Encyclopedia for Writers
Writing with ai, coherence – how to achieve coherence in writing.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - Founder, Writing Commons
Coherence refers to a style of writing where ideas, themes, and language connect logically, consistently, and clearly to guide the reader's understanding. By mastering coherence , alongside flow , inclusiveness , simplicity, and unity , you'll be well-equipped to craft professional or academic pieces that engage and inform effectively. Acquire the skills to instill coherence in your work and discern it in the writings of others.

Table of Contents

What is Coherence?
Coherence in writing refers to the logical connections and consistency that hold a text together, making it understandable and meaningful to the reader. Writers create coherence in three ways:
- logical consistency
- conceptual consistency
- linguistic consistency.
What is Logical Consistency?
- For instance, if they argue, “If it rains, the ground gets wet,” and later state, “It’s raining but the ground isn’t wet,” without additional explanation, this represents a logical inconsistency.
What is Conceptual Consistency?
- For example, if you are writing an essay arguing that regular exercise has multiple benefits for mental health, each paragraph should introduce and discuss a different benefit of exercise, all contributing to your main argument. Including a paragraph discussing the nutritional value of various foods, while interesting, would break the conceptual consistency, as it doesn’t directly relate to the benefits of exercise for mental health.
What is Linguistic Consistency?
- For example, if a writer jumps erratically between different tenses or switches point of view without clear demarcation, the reader might find it hard to follow the narrative, leading to a lack of linguistic coherence.
Related Concepts: Flow ; Given to New Contract ; Grammar ; Organization ; Organizational Structures ; Organizational Patterns ; Sentence Errors
Why Does Coherence Matter?
Coherence is crucial in writing as it ensures that the text is understandable and that the ideas flow logically from one to the next. When writing is coherent, readers can easily follow the progression of ideas, making the content more engaging and easier to comprehend. Coherence connects the dots for the reader, linking concepts, arguments, and details in a clear, logical manner.
Without coherence, even the most interesting or groundbreaking ideas can become muddled and lose their impact. A coherent piece of writing keeps the reader’s attention, demonstrates the writer’s control over their subject matter, and can effectively persuade, inform, or entertain. Thus, coherence contributes significantly to the effectiveness of writing in achieving its intended purpose.
How Do Writers Create Coherence in Writing?
- Your thesis statement serves as the guiding star of your paper. It sets the direction and focus, ensuring all subsequent points relate back to this central idea.
- Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments to strengthen your position and add depth to your writing.
- Use the genres and organizational patterns appropriate for your rhetorical situation . A deductive structure (general to specific) is often effective, guiding the reader logically through your argument. Yet different disciplines may privilege more inductive approaches , such as law and philosophy.
- When following a given-to-new order, writers move from what the reader already knows to new information. In formal or persuasive contexts, writers are careful to vet new information for the reader following information literacy laws and conventions .
- Strategic repetition of crucial terms and your thesis helps your readers follow your main ideas and evidence for claims
- While repetition is useful, varying language with synonyms can prevent redundancy and keep the reader engaged.
- Parallelism in sentences can provide rhythm and clarity, making complex ideas easier to follow.
- Consistent use of pronouns avoids confusion and helps in maintaining a clear line of thought.
- Arrange your ideas in a sequence that naturally builds from one point to the next, ensuring each paragraph flows smoothly into the next .
- Signposting , or using phrases that indicate what’s coming next or what just happened, can help orient the reader within your argument.
- Don’t bother repeating your argument in your conclusion. Prioritize conciseness. Yet end with a call to action or appeal to kairos and ethos .
Recommended Resources
- Organization
- Organizational Patterns
The Elements of Style

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Recommended

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Structured Revision – How to Revise Your Work

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Authority & Credibility – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing

Citation Guide – Learn How to Cite Sources in Academic and Professional Writing

Page Design – How to Design Messages for Maximum Impact
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Comments This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - How to Differentiate Quality Information from Misinformation & Rhetrickery
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. You need to be strategic about how you consume and use information in order to thrive,...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

| Essay writing Essay writing |
Achieving coherence
“A piece of writing is coherent when it elicits the response: ‘I follow you. I see what you mean.’ It is incoherent when it elicits the response: ‘I see what you're saying here, but what has it got to do with the topic at hand or with what you just told me above?’ ” - Johns, A.M
Transitions
Parallelism, challenge task, what is coherence.
Coherence in a piece of writing means that the reader can easily understand it. Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly. The reader can see that everything is logically arranged and connected, and relevance to the central focus of the essay is maintained throughout.

Pronouns are useful cohesive devices because they make it unnecessary to repeat words too often. Consider the following:
Repetitious referencing:
When Gillette first invented disposable razor blades, he found it very hard to sell the disposable razor blades . He found it very hard to sell the disposable razor blades because nobody had marketed a throw-away product before.
When Gillette first invented disposable razor blades, he found it very hard to sell them . This was because nobody had marketed a throw-away product before.
Pronouns as cohesive devices
This following presentation shows how pronouns can be used effectively to achieve coherence within a text and some common problems of use.

Repetition in a piece of writing does not always demonstrate cohesion. Study these sentences:
|
So, how does repetition as a cohesive device work?
When a pronoun is used, sometimes what the pronoun refers to (ie, the referent) is not always clear. Clarity is achieved by repeating a key noun or synonym . Repetition is a cohesive device used deliberately to improve coherence in a text.
In the following text, decide ifthe referent for the pronoun it is clear. Otherwise, replace it with the key noun English where clarity is needed.
English has almost become an international language. Except for Chinese, more people speak it ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select3" ).html( document.getElementById( "select3" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); than any other language. Spanish is the official language of more countries in the world, but more countries have English ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select4" ).html( document.getElementById( "select4" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); as their official or unofficial second language. More than 70% of the world's mail is written in English ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select5" ).html( document.getElementById( "select5" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); It ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select6" ).html( document.getElementById( "select6" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); is the primary language on the Internet. (p.23). Text source: Oshima, A. and Hogue. A. (2006). (4th ed.). NY: Pearson Education |
Click here to view the revised text.
Suggested improvement
English has almost become an international language. Except for Chinese, more people speak it (clear reference; retain) than any other language. Spanish is the official language of more countries in the world, but more countries have English ( it is replaced with a key noun) as their official or unofficial second language. More than 70% of the world's mail is written in English ( it is replaced with a key noun). It (clear reference; retain) is the primary language on the Internet.
Sometimes, repetition of a key noun is preferred even when the reference is clear. In the following text, it is clear that it refers to the key noun gold , but when used throughout the text, the style becomes monotonous.
Gold, a precious metal, is prized for two important characteristics. First of all, has a lustrous beauty that is resistant to corrosion. Therefore, is suitable for jewellery, coins and ornamental purposes. never needs to be polished and will remain beautiful forever. For example, a Macedonian coin remains as untarnished today as the day it was minted 23 centuries ago. Another characteristic of is its usefulness to industry and science. For many years, has been used in hundreds of industrial applications, such as photography and dentistry. Its most recent use is in astronauts’ suits. Astronauts wear heat shields made from for protection when they go outside spaceships in space. In conclusion, is treasured not only for its beauty but also its utility. (p.22). Text source: Oshima, A. and Hogue, A. (2006). (4th ed.). NY: Pearson Education |
Improved text: Note where the key noun gold is repeated. The deliberate repetition creates interest and adds maturity to the writing style.
Gold , a precious metal, is prized for two important characteristics. First of all, gold has a lustrous beauty that is resistant to corrosion. Therefore, it is suitable for jewellery, coins and ornamental purposes. Gold never needs to be polished and will remain beautiful forever. For example, a Macedonian coin remains as untarnished today as the day it was made 23 centuries ago. Another important characteristic of gold is its usefulness to industry and science. For many years, it has been used in hundreds of industrial applications. The most recent use of gold is in astronauts’ suits. Astronauts wear gold -plated shields when they go outside spaceships in space. In conclusion, gold is treasured not only for its beauty but also its utility.
Pronoun + Repetition of key noun
Sometimes, greater cohesion can be achieved by using a pronoun followed by an appropriate key noun or synonym (a word with a similar meaning).
In the two main studies, no dramatic change was found in the rate of corrosion. could be due to several reasons. Generally speaking, crime rates in Europe have fallen over the past two years. has been the result of new approaches to punishment. When a group of school children was interviewed, the majority said they preferred their teachers to be humorous yet kind. However, were not as highly rated by teachers. |
Transitions are like traffic signals. They guide the reader from one idea to the next. They signal a range of relationships between sentences, such as comparison, contrast, example and result. Click here for a more comprehensive list of Transitions (Logical Organisers) .
Test yourself: How well do you understand transitions?
Which of the three alternatives should follow the transition or logical organiser in capital letters to complete the second sentence?
Using transitions/logical organisers
Improve the coherence of the following paragraph by adding transitions in the blank spaces. Use the italicised hint in brackets to help you choose an apporpriate transition for each blank. If you need to, review the list of Transitions (Logical Organisers) before you start.
First, CDs brought digital sound into people's homes. Then DVD technology brought digital sound and video and completely revolutionised the movie industry. Soon there will be 1. ( ) revolution: Blu-ray *BDs. A Blu-ray disc will have several advantages. 2. ( ), it has an enormous data storage capacity. A single-sided DVD can hold 4.7 gigabytes of information, about the size of an average 2-hour movie. A single-sided BD, 3. ( ) can hold up to 27 gigabytes, enough for 13 hours of standard video. A 4. ( ) advantage is that a BD can record, store, and play back high-definition video because of its larger capacity. A double-layer BD can store about 50 gigabytes, enough for 4.5 hours of high-definition video. The cost will be the same. 5. ( ), a BD has a higher data transfer rate - 36 megabits per second - than today's DVDs, which transfer at 10 megabits per second. 6. ( ), a BD can record 25 gigabytes of data in just over an hour and a half. 7. ( , because of their storage capacity and comparable cost, BDs will probably take over the market when they become widely available. (p.31). Text source: Oshima, A. and Hogue, A. (2008). 4th ed.). NY: Pearson Longman Ltd. |
Using transitions
Choose the most appropriate transition from the options given to complete the article:
There are three separate sources of hazards related to the use of nuclear reactions to supply us with energy. Firstly ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select14" ).html( document.getElementById( "select14" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , the radioactive material must travel from its place of manufacture to the power station. Although ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select15" ).html( document.getElementById( "select15" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); the power stations themselves are solidly built, the containers used for the transport of the material are not. Unfortunately, there are normally only two methods of transport available, namely ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select16" ).html( document.getElementById( "select16" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); road or rail, and both of these involve close contact with the general public, since ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select17" ).html( document.getElementById( "select17" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); the routes are bound to pass near or through heavily-populated areas. Secondly ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select18" ).html( document.getElementById( "select18" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , there is the problem of waste. All nuclear power stations produce wastes which in most cases will remain radioactive for thousands of years. It is impossible to de-activiate these wastes; consequently ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select19" ).html( document.getElementById( "select19" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , they must be disposed of carefully. For example ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select20" ).html( document.getElementById( "select20" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , they may be buried under the ground, dropped into disused mineshafts, or sunk in the sea. However ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select21" ).html( document.getElementById( "select21" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , these methods do not solve the problem; they merely store it, since ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select22" ).html( document.getElementById( "select22" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); an earthquake could crack open the containers. Thirdly ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select23" ).html( document.getElementById( "select23" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , there is the problem of accidental exposure due to a leak or an explosion at the power station. As with the other two hazards, this is extremely unlikely. Nevertheless ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select24" ).html( document.getElementById( "select24" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); it can happen. Separately, and during short periods, these three types of risk are no great cause for concern. Taken together, though ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select25" ).html( document.getElementById( "select25" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , and especially over much longer periods, the probability of a disaster is extremely high. (p. 62). Text source: Coe, N., Rycroft, R., & Ernest, P. (1983). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
Overusing transitions
While the use of appropriate transitions can improve coherence (as the previous practice activity shows), it can also be counterproductive if transitions are overused. Use transitions carefully to enhance and clarify the logical connection between ideas in extended texts. Write a range of sentences and vary sentence openings.
Study the following examples:
: If people stopped drinking, they might be able to prevent the onset of liver disease. , governments permit the production and sale of alcohol. , they should help in preventing this disease. , government resources are limited. : If people stopped drinking, they might be able to prevent the onset of liver disease. Governments permit the production and sale of alcohol. They should help in preventing this disease. Government resources are limited.
If people stopped drinking, they might be able to prevent the onset of liver disease. The government should help in preventing this disease they permit the production and sale of alcohol. Government resources, , are limited. |
Identifying cohesive devices

1. Repetition of key noun
2. Repetition of key noun
3. Pronoun + Repetition
4. Repetition with synonym
5. Pronoun
6. Pronoun
7. Transition
8. Transition
9. Repetition of key noun
10. Pronoun
11. Pronoun + Repetition
Write the name of the cohesive device - pronoun , repetition or transition - in the space after each underlined word or phrase before the blank.
The Sinking of the Titanic
In 1912, the Titanic, the largest and best equipped transatlantic liner of pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select26" ).html( document.getElementById( "select26" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); time, hit an iceberg on pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select27" ).html( document.getElementById( "select27" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); first crossing from England to America and sank. Of the 2,235 parrengers and crew, only 718 survivived. Research has shown that a number of factors played an important part in the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select28" ).html( document.getElementById( "select28" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); . transition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select29" ).html( document.getElementById( "select29" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select30" ).html( document.getElementById( "select30" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); carried only sixteen lifeboats, with room for about 1,100 people. pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select31" ).html( document.getElementById( "select31" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); was clearly not enough for a ship of the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select32" ).html( document.getElementById( "select32" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); size. transition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select33" ).html( document.getElementById( "select33" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , the designer of the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select34" ).html( document.getElementById( "select34" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); originally planned to equip the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select35" ).html( document.getElementById( "select35" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); with forty-eight repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select36" ).html( document.getElementById( "select36" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); ; transition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select37" ).html( document.getElementById( "select37" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , in order to reduce pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select38" ).html( document.getElementById( "select38" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); costs for building the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select39" ).html( document.getElementById( "select39" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , the owners of the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select40" ).html( document.getElementById( "select40" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); decided to give pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select41" ).html( document.getElementById( "select41" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); only sixteen repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select42" ).html( document.getElementById( "select42" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); . A transition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select43" ).html( document.getElementById( "select43" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select44" ).html( document.getElementById( "select44" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); was that the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select45" ).html( document.getElementById( "select45" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); crew were not given enough time to become familiar with the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select46" ).html( document.getElementById( "select46" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , especially with pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select47" ).html( document.getElementById( "select47" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); emergency equipment. transition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select48" ).html( document.getElementById( "select48" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , many repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select49" ).html( document.getElementById( "select49" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); left the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select50" ).html( document.getElementById( "select50" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); only half-full and many more people died than needed to. The transition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select51" ).html( document.getElementById( "select51" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select52" ).html( document.getElementById( "select52" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); in the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select53" ).html( document.getElementById( "select53" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); was the behaviour of the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select54" ).html( document.getElementById( "select54" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); officers on the night of the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select55" ).html( document.getElementById( "select55" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); . In the twenty-four hours before the repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select56" ).html( document.getElementById( "select56" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); , pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select57" ).html( document.getElementById( "select57" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); received a number of warnings about repetition ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select58" ).html( document.getElementById( "select58" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); in the area, but pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select59" ).html( document.getElementById( "select59" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); took no precautions. pronoun ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); tmpAr.push( ' ' ); jQuery( "#select60" ).html( document.getElementById( "select60" ).innerHTML + tmpAr.join( '' )); did not change direction or even reduce speed. (p. 22). Source: Pakenham, K.J. (1998). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
Using cohesive devices - pronouns and repetition
Read through the text below and consider how you might use pronouns and repetition (either with a key noun or synonym) to replace the bolded expressions. Write your revised text in the submission box.
| Facebook did not invent social networking, but the company has fine-tuned into a science. When a newcomer logs in, the experience is designed to generate something Facebook calls the aha! moment. is an observable emotional connection, gleaned by videotaping the expressions of test users navigating for the first time. Facebook has developed a formula for the precise number of aha! moments users must have before are hooked. Company officials will not say exactly what that magic number is, but everything about Facebook is geared to reach as quickly as possible. So far, at least, Facebook has avoided the digital exoduses that beset predecessors, MySpace and Friendster. is partly because Facebook is so good at making indispensable. Losing Facebook hurts. Source: Fletcher, D. (2010, May 31). Friends without borders. , 21, 16-22. |
| Write the revised text here: |
Click here to view a suggested answer.
Suggested answer :
The Aha! Moment
Facebook did not invent social networking, but the company has fine-tuned it ( pronoun-first person ) into a science. When a newcomer logs in, the experience is designed to generate something Facebook calls the aha! moment. This ( pronoun-determiner ) is an observable emotional connection, gleaned by videotaping the expressions of test users navigating the site ( repetition with synonym ) for the first time. Facebook has developed a formula for the precise number of aha! moments users must have before they ( pronoun-third person ) are hooked. Company officials will not say exactly what that magic number is, but everything about the site ( repetition with synonym ) is geared to reach it as quickly as possible.
So far, at least, Facebook has avoided the digital exoduses that beset its ( pronoun-possessive ) predecessors, MySpace and Friendster. This is partly because Facebook is so good at making itself ( pronoun-reflexive ) indispensable. Losing Facebook hurts.
Cohesion between paragraphs
So far, we have looked at cohesion within paragraphs. In longer texts of several paragraphs, a combination of pronouns, transition and reptition can be used to maintain logical flow and connection between paragraphs.
The extract presented here consists of four paragraphs of an expository essay entitled Sustainable Development from a Historical Perspective: The Mayan Civilisation . Note how the bolded expressions at the start of the second, third and fourth paragraphs provide cohesive links to the paragraph preceding them.
Click to view Cohesion between paragraphs.
Sometimes known as parallel structures or balanced constructions, parallelism is the use of similar grammatical forms or sentence structures when listing or when comparing two or more items.
When used correctly, parallelism can improve the clarity of your writing.
): : The elderly residents enjoy many recreational activities: swimming, *read and *to garden. : The elderly residents enjoy many recreational activities: , , and .
: The academic conversation group consists of students from China, Japan, Korea and *some Germans. : The academic conversation group consists of students from , , , and
: This paper discusses the main features of the AST system, the functionalities, and *the system also has a number of limitations. : This paper discusses the , , and |
Parallelism in extended texts
The following excerpt from Bertrand Russell's famous prologue to his autobiography has some classic examples of parallelism:

: The computer is both fast and *it has reliability
: The computer is both and .
: The problem with electronic banking is neither the lack of security nor *the fact that you pay high interest rates.
: The problem with electronic banking is neither nor .
: The aim of the new law is not only to reduce the incidence of boy racing but also *setting up new standards for noise tolerance in the whole neighbourhood.
: The aim of the new law is not only ... but also new standards for noise tolerance in the whole neighbourhood.
Correcting faulty parallel constructions
Correct the faulty parallel constructions ( bold ) in the following sentences.
1. The researcher wanted to find out where the new immigrants came from and to talk about their future plans.
2. The earthquake victims were both concerned about water contamination and the slow response from the government also made them angry.
3. An ideal environment for studying includes good lighting, a spacious room, and the furniture must be comfortable.
4. Computers have changed the way people live, for their work, and how they use their leisure time.
5. Houses play an important role not only to provide a place to live, but also for giving a sense of security.
| Write your corrections here: |
Click here to view the suggested answers.
Suggested answers :
1 The researcher wanted to find out where the new immigrants came from and what their future plans were.
2. The earthquake victims were both concerned about water contamination and angry at the the slow response from the government.
3. An ideal environment for studying includes good lighting, a spacious room, and comfortable furniture.
4. Computers have changed the way people live, work, and use their leisure time.
5. Houses play an important role not only to provide a place to live, but also to give a sense of security.
Recognising parallel structures
Read through the text and underline the examples of parallel structures (there are five of them). If you can, write the type of grammatical form used in each case. The first one has been done for you as an example.
Write out the entire paragraph in the submission box if it is easier.
Now you try :
Not only have geneticists found beneficial uses of genetically engineered organisms in agriculture, but they have also found ( 1. paired conjunctions ) useful ways to use these organisms advantageously in the larger environment. According to the Monsanto company, a leader in genetic engineering research, recombinant DNA techniques may provide scientists with new ways to clean up the environment and with more efficient methods of producing chemicals. By using genetically engineered organisms, scientists have been able to produce natural gas. This process will decrease society's dependence on the environment and will reduce the rate at which natural resources are depleted. In other processes, genetically engineered bacteria are being used both to extract metals from their geological setting and to speed the breakup of complex petroleum mixtures which will help to clean up oil spills. (p. 523).
Source: Rosen, L.J. (1995). Discovery and commitment: A guide for college writers. Mass.: Allyn and Bacon.
| Write your answer here. |
Click here to view the answer to the question above

| « | » |
- Select text to style.
- Paste youtube/vimeo url to add embeded video.
- Click + sign or type / at the beginning of line to show plugins selection.
- Use image plugin to upload or copy/paste image searched from internet or paste in snip/sketched image from snap tool
Pasco-Hernando State College
- Unity and Coherence in Essays
- The Writing Process
- Paragraphs and Essays
- Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking
- Appropriate Language
Test Yourself
- Essay Organization Quiz
- Sample Essay - Fairies
- Sample Essay - Modern Technology
Related Pages
- Proving the Thesis
Unity is the idea that all parts of the writing work to achieve the same goal: proving the thesis. Just as the content of a paragraph should focus on a topic sentence, the content of an essay must focus on the thesis. The introduction paragraph introduces the thesis, the body paragraphs each have a proof point (topic sentence) with content that proves the thesis, and the concluding paragraph sums up the proof and restates the thesis. Extraneous information in any part of the essay that is not related to the thesis is distracting and takes away from the strength of proving the thesis.
An essay must have coherence. The sentences must flow smoothly and logically from one to the next as they support the purpose of each paragraph in proving the thesis.
Just as the last sentence in a paragraph must connect back to the topic sentence of the paragraph, the last paragraph of the essay should connect back to the thesis by reviewing the proof and restating the thesis.
Example of Essay with Problems of Unity and Coherence
Here is an example of a brief essay that includes a paragraph that does not support the thesis “Many people are changing their diets to be healthier.”
People are concerned about pesticides, steroids, and antibiotics in the food they eat. Many now shop for organic foods since they don’t have the pesticides used in conventionally grown food. Meat from chicken and cows that are not given steroids or antibiotics are gaining popularity even though they are much more expensive. More and more, people are eliminating pesticides, steroids, and antibiotics from their diets. Eating healthier also is beneficial to the environment since there are less pesticides poisoning the earth. Pesticides getting into the waterways is creating a problem with drinking water. Historically, safe drinking water has been a problem. It is believed the Ancient Egyptians drank beer since the water was not safe to drink. Brewing beer killed the harmful organisms and bacteria in the water from the Nile. There is a growing concern about eating genetically modified foods, and people are opting for non-GMO diets. Some people say there are more allergic reactions and other health problems resulting from these foods. Others are concerned because there are no long-term studies that clearly show no adverse health effects such as cancers or other illnesses. Avoiding GMO food is another way people are eating healthier food.
See how just one paragraph can take away from the effectiveness of the essay in showing how people are changing to healthier food since unity and coherence are affected. There is no longer unity among all the paragraphs. The thought pattern is disjointed and the essay loses its coherence.
Transitions and Logical Flow of Ideas
Transitions are words, groups of words, or sentences that connect one sentence to another or one paragraph to another.
They promote a logical flow from one idea to the next and overall unity and coherence.
While transitions are not needed in every sentence or at the end of every paragraph, they are missed when they are omitted since the flow of thoughts becomes disjointed or even confusing.
There are different types of transitions:
- Time – before, after, during, in the meantime, nowadays
- Space – over, around, under
- Examples – for instance, one example is
- Comparison – on the other hand, the opposing view
- Consequence – as a result, subsequently
These are just a few examples. The idea is to paint a clear, logical connection between sentences and between paragraphs.
- Printer-friendly version

Paragraph Unity, Coherence, and Development
In each paragraph of an essay, one particular idea or topic is developed and explained. In order to successfully do so, however, it is essential that the paragraph be written in a unified and coherent manner.
A unified paragraph must follow the idea mentioned in the topic sentence and must not deviate from it. For a further explanation on topic sentences, see the Write Right on Topic Sentences .
A coherent paragraph has sentences that all logically follow each other; they are not isolated thoughts. Coherence can be achieved in several ways. First, using transitions helps connect ideas from one sentence to the next. For more on transitions, see the Write Right on Transitions . Second, ordering thoughts in numerical sequence helps to direct the reader from one point to the next. Third, structuring each paragraph according to one of the following patterns helps to organize sentences: general to particular; particular to general; whole to parts; question to answer; or effect to cause.
Remember that a paragraph should have enough sentences so that the main idea of the topic sentence is completely developed. Generalizations should be supported with examples or illustrations. Also, details and descriptions help the reader to understand what you mean. Don't ever assume that the reader can read your mind: be specific enough to develop your ideas thoroughly, but avoid repetition
An effective paragraph might look like this:
It is commonly recognized that dogs have an extreme antagonism toward cats. This enmity between these two species can be traced back to the time of the early Egyptian dynasties. Archaeologists in recent years have discovered Egyptian texts in which there are detailed accounts of canines brutally mauling felines. Today this type of cruelty between these two domestic pets can be witnessed in regions as close as your own neighborhood. For example, when dogs are walked by their masters (and they happen to catch sight of a stray cat), they will pull with all their strength on their leash until the master is forced to yield; the typical result is that a feline is chased up a tree. The hatred between dogs and cats has lasted for many centuries, so it is unlikely that this conflict will ever end.
This paragraph is effective for the following reasons:
- The paragraph shows unity. All the sentences effectively relate back to the topic sentence at the beginning of the paragraph.
- The paragraph shows coherence. There is a flow of thoughts and ideas among the sentences in this paragraph. There are good transitions employed in the paragraph. The writer also presents her sub-topics in an orderly fashion that the reader can follow easily.
- The paragraph is developed. The writer gives herself enough space to develop the topic. She gives us at least two reasons to accept her argument and incorporates some examples in order to give those reasons more validity.
Reference: Strunk, Wiliam Jr., and E. B. White. The Elements of Style . 4th ed., Allyn and Bacon, 2000.
Copyright © 2009 Wheaton College Writing Center
Cohesion And Coherence In Essay Writing
Table of contents, introduction, definitions cohesion and coherence, what is coherence, what is cohesion, how to achieve cohesion and coherence in essay writing, lexical cohesion, grammatical cohesion, substitutions, conjunctions transition words, cohesive but not coherent texts.
The player threw the ball toward the goalkeeper. Balls are used in many sports. Most balls are spheres, but American football is an ellipsoid. Fortunately, the goalkeeper jumped to catch the ball. The crossbar in the soccer game is made of iron. The goalkeeper was standing there.
How to write a coherent essay?
1. start with an outline, 2. structure your essay.
| Parts of the essay | Content |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Introduces the topic. Provides background information Presents the thesis statement of the essay |
| Body | The body of the essay is made up of several paragraphs depending on the complexity of your argument and the points you want to discuss. Each paragraph discusses one main point. Each paragraph includes a topic sentence, supporting details, and a concluding sentence. All paragraphs must relate to the thesis. |
| Conclusion | The conclusion summarizes the main points of the essay. It must not include new ideas. It draws a final decision or judgment about the issues you have been discussing. May connect the essay to larger topics or areas of further study. |
3. Structure your paragraphs
4. relevance to the main topic, 5. stick to the purpose of the type of essay you’re-writing, 6. use cohesive devices and signposting phrases.
| Cohesive device | Examples |
|---|---|
| Lexical | Repetition. Synonymy. Antonymy. Hyponymy. Meronymy. |
| Grammatical | Anaphora. Cataphora. Ellipsis. Substitutions. Conjunctions and transition words. |
What is signposting in writing?
Essay signposting phrases.
| Signposting | Functions | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Transition words | Expressing addition | in addition – as well as – moreover – what is more… |
| Expressing contrast | however – yet – nevertheless – nonetheless – on the contrary – whereas… | |
| Expressing cause and effect | consequently – as a consequence – as a result – therefore… | |
| Expressing purpose | in order to – in order not to – so as to… | |
| Summarizing | in conclusion – to conclude – to sum up | |
| Other signposting expressions | To introduce the essay | – This essay aims at… – This essay will be concerned with… – It shall be argued in this essay… – This essay will focus on… |
| To introduce a new idea | – Having established…, it is possible now to consider… – … is one key issue; another of equal importance is… – Also of significant importance is the issue of… – With regard to… – With respect to… – Firstly, … – Secondly, … – Finally, … | |
| To illustrate something | – One aspect that illustrates … is … – An example of… – …can be identified as… – The current debate about… illustrates – This highlights… | |
| To be more specific and emphasize a point | – Importantly, – Indeed, – In fact, – More importantly, – It is also important to highlight – In particular, In relation to, More specifically, With respect to, In terms of | |
| Changing direction | – To get back to the topic of this paper, … – Speaking of…, … – That reminds me of… – That brings to mind… – On a happier/sad note, … – Another point to consider is … | |
| Comparing | – In comparison, … – Compared to… – Similarly, … – Likewise,… – Conversely – In contrast, … – On the one hand, … – On the other hand, … | |
| Going into more detail on a point | – In particular… – Specifically… – Concentrating on … – By focusing on …. in more detail, it is possible… to… – To be more precise … | |
| Rephrasing | – In other words, … – To put it simply, … – That is to say… – To put it differently, … – To rephrase it, … – In plain English, … | |
| Reintroducing a topic | – As discussed/explained earlier, … – The earlier discussion on… can be developed further here, … – As stated previously, … – As noted above,… | |
| Introducing an opposing/alternative view | – An alternative perspective is given by… who suggests/argues that… – This conflicts with the view held by… – Alternatively, … | |
| Concluding | – It could be concluded that… – From this, it can be concluded that… – The evidence shows that… – In conclusion,… -In summary, … |
7. Draft, revise, and edit

How Coherence in Writing Facilitates Manuscript Acceptance
Coherence is an essential quality for good academic writing . In academic writing, the flow of ideas from one sentence to the next should be smooth and logical. Without cohesion, the reader will not understand the main points that you are trying to make. It also hampers readability. Cohesion necessarily precedes coherence. There is a difference between cohesion and coherence: cohesion is achieved when sentences are connected at the sentence level, whereas as coherence is achieved when ideas are connected. In addition, cohesion focuses on the grammar and style of your paper.
What is Coherence in Writing?
Coherence also means “clarity of expression” and it is created when correct vocabulary and grammar are used. After all, the goal of writing is to benefit the readers. Without both coherence and cohesion, the readers may detect choppiness in the text and feel as if there are gaps in the ideas presented. Needless to say, texts without coherence are difficult to read and understand. It defeats the whole purpose of writing, which is to relay ideas in a clear and efficient manner. There are strategies that you can use to ensure coherence and cohesion in academic writing.
Examples of Cohesive and Non-Cohesive Paragraphs
Paragraph coherence and cohesion results in paragraph unity . To ensure that your paragraphs have unity, there are two things to keep in mind: it must have a single topic (found in the topic sentence) and sentences provide more detail than the topic sentence, while maintaining the focus on the idea presented. The paragraph below shows a lack of unity:
Non-cohesive sample: Dogs are canines that people domesticated a long time ago. Wolves are predecessors of dogs and they help people in a variety of ways. There are various reasons for owning a dog, and the most important is companionship.
Cohesive sample: Dogs are canines that people domesticated a long time ago, primarily for practical reasons. Even though dogs descended from wolves, they are tame and can be kept in households. Since they are tame, people have various reasons for owning a dog, such as companionship.
Notice that the ideas in the non-cohesive sample are not arranged logically. The sentences are not connected by transitions and give the readers new ideas that are not found in the topic sentence. Thus, the paragraph is hard to read, leaving readers confused about the topic. On the other hand, the cohesive sample has ideas arranged logically. All ideas in this sample flow from the topic sentence. In addition, they give more details about the topic while maintaining their focus on the topic sentence.
Establishing Coherence
It is important to focus on coherence when writing at the sentence level. However, cohesion smoothens the flow of writing and should be established. There are various ways to ensure coherent writing :
- Write sentences that flow by varying the lengths and structures, the use of correct punctuation, and broadening your word choices
- Use simple transitions, such as “in addition, additionally, furthermore, therefore, thus, on the contrary, by the same token, at the same time, in other words, etc.”
- Repeat your keywords but be careful of excessive repetition
- Repeat sentence structures, which is used as a rhetorical technique rather than cohesion to highlight parallelism between sentences
- Ensure thematic consistency
- Start every sentence or paragraph with information that hints at the content of the next sentence
Academic writing is improved by coherence and cohesion. Without coherence and cohesion, readers will become confused and eventually disinterested in the article. Your ideas then become lost and the primary objective of writing is not achieved.
Tips and Strategies
There are six ways for creating coherence, which you will find useful while polishing your manuscript. Creating coherence is not as difficult as it seems, but you will need the right tools and strategies to achieve it.
- >Lexis creates cohesion using synonyms, hyponyms, and superordinates. The use of lexical chains creates variety in writing and avoids monotony.
- Reference creates cohesion by using possessive pronouns (e.g. your, their, etc.), pronouns (e.g. she, me, etc.), and determiners (e.g. those, these, etc.).
- Substitution, which is the use of a different word in place of a previously mentioned word (e.g. “I bought a designer bag today. She did the same.”)
- Ellipsis is the removal or omission of words because their meaning is implied through context (e.g. “He goes to yoga classes in the afternoon. I hope I can too.”)
- Cohesive nouns are also called umbrella nouns because they summarize many words in one.
- Conjunctions include words that list ideas (e.g. first, next, then, lastly, etc.)
Academic writing should be concise, coherent, and cohesive. Maintaining these three qualities involves using a number of strategies to impart ideas to the reader. After all, that is the whole point of any type of writing.
Thanks for this nice post. It is very useful.
rich info, thank you.
Thanks for the well explained meaning of cohesion and coherence, how ever, I rated this post with 5 🌟 to show my appreciation, once again thanks 😂😀😀
Nice content 👍🏻
Very interesting content
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Language & Grammar
- Reporting Research
How to Avoid Run-on Sentences in Academic Writing
When writing a paper, are you more focused on ideas or writing style? For most…

How to Improve Your Academic Writing Using Language Corpora
No matter how brilliant a researcher you are, you must be able to write about…

- Global Spanish Webinars
- Old Webinars
Cómo Dominar el Arte de Escribir Manuscritos en Inglés
Consejos de corrección Errores comunes de manuscritos Aplicación de la gramática inglesa Consejos sobre redacción…
- Global Japanese Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
英語での論文執筆をマスターする
英語でのライティングスキルの重要性 論文英語の組み立て 日本人によくある英語の間違い 論文執筆の基本

- Infographic
Top 10 Tips to Increase Academic Vocabulary for Researchers
Improving academic vocabulary is an important skill for all researchers. Academic vocabulary refers to the words…
Avoid These Common Grammatical Errors in Your Paper
Manuscript Drafting: Why is Subject-Verb Agreement Important?

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

Which among these features would you prefer the most in a peer review assistant?

- WRITING SKILLS
Coherence in Writing
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Writing Skills:
- A - Z List of Writing Skills
The Essentials of Writing
- Common Mistakes in Writing
- Introduction to Grammar
- Improving Your Grammar
- Active and Passive Voice
- Punctuation
- Clarity in Writing
- Writing Concisely
- Gender Neutral Language
- Figurative Language
- When to Use Capital Letters
- Using Plain English
- Writing in UK and US English
- Understanding (and Avoiding) Clichés
- The Importance of Structure
- Know Your Audience
- Know Your Medium
- Formal and Informal Writing Styles
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Creative Writing
- Top Tips for Writing Fiction
- Writer's Voice
- Writing for Children
- Writing for Pleasure
- Writing for the Internet
- Journalistic Writing
- Technical Writing
- Academic Writing
- Editing and Proofreading
Writing Specific Documents
- Writing a CV or Résumé
- Writing a Covering Letter
- Writing a Personal Statement
- Writing Reviews
- Using LinkedIn Effectively
- Business Writing
- Study Skills
- Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Have you ever read a piece of writing and wondered what point the writer was trying to make? If so, that piece of writing probably lacked coherence. Coherence is an important aspect of good writing—as important as good grammar or spelling. However, it is also rather harder to learn how to do it, because it is not a matter of simple rules.
Coherent writing moves smoothly between ideas. It guides the reader through an argument or series of points using signposts and connectors. It generally has a clear structure and consistent tone, with little or no repetition. Coherent writing feels planned —usually because it is. This page provides some tips to help you to develop your ability to write coherently.
Defining Coherence
Dictionary definition of coherence
cohere , v. to stick together, to be consistent, to fit together in a consistent, orderly whole.
coherence , a sticking together, consistency.
Source: Chambers English Dictionary, 1989 edition.
The dictionary definition of coherence is clear enough—but what does that mean in practical terms for writers?
Once you have achieved coherence in your writing, you will find that:
Your sentences and ideas are connected and flow together;
Readers can move easily through the text from one sentence, paragraph or idea to the next; and
Readers will be able to follow the ideas and main points of the text.
On the other hand, a text that is NOT coherent jumps between ideas without making clear connections between them. It is often hard to follow the argument. Readers may find themselves unclear about the point of particular paragraphs or even whole sections. There may be odd sentences that do not fit well with the previous or following sentence, or paragraphs that repeat earlier ideas.
All these issues provide pointers for how to develop coherence.
Elements of Coherence
There are several different elements that contribute to coherence, or are closely linked to the concept.
They include:
Cohesion , or whether ideas are linked within and between sentences.
Unity , or the extent to which a sentence, paragraph or section focuses on a single idea or group or ideas. In any given paragraph, every sentence should be relevant to a single focus.
A joint effort
Together, cohesion and unity mean that sentences and paragraphs are connected around a central theme.
- Flow , or how the reader is led through the text. Some of this is about the ordering of ideas, but it also takes into account issues like phrasing, rhythm and style. Some people define flow as the quality that makes writing engaging and easy to read.
Levels of Coherence
We can consider coherence at several different levels. These include:
Within sentences. A sentence is coherent when it flows naturally, and uses correct grammar , spelling and punctuation . Coherence also includes the use of the most appropriate words, and avoidance of redundancy.
Between sentences . Coherence between sentences means that each sentence flows logically and naturally from the previous one. Connections are made between them so that readers can see the flow of ideas, and how each sentence is linked to the previous one.
Within paragraphs . This is a logical extension of coherence between sentences. Coherence within a paragraph means that the sentences within the paragraph work together as a whole to present a complete thesis or idea.
Why single-sentence paragraphs don’t work
This definition of ‘within paragraph’ coherence explains why you should (almost) never use single-sentence paragraphs. A single sentence is (almost) never going to be able to provide a complete summary of your thesis or idea.
Between paragraphs . For most pieces of writing, you will also need to consider how the paragraphs fit together. Each paragraph covers an idea or thesis—and must then be connected logically to the next paragraph, so that your overall thesis is built step-by-step.
Between subsections or sections . This final level of coherence is only really important for longer documents. You must create a logical flow between different sections, to guide your reader from one to the next so that they can follow the development of your ideas.
Techniques to Improve Coherence
The first step to improving coherence is to plan your writing in advance.
Decide on the main point that you want to make, and the ideas that will lead your reader towards your point. It is also helpful to consider your planned audience, and what they want from your text.
There is more about this in our page on Know Your Audience . You may also find it helpful to read our page on Know Your Medium , to check whether there is anything about your publishing medium that you need to consider ahead of starting to write.
There are some techniques that you can use to help improve coherence within your writing. These include:
Using transitional expressions and phrases to signal connections
Words and phrases like ‘however’, ‘because’, ‘therefore’, ‘additionally’, and ‘on the one hand... on the other’ can be used to signal connections between sentences and paragraphs.
WARNING! Real connections needed!
Transitional phrases and words should only be used where the ideas really are connected.
Just inserting transitional expressions will not connect your ideas. Instead, you need to create a reasonable progression of ideas through a paragraph or section.
You also need to use transitional expressions sparingly. Not all ideas need an obvious link—and sometimes putting one in can seem awkward and contrived.
Using repeating forms or parallel structures to emphasise links between ideas
Generally speaking, repetition of words and phrases is unadvisable.
However, used sparingly, you may be able to harness repetition as a way to signal connections between sentences or ideas.
For example, many research papers have a section setting out the limitations of the study. These limitations can often be quite diverse, which makes for a rather disjointed section. To overcome this issue, writers often use the form ‘First... Second... Finally...’ to demonstrate the links between the disparate ideas.
Using pronouns and synonyms to eliminate unnecessary repetition
Repetition is often the enemy of coherence because it interrupts your movement through the writing. You tend to get distracted by the repeated words, and lose the thread of the argument or idea.
Pronouns and synonyms are a good way to avoid repeating words and phrases. However, care is needed when using them, to avoid ambiguity. It is advisable NOT to use pronouns following a sentence with two elements that might take the same pronoun.
For example:
John was sure that Tom was wrong. He had made the same argument last week.
Who made the same argument last week? John or Tom?
It is better to use at least one name again than create ambiguity.
TOP TIP! Come back later
It is often hard to detect ambiguity in your own writing because you know what you wanted to say.
It is therefore a good idea to leave any piece of writing overnight, and read it again in the morning. This will often identify problems such as ambiguous pronouns, and give you a chance to revise them.
Revisit, Revise and Review
Alongside planning, the single most important thing that you can do to improve the coherence of a piece of writing is to review and revise it with the reader’s needs in mind.
When you have finished a piece of writing, put it aside for a while. Overnight is ideal, but longer is fine. Once you have had a chance to forget precisely what you meant, read it over again as if you were coming to it for the first time.
As you start to read, consider the focus of your text: the main point that you want to make.
With that in mind, consciously examine whether the ideas flow clearly through your sentences, paragraphs and sections. Can the reader grasp your argument and follow it through the text? Is there an obvious conclusion?
While you are reading, you should also consider whether there are any very long sentences. If so, shorten them, using transitional words or phrases to link them together effectively. This will make your writing easier to read, and it will naturally flow better.
A Final Thought
It is not always easy to know how to create more coherent writing.
The best way to do so is to plan your writing, and then review it carefully. You should particularly consider your focus, and your readers’ needs. In doing so, you may find it helpful to use some of the techniques described on this page—but they will not, in themselves, be sufficient without the planning and review.
Continue to: Writing Concisely Using Plain English
See also: The Importance of Structure in Writing Editing and Proofreading Copywriting
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence

Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
| --> |
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
|
|
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Cohesion How to make texts stick together
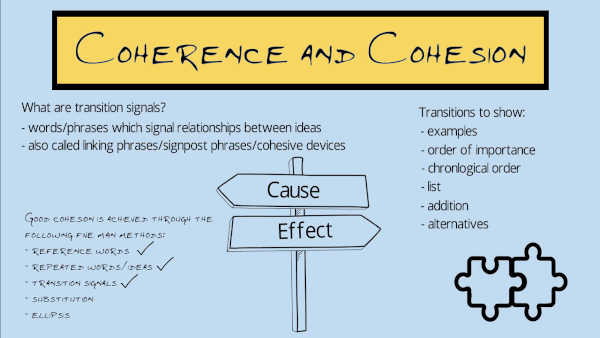
Cohesion and coherence are important features of academic writing. They are one of the features tested in exams of academic English, including the IELTS test and the TOEFL test . This page gives information on what cohesion is and how to achieve good cohesion. It also explains the difference between cohesion and coherence , and how to achieve good coherence. There is also an example essay to highlight the main features of cohesion mentioned in this section, as well as some exercises to help you practise.
For another look at the same content, check out YouTube or Youku , or the infographic .
It is important for the parts of a written text to be connected together. Another word for this is cohesion . This word comes from the verb cohere , which means 'to stick together'. Cohesion is therefore related to ensuring that the words and sentences you use stick together.
Good cohesion is achieved through the following five main methods, each of which is described in more detail below:
- repeated words/ideas
- reference words
- transition signals
- substitution
Two other ways in which cohesion is achieved in a text, which are covered less frequently in academic English courses, are shell nouns and thematic development . These are also considered below.
Repeated words/ideas

Check out the cohesion infographic »
One way to achieve cohesion is to repeat words, or to repeat ideas using different words (synonyms). Study the following example. Repeated words (or synonyms) are shown in bold.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing . It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report . You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features . The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
In this example, the word cohesion is used several times, including as a verb ( coheres ). It is important, in academic writing, to avoid too much repetition, so using different word forms or synonyms is common. The word writing is also used several times, including the phrase essay or report , which is a synonym for writing . The words important features are also repeated, again using synonyms: key feature , important aspect .
Reference words
Reference words are words which are used to refer to something which is mentioned elsewhere in the text, usually in a preceding sentence. The most common type is pronouns, such as 'it' or 'this' or 'these'. Study the previous example again. This time, the reference words are shown in bold.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing. It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report. You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features. The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
The words it , which and these are reference words. The first two of these, it and which , both refer to 'cohesion' used in the preceding sentence. The final example, these , refers to 'important features', again used in the sentence that precedes it.
Transition signals, also called cohesive devices or linking words, are words or phrases which show the relationship between ideas. There are many different types, the most common of which are explained in the next section on transition signals . Some examples of transition signals are:
- for example - used to give examples
- in contrast - used to show a contrasting or opposite idea
- first - used to show the first item in a list
- as a result - used to show a result or effect
Study the previous example again. This time, the transition signals are shown in bold. Here the transition signals simply give a list, relating to the five important features: first , second , third , fourth , and final .
Substitution
Substitution means using one or more words to replace (substitute) for one or more words used earlier in the text. Grammatically, it is similar to reference words, the main difference being that substitution is usually limited to the clause which follows the word(s) being substituted, whereas reference words can refer to something far back in the text. The most common words used for substitution are one , so , and auxiliary verbs such as do, have and be . The following is an example.
- Drinking alcohol before driving is illegal in many countries, since doing so can seriously impair one's ability to drive safely.
In this sentence, the phrase 'doing so' substitutes for the phrase 'drinking alcohol before driving' which appears at the beginning of the sentence.
Below is the example used throughout this section. There is just one example of substitution: the word one , which substitutes for the phrase 'important features'.
Ellipsis means leaving out one or more words, because the meaning is clear from the context. Ellipsis is sometimes called substitution by zero , since essentially one or more words are substituted with no word taking their place.
Below is the example passage again. There is one example of ellipsis: the phrase 'The fourth is', which means 'The fourth [important feature] is', so the words 'important feature' have been omitted.
Shell nouns
Shell nouns are abstract nouns which summarise the meaning of preceding or succeeding information. This summarising helps to generate cohesion. Shell nouns may also be called carrier nouns , signalling nouns , or anaphoric nouns . Examples are: approach, aspect, category, challenge, change, characteristics, class, difficulty, effect, event, fact, factor, feature, form, issue, manner, method, problem, process, purpose, reason, result, stage, subject, system, task, tendency, trend, and type . They are often used with pronouns 'this', 'these', 'that' or 'those', or with the definite article 'the'. For example:
- Virus transmission can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals. These methods , however, are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals.
- An increasing number of overseas students are attending university in the UK. This trend has led to increased support networks for overseas students.
In the example passage used throughout this section, the word features serves as a shell noun, summarising the information later in the passage.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing. It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report. You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features . The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
Thematic development
Cohesion can also be achieved by thematic development. The term theme refers to the first element of a sentence or clause. The development of the theme in the rest of the sentence is called the rheme . It is common for the rheme of one sentence to form the theme of the next sentence; this type of organisation is often referred to as given-to-new structure, and helps to make writing cohere.
Consider the following short passage, which is an extension of the first example above.
- Virus transmission can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals. These methods, however, are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals. It is important for such health workers to pay particular attention to transmission methods and undergo regular screening.
Here we have the following pattern:
- Virus transmission [ theme ]
- can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals [ rheme ]
- These methods [ theme = rheme of preceding sentence ]
- are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals [ rheme ]
- health workers [ theme, contained in rheme of preceding sentence ]
- [need to] to pay particular attention to transmission methods and undergo regular screening [ rheme ]
Cohesion vs. coherence
The words 'cohesion' and 'coherence' are often used together with a similar meaning, which relates to how a text joins together to make a unified whole. Although they are similar, they are not the same. Cohesion relates to the micro level of the text, i.e. the words and sentences and how they join together. Coherence , in contrast, relates to the organisation and connection of ideas and whether they can be understood by the reader, and as such is concerned with the macro level features of a text, such as topic sentences , thesis statement , the summary in the concluding paragraph (dealt with in the essay structure section), and other 'bigger' features including headings such as those used in reports .
Coherence can be improved by using an outline before writing (or a reverse outline , which is an outline written after the writing is finished), to check that the ideas are logical and well organised. Asking a peer to check the writing to see if it makes sense, i.e. peer feedback , is another way to help improve coherence in your writing.
Example essay
Below is an example essay. It is the one used in the persuasion essay section. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different cohesive aspects in this essay, i.e. repeated words/ideas, reference words, transition signals, substitution and ellipsis.
Title: Consider whether human activity has made the world a better place.
History shows that human beings have come a long way from where they started. They have developed new technologies which means that everybody can enjoy luxuries they never previously imagined. However , the technologies that are temporarily making this world a better place to live could well prove to be an ultimate disaster due to , among other things, the creation of nuclear weapons , increasing pollution , and loss of animal species . The biggest threat to the earth caused by modern human activity comes from the creation of nuclear weapons . Although it cannot be denied that countries have to defend themselves, the kind of weapons that some of them currently possess are far in excess of what is needed for defence . If these [nuclear] weapons were used, they could lead to the destruction of the entire planet . Another harm caused by human activity to this earth is pollution . People have become reliant on modern technology, which can have adverse effects on the environment . For example , reliance on cars causes air and noise pollution . Even seemingly innocent devices, such as computers and mobile phones, use electricity, most of which is produced from coal-burning power stations, which further adds to environmental pollution . If we do not curb our direct and indirect use of fossil fuels, the harm to the environment may be catastrophic. Animals are an important feature of this earth and the past decades have witnessed the extinction of a considerable number of animal species . This is the consequence of human encroachment on wildlife habitats, for example deforestation to expand cities. Some may argue that such loss of [animal] species is natural and has occurred throughout earth's history. However , the current rate of [animal] species loss far exceeds normal levels [of animal species loss] , and is threatening to become a mass extinction event. In summary , there is no doubt that current human activities such as the creation of nuclear weapons , pollution , and destruction of wildlife , are harmful to the earth . It is important for us to see not only the short-term effects of our actions, but their long-term ones as well. Otherwise , human activities will be just another step towards destruction .
Aktas, R.N. and Cortes, V. (2008), 'Shell nouns as cohesive devices in published and ESL student writing', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 7 (2008) 3-14.
Alexander, O., Argent, S. and Spencer, J. (2008) EAP Essentials: A teacher's guide to principles and practice . Reading: Garnet Publishing Ltd.
Gray, B. (2010) 'On the use of demonstrative pronouns and determiners as cohesive devices: A focus on sentence-initial this/these in academic prose', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 9 (2010) 167-183.
Halliday, M. A. K., and Hasan, R. (1976). Cohesion in English . London: Longman.
Hinkel, E. (2004). Teaching Academic ESL Writing: Practical Techniques in Vocabulary and Grammar . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc Publishers.
Hyland, K. (2006) English for Academic Purposes: An advanced resource book . Abingdon: Routledge.
Thornbury, S. (2005) Beyond the Sentence: Introducing discourse analysis . Oxford: Macmillan Education.

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for essay cohesion and coherence. Use it to check your own writing, or get a peer (another student) to help you.
| There is good use of (including synonyms). | ||
| There is good use of (e.g. 'it', 'this', 'these'). | ||
| There is good use of (e.g. 'for example', 'in contrast'). | ||
| is used, where appropriate. | ||
| is used, if necessary. | ||
| Other aspects of cohesion are used appropriately, i.e. (e.g. 'effect', 'trend') and | ||
| There is good via the thesis statement, topic sentences and summary. |
Next section
Find out more about transition signals in the next section.
- Transitions
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about paraphrasing .
- Paraphrasing
Exercises & Activities Some ways to practise this area of EAP
You need to login to view the exercises. If you do not already have an account, you can register for free.
- Register
- Forgot password
- Resend activiation email

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 03 February 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
Coherence And Cohesion: Writing Tips For Seamless Texts
Learn coherence and cohesion secrets to create seamlessly flowing, impactful writing. Read this content and understand both.
Understanding the importance of coherence and cohesion in writing is fundamental, as these principles significantly impact how well your message is conveyed to the reader. These concepts empower you to create clear, logical, and organized content.
When your writing lacks coherence, it may appear disjointed, confusing, and challenging for the reader to follow. On the other hand, without cohesion, your ideas may seem scattered and unrelated. Mastering these aspects not only enhances the overall quality of your writing but also ensures your audience can easily grasp and appreciate the information you’re presenting.
In this article, you will gain an in-depth understanding of these essential elements. The exploration begins with a clear definition of coherence and cohesion, followed by an examination of their intricate relationship.
Definition Of Coherence
Coherence is a fundamental aspect of effective communication through written language. It encompasses the logical and orderly arrangement of ideas, details, and arguments within a text, ensuring that they connect seamlessly to convey a clear and unified message. Coherent writing allows readers to follow the author’s thought process without confusion or disruption.
This connection of ideas is achieved through the strategic use of organization, structure, transitional elements, and logical progression. In essence, coherence is the glue that binds individual sentences, paragraphs, and sections into a cohesive and comprehensible whole, making it an indispensable element for conveying information, presenting arguments, and telling compelling stories in written form.
Definition Of Cohesion
Cohesion refers to the quality of a written text that makes it clear, organized, and logically connected. It is achieved through various linguistic devices such as transitional words, pronoun references, repetition, and logical sequencing.
Cohesion ensures that the ideas within a text flow smoothly and are linked together, making the text easier to understand and follow. In essence, cohesion contributes to the overall coherence of a written piece, ensuring that it is cohesive and well-structured.
Relationship Between Coherence And Cohesion
The relationship between coherence and cohesion in writing is a close and interdependent one. Coherence and cohesion work together to create well-structured and easily understandable texts.
Coherence primarily deals with the overall clarity and logical flow of ideas in a piece of writing. It involves the organization of content in a way that makes sense to the reader. Coherent writing maintains a clear and consistent focus on the topic, using logical transitions between sentences and paragraphs.
On the other hand, cohesion focuses on the specific linguistic devices and techniques used to connect different parts of a text. These devices include transitional words (e.g., “therefore,” “however”), pronoun references (e.g., “it,” “they”), repetition of key terms, and logical sequencing of ideas. Cohesion ensures that the sentences within a text are linked together smoothly, enhancing the readability and comprehension of the content.
In essence, cohesion serves as a tool to achieve coherence. When a writer effectively employs cohesive elements in their writing, it enhances the overall coherence of the text. Without cohesion, even well-structured ideas may appear disjointed or confusing to the reader. Therefore, coherence and cohesion are complementary aspects of effective writing, working hand in hand to convey ideas clearly and persuasively.
Types Of Cohesion
Cohesion plays a vital role in the coherence and flow of your writing. In this section, we will explore different types of cohesion, each contributing to the overall clarity and structure of your text.
Grammatical Cohesion
Grammatical cohesion focuses on the grammatical and structural elements within a text that contribute to its coherence. It involves using linguistic devices, like pronouns and sentence structure, to create clear relationships between ideas and sentences. This type of cohesion ensures smooth writing flow and aids readers in understanding connections between different parts of your text.
For instance, pronouns like “it,” “they,” and “this” refer back to previously mentioned nouns, preventing repetition. Sentence structure, including parallelism and transitional words, also plays a crucial role in achieving grammatical cohesion. It ensures consistent presentation of similar ideas and guides readers through your writing.
Reiterative Cohesion
Reiterative cohesion involves the repetition of words, phrases, or ideas within a text to reinforce key concepts and enhance clarity. This type of cohesion is particularly useful when you want to emphasize specific points or themes throughout your writing.
By restating essential elements, you create a sense of continuity and remind readers of the central message. However, it’s crucial to use reiteration judiciously to avoid redundancy and monotony.
Lexical/Semantic/Logical Cohesion
Lexical, semantic, or logical cohesion ensures meaningful connections in your text. Writers use techniques like synonyms, antonyms, and precise vocabulary to clarify complex ideas. It also maintains consistency in word meanings and logical progression, enhancing clarity and engagement.
Referential Cohesion
Referential cohesion involves linking ideas and information within a text. It’s achieved by using pronouns, demonstratives, or repetition to connect concepts. This cohesion helps readers follow the flow of the text and understand the relationships between different parts of the content.
Textual Or Interpersonal Cohesion
Textual or interpersonal cohesion focuses on how language is used to engage and communicate with the reader. It involves strategies such as addressing the reader directly, using inclusive language, and creating a sense of connection. This type of cohesion aims to make the text more relatable and interactive, enhancing the reader’s overall experience.
Tips For Using Coherence And Cohesion In Writing
When it comes to effective writing, coherence, and cohesion play a pivotal role in shaping the clarity and flow of your text. In this section, we’ll delve into practical tips for harnessing these vital elements to create well-structured and engaging content.
Develop Topic Sentences And Themes
Effective writing hinges on clear topic sentences and well-defined themes. These elements act as your text’s structural framework, ensuring both you and your readers follow a logical path through your content.
- Identify Core Ideas: Before you begin writing, pinpoint the central concepts or themes you want to convey. These serve as the core messages or arguments you’ll explore.
- Craft Concise Topic Sentences: Start each paragraph with a concise topic sentence that introduces its main idea. Think of these sentences as guideposts, signaling what’s ahead and providing clarity.
- Establish a Strong Base: Topic sentences and themes set your text’s direction and purpose. Without them, your writing can seem disjointed and confusing.
- Map Out Content: Effective topic sentences not only introduce a paragraph’s main point but also outline the supporting details. They create a roadmap, making your content structure clear.
- Improve Readability: Strong topic sentences and themes make your writing more accessible. They help readers grasp ideas quickly and navigate your text effortlessly, making your message compelling.
By integrating these techniques into your writing, you enhance your content’s coherence and cohesion, making it more engaging and persuasive. Crafting clear topic sentences and themes provides a foundation for your ideas to shine and resonate with your audience.
Make Connections Between Ideas And Sentences
Writing with coherence involves crafting a seamless path for your readers. This means ensuring that your ideas flow logically and cohesively from one to the next. To achieve this, use transition words and phrases like “however,” “therefore,” “in contrast,” and “moreover” to signal relationships between ideas.
Avoid abrupt shifts, as these can confuse readers and disrupt the flow. By making these connections, you not only maintain coherence but also enhance clarity and engagement, providing your audience with a richer and more enjoyable reading experience.
Utilize Transition Words To Enhance Understanding
Transition words are the glue that holds your writing together, creating a bridge between sentences and paragraphs. These words and phrases, such as “however,” “in addition,” “consequently,” and “for instance,” help guide readers through your text, making it easier for them to follow your line of thought.
When used effectively, transition words create a smooth and logical flow, enhancing the coherence of your writing. They clarify relationships between ideas, signal shifts in focus, and add depth to your arguments. By incorporating these linguistic tools into your writing, you not only boost comprehension but also elevate the overall quality of your work.
Use Repetition When Appropriate
Repetition in writing, when used judiciously, can be a powerful tool to reinforce key ideas, engage readers, and create memorable content. By repeating certain words, phrases, or concepts, you can emphasize their significance and drive your point home effectively.
However, the key is to use repetition purposefully and sparingly, ensuring that it aligns with your writing’s objectives. Whether it’s repeating a central theme, a thought-provoking question, or a striking metaphor, strategic repetition can enhance the cohesiveness and impact of your writing, leaving a lasting impression on your audience.
Checklist For Essay Coherence And Cohesiveness
When crafting an essay, ensuring that it has both coherence and cohesion is paramount to engage your audience and effectively convey your message. Follow this checklist to enhance the quality of your writing:
- Clear Thesis Statement: Begin with a concise and well-defined thesis statement that sets the tone for your essay.
- Logical Flow: Organize your ideas logically, ensuring each paragraph connects seamlessly to the next.
- Transitions: Use transitional words and phrases like “however,” “therefore,” and “in addition” to guide your reader through your essay.
- Topic Sentences: Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that previews the content to follow.
- Consistent Point of View: Maintain a consistent perspective (first, second, or third person) throughout your essay.
- Repetition with Purpose: Use repetition thoughtfully to reinforce key points or themes.
- Parallel Structure: Structure sentences and lists in a parallel format for clarity.
- Pronoun Clarity: Ensure pronouns have clear antecedents to avoid confusion.
- Sentence Variety: Vary your sentence structure for rhythm and engagement.
- Proofreading: Thoroughly proofread your essay for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors.
By implementing these strategies, you can create essays that are not only coherent and cohesive but also compelling and impactful.
High Impact And Greater Visibility For Your Work
Mind the Graph can bring high impact and greater visibility to your work by transforming your research findings into engaging visuals that are easily understood and shared. This can help you reach a broader audience, foster collaboration, and ultimately enhance the recognition and influence of your scientific contributions.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags

- Peterborough

Creating Coherence (or Flow)
- Transitions within Paragraphs
- Transitions between Paragraphs
Transitional Paragraphs
The importance of transitions in making connections within paragraphs.
Good paragraphs make clear connections between sentences and ideas, both within and between paragraphs. Internally, paragraphs should move smoothly from one idea to the next; the reader should be able to see how each sentence relates to the controlling idea.The paragraph must have internal cohesian and advance the main idea. Do not simply expect the reader to see connections: you may find, when your essay is returned, that you have been misinterpreted.
Transitional words and phrases are essential tools for connecting ideas. They can join ideas together in a sentence, sentences together in a paragraph, and paragraphs together in an essay. Transitions are words such as “subsequently” and “conversely,” or phrases such as “as a result” and “in conclusion.” They link ideas and signal the logical connection between ideas.
Common Transitional Words and Phrases
- Adding Ideas: again, also, and, and then, as well as, besides, equally important, finally, first (second, third, etc.), for one thing, further, furthermore, in addition, in the first place, last, likewise, more, moreover, next, nor, similarly, too
- Emphasizing Ideas: above all, after all, equally important, especially, indeed, in fact, in particular, it is true, most important, of course, truly
- Illustrating Ideas: an illustration of, for example, for instance, in other words, in particular, namely, specifically, such as, that is, thus, to illustrate
- Comparing Ideas : in the same way, likewise, similarly
- Contrasting Ideas : and yet, but, but at the same time, conversely, despite, differently, even so, for all that, however, in contrast, in spite of, nevertheless, notwithstanding, on the contrary, on the other hand, or, otherwise, rather, regardless, still, though, unfortunately, yet
- Showing Cause and Effect : accordingly, as a result, consequently, for that reason, for this purpose, hence, otherwise, so, then, therefore, thereupon, thus, to this end, with this object
- Placing Ideas in Time: again, already, always, at first, at least, at length, at once, at that time, at the same time, briefly, during this time, earlier, eventually, finally, first (second, third, fourth, etc.), formerly, gradually, immediately, in future, in the meantime, in the past, last, lately, later, meanwhile, next, never, now, once, presently, promptly, recently, shortly, simultaneously, so far, sometimes, soon, subsequently, suddenly, then, thereafter, until now
- Summarizing Ideas: all in all, altogether, as has been noted, finally, in brief, in conclusion, in other words, in short, in simpler terms, in summary, on the whole, that is, to put it differently, to summarize
Using Transitions Between Paragraphs
Transitions also make connections between paragraphs; it is important to make sure that each paragraph connects to the one preceding it. Use the following transitional strategies to ensure that connections are clear for the reader.
Strategy One: Connect the preceding paragraph with the new one by reminding the reader of your thesis as you begin the paragraph.
Example: Clearly, then, our obstetrical procedures have not kept pace with our knowledge of infant psychology. Especially serious has been the early separation of the newborn from its mother.
Strategy Two: Use a transitional word or phrase. (See the previous explanation and the list of transitions above)
Example: Conversely, some non-traditional birthing centres have attempted to create areas where mothers, fathers, and babies can sleep together during their first days together.
Strategy Three: Use a key word from the preceding paragraph.
Example: Our increased attention to psychological tendencies such as bonding [discussed in previous paragraph] should lead to new hospital procedures.
Strategy Four: Begin the paragraph with a sentence that glances backward to the last paragraph and forward to the new one.
Example: If the last decade has witnessed many changes in theory [subject of preceding paragraph], practice has not kept pace.
Transitional paragraphs are used after major sections of essays to pause, regroup, and show where you are in your argument. In them, you can sum up the major points and evidence considered in the previous section of the essay, and relate the previous section to the thesis of the paper. After reviewing what you have covered, you may then go on to explain how it connects to what will follow. Will the next section offer a similar or a contrasting point? Where you will go next in your argument?
For context, please review the thesis of the essay:
Although Twelfth Night and A Midsummer Night’s Dream are alike in many ways, they differ primarily because of two characters—Malvolio and Bottom—whose differences make Twelfth Night less a purely comic play than A Midsummer’s Night Dream; Twelfth Night thwarts illusion, and acquires wistfulness, whereas A Midsummer Night’s Dream does not.
This transitional paragraph refers to important essay themes and shows the relationship between the section that has just been developed and the section that follows it:
Clearly, illusion, romance, and mistaken identity are found within both Twelfth Night and A Midsummer Night’s Dream. Indeed, the settings and story lines seem almost interchangeable (topic of previous section). The important difference between the two plays lies in Shakespeare’s treatment of Malvolio and Bottom (topic of next section).
Use of cookies
Lund University uses cookies to ensure that the website functions properly and to improve your experience.
Read more in our cookie policy
- AWELU contents
- Writing at university
- Different kinds of student texts
- Understanding instructions and stylesheets
- Understanding essay/exam questions
- Peer review instructions
- Dealing with feedback
- Checklist for writers
- Research writing resources
- Administrative writing resources
- LU language policy
- Introduction
- What characterises academic writing?
- The heterogeneity of academic writing
- Three-part essays
- IMRaD essays
- How to get started on your response paper
- Student literature review
- Annotated bibliography
- Three versions of the RA
- Examples of specificity within disciplines
- Reviews (review articles and book reviews)
- Popular science writing
- Research posters
- Grant proposals
- Writing for Publication
- Salutations
- Structuring your email
- Direct and indirect approaches
- Useful email phrases
- Language tips for email writers
- Writing memos
- Meeting terminology
- The writing process
- Identifying your audience
- Using invention techniques
- Research question
- Thesis statement
- Developing reading strategies
- Taking notes
- Identifying language resources
- Choosing a writing tool
- Framing the text: Title and reference list
- Structure of the whole text
- Structuring the argument
- Structure of introductions
- Structure within sections of the text
- Structure within paragraphs
- Signposting the structure
- Using sources
- What needs to be revised?
- How to revise
- Many vs. much
- Other quantifiers
- Quantifiers in a table
- Miscellaneous quantifiers
- Adjectives and adverbs
- Capitalisation
- Sentence fragment
- Run-on sentences
- What or which?
- Singular noun phrases connected by "or"
- Singular noun phrases connected by "either/or"
- Connected singular and plural noun phrases
- Noun phrases conjoined by "and"
- Subjects containing "along with", "as well as", and "besides"
- Indefinite pronouns and agreement
- Sums of money and periods of time
- Words that indicate portions
- Uncountable nouns
- Dependent clauses and agreement
- Agreement with the right noun phrase
- Some important exceptions and words of advice
- Atypical nouns
- The major word classes
- The morphology of the major word classes
- Words and phrases
- Elements in the noun phrase
- Classes of nouns
- Determiners
- Elements in the verb phrase
- Classes of main verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Primary auxiliary verbs
- Modal auxiliary verbs
- Meanings of modal auxiliaries
- Marginal auxiliary verbs
- Time and tense
- Simple and progressive forms
- The perfect
- Active and passive voice
- Adjective phrases
- Adverb phrases
- Personal pronouns
- Dummy pronouns
- Possessive pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns
- Indefinite pronouns
- Quantifiers
- Prepositions and prepositional phrases
- More on adverbials
- The order of subjects and verbs
- Subject-Verb agreement
- Hyphen and dash
- English spelling rules
- Commonly confused words
- Differences between British and American spelling
- Vocabulary awareness
- Useful words and phrases
- Using abbreviations
- Register types
- Formal vs. informal
- DOs & DON'Ts
- General information on dictionary use
- Online dictionary resources
- What is a corpus?
- Examples of the usefulness of a corpus
- Using the World Wide Web as a corpus
- Online corpus resources
- Different kinds of sources
- The functions of references
- Paraphrasing
- Summarising
- Reference accuracy
- Reference management tools
- Different kinds of reference styles
- Style format
- Elements of the reference list
- Documentary note style
- Writing acknowledgements
- What is academic integrity?
- Academic integrity and writing
- Academic integrity at LU
- Different kinds of plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- About Awelu

- Start here AWELU contents Student writing resources Research writing resources Administrative writing resources LU language policy
- Genres Introduction The Nature of Academic Writing Student writing genres Writing in Academic Genres Writing for Publication Writing for Administrative Purposes
- Writing The writing process Pre-writing stage Writing stage Rewriting stage
- Language Introduction Common problems and how to avoid them Selective mini grammar Coherence Punctuation Spelling Focus on vocabulary Register and style Dictionaries Corpora - resources for writer autonomy References
- Referencing Introduction Different kinds of sources The functions of references How to give references Reference accuracy Reference management tools Using a reference style Quick guides to reference styles Writing acknowledgements
- Academic integrity What is academic integrity? Academic integrity and writing Academic integrity at LU Plagiarism
- Repeating key nouns
- Using consistent pronouns
- Using transition signals to link ideas
- Arranging your ideas in logical order
A list of linking words for different purposes (Björk & Räisänen 1997)
| addition | ||
| contrast | ||
similarity | ||
| exemplification | ||
| chronology | ||
| causality | ||
| attitude | ||
| summary | ||
|
Connecting events in a text (Hamp Lyons & Heasley 2006)
Hamp Lyons & Heasley (2006, p. 80)
- Staff Directory
- Library Policies
- Hege Research Award
- Quaker Archives
- Art Gallery
- Student Support
- Teaching & Learning
- Reserving spaces
- Technology Lending
- Interlibrary Loan
- Course Reserves
- Copyright & Fair Use
- Poster Printing
- Virtual Reference
- Research Guides
- Off-campus access
- Digital Scholarship
- Guilford Sources
- Open Educational Resources
- Quaker Collections
- Digital Collections
- College Archives
- Underground Railroad
- Universities Studying Slavery
- Images & Exhibitions
Service Alert

Hege Library & Learning Technologies
- Guilford College
- Campus Partners
Guilford College Writing Manual
Revising to improve coherence.
- Practical Considerations
- Write to Learn
- Defining and Freeing the Self
- Joining a Community of Seekers
- Final Thoughts
- A Proposed Categorization of the Academic Writer's Responsibilities
- Required Writing Courses
- Placement in First-Year Writing Courses
- Writing Courses Beyond First-Year English
- Informal vs. Formal Writing
- Essay vs. Article
- Two Models of Papers
- What is the Real Difference?
- Specific Expectations of Papers
- Grade Descriptions
- The A Paper
- The B Paper
- The C Paper
- The D Paper
- The F Paper
- What makes college reading different?
- Levels of Reading
- An Overview
- Sample Schedule
- Suggestions for Prewriting
- Modes of Invention
- Four Categories of Invention
- Intuition Heuristics
- The Five Perspectives
- Loosening Heuristics
- Closing Observations
- Introduction
- Preliminary Tasks
- The Search Strategy
- Finding Materials
- Finding Appropriate Websites
- Selected Websites
- Documenting Your Sources
- Open Form vs. Fixed Form
- Geography of a Thesis and Proof Essay
- Introductions
- Body Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Maintaining Control
- Geography of an Issues and Exploration Paper
- Reader Expectations
- What is Style?
- Festival of Verbs
- Two Zones of the Word Stock
- Levels of Generality
- Writing with Nouns and Verbs
- Avoiding Cliches
- The Two Faces of Jargon
- Using "I" in Academic Writing
- What Kinds of Sentences to Use
- Hemingway vs. Faulkner
- Three Syntactic Devices Worth Using
- Subject-Verb-Object
- Touches of Elegance
- Gunning's Fog Index
- Why It's Important
- Two General Principles
- Some College-Level Problems
- A Word on Typos
- An Important General Rap
- Revising Checklist
- Revising for Concreteness
- Revising to Eliminate Wordiness
- Revising to Sharpen
- Revising to Make More Effective Use of Quotations
- Revising to Make Language More Inclusive
- Revising to Brighten
- What It Is and Why We Do It
- Sample Edit Guide
REVISING TO IMPROVE COHERENCE
Coherence describes the way that the elements in our sentences and paragraphs hang together to produce meaning. Usually when we write rough drafts, we are concerned mainly with getting our thoughts on paper, not with making sure that they interconnect well so that a reader can process our reasoning easily. We may even leave logical steps out.
Revising for coherence means going back to the draft with the reader's needs in mind. It may mean inserting transitional words and phrases, or creating parallelism so that the reader can see at a glance that a pair of elements carry the same weight, or rearranging material within a sentence so that the reader gets an accurate sense of what’s important and what’s not. Generally, it means instructing the reader on how to read our discourse.
The goal? Sharp focus.
It may be profitable to think of focus in terms of its original meaning. Borrowed without change from Latin, this word surprisingly first meant "hearth" or "fireplace" (compare fellow derivatives FOYER and FUEL)—in other words, that central point from which heat and light radiate throughout a structure. Focus entered the language of optical science with the sense of a place where things converge, and it is this sense of convergence and centrality and the sharp image that a correctly focused lens produces that we intend when we speak of FOCUS in writing.
Original paragraph :
Vegetation covers the earth, except for those areas continuously covered with ice or utterly scorched by continual heat. Richly fertilized plains and river valleys are places where plants grow, as well as at the edge of perpetual snow in high mountains. There is plant growth not only in and around lakes and swamps but under the ocean and next to it. The cracks of busy city sidewalks have plants in them as well as in barren rocks. Before man existed the earth was covered with vegetation, and the earth will have vegetation long after evolutionary history swallows us up.
(from Joseph Williams, Style )
The sentences contain sufficient information, but when read together they seem hazy, disconnected. It's not clear‑‑really‑‑what the main point is, even though one can sense the underlying logic. Note how the revising choices in the following version alleviate the problem. Then we'll look at the specific changes that were made.
Revised paragraph :
Except in those areas continually covered with ice or scorched by continual heat, the earth is covered with vegetation. Plants grow not only in richly fertilized plains and river valleys but at the edge of perpetual snow in high mountains, not only in and around lakes and swamps but under the ocean and next to it. They survive in the cracks of busy city sidewalks as well as in barren rocks. Vegetation covered the earth before we existed and will cover the earth after evolution swallows us up.
This version is much more reader‑friendly because the writer has made the following changes:
(1) Shifted the material in the first sentence so that the main point comes at the end of the sentence. Readers expect the most important information to come at the end. By putting it there, the writer has insured that the reader will not interpret the exception ("except for . . .") to be what this paragraph is about. Instead, the reader can confidently go to the next sentence looking for examples of "the earth is covered with vegetation."
(2) Taken the six examples which make up the meat of the paragraph and put them in grammatically parallel constructions so the reader can see at a glance that they are all being used in the same way‑‑as examples. Note how in the revision, the grammatical subject is "plants" throughout the middle sentences, whereas in the previous version the subjects are "plains and river valleys," "plants," "plant growth," "the cracks of busy city sidewalks." The subject‑shifts in the original are abrupt and confusing.
(3) Strengthened the continuity from second last sentence to final sentence by beginning with "vegetation." "Vegetation" connects immediately with the previous sentences, whereas in the original version, the opening clause suddenly shifts us into a historical perspective in which the first grammatical subject is "man." Note also how the writer has sharpened the paragraph's focus‑-and hence the coherence‑‑by eliminating wordiness and strengthening the verbs.
Using transitions
Another sure‑fire way of improving coherence is to use transitional words and phrases. Such devices function like road signs. They signal immediately the logical relationship between parts of a sentence, or, if positioned near the beginning of a sentence, the relationship between that sentence and the sentence that preceded it. Any two consecutive sentences have an implicit logical relationship; often it helps the reader if you make the relationship explicit. In looking at the following list of transitions drawn from the Harbrace College Handbook , note the logical relationships indicated by the category headings:
1. Alternative and addition : or, nor, and, and then, moreover, further, furthermore, besides, likewise, also, too, again, in addition, even more important, next, first, second, third, in the first place, in the second place, finally, last.
2. Comparison : similarly, likewise, in like manner.
3. Contrast : but, yet, or, and yet, however, still, nevertheless, on the other hand, on the contrary, conversely, even so, notwithstanding, for all that, in contrast, at the same time, although this may be true, otherwise, nonetheless.
4. Place : here, beyond, nearby, opposite to, adjacent to, on the opposite side.
5. Purpose : to this end, for this purpose, with this object.
6. Cause, result : so, for, hence, therefore, accordingly, consequently, thus, thereupon, as a result, then, because.
7. Summary, repetition, exemplification, intensification : to sum up, in brief, on the whole, in sum, in short, as I have said, in other words, that is, to be sure, as has been noted, for example, for instance, in fact, indeed, to tell the truth, in any event.
8. Time : meanwhile, at length, soon, after a few days, in the meantime, afterward, later, now, then, in the past, while.
See the improvement in coherence that results when transitions are added to the following paragraph:
Cable television sounds like a good deal at first. All available local channels can be piped into a television set for a relatively low cost per month. The reception is clear‑‑a real bonus in fringe and rural areas. Several channels for news and local access are in the basic monthly fee. A cable connection to a second or third TV set costs extra. In most places subscribers have to pay as much as thirty dollars a month extra to get the channels like Home Box Office and The Disney Channel. The movies change each month. The pay‑TV movie channels run the same films over and over during a month's time. Many of the films offered each month are box office flops or reruns of old movies that can be viewed on regular channels. Cable television isn't really a bargain.
from Harbrace College Handbook
Cable television sounds like a good deal at first. All available local channels can be piped into a television set for a relatively low cost per month. And the reception is clear‑‑a real bonus in fringe and rural areas. Moreover , several channels for news and local access are in the basic monthly fee. On the other hand , a cable connection to a second or third TV set costs extra. And in most places subscribers have to pay as much as thirty dollars a month extra to get the channels like Home Box Office and The Disney Channel. While it is true that the movies change each month, the pay‑TV channels run the same films over and over during a month's time, and many of the films offered each month are box office flops or reruns of old movies that can be viewed on regular channels. In sum , cable television isn't really a bargain.
A final comment about transitional words and phrases : don’t overuse them. As historian Richard Marius observes, “when we use them too frequently to hold an essay together, they leave the rivets in our writing showing."
- << Previous: Revising to Sharpen
- Next: Revising to Make More Effective Use of Quotations >>
- Last Updated: Dec 8, 2015 1:59 AM
- URL: https://library.guilford.edu/writingmanual

How to Make Academic Writing more Coherent (7 Methods)
Enhance clarity, coherence, and cohesion in your academic writing for more persuasive papers. Explore techniques for effective academic communication.

Make Your Writing Coherent
In today’s newsletter, we'll be discussing how to make your writing more coherent. As you know, effective communication is crucial to success in academia. Writing with clarity and coherence is crucial to convey ideas and research effectively to readers. One of the most important skills for writers is to make their writing coherent. Cohesion helps readers understand complex ideas and arguments, and facilitates the construction of rigorous and nuanced arguments. Therefore, producing work that is both persuasive and impactful is vital to succeed in academic writing.
However, many writers struggle with coherence in their writing. Their writing suffers from unclear connections between ideas, poor organization, and a lack of cohesion within paragraphs. These issues can cause confusion and frustration for readers, making it difficult for the writer to get their point across and potentially decreasing the effectiveness of their work. However, there are techniques and practices that can be used to overcome these issues. This newsletter issue provides some strategies and methods that help you create writing that is clear and interesting.
A well-written paper ties together different ideas and concepts in a way that makes sense. Cohesion and coherence are achieved by linking ideas well within and between paragraphs, reiterating the main point, and, if necessary, giving detailed explanations. Transitions are the most obvious way to show how different ideas are related to each other, but there are other ways and examples that writers can use to do the same thing.
So, before I dive into transitions below with a great list of examples that you can use right away, let’s discuss some other ways to make your writing more coherent.
Parallelism
Parallel sentence structure is a technique that can make academic writing easier for readers to follow. You essentially repeat similar phrase structures, which may help generate a feeling of rhythm and balance in your paper. By adopting parallel sentence patterns, you are able to emphasize significant ideas and facilitate the comprehension of difficult issues.
Consider using parallel sentence structures as you write your paper to create a sense of progression in your ideas. For example, you can use parallel sentence structures to describe different aspects of a complex concept, such as "The first aspect of X is..., the second aspect of X is..., and the third aspect of X is...". This breaks down the concept into manageable parts and makes it easier for readers to understand.
Another way to use this technique is to emphasize key points or arguments. For instance, you might use parallel sentence structures to describe different examples that support your argument, such as "Example A demonstrates..., Example B illustrates..., and Example C confirms...". This can help reinforce your argument and make it more persuasive for the reader.
Parallel sentence patterns support readers in digesting complicated ideas and following the progression of ideas. They also create a feeling of rhythm and balance in your writing, emphasizing key themes in within your paper structure.
Repetition of essential words, ideas, or phrases is an effective method that can strengthen the structure of an academic paper and make it simpler for the reader to follow the argument's major themes. By consistently using these core phrases throughout the document, authors can establish coherence and unity that reinforce the overall message.
For instance, when you are discussing a complex concept like "postmodernism," you may use this term repeatedly throughout the text to help readers understand the main idea. You may also use specific terms and phrases like "postmodern philosophy" or "postmodern literature" to emphasize this concept and make the paper easier to comprehend.
This strategy may also be used by repeating significant ideas or arguments throughout the document. You may, for instance, offer an important idea in the opening and then repeat it in the conclusion to underline its significance and make a lasting impact on the reader. This may also help to generate a feeling of cohesion and unity throughout the various sections of the article.
Synonyms are a way to improve the flow of academic writing by varying word choice. Synonyms are words that have the same or a similar meaning. They can prevent repetition in a document while maintaining emphasis. This method can also add variety to a document, making it more interesting for the reader.
You have to be careful though with core concepts in your paper, those should be used consistently throughout for clarity. Repeat your key words for clarity (but do not do this excessively). So, for anything directly relevant to your experiment or theory, I do not advise switching out synonyms because this will just confuse your reviewers. However, when it comes to words that clarify important ideas, feel free to use different terms to add diversity to your paper.
Lexical Chains
Lexical chains are sequences of related words that illustrate the consistency and relevance of vocabulary choices to the paper's topic. Using lexical chains creates variety in writing and prevents monotony. For your paper, consider using synonyms, antonyms, hyponyms, superordinates, and other related words to create lexical chains that maintain coherence within a paragraph or section.
For instance, when discussing user interface design, you could use a lexical chain such as "usability - user experience - user satisfaction - user engagement - user loyalty" to maintain coherence and emphasize the significance of these related concepts. Similarly, when discussing artificial intelligence and machine learning, you might use a lexical chain like "data processing - algorithms - learning models - neural networks - deep learning" to illustrate the various stages of the machine learning process and ensure coherence in your discussion.
Lexical chains create coherent flow in your academic paper, making it easier for readers to follow your argument and understand the relevance of your vocabulary choices to the topic at hand.
Topic Sentences
Topic sentences establish order in your writing. You begin each paragraph with a clear and succinct topic sentence. This helps your readers comprehend the paragraph's key point and its relationship to your main research question or hypothesis. Consider using topic sentences to establish a focused framework that takes the reader through your argument as you compose your paper.
For instance, if you are addressing the design principles of user interfaces, you may begin a paragraph with a subject phrase such as "The concept of simplicity is an important factor in user interface design." Afterwards, you may add supporting data and specifics to explain how this idea pertains to the design of user interfaces. In the same way, if you are addressing the ethical implications of artificial intelligence, you may begin a paragraph with a subject phrase such as "The potential misapplication of AI creates a huge ethical concern." You might then provide supporting information and evidence to show the possible hazards and difficulties involved with the use of artificial intelligence.
The topic sentence sets the tone for your paragraph. It ties each paragraph back to your overarching question. Start each sentence or paragraph with information that hints at the content of the next sentence. Using this structure in your writing may not only make the entire paper more coherent but also help you be more convincing in your argumentation.
Cohesive Nouns
Cohesive nouns, also known as "umbrella nouns," summarize multiple related words or concepts into one term. For example, the cohesive noun "family" encompasses a group of individuals who are related by blood or marriage and who live together in a household unit. By using cohesive nouns, you can reduce wordiness and improve the clarity and flow of your writing by condensing multiple related ideas into a single, broad term.
Using cohesive nouns can help you avoid repetition and create a more sophisticated tone in your writing. For example, when discussing the various components of a user interface, you can use the cohesive noun "interface elements" to refer to buttons, menus, and other related components. This not only avoids repeating the same words multiple times but also creates a more concise and polished sentence. Similarly, when discussing the impact of technology on society, you can use the cohesive noun "digital technologies" to refer to computers, smartphones, and other related technologies.
With cohesive nouns, you can create a more efficient and streamlined paper that avoids unnecessary repetition and keeps the focus on your central argument. Additionally, cohesive nouns can also help to clarify complex topics and make them more accessible to a wider audience by simplifying the language and reducing confusion.
Transitions
Transitions are crucial in academic writing, as they play a vital role in connecting different parts of a paper and making the writer's argument clear and easy to follow. In addition to using simple words (e.g., "however", "therefore", "in addition", "on the other hand") to indicate relationships between sentences or paragraphs, full transition sentences and templates can be extremely helpful in crafting an effective academic paper. These templates provide writers with a clear structure and framework for their writing, helping them to maintain coherence and clarity throughout the paper.
To this end, I have compiled a comprehensive list of transitions that I use in my paper writing. Each of these transitions is the start of an example sentence, providing me with a solid starting point to create structure and better coherence in my writing. By using these transitions, I can help my readers follow the flow of my argument, understand how my ideas are connected, and ultimately create a more convincing and compelling academic paper.
Transitions are key to clear and coherent academic writing. Using both simple and longer phrases helps connect sentences and paragraphs, keeping your work consistent. Templates can speed up the writing process by providing a framework and structure, ensuring clarity and uniformity. This list of transitions will help you start crafting a well-structured and engaging academic paper.
To wrap up today’s issue, ensuring coherence in your writing is essential to effectively conveying your ideas and research. You can achieve cohesion and coherence in various ways, such as using parallelism , repetition , synonyms , lexical chains , topic sentences , and cohesive nouns . Additionally, transitions are crucial for connecting different parts of your paper and making your argument clear and easy to follow. Using templates and transition words helps connect sentences and paragraphs, keeping your writing clear and consistent. Think about your readers and use these tools wisely.
Curious to explore how we can tackle your writing struggles? I've got 3 suggestions that could be a great fit.
- Get my CHI paper writing masterclass : Unlock your potential with the How to Write Better Papers Course for HCI researchers. This course offers concise, actionable video lessons you can absorb at your own pace, saving you time. Get expert guidance tailored for CHI and HCI publications with proven strategies. Gain the skills to succeed in a competitive field.
- Learn how to write papers with AI ethically : Access the AI Research Tools Webinar to improve your research and writing skills. Enjoy a 3-hour tutorial with subtitles in 19 languages, 46 detailed slides, and a 1-hour ChatGPT bonus tutorial with 39 prompts. Learn from 3 app tutorials (Yomu AI, SciSpace, and Sourcely) and get a 184-page Mastery Guide on 34 AI tools. This bundle provides everything you need for AI-powered academic success.
- Defend your thesis with confidence : Increase your productivity and graduate success with this thesis workshop. Get instant access to a 3-hour video, 64 instructional slides, and curated productivity software. Use our online whiteboard and a 7-page workbook of checklists and prompts. Prepare confidently with a 10-page Viva questions guide and a PhD exam checklist. Optimize your thesis workflow and excel in your studies.

How to Pick a Research Topic (and Actually Love It)
Ever feel like choosing a research topic is like swiping on a never-ending social app? Up, down, like, but nothing feels just right? Trust me, I've been there - staring at a blank screen, juggling a dozen ideas, and questioning all my life choices.

How to go from research idea to published paper in 10 (mostly painless) phases
Ever wonder why some researchers breeze through projects while others struggle? It's not about IQ or experience. The secret is in research strategy.

How to master 14 literature review types
Most academics only use 2 types of literature reviews, but there are actually 14—and mastering them all can change your research career.
21 Coherence Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Coherence refers to the qualities of consistency, harmony, and logical connection within a set of ideas or elements.
To be coherence means to make seamless connections between ideas and use an understandable flow during communication.
The term can be applied to many concepts, including:
- The storyline in a novel
- A person’s debate speech
- A politician’s policy platform
The more coherent something is, the easier it is to logically follow and understand. The degree of coherence in an idea also often serves as an indicator of its efficiency or effectiveness.
In order to be coherent, you may need to plan-out how you will communicate an idea, write drafts, organize your thoughts, and pay attention to the logic and flow of your key points.
Coherence Examples
1. demonstrating cause and effect.
A story that is coherent will clearly explain the chain of events in the story. One way to do this is to demonstrate cause and effect.
To explain it another way, imagine if something happened in a story that seems odd, and there’s no explanation as to why or how it happened. You would be left feeling as if the story was incoherent .
So, clearly explaining cause and effect allows a reader to follow the chain of events or ideas logically, enhancing overall understanding and agreement with your points.
See Also: Cause and Effect Examples
2. Using Logical Reasoning
The use of logical reasoning is a powerful way to enhance coherence in your communication.
Logical reasoning is the act of drawing conclusions based on premises that are true, and it operates under the guiding principles of sound logic. This enhances your credibility and the value of your ideas.
Imagine, for example, if someone told a story and there were points within it that were illogical . This, in itself, will be an incoherent story!
See Also: The Types of Fallacy
3. Avoiding Fallacies and Heuristics
Resorting to fallacies and heuristics tends to tarnish a part of the coherence of your communication.
Fallacies are mistakes or errors in reasoning, while heuristics are mental shortcuts people take that can sometimes lead to faulty decision making.
For instance, allowing logical fallacies such as the strawman argument, where the argument’s viewpoint is misrepresented to weaken it, obstructs the coherence by distorting the logical reasoning.
Staying clear from such tendencies ensures that your position is firmly anchored in solid reasoning, thus increasing the coherence of your message.
See Also: The Multiple Types of Fallacy
4. Staying on Topic
Veering off the topic is perhaps the most common way that my students fail to maintain coherence in their essays.
Imagine trying to understand a text where the author jumps randomly from topic to topic with no clear connection. This would be hard to follow and would seem incoherent.
And yet, too often, students will start a paragraph talking about one concept and end it on a completely random tangent. Avoid this, and you’ll be on track to greater coherence.
5. Using Clear Language
Sometimes, lack of clarity in word choice can make something incoherent. Take, for example, talking to a toddler. The toddler is trying to communicate something, and you have to strain very hard to understand their baby talk. Their incoherence is rooted in their inability to speak clearly.
Similarly, jargon or overly complex language can lead to confusion and misinterpretation, damaging the coherence of your message.
6. Organizing Ideas Logically
Sometimes, the most straightforward way of improving the coherence of student essays is to simply think a little harder while essay planning about what to say first, second, and third.
Consider, for example, why one idea would come before another. Oftentimes, we need to use basic ideas like defining terms before we move on to analyzing them. By simply paying attention to how you organize your points, you can make your work appear much more coherent.
7. Using Clear Transitions Between Ideas
Strong coherence can be achieved through effective use of transitions between ideas. Imagine you’re being told a story, and suddenly, without any warning, the topic changes. You’re left confused and it feels like the story is jumping around.
This happens without clear transitions.
But a well-placed transition clearly shows the link between the two ideas, meaning the reader can follow along easily.
You can use transitions for contrast, like “however”, “by contrast” and “on the other hand”. These simple transition words can help the reader or listener understand the relationship between the first and second ideas you’re presenting.
8. Using Relevant Examples
When you provide relevant examples in your writing, you increase the coherence of your message because examples help people to understand you better.
Picture trying to understand a complex idea, and the person teaching you tries to clarify it using an example that is relevant to you. This, often, is when you have that ‘lightbulb moment’ and finally understand the idea.
Providing examples directly tied to your main idea help elucidate your point, making the message clear and coherent for the audience.
9. Addressing and Debunking Counterarguments
Addressing and debunking counterarguments can underpin the logic of your own point of view, and therefore, improve the coherence of your arguments.
Consider presenting an idea without addressing the possible counterarguments that might arise against it. It can lead to a feeling of imbalance or a lack of full perspective.
However, by addressing those counterpoints openly, you demonstrate that you consider your position from multiple perspectives, lending your argument a sense of robustness, wholeness, and ultimately, coherence.
10. Using Consistent Tone and Style
Having a consistent tone and style is key to maintaining coherence in your text.
Visualize reading a serious political commentary article and, midway through, it starts using humor and colloquial language. It would feel disjointed, disrupting the reader’s understanding.
By maintaining a consistent tone and style throughout your text, you ensure a smooth, coherent experience for the reader, making your message more accessible and easier to understand.
My Full List of Ways to be Coherent
- Demonstrating Cause and Effect
- Using Logical Reasoning
- Avoiding Fallacies and Heuristics
- Staying on Topic
- Using Clear Language
- Organizing Ideas Logically
- Using Clear Transitions Between Ideas
- Using Relevant Examples
- Addressing and Debunking Counterarguments
- Using Consistent Tone and Style
- Remaining Consistent in your Worldview
- Structuring Sentences Clearly
- Using Analogies to Clarify Complex Ideas
- Clearly Linking Sub-Points to the Main Topic
- Using Consistent Terminology
- Using Signposting
- Providing Context for Ambiguous Statements
- Avoiding Overly Complex Sentence Structures
- Using Visual Aids (like charts or graphs) Appropriately
- Summarizing Points Periodically
- Avoiding Contradictions
- Proofreading for Clarity
Coherence vs Cohesion
Coherence and cohesion are both essential elements in effective writing. Coherence is about the higher-level ideas and arguments, while cohesion is about the syntax and grammar of the writing at the sentence level.
While the terms are interconnected and overlap, they are different concepts:
- Coherence refers to the logical and consistent interconnection of ideas in a piece of writing. This concept is about the ideas and the arguments that are being made connecting logically to create a clear, easy-to-follow narrative.
- Cohesion is about the grammatical and linguistic elements of writing that make it readable and understandable. It involves things like transitions, reference words, and sentence structure. It refers to the way you connect sentences and paragraphs to each other through various linguistic and grammatical devices.
A piece of writing can have one without the other. It is possible to have a text that is cohesive with excellent syntax, yet lacks coherence because the ideas aren’t logically connected. Similarly, a text’s ideas could theoretically be logically interconnected (coherent) while the syntax and grammar that connects the sentences are lacking (cohesive).
See More: Cohesion Examples
Coherence is the backbone of clear and effective communication. Its role in organizing ideas, synthesizing information, and facilitating understanding can’t be overemphasized. Lacking coherence can make even the most profound ideas seem jumbled and difficult to comprehend. Therefore, for students, we need to keep our focus on maintaining coherence in our communication style in order to achieve clarity, precision, and persuasive power. Through this, you’ll see your grades grow!

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
English Studies
This website is dedicated to English Literature, Literary Criticism, Literary Theory, English Language and its teaching and learning.
Coherence in Writing
Coherence in writing is the quality that ensures a text flows logically and smoothly, making it easy for readers to understand the writer’s intended message.
Introduction: Coherence in Writing
Table of Contents
Coherence in writing is the quality that ensures a text flows logically and smoothly, making it easy for readers to understand the writer’s intended message. Achieving coherence involves creating clear connections between sentences and paragraphs, using transitional words and phrases to guide the reader through the text, and maintaining a consistent and well-organized structure.
This coherence is essential for effective communication in both academic and non-academic contexts, as it enables readers to follow the writer’s argument or narrative, enhancing comprehension and engagement with the text.
How to Create Coherence in Writing
| Organize Your Ideas | Start with a clear and well-organized structure. Plan your writing with a logical sequence of ideas, using an outline if necessary. | Example: When writing an essay, create an outline with a clear introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion to structure your thoughts. |
| Employ transitional words and phrases (e.g., “however,” “therefore,” “in addition”) to connect sentences and paragraphs, guiding the reader through your text. | Example: “Moreover, the study’s findings suggest a strong correlation between X and Y.” | |
| Maintain Consistency | Ensure consistency in tone, style, and point of view throughout your writing to avoid confusion. | Example: If you start with a formal tone, maintain that tone consistently throughout the document. |
| Begin each paragraph with a strong topic sentence that introduces the main point or idea, providing a clear focus for the reader. | Example: In an article about climate change, the topic sentence of a paragraph might be, “Rising global temperatures have far-reaching consequences.” | |
| with Purpose | Reiterate key concepts and phrases when necessary, but do so with a purpose, emphasizing the importance of those ideas. | Example: In a persuasive speech, you can strategically repeat the central message to reinforce its significance. |
| Pronoun Usage | Use pronouns effectively to refer back to previously mentioned concepts, enhancing the flow of your text. | Example: “The research indicated a significant impact on the economy. This impact was particularly evident in the job market.” |
| Revise and Edit | After writing, revise your work for clarity and coherence. Eliminate irrelevant information and ensure all sentences and paragraphs contribute to the overall message. | Example: When editing, remove redundant sentences and ensure that each paragraph aligns with the central thesis of the paper. |
Benefits of Using Coherence in Writing
- Enhanced Clarity : Coherence in writing makes your text more understandable and ensures that readers can easily follow your ideas.
- Improved Flow : Coherent writing leads to smoother transitions between sentences and paragraphs, resulting in a more enjoyable reading experience.
- Effective Communication : Coherence helps you convey your message effectively, ensuring that your intended meaning is accurately and clearly delivered to the reader.
- Engaged Audience : When writing is coherent, readers are more likely to stay engaged, as they can focus on the content rather than deciphering the structure.
- Credibility : Coherent writing reflects professionalism and credibility, enhancing your reputation as a writer or communicator.
- Logical Structure : A coherent structure aids in organizing information logically, which is crucial for essays, reports, and academic papers.
- Supports Argumentation : Coherence is vital in persuasive writing, as it helps build a compelling argument by presenting ideas in a logical sequence.
- Efficient Proofreading : Coherent writing is easier to proofread and edit because it follows a clear structure, making it simpler to identify and correct errors.
- Reader’s Trust : Coherent writing builds trust with the reader, demonstrating that you have taken care in presenting your ideas.
- Professionalism : Coherence is a hallmark of professional writing, whether it’s in business communication, academic papers, or creative works.
Coherence in Literary Theories
- Structuralism and Formalism : These theories focus on the inherent structure of a text. Coherence is critical in maintaining the consistency and integrity of a text’s structure, as it helps in identifying patterns and relationships among elements in the narrative.
- Reader-Response Theory : Coherence can influence readers’ interpretations of a text. A well-structured and coherent narrative is more likely to elicit the intended responses from readers, while a lack of coherence can lead to confusion or misinterpretation.
- Narrative Theory : Narrative coherence is a fundamental aspect of narrative theory. Coherence in storytelling ensures that the plot and events are logically connected, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the narrative.
- Post-Structuralism and Deconstruction : While these theories often challenge traditional notions of coherence, they do so by deconstructing and reevaluating how coherence is achieved or subverted in texts. Understanding coherence is crucial for deconstructive analysis.
- Feminist and Gender Studies : Coherence can be examined in terms of how gender roles and expectations influence the portrayal of characters and the development of plot in literary works, contributing to the analysis of gender representation.
- Cultural and Historical Contexts : In literary analysis that considers the cultural and historical contexts of a work, coherence helps in understanding how the text aligns with or challenges prevailing social norms and expectations.
- Psychoanalytic Theory : Coherence in character development and psychological aspects of the narrative is integral to psychoanalytic interpretations, as it helps uncover hidden meanings and motivations in the text.
- Marxist Criticism : Coherence can be explored in relation to social and economic aspects of the text, helping to analyze how the narrative reflects class structures and power dynamics.
- Postcolonial and Global Studies : Coherence may be relevant when considering how colonialism or globalization affects the narrative and the interconnectedness of different cultures and societies.
- Ecocriticism : Coherence can be applied to ecological themes within a text, examining how the representation of nature and the environment aligns with or challenges prevailing ecological concerns and values.
Suggested Readings
- Kolln, Martha J. Rhetorical Grammar: Grammatical Choices, Rhetorical Effects . Pearson, 2016.
- Rose, Mike. Lives on the Boundary: A Moving Account of the Struggles and Achievements of America’s Educationally Underprepared . Penguin Books, 2005.
- Williams, Joseph M. Style: Toward Clarity and Grace . University of Chicago Press, 1990.
- Zinsser, William. On Writing Well: The Classic Guide to Writing Nonfiction . HarperCollins, 2006.
Related posts:
- Using Repetition in Writing
- Sonnet: A Poetic Genre
- Internal Rhyme: Using and Critiquing
- Narrative: Using and Creating It
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

COMMENTS
Coherence is crucial in writing as it ensures that the text is understandable and that the ideas flow logically from one to the next. When writing is coherent, readers can easily follow the progression of ideas, making the content more engaging and easier to comprehend. Coherence connects the dots for the reader, linking concepts, arguments ...
Two key aspects of coherence. Cohesion: This relates to the linking of ideas within a sentence, the linking of sentences (the ties between sentences) within a paragraph and the linking between paragraphs. Unity: This relates to the question of relevance and maintaining the central focus of a single paragraph and throughout the essay.
Unity. Unity is the idea that all parts of the writing work to achieve the same goal: proving the thesis. Just as the content of a paragraph should focus on a topic sentence, the content of an essay must focus on the thesis. The introduction paragraph introduces the thesis, the body paragraphs each have a proof point (topic sentence) with ...
2. Through the use of pronouns that not only stand in for nouns but also carry the idea the noun represents through a passage. 3. Through the use of recycled words or through repetition, which connects paragraphs or sentences by making a transition from a given use of a word or phrase to a new use. In short, then, coherence means creating a ...
A coherent paragraph has sentences that all logically follow each other; they are not isolated thoughts. Coherence can be achieved in several ways. First, using transitions helps connect ideas from one sentence to the next. For more on transitions, see the Write Right on Transitions. Second, ordering thoughts in numerical sequence helps to ...
Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly to create unity. So, sentences and ideas must be relevant to the central thesis statement. The writer has to maintain the flow of ideas to serve the main focus of the essay. 5. Stick to the purpose of the type of essay you're-writing.
Total: 4) Coherence is an essential quality for good academic writing. In academic writing, the flow of ideas from one sentence to the next should be smooth and logical. Without cohesion, the reader will not understand the main points that you are trying to make. It also hampers readability.
Coherence is an important aspect of good writing—as important as good grammar or spelling. However, it is also rather harder to learn how to do it, because it is not a matter of simple rules. Coherent writing moves smoothly between ideas. It guides the reader through an argument or series of points using signposts and connectors.
Good cohesion is achieved through the following five main methods, each of which is described in more detail below: repeated words/ideas; ... i.e. peer feedback, is another way to help improve coherence in your writing. Example essay. Below is an example essay. It is the one used in the persuasion essay section. Click on the different areas (in ...
Writing with coherence involves crafting a seamless path for your readers. This means ensuring that your ideas flow logically and cohesively from one to the next. To achieve this, use transition words and phrases like "however," "therefore," "in contrast," and "moreover" to signal relationships between ideas.
Coherence is built in first drafts essay as whole - by relationships into the paper of language, the sentence, paragraph, takes more images, and to constructing these that occur patterns. throughout a strategies can celebrated begin with sentence gay activist structures from "Invisibility Adrienne that seem in Academe," to As you read, if by.
Strategy Three: Use a key word from the preceding paragraph. Example: Our increased attention to psychological tendencies such as bonding [discussed in previous paragraph] should lead to new hospital procedures. Strategy Four: Begin the paragraph with a sentence that glances backward to the last paragraph and forward to the new one.
Cohesion and Coherence. A well-organized paper uses techniques to build cohesion and coherence between and within paragraphs to guide the reader through the paper by connecting ideas, building details, and strengthening the argument. Although transitions are the most obvious way to display the relationship between ideas, consider some of the ...
A writer must maximise understanding of a text by making it as clear and logical as possible. Coherence can be achieved in a number of ways. Oshima & Hogue (2006) suggest the following four: Repeating key nouns. Using consistent pronouns. Using transition signals to link ideas. Arranging your ideas in logical order.
Coherence ensures that the bigger picture is clear. Coherence in writing can be achieved through the use of words, but also through context. Kies (2003) offers the following advice: "Coherence is a product of many different factors, which combine to make every paragraph, every
Maintaining Coherence and Cohesion. Coherence refers to maintaining a clear focus within paragraphs, making connections between paragraphs, and connecting each paragraph to a central claim or thesis. Here are some ways to create coherence: Begin each paragraph with a sentence that not only forecasts the content of the paragraph but also links ...
To Improve Coherence Coherence is established in two ways: 1. Topics of individual sentences are clear 2. Topics of paragraphs are clear A paragraph is much more than a group of sentences set off by an indentation. If you can't quickly and succinctly say what a paragraph's main point is, it lacks coherence. Here's an example passage:
Coherence is the quality of hanging together, of providing the reader an easily followed path. ... Paragraph development is achieved partly through the specific strategies of exemplification, analysis, comparison and contrast, definition, enumeration, and description, all of which furnish distinct approaches to developing ideas.
Coherence describes the way that the elements in our sentences and paragraphs hang together to produce meaning. Usually when we write rough drafts, we are concerned mainly with getting our thoughts on paper, not with making sure that they interconnect well so that a reader can process our reasoning easily. We may even leave logical steps out.
Wrap-Up. To wrap up today's issue, ensuring coherence in your writing is essential to effectively conveying your ideas and research. You can achieve cohesion and coherence in various ways, such as using parallelism, repetition, synonyms, lexical chains, topic sentences, and cohesive nouns.
Coherence refers to the qualities of consistency, harmony, and logical connection within a set of ideas or elements. To be coherence means to make seamless connections between ideas and use an understandable flow during communication. The term can be applied to many concepts, including: The storyline in a novel. A person's debate speech.
Table of Contents. Coherence in writing is the quality that ensures a text flows logically and smoothly, making it easy for readers to understand the writer's intended message. Achieving coherence involves creating clear connections between sentences and paragraphs, using transitional words and phrases to guide the reader through the text ...