current employees as they go through the HRP process. These gaps degrade the overall performance of the business. A good human resource plan will weigh the ability to train the existing workforce to meet demand vs. the need to hire new employees.
Because HR managers must work closely with department heads for this alignment to occur, they’re always acutely aware of where performance issues are arising and can adapt the planning process to mitigate those problems.
Another area where HRP can boost a company’s performance is by facilitating organizational innovation. A business must have a skilled and dynamic employee pool to be innovative. With a well-developed HR plan, the company can identify potential employees who can fulfill those needs.

While the human resource planning process is vital to organizational management, it doesn’t come without challenges. Without a plan to overcome these challenges, they can derail the plan’s effectiveness. Strategic planning must anticipate the challenges an HR team will encounter during HRP, ranging from market fluctuations to internal workforce dynamics.
Business objective alignment
We’ve talked quite a bit about the need to balance a human resource strategy with the objectives of the business. This, essentially, is the core of HRP and one of the biggest challenges HR managers face when developing a plan. The ever-evolving market conditions and organizational priorities add a layer of complexity to the already challenging task of strategic human resource planning.
To counter this, HR departments must maintain a continuous approach to HRP and constantly consult with department heads to update the direction of the company and the needs of individual departments.
Accurate forecasting
A big part of human resource planning involves forecasting the demand for current employees and future talent. Business growth can be unpredictable, technological advancements can change needs rapidly, and economic changes can shift priorities.
Investing in HR software such as data analytics and forecasting tools will help HR plan more accurately for these changes. These tools used advanced machine learning and large amounts of data to create forecasts more accurately than humans alone can.
Maintaining balance
There’s a delicate balance to be maintained between the current workforce needs and future requirements. This planning process can be overwhelming, especially for small HR teams. Teams at larger companies may struggle to stay connected with the needs of frontline employees.
Smaller teams especially must rely on talent management software that will automate much of the work in predicting when new employees or skills will be needed. Larger companies must create and maintain a direct line of communication between HR and frontline employees so their concerns are always a part of the human resource planning process.
Integrating the planning processes
Human resource planning must not only consider the business’s goals but must be tightly integrated with the company’s overall planning process. This ensures that actions taken by HR aren’t just reactive but that a proactive approach to hiring and training employees is taken.
This requires a strategic approach to resource planning. HR managers should be a part of every discussion about the company’s future so they can provide input that shapes the company’s direction and receive input that shapes HR’s approach.

We’ve seen several instances where HR planning software will help teams better prepare for the business’s staffing needs. Technology has evolved rapidly in recent years, making it a vital part of strategic human resources planning. Chief among these advancements has been the growth of artificial intelligence , revolutionizing how companies manage their workforce through machine learning.
The rise of remote work has further driven the adoption of new technologies. An HR department must emphasize a flexible and dynamic human resource planning process with a dispersed workforce. Innovative tools and workforce planning software can help support these growing HR needs.
ClickUp is an all-in-one productivity platform. In addition to comprehensive project planning tools , the software has useful features for human resources planning. Its capabilities extend to various HR functions but also work well for every department in the company, making it ideally suited to keeping HR departments on the same page as other departments and the overall company direction.
As you can tell, it’s obvious how vital performance management is for strategic human resource planning. ClickUp provides a robust set of performance management tools, helping HR staff give and receive continuous feedback and set employee goals. By taking advantage of these features, your company can foster a constant learning and development culture that better prepares it for changing needs.
One of ClickUp’s biggest strengths is the extensive set of available templates. For nearly any productivity task your company needs to accomplish, a template shows you exactly how to put the software’s features to work on it.
ClickUp’s HR Standard Operating Procedures template is handy for identifying skill gaps and developing a plan to close them. To keep existing employees up-to-date and prepared for changing requirements, the ClickUp HR knowledge base template shines.
Technology has rapidly changed the landscape of human resources and shows no signs of slowing down. Changing attitudes and shifting priorities will also affect how strategic human resource planning evolves over the coming years.
Companies will no doubt find that artificial intelligence and data analytics tools will emerge that further refine processes and increase the accuracy of forecasts. As these tools improve the ability of an HR team to forecast staffing needs and identify skill gaps, smaller HR teams will be able to better compete with their larger counterparts.
We’re also seeing significant shifts in the way companies approach employment. More focus than ever is being placed on employee well-being and work-life balance. These priorities pay dividends by reducing burnout and improving productivity.
Human resources departments will increasingly shift from mere recruitment and training to working on building an inclusive and supportive workplace culture.
The trend of remote work and the gig economy will likely continue. The gig economy could provide opportunities for HR teams to rely on independent contractors for temporary surges in staffing requirements to keep the in-house staffing optimized during slow times but not overwhelmed during the busy ones.
Wrapping It Up

While many challenges are involved in keeping a company’s workforce as tightly tuned to its actual needs as possible, doing so provides the most efficient use of human resources and a substantial competitive advantage.
Thankfully, there are many tools available to help companies achieve this. Several free HR planning templates can help keep your staff organized and their processes streamlined. By combining this with effective employee management software , like ClickUp, even small teams can develop comprehensive human resource plans.
ClickUp is free to try. Sign up today to see how this powerful productivity tool can benefit your company.
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
Maximizing HR Impact: Your Strategic HRM Plan Explained

What is a strategic HRM plan?
Why do organizations need a strategic hrm plan, stronger employee engagement, increased manager efficiency, better alignment between hr and business goals, greater business impact, mission, vision, and values statement, workforce analysis, skills inventory, job analysis and design, employee engagement and communication, performance management, training and development, succession planning, define hr objectives and align with business goals, analyze current hr practices and processes, identify areas for improvement and implement changes, monitor and evaluate the impact of your strategic hrm plan, the future of strategic hrm planning, amplify hr’s value with a strategic hrm plan .
Today’s HR leaders are under tremendous pressure to optimize their workforces for today’s demands while building agility for the future. To bring this new model to life, you need a strategic HRM plan that outlines how people will find their full potential within your organization.
According to a recent report from the HR Research Institute , only 8% of business leaders strongly agree that their workforce and business are prepared to adapt to changing work trends, while 42% don’t agree at all. Preparing your workforce to meet business needs today and in the future requires more strategic use of your talent resources — and a modern HRM plan can help you get there.
Learn more about what a comprehensive strategic HRM plan looks like, the benefits of a modern one, and steps to take to strengthen yours.
A strategic HRM plan is a comprehensive document outlining an organization’s HR goals, objectives, and strategies. Such a plan compares business goals against the people resources needed to accomplish them, including the skills, abilities, traits, talents, and competencies housed within your workforce.
The plan should include a detailed overview of the organization’s HR goals and how they link to business objectives. It should also analyze the current environment, review applicable policies and procedures, and offer a road map for implementing and managing HRM initiatives. Additionally, the plan should address how the organization will measure and track progress.
Strategic HRM planning lives at a higher level than operational HR planning, which takes a more tactical approach. Strategic HRM planning sets aspirational, ambitious goals based on the company’s vision. Generally, a strategic HRM plan guides operational HR planning, which builds the long-term plan into daily operations and processes.
A strategic HRM plan details the resources needed by the business — including by departments and teams — to achieve objectives. It also specifies what actions to take to identify and fill gaps. Without an HRM plan, an organization might begin an ambitious project only to discover halfway through that the workforce doesn’t have the skills needed to deliver.
Ultimately, an HRM plan helps businesses understand what human resources they have and how to maximize their value. These plans balance available resources against demand and factor in upcoming initiatives and goals to ensure the right skills, abilities, and competencies are available when needed.
4 benefits of strategic HRM planning
HRM planning provides a line of sight into your workforce’s strengths and weaknesses and outlines your plans to sustainably develop your people in line with business objectives. Strategically deploying people where they’ll have the greatest impact produces several benefits for the workforce and the business.
Strategic HRM planning improves employee engagement by creating an inherently motivating environment for employees. When all projects and teams are adequately staffed, and people have the skills and abilities they need to succeed, they work more effectively. Doing better work helps employees feel a greater sense of progress and satisfaction, which often drives higher engagement.
An effective strategic HRM plan takes each employee’s strongest skills into account. To maximize value, it places workers in situations where they do their best work, which can be especially motivating. Moreover, people tend to enjoy doing work they’re good at, which supports higher employee satisfaction and engagement.
Strategic HRM planning can make a manager’s job easier by matching people’s skill sets with job assignments that make sense. A strong job fit helps people contribute to the team’s goals. When everyone is engaged and empowered to do their best work, the entire team’s efficiency increases.
A strategic HRM plan also serves as a tool for training managers to learn to allocate their team resources more effectively. By seeing the skills, abilities, and competencies available on their team, managers learn how to delegate tasks effectively over time.
Strategic HRM planning is a living example of how the HR teams’ goals connect with business goals. These plans demonstrate how you’ll overcome HR challenges while keeping strategic goals top of mind. They outline how HR leaders will deploy people resources strategically to best support what the business wants to accomplish.
If one of your business goals is to improve product quality, for example, your HRM plan may include developing a new training program for product testers.
Strategic HRM planning helps HR leaders (and other executives) more easily grasp the landscape of the organization’s available people resources. This knowledge informs decisions around reallocating talent, improving operational efficiency, and increasing customer satisfaction.

8 key elements of a strategic HRM plan
Every strategic HRM plan differs based on the needs of the business. As you create a strategic HR plan, consider these eight essential elements.
Your organization’s mission statement provides a framework for decision-making and goal-setting. Your vision statement states long-term goals at a high level and can be a guide for setting objectives.
These statements provide a North Star for HRM planning. For example, your mission and vision statement should already inform how you recruit, train, and build company culture. By looking at them through a strategic lens, these statements help you identify the skills, values, and traits you need to achieve business goals.
A workforce analysis is a crucial exercise for understanding your current state. Going through this process means looking at the existing workforce’s skills, knowledge, and experience and the projected business needs. The analysis helps identify gaps between current and future workforce requirements and guides recruitment, training, retention, and succession planning decisions.
Equipped with this information, you can make more informed decisions about allocating resources in the near and long term.
Skills inventories allow you to identify and assess workforce competencies, providing a better understanding of your human resources. Use this information to develop strategies tailored to the strengths and weaknesses of your workforce.
For example, if the skills inventory reveals a lack of technical expertise in a certain area, you can create training programs to fill the gap or emphasize hiring people with this skill set.
Job analysis exercises affect strategic HRM planning by providing valuable information about organizational staffing. This process identifies each job’s duties, tasks, responsibilities, and required skills and knowledge. When HR leaders understand job architectures, they can properly update job descriptions.
Like any strategy, an HRM plan needs to be communicated to managers and front-line employees. Make sure they understand their responsibilities and the potential benefits.
Some employees might worry that an HRM plan reduces their value to what the business can get from them. But strategic HRM planning allows team members to exercise their strongest talents and develop new ones. Emphasize communication that explains how HRM planning helps employees reach their full potential.
Performance management is a framework for aligning individual goals and objectives with those of the organization. This provides strategic value by guaranteeing that everyone in the company is working to achieve aligned goals.
The data gathered from performance management software and processes helps HR identify skill gaps, evaluate workforce performance and career aspirations, and gauge progress toward goals. You can use this data to refine existing goals and inform performance improvement plans.
Training and employee development are important components of a strategic HRM plan. Training keeps employees up to date with the latest industry trends, technology, and procedures, which improves operations and efficiency.
Employee development is more strategic — increasing employee skills and expertise for the long term. This approach helps team members explore their career path, including the education they need to advance.
Succession planning is the process of identifying and developing potential leaders to fill critical positions. Strategic HRM planning recognizes this importance by identifying what roles are most important to fill quickly — and which roles are at risk of not having a successor ready.
Succession plans help companies ensure that internal candidates can fill any key vacancy with the skills and knowledge to maintain business continuity and achieve strategic objectives.

4 steps for strategic HRM planning
Like any HR initiative, you need a sound approach. Here are four steps for creating an HRM plan, with examples, at your organization.
The HRM plan always takes its cue from the larger business plan. To create a strategic HRM plan, start by evaluating the organization’s goals and objectives. Next, assess the results of your workforce analysis and skills inventory and compare them against the needs of the business plan. Identify places where resources are low, and draw up plans to close the gaps.
Work with executive-level peers to identify HR-specific needs that will help them execute the business plan. At this stage, flag any strategic actions the organization lacks the resources to accomplish.
Your HRM plan, for example, comes into play if the chief risk officer wants to adopt new risk management software within the quarter. You might push back against such a tight timeline if you lack the capacity to gain buy-in, communicate the transition plan, and train people on new processes.
Distill your HR objectives into a measurable, achievable HRM plan. Break down the plan’s goals into objectives and key results, and assign accountability and ownership for each smaller objective to ensure they’re accomplished.
Don’t assume your existing processes make sense for tomorrow’s business goals. Start by evaluating HR policies, procedures, and systems. Are they the right fit for producing the outcomes you need? How could they be improved, refined, or redefined?
If the business is focused on long-term continuity, for example, it needs a more resilient workforce. For HR leaders, that means they might look at the organization’s traditionally linear career paths. They might discover knowledge silos and higher turnover among employees who don’t see a path upward. A strategic HRM plan that emphasizes open and lateral career paths can break down silos so everyone has better visibility into other parts of the business and help employees see a future within the organization — both of which contribute to business continuity.
One of the most important steps of HRM planning is plotting the actions you’ll take to close resource gaps. Doing so often requires changing processes or workflows. Include a timeline for implementing changes and a detailed budget.
For example, a business traditionally hires contractors where your workforce lacks the requisite skill sets. But as the business evolves, you see an opportunity to build out those capabilities in-house — either by upskilling employees or hiring from the outside. A strategic HRM plan lays out the reasoning for this shift in spending, hiring, and structure.
All strategic HR plans need to be monitored. If the plan isn’t progressing or doing so quickly enough, take a step back to assess why.
Perhaps the HRM plan intended to fill skills gaps through external recruiting and hiring. But if those skills aren’t readily available or come at a premium cost, you might have to pivot to internal skills development.

The future of strategic HRM planning increasingly intersects with technology, analytics, and data. Companies want data-driven approaches to everything in business, including talent.
Automation and artificial intelligence are already commonplace in transactional areas of HR, such as recruitment, training, and onboarding. These technologies will gain ground in more strategic areas, such as interpreting key HR metrics . The more you understand your HR data, the more effectively you can deploy talent to support the business.
Companies are also looking for a more holistic approach to HR management and greater emphasis on employee engagement and well-being. Employees are reprioritizing their responsibilities, increasingly demanding flexibility and better benefits. Strategic HRM plans need to respond to these trends, both in terms of organizational design and the allocation of people resources.
The importance of having a strategic HRM plan can’t be overstated. Proactive resource planning by HR leaders ensures that the business has the skills, abilities, and competencies needed to achieve strategic objectives.
HR leaders increasingly have a seat at the table. Your HRM plan is how you showcase your value, build a successful and sustainable workforce, and help the organization reap the rewards.
Want to learn more about strategic HR?
Related Blog Posts

Defining Success Before Implementation: The True Key to Performance Program Impact
Set clear metrics and benchmarks from the outset to empower your organization to achieve measurable,…

Crafting a Winning Performance Management Strategy: Best Practices and Insights
Learn how to develop and implement an effective performance management strategy. Discover best practices and…

Best Performance Management Approaches and Models
Explore various performance management approaches and best practices. Learn how to enhance employee performance and…
Upcoming Events

The Future of HR: Merging Skills Growth with Performance Excellence

Gartner ReimagineHR: London

HR Tech: Las Vegas
Subscribe to the betterworks magazine, you might find interesting.

Performance Management Goal Setting: Examples and Best Practices

- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Pinterest
- Share through Email
HR Planning: Complete Guide 2024
Finn is an editor at People Managing People . He's passionate about growing organizations where people are empowered to continuously improve and genuinely enjoy coming to work. If not at his desk, you can find him playing sports or enjoying the great outdoors.
Use this guide to help you create a forward-looking and adaptable HR plan that aligns talent with organizational goals and objectives.

HR planning is a valuable process for any organization, ensuring that the right people are in the right roles at the right time.
Whether you're a small business owner or a seasoned HR professional, understanding HR planning can help you optimize your workforce, improve employee satisfaction, and drive organizational success.
In this article, we'll explore the key components, benefits, and best practices of HR planning to help you navigate this essential aspect of human resource management.
What Is HR Planning?
HR planning is a strategic process that seeks to align an organization’s talent management strategies with its business goals and objectives.
The HR planning process involves forecasting future workforce needs, assessing current workforce capabilities and needs, analyzing the market, and identifying specific issues related to talent management e.g. retention.
How HR Planning is Used
Think of HR planning as a roadmap for your company’s workforce needs. You wouldn’t set off on a road trip without a map or GPS. Similarly, businesses shouldn’t navigate their growth without a solid HR plan.
By anticipating future staffing needs and aligning them with your company’s goals, HR planning helps ensure you have the right people in the right roles at the right times. Some the business outcomes you can use HR planning to influence include:
Improved Resource Allocation: Ensure your company has the necessary human resources to meet demands, preventing the scramble to fill positions last minute.
Enhanced Employee Performance: HR planning provides clarity for your workforce, outlining clear roles, expectations, and career paths.
Better Alignment with Business Objectives: HR planning ensures that your staffing strategy aligns with your overall business objectives and drives the company towards its goals efficiently and effectively.
Goals of HR Planning
HR planning isn't just about filling positions; it's about strategically shaping the future of your workforce to meet the needs of your business. Here are the primary goals:
Forecasting Future Needs
Just like weather forecasting helps us prepare for the elements, HR planning involves predicting future workforce needs based on business goals, market trends, and upcoming projects. This proactive approach helps prevent talent shortages and ensures that the company is always ready to scale up or down as needed.
Bridging Skill Gaps
HR planning identifies missing skills within your workforce and finds ways to fill them, either through hiring, training, or development programs.

Get weekly insights and how-tos on leadership and HR’s biggest and most pressing topics—right to your inbox.
- Your email *
- By submitting this form, you agree to receive our newsletter, and occasional emails related to People Managing People. You can unsubscribe at any time. For more details, please review our privacy policy . We're protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Supporting Growth and Expansion
If your company is looking to grow, whether by expanding into new markets or launching new products, HR planning identifies the people needed for this growth, ensuring you have the right mix of talent to support your ambitions.
Enhancing Employee Development
Good HR planning also focuses on the growth and development of existing employees. It creates pathways for career advancement, which not only helps in retaining top talent but also ensures that your workforce is continually evolving and improving.
Ensuring Compliance and Risk Management
With constantly changing labor laws and regulations, HR planning helps businesses stay compliant and manage risks effectively. This includes everything from ensuring fair hiring practices to maintaining proper documentation and managing employee relations.
Optimizing Costs
Efficient HR planning can optimize costs by reducing turnover, improving hiring processes, and ensuring that resources are used effectively. This cost efficiency supports the overall financial health of the business.
Challenges Of Human Resource Planning
The future is notoriously difficult to predict and several internal and external factors can complicate the HR planning process.
- Competing priorities . Sometimes, a lack of clear priorities from business leaders makes planning for future talent needs difficult. Organizations often struggle to balance immediate staffing needs with long-term strategic goals, leading to potential misalignments between workforce capabilities and organizational objectives.
- Data management and analytics : Collecting and analyzing reliable workforce data to inform HR planning decisions can be tricky, especially for organizations that lack the necessary tools or expertise.
- Adapting to market changes : Fluctuations in the labor market, such as skill shortages, can complicate the planning process.
9-Step HR Planning Process
The HR planning process is both forward-looking and adaptable, aiming to align workforce capabilities with the organization’s goals and objectives. The key steps in the HR planning process are:
1. Understanding organizational objectives
- Begin by thoroughly understanding the organization's strategic plan, including its long-term goals, competitive positioning, and key business drivers.
2. Workforce analysis
- Conduct a talent review to assess the current workforce in terms of size, skills, competencies, age, turnover rates, and other relevant factors.
- Assess the external labor market for the availability of required skills and competencies.
- Assess employee feedback about any challenges they’re facing in the organization and how they’d improve things.
3. Forecasting demand for talent
- Predict future workforce requirements based on organizational objectives, projected turnover, technological advancements, and market trends.
- Consider both the quantity and quality of employees needed to achieve organizational objectives.
4. Identifying skills gaps
- Perform a skills gap analysis to compare the demand for labor with the current supply, both internally and externally. The aim is to identify where the organization may face shortages or surpluses of specific skills or roles.
5. Developing HR strategies to address gaps
- Formulate strategies to bridge identified gaps and optimize talent usage This could include recruitment, training and development, restructuring, outsourcing, workforce reduction, and retention strategies
- Create goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) to make it easier to track progress
- Consider long-term strategies like succession planning.
6. Assessing HR’s capabilities
- Complete the above steps for the HR department. Is there capability within the team to meet the new objectives and deliver projects?
- What HR software solutions could help and which processes could be improved?
- Assess where there are opportunities for automation of HR processes.
7. Plan and implement HR Initiatives and Programs
- Plan how these initiatives will be implemented, including timelines, responsibilities, and required resources.
- Implement initiatives in accordance with project plans and timelines.
8. Monitoring, evaluation, and feedback:
- Periodically monitor the implementation of HR plans against set objectives.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of HR strategies and make adjustments as needed.
- Collect feedback from stakeholders to inform future HR planning efforts.
9. Review and revision:
- Regularly review HR planning processes and outcomes in light of changing organizational needs and external conditions.
- Revise HR plans to ensure they remain aligned with organizational goals and responsive to the dynamic nature of the labor market.
HR Planning Best Practices
There are a lot of moving parts when it comes to talent management and the HR planning process.
Use these best practices to help make the process more accurate and efficient.
- Engage senior management : Ensure that senior executives understand and support the HR strategy. Leadership buy-in is critical for securing the necessary resources and for cascading the importance of the strategy throughout the organization.
- Keep good data hygiene . Being able to accurately measure key HR metrics such as attrition and retention rates is vital for HR planning. Technology such as HR analytics software can help here.
- Set clear KPIs . Your human resources strategies and initiatives should always be mapped back to your organizational strategies. Likewise, your HR KPIs should be able to articulate how HR professionals are providing real value realization against those same strategies.
- Gather feedback from employees. Great ideas can come from anywhere and employee listening should inform any HR planning process.
- Create a skills library . Many organizations are now moving from a roles-based approach to talent management to a skills-based one. Part of this is building out skills libraries that define what skills mean in an organization and make it easier to track them.
- Deconstruct complex processes. As part of your HR planning efforts, segment complex HR challenges into simpler, easier-to-implement components. For example, can you condense you streamline your technology needs or integrate HR systems that could minimize the need for repetitive tasks and manual data entry.
Join The People Managing People Community
For further advice on HR planning and other strategic initiatives, join our supportive community of HR and business leaders sharing knowledge and best practices to help you grow in your career and make greater impact in your org.
Mission Possible: HR’s Crucial Role In Sustainability

Small Business HR: Does Your Small Business Need It? A Comprehensive Guide
Developing Your International Strategy: 9-Step Process For Success
- Book a Speaker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Vivamus convallis sem tellus, vitae egestas felis vestibule ut.
Error message details.
Reuse Permissions
Request permission to republish or redistribute SHRM content and materials.
Practicing Strategic Human Resources
Overview Background Benefits of HR Strategic Planning Developing a Strategic HR Plan
Assess the Current Situation
Envision the future, develop strategic hr objectives, monitor and evaluate, additional resources.
This article provides a definition, background, information, resources and suggested reading on how to begin the process of strategic human resources. Topics include the following:
- Benefits to HR to engage in strategic planning.
- Developing a strategic HR plan.
- Assessing the organization's current environment.
- Creating statements of vision, mission and values.
- Implementing, monitoring and evaluating the HR strategic plan.
Strategic human resource management involves a future-oriented process of developing and implementing HR programs that address and solve business problems and directly contribute to major long-term business objectives.
HR management was once largely an administrative function focused on day-to-day responsibilities such as employee recruiting and selection and managing employee benefits. Changing labor market conditions and new business thinking call for HR business strategies that include recruiting and retaining the right people, as well as providing ethical and cultural leadership.
Strategic planning presents great challenges and opportunities for HR professionals. Nearly all HR leaders in the largest global companies are involved in strategic decision-making and participate on the organization's strategy team, and a majority of HR professionals report that strategic planning is part of their function. In contrast, HR professionals in many medium and small organizations are not often involved in organizational or functional strategic planning. Consequently, to achieve long-term strategic HR objectives and to be a key player in the organization's strategic planning process, some HR departments may need to convince senior management of the value and contribution HR can provide.
Benefits of HR Strategic Planning
The closer the alignment between HR and an organization's overall business strategy, the better the company's ability to anticipate and respond to customer needs and to maintain competitive advantage. Rigorous research, planning and development involving workforce culture, behaviors and competencies promote the successful execution of business strategy.
Particular benefits of HR strategic planning include the following:
- Avoiding costly and disruptive surprises that interfere with achieving goals.
- Addressing key issues in a timely manner to avoid crises.
- Promoting employee productivity and overall organizational success.
- Providing a sense of direction to positively affect how work gets done.
- Keeping employees focused on organizational goals.
- Providing a strategic focus to guide training and development initiatives.
- Giving leaders tools to help focus and implement their strategic initiatives.
Developing a Strategic HR Plan
HR's role includes developing a plan of HR initiatives to achieve and promote the behaviors, culture and competencies needed to achieve organizational goals.
Results-oriented goals broadly include the following:
- Correctly assessing staffing and skills needs and keeping training up-to-date.
- Developing and maintaining competitive pay and benefits.
- Managing performance and designing a rewards system that keeps employees motivated.
- Knowing what competitors are doing to recruit and retain talent.
- Providing training, including ethics, which reinforces corporate values.
The strategic planning process begins with four critical questions:
- Where are we now? (Assess the current situation.)
- Where do we want to be? (Envision and articulate a desired future.)
- How do we get there? (Formulate and implement a strategy and strategic objectives.)
- How will we know if we are on track toward our intended destination? (Establish a mechanism to evaluate progress.)
See HR as Strategic Planning Facilitator .
The following sections examine each step in greater detail.
Being a strategic business partner means carrying out HR activities with the long-range goals of the organization in mind. To do this, HR professionals must do the following:
- Understand how the various organizational components interact and recognize the long-term implications of HR decisions. The impact of HR decisions must be thoroughly researched and analyzed before changes are implemented.
- Have a firm grounding in business basics, including finance, marketing, sales, operations and IT. These skills help with budgeting and with maintaining a workforce with the correct mix of skills.
- Develop and exercise analytic skills directed at "the why" as well as "the what." This may mean spending more time on so-called translational work (such as coaching business leaders, planning and implementing HR practices that effectively execute strategy, and helping teams manage change) than on transactional work (such as recruitment, training, human resource information systems and other traditional HR functions).
- Conduct a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats (SWOT) analysis of their organizations. The SWOT approach offers a clearer picture of customers, markets and competitors.
What are the basics of environmental scanning as part of the strategic planning process?
What is SWOT analysis, and how does it apply to an HR department?
How to Make Strategic Choices in Uncertain Conditions
Aligning the HR function to the organization's business strategy
For HR departments, intradepartmental strategic planning can be a good way to start the functional alignment process. However, regardless of whether strategic planning begins in the HR department or in another department, or is managed on an organization wide scale, the actions of the HR department will be integral to the success of the strategic plan. Thus, HR professionals must take care to align the HR function with every aspect of the strategic plan, even if the strategic plan does not explicitly address HR issues. Recent SHRM research reveals that HR professionals foresee significant workplace challenges, including rising health care costs, the retirement of large numbers of Baby Boomers and the increased demand for work/life balance. Retention programs, work/life programs, succession planning, and health, safety and security programs are among the HR efforts that are viewed as key workplace challenges through which HR can strategically contribute to organizations. See Aligning Workforce Strategies with Business Objectives.
The HR alignment process is often driven by workforce composition issues. Although every organization's particular strategic plan is unique, the demographics and other characteristics of the available workforce have a major effect on the way businesses are staffed. In turn, the way organizations are staffed has a significant impact on the execution of the organization's strategy.
HR professionals should monitor and respond accordingly to factors that may affect workforce composition, including the following:
- Age. The age of the existing employees, the age of the available workforce, and the patterns of retirement for older workers and for the entrance of younger workers can significantly affect workforce availability.
- Current economic conditions. Unemployment rates, natural disasters and political changes can also have an impact the availability of workers.
- Globalization. One aspect of globalization that will affect almost all organizations is the increasing diversity of the workforce. Another aspect of globalization is the economic incentive to outsource labor and production activities to wherever such costs are lower. A third, and related, aspect is immigration, both legal and illegal, in the United States and abroad.
Conducting a SWOT analysis
Understanding of the current situation can be enhanced by conducting a SWOT analysis. This analysis includes an internal assessment of the organization's capabilities and limitations as well as an external environmental scan to review its customers, markets and competitors, and to forecast to external opportunities and threats.
What is a S.W.O.T. analysis, and how does it apply to an HR department?
Cultivate Critical Evaluation with a PESTLE Analysis
How To Build On Your Organization's Strengths
Major areas to consider during an external scan include economic, demographic, political, social and technological trends. An analysis of customers, markets and competitors is used to determine how the market is changing, to predict who the future customers will be and to analyze competitors in the marketplace. See Strategic Planning: What are the basics of environmental scanning? and Report: HR Lags in Using Data to Make Decisions .
When conducting a customer/market/competitor analysis, HR professionals should answer the following questions:
- What business are we in?
- What is going on in the world in which we do business?
- What business should we be in?
- What are our resources?
- What are our core competencies?
- Who are our competitors?
- How will we compete?
When the HR strategic planning team has fully evaluated the current situation, it should consider what the ideal future would look like from an organizational perspective.
The question "Where do we want to be?" can be answered and clearly articulated by creating statements of vision, mission and values. A vision statement provides a description of what an organization wants to become or hopes to accomplish in the future. An effective vision statement paints a mental picture of the organization's preferred future that is inspirational, aspirational, compelling and concise. See Human Resources Mission Statement Examples .
A values statement describes what the organization believes in and how it will behave. This statement can serve as the organization's moral compass and should be used to guide decision-making and assess actions taken. See Mission: What Is the Difference Between a Company's Mission, Vision and Values Statements?
Setting strategic objectives is an important part of the strategic planning process. Therefore, these objectives must be aligned with the organization's mission, vision and overall strategy. Strategic objectives will vary from organization to organization.
To identify whether strategic objectives have a solid foundation for success, HR should consider the following questions:
- Have the benefits of obtaining the defined objectives been outlined and communicated?
- Are the strategic objectives relevant to the organization's position in the external market? For example, do they consider competitor positions, organizational size and financial strength?
- Do the strategic objectives recognize the organization's strengths and weaknesses?
- Do employees throughout the company understand how these objectives affect them and how they contribute independently and collectively to the defined objectives?
- Are the strategic objectives realistic and feasible? Unrealistic objectives typically result in disappointment for all involved.
- Have timelines for benchmarking progress and targets for completed objectives been set?
- Will the organization realistically be able to identify the success or lack of success in the accomplishment of strategic objectives in some quantitative fashion?
- Can the strategic objectives be linked back to the organization's overall strategy?
As an example, ABC Company may identify in its strategic planning analysis a need to improve the talent acquisition process. The strategic objective to address this issue is to design selection criteria to ensure best-fit hiring while reducing the time-to-fill positions.
Once a key initiative is identified, the organization should do the following:
- Continuously ensure that the objective and action plan are aligned with the organizational and HR strategy.
- Identify the primary actions required to achieve the objective.
- Set milestones for each action, and plan for contingencies.
- Identify the required resources, including budget and staff.
- Establish success measures.
- Communicate key messages.
Ultimately, a strategic objective is only as good as the overall strategic plan.
At this step of the strategic planning process, the focus is on specifying short-term answers to the question "How do we get there?" Specific, concrete short-term objectives that can be completed within six months to a year should be established to answer this question.
Although many organizations engage in strategic planning, very few of them believe they are highly successful at strategy execution. According to a survey by the American Management Association and the Human Resources Institute, only 3 percent of executives polled said their organizations were very successful at executing corporate strategy, whereas 62 percent stated their organizations were moderately successful. However, the companies that reported relatively high success in strategy execution were more likely to realize favorable revenue growth, market share, profitability and customer satisfaction.
Though every organization has its own strategy execution challenges, this study found that mastering the following areas is essential to successfully implementing strategic plans:
- Clarity of communication.
- Alignment of practices.
- Leadership.
- An adaptive organizational infrastructure.
- Resource management.
The single greatest barrier to executing strategy is the lack of adequate resources, the study found.
The final step should be establishing a mechanism to monitor and evaluate progress toward the achievement of strategic objectives. Most organizations conduct annual or quarterly strategic reviews for this purpose. These reviews do the following:
- Determine whether the organization is on track to achieve key objectives.
- Provide the opportunity to identify and adapt to significant internal or external changes that affect the strategic plan.
- Update annual action priorities.
Some organizations may find that systems or tools such as balanced scorecards, benchmarking and dashboards are helpful for keeping focus and monitoring results.
How can the balanced scorecard be applied to human resources?
How do I determine which HR metrics to measure and report?
9 Tips for Using HR Metrics Strategically
How AI Is Changing HR Jobs and Tasks
Wilkinson, Michael (2011) The Executive Guide to Facilitating Strategy Atlanta, GA: Leadership Strategies Publishing.
Stroble, K. R., Kurtessis, J. N., Cohen, D. J., & Alexander, A. (2015). Defining HR Success: 9 critical competencies for HR professionals. Alexandria, VA: Society for Human Resource Management.
Related Articles

Why AI+HI Is Essential to Compliance
HR must always include human intelligence and oversight of AI in decision-making in hiring and firing, a legal expert said at SHRM24. She added that HR can ensure compliance by meeting the strictest AI standards, which will be in Colorado’s upcoming AI law.

A 4-Day Workweek? AI-Fueled Efficiencies Could Make It Happen
The proliferation of artificial intelligence in the workplace, and the ensuing expected increase in productivity and efficiency, could help usher in the four-day workweek, some experts predict.

How One Company Uses Digital Tools to Boost Employee Well-Being
Learn how Marsh McLennan successfully boosts staff well-being with digital tools, improving productivity and work satisfaction for more than 20,000 employees.
HR Daily Newsletter
News, trends, analysis and breaking news alerts to help HR professionals do their jobs better each business day.
Success title
Success caption

Enter your information to receive our Learning and Development Offerings Catalog

- Erin Aldridge
- February 16, 2023
Align Human Resources (HR) with Business Strategy
A business strategy consists of clearly defined plans, actions, and goals that map how a business will use its products or services to compete in one or more markets. Compared to most business functions, Human Resources (HR) intersects with all other departments, making it a vital part of any good business strategy.
More businesses are giving HR a seat at the leadership table and tapping into workforce data to identify and reach critical business objectives. Companies that weave HR activities such as recruitment, retention, and training into their overall business strategy gain a competitive edge that sets them up for long-term success. This article will explain the role of human resources in strategic planning, provide examples demonstrating how to align human resources with business strategy, and more.

Discover the Top Training Trends for 2024
Stay ahead with the latest trends and strategies in corporate training.
On this page:
The Role of Human Resources in Strategic Planning
How to align hr strategy with business strategy, examples of aligning hr strategy with business strategy.
HR is often viewed as a day-to-day administrative business unit responsible for managing talent acquisition efforts, employee benefits, performance management, training and development , compensation, and more. Given the rapidly changing nature of business, HR can no longer operate in a silo. Technology is changing entire industries at a fantastic speed and altering labor markets in a way that has a real impact on people.
With this change comes opportunity, and it requires leveraging human resources as a long-term strategic partner in business. HR can communicate business goals to personnel and help them thrive amid subsequent organizational changes. Using HR to coordinate strategic initiatives directly improves a business’s ability to remain competitive.
Other benefits of aligning HR with the business strategy at large include:
- Improving communication between leaders and the rest of the business
- Helping maintain employee and business focus on strategic goals
- Augmenting productivity
- Promoting employee engagement and retention
Human Resources can no longer be viewed as just a service-oriented department but rather an essential partner in business decision-making. Whether defining business goals and forming strategic plans starts with the executive team, the HR team, or another department, HR will play an essential role in achieving success.
Dramatic changes to the workplace are already underway, from increasing remote work to rising healthcare costs. Executing a strategic plan requires understanding these challenges. Knowing the long-term business objectives allows the HR department to navigate these challenges in a way that contributes to the business.
To successfully align their efforts with business strategy, HR experts must complete the following:
- Understand the business strategy and how it impacts other departments
- Evaluate external and internal workforce conditions
- Plan and implement the HR strategy that includes key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Automate applicable tasks
- Measure and evaluate results

A typical HR team is responsible for a range of business operations that impact how all other business units operate. Here are a couple of examples demonstrating what it means to align HR initiatives with business strategy:
Example 1: Organizational Restructuring
A corporate restructure can take many forms, from moving to a hybrid work model to consolidating departments or choosing a new corporate headquarters. No matter what the organizational change is, it will impact all employees. The restructuring can make them fearful for job security, upend their work schedule, and require them to change teams.
HR should be looped into the goal of the restructuring and play a central role during the transition. If your business is moving towards remote work, HR can find the best technology and processes to help with the change. Are you opening an office in a new city? HR can find the best local talent and onboard them. Overall, aligning HR to the restructuring goal can help retain and recruit essential employees , ultimately preserving productivity and saving money.
Example 2: Employee Retention
In a competitive job market, employees can resign for many reasons. Better pay, flexible work options, and a better work/life balance are a few common reasons. Business leaders prioritizing employee retention should tap HR to execute a plan to stifle employee resignations. HR can run an employee satisfaction survey to determine why staff leave the company and recommend changes to address them.
Example 3: Social Responsibility
More companies are prioritizing social responsibility and looking to make it a central part of their corporate values. Baking social responsibility into a business’s DNA requires significant input from the Human Resources department. Depending on the specific goals the company wants to achieve, HR might introduce diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) training, organize volunteer dates with local charities, or establish a plan for integrating environmentally-friendly business practices.
Example 4: Crisis Management
Nearly every business received a wake-up call during the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. Many had to significantly cut costs, including laying off employees, dealing a blow to morale and the bottom line. For businesses eager to be better prepared for potential crises, HR should take the lead by creating a business continuity plan (BCP) to mitigate disruptions in the case of disaster.
Keeping pace with the constant change affecting business requires using HR more strategically than ever. The core responsibilities of managing employee engagement, training, performance, and benefits will always be there. Aligning HR with the business strategy is essential for unlocking productivity, sustaining growth, achieving corporate objectives, and remaining competitive. Today’s HR function is more than just administrative cost-centers. It is a crucial partner that keeps the entire business working towards the same goals.
Receive our newsletter to stay on top of the latest posts
- Business Analysis
- Corporate Training
- Cybersecurity
- Data Analysis
- Digital Transformation
- Human Resources
- Learning & Development
- Project Management
- Technical Training
Related Blog Posts

- Corporate Training , Uncategorized

Revealing the Numbers: Key Statistics on the Widening Skills Gap

- Corporate Training , Cybersecurity
Closing the Cybersecurity Skills Gap: Key Skills and Effective Solutions

Navigating Digital Transformation: Bridging the Skills Gap
Training and development.
Training Solutions Areas of Expertise Our Brands
Resources and Insights
Blog Webinars Resources
- (877) 243-6690
- [email protected]
- Mon - Fri | 8 AM - 6 PM EST
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Human Resource Planning (HRP)
- Understanding HRP
What Is the Goal of Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
- Human Resource Planning FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Human Resource Planning (HRP) Meaning, Process, and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
Human resource planning (HRP) is the continuous process of systematic planning to achieve optimum use of an organization's most valuable asset—quality employees. HR planning ensures the best fit between employees and jobs while avoiding manpower shortages or surpluses.
There are four key steps to the HRP process. They include analyzing present labor supply, forecasting labor demand, balancing projected labor demand with supply, and supporting organizational goals. HRP is an important investment for any business as it allows companies to remain both productive and profitable.
Key Takeaways
- Human resource planning (HRP) is a strategy companies use to maintain a steady supply of skilled employees while avoiding staffing shortages or surpluses.
- HRP needs to meet short-term staffing challenges while adapting to changing conditions in the business environment over the longer term.
- Having a good HRP strategy in place can mean productivity and profitability for a company.
- HRP is made harder by the fact that not everything can be predicted.
- There are four general steps in the HRP process: identifying the current supply of employees, determining the future of the workforce, balancing between labor supply and demand, and developing plans that support the company's goals.
Michela Buttignol
What Is Human Resource Planning (HRP) Used For?
Employees are a key part of any business. Without a strong workforce, income will likely dry up and the company will go out of business. HRP is designed to prevent this from happening. Its mission is to identify current and future hiring and training needs.
HRP allows companies to plan ahead so they can maintain a steady supply of skilled employees. The process is used to help companies evaluate their needs and to plan ahead to meet those needs.
HRP needs to be flexible enough to meet short-term staffing challenges while adapting to changing conditions in the business environment over the longer term. To help prevent future roadblocks and satisfy their objectives, HR managers have to make plans to do the following:
- Find and attract skilled employees
- Select, train, and reward the best candidates
- Keep employees motivated
- Cope with absences and deal with conflicts
- Succession planning
- Promote employees or let some of them go
- Keep tabs on trends that could impact future supply and demand
Identifying a company's skill set and targeting the skills a company needs enables it to strategically reach business goals and be equipped for future challenges.
The goal of HR planning is to have the optimal number of staff to make the most money for the company. Staying on top of this and achieving effective HRP can ensure that the company:
- Gets the best out of current employees and increases their value
- Has a competitive advantage in its industry
- Is better placed to respond to challenges and adapt to changes
Challenges of Human Resource Planning (HRP)
HRP offers many advantages but it isn't without challenges. The future isn't easy to predict. A technology breakthrough can change everything, as can a black swan event. Issues such as employees getting sick and wealthier or more prestigious competitors poaching staff can also cause serious problems.
Additionally, as globalization increases, HR departments will face the need to implement new practices to accommodate government labor regulations that vary from country to country. The increased use of remote workers by many corporations will also impact HRP and will require HR departments to use new methods and tools to recruit, train, and retain workers.
Companies can set themselves up to better deal with these types of challenges if they are adaptable and continuously keep tabs on the world around them. The more prepared a company is for an event that impacts its human resources, the better it can handle and potentially take advantage of it.
HRP strategies must frequently be revised to match not only the company's changing needs but also external changes.
There's also the challenge of HRP being time consuming and potentially costly. HRP offers benefits but it can take a while to reap them.
A high level of employee engagement can be essential for a company's success. If a company has the best employees and the best practices in place, it can mean the difference between sluggishness and productivity, helping to lead a company to profitability. However, like most important investments, it can take a while for these efforts to pay off. In the beginning, HRP will be a drag on profits.
What Are the Four Steps to Human Resource Planning (HRP)?
There are four general, broad steps involved in the HRP process. Each step needs to be taken in sequence in order to arrive at the end goal, which is to develop a strategy that enables the company to successfully find and retain enough qualified employees to meet its needs.
1. Analyzing Labor Supply
The first step of HRP is to identify the company's current human resources supply. In this step, the HR department studies the strength of the organization based on the number of employees, their skills, qualifications, positions, benefits, and performance levels.
2. Forecasting Labor Demand
The second step requires the company to outline the future of its workforce. Here, the HR department can consider anything that factors into the future needs of the company, including promotions, retirements, layoffs, and transfers. The HR department can also look at external conditions impacting labor demand , such as new technology that might increase or decrease the need for workers.
3. Balancing Labor Demand With Supply
The third step in the HRP process is forecasting the employment demand. HR creates a gap analysis that lays out specific needs to narrow the supply of the company's labor versus future demand. This analysis will often generate a series of questions, such as:
- Should employees learn new skills?
- Does the company need more managers?
- Do all employees play to their strengths in their current roles?
4. Developing and Implementing a Plan
The answers to questions from the gap analysis help HR determine how to proceed, which is the final phase of the HRP process. HR must now take practical steps to integrate its plan with the rest of the company. The department needs a budget , the ability to implement the plan, and a collaborative effort with all departments to execute that plan.
Common HR policies put in place after this fourth step may include policies regarding vacation, holidays, sick days, overtime compensation, and termination.
Why Is Human Resource Planning Important?
Human resource planning (HRP) allows a business to better maintain and target the right kind of talent to employ—having the right technical and soft skills to optimize their function within the company. It also allows managers to better train the workforce and help them develop the required skills.
What Is "Hard" vs. "Soft" Human Resource Planning?
Hard HRP evaluates various quantitative metrics to ensure that the right number of the right sort of people are available when needed by the company. Soft HRP focuses more on finding employees with the right corporate culture, motivation, and attitude. Often these are used in tandem.
What Are the Basic Steps in HRP?
HRP begins with an analysis of the available labor pool from which a company can draw. It then evaluates the firm's present and future demand for various types of labor and attempts to match that demand with the supply of job applicants.
Quality employees are a company's most valuable asset. HRP involves the development of strategies to ensure that a business has an adequate supply of employees to meet its needs and can avoid either a surplus or a lack of workers.
There are four general steps in developing such a strategy: first, analyzing the company's current labor supply; second, determining the company's future labor needs; third, balancing the company's labor needs with its supply of employees; and fourth, developing and implementing the HR plan throughout the organization.
A solid HRP strategy can help a company be both productive and profitable.
International Journal of Business and Management Invention. K. Prashanthi. " Human Resource Planning-An Analytical Study ," Page 64.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/knowrisk-56fd587a5f9b586195c69845.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
HR Business Plan Template: Everything You Need to Know
With an HR business plan template, you can help your company recruit new employees, retain existing employees, and guide the development of the workforce. 4 min read updated on September 19, 2022
With an HR business plan template, you can help your company recruit new employees, retain existing employees, and guide the development of the workforce so that you collectively meet your business objectives, regardless of any changes in the industry or economy.
When creating your HR business plan, you need to perform a needs analysis of your workplace to tailor the plan to your company's requirements. You'll also need to learn about the industry standards for your field to make sure you're competitive.
Without such a plan in place, your workers will feel unprepared and won't know how to work towards your company's overall goals.
Steps for Developing a Human Resources Department Business Plan
There are several steps to creating an HR business plan. They include:
- Clarify the requirements . While you might be tempted to create a detailed plan that encompasses the entire company's next 10 years, hold off. Always talk with your boss to see how much detail he or she would like in the plan. This will save you time and help streamline the process. However, there's no harm in creating your own personalized strategic plan for your specific department.
- Read through the HR job descriptions . The HR department typically has employees such as HR assistants, HR generalists, and an HR director . Read through the job descriptions for each worker in the department and see what kind of duties are missing. Brainstorm additional functions that each job role could provide to the company.
- Curate your list . Take the different functions you've brainstormed and compare them to what each member of the HR department is already doing. Are there functions you could add or subtract from each employee for more productivity? You don't have to go into detail here, but just think about how you could improve each role.
- Schedule a meeting with the executives . Before you make any changes, you'll obviously need to get input and approval from the company's executives. They may have more feedback on how the HR department can provide additional services and support the company's overall goals and mission.
- Create a feedback form . Come up with a list of questions to ask leadership about HR's role in the company and provide it to them in advance of the meeting so they have time to think it over and talk with their staff. You may even want to provide a rating and ranking format for the questions, as this will make their responses easy to understand and implement. Overall, this is a key process to understanding what management and employees want and need from the HR department.
- Look at external resources . While the internal information you're collecting is the most important, it also doesn't hurt to take a look at data from professional organizations and websites, such as the Society for Human Resource Management , The Balance , or HR Magazine . You can also ask colleagues from other local organizations for tips on creating your business plan.
- Use this information to make a plan . With your ideas, feedback from executives, and tips from external resources, you should have a clear idea of what your plan should look like. The things that are missing from the HR department should now be clear, and this should guide you on what to focus on to improve HR's contribution to the company.
- Identify goals for this year and next . While your plan can have long-term goals, keep the majority of them a little bit shorter in scope to see how things work out. This gives you the chance to reorganize and restructure if things aren't going right. Consider creating a list of accomplishments you can reach for the end of this year and into the next.
A Real Life Example
If you're seeking more guidance on how to create a successful HR business plan, look to Starbucks as an example.
As the world's largest coffee chain, Starbucks had $21.3 billion in sales in 2016.
Despite these massive numbers, Starbucks maintains the same approach to their human resources department. All of the HR planning is guided by the company's organizational strategy and brand.
Their strategy is to use specific interview techniques when hiring new employees. This lets them identify potential leaders and place them in a "New Partner Orientation and Immersion" training program. With this system, Starbucks has achieved the lowest employee turnover rate in the quick-service restaurant industry.
Starbucks also offers numerous employee perks and dedicates a lot of time to employee training through an online portal that teaches employees essential job skills.
If you need help with your HR business plan template, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- HR Compliance
- SPHR Certification
- Human Resources Management
- LLC Business Plan Template
- Details of a Business Plan
- Business Plan Management Structure: What You Need to Know
- CCP Certification
- Service Business Plan
- Creating a Business Plan
Human Resource Planning: Meaning, Process, Types, & Importance

Human Resource Planning (HRP) is a critical component of an organization’s strategic framework. It involves forecasting the organization’s future human resource needs and developing strategies to meet those needs. Effective HRP ensures that the organization has the right number of people, with the right skills, in the right places, at the right times. This comprehensive process helps organizations achieve their goals, improve efficiency, and maintain a competitive edge. This article delves into the meaning, process, types, and importance of Human Resource Planning.
Meaning of Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning, also known as workforce planning , is a systematic process aimed at ensuring that an organization has the necessary human capital to meet its objectives. It involves analyzing and forecasting the human resource requirements, considering both the internal and external factors that could affect the availability of people with the necessary skills and competencies.
HRP is a proactive process that helps organizations anticipate and manage their workforce needs. It aligns human resource management with the overall strategic plan of the organization. By doing so, HRP ensures that the organization can respond effectively to changes in the business environment and maintain a competitive advantage.
The Process of Human Resource Planning
The HRP process typically involves several key steps:
1. Analyzing Organizational Objectives
The first step in HRP is to understand the organization’s long-term goals and objectives. This involves analyzing the strategic plan and identifying the human resources needed to achieve these objectives. Understanding the direction in which the organization is headed helps in determining the type and quantity of workforce required.
2. Assessing Current Human Resources
The next step is to assess the current human resource inventory. This involves evaluating the existing workforce in terms of numbers, skills, competencies, qualifications, and performance levels. Tools such as skills inventories, performance appraisals , and employee databases are often used in this step.
3. Forecasting Future Human Resource Needs
Once the current human resources are assessed, the next step is to forecast future HR needs. This involves predicting the demand for various types of jobs and skills in the future. Factors such as business expansion, technological advancements, and market trends are considered in this forecast.
4. Identifying Gaps in Human Resources
After forecasting future needs, the next step is to identify the gaps between the current HR inventory and the future HR requirements. This involves determining the number and type of employees needed in the future and comparing it with the current workforce.
5. Developing HR Strategies
To address the identified gaps, organizations develop HR strategies. These strategies may include recruitment, training and development, succession planning, and workforce reduction plans. The aim is to ensure that the organization has the right people with the right skills at the right time.
6. Implementing HR Plans
Once the strategies are developed, they need to be implemented. This involves putting the plans into action and managing the changes required to achieve the desired workforce composition. Effective communication and collaboration across various departments are crucial during this phase.
7. Monitoring and Evaluation
The final step in the HRP process is to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the HR plans. This involves tracking the progress of the implemented strategies, assessing their impact on organizational performance, and making necessary adjustments. Continuous monitoring helps in ensuring that the HR plans remain aligned with the organizational objectives.
Types of Human Resource Planning
There are different types of HRP, depending on the scope and focus of the planning process. These include:
1. Strategic Human Resource Planning
Strategic HRP is a long-term approach that aligns human resource management with the overall strategic goals of the organization. It involves forecasting the future HR needs based on the strategic direction of the company and developing plans to meet those needs. Strategic HRP focuses on building a workforce that can support the organization’s long-term objectives and adapt to changes in the business environment.
2. Operational Human Resource Planning
Operational HRP is a short-term approach that focuses on the day-to-day management of human resources. It involves planning for immediate HR needs based on the current operations of the organization. This type of planning is more tactical and focuses on managing the existing workforce to ensure smooth operations. It includes activities such as scheduling, staffing, and addressing immediate HR issues.
3. Workforce Planning
Workforce planning is a subset of HRP that focuses specifically on the supply and demand of labor. It involves analyzing the current workforce, forecasting future labor needs, and developing strategies to ensure that the organization has the right number of employees with the right skills. Workforce planning is often used to address specific labor market challenges, such as skill shortages or high turnover rates.
4. Succession Planning
Succession planning is a type of HRP that focuses on identifying and developing internal talent to fill key leadership positions in the future. It involves assessing the potential of current employees, providing them with development opportunities, and preparing them for future leadership roles. Succession planning helps in ensuring a smooth transition of leadership and maintaining organizational stability.
5. Contingency Planning
Contingency planning is a type of HRP that focuses on preparing for unexpected events that could impact the workforce. It involves identifying potential risks, such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or sudden loss of key employees, and developing plans to address these risks. Contingency planning helps in ensuring business continuity and minimizing the impact of unforeseen events on the workforce.
Importance of Human Resource Planning
Human Resource Planning is essential for several reasons:
1. Aligning HR with Organizational Goals
HRP ensures that human resource management is aligned with the overall strategic goals of the organization. By understanding the long-term objectives, HR professionals can develop plans to meet the future workforce needs. This alignment helps in achieving organizational goals more efficiently and effectively.
2. Improving Workforce Utilization
Effective HRP helps in optimizing the utilization of the workforce. By accurately forecasting the demand and supply of labor, organizations can avoid overstaffing or understaffing situations. This leads to better utilization of human resources, improved productivity, and reduced labor costs.
3. Addressing Skill Gaps
HRP helps in identifying and addressing skill gaps in the workforce. By analyzing the current HR inventory and forecasting future needs, organizations can identify the skills that are lacking and develop training and development programs to address these gaps. This ensures that the organization has the necessary skills to achieve its objectives.
4. Enhancing Employee Development
HRP plays a crucial role in employee development. By identifying the future HR needs and the skills required, organizations can provide targeted development opportunities for their employees. This not only helps in building a skilled workforce but also enhances employee satisfaction and retention.
5. Ensuring Business Continuity
Effective HRP helps in ensuring business continuity by preparing for potential risks and uncertainties. By developing contingency plans and succession plans, organizations can minimize the impact of unexpected events on the workforce and maintain business operations.
6. Supporting Change Management
HRP is essential for managing change effectively. As organizations undergo changes such as mergers, acquisitions, or restructuring, HRP helps in managing the workforce transition smoothly. It involves planning for the new workforce requirements, addressing employee concerns, and ensuring that the organization has the necessary talent to support the changes.
7. Legal Compliance
HRP helps organizations comply with labor laws and regulations. By understanding the legal requirements related to employment, organizations can develop HR plans that ensure compliance with these laws. This helps in avoiding legal issues and maintaining a positive reputation.
8. Enhancing Organizational Agility
HRP enhances organizational agility by enabling organizations to respond quickly to changes in the business environment. By forecasting future HR needs and developing flexible HR plans, organizations can adapt to changes such as technological advancements, market trends, and competitive pressures. This agility helps in maintaining a competitive edge.
9. Promoting a Proactive Approach
HRP promotes a proactive approach to human resource management . Instead of reacting to workforce issues as they arise, HRP involves anticipating future needs and developing plans to address them. This proactive approach helps in minimizing workforce disruptions and improving organizational performance.
Human Resource Planning is a vital process that helps organizations align their human resource management with their strategic objectives. By forecasting future HR needs and developing strategies to meet those needs, HRP ensures that organizations have the right people, with the right skills, in the right places, at the right times. The process of HRP involves analyzing organizational objectives, assessing current human resources, forecasting future needs, identifying gaps, developing HR strategies, implementing plans, and monitoring and evaluating their effectiveness.
There are different types of HRP, including strategic HRP, operational HRP, workforce planning, succession planning , and contingency planning. Each type focuses on different aspects of human resource management and addresses specific organizational needs.
The importance of HRP cannot be overstated. It helps in aligning HR with organizational goals, improving workforce utilization, addressing skill gaps, enhancing employee development, ensuring business continuity, supporting change management, ensuring legal compliance, enhancing organizational agility, and promoting a proactive approach to HR management.
In an ever-changing business environment, effective HRP is crucial for organizations to maintain a competitive edge and achieve long-term success. By investing in HRP, organizations can build a skilled and adaptable workforce that can support their strategic goals and drive organizational growth.
Related Content

10 Types of Employment Contracts
Employment contracts are the foundation of the employer-employee relationship, defining the terms and conditions that govern the professional alliance between ...

The Role of Generative AI in HR Development
Human Resources (HR) plays a critical role in the success of any organization by managing the most valuable asset: its ...

Asking Applicants to Disclose Salary Requirements
If you work in human resource or are a hiring manager, you are accustomed to asking for salary requirements. It ...
The Best 5 Tools
Find the recruiting firm you need
Any Industry. Anywhere.


Access to 13 certificate programs, courses and all future releases
Personal Coaching and Career Guidance
Community and live events
Resource and template library

- 11 Successful HR Strategy Examples...
11 Successful HR Strategy Examples To Consider for 2024

What is an HR strategy?
- A thorough analysis of both the organization and its external surroundings
- The ability to allocate vital organizational resources such as finances, time, and personnel effectively
- It’s numbers-driven and built on data-driven insights
- It’s subject to annual revisions
- It incorporates the insights and expertise of senior HR management
- It relies on and ultimately drives specific behaviors
- It’s a roadmap for how a business intends to manage its workforce.

7 Steps to creating an HR strategy

11 Successful HR strategy examples

Key HR actions Actions that Google’s HR team took include: Predictive modeling to address future people management challenges and opportunities Effective hiring algorithms to predict candidate success Using data to enhance workforce planning in a growing and changing firm.
2. Salesforce
Key HR actions Actions that the Salesforce HR team took include: Emphasizing family and community to employees, customers, and partners Linking the idea of Ohana with Salesforce’s core values Encouraging teamwork and support for employees’ well-being and engaging in philanthropic activities to strengthen the sense of togetherness.
Key HR actions Actively promoting and reinforcing alignment between mission and culture, making it a central part of the company’s identity Encouraging employees to identify and maximize their strengths Supporting employees’ personal lives by helping them manage their responsibilities both inside and outside of work.
Key HR actions Strong emphasis on talent development and motivation, including skill enhancement, career growth, and personal development A geocentric approach ensures that the right talent is in the right place to drive efficient international operations A commitment to CSR by investing in education, community improvement, and promoting gender diversity within its workforce to grow its reputation as a socially responsible organization.
5. Microsoft
Key HR actions Clear alignment with core values provides a strong foundation for cultural change Authentic leadership to inspire and guide employees Technology to accelerate cultural change, monitor progress, and help employees to adapt to the evolving culture.
Key HR actions Hiring and retaining top-tier talent, even during challenging periods Emphasizing performance over seniority to create an agile workforce aligned with Netflix’s evolving needs Adopting a flexible holiday policy, allowing employees to take as much time off as they want.
7. Johnson & Johnson
Key HR actions Investing in leadership development programs, recognizing the pivotal role of strong leadership in the company’s success Creating a culture of inclusion and diversity where all employees feel valued and respected Ensuring that employees can maintain a healthy work-life balance and overall wellbeing. This commitment to employee welfare contributes to a motivated and engaged workforce.
Key HR actions Implementing a philosophy that promotes a culture of continuous improvement among the workforce Selecting top-tier talent and empowering them to improve their skills continually Granting leaders the autonomy to build their teams and maintaining transparent salary scales.
Key HR actions Instilling a culture of exceptional discipline throughout the organization Providing training and skill development opportunities for employees Prioritizing data and discipline over emotion to ensure efficient decision-making.
10. Marks & Spencer
Key HR actions Prioritizing communication and actively involving employees in decision-making processes Maintaining positive employee relations and treating the workforce with respect Ensuring that employees are well-informed and engaged in the company’s operations.
11. Mayo Clinic
Key HR actions Compensation to attract outstanding talent Promoting teamwork that contributes to the organization’s success Instilling trust and confidence among employees to create a positive and supportive work environment.
Key takeaways

Monique Verduyn
Related articles.

HR SOP Template & Guide for HR Leaders

HR Technology Strategy: How HR Leaders Can Succeed

When To Implement an HRBP Model: 5 Signs You’re Ready
New articles.

27 Key Drivers of Employee Engagement To Benefit Your Workforce

13 Best Practices To Observe for Recruiting Top Talent

How To Develop a Performance Management Framework: Your All-In-One Guide
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter, are you ready for the future of hr.
Learn modern and relevant HR skills, online

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
Management and Human Resources Business Plans
The management portion of your business plan, the hr portion of your business plan, frequently asked questions (faqs).
As a startup, it’s never easy to come up with a business plan, let alone the management and human resources sections of a business plan. Despite that, it’s important that you start your business plan for human resources as soon as possible. Doing so gives your management goals a plan that will guide you and keep your business on track as it grows.
The key components of your human resources business plan should include your organizational structure, the philosophy and needs of your HR department, the number of employees you want to hire, how you plan to manage them, and all the estimated costs related with personnel.
You’ll want to start your HR business plan by outlining your own managerial experience and skills as well as those of your team. Highlight the roles of each member of your team, and any particular areas of strength or deficiency in your personnel lineup. For example, your HR team may be strong in compliance and conflict resolution but weak in hiring.
Don't worry if you don’t have a complete team in place when you write your HR business plan. Simply use this section to outline the organizational structure along with job descriptions, how you plan to recruit key team members, and what their responsibilities will be.
This section should look like a pyramid with you at the top and will likely have lateral positions. Be as specific as possible when defining an employee's responsibilities because this is what will drive your business.
Do You Need an HR Manager?
If you’re a solo practitioner, you may not think of including an HR manager in your management business plan. However, if you expect to hire non-managerial employees (such as salespeople or clerical workers), you should consider recruiting a human resources manager.
If hiring a human resources manager can’t be done, consider a human resources consultant. Human resource management requires an immense amount of time and paperwork, and an experienced HR consultant will be able to quickly get your payroll and benefits program up and running, affording you more time to concentrate on growing the business. Human resource responsibilities should include:
- Handling FICA and unemployment taxes and paperwork
- Ensuring compliance with the Family and Medical Leave Act
- Staying on top of IRS filings
There are plenty of companies that offer HR management platforms tailored to each business's needs. Research these companies and be sure to include their estimated cost in your HR business plan.
When you develop the HR portion of your business plan, begin by including a brief overview of your HR strategy. Investors may be curious about how your payroll will be handled and the associated costs of administering it, as well as the type of corporate culture you plan to create. Specific items to highlight in the HR section include:
- Payscale: Show the salaries for managers and non-managers based on the market for those jobs.
- Vacation time: Describe your vacation-time policy. How much time do employees get? How quickly does it accrue? Vacation time is not required by law, but most firms offer vacation time to stay competitive and keep employees refreshed.
- Insurance: Health insurance is a common staple benefit, although skyrocketing prices have forced many firms to cut back on this benefit. If you can’t afford a health plan, look into subsidizing one with employees paying the rest. Alternatively, inquire if a professional insurance representative can help you get a bulk rate.
- Additional benefits: Other things to consider include life insurance, a 401(k) and matching funds, bereavement leave, religious and floating holidays, and a bonus structure, if applicable.
In addition to the key elements above, it helps to have a framework from which to build your HR business plan. Here’s a basic outline that can help you get started:
- Figure out what your human resources department would need.
- Determine a strategy for recruiting talent.
- Formulate your hiring process.
- Develop a training program for new employees.
- Determine how much you want to pay your team (this is a good spot for payscale info)
- Create performance standards
It may be overwhelming to contemplate these benefits and their costs in the early stages of setting up your business, but in a competitive labor market, your firm needs to offer enough to entice qualified people and, more importantly, to keep them happy.
Consider revisiting your management and HR business plans every couple of years to see if you need to create action steps to refine your processes.
What should be in an HR business plan?
An HR business plan should include a mix of the steps you plan to take to launch an effective HR department, as well as specifics about how you plan to handle time off, insurance, and other benefits you plan to offer.
How do I write a human resources plan?
It helps to start with a simple framework. Try to break the plan down into sections: HR needs, recruitment, hiring, training, pay, and performance reviews. From there, incorporate other aspects of HR, like benefits and promotions.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce. " Does Your Small Business Need an HR Department? "
University of Minnesota. “ Human Resources Management: 2.2 Writing the HRM Plan .”
Mecklenburg County, North Carolina. “ FY 2020-2022 Strategic Business Plan: Human Resources .”
The new possible: How HR can help build the organization of the future
Business leaders watching their organizations experience profound upheaval because of the COVID-19 crisis may find it difficult to understand what it all means until the dust settles.
But the pandemic hasn’t afforded them, or any of us, that luxury. It has created profound and immediate changes to how societies operate and how individuals interact and work. We have all witnessed an at-scale shift to remote work, the dynamic reallocation of resources, and the acceleration of digitization and automation to meet changing individual and organizational needs.
Organizations have by and large met the challenges of this crisis moment. But as we move toward imagining a postpandemic era , a management system based on old rules—a hierarchy that solves for uniformity, bureaucracy, and control—will no longer be effective. Taking its place should be a model that is more flexible and responsive, built around four interrelated trends: more connection, unprecedented automation, lower transaction costs, and demographic shifts.
To usher in the organization of the future, chief human-resources officers (CHROs) and other leaders should do nothing less than reimagine the basic tenets of organization. Emerging models are creative, adaptable, and antifragile . 1 Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Antifragile: Things That Gain from Disorder , New York, NY: Random House Trade Paperbacks, 2012. Corporate purpose fuels bold business moves. “Labor” becomes “talent.” Hierarchies become networks of teams . Competitors become ecosystem collaborators. And companies become more human: inspiring, collaborative, and bent on creating an employee experience that is meaningful and enjoyable .
After the pandemic erupted last year, we spoke with 350 HR leaders about the role of uncertainty in their function. They told us that over the next two years they wanted to prioritize initiatives that strengthen their organization’s ability to drive change in leadership, culture, and employee experience.
How are they doing? In this article, we discuss ways that CHROs can continue to meet the moment by rethinking processes in three fundamental areas: identity, agility, and scalability.
How HR fits in the big picture
McKinsey has recently conducted research on how businesses can best organize for the future . The experimentation underway suggests that future-ready companies share three characteristics: they know what they are and what they stand for; they operate with a fixation on speed and simplicity; and they grow by scaling up their ability to learn and innovate.
HR can help propel this transformation by facilitating positive change in these three key areas, as well as with nine imperatives that radiate out from them (Exhibit 1).
Identity: HR can clarify the meaning of purpose, value, and culture
Companies that execute with purpose have greater odds of creating significant long-term value generation , which can lead to stronger financial performance, increased employee engagement, and higher customer trust.
Home in on the organization’s purpose
What is your company’s core reason for being, and where can you have a unique, positive impact on society? Now more than ever, you need good answers to those questions—purpose is not a choice but a necessity.
CHROs play a vital role in making sure the organization is living its purpose and values . HR can articulate and role-model desired individual mindsets and behaviors linked to purpose by identifying “moments that matter” in the company’s culture and translating purpose into a set of leadership and employee norms and behaviors.
For instance, commercial-vehicle manufacturer Scania holds an annual “Climate Day,” during which the company stops operations for one hour to hold sustainability training, in line with its purpose to “drive the shift toward a sustainable transport system.” 2 Scania Annual and Sustainability Report 2019 , Scania, scania.com.
HR can also ensure that clear changes are made to recruitment and capability-building processes by determining the characteristics of a “purpose driven” employee and embedding these attributes within recruitment, development, and succession planning.
HR can also incorporate purpose-driven metrics into compensation and performance decisions. Companies across industries have embarked on these metrics lately. For example, Seventh Generation, a maker of cleaning and personal-care products, recently built into its incentive system sustainability targets for the company’s entire workforce, in service of its goal of being a zero-waste company by 2025. Shell has plans to set short-term carbon-emissions targets and link executive compensation to performance against them.
Think deeply about talent
Organizations that can reallocate talent in step with their strategic plans are more than twice as likely to outperform their peers. To link talent to value, the best talent should be shifted into critical value-driving roles. That means moving away from a traditional approach, in which critical roles and talent are interchangeable and based on hierarchy.
Getting the best people into the most important roles requires a disciplined look at where the organization really creates value and how top talent contributes . Consider Tesla’s effort to create a culture of fast-moving innovation, or Apple’s obsessive focus on user experience. These cultural priorities are at the core of these companies’ value agendas. The roles needed to turn such priorities into value are often related to R&D and filled with talented, creative people.
To enable this shift, HR should manage talent rigorously by building an analytics capability to mine data to hire, develop, and retain the best employees. HR business partners, who articulate these staffing needs to the executive management team, should consider themselves internal service providers that ensure high returns on human-capital investments. For example, to engage business leaders in a regular review of talent, they can develop semiautomated data dashboards that track the most important metrics for critical roles.
Create the best employee experience possible
Companies know that a better employee experience means a better bottom line. Successful organizations work together with their people to create personalized, authentic, and motivating experiences that tap into purpose to strengthen individual, team, and company performance.
The HR team plays a crucial role in forming employee experience. Organizations in which HR facilitates a positive employee experience are 1.3 times more likely to report organizational outperformance, McKinsey research has shown . This has become even more important throughout the pandemic, as organizations work to build team morale and positive mindsets .
HR should facilitate and coordinate employee experience. Organizations can support this by helping HR evolve, strengthening the function’s capability so that it becomes the architect of the employee experience. Airbnb, for instance, rebranded the CHRO role as global head of employee experience. PayPal focused on HR’s capability and processes to create a better experience for employees, including coaching HR professionals on measuring and understanding that experience, and using technology more effectively.
Strengthen leadership and build capacity for change
Culture is the foundation on which exceptional financial performance is built. Companies with top-quartile cultures (as measured by McKinsey’s Organizational Health Index ) post a return to shareholders 60 percent higher than median companies and 200 percent higher than those in the bottom quartile.
Culture change should be business-led, with clear and highly visible leadership from the top, and execution should be rigorous and consistent. Companies are more than five times more likely to have a successful transformation when leaders have role-modeled the behavior changes they were asking their employees to make.
To strengthen an organization’s identity, HR should ask the following questions:
- How can we develop an energizing sense of purpose that has a tangible impact on our strategic choices and ways of working?
- How can we identify key talent roles and focus them on creating value?
- How can we build a data-driven, systemic understanding of our organizational health?
Agility: HR’s role in flattening the organization
Organizational agility improves both company performance and employee satisfaction . HR can be instrumental in shifting an organization from a traditional hierarchy to a marketplace that provides talent and resources to a collection of empowered small teams, helping them to achieve their missions and acting as a common guiding star.
Adopt new organizational models
For instance, as a part of a multiyear agile transformation, a large European bank worked to establish an in-house agile academy led jointly by coaches and the HR function to drive capability building for the transformation.
To be successful, a transformation should touch every facet of an organization—people, process, strategy, structure, and technology. HR can help create an iterative approach by developing core elements of the people-management process, including new career paths for agile teams, revamped performance management, and capability building. It should lead by example as well, by shifting to agile “flow to work” pools in which individuals are staffed to prioritized tasks.
Create a flexible—and magnetic—workforce
Because many roles are becoming disaggregated and fluid, work will increasingly be defined in terms of skills . The accelerating pace of technological change is widening skill gaps, making them more common and more quick to develop. To survive and deliver on their strategic objectives, all organizations will need to reskill and upskill significant portions of their workforce over the next ten years.
According to a 2018 McKinsey survey , 66 percent of executives said that “addressing potential skills gaps related to automation/digitization” within their workforces was at least a “top ten priority.” HR should help prioritize these talent shifts.
In a more recent survey McKinsey conducted with global executives about the postpandemic workforce, more than a third of respondents said that their organizations were unprepared to address the skill gaps exacerbated by automation and digitization. The shift to digitization has accelerated during the pandemic: 85 percent of companies have picked up the pace of their digitization (including a 48 percent rise in the digitization of customer channels). In light of these trends and the need to shift skills, there is a clear business rationale behind workforce strategy and planning.
HR should be a strategic partner for the business in this regard, by ensuring that the right talent is in place to deliver on core company objectives. HR can also drive workforce planning by reviewing how disruptive trends affect employees, identifying future core capabilities, and assessing how supply and demand apply to future skills gaps.
Moving to a skills focus also requires innovative sourcing to meet specific work-activity needs (for example, the gig economy and automation), and changing which roles companies need to source with traditional full-time-equivalent positions and which can be done by temporary workers or contractors. In the survey with global executives, about 70 percent said that two years from now they expect to use more temporary workers and contractors than they did before the COVID-19 crisis.
During the pandemic, we’ve seen how organizations have come together to utilize talent with transferable skills. For instance, McKinsey has supported Talent Exchange , a platform that uses artificial intelligence to help workers displaced by the crisis.
Make better decisions—faster
Companies that make decisions at the right organizational level and that have fewer reporting layers are more likely to deliver consistently on quality, velocity, and performance outcomes and thus outperform their industry peers. The pandemic has trained the spotlight on the power of fast decision making, as many organizations have had to move dramatically more quickly than they had originally envisioned. For example, one retailer had a plan for curbside delivery that would take 18 months to roll out; once the COVID-19 crisis hit, the plan went operational in just two days.
HR can help with strong decision making by empowering employees to take risks in a culture that rewards them for doing so. McKinsey research revealed that employees who are empowered to make decisions and who receive sufficient coaching from leaders were three times more likely to say that their companies’ delegated decisions were both high quality and speedy .
Introduce next-generation performance management
Companies are experimenting with a wide variety of approaches to improve how they manage performance. According to a McKinsey Global Survey , half of respondents said that performance management had not had a positive effect on employee or organizational performance. Two-thirds reported the implementation of at least one meaningful modification to their performance-management systems.
We identified three practices—managers’ coaching, linking employee goals to business priorities, and differentiated compensation—that increase the chances that a performance-management system will positively affect employee performance. HR plays an important role in embedding these practices in performance management by supporting the goal-setting process, decoupling the compensation and development discussion, investing in manager’s capability building, and embedding technology and analytics to simplify the performance-management process.
To strengthen an organization’s agility, HR should ask the following questions:
- Can we enable more effective decision making by pushing decisions to the edges of the organization, creating psychological safety that empowers people, and building capabilities?
- How do we accelerate the shift to a more diverse and deeply motivated talent base, one that is supported through a human-centric culture that enables outperformance and superior experience?
- Which organizational areas or end-to-end value-creation streams would most benefit from a shift to new ways of working and organizing?
Scalability: How HR can drive value creation
The new normal of large, rapidly recurring skills gaps means that reskilling efforts must be transformational, not business as usual or piecemeal.
Lean into a learning culture by reskilling and upskilling
Effective reskilling and upskilling will require employees to embark on a blended-learning journey that includes traditional learning (training, digital courses, job aids) with nontraditional methods (enhanced peer coaching, learning networks, the mass personalization of change , “nudging” techniques).
For instance, Microsoft shifted from a “know it all” to a “learn it all” ethos, incorporating open learning days, informal social learning opportunities, learning data for internal career paths, and new platforms and products for its partner network.
Memo to HR: Look in the mirror
To drive and facilitate these workforce initiatives, HR must transform itself first. Talent is consistently ranked as a top three priority for CEOs, yet many lack confidence in HR’s ability to deliver. 3 Dominic Barton, Dennis Carey, and Ram Charan, “People before strategy: A new role for the CHRO,” Harvard Business Review , July– August 2015, Volume 93, Number 7–8, pp. 62–71, hbr.org. The HR function is often overburdened with transactional work and not well equipped to create value for the enterprise.
Yet people-first organizations look at business problems from the perspective of how talent creates value, and HR is well positioned to bring data-driven insights to talent decisions. HR can arm itself with data-driven insights and people analytics to support talent-driven transformation, and HR business partners can then consistently make talent decisions based on data.
Create a value-enhancing HR ecosystem
McKinsey analysis has shown that a preponderance of executives recognize how much external partnerships help companies differentiate themselves. Increased value can be created through ecosystems where partners share data, code, and skills. Success now requires “blurry boundaries” and mutually dependent relationships to share value. The need of the hour is for HR to collaborate on and leverage the landscape of HR tech solutions across the employee life cycle—from learning, talent acquisition, and performance management to workforce productivity—to build an effective HR ecosystem.
To strengthen an organization’s scalability, HR should ask the following questions:
- How can we set up platforms spanning multiple players in the ecosystem and enable new sources of value and employee experience through them?
- How can we become the best company to partner with in the ecosystem? How can we set ourselves up for fast partnering and make the ecosystem accessible?
- What are the critical skills that drive future value creation and how can we upskill our talent base accordingly?
Looking ahead: How transformation happens
As the organization of the future takes shape, HR will be the driving force for many initiatives: mapping talent to value; making the workforce more flexible; prioritizing strategic workforce planning, performance management, and reskilling; building an HR platform; and developing an HR tech ecosystem. For other initiatives, HR can help C-suite leaders push forward on establishing and radiating purpose, improving employee experience, driving leadership and culture, and simplifying the organization.
Given the magnitude of the task and the broad portfolio of value-creating HR initiatives, prioritization is critical.
In May of 2020, HR leaders attending a McKinsey virtual conference indicated that over the next two years, they wanted to prioritize initiatives that strengthen agility and identity. That included 27 percent who said that they would focus on responding with agility and 25 percent who prioritized driving leadership, culture, and employee experience. Next came mapping talent to value and establishing and radiating purpose, each at 13 percent (Exhibit 2).
At a second conference for HR leaders, 4 Survey of human-resources leaders at “Reimagine: Organizing for the future,” a McKinsey virtual conference held in June 2020. about half of the assembled CHROs said that they were focusing on reimagining the fundamentals of the organization and rethinking the operating model and ways of working in the next normal.
We see organizations making this shift. Throughout the pandemic, HR has played a central role in how companies build organizational resilience and drive value . CHROs and their teams can continue on this path by connecting talent to business strategy and by implementing changes in the three core areas of identity, agility, and scalability, as well as the nine imperatives that flow from them.
A more flexible and responsive model will also help organizations meet coming demographic shifts and other workforce changes. Millennials are becoming the dominant group in the workforce (with Gen Z close behind), creating novel challenges for organizations to meet their needs. The prominence of the gig economy and alternate models of working will only grow, with 162 million workers in the European Union and the United States working independently— 70 percent of them by choice . And the rapid spread of digital technology and automation is dramatically reshaping the global economy, with half the tasks people perform already automatable today.
These trends are not new, but they are approaching tipping points, placing organization at the top of the CEO agenda. CHROs can help leadership by transforming their own HR organizations: developing and reinforcing clear priorities; embracing new ways of working, including rapid iteration and testing with the business and seeking explicit feedback; and revamping the HR skill set by embracing agility and digital capabilities.
While clearly a trial by fire, the pandemic also provides an opportunity for HR to accelerate its shift from a service to a strategic function, helping to shape a more dynamic organization that is ready to meet the postcrisis future.
Asmus Komm is a partner in McKinsey’s Hamburg office, Florian Pollner is a partner in the Zurich office, Bill Schaninger is a senior partner in the Philadelphia office, and Surbhi Sikka is a consultant in the Gurugram office.
The authors wish to thank Talha Khan for his contributions to this article.
This article was edited by Barbara Tierney, a senior editor in the New York office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Organizing for the future: Nine keys to becoming a future-ready company

HR says talent is crucial for performance—and the pandemic proves it

The future of work after COVID-19
- Newsletters
- Announcements
- Business Strategy
- Executive Networking
- Leadership Development
- Publishing With Forbes Councils
- Research And Data
- Sharing Expert Insights
- Women in Leadership
Organizational Structure in Business: The Role of Human Resources
Forbes Human Resources Council | March 16, 2023

Organizational structure is a critical aspect of any business, as it provides the framework for how tasks are allocated and resources are managed. Human resources plays a key role in designing and implementing the organizational structure, as well as managing the people who work within it. In this blog post, we will explore the importance of HR leaders in organizational structure and the various ways HR executives can contribute to organizational development.
HR Department Structure and Functions
The HR department’s structure and functions should align with the overall organizational structure and support its goals. HR team structure can vary depending on the size and complexity of the organization, but may include specialists in areas such as recruitment, training, compensation and benefits, employee relations and retention, and performance management. HR specialists should work closely with managers to support the needs of the organization.
Human Resources and Organizational Development
Organizational development — the process of improving the effectiveness and efficiency of an organization by aligning its people, processes, and culture with goals and strategies — is a crucial aspect of any successful organization.
HR’s role in organizational development is focused on human resource management — that is, creating policies and procedures for finding, supporting, and developing the people within the organization. This can include needs assessment, training and development, career planning, and performance management.
Key Elements of HR Organizational Development
HR’s role in organizational development includes several key elements:
Needs Assessment
A needs assessment involves identifying the skills, knowledge, and capabilities required for employees to meet the changing needs of the organization. This involves analyzing the current state of the organization and identifying any gaps in employee performance.
Benefit: Carefully defining the skills and traits needed for a given team or position results in better fits and more successful hires.
Training and Development
Employee training and development programs are designed to develop the skills, knowledge, and capabilities of the teams who comprise the organization. This includes both formal training programs and on-the-job training opportunities.
Benefit: Developing the skills and capabilities of employees leads to increased productivity, efficiency, and effectiveness.
Career Planning
Career planning and development programs help employees to plan and develop their careers within the organization. This includes identifying career paths and offering opportunities for growth and advancement.
Benefit: Opportunities for growth and career advancement result in engaged employees who are committed to the organization.
Performance Management
Performance management involves setting performance goals, providing feedback on performance, and evaluating employee performance.
Benefit: Performance management programs help to ensure that employees are meeting the expectations of the organization and are performing at their best.
Human Resource Management and Organizational Change
When an established business is running smoothly, the programs and functions created by HR to keep teams filled and efficient also tend to run smoothly.
But advancing technology and a competitive market introduce constant change to the equation. Just when you get a strong process in place, something shifts, and businesses have to keep up. That’s when HR executives take on organizational change.

What is Organizational Change?
Organizational change is a process of making changes to an organization's structure, processes, and culture to improve its performance and keep it competitive. These changes may include restructuring, downsizing, mergers and acquisitions, introducing new technologies, and organizational culture refreshes.
HR’s Contributions to Organizational Change
HR executives have a critical role to play as they evaluate the changing needs of each team and help employees navigate transitions. Human resource management helps organizations achieve successful change by:
Overseeing organizational design:
HR assesses a business’s structure, including its hierarchy, reporting relationships, and the distribution of responsibilities, to identify and make needed updates.
Identifying and prioritizing responsibilities:
HR identifies new tasks and responsibilities that need to be performed, prioritizes them based on importance and urgency, ensuring that teams will be established to meet changing needs appropriately.
Providing guidance and support:
The HR team is responsible for ensuring that employees understand the reasons for changes and the benefits that it will bring. This can help to reduce anxiety and resistance to change and increase employee engagement and commitment.
Managing employee training and development:
Organizational change often requires employees to learn new skills or adapt to new processes. HR manages training and development programs to ensure that employees have what they need to perform their new roles effectively.
Human resources executives’ contributions to organizational structure, development, and change are essential to keep a company functioning effectively. HR’s role in organizational development includes overseeing needs assessment, training and development, career planning, and performance management.
When organizational change comes around, HR leaders oversee organizational design, identify and prioritize responsibilities, provide guidance and support, and manage employee training and development to help ensure that everyone in the company is up to speed and on board.
If you’re an HR executive who would like to compare ideas and expertise on organizational structure or other challenges with vetted senior HR leaders, check out Forbes Human Resources Council and see if you qualify to join.

More From Forbes
Why hr is key to executive success: how the human resources function impacts business growth.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Joey Price is CEO of Jumpstart:HR , a workplace culture-focused HR consulting firm and host of the While We Were Working weekly podcast.
In my years as a professional consultant, I've learned to spot the difference between thriving organizations and underperforming ones rather quickly. Sometimes I can tell from the first interaction on a call. Other times it becomes apparent once we're in a rhythm with the full team. At some point in our engagement, corporates tend to show me and my team "how they really are" and if they want to build a winning workforce culture.
What's the secret behind high-performing organizations? They are most keenly aware of the critical role that their organization's human resources function plays in activating its overall success. If you think human resources is just a support system (*cough* "back office" *cough*) for your business, it's time to reimagine your relationship. HR is a key driver of growth and competitiveness.
Here are five key reasons why HR is essential to organizational success and how leveraging its full potential can impact your business in a positive way.
1. Attracting And Retaining Top Talent
Attracting and retaining top talent is essential for the growth and success of any business. An older study found that organizations with a strong talent recruiting strategy saw 3.5 times the revenue growth than those without. Building a diverse and skilled workforce is crucial for meeting the challenges of a rapidly changing business environment. A team of motivated and highly skilled employees can lead to increased productivity, improved customer satisfaction, and a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Reducing turnover is another key benefit of effective recruitment and retention strategies. The cost of replacing an employee "can range from one-half to two times the employee's annual salary ," according to Gallup. Investing in effective recruitment and retention strategies can help businesses attract and retain the best talent, which is essential for long-term success. The HR function plays a vital role in this process, by finding not only candidates with the right skills and experience but also those who align with the company's culture and values. By building a strong and diverse workforce, organizations can better equip themselves to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing business environment and retain top talent.
2. Building A Positive Workplace Culture
Building a positive workplace culture is essential for the success of any business. This aspect of growing your organization is truly the sweet spot of effective HR. No one is thinking about the entire organization except the HR function. According to a study by Gallup, organizations with high employee engagement have 23% higher profitability . A positive culture not only improves employee morale, but it also has been shown to increase productivity, reduce absenteeism and turnover, and improve customer satisfaction. By fostering a culture of trust, respect and inclusivity, businesses can create an environment where employees feel valued, respected and motivated to contribute their best efforts. This not only benefits the employees but also makes the company an attractive destination for top talent, which is essential for long-term success. The HR function plays a crucial role in creating and maintaining a positive and engaging workplace culture.
3. Managing And Mitigating Risk
Managing and mitigating risk is a critical need for thriving businesses as it is essential for protecting the organization's reputation, stability and long-term success. Sadly, not every organization relies on risk management procedures, and while the data is older, one survey gives a glimpse into what the practice of these procedures can look like. A 2017 survey from PMI showed that 26% of respondents used risk management practices "sometimes" and 34% of respondents used risk management practices "often." The HR function plays a vital role in this process by ensuring compliance with labor laws and regulations, identifying potential areas of liability and implementing procedures to mitigate them. This not only helps to protect the organization from costly fines and lawsuits but also helps maintain trust with customers, shareholders and other stakeholders. By effectively managing and mitigating risk, organizations can ensure their long-term stability and success.
4. Driving Business Strategy
Driving business strategy is a critical need for thriving businesses as it helps align the organization's human capital with its overall business goals. According to Gartner, " 38% of HR leaders state that their HR strategic planning process is not aligned to the business strategic planning calendar , and changes are not triggered by shifts in the business plans." The HR function plays a crucial role in this process by identifying the skills and capabilities that the organization needs to achieve its goals and developing and implementing programs to acquire and develop those skills. By aligning HR initiatives with the business strategy, organizations can ensure that they have the right people, with the right skills, in the right roles, to achieve their goals. This not only helps organizations stay competitive in a rapidly changing business environment but also creates a clear direction and vision for the organization that all employees can work toward.
5. Improving Organizational Performance
Improving organizational performance is not only essential for achieving goals and increasing efficiency, but it also has a direct impact on the bottom line. According to The People IQ study, 13% of managers and workers expressed the belief that their organization's PM system is useful . The HR function plays a critical role in driving this performance by managing and motivating employees, creating systems and processes to measure and improve performance and providing development opportunities. By implementing effective performance management systems and providing development opportunities, organizations can improve the performance of individual employees, teams and the organization as a whole. This can ultimately lead to improved productivity, increased revenue and greater success in achieving organizational goals. Additionally, effective performance management can also help organizations identify areas for improvement and make necessary changes, allowing them to stay competitive in the long term.
In conclusion, the HR function is a critical driver of growth and competitiveness for any organization. By leveraging the full potential of the HR function, organizations can attract and retain top talent, build a positive workplace culture, manage and mitigate risk, drive business strategy and improve organizational performance. Remember, investing in the HR function is not just a cost, but an opportunity for your business to thrive and succeed.
Forbes Human Resources Council is an invitation-only organization for HR executives across all industries. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
1.1 What is Human Resources?
Learning objectives.
- Explain the role of HRM in organizations.
- Define and discuss some of the major HRM activities.
Every organization, large or small, uses a variety of capital to make the business work. Capital includes cash, valuables, or goods used to generate income for a business. For example, a retail store uses registers and inventory, while a consulting firm may have proprietary software or buildings. No matter the industry, all companies have one thing in common: they must have people to make their capital work for them. This will be our focus throughout the text: generation of revenue through the use of people’s skills and abilities.
What Is HRM?
Human resource management (HRM) is the process of employing people, training them, compensating them, developing policies relating to them, and developing strategies to retain them. As a field, HRM has undergone many changes over the last twenty years, giving it an even more important role in today’s organizations. In the past, HRM meant processing payroll, sending birthday gifts to employees, arranging company outings, and making sure forms were filled out correctly—in other words, more of an administrative role rather than a strategic role crucial to the success of the organization.
CEOs believe that the time is now for HRM. “Now is the time for HRM for critical shifts to bring the organization to success through, Being Embedded Throughout the Organization, Focus on Performance, Leveraging Tech, Creating Fulfilling Work, and Sustained Culture” (Brower, 2023).
It’s necessary to point out here, at the very beginning of this text, that every manager has some role relating to human resource management. Just because we do not have the title of HR manager doesn’t mean we won’t perform all or at least some of the HRM tasks. For example, most managers deal with compensation, motivation, and retention of employees—making these aspects not only part of HRM but also part of management. As a result, this book is equally important to someone who wants to be an HR manager and to someone who will manage a business.
Human Resource Recall
Have you ever had to work with a human resource department at your job? What was the interaction like? What was the department’s role in that specific organization?
The Role of HRM
Keep in mind that many functions of HRM are also tasks other department managers perform, which is what makes this information important, despite the career path taken. Most experts agree on seven main roles that HRM plays in organizations. These are described in the following sections.
You need people to perform tasks and get work done in the organization. Even with the most sophisticated machines, humans are still needed. Because of this, one of the major tasks in HRM is staffing. Staffing involves the entire hiring process from posting a job to negotiating a salary package. Within the staffing function, there are four main steps:
- Development of a staffing plan. This plan allows HRM to see how many people they should hire based on revenue expectations.
- Development of policies to encourage multiculturalism at work. Multiculturalism in the workplace is becoming more and more important, as we have many more people from a variety of backgrounds in the workforce.
- Recruitment. This involves finding people to fill the open positions.
- Selection. In this stage, people will be interviewed and selected, and a proper compensation package will be negotiated. This step is followed by training, retention, and motivation.
Development of Workplace Policies
Every organization has policies to ensure fairness and continuity within the organization. One of the jobs of HRM is to develop the verbiage surrounding these policies. In the development of policies, HRM, management, and executives are involved in the process. For example, the HRM professional will likely recognize the need for a policy or a change of policy, seek opinions on the policy, write the policy, and then communicate that policy to employees. It is key to note here that HR departments do not and cannot work alone. Everything they do needs to involve all other departments in the organization. Some examples of workplace policies might be the following:
- Discipline process policy
- Vacation time policy
- Ethics policy
- Internet usage policy
These topics are addressed further in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits”, Chapter 7 “Retention and Motivation”, Chapter 8 “Training and Development”, and Chapter 9 “Successful Employee Communication”.
Compensation and Benefits Administration
HRM professionals need to determine that compensation is fair, meets industry standards, and is high enough to entice people to work for the organization. Compensation includes anything the employee receives for his or her work. In addition, HRM professionals need to make sure the pay is comparable to what other people performing similar jobs are being paid. This involves setting up pay systems that take into consideration the number of years with the organization, years of experience, education, and similar aspects. Examples of employee compensation include the following:
- Health benefits
- 401(k) (retirement plans)
- Stock purchase plans
- Vacation time
- Tuition reimbursement
Since this is not an exhaustive list, compensation is discussed further in Chapter 6 “Compensation and Benefits.”
Retention involves keeping and motivating employees to stay with the organization. Compensation is a major factor in employee retention, but there are other factors as well. Ninety percent of employees leave a company for the following reasons:
- Issues around the job they are performing
- Challenges with their manager
- Poor fit with organizational culture
- Poor workplace environment
Chapter 7 “Retention and Motivation” and Chapter 11 “Employee Assessment” discuss some strategies to retain the best employees based on these four factors.
Training and Development
Once we have spent the time to hire new employees, we want to make sure they not only are trained to do the job but also continue to grow and develop new skills in their job. This results in higher productivity for the organization. Training is also a key component in employee motivation. Employees who feel they are developing their skills tend to be happier in their jobs, which results in increased employee retention. Examples of training programs might include the following:
- Job skills training, such as how to run a particular computer program
- Training on communication
- Team-building activities
- Policy and legal training, such as sexual harassment training and ethics training
We address each of these types of training and more in detail in Chapter 8 “Training and Development”.
Dealing with Laws Affecting Employment
Human resource employees must be aware of all the laws that affect the workplace. An HRM professional might work with some of these laws:
- Discrimination laws
- Health-care requirements
- Compensation requirements such as the minimum wage
- Worker safety laws
The legal environment of HRM is always changing, so HRM must always be aware of changes taking place and then communicate those changes to the entire management organization. Rather than presenting a chapter focused on HRM laws, we will address these laws in each relevant chapter.
Worker Protection
Safety is a major consideration in all organizations. Oftentimes new laws are created with the goal of setting federal or state standards to ensure worker safety. Unions and union contracts can also impact the requirements for worker safety in a workplace. It is up to the human resource manager to be aware of worker protection requirements and ensure the workplace is meeting both federal and union standards. Worker protection issues might include the following:
- Chemical hazards
- Heating and ventilation requirements
- Use of “no fragrance” zones
- Protection of private employee information
We take a closer look at these issues in Chapter 12 “Working with Labor Unions” and Chapter 13 “Safety and Health at Work”.

Communication
Besides these major roles, good communication skills and excellent management skills are key to successful human resource management as well as general management. We discuss these issues in Chapter 9 “Successful Employee Communication”.
Awareness of External Factors
In addition to managing internal factors, the HR manager needs to consider the outside forces at play that may affect the organization. Outside forces, or external factors, are those things the company has no direct control over; however, they may be things that could positively or negatively impact human resources. External factors might include the following:
- Globalization and offshoring
- Changes to employment law
- Health-care costs
- Employee expectations
- Diversity of the workforce
- Changing demographics of the workforce
- A more highly educated workforce
- Layoffs and downsizing
- Technology used, such as HR databases
- Increased use of social networking to distribute information to employees
For example, the recent trend in flexible work schedules (allowing employees to set their own schedules) and telecommuting (allowing employees to work from home or a remote location for a specified period of time, such as one day per week) are external factors that have affected HR. HRM has to be aware of these outside issues, so they can develop policies that meet not only the needs of the company but also the needs of the individuals.

One way managers can be aware of the outside forces is to attend conferences and read various articles on the web. For example, the website of the Society for Human Resource Management, SHRM Online , not only has job postings in the field but discusses many contemporary human resource issues that may help the manager make better decisions when it comes to people management. In Section 1.3 “Today’s HRM Challenges”, we go into more depth about some recent external issues that are affecting human resource management roles. In Section 1.1.2 “The Role of HRM”, we discuss some of the skills needed to be successful in HRM.

Key Takeaways
- Capital includes all resources a company uses to generate revenue. Human resources or the people working in the organization are the most important resource.
- Human resource management is the process of employing people, training them, compensating them, developing policies relating to the workplace, and developing strategies to retain employees.
- There are seven main responsibilities of HRM managers: staffing, setting policies, compensation and benefits, retention, training, employment laws, and worker protection. In this book, each of these major areas will be included in a chapter or two.
- In addition to being concerned with the seven internal aspects, HRM managers must keep up to date with changes in the external environment that may impact their employees. The trends toward flexible schedules and telecommuting are examples of external aspects.
- To effectively understand how the external forces might affect human resources, it is important for the HR manager to read the HR literature, attend conferences, and utilize other ways to stay up to date with new laws, trends, and policies.
- State arguments for and against the following statement: there are other things more valuable in an organization besides the people who work there.
- Of the seven tasks an HR manager does, which do you think is the most challenging? Why?
Brower, T. (2023). CEOS say HR is central to business success: 5 critical shifts . Forbes. https://www.forbes.com/sites/tracybrower/2023/01/22/ceos-say-hr-is-central-to-business-success-5-critical-shifts/?sh=170618f262f8
Mayer, K. (2022). Employers anticipating big jump in cost of health benefits next year . Human Resource Executive. https://hrexecutive.com/employers-anticipating-big-jump-in-cost-of-health-benefits-next-year/

COMMENTS
Strategic Human Resource Management (2024 Guide)
Aligning with business strategy gives HR a strategic focus and helps prioritize goals. Secure the right talent: Good talent is always valuable, but companies may need to invest in different skill sets or roles at different times. Understanding the strategic goals of the business will help HR attract and retain the right talent at the right time.
To drive HR strategic planning and any HR transformation initiatives, follow these five steps to create an effective human resources strategy that supports enterprise business goals:. Understand your organization's mission, strategy and business goals.; Identify the critical capabilities and skills.; Evaluate the current capabilities and skills of your talent and the HR function, and ...
Here are six steps to help you succeed at the human resource planning process. 1. Assess current employees' skill levels. The first step to creating a future-forward HR plan is to assess employees' current skill sets, and compare them to your operational needs moving forward.
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, having a plan in place for managing your human capital is key — and that's where human resource planning (HRP) comes in. Human resource planning plays a critical role in making sure that your organization is well-equipped with the right talent at the right time.
In "hard" human resource planning, a quantitative approach is taken. The focus is on workforce capabilities and resource planning. Supply forecasting and skills inventory data is used to predict future workforce requirements. The sole mission is getting that sweet alignment between human resources and the business's needs.
A strategic HRM plan is a comprehensive document outlining an organization's HR goals, objectives, and strategies. Such a plan compares business goals against the people resources needed to accomplish them, including the skills, abilities, traits, talents, and competencies housed within your workforce. The plan should include a detailed ...
In order to plan the staffing that your organization will require in the future, you'll first need to analyze the overall objectives of the company in terms of expansion, sales, finance, marketing and production. 2. Evaluate the current HR capacity. Next, you will need to create a catalog of your company's current supply of human resources.
HR planning is a valuable process for any organization, ensuring that the right people are in the right roles at the right time. Whether you're a small business owner or a seasoned HR professional, understanding HR planning can help you optimize your workforce, improve employee satisfaction, and drive organizational success.
Developing a Strategic HR Plan. HR's role includes developing a plan of HR initiatives to achieve and promote the behaviors, culture and competencies needed to achieve organizational goals ...
Understand the business strategy and how it impacts other departments. Evaluate external and internal workforce conditions. Plan and implement the HR strategy that includes key performance indicators (KPIs) Automate applicable tasks. Measure and evaluate results. 5 Steps to Align HR with Business Strategy.
Human resource planning (HRP) is the continuous process of systematic planning to achieve optimum use of an organization's most valuable asset—quality employees. HR planning ensures the best fit ...
Without such a plan in place, your workers will feel unprepared and won't know how to work towards your company's overall goals. Steps for Developing a Human Resources Department Business Plan. There are several steps to creating an HR business plan. They include: Clarify the requirements. While you might be tempted to create a detailed plan ...
The Process of Human Resource Planning. The HRP process typically involves several key steps: 1. Analyzing Organizational Objectives. The first step in HRP is to understand the organization's long-term goals and objectives. This involves analyzing the strategic plan and identifying the human resources needed to achieve these objectives.
Human resource planning steps. Here are some of the steps you can take for effective human resource planning: 1. Analyze the company's current employees and their offerings. Analyzing a company's current offerings, staff skills and business goals are essential to planning. This helps you understand what you might need to improve or what works well.
7 Steps to creating an HR strategy. We've outlined 7 key steps based on Deloitte's HR Strategy Framework to help you design an HR strategy:. 1. Consider the market and trends: Analyze the external market and trends that are impacting your industry. 2. Understand the business strategy: Know the business strategy and be clear on the must-win battles for the business, the key value drivers ...
The key components of your human resources business plan should include your organizational structure, the philosophy and needs of your HR department, the number of employees you want to hire, how you plan to manage them, and all the estimated costs related with personnel. ... Highlight the roles of each member of your team, and any particular ...
To usher in the organization of the future, chief human-resources officers (CHROs) and other leaders should do nothing less than reimagine the basic tenets of organization. Emerging models are creative, adaptable, and antifragile. 1 Corporate purpose fuels bold business moves. "Labor" becomes "talent.".
Naturally, this is when addressed up front in the HR business plan. Three Key Elements of HR in the Planning Process 1. Resource Planning. Once the business goals are set, it is people involved who will carry them out. So, having the right people in the right roles at the right time is key. A resource plan is the people equivalent of a ...
Identifying the key priorities will naturally drive alignment among talent, strategic objectives and results. Often, HR professionals overlook the importance of focusing on the key issues that the ...
Human resources executives' contributions to organizational structure, development, and change are essential to keep a company functioning effectively. HR's role in organizational development includes overseeing needs assessment, training and development, career planning, and performance management. When organizational change comes around ...
The HR function plays a crucial role in creating and maintaining a positive and engaging workplace culture. 3. Managing And Mitigating Risk. Managing and mitigating risk is a critical need for ...
5. Reducing costs. Predictable HR requirements, enhanced productivity, increased retention and optimised performance are all factors that can help a business reduce its costs. When a business can predict its HR needs and optimise performance, it can have the right people in the right roles working the right shifts.
Development of a staffing plan. ... Not understanding the external factors can also mean breaking the law, which has a concerning set of implications as well. Figure 1.2. Click the image to open in a full-screen window. ... The Role of Human Resources Toggle "Chapter 1: The Role of Human Resources" submenu.