- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

References in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Outline – Types, Example, Template

APA Research Paper Format – Example, Sample and...

Research Approach – Types Methods and Examples

Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and...
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free

How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, apa format: basic guide for researchers, how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements, how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to write a high-quality conference paper.

How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to start your research paper [step-by-step guide]
1. Choose your topic
2. find information on your topic, 3. create a thesis statement, 4. create a research paper outline, 5. organize your notes, 6. write your introduction, 7. write your first draft of the body, 9. write your conclusion, 10. revise again, edit, and proofread, frequently asked questions about starting your research paper, related articles.
Research papers can be short or in-depth, but no matter what type of research paper, they all follow pretty much the same pattern and have the same structure .
A research paper is a paper that makes an argument about a topic based on research and analysis.
There will be some basic differences, but if you can write one type of research paper, you can write another. Below is a step-by-step guide to starting and completing your research paper.
Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about. Your interest will show in the way you write and effort you put into the paper. Consider these issues when coming up with a topic:
- make sure your topic is not too broad
- narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general
Academic search engines are a great source to find background information on your topic. Your institution's library will most likely provide access to plenty of online research databases. Take a look at our guide on how to efficiently search online databases for academic research to learn how to gather all the information needed on your topic.
Tip: If you’re struggling with finding research, consider meeting with an academic librarian to help you come up with more balanced keywords.
If you’re struggling to find a topic for your thesis, take a look at our guide on how to come up with a thesis topic .
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing. It can be defined as a very brief statement of what the main point or central message of your paper is. Our thesis statement guide will help you write an excellent thesis statement.
In the next step, you need to create your research paper outline . The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
Then, fill out your outline with the following components:
- the main ideas that you want to cover in the paper
- the types of evidence that you will use to support your argument
- quotes from secondary sources that you may want to use
Organizing all the information you have gathered according to your outline will help you later on in the writing process. Analyze your notes, check for accuracy, verify the information, and make sure you understand all the information you have gathered in a way that you can communicate your findings effectively.
Start with the introduction. It will set the direction of your paper and help you a lot as you write. Waiting to write it at the end can leave you with a poorly written setup to an otherwise well-written paper.
The body of your paper argues, explains or describes your topic. Start with the first topic from your outline. Ideally, you have organized your notes in a way that you can work through your research paper outline and have all the notes ready.
After your first draft, take some time to check the paper for content errors. Rearrange ideas, make changes and check if the order of your paragraphs makes sense. At this point, it is helpful to re-read the research paper guidelines and make sure you have followed the format requirements. You can also use free grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .
Tip: Consider reading your paper from back to front when you undertake your initial revision. This will help you ensure that your argument and organization are sound.
Write your conclusion last and avoid including any new information that has not already been presented in the body of the paper. Your conclusion should wrap up your paper and show that your research question has been answered.
Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit, and proofread your paper.
Tip: Take a break from your paper before you start your final revisions. Then, you’ll be able to approach your paper with fresh eyes.
As part of your final revision, be sure to check that you’ve cited everything correctly and that you have a full bibliography. Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize your research and to create accurate citations.
The first step to start writing a research paper is to choose a topic. Make sure your topic is not too broad; narrow it down if you're using terms that are too general.
The format of your research paper will vary depending on the journal you submit to. Make sure to check first which citation style does the journal follow, in order to format your paper accordingly. Check Getting started with your research paper outline to have an idea of what a research paper looks like.
The last step of your research paper should be proofreading. Allow a few days to pass after you finished writing the final draft of your research paper, and then start making your final corrections. The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill gives some great advice here on how to revise, edit and proofread your paper.
There are plenty of software you can use to write a research paper. We recommend our own citation software, Paperpile , as well as grammar and proof reading checkers such as Grammarly .

How to Write a Research Paper

If you already have a headache trying to understand what research paper is all about, we have created an ultimate guide for you on how to write a research paper. You will find all the answers to your questions regarding structure, planning, doing investigation, finding the topic that appeals to you. Plus, you will find out the secret to an excellent paper. Are you at the edge of your seat? Let us start with the basics then.
- What is a Research Paper
- Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
- Report Papers and Thesis Papers
- How to Start a Research Paper
- How to Choose a Topic for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Plan
- How to Do Research
- How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Rough Draft
- How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Body of a Research Paper
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Revise and Edit a Research Paper
- How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper
- What Makes a Good Research Paper
Research Paper Writing Services
What is a research paper.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
You probably know the saying ‘the devil is not as black as he is painted’. This particular saying is absolutely true when it comes to writing a research paper. Your feet are cold even with the thought of this assignment. You have heard terrifying stories from older students. You have never done this before, so certainly you are scared. What is a research paper? How should I start? What are all these requirements about?
Luckily, you have a friend in need. That is our writing service. First and foremost, let us clarify the definition. A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides information about a particular topic that you’ve researched . In other words, you choose a topic: about historical events, the work of some artist, some social issues etc. Then you collect data on the given topic and analyze it. Finally, you put your analysis on paper. See, it is not as scary as it seems. If you are still having doubts, whether you can handle it yourself, we are here to help you. Our team of writers can help you choose the topic, or give you advice on how to plan your work, or how to start, or craft a paper for you. Just contact us 24/7 and see everything yourself.
5 Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
Why should I spend my time writing some academic paper? What is the use of it? Is not some practical knowledge more important? The list of questions is endless when it comes to a research paper. That is why we have outlined 5 main reasons why writing a research paper is a good thing.
- You will learn how to organize your time
If you want to write a research paper, you will have to learn how to manage your time. This type of assignment cannot be done overnight. It requires careful planning and you will need to learn how to do it. Later, you will be able to use these time-managing skills in your personal life, so why not developing them?
- You will discover your writing skills
You cannot know something before you try it. This rule relates to writing as well. You cannot claim that you cannot write until you try it yourself. It will be really difficult at the beginning, but then the words will come to your head themselves.
- You will improve your analytical skills
Writing a research paper is all about investigation and analysis. You will need to collect data, examine and classify it. These skills are needed in modern life more than anything else is.
- You will gain confidence
Once you do your own research, it gives you the feeling of confidence in yourself. The reason is simple human brain likes solving puzzles and your assignment is just another puzzle to be solved.
- You will learn how to persuade the reader
When you write your paper, you should always remember that you are writing it for someone to read. Moreover, you want this someone to believe in your ideas. For this reason, you will have to learn different convincing methods and techniques. You will learn how to make your writing persuasive. In turns, you will be able to use these methods in real life.
What is the Difference between Report and Thesis Papers?
A common question is ‘what is the difference between a report paper and a thesis paper?’ The difference lies in the aim of these two assignments. While the former aims at presenting the information, the latter aims at providing your opinion on the matter. In other words, in a report paper you have to summarize your findings. In a thesis paper, you choose some issue and defend your point of view by persuading the reader. It is that simple.
A thesis paper is a more common assignment than a report paper. This task will help a professor to evaluate your analytical skills and skills to present your ideas logically. These skills are more important than just the ability to collect and summarize data.
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
Research comes from the French word rechercher , meaning “to seek out.” Writing a research paper requires you to seek out information about a subject, take a stand on it, and back it up with the opinions, ideas, and views of others. What results is a printed paper variously known as a term paper or library paper, usually between five and fifteen pages long—most instructors specify a minimum length—in which you present your views and findings on the chosen subject.

It is not a secret that the majority of students hate writing a research paper. The reason is simple it steals your time and energy. Not to mention, constant anxiety that you will not be able to meet the deadline or that you will forget about some academic requirement.
We will not lie to you; a research paper is a difficult assignment. You will have to spend a lot of time. You will need to read, to analyze, and to search for the material. You will probably be stuck sometimes. However, if you organize your work smart, you will gain something that is worth all the effort – knowledge, experience, and high grades.
The reason why many students fail writing a research paper is that nobody explained them how to start and how to plan their work. Luckily, you have found our writing service and we are ready to shed the light on this dark matter.
We have created a step by step guide for you on how to write a research paper. We will dwell upon the structure, the writing tips, the writing strategies as well as academic requirements. Read this whole article and you will see that you can handle writing this assignment and our team of writers is here to assist you.
How to Start a Research Paper?

It all starts with the assignment. Your professor gives you the task. It may be either some general issue or specific topic to write about. Your assignment is your first guide to success. If you understand what you need to do according to the assignment, you are on the road to high results. Do not be scared to clarify your task if you need to. There is nothing wrong in asking a question if you want to do something right. You can ask your professor or you can ask our writers who know a thing or two in academic writing.
It is essential to understand the assignment. A good beginning makes a good ending, so start smart.
Learn how to start a research paper .
Choosing a Topic for a Research Paper

We have already mentioned that it is not enough to do great research. You need to persuade the reader that you have made some great research. What convinces better that an eye-catching topic? That is why it is important to understand how to choose a topic for a research paper.
First, you need to delimit the general idea to a more specific one. Secondly, you need to find what makes this topic interesting for you and for the academia. Finally, you need to refine you topic. Remember, it is not something you will do in one day. You can be reshaping your topic throughout your whole writing process. Still, reshaping not changing it completely. That is why keep in your head one main idea: your topic should be precise and compelling .
Learn how to choose a topic for a research paper .
How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper?

If you do not know what a proposal is, let us explain it to you. A proposal should answer three main questions:
- What is the main aim of your investigation?
- Why is your investigation important?
- How are you going to achieve the results?
In other words, proposal should show why your topic is interesting and how you are going to prove it. As to writing requirements, they may differ. That is why make sure you find out all the details at your department. You can ask your departmental administrator or find information online at department’s site. It is crucial to follow all the administrative requirements, as it will influence your grade.
Learn how to write a proposal for a research paper .
How to Write a Research Plan?

The next step is writing a plan. You have already decided on the main issues, you have chosen the bibliography, and you have clarified the methods. Here comes the planning. If you want to avoid writer’s block, you have to structure you work. Discuss your strategies and ideas with your instructor. Think thoroughly why you need to present some data and ideas first and others second. Remember that there are basic structure elements that your research paper should include:
- Thesis Statement
- Introduction
- Bibliography
You should keep in mind this skeleton when planning your work. This will keep your mind sharp and your ideas will flow logically.
Learn how to write a research plan .
How to Do Research?

Your research will include three stages: collecting data, reading and analyzing it, and writing itself.
First, you need to collect all the material that you will need for you investigation: films, documents, surveys, interviews, and others. Secondly, you will have to read and analyze. This step is tricky, as you need to do this part smart. It is not enough just to read, as you cannot keep in mind all the information. It is essential that you make notes and write down your ideas while analyzing some data. When you get down to the stage number three, writing itself, you will already have the main ideas written on your notes. Plus, remember to jot down the reference details. You will then appreciate this trick when you will have to write the bibliography.
If you do your research this way, it will be much easier for you to write the paper. You will already have blocks of your ideas written down and you will just need to add some material and refine your paper.
Learn how to do research .
How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper?

To make your paper well organized you need to write an outline. Your outline will serve as your guiding star through the writing process. With a great outline you will not get sidetracked, because you will have a structured plan to follow. Both you and the reader will benefit from your outline. You present your ideas logically and you make your writing coherent according to your plan. As a result, this outline guides the reader through your paper and the reader enjoys the way you demonstrate your ideas.
Learn how to write an outline for a research paper . See research paper outline examples .
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper?

Briefly, the thesis is the main argument of your research paper. It should be precise, convincing and logical. Your thesis statement should include your point of view supported by evidence or logic. Still, remember it should be precise. You should not beat around the bush, or provide all the possible evidence you have found. It is usually a single sentence that shows your argument. In on sentence you should make a claim, explain why it significant and convince the reader that your point of view is important.
Learn how to write a thesis statement for a research paper . See research paper thesis statement examples .
Should I Write a Rough Draft for a Research Paper?

Do you know any writer who put their ideas on paper, then never edited them and just published? Probably, no writer did so. Writing a research paper is no exception. It is impossible to cope with this assignment without writing a rough draft.
Your draft will help you understand what you need to polish to make your paper perfect. All the requirements, academic standards make it difficult to do everything flawlessly at the first attempt. Make sure you know all the formatting requirements: margins, words quantity, reference requirements, formatting styles etc.
Learn how to write a rough draft for a research paper .
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper?

Let us make it more vivid for you. We have narrowed down the tips on writing an introduction to the three main ones:
- Include your thesis in your introduction
Remember to include the thesis statement in your introduction. Usually, it goes at the end of the first paragraph.
- Present the main ideas of the body
You should tell the main topics you are going to discuss in the main body. For this reason, before writing this part of introduction, make sure you know what is your main body is going to be about. It should include your main ideas.
- Polish your thesis and introduction
When you finish the main body of your paper, come back to the thesis statement and introduction. Restate something if needed. Just make it perfect; because introduction is like the trailer to your paper, it should make the reader want to read the whole piece.
Learn how to write an introduction for a research paper . See research paper introduction examples .
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper?

A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument.
It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic. Stay focused and do not be sidetracked. You have your outline, so follow it.
Here are the main tips to keep in head when writing a body of a research paper:
- Let the ideas flow logically
- Include only relevant information
- Provide the evidence
- Structure the paragraphs
- Make the coherent transition from one paragraph to another
See? When it is all structured, it is not as scary as it seemed at the beginning. Still, if you have doubts, you can always ask our writers for help.
Learn how to write a body of a research paper . See research paper transition examples .
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper?

Writing a good conclusion is important as writing any other part of the paper. Remember that conclusion is not a summary of what you have mentioned before. A good conclusion should include your last strong statement.
If you have written everything according to the plan, the reader already knows why your investigation is important. The reader has already seen the evidence. The only thing left is a strong concluding thought that will organize all your findings.
Never include any new information in conclusion. You need to conclude, not to start a new discussion.
Learn how to write a conclusion for a research paper .
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper?

An abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually 100-200 words. You should provide the main gist of your paper in this short summary. An abstract can be informative, descriptive or proposal. Depending on the type of abstract, you need to write, the requirements will differ.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research.
To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery. You should write a short teaser of your paper. That is to say, you need to write an overview of your paper. The aim of a descriptive abstract is to interest the reader.
Finally, to write a proposal abstract you will need to write the basic summary as for the informative abstract. However, the difference is the following: you aim at persuading someone to let you write on the topic. That is why, a proposal abstract should present your topic as the one worth investigating.
Learn how to write an abstract for a research paper .
Should I Revise and Edit a Research Paper?

Revising and editing your paper is essential if you want to get high grades. Let us help you revise your paper smart:
- Check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes
- Sharpen the vocabulary
- Make sure there are no slang words in your paper
- Examine your paper in terms of structure
- Compare your topic, thesis statement to the whole piece
- Check your paper for plagiarism
If you need assistance with proofreading and editing your paper, you can turn to the professional editors at our service. They will help you polish your paper to perfection.
Learn how to revise and edit a research paper .
How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper?

First, let us make it clear that bibliography and works cited are two different things. Works cited are those that you cited in your paper. Bibliography should include all the materials you used to do your research. Still, remember that bibliography requirements differ depending on the formatting style of your paper. For this reason, make sure you ask you professor all the requirements you need to meet to avoid any misunderstanding.
Learn how to write a bibliography for a research paper .
The Key Secret to a Good Research Paper
Now when you know all the stages of writing a research paper, you are ready to find the key to a good research paper:
- Choose the topic that really interests you
- Make the topic interesting for you even if it is not at the beginning
- Follow the step by step guide and do not get sidetracked
- Be persistent and believe in yourself
- Really do research and write your paper from scratch
- Learn the convincing writing techniques and use them
- Follow the requirements of your assignment
- Ask for help if needed from real professionals
Feeling more confident about your paper now? We are sure you do. Still, if you need help, you can always rely on us 24/7.
We hope we have made writing a research paper much easier for you. We realize that it requires lots of time and energy. We believe when you say that you cannot handle it anymore. For this reason, we have been helping students like you for years. Our professional team of writers is ready to tackle any challenge.
All our authors are experienced writers crafting excellent academic papers. We help students meet the deadline and get the top grades they want. You can see everything yourself. All you need to do is to place your order online and we will contact you. Writing a research paper with us is truly easy, so why do not you check it yourself?
Additional Resources for Research Paper Writing:
- Anthropology Research
- Career Research
- Communication Research
- Criminal Justice Research
- Health Research
- Political Science Research
- Psychology Research
- Sociology Research
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia
How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
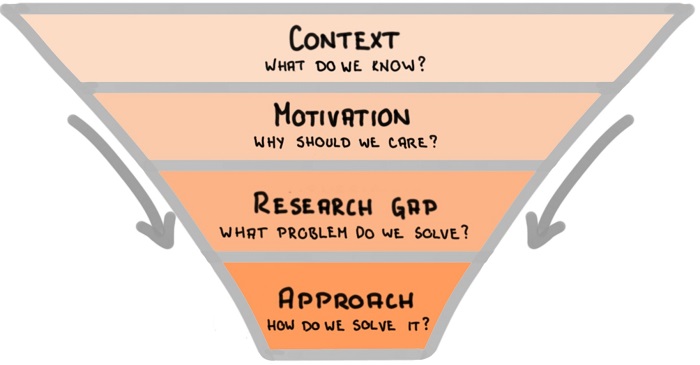
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
Writing a Research Paper
This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper.
Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
Discovering, Narrowing, and Focusing a Researchable Topic
- Try to find a topic that truly interests you
- Try writing your way to a topic
- Talk with your course instructor and classmates about your topic
- Pose your topic as a question to be answered or a problem to be solved
Finding, Selecting, and Reading Sources
You will need to look at the following types of sources:
- library catalog, periodical indexes, bibliographies, suggestions from your instructor
- primary vs. secondary sources
- journals, books, other documents
Grouping, Sequencing, and Documenting Information
The following systems will help keep you organized:
- a system for noting sources on bibliography cards
- a system for organizing material according to its relative importance
- a system for taking notes
Writing an Outline and a Prospectus for Yourself
Consider the following questions:
- What is the topic?
- Why is it significant?
- What background material is relevant?
- What is my thesis or purpose statement?
- What organizational plan will best support my purpose?
Writing the Introduction
In the introduction you will need to do the following things:
- present relevant background or contextual material
- define terms or concepts when necessary
- explain the focus of the paper and your specific purpose
- reveal your plan of organization
Writing the Body
- Use your outline and prospectus as flexible guides
- Build your essay around points you want to make (i.e., don’t let your sources organize your paper)
- Integrate your sources into your discussion
- Summarize, analyze, explain, and evaluate published work rather than merely reporting it
- Move up and down the “ladder of abstraction” from generalization to varying levels of detail back to generalization
Writing the Conclusion
- If the argument or point of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to add your points up, to explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction.
- Perhaps suggest what about this topic needs further research.
Revising the Final Draft
- Check overall organization : logical flow of introduction, coherence and depth of discussion in body, effectiveness of conclusion.
- Paragraph level concerns : topic sentences, sequence of ideas within paragraphs, use of details to support generalizations, summary sentences where necessary, use of transitions within and between paragraphs.
- Sentence level concerns: sentence structure, word choices, punctuation, spelling.
- Documentation: consistent use of one system, citation of all material not considered common knowledge, appropriate use of endnotes or footnotes, accuracy of list of works cited.


Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1970 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 41,568 quotes across 1970 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!


How to Write a Research Paper: Parts of the Paper
- Choosing Your Topic
- Citation & Style Guides This link opens in a new window
- Critical Thinking
- Evaluating Information
- Parts of the Paper
- Writing Tips from UNC-Chapel Hill
- Librarian Contact
Parts of the Research Paper Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea, and indicate how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas.
1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses. Use keywords that help explain your paper's topic to the reader. Try to avoid abbreviations and jargon. Think about keywords that people would use to search for your paper and include them in your title.
2. The Abstract The abstract is used by readers to get a quick overview of your paper. Typically, they are about 200 words in length (120 words minimum to 250 words maximum). The abstract should introduce the topic and thesis, and should provide a general statement about what you have found in your research. The abstract allows you to mention each major aspect of your topic and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Because it is a summary of the entire research paper, it is often written last.
3. The Introduction The introduction should be designed to attract the reader's attention and explain the focus of the research. You will introduce your overview of the topic, your main points of information, and why this subject is important. You can introduce the current understanding and background information about the topic. Toward the end of the introduction, you add your thesis statement, and explain how you will provide information to support your research questions. This provides the purpose and focus for the rest of the paper.
4. Thesis Statement Most papers will have a thesis statement or main idea and supporting facts/ideas/arguments. State your main idea (something of interest or something to be proven or argued for or against) as your thesis statement, and then provide your supporting facts and arguments. A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. It also points toward the paper's development. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.
Students often learn to write a thesis as a first step in the writing process, but often, after research, a writer's viewpoint may change. Therefore a thesis statement may be one of the final steps in writing.
Examples of Thesis Statements from Purdue OWL
5. The Literature Review The purpose of the literature review is to describe past important research and how it specifically relates to the research thesis. It should be a synthesis of the previous literature and the new idea being researched. The review should examine the major theories related to the topic to date and their contributors. It should include all relevant findings from credible sources, such as academic books and peer-reviewed journal articles. You will want to:
- Explain how the literature helps the researcher understand the topic.
- Try to show connections and any disparities between the literature.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
More about writing a literature review. . .
6. The Discussion The purpose of the discussion is to interpret and describe what you have learned from your research. Make the reader understand why your topic is important. The discussion should always demonstrate what you have learned from your readings (and viewings) and how that learning has made the topic evolve, especially from the short description of main points in the introduction.Explain any new understanding or insights you have had after reading your articles and/or books. Paragraphs should use transitioning sentences to develop how one paragraph idea leads to the next. The discussion will always connect to the introduction, your thesis statement, and the literature you reviewed, but it does not simply repeat or rearrange the introduction. You want to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking, not just reporting back facts that you gathered.
- If possible, tell how the topic has evolved over the past and give it's implications for the future.
- Fully explain your main ideas with supporting information.
- Explain why your thesis is correct giving arguments to counter points.
7. The Conclusion A concluding paragraph is a brief summary of your main ideas and restates the paper's main thesis, giving the reader the sense that the stated goal of the paper has been accomplished. What have you learned by doing this research that you didn't know before? What conclusions have you drawn? You may also want to suggest further areas of study, improvement of research possibilities, etc. to demonstrate your critical thinking regarding your research.
- << Previous: Evaluating Information
- Next: Research >>
- Last Updated: Feb 13, 2024 8:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ucc.edu/research_paper
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- The 10 Best Free Character and Word Counters of 2024
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Creating a Dissertation Title Page (Examples & Templates)
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
- Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top 10 Essay Writing Tools in 2024 | Plan, Write, Get Feedback
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.

- Tags: Academic Research , Academic Writing , Research , Research Paper
Learning how to start a research paper is the first checklist item of your academic writing journey. A compelling research paper introduction sets the stage for everything that follows. It clearly defines your argument and gives readers a roadmap for what’s in store.
But why is a strong introduction to a research paper so important? Simple. It grabs attention and lays the foundation stone of your argument. Through this practical guide, we’ll explore the various elements to include in your introduction for a research paper. We’ll try to shed light through practical tips and examples. So let’s dive in!
Want to elevate the quality of your research paper? Learn more
How to write a research paper introduction?
First impressions always matter, and this is why adding a strong introduction to a research paper is so important. But what does it constitute? There are 3 main parts broadly – The hook, the background information, and the thesis statement.
Let’s look at each one in detail:
The first sentence is your hook, designed to capture the reader’s attention. It can be a provocative question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement. The aim is to pique interest and pose the overarching question that your research seeks to answer. A well-crafted hook is like a magnet—it draws the reader into your intellectual arena.
Example: Did you know chocolate was once used as currency in ancient civilizations?
Background information
When it comes to writing a research paper introduction , your reader needs context but not information overload. Here, you set the stage by providing just enough background information on the topic at hand.
It can include previous studies on the same topic, the scope, and some context. Consider this your chance to orient your audience before delving into the complexities of your argument.
Example : “There has been a significant increase in the incidence of diabetes in recent years. This has led to an increased demand for effective diabetes management strategies. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the effectiveness of a new diabetes management program in improving patient outcomes.”
The thesis statement
This is the core of your research paper introduction paragraph. It succinctly outlines the aim and focus of your paper. This is usually the first sentence in the introductory paragraph of a research paper.
Example: This paper reviews the recent research in cultural psychology and how culture is the byproduct of interpersonal relations and evolution.
Some practical tips:
- Keep your thesis statement specific.
- Express a single main idea in your statement.
- Make your thesis statement invite the main discussion.
In Summary:
- A compelling hook grabs attention.
- Just enough background sets the stage and orients the reader.
- A clear thesis statement should warrant discussion and take some sort of a stand.
Armed with these three pillars, you’re well on your way to crafting an introduction paragraph of a research paper that captivates and informs.
In the following sections, we’ll dive deeper into how to start a research paper , offering tailored advice for various types of research undertakings.
How to Start A Research Paper: Actionable Tips
So you’re staring at that blinking cursor, feeling the weight of a thousand academic journals on your shoulders. The task: figure out how to start a research paper. Let’s ditch the anxiety and get right to the point!
Understand your audience
First and foremost, know who you’re talking to. Is your audience a group of academics or a more general readership? Understanding your audience is like knowing your stage and adjusting your tone and language accordingly.
To define your audience, try to create a persona – age, sex, economic level, social status, and so on. You can do this by:
- Conducting an online survey
- Organizing focus groups
- Talking to your audience directly via phone calls
Research beforehand
Before you even type the first word, dig deep into your topic. Consult sources, both primary and secondary, to have a well-rounded understanding of the issue.
Check the following aspects before moving to the next step:
- Identify Keywords : Find relevant keywords that are related to your topic.
- Database Diving : Utilize academic databases like PubMed for medical research or JSTOR for humanities.
- Cross-Reference : Always double-check facts from multiple sources.
You can rely on two kinds of sources for your research, as mentioned below:
Primary Sources : These are your firsthand accounts or direct evidence. If you’re tackling a historical topic, primary sources could be letters, diaries, or newspaper articles from the time. In scientific research, it might be the raw data from experiments.
Secondary Sources : These are interpretations or analyses of primary sources. Academic articles, reviews, and most books fall under this category.
Craft a strong thesis statement
A thesis statement focuses on a specific topic. So make your thesis statement is clear and concise.
Follow the steps mentioned below to craft a strong thesis statement:
- Be specific : Aim for specificity. Instead of saying, “Social media affects mental health,” say, “Excessive use of social media contributes to increased levels of anxiety among teenagers.”
- Keep an arguable point : Your thesis should make a claim that can be debated. If it’s a universally accepted fact, there’s no point in arguing.
- Be focused : Keep it tight and focused. Your thesis statement should be one to two sentences max. It’s the tagline of your paper; it should be concise and to the point.
- Position it well : Generally, your thesis should appear towards the end of your introduction. It’s like the crescendo in a musical piece, building up to the main event.
- Revise : Don’t be afraid to go back and tweak it as your paper evolves.
Example: An analysis of the college admission process reveals one challenge facing counselors: accepting students with high test scores or students with strong extracurricular backgrounds.
Outline your points
Before diving into the writing, sketch out an outline. This serves as your roadmap, outlining the key points and sub-points you’ll tackle. In essence, it’s the blueprint of your academic paper.
Follow these points to create an outline of the research:
- Identify the main points : These are the arguments or topics that are crucial to your research. List them in the order you plan to address them.
- Keep solid sub-points and supporting evidence : For each main point, jot down sub-points or examples that support it.
- Maintain a logical flow : Make sure your points follow a logical sequence. Your arguments should build upon each other.
- Use transitional phrases : Consider how you’ll transition from one point to the next.
- Maintain flexibility : Your outline isn’t set in stone. As you dig deeper into your research, you may discover new points that fit better.
Start writing
Once you outline your points, it’s time to venture forth. A strong start incorporates the hook, background, and thesis statement, as we’ve discussed. But don’t get stuck striving for perfection; you can always revisit and refine.
Key Takeaways:
- Know your audience.
- Pre-research is your scouting phase.
- Your thesis is your anchor.
- Outlining sets the stage.
- Just start—perfection comes later.
By following these tips, you’ll be well-equipped to begin your research paper. In the sections that follow, we’ll explore how to write an introduction for a research paper, focusing on specific types for a more targeted approach.
How to Write a Research Paper Introduction for Different Types of Papers?
Research papers come in various types – argumentative, empirical, and review papers. Writing an introduction for a research paper of each type comes with its own specific nuances.
Below are distinctive elements for crafting introductions across various research paper types:
Argumentative paper
An argumentative paper aims to persuade. Your introduction here should not only present your thesis but also hint at the counterarguments you’ll dismantle. Think of it as a debate stage; you’re not just stating your case but also preempting the opposing views.
Example: “School uniforms: they’re a subject of constant debate in the field of education. Supporters argue they create a sense of unity and reduce distractions, leading to better academic performance. Critics claim they stifle individuality and have no real impact on learning. This paper will argue that implementing school uniforms in public schools leads to improved academic performance by fostering a focused learning environment.”
Empirical paper
Here, you’re the scientist, the explorer. Your introduction should outline the research question and the methods you’ll use to answer it. If a specific hypothesis needs testing, it should be mentioned in the research question.
Topic – Empirical Studies on Product-Service Systems – A Systematic Literature Review
Introduction Example – The rising global population, accelerating technological development, increasing resource usage, and intensifying environmental impacts make sustainability the key issue for the entire society. This has resulted in the growing importance of product-service systems (PSS) in academics and industrial fields.
As an ‘integrated bundle of products and services which aims at creating customer utility and generating value’ [1], PSS is one of the most effective instruments that move society towards sustainability [2]. According to its evolution, the classical categorization of PSS includes product-oriented PSS, user-oriented PSS, and result-oriented PSS [3]
Review paper
In a review paper, you summarize existing studies on a topic. Your introduction should highlight the main findings so far and where your paper fits into the dialogue.
Example: “Over the past decade, remote work has transitioned from a corporate perk to a standard practice, especially in tech industries. While some argue that remote work increases productivity and employee satisfaction, others point to challenges like communication breakdowns and feelings of isolation. This paper will review existing literature on the effectiveness of remote work, examining its impact on employee productivity, mental health, and organizational cohesion.”
Remember the following points:
- Argumentative papers need a persuasive touch.
- Empirical papers require a hint of methodology.
- Review papers demand an overview of existing research.
Tips for All Types:
- Be concise: Whether you’re persuading, exploring, or reviewing, get to the point.
- Be focused: Keep your thesis statement tight and direct.
- Be engaging: Use your hook to draw readers in, no matter the type of paper.
By tailoring your introduction to the type of paper you’re writing, you’ll align your research with the expectations of your audience. Each type has its nuances, but the core principles of how to write an introduction for a research paper across these diverse types—capturing attention, providing context, and stating your thesis—remain constant. In the end, it’s all about setting the stage for the research that follows.
Research paper introduction example
Imagine you’re crafting an empirical research paper on the impact of social media on mental health. How would a compelling introduction of a research paper look?
Let’s break it down via a concrete research paper introduction example:
“In today’s digital age, social media platforms have become ubiquitous, shaping our interactions and emotional landscapes. While these platforms promise connectivity, emerging research suggests a darker narrative: a potential link between social media usage and declining mental health. This study aims to explore this complex relationship through a comprehensive analysis of survey data and psychological assessments. Employing both qualitative and quantitative methods, we endeavor to answer the pressing question: Does social media negatively impact mental health?”
In this example, the hook points out how common social media use is. The background information provides context by acknowledging both the positive and negative aspects of social media. Finally, the thesis statement outlines the research question and the methodology.
Key Elements:
- A relatable hook draws the reader in.
- Contextual background sets the stage.
- A clear thesis statement outlines the research aim and method.
In a nutshell, the introduction of a research paper serves as a mini-blueprint for the paper. It sets the stage, intrigues the reader, and outlines the research scope—all in a concise manner.
This guide should serve as a useful starting point in understanding how to start an introduction for a research paper. Explore research paper editing services to structure and articulate your ideas in a polished manner effectively. This can ensure you write your research paper with no typos and in refined academic language.
Keep reading to further enhance your knowledge of writing research papers!
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you start a research paper example, what is a good starting sentence for a research paper, what is a good way to start a research topic.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
8 Key Elements of a Research Paper Structure + Free Template (2024)
.webp)
Table of contents

Brinda Gulati
Welcome to the twilight zone of research writing. You’ve got your thesis statement and research evidence, and before you write the first draft, you need a wireframe — a structure on which your research paper can stand tall.
When you’re looking to share your research with the wider scientific community, your discoveries and breakthroughs are important, yes. But what’s more important is that you’re able to communicate your research in an accessible format. For this, you need to publish your paper in journals. And to have your research published in a journal, you need to know how to structure a research paper.
Here, you’ll find a template of a research paper structure, a section-by-section breakdown of the eight structural elements, and actionable insights from three published researchers.
Let’s begin!
Why is the Structure of a Research Paper Important?
A research paper built on a solid structure is the literary equivalent of calcium supplements for weak bones.
Richard Smith of BMJ says, “...no amount of clever language can compensate for a weak structure."
There’s space for your voice and creativity in your research, but without a structure, your paper is as good as a beached whale — stranded and bloated.
A well-structured research paper:
- Communicates your credibility as a student scholar in the wider academic community.
- Facilitates accessibility for readers who may not be in your field but are interested in your research.
- Promotes clear communication between disciplines, thereby eliminating “concept transfer” as a rate-limiting step in scientific cross-pollination.
- Increases your chances of getting published!
Research Paper Structure Template
.webp)
Why Was My Research Paper Rejected?
A desk rejection hurts — sometimes more than stubbing your pinky toe against a table.
Oftentimes, journals will reject your research paper before sending it off for peer review if the architecture of your manuscript is shoddy.
The JAMA Internal Medicine , for example, rejected 78% of the manuscripts it received in 2017 without review. Among the top 10 reasons? Poor presentation and poor English . (We’ve got fixes for both here, don’t you worry.)
5 Common Mistakes in a Research Paper Structure
- Choppy transitions : Missing or abrupt transitions between sections disrupt the flow of your paper. Read our guide on transition words here.
- Long headings : Long headings can take away from your main points. Be concise and informative, using parallel structure throughout.
- Disjointed thoughts : Make sure your paragraphs flow logically from one another and support your central point.
- Misformatting : An inconsistent or incorrect layout can make your paper look unprofessional and hard to read. For font, spacing, margins, and section headings, strictly follow your target journal's guidelines.
- Disordered floating elements : Ill-placed and unlabeled tables, figures, and appendices can disrupt your paper's structure. Label, caption, and reference all floating elements in the main text.
What Is the Structure of a Research Paper?
The structure of a research paper closely resembles the shape of a diamond flowing from the general ➞ specific ➞ general.
We’ll follow the IMRaD ( I ntroduction , M ethods , R esults , and D iscussion) format within the overarching “context-content-conclusion” approach:
➞ The context sets the stage for the paper where you tell your readers, “This is what we already know, and here’s why my research matters.”
➞ The content is the meat of the paper where you present your methods, results, and discussion. This is the IMRad (Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion) format — the most popular way to organize the body of a research paper.
➞ The conclusion is where you bring it home — “Here’s what we’ve learned, and here’s where it plays out in the grand scheme of things.”
Now, let’s see what this means section by section.
1. Research Paper Title
A research paper title is read first, and read the most.
The title serves two purposes: informing readers and attracting attention . Therefore, your research paper title should be clear, descriptive, and concise . If you can, avoid technical jargon and abbreviations. Your goal is to get as many readers as possible.
In fact, research articles with shorter titles describing the results are cited more often .
An impactful title is usually 10 words long, plus or minus three words.
For example:
- "Mortality in Puerto Rico after Hurricane Maria" (word count = 7)
- “A Review of Practical Techniques For the Diagnosis of Malaria” (word count = 10)
2. Research Paper Abstract
In an abstract, you have to answer the two whats :
- What has been done?
- What are the main findings?
The abstract is the elevator pitch for your research. Is your paper worth reading? Convince the reader here.

✏️ NOTE : According to different journals’ guidelines, sometimes the title page and abstract section are on the same page.
An abstract ranges from 200-300 words and doubles down on the relevance and significance of your research. Succinctly.
This is your chance to make a second first impression.
If you’re stuck with a blob of text and can’t seem to cut it down, a smart AI elf like Wordtune can help you write a concise abstract! The AI research assistant also offers suggestions for improved clarity and grammar so your elevator pitch doesn’t fall by the wayside.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
3. Introduction Section
What does it do.
Asks the central research question.
Pre-Writing Questions For the Introduction Section
The introduction section of your research paper explains the scope, context, and importance of your project.
I talked to Swagatama Mukherjee , a published researcher and graduate student in Neuro-Oncology studying Glioblastoma Progression. For the Introduction, she says, focus on answering three key questions:
- What isn’t known in the field?
- How is that knowledge gap holding us back?
- How does your research focus on answering this problem?
When Should You Write It?
Write it last. As you go along filling in the body of your research paper, you may find that the writing is evolving in a different direction than when you first started.
Organizing the Introduction
Visualize the introduction as an upside-down triangle when considering the overall outline of this section. You'll need to give a broad introduction to the topic, provide background information, and then narrow it down to specific research. Finally, you'll need a focused research question, hypothesis, or thesis statement. The move is from general ➞ specific.
✨️ BONUS TIP: Use the famous CARS model by John Swales to nail this upside-down triangle.
4. methods section.
Describes what was done to answer the research question, and how.
Write it first . Just list everything you’ve done, and go from there. How did you assign participants into groups? What kind of questionnaires have you used? How did you analyze your data?
Write as if the reader were following an instruction manual on how to duplicate your research methodology to the letter.
Organizing the Methods Section
Here, you’re telling the story of your research.
Write in as much detail as possible, and in the chronological order of the experiments. Follow the order of the results, so your readers can track the gradual development of your research. Use headings and subheadings to visually format the section.

This skeleton isn’t set in stone. The exact headings will be determined by your field of study and the journal you’re submitting to.
✨️ BONUS TIP : Drowning in research? Ask Wordtune to summarize your PDFs for you!
5. results section .
Reports the findings of your study in connection to your research question.
Write the section only after you've written a draft of your Methods section, and before the Discussion.
This section is the star of your research paper. But don't get carried away just yet. Focus on factual, unbiased information only. Tell the reader how you're going to change the world in the next section. The Results section is strictly a no-opinions zone.
How To Organize Your Results
A tried-and-true structure for presenting your findings is to outline your results based on the research questions outlined in the figures.
Whenever you address a research question, include the data that directly relates to that question.
What does this mean? Let’s look at an example:
Here's a sample research question:
How does the use of social media affect the academic performance of college students?
Make a statement based on the data:
College students who spent more than 3 hours per day on social media had significantly lower GPAs compared to those who spent less than 1 hour per day (M=2.8 vs. M=3.4; see Fig. 2).
You can elaborate on this finding with secondary information:
The negative impact of social media use on academic performance was more pronounced among freshmen and sophomores compared to juniors and seniors ((F>25), (S>20), (J>15), and (Sr>10); see Fig. 4).
Finally, caption your figures in the same way — use the data and your research question to construct contextual phrases. The phrases should give your readers a framework for understanding the data:
Figure 4. Percentage of college students reporting a negative impact of social media on academic performance, by year in school.
Dos and Don’ts For The Results Section

✔️ Related : How to Write a Research Paper (+ Free AI Research Paper Writer)
6. discussion section.
Explains the importance and implications of your findings, both in your specific area of research, as well as in a broader context.
Pre-Writing Questions For the Discussion Section
- What is the relationship between these results and the original question in the Introduction section?
- How do your results compare with those of previous research? Are they supportive, extending, or contradictory to existing knowledge?
- What is the potential impact of your findings on theory, practice, or policy in your field?
- Are there any strengths or weaknesses in your study design, methods, or analysis? Can these factors affect how you interpret your results?
- Based on your findings, what are the next steps or directions for research? Have you got any new questions or hypotheses?
Before the Introduction section, and after the Results section.
Based on the pre-writing questions, five main elements can help you structure your Discussion section paragraph by paragraph:
- Summary : Restate your research question/problem and summarize your major findings.
- Interpretations : Identify patterns, contextualize your findings, explain unexpected results, and discuss if and how your results satisfied your hypotheses.
- Implications: Explore if your findings challenge or support existing research, share new insights, and discuss the consequences in theory or practice.
- Limitations : Acknowledge what your results couldn’t achieve because of research design or methodological choices.
- Recommendations : Give concrete ideas about how further research can be conducted to explore new avenues in your field of study.
Dos and Don’ts For the Discussion Section

Aritra Chatterjee , a licensed clinical psychologist and published mental health researcher, advises, “If your findings are not what you expected, disclose this honestly. That’s what good research is about.”
7. Acknowledgments
Expresses gratitude to mentors, colleagues, and funding sources who’ve helped your research.
Write this section after all the parts of IMRaD are done to reflect on your research journey without getting distracted midway.
After a lot of scientific writing, you might get stumped trying to write a few lines to say thanks. Don’t let this be the reason for a late or no-submission.
Wordtune can make a rough draft for you.

All you then have to do is edit the AI-generated content to suit your voice, and replace any text placeholders as needed:

8. References
Lists all the works/sources used in your research with proper citations.
The two most important aspects of referencing are:
- Following the correct format; and
- Properly citing the sources.
Keep a working document of the works you’ve referenced as you go along, but leave the finishing touches for last after you’ve completed the body of your research paper — the IMRaD.
Tips For Writing the References Section
The error rate of references in several scientific disciplines is 25%-54% .
Don’t want to be a part of this statistic? We got you.
- Choose quality over quantity : While it's tempting to pad your bibliography to seem more scholarly, this is a rookie mistake. Samantha Summers , a museum professional based in Canada, is a published researcher in Medieval History and Critical Philanthropy studies. According to her, “Adding in a citation just to lengthen your bibliography and without engaging deeply with the cited work doesn’t make for good writing.” We ought to listen to her advice — she has three Master’s degrees to her name for a reason.
- Select the correct referencing guide : Always cross-check with your chosen journal’s or institution’s preference for either Harvard, MLA, APA, Chicago, or IEEE.
- Include recent studies and research : Aim to cite academically ripe sources — not overripe. Research from the past half-decade or so is ideal, whereas studies from the 80s or 90s run a higher risk of being stale.
- Use a reliable reference manager software : Swagatama recommends several free resources that have helped her get her research organized and published — Zotero and Mendeley are top contenders, followed by EndNote .
By the end, your References section will look something like this:

Ready, Get, Set, Publish!
Dust yourself off, we've made it out of the twilight zone. You’ve now got the diamond of the structure of a research paper — the IMRaD format within the “context-content-conclusion” model.
Keep this structure handy as you fill in the bones of your research paper. And if you’re stuck staring at a blinking cursor, fresh out of brain juice?
An AI-powered writing assistant like Wordtune can help you polish your diamond, craft great abstracts, and speed through drafts!
You've got this.
Share This Article:
%20(1).webp)
8 Tips for E-commerce Copywriting Success (with Examples!)
.webp)
The Brand Strategy Deck You Need to Drive Social Media Results + 5 Examples

Grammarly Alternatives: Which Writing Assistant is the Best Choice for You?
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
Welcome to 2024! Happy New Year!

Research Writing ~ How to Write a Research Paper
- Choosing A Topic
- Critical Thinking
- Domain Names
- Starting Your Research
- Writing Tips
- Parts of the Paper
- Edit & Rewrite
- Citations This link opens in a new window
Use your notes to write your paper. As you read over your notes, look for main themes and points of interest. These can be the main ideas you read about in your research sources. Try to support these main ideas with facts and statistics you have collected. If the paper is argumentative, remember to provide an argument for counterpoints to your main ideas.
Try outlining you ideas. Outlining is a way to organize your information into a series of well-ordered and understandable thoughts. What ideas are your main points and what ideas are supporting information. You may also find gaps in your ideas and reasoning. Use the outline to give yourself a better idea of what structure you paper is going to take. It will create a map for where information should be placed; how the placement of the information will create a flow of ideas.
Try to state the main theme and supporting points in your own words. See the Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing Guidelines from Purdue Owl. Try to explain the major ideas. Begin a new paragraph for each main idea. Remember to integrate the research you have found and acknowledge ideas and information you have learned with in-text citations. A research paper is not an essay, in other words, this is not about your opinions. Do not use first person nouns such as "I" or "my." If you have developed new interpretations or concepts related to your research, great! But, you need to back up these ideas with facts. Read the paper out loud. In addition to helping you express ideas in your own words, this exercise may stimulate your own thoughts and viewpoints concerning your topic. Reading out loud also helps with your phrasing and organization of ideas. Even better, read your paper out loud to someone else. You may be more aware of how your words sound when you have an audience, and they may also give you some good feedback.
- << Previous: Starting Your Research
- Next: Writing Tips >>
- Last Updated: Feb 1, 2024 4:06 PM
- URL: https://library.hccc.edu/research_paper
Gabert Library

NHC Library

- Database A-Z
- Research Guides
- Citation Help
- Ask a Librarian
- Library Instruction
- Academic Liaisons
- Library Staff Login
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Start Writing a Research Paper: 10 Steps You Should Not Skip
Writing a research paper can be daunting; early career researchers often find themselves at a crossroads, not knowing how to start writing a research paper. Working on a research project, conducting experiments, and gathering data can be exciting work, but many tend to procrastinate when it comes to actually writing it all down and producing a quality research paper. Unfamiliarity with the language, inexperience with academic writing, and uncertainty about how to present data and information in a simple, accurate way are all real obstacles. Yet, writing a well-structured, compelling research paper is essential to communicate your findings, make an impact in your field, and grow your academic career. So in this comprehensive article, we’ll walk you through how to start writing a research paper, from formulating a research question to organizing your thoughts and staying on track.
Not all research papers are the same. Academic writing requirements can vary based on the type of article, its purpose, or even the field of research. Regardless, the basic steps in writing a research paper remain broadly the same. With proper planning and preparation, and consistent effort, you can overcome procrastination and become a better academic writer.
Table of Contents
Define a clear, focused research question
Knowledge without direction is like a boat on dry land. So, the first step in writing a research paper is to craft a strong research question that sets the foundation for your paper and guides your study’s objectives. Consider your area of interest, review existing literature, and identify gaps or areas needing further exploration to craft a clear and focused research question.
Conduct a thorough literature review
Before diving into your research, conduct a comprehensive literature review to gain insights into the existing body of knowledge on your topic and in related areas. This step will help you identify key theories, findings, and methodologies used in related studies, help you understand how your work fits into the broader academic landscape, and add credibility to your work as an expert.
Formulate a research statement
Your research statement serves as the core of your research paper, allowing readers to understand the main argument or purpose of your study. With the insights from your literature review, craft a concise and compelling research statement that encapsulates the essence of your research question and sets the direction for your paper.
Create a strong research paper outline
Now that you have a clear research question and statement in place, organize your research and data systematically. Create a cohesive outline that outlines the main sections of your research paper (the introduction, methodology, results, discussions, and conclusion) to ensure focus and coherence in your writing. Having a mind map of how information is to be presented in your article is a critical step in simplifying the process of writing a research paper.
Begin working on the first draft
Don’t expect perfection when you start writing a research paper; the first draft should focus on getting your research out onto paper. If you’ve followed the steps so far, this becomes an easier task. You only need to focus on the outline and what you want to communicate in each section, then just fill in the gaps. While many researchers put off writing a research paper until they’ve finished the study, experts suggest that working on your manuscript along with your research may actually help ensure all the details are captured accurately and completely.
Writing a compelling Introduction
The introduction is your paper’s gateway, capturing the reader’s attention and setting the stage for what follows. Consider beginning with a hook or an engaging anecdote to pique the reader’s interest and entice them to delve deeper into your research. Be sure to clearly state the research question and statement, providing context and significance for your study. A well-crafted introduction will entice readers to delve deeper into your research.
Spend time on your Abstract and Title
When writing a research paper, it’s common to focus on the Methods, Results, and Discussion while neglecting the Title and Abstract. However, this is a sure way to fail. These two sections are often what a reader typically encounters of your paper, so spend enough time fine-tuning them. Ensure the title is clear, specific, and reflective of your research with the keywords to make sure your paper is found, read, and cited. Include the research question and main premise of your research when writing the abstract , which should effectively summarize your manuscript.
Wrap up with a well-rounded Conclusion
When writing a research paper conclusion, highlight the key points but take care not to include any concepts or points that have not been discussed in the body of your research paper. Ensure that in summarizing your work, you present the answer to your research question in an interesting, easy to understand way.
Align with the target journal guidelines
One of the most important final steps in writing a research paper is checking to ensure it aligns with journal guidelines. This not only ensures the likelihood of acceptance by the journal; it also reflects your commitment and professionalism as an academic. Double check that your research fits within the journal’s scope and aligns with its specific aims and objectives. Thoroughly review the journal’s website or guidelines document, paying attention to formatting requirements, citation styles, word limits, and preferred article structure. Confirm you have addressed requests for additional data or ethical declarations to avoid potential delays or rejections.
Revise and polish your academic writing
Poor language and comprehension is often one of the top reasons for manuscript rejection. So after you have completed the first draft, take time to edit and proofread your work. Avoid using too much jargon and technical terms and create simple, concise sentences to convey your message. Check for grammar errors, punctuation and spelling mistakes, correct word choice and sentence structure, and any unintended plagiarism.
Knowing how to start writing a research paper is just the first step in a crucial and often challenging process. We hope the detailed steps listed above will help you overcome any hesitation and lay the foundation for a well-crafted, engaging, and impactful research paper, with the best chance of publication success.
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What is Cluster Sampling? Definition, Method, and Examples

Why is Citing Sources Important in Research?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
A Beginner's Guide to Starting the Research Process

When you have to write a thesis or dissertation , it can be hard to know where to begin, but there are some clear steps you can follow.
The research process often begins with a very broad idea for a topic you’d like to know more about. You do some preliminary research to identify a problem . After refining your research questions , you can lay out the foundations of your research design , leading to a proposal that outlines your ideas and plans.
This article takes you through the first steps of the research process, helping you narrow down your ideas and build up a strong foundation for your research project.
Table of contents
Step 1: choose your topic, step 2: identify a problem, step 3: formulate research questions, step 4: create a research design, step 5: write a research proposal, other interesting articles.
First you have to come up with some ideas. Your thesis or dissertation topic can start out very broad. Think about the general area or field you’re interested in—maybe you already have specific research interests based on classes you’ve taken, or maybe you had to consider your topic when applying to graduate school and writing a statement of purpose .
Even if you already have a good sense of your topic, you’ll need to read widely to build background knowledge and begin narrowing down your ideas. Conduct an initial literature review to begin gathering relevant sources. As you read, take notes and try to identify problems, questions, debates, contradictions and gaps. Your aim is to narrow down from a broad area of interest to a specific niche.
Make sure to consider the practicalities: the requirements of your programme, the amount of time you have to complete the research, and how difficult it will be to access sources and data on the topic. Before moving onto the next stage, it’s a good idea to discuss the topic with your thesis supervisor.
>>Read more about narrowing down a research topic
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
So you’ve settled on a topic and found a niche—but what exactly will your research investigate, and why does it matter? To give your project focus and purpose, you have to define a research problem .
The problem might be a practical issue—for example, a process or practice that isn’t working well, an area of concern in an organization’s performance, or a difficulty faced by a specific group of people in society.
Alternatively, you might choose to investigate a theoretical problem—for example, an underexplored phenomenon or relationship, a contradiction between different models or theories, or an unresolved debate among scholars.
To put the problem in context and set your objectives, you can write a problem statement . This describes who the problem affects, why research is needed, and how your research project will contribute to solving it.
>>Read more about defining a research problem
Next, based on the problem statement, you need to write one or more research questions . These target exactly what you want to find out. They might focus on describing, comparing, evaluating, or explaining the research problem.
A strong research question should be specific enough that you can answer it thoroughly using appropriate qualitative or quantitative research methods. It should also be complex enough to require in-depth investigation, analysis, and argument. Questions that can be answered with “yes/no” or with easily available facts are not complex enough for a thesis or dissertation.
In some types of research, at this stage you might also have to develop a conceptual framework and testable hypotheses .
>>See research question examples
The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you’ll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research.
There are often many possible paths you can take to answering your questions. The decisions you make will partly be based on your priorities. For example, do you want to determine causes and effects, draw generalizable conclusions, or understand the details of a specific context?
You need to decide whether you will use primary or secondary data and qualitative or quantitative methods . You also need to determine the specific tools, procedures, and materials you’ll use to collect and analyze your data, as well as your criteria for selecting participants or sources.
>>Read more about creating a research design
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Finally, after completing these steps, you are ready to complete a research proposal . The proposal outlines the context, relevance, purpose, and plan of your research.
As well as outlining the background, problem statement, and research questions, the proposal should also include a literature review that shows how your project will fit into existing work on the topic. The research design section describes your approach and explains exactly what you will do.
You might have to get the proposal approved by your supervisor before you get started, and it will guide the process of writing your thesis or dissertation.
>>Read more about writing a research proposal
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
More interesting articles
- 10 Research Question Examples to Guide Your Research Project
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
- How to Define a Research Problem | Ideas & Examples
- How to Write a Problem Statement | Guide & Examples
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Objectives | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Fishbone Diagram? | Templates & Examples
- What Is Root Cause Analysis? | Definition & Examples
Get unlimited documents corrected
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Jessie Ball duPont Library
Research writing.
- What is Research?
- The Research Process
- Choosing a Topic
- Finding Sources
Thesis Statements
- What is your Main Idea?
- Presenting your Sources
- Organizing your Material
- Discipline-Specific Research
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements This resource from Purdue University's Online Writing Lab (OWL) provides tips for creating a thesis statement and examples of different types of thesis statements.
Need more help writing a thesis statement? Check out this video from East Tennessee State University
Hypothesis or Theory?
The terms theory and hypothesis are often used interchangeably in everyday use. However, the difference between them in scholarly research is important, particularly when using an experimental design.
The key distinctions are:
- A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances.
- A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested.
Hypothesis Example
A worker on a fish-farm notices that his trout seem to have more fish lice in the summer, when the water levels are low, and wants to find out why. His research leads him to believe that the amount of oxygen is the reason - fish that are oxygen stressed tend to be more susceptible to disease and parasites.
He proposes a general hypothesis.
“Water levels affect the amount of lice suffered by rainbow trout.”
This is a good general hypothesis, but it gives no guide to how to design the research or experiment . The hypothesis must be refined to give a little direction.
“Rainbow trout suffer more lice when water levels are low.”
Now there is some directionality, but the hypothesis is not really testable , so the final stage is to design an experiment around which research can be designed, a testable hypothesis.
“Rainbow trout suffer more lice in low water conditions because there is less oxygen in the water.”
This is a testable hypothesis - he has established variables , and by measuring the amount of oxygen in the water, eliminating other controlled variables , such as temperature, he can see if there is a correlation against the number of lice on the fish.
This is an example of how a gradual focusing of research helps to define how to write a hypothesis .
Material adapted from "Research Methods: Hypothesis" by George A. Spiva Library, Missouri Southern State University
- << Previous: Finding Sources
- Next: Presenting your Sources >>
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 11:45 AM
- URL: https://library.sewanee.edu/researchwriting
Research Tools
- Find Articles
- Find Research Guides
- Find Databases
- Ask a Librarian
- Learn Research Skills
- How-To Videos
- Borrow from Another Library (Sewanee ILL)
- Find Audio and Video
- Find Reserves
- Access Electronic Resources
Services for...
- College Students
- The School of Theology
- The School of Letters
- Community Members
Spaces & Places
- Center for Leadership
- Center for Speaking and Listening
- Center for Teaching
- Floor Maps & Locations
- Ralston Listening Library
- Research Help
- Study Spaces
- Tech Help Desk
- Writing Center
About the Library
- Where is the Library?
- Library Collections
- New Items & Themed Collections
- Library Policies
- Library Staff
- Friends of the Library
Jessie Ball duPont Library, University of the South
178 Georgia Avenue, Sewanee, TN 37383
931.598.1664
- Open access
- Published: 29 July 2024
Co-creating and hosting PxP: a conference about patient engagement in research for and by patient partners
- Dawn P. Richards 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Hetty Mulhall 1 ,
- Joletta Belton 4 ,
- Savia de Souza 5 ,
- Trudy Flynn 6 ,
- Alex Haagaard 7 ,
- Linda Hunter 8 ,
- Amy Price 9 , 10 , 11 ,
- Sara Riggare 12 , 13 ,
- Janice Tufte 14 , 15 ,
- Rosie Twomey 1 &
- Karim M. Khan 1
Research Involvement and Engagement volume 10 , Article number: 77 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Research projects, initiatives and conferences that include patients as partners rather than as participants are becoming more common. Including patients as partners (what we will call ‘patient partners’) is an approach called patient engagement or involvement in research, and we will call it patient engagement throughout this paper. Patient engagement moves traditional health research conferences and events to include a broader audience for their knowledge exchange and community building efforts, beyond academics and healthcare professionals. However, there are few examples of conferences where patients are given the opportunity to fully lead. Our conference went beyond patient engagement – it was patient-led. Patient partners conceived, planned, and decided on all aspects of a virtual conference.
We present the work and processes we undertook throughout 2023 to create and produce a free conference called “PxP: For patients, by patients” or PxP for short, with a tagline of “Partnering to make research stronger.” PxP was patient-led and about patient engagement in research rather than a specific disease or condition. PxP was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis. The PxP website, known as the PxP Hub, now houses the conference recordings along with resources about patient engagement in research. These resources were recommended by the PxP Steering Committee members, speakers, and others who attended the 2023 conference. Here we lead you through how the idea for PxP was generated; how the international patient partner Steering Committee was convened and supported; how PxP was brought to life over nine months; the PxP 3-day event and feedback collected to improve future efforts; trade-offs, challenges and learnings; and resources required to support this type of event. We close with what the future holds for PxP in 2024 and beyond.
It’s time to elevate patients into leadership roles for conferences and events, and we encourage you to adopt the PxP ethos by using or adapting our approach and resources to support your opportunity.
Plain English summary
Patients are often included in health research as study participants. Involving patients as partners in research projects or conferences is becoming more common. This approach is called patient engagement or involvement. Traditional health research conferences are by and for academic researchers or healthcare professionals. These events rarely include patients as the main attendees or in the planning. While some research conferences are starting to use patient engagement, few are designed and led by patients. We share our work on a conference led and designed by patients. In 2023, our team co-created a free conference called “PxP.” PxP is short for “For patients, by patients.” The conference tagline was “Partnering to make research stronger.” PxP was focused on patient engagement in research rather than any one health problem. PxP was supported by the Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis. This is one of 13 Canadian Institutes of Health Research. A free online PxP Hub now hosts all of the conference recordings and many resources. We share how the idea for PxP came about, how the international patient partner Steering Committee came together and was supported to plan and bring PxP to life, the PxP conference and feedback, challenges and what we learned, and resources needed. It’s time for patients to have a leadership role for conferences and events. Through sharing this example, we encourage others to adopt the PxP ethos.
Peer Review reports
While there are increasingly more research projects, initiatives and conferences that include patients as partners and not just participants, examples where patients fully lead are rare in these settings [ 1 , 2 ]. To date, most of the focus in these spaces has been on co-creation or co-production aspects. The approach of including patients as partners (which we call ‘patient partners’) is referred to as patient engagement (in North America) [ 1 ], patient involvement (in Europe) [ 3 ], or consumer involvement (in Australia) [ 4 ]. Here we use the term patient engagement as a ‘catch all’ for these phrases.
Health research conferences and events provide an opportunity for knowledge exchange and community building, though have traditionally been restricted to a narrow audience of academics and health professionals. While some conferences are patient-led through conception, design, delivery and dissemination, these tend to be patient organization-run conferences that offer support and education to their specific communities (e.g., arthritis, pain, cancer, etc.) [ 5 , 6 ]. To our knowledge, there is little in the academic literature about patient-led health research conferences [ 7 , 8 ] and we were unable to locate any literature about patient-led conferences on the topic of patient engagement in research.
Here we describe the processes to plan and organize a free conference all about patient engagement in research called “PxP: For Patients, by Patients” and share the outputs of the conference [ 9 ]. The conference’s tagline was “Partnering to Make Research Stronger.” The free PxP conference was virtually hosted in September 2023, and was fully designed and driven by an international Steering Committee of individuals who identify as patient partners [ 1 ]. PxP was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis (IMHA) [ 10 ]. IMHA’s mandate includes supporting research related to: active living, mobility and the wide range of conditions related to bones, joints, muscles, connective tissue, skin as well as the mouth, teeth and craniofacial region. IMHA has a history of engaging patients as partners for over 20 years [ 11 ]. Recently, IMHA and its Patient Engagement Research Ambassadors (PERA) fully co-created and launched free, online learning modules as a How-To Guide for Patient Engagement in Research which is ‘disease agnostic,’ meaning that it is not specific to any one disease area [ 12 , 13 ]. PxP is another example of work that IMHA is supporting in the patient engagement in research space that is also disease agnostic.
This paper aims to describe what we did and learned following a planning and executing timeline so that people who are interested in elements of PxP may benefit when planning their own patient-led conferences or events. We detail the processes, provide templates and resources, and share our learnings by highlighting the expertise, time and other resources that were necessary to make PxP a success. In the spirit of PxP, this paper was co-written with many of its patient partner Steering Committee members (JB, SdS, TF, AH, LH, AP, SR, JT).
Below we outline the PxP conference process, including its inputs and outputs, in a manner that is linear to PxP’s overall planning and executing timeline.
Generating the idea for the PxP
The idea for the PxP conference came from conversations in 2022 with IMHA’s PERA members [ 12 ]. PERA is composed of individuals who live with conditions that fall under IMHA’s research mandate. PERA meets every 1–2 months virtually to provide bidirectional insights and lived experiences to help IMHA achieve its goals and priorities while also carrying out its own mandate. PERA’s mandate is to inform IMHA and CIHR of patient priorities in research; inform their respective communities about IMHA, CIHR, and their work with PERA; advocate to benchmark best practice in patient-oriented research (POR) across IMHA’s activities (including priority setting); curate quality POR assets (for example, videos, websites etc.) for IMHA and the broader CIHR community, and create new POR assets to fill gaps; and, evaluate progress of PERA [ 11 ]. PERA members who wished to contribute to the conference were invited to be part of the conference’s 2023 Steering Committee (SC; noting there were 6 PERA members at the time).
An initial discussion with interested PERA members (TF, LH, plus one other) was hosted in November 2022 to gain further insights. This initial conference discussion was supported by IMHA’s Scientific Director, a staff member, and a patient engagement consultant (DPR, who also identifies as a patient partner). Terms of reference for the SC were drafted (see Additional File 1 ) and a timeline of SC meetings with high-level agenda topics was created for internal IMHA purposes. The decision about the conference name was reserved for the patient-led SC. The only pre-determined parameters around the conference were that it would be: free, virtual, led by patient partners, about patient engagement in research, disease agnostic, and for patients (as a primary audience), though anyone would be welcome to attend (and those in academic roles heard about it through IMHA’s regular newsletter and other targeted newsletters). Patients being the primary audience was a decision purposefully made so that patients could explore topics about patient engagement that were most important to them in a safe space. After this meeting, in late 2022 and in early 2023, additional patient partners from across the globe were invited to be part of the SC (based on the diversity of their locations, experiences, etc.), with an aim to have a total of 10 members. SC members who were invited beyond PERA members were known to IMHA through various research and personal networks and social media interactions. One SC member left for personal reasons in spring 2023.
Bringing the PxP conference to life
An overview of the inputs and outputs of PxP 2023 (see Fig. 1 ) are described in more detail in the following sections.

PxP Inputs and Outputs. An overview is provided of the human, financial and operational resources as well as the expertise, insights and skills that went in to PxP 2023. The various outputs include the 3-day conference, a community, and learning and resources
Championing the patient-led ethos
The international SC first met virtually in February 2023 and then monthly (except August and September) until October 2023 [ 14 ]. Two hours were reserved for each virtual meeting. The initial conference concept and parameters were brought to the SC during the February meeting so they could develop their collective vision. The development of the conference was guided by the five PatientsIncluded™ criteria [ 15 ], and went beyond patient co-creation to patient leadership. As outlined below, all elements of the conference were decided by the SC and facilitated through IMHA resources (time, financial, and skills).
The SC meetings were facilitated by the IMHA patient engagement consultant (DPR) and were attended by additional members of the IMHA team as needed to capture relevant action points to fulfill the logistical needs of the conference. DPR developed draft agendas for each meeting (which were open to changes made by SC members), took meeting notes (finalized upon review at each subsequent meeting) and facilitated meetings to ensure meetings supported psychological safety, respect, transparency and collaboration [ 16 ]. If SC members could not attend meetings, they were invited to provide their ideas separately via email or to meet one on one with DPR who incorporated their ideas in to planning. Meetings were kept to a minimum to be respectful of SC members’ time and other commitments. SC members were provided regular updates via email about operational progress between meetings. Email updates also included communication assets (such as social media graphics) so that the SC could share news about PxP with their own networks and on social media; with the opportunity to request additional assets, information or communication support at any point.
All SC members were offered honoraria aligned with the IMHA Patient Engagement Compensation Guidelines, which were developed after this work started [ 17 ]. Honoraria covered all aspects of SC members’ work and contributions for conference planning, and additional honoraria were offered for their time to participate in and attend the conference even if they chose not to be part of the program. Offering honoraria to SC members aligns with principles of equity, diversity and inclusion, and with best practices related to patient engagement in research [ 18 ].
Determining the path of PxP
Launching a new conference and an associated community required a significant amount of work and a focus on both the big picture and the more detailed elements (more on resources required is provided near the end of the paper). The patient-led and operations elements throughout the course of the PxP are detailed in Table 1 . Over the course of conference planning, the SC decided on the following for the conference:
its name (For Patients, By Patients) which was shortened to PxP;
its goal of partnering to make research stronger;
its mission to bring resources, mentorship and community to other patient partners in any kind of health research, no matter their experiences as a patient partner;
its logo design and colours;
the dates, format and length;
its agenda, including each day’s themes, sub-themes and speakers;
the platform (Zoom Webinars);
the preferred communications channels (X/Twitter, LinkedIn, Instagram and newsletter); and,
the post-conference survey questions for attendees, hosts, moderators, and speakers.
Additionally, the SC advised on the PxP website (also called the PxP Hub) [ 19 ] by providing thoughts on: user journey, functionality, content and accessibility features. Each member also provided up to 3 resources about patient engagement in research that are posted on the site. The PxP website was created by an agency and is updated by an IMHA staff member.
Co-developing the program
The themes for each day of the conference and for the sessions themselves were selected based on several SC conversations at the monthly meetings. The conference agenda including each day’s theme and sessions is provided in Table 2 , with the full conference agenda that includes dates, times, hosts, moderators, and speakers/panelists in Additional File 2 . Day 1 was considered to be introductory to help equip attendees with the language and baseline knowledge necessary to get involved in patient and public engagement in research, as well as to get the most out of the program [ 20 ]. Day 2 was designed to highlight self-research (where speakers shared doing their own research on themselves as part of their own healthcare journeys), patient-led research, and researcher perspectives on the how and why of their patient engaged research [ 20 ]. On Day 3, the SC wanted to tackle difficult conversations around real-world challenges for patient partners and those who have historically been excluded from health research in the safe space of this patient-led conference, and finished with a session providing practical tips around knowledge dissemination and amplifying the impact of health research [ 20 ]. The themes and session topics were of importance to the SC as patient partners rather than those researchers thought would be important to them.
All SC members had multiple opportunities to suggest specific people or organizations as speakers. They also had the opportunity to be as involved or uninvolved as they wished with the program itself, including as hosts (opened and closed each day and handed each session over to the session moderator), moderators (facilitated sessions by introducing the topic, speakers, and asking audience questions), and speakers, or, if time-zones permitted, as attendees who contributed to the live chats and encouraged discussion amongst attendees. SC members also contributed to how each conference session would be structured, being purposeful about having different approaches to each session (some included presentations, most were moderated discussions). DPR collected, compiled and reviewed all suggestions, and then proposed a draft agenda with a number of options for speakers, which took in to account equity, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) principles [ 16 ]. This agenda was subject to additional discussion, changes, and then approval by the SC before speakers were invited.
Conference supports
SC members who participated as hosts, moderators, and speakers/panelists were supported by the IMHA staff and DPR, as were all other moderators and speakers/panelists. All hosts, moderators and speakers/panelists were offered monetary compensation for their time in preparing for and being involved in the conference, with the exception of those who had an academic appointment and whose involvement in such a conference was considered part of their role in academia. For each session of the conference, a meeting was set up and facilitated by DPR so the moderator and speakers/panelists of that session could meet and get to know one another in the month leading up to PxP. At these virtual meetings, logistics about the conference were reviewed and notes were taken that were provided back to attendees. In most cases, the participants worked together to co-create the session content (often with suggestions from SC members).
A ‘run of show’ was created in Google Docs and was shared with all SC members for comment. The ‘run of show’ included each day’s schedule, logistics comments for daily hosts to share with all PxP attendees at the start and close of each day, transitions to breaks, and notes for each session about how it would run, who the moderator and speakers were, etc. The daily hosts were encouraged to make the logistics comments and all commentary their own by copying and pasting content out of the Google Doc. The ‘run of show’ for each session was shared with each session’s moderator, speakers or panelists. Two drop-in sessions on different times and days (to accommodate a variety of time-zones) were offered to all session speakers or panelists and hosts the week before the conference as an opportunity to gain familiarity with the platform, ask logistical questions, and test out slide sharing functionality. Communications to moderators and speakers and panelists were intentionally minimized, but carefully crafted to ensure language was clear and support was available if needed. Formal and informal feedback indicated that hosts, moderators and speakers felt well-prepared for and supported at the conference.
Being purposeful about accessibility
The SC was clear about the importance of accessibility, that is removing barriers to attend and fully participate, being mindful that the conference audience would include people with a wide range of disabilities and access needs, including energy-limiting chronic illness and neurodivergence. Registrants were invited to contact the IMHA team to make it aware of any access or accommodation needs that were not being provided so that it could do its best to support them. The conference was free and the program was purposefully designed with 30-min breaks between sessions. The timings of the program were intended to suit people joining from different time-zones around the world, with Day 3 run during different hours to better include attendees and speakers in Oceania and parts of Asia. To help reduce the burden of converting between time-zones, a table was provided on the PxP website [ 21 ].
As an ongoing consideration to accessibility and inclusivity, all sessions were recorded (with consent) and are available to view directly on the PxP YouTube Channel [ 22 ] or via the PxP Hub [ 9 ]. Asynchronous viewing was considered important for those who could not join live (for example, due to time-zone, medical needs, or other responsibilities) or who would like to re-watch the sessions. The entire transcript was manually edited with Adobe Premiere Pro to help improve accuracy of closed captions. The Adobe software was available through an institutional subscription and there may be alternative options for those who do have access to this product. Anonymized chat summaries from the live sessions are also available for each day on the PxP Hub resource page.
Accessibility for all participants was a priority with the logo and website design, and highlighted in the logo brief and website scope of work. The logo and website have sufficient colour contrast to meet Web-Content Accessibility Guidelines and the colour palette was chosen to not be visually overwhelming for people with visual processing challenges [ 23 ]. The decision to exclude icons was purposeful; different images may not translate well between patient communities and across different cultures. An easy-to-read font was chosen. The premium version of UserWay was added to the site which includes a range of tools for users such as the ability to adjust font, line height or contrast; to pause animations; and to utilise a screen reader, reading mask or reading guide [ 24 ]. There can be limitations and problems that may arise from using automated accessibility overlays which should be investigated and understood before using one. A web page to explain these features and signpost to contact details for additional support is featured prominently on the main menu of the website [ 25 ]. The website is bilingual, offered in both of Canada’s official languages, English and French. Speaker biographies were provided in three different options, in recognition of different preferences or needs for content format: html, PDF with selectable text, and digital flipbook optimized for mobile devices [ 26 ].
The SC chose Zoom Webinars as the conference platform to help promote inclusivity given the familiarity that many people have with it. To keep things simple with the first PxP, a conscious decision was made to use Webinar without any breakout rooms or networking sessions. Attendee and speaker/panelist versions of a PxP 2023 Zoom Webinars guide were created with images to help people get set up at the conference [ 27 ]. See Additional File 3 for the attendee Zoom Webinar guide. A member of the IMHA logistics team was available throughout the conference as technical support for attendees, and a second Zoom room was set up for speaker/panelist questions. At the start of each day of the conference, the daily host provided information to attendees about supports provided and how to access them (e.g., closed captions for sessions, etc.). A Zoom Webinars background was automatically provided for speakers/panelists when they logged in to the webinar, and the colour was chosen to reduce brightness for those with visual processing needs. The logistics team ensured the Zoom platform had the live translated captions as an add-on in over 30 languages. While the addition of live interpreters in other languages including sign-language is preferred, this was not viable due to the number of countries and languages represented in the audience, the conference budget, and other resource considerations.
PxP live and feedback
PxP 2023 took place virtually on September 12, 13 and 14/15, 2023 UTC over a total of 4 h (including breaks) on each day (see Additional File 2 for the full agenda). There were a number of powerful quotes as takeaways from the sessions, some of which are provided in Table 3 . PxP 2023 had 617 registrants from 34 countries, with 310 live attendees self-identifying that they were from 18 countries (note SC members and IMHA staff are included in this number). Attendees were from around the globe including from North America (Canada, United States), South America (Brazil, Colombia), Europe (Denmark, France, Ireland, Italy, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom), Asia (India, Israel), Africa (Nigeria), and Oceania (Australia, New Zealand). The majority of attendees were from Canada (57%), United States (18%), United Kingdom (11%) and Australia (7%), respectively. Attendees were provided the option at the start of each day to identify the perspective they brought in a Zoom poll (they were allowed to select more than one option), and in these polls (data are summarized across all 3 days), attendees identified themselves as a patient partner/person with lived experience (59%), a researcher (35%), a caregiver or relative (20%), a clinician (9%), or a trainee or student (6%).
One member of the IMHA team hosted Zoom Webinars and DPR was also on the ‘back-end’ of Zoom Webinars to support each session’s participants if/as required. SC members took on a variety of roles including as hosts, moderators, presenters, or active participants watching and participating in the Zoom chats. In addition to housekeeping, a Land Acknowledgement [ 28 ], and a bit of information about the day, daily hosts encouraged engagement from the start by asking the audience to respond to the Zoom poll mentioned above.
A graphic artist sketched each speaker/panelist in each day’s first session along with one of their quotes from the session. Once these sketches were signed off by the sketched speakers/panelists, they were shared on social media. There are plans to build on this idea for the 2024 conference by engaging an artist who identifies as a patient to do this for all sessions of the conference.
Attendee interactions and social media
Before the conference, all individuals who registered were provided with a link to a guide to make the most of Zoom Webinars and encouraged to share anything they wished in the chat and on social media with the hashtag #PxP23. At the start of each day, hosts provided introductory comments that included a short overview on using Zoom’s chat, question and answer (Q&A), and emoji functions, the latter to provide live feedback to hosts, speakers and moderators. These appeared to be successful tactics for audience participation as there was a great deal of commenting and sharing of resources in the chat, of emojis during presentations and conversations, and efforts made to include questions from the audience into each session (at the end for a dedicated question and answer session or throughout if the session was a moderated discussion). Since permission was not sought of attendees to copy and share the chats verbatim, two IMHA staff created anonymous summaries of each session’s chat comments and resources that were shared in the chat, which are available on PxP Hub in its resources section. [ 29 ].
Leading up to PxP, a newsletter and social media handles were created on Twitter/X (@PxPHub), Instagram (PxPHub), Threads (PxPHub), and LinkedIn (PxPHub). On the days of the event, PxP live updates and threads were shared primarily on X, in addition to Instagram Stories and LinkedIn. A social media graphic was prepared in advance to be used for event quotes and all images were shared with Alt text. In September 2023 (the month of the conference), the PxP X account gained 94.5 k organic (i.e., not paid for) impressions with a 2.4% engagement rate; on PxP LinkedIn, organic impressions were 3,859 with a 12.2% average engagement rate (which is the engagement rate for each post divided by the total number of posts). The newsletter has over 700 subscribers with an average open rate of 57% and an average click rate of 10%.
Between its launch on July 19, 2023, and December 31, 2023, the PxP website had 5.9 k unique visitors, 16.3 k page views, and an average visit duration of over 2 min. The top four countries for website views were Canada (46%), United States (20.9%), United Kingdom (12.3%) and Australia (9.5%), which mirrors the geographic makeup of PxP attendees. Most people were accessing the site directly (for example, through email share), followed by through X, Google, LinkedIn and Facebook. Other than the homepage, the most frequently accessed pages related to the event tickets and program and the PxP resource page, which is a collation of PxP and external resources.
All PxP 2023 session recordings were made available to view on the PxP YouTube Channel [ 22 ] following manual editing of the closed captions. Day 1 recordings were shared in September 2023, Day 2 recordings in October 2023, and Day 3 recordings in November 2023. As of December 31, 2023, the recordings have already garnered 546 views from over 200 unique viewers, with a combined watch time of 90.5 hours; the videos also have 2 k impressions (which is the times the video thumbnails were shown on YouTube) and an impressions click-through rate of 4.8%, this includes people who have been shown the content in their suggested videos, or Browse features (for example).
Conference feedback
A Project Ethics Community Consensus Initiative (ARECCI) framework was used to assess for and mitigate ethical risks for a survey of PxP participants (hosts, speakers, moderators, and attendees), including the four-step ARECCI Ethics Screening Tool and the ARECCI Ethics Guidelines [ 30 , 31 ]. The survey was deemed as minimal risk to participants and did not require review from a Research Ethics Board. All PxP participants (hosts, speakers/panelists, moderators and attendees) were provided a link to an online, voluntary, self-reported anonymous survey to complete. The survey included a consent statement at the beginning about the potential use of their results and open-ended responses for learning purposes or for publication purposes. Respondents could opt-out of their survey responses being used for publication purposes if they wished. The survey was issued using a modified Dillman’s method to achieve a better response rate [ 32 ].
All 310 attendees were invited to respond to a survey about the conference. One-hundred and thirty-seven (137) attendees voluntarily submitted survey responses (response rate of 44%). Of these respondents, 136 respondents consented to their responses being used for publication purposes and 1 respondent agreed for their responses only to be used for learning purposes, not for publication purposes. The survey results from the 136 attendees were overwhelmingly positive:
96% (130) of respondents agreed or strongly agreed that the themes and topics discussed were relevant to them;
96% (130) of respondents agreed or strongly agreed the question and discussion periods were well-organized and helpful in their learning;
74% (100) agreed or strongly agreed that there were opportunities to interact, engage and network with other attendees during the conference;
88% (120) of respondents agreed or strongly agreed they learned something new that will be useful in their future approach in patient partnership/engagement;
95% (129) of respondents agreed or strongly agreed that the conference environment was inclusive and safe;
95% (129) of respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they would recommend the PxP conference to a friend or colleague;
95% (129) of respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they were satisfied with Zoom Webinars as the conference platform; and,
94% (128) of respondents agreed or strongly agreed that they were satisfied with the sessions they attended.
In response to 5 comments on main areas for improvement, increased diversity (gender, ethnicity, geography) for SC members and speakers will be a focus for PxP2024.
SC members were also issued a separate online survey based on the validated Patient and Public Engagement Evaluation Tool to respond to anonymously about their experiences of being a SC member between February to September 2023 [ 33 ]. This survey also had a consent statement at the start about potential uses of the survey data and from which respondents could opt-out. All 9 SC members responded anonymously to this survey. The results indicated that their experiences were positive overall with respect to planning and carrying out the conference. Overall, they indicated that the SC was a safe environment where they could express their views, they felt supported by IMHA in a number of ways (e.g., through being offered one on one meetings if they were unable to attend scheduled meetings), they felt that their feedback was taken into account by IMHA, and that they were proud of the conference. Like conference attendees, they felt that the SC’s diversity of experiences, ethnicity, gender, geography, etc., should be expanded in future years.
Trade-offs, challenges and learnings
The SC aimed to minimize the burden of registering for and attending the conference. The SC decided a conference platform was not necessary, and instead opted to use Zoom alone given familiarity with Zoom due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Further, the SC considered the options of separate registrations and links for each session vs. each day of the conference, and opted to have each day run as one long Zoom Webinar. It was thought that this registration/link approach would minimize potential for confusion around different time-zones for an international event. With this approach, each attendee registered for each day and was provided with a personalized link for that day. Using Zoom Webinar meant that for the starting session of each day, session hosts and speakers/panelists were in a private Zoom Webinar room before the event went live and could prepare without the audience seeing or hearing them. However, after that first session and during breaks, new session speakers/panelists joined and if audience members kept their Zoom Webinar open, they were privy to these preparations. Using Zoom Webinar also meant that attendees could not direct message each other, rather only had the option to post to everyone in the chat. Visual messaging on the screen and in the chats was used during the breaks to let attendees know when sessions would start again. Even with these trade-offs, evaluation results and comments indicated that Zoom Webinar was an appropriate platform for PxP 2023.
Some audience members found the action in the Zoom Webinar chat during the sessions to be distracting and struggled to keep up with the amount of participation in the chat. Part of this may have had to do with how their chat settings were set up (some participants indicated that the chat kept ‘popping up’). For PxP 2024, some suggestions will be offered to deal with the chat and how it can be minimized, and attendees will be informed that the chats will be summarized (including the resources shared in the chats) and posted on the PxP resource hub after the conference.
Future conferences will see an increased diversity (gender, ethnicity, etc.) of the SC members and the invited speakers. Four survey comments indicated gender diversity is an area for improvement given they observed few who appeared to identify as men presenting in the sessions (note that organizers did not ask hosts, moderators or speakers/panelists to disclose their gender). A study of the demographics of patient partners in Canada indicates that this gender uniformity is fairly reflective of the patient partner demographic in many initiatives [ 34 ].
Even though this event was all about patient engagement in research and aimed to execute well on best practices, we experienced process challenges at IMHA’s home institution with respect to issuing honoraria for international participants. The IMHA team has developed an approach to minimize these process issues by working with its home institution for subsequent events.
Resource requirements
The conference required certain resources from IMHA. In addition to a financial budget, a conference platform, communication tools (e.g., a website, social media accounts, a newsletter, etc.), and human resources were required. Without these resources, it would have been difficult to host the same quality of PxP.
It is estimated that in addition to IMHA human resource costs (see below for information on time of various roles), the cost for the first PxP was approximately $27,500 CDN (all figures here in Canadian dollars). This amount includes honoraria offered to SC members (to attend meetings and for various roles in the conference) and all speakers/panelists ($20,000), building the website ($6,000, excluding an annual maintenance fee of $900), and the Zoom platform (~ $1,500). For PxP2024, the only item that will come off the budget is the cost to build the website.
While time commitment varied and especially ramped up closer to the conference itself, a number of IMHA team members contributed to the conference. The financial cost of these human resources is not provided as a dollar amount as this will vary for organizations. Balancing other IMHA-related work within her one-day a week commitment to IMHA (that is, less than 0.2 full time equivalents), DPR prepared materials for and hosted all SC meetings, met with SC members individually if they could not attend scheduled meetings, invited speakers and panelists, hosted 9 conference planning sessions/introductory meetings for sessions, attended the 2 pre-conference drop-ins for all speakers, hosts, and panelists, led developing the ‘run of show,’ shared information about the conference on social media and in her networks, and supported speakers, hosts and panelists on the back-end of Zoom Webinars each day of the conference. RT worked closely with DPR and attended all SC meetings and provided technical support for speakers, hosts and panelists at the conference. HM worked closely with DPR, attending most SC meetings, co-designed all communications and social media assets for the conference, coordinated all IMHA communications about the conference, coordinated PxP logo and website development, created all conference agendas and guides for using Zoom Webinar, etc., and hosted Zoom Webinar for the conference. HM’s time commitment was between 0.25–0.5 full time equivalents in the 6 months leading up to the conference. Another member of the IMHA team supported compensation processes for all SC members, speakers and panelists, through setting up individuals with a finance system and ensuring payments were received. And one other member of the IMHA team co-created the evaluation materials and uploaded them in to an online survey software (Qualtrics), and helped with analyzing all survey results. KK supported the entire project by attending SC meetings, the conference itself, and allowing IMHA resources to be used to support the PxP.
Next steps for PxP and beyond
Planning for PxP 2024 has already started, and PxP will continue until at least 2025 with IMHA support. Beyond 2025, a new Scientific Director will be appointed to IMHA (Scientific Directors’ terms are for a maximum of 8 years, with the current Scientific Director completing his term in 2025), and their support for PxP is not guaranteed. With a commitment to provide new patient partners the opportunity to plan and participate in the conference, a new SC is being formed for 2024 with efforts to expand its diversity (patient partner experience, gender, ethnicity, geography, etc.), and based on suggestions made by 2023’s SC members. The 2023 SC has become an Alumnus Committee and their interaction with the 2024 SC and involvement in PxP 2024 will be decided by the incoming SC. As was the case with the 2023 event, the 2024 SC will decide on all aspects of the conference, building on the successes and learning from the challenges of PxP 2023.
As individuals who were involved in designing and executing PxP, we encourage others to use the PxP template and build on it to find ways to support and create conferences and events for patients and by patients. Support may take the form of any of a number of resources, such as people, funding, and skills. One of the main challenges for patients planning and carrying out their own conferences is funding, and we urge organizations to consider how they can provide this type of financial support. There may also be more innovative partnership models waiting to be created and learned from.
Conclusions
We present work we undertook throughout 2023 to co-create and produce PxP, a conference for patients and by patients, all about patient engagement in research, and its associated PxP Hub. We share how the conference prioritized the patient partner community and accessibility, and provided an opportunity for knowledge exchange and nuanced discussions on all aspects of patient engagement in research. The conference has convened an active community of over 700 people that we hope will grow. We aim to engage in future events, with a deeper focus on equity, diversity and inclusion. In addition to working with knowledgeable patients who have their own networks, having support (funding, project management and communications skills and expertise, people, etc.) is required to carry out such an event. The time is now to elevate patients into leadership roles for conferences and events. We encourage you to adopt the PxP ethos by using or adapting our approach and resources to support this model.
Availability of data and materials
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
Canadian Institutes of Health Research
Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis
Patient Engagement in Research Ambassadors
Patient-Oriented Research
For Patients, by Patients
Steering Committee
Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Definitions of Patient and Patient Engagement. Available from: http://www.cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/48413.html . Cited 2024 Jan 8.
European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR). EULAR Online Course for Patient Research Partners. https://esor.eular.org/ . European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology; 2024.
National Institute for Health and Care Research. Definition of Patient and Public Involvement. Available from: https://www.rds-sc.nihr.ac.uk/ppi-information-resources/#:~:text=Patient%20and%20Public%20involvement%20in%20research%20refers%20to%20an%20active,and%20possibly%20as%20co%2Dresearchers . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
Definition of Consumer Involvement [web page]. https://www.nhmrc.gov.au/guidelinesforguidelines/plan/consumer-involvement . National Health and Medical Research Council. Cited 2023 Dec 6.
European Conference on Rare Diseases 2024 https://www.eurordis.org/ecrd-2024/ . EURODIS; 2024.
Putting the Pieces Together Conference [website]. Pain Canada. Available from: https://www.paincanada.ca/events/putting-the-pieces-together . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
Levy M. Patient led conferences: an education for doctors. BMJ. 2001;323(323):270.
Zakrzewska JM, Jorns TP, Spatz A. Patient led conferences–who attends, are their expectations met and do they vary in three different countries? Eur J Pain. 2009;13(5):486–91.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
PxP: For Patients, By Patients: Partnering to Make Research Stronger [website]. www.pxphub.org . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/13217.html . Canadian Institutes of Health Research; 2024. 2023 Dec 6.
Richards D, Twomey R, Flynn T, Hunter L, Lui E, Stordy A, et al. Patient engagement in a Canadian Health Research Funding Institute: Implementation and Impact. 2023. Preprint.
Google Scholar
Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis Patient Engagement Research Ambassadors. Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Available from: https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/27297.html#a1 . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
A How-to Guide for Patient Engagement in Research https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/27297.html#a2 . Canadian Institutes of Health Research; 2022. Cited 2023 Dec 6.
PxP 2023 Steering Committee Members. Available from: https://pxphub.org/event/steering-committee-2023 . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
PatientsIncluded [webpage]. Available from: www.patientsincluded.org . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
Clareborn A, Degsell E, Kannisto K, Haag M, Friedman M, Riggare S, et al. Patient and next-of-kin collaboration for better reserch and healthcare. 2024.
CIHR Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthrits Patient Compensation Guideline. Available from: https://cihr-irsc.gc.ca/e/27297.html#a4 . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
Richards DP, Jordan I, Strain K, Press Z. Patient partner compensation in research and health care: the patient perspective on why and how. Patient Exp J. 2018;5(3):6–12.
Article Google Scholar
PxP Resource Hub [website]. https://pxphub.org/resource . PxP; 2023. Cited 2023 Dec 6.
PxP 2023 Program Agenda: PxP; 2023. Available from: https://pxphub.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/PxP-Full-Agenda-English-FINAL.pdf . Cited 2023 Dec 6.
PxP Registration Page with Time-Zone Conversion Table PxPHub.org: PxP; 2023. Available from: https://pxphub.org/event/registration-information-2023/ . Cited 2024 Jan 30.
PxP YouTube Channel [YouTube Channel]. pxphub.org: PxP; 2023 Available from: https://www.youtube.com/@PxPHub .
WebAIM (web accessibility in mind). Available from: https://webaim.org/resources/contrastchecker/ . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
UserWay. Available from: https://userway.org/about/ . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
PxP Accessibility webpage pxphub.org: PxP; 2023. Available from: https://pxphub.org/accessibility/ . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
PxP 2023 Speakers pxphub.org: PxP; 2023. Available from: https://pxphub.org/event/speakers-2023/ . Cited 2024 Jan 24.
PxP 2023 Zoom Webinar Guide pxphub.org: PxP; 2023. Available from: https://pxphub.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/PxP-2023-Zoom-Webinars-Guide-for-Attendees-FINAL.pdf . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
Native Land Digital - Territory Acknowledgement https://native-land.ca/ . Native Land Digital. Available from: https://native-land.ca/resources/territory-acknowledgement/ . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
PxP Hub Resources webpage pxphub.org: PxP; 2023. Available from: https://pxphub.org/resource . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
A project Ethics Community Consensus Initiative (ARECCI) Ethics Screening Tool: Alberta Innovates. Available from: https://arecci.albertainnovates.ca/ . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
A pRoject Ethics Community Consensus Initiative (ARECCI) Ethics Guideline Tool January 12, 2024. Available from: https://albertainnovates.ca/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/ARECCI-Ethics-Guideline-Tool.pdf . Cited 2024 Jan 12.
Dillman D. Mail and Internet Surveys: The Tailored Design Method. 2nd ed. New York: Wiley; 2000.
Abelson J, Li K, Wilson G, Shields K, Schneider C, Boesveld S. Supporting quality public and patient engagement in health system organizations: development and usability testing of the Public and Patient Engagement Evaluation Tool. Health Expect. 2016;19(4):817–27.
Abelson J, Canfield C, Leslie M, Levasseur MA, Rowland P, Tripp L, et al. Understanding patient partnership in health systems: lessons from the Canadian patient partner survey. BMJ Open. 2022;12(9):e061465.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Eileen Davidson as a Steering Committee member of PxP 2023, Eunice Lui for her work related to the conference evaluation, and Mike Brennan for his speaker sketches.
All SC members who are authors were offered an honorarium for their involvement in developing and writing this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Dawn P. Richards, Hetty Mulhall, Rosie Twomey & Karim M. Khan
Five02 Labs Inc., Toronto, ON, Canada
Dawn P. Richards
Patient Partner and Patient Author, Toronto, ON, Canada
Patient Partner and Patient Author, Fraser, CO, USA
Joletta Belton
Patient Partner and Patient Author, London, UK
Savia de Souza
Patient Partner and Patient Author, Halifax, NS, Canada
Trudy Flynn
Patient Partner and Patient Author, Kingston, ON, Canada
Alex Haagaard
Patient Partner and Patient Author, Ottawa, ON, Canada
Linda Hunter
Patient Author, London, UK
Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Practice (TDI), Geisel School of Medicine, Dartmouth College, Hanover, NH, USA
Patient Editor BMJ, London, UK
Patient Partner and Patient Author, Stockholm, Sweden
Sara Riggare
Participatory eHealth and Health Data, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
Patient Partner and Patient Author, Seattle, WA, USA
Janice Tufte
PCORI, Seattle, WA, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
DPR, HM and RT led conception of the work, DPR convened the writing group and discussions (JB, SdS, TF, AH, LH, KK, HM, AP, SR, JT, RT). DPR led writing of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the design, analysis of the work and in writing and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Authors’ information
We have not filled in the GRIPP2 for this commentary as a number of the authors identify as patient partners. All author contributions are noted above. The following authors can be found and tagged on X: DPR (@TO_dpr), TF (@trudyflynn_), AH (@alexhaagaard), LH (@lhunter1310), HM (@HettyMulhall), AP (@AmyPricePhD), JT (@Hassanah2017).
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dawn P. Richards .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
A Project Ethics Community Consensus Initiative (ARECCI) framework was used to assess for and mitigate ethical risks for a survey of PxP participants (attendees, hosts, session participants) as well as SC members, including the four-step ARECCI Ethics Screening Tool and the ARECCI Ethics Guidelines. The surveys were deemed as minimal risk to participants, and did not require review from a Research Ethics Board. The surveys were answered anonymously (no identifying information was collected) and voluntary, and there was a consent statement before the survey start so they could opt out of if they wished.
Consent for publication
Individuals who chose to complete the survey (see above) were consented for their results to be part of a discussion in a publication. One person did not consent to their survey results being used for this purpose, and their results were removed from those discussed in this paper.
Competing interests
DPR is a full-time employee of Five02 Labs, Inc., and is under contract to the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Institute of Musculoskeletal Health and Arthritis to support its patient engagement efforts.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. steering committee terms of reference., 40900_2024_603_moesm2_esm.pdf.
Additional file 2. Full version of the conference agenda which includes dates, times, hosts, session names and their respective moderators and speakers.
40900_2024_603_MOESM3_ESM.pdf
Additional file 3. Zoom Webinar Guide that was created for conference attendees to make the most of attending the conference on the Zoom Webinar platform.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Richards, D.P., Mulhall, H., Belton, J. et al. Co-creating and hosting PxP: a conference about patient engagement in research for and by patient partners. Res Involv Engagem 10 , 77 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-024-00603-0
Download citation
Received : 02 February 2024
Accepted : 28 June 2024
Published : 29 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40900-024-00603-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Patient engagement in research
- Patient and public involvement
- Consumer involvement
- Service user research
- Patient-led conference
- Co-production
- PatientsIncluded
- Patient author
- Patient partner
Research Involvement and Engagement
ISSN: 2056-7529
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Grassland ecosystem services: their economic evaluation through a systematic review.

1. Introduction
2. materials and methods, 2.1. the science mapping, 2.2. the systematic review process, 3.1. the descriptive and bibliometric analysis of the literature on grasslands ecosystem services, 3.2. the analysis of the documents referring to the economic evaluation methodologies of the grassland es, 4. discussion, 4.1. main findings, 4.2. limitations of the study, 5. conclusions, author contributions, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Data on Land Cover (Grassland). FAOSTAT. 2021. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/LC (accessed on 10 May 2024).
- FAO. Guidelines: Land Evaluation for Extensive Grazing, 1990. FAO Soil Bulletin 58. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/t0412e/t0412e.pdf (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Faber-Langendoen, D.; Keeler-Wolf, T.; Meidinger, D.; Josse, C.; Weakley, A.; Tart, D.; Navarro, G.; Hoagland, B.; Ponomarenko, S.; Fults, G.; et al. Classification and Description of World Formation Types ; Gen. Tech. Rep. RMRS-GTR-2016; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Fort Collins, CO, USA, 2016; Volume 346, p. 222. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dixon, A.P.; Faber-Langendoen, D.; Josse, C.; Morrison, J.; Loucks, C.J. Distribution mapping of world grassland types. J. Biogeogr. 2014 , 41 , 2003–2019. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Allen, V.G.; Batello, C.; Berretta, E.J.; Hodgson, J.; Kothmann, M.; Li, X.; Mcivor, J.; Milne, J.; Morris, C.; Peeters, A.; et al. An international terminology for grazing lands and grazing animals. Grass Forage Sci. 2011 , 66 , 2–28. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Shao, C. Types and Distribution of Chinese Grassland Ecosystems. In Grassland Ecosystems of China. Ecosystems of China ; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 2. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lezama, F.; Cáceres, D.; Pañella, P.; del Pino, A. Land-Use Intensification by Overseeding Legumes on Natural Grasslands: Impacts on Plant Diversity. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2024 , 93 , 95–103. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Colman, C.B.; Guerra, A.; Almagro, A.; de Oliveira, R.F.; Rosa, I.M.D.; Fernandes, G.W.; Oliveira, P.T.S. Modeling the Brazilian Cerrado land use change highlights the need to account for private property sizes for biodiversity conservation. Sci. Rep. 2024 , 14 , 4559. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Noellemeyer, E.; Álvarez, L.; Álvarez, C.; Dillchneider, A.; Farrell, M.; Fernández, R.; Buss, E.F.; Frasier, I.; Gaggioli, C.; Gili, A.; et al. From science to practice: The AGSUS protocol for monitoring and certification of sustainable soil management and carbon sequestration. Soil Till Res. 2024 , 241 , 106102. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Peeters, A.; Beaufoy, G.; Canals, R.M.; De Vliegher, A.; Huyghe, C.; Isselstein, J.; Jones, G.; Kessler, W.; Kirilov, A.; Mosquera-Losada, M.R.; et al. Grassland term definitions and classifications adapted to the diversity of European grassland-based systems. In Grassland Science in Europe—EGF at 50: The Future of European Grasslands ; Hopkins, A., Collins, R.P., Fraser, M.D., King, V.R., Lloyd, D.C., Moorby, J.M., Robson, P.R.H., Eds.; IBERS, Aberystwyth University: Gogerddan, UK, 2014; Volume 19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dengler, J.; Janišová, M.; Török, P.; Wellstein, C. Biodiversity of palaearctic grasslands: A synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014 , 182 , 1–14. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Richter, F.; Jan, P.; El Benni, N.; Lüscher, A.; Buchmann, N.; Klaus, V.H. A guide to assess and value ecosystem services of grasslands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021 , 52 , 101376. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bengtsson, J.; Bullock, J.M.; Egoh, B.; Everson, C.; Everson, T.; O’Connor, T.; O’Farrell, P.J.; Smith, H.G.; Lindborg, R. Grasslands—More important for ecosystem services than you might think. Ecosphere 2019 , 10 , 1–20. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Costanza, R.; Dange, R.; Degroot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J.; et al. The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 1997 , 387 , 253–260. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Egoh, B.J.; Bengtsson, R.; Lindborg, J.M.; Bullock, A.; Dixon, P.; Rouget, M. The importance of grasslands in providing ecosystem services: Opportunities for poverty alleviation. In Routledge Handbook of Ecosystem Services ; Potschin, M., Haines-Young, R., Fish, R., Turner, R.K., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 421–441. [ Google Scholar ]
- Basso, F.; Santilocchi, R.; Postiglione, L.; Cavallero, A.; Grignani, C.; Reyneri, A.; Acutis, M.; Costa, G.; Pascal, G.; Ziliotto, U.; et al. Gestione e miglioramento di pascoli italiani. Riv. Agron. 1992 , 26 , 344–359. [ Google Scholar ]
- Queiroz, C.; Beilin, R.; Folke, C.; Lindborg, R. Farmland abandonment: Threat or opportunity for biodiversity conservation? Front. Ecol. Environ. 2014 , 12 , 288–296. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bojārs, E.; Ruskule, A.; Veidemane, K.; Fammler, H.; Kuris, M.; Norvaišaite, R.; Burkhard, B. How do Grasslands Benefit Humans-Introduction to Grassland Ecosystem Services. Baltic Environmental Forum. 2017. Available online: https://vivagrass.eu/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/broshure-final-how-grasslands-benefit-human-introduction-to-grassland-ecosystem-services-download.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- O’Mara, F.P. The role of grasslands in food security and climate change. Ann. Bot. 2012 , 110 , 1263–1270. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Erb, K.H.; Kastner, T.; Plutzar, C.; Bais, A.L.S.; Carvalhais, N.; Fetzel, T.; Gingrich, S.; Haberl, H.; Lauk, C.; Niedertscheider, M.; et al. Unexpectedly large impact of forest management and grazing on global vegetation biomass. Nature 2018 , 553 , 73–76. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Veen, P.; Jefferson, R.; de Smidt, J.; van der Straaten, J. Grasslands in Europe of High Nature Value ; KNNV Publishing: Zeist, The Netherlands, 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Habel, J.C.; Dengler, J.; Janišová, M.; Török, P.; Wellstein, C.; Wiezik, M. European grassland ecosystems: Threatened hotspots of biodiversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2013 , 22 , 2131–2138. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Helgadóttir, Á.; Frankow-Lindberg, B.E.; Seppänen, M.M.; Søegaard, K.; Østrem, L. European grasslands overview: Nordic region. In Grassland Science in Europe—EGF at 50: The Future of European Grasslands ; Hopkins, A., Collins, R.P., Fraser, M.D., King, V.R., Lloyd, D.C., Moorby, J.M., Robson, P.R.H., Eds.; IBERS, Aberystwyth University: Gogerddan, UK, 2014; Volume 19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Huyghe, C.; De Vliegher, A.; Goliński, P. European grasslands overview: Temperate region. In Grassland Science in Europe, EGF at 50: The Future of European Grasslands ; Hopkins, A., Collins, R.P., Fraser, M.D., King, V.R., Lloyd, D.C., Moorby, J.M., Robson, P.R.H., Eds.; IBERS, Aberystwyth University: Gogerddan, UK, 2014; Volume 19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cosentino, S.L.; Porqueddu, C.; Copani, V.; Patanè, C.; Testa, G.; Scordia, D.; Melis, R. European grasslands overview: Mediterranean region. In Grassland Science in Europe, EGF at 50: The Future of European Grasslands ; Hopkins, A., Collins, R.P., Fraser, M.D., King, V.R., Lloyd, D.C., Moorby, J.M., Robson, P.R.H., Eds.; IBERS, Aberystwyth University: Gogerddan, UK, 2014; Volume 19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jouven, M.; Lapeyronie, P.; Moulin, C.H.; Bocquier, F. Rangeland utilization in Mediterranean farming systems. Animal 2010 , 4 , 1746–1757. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Perevolotsky, A. Integrating landscape ecology in the conservation of Mediterranean ecosystems. The Israeli experience. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2005 , 53 , 203–213. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gómez-Baggethun, E.; Barton, D.N.; Berry, P.; Dunford, R.; Harrison, P.A. Concepts and methods in ecosystem services valuation. In Routledge Handbook of Ecosystem Services ; Potschin, M., Haines-Young, R., Fish, R., Turner, R.K., Eds.; Routledge Handbooks Online: London, UK, 2016; pp. 99–111. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kang, B.; Shao, Q.; Xu, H.; Jiang, F.; Wei, X.; Shao, X. Research on grassland ecosystem service value in China under climate change based on meta-analysis: A case study of Qinghai province. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2020 , 12 , 617–637. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, H.; Hou, L.; Kang, N.; Nan, Z.; Huang, J. A meta-regression analysis of the economic value of grassland ecosystem services in China. Ecol. Indic. 2022 , 138 , 108793. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, H.; Hou, L.; Kang, N.; Nan, Z.; Huang, J. The economic value of grassland ecosystem services: A global meta-analysis. Grassl. Res. 2022 , 1 , 63–74. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Merli, R.; Preziosi, M.; Acampora, A. How do scholars approach the circular economy? A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018 , 178 , 703–722. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Denyer, D.; Tranfield, D. Producing a systematic review. In The Sage Handbook of Organizational Research Methods ; Buchanan, D.A., Bryman, A., Eds.; Sage Publications Ltd.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 671–689. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pergola, M.; De Falco, E.; Belliggiano, A.; Ievoli, C. The Most Relevant Socio-Economic Aspects of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants through a Literature Review. Agriculture 2024 , 14 , 405. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021 , 133 , 285–296. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Manual for VOSviewer Version 1.6.20. 2023. Available online: https://www.vosviewer.com/documentation/Manual_VOSviewer_1.6.20.pdf (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Muley, A.; Medithi, S. A Quantitative Literature Analysis of the Research on Holy Basil (Tulsi). J. Scientometr. Res. 2022 , 11 , 30–36. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sánchez, A.D.; de la Cruz Del Río Rama, M.; García, J.Á. Bibliometric analysis of publications on wine tourism in the databases Scopus and WoS. Eur. Res. Manag. Bus. Econ. 2017 , 23 , 8–15. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aghaei Chadegani, A.; Salehi, H.; Md Yunus, M.M.; Farhadi, H.; Fooladi, M.; Farhadi, M.; Ale Ebrahim, N. A comparison between two main academic literature collections: Web of science and Scopus databases. Asian Soc. Sci. 2013 , 9 , 18–26. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Guz, A.N.; Rushchitsky, J.J. Scopus: A system for the evaluation of scientific journals. Int. Appl. Mech. 2009 , 45 , 351–362. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Parton, W.J.; Wright, R.G.; Risser, P.G. Simulated grazing responses on the proposed prairies National Park. Environ. Manag. 1980 , 4 , 165–170. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Loreau, M.; Hector, A. Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature 2001 , 412 , 72–76. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Balvanera, P.; Pfisterer, A.B.; Buchmann, N.; He, J.; Nakashizuka, T.; Raffaelli, D.G.; Schmid, B. Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and services. Ecol. Lett. 2006 , 9 , 1146–1156. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tilman, D.; Reich, P.; Knops, J. Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature 2006 , 441 , 629–632. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wagg, C.; Bender, S.F.; Widmer, F.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014 , 111 , 5266–5270. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hoekstra, J.M.; Boucher, T.; Ricketts, T.H.; Roberts, C.S. Confronting a biome crisis: Global disparities of habitat loss and protection. Ecol. Lett. 2004 , 8 , 23–29. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.; Reich, P.B.; Jeffries, T.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Encinar, D.; Berdugo, M.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2016 , 7 , 10541. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Díaz, S.M.; Lavorel, S.; de Bello, F.; Quétier, F.; Grigulis, K.; Robson, T.M. Incorporating plant functional diversity effects in ecosystem service assessments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2007 , 104 , 20684–20689. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Ouyang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Polasky, S.; Liu, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Rao, E.; et al. Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital. Science 2016 , 17 , 1455–1459. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Isbell, F.; Calcagno, V.; Hector, A.; Connolly, J.; Harpole, W.S.; Reich, P.B.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Schmid, B.; Tilman, D.; van Ruijven, J.; et al. High plant diversity is needed to maintain ecosystem services. Nature 2011 , 477 , 199–202. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Ouyang, Z.; Tam, C.; Chen, X. Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008 , 15 , 9477–9482. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, C.; Li, J.; Jiang, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, W.; Duan, H.; Wei, Z.; Huang, Y. The Impacts of Land-Use Changes on Ecosystem Service Value in the Yunnan–Kweichow Plateau, China. Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 1062. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhu, L.N.; Zhao, M.; Li, Y.F.; Fan, Y.; Wang, J. The Space-time Relationship between the Ecosystem Service Value and the Human Activity Intensity in Xi’an Metropolitan Area. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2024 , 40 , 325–334. [ Google Scholar ]
- Li, J.; Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; Chu, J.; Yin, H.; Ma, M. Study of identification and simulation of ecological zoning through integration of landscape ecological risk and ecosystem service value. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024 , 107 , 105442. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hong, X.; Peng, Q.; Zheng, R.; Lin, W.; Fan, S.; Su, K. Evaluating the Spatial Evolution of the Eco-Economy Harmony in Anxi County, China, Based on Ecosystem Services Value. Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 1491. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xia, F.; Huang, Y.; Dong, L. Comparison of comprehensive benefits of land-use systems under multi- and single-element governance. Land Use Policy 2024 , 141 , 107164. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- You, C.; Qu, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L. Assessment of Uncertainties in Ecological Risk Based on the Prediction of Land Use Change and Ecosystem Service Evolution. Land 2024 , 13 , 535. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dammag, A.Q.; Dai, J.; Cong, G.; Derhem, B.Q.; Latif, H.Z. Assessing and predicting changes of ecosystem service values in response to land use/land cover dynamics in Ibb City, Yemen: A three-decade analysis and future outlook. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024 , 17 , 137–147. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, T.; Shi, D.; Jiang, S.; Li, Y.; Yu, H. Analysis of Spatial—Temporal Variation in Ecosystem Service Value in Shandong Province over the Last Two Decades. Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 515. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zuo, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, P. Analysis of the gains and losses of ecosystem service value under land use change and zoning in Qiqihar. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023 , 11 , 1192952. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yin, D.; Yu, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, X. Spatial pattern evolution of territorial space and its effects on ecological response in the Yellow River Basin during 2000–2020. Nongye Gongcheng Xuebao/Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023 , 39 , 217–228. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bao, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, T. Spatiotemporal Changes of Ecosystem Service Values in Response to Land Cover Dynamics in China from 1992 to 2020. Sustainability 2023 , 15 , 7210. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jin, T.; Chen, Y.; Shu, B.; Gao, M.; Qiu, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service value and topographic gradient effect in the Da-Xiao Liangshan Mountains in Sichuan Province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2023 , 20 , 2344–2357. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chi, Y.; He, C. Impact of Land Use Change on the Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Ecosystem Service Values in South China Karst Areas. Forests 2023 , 14 , 893. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zeng, J.; Bian, J.; Chen, W. Impact of slope farmland use change on ecosystem services value in China, 2000–2020. J. Mt. Sci. 2023 , 20 , 821–833. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xu, X.; Peng, Y. Ecological Compensation in Zhijiang City Based on Ecosystem Service Value and Ecological Risk. Sustainability 2023 , 15 , 4783. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xie, J.; Lu, Z.; Xiao, S.; Xiao, S.; Yan, C. Driving Force and Ecosystem Service Values Estimation in the Extreme Arid Region from 1975 to 2015: A Case Study of Alxa League, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2021 , 31 , 1097–1107. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gong, X.; Chang, C. Correlation and trade-off analysis of ecosystem service value and human activity intensity: A case study of Changsha, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023 , 43 , 100738. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, H.; Niu, W.; Song, M.; Zhang, B.; Jin, Y. Construction and spatial optimization of ecological network in Shaanxi Province based on LUCC and its ESV response. Resour. Sci. 2023 , 45 , 1380–1395. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xin, X.; Zhang, T.; He, F.; Zhang, W.; Chen, K. Assessing and simulating changes in ecosystem service value based on land use/cover change in coastal cities: A case study of Shanghai, China. Ocean Coast Manag. 2023 , 239 , 106591. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huang, X.; Xie, Y.; Lei, F.; Cao, L.; Zeng, H. Analysis on spatio-temporal evolution and influencing factors of ecosystem service in the Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan urban agglomeration, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023 , 11 . [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Farley, K.A.; Bremer, L.L. “Water Is Life”: Local Perceptions of Páramo Grasslands and Land Management Strategies Associated with Payment for Ecosystem Services. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2017 , 107 , 371–381. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Byrne, A.T.; Hadrich, J.C.; Robinson, B.E.; Han, G. A factor-income approach to estimating grassland protection subsidy payments to livestock herders in Inner Mongolia, China. Land Use Policy 2020 , 91 , 104352. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fan, S.; Zhao, C.; Zha, S. Analysis of the Impact of Policy Instruments on Payment for Grasslands Ecosystem Services (PGES) Implementation: A Case Study from Northwest China. Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 13779. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Behrendt, K.; Brown, C.; Qiao, G.; Zhang, B. Assessing the opportunity costs of Chinese herder compliance with a payment for environmental services scheme. Ecol. Econ. 2022 , 193 , 107313. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xue, J.; Liu, Z.; Han, X.; Huang, J. China’s new rural “separating three property rights” land reform results in grassland degradation: Evidence from Inner Mongolia. Land Use Policy 2018 , 71 , 170–182. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bremer, L.L.; Farley, K.A.; Lopez-Carr, D.; Romero, J. Conservation and livelihood outcomes of payment for ecosystem services in the Ecuadorian Andes: What is the potential for ‘win-win’? Ecosyst. Serv. 2014 , 8 , 148–165. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ranjan, R. Creating synergies between payments for ecosystem services, green bonds, and catastrophe insurance markets for enhanced environmental resilience. Land Use Policy 2024 , 136 , 106970. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fan, S.; He, M.; Zhang, T.; Huo, Y.; Fan, D. Credibility measurement as a tool for conserving nature: Chinese herders’ livelihood capitals and payment for grassland ecosystem services. Land Use Policy 2022 , 115 , 106032. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Joslin, A. Dividing “Above” and “Below”: Constructing Territory for Ecosystem Service Conservation in the Ecuadorian Highlands. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2020 , 110 , 1874–1890. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Chase, L.; Strong, A.M.; Swallow, S.K. Making markets for private provision of ecosystem services: The Bobolink Project. Ecosyst. Serv. 2019 , 37 , 100936. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Russi, D.; Margue, H.; Oppermann, R.; Keenleyside, C. Result-based agri-environment measures: Market-based instruments, incentives or rewards? The case of Baden-Württemberg. Land Use Policy 2016 , 54 , 69–77. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bremer, L.L.; Farley, K.A.; Lopez-Carr, D. What factors influence participation in payment for ecosystem services programs? An evaluation of Ecuador’s Socio Páramo program. Land Use Policy 2014 , 36 , 122–133. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Groth, M. Cost-effective Biodiversity Conservation: Procurement Auctions and Payment-by-Results. EuroChoices 2011 , 10 , 32–37. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wätzold, F.; Drechsler, M.; Johst, K.; Mewes, M.; Sturm, A. A Novel, Spatiotemporally Explicit Ecological-Economic Modeling Procedure for the Design of Cost-Effective Agri-Environment Schemes to Conserve Biodiversity. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2016 , 98 , 489–512. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hecker, L.P.; Sturm, A.; Querhammer, L.; Wätzold, F. Cost-effectiveness of state-dependent versus state-independent agri-environment schemes for biodiversity conservation. Ecol. Econ. 2024 , 217 , 108088. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ward, A.; Dargusch, P.; Thomas, S.; Liu, Y.; Fulton, E.A. A global estimate of carbon stored in the world’s mountain grasslands and shrublands, and the implications for climate policy. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014 , 28 , 14–24. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Deng, H. Construction and Influencing Factors of Voluntary Compensation Subjects for Herders—From the Perspective of Sustainable Utilization of Grassland Resources. Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 2576. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Deng, Y.J.; Hou, M.Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.; Yao, S.B. Ecological compensation strategy of the old revolutionary base areas along the route of Long March based on ecosystem service value evaluation. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2022 , 33 , 159–168. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Horák, I.; Marada, P. Erosion and the Economic Evaluation of the Conservation Grassland as an Existing Effective Tool to Reduce Erosion. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendelianae Brun. 2023 , 71 , 141–153. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lai, M.; Wu, S.H.; Yin, Y.H.; Pan, T. Accounting for eco-compensation in the three-river headwaters region based on ecosystem service value. Shengtai Xuebao 2015 , 35 , 227–236. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dai, Q.-W.; Zhao, X.-Y. Discussion on Several Key Scientific Issues of Eco-compensation Mechanism in Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2010 , 65 , 494–506. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Bhatt, S.; Rahmat, S.; Paul, S.K.; Sen, S. Estimating global ecosystem service values and its response to land surface dynamics during 1995–2015. J. Environ. Manag. 2018 , 223 , 115–131. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Blignaut, J.; Mander, M.; Schulze, R.; Horan, M.; Dickens, C.; Pringle, C.; Mavundla, K.; Mahlangu, I.; Wilson, A.; McKenzie, M.; et al. Restoring and managing natural capital towards fostering economic development: Evidence from the Drakensberg, South Africa. Ecol. Econ. 2010 , 69 , 1313–1323. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Du, J.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, C.; Wang, W. A Review of Ecosystem Services Assessment and Valuation of Protected Areas. Res. Environ. 2019 , 32 , 1475–1482. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Inoue, M. Change of Landscape and Ecosystem Services of Semi-natural Grassland in Mt. Sanbe, Shimane Prefecture, Japan. In Landscape Ecology for Sustainable Society ; Hong, S.K., Nakagoshi, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhao, X.; Yi, P.; Xia, J.; He, W.; Gao, X. Temporal and spatial analysis of the ecosystem service values in the Three Gorges Reservoir area of China based on land use change. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022 , 29 , 26549–26563. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Gascoigne, W.R.; Hoag, D.; Koontz, L.; Tangen, B.A.; Shaffer, T.L.; Gleason, R.A. Valuing ecosystem and economic services across land-use scenarios in the Prairie Pothole Region of the Dakotas, USA. Ecol. Econ. 2011 , 70 , 1715–1725. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Assessment of Grassland Ecosystem Services and Analysis on Its Driving Factors: A Case Study in Hulunbuir Grassland. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022 , 10 , 841943. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mulwa, R.; Siikamaki, J.; Ndwiga, M.; Alvsilver, J. Influence of proximity to and type of foraging habitat on value of insect pollination in the tropics, with applications to Kenya. Afr. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2022 , 17 , 171–191. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Rewitzer, S.; Huber, R.; Grêt-Regamey, A.; Barkmann, J. Economic valuation of cultural ecosystem service changes to a landscape in the Swiss Alps. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017 , 26 , 197–208. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kusi, K.K.; Khattabi, A.; Mhammdi, N. Analyzing the impact of land use change on ecosystem service value in the main watersheds of Morocco. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023 , 25 , 2688–2715. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Admasu, S. Assessing the impact of Land use changes on ecosystem services in the Alledighe rangeland, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2024 , 10 , 28798. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aziz, T. Changes in land use and ecosystem services values in Pakistan, 1950–2050. Environ. Dev. 2021 , 37 , 100576. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yi, F.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yao, B.; Lu, Q. Changes in Land Use and Ecosystem Service Values of Dunhuang Oasis from 1990 to 2030. Remote Sens. 2023 , 15 , 564. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mendoza-González, G.; Martínez, M.L.; Lithgow, D.; Pérez-Maqueo, O.; Simonin, P.W. Land use change and its effects on the value of ecosystem services along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. Ecol. Econ. 2012 , 82 , 23–32. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gren, I.M.; Groth, K.H.; Sylvén, M. Economic Values of Danube Floodplains. J. Environ. Manag. 1995 , 45 , 333–345. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hardaker, A.; Pagella, T.; Rayment, M. Ecosystem service and dis-service impacts of increasing tree cover on agricultural land by land-sparing and land-sharing in the Welsh uplands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021 , 48 , 101253. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Jayalath, T.A.; Grala, R.K.; Grado, S.C.; Evans, D.L. Increasing provision of ecosystem services through participation in a conservation program. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021 , 50 , 101303. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dong, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Pastoral Differentiations’ Effects on Willingness to Accept Valuation for Grassland Eco-Subsidy—Empirical Study of 410 Herder Households in Grass–Livestock Balance Sub-Policy Zones in Inner Mongolia, China. Sustainability 2023 , 15 , 10001. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ingram, S.; Belcher, K.; Hesseln, H. Policy development to support ecosystem services on pasture systems in Saskatchewan: A case study. Land Use Policy 2023 , 134 , 106885. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huber, R.; Finger, R. A Meta-analysis of the Willingness to Pay for Cultural Services from Grasslands in Europe. J. Agric. Econ. 2020 , 71 , 357–383. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ning, J.; Jin, J.; Kuang, F.; Wan, X.; Zhang, C.; Guan, T. The Valuation of Grassland Ecosystem Services in Inner Mongolia of China and Its Spatial Differences. Sustainability 2019 , 11 , 7117. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Huber, R.; Le’Clec’h, S.; Buchmann, N.; Finger, R. Economic value of three grassland ecosystem services when managed at the regional and farm scale. Sci. Rep. 2022 , 12 , 4194. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Divinsky, I.; Becker, N.; Kutiel, P.B. Ecosystem service tradeoff between grazing intensity and other services—A case study in Karei-Deshe experimental cattle range in northern Israel. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017 , 24 , 16–27. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shen, P.; Wu, L.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, J. A Study on the Spatial Pattern of the Ecological Product Value of China’s County-Level Regions Based on GEP Evaluation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023 , 20 , 3181. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Yu, F.; Li, X.B.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.J.; Xu, W.H.; Fu, R. Accounting of gross ecosystem product based on emergy analysis and ecological land classification in China. Shengtai Xuebao 2016 , 36 , 1663–1675. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dolkar, P.; Xiao, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Wang, L. Assessment of ecological conservation effect in Xishui county based on gross ecosystem product. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020 , 40 , 499–509. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhao, N.; Wang, H.; Zhong, J.; Bai, Y.; Yi, S. Evaluation of the Gross Ecosystem Product and Analysis of the Transformation Path of “Two Mountains” in Hulunbuir City, China. Land 2023 , 12 , 63. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dong, X.; Brown, M.T.; Pfahler, D.; Ingwersen, W.W.; Kang, M.; Jin, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhang, X.; Ulgiati, S. Carbon modeling and emergy evaluation of grassland management schemes in Inner Mongolia. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012 , 158 , 49–57. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wanga, C.; Lic, X.; Yua, H.; Wang, Y. Tracing the spatial variation and value change of ecosystem services in Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2019 , 96 , 270–277. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, Q.; Liu, G.; Giannetti, B.F.; Agostinho, F.; Almeida, C.M.V.B.; Casazza, M. Emergy-based ecosystem services valuation and classification management applied to China’s grasslands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020 , 42 , 101073. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Dong, X.B.; Yu, B.H.; Brown, M.T.; Zhang, Y.S.; Kang, M.Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.S.; Ulgiati, S. Environmental and economic consequences of the overexploitation of natural capital and ecosystem services in Xilinguole League, China. Energy Policy 2014 , 67 , 767–780. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tindale, S.; Vicario-Modroño, V.; Gallardo-Cobos, R.; Hunter, E.; Miškolci, S.; Price, P.N.; Sánchez-Zamora, P.; Sonnevelt, M.; Ojo, M.; McInnes, K.; et al. Citizen perceptions and values associated with ecosystem services from European grassland landscapes. Land Use Policy 2023 , 127 , 106574. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cebrián-Piqueras, M.A.; Karrasch, L.; Kleyer, M. Coupling stakeholder assessments of ecosystem services with biophysical ecosystem properties reveals importance of social contexts. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017 , 23 , 108–115. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sigwela, A.; Elbakidze, M.; Powell, M.; Angelstam, P. Defining core areas of ecological infrastructure to secure rural livelihoods in South Africa. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017 , 27 , 272–280. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shi, Q.; Chen, H.; Liang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D. Cultural ecosystem services valuation and its multilevel drivers: A case study of Gaoqu Township in Shaanxi Province, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020 , 41 , 101052. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, C. Estimation of the Value of Ecosystem Carbon Sequestration Services under Different Scenarios in the Central China (the Qinling-Daba Mountain Area). Sustainability 2020 , 12 , 337. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Peacock, R.; Bently, M.A.; Rees, P.; Blignaut, J.N. The benefits of ecological restoration exceed its cost in South Africa: An evidence-based approach. Ecosyst. Serv. 2023 , 61 , 101528. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zang, Z.; Zou, X.Q. Connotation characterization and evaluation of ecological well-being based on ecosystem service theory. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao 2016 , 27 , 1085–1094. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Durán, M.; Canals, R.M.; Sáez, J.L.; Ferrer, V.; Lera-López, F. Disruption of traditional land use regimes causes an economic loss of provisioning services in high-mountain grasslands. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020 , 46 , 101200. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pei, S.; Xie, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Chen, L. Dynamic Changes of Water Conservation Service of Typical Ecosystems in China within a Year Based on Data from CERN. Sustainability 2015 , 7 , 16513–16531. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, C.; Xu, C.; He, L.; Wang, S.T.; Chen, Y.H.; Xu, H. Purification function of coastal-terrestrial ecosystems and its evaluation: A case study of Huanghua City. J. Ecol. Rural. Environ. 2015 , 31 , 506–513. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Raviv, O.; Zemah-Shamir, S.; Izhaki, I.; Lotan, A. The effect of wildfire and land-cover changes on the economic value of ecosystem services in Mount Carmel Biosphere Reserve, Israel. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021 , 49 , 101291. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Brandão, M. Chapter 16: A Life Cycle Approach for Assessing the Impacts of Land-Use Systems on the Economy and Environment: Climate Change, Ecosystem Services, and Biodiversity. In Life Cycle Assessment ; World Scientific: Singapore, 2022; pp. 285–298. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sallustio, L.; Quatrini, V.; Geneletti, D.; Corona, P.; Marchetti, M. Assessing land take by urban development and its impact on carbon storage: Findings from two case studies in Italy. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2015 , 54 , 80–90. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Cai, Y.; Zhao, M.; Shi, Y.; Khan, I. Assessing restoration benefit of grassland ecosystem incorporating preference heterogeneity empirical data from Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Ecol. Indic. 2020 , 117 , 106705. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J. Identifying priority areas for biodiversity conservation based on Marxan and InVEST model. Landsc. Ecol. 2022 , 37 , 3043–3058. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xie, G.; Lu, C.; Xiao, Y. The Economic Evaluation of Grassland Ecosystem Services in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2003 , 21 , 50–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lipton, J.; Özdemiroglu, E.; LeJeune, K.; Peers, J. Resource equivalency methods in the European Union: A ‘toolkit’ for calculating environmental liability. In Equivalency Methods for Environmental Liability ; Lipton, J., Özdemiroğlu, E., Chapman, D., Peers, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ouyang, Z.Y.; Zhu, C.Q.; Yang, G.B.; Xu, W.H.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y. Gross ecosystem product: Concept, accounting framework and case study. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013 , 33 , 6747–6761. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Odum, H.T. Environmental Accounting: Emergy and Environmental Decision Making ; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Reid, W.V.; Mooney, H.A.; Cropper, A.; Capistrano, D.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chopra, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Hassan, R.; et al. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being-Synthesis: A Report of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment ; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Type of Grasslands | Description |
|---|---|
| Annual | The forage is established annually |
| Cultivated | The forage is established with domesticated species that receive periodic agricultural treatments |
| Permanent | With perennial or self-seeding annual forage species that may survive indefinitely or often due to limiting factors that prevent other uses (excessive slope, shallow soil depth, outcropping rockiness, stoniness) |
| Temporary | The vegetation is composed of annual, biennial, or perennial forage species kept for only a few years |
| Naturalized | The forage species are mainly introduced from other geographical places that have established themselves and have persisted for a long time in existing environmental and management conditions |
| Semi-natural | A managed ecosystem dominated by native or naturally occurring herbs and other herbaceous species |
| European Area | Grasslands Type | Main Functions Provided | Ecosystem Services Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden) | Natural | livestock production | Provisioning |
| Semi-natural | grazing maintaining biodiversity maintaining landscape | Provisioning Supporting | |
| Cultivated | winter fodder milk in summer | Provisioning | |
| Temperate regions (such as Ireland, the UK, France, the Benelux, Germany, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Poland) | Permanent | feed production maintaining biodiversity soil erosion control | Provisioning Supporting Regulating |
| Temporary | feed production maintaining biodiversity | Provisioning Supporting | |
| Mediterranean basin | Natural/ Semi-natural | livestock production soil erosion control carbon sequestration biodiversity conservation maintaining landscape | Multiple |
| Source Title | Number of Documents | % of Documents |
|---|---|---|
| Ecological indicators | 176 | 4% |
| Shengtai xuebao | 175 | 4% |
| Science of the total environment | 138 | 3% |
| Sustainability Switzerland | 131 | 3% |
| Land | 115 | 2% |
| Agriculture ecosystems and environment | 110 | 2% |
| Journal of Environmental Management | 95 | 2% |
| Remote sensing | 71 | 2% |
| Plos one | 70 | 2% |
| Journal of Applied Ecology | 65 | 1% |
| Total of the top ten journals | 1146 | 25% |
| Number of documents published in journals | 4304 | 93% |
| Number of documents related to grassland ESs | 4608 | 100% |
| Title of the Top Ten Cited Manuscripts | Journal’s Name | Year of Publication | Number of Citations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments [ ] | Nature | 2001 | 2242 |
| Quantifying the evidence for biodiversity effects on ecosystem functioning and services [ ] | Ecology letters | 2006 | 2006 |
| Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment [ ] | Nature | 2006 | 1611 |
| Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality [ ] | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. | 2014 | 1495 |
| Confronting a biome crisis: Global disparities of habitat loss and protection [ ] | Ecology letters | 2004 | 1321 |
| Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems [ ] | Nature Communications | 2016 | 1306 |
| Incorporating plant functional diversity effects in ecosystem service assessments [ ] | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. | 2007 | 1250 |
| Improvements in ecosystem services from investments in natural capital [ ] | Science | 2016 | 1228 |
| High plant diversity is needed to maintain ecosystem services [ ] | Nature | 2011 | 1150 |
| Ecological and socioeconomic effects of China’s policies for ecosystem services [ ] | Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. | 2008 | 1125 |
| Methodologies | Number of Documents | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ecosystem Service Value (ESV) Assessment | 91 | [ , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ] * |
| Resource Equivalency Approach | 22 | [ , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ] |
| Econometric Models | 11 | [ , , , , , , , , , ] |
| Benefit Transfer Method | 7 | [ , , , , , , ] |
| Contingent Valuation Method (CVM) | 7 | [ , , , , , , ] |
| Gross Ecosystem Product (GEP) | 4 | [ , , , ] |
| Emergy Value Method | 4 | [ , , ] |
| Focus Groups, Perception/Social Preference Method | 4 | [ , , , ] |
| Net Present Value | 3 | [ , , ] |
| Replacement Cost Method | 3 | [ , , , ] |
| Market and Shadow Price Method | 2 | [ , ] |
| Life Cycle Assessment Approach | 1 | [ ] |
| Social Cost | 1 | [ ] |
| Theory of Value and Random Utility | 1 | [ ] |
| Cost–Benefit Analysis | 1 | [ ] |
| Type of Data | Number of Documents |
|---|---|
| Land use/cover change (LUCC) | 60 |
| Data from structured and semi-structured interviews (SSIs) | 22 |
| Land cover data, net primary productivity, precipitation, and soil erosion data (LNPS) | 21 |
| Multi-source data (MS) | 14 |
| Bio-economic modeling approach (BEM) | 12 |
| Data from others research (R) | 12 |
| Land use data and socio-economic data (LSE) | 9 |
| LUCC, climatic, socioeconomic, and biophysical data (LCSEB) | 7 |
| Socio-economic data (SE) | 4 |
| Total | 161 |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Pergola, M.; De Falco, E.; Cerrato, M. Grassland Ecosystem Services: Their Economic Evaluation through a Systematic Review. Land 2024 , 13 , 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081143
Pergola M, De Falco E, Cerrato M. Grassland Ecosystem Services: Their Economic Evaluation through a Systematic Review. Land . 2024; 13(8):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081143
Pergola, Maria, Enrica De Falco, and Michele Cerrato. 2024. "Grassland Ecosystem Services: Their Economic Evaluation through a Systematic Review" Land 13, no. 8: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/land13081143
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers. 5. Write a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction.
As we've discussed, all introductions begin broadly. The audience, format, and purpose of your paper influence how broad it should be. You can expect more background knowledge from readers of a technical journal than you can from readers of a popular magazine. Use a 'hook' to capture readers' interest.
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
After you've done some extra polishing, I suggest a simple test for the introductory section. As an experiment, chop off the first few paragraphs. Let the paper begin on, say, paragraph 2 or even page 2. If you don't lose much, or actually gain in clarity and pace, then you've got a problem. There are two solutions.
Step 2: Develop a structure and outline. With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it's time to move on to planning your actual research paper. It might sound obvious, but it's really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper.
Below is a step-by-step guide to starting and completing your research paper. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. 1. Choose your topic. Choose a topic that interests you. Writing your research paper will be so much more pleasant with a topic that you actually want to know more about.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research. To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery.
Step 4: Create a Research Paper Outline. Outlining is a key part of crafting an effective essay. Your research paper outline should include a rough introduction to the topic, a thesis statement, supporting details for each main idea, and a brief conclusion. You can outline in whatever way feels most comfortable for you.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts. You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on - diving into the results.
3. Research your topic. Once you've settled on a topic your next in how to write a research paper is, to begin the preliminary research. You can take a deeper dive into some sources you examined while choosing your topic. Look for data and evidence that answer the questions you developed in step 2.
Writing a Research Paper. This page lists some of the stages involved in writing a library-based research paper. Although this list suggests that there is a simple, linear process to writing such a paper, the actual process of writing a research paper is often a messy and recursive one, so please use this outline as a flexible guide.
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
Writing Your Paper. Parts of the Research Paper. Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea, and indicate how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the ...
Follow these points to create an outline of the research: Identify the main points: These are the arguments or topics that are crucial to your research. List them in the order you plan to address them. Keep solid sub-points and supporting evidence: For each main point, jot down sub-points or examples that support it.
1. Research Paper Title. A research paper title is read first, and read the most. The title serves two purposes: informing readers and attracting attention. Therefore, your research paper title should be clear, descriptive, and concise. If you can, avoid technical jargon and abbreviations.
Begin a new paragraph for each main idea. Remember to integrate the research you have found and acknowledge ideas and information you have learned with in-text citations. A research paper is not an essay, in other words, this is not about your opinions. Do not use first person nouns such as "I" or "my." If you have developed new interpretations ...
Conduct a thorough literature review. Formulate a research statement. Create a strong research paper outline. Begin working on the first draft. Writing a compelling Introduction. Spend time on your Abstract and Title. Wrap up with a well-rounded Conclusion. Align with the target journal guidelines.
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research. There are often many possible paths you can take to answering ...
The key distinctions are: A theory predicts events in a broad, general context; a hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a specified set of circumstances. A theory has been extensively tested and is generally accepted among scholars; a hypothesis is a speculative guess that has yet to be tested. Hypothesis Example.
DALL·E 2 began as a research project and is now available in beta. Safety mitigations we have developed and continue to improve upon include: Preventing harmful generations We've limited the ability for DALL·E 2 to generate violent, hate, or adult images.
Research projects, initiatives and conferences that include patients as partners rather than as participants are becoming more common. Including patients as partners (what we will call 'patient partners') is an approach called patient engagement or involvement in research, and we will call it patient engagement throughout this paper. Patient engagement moves traditional health research ...
Grasslands provide a wide range of provision, support, regulation, and cultural ecosystem services (ESs), whose valuation methods can be grouped into three categories (ecological, sociocultural, and economic). The present manuscript aims to provide an overview of academic studies on grassland ESs and of the most used economic evaluation methods. To this end, a systematic and bibliometric ...