- Validity of the Marketing Mix Model Words: 15103
- Service Marketing and Product Marketing Definition Words: 691
- Overview of the World of the Marketing Words: 585
- The 7P Marketing Mix for Customers Words: 550
- Service and Product Marketing Words: 597
- Apple Company’s Innovations and Marketing Mix Words: 667
- Managing the Marketing Environment Words: 743
- Wal-Mart Business Strategy and Marketing Mix Words: 1686
- The 7Ps Marketing Model Evaluation Words: 1511
- Product Portfolio Management for Marketing Words: 2960
- The Wilson Company’s Marketing Mix Words: 1164

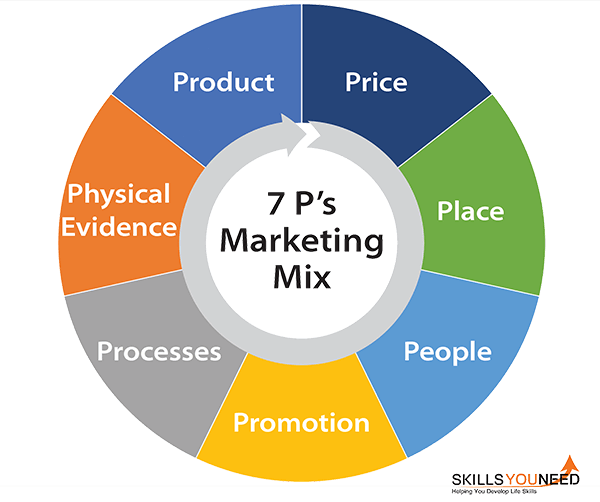
7Ps of the Marketing Mix
A marketing strategy is a company’s battle plan in the struggle of market competition. However, its task is in effect to outline the way the company plans to act in the market, which is made in a general way. To realize the marketing strategy, a company develops a marketing mix, which is a set of marketing tools used to influence the demand for the product (Kotler et al 2008, p.49). The first formula of the marketing mix included four elements, so-called 4Ps, which were: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Gradually the notion of the marketing mix has been extended to 7Ps by adding such elements as Processes, Physical Evidence, ad People (Schneider & Bowen 1998, p. 213).
Product is a service produced by the company; it can be tangible or intangible, produced on a large scale or individually. Each product has its life cycle, which includes the stages of development, introduction, growth, maturity, and decline (Kurtz, MacKenzie & Snow 2009, p.341). Each of the stages requires specific marketing decisions. Another important point is a product’s competitive advantage, which also defines the product’s marketing: it helps to expand the company’s market segment and to increase the price.
Price is not simply the cost of the product for the buyer; it is a point of communication between the producer and the customer. Price defines the product’s position in the market, informing the client about its quality and originality. Depending on a good’s parameters and the life cycle stage, different pricing strategies can be used (Bangs 2002, p. 72): premium pricing (high quality or unique products), penetration pricing (lowering the price when entering the market), economy pricing, and price skimming (the product is new or has a strong competitive advantage). There are also some alternative approaches, such as psychological pricing ($99 instead of $100), optional product pricing (setting price for the additional services), etc (Armstrong et al 2009, p. 328).
The element of Place outlines the approach of the product’s distribution and includes the distribution chain which delivers the product from the manufacturer to the customer (Kotler et al 2008, p. 50). The product can be sold directly to the customer or the dealer; the shop can be physical or virtual. The place is defined according to the peculiarities of the product sold.
Promotion is a set of tools that help to communicate to the client, which is to attract his attention, provide information about the product, and stimulate the decision to buy. The company can use such tools as direct selling, personal selling, public relations, advertising, sponsorship, etc. As a rule, they are used in complex (p.51).
Schneider and Bowen emphasize the meaning of the last 3Ps: these factors help to overgrow the marketing of products and services and embrace marketing of the whole organization with its attributes, such as people, tangibles, etc. (1998, p. 213).
The component of People includes the company’s staff with its skills and knowledge. The staff which has appropriate interpersonal skills and attitude to the work, as well as the professional competence, creates an additional competitive advantage, becoming a face of the company.
Processes also make the company competitive, increasing the customers’ loyalty. They include efficient service delivery which meets the needs and requirements of the clients, for ex., preparing a burger the way a client wants (Strydom 2005, p. 196).
Physical Evidence implies taking care of the services’ performance which influences the judgments about the company. Providing a clean environment of the restaurant or comfortable accommodation for the college students, as well as the website and brochures about the company’s service or a logo at the ticket, are examples of this element (Strydom 2004, p. 197).
Some attempts to extend 7Ps to 9Ps take place (Dacko 2008, p. 335); however, the additional elements are disputable: for example, Packaging can be considered a separate element or be included in the category of the Product, and Professionalism can be combined with People.
- Armstrong, G et al 2009, Marketing: an introduction. Harlow, England, Financial Times Prentice Hall.
- Bangs, DH 2002, The market planning guide: creating a plan to successfully market your business, product, or service. Chicago, Dearborn Trade Pub.
- Dacko, SG 2008, The advanced dictionary of marketing: putting theory to use. Oxford; New York, Oxford University Press.
- Kotler, P et al 2008, Principles of marketing. Upper Saddle River, N.J., Pearson Prentice Hall.
- Kurtz, DL, MacKenzie, HF & Snow, K 2009, Contemporary marketing. Toronto, Nelson Education.
- Schneider, B & Bowen, DE 1998, Winning the service game. Boston, Mass., Harvard Business School Press.
- Strydom, J 2004, Introduction to marketing. Lansdowne, Cape Town, S.A., Juta.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, November 26). 7Ps of the Marketing Mix. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/
"7Ps of the Marketing Mix." StudyCorgi , 26 Nov. 2021, studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '7Ps of the Marketing Mix'. 26 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "7Ps of the Marketing Mix." November 26, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "7Ps of the Marketing Mix." November 26, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "7Ps of the Marketing Mix." November 26, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/7ps-of-the-marketing-mix/.
This paper, “7Ps of the Marketing Mix”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 26, 2021 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

- Digital Marketing Strategy and Planning
- Content Marketing
- Digital Experience Management (Desktop/mobile website)
- Email Marketing
- Google Analytics
- Marketing Campaign Planning
- Search Engine Optimisation (SEO)
- Social Media Marketing
- Agency growth
- Business-to-Business
- Charity and Not-for-profit
- E-commerce / Retail
- Managing Digital Teams
- Managing Digital Branding
- Managing Digital Transformation
- Managing Lifecycle Marketing
- Managing International Marketing
- Startup and Small Businesses
How to use the 7Ps Marketing Mix
What is the 7Ps Marketing Mix and how should it be used?
The marketing mix is a familiar marketing strategy tool, which as you will probably know, was traditionally limited to the core 4Ps of Product, Price, Place and Promotion. It is one of the top 3 classic marketing models according to a poll on Smart Insights.
It's an essential part of a marketing plan structure that defines the tactics to be used to implement the marketing strategy.
The traditional 7Ps of marketing consist of:
- Physical evidence

Free marketing plan template
Download for recommendations on how to structure different types of marketing plans including marketing plans, campaign plans and digital plans. Join Smart Insights as a Free Member to download our marketing plan template today
Access the How to structure different types of marketing plans
Who created the 7Ps marketing mix model?
The 7Ps marketing model was originally devised by E. Jerome McCarthy and published in 1960 in his book Basic Marketing. A Managerial Approach.
We've created the graphic below so you can see the key elements of the 7Ps marketing mix. More details are provided in the next visual.
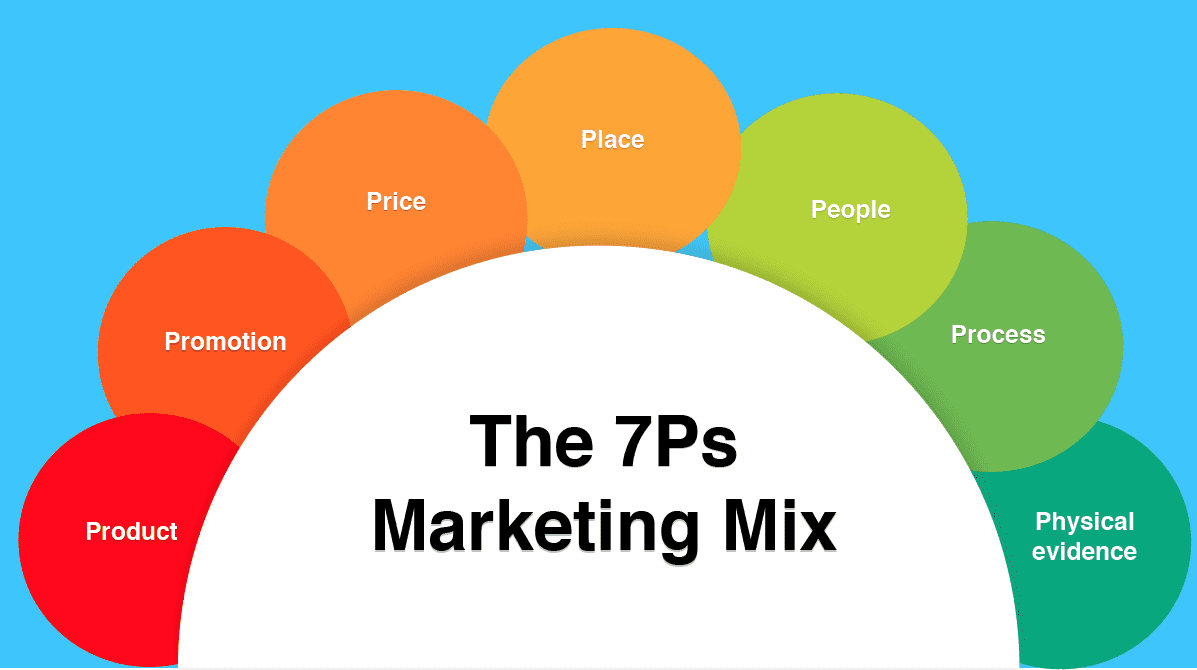
The 4Ps vs The 7Ps
The 4Ps marketing mix was designed at a time when businesses were more likely to sell products, rather than services. The 4 Ps represented an early focus on product marketing, when the role of customer service in helping brand development wasn't so well known.
Over time, Booms and Pitner added three extended ‘service mix P’s' : Participants or People, Physical evidence, and Processes. Later 'Participants' was renamed as 'People' - the marketing mix covering marketers, customer service reps, recruitment, culture, training and remuneration.
Today, it's recommended that the full 7 elements of the marketing mix are considered when reviewing competitive strategies - across product, customer service and more.
The 7Ps helps companies to review and define key issues that affect the marketing of its products and services. A popular marketing model, the marketing mix is can also be referred to as the 7Ps framework for the digital marketing mix.
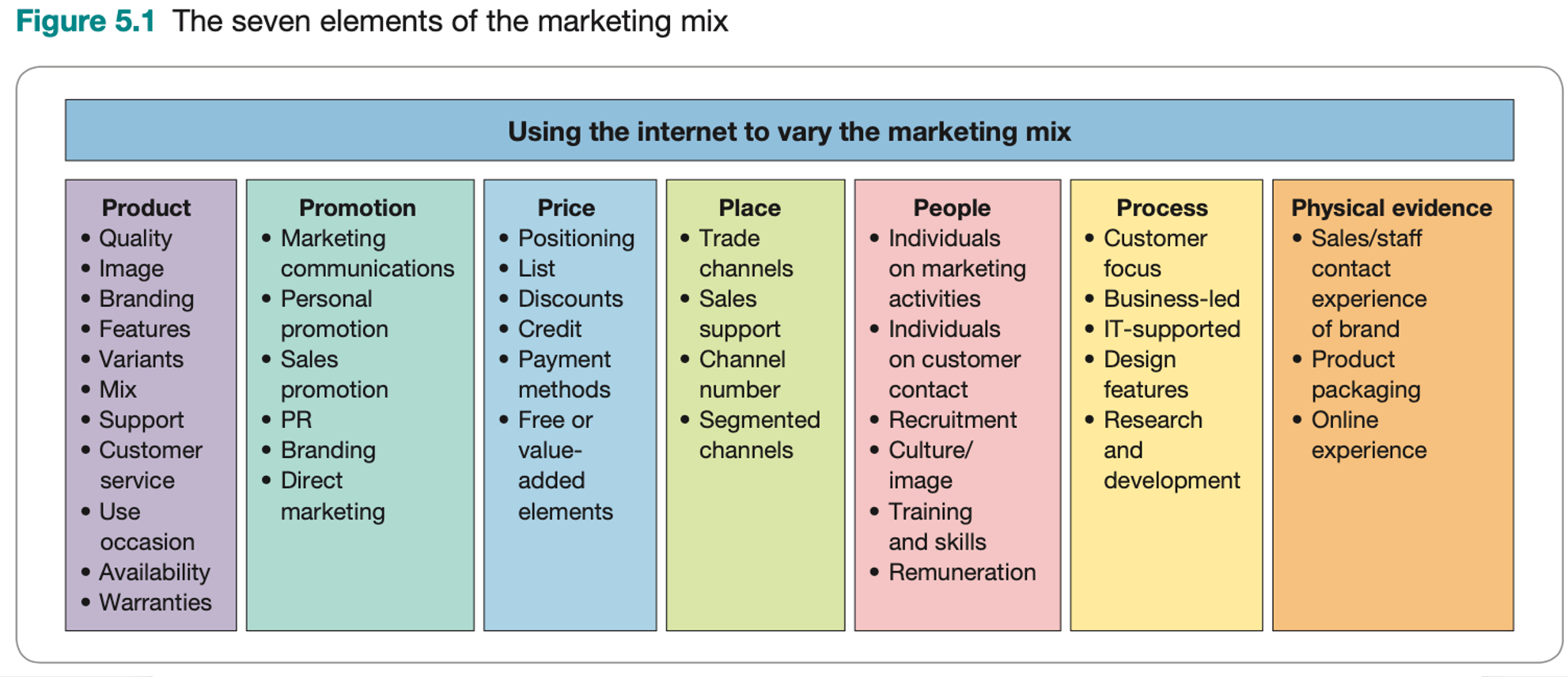
In Dave Chaffey's book: Digital Marketing: Strategy, Implementation and Practice , this model was refreshed and applied to online channels to give a practical approach which works well for multichannel businesses. An eighth P, ‘Partners’ is often recommended for businesses to gain reach online (first mentioned in Digital mMarketing Excellence by Dave Chaffey and PR Smith although some would argue it's part of Place).
How can I use this marketing model?
Although it's sometimes viewed as dated, we believe the 4Ps are an essential strategy tool to select their scope and is particularly useful for small businesses. For startups reviewing price and revenue models today, using the Business Model Canvas for marketing strategy is a great alternative since it gives you a good structure to follow.
Companies can also use the 7Ps model to set objectives, conduct a SWOT analysis and undertake competitive analysis. It's a practical framework to evaluate an existing business and work through appropriate approaches whilst evaluating the marketing mix elements.
What are the 7Ps of marketing?
- Products/Services: How can you develop your products or services
- Prices/Fees: How can we change our pricing model
- Place/Access: What new distribution options are there for customers to experience our product, e.g. online, in-store, mobile etc
- Promotion: How can we add to or substitute the combination within paid, owned and earned media channels
- Physical Evidence: How we reassure our customers, e.g. impressive buildings, well-trained staff, great website
- Processes: Are there internal process barriers in the way to delivering the best customer value
- People: Who are our people and are there skills gaps
- Partners: Are we seeking new partners and managing existing partners well?
An example of a company using the 7Ps marketing mix in their strategy
Take a look at HubSpot as an example, which was founded in 2006; Hubspot now boasts over 86,000 total customers in more than 120 countries. Comprised of Marketing Hub, Sales Hub, Service Hub, CMS Hub, and a powerful free CRM, HubSpot adds value for customers in every aspect of the 7Ps.
What does an example of a successful marketing mix look like?
This is a top-level overview; you would take this into greater detail and ask the following questions:
1. Products/Services: Integrated toolset for SEO, blogging, social media, website, email and lead intelligence tools.
2. Prices/Fees: Subscription-based monthly, Software-As-Service model based on number of contacts in database and number of users of the service.
3. Place/Access: Online! Network of Partners, Country User Groups.
4. Promotion: Directors speak at events, webinars, useful guides that are amplified by SEO. Social media advertising, e.g. LinkedIn.
5. Physical Evidence: Consistent branding across communications.
6. Processes: More sales staff are now involved in conversion.
7: People : Investment in online services.
8. Partners: Hubspot looks to form partnerships with major media companies such as Facebook and Google plus local partners including Smart Insights who it is collaborating with on research in Europe.
What to watch for
When using the 7Ps as a model to conduct a marketing audit, I look at each of the Ps. It’s unwise to ignore an area unless it is completely outside your control.
We are now seeing AI and machine learning techniques informing more developed Marketing Mix Modeling techniques such as regression and forecasting. Note that this is different to the different elements of the marketing mix described in this article and focuses more on the mix of budget investment in different media.
9Ps of marketing?
As the scope of marketing continues to develop, so does the marketing mix. Since 2007, Larry Londre's 9Ps of marketing has included:
- Planning, Process or Marketing Process
- People/Prospects/Potential Purchasers/Purchasers (Target Market)
- Price/Pricing
- Place/Distribution
- Partners/Strategic Alliances
- Presentation
Original References and sources of 7Ps marketing mix
Bitner, M. J. and Booms, H. (1981). Marketing Strategies and Organization: Structure for Service Firms. In Donnelly, J. H. and George, W. R. (Eds). Marketing of Services, Conference Proceeding s. Chicago, IL. American Marketing Association. p. 47- 52.
McCarthy, E. J. (1964). Basic Marketing . Richard D. Irwin. Homewood, IL.

Free essential marketing models
Our free guide details 15 classic planning tools to help you use data and analysis to develop your marketing strategy.
Access the Essential marketing models for business growth
By Annmarie Hanlon
Annmarie Hanlon PhD is an academic and practitioner in strategic digital marketing and the application of social media for business. Dr Hanlon has expertise in the strategic application of social media for business and the move from digitization, to digitalization and digital transformation for business. Her expertise spans consumer touch points, online customer service, the use of reviews, the role of influencers, online engagement and digital content. You can follow her update on Twitter https://twitter.com/annmariehanlon
This blog post has been tagged with:
Turbocharge your results with this toolkit containing 7 resources
- Marketing campaign plan template
- Campaign timeline/project plan template and example
- Editorial calendar spreadsheet
- View the Toolkit
The Marketing Campaign Planning toolkit contains:

FREE marketing planning templates
Start your Digital Marketing Plan today with our Free membership.
- FREE practical guides to review your approach
- FREE digital marketing plan templates
- FREE alerts on the latest developments
Solutions to your marketing challenges
- Digital Transformation
- Email Marketing and Marketing Automation
- Managing Digital Marketing Teams
- Marketing Strategy and Planning
- Multichannel lifecycle marketing
Expert advice by sector
- Business-to-Business (B2B)
- Charity and Not-For-Profit
- E-commerce and Retail
- Sector Technology Innovation
- Startups and Small Businesses
Improve your digital marketing skills with our FREE guides and templates

Join the Conversation
Recommended Blog Posts
Free 3-page marketing plan template for a small business
Use our simple, 15 section download to quickly create a marketing plan for your business Many marketing plan templates you will find online were created long ago for larger businesses and aren’t so relevant to small and startup business competing …..
How to create a marketing plan in 2024
A Marketing Plan is a bit like a job description for your company. Everyone should have one, but they’re often not fit for purpose, out of date and reviewed infrequently… Research has shown that businesses with plans succeed…
How to structure an effective marketing plan in 15 sections
Using the RACE OSA process to structure a marketing plan A marketing plan is an essential tool to compete and grow your business since it gives focus to your marketing activities by setting realistic, achievable priorities within your budget. It …..

The Marketing Mix: The 7 Ps
The 7 Ps of the marketing mix (product, price, place, promotion, people, process and physical evidence) provide a helpful checklist to evaluate a product or service by ensuring that the critical areas of a value proposition are considered for the target market.

MBA Management Models
In modern competitive markets, potential customers have a wealth of options. This abundance of choice means that it is imperative that marketers identify appropriate market segments and provide attractive offerings that meet their needs. Once market segmentation has taken place, and a target is selected, attention must be paid to a wide range of aspects that influence the buying decision of customers. The marketing mix is a list of considerations to be taken into account when launching a new product or service into a market segment. The 7 Ps are:
- Product/service - what product features will users be attracted to?
- Price - how much will our target customers be prepared to pay?
- Place - where would our target customers go to purchase the product?
- Promotion - how will we let our target customers know about the product?
- People - how can other people help facilitate the sale?
- Process - what processes will be needed to satisfy customer demand?
- Physical evidence - how will our target customers experience the product?
All components must be evaluated against the target market and brand positioning to ensure that the offering satisfies the target market.

The concept of the 'marketing mix' originates from a 1964 article by Harvard Business School professor Neil Borden in the Journal of Advertising Research (see Further reading ). In his article, Borden stated that:
"Marketing is still an art, and the marketing manager, as head chef, must creatively marshal all his marketing activities to advance the short and long term interests of his firm."
Borden identified the vital role that market segmentation plays in ensuring that all aspects of the product or service directly address the needs of a well-defined and specific target customer group.
In 1964, E. Jerome McCarthy categorised the original 4 Ps of the marketing mix, product/service, price, place and promotion, based on Borden's earlier work.
Given the complexity of modern markets and societal needs, Philip Kotler (see Further reading ) added an additional three components, people, process and physical evidence, to create the 7 Ps of the marketing mix that is in common usage today.
When to use it
- To evaluate the brand positioning of a new product or service to ensure it meets the target market's needs.
- To appraise the current marketing strategy and identify areas for enhancement.
- To conduct competitor analysis.
How to use it
Begin by identifying the product or service that you want to examine and then reflect on each of the 7 Ps of the marketing mix for the customer segment being targeted. Ensure that each area is thoroughly inspected, ignoring only elements that are entirely outside your control.
The following sections provide a guide to help you define the questions you need to answer for each of the 7 Ps for your particular scenario by providing examples:
Product/Service
- What problem or issue does the product solve for customers within the target market segment?
- What makes this product the best solution for people with this problem or issue?
- Which product attributes are most important to the target market - quality, price, convenience, brand affiliation?
- How is your product different to your competitors?
- How does your product negate the unique selling points of competitors?
- Why would customers choose a competitors product/service over yours?
- What features of the product will be most attractive to customers?
- What about the packaging will help to attract customers?
- What range of colours and sizes will you offer?
- How will you deal with warranties, services, repairs and returns?
- What is the value of the product or service to a potential customer within the target market segment?
- What would customers in your target segment be prepared to pay for the product?
- How price-sensitive are the customers within your target market?
- How does your pricing compare to competitors?
- Are subscriptions, memberships or extended warranties appropriate?
- What is your pricing strategy for repairs, maintenance and servicing?
- Will you offer discounted prices at launch or at any other time? What about for existing customer upgrades, bulk purchases or trade customers?
- Will you provide credit terms or other customer finance options?
- How will you deal with elapsed subscriptions or failed payments?
- Where would your target customers usually go to purchase the product?
- What distribution channels will you target - online, retail, wholesale?
- How are your competitors distributing their products?
- Do you have appropriate supply networks in place?
- Where are customers within your target market segment most likely to see or hear your promotional messages - websites, social media, magazines, direct mail, billboards, television, radio, podcasts, email?
- What are the main messaging points and tone-of-voice for marketing?
- What advertising, direct marketing and in-store activities will be required?
- How can you leverage digital marketing - online events, social media, pay-per-click advertising, sponsorship?
- How can you inspire word-of-mouth and other forms of free advertising? Can you utilise social media to accomplish this?
- When is the best time to promote the product? Is there any seasonality in the market?
- How will customers interact with sales and customer service team members?
- How can you provide a range of ways for customers to speak with staff members at their own convenience?
- What training will be required by sales and customer service teams?
- How can you encourage customer referrals?
- How will you manage online reviews and other forms of feedback?
- How will you deal with service failure?
- What touch-points will you set up with customers during the sales process and lifetime of your product or service?
- How can you ensure an efficient and reliable delivery experience for the customer?
- How will the delivery experience match up with your brand reputation and corporate social responsibility?
- What processes will you need to put in place to provide excellent customer service for the lifetime of the product?
- How will you deal with spikes in demand?
- Are self-service technologies appropriate?
- How will you manage service variability?
- How will you manage complaints, returns and refunds?
Physical evidence
- How will you manage the sensory experience for the customer - touch, taste, smell, sound and sight - in-store, online and through other media?
- What retail point-of-sale assets will be required?
- How will the packaging complement your existing branded products?
- Do you have sufficient and appropriate digital marketing assets available?
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What should i do if i don't know all the information required for each of the 7 ps of the marketing mix.
Although tempting, avoid basing your answers on untested assumptions. Keep strictly to verified facts and seek out that information if it is not currently available to you.
Can I compare with competitors in different market segments?
When comparing your product with the competition, be sure to consider not only the type of product but also the market segment that they are targeting. The optimal marketing and distribution channels can vary significantly for even slight variations in the target market. This is particularly true for segments where age or relative wealth is a factor.
How often should the marketing mix be reviewed?
Review the marketing mix regularly to account for changes in your product or service and those of your competitors and for changing market conditions. Triggers for a review of your marketing mix may include:
- a new competitor or product entering the market
- a change to an existing competitor product
- in response to new marketing campaigns by competitors
- the introduction of a new product, or a significant change to an existing product, by your company
- if 12-months have passed since the last review
Further reading
Borden, N. H. (1964) The Concept of the Marketing Mix. Journal of Advertising Research. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. Available from https://motamem.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/07/Borden-1984_The-concept-of-marketing-mix.pdf [accessed 30 August 2021].
Kotler, P., Keller, K. L., Brady, M., Goodman, M. and Hansen, T. (2019) Marketing Management, 4th European edition. Harlow, UK: Pearson Education.
McCarthy, E. J. (1964) Basic Marketing: A managerial approach. Homewood, IL: Irwin.
Some of the links to products provided in this article are affiliate links. This means that the supplier may pay the owner of this website a small amount of money for purchases made via the link. This will have absolutely no impact on the amount you pay.
Sign up for more like this.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- United Kingdom
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
7 Ps of Marketing and How They Apply to Your Marketing Mix Looking for picture perfect marketing formulas that will likely outlast and adapt to any trend? Read on.
By Brian Tracy Apr 26, 2023
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
No matter what industry your business operates in, there is competition to outperform and ever-evolving trends to keep up with.
You must find a way to get your business to stand out. Whether you are trying to build a name for your business or maintain its stature, marketing is the key to getting people's attention and showing them what you can do.
Marketing strategies are roadmaps that allow your company to grow brand awareness and boost consumer engagement, relationships, and trust. It takes time, effort, and sometimes budget to build a marketing plan; however, it can pay huge dividends.
Once you've developed your marketing strategy, there is a "Seven P Formula" you should use to continually evaluate and reevaluate your business activities. The formula can help you create a system of checks and balances for physical evidence that your business is constantly evolving to ensure your marketing efforts reach your target audience .
With technology as an ever-evolving factor, updating your marketing campaigns to include more than just word of mouth is essential. Nowadays, you can use many distribution channels, like digital marketing, social media, and podcasts.
No matter which platforms you choose as your marketing tools, the seven Ps can serve as tried and true basic marketing tactics that you can adapt into your marketing efforts to best fit your business.
The 7 Ps of Marketing include:
- Positioning
Read on to learn more about the 7 Ps.
To begin with, develop the habit of looking at your product as though you were an outside marketing consultant brought in to help your company decide whether or not it's in the right business at this time. Ask critical questions such as, "Is your current product or service, or mix of products and services, appropriate and suitable for the market and the customers of today? Is this product offering any remedy to a customer's pain point?"
Whenever you're having difficulty selling as much of your products or services as you'd like, you need to develop the habit of assessing your business honestly and asking, "Are these the right products or services for our customers today?"
Is there any product or service you're offering today that, knowing what you now know, you would not bring out again today? Compared to your competitors, is your product or service superior in some significant way to anything else available? If so, what is it? If not, could you develop an area of superiority? Should you be offering this product or service at all in the current marketplace?
The second P in the formula is price. Develop the habit of continually examining and reexamining the pricing strategy of the products and services you sell to make sure they're still appropriate to the realities of the current market. Sometimes you need to lower your prices. At other times, it may be appropriate to raise your prices.
And other times, you need to research the competition to see what similar products in your industry space are going for, to ensure you are listing competitive pricing. Many companies have found that the profitability of certain new products or services doesn't justify the amount of effort and resources that go into producing them. By raising their prices, they may lose a percentage of their customers, but the remaining percentage generates a profit on every sale. Could this be appropriate for you?
Sometimes you need to change your terms and conditions of sale. Sometimes, by spreading your price over a series of months or years, you can sell far more than you are today, and the interest you can charge will more than make up for the delay in cash receipts. Sometimes you can combine products and services together with special offers and special promotions. Sometimes you can include free additional items that cost you very little to produce but make your product prices appear far more attractive to your customers.
In business, as in nature, whenever you experience resistance or frustration in any part of your sales or marketing plan, be open to revisiting that area. Be open to the possibility that your current pricing structure is not ideal for the current market. Be open to the need to revise your prices, if necessary, to remain competitive, to survive and thrive in a fast-changing marketplace.
Related: How to Create a Marketing Plan - Entrepreneur.com
3. Promotion
The third habit in marketing and sales is to think in terms of promotion all the time. Promotion includes all the ways you tell your target market about your products or services and how you then market and sell to them.
Small changes in the way you promote and sell your products based on segmentation can lead to dramatic changes and booms in your results. Even small changes in your advertising can lead immediately to higher sales. Experienced copywriters can often increase the response rate from advertising by 500 percent by simply changing the headline on an advertisement.
Large and small companies in every industry continually experiment with different ways of advertising, promoting, and selling their products and services. Right now? Search Engine Optimization (SEO) , is meant to improve the quality and quantity of traffic to a website.
But no matter what the favored method of the time, there is one tried and true rule. Whatever method of marketing and sales you're using today will, sooner or later, stop working. Sometimes it will stop working for reasons you know, and sometimes it will be for reasons you don't know. In either case, your methods of marketing and sales will eventually stop working, and you'll have to develop new sales, marketing and advertising approaches, offerings, and strategies.
While many might guess that email marketing and Facebook ads are today's most popular marketing activities, much of the market has already moved on to new methods.
The top five advertising techniques in 2022 include:
- Sound-free, short-form video ads.
- Advertising on mobile games.
- Machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- Collecting and advertising third-party data.
- LinkedIn and other social media platforms.
The fourth P in the extended marketing mix is the place where your product or service is actually sold. Develop the habit of reviewing and reflecting upon the exact physical location where the customer meets the salesperson. Sometimes a change in place can lead to a rapid increase in sales.
You can sell your product in many different places. Some companies use direct selling, sending their salespeople out to personally meet and talk with the prospect. Some sell by telemarketing. Some sell through catalogs or mail order. Some sell at trade shows or in retail establishments. Some sell in joint ventures with other similar products or services. Some companies use manufacturers' representatives or distributors. Many companies use a combination of one or more of these methods.
In each case, the entrepreneur must make the right choice about the very best location or place for the customer to receive essential buying information on the product or service needed to make a buying decision. What is yours? In what way should you change it? Where else could you offer your products or services?
5. Packaging
The fifth element of the marketing mix is the packaging. Develop the habit of standing back and looking at every visual element in the packaging of your physical product or service through the eyes of a critical prospect. Remember, people form their first impression about you within the first 30 seconds of seeing you or some element of your company. Small improvements in the packaging or external appearance of your product or service can often lead to completely different reactions from your customers.
With regard to the packaging of your company, your product or service, you should think in terms of everything customer experience —what they see from the first moment of contact with your company through the purchasing process. Consider branded packaging to make an impactful first impression.
If your customer begins experiencing your brand with an eye-catching design, they are more likely to remember that experience with fond associations. Including your business logo and social media handles is another great addition to custom packaging that can invite customers to engage with your brand and promote repeat interactions.
Packaging refers to the way your product or service appears from the outside. Packaging also refers to your people and how they dress and groom. It refers to your offices, your waiting rooms, your brochures, your correspondence and every single visual element about your company. Everything counts. Everything helps or hurts. Everything affects your customer's confidence about dealing with you.
When IBM started under the guidance of Thomas J. Watson, Sr., he very early concluded that fully 99 percent of the visual contact a customer would have with his company, at least initially, would be represented by IBM salespeople. Because IBM was selling relatively sophisticated high-tech equipment, Watson knew customers would have to have a high level of confidence in the credibility of the salesperson. He therefore instituted a dress and grooming code that became an inflexible set of rules and regulations within IBM.
As a result, every salesperson was required to look like a professional in every respect. Every element of their clothing-including dark suits, dark ties, white shirts, conservative hairstyles, shined shoes, clean fingernails-and every other feature gave off the message of professionalism and competence. One of the highest compliments a person could receive was, "You look like someone from IBM."
6. Positioning
The next P is positioning. You should develop the habit of thinking continually about how you are positioned in the hearts and minds of your customers. How do people think and talk about you when you're not present? How do people think and talk about your company? What positioning do you have in your market, in terms of the specific words people use when they describe you and your offerings to others?
In the famous book by Al Reis and Jack Trout, Positioning , the authors point out that how you are seen and thought about by your customers is the critical determinant of your success in a competitive marketplace. Attribution theory says that most customers think of you in terms of a single attribute, either positive or negative. Sometimes it's "service." Sometimes it's "excellence." Sometimes it's "quality engineering," as with Mercedes Benz. Sometimes it's "the ultimate driving machine," as with BMW. In every case, how deeply entrenched that attribute is in the minds of your customers and prospective customers determines how readily they'll buy your product or service and how much they'll pay.
Develop the habit of thinking about how you could improve your positioning. Begin by determining the position you'd like to have. If you could create the ideal impression in the hearts and minds of your customers, what would it be? What would you have to do in every customer interaction to get your customers to think and talk about in that specific way? What changes do you need to make in the way you interact with customers today in order to be seen as the very best choice for the customer needs of tomorrow?
The final P of the marketing mix is people. Develop the habit of thinking in terms of the people inside and outside of your business who are responsible for every element of your sales, marketing strategies, and activities.
It's amazing how many entrepreneurs and businesspeople will work extremely hard to think through every element of the marketing strategy and the marketing mix, and then pay little attention to the fact that every single decision and policy has to be carried out by a specific person, in a specific way. Your ability to select, recruit, hire and retain the proper people, with the skills and abilities to do the job you need to have done, is more important than everything else put together.
In his best-selling book, Good to Great , Jim Collins discovered the most important factor applied by the best companies was that they first of all "got the right people on the bus, and the wrong people off the bus." Once these companies had hired the right people, the second step was to "get the right people in the right seats on the bus."
To be successful in business, you must develop the habit of thinking in terms of exactly who is going to carry out each task and responsibility. In many cases, it's not possible to move forward until you can attract and put the right person into the right position. Many of the best business plans ever developed sit on shelves today because the [people who created them] could not find the key people who could execute those plans.
Excerpted from Million Dollar Habits
The Ps of marketing
Marketing is essential whether you run an eCommerce business, a physical store, a small business, or a large corporation. While trends may evolve, the 7Ps of marketing will likely remain true and evolve with any new trend.
Remember, as products, markets, customers and needs change rapidly, you must continually revisit the seven Ps marketing model to ensure you're on track and achieving the maximum results possible for you in today's marketplace.
Looking for more marketing resources? Explore Entrepreneur's Marketing Hub here to help grow your business .
Chairman and CEO of Brian Tracy International, Speaker and Author
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Nick Offerman's Side Hustle as an Actor Helps Fund the Business He Started 23 Years Ago — and Still Works at Every Day
- Lock 8 Evening Routines With Surprising Effects on Your Ability to Get Things Done
- His Ex-Boss Issued Him a Cease-and-Desist Order . Neither Man Expected What Happened in a Parking Lot Next: 'I Bleed This Business. It's Cold-Blooded.'
- Lock I Sent My Role Model a DM, Never Imagining She'd Respond — Then This Happened
- Lock This Couple's Weekend Side Hustle Began With a $50 Facebook Marketplace Purchase — Now It Earns Millions of Dollars a Year: 'You Don't Need Money to Start'
- Walmart and Burger King's New Partnership Is Poised to Give a Boost to Franchise Traffic
Most Popular Red Arrow
Canva says massive subscription price increase is due to new ai features.
Canva hiked fees on some subscriptions by 300%.
DirecTV Issuing Credits to Customers as Disney Channels Go Dark. Here's How to Collect.
DirecTV is giving $20 credits to customers.
AI Slop is Everywhere We Look — Here's How Businesses Can Avoid the AI Slop Cycle
AI slop is the latest iteration of digital clutter. It's the filler content produced by AI tools that prioritize speed and quantity over substance and quality. Here's how to avoid it as a business owner.
5 Unforgettable Lessons I Learned Spending $1 Million on a Domain Name
After buying my company domain name for over $1 million USD and completing hundreds of six and seven-figure transactions since, here are the five best pieces of advice I can offer to anyone looking to purchase ultra-premium digital real estate.
I've Interviewed Over 2000 Candidates — Here Are the 2 Questions I've Asked the Best Hires
I've learned that there are only two questions that really matter when hiring.
You're Busy Running Your Business, So Get Your Shopping Done at BJ's
With a BJ's 1-year membership, you can grab groceries, tech, and more in one place.
Successfully copied link
BRAND-LED GROWTH
OUR OFFICES
Registered Address: St Christophers House 126 Ridge Road Letchworth Garden City Hertfordshire SG6 1PT
Community House Portholme Road Selby North Yorkshire Y08 4QQ
- 01462 262362
- [email protected]

Understanding the 7Ps of a Marketing Mix
Marketing is like baking. With the right ingredients, measurements and conditions, your recipe is sure to be a success. Find out the 7 ingredients for the perfect marketing mix … or risk a soggy bottom!
A marketing mix is a set of actions that businesses and marketers use to help promote their brand, or to sell a product or service they offer. When selling a new product or service, it’s important to create a marketing mix strategy that essentially blends the key marketing ingredients together to achieve the desired result.
What are the 7Ps of a marketing mix?
A marketing mix always begins with a product to sell. In the early development phase of your product, it is extremely important to carry out extensive research on the life cycle of the product you are creating.
All products have their own life cycle including the growth phase, the maturity phase, and the sales decline phase. Once a product reaches the sales decline phase, marketers need to find new ways to increase sales again.
When developing the right product, it’s important to ask yourself a series of questions to make sure your product is better than your competitors, i.e. what does the client want from the product? Or, how, where and why the client uses the product?
In a marketing mix, place refers to the position and distribution of the product you are selling in a place that is accessible to your target audience, this could be a high street shop, an online store, or mail order. Examples of distribution strategies include: intensive, exclusive, selective and franchising.
To make sure you position your product in the best possible place, it’s vital to understand your customer and what their shopping habits may be. Therefore, to develop a distribution strategy, you need to ask yourself the following questions:
- Where do clients look for my product?
- Where do clients usually shop for products?
- Should I sell the product online?
Pricing is an extremely important component to your marketing mix as it determines your profit and costing of your product. Altering the price of a product can affect the entire marketing strategy, whilst also affecting the sales and demand of your product.
As a newcomer to the market, it’s tempting to set your prices high, especially if you know your product is worth the price you are asking for. However, it’s unlikely that your target audience will be willing to pay the price, simply because your brand is only starting out so you’re not as recognisable or trustworthy – this comes with time.
Pricing also helps consumers to determine the perception of your product. For example, a lower priced product is deemed less inferior in terms of quality and ability, as opposed to a highly priced product.
In a marketing mix, promotion is an element that can boost sales and brand recognition through advertising, sales promotion, sales organisation, and public relations.
When promoting a product, you may decide on all of the promotion elements above, or simply choose the techniques that will target your audience more effectively. However, in order to create a successful product promotion strategy, here are a number of questions to ask yourself first:
- When is the best time to promote my product?
- What is the strategy my competitors are using?
- Should I use social media to promote the product?
- How can I send marketing messages to my target audience?
- What marketing channel is the best to promote my product for my audience?
The promotional strategy you use is also dependent on your budget, your communication and how you want to get your message across, and your target market.
Another important element in the marketing mix is people. This includes whether or not your target audience is large enough, and if there is a large enough demand for your product or not.
Consumers aren’t the only important people to consider in your marketing strategy, you also have to take into the account the people who will be delivering the marketing and sales of your product. To make sure you deliver excellent service and marketing, you’ll need people who are fully trained for the job, whether this is customer service assistants, copywriters, designers or a sales representative for example.
As for processes in the marketing mix, the process of your organisation can affect the performance of the service you provide, involving the delivery of your product to consumers.
As a business, it’s crucial to make sure you’re easy to do business with, meaning you’re efficient, helpful and timely.
By making sure your business has a good process in place, you will also save time and money due to greater efficiency, and your standard of service to customers will remain consistent, which is excellent for developing a brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Physical Evidence
The final P in a marketing mix stands for physical evidence and it refers to everything your customers sees or hears when interacting with your business.
T his includes your branding, your product packaging, a physical space such as a shop, and even the way your staff and sales representatives act and dress – it’s not all about the product! The way that you portray your brand physically has a great impact on consumers and can either lead or an increase, or decrease, in sales.
Using the Marketing Mix
Each of the 7Ps found in a marketing mix work together to ensure your business is a success. The 7Ps also have an impact on your positioning, targeting, and segmentation decisions, so it’s crucial to understand their benefits to create your own marketing mix.
If you would like more information on how you can create your own marketing mix, please call our strategic team on 01462 262020 or a no obligation chat, or email us at [email protected]
You can also view some case studies over at our client work area to see how we’ve already successfully helped businesses with their marketing mix.
Like what you see? Be the first to read our blogs
Get our latest blogs in a handy newsletter - go on, try it, you can unsubscribe in one click
RELATED POSTS
The art of storytelling: crafting your brand’s unique narrative, navigating mergers and acquisitions: the indispensable role of branding, achieving brand fitness: harnessing the power of brand alignment, unleashing the power of design in branding, world creativity and innovation day 2023, unlocking business potential: the power of brand-fit in mergers and acquisitions, business plan for the year, hubspot – 10 best things to know.
- Why Hurree?
The 7Ps of The Marketing Mix: Streamline your Strategy
As marketers, we should never underestimate the power of planning. For most of us, that means creating a water-tight marketing strategy, informed by analysis and data - one that has objectives, a target market, and proven tactics.
We all use different blueprints depending on our industry, our target audience and our products and services. But there’s one, timeless model that any marketer can utilise regardless of their field of work and that is the marketing mix.
What is the marketing mix?
Traditionally, the marketing mix is a framework for your marketing strategy containing four key elements: Product, Place, Price and Promotion. Then we have the extended marketing mix - or the 7Ps - which contains the first four elements, plus Physical Evidence, People and Processes.
It’s important to note that while the marketing mix can influence your strategy and provide a greater understanding of the wider market, as well as your business internally, it doesn’t work in isolation. The marketing mix is a tactic that works best when it’s implemented regularly or semi-regularly as a structure for planning, executing, evaluating and re-evaluating your marketing activities.
Who created the marketing mix?
The marketing mix is a concept developed by professor and academic, Neil H. Borden , who elaborated on James Culliton’s concept of business executives being mixers of ingredients - ingredients being different marketing features and practices. The marketing mix was later refined by professor and author, Jerome McCarthy, to specifically include four key components: Product, Place, Price and Promotion. McCarthy wrote about the 4Ps in the 1960s in his book Basic Marketing: A Managerial Approach .
The 4Ps vs the 7Ps
These original 4Ps of the marketing mix covered the fundamental factors of business and marketing at the time. But as we know, marketing and business as a whole have evolved exponentially since then, so it was only a matter of time before the marketing mix needed to be expanded. In 1981, the 4Ps were built upon by two modern academics, B.H. Booms and M.J. Bitner, who identified three additional elements they saw as key to the marketing mix: Physical Evidence, People, and Process, thus providing us with what we now know as the 7Ps of the marketing mix. And it makes sense that these three were the elements Booms and Bitner added to the marketing mix framework. People are at the heart of every business. Without people, you have no one to market to; no one is there to buy your product or make use of your services. It’s a no-brainer.
What are the 7Ps of the marketing mix?
Now that you know what the 7 Ps of the marketing mix are and their origins, let’s dive a little deeper into the definition of each aspect.
Product refers to what is being sold - a physical product, service, or experience. No matter how you position yourself as a brand, your product or service is always going to be at the centre of your strategy and will influence every aspect of the marketing mix. When you think of your product, consider factors such as:
- Specific features
- Packaging/presentation
- The problem that it will solve for your customers
Product in this case, then, is about crafting something that meets the needs and desires of your target audience. This means understanding their preferences, pain points, and aspirations. By meticulously aligning your product with customer expectations, you create a solid starting point for your marketing endeavours. Over 30,000 consumer products are launched yearly. Out of these 30,000 new products, 95% of them fail woefully without having any significant impact on the market.
Choosing the right distribution channels significantly impacts your product's accessibility and visibility. Effective placement ensures your product is available when and where your target audience needs it. Place in the marketing mix doesn't just mean physical locations—it encompasses websites, catalogues, social media, trade shows, and brick-and-mortar stores.

Source: Zippia
Place covers all distribution channels. Factors like your target audience influence your choices. Selling via a single high-street store won't work if your audience is mostly online or global. Test options—could an eCommerce site or a pop-up store work? A mix might suit your business. Understanding your target audience is vital for the right distribution. To profit consistently, distribute where your brand fits and your audience can access. Make your presence felt where it matters most.
The right pricing strategy is critical for a product's success. A misstep in pricing can jeopardize your ROI. Bain & Company research found that 18% of companies lack internal processes for pricing decisions. Your price should mirror customer perception, align with your budget, and ensure profitability. Pricing significantly impacts your business's success, affecting marketing, sales, and demand. Various pricing strategies exist , each with unique benefits and considerations, depending on your product and brand image.
6 Common pricing strategies:
- Price Skimming : Begin with a high price, gradually lowering it over time.
- Competition-Based Pricing : Set prices above or below competitors' rates.
- Economy Pricing : Target budget-conscious buyers with lower prices.
- Premium Pricing : Attach a high price, emphasizing product quality.
- Value-Based Pricing : Determine price based on perceived customer value.
- Cost-Plus Pricing : Set price based on production cost plus markup.
Whatever your pricing strategy is, ensure it aligns with your brand, appeals to customers, and maintains profitability. Monitor the market, economy, and competitors to adjust as needed.

4. Promotion
Promotion is at the core of our marketing expertise. Whether through direct marketing, PR, advertising, content strategies, or in-store presentations, as marketers, we excel in raising awareness and engagement. Promotion involves telling a compelling brand story that resonates with consumers, guiding them to consider your offerings. Effective promotional strategies achieve various goals, from elevating brand recognition to driving sales and revenue. Addressing key questions sets the stage:
Where is your audience able to find you? Online or in a physical store?
Does seasonal impact influence your business?
What is your brand personality and how does it shape your messaging and design?
- How do competitors promote themselves? A SWOT analysis helps here.
Promotional tactics fall into two categories: traditional and digital . Traditional methods encompass print media, broadcasting, mail, billboards, and word of mouth. Digital avenues include email, social media, content marketing, SEO , mobile outreach, and paid ads. Digital marketing generates 50% more customer interactions than traditional methods.
Source: MarTech Alliance
The way you communicate and promote directly affects your brand's success. Misplaced messages or poor timing can negatively impact sales. Understanding your audience through segmentation and targeting, along with integrating marketing data, helps cater to their needs and ensures seamless omnichannel campaigns.
5. Physical Evidence
Physical evidence means more than just proof of purchase - it encompasses the overall existence of your brand. Think website, branding, social media, the logo on your building, your store’s decor, the packaging of your product, the post-purchase thank you email, even the ambience of your store. All of these elements offer your customer the physical evidence they need to be certain that your business is viable, reliable and legitimate. For consumers to truly be comfortable with you, to complete a purchase, remain loyal and advocate for your brand, they need to be confident that you’re legitimate and worth their time.
To create a well-crafted strategy that ensures you offer great customer support, be sure to deliver products and receipts efficiently and reliably, and provide a customer experience that is seamless across each and every touchpoint.
6. People People, in the marketing mix, refers to anyone directly or indirectly involved in the business side of the enterprise. That means anyone involved in selling a product or service, designing it, marketing, managing teams, representing customers, recruiting and training. It’s critical to the success of your brand, and the satisfaction of your customers, that everyone who represents the company (including the chatbots) is polite, professional, knowledgeable and fully trained. Employees need to be able to solve the problems that customers have, so as a business, you need to offer training, good working environments and anything that will safeguard the contentment of your employees.

50% of consumers will switch to a competitor after a single bad experience, while 80% will switch after multiple bad experiences. Excellent customer service is a must for any brand operating in today’s customer-centric market. Digital strategist, Dave Chaffey, says that people buy from people because of the human connection that we all typically crave. When marketers create a strategy that’s highly tailored and personalised, they can be as influential as the best, most persuasive salesperson. Having the right people is key for both long and short-term success. Each part of the marketing mix can help your customers see you as reliable and dependable, which is crucial to any branding strategy.
Process encompasses what goes into every step of the customer journey - from making an enquiry to requesting information and making a purchase. The efficiency and consistency of your processes can significantly impact your overall effectiveness. From lead generation to customer support, having well-defined and streamlined processes ensures a seamless customer journey. The more intentional and personalised your processes are, the happier your customers will be. Even with the best product in the world, your business can be let down by processes.
You want your customer interactions to be seamless from beginning to end, so think about things like:
- Your customer response time
- The time between booking with sales and actually having a meeting
- What happens once they make a purchase
- How to generate positive reviews after purchase
- What tools can make your processes more efficient i.e. AI, CRMs, email clients, KPI tracking , etc.
Source: Oracle
Marketers who plan their projects and campaigns against their strategy are 365% more likely to report success. Regularly assessing, adjusting and adapting your processes will help to structure your business efforts so that you can function at optimal efficiency.

Why are the 7Ps of the marketing mix important?
In the dynamic realm of marketing, where strategies evolve and consumer behaviours shift, having a reliable and comprehensive framework is essential. The 7Ps of the marketing mix provide precisely that – a versatile toolkit that empowers intermediate marketers to construct impactful strategies and achieve sustainable success. At the core of the 7Ps framework lies a profound focus on understanding and catering to the needs of your target audience. This customer-centric approach is a cornerstone of successful marketing. By delving deep into your customers' preferences, pain points, and aspirations, you gain insights that guide your decisions across the 7Ps. This empathetic understanding ensures that your product is tailored to meet specific demands, your pricing resonates with perceived value, your distribution channels are optimized for accessibility, and your promotional efforts strike a chord. The 7Ps framework also equips marketers with the agility to respond to shifting market dynamics. Whether it's adjusting pricing strategies to remain competitive, leveraging new promotional platforms to reach wider audiences, or refining product offerings based on customer feedback, the flexibility inherent in the 7Ps allows marketers to stay relevant and effective. Additionally, the 7Ps facilitate measurement and optimisation, a key element of any successful marketing strategy. Each "P" provides distinct metrics that can be tracked and analysed which allows marketers to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, leading to continuous refinement and enhanced results.

How can I use the 7Ps?
The 7Ps marketing mix is more than just a theoretical concept; it's a versatile toolkit that can be wielded by intermediate marketers to create impactful and effective strategies. Here's a concise guide on how you can leverage this model to your advantage: 1. Start with Solid Research Understanding your target audience is paramount. Conduct thorough market research to unearth insights into their preferences, behaviours, and needs. This foundational knowledge will inform every decision you make across the 7Ps. 2. Tailor Your Product Offering Craft your product or service with your audience in mind. Strive to meet their unique needs and desires, differentiating yourself from competitors by adding value and addressing pain points. 3. Pricing Precision Develop a pricing strategy that aligns with customer expectations and provides a clear reflection of the value you offer. Consider factors such as production costs, competitor pricing, and perceived value when setting your prices. 4. Strategic Placement Determine the optimal distribution channels to ensure your product or service reaches your target audience conveniently. Whether it's through physical stores, online platforms, or a combination of both, choose avenues that enhance accessibility and visibility. 5. Powerful Promotions Craft compelling promotional campaigns that resonate with your audience. Utilize a mix of advertising, public relations, social media, and other marketing channels to amplify your message and create a buzz around your offering. 6. Prioritize People Invest in your employees and ensure they are well-trained and aligned with your brand's values. Their interactions with customers can significantly impact their experience and perception of your brand. 7. Streamline Processes Efficiency is key. Optimize your marketing processes to ensure a seamless customer journey from awareness to purchase and beyond. This includes lead generation, customer support, and post-purchase interactions. In the ever-evolving landscape of marketing, a robust framework is essential, and the 7Ps of the marketing mix offer just that. As marketers, this versatile toolkit empowers us to craft impactful strategies for enduring success. By delving into customer preferences, pain points, and dreams, we tailor our decisions across the 7Ps. Harnessing the power of the 7Ps, allows us to shape strategies that resonate, adapting to the ever-shifting marketing landscape, and ensuring lasting success.
Track and visualise your KPIs in real-time with Hurree. Try Hurree today and discover how to truly harness the power of analytics and transform your company reporting using cross-platform dashboards. If you have any questions then feel free to get in touch !

You May Also Like
These Related Stories

What Are The Major Components of a Marketing Strategy?

Experiential Marketing: 4 Es to Future-proof Your Strategy

Market Targeting: Why it Pays to Differentiate
Get email notifications.

- LEADERSHIP SKILLS
- Marketing Skills
- The 7 P's of Marketing Mix
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Leadership Skills:
- What Sort of Leader are You? Quiz
- Management Skills Self-Assessment
- Top Leadership Skills You Need
- Deciphering Business Jargon
- A - Z List of Leadership Skills
- Understanding Leadership
- Planning and Organising Skills
- Strategic Marketing
- Writing a Marketing Strategy
- Understanding Marketing Mediums
- Understanding Return on Investment (ROI) in Strategic Marketing
- The 7 P's of Marketing
- Pricing Strategies
- Customer Segmentation
- Social Media Marketing
- Writing Marketing Copy
- Content Marketing
- Storytelling in Business
- Strategic Thinking Skills
- Management Skills
- Entrepreneurship and Self-Employment Skills
- Change Management
- Persuasion and Influencing Skills
Our eBooks:
The Skills You Need Guide to Leadership

Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
The 7 Ps of Marketing Mix
The Seven Ps of Marketing is a relatively simple framework that can be used by any organisation or manager to plan marketing activities and a marketing strategy .
It is useful because it ensures that you look across each area together, and consider how they might be related.
The Seven Ps started as just four: product, price, place and promotion. Over time, as marketers became more aware, and practices and businesses changed, three more have been added: people, processes, and physical evidence.
This page explores each of these areas in turn, looking at the important aspects to consider when planning marketing activity.
Product first, or customer?
Apple is said to have developed the iPod without checking for customer demand first. Steve Jobs was apparently convinced — correctly, as it turned out — that people would want to buy his product.
History, however, is littered with less successful examples of companies who have developed a product first, and worried about finding customers later. It is true that customers do not always know what they want . They do, however, often have an idea of what they lack, or the problem they are trying to solve.
Doing some good customer research in advance of any development costs will ensure that you do not waste any time or money on products that nobody wants to buy.
It is also helpful to check back with your customers during the development to ensure that you are still developing the right product. In particular, check that you are not over-engineering the quality: sometimes good enough is all that is necessary or required.
The price that you charge is important, because it will determine the profit that you make on the product or service.
It must, therefore, be greater than the cost of producing the goods or services.
However, a product is only worth what someone is prepared to pay for it, so it needs to be priced competitively: consistent with what others are charging for similar goods or services.
Pricing also sends a signal to your customers:
- Cheap often indicates a ‘no-frills’ product, without any added extras.
- Expensive may indicate a ‘luxury’ product, or one that has some added value such as improved customer service.
What you charge will therefore influence your customers’ expectations of your product or service, and you need to ensure that you meet those expectations .
‘Place’ describes where and how your customers will buy your product or service, and how it will reach them.
This might be, for example, through your website, or in a particular shop or shops.
In considering ‘place’, you need to decide two things:
- How you will get the goods to that place; and
- How you will get the goods to the customer.
Research shows that delivery of goods bought online is very important to overall customer satisfaction, so should be a part of your overall strategy.
Promotion is how you communicate what you do and/or sell to your customers.
'Promotion' includes a whole range of activities, from branding through social media activity and advertising to sales management and special offers. It is designed to show customers why they should buy your product or service , and should therefore focus on benefits, and not just features.
Perhaps the most important thing to remember is that promotion is NOT one-way . Instead, you should see it as the way to start a conversation with your customers, and with your employees, who also need to understand the product.
It is important to look at a variety of channels, including print, online and mobile. Your promotion activity should focus on where your customers are, whether that is particular social media sites, or newspapers.
Your customers are unlikely to separate the product or service from those who provide it.
Your staff—and that means anyone who comes into contact with customers, even remotely, through something that they have written for the company website—are therefore vital. They will have an important effect on customer satisfaction . This is even more important now, because so many people are active on social media, and staff therefore can (and will) communicate with customers directly.
Staff will need to be adequately trained to understand their importance, and how to deal with customers.
Further Reading from Skills You Need

The Skills You Need Guide to Business Strategy and Analysis
Based on our popular management and analysis content the Skills You Need Guide to Business Strategy and Analysis is a straightforward and practical guide to business analysis.
This eBook is designed to give you the skills to help you understand your business, your market and your competitors.
It will help you understand why business analysis is important for strategy—and then enable you to use analytical tools effectively to position your business.
Processes was originally added for service industries, but there is increasing recognition that processes also affect customer experience in product companies.
What’s more, it is very clear that customer experience shapes customer satisfaction.
The experience starts from the first point of contact, and goes on until after the sale, including after-sales service. The process of handling customers at first contact, during sales and beyond, is therefore crucial to overall customer satisfaction. This might include:
- The website, and how the pages load;
- The ordering process: one-click or not, how the customer can pay and so on;
- The information provided to customers after purchase, including about any delays in delivery;
- The delivery time and method, and the way that the person delivering the product behaves; and
- The helpfulness of staff if the customer has to telephone or message for any reason.
Considering the process from end-to-end and from the customer’s perspective can help to avoid problems later on.
Physical evidence
Physical evidence refers to what the customer ‘sees’ of your product. It shows them what it would be like to own or use it.
It therefore includes your website, or your business premises or shop, models wearing your clothes, or photos of them doing so. It also includes customer testimonials, especially if they are on an independent reviewing site, and not under your control.
Like price, the physical evidence sends an important signal to your customer about your product , so it is important that, for example, your website sends the right impression of your product or service.
A collective endeavour
Marketing as a whole relies on all seven Ps.
It is essential to consider them as a whole, and not in isolation. Customers must experience a coherent view of your company and your product, and that can only come from viewing the customer experience from end-to-end across all seven Ps.
Continue to: Customer Segmentation Strategic Marketing
See also: 5 Marketing-Based Skills to Learn During Lockdown Workplace Confidentiality
Mastering the Marketing Mix: A Comprehensive Guide to 7Ps
Home » Marketing » Mastering the Marketing Mix: A Comprehensive Guide to 7Ps

In the world of marketing, the concept of Marketing Mix is crucial. It is a set of tools and tactics that businesses use to promote their products or services to the target market. The traditional Marketing Mix consisted of four Ps: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. However, with the changing times, businesses realized that to provide a better experience to customers, they need to consider more elements than the traditional four Ps. Thus, the Marketing Mix 7P was introduced. In this article, we will take an in-depth look at the Marketing Mix 7P and understand how businesses can benefit from it.
Table of Contents
The 7Ps of Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix 7P is an extension of the traditional Marketing Mix , and it includes the seven Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence. Let’s take a look at each of these elements in detail.
The product P refers to the goods or services that a business offers to its customers. The product includes the design, features, quality, packaging, and branding of the product. The key to creating a successful product is to understand the needs and wants of your target market and to differentiate your product from your competitors.
- Conduct market research to understand the needs and wants of your target market.
- Conduct a competitive analysis to understand your competitors’ products and identify areas where you can differentiate.
- Use customer feedback to improve your product.
- Continuously innovate and improve your product to stay ahead of the competition.
The price P refers to the cost of the product or service. The pricing strategy of a business must be aligned with its overall marketing objectives and target market. The price of a product must reflect its perceived value and the cost of producing it.
- Conduct a pricing analysis to understand the pricing strategies of your competitors.
- Determine the perceived value of your product and price it accordingly.
- Consider the cost of producing and delivering the product when setting the price.
- Use promotions and discounts strategically to encourage customers to buy your product.
The place P refers to the distribution channels that a business uses to reach its target market. The distribution strategy must be tailored to the target market, and the product must be available at the right time and in the right place.
- Identify the most effective distribution channels for your target market.
- Ensure that your product is available in the right locations and at the right times.
- Use technology to improve the efficiency of your distribution channels.
- Continuously evaluate and optimize your distribution strategy to ensure that it is meeting the needs of your target market.
The promotion P refers to the communication strategies that a business uses to promote its product or service to its target market. The promotion mix includes advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, direct marketing, and public relations.

Promotion drives sales by creating awareness and communicating value
- Develop a clear and compelling brand message that resonates with your target market.
- Use a mix of advertising, personal selling, and other promotional techniques to reach your target market.
- Use social media and other digital channels to reach your target market.
- Continuously monitor the effectiveness of your promotional activities and adjust them as needed.
The people P refers to the employees who interact with customers and provide support to them. The staff must be well-trained and motivated to provide excellent customer service.
- Hire employees who have the skills and qualities needed to provide excellent customer service.
- Train employees on how to interact with customers and provide support to them.
- Encourage employees to take ownership of their work and to be proactive in solving customer problems.
- Recognize and reward employees who provide excellent customer service.
The process P refers to the processes and procedures that a business uses to deliver its product or service to its customers. The processes must be efficient and effective, and they must be designed to meet the needs and wants of the target market.
- Identify the key processes that are involved in delivering your product or service to customers.
- Streamline and optimize these processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Ensure that the processes are designed to meet the needs and wants of your target market.
- Continuously evaluate and improve your processes to ensure that they are meeting the needs of your customers.
Physical Evidence
The physical evidence P refers to the tangible elements that customers can see and touch when they interact with a business. This includes the physical environment, packaging, and branding. The physical evidence must be aligned with the overall brand image of the business.
- Ensure that your physical environment is clean, comfortable, and visually appealing.
- Use packaging that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
- Use branding that is consistent across all physical touchpoints.
- Pay attention to the details, such as signage, lighting, and decor, to create a positive customer experience.

Physical evidence refers to tangible elements customers use to evaluate a product or service, such as packaging or store atmosphere
Importance of 7Ps Marketing Mix
The Marketing Mix 7P is important for businesses as it helps them to provide a better experience to their customers. By considering all the elements of the Marketing Mix, a business can ensure that its products or services meet the customers’ needs, preferences, and expectations.
It also helps businesses to differentiate themselves from their competitors and create a unique brand image. Furthermore, by adapting the Marketing Mix to different industries and target markets, businesses can increase their reach and effectiveness.
Marketing Mix 7P vs 4P
The Marketing Mix 4Ps model and the Marketing Mix 7Ps model are both frameworks used by marketers to develop effective marketing strategies. The Marketing Mix model was originally proposed by E. Jerome McCarthy in 1960, including Product, Price, Promotion, and Place.
The model was later expanded by Booms and Bitner in 1981 to include three additional Ps: People, Process, and Physical evidence. Today, the 7Ps Marketing Mix model is widely used in marketing theory and practice.
Examples of 7Ps Marketing Mix in Action
Let’s take a look at some examples of companies that have successfully implemented the 7Ps Marketing Mix:
Apple is a company that is known for its innovative products and excellent customer experience. Their products have a unique design, packaging, and features that set them apart from their competitors. Apple also offers excellent customer service and has a well-trained staff that provides support to customers. Its physical stores have a unique layout and atmosphere that creates a premium brand image. Apple’s Marketing Mix is an excellent example of how a company can create a unique brand image by considering all the elements of the Marketing Mix.
Starbucks is another example of a company that has successfully implemented the 7Ps Marketing Mix. Starbucks has a unique product range, which includes coffee, tea, food, and merchandise. Its pricing strategy is based on the premium experience that it offers to its customers.
Starbucks has a strong distribution network, and its stores are located in prime locations to reach its target market effectively. Starbucks’ promotional activities focus on creating a unique experience for its customers, such as personalized drinks and promotions. The staff at Starbucks are well-trained to provide excellent customer service, and the physical stores have a unique atmosphere that creates a premium brand image.

How to apply Marketing Mix 7P?
As a marketer or business owner, you can use the 7Ps Marketing Mix model to design and implement an effective marketing strategy that meets the needs and wants of your target market, drives sales and revenue, and establishes a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Here are some steps you can follow to use this model effectively:
- Understand your target market: Conduct market research to understand the needs, wants, and preferences of your target market.
- Define your marketing objectives: Identify your marketing objectives, such as increasing sales, launching a new product, expanding into new markets, or improving customer retention.
- Develop a product or service: Use the insights from your market research to design a product or service that meets the needs of your target market.
- Determine your pricing strategy: Decide on a pricing strategy that reflects the perceived value of your product or service and aligns with your marketing objectives.
- Choose your distribution channels: Identify the most effective distribution channels to reach your target market. Ensure that your product or service is available in the right locations and at the right times.
- Develop a promotional strategy: Develop a promotional strategy that effectively reaches your target market. This may include a mix of advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, direct marketing, and public relations.
- Train and motivate your staff: Ensure that your staff are well-trained and motivated to provide excellent customer service.
- Streamline your processes: Streamline your processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
- Create a positive physical environment: Pay attention to the physical environment, packaging, and branding to create a positive customer experience.
In conclusion, the Marketing Mix 7P is a powerful tool that businesses can use to provide a better experience to their customers. By considering all the elements of the Marketing Mix, businesses can create a unique brand image and differentiate themselves from their competitors. Furthermore, by adapting the Marketing Mix to different industries and target markets, businesses can increase their reach and effectiveness. We hope this guide has helped you understand the importance of the Marketing Mix 7P and how businesses can benefit from it. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below.
You might be interested in:
- Marketing Metrics : Everything You Need to Know
- Facebook Ad Metrics : Master in 5 Minutes
- Crafting an Effective Marketing Strategy : Tips and Best Practices
- Digital Marketing Quotes & Phrases to Inspire & Motivate

Table of Contents
Top 12 marketing models , 7 ps of marketing, importance of 7 ps of marketing, steps to develop a successful marketing mix, what are the 7 ps of marketing.
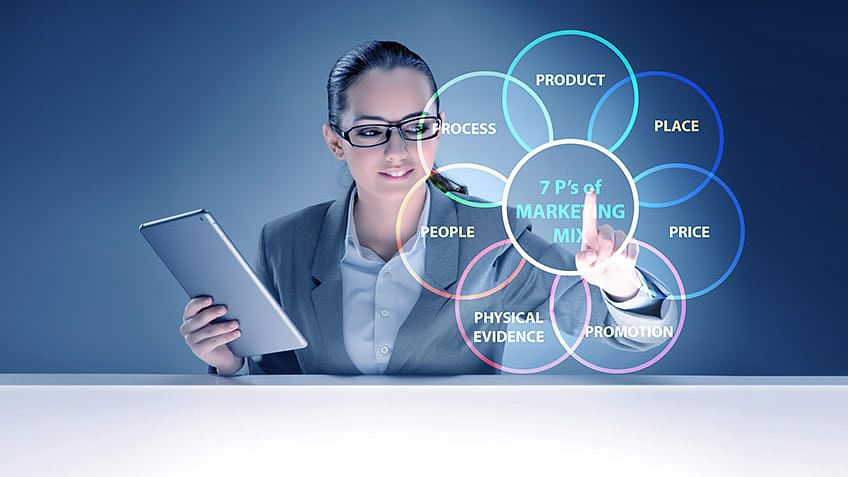

Marketing communicates the value of goods and services to the customers. While marketing is often thought of as the end promotional activity, marketing is a combination of activities that delivers an optimal mix of pricing, product development, distribution, and advertising for a business to achieve success. It is both a science and an art, and overlaps, but is not synonymous, with the concepts of advertising , promotion, market research, and sales. Several marketing models are available that help develop and implement the marketing strategies as per the business requirements and customer needs. To begin with, here are some of the most common marketing models.
Some of the popular marketing models that have stood the test of time and are relevant in today’s era of omnichannel marketing have been listed below:
- 7 Ps of marketing
- USP (Unique Selling Proposition)
- Boston Consulting Group Matrix
- Brand positioning map
- Customer Lifetime Value marketing models
- Growth strategy matrix
- Loyalty ladder marketing models
- PESTLE (Asses impact on political, economic, social, technological, legal, and economic factors)
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Product Life Cycle
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
- PR Smith's SOSTAC (Situation, Objectives, Strategy, Tactics, Actions, Control) model
In this article we will learn about one such commonly used marketing model mix, i.e., 7 Ps of marketing!
The 7 Ps of marketing is a set of recognized marketing tactics, which can be used in any combination to satisfy customers in the target market. Combining these marketing tactics to meet the customers' needs and wants is known as using a 'tactical marketing mix'.
This marketing mix is a familiar marketing strategy tool that was traditionally limited to the core 4Ps - Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. In the 7 Ps, the new additions are People, Process, Physical evidence.
Let's dive into these marketing tactics, starting with the most important one, product.
It definitely goes without saying that your product must be at the centre of your entire strategy. The entire marketing mix is about the product itself. Concentrate on what is the pain point that your product or service is solving. How your product is more efficient than other similar ones in the market.
You can use research and development to help your company develop new products or create awareness about the existing one. The digital marketing mix is ideal for showcasing your products, such as through SEO , blogs or articles, paid advertising, influencer marketing , and viral video campaigns.
This refers to your pricing strategy for products and services, as well as how it will affect your customers. You should determine how much your customers are willing to pay, how much you need to mark up to cover overheads, your profit margins and payment methods, and other costs. You may also want to consider the possibility of discounts and seasonal pricing, subscription and membership programmes, or email marketing of promotions and sales to attract customers and maintain your competitive advantage.
The location of your products and services is where they are seen, made, sold, or distributed. Customer access to your products is critical, and it is critical that customers can find you.
You can distinguish yourself from the competition by designing your retail space and employing effective visual merchandising techniques. Even if you are not a retail business, location is an important part of your marketing strategy. Your customers may require a quick turnaround or prefer to purchase locally manufactured goods.
Finding the right business location will be an important marketing tactic if you are starting a new business.
All promotional activities across the marketing mix, including advertising, direct marketing, and in-store promotional activities, are included in successful marketing strategies. Digital promotion is only limited by your imagination and can include online events, chats, social media groups, and livestreams.
People refer to the employees and salespeople who work for your company, including you.
When you provide excellent customer service, you create a positive experience for your customers and, as a result, market to them. As a result, current customers may spread the word about your excellent service, and you may receive referrals.
Give your company a competitive advantage by hiring the right people, training them to improve their skills, and retaining good employees.
The process of getting your product to the consumer should be designed for maximum efficiency and dependability, but it should also include features that are consistent with your brand, such as being environmentally or sustainably focused.
With the rise of online shopping, digital partnerships and logistics have become critical components of the marketing mix. Having a good process in place ensures that you consistently provide the same level of service to your customers while also saving time and money through increased efficiency.
Physical Evidence
Physical evidence includes elements that demonstrate your brand's existence and that a purchase occurred.
A physical store or office for your business, a website if your business only operates online, and printed business cards that you exchange when meeting people are all examples of proof that your brand exists. Physical or digital receipts, invoices, or follow-up email newsletters sent to customers as a retention exercise are all examples of proof of purchase.
Your marketing mix must also account for everything your customer sees, hears, and sometimes even smells in relation to your product or service.
This includes, of course, packaging and branding , but it should also include how products are displayed in stores, where they are placed, and the context in which they sit, as well as digital placement, such as on your website and social media.
The marketing mix of 7Ps is the mix of tactics applied and coordinated that positions the organization clearly in the minds of the customer.
The 7Ps model helps us to:
- Set objectives and provide a roadmap for your business objectives.
- Conduct SWOT analysis , and undertake competitive analysis.
- Review and define key issues that affect the marketing of its products and services.
- Evaluate existing business and work through appropriate approaches whilst evaluating the marketing mix elements.
- Market the right product, to the right people, at the right price and time.
- Help develop products and services that better serve the wants and needs of the target market.
- Help customers understand why the product or service is better than those of competitors.
The advantages of using the 7Ps model can be achieved only if each of the Ps is correctly understood and appropriate strategies are devised for them. It will be unwise to ignore an area unless it is completely outside one’s control.
Become a Business and Leadership Professional
- 3rd Best Job among overall jobs in the US
- 1.1 Million Jobs is the total management job openings each year, on average
- 60% Companies see management driving annual planning
Executive Certificate Program in General Management
- The capstone project mentored by IIM Indore faculty
Post Graduate Program in Digital Marketing
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Peeyush Gupta
Regional sales manager , rspl ltd (hcd).
Simplilearn's general management course, featuring expert faculty from IIM Indore, provided enriching learning. The curriculum's direct applicability and a visit to the campus made it a positive and valuable experience in general management training.
Allan Joaquin
Senior copywriter , ami group.
Completing the PGP in Digital Marketing and gaining knowledge allowed me to service new clients needing consultancy on digital marketing strategies. After upskilling with Simplilearn's digital marketing course, I increased my revenue by 50%.
The following 10 steps will assist you in developing the perfect marketing mix:
Step 1. Set the Goals and Objectives - Clearly define the required result. For example, more customers, brand awareness, higher sales, etc. Every marketing plan will have its own marketing goals. Set a specific time frame in which to achieve the results.
Step 2. Prepare the Budget – Identify the amount that will be spent on product innovation, consumer research, product promotion, etc.
Step 3. Determine the Unique Selling Proposition (USP) - Identify the benefits users will experience from using your product or service. Also, determine the unique problem that the product/ service is solving better than anyone else.
Step 4. Identify the target Target Market – Understand the target audience and know who they are and how they prefer to be communicated. Create an in-depth profile of the ideal customer .
Step 5. Seek Customer Feedback – Understand from the customers what they think of the product, how satisfied they are with the quality, is the product effectively meeting their needs, etc. This will help to make the products more relatable and approachable to the audience.
Step 6. Define the Product in Detail - Describe the specific qualities and value of your product. Look for the unique features that define the product’s worth.
Step 7. Know the Distribution Channels - Identify the places your product will be marketed and which distribution channels you’ll make use of. This will influence your pricing and your promotion decisions.
Step 8. Create Pricing Strategy - Discover ways of differentiating your product on price. Know the competitors and make sure the customers are not overcharged. Also, understand what the target audience might be willing to pay and what it costs to produce the product.
Step 9. Choose Promotional Techniques - The target audience needs to be made aware of the product offering. Successful promotion of the product includes various elements, like direct marketing, public relations, advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, word of mouth, etc.
Step 10. Use Inbound Marketing - Inbound marketing also plays a vital role in developing your marketing mix.An effective inbound marketing mix includes a website, email marketing, social media , and blogging .
Every business, whether local or international, requires well-versed marketing professionals. Hence, an understanding marketing is one of the sought-after disciplines among students. The Digital Marketing Course offered by Simplilearn will make the students job-ready for the marketing industry. Upon completion of marketing program, they will be able to skillfully identify marketing strategies and help their companies grow.
Led by Simplilearn the Executive Certificate Program in General Management program covers essential topics such as strategy formulation, financial management, leadership, marketing, and more. With a strong focus on practical application, you'll gain valuable insights and tools that can be immediately implemented in your organization. Elevate your career and join the ranks of successful business leaders by enrolling in this prestigious program today. Don't miss this opportunity to enhance your management capabilities and drive your career to new heights.
Our Business And Leadership Courses Duration And Fees
Business And Leadership Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 2,499 |
| Cohort Starts: | 6 Months | € 1,990 |
| Cohort Starts: | 5 months | € 3,190 |
| 11 Months | € 1,299 |
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing Tools and Techniques
Introduction to Digital Marketing Fundamentals Course
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Business and leadership.
Discover How AI Will Help Good Managers Become Great
Why our Indore General Management program should be the next big move for your career
Climb the General Management Career Ladder in 2024 with IIM Indore
Recommended Reads
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
Top 7 Marketing Strategies That Can Help You Become a Marketing Wizard Today
What is Digital Marketing and How Does It Work?
Digital Marketing Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Digital Marketing Specialist
Top Benefits of Content Marketing
25 Digital Marketing Skills To Master
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
What is Marketing Mix? – The 4Ps & 7Ps Of Marketing Explained

The marketing mix theory, first coined by E. Jerome McCarthy in the 1960s, forms the foundation model for every business today.
Earlier, the marketing framework was confined to the characteristics of marketing systems and their functions. McCarthy provided a framework for marketing decision-making centered around the product, price, place, and promotion through his marketing mix theory.
Today, every company’s marketing decision-making revolves around these marketing mix principles. However, experts have further increased the number of principles influencing the marketing decision-making process.
But before explaining the 4Ps and 7Ps of the marketing mix theory, here’s an example of how Coca-Cola markets itself.
Coca Cola is one of the most valued brands in the world :
- It has a well-diversified portfolio of 3500+ products.
- It operates throughout the world and distributes its products using a franchise system .
- All of its products are competitively priced (since the FMCG industry sees a lot of competition), and
- It aggressively promotes its brand and offerings using advertisements, sales promotions, PR, and even CSR activities.
This is Coca-Cola’s marketing mix where it develops the product according to the customer needs , distributes it efficiently, prices it competitively according to the demand, and promotes it effectively to boost sales.
But what is marketing mix? What are the four pillars or 4ps of marketing?
What Is Marketing Mix?
Marketing mix is a set of tools and tactics a business use to pursue its marketing objectives and sell its offerings to the target audience.
Also called the elements of marketing, these tactics include how the marketers develop the offerings and decide their prices, places where they will be sold, and communication and promotional strategies.
In simple terms, marketing mix refers to the set of decisions that marketers use to develop and execute their marketing plans that can
- Create the highest level of consumer satisfaction, and
- Meet its organisational objectives.
This marketing mix concept derives its framework from the basic definition of marketing – identifying customer’s needs and satiating those needs through offerings. So the business:
- Develops a product according to the customers’ needs and wants
- Make it available at a price that customers find reasonable
- Supply the offering using distribution channels (places) that are convenient for the customer to buy from
- Inform the customer about the offering and its characteristics through various promotional channels
The Four Ps Of Marketing

According to Philip Kotler, “Marketing mix is the set of controllable variables that the firm can use to influence the buyer’s response”.
These controllable variables constitute the 4ps or the four pillars of marketing –
- Product: the tangible, physical good or intangible service being marketed;
- Price: how much it costs to buy the product;
- Place: where and through what channels can one purchase the product;
- Promotion: how the business promotes its product.
Product is the offering that the business builds, designs, or procures to satisfy customers’ needs and wants.
The product isn’t limited to a tangible offering. It can also be an intangible offering or a service like air travel, massage, etc.
The customer doesn’t pay for the tangible or intangible product, but for the benefit it provides. For example, customers pay for shoes because they look for comfort and style. They pay for ice cream because it’s tasty and provides relief on a hot summer day. They pay their internet bills because it lets them access the world wide web at the browsing speed decided.
Hence, a product can also be defined as the bundle of benefits offered to the customer at a price.
Price is the amount the business charges for its offering.
Various factors influence the price of the offering. They include its demand, total cost incurred by the customer (including monetary and non-monetary cost), customer’s ability to pay, prices charged by competitors, government policies and restrictions, etc.
Price has a significant effect on the entire marketing mix and determines the business’s sustainability in the market. Besides this, it also influences:
- Product’s demand
- Brand positioning
- Buyer’s perception
- Business’s profitability
Businesses usually use one of these pricing strategies to price their offerings –
- Cost-Based Pricing: adds a set percentage of profits above the production cost of the product.
- Value-Based Pricing: sets the price based on the buyer’s perception of value rather than the actual costs.
- Competitive Pricing: sets the price based on prices charged by the competing businesses.
- Going-Rate Pricing: sets the price based on the going rate in the market. It is used where the business has little or no control over market rates.
Place is the physical location where the customers get, access, purchase, or use the offering.
It includes the distribution channels the business uses to take the products to the customers. These comprise the chain of individuals or institutions like manufacturers, agents, distributors, wholesalers, and retailers , who form the distribution network of the business.
The distribution-related decisions are majorly influenced by a host of factors, mainly:
- Nature of market
- Nature of product
- Nature of the company
- Middlemen considerations
Usually, businesses choose any of the four prevalent distribution strategies. These are:
- Intensive Distribution: where the business try to distribute its offering to all the vendors who are ready to sell the offering. This strategy helps in covering as much market as possible. For example, surf products, soft drinks, etc.
- Selective Distribution: where the business us a limited number of outlets in a geographical area to sell its offerings. For example, Zara, Adidas, etc.
- Exclusive Distribution: where only one distributor is used in a specific geographical area. For example, Lamborghini.
- Franchise System: Where small businesses purchase rights from the business to sell its offerings. For example, McDonald’s.
A business can also decide between direct and indirect distribution:
- Direct Distribution: When the business sells directly to the customers without involving any intermediaries.
- Indirect Distribution: When the business involves intermediaries in their distribution strategy.
Promotion is the process of informing, persuading, and influencing a customer to buy’s the business’s offering.
In simple terms, it comprises all the marketing communication efforts a business undertakes to promote its offering to the target audience. Usually, a business undertakes four strategies to promote its offerings:
- Advertising : Calling public attention to the business’s offering through paid announcements on offline and online channels.
- Public Relations : Strategic communication process business uses to build mutually beneficial relationships with the public.
- Personal Selling : Personalised sales method employs person-to-person interaction between the business and prospective customers to influence the customer’s purchase decision.
- Sales Promotion: Using attractive short-term initiatives to stimulate the offering’s demand and increase its sales.
The main objective of promotion is to provide information about the offering to the prospective customer to:
- Arouse potential customers’ interest in the offering,
- Compare it with competitor’s offerings, and
- Convince the customers to purchase this product.
The Extended Marketing Mix – The 7Ps of Marketing
The changing customer needs, behaviour, and trends force marketing to become a continually evolving discipline. Today, the marketing mix isn’t limited to just four pillars. Three more pillars have found their place in the extended marketing mix that shape marketers’ decision-making process.
- People: Business’s human resource that enables it to deliver the offering to the target audience.
- Process: The series of actions involved in delivering the offering to the customer.
- Physical Evidence: The tangible elements surrounding the product and the physical environment where the product or service is provided to the customers.
The business’s human resource form an important component of the extended marketing mix as they are key to offering’s delivery to the target market.
People include all the employees involved in the marketing and sales processes, be it those who directly interact with the customers and those who indirectly connect with the audience.
This element of the marketing mix is essential as customers don’t differentiate employees who contact them from the business these employees work with.
People include:
- Human resource responsible for service delivery,
- Personnel who represents the company’s value and conveys the brand message to the customers,
- Every other brand personnel who comes in contact with the target customers.
Process is the series of actions involved in the delivery of the offering to the target customers. It includes all the procedures, mechanisms, and activities that impact how the offering is handled by the business and delivered to consumers.
In simple terms, process is the route the offering takes from the business to the customer. It includes the holistic customer experience that starts when the customer discovers the business and its offering and lasts through purchase and even beyond.
The process can be a sequential order of tasks an employee takes or a mixture of related or unrelated activities divided among the employees and the customers, resulting in the transfer of ownership from the business to the customer.
Physical Evidence
Physical evidence includes all the tangible elements surrounding the product and the physical environment where the product or service is provided to the target customer.
It includes all the non-human elements of the marketing experience developed to transfer the ownership of the offering from the business to the customer.
This includes:
- The touch points where customers interact with the business.
- Tangible branding elements like POPs , packaging, bills, carrybags, etc.
- Visual merchandising
- Every other non-human element that the customer sees, hears, and even smells in relation to the offering.
Importance Of Marketing Mix
Marketing as a whole depends on its seven pillars. The marketing mix forms the ingredients to the business’s key to marketing success.
A business can never consider a single element of the market mix in isolation. For example, one cannot develop a product without deciding on its price or distribution channel.
The process where the business considers the seven Ps of marketing mix together to form a cohesive strategy is called marketing planning. It’s vital for a business’s survival and sustainability in the market.
Besides this, a sound knowledge of marketing mix is important –
- For new product development,
- To make an offering sustain in the market for long,
- To tackle business competition,
- To tackle dynamic market demand and trends, and
- To develop a unique brand positioning.
Ideal use of marketing mix results in creating synergy that gives the right direction to all the marketing efforts towards a set objective.
What Factors Determine The Marketing Mix?
There’s no one shoe fits all when it comes to the marketing mix. Different companies selling different products have different marketing mixes. Two major factors influence their marketing mix –
- Nature of the offering
- Offering’s stage in its lifecycle
- Business’s objectives
- Business’s finance
- Competition degree
- Marketing channel’s efficiency
- Market trends
- Customer buying behaviour
- Government restrictions and policies
Marketing Mix Examples
Every company that exists today makes use of marketing mix in its marketing plans . Here are two renowned examples of the marketing mix.
Marketing Mix Of Nestle
Nestle is the world’s largest food and beverage company with more than 2000 brands serving almost every sub-industry of the FMCG industry.
Product Mix of Nestle
Nestle focuses on fulfilling the instant food needs of its customers. In addition, the company focuses on ready-to-consume and processed food items. Nestle’s product mix consists of:
- Dairy products: Nestle Milk, Nestle Slim, and Nestle Everyday.
- Chocolates : KitKat, Munch, Polo, Milky bar, Crunch, etc.
- Coffee : Nescafe, Nescafe Dolce Gusto, Nespresso, etc.
- Ready to cook or instant food : Nestle Maggi, Buitoni, Jacks, Herta etc.
Price Mix Of Nestle
Nestle usually follows only two pricing strategies for its products:
- Competitive Pricing : The company prices its products according to the competitor’s products prices for its products that operate in a competitive market like chocolates, instant food, etc.
- Skimming Pricing : The company sets a price higher than the competition for the products where Nestle stands out. These include products like Nestle A+ Slim, Nestle A+ Toned, etc.
Place Mix Of Nestle
Nestle makes use of mass distribution and uses a four-to-five level distribution channel involving manufacturers, agents (sometimes more than one), wholesalers, and retailers to deliver its offerings to the customers.
The company even uses modern distribution channels like eCommerce stores and online marketplaces to sell its offerings.
Promotion Mix Of Nestle
Nestle uses a mix of ATL, BTL , and digital marketing channels to promote its offerings to the customers. It includes:
- Advertisements: TV ads, radio ads, print ads, and digital marketing ads.
- Sales Promotion: Active promotions to increase POS sales.
- Public Relations: It maintains a good image of the brand through news articles, events, etc.
People Mix Of Nestle
The company maintains a healthy engagement with the target audience through social media channels. Also, it makes sure its salespersons are trained well before they contact the customers and other stakeholders like media, retailers, wholesalers, etc.
Process Mix Of Nestle
The company tries to develop its offerings using modern and robust technology and try to make sure that its offerings are always available at the point of sales .
The company is also involved in actively researching and understanding the evolving needs of its target customers to develop and deliver better offerings.
Physical Evidence Mix Of Nestle
Nestle uses distinctive packaging and branding strategies to deliver its offerings. It even makes sure to design the shelves its products are placed on to develop a holistic physical evidence mix for its offerings.
The company even has a user-friendly and branded website that allows its customers to view its products and interact with the brand.
Marketing Mix Of Facebook
Facebook is the world’s number one social media network that helps its users connect with their friends, families, and others over the internet.
Product Mix Of Facebook
Facebook offers a family of social media networks for users to connect with others and share their memories. These products include:
Price Mix Of Facebook
The company keeps its products free of charge for the users while charges a competitive price from the advertisers who advertise on the platform targeting these users.
Place Mix Of Facebook
Facebook uses all possible digital channels in its place mix to reach out to its customers. They include the desktop version of the platform and mobile applications compatible with almost every available mobile OS.
Promotion Mix Of Facebook
Facebook uses a mix of advertisements, PR, referral, and word-of-mouth marketing strategies to promote its offerings to customers.
People Mix Of Facebook
Facebook makes sure its support staff is highly trained before connecting with business customers. It also maintains its brand by teaching its employees personal branding etiquettes over social media channels.
Process Mix Of Facebook
Facebook keeps updating its platform’s algorithm to make sure customers get the best trends while fulfilling their socialising needs.
Physical Evidence Mix Of Facebook
For Facebook, the physical evidence includes website branding, design, and user experience, which the company takes good care of.
What Is Digital Marketing Mix?
A digital marketing mix is an adaptation of the traditional marketing mix on to digital marketing platform. That is, the business develops its digital marketing plans by considering the seven Ps of marketing – price, place, product, promotion, people, process, and physical evidence.
Go On, Tell Us What You Think!
Did we miss something? Come on! Tell us what you think of this article in the comment section.
A startup consultant, digital marketer, traveller, and philomath. Aashish has worked with over 20 startups and successfully helped them ideate, raise money, and succeed. When not working, he can be found hiking, camping, and stargazing.
Related Posts:

Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Using the 7Ps as a generic marketing mix: an exploratory survey of UK and European marketing academics

1995, Marketing Intelligence & Planning
Related Papers
International Journal of Entrepreneurship
This is a theoretical paper about managerial marketing variables that describe new dimensions of the marketing mix. The paper discusses the current 4P's model of marketing and its variables: Product, Price, Place and Promotion. The article suggests a more complete view of the today's marketing management variables. Updating the management model of controllable marketing factors is necessary as the socioeconomic evolution must be considered in a business application model. The article explains the reviews the new p's and the state of science and proposes new dimensions for strategic decision making in marketing departments and organizations. The proposed model or enlarged P model is composed of 4 2 variables (4x4=16p) :
Journal of Marketing Education
Gordon Bruner
Are the presently used paradigms of the marketing mix adequate for describing the breadth of marketing applications in the 1980s and beyond? Previously proposed models of the mix are evaluated and found to have shortcomings. Criteria are established for evaluating presently available models as well as any paradigm offered in the future.
Journal of Marketing Management
Margarita Išoraitė
Aim of article is to analyze marketing mix theoretical aspects. The article discusses that marketing mix is one of the main objectives of the marketing mix elements for setting objectives and marketing budget measures. The importance of each element depends not only on the company and its activities, but also on the competition and time. All marketing elements are interrelated and should be seen in the whole of their actions. Some items may have greater importance than others; it depends mainly on the company's strategy and its activities. Companies that provide services-the provision of services will be a key element. Article arises research questions is marketing mix create added value for enterprises. There are used scientific literature and analysis methods in article. An analysis of the scientific literature, it can be said that the marketing mix measures are the actions and measures necessary to achieve marketing goals. Marketing elements: product, price, place and promoti...
Fulga Bogdan
BUSINESS SCIENCES INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL
ismat ara eti
The world is relentlessly changing which creating new trades. A few ages past, speediness of these revolutions, maybe it was every fasten of years or every decade, but straightaway, every year or every month we are nearsighted new goods and products that in the history there was not any kind of them. Every company should not neglect to take virtuous maintenance of customers that helps to partake the right planning and aiming people, the right product or service, right place or distribution, right price, right promotion, right physical and psychological evidence, with the right amount of productivity & quality performance in carrying the Ps of Marketing. This paper aims to undertake an extensive literature review from the past studies related to the concept of the marketing mix and descriptive analysis is used to analyze the best practice among the 8Ps or more Ps of marketing mix towards business performance. Equally, a tool of marketing strategy and theoretical framework grants a vi...
Journal of Historical Research in Marketing
Boryana Dimitrova
Azam Haghkhah
This research aims to study marketing mix and its elements – especially the Four Ps including product, price, place and promotion- in the industrial market. It reviews the concept of marketing mix and deals with its elements and then, studies in brief the impact of each element on the success of industrial market. The research showed that industrial marketing is different from marketing for final consumer goods and services in that it is a business-to-business marketing and the number of buyers is limited. Therefore, it is even more sensitive to attract other companies to buy from the seller industry and keep them satisfied for a continuous business relationship.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Brasov. Series V : Economic Sciences
Simona Balasescu
ashenafi haile
Journal of Advertising Research
Rumeninng Abrantes dos Santos
Jurnal Manajemen Bisnis
Naelati Tubastuvi
Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)
Sohan Kumar
Kholivan Renaldi
Rahul Gupta Choudhury
The Marketing Review
Graham Hughes
Journal of Retailing
Dian Utami Sutiksno
Management decision
Abraham Efua Dufu
Dinmukhamed Kelesbayev
International Journal of Review Management Business and Entrepreneurship (RMBE)
Ivana Tanjung
eduardo calva leon
Roger Mason
Perspectiva Empresarial
Alvaro Dias
Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing
Jaqueline Pels
Revista Perspectiva Empresarial
International journal of business and management
Gandolfo Dominici
International Journal of Advanced Research (IJAR)
IJAR Indexing
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

The 7Ps of marketing
- 10 March 2023
The 7Ps of marketing are product, price, place, promotion, people, process and physical evidence.
This post and more is contained within our CIM ebook, 7Ps: a brief summary of marketing and how it works .
Learn the 7Ps and you're well on your way to having your marketing fundamentals completed. Use the links below to jump to the one you want to learn more about:
- Physical Evidence
P1 - Product
There is no point in developing a product or service that no one wants to buy, yet many businesses decide what to offer first, then hope to find a market for it afterwards. Successful companies find out what customers need or want and then develop the right product with the right level of quality to meet their expectations, both now and in the future.
- A product does not have to be tangible – an insurance policy can be a product.
- The perfect product provides value for the customer. This value is in the eye of the beholder — we must give our customers what they want, not what we think they want.
- Ask yourself whether you have a system in place to regularly check what your customers think of your product and your supporting services.
- Find out what their needs are now and whether they believe these will change in future.
- Beware the product quality trap – don’t take it too far by trying to sell a Rolls-Royce when the customer really wants a Nissan Micra.
A product is only worth what customers are prepared to pay for it. The price needs to be competitive, but this doesn’t mean you have to be the cheapest in your market – small businesses can compete with larger rivals by offering a more personal service, value-adds or better value for money. You also need to make a profit. Pricing is the only element of the marketing mix that generates revenue — everything else represents a cost to you. When considering the price of your product, it’s important to look at it from the customer’s perspective:
- Price positions you in the marketplace — it tells customers where to place you in relation to your competitors.
- The more you charge, the more value or quality your customers will expect for their money.
- This is a relative measure. If you are the most expensive provider in your market, customers will expect you to provide a better service.
- Everything that the customer sees must be consistent with these higher quality expectations — packaging, environment, promotional materials, website, letterheads, invoices, etc.
- Existing customers are generally less sensitive about price than new customers — a good reason to look after them well.
The product must be available in the right place, at the right time and in the right quantity, while keeping storage, inventory and distribution costs at an acceptable level. The place where customers buy a product, and the means of distributing your product to that place, must be appropriate and convenient for the customer. This applies to brick-and-mortar operations, but is even more important in e-commerce.
- Customer surveys show that delivery performance is one of the most important criteria when choosing a supplier.
- Place also means ways of displaying your product to customer groups. This could be in a shop window, but it could also be online.
- E-commerce operations that sell exclusively on the internet must place even more emphasis on the company website and other online activities, as there are fewer points where the customer will interact with the company.
- For the same reason, all firms that sell online should consider how the product will be delivered to the consumer – even if this is handled by a third party.
- Mobile is an increasingly important purchasing channel for consumers, so it may be a good time to optimise your website. Does yours conform to the latest standards? For example, Google search now penalises websites that are not optimised for mobile, potentially making it more difficult for consumers to find you.
P4 - Promotion
Promotion is the way a company communicates what it does and what it can offer customers. It includes branding, advertising, PR, corporate identity, social media outreach, sales management, special offers and exhibitions. Promotion must gain attention, be appealing, send a consistent message and - above all - give the customer a reason to choose your product rather than someone else’s.
- Good promotion is not one-way communication — it paves the way for a dialogue with customers, whether in person or online.
- Promotion should communicate the benefits that a customer receives from a product, not just its features.
- Your website is often the customer’s first experience of your company – you only have one chance to make a good first impression, so make sure that information on the site is always kept up to date and the design is updated to keep it fresh.
- Explore new channels – from traditional print ads to the latest social media trends, there is now a world of possibilities to explore. The important principle is to always advertise where your target consumer goes.
- Printed promotional material must grab the attention of your customers. It should be easy to read and enable the customer to identify why they should buy your product – A brochure isn’t necessarily the best way of promoting your business. Unlike your website, the information is fixed once a brochure has been printed. A more cost-effective and flexible option might be a folder with a professionally designed sheet inside, over a series of your own information sheets produced in-house. These sheets can be customised by varying them to suit the target customers and/or changing them as required
- Promotion does not just mean communicating with your customers. It is just as important to communicate with staff/fellow employees about the value and attributes of your products. They can then pass on the knowledge to their customers.
P5 - People
Everyone who comes into contact with your customers will make an impression. Many customers cannot separate the product or service from the staff member who provides it, so your people will have a profound effect — positive or negative — on customer satisfaction.
- The reputation of your brand rests in the hands of your staff. They must be appropriately trained, well-motivated and have the right attitude.
- All employees who have contact with customers should be well-suited to the role.
- In the age of social media, every employee can potentially reach a mass audience. Formulate a policy for online interaction and make sure everyone stays on message.
- Likewise, happy customers are excellent advocates for your business. Curate good opinion on review sites.
- Superior after-sales support and advice adds value to your offering, and can give you a competitive edge. These services will probably become more important than price for many customers over time.
- Look regularly at the products that account for the highest percentage of your sales. Do these products have adequate after-sales support, or are you being complacent with them? Could you enhance your support without too much additional cost?
P6 - Process
Many customers no longer simply buy a product or service - they invest in an entire experience that starts from the moment they discover your company and lasts through to purchase and beyond.
- That means the process of delivering the product or service, and the behaviour of those who deliver it, are crucial to customer satisfaction. A user-friendly internet experience, waiting times, the information given to customers and the helpfulness of staff are vital to keep customers happy.
- Customers are not interested in the detail of how your business runs, just that the system works. However, they may want reassurance they are buying from a reputable or ‘authentic’ supplier.
- Remember the value of a good first impression. Identify where most customers initially come into contact with your company - whether online or offline - and ensure the process there, from encounter to purchase, is seamless.
- Do customers have to wait?
- Are they kept informed?
- Is your website fast enough and available on the right devices?
- Are your people helpful?
- Is your service efficiently carried out?
- Do your staff interact in a manner appropriate to your pricing?
Customers trying to reach your company by phone are a vital source of income and returning value, but all too often they're left on hold. Many will give up, go elsewhere and tell their friends not to use your company - just because of the poor process.
P7 - Physical evidence
Choosing an unfamiliar product or service is risky for the consumer, because they don’t know how good it will be until after purchase. You can reduce this uncertainty by helping potential customers ‘see’ what they are buying.
- A clean, tidy and well-decorated reception area – or homepage - is reassuring. If your digital or physical premises aren’t up to scratch, why would the customer think your service is?
- The physical evidence demonstrated by an organisation must confirm the assumptions of the customer — a financial services product will need to be delivered in a formal setting, while a children’s birthday entertainment company should adopt a more relaxed approach.
- Some companies engage customers and ask for their feedback, so that they can develop reference materials. New customers can then see these testimonials and are more likely to purchase with confidence.
- Although the customer cannot experience the service before purchase, he or she can talk to other people with experience of the service. Their testimony is credible, because their views do not come from the company. Alternatively, well-shot video testimonials and reviews on independent websites will add authenticity.
Each of the ‘ingredients’ of the marketing mix is key to success. No element can be considered in isolation — you cannot, for example, develop a product without considering a price, or how it will reach the customer.
The process of considering the seven Ps and pulling them together to form a cohesive strategy is called marketing planning.
Want to read more about the fundamentals of marketing? Check out our other posts in the series, What is marketing and Planning a marketing strategy , or take a look at our marketing fundamentals course which has all of this info and more to get you immersed in everything marketing.
More marketing fundamentals
You may also like

What is Marketing?

Planning a marketing strategy

- Your Project
- 7P Marketing Mix
What is the 7P Marketing Mix?
The 7P Marketing Mix is a set of 7 factors you should focus on when developing your Marketing Strategy .
Why is this definition so similar to the 4P Marketing Mix one? Because is the same concept.
The 7P Marketing Mix is nothing but an extended 4P Marketing Mix .
While the classic 4P Marketing Mix analyzes the:
- Promotion .
The 7P Marketing Mix , simply adds the next 3 factors to this:
Physical Evidence .
We explained in our “ 4P Marketing Mix ” page, the main factors to study within a 4P analysis.
- If you have not visited that page yet, we encourage you to do so right now since here, we’ll just explain the additional 3 factors that a 7P Marketing Mix includes .
What do these 3 new factors mean?
Now, we’ll explain you what these new factors add with some examples and why should you worry about them:
1. Physical Evidence - 7P Marketing Mix
This factor tends to have more than one meaning.
Depending on who you ask you can receive a different answer.
It Usually means 2 things :
- Literally, giving the customer Physical Evidence about what they are buying .
- Show, with Physical Evidence, why your product is the best in the Market .
We know that both of them seem to be the same.
Now, we’ll explain the difference with helpful examples:
1.1 Give Physical Evidence about what they are buying
Sometimes, Companies offer intangible products or some intangible values that are associated to their physical products.
Customers are like “serial killers”: they like keeping evidences about what they purchased .
- The higher the price of the product, the bigger the evidence should be.
This evidence can be in :
- With the Logo of the Brand everywhere.
- Usually in luxury brands.
- With VIP Memberships, for example.
Rolex - Physical Evidence - 7P Marketing Mix example

The Rolex example is the best one we could have chosen since it offers lots of Physical Evidences.
1. As soon as you enter in an authorized Rolex shop :
- If you are intended to buy a Rolex, you’ll surely receive a glass of Champagne .
2. Together with your Watch, you’ll receive:
- A serial number that guarantees that it is not a fake watch.
- A high quality leather box containing the watch.
- Access to the Rolex community ; events, notifications, etc.
3. The watch has a perfectly identifiable design .
- You receive a watch that everybody identifies as synonym of high economical status.

All these things are not assuring you that Rolex is the best technical option you could have made.
These Physical Evidences tell you that you are purchasing a luxury product, nothing else :
- The box may seem very beautiful, but its price is nothing compared to the watch you are acquiring.
- The glass of Champagne may feel very sophisticated, but it represents nothing to the shop: the whole bottle may cost $50.
- If Rolex changed its famous designs, the people wouldn’t identify their watches so easily (and lets be honest; 80% of the people owning a Rolex want to brag about it).
1.2. Physical Evidence about why your product is the best in the Market
This is a different Physical Evidence approach.
While the previous one was more “whim-oriented”, this one is a more Technical approach .
When you are stating that your product is either the best one, or different, you have to give proof about it to your customers before they buy your product .
We will give you an example about what may happen if you don’t or can’t give Physical Evidence to your customers :
Nintendo 3DS - Physical Evidence - 7P Marketing Mix example

As soon as Nintendo announced the Nintendo 3DS we were sure about its success.
- A portable device that can generate 3D images without any glasses : Amazing!
However it didn’t succeeded as much as Nintendo expected … Why?
The problem they had was that Nintendo couldn’t give Physical Evidence about its technically-amazing product through conventional Marketing campaigns .
- You could see a TV commercial where they explained to you how good the 3D images were, but unless you were in front of it, you would never experience the effect .
Nintendo 3DS case is very curious, because Nintendo couldn’t do much for giving Physical Evidence about its product .
This example shows how, sometimes, having the best product in not enough: you always have to give proof about what you offer .
- That is why that many food brands offer you little pieces of cheese, chocolate, drinks… at the supermarkets.
2. Process - 7P Marketing Mix
The process represents all the actions that take place when developing, showing and delivering your product to the final customer .
This is a commonly forgotten factor but for some companies, it represents the real key to success.
Think about how many businesses success mainly, because they have a proper process:
- Automotive companies that elaborate their cars efficiently .
- Websites that have a nice and friendly user interface.
- Fast food companies that have defined a elaboration process that saves time and money.
A proper process can :
- Increase your margins by reducing the costs .
- Allow you to engage more with your customers .
- Ensure the best quality .
Nespresso - Process - 7P Marketing Mix example

If there is a company that has understood how important the “purchasing process” is for engaging your customers, is Nespresso .
- Nespresso is a good example for lots of things: Design, Physical Evidence, Branding…
However, we’ll focus on how good its selling process is :
- They design elegant stores that customers identify with the company’s essence.
- As soon as you enter in its stores, you find stylish people that are always very kind to you .
- The product is placed in perfectly neat shelves .
- They offer you a free coffee .
- You can enter in the Nespresso club , with nice discounts and access to promotions.
- Finally, there are always new flavors so you “feel the obligation” of coming back periodically .

This “purchasing process” generates a desirable experience for the customers and allows Nespresso to project its coffee as a more exclusive product.
If you think about it, Nespresso just sells coffee, nothing else (ok, coffee machines) then… Why do you feel that they are offering you something else?
So, from now on, don’t focus just on the product itself.
Regard it as an entire Manufacturing and Delivery Process :
- From the moment it was being developed to the moment the final client received it.
3. People - 7P Marketing Mix
The People factor refers to everyone involved in the Marketing and Manufacturing process .
Sometimes, this factor only considers people within a Company: Designers, Managers… but Clients should also be taken into account .
Hence, we’ll divide this factor into 2:
- The People involved in the product’s development .
- Clients ‘ profiles.
3.1 People involved in the product's development
This is an extension of the 7P Process factor, previously explained.
A company is as good as the people integrating it , so you should analyze all the professionals involved at key positions:
- Commercials.
Apollo XI - People - 7P Marketing Mix example

It’s been 50 years since the first man reached the moon with the Apollo XI.
Undoubtedly, it is one of the biggest achievements in history of mankind.
But, how on earth could they reach the moon with 1969’s technology?
- They had the best scientists and engineers in the world . That is how.
If you wanted to replicate this big achievement, you would have to hire the best brains in the world.
This simple but effective example shows how sometimes, the key thing for guaranteeing a project’s success is the people involved .
- You can also appreciate this fact at Movies, where the success normally relies on one single actor’s interpretation.
3.2 Clients' profiles
This factor highlights how important is to take into account your clients:
- Who they are .
- Where they come from .
- What they like .
YouTube - People - 7P Marketing Mix example

Some years ago, while I was having a beer at a friend’s house and, I remembered an interesting video I had watched on YouTube.
It was a video that had been suggested to me repeatedly, so I expected to find the same video at the first page of my friend’s computer .
However, I found completely different suggestions at his main page.
Now, we all know that YouTube suggests certain videos to certain profiles.
But at that moment that shocked me, since it was a similar person, with similar cultural background , from the same city, with the same age.
- We went to the same school… so I was surprised YouTube had not suggested this video to my friend.
YouTube analyzes all the videos you have seen so far, the ones that you liked the most, the language of the videos, where you come from… So they can suggest the content that better fits you .
And that is why YouTube is of king of content nowadays.
Categorize customers is very difficult.
Even between brothers and sisters you would have it difficult: how different we are from our parents, cousins, brothers…
No matter how difficult it is: you have to adapt your Marketing strategies to your client’s tastes, cultural backgrounds and preferences .
Otherwise you’ll never engage with them.
Never forget: Your client must be the centre of all the decisions you take .
Summarizing
The 7P Marketing Mix is nothing but an amplified 4P analysis.
To the traditional:
The 7P Marketing Mix adds :
- Give physical evidence about what the customer is buying .
- Give proof about why your product is the best in the market.
- Analyze the actions that take place when developing, showing and delivering your product to the final customer .
- Which are the clients’ profiles .
- Economies of Scale
- Business Plan for Beginners
- Business Plan Basics
- How to write a Business Plan
- Cash Flow Calculation
- Raising Funds for a Business
- 4 C’s of Credit
- Business Plan Templates
- Customer Insight
- Customer Experience
- Customer Pain Points
- 4C Marketing Model
- RATER Model
- Augmented Product
- Product Mix
- Unique Selling Proposition
- DAGMAR Model
- Marketing Storytelling
- Content Marketing
- Psychographics
- Barnum Effect
- Market Segmentation
- Market Research & Big Data
- Marketing to Generation Z
- 4P Marketing Mix
- Sales Funnel
- Loyalty Ladder
- RACE Planning
- Push and Pull Marketing
- Marketing Strategy
- Marketing Templates
- Starting your own business
- From Startup to a Business
- Entrepreneur FAQs
- Start your Business Idea
- Entrepreneur Golden Rules
- Innovate or Imitate?
- Design Thinking
- SCAMPER Model
- AAR Process
- Work From Home
- Growth strategies for Startups
- VMOST Analysis
- 3P Framework
- SOAR Analysis
- TELOS Analysis
- 5 C’s of Entrepreneurship
- Crowdfunding
- BATNA & ZOPA Negotiation
- Entrepreneur with no Money
- Entrepreneurship Templates
- Strategy vs Tactics
- Mission and Vision
- Business Values
- Value Chain
- Scenario Planning
- Porter 6 Forces
- Bowman’s Strategy Clock
- GE-McKinsey Matrix
- Delta Model
- PEST Analysis
- PESTEL Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- VRIO Framework
- Strategy Canvas
- Competitive Advantages
- Porter’s Four Corners
- 5 Ps of Strategy
- Porter’s Generic Strategies
- Porter’s Diamond Model
- Wardley Map
- Core Competencies
- Resource Based View
- Bridges Transition Model
- CAGE Distance Framework
- McKinsey’s 3 Horizons
- Vertical Integration
- Horizontal Integration
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Red Ocean Strategy
- Porter 5 Forces
- Ansoff Matrix
- McKinsey 7S Framework
- CATWOE Analysis
- Strategy Pyramid
- Bain’s RAPID Framework
- Balanced Scorecard
- Resources and Capabilities
- Strategy of Apple
- Strategy of Amazon
- Strategy of Starbucks
- Strategy Templates
- Communicate Effectively
- COIN Conversation Model
- SCARF Model
- SBI Feedback Model
- CEDAR Feedback Model
- How to behave at a meeting
- Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
- Bloom’s Taxonomy
- 5E Learning Model
- 9-Box Performance Grid
- SEEDS Bias Model
- Halo Effect
- Pygmalion Rosenthal Effect
- Dunning-Kruger Effect
- How to be an Entrepreneur
- How to be a Leader
- Mintzberg Managerial Roles
- Cog’s Ladder
- The Peter Principle
- How to Negotiate
- Teamwork Skills and Profiles
- Gantt Chart
- RACI Matrix
- Eisenhower Matrix
- MoSCoW Method
- FMEA Process
- Problem Solving
- Ishikawa Fishbone diagram
- 5 Whys Method
- 8 Disciplines Method
- ADDIE Model
- ORAPAPA Method
- Cynefin Framework
- Just In Time
- SMART Goals
- KISS Principle
- Birkinshaw’s 4 Dimensions
- Parkinson’s Law
- OGSM Framework
- OKR Methodology
- APQP Framework
- Theory of Constraints
- Success through Organization
- ADKAR Model
- Lewin’s Change Model
- Kotter’s 8-Step Model
- The Greiner Curve
- GAP Analysis
- Planning Templates
- Mean, Median and Mode
- Define your Data
- Pareto Principle 80/20 Rule
- Decision Matrix
- Decision Tree
- TARA Framework
- Root Cause Analysis
- Simplex Process
- Forecasting Methods
- Product Life Cycle
- How to use Google Trends
- Correlation vs Causation
© 2024 - Consuunt .
We're not around right now. But you can send us an email and we'll get back to you, asap.
Log in with your credentials
Forgot your details.
Marketing Mix paper Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Introduction
Coca cola company, promotion strategies, pricing methods.
Over the recent past, marketing has grown to become one of the key functional areas of business organizations. This growth has come in the wake of the realization that the traditional business practice methods are no longer relevant in the modern day business environment (Michael & Saren, 2010).
For a long time, business managers ignored the aspect of marketing and paid much emphasis on the production of goods and services. However, in the current day business world where competition is a major determinant of the adoptability of a product by the consumers, marketing has become an inevitable functional area of most organizations.
The importance of marketing comes in that the various products; both goods and services offered by an organization ought to be presented to the target consumers. More so, due to the availability of competitor products and supplementary products, marketing is necessary so as to help push the products to the consumers (Richard, 2009). Marketing therefore takes different forms and the final aim of any marketing activity is to enable the product being marketed to get adopted by the target consumers.
The success of a marketing strategy and subsequent marketing activities is judged by the increase in the amount of sales generated from the marketing activity (Marian, 2010). This essay presents and explains the four elements of marketing mix; Product, Pricing, Promotion and Place. The Coca cola Company will be analyzed in this essay.
Coca Cola Company is the world’s number one manufacturer, marketer and distributor of non-alcoholic drinks. It is a multinational giant that has headquarters in the United States of America. The company has managed to produce top brands in the beverage industry such as Fanta, Coke, and Sprite and so on. Its main objective is to maintain its global leadership in the production and distribution of the soft drinks.
This objective has largely been achieved because most of the coca cola company products are house hold brands and continue to be used by many. The challenge is however maintaining this status and in order to achieve this, the company has come up with ways in which it can effectively use the 4 Ps of marketing to ensure that its brand remains visible all over the world. The following text discusses how the different P’s of marketing have affected the Coca-cola company marketing strategy.
Product is one of the four main elements of marketing mix that concerns with the product itself. A company’s product is the sole reason for the existence of the company. This is because it is what meets the customers’ needs (Michael & Saren, 2010). There are various attributes of a product that help in marketing. These include the product lifecycle, product line and the product mix. A marketer should be able to manage the product in such a manner that its relevant to the consumers’ needs remain unaffected (Richard, 2009).
Coca-cola Company has managed to incorporate this marketing element to be able to achieve some marketing objective. One way of dealing with the product is through having a continual reinvention of the product that makes sure that the consumers continue to enjoy and derive benefits from that particular product.
The other way is by extending the product life cycle. The company has managed to continually re-invent its products over the years and this has offered a great deal of help in retaining the brand visibility among majority of consumers in the world.
The various Coca-cola Company products such as the Coke, Fanta, and Sprite have maintained their visibility among the consumers over the years. These products have been regularly associated with the young people and as such, the marketing strategy for these products revolves round the young people. This has been a successful strategy since the products have remained house hold brands among many individuals.
Promotion is the other marketing mix element that deals with a company’s act of driving the products to the consumers. This is achieved through employing marketing activities that convince the consumers to purchase the particular product (Christ, 2011). There are various available promotional strategies. The most common ones are the push-pull strategy and the message & media strategy.
The push-pull strategy deals with the manufacturer promoting the product to the retailers directly so as to ensure that they keep the goods in their stock. The message & media strategy deals with the manufacturer performing the promotional activities independent of the retailer and this is aimed at creating a demand for the product among the consumers such that the retailers will act on the demand and therefore stock the product (Richard, 2009).
Coca-cola Company has majorly employed the message & media strategy. Their products are marketed via the different media such as the televisions, bill-boards, Social media, and so on. This element of promotion has affected the company’s marketing strategy since the company majorly employs promotion as the key marketing activity for its products.
The company gains a lot from this strategy since the consumers who regularly see these promotional messages in the mass media become accustomed to the products and as such, develop loyalty on the products. The brands that have managed to achieve success through this method are Coke and Fanta.
Pricing is another element of marketing mix that deals with the setting of the product price. Price is usually the factor that determines the consumers’ willingness and ability to pay for the particular product (Christ, 2011). This is because of the fact that money is usually a scarce resource and as such, the available limited disposable income is allocated to the unlimited competing needs. Companies therefore ought to have a pricing strategy that does not exploit the consumers hence scaring them from purchasing the products.
The Coca-Cola Company effectively employs the pricing strategy and as such, it is able to gain a competitive advantage over other competitors’ such as Pepsi. The Coca-cola products are sold at relative lower prices comparing to the competitors. this has been achieved through the ability to gain on the economies of scale therefore having low products cost per unit.
The strategy that the company has used in this area is through having a suggested retail price. This prevents that consumers from being exploited by the retailers and also helps maintain the confidence the consumers have on the brand.
This marketing element has to deal with the businesses’ act of ensuring that the products are presented at a convenient location to the consumers. Place also forms a type of utility where the consumer needs the product being offered by the business to be in an accessible location or a convenient one (Marian, 2010).
This is done either through transporting the products to the areas near the consumer or carrying out production near the consumers. The boon in this is that the consumer is allowed is able to purchase the product without major logistical issues.
Coca-cola Company has been able to put this element into consideration when coming up with marketing strategy. The company has expanded its tentacles to almost all the countries of the world and as such, it is able to carry out production and subsequent distribution to the consumers at their convenience.
Companies that have moved their products closer to the consumers not only enjoy brand visibility and recognition among the consumers but they also incur fewer expenses during production. The advantage of this is that the company is able to sell at lower prices and thus attract more customers who result in growth in the revenues.
Coca-cola Company has set numerous bottling plants in many countries and this has greatly helped in achieving low production costs. This has also ensured that the consumers purchase these goods at their own convenience. The strategy involved by Coca-Cola Company in this case is referred to as exclusive distribution.
This is where the company opts to solely and exclusively carry out its own distribution process without engaging other third parties. This helps in the consumers’ appreciation of the products and also increased the brand value of the company among the various consumers.
The importance of incorporating the 4Ps of marketing in crafting the marketing strategy cannot be overemphasized. Once a company has fully articulated the requirements of the 4ps of marketing, the marketers need to incorporate the customer focus marketing approach that leads to the 4Cs of marketing mix. These are the Commodity, cost, channel, and Communication. Once all these factors are put in place, the marketing strategy can be said to be complete and as such positive results can be expected from such an approach.
Christ, P. (2011). Principles of Marketing. New York: Butterworth- Heinemann.
Marian, B. W. (2010). Essential Guide to Marketing Planning. New York: Pearson Publishers.
Michael, J. B., & Saren, M. (2010). marketing Theory. London: Sage Publishers.
Richard, H. (2009). Brilliant Marketing: What the Best Marketers Know, Do and Say (3rd Edition ed.). New York: Pearson.
- BatesManor Furniture Marketing Plan
- Marketing's Definition and Developmnt
- Brand Overview: Diet Coke
- “The Corporation” Documentary Analysis
- Cola Wars Continue: Coke and Pepsi in 2010
- Palisades Promotional Assessment
- Australian Beauty Industry
- Ford Mustang Market Environment Research
- Marketing Research on Biotech Industry
- Marketing Strategy: Product Perceptual Map
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, November 6). Marketing Mix paper. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/
"Marketing Mix paper." IvyPanda , 6 Nov. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Marketing Mix paper'. 6 November.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Marketing Mix paper." November 6, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.
1. IvyPanda . "Marketing Mix paper." November 6, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Marketing Mix paper." November 6, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/marketing-mix-paper/.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The first formula of the marketing mix included four elements, so-called 4Ps, which were: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. Gradually the notion of the marketing mix has been extended to 7Ps by adding such elements as Processes, Physical Evidence, ad People (Schneider & Bowen 1998, p. 213). Product is a service produced by the company; it ...
The Marketing Mix is a framework to help marketers develop a marketing strategy. The traditional marketing mix contains four elements, often referred to in marketing textbooks as ' The 4Ps ', which are, namely, Product, Price, Promotion and Place, extending into ' The 7Ps ' with People, Process and Physical Evidence.
An example of a company using the 7Ps marketing mix in their strategy. Take a look at HubSpot as an example, which was founded in 2006; Hubspot now boasts over 86,000 total customers in more than 120 countries. Comprised of Marketing Hub, Sales Hub, Service Hub, CMS Hub, and a powerful free CRM, HubSpot adds value for customers in every aspect ...
In the realm of marketing, the "seven P's of marketing" stand as fundamental principles guiding our efforts. These seven elements, namely Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Processes, and Physical Evidence, collectively constitute the marketing mix. They provide a framework for marketers to evaluate and optimize their campaigns, making ...
The marketing mix or 7Ps is a foundation model in marketing. it helps to define the tactics to make the marketing plan happen. A planned approach to marketing helps us to set clear objectives based on the current situation a company is facing. The strategy defines how those objectives will be achieved, including the target market to focus on ...
This will have absolutely no impact on the amount you pay. The 7 Ps of the marketing mix (product, price, place, promotion, people, process and physical evidence) provide a helpful checklist to evaluate a product or service by ensuring that the critical areas of a value proposition are considered for the target market.
Contends that the numerous and ad hoc conceptualizations undermine the concept of the marketing mix and proposes that Booms and Bitner′s (1981) 7Ps mix for services be extended to other areas of ...
No matter which platforms you choose as your marketing tools, the seven Ps can serve as tried and true basic marketing tactics that you can adapt into your marketing efforts to best fit your ...
Marketing mix is simply placing he right product in the right place for the right customer at the right price. There is no universal definition of what is right, it is instead a relative concept and depends on the nature of the product and organisation's skills and resources. Marketers must have a detailed idea of the business plan in order ...
Using the Marketing Mix. Each of the 7Ps found in a marketing mix work together to ensure your business is a success. The 7Ps also have an impact on your positioning, targeting, and segmentation decisions, so it's crucial to understand their benefits to create your own marketing mix. If you would like more information on how you can create ...
Check our 💯 free 7Ps marketing mix examples submitted by straight-A students. Find inspiration or ideas for your own 7Ps matrix. ️ Daily updates. ... The IvyPanda's free database of academic samples contains thousands of essays on any topic. Use them for inspiration, insights into a specific topic, as a reference, or even as a template for ...
Traditionally, the marketing mix is a framework for your marketing strategy containing four key elements: Product, Place, Price and Promotion. Then we have the extended marketing mix - or the 7Ps - which contains the first four elements, plus Physical Evidence, People and Processes. It's important to note that while the marketing mix can ...
The Seven Ps of Marketing is a relatively simple framework that can be used by any organisation or manager to plan marketing activities and a marketing strategy. It is useful because it ensures that you look across each area together, and consider how they might be related. The Seven Ps started as just four: product, price, place and promotion.
The 7Ps of Marketing Mix. The Marketing Mix 7P is an extension of the traditional Marketing Mix, and it includes the seven Ps: Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence.Let's take a look at each of these elements in detail. Product. The product P refers to the goods or services that a business offers to its customers.
Combining these marketing tactics to meet the customers' needs and wants is known as using a 'tactical marketing mix'. This marketing mix is a familiar marketing strategy tool that was traditionally limited to the core 4Ps - Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. In the 7 Ps, the new additions are People, Process, Physical evidence.
The marketing mix theory, first coined by E. Jerome McCarthy in the 1960s, forms the foundation model for every business today. Earlier, the marketing framework was confined to the characteristics of marketing systems and their functions. McCarthy provided a framework for marketing decision-making centered around the product, price, place, and promotion through his marketing mix theory.
Question. What are the 4Ps & 7Ps of the marketing mix? Answer. The marketing mix is a tool used when developing a marketing strategy. The four P's of the marketing mix consist of product, place, price and promotion: Product - This refers to an item which can satisfy customer needs or demands, which can be either a tangible good (physical existence) or an intangible service.
Usefulness of the 7Ps mix with respect to its general applicability (i.e. across a wide range of subjects) Degree of usefulness Very useful extension Useful extension Neither superior nor inferior Of little use Of no use Total (per cent) Number of respondents UK % Respondents European % All % 17.4 47.8 17.4 17.4 0.0 100 46 1.9 50.0 26.9 11.5 10 ...
service marketin. from product marketing. In their market-ing mix, three Ps namely personnel, physical assets and procedur. s were added and. inally 7Ps were shaped. (Culliton, 1948). Below, one can find the definition of marketing mix elements: Product is a. l necessary components and elements to doa service which.
The 7Ps of marketing. The 7Ps of marketing are product, price, place, promotion, people, process and physical evidence. This post and more is contained within our CIM ebook, 7Ps: a brief summary of marketing and how it works . Learn the 7Ps and you're well on your way to having your marketing fundamentals completed.
Rolex - Physical Evidence - 7P Marketing Mix example. The Rolex example is the best one we could have chosen since it offers lots of Physical Evidences. 1. As soon as you enter in an authorized Rolex shop: If you are intended to buy a Rolex, you'll surely receive a glass of Champagne. 2.
Here main emphasis has been given on the service sector & hence aim of article is to analyze the marketing mix. It's a part of service marketing, where Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People ...
The success of a marketing strategy and subsequent marketing activities is judged by the increase in the amount of sales generated from the marketing activity (Marian, 2010). This essay presents and explains the four elements of marketing mix; Product, Pricing, Promotion and Place. The Coca cola Company will be analyzed in this essay.