- General SEO
- Keyword Research
- On-Page SEO
- Link Building
- Technical SEO
- Enterprise SEO
- General Marketing
- Content Marketing
- Affiliate Marketing
- Paid Marketing
- Video Marketing


Market Research: What It Is and How to Do It

- Linking websites 193
The number of websites linking to this post.
This post's estimated monthly organic search traffic.

In other words, it’s the process of understanding who your business is targeting so you can better position your marketing strategy.
In this guide, you’ll learn:
- The role of market research in a marketing strategy
- When to conduct market research
Types of market research
- Market research methods and their benefits
- How to conduct market research (example included)
- Market research tools and resources
What is the role of market research in a marketing strategy?
A marketing strategy is a business’s overall game plan for reaching consumers and turning them into customers.
The key word in the above definition is “game plan”. Entering a market with a product is like starting a new game. Since you’re new to the game, you don’t know the rules, and you don’t know who you’re playing against.
This is exactly where market research comes in . Market research allows you to discover the rules of the marketing game by understanding your target audience. Moreover, it allows you to understand who your opponent is by assessing the strengths and weaknesses of your competition.
Research is what marketing pros do to plan their moves, and outperform their competition. It’s also what marketing pros use to identify the strengths and weaknesses of their own marketing strategy .
But is market research the ultimate business oracle? Unfortunately no. Even companies that specialize in market research admit it - here’s a quote from one of them :
(…) it cannot be assumed that market research is an exact science, as it would be unrealistic and unreasonable to expect market researchers to predict the precise demand for a new concept, given that there are numerous variables that can impact demand outside of the market researchers’ remit.
That’s why market research with all of its significance is “only” a part of marketing, and it’s “only” an experiment. It’s up to you whether you will conduct your experiment, and when you will end it.
For example, Crystal Pepsi seemed very promising in the market research phase, yet it failed when released onto the market (a similar thing happened to New Coke). Xerox’s idea for a commercial photocopier was a no-go in the eyes of research analysts; Xerox did it anyway, and the rest is history.
When should you conduct market research?
Paul N. Hauge and Peter Jackson in their book “Do Your Own Market Research” point to three specific situations when market research is really useful:
- Setting goals . Knowing things like the size of the market, or defining your potential customers can help you set your sales goals.
- Problem-solving . Low sales? Low profitability? Market research will help you understand whether your problems are internal, like a low-quality product, or external, like aggressive competition.
- Supporting company growth. Understanding how and why consumers decide on products will help you decide what products to introduce to the market.
Another answer to the “when” is the importance of the decision that you need to make. The more important the marketing issue you’re tackling, the more market research comes in handy.
For example, launching a new car on the market is quite a big event, right? So maybe Ford could have avoided losing 350 million dollars with the Ford Edsel if they had done their research properly. I mean, with the right methods in place it shouldn’t be that hard to predict that consumers will deem the car overpriced and ugly.
That said, market research doesn’t always have to be a large, complex project. The relatively new trend of agile market research allows you to research the market regularly and in a cost-effective way. This is where you employ bite-size, iterative, and evolutionary methods to react to fast-changing circumstances and adapt to unknown market territories.
Furthermore, if you’re working in startup conditions, especially if you’re developing an innovative product, you may be interested in customer development . In this methodology market research is at its “agilest” and it’s tightly woven into the product development process.
Take Ahrefs for example. We stick to agile market research hacks anyone can use. As you will see later in the article, we use simple (but effective!) stuff like social media polls, crowdsourcing, in-house competitive analysis, or just tracking the pricing of our competitors.
Case in point, just recently we asked our fellow marketers on Twitter how they go about researching the market. It seems that market research comes in all shapes and sizes:
Have you ever performed “market research?“ What was it for? — Tim Soulo (@timsoulo) May 3, 2021
Just because somebody does market research in a certain way doesn’t mean that you need to copy that. You should know your options, and they start with the different types of market research.
Primary research
Whenever the research is done by you or on your behalf, and you need to create the data to solve a given problem, that is called primary market research.
Examples: Focus groups, interviews, surveys (more on those later in the article).
Key benefits: It’s specific to your brand and products or services, and you can control the quality of the data.
Secondary research
Whenever you’re using already existing data, such as that put together by other businesses and organizations, you’re doing secondary market research.
Examples: Second-party and third-party sources like articles, whitepapers, reports, industry statistics, already collected internal data.
Key benefits: Get a macro perspective of your marketplace, as secondary research includes other players in the market, and most probably utilizes a bigger set of data than your primary sources.
Primary research vs. secondary research
Primary and secondary market research are different but by no means opposite. It’s actually recommended to use both.
While primary sources will give you a focused, micro perspective of your business, secondary research will tell you how other businesses are doing and how your research findings compare to bigger research sample sizes.
Market research subtypes
A bit more theory for all you marketing geeks out there. Professional market researchers distinguish between the following primary and secondary market research subtypes:
- Qualitative research. Think interviews, open-ended questions, results expressed in words rather than numbers and graphs. This type of research is used to understand underlying reasons, opinions, and motivations.
- Quantitative research. Think surveys, polls, usually closed-ended questions, results expressed in numbers and statistics. This type of research is used to test or confirm hypotheses or assumptions by quantifying defined variables (such as opinions or behaviours) and generalizing results from larger data samples.
Overview of market research methods
Let’s go over some popular market research methods you can use yourself and/or outsource.
Internal data analysis
The data you’ve already collected in your company is an invaluable secondary research data source. The more time you’re in the business, the more data you have on your hands.
The best thing about your internal data is that it’s been put into practice in real-life market conditions, so you just need to find the patterns and draw conclusions.
Here are some internal data sources you can leverage :
- Website data (like Google Analytics)
- Past campaigns performance data
- Internal interviews with employees
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions and are great for exploratory qualitative research.
In unstructured interviews, you have an informal, free-flowing conversation on a given set of topics.
In structured interviews, you prepare a detailed, rigorous interview protocol where you list every question you want to ask and you can’t divert from them.
You can also choose the “middle way” with semi-structured interviews which revolve around predefined themes or questions, but allow for open-ended discussion.
A word of advice here would be to always remain neutral and unbiased, even during unstructured interviews. Also, it’s helpful to perform a pilot test of the interview to quickly spot some defects of your protocol.
Recording the interview may influence the answers, so use it wisely.
Focus groups
Focus groups are where 5 to 10 people with common characteristics take part in an interactive discussion with a moderator. They’re used to learn how a particular group thinks about a given issue or to provide feedback on a product.
Now, you might know that Steve Jobs famously hated focus groups. He’s on record saying:
It’s really hard to design products by focus groups. A lot of times, people don’t know what they want until you show it to them.
If you’re trying to create a leapfrog product like the iPhone, there’s probably some validity to this statement. But most of us aren’t wrestling with that level of ambition. We just want to know if customers will like a proposed new feature or not. For this, focus groups are super useful.
Surveys involve polling your audience. They’re usually performed online for customer satisfaction and loyalty research, and are one of the most popular and cost-effective market research methods.
Some of the tried and tested use cases of online surveys are:
- Product feature desirability
- User satisfaction feedback
- Quantitative analysis of certain issue occurrences
- Identifying friction points in your customer journey
- Discovering the reasons to convert to or cancel your service
- During product onboarding to create a customer profile (and for marketing automation)
- Opinion about a recently made change
An interesting example of surveying the market is crowdsourcing . That’s what Ahrefs does to understand what features to build, how important they are, and what customers expect from them.
What’s unique about crowdsourcing is that it allows the users to add their own ideas, and upvote or comment on existing ideas rather than answer predetermined questions, so this method leaves less room for marketing myopia. You improve your business, and the users get a better product—everybody wins.
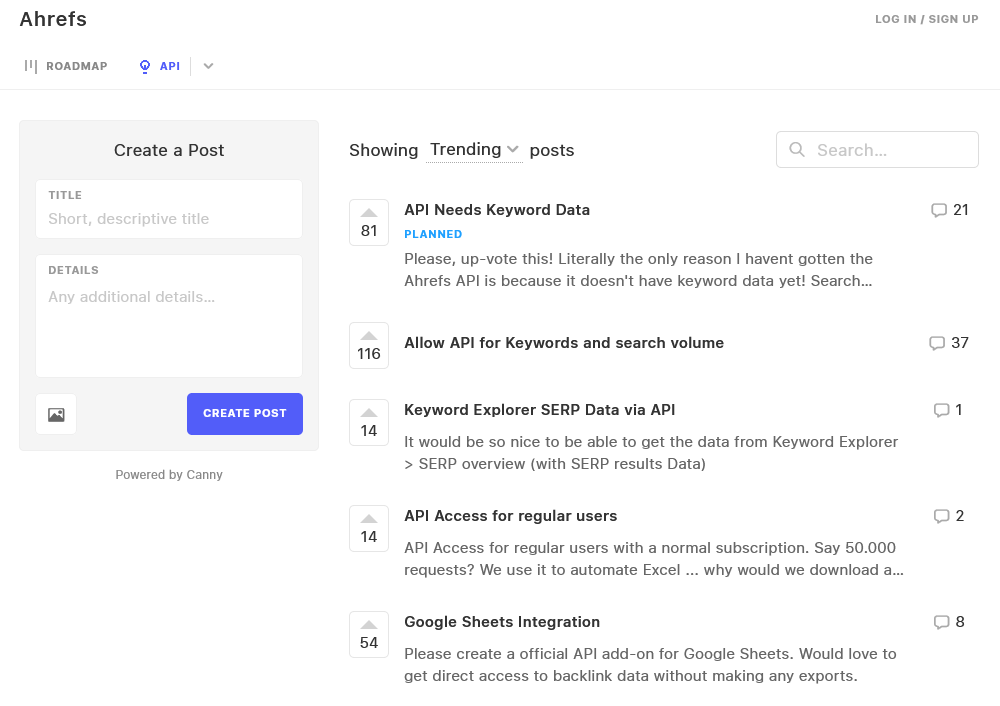
How we crowdsource ideas at Ahrefs
Social media is another great place to survey the marketplace.
How many of you have disavowed links in GSC this year? — Tim Soulo (@timsoulo) October 8, 2020
Market segmentation
Market segmentation is the practice of categorizing a market into homogeneous groups based on specific criteria, also called segmentation variables (like age, sex, company size, country, etc.).
If you think you’re building a product for everyone, think again. Not everyone will want to buy from you.
Smart companies pick their target audience carefully. They pinpoint groups of people or organizations that could be valuable customers for the business. That way they also discover their non-ideal customers and develop a plan to attract customer segments gradually.
Ever wondered why Procter and Gamble creates so many, often competing, brands? You guessed it: market segmentation. P&G simply divides and conquers. Different people have different needs, so they need different products (and possibly brands).

Competitive analysis
Another powerful, yet often overlooked, market research method is the process of understanding one’s market environment. Seriously, if there’s only one thing you could do to learn what works and what doesn’t in your market, you should do a competitive analysis.
“Whenever we discuss building a certain feature, we would definitely research our competitors and see how they do it.” Tim Soulo, CMO
You’d be surprised by how much you can learn about and from your competition and how much of it can be done online. There are certain tried and tested techniques, hacks, and tools for this type of research, and you can find them in this guide .
Analyze commercial data
Secondary market research data is relatively affordable, fast to acquire, and easy to use. Think market reports, industry insights, and a ton of research data someone has already gathered and analyzed so you don’t have to.
The most reputable sources are Gartner , Forrester , and Pew . Apart from those, make sure to check if there is a trustworthy commercial data source specific to your niche.
Sites like G2, Capterra and Trust Pilot also count. Not only do they give you an overview of your industry, but you can also find some real gems in your users’ reviews and your competitors’ reviews as well. Ahrefs uses that data source regularly internally and externally, like for this section of our Ahrefs vs Semrush vs Moz landing page:

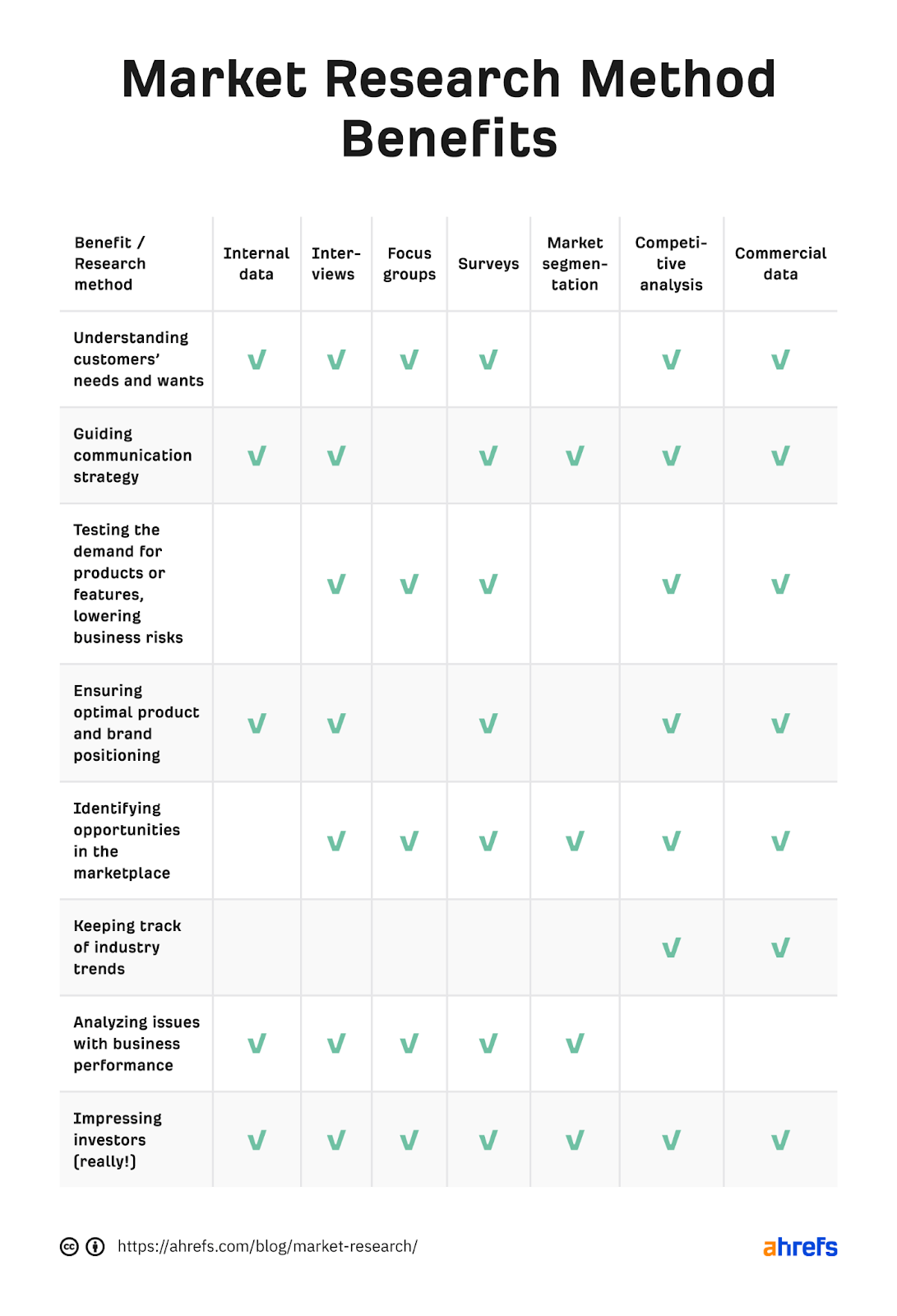
Benefits of market research - a comparison
Let’s quickly summarize the above 7 different methods of market research by their key benefits.
How to do market research process in 5 key steps
So now we know what market research is, why and when to do it, and we’ve learned about all of the important types and methods.
Let’s see how we can use that knowledge to conduct any type of market research in 5 steps. As an example of market research, I’ll tell you about some of my past experiences with a 3D printing company.
- Identify the market research problem
- Choose the sample and research method
- Collect the data
- Analyze the data
- Interpret and present conclusions
1. Identify the market research problem
This is where every research project starts. You will also find that market research, in general, follows the pattern of the scientific method . First, you need to establish what exactly you are researching.
Do you have a question about your business you want to answer? Maybe you see an opportunity in the market. Or maybe you’ve observed something curious about your product use and you have a hypothesis that you want to validate? State that in the first step of the market research process.
Let me share an example.
In the past, I ran marketing for a few companies, and one of them was a 3D printer manufacturer. Early on I stumbled upon two problems with that company.
First: one of our market segments was saturated with similar products of similar quality at significantly lower price (classic, right?). Second: more and more 3D printing manufacturers seemed to be drifting away from the hobby segment to tackle the professional segments with more expensive products, yet we remained in the hobby/DIY niche. So we were too expensive for hobbyists but too hobbyist for customers who could afford us.
The hypothesis that I wanted to verify was that if the marketplace was showing a trend towards more professional use cases of 3D printing, our company should follow that trend. In other words, I wanted to check the viability of shifting the brand positioning into the professional/premium sector.
2. Choose the sample and research method
We’ve already covered the main types and methods of market research. You should already have a good idea of the differences between primary and secondary research, or whether qualitative or quantitative methods would best suit your needs.
As for the sample of your research, this refers to the portion of the entire data source in question that you will use. For example, if you want to run a survey among your customers, the sample will refer to the selection of customers you will include in your survey. There are a few options for choosing a sample:
- Use the entire data source . Obviously, it’s not a sample per se. Nevertheless, if sending a survey to all of your customers is doable (and reasonable), this is a perfectly good choice.
- Choose a random sample. Systematic sampling is the easiest way to choose a random sample. This is where you select every x/nth individual for the sample, where x is the population, n is the sample. For example, if you want a sample size of 100 from a population of 1000, select every 1000/100 = 10th member of the population.
- Convenience sampling: choose respondents available and willing to take part in the survey.
- Purposive sampling: choose respondents that in your judgement will be representative or possess some other feature that is important to the research.
- Quota sampling: choose some arbitrary quota of respondents, e.g. 10 non-paying customers, 10 paying small companies and 10 paying large companies.
Back to our example. As a method for verifying my hypotheses, I chose a mix of:
- Surveys sent to all of our resellers. We wanted to see if they also had seen a paradigm shift in the market and what segment of clients they had encountered the most. We also wanted to know their perspective on the longevity of that trend, and whether they potentially be interested in a more premium version of our product.
- In-depth interviews on the phone with our resellers conducted by our sales team. We used purposive sampling here. Our sample comprised resellers with which we had the best relations (we knew they would be more eager to share).
- Competitive analysis. We were mostly interested in market players who tried to penetrate the professional/industrial segment, so this was our sample ( purposive sampling ). We were interested in stuff like: what features were they building into their 3D printers, what was their brand positioning, what was their pricing, what language they used to communicate with their target audience, etc.
- Wohler’s industry report, anything 3D printing from Gartner and the like, reports by 3D printing services providers, and basically any scrape of serious data we could find ( convenience sampling ).
- Internal data: customer satisfaction issues, and just general current customer profile based on Google Analytics and Facebook data.
3. Collect the data
Once you’ve got your problem, method, and sample nailed, all you need to do is to gather the data. This is the step where you send out your surveys, conduct your interviews, or reach out for industry insights.
A word of advice, choose your market research tool carefully; it will greatly influence the amount of work you will have with analyzing the data. For example, Google Forms automatically makes graphs out of quantifiable data (plus it’s free).
Here’s the data we collected for the 3D printing company:
- Reseller survey data (both quantitative and qualitative data).
- Reseller interview data (qualitative data).
- Customer satisfaction issues (qualitative data gathered through all customer support channels, we analysed about 200 issues and requests).
- Competitive analysis data (from about 10 competitors).
- We managed to gather 3 comprehensive, independent industry reports, a few smaller reports made by other 3D printing companies, and dozens of scrapes of data, like statistics and noteworthy insights. We pulled out data like: 3D printer manufacturer market share, market growth in time, market segmentation, key 3D printing applications, 3D printing adoption by region, key players’ sales numbers.
- Any demographic, sociographic and psychographic data on customers and website visitors we could find in our internal data.
4. Analyze the data
Now that you have your data collected, the next step is to look for patterns, trends, concepts, or often repeated words—all dependent on whether your method was qualitative or quantitative (or both).
Simple research performed on a small sample will be relatively easy to analyze, or even analyzed automatically, like with the aforementioned Google Forms. Sometimes you will have to use expensive and harder to master software like Tableau , NVivo , PowerBI , or SPSS . Or you can use Python or R for data analysis (if you have a data analyst or data scientist on board, you’re in luck).
Continuing the example: Google Forms made it easy for us to spot patterns in surveys since quantitative data was calculated automatically. The most time-consuming part was reading through all of the responses and manually looking for patterns (back then I wasn’t aware of any tool that could do the job). Both sales and marketing teams worked on analyzing some of the qualitative data to have more than one reference point.
When it comes to researching the competition, coming up with some kind of data structure makes the work more comprehensive (and saner). We put our competitors’ data in specific categories, like products & services (prices included), target market, benefits, values, and brand message. We also used something called a brand positioning map which looks like this:
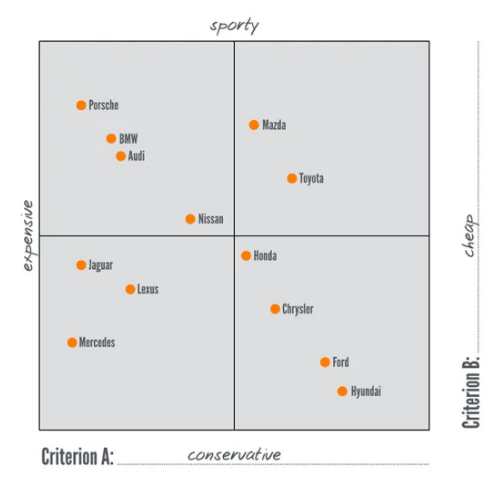
Analyzing secondary data was probably the easiest part, as the data we needed was already prepared in ready-to-use graphs, statistics and insights. We just had to sift through the contents to look for answers to our questions.
5. Interpret and present conclusions
Analyzing the data is not enough. You need to compile your data in a communicative, actionable way for the decision makers. A good practice is to include in your report: all your information, a description of your research process, the results, conclusions, and recommended actions.
Summing up my 3D printing example, I hypothesised that our market was experiencing a major shift and that the company should follow that trend. The research we did verified that hypothesis positively:
- Our resellers were getting more and more inquiries about professional/industrial use cases and machines. As you can imagine, the budget of this kind of client was significantly higher than hobbyists but so were the expectations.
- Our resellers indicated that this phenomenon is here to stay. Moreover, they declared interest in a new 3D printer tailored to the needs of their more demanding clientele.
- Our customers were outgrowing their early-adopter habits and wanted something easier to use, something plug-and-play that just worked reliably. Tinkering with the printer was something only hardcore makers were interested in.
- The companies we were interested in had already started adapting to the professional/premium market both with their offer and smart marketing communication.
- We also found a ton of other interesting data that we used later on. For example, we found that apart from engineers and designers, an equally interesting segment was educational institutions.
Our initial market research lasted for about two months. We also came back to it whenever we had the chance (or the necessity) and reiterated it to see if we were on the right track.
Was it worth it? Let me tell you this: it saved the company. Our research showed us that this was the last call to reposition the brand and the product. Our original target segment was being gradually dominated by companies we couldn’t compete with.
It took us some time to get buy-in from key stakeholders and implement the conclusions throughout the whole company (eventually, we got it right). As a result, we increased sales, increased customer satisfaction and put ourselves on a more profitable growth track—a win-win for everyone. We even went as far as merging with another manufacturer to shorten the time to get to that sweet market spot.
Looking back, no one from our close competitors survived. They didn’t adapt as we did, and we owed everything to market research.
Whatever you do, avoid these common market research mistakes :
- Poor sampling.
- Ambiguous questions.
- Leading or loaded questions (questions that show bias or contain controversial assumptions).
- Unclear or too many research objectives.
- Mixing correlation with causation.
- Ignoring competitive analysis.
- Allowing biases to influence your research ( confirmation bias being arguably the most common and the most dangerous one).
- Not tracking data on a regular basis.
Online market research tools and resources
Market research reaches back to the 1930s and it’s probably rooted even “deeper” than the 20th century. Everything you could do then you can do now better, faster and cheaper thanks to these online tools and resources.
SEO tools - research the market with Ahrefs
I’ve put together 3 quick wins that can help with your market research—and that’s only a taste of what you can do with Ahrefs.
1. Brand awareness
In the early 20th century, you’d have to hire market researchers to spend days or even weeks asking people “have you heard about brand X”. Today, you can simply look up the search volume for that brand.
So let’s say you run a drone manufacturing brand, and you want to check out your competitors’ brand awareness in France. Go to Ahrefs Keywords Explorer , input the names of the brands, select “France” as your market, and in a flash you get:
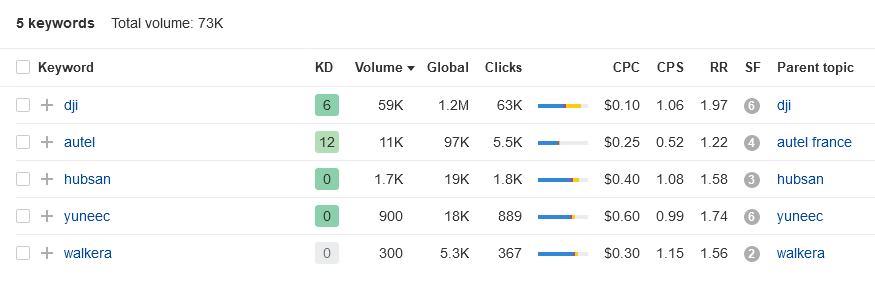
The branded keyword volume indicates the brand awareness of that brand in a particular market. You can also keep track of that data by performing this search regularly to see if there are significant changes over time (for example, impacted by a recent campaign).
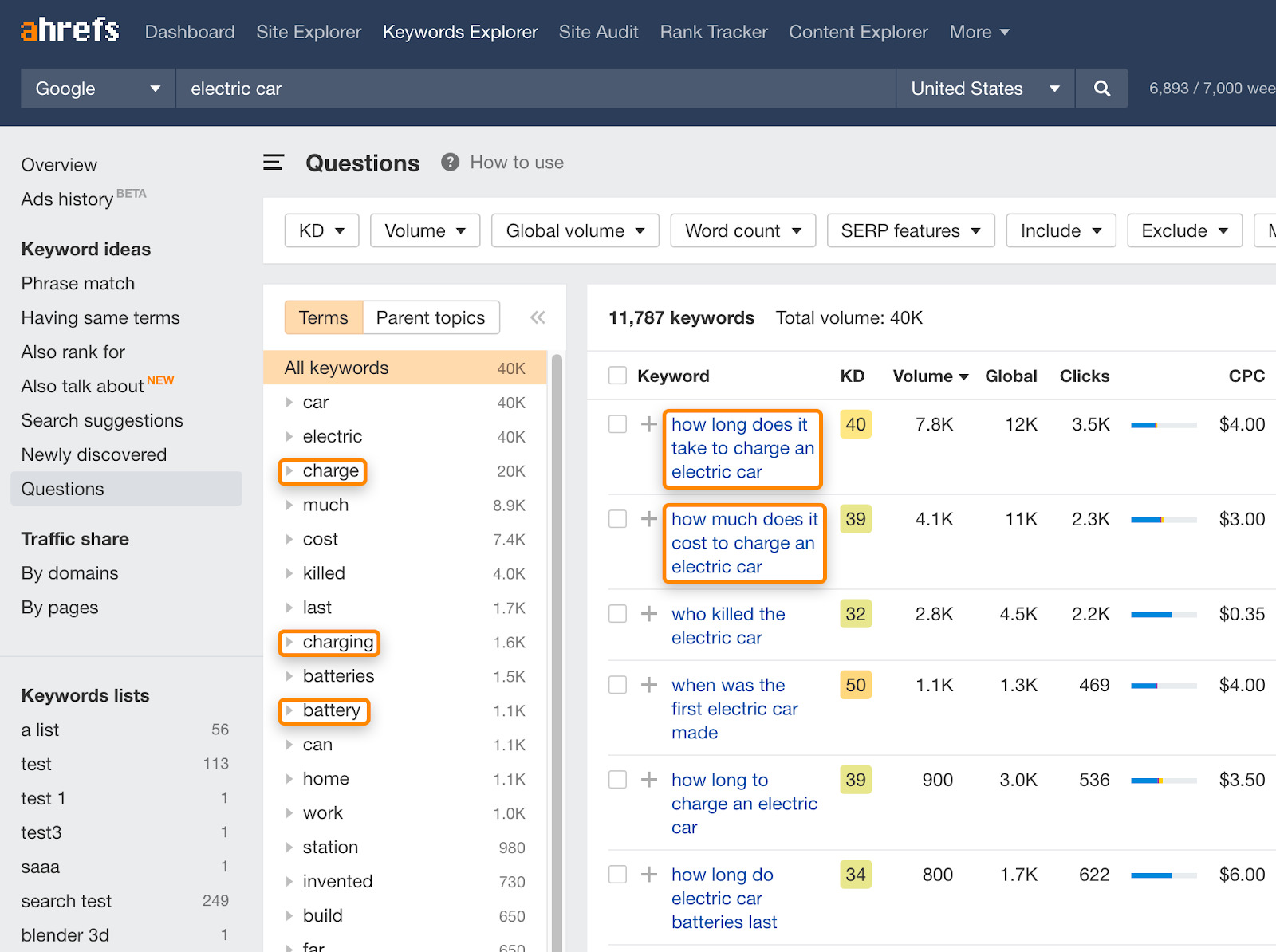
2. Feature demand
The next game-changing feature for electric cars will concern batteries, charging time, and charging cost (and not autopilot). How do I know?
Well, I opened Ahrefs Keywords Explorer , typed in “electric cars”, and went to the Questions report to find out what people search for. This gave me an idea of what problems electric car owners have (and potential owners worry about). You can easily perform similar research for your niche.
3. Understand the language of your market
Gerald Zaltman in his popular book “How Customers Think” proposes the idea that one of the major erroneous assumptions of marketing is that consumers think in words.
On the other hand, when consumers Google something they have to think in words. And when we market to those consumers we have to think in words as well. The question is: which words?
Let’s say that you want to enter a new and innovative market in the USA, for example the synthetic fermentation-derived dairy industry, also called animal-free dairy.
To you, this set of words “animal-free dairy” may be the very center of your business and marketing efforts. But let’s see what other people think. Let’s use Keywords Explorer to see how many people search Google in the U.S. just for that phrase:
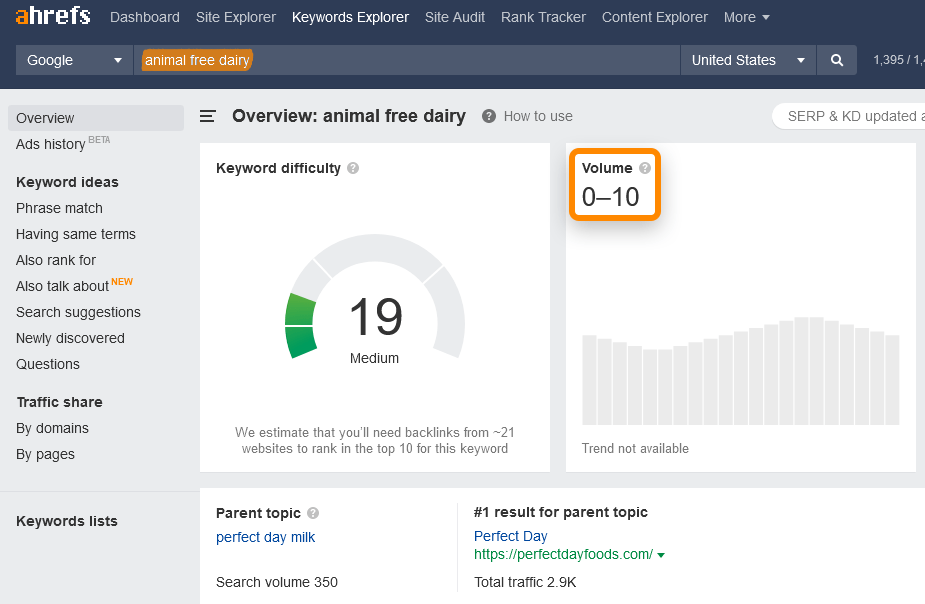
Whoops! Looks like your product category has disappointingly low awareness. Does this mean you’re doomed? Not necessarily.
Let’s try other words. Words that mean something different, but still closely related to your new product.
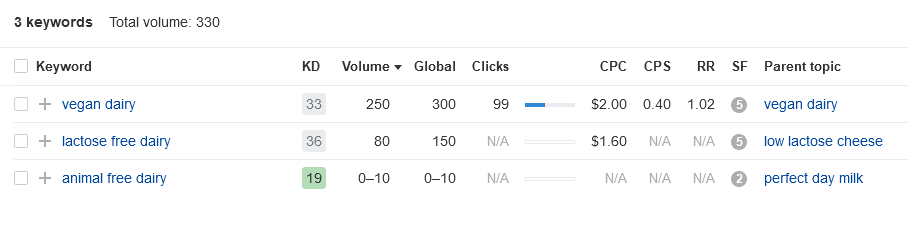
Now we’re onto something. People search for “vegan dairy” and “lactose free dairy” more often. Not the same, but closely related. Yet, look at the difference in search volume.
Words make a huge difference. And Google knows that.
The only reason you were able to put all of those three phrases in the same bucket was that you knew the connection between those words. The problem is that your target audience may not know that connection; they may not even know that this kind of product exists. This quick analysis of search volume shows that you may want to make that connection, for example with content marketing .
If you create content around related higher volume keywords, you can potentially get more organic traffic than simply focusing on the keyword designating your product category. Look, even though you might believe the main benefit of your animal-free product is something unrelated to lactose, e.g., cruelty-free production, you might want to address the problem of lactose intolerance to appeal to people with this condition.
But that’s not all. You may have noticed “low lactose cheese” in the bottom right corner. This refers to the nifty feature of Ahrefs’ Keyword Explorer called “Parent topic”. Parent topic indicates that Google sees a given keyword as part of a broader topic.
If we click on this Parent topic, we uncover even more search demand:
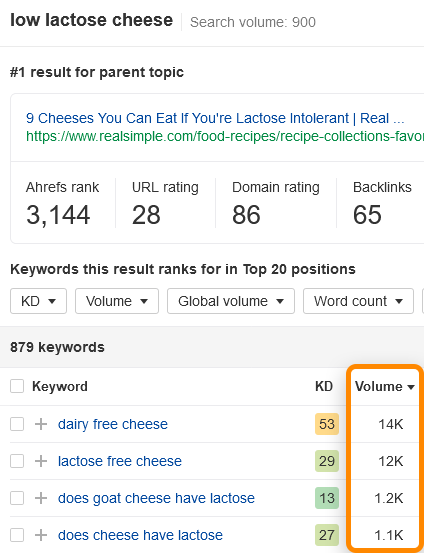
We can see that the search for the topic “low lactose cheese” exceeds the “vegan dairy” topic by almost 300% in the US. Also, uncovering that parent topic gave us 879 potential keyword ideas (some of them have even higher search volume, like “lactose free cheese”).
Want to discover even more topic associations? No problem. You can dive deeper into this research by using other features of Ahrefs’ Keyword explorer. For example,the Also rank for report allows you to see which other keywords (and topics) the top 100 ranking pages for your target keyword also rank for.
This market research quick-win ties into the broader topic of keyword research. If you want to uncover even more keyword ideas and learn how to analyze them, read our keyword research guide .
Source: https://hubspot.com
Customer Relationship Management software is used to manage and track interactions between a company and its customers and prospects. Usually, it works in tandem with sales or marketing automation software (or has integrations for them). If used properly, it is a true cornucopia of market insight.
As I pointed out earlier, it’s one of those primary data sources that you can leverage to discover patterns in your customer behaviour or characteristics. Popular choices are Hubspot, Salesforce, Intercom, but there is a ton of CRM software out there, so check out a software comparison like G2 to see what best suits your needs.
User feedback tools

This type of tool allows you to carry out our aforementioned survey research method online.
Create targeted, user-specific surveys and analyze answers with tools like Google Forms , SurveyMonkey , Typeform , or Qualaroo .
Sending out your typical email with a survey is not the only option, for example with Qualaroo you can display surveys:
- In your digital product
- In your SaaS product
- Inside your web app
- Inside your mobile app
- On your website
- On your mobile site
- On your prototypes.
- On most public URLs. Even competitor sites
Need more? No problem, check out SurveyMonkey’s Market Research solution . It taps into the agile market research models we’ve discussed. They’ve got 14 online solutions that help you stay on top of your game, including customer segmentation, monitoring market dynamics, brand, creative analysis, feature importance, finding the right price for your products, and more.
So you think you have a tough business challenge? This daring gentleman is trying to disrupt… eggs. Extremely hard, but doable with market research on his side.
Website/app analytics
Tracking your website or app traffic is absolute marketing basics. Just look at some data dimensions Google Analytics offers:
- Demographics
Sounds familiar? Yup, that sounds like good ol’ market segmentation. Here’s the best part: it’s free, quick to perform and it’s based on your primary data.
If you’ve never dug deeper into Google Analytics, or similar analytics software (e.g., Matomo , Woopra ) here are some questions that this marketing technology can answer for you:
- What do people search for once they’re on my site?
- What differentiates customers who have made a purchase from the ones that haven’t?
- What are my top countries by revenue?
- What are my best selling products?
If you’re already using Google Analytics, see if you’re not making these Google Analytics tracking mistakes.
User experience research tools
Commonly used by UX designers, but just listen to the value propositions of these tools:
- “See and hear real people using your website, online shop or app.” ( https://userpeek.com/ )
- “Real-time feedback. From real customers. Wherever you work. So you can create experiences that get real results.” ( https://www.usertesting.com/ )
- “Scalable & Customized User Research” ( https://www.userlytics.com/ )
- “Record video and audio of your users, so you see and hear their exact experience with your product.” ( https://www.loop11.com/ )
Again, sounds much like our market research methods, right? And it’s no joke, thousands of companies use these tools.
User experience research tools allow you to get user feedback and insights on your products, prototypes, websites, and apps.
Testing is based on tasks your test-takers perform. You can either use your own user base or define a custom base using their services. You’ll get written reports and even recorded videos that you can incorporate into your market research and make sure you’re properly taking advantage of that market opportunity.
Ad planning tools
That’s right—the Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter ad planner you already use for running ads can give you some insight into the numbers behind the market segments you’re interested in.
30+ males with higher education interested in technology gadgets? No problem. Female C-suite decision-makers from Europe? It’s all there.
Census data
The availability of this kind of data may vary based on your target market. For example, in the US the Census Bureau offers a free resource for searching the country’s census data. You can filter the data by topics, years, geography, surveys, or industry codes. You can also access premade interactive tables (which you can also download) or simply explore certain regions of the country using their maps.
Business intelligence tools
With business intelligence tools like Tableau , Looker or Sisense , you can connect to any data source to perform data cleaning, statistical operations, and data visualization. They are designed to allow you to glean insights into your data, and communicate effectively with your stakeholders. It’s like SQL combined with R, but you don’t need coding skills and you get a user-friendly interface.
Because these tools are overflowing with functionality and because they are usually pricey, they are overkill for small companies with basic market research needs. Often you will find that the tool that you are already using for your research method comes with some data analysis and visualization functions. And if not, you can always import your data to Excel or Google Docs and use Google Data Studio for a shareable interactive presentation.
Other noteworthy tools and services
- Think with Google
- Living Facts
Final thoughts
Market research is no easy feat. If you feel intimidated by it, you’re not the only one. But don’t shy away from it. The benefits of conducting even sporadic market research can have benefits for your business you simply can’t ignore. You won’t turn into a market research pro overnight, but the good news is you don’t have to. You can go the agile way (like Ahrefs), use affordable self-service online tools and resources, or you can even outsource your research. As long as you base your marketing game plan on valid data, you dramatically improve your chances for success.
Got questions? Ping me on Twitter .

How to Conduct a Market Analysis? (+ Examples)
Appinio Research · 04.10.2023 · 29min read

Are you ready to transform your business with the unparalleled advantages of market analysis? Discover how harnessing the power of data-driven insights can propel your decision-making and unlock exceptional growth opportunities.
In this guide, we delve deep into the art of market analysis, showing you how to gain a competitive edge, tailor your strategies with precision, and, ultimately, boost your success. Let's embark on this journey of discovery together.
What is Market Analysis?
Market analysis is the process of evaluating market conditions and dynamics to understand its potential and make informed decisions. It helps you answer crucial questions:
- Who are your customers?
- What are their needs and preferences?
- Who are your competitors?
- What market trends should you be aware of?
Market analysis is crucial because it empowers you to make data-driven choices, minimize risks, and maximize opportunities.
Why is Market Analysis Important?
Before diving into the analysis, you need to define your objectives. Common goals of market analysis include:
- Market Entry: Evaluating the feasibility of entering a new market.
- Product Development : Identifying market gaps for new product development.
- Competitor Analysis: Understanding your competition's strengths and weaknesses.
- Strategic Planning: Shaping your business strategies based on market insights.
Benefits of Effective Market Analysis
Conducting a thorough market analysis brings several benefits:
- Risk Mitigation: Minimize the risk of entering an unprofitable market.
- Resource Allocation: Optimize resource allocation for marketing and product development.
- Competitive Advantage: Gain a competitive edge by understanding your market better.
- Innovation: Identify opportunities for innovation and growth.
Now that you understand the importance of market analysis, let's move on to the practical steps involved.
How to Prepare for Market Analysis?
Before diving into market analysis, setting the stage for success is essential. Here are the key steps to prepare for market analysis:
- Set Clear Objectives: Define your specific goals and objectives for the analysis. Be clear about what you want to achieve. For example, if you're planning to enter a new market, your purpose might be to determine market demand and competition.
- Identify Target Audience: Knowing your audience is crucial. Identify the demographics, preferences, and behaviors of your target market. This information will guide your data collection methods.
- Gather Necessary Resources: Market analysis requires data, tools, and expertise. Ensure you have access to the resources you need. This might include budget allocation for research tools, hiring analysts, or outsourcing data collection.
- Consider Ethical Considerations: Ethical guidelines are paramount in market analysis. Ensure that your data collection methods and analysis processes adhere to ethical standards, respecting privacy and confidentiality.
With your preparations in place, you're ready to collect the data necessary for your market analysis.
Data Collection for Market Analysis
Accurate and relevant data is the lifeblood of market analysis. Here's how you can gather the information you need:
Primary Data Sources
Primary data refers to information collected directly from the source. You can obtain primary data through:
- Surveys: Conducting surveys to gather insights from your target audience.
- Interviews: Engaging in one-on-one interviews with industry experts or potential customers .
- Observations: Collecting data by observing customer behavior or market trends.
Secondary Data Sources
Secondary data is information that already exists and is collected by someone else. Sources of secondary data include:
- Market Reports: Industry-specific reports and publications.
- Government Data: Data provided by government agencies.
- Competitor Reports: Analyzing reports and information about your competitors.
Qualitative Data Collection Methods
Qualitative data provides in-depth insights into customer attitudes and behaviors. Qualitative methods include:
- Focus Groups: Gathering a small group of participants to discuss specific topics.
- In-Depth Interviews: Conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their perspectives.
Quantitative Data Collection Methods
Quantitative data is numerical and can be analyzed statistically. Common quantitative methods include:
- Surveys: Creating structured questionnaires for large-scale data collection.
- Online Analytics: Analyzing website and social media metrics for user behavior.
With your data collected, it's time to move on to the next crucial step: analyzing and interpreting the data.
Market Research Techniques
Analyzing the data you've collected is where the real insights come to light. Let's explore various market research techniques that help you make sense of your data.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are powerful tools for collecting quantitative data. They allow you to gather structured responses from a large sample of participants. When designing surveys, consider:
- Question Types: Crafting survey questions that are clear and unbiased.
- Sampling Techniques: Ensuring your sample is representative of your target audience.
- Data Analysis: Applying statistical methods to analyze survey data.
Interviews provide qualitative data through in-depth conversations with individuals. Key considerations include:
- Interview Structure: Developing a structured interview guide.
- Listening Skills: Active listening to uncover valuable insights.
- Transcribing and Coding: Transcribing interviews and coding responses for analysis.
Focus Groups
Focus groups involve small group discussions, providing rich qualitative data. To conduct effective focus groups:
- Moderation Skills: Skillfully moderating group discussions.
- Participant Selection: Recruiting diverse participants for varied perspectives.
- Thematic Analysis: Identifying themes and patterns in focus group discussions.
Observational Research
Observational research involves watching and recording customer behavior.
- Research Setting: Choosing the right environment for observations.
- Data Recording: Accurate and detailed recording of observations.
- Interpretation: Interpreting observed behaviors in the context of your objectives.
Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis involves evaluating your rivals to understand their strengths and weaknesses.
- Identifying Competitors: Determine who your main competitors are.
- Competitive Metrics: Choose relevant metrics to assess competition.
- Benchmarking: Comparing your performance against competitors.
By mastering these market research techniques, you'll be well-prepared to extract valuable insights from your data. The next step is to interpret these insights effectively.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Analyzing and interpreting data is the heart of market analysis. This process involves converting raw data into actionable insights.
Data Cleaning and Preparation
Data can be messy, and cleaning and preparing it for analysis is essential. This involves:
- Data Cleaning: Removing outliers, errors, and inconsistencies.
- Data Transformation: Converting data into a consistent format.
- Data Validation: Ensuring data accuracy and completeness.
Descriptive Analysis
Descriptive analysis involves summarizing and visualizing data to understand its basic characteristics. Techniques include:
- Summary Statistics: Calculating measures like mean, median, and standard deviation.
- Data Visualization: Creating charts and graphs to represent data visually.
- Data Distribution Analysis: Understanding how data is distributed.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis allows you to draw meaningful conclusions from your data. Techniques include:
- Hypothesis Testing: Testing hypotheses to make data-driven decisions.
- Regression Analysis: Examining relationships between variables.
- Segmentation Analysis: Grouping data for more targeted insights.
Identify Trends and Patterns
Identifying trends and patterns in your data helps you make predictions and formulate strategies.
- Time Series Analysis: Analyzing data over time to identify trends.
- Pattern Recognition: Spotting recurring patterns in customer behavior.
- Predictive Modeling: Using data to make future predictions.
Armed with these analytical skills, you can effectively uncover valuable insights that inform your business decisions.
Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is crucial in understanding your audience better and tailoring your strategies accordingly.
What is Market Segmentation?
Market segmentation involves dividing your market into distinct groups based on shared characteristics. This is significant because it allows you to:
- Target Specific Audiences: Tailor your marketing efforts to specific segments.
- Personalize Products: Customize products and services to meet segment needs.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on high-potential segments.
Types of Market Segmentation
There are various ways to segment a market, including:
- Demographic Segmentation : Dividing based on age, gender, income, etc.
- Psychographic Segmentation : Grouping by lifestyles, values, and attitudes.
- Geographic Segmentation: Segmenting by location or region.
- Behavioral Segmentation: Dividing based on buying behavior and preferences.
Targeting Specific Market Segments
After segmentation, you must target your chosen segments effectively. This involves:
- Positioning: Crafting a unique value proposition for each segment.
- Messaging: Tailoring your marketing messages to resonate with each segment.
- Product Development: Adapting products to meet segment-specific needs.
By understanding your market segments, you can connect with your audience on a deeper level and increase your chances of success.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for assessing your business's internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
Identify and leverage your strengths, such as:
- Unique Products: What sets your products apart from the competition?
- Skilled Workforce: Highlight the expertise of your team.
- Strong Brand: Emphasize your brand reputation and recognition.
Acknowledge and address your weaknesses, including:
- Limited Resources: Recognize budget constraints or resource shortages.
- Market Share: Assess areas where competitors outperform you.
- Operational Challenges: Identify internal issues that need improvement.
Opportunities
Exploit opportunities in your market, such as:
- Market Growth: Explore emerging markets and trends.
- Partnerships: Seek collaboration with complementary businesses.
- New Technologies: Embrace innovations that can improve your operations.
Mitigate potential threats, such as:
- Competition: Analyze the competitive landscape and potential disruptors.
- Economic Trends: Consider how economic fluctuations may affect your business.
- Regulatory Changes: Stay updated on industry regulations and compliance.
Conducting a SWOT analysis helps you develop strategies that capitalize on strengths, mitigate weaknesses, seize opportunities, and guard against threats.
How to Conduct Competitive Market Analysis?
Competitive market analysis is a critical component of your overall market analysis strategy. Understanding who your competitors are, analyzing their strengths and weaknesses, and conducting competitive benchmarking are essential steps to gain a strategic advantage in your market.
1. Identify Key Competitors
Identifying your key competitors is the first step in a competitive market analysis. Key competitors are those businesses that directly compete with you for the same target audience or market share. Here's how to identify them:
- Market Research : Conduct thorough market research to identify businesses offering similar products or services in your industry or niche.
- Customer Feedback: Listen to your customers. Often, they will mention your competitors when discussing alternatives or choices.
- Industry Associations: Explore industry associations, directories, or trade publications to find a list of competitors.
- Online Search: Use search engines and social media platforms to discover businesses that appear in similar search results or target similar keywords.
Once you have identified your key competitors, you can move on to a more in-depth analysis of their strengths and weaknesses.
2. Analyze Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Analyzing competitor strengths and weaknesses provides valuable insights into their strategies and helps you identify opportunities and threats. Here's how to conduct this analysis effectively:
Product or Service Offering
- Strengths: Determine what your competitors excel at regarding product quality, features, and innovation.
- Weaknesses: Identify areas where their products or services fall short compared to yours.
Pricing Strategies
- Strengths: Analyze whether competitors offer competitive pricing or unique pricing models.
- Weaknesses: Look for instances where their pricing may be less competitive or prohibitive.
Market Share and Customer Base
- Strengths: Assess the size of their customer base and market share in your industry.
- Weaknesses: Investigate whether they have any vulnerabilities or dependencies on a specific customer segment.
Marketing and Branding
- Strengths: Analyze their marketing strategies, branding efforts, and customer engagement tactics.
- Weaknesses: Identify any gaps or areas where their marketing efforts may be less effective.
Customer Reviews and Feedback
- Strengths: Look for positive customer reviews and feedback to understand what your competitors are doing well.
- Weaknesses: Pay attention to negative reviews and areas where customers express dissatisfaction.
This analysis will help you identify areas where you can differentiate yourself and gain a competitive edge. It also enables you to anticipate how competitors might respond to your strategies.
3. Competitive Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking involves comparing your performance and strategies against those of your key competitors. It allows you to set performance goals, identify best practices, and continuously improve.
- Select Key Metrics: Choose the key performance metrics that matter most to your business. These could include revenue growth, customer acquisition costs, customer satisfaction scores, or market share.
- Gather Data: Collect data on these selected metrics for both your business and your competitors. This data can come from public sources, industry reports, or your own internal records.
- Analyze and Compare: Compare your performance against that of your competitors using the selected metrics. Pay close attention to areas where you outperform them and areas where you lag behind.
- Identify Best Practices: Identify the strategies and practices that contribute to your competitors' success. Learn from their best practices and consider implementing similar strategies in your business.
- Set Improvement Goals: Based on your analysis, set specific improvement goals for your business. These goals should be realistic and aligned with your overall business objectives.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly monitor your progress toward achieving your improvement goals. Adjust your strategies and tactics as needed to stay competitive.
Competitive benchmarking is an ongoing process. By continuously assessing your performance compared to your competitors, you can adapt and refine your strategies to maintain a competitive advantage in the market.
How to Conduct Comparative Market Analysis?
Comparative market analysis involves assessing your market position, understanding competitor strategies and performance, and identifying opportunities for growth. Let's explore each aspect in more detail.
What is Comparative Analysis in Market Research?
Comparative analysis involves examining your business in relation to your competitors and the overall market. It helps you:
- Gain Perspective: Understand where your business stands in the market landscape.
- Identify Trends: Recognize industry trends and shifts.
- Spot Opportunities: Discover areas where your business can excel or innovate.
To conduct an effective comparative analysis:
- Collect Data: Gather data on your business, competitors, and the market as a whole.
- Use Key Metrics: Focus on key performance metrics relevant to your industry.
- Benchmark Against Competitors: Compare your performance against that of your direct competitors.
Analyzing Competitor Strategies and Performance
Analyzing competitor strategies and performance is a critical aspect of comparative analysis. Here's how to go about it:
1. Competitor Strategies
Product and Service Strategies: Examine their product/service offerings and pricing strategies.
- Marketing and Promotion: Analyze their marketing campaigns, messaging, and customer engagement tactics.
- Distribution Channels: Understand how they reach and distribute products or services to customers.
- Innovation: Identify areas where they innovate or introduce new features.
2. Financial Performance
- Revenue and Growth: Assess their revenue figures and growth rates over time.
- Profit Margins: Analyze their profit margins and how they compare to industry standards.
- Investment and Funding: Explore whether they have secured significant investments or funding.
3. Customer Engagement
- Customer Base: Understand the size and composition of their customer base.
- Customer Satisfaction: Look for indicators of customer satisfaction, such as reviews or feedback.
4. Market Presence
Market Share: Determine their market share in your industry or niche.
Geographic Reach: Explore the regions or markets they serve.
Identifying Market Position and Opportunities
Identifying your market position and opportunities is the ultimate goal of comparative market analysis. Here's how to accomplish this:
1. Market Position
- Relative Strengths: Determine where your business excels compared to competitors.
- Areas of Improvement: Identify areas where you lag and need improvement.
- Market Niche: Define your unique value proposition and niche within the market.
2. Opportunities
- Competitive Gaps: Recognize gaps in the market that your business can fill.
- Unmet Customer Needs: Explore customer needs that competitors are not effectively addressing.
- Emerging Trends: Stay alert to emerging industry trends and adapt your strategies accordingly.
3. Strategic Planning
- Strategy Development: Formulate strategies that capitalize on your strengths and address weaknesses.
- Innovation: Consider innovative approaches to differentiate your business.
- Risk Mitigation: Develop plans to mitigate risks associated with market dynamics.
By conducting a comprehensive comparative market analysis, you gain a deeper understanding of your competitive landscape, enabling you to make informed decisions, refine your strategies, and seize growth opportunities effectively. This process should be ongoing, as the market is dynamic and ever-changing.
Competitive Market Analysis vs. Comparative Market Analysis
While these approaches share some similarities, they serve distinct purposes and offer unique insights. Let's explore the key differences and applications of each.
Competitive Market Analysis
Objective: Competitive Market Analysis primarily focuses on assessing your direct competitors and understanding their strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and overall market position. Its main goal is to help you gain a competitive edge by learning from and responding to your rivals effectively.
Key Aspects:
- Competitor-Centric: It revolves around thoroughly examining specific competitors that directly impact your business.
- Strategy-Oriented: The emphasis is on understanding your competitors' strategies, pricing models, product offerings, and marketing tactics.
- Market Positioning: It helps you define your position in relation to your immediate competitors and identify areas for differentiation.
- Direct Impact: Competitive Market Analysis is often employed for short-term decision-making, such as refining marketing strategies or adjusting pricing to respond to competitor moves.
Comparative Market Analysis
Objective: Comparative Market Analysis takes a broader perspective by evaluating your business within the context of the entire market. It aims to provide a comprehensive view of your market's dynamics, trends, and opportunities, helping you make informed, long-term strategic decisions.
- Market-Centric: It considers a broader view of the market, including competitors, potential entrants, and industry dynamics.
- Trend Analysis: Comparative Market Analysis looks at industry trends, market growth, consumer behavior, and emerging technologies that may impact your business.
- Strategic Insights: It provides strategic insights that extend beyond immediate competition, helping you identify opportunities for market expansion, diversification, or innovation.
- Long-Term Planning: This approach is suitable for long-term strategic planning, such as entering new markets, launching new products, or adapting to evolving market conditions.
How to Choose the Right Approach?
The choice between Competitive Market Analysis and Comparative Market Analysis depends on your specific business goals and the depth of insights you seek:
- Use Competitive Market Analysis when you need to closely monitor and respond to specific competitors' actions, refine short-term strategies, or differentiate your offerings within a crowded market segment.
- Opt for Comparative Market Analysis when you are making long-term strategic decisions, considering market expansion, or seeking to innovate based on broader industry trends. This approach provides a holistic view that extends beyond immediate competitors.
In practice, many businesses find value in combining elements of both approaches to gain a comprehensive understanding of their market environment. The key is to align your analysis with your strategic objectives and adapt your approach as your business evolves.
Market Analysis Template
A well-structured market analysis template is invaluable for streamlining the market research process, ensuring you cover all essential aspects and gather data systematically. Let's explore the components of an effective market analysis template and how to customize it to your specific needs.
How to Create a Structured Market Analysis Framework?
A comprehensive market analysis template typically includes the following sections:
1. Market Overview
- Market Size: Describe the current size and potential growth of the market.
- Market Segmentation: Identify key segments within the market.
- Market Trends: Highlight recent trends and developments.
2. Competitive Landscape
- Competitor Identification: List your main competitors and potential disruptors.
- Competitor Analysis: Evaluate their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT).
- Competitive Advantage: Explore ways in which your business can gain a competitive edge.
3. Target Market Analysis
- Customer Personas: Develop detailed customer personas based on demographics, behavior, and preferences.
- Customer Needs: Understand your target audience's specific needs and pain points.
- Market Demand: Assess the demand for your products or services within your target market.
4. SWOT Analysis
- Strengths: Identify your business's internal strengths and advantages.
- Weaknesses: Acknowledge areas where your business may be vulnerable.
- Opportunities: Explore external factors that can be leveraged for growth.
- Threats: Recognize potential challenges and external risks.
5. Trends and Forecast
- Market Trends: Analyze current trends and their potential impact on your business.
- Market Forecast: Make data-driven predictions about the future of the market.
- Emerging Technologies: Assess how emerging technologies may influence your industry.
How to Utilize Template for Efficient Market Analysis?
Templates not only save time but also ensure that you cover all critical aspects of market analysis. To effectively utilize a template:
1. Identify Relevant Sections
Review the template to identify sections that are relevant to your specific market analysis objectives. Not all sections may be necessary for every analysis.
2. Customize Sections
Tailor each section to your business and market. For example:
- In the "Market Overview" section , provide market data specific to your industry or region.
- In the "Competitive Landscape" section , focus on competitors directly impacting your business.
3. Collect Data Methodically
Use the template as a guide to collect data methodically. It ensures that you gather the right information in a structured manner.
4. Analyze and Interpret Data
After collecting data, analyze and interpret it within the context of each section of the template.
This step provides actionable insights.
5. Draw Conclusions and Recommendations
Utilize the insights gained from your analysis to draw conclusions and formulate recommendations that address your initial market analysis objectives.
6. Report Compilation
Compile the information from your template into a well-organized market analysis report that can be easily shared with stakeholders, investors, or team members.
How to Customize the Market Analysis Template?
Market analysis templates should not be rigid but rather adaptable to meet your unique requirements.
- Additional Sections: If your analysis requires sections not covered in the template, feel free to add them. For example, you might include a section on environmental or sustainability factors.
- Data Sources and Tools: Specify the data sources and analysis tools you'll use for each section. This ensures transparency and accountability in your analysis process.
- Visual Elements: Incorporate charts, graphs, and visual representations where relevant. Graphic elements can make complex data more digestible.
- Timelines and Milestones: If your market analysis is part of a larger project or business plan, include timelines and milestones to track progress.
- Appendices: Consider including appendices with supplementary materials such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or detailed calculations to support your analysis.
Market Analysis Examples
To gain a deeper understanding of how market analysis is applied in real-world scenarios, let's explore a variety of detailed examples that showcase different aspects of this crucial business practice.
Example 1: Entering a New Market
Scenario: Imagine you are the marketing manager of a well-established electronics company considering expansion into a new geographic market. Let's call it Market X.
Market Analysis Objective: Your goal is to assess the feasibility and potential success of entering Market X.
Data Collection and Analysis
- Market Research: Begin by collecting data on Market X, such as population demographics, economic indicators, and consumer behavior.
- Competitor Analysis: Identify and analyze competitors already operating in Market X. Assess their market share, product offerings, pricing strategies, and customer reviews.
- Consumer Surveys: Conduct surveys in Market X to understand consumer preferences, needs, and willingness to adopt your products.
- Regulatory Environment: Investigate the regulatory framework in Market X, including import/export regulations, industry standards, and compliance requirements.
Findings and Insights
- Market Potential: Through extensive data analysis, you discover that Market X has a growing population with a high demand for electronics, indicating market potential.
- Competitive Landscape: You identify several established competitors, but their product offerings are limited in comparison to your company's range.
- Consumer Preferences: Survey results reveal a preference for high-quality, durable electronics aligning with your product portfolio.
- Regulatory Insights: Understanding the regulatory environment helps you plan for compliance, ensuring a smooth market entry.
Recommendations
Based on your analysis, you can make informed recommendations:
- Market Entry Strategy: Develop a comprehensive market entry strategy tailored to Market X, including distribution channels and pricing strategies.
- Product Localization: Customize certain product features to align with local preferences and regulatory requirements.
- Competitive Edge: Leverage your wider product range as a competitive advantage.
Example 2: Product Launch Strategy
Scenario: You work for a startup that has developed an innovative health and fitness wearable device. Your goal is to create an effective product launch strategy.
Market Analysis Objective: Understand your target market, competition, and market trends to launch the wearable successfully.
- Target Audience Profiling: Create detailed customer personas based on demographics, interests, and health and fitness habits.
- Competitor Analysis: Examine the market for similar wearable devices, assessing their features, pricing, and customer reviews.
- Market Trends and Consumer Behavior: Analyze market trends related to health and fitness, wearable technology adoption, and consumer preferences.
- Market Size and Growth: Determine the size of the wearable technology market and its growth rate.
- Target Audience: Detailed personas reveal that your primary customer segments include health-conscious individuals, athletes, and tech enthusiasts.
- Competition: While there are competitors in the market, a gap exists for a wearable that combines health monitoring with advanced fitness tracking.
- Market Trends: Trends show an increasing demand for health-related wearables due to a growing focus on fitness and well-being.
- Market Size: The market is substantial and expected to grow steadily over the next few years.
- Product Features: Focus your product's features on health monitoring and advanced fitness tracking to cater to the identified target segments.
- Pricing Strategy: Set a competitive yet profitable price point for your wearable.
- Marketing Campaign: Develop a marketing campaign highlighting the unique features of your wearable and its benefits for health-conscious consumers, athletes, and tech enthusiasts.
Example 3: Competitive Analysis for an E-commerce Startup
Scenario: You're part of a startup team launching an e-commerce platform that sells handmade artisanal products. You need to understand the competitive landscape to formulate a successful business strategy.
Market Analysis Objective: Gain insights into the e-commerce market for handmade products and identify opportunities for differentiation.
- Competitor Identification: Identify existing e-commerce platforms specializing in handmade products.
- Product Range and Quality: Assess the variety and quality of products offered by competitors.
- Pricing Strategies: Analyze pricing strategies and discount offers of competitors.
- Customer Reviews: Study customer reviews and ratings for competing platforms.
- Competitor Landscape: You discover several established e-commerce platforms in the handmade product niche, but none seem to offer a comprehensive range of unique artisanal items.
- Product Quality: Competitors mainly offer mass-produced items with limited emphasis on craftsmanship and uniqueness.
- Pricing: Pricing strategies appear to be competitive, but customer reviews indicate a desire for more affordable options.
- Product Curation: Focus on curating a selection of high-quality, truly artisanal products to differentiate your platform.
- Competitive Pricing: Offer competitive pricing while maintaining the unique value proposition of handmade items.
- Customer Engagement: Implement strategies to engage customers and gather feedback for continuous improvement.
These examples illustrate how market analysis informs critical business decisions. Whether entering a new market, launching a product, or competing in e-commerce, a data-driven approach empowers you to make informed choices and increase your chances of success.
Remember that market analysis is an ongoing process, and staying updated with evolving market dynamics is essential for long-term success.
Market analysis is your secret weapon for success in the ever-evolving business landscape. By understanding your market, customers, and competition, you gain the knowledge to make informed decisions, identify growth opportunities, and stay ahead of the curve.
Remember, market analysis is not a one-time task; it's an ongoing journey. Continuously gather data, adapt your strategies, and embrace the power of real-time insights. With the right tools and knowledge, you have the potential to turn market analysis into a dynamic force that propels your business to new heights.
How to Conduct Market Analysis in Minutes?
Looking to supercharge your market analysis? Look no further than Appinio , the real-time market research platform changing the game. With Appinio, you can harness the power of real-time consumer insights to make data-driven decisions that drive your business forward.
- Lightning-Fast Insights: Say goodbye to waiting weeks for market research results. Appinio delivers answers to your burning questions in minutes.
- Instant Decision-Making: With real-time consumer insights at your fingertips, you can make informed decisions on the fly, giving your business a competitive edge.
- User-Friendly and Intuitive: Market research doesn't have to be a daunting task. Appinio's user-friendly platform makes it easy for anyone to access and interpret valuable data.
Say goodbye to the old stigma of market research being boring, intimidating, and overpriced. It's time to unlock the power of real-time insights and drive your success.
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

11.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Data Analysis? Definition, Tools, Examples
09.04.2024 | 29min read
What is a Confidence Interval and How to Calculate It?

05.04.2024 | 28min read
What is Field Research? Definition, Types, Methods, Examples
What is Market Research Analysis? Definition, Steps, Benefits, and Best Practices
By Nick Jain
Published on: September 8, 2023
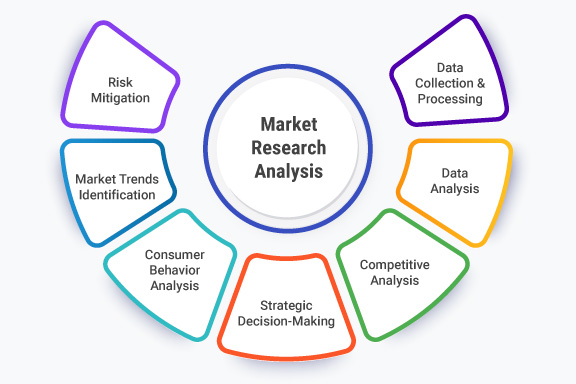
Table of Contents
What is Market Research Analysis?
Market research analysis steps, market research analysis benefits, 15 market research analysis best practices.
Market research analysis is defined as the systematic process of collecting, processing, interpreting, and evaluating data related to a specific market, industry, or business environment. Its primary purpose is to gain insights into various aspects of the market, including consumer behavior, market trends, competitive landscape, and other relevant factors. Market research analysis aims to provide businesses with actionable information that can inform their decision-making processes and strategies.
Here are the key components and objectives of market research analysis:
- Data Collection: The process begins with gathering data from a variety of sources. This data can be classified into two main categories:
Primary Data: Data collected directly from original sources, such as surveys, interviews, focus groups , observations, and experiments.
Secondary Data: Existing data collected by third parties, such as market reports, government publications, industry publications, and academic studies.
- Data Processing: Once collected, the data is processed to ensure its accuracy and reliability. This step involves cleaning the data to remove errors or inconsistencies and structuring it in a way that is suitable for analysis. Data processing may also involve data coding, categorization, and transformation.
- Data Analysis: The heart of market research analysis involves examining and interpreting the data to extract meaningful insights. Various analytical techniques and statistical tools are used to identify patterns, relationships, trends, and correlations within the data. This analysis supports businesses in making knowledgeable decisions.
- Competitive Analysis: Assessing the competitive landscape is an essential aspect of market research analysis. This includes studying competitors’ strengths, weaknesses, strategies, market share, and customer perceptions. Understanding the competitive environment is crucial for shaping a company’s strategy and positioning in the market.
- Consumer Behavior Analysis: Understanding how consumers think, feel, and act is a central objective of market research analysis. It involves identifying consumer preferences, purchasing habits, motivations, and pain points. This information helps businesses tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to meet customer needs effectively.
- Market Trends Identification: Market research analysis helps businesses stay updated on the latest market trends, industry developments, and emerging technologies. Recognizing these trends allows companies to adapt, innovate, and remain competitive in their respective markets.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Ultimately, the goal of market research analysis is to provide actionable insights that inform strategic decision-making. These decisions can relate to product development, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, market entry or expansion, and more.
- Risk Mitigation: By understanding market dynamics and potential challenges, businesses can proactively identify and mitigate risks. This reduces the likelihood of unexpected setbacks and allows for more effective crisis management.
Market research analysis is a vital tool that helps businesses gather and interpret data to make informed decisions, mitigate risks, identify opportunities for growth, and stay competitive in their respective markets. It plays a pivotal role in shaping business strategies and ensuring that resources are allocated effectively to achieve business objectives.
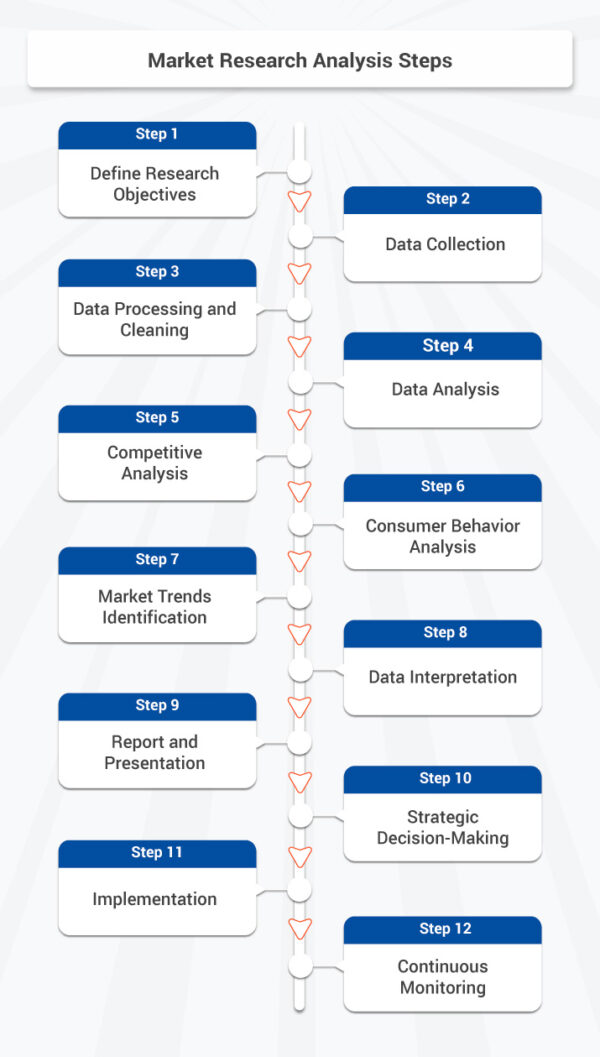
Market research analysis involves a series of systematic steps to gather, process, and interpret data to gain insights into a specific market or industry. These steps are crucial for making informed business decisions and developing effective strategies. Here are the key steps in the market research analysis process:
Step 1: Define Research Objectives
Precisely outline the goals and objectives of your market research . What specific insights or data are you aiming to acquire? What are your research questions? Understanding your objectives is essential for guiding the entire process.
Step 2: Data Collection
Collect relevant data from various sources. This can include primary data (directly collected from surveys, interviews, focus groups , observations, etc.) and secondary data (existing data from reports, publications, databases, etc.). Make certain that your data-gathering approaches are in harmony with your research objectives.
Step 3: Data Processing and Cleaning
Clean and preprocess the collected data to ensure its accuracy and reliability. This step may involve removing duplicate records, correcting errors, and organizing the data for analysis.
Step 4: Data Analysis
Perform data analysis using appropriate techniques and tools. Common analytical methods include statistical analysis, regression analysis, trend analysis, customer segmentation, and sentiment analysis. The objective is to derive significant insights from the data.
Step 5: Competitive Analysis
Assess the competitive landscape by studying your competitors. Analyze their strengths, weaknesses, market share, strategies, and customer perceptions. Recognize potential opportunities and vulnerabilities within the competitive landscape.
Step 6: Consumer Behavior Analysis
Examine consumer behavior by analyzing data related to preferences, purchasing habits, motivations, and demographics. Gain insights into what drives consumer decisions and how they interact with your products or services.
Step 7: Market Trends Identification
Identify and analyze current market trends, industry developments, and emerging technologies. Stay up-to-date with changes in the market that could impact your business.
Step 8: Data Interpretation
Interpret the outcomes of your data analysis within the framework of your research goals. What do the findings mean for your business? Are there actionable insights that can inform your decisions?
Step 9: Report and Presentation
Create a comprehensive report or presentation that summarizes your research findings. Use clear visuals, charts, and graphs to convey the information effectively. Include recommendations and insights that can guide decision-making.
Step 10: Strategic Decision-Making
Use the insights gained from your market research analysis to make informed strategic decisions. These decisions can relate to product development, pricing strategies, marketing campaigns, market entry or expansion, and more.
Step 11: Implementation
Put your strategic decisions into action. Implement the changes and strategies based on your market research analysis. Continuously track progress and adapt your approach as necessary.
Step 12: Continuous Monitoring
Market research analysis is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor market conditions, consumer behavior, and competitive developments to stay adaptable and responsive to changes in the market.
By following these steps, businesses can harness the power of market research analysis to make informed decisions, gain a competitive edge, and drive growth and innovation in their respective industries.
Learn more: What is Research Design?
Market research analysis offers numerous benefits to businesses and organizations across various industries. These benefits are instrumental in making informed decisions, shaping strategies, and ultimately achieving business objectives. Here are some of the key advantages of conducting market research analysis:
- Informed Decision-Making: Market research analysis provides valuable insights and data-driven information that support informed decision-making. By understanding market dynamics, consumer behavior, and trends, businesses can make strategic choices that are more likely to lead to success.
- Risk Mitigation: Through market research , organizations can identify potential risks and challenges in advance. This proactive approach allows them to develop strategies for risk mitigation and crisis management, reducing the impact of unforeseen events.
- Market Understanding: Market research analysis helps companies gain a deeper understanding of their target audience, including demographics, preferences, and purchasing behavior. This knowledge is critical for tailoring products, services, and marketing efforts to meet customer needs effectively.
- Competitive Advantage: By analyzing the competitive landscape, businesses can identify their competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. This information enables them to develop strategies that capitalize on their strengths and exploit competitors’ weaknesses, leading to a competitive advantage.
- Product Development: Market research analysis guides product development by uncovering consumer preferences, pain points, and unmet needs. This ensures that companies create products that resonate with their target market, increasing the likelihood of success in the market.
- Effective Marketing Strategies: Understanding consumer behavior and preferences helps in crafting more effective marketing campaigns. Market research analysis can identify the most suitable marketing channels, messaging, and timing to reach and engage the target audience.
- Optimized Pricing Strategies: Businesses can determine the optimal pricing strategies for their products or services through market research analysis. This includes assessing price sensitivity, competitive pricing, and value perception among customers.
- Market Expansion and Diversification: Market research analysis can reveal new market opportunities and potential areas for diversification. Companies can use this information to expand their reach into new markets or introduce new product lines.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: By aligning products and services with customer preferences, companies can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Contented customers are increasingly inclined to become returning purchasers and enthusiastic brand supporters.
- Cost Efficiency: Market research analysis can help companies allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on strategies and initiatives that are most likely to yield positive results. This reduces wasteful spending on ineffective activities.
- Measurable Results: Market research provides a basis for measuring the success of strategies and initiatives. It allows companies to set benchmarks, track progress, and assess the return on investment (ROI) of various marketing and business efforts.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Market research analysis keeps businesses up-to-date with market trends and emerging technologies. This knowledge encourages innovation and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Enhanced Reputation: Companies that demonstrate a commitment to understanding their market and meeting customer needs often enjoy an enhanced reputation in the eyes of consumers, partners, and investors.
Market research analysis is a valuable tool that empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions, minimize risks, gain a competitive edge, and achieve sustainable growth. It is an investment that can yield substantial returns by helping organizations align their strategies and resources with market realities and customer expectations.
Learn more: What is Primary Market Research?
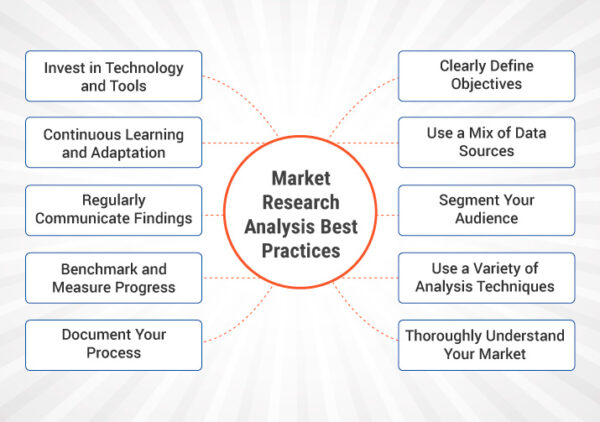
Effective market research analysis is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions and stay competitive in their respective industries. To ensure that your market research analysis yields valuable insights, consider these best practices:
1. Clearly Define Objectives
Begin by clearly defining the objectives of your market research analysis. What particular inquiries do you aim to address? What are your goals and desired outcomes? Having a well-defined purpose will guide your research efforts.
2. Use a Mix of Data Sources
Combine both primary and secondary data sources. Primary data is collected directly from your target audience, while secondary data comes from existing sources. Using a mix of data sources enhances the comprehensiveness of your analysis.
3. Ensure Data Quality
Data quality is paramount. Take steps to ensure the data you collect is accurate, relevant, and reliable. Verify the credibility of your sources and implement data-cleaning processes to remove errors and inconsistencies.
4. Segment Your Audience
Segment your target audience into distinct groups based on demographics, behaviors, or other relevant criteria. This allows for more tailored insights and strategies.
5. Use a Variety of Analysis Techniques
Employ a range of analysis techniques such as quantitative and qualitative methods . Quantitative analysis involves numerical data, while qualitative analysis explores insights from open-ended questions and interviews. This all-encompassing strategy offers a more complete perspective.
6. Stay Objective and Unbiased
Avoid bias in your research by maintaining objectivity. Be aware of any preconceived notions or assumptions that might influence your analysis. Use unbiased language and interpretation of results.
7. Thoroughly Understand Your Market
Before conducting research , gain a deep understanding of the market and industry you’re investigating. This background knowledge will help you ask the right questions and interpret findings effectively.
8. Invest in Technology and Tools
Utilize advanced tools and software for data analysis. These tools can streamline the process, handle large datasets, and provide more robust insights. Consider investing in data visualization tools to present findings effectively.
9. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Keep yourself informed about the most current research methodologies and industry developments. Market conditions evolve, so it’s essential to adapt your research methods accordingly.
10. Ethical Considerations
Adhere to ethical standards in data collection and analysis. Respect privacy and confidentiality, obtain informed consent when necessary, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
11. Regularly Communicate Findings
Share research findings with relevant stakeholders within your organization. Effective communication ensures that insights are used to inform decision-making and strategy development.
12. Iterative Process
Market research analysis should be an iterative process. As you implement strategies based on your findings, continue to monitor and analyze the market to stay responsive to changes.
13. Benchmark and Measure Progress
Set benchmarks and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your strategies. Regularly assess whether you are meeting your objectives and adjust your approach as needed.
14. Seek External Expertise
Consider consulting with external experts or hiring market research professionals when needed. Their expertise can enhance the quality and reliability of your analysis.
15. Document Your Process
Maintain thorough documentation of your research process , including data sources, methodologies, and assumptions. This documentation is valuable for transparency and future reference.
By following these best practices, businesses can conduct market research analysis that provides actionable insights, informs decision-making, and contributes to long-term success in a competitive market.
Learn more: What is Qualitative Market Research?
Enhance Your Research
Collect feedback and conduct research with IdeaScale’s award-winning software
Elevate Research And Feedback With Your IdeaScale Community!
IdeaScale is an innovation management solution that inspires people to take action on their ideas. Your community’s ideas can change lives, your business and the world. Connect to the ideas that matter and start co-creating the future.
Copyright © 2024 IdeaScale
Privacy Overview
BRAND NEW Two-Day LIVE Summit with 20+ Ecommerce Trailblazers.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
A magazine for young entrepreneurs
The best advice in entrepreneurship
Subscribe for exclusive access, the complete guide to market research: what it is, why you need it, and how to do it.

Written by Mary Kate Miller | June 1, 2021
Comments -->

Get real-time frameworks, tools, and inspiration to start and build your business. Subscribe here
Market research is a cornerstone of all successful, strategic businesses. It can also be daunting for entrepreneurs looking to launch a startup or start a side hustle . What is market research, anyway? And how do you…do it?
We’ll walk you through absolutely everything you need to know about the market research process so that by the end of this guide, you’ll be an expert in market research too. And what’s more important: you’ll have actionable steps you can take to start collecting your own market research.
What Is Market Research?
Market research is the organized process of gathering information about your target customers and market. Market research can help you better understand customer behavior and competitor strengths and weaknesses, as well as provide insight for the best strategies in launching new businesses and products. There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four.
“Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research,” says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing . “Market research can help you piece together your [business’s] strengths and weaknesses, along with your prospective opportunities, so that you can understand where your unique differentiators may lie.” Well-honed market research will help your brand stand out from the competition and help you see what you need to do to lead the market. It can also do so much more.
The Purposes of Market Research
Why do market research? It can help you…
- Pinpoint your target market, create buyer personas, and develop a more holistic understanding of your customer base and market.
- Understand current market conditions to evaluate risks and anticipate how your product or service will perform.
- Validate a concept prior to launch.
- Identify gaps in the market that your competitors have created or overlooked.
- Solve problems that have been left unresolved by the existing product/brand offerings.
- Identify opportunities and solutions for new products or services.
- Develop killer marketing strategies .
What Are the Benefits of Market Research?
Strong market research can help your business in many ways. It can…
- Strengthen your market position.
- Help you identify your strengths and weaknesses.
- Help you identify your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Minimize risk.
- Center your customers’ experience from the get-go.
- Help you create a dynamic strategy based on market conditions and customer needs/demands.
What Are the Basic Methods of Market Research?
The basic methods of market research include surveys, personal interviews, customer observation, and the review of secondary research. In addition to these basic methods, a forward-thinking market research approach incorporates data from the digital landscape like social media analysis, SEO research, gathering feedback via forums, and more. Throughout this guide, we will cover each of the methods commonly used in market research to give you a comprehensive overview.
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
Primary and secondary are the two main types of market research you can do. The latter relies on research conducted by others. Primary research, on the other hand, refers to the fact-finding efforts you conduct on your own.
This approach is limited, however. It’s likely that the research objectives of these secondary data points differ from your own, and it can be difficult to confirm the veracity of their findings.
Primary Market Research
Primary research is more labor intensive, but it generally yields data that is exponentially more actionable. It can be conducted through interviews, surveys, online research, and your own data collection. Every new business should engage in primary market research prior to launch. It will help you validate that your idea has traction, and it will give you the information you need to help minimize financial risk.
You can hire an agency to conduct this research on your behalf. This brings the benefit of expertise, as you’ll likely work with a market research analyst. The downside is that hiring an agency can be expensive—too expensive for many burgeoning entrepreneurs. That brings us to the second approach. You can also do the market research yourself, which substantially reduces the financial burden of starting a new business .
Secondary Market Research
Secondary research includes resources like government databases and industry-specific data and publications. It can be beneficial to start your market research with secondary sources because it’s widely available and often free-to-access. This information will help you gain a broad overview of the market conditions for your new business.
Identify Your Goals and Your Audience
Before you begin conducting interviews or sending out surveys, you need to set your market research goals. At the end of your market research process, you want to have a clear idea of who your target market is—including demographic information like age, gender, and where they live—but you also want to start with a rough idea of who your audience might be and what you’re trying to achieve with market research.
You can pinpoint your objectives by asking yourself a series of guiding questions:
- What are you hoping to discover through your research?
- Who are you hoping to serve better because of your findings?
- What do you think your market is?
- Who are your competitors?
- Are you testing the reception of a new product category or do you want to see if your product or service solves the problem left by a current gap in the market?
- Are you just…testing the waters to get a sense of how people would react to a new brand?
Once you’ve narrowed down the “what” of your market research goals, you’re ready to move onto how you can best achieve them. Think of it like algebra. Many math problems start with “solve for x.” Once you know what you’re looking for, you can get to work trying to find it. It’s a heck of a lot easier to solve a problem when you know you’re looking for “x” than if you were to say “I’m gonna throw some numbers out there and see if I find a variable.”

How to Do Market Research
This guide outlines every component of a comprehensive market research effort. Take into consideration the goals you have established for your market research, as they will influence which of these elements you’ll want to include in your market research strategy.
Secondary Data
Secondary data allows you to utilize pre-existing data to garner a sense of market conditions and opportunities. You can rely on published market studies, white papers, and public competitive information to start your market research journey.
Secondary data, while useful, is limited and cannot substitute your own primary data. It’s best used for quantitative data that can provide background to your more specific inquiries.
Find Your Customers Online
Once you’ve identified your target market, you can use online gathering spaces and forums to gain insights and give yourself a competitive advantage. Rebecca McCusker of The Creative Content Shop recommends internet recon as a vital tool for gaining a sense of customer needs and sentiment. “Read their posts and comments on forums, YouTube video comments, Facebook group [comments], and even Amazon/Goodreads book comments to get in their heads and see what people are saying.”
If you’re interested in engaging with your target demographic online, there are some general rules you should follow. First, secure the consent of any group moderators to ensure that you are acting within the group guidelines. Failure to do so could result in your eviction from the group.
Not all comments have the same research value. “Focus on the comments and posts with the most comments and highest engagement,” says McCusker. These high-engagement posts can give you a sense of what is already connecting and gaining traction within the group.
Social media can also be a great avenue for finding interview subjects. “LinkedIn is very useful if your [target customer] has a very specific job or works in a very specific industry or sector. It’s amazing the amount of people that will be willing to help,” explains Miguel González, a marketing executive at Dealers League . “My advice here is BE BRAVE, go to LinkedIn, or even to people you know and ask them, do quick interviews and ask real people that belong to that market and segment and get your buyer persona information first hand.”
Market research interviews can provide direct feedback on your brand, product, or service and give you a better understanding of consumer pain points and interests.
When organizing your market research interviews, you want to pay special attention to the sample group you’re selecting, as it will directly impact the information you receive. According to Tanya Zhang, the co-founder of Nimble Made , you want to first determine whether you want to choose a representative sample—for example, interviewing people who match each of the buyer persona/customer profiles you’ve developed—or a random sample.
“A sampling of your usual persona styles, for example, can validate details that you’ve already established about your product, while a random sampling may [help you] discover a new way people may use your product,” Zhang says.
Market Surveys
Market surveys solicit customer inclinations regarding your potential product or service through a series of open-ended questions. This direct outreach to your target audience can provide information on your customers’ preferences, attitudes, buying potential, and more.
Every expert we asked voiced unanimous support for market surveys as a powerful tool for market research. With the advent of various survey tools with accessible pricing—or free use—it’s never been easier to assemble, disseminate, and gather market surveys. While it should also be noted that surveys shouldn’t replace customer interviews , they can be used to supplement customer interviews to give you feedback from a broader audience.
Who to Include in Market Surveys
- Current customers
- Past customers
- Your existing audience (such as social media/newsletter audiences)
Example Questions to Include in Market Surveys
While the exact questions will vary for each business, here are some common, helpful questions that you may want to consider for your market survey. Demographic Questions: the questions that help you understand, demographically, who your target customers are:
- “What is your age?”
- “Where do you live?”
- “What is your gender identity?”
- “What is your household income?”
- “What is your household size?”
- “What do you do for a living?”
- “What is your highest level of education?”
Product-Based Questions: Whether you’re seeking feedback for an existing brand or an entirely new one, these questions will help you get a sense of how people feel about your business, product, or service:
- “How well does/would our product/service meet your needs?”
- “How does our product/service compare to similar products/services that you use?”
- “How long have you been a customer?” or “What is the likelihood that you would be a customer of our brand?
Personal/Informative Questions: the deeper questions that help you understand how your audience thinks and what they care about.
- “What are your biggest challenges?”
- “What’s most important to you?”
- “What do you do for fun (hobbies, interests, activities)?”
- “Where do you seek new information when researching a new product?”
- “How do you like to make purchases?”
- “What is your preferred method for interacting with a brand?”
Survey Tools
Online survey tools make it easy to distribute surveys and collect responses. The best part is that there are many free tools available. If you’re making your own online survey, you may want to consider SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Google Forms, or Zoho Survey.
Competitive Analysis
A competitive analysis is a breakdown of how your business stacks up against the competition. There are many different ways to conduct this analysis. One of the most popular methods is a SWOT analysis, which stands for “strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.” This type of analysis is helpful because it gives you a more robust understanding of why a customer might choose a competitor over your business. Seeing how you stack up against the competition can give you the direction you need to carve out your place as a market leader.
Social Media Analysis
Social media has fundamentally changed the market research landscape, making it easier than ever to engage with a wide swath of consumers. Follow your current or potential competitors on social media to see what they’re posting and how their audience is engaging with it. Social media can also give you a lower cost opportunity for testing different messaging and brand positioning.
SEO Analysis and Opportunities
SEO analysis can help you identify the digital competition for getting the word out about your brand, product, or service. You won’t want to overlook this valuable information. Search listening tools offer a novel approach to understanding the market and generating the content strategy that will drive business. Tools like Google Trends and Awario can streamline this process.
Ready to Kick Your Business Into High Gear?
Now that you’ve completed the guide to market research you know you’re ready to put on your researcher hat to give your business the best start. Still not sure how actually… launch the thing? Our free mini-course can run you through the essentials for starting your side hustle .

About Mary Kate Miller
Mary Kate Miller writes about small business, real estate, and finance. In addition to writing for Foundr, her work has been published by The Washington Post, Teen Vogue, Bustle, and more. She lives in Chicago.
Related Posts

12 Instagram Growth Hacks For More Engaged Followers (Without Running Ads)

Create Viral Infographics That Boost Your Organic Traffic
How to Create a Video Sales Letter (Tips and Tricks from a 7-Figure Copywriter)

How to Write a Sales Email That Converts in 2024

What Is a Media Kit: How to Make One in 2024 (With Examples)

Namestorming: How to Choose a Brand Name in 20 Minutes or Less

10 Ways to Increase Brand Awareness without Increasing Your Budget

What Is a Content Creator? A Deep Dive Into This Evolving Industry

Content Creator vs Influencer: What’s the Difference?

How Much Do YouTube Ads Cost? A Beginner’s Pricing Breakdown

How to Get Podcast Sponsors Before Airing an Episode

How Founders Can Overcome Their Sales Fears with AJ Cassata

How to Grow Your YouTube Channel & Gain Subscribers Quickly

How to Write Good Instagram Captions That Hook Your Audience

Discovering the Best CRM for Consultants
FREE TRAINING FROM LEGIT FOUNDERS
Actionable Strategies for Starting & Growing Any Business.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Market Research?
- How It Works
- Primary vs. Secondary
- How to Conduct Research
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials
How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dd453b82d4ef4ce8aac2e858ed00a114__alexandra_twin-5bfc262b46e0fb0026006b77.jpeg)
Joules Garcia / Investopedia
Market research examines consumer behavior and trends in the economy to help a business develop and fine-tune its business idea and strategy. It helps a business understand its target market by gathering and analyzing data.
Market research is the process of evaluating the viability of a new service or product through research conducted directly with potential customers. It allows a company to define its target market and get opinions and other feedback from consumers about their interest in a product or service.
Research may be conducted in-house or by a third party that specializes in market research. It can be done through surveys and focus groups, among other ways. Test subjects are usually compensated with product samples or a small stipend for their time.
Key Takeaways
- Companies conduct market research before introducing new products to determine their appeal to potential customers.
- Tools include focus groups, telephone interviews, and questionnaires.
- The results of market research inform the final design of the product and determine how it will be positioned in the marketplace.
- Market research usually combines primary information, gathered directly from consumers, and secondary information, which is data available from external sources.
Market Research
How market research works.
Market research is used to determine the viability of a new product or service. The results may be used to revise the product design and fine-tune the strategy for introducing it to the public. This can include information gathered for the purpose of determining market segmentation . It also informs product differentiation , which is used to tailor advertising.
A business engages in various tasks to complete the market research process. It gathers information based on the market sector being targeted by the product. This information is then analyzed and relevant data points are interpreted to draw conclusions about how the product may be optimally designed and marketed to the market segment for which it is intended.
It is a critical component in the research and development (R&D) phase of a new product or service introduction. Market research can be conducted in many different ways, including surveys, product testing, interviews, and focus groups.
Market research is a critical tool that companies use to understand what consumers want, develop products that those consumers will use, and maintain a competitive advantage over other companies in their industry.
Primary Market Research vs. Secondary Market Research
Market research usually consists of a combination of:
- Primary research, gathered by the company or by an outside company that it hires
- Secondary research, which draws on external sources of data
Primary Market Research
Primary research generally falls into two categories: exploratory and specific research.
- Exploratory research is less structured and functions via open-ended questions. The questions may be posed in a focus group setting, telephone interviews, or questionnaires. It results in questions or issues that the company needs to address about a product that it has under development.
- Specific research delves more deeply into the problems or issues identified in exploratory research.
Secondary Market Research
All market research is informed by the findings of other researchers about the needs and wants of consumers. Today, much of this research can be found online.
Secondary research can include population information from government census data , trade association research reports , polling results, and research from other businesses operating in the same market sector.
History of Market Research
Formal market research began in Germany during the 1920s. In the United States, it soon took off with the advent of the Golden Age of Radio.
Companies that created advertisements for this new entertainment medium began to look at the demographics of the audiences who listened to each of the radio plays, music programs, and comedy skits that were presented.
They had once tried to reach the widest possible audience by placing their messages on billboards or in the most popular magazines. With radio programming, they had the chance to target rural or urban consumers, teenagers or families, and judge the results by the sales numbers that followed.
Types of Market Research
Face-to-face interviews.
From their earliest days, market research companies would interview people on the street about the newspapers and magazines that they read regularly and ask whether they recalled any of the ads or brands that were published in them. Data collected from these interviews were compared to the circulation of the publication to determine the effectiveness of those ads.
Market research and surveys were adapted from these early techniques.
To get a strong understanding of your market, it’s essential to understand demand, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing.
Focus Groups
A focus group is a small number of representative consumers chosen to try a product or watch an advertisement.
Afterward, the group is asked for feedback on their perceptions of the product, the company’s brand, or competing products. The company then takes that information and makes decisions about what to do with the product or service, whether that's releasing it, making changes, or abandoning it altogether.
Phone Research
The man-on-the-street interview technique soon gave way to the telephone interview. A telephone interviewer could collect information in a more efficient and cost-effective fashion.
Telephone research was a preferred tactic of market researchers for many years. It has become much more difficult in recent years as landline phone service dwindles and is replaced by less accessible mobile phones.
Survey Research
As an alternative to focus groups, surveys represent a cost-effective way to determine consumer attitudes without having to interview anyone in person. Consumers are sent surveys in the mail, usually with a coupon or voucher to incentivize participation. These surveys help determine how consumers feel about the product, brand, and price point.
Online Market Research
With people spending more time online, market research activities have shifted online as well. Data collection still uses a survey-style form. But instead of companies actively seeking participants by finding them on the street or cold calling them on the phone, people can choose to sign up, take surveys, and offer opinions when they have time.
This makes the process far less intrusive and less rushed, since people can participate on their own time and of their own volition.
How to Conduct Market Research
The first step to effective market research is to determine the goals of the study. Each study should seek to answer a clear, well-defined problem. For example, a company might seek to identify consumer preferences, brand recognition, or the comparative effectiveness of different types of ad campaigns.
After that, the next step is to determine who will be included in the research. Market research is an expensive process, and a company cannot waste resources collecting unnecessary data. The firm should decide in advance which types of consumers will be included in the research, and how the data will be collected. They should also account for the probability of statistical errors or sampling bias .
The next step is to collect the data and analyze the results. If the two previous steps have been completed accurately, this should be straightforward. The researchers will collect the results of their study, keeping track of the ages, gender, and other relevant data of each respondent. This is then analyzed in a marketing report that explains the results of their research.
The last step is for company executives to use their market research to make business decisions. Depending on the results of their research, they may choose to target a different group of consumers, or they may change their price point or some product features.
The results of these changes may eventually be measured in further market research, and the process will begin all over again.
Benefits of Market Research
Market research is essential for developing brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. Since it is unlikely for a product to appeal equally to every consumer, a strong market research program can help identify the key demographics and market segments that are most likely to use a given product.
Market research is also important for developing a company’s advertising efforts. For example, if a company’s market research determines that its consumers are more likely to use Facebook than X (formerly Twitter), it can then target its advertisements to one platform instead of another. Or, if they determine that their target market is value-sensitive rather than price-sensitive, they can work on improving the product rather than reducing their prices.
Market research only works when subjects are honest and open to participating.
Example of Market Research
Many companies use market research to test new products or get information from consumers about what kinds of products or services they need and don’t currently have.
For example, a company that’s considering starting a business might conduct market research to test the viability of its product or service. If the market research confirms consumer interest, the business can proceed confidently with its business plan . If not, the company can use the results of the market research to make adjustments to the product to bring it in line with customer desires.
What Are the Main Types of Market Research?
The main types of market research are primary research and secondary research. Primary research includes focus groups, polls, and surveys. Secondary research includes academic articles, infographics, and white papers.
Qualitative research gives insights into how customers feel and think. Quantitative research uses data and statistics such as website views, social media engagement, and subscriber numbers.
What Is Online Market Research?
Online market research uses the same strategies and techniques as traditional primary and secondary market research, but it is conducted on the Internet. Potential customers may be asked to participate in a survey or give feedback on a product. The responses may help the researchers create a profile of the likely customer for a new product.
What Are Paid Market Research Surveys?
Paid market research involves rewarding individuals who agree to participate in a study. They may be offered a small payment for their time or a discount coupon in return for filling out a questionnaire or participating in a focus group.
What Is a Market Study?
A market study is an analysis of consumer demand for a product or service. It looks at all of the factors that influence demand for a product or service. These include the product’s price, location, competition, and substitutes as well as general economic factors that could influence the new product’s adoption, for better or worse.
Market research is a key component of a company’s research and development (R&D) stage. It helps companies understand in advance the viability of a new product that they have in development and to see how it might perform in the real world.
Britannica Money. “ Market Research .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1327127856-ce97892716b346b99dcf1d14af294a97.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Market research
- Sales and marketing
- Business management

How to Measure Inclusion in the Workplace
- Lauren Romansky
- Katie Brown
- May 27, 2021

What Customers Want from the Collaborative Economy
- Alexandra Samuel
- October 08, 2015

3 Questions Sales Teams Should Ask After Losing (or Winning) a Deal
- Lisa Earle McLeod
- July 24, 2023

Maybe Failure Isn't the Best Teacher
- Lauren Eskreis-Winkler
- Eben Harrell
- From the May–June 2020 Issue
Women Too Respond to Sexual Cues by Taking More Risks
- Anouk Festjens
- Alison Beard
- From the April 2014 Issue

Research: When Consumers Feel Less Powerful, They Seek More Variety
- Dinesh Gauri
- Raj Raghunathan
- Wangshuai Wang
- October 19, 2022
Cost-Conscious Marketing Research
- Alan R. Andreasen
- From the July 1983 Issue
Riding the Marketing Information Wave
- From the September–October 1993 Issue

The Paradox of Marketing to Caregivers
- Ximena Garcia-Rada
- Mary Steffel
- Elanor F. Williams
- Michael I. Norton
- September 28, 2021
Competing on the Eight Dimensions of Quality
- David A. Garvin
- From the November 1987 Issue
What? Me, Worry?
- Gardiner Morse
- From the November 2005 Issue

Expand Your Pricing Paradigm
- Rafi Mohammed
- From the January–February 2023 Issue
Why Digital Media Require a Strategic Rethink
- Michael D. Smith
- Rahul Telang
- From the October 2012 Issue
What Men Think They Know About Executive Women
- Dawn S. Carlson
- K. Michele Kacmar
- Dwayne Whitten
- From the September 2006 Issue

Does Original Content Help Streaming Services Attract More Subscribers?
- Jeff Prince
- Shane Greenstein
- April 24, 2018

Rethinking Retraining
- Willy C Shih
- Howard Rudnick
- Colleen Tapen
- November 09, 2018

How Companies Can Meet the Needs of a Changing Workforce
- Avivah Wittenberg-Cox
- December 18, 2020
It's Not Necessarily Best to Be First
- Elena Reutskaja
- Barbara Fasolo
- From the January–February 2013 Issue

Listen to Your Employees, Not Just Your Customers
- Beth Benjamin
- August 15, 2016

Marketing Meets Mission
- Myriam Sidibe

United Breaks Guitars
- John Deighton
- Leora Kornfeld
- January 06, 2010
Vibrance Kegel Device: Capturing Mindshare
- June 28, 2016
Corning: 156 Years of Innovation
- H. Kent Bowen
- Courtney Purrington
- March 05, 2008
Flipkart: Grappling with Product Returns
- Sanjeev Prashar
- Mukesh Kumar
- Amit Kumar Mukul
- July 13, 2018
Sony and the JK Wedding Dance
- December 22, 2009
Apple Watch (B): Would You Bet On It?
- Gary Ottley
- Ken Matsuno
- October 01, 2017
Note on the Impact of Millennials on the Food System
- Jose B. Alvarez
- James Weber
- Natalie Kindred
- November 13, 2016
L'Oreal of Paris: Bringing "Class to Mass" with Plenitude
- Robert J. Dolan
- August 08, 2002
Jess Westerly at Kauflauf GmbH
- John J. Gabarro
- Colleen Kaftan
- August 24, 2012
Electronic Arts Introduces The Sims Online
- Youngme Moon
- August 23, 2002

Marketplace Tutorial: Price Elasticity in Practice
- Marketplace Simulations
- Ernest R. Cadotte
- December 13, 2022
Yla Eason (A)
- Kathleen Meyer
- Suzanne Allen
- Laura Wattenberg
- December 15, 1996
Compaq Computer: Focus Groups 1 and 2, Video Transcript
- Compaq Computer
- June 04, 1999
Shanty Real Estate: Confidential Information for iBuyer 2
- Michael Luca
- Jesse M. Shapiro
- October 11, 2022
Howard Schultz and Starbucks Coffee Company
- Nancy F. Koehn
- September 30, 2005
Keroche (A): Fighting for Share in the Kenyan Alcoholic Drinks Market
- Ramon Casadesus-Masanell
- Pippa Tubman Armerding
- September 23, 2019

Customer Data and Privacy: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business Review
- Harvard Business Review
- Timothy Morey
- Andrew Burt
- Christine Moorman
- Thomas C. Redman
- September 22, 2020
Aqualisa Quartz: Simply a Better Shower
- Kerry Herman
- January 16, 2002

Understanding the Brand Equity of Nestlé Crunch Bar: A Market Research Case
- Gerald Zaltman
- January 12, 2019

Marketing Reading: Customer Centricity
- Rohit Deshpande
- June 30, 2014

The Flaxil Label (A), (B), and (C), Teaching Note
- Gregory Barron
- August 24, 2008
Popular Topics
Partner center.

How to do Market Analysis in 6 Easy Steps

Knowing how to do market analysis is pivotal for many roles, benefiting any organization, regardless of its size, scope, or sector.
Regular market analysis levels up your individual ability to spot potential opportunities, stay on top of current trends, and gives you insights into the competitive landscape .
This article will cover why you need to analyze a market frequently and shows you how to do a basic market analysis in 6 straightforward steps.
What is a market analysis?
Market analysis is the process of gathering data about a target market . It examines the competitive landscape, consumers, and conditions that impact the marketplace.
The benefits of market analysis
Here are eight reasons why a regular market analysis is beneficial:
- Understand the competitive landscape
- Spot trends in your market
- Uncover opportunities for growth or diversification
- Reduce either risk or cost for launching new products or services
- Develop a deeper understanding of a target audience
- Enhance marketing efforts or discover ways to change
- Analyze business performance within a market
- Identify new segments of a market to target
Why you should conduct a market analysis
Aside from the benefits we’ve already listed, reviewing and redoing your market analysis regularly is important . Here’s why.
- Markets shift
- Consumer behaviors change
- New players enter existing markets
- Disruptive technologies and enhancements to rival offerings can shift the landscape
- External events impact market conditions that drive changes
If you already know how to do market analysis, ask yourself how frequently you undertake the task: is it annually or quarterly? And consider the time it takes and the tools you used to obtain your information.
With this in mind, we’ll walk you through the most effective market analysis methods. Showing you the steps to take, with market analysis examples, to bring these steps to life.
How to conduct a market analysis
These six steps break down how to analyze a market into easy-to-follow, digestible stages.
Before you start: Use a framework to record your findings. There are plenty of visualization tools, but a basic excel sheet will be fine if you want to keep it simple. Why? Because when you return to review this analysis and repeat this exercise, you’ll want to have everything recorded in a single place. It will save you time and make any future comparisons easier.
Step 1 – Market segmentation
What: Whether you want to enter a new market , launch a new product, or simply assess opportunities for an existing business, this first step in the market analysis process is crucial yet often overlooked.
Why: Market segmentation helps you identify the core segments of a market to target. By identifying the portion of a market your products will be suitable for, you can accurately define the market size and better understand your potential customers’ specific needs and preferences.
How: There are multiple ways you can segment a market, and the right approach will depend on your product, its customers, and its target profiles.
Here, we can see how a segment is built using Similarweb’s website segment feature. I specifically want to view the credit card sector in the US, a market made up of pure players (think Amex or Visa ) and individual players with credit card lines as one of their segments (think Wells Fargo or USAA ). By splitting up a market like this, I can analyze the areas of business I care about more for my market analysis.
So, instead of viewing data that encompasses the other lines of business the likes of Wells Fargo and the USAA handle, such as loans, I get to hone in on their credit card segments only.
This is just one example of market segmentation. You can also segment a market based on consumer needs, ideal consumer profiles, regions, and other demographic data.
Step 2 – Market sizing
What: Market sizing determines your target market’s potential volume or sales revenue. It’s an essential component of market analysis that uses either secondary or primary research to explore the actual size of the market you are in or wish to enter.
Total Addressable Market (TAM) – This gives you the complete value of the overall market and the first step in the market sizing process . Let’s say we want to analyze the US credit card market, the TAM would account for the whole of this market. Service Addressable Market (SAM) looks at potential audience volumes for a product or service in a target region. Sticking with the credit card sector example, this could be the total value of the credit card business that specifically targets the ‘poor credit rating’ segment of this market. Share of Market (SOM) – Also known as ‘service addressable market,’ it represents the proportion of your SAM that you are likely to achieve. SOM is always lower than SAM, taking a range of estimates based on the previous year’s performance or current market share + project growth to arrive at this figure.
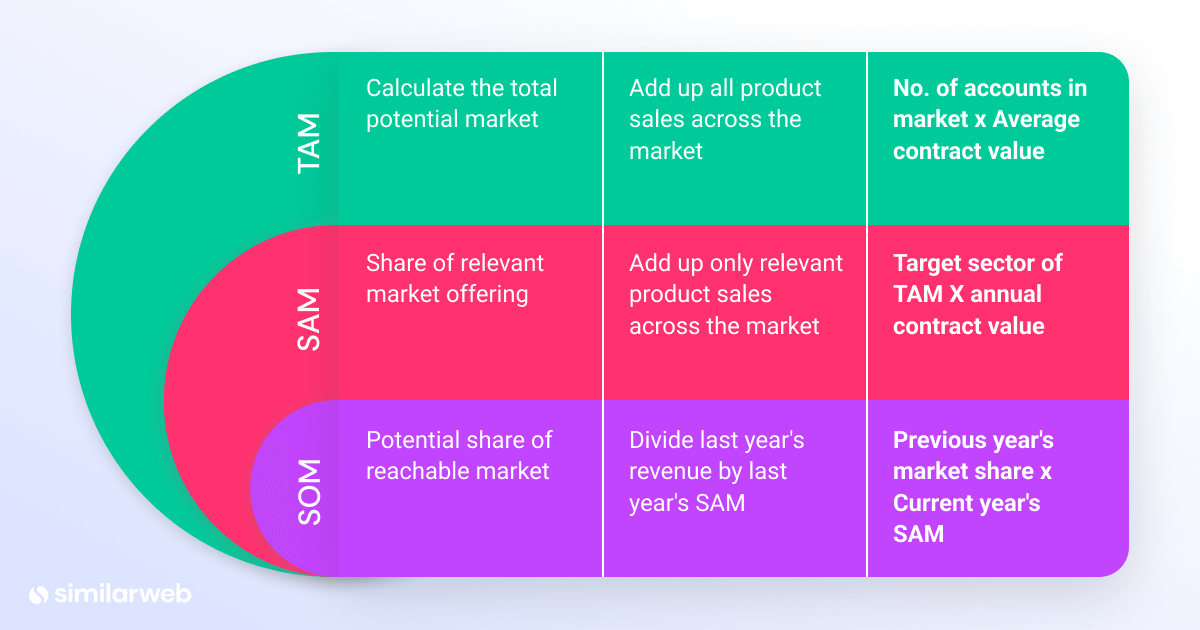
Why: Market sizing helps businesses understand the size of their opportunity. By understanding the size and scope of a market, companies can better assess the potential profitability of the market. Tracking market share over time can also show who wins or loses at any given time.
Power-up Your Market Analysis with Similarweb Today
Market analysis example: market sizing.
Using a metric known as traffic share , we can estimate the potential market size by showing the total reachable audience you have or could have with a product or service.

Using Similarweb Industry Analysis , I can see a real-time snapshot of my market’s performance. With it, I can see the total number of people in a market (unique visitors) and establish how much of that share I have or will target this year.
When sizing a market, it’s easy to fall into the habit of analyzing the market quarterly or annually. But often, the best insights are dynamic in nature. They appear to show shifts, sometimes unexpectedly or can indicate growth and changing behaviors as the year progresses. This is why we place a high emphasis on continuing a market analysis throughout the year.
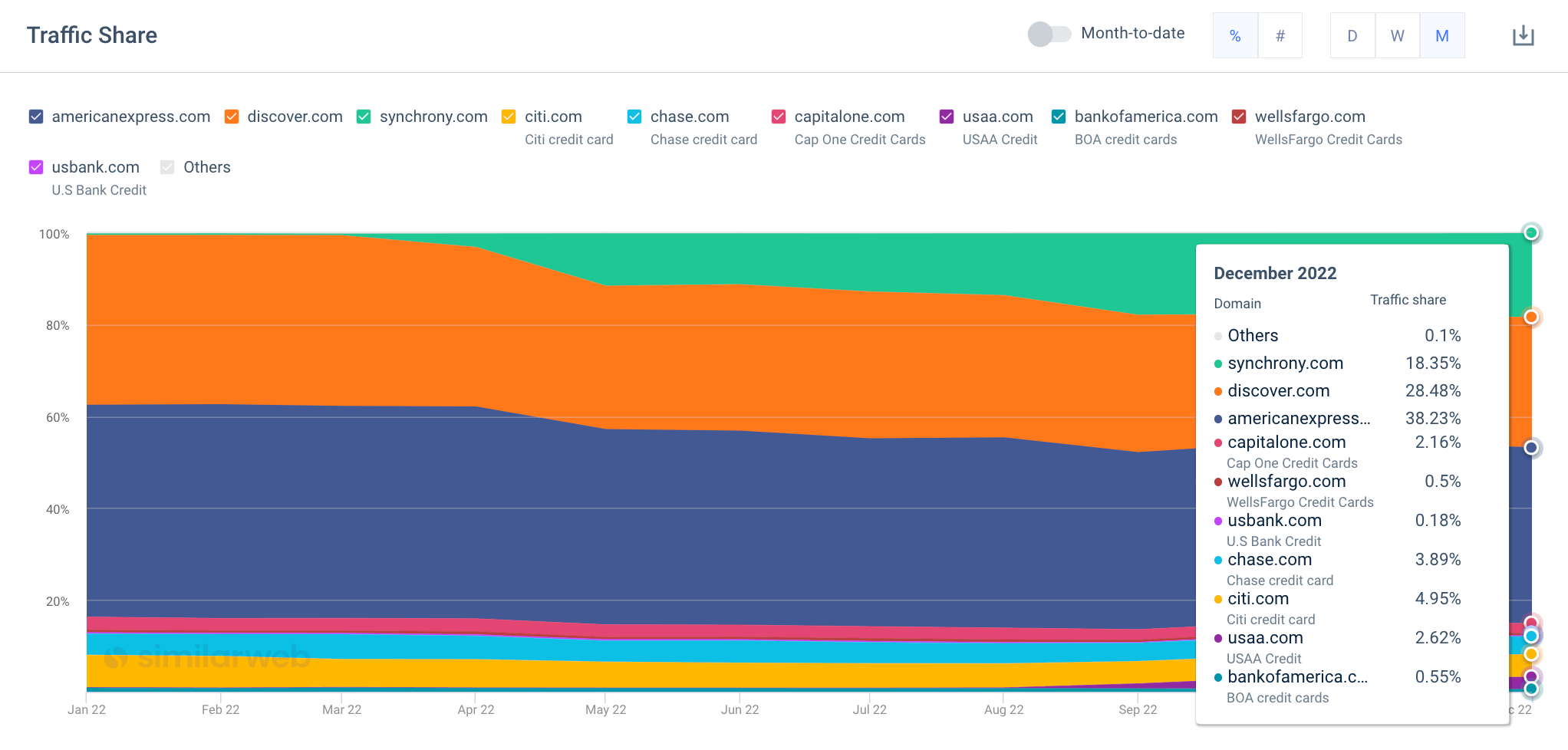
Here, we’re looking at traffic share changes over time using Similarweb’s market trends. You can see the impact of Snychrony’s growth (in green) as they gain traction, along with USAA (purple). At the start of the year, these two players had no impact on the market. By the end of 2022, they’re showing gains and would be two key competitors to track when you reach step 4 of the market analysis process.
Those analyzing a market annually would miss out on key insights that show the rise of these two emerging players. At the end of the year, they’ve already grabbed a chunk of the market and, if they continue on the same trajectory, will continue to do so in 2023.
With the right tools, you get a dynamic view of the market data you need, allowing you to change tactics when markets shift.
Step 3 – Market trends
What: Reviewing current trends is key to any good market analysis. As we all know, trends can rise and fall at a moment’s notice. This is why this activity, in particular, is one you should routinely perform.
Why: Keeping a finger on the pulse can help you adapt and flex, at the right time, in the right way. Market trends give you insights into the current market situation and potential opportunities and challenges. Doing so can help you identify areas for growth, spot potential risks, and plan effective strategies. Market trends can also provide valuable information about customer preferences, competition, and economic and technological developments. By monitoring these trends, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions that will benefit their bottom line.
You may have heard about ChatGPT in the press ; this is an example of a highly-disruptive technology that has the potential to completely shift an entire market; many, in fact. It managed to gain over 1 million users within its first week on the market. And it’s a great example of why regular market trends analysis should occur.

How: There are lots of ways new market trends can surface. Consumer behavior, economic trends, technological advancements, and the competitive landscape can impact how markets behave. Legal and regulatory changes can also influence trends and changes too.
Staying up to date with industry news and legislation changes is useful. But it takes time, and it’s not always the most effective way to know when consumer sentiment changes.
Market research surveys are one way to understand customer attitudes and needs and how they shift over time. However, it’s not the most effective way to inform your market analysis. Particularly when you want real-time market intel.
Market analysis example: trend detection
Similarweb analyzes billions of data signals daily to deliver game-changing insights about any market, region, or individual company. So, as we look at how to do market analysis, I wanted to share a practical example of how clients use Similarweb to spot trends in a market.
Wonderbly , a global business, provides personalized books, serving over 6 million customers. To grow its business, it conducts regular market analysis. As part of this process, they analyzed seasonal trending keywords within Similarweb. Let’s look at what it found out and how it impacted the business.

Wonderbly was able to spot an emerging category (anniversaries and weddings) that was not currently catered for within its own product set. In addition to being able to capitalize on seasonal trends in its market, it achieved a 69% revenue in books purchased by a more mature demographic and a completely new audience for its business.
Read more: Wonderbly’s market analysis success story .
Step 4 – Competitive analysis
What: A competitive analysis involves collecting and reviewing data about key industry players, rivals, or emerging stars in your market. It unpacks and tracks their activities and successes, letting you see what’s working, how they go to market and the various marketing strategies they use to attract and retain customers.
Why: Regardless of your size or scope, understanding the competitive landscape is key. Your target audience knows your competitors and will likely size up the pros and cons of buying from thesm before considering whether to do business with you. A robust competitive analysis can help you refine your own offerings, make informed pricing decisions, show where you can beat out your rivals, and identify areas for improvement or diversification.
How: A tried and trusted tool for this process is the well-known SWOT analysis . It lets you map and view what and how each competitor takes its products to market. Considering things like pricing, positioning, marketing, services, and more. A competitive matrix is another tool used to visualize data about rivals in a market.
To do it, download our free competitive analysis framework . Then, pick five competitors in your market to track. Complete each section, and analyze the results to discover your biggest opportunities.
Step 5 – Develop strategies
What: Use the results of your market analysis to make data-driven decisions .
Why: When you read a post about how to do market analysis, the chances are you’ve got a goal in mind. Perhaps you want to explore a new market before deciding if it’s ripe for entry. You may want to introduce a new product or service or acquire an existing company. Whatever your goal is, ensure you put the insights and data you’ve obtained to good use.
How: Create a list of potential opportunities, then build strategies around each. Here, you might evaluate potential ideas based on project costs or timeframes. Once you’ve clearly mapped out each opportunity, and understand the potential impact it will have, along with associated costs and timeframes, you can think strategically about which ideas to move forward with from both a short and long-term perspective.
Pro Tip: Use a framework to record, capture, and review the data you’ve collected about market segmentation, size, trends, and key competitors. You can draw inspiration from our downloadable competitive analysis frameworks. However, what’s key is that you systematically record your findings and review them regularly.
Step 6 – Monitor the market
What: Keep track of your market and its key players; monitor changes over time.
Why: We know markets shift, whether they’re impacted by consumer behaviors, external factors, or something else. So, it’s important to monitor changes over time.
How: We may be a little biased, but Similarweb gives you a real-time bird-eye view of your market. Letting you dive into the details and unpick changes and tactics whenever you need. With it, you can track key growth metrics, marketing channels, emerging players, trending topics , and much more.
Using the Industry Analysis tab in Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence , I can identify the market leaders and rising stars quickly. Here, I immediately see a company to track, Synchrony . As an emerging player showing exponential growth (2700%), I’ll take my market analysis a step further by investigating their successes later.
Similarweb shows me key insights, such as website traffic , the marketing channels it’s getting traffic from, audience demographics , geography , organic search insights, and more. As part of any good market analysis, the ability to spot rising players and unpack their successes can be crucial, particularly when they’re showing such growth.
Analyzing a market: Conclusions
Learning how to do market analysis is the first step. Aside from analyzing the results and making key strategic decisions, the ability to track changes over time is key. Similarweb makes it easy to segment, size, and analyze a market fast. With it, you can spot opportunities, benchmark your performance, and monitor shifts and changes as they happen, not a month or quarter later.
What are the 4 types of market analysis?
The four types of market analysis are market segmentation, market sizing, market trends, and competitive analysis.
What are the five components of market analysis?
The five components of market analysis are: customer segmentation, customer needs and trends, competitors, market size and trend, and pricing.
What makes a good market analysis?
A good market analysis should include accurate, up-to-date data, clear objectives, and a thorough market and customer needs analysis.
Is market analysis the same as a SWOT analysis?
No, market analysis and SWOT analysis are not the same. While a SWOT analysis evaluates an organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, a market analysis focuses on the external environment, such as customer needs, market trends, and competitors.
Related Posts

The Future of UK Finance: Top Trends to Watch in 2024

From AI to Buy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Retail
How to Conduct a Social Media Competitor Analysis: 5 Quick Steps

Industry Research: The Data-Backed Approach
How to Do a Competitive Analysis: A Complete Guide
How to Check Website Traffic: Analyzing the Digital Data
Wondering what similarweb can do for you.
Here are two ways you can get started with Similarweb today!

- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

- 01 Apr 2024
- In Practice
Navigating the Mood of Customers Weary of Price Hikes
Price increases might be tempering after historic surges, but companies continue to wrestle with pinched consumers. Alexander MacKay, Chiara Farronato, and Emily Williams make sense of the economic whiplash of inflation and offer insights for business leaders trying to find equilibrium.

- 27 Feb 2024
- Research & Ideas
Why Companies Should Share Their DEI Data (Even When It’s Unflattering)
Companies that make their workforce demographics public earn consumer goodwill, even if the numbers show limited progress on diversity, says research by Ryan Buell, Maya Balakrishnan, and Jimin Nam. How can brands make transparency a differentiator?

- 17 Jan 2024
Psychological Pricing Tactics to Fight the Inflation Blues
Inflation has slowed from the epic rates of 2021 and 2022, but many consumers still feel pinched. What will it take to encourage them to spend? Thoughtful pricing strategies that empower customers as they make purchasing decisions, says research by Elie Ofek.

- 05 Dec 2023
- Cold Call Podcast
Tommy Hilfiger’s Adaptive Clothing Line: Making Fashion Inclusive
In 2017, Tommy Hilfiger launched its adaptive fashion line to provide fashion apparel that aims to make dressing easier. By 2020, it was still a relatively unknown line in the U.S. and the Tommy Hilfiger team was continuing to learn more about how to serve these new customers. Should the team make adaptive clothing available beyond the U.S., or is a global expansion premature? Assistant Professor Elizabeth Keenan discusses the opportunities and challenges that accompanied the introduction of a new product line that effectively serves an entirely new customer while simultaneously starting a movement to provide fashion for all in the case, “Tommy Hilfiger Adaptive: Fashion for All.”

- 24 Oct 2023
When Tech Platforms Identify Black-Owned Businesses, White Customers Buy
Demand for Black-owned restaurants rises when they're easier to find on Yelp. Research by Michael Luca shows how companies can mobilize their own technology to advance racial equity.

- 17 Oct 2023
With Subscription Fatigue Setting In, Companies Need to Think Hard About Fees
Subscriptions are available for everything from dental floss to dog toys, but are consumers tiring of monthly fees? Elie Ofek says that subscription revenue can provide stability, but companies need to tread carefully or risk alienating customers.

- 31 May 2023
With Predictive Analytics, Companies Can Tap the Ultimate Opportunity: Customers’ Routines
Armed with more data than ever, many companies know what key customers need. But how many know exactly when they need it? An analysis of 2,000 ridesharing commuters by Eva Ascarza and colleagues shows what's possible for companies that can anticipate a customer's routine.

- 30 May 2023
Can AI Predict Whether Shoppers Would Pick Crest Over Colgate?
Is it the end of customer surveys? Definitely not, but research by Ayelet Israeli sheds light on the potential for generative AI to improve market research. But first, businesses will need to learn to harness the technology.

- 25 Apr 2023
How SHEIN and Temu Conquered Fast Fashion—and Forged a New Business Model
The platforms SHEIN and Temu match consumer demand and factory output, bringing Chinese production to the rest of the world. The companies have remade fast fashion, but their pioneering approach has the potential to go far beyond retail, says John Deighton.

- 21 Apr 2023
The $15 Billion Question: Have Loot Boxes Turned Video Gaming into Gambling?
Critics say loot boxes—major revenue streams for video game companies—entice young players to overspend. Can regulators protect consumers without dampening the thrill of the game? Research by Tomomichi Amano and colleague.

- 06 Dec 2022
Latest Isn’t Always Greatest: Why Product Updates Capture Consumers
Consumers can't pass up a product update—even if there's no improvement. Research by Leslie John, Michael Norton, and Ximena Garcia-Rada illustrates the powerful allure of change. Are we really that naïve?

- 04 Oct 2022
- What Do You Think?
Have Managers Underestimated the Need for Face-to-Face Contact?
COVID-19 made remote work and instant delivery mainstays of life for many people, but will the need for community erode these concepts after the pandemic ends? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 26 Jul 2022
Burgers with Bugs? What Happens When Restaurants Ignore Online Reviews
Negative Yelp reviews hold more sway with consumers than restaurateurs might think. A machine learning study by Chiara Farronato reveals how online platforms amplify the customer voice, and why business owners should listen.

- 18 Jul 2022
After the 'Crypto Crash,' What's Next for Digital Currencies?
After soaring to dizzying levels, Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have lost more than half of their value in recent months. Scott Duke Kominers discusses crypto's volatility, potential for regulation, and why these digital assets are likely here to stay.

- 17 May 2022
Delivering a Personalized Shopping Experience with AI
THE YES, a shopping app for fashion brands, uses a sophisticated algorithm to create and deliver a personalized store for every shopper, based on her style preferences, size, and budget. After launching the app in 2020, the founders had to decide whether to continue developing the algorithm to deliver on the company’s customer value proposition or to focus their resources on new customer acquisition, with the idea that more users on the app would improve the algorithm's performance. Senior Lecturer Jill Avery and The YES co-founder and CEO Julie Bornstein discuss this make-or-break dilemma in the case, The YES: Reimagining the Future of e-Commerce with Artificial Intelligence (AI). This episode was recorded live at Harvard Business School on March 30, 2022 as part of our Case Method 100 celebration.

- 05 May 2022
Why Companies Raise Their Prices: Because They Can
Markups on household items started climbing years before the COVID-19 pandemic. Companies have realized just how much consumers will pay for the brands they love, says research by Alexander MacKay. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.

- 23 Nov 2021
The Vinyl Renaissance: Take Those Old Records Off the Shelf
If listeners today can stream just about any song they want, why are so many music aficionados still buying records? Ryan Raffaelli and Gold Rush Vinyl CEO Caren Kelleher discuss the resurgence of vinyl. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 12 Oct 2021
What Actually Draws Sports Fans to Games? It's Not Star Athletes.
Team owners think they need marquee names or slick stadiums to prosper, but research by Karim Lakhani and Patrick Ferguson suggests that fans want something far simpler: suspense. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 23 Jun 2021
One More Way the Startup World Hampers Women Entrepreneurs
Early feedback is essential to launching new products, but women entrepreneurs are more likely to receive input from men. Research by Rembrand Koning, Ramana Nanda, and Ruiqing Cao. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 15 Jun 2021
IKEA Navigates the Future While Staying True to its Culture
After years of success in providing quality furniture at affordable prices, Swedish furniture maker IKEA is challenged by the rise of online shopping and changing consumer behavior, plus the arrival of a new leader. The company's top executives know they had to step out of their comfort zones and embrace new strategic initiatives to stay relevant. But which initiatives will best enable IKEA to evolve while staying true to the company’s core values? Harvard Business School professors Juan Alcacer and Cynthia Montgomery discuss navigating a new future while preserving the company’s culture and identity in their case, “Which IKEA Do We Want?” Open for comment; 0 Comments.
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
What is market analysis? Definition, examples, and template

Product management is full of processes and frameworks, and product managers must think through them before deciding to invest in or build significant new products or services. As part of that process, one of the very first steps is market research and market analysis.

Well-executed market analysis will give you a clear indication of how successful the right product can be when introduced to the right target market for the right price. In this article, we’ll talk about market analysis and how to do it effectively, as well as walk through examples and a free template.
What is market analysis?
Simply put, market analysis is all the market research and competitive analysis done to determine a product-market fit . Sounds easy right? Well, there is a bit more that goes into conducting market analysis for your product than may meet the eye. But when done thoroughly, market analysis can lead to a very successful launch and future for your product.
Typically, market analysis is done before your product strategy is created. You need to know the details uncovered in this research to build out an effective, informed product strategy and vision.
The importance of market analysis in product management
To develop a strong product strategy, you’ll need to have a deep understanding of your target customers, the market, and where or how your product will fit in.
Here’s a basic but great example — let’s say you want to open a donut shop. Would you just jump right in with the first open space you see, fill your store with donuts, open the doors, and expect the masses to come? How do you know people even want donuts in that area? Are there other donut shops nearby? What price do you sell your donuts for and to whom?
Not conducting this type of detailed research upfront can lead to failed launches, lost money, and lost time. It would be much better if you planned ahead and did the research to determine that there is, indeed, a need for donuts in the area. The competition is slim and your customers are kids with no more than allowance money to spend on donuts too! I bet if you knew those details upfront, you would make vastly different decisions about your launch.
This is where conducting market analysis comes into play. It’s understanding that landscape ahead of time to eliminate risk and ensure from both a qualitative and quantitative perspective there is indeed a need for your product (or service).
Essential components in crafting your analysis
There are six main buckets to dive into to create your market analysis. A complete analysis will be a combination of the qualitative and quantitative info below. Once you have these pieces identified, you will easily be able to craft your strategy and have a solid foundation to pitch from when discussing your product with stakeholders.
For the purpose of breaking these down let’s use the following example objective:
“You currently have a social platform that is used daily by 1.2 million users for free and want to introduce a premium version.”
Know your industry
This may seem like a given, but as part of your analysis, you will want to make sure you have a firm understanding of your industry and any current trends. Be able to answer what is going on in your industry, any big changes that may have recently occurred, as well as where the industry is headed.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Describe the opportunity
Use this section to pitch your product or service and what value you think it can provide to the market. This section could also include a brief summary of who you think this product or service is for and anything high-level about the opportunity that you want stakeholders to know upfront.
Define your target market and customers
Your product is likely not relevant for everyone and that is OK! What is important in this step is to first identify the market you want to bring your product or service into and then identify what personas could benefit from it . Alternatively, it’s good to figure out who would not be your ideal customer too. Get as specific as you can here.
Questions to answer in this section include:
- What audience would this product or service best serve? Why?
- What are their demographics? (age, gender, race, ethnicity, etc.)
- What are their likes and dislikes?
- Where would they use this product or service? (online, in person, etc.)
- Who would not benefit from this offering and why?
Using our example above, we will want to understand from our existing user base what types of users would benefit most from this premium service. So let’s say we identified that our target premium users would be 13–35 years old.
Size up the opportunity
Now that you have identified who your target customers are and aren’t, the next step is to understand how big the market is for that persona. This is where you’ll want to provide specific data on the demographic you are trying to reach crossed with the total market in that area. This can be done by calculating the TAM, SAM, and SOM.
Let’s take these terms combined with our example from above and break it down a bit more:
This article on the TAM, SAM, and SOM can walk you through calculating these numbers. Having this prepared aids product teams (as well as finance teams) in understanding the revenue opportunity with your product before it even gets built. It is the backbone of creating a compelling market analysis for stakeholders as well.
Once you have these numbers, you can then enter them into a diagram to represent the bigger picture. You may recall seeing these values often represented in an onion-shaped char that looks something like this:
Identify any barriers to entry
Next, identify any major barriers to entry into the market with this product or service offering. Outline any steps you think you need to take to remove those barriers if known.
Evaluate the current market
The last but most important step is to take all the information above and plug it in side-by-side with the competition in that market to see how your offering would stack up. By mapping out what your competition has versus your offering, you will be visually able to see any opportunities or areas to look further into.
For example, if you find within your market there is a lot of competition with similar offerings, this may lead you to evaluate whether this is the right market to jump into or if you should explore elsewhere. Or perhaps you discover that no one is offering this product or service in your market. In this case, you have an opportunity to get ahead with a new offering or do deeper research into why no one has introduced something similar yet.
Take time to compare your offering to several competitors in the market (I recommend between three and five). You’ll want to dig deep to understand anything you can about their offering including who they offer it to, how long they have been providing that option, pricing, and more.
Market analysis template
Now that you know what a market analysis is and its components, here is a free template that you can use to craft your own market analysis. Please click File > Make a copy to download it to your own Google account and customize it as needed.
Here’s what the template above would look like when populated for our fitness app example:

Key Takeaways
When you have a new idea for a product or service, take time to thoroughly research the market and competition before diving headfirst. This will help you make informed product decisions that won’t turn out to be expensive mistakes.
Hopefully, this article took away some of the mystery behind market analysis in product management!
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.

A guide to optimizing the digital customer experience
The digital customer experience (DCX) refers to the journey your customers embark on when they interact with your product.
Leader Spotlight: Improving product development through documentation, with Mark Francis
Mark Francis discusses the importance of stakeholders across all business groups embracing the need for documentation and transparency.

A guide to crafting your brand strategy
Brand strategy is one of the most underestimated forces that shapes the trajectory of your products and services.

Leader Spotlight: Helping turn Apple’s business around, with Steve Chazin
Steve Chazin, VP of Products at Alarm.com, shares how he was re-hired by Steve Jobs to help turn Apple around.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Cryptocurrencies: market analysis and perspectives
- Published: 17 September 2019
- Volume 47 , pages 1–18, ( 2020 )
Cite this article
- Giancarlo Giudici 1 ,
- Alistair Milne 2 &
- Dmitri Vinogradov ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5426-1690 3 , 4
123k Accesses
108 Citations
38 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The papers in this special issue focus on the emerging phenomenon of cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are digital financial assets, for which ownership and transfers of ownership are guaranteed by a cryptographic decentralized technology. The rise of cryptocurrencies’ value on the market and the growing popularity around the world open a number of challenges and concerns for business and industrial economics. Using the lenses of both neoclassical and behavioral theories, this introductory article discusses the main trends in the academic research related to cryptocurrencies and highlights the contributions of the selected works to the literature. A particular emphasis is on socio-economic, misconduct and sustainability issues. We posit that cryptocurrencies may perform some useful functions and add economic value, but there are reasons to favor the regulation of the market. While this would go against the original libertarian rationale behind cryptocurrencies, it appears a necessary step to improve social welfare.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Cryptocurrencies continue to draw a lot of attention from investors, entrepreneurs, regulators and the general public. Much recent public discussions of cryptocurrencies have been triggered by the substantial changes in their prices, claims that the market for cryptocurrencies is a bubble without any fundamental value, and also concerns about evasion of regulatory and legal oversight. These concerns have led to calls for increased regulation or even a total ban. Further debates concern inter alia: the classification of cryptocurrencies as commodities, money or something else; the potential development of cryptocurrency derivatives and of credit contracts in cryptocurrency; the use of initial coin offerings (ICO) employing cryptocurrency technology to finance start-up initiatives; and the issue of digital currencies by central banks employing cryptocurrency technologies.
These discussions often shed more heat than light. There is as yet little clearly established scientific knowledge about the markets for cryptocurrencies and their impact on economies, businesses and people. This special issue of the Journal of Industrial and Business Economics aims at contributing to fill this gap. The collection of papers in the special issue offers six distinct perspectives on cryptocurrencies, written from both traditional and behavioural viewpoints and addressing both financial questions and broader issues of the relationship of cryptocurrencies to socio-economic development and sustainability.
Here in this introduction we set the stage by defining and discussing the main concepts and issues addressed in the papers collected in this special issue and previewing their individual contributions. Cryptocurrencies are digital financial assets, for which records and transfers of ownership are guaranteed by a cryptographic technology rather than a bank or other trusted third party. They can be viewed as financial assets because they bear some value (discussed below) for cryptocurrency holders, even though they represent no matching liability of any other party and are not backed by any physical asset of value (such as gold, for example, or the equipment stock of an enterprise). Footnote 1
As the word cryptocurrency, and the other terminology employing ‘coin’, ‘wallets’ in the original whitepaper proposing the supporting technology for Bitcoin (Nakamoto 2008 ) all suggest, the original developers consciously attempted to develop a digital transfer mechanism that corresponded to direct transfer of physical cash used for payments or other financial assets—such as a precious metals and ‘bearer bonds’—that like cash also change hands through physical transfer.
What about the arrangements used for financial assets recorded in digital form (such as bank deposits, equities or bonds but not bearer bonds or bank notes)? Ownership arrangements for these assets depend on the information system maintained by a financial institution (commercial bank, custodian bank, fund manager) determining who is entitled to any income or other rights it offers and has the right of sale or transfer. Originally these systems were paper based, but since the 1960s they have utilised first mainframe and more recently computer systems. Footnote 2 If there is a shortcoming in their information system, for example a breach of security that leads to theft or loss or failure to carry out an instruction for transfer, then the financial institution is legally responsible for compensating the owner of the asset.
In the case of cryptocurrencies, it is the supporting software that both verifies ownership and executes transfers. Footnote 3 There is no requirement for a ‘trusted third party’. Footnote 4 This approach though requires a complete historical record of previous cryptocurrency transfers, tracing back each holding of cryptocurrency to its initial creation. This historical record is based on a “blockchain”, a linking of records (“blocks”) to each other in such a way that each new block contains information about the previous blocks in the growing list (“chain”) of digital records. So that every participant in the cryptocurrency network sees the same transaction history, a new block is accepted by agreement across the entire network.
The applications of this technology are not necessarily finance-related; it can be applied to any form of record-keeping; however if the block refers to a financial transaction then each transaction in the blockchain, by definition, includes information about previous transactions, and thus verifies the ownership of the financial asset being transferred. Falsifying ownership, i.e. counterfeiting (which, one could imagine, is easy, as digital objects can be easily duplicated by copying), is impossible because one would have to alter preceding records in the whole chain. Since records are kept in the network of many users’ computers, a “distributed ledger”, this is rather unthinkable.
There is a substantial computer science literature on the supporting cryptocurrency technologies, including on the security of public key cryptography, efficient search tools for finding transactions on the blockchain, and the ‘consensus’ mechanisms used to establish agreement on ledger contents across the network. Footnote 5 Commentators expect new more efficient approaches will replace the mechanisms currently used in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Footnote 6 This though would not affect our definition of cryptocurrencies (as an asset and some technology which verifies ownership of the asset), which is independent of any particular technological implementation. Footnote 7
Cryptocurrencies can be seen as part of a broader class of financial assets, “cryptoassets” with similar peer-to-peer digital transfers of value, without involving third party institutions for transaction certification purposes. What distinguishes cryptocurrencies from other cryptoassets? This depends on their purpose, i.e. whether they are issued only for transfer or whether they also fulfil other functions. Within the overall category of cryptoassets, we can follow the distinctions drawn in recent regulatory reports, distinguishing two further sub-categories of cryptoassets, on top of cryptocurrencies: Footnote 8
Cryptocurrencies : an asset on a blockchain that can be exchanged or transferred between network participants and hence used as a means of payment—but offers no other benefits.
Within cryptocurrencies it is then possible to distinguish those whose quantity is fixed and price market determined (floating cryptocurrencies) and those where a supporting arrangement, software or institutional, alters the supply in order to maintain a fixed price against other assets (stable coins, for example Tether or the planned Facebook Libra).
Crypto securities : an asset on a blockchain that, in addition, offers the prospect of future payments, for example a share of profits.
Crypto utility assets : an asset on a blockchain that, in addition, can be redeemed for or give access to some pre-specified products or services.
A further distinguishing feature of crypto securities and crypto utility assets is that they are issued through a public sale (in so called initial coin offerings or ICOs). ICOs have been a substantial source of funding for technology orientated start-up companies using blockchain based business models. These classifications of cryptoassets are critical for global regulators, since they need to determine whether a particular cryptoasset should be regulated as an e-money, as a security or as some other form of financial instrument, especially in relation to potential concerns about investor protection in ICOs. Footnote 9
Floating cryptocurrencies account for the very large majority of the cryptoasset market capitalisation (Tether, a stablecoin, and Bitfinex’s UNUS SED LEO, a utility coin, are in the top 12 cryptoassets by market capitalisation, all the rest are floating cryptocurrencies). Table 1 summarises the market share of leading cryptocurrencies at the time of writing.
What is the value of cryptocurrencies? On the one hand, cryptocurrencies should be able to ease financial transactions through elimination of the intermediaries, reduction of transaction costs, accessibility to everyone connected to the Internet, greater privacy and security (see, e.g., discussions in Böhme et al. 2015 ; Richter et al., 2015 ). Footnote 10 On the other hand, the real economic value transferred in the transactions of freely floating cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin’s BTC and Ethereum’s Ether remains unclear. Despite the exhaustive and unfalsifiable record of all previous transactions held cryptographically, as in the Bitcoin blockchain, the information only refers to nominal numbers, i.e. the amount of cryptocurrency units transferred. One can, however, get an idea of the market value of cryptocurrencies by looking at their exchange rates against existing fiat currencies. This is possible thanks to cryptocurrency exchanges, which provide a nearly continuous price record for all actively traded cryptocurrencies. Although the resulting exchange rates are highly volatile, they reveal that cryptocurrencies have a non-zero value for those prepared to pay fiat currency in order to purchase them.
What drives this value in the absence of a backing asset or an issuer’s liability? Some advocate it is the cost of “mining” (energy and time spent on computational efforts required to complete formation of a new block in the chain, and rewarded by a newly issued cryptocurrency unit), however the cost borne by one member of the network does not justify the value of the new cryptocurrency unit for other members of the network (see also Dwyer 2015 , who argues the cost of mining is sunk and as such should be disregarded in the market value analysis). Others claim their market value is driven by the speculative bubble; yet, strictly speaking, the bubble is manifested in upward price deviations from the fundamental value (see, e.g., Siegel 2003 , for a review of definitions), hence the bubble explanation is only partial and raises further questions about what drives investors’ beliefs that feed their demand and thus support the bubble.
If it is the ease and the speed of transactions, then new transaction technologies and fund transfer systems that greatly improved in the recent decade (such as Transferwise and similar systems) should have wiped out a big chunk of the cryptocurrency value, yet this does not seem to be the case. A possible answer may lie in the features that distinguish cryptocurrencies from other assets and payment systems. Privacy, or rather anonymity, is a prominent distinctive feature popping up in most discussions of cryptocurrencies. The value of a cryptocurrency is then effectively a measure of how much users value anonymity of their transactions. While anonymity may be attractive for illegal activities (and some research reviewed below suggests cryptocurrencies are often used for these purposes), one cannot rule out users may simply wish more privacy, trying to avoid the “Big Brother” effect of traditional transactions. Of course, there may be other factors, for example, fashion (users want to use the technology others are talking about), hi-tech appeal (the desire to use the most modern technology) or curiosity (the desire to try something new), among others, but these phenomena appear shorter-lived than the allure of anonymity.
A key development in the rise of cryptocurrencies and other cryptoassets has been the emergence of cryptoexchanges where anyone can open accounts and trade cryptoassets both against each other and against fiat currencies. In a survey by Hileman and Rauchs ( 2017 ), the US dollar, the Euro and the British Pound are currently most widely traded against cryptocurrencies, while the importance of the Chinese Renminbi (CNY) significantly diminished after the tightening of the regulation by the People’s Bank of China; about three-quarters of large exchanges provide trading support for two or more cryptocurrencies. Above, we highlighted that cryptoexchanges provide extensive cryptocurrency pricing and trading information in the public domain. The emergence of these exchanges has created an entire ‘ecosystem’ of services and participants, seeking to provide liquidity, exploit price discrepancies for profit and to support investment by both retail and professional investors.
Academic interest in cryptocurrencies started to soar in 2014 (see Fig. 1 ): the Scopus database lists 127 publications containing the word ‘Bitcoin’ in the title or abstract or keywords and 24 containing ‘cryptocurrency’ or ‘cryptocurrencies’ in 2014. In 2017 and especially in 2018 the number of publications grew fast, and in 2019 the trend is continuing. Interestingly, academic work focuses much more on the Bitcoin than on the more general topic of cryptocurrencies, although in 2018 and in 2019 the gap narrowed. It appears that—apart from the Bitcoin frenzy—there is a growing attention to the general phenomenon of cryptocurrencies. However, focusing only on the ‘Economics, Econometrics & Finance’ and ‘Business, Management & Accounting’ sections of Scopus reveals that the interest in the topic surged a few years later Footnote 11 , although the number of publications is still rather low: in 2018 there were just over 100 titles on the topic in the above fields. The remaining contributions come from the ‘Computer Science’, ‘Engineering’ and ‘Mathematics’ disciplines.
Publications listed on the Scopus database containing ‘Cryptocurrency/ies’ and ‘Bitcoin’ in the title or abstract or keywords. The graph reports the number of publications tracked by the Scopus database ( http://www.scopus.com ) accessed on August 10, 2019 containing the words “Cryptocurrency/ies” or “Bitcoin” in the title or abstract or keywords. The subsample ECON refers to the category Economics, Econometrics & Finance while the subsample BUS refers to Business, Management & Accounting
This special issue of the Journal of Industrial & Business Economics offers a multifaceted view on the cryptocurrency phenomenon. Contributions have been selected with the objective to extend the existing knowledge about cryptocurrencies, which themselves embody innovations and technological change, and may appear to be a lucrative form of fund raising for small businesses; extra emphasis is made on areas of the journal’s particular interest, such as environment, sustainability and social responsibility. The remainder of this editorial proceeds as follows. In Sect. 2 we describe the contributions that shed light on the relationship between cryptocurrencies and financial investments. In Sect. 3 we focus on behavioral issues, while in Sect. 4 we introduce the development of the socio-economic perspectives related to cryptocurrencies and discuss initial coin offerings as a potential source of funds for small businesses. Finally, Sect. 5 concludes discussing the research agenda for the future.
2 Cryptocurrencies and neoclassical finance
Cryptocurrencies can be used both as a means of payment and as a financial asset. Glaser et al. ( 2014 ) provide evidence that, at least for the Bitcoin, the main reason to purchase a cryptocurrency is speculative investment. Financial securities, such as ETNs (exchange traded notes) and CFDs (derivative products) that replicate Bitcoin’s price performance are made available by brokers, expanding the speculative investment opportunities to an even larger set of investors. With this in mind, it makes sense to evaluate cryptocurrencies as financial assets.
The cross-section of cryptocurrency returns has been analyzed in a number of papers. Urquhart ( 2016 ) shows that Bitcoin returns do not follow random walk, based on which he concludes the Bitcoin market exhibits a significant degree of inefficiency, especially in the early years of existence. Corbet et al. ( 2018 )analyze, in the time and frequency domains, the relationship between the return of three different cryptocurrencies and a variety of other financial assets, showing lack of relationship between crypto- and other assets. Liu and Tsyvinski ( 2018 ) investigate whether cryptocurrency pricing bears similarity to stocks: none of the risk factors explaining movements in stock prices applies to cryptocurrencies in their sample. Moreover, movements in exchange rates, commodity prices, or macroeconomic factors of traditional significance for other assets play little to none role for most cryptocurrencies. The latter invalidates the view on cryptocurrencies as substitutes to monies, or as a store of value (like gold), and rather stresses they are assets of their own class. The review of the literature in Corbet et al. ( 2019 ) summarizes the most interesting findings on the role of cryptocurrencies as a credible investment asset class and as a valuable and legitimate payment system.
The relative isolation of cryptocurrencies from more traditional financial assets suggests cryptocurrencies may offer diversification benefits for investors with short investment horizons. Bouri et al. ( 2017 ) as well as Baur et al. ( 2018 ) find that Bitcoin is suitable for diversification purposes as its returns are uncorrelated with those of most major assets. Interestingly, they provide empirical evidence of the predominant usage of Bitcoins as speculative assets, though this is done on the data on USD transactions only and thus likely reflects the behavior of U.S. cryptocurrency investors mainly. Relatedly, Adhami and Guegan ( 2020 ) find that similarly to cryptocurrencies, cryptotokens are also a useful diversification device though not a hedge.
One way to understand similarities and differences between cryptocurrencies and more traditional financial assets is to estimate relationships known for traditional assets. A pattern that has received a lot of attention in the finance literature is the co-movement of the trading volume and returns/volatility of financial assets (a by far non-exhaustive list of examples would include Admati and Pfleiderer ( 1988 ), Foster and Viswanathan ( 1993 ), and Andersen ( 1996 )—for equity markets; Bessembinder and Seguin ( 1993 )—for futures; notably, no clear evidence of such a relationship exists for currencies, i.e. for exchange rates, see, e.g. Côté 1994 ). This special issue includes a contribution by Figà-Talamanca ( 2020 ), who, inter alia , investigate this relationship for cryptocurrencies, along with the impact of “relevant events”, which are key disruptive changes to the market infrastructure. They find that Bitcoin trading volume does not affect its returns but detect a positive effect of Bitcoin trading volumes on return volatility. While their focus is mainly on market attention, these results highlight similar forces rule cryptocurrency markets and those for more traditional financial assets, again supporting the view of cryptocurrencies as investment assets. Footnote 12
The risk of holding cryptocurrencies is discussed in this special issue by Fantazzini and Zimin ( 2020 ). Cryptocurrency prices may drop dramatically because of a revealed scam or suspected hack, or other hidden problems. For example, on June 26th, 2019, the Bitcoin price lost more than 10 % of the value in a few minutes because of the crashes and outages of the Coinbase digital exchange. As a consequence, a cryptocoin may become illiquid and its value may substantially decline. Fantazzini and Zimin ( 2020 ) propose a set of models to estimate the risk of default of cryptocurrencies, which is back-tested on 42 digital coins. The authors make an important point in extending the traditional risk analysis to cryptocurrencies and making an attempt to distinguish between market risk and credit risk for them. The former, as typical in the finance literature, is associated with movements in prices of other assets. The latter is associated in traditional finance with the failure of the counterparty to repay, but as cryptocurrencies presume no repayments, defining credit risk for them is tricky. The authors’ approach is to see the “credit” risk of cryptocurrency in the possibility of them losing credibility among users, and thus becoming value-less, or “dead”. The authors find, notably, that the market risk of cryptocurrencies is driven by Bitcoin, suggesting some degree of homogeneity in the cryptomarket. As for the credit risk, the traditional credit scoring models based on the previous month trading volume, the one-year trading volume and the average yearly Google search volume work remarkably well, suggesting indeed a similarity between the newly defined credit risk for cryptocurrencies and the one traditionally used for other asset classes.
3 Cryptocurrencies and behavioral finance and economics
A large strand of the literature explains market phenomena that work against the neo-classical predictions, from the perspective of unquantifiable risk, or ambiguity. Most commonly, ambiguity is associated with the impossibility to assign probability values to events that may or may not occur. In the case of cryptocurrencies, this type of uncertainty may arise for two reasons: (1) the technology is rather complicated and opaque to unsophisticated traders, and (2) the fundamental value of cryptocurrencies is unclear. As we highlighted above, even if it is strictly positive, it is likely to derive from intangible factors and as such is rather uncertain. Dow and da Costa Werlang ( 1992 ) demonstrate that under pessimism (ambiguity aversion) uncertainty about fundamentals leads to zero trading in financial markets, yet this does not seem to apply to cryptocurrencies. In Vinogradov ( 2012 ) not only does the no-trade outcome depend on the degrees of optimism and pessimism, which may vary, but it also manifests only under high risk (in the standard sense). Still, again, although cryptocurrency returns exhibit high volatility, trade volumes are significant. In Caballero and Krishnamurthy ( 2008 ) uncertainty leads to “flights to quality” in traditional asset markets, which, if properly applied to cryptocurrencies, might also explain the crashes we recently observed.
Obtaining information is crucial to reduce uncertainty. Figà-Talamanca ( 2020 ) focus on a rather general definition of the demand for information, as manifested in the google search index. According to them, the intensity of the internet search for cryptocurrency-related keywords significantly affects cryptocurrency volatility (but not return); this impact vanishes once one controls for “relevant events”. These relevant events are effectively announcements of either restrictions (and even bans) on cryptocurrency usage, or of the widening of the cryptocurrency market. While we remain largely agnostic regarding what people find when they search for cryptocurrency related terms on the Internet, the events give us an indication of the type of information that actually matters for cryptocurrency investment decisions, and hence for pricing. In uncertainty, when finding relevant information is uneasy, investors might resort to watching and mimicking other, presumably better informed, investors’ decisions, resulting in herding (Trueman 1994 ; Devenow and Welch 1996 ), addressed in this special issue by Haryanto et al. ( 2020 ), see below.
Uncertainty and attitudes to it are not the only reasons why neoclassical predictions may fail. Shiller ( 2003 ) notes that market participants are humans and can make irrational systematic errors contrary to the assumption of rationality. Such errors affect prices and returns of assets, creating market inefficiencies. Studies in behavioral economics highlight inefficiencies, such as under- or over-reactions to information, as causes of market trends and, in extreme cases, of bubbles and crashes. Such reactions have been attributed to limited investor attention, overconfidence, mimicry and noise trading, explanations of many of which find roots in Kahneman and Tversky’s ( 1979 ) prospect theory, which postulates that decision makers evaluate outcomes from the perspective of their current endowment (and are predominantly loss-averse) and “revise” probabilities of outcomes when making decisions (predominantly overweighting probabilities of bad outcomes and underweighting those of good ones). The loss-aversion led Shefrin and Statman ( 1985 ) to formulate the ‘disposition effect’ in investment decisions: investors in traditional assets tend to keep assets that lose value too long and sell those that gain in value too early.
Three features distinguish cryptocurrency markets: investors are non-institutional, risk (volatility of returns) is high, and the fundamental value is unclear. Under these conditions behavioral biases should be even more pronounced than in traditional asset markets. In this special issue Haryanto et al. ( 2020 ) study the disposition effect and the herding behavior in the cryptocurrency realm by investigating the trading behavior at a cryptoexchange: they find a reverse disposition effect in bullish periods where the Bitcoin price increases while a positive disposition effect is observed in bearish periods. They also find that in different market conditions herding moves along with market trend (in the bullish market a positive market return increases herding, while in the bearish market a negative market return has the same effect). The reverse disposition effect in the bullish market indicates investors exhibit more optimism and expect returns to further grow, which is consistent with the exponential price growth in a bubble in the absence of a clearly defined fundamental value. This lack of clarity regarding the fundamental value is also supported by the asymmetric herding behavior: when the price grows in a bullish market, investors look at other market participants to see whether others also think the price will continue to grow (similarly but with the opposite sign for the bearish market).
This special issue also contributes to the debate on the existence of a ‘bubble’ in the cryptocurrency market (see Baek and Elbeck 2015 ; Cheah and Fry 2015 ). The contribution by Moosa ( 2020 ) highlights that the Bitcoin was in a bubble up to the end of 2017. The analysis claims that the volume of trading in Bitcoin can be explained predominantly in terms of price dynamics considering past price movements, particularly positive price changes, and that the path of the price is well described by an explosive process.
4 Socio-economic perspectives
Critiques emphasize cryptocurrencies are not exempt from frauds and scandals. For example, several millions in Bitcoin from the Japanese platform Mt. Gox in 2014 and $50 million in Ether during the Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) attack in 2016 were stolen. Moreover, cryptocurrency payments, being largely unregulated, do not restrict any purchases, including those illegal. Böhme et al. ( 2015 ) provide summary data showing that, at least in the beginning of the Bitcoin era, most transactions were used for drug purchases. Foley et al. ( 2019 ) estimate that about 46 % of Bitcoin transactions are associated with illicit activities, but that the illegal share of Bitcoin activity declined over time with the emergence of more opaque cryptocurrencies. On top of that, users appear unprotected as payments are often irreversible, and an erroneous transfer cannot be cancelled, unlike credit card payments (Böhme et al. 2015 ).
On the positive side, the development of the cryptocurrency market contributes to the dynamics of access to finance (Adhami et al. 2018 ). The advent of the blockchain technology allowed entrepreneurial teams to raise capital in cryptocurrencies and fiat money (which has to be exchanged into a cryptocurrency) through the issuance of digital tokens (Initial Coin Offerings, ICOs) and the development of ‘smart contracts’ (Giudici and Adhami 2019 ). Tokens give their buyers a right to use certain services or products of the issuer, or to share profits, in which case they resemble equity. Special cryptoexchanges then serve the secondary market for tokens. The OECD ( 2019 ) lays out basic principles and typical steps of an ICO. An important distinction between tokens and cryptocurrencies is though that there is a liability or some sort of commitment behind the token, and this liability determines its value. Now that this cryptoasset bears more similarity with traditional assets, one would expect also the main predictions of neoclassical finance to come true. In fact, in a recent empirical study of cryptotokens, Howell et al. ( 2018 ) demonstrate the effects of asymmetric information on tokens trading: their liquidity and trading volume are positively associated with the information inflow. The latter is achieved through voluntary disclosure of information (including the operating budget and their business plans), and quality signaling (e.g. information on prior venture capital funding of the issuer).
Cryptocurrencies, which underlie the ICO procedure, are claimed to provide much more equitable and democratic access to capital as well as greater efficiency, compared to fiat money, allowing peer-to-peer transactions and avoiding the intermediation of banks (Nakamoto 2008 ; Karlstrøm 2014 ). This is normally done via an ICO, and could be a relevant opportunity for small business, which often experience a gap in funding and miss competences to relate with professional investors (Giudici and Paleari 2000 ). OECD ( 2019 ) also reports ICOs are a potential route for low cost finance for SMEs.
Will cryptocurrencies favor a process of “democratization” of funding? This has been widely discussed by practitioners and investors, with a great variety of views. For example, The World Economic Forum White Paper (WEF 2018 ), claims that cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies could increase the worldwide trading volume, moving to better levels of service and lower transaction fees. To this extent, the contribution by Ricci ( 2020 ) in this special issue considers the geographical network of Bitcoin transactions in order to discover potential relationships between Bitcoin exchange activity among countries and national levels of economic freedom. The study shows that high levels of freedom to trade internationally, that guarantee low tariffs and facilitate international trade, are strongly connected to the Bitcoin diffusion. On the one hand, the freedom to trade internationally could increase the foreign trade through the use of alternative payment instruments capable of reducing transaction costs (like cryptocurrencies), on the other, low capital controls could encourage the use of cryptocurrencies for illegal conduct, such as money laundering.
The reward system for cryptocurrency ‘miners’ creates an incentive to leverage on computing power, increasing the consumption of energy. For example, Böhme et al. ( 2015 ) note that computational efforts of miners are costly, mainly because the proof-of-work calculations are “power-intensive, consuming more than 173 megawatts of electricity continuously. For perspective, that amount is … approximately $178 million per year at average US residential electricity prices.” The sustainability topic is raised in this special issue by Vaz and Brown ( 2020 ). They posit that there are significant sustainability issues in the cryptocurrency development exceeding potential benefits, that are captured typically by a few people. Therefore, they call for different institutional models with government and public engagement, as to avoid that the market is driven mostly by private money and profit motivations.
5 Conclusions
Growing attention has been paid to cryptocurrencies in the academic literature, discussing whether they are supposed to disrupt the economy or are a speculative bubble which could crash and burn or favor money laundering and criminals. In support of the first view, it is often argued they meet a market need for a faster and more secure payment and transaction system, disintermediating monopolies, banks and credit cards. Critics, on the other hand, point out that the unstable value of cryptocurrencies make them more a purely speculative asset than a new type of money.
The reality is somewhere in between these two positions, with cryptocurrencies performing some useful functions and hence adding economic value, and yet being potentially highly unstable. The trend is towards a regulation of cryptocurrencies, and more generally of all crypto-assets, and to their increased trading on organized and regulated exchanges. This would go against the original libertarian rationale that originated the Bitcoin but is a necessary step to provide protection for market participants and reduce moral hazard and information asymmetries.
How will future research build on the articles in this special issue and on other recent studies of cryptocurrencies? It is of course always difficult to anticipate substantial future research contributions, especially in relation to such a recent and novel phenomenon like cryptocurrencies. But we would argue that there are a few major issues that deserve continued attention from scholars in finance, economics and related disciplines.
One is the need for a much closer examination of the ‘market microstructure’ of cryptoexchanges. Some recent research already draws attention to the functioning of cryptoexchanges. For example, Gandal et al. ( 2018 ) investigate price manipulations at the Mt. Gox Bitcoin exchange; a notable by-product of their research is the finding that suspicious trading on one exchange led to equal price changes on other exchanges, suggesting traders can effectively engage in arbitrage activities across exchanges. Similarly, signs of efficiency are detected in Akyildirim et al. ( 2019 ) who investigate pricing of Bitcoin futures on traditional exchanges—Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE). Importantly, in their study information flows and price discovery go from futures to spot markets, in contrast to previous results for traditional assets; a likely explanation is the difference in the type of traders at cryptoexchanges (that determine the spot price) and both CME and CBOE. Footnote 13 Yet more has to be learnt about cryptoexchanges. Their open nature distinguishes them from conventional stock exchanges and dealer markets with transactors directly accessing the market rather than relying on brokers as intermediaries. Is this open nature helpful, providing greater liquidity and narrowing trading spreads? Or does it disadvantage some investors, limiting regulatory oversight and allowing a core of participants to manipulate market prices at the expense of other investors? Do the technical arrangements supporting cryptoexchanges, notably the use of distributed ledger or blockchain technology which eliminates the need for post-trade settlement, lead to more efficient trading outcomes in terms of price, liquidity and speed of execution? Could these technologies also improve the efficiency of outcomes in conventional financial exchange?
The second issue, widely debated in the cryptocurrency literature, is whether cryptocurrencies have a fundamental own value. Dwyer ( 2015 ) conjectures the limitation of the quantity produced can create an equilibrium in which a digital currency has a positive value: this limitation is a form of commitment, replacing the implicit obligation of Central banks to exchange fiat money into gold. Hayes ( 2017 ) advocates the cost of production view on cryptocurrency pricing; yet, as we discussed earlier, from a market equilibrium perspective, being sunk cost (as in Dwyer 2015 ), it does not matter for the pricing of existing coins. Footnote 14 A concurrent work by Bolt and Van Oordt ( 2019 ) outlines three key elements of the cryptocurrency value: convertibility into fiat money or ability to buy goods and services, investors’ expectations, and factors that determine acceptance of the cryptocurrency in the future, by both vendors and buyers. Simultaneously, Schilling and Uhlig ( 2019 ) offer a model where cryptocurrencies are a reliable medium of exchange and compete against fiat money: this role implies the current price of cryptocurrencies is the expectation of their future value (a martingale), yet interestingly, competition and substitutability between the two imply in their analysis cryptocurrencies should disappear in the long run equilibrium. The authors admit that their analysis abstracts away such distinctive features of cryptocurrencies as “censorship resistance, transparency, and speed of trading”. Above we have provided a simplified argument explaining that cryptocurrencies may have a value by offering features, such as anonymity of transactions, not covered by traditional currencies. Many findings, also those included in this special issue, point towards the intangible nature of the cryptocurrency value. Knowing more about it, we would be better equipped to understand the price dynamics and, reciprocally, the price dynamics would improve our understanding of decisions made by investors. So far, we remain very much agnostic in this respect.
The third issue is the societal role of cryptocurrencies and their regulation. While many discussions of cryptocurrencies stress that they are free of regulation, and the desire to be unregulated was one of drivers behind their creation, there is considerable controversy both about the application of existing regulation to cryptocurrencies and other cryptoassets and also what if any new regulations may be needed to protect investors, prevent financial crime and ensure financial stability. Are crypto investments securities and therefore subject to securities law (in the US this has been determined by the so-called Howey test)? What about the regulation of cryptoexchanges and the problems of hacking with some prominent examples of theft and failure to enforce “know-your-customer” (KYC) and anti-money-laundering (ALM) regulations?
Globally, regulators are shifting towards a tougher stance. Some exchanges are seeking to engage with regulators and be fully compliant. Others prefer to operate outside of regulation. A simple argument is that one has to protect investors and users from financial and technological risks they face. However, as papers presented in this special issue demonstrate, cryptocurrencies differ from traditional assets, hence the validity of traditional arguments, such as systemic stability, consumer protection and promotion of competition, is not clear. As our literature review and papers in this special issue underscore, cryptocurrencies do not comove with other assets; they help diversification and do not pose an immediate danger for systemic stability. There appears to be a significant and growing degree of competition between different cryptocurrencies and cryptoexchanges, and yet we have to understand whether and why such a competition is desirable for the society.
Similarly, we need to understand whether there is a need to protect consumers. In traditional asset markets and in banking such protection improves allocation of resources and promotes economic growth and welfare, which is not straightforwardly applicable to cryptocurrencies and existing other cryptoassets. An extra dimension that arises from the studies in our special issue is the sustainability and environmental impact of cryptocurrencies, and this is again different from other asset classes.
Last but not the least, yet another major issue is how cryptocurrency technologies may affect conventional fiat currency issued by central banks. Footnote 15 Emerging literature on the competition between cryptocurrencies and fiat money raises concerns that the emergence of privately issued cryptocurrencies could weaken the monetary policy tools employed by the central bank and result in welfare losses (Zhu and Hendry 2018 ; Schilling and Uhlig 2019 ). Fernández-Villaverde and Sanches ( 2019 ) find that when private currency competes with a central bank issued e-money the former should vanish in equilibrium, yet it remains unclear what happens if cryptocurrencies are not a perfect substitute to fiat money. Footnote 16 Cukierman ( 2019 ), building on the analysis by Roubini ( 2018 ), brings the discussion to a further level by discussing the potential also for cryptocurrency issue by the central bank being used to implement fully reserved or narrow banking and thus to promote financial stability.
We hope this special issue contributes to our understanding of cryptocurrencies and surrounding issues. We also reckon it helps generate knowledge and materials useful for practitioners and scholars, involved in studying and shaping the cryptocurrency market for the future. Very possibly this will evolve and become very different from what we observe today, but for sure already now cryptocurrencies embody an innovation capable of moving our financial markets and economies forward in terms of efficiency and growth. We just need to learn using this innovation properly.
From the accounting perspective, cryptocurrencies are investment assets, sometimes even treated similarly to stocks for accounting purposes (Raiborn and Sivitanides 2015 ).
Milne ( 2015 ) provides a history of the information systems used in securities markets.
A more detailed yet still accessible overview of the key features of the current technology behind cryptocurrencies can be found in Böhme et al. ( 2015 ). Narayanan et al. ( 2016 ) provide a detailed textbook description. A key feature is that ownership is identified with a public cryptographic key. The matching private cryptographic key can then be used both to confirm ownership of the associated public key and to instruct transfers of the cryptocurrency to other public keys. The number of these keys is effectively unlimited. In the case of Bitcoin these keys are 256-bit binary numbers, so in consequence there are 2 256 possible public keys; an almost unimaginably large number.
Third parties may still play a role in the functioning of a cryptocurrency. For example, 5 % of XRP, the cryptocurrency that supports Ripple international payments platform is held by Ripple themselves, and their decisions to buy or sell affect market supply. Third parties also support stablecoins such as Tether or Facebook’s proposed Libra currency.
Blockchains are validated and updated within peer-to-peer networks using a ‘consensus mechanism’ (for example “proof of work” or “proof of stake”, see Tschorsch and Scheuermann 2016 ) that prevents members of the network from creating a false version of history. This consensus then supports a fully decentralized secure verification of ownership and exchange (Pilkington 2016 ; Goldstein et al. 2019 ). In the case of Bitcoin, the term block was originally used because its consensus mechanism (‘mining’) is applied to append ‘blocks’ of around 1000 transactions at a time to the chain of transaction records.
For a review of several prominent consensus mechanisms see Baliga ( 2017 ).
Ripple (XRP) is an example of a cryptoasset that does not use blockchain. However, it has a different purpose designed primarily to mediate conversions from currency to currency, or from any asset A to asset B.
For example (Bank of England, Financial Conduct Authority, and HM Treasury 2018 ; ESMA 2019 ; EBA 2019 ) and also (Hacker and Thomale 2017 ). The term ‘token’ is often used as a shorthand reference to cryptoassets, especially for crypto securities and crypto utility assets (e.g. Adhami and Guegan 2020 ), though Milne ( 2018 ) argues that this usage can be misleading, disguising similarities with more conventional financial assets.
Recent discussion of these issues includes FSB ( 2018 ), FCA ( 2019 ) and Blandin et al. ( 2019 ).
Note that transactions in cryptocurrencies are subject to such restrictions as the lack of reversibility, i.e. an erroneous transaction cannot be cancelled as soon as it is written in the block. More traditional payment systems, such as bank transfers and credit card payments, are more flexible in this respect.
This delay may also reflect slower publication process in our field, with most papers going through a few not so fast rounds of revisions (let alone rejections) before they get published. Huisman and Smits ( 2017 ) review recent evidence on the duration of the publication process; their sample shows, for example, that tit takes twice as long to publish in Economics than, e.g. in Medicine, with an average first response time in Economics and Finance being 16–18 weeks (comparable to Azar’s 2007 , estimate of 3–6 months). Their sample does not account for the number of previous rejections though. John Cochrane witnesses most of his publications were rejected 2–3 times before getting eventually published ( https://johnhcochrane.blogspot.com/2017/09/a-paper-and-publishing.html ); further anecdotal evidences are in Shepherd ( 1995 ).
“Similar forces” here does not mean similar factors: like Liu and Tsyvinski ( 2018 ), Figà-Talamanca ( 2020 ) find a strong dependence of cryptocurrency returns of their past values, which distinguishes them from other asset classes.
Interestingly, CBOE futures present an informational advantage over the CME alternative, possibly because of the smaller size of contracts and hence the larger number of investors actively trading.
It may matter though for the decision to mine new coins (the marginal cost of coin production should be below market price, which stands for the marginal profit). Hayes ( 2017 ) also points at the difficulty of the mining algorithm as a driver of cryptocurrency prices. This measure may be an indicator of the reliability of the cryptographic technology behind the cryptocurrency, and thus part of the fundamental value, as it represents security of transactions, valued by the users.
Pieters ( 2020 , forthcoming) provides a useful wider review of central banks and digital payments technologies.
Fernández-Villaverde and Sanches ( 2019 ) also advance an interesting idea that cryptocurrencies, being “private money”, create limits for monetary policy and, at the same time, provides market discipline for the government.
Adhami, S., Giudici, G., & Martinazzi, S. (2018). Why do businesses go crypto? An empirical analysis of initial coin offerings. Journal of Economics & Business, 100, 64–75.
Google Scholar
Adhami, S. & Guegan, D. (2020). Crypto assets: the role of ICO tokens within a well-diversified portfolio. Journal of Industrial & Business Economics (forthcoming) .
Admati, A. R., & Pfleiderer, P. (1988). A theory of intraday patterns: Volume and price variability. The Review of Financial Studies, 1 (1), 3–40.
Akyildirim, E., Corbet, S., Katsiampa, P., Kellard, N., & Sensoy, A. (2019). The development of Bitcoin futures: Exploring the interactions between cryptocurrency derivatives. Finance Research Letters . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.frl.2019.07.007 . (in press) .
Article Google Scholar
Andersen, T. G. (1996). Return volatility and trading volume: An information flow interpretation of stochastic volatility. The Journal of Finance, 51 (1), 169–204.
Azar, O. H. (2007). The slowdown in first-response times of economics journals: Can it be beneficial? Economic Inquiry, 45 (1), 179–187.
Baek, C., & Elbeck, M. (2015). Bitcoins as an investment or speculative vehicle? A first look. Applied Economics Letters, 22 (1), 30–34.
Baliga, A. (2017). Understanding Blockchain Consensus Models. Persistent White paper. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/da8a/37b10bc1521a4d3de925d7ebc44bb606d740.pdf . Accessed 14 Sept 2019.
Bank of England, Financial Conduct Authority, and HM Treasury. (2018). Cryptoassets taskforce: Final report. London.
Baur, D. G., Hong, K., & Lee, A. D. (2018). Bitcoin: Medium of exchange or speculative assets? Journal of International Financial Markets, Institutions and Money, 54, 177–189.
Bessembinder, H., & Seguin, P. J. (1993). Price volatility, trading volume, and market depth: Evidence from futures markets. Journal of financial and Quantitative Analysis, 28 (1), 21–39.
Blandin, A., Cloots, A. S., Hussain, H., Rauchs, M., Saleuddin, R., Allen, J. G., et al. (2019). Global cryptoasset regulatory landscape study . Cambridge: Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance.
Böhme, R., Christin, N., Edelman, B., & Moore, T. (2015). Bitcoin: Economics, technology, and governance. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 29 (2), 213–238.
Bolt, W., & Van Oordt, M. R. (2019). On the value of virtual currencies. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking . https://doi.org/10.1111/jmcb.12619 .
Bouri, E., Molnár, P., Azzi, G., Roubaud, D., & Hagfors, L. (2017). On the hedge and safe haven properties of Bitcoin: Is it really more than a diversifier? Finance Research Letters, 20, 192–198.
Caballero, R. J., & Krishnamurthy, A. (2008). Collective risk management in a flight to quality episode. The Journal of Finance, 63 (5), 2195–2230.
Cheah, E.-T., & Fry, J. (2015). Speculative bubbles in bitcoin markets? An empirical investigation into the fundamental value of bitcoin. Economics Letters, 130, 32–36.
Corbet, S., Lucey, B., Urquhart, A., & Yarovaya, L. (2019). Cryptocurrencies as a financial asset: A systematic analysis. International Review of Financial Analysis, 62, 182–199.
Corbet, S., Meegan, A., Larkin, C., Lucey, B., & Yarovaya, L. (2018). Exploring the dynamic relationships between cryptocurrencies and other financial assets. Economics Letters, 156, 28–34.
Côté, A. (1994). Exchange rate volatility and trade. Bank of Canada .
Cukierman, A. (2019) Welfare and political economy aspects of a central bank digital currency. Centre for Economic Policy Research, discussion paper DP13728, May 2019.
Devenow, A., & Welch, I. (1996). Rational herding in financial economics. European Economic Review, 40 (3–5), 603–615.
Dow, J., & da Costa Werlang, S. R. (1992). Uncertainty aversion, risk aversion, and the optimal choice of portfolio. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society , 60 (1), 197–204.
Dwyer, G. P. (2015). The economics of bitcoin and similar private digital currencies. Journal of Financial Stability, 17, 81–91.
EBA. (2019). Report with Advice for the European Commission on crypto-assets. https://eba.europa.eu/documents/10180/2545547/EBA+Report+on+crypto+assets.pdf . Accessed 14 Sept 2019.
ESMA. (2019). “Advice: Initial coin offerings and crypto-assets. https://www.esma.europa.eu/sites/default/files/library/esma50-157-1391_crypto_advice.pdf . Accessed 14 Sept 2019.
Fantazzini, D., & Zimin, S. (2020). A multivariate approach for the joint modelling of market risk and credit risk for cryptocurrencies. Journal of Industrial & Business Economics (this issue) .
FCA. (2019). Guidance on cryptoassets feedback and final guidance to CP 19/3. Policy Statement PS19/22. Financial Conduct Authority July 2019.
Fernández-Villaverde, J., & Sanches, D. (2019). Can currency competition work? Journal of Monetary Economics, in press, . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoneco.2019.07.003 .
Figà-Talamanca, G., & Patacca M. (2020). Disentangling the relationship between Bitcoin and market attention measures. Journal of Industrial & Business Economics (this issue) .
Foley, S., Karlsen, J., & Putnins, T. (2019). Sex, drugs, and bitcoin: How much illegal activity is financed through cryptocurrencies? Review of Financial Studies, 32 (5), 1798–1853.
Foster, F. D., & Viswanathan, S. (1993). Variations in trading volume, return volatility, and trading costs: Evidence on recent price formation models. The Journal of Finance, 48 (1), 187–211.
FSB. (2018). Crypto-asset markets Potential channels for future financial stability implications (p. 10). Basel: Financial Stability Board.
Gandal, N., Hamrick, J. T., Moore, T., & Oberman, T. (2018). Price manipulation in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Journal of Monetary Economics, 95, 86–96.
Giudici, G., & Adhami, S. (2019). The governance of ICO projects: Assessing the impact on fundraising success. Journal of Industrial and Business Economics, 46 (2), 283–312.
Giudici, G., & Paleari, S. (2000). The provision of finance to innovation: A survey conducted among Italian technology-based small firms. Small Business Economics, 14 (1), 37–53. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008187416389 .
Glaser, F., Zimmermann, K., Haferkorn, M., Weber, M. C., & Siering, M. (2014). Bitcoin-asset or currency? revealing users’ hidden intentions. Revealing Users’ Hidden Intentions (April 15, 2014). ECIS.
Goldstein, I., Wei Jiang, W., & Karolyi, G. A. (2019). To FinTech and Beyond. The Review of Financial Studies, 32 (5), 1647–1661. https://doi.org/10.1093/rfs/hhz025 .
Hacker, P., & Thomale, S. (2017). Crypto-securities regulation: ICOs, token sales and cryptocurrencies under EU financial law. European Company and Financial Law Review, 15 (4), 645–696.
Hayes, A. S. (2017). Cryptocurrency value formation: an empirical study leading to a cost of production model for valuing bitcoin. Telematics and Informatics , 34 (7), 1308–1321.
Haryanto, S., Subroto A., & Ulpah M. (2020). Disposition effect and herding behavior in the cryptocurrency market. Journal of Industrial & Business Economics (this issue) .
Hileman, G., & Rauchs, M. (2017). Global cryptocurrency benchmarking study. Cambridge Centre for Alternative Finance . https://cdn.crowdfundinsider.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/Global-Cryptocurrency-Benchmarking-Study.pdf . Accessed 14 Sept 2019.
Howell, S. T., Niessner, M., & Yermack, D. (2018). Initial coin offerings: Financing growth with cryptocurrency token sales (No. w24774). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Huisman, J., & Smits, J. (2017). Duration and quality of the peer review process: The author’s perspective. Scientometrics, 113 (1), 633–650.
Kahneman, D., & Tversky, A. (1979). Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica, 47 (2), 263–292.
Karlstrøm, H. (2014). Do libertarians dream of electric coins? The material embeddedness of bitcoin. Scandinavian Journal of Social Theory, 15 (1), 25–36.
Liu, Y., & Tsyvinski, A. (2018). Risks and returns of cryptocurrency (No. w24877). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Milne, A. (2015). Central securities depositories and securities clearing and settlement: Business practice and public policy concern. In M. Diehl, B. Alexandrova-Kabadjova, R. Heuver, & S. Martínez-Jaramillo (Eds.), Analyzing the economics of financial market infrastructures . Hershey: IGI Global.
Milne, A. K. L. (2018) Argument by False analogy: The mistaken classification of Bitcoin as token money (November 25, 2018). https://ssrn.com/abstract=3290325 .
Moosa, I. (2020). The Bitcoin: A Sparkling Bubble or Price Discovery? Journal of Industrial & Business Economics (this issue) .
Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: a peer-to-peer electronic cash system. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf . Accessed 14 Sept 2019.
Narayanan, A., Bonneau, B., Felten, E., Miller, A., & Goldfeder, S. (2016). Bitcoin and cryptocurrency technologies: A comprehensive introduction . Princeton: Princeton University Press.
OECD. (2019). Initial coin offerings (ICOs) for SME financing, http://www.oecd.org/finance/initial-coin-offerings-for-sme-financing.htm .
Pieters, G. (2020). Central banks and digital currencies. In R. Rau, R. Wardrop, & L. Zingales (Eds.), The Palgrave handbook of alternative finance . Basingstoke: Palgrave MacMillan.
Pilkington, M. (2016). Blockchain technology: Principles and applications. In F. Xavier Olleros & M. Zhegu (Eds.), Research handbooks on digital transformations (pp. 225–253). Cheltenham: Edward Elgar.
Raiborn, C., & Sivitanides, M. (2015). Accounting issues related to Bitcoins. Journal of Corporate Accounting & Finance, 26 (2), 25–34.
Ricci, P. (2020). How economic freedom reflects on the Bitcoin transaction network. Journal of Industrial & Business Economics (this issue) .
Richter, C., Kraus, S., & Bouncken, R. C. (2015). Virtual currencies like Bitcoin as a paradigm shift in the field of transactions . International Business & Economics Research Journal, 14 (4), 575–586.
Roubini, N. (2018). Exploring the cryptocurrency and blockchain ecosystem . Washington, DC: Testimony for the Hearing of the US Senate Committee on Banking, Housing and Community Affairs.
Schilling, L., & Uhlig, H. (2019). Some simple bitcoin economics. Journal of Monetary Economics (forthcoming).
Shefrin, H., & Statman, M. (1985). The disposition to sell winners too early and ride losers too long: Theory and evidence. The Journal of Finance, 40 (3), 777–790.
Shepherd, G. B. (1995). Rejected: Leading economists ponder the publication process . Sun Lakes: T. Horton and Daughters.
Shiller, R. J. (2003). From efficient markets theory to behavioral finance. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 17 (1), 83–104.
Siegel, J. J. (2003). What is an asset price bubble? An operational definition. European Financial Management, 9 (1), 11–24.
Trueman, B. (1994). Analyst forecasts and herding behavior. The Review of Financial Studies, 7 (1), 97–124.
Tschorsch, F., & Scheuermann, B. (2016). Bitcoin and beyond: A technical survey on decentralized digital currencies. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 18 (3), 2084–2123.
Urquhart, A. (2016). The inefficiency of Bitcoin. Economics Letters, 148 (1), 80–82.
Vaz, J., & Brown, K. (2020). Sustainable development and cryptocurrencies as private money. Journal of Industrial & Business Economics (this issue) .
Vinogradov, D. (2012). Destructive effects of constructive ambiguity in risky times. Journal of International Money and Finance, 31 (6), 1459–1481.
WEF. (2018). Trade Tech—A new age for trade and supply chain finance, The World Economic Forum in collaboration with Bain & Company. World Economic Forum, January 2018. http://www3.weforum.org/docs/White_Paper_Trade_Tech_report_2018.pdf . Accessed 14 Sept 2019.
Zhu, Y., & Hendry, S. (2018). A framework for analyzing monetary policy in an economy with e - money (December 31, 2018). https://ssrn.com/abstract=3318915 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3318915 . Accessed 14 Sept 2019.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy
Giancarlo Giudici
University of Loughborough, Loughborough, UK
Alistair Milne
University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK
Dmitri Vinogradov
National Research University Higher School of Economics, Russian Federation, Perm, Russia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Dmitri Vinogradov .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Giudici, G., Milne, A. & Vinogradov, D. Cryptocurrencies: market analysis and perspectives. J. Ind. Bus. Econ. 47 , 1–18 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40812-019-00138-6
Download citation
Received : 07 September 2019
Revised : 07 September 2019
Accepted : 11 September 2019
Published : 17 September 2019
Issue Date : March 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40812-019-00138-6
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Cryptocurrencies
- Cryptoassets
JEL Classification
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
Market Research Articles and Resources
We've put together this comprehensive and thorough Market Research guide to give you the tools and information you need to manage, strategize, measure and impact all aspects of the Market Research for your business.
Select a topic
Analysis & Reporting
Panels & Samples
Market Segmentation
Focus Groups
Text Analytics
Distribution & Response
Survey data analysis and best practices for reporting
Data can do beautiful things, but turning your survey results into clear, compelling analysis isn’t always a straightforward task. We’ve collected our tips for survey analysis along with a beginner’s guide to survey data and analysis tools. 20 min read
More Analysis & Reporting articles
What is a research panel (and should we have one)?
There is often confusion between having a research panel and buying a sample from a third party panel provider. In fact, these are two different solutions to the same need. To help you decide what’s right for you, we break down the difference between managing your own research panel and buying a sample. 10 min read
More Panels & Samples articles
How to determine sample size
Sample size can make or break your research project. Here’s how to master the delicate art of choosing the right sample size. 12 min read
More Sampling articles
What is a user persona and how do I make one?
Creating personas can be extremely beneficial for making effective design, product and content decisions. Learn how to make and utilize user personas with our guide below. 14 min read
More Market Segmentation articles
The ultimate guide to market research: How to conduct it like a pro
Wondering how to do market research? Or even where to start learning about it? Use our ultimate guide to understand the basics and discover how you can use market research to help your business. 27 min read
More Market Research articles
The definitive guide to focus groups
Interested in focus groups but not sure where to start? Use our definitive guide to grasp the essentials and learn how you can leverage focus groups to better know your audience. 15 min read
More Focus Groups articles
What is a survey? (Benefits, tips, best practices & free survey tools)
It’s a simple question. But as with many things, the answer is more complex than you’d think. Surveys can take many forms but are most common as a questionnaire, either written or online. 18 min read
More Surveys articles
Text analysis: definition, benefits & examples
Find out how text analysis software works, and how you can use it to find breakthrough insights in unstructured data to take your customer, employee, brand, and product experience programs to another level. Written by Rohan Sinha, Senior Principal CX at Qualtrics. 45 min read
More Text Analytics articles
User interviews: definition & questions to ask
What do your users need — and how should you engage with them? Here we explain how you can get to know your users, and their expectations of your products and services, with our complete guide to user interviews. 25 min read
More Interviews articles
How your survey distribution methods can impact your research results
Effective survey distribution means you can reach your target customers more effectively, get better response rates, and better quality data. Learn which survey distribution methods will give your team the best chance of success. 23 min read
More Distribution & Response articles
Real-time market research insights drive better decisions.
Modern market research means you can track consumer behavior across diverse segments, benchmark your company versus competitors, conduct complex academic research, and capture the insights you need to move the needle.
Today’s market research is predictive and collaborative so everyone in your organization has the same information to drive the business forward.
Research today shouldn’t just track change, it should provoke it.
Request Demo
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

- SVP Experience
- Ethical Business Decisions Playbook
- Silicon Valley Hiring Guide
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- GMAT/GRE Waiver
- Admissions Requirements
- Application Deadlines
- How to Apply
- Networking Opportunities
- Student Success
How to Conduct Marketing Research and Analysis

A key component of running any successful business is regularly conducting market analysis—a process that provides insight into where the company is and where it's heading. This analysis contains qualitative and quantitative marketing research, primary and secondary research, and additional data points regarding positioning, industry and market statistics, insights into consumer attitudes and buying habits, customer satisfaction, and more.
According to the global data and business intelligence platform Statista, the worldwide market research industry surpassed $81 billion in 2022. 1 The United States Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects that employment in the industry is due to grow 13% over the next ten years. 2 In light of that strength and likely rapid expansion, facility with marketing research and analysis is an increasingly valuable skill. Keep reading to explore some of the key elements of this essential process.
Market Research, Marketing Research, and Other Key Terms
It’s important to understand the differences between market research/analysis and marketing research/analysis. The terms are similar but the meanings are distinct: 3
- Market research: A study done to collect statistics on a given market within a specific industry
- Market analysis: Interpretation of market information to determine a market’s size, growth potential, audience, and competitive landscape 4
- Marketing research: The process of collecting data to understand consumer behaviors, preferences, and market dynamics
- Marketing analysis: Evaluating and interpreting collected data to draw conclusions, derive actionable insights, and make informed, data-driven marketing decisions
In addition, as you get further into marketing research and analysis, you’ll need to be familiar with these terms:
- Quantitative marketing research involves gathering numerical data to quantify and analyze patterns and relationships in consumer behavior
- Qualitative marketing research involves gathering information that isn't expressed in numbers to gain insights into consumer behaviors, attitudes, and motivations
- Ethnographic research is the process of studying a target audience's environment to gain a clearer understanding of potential customers’ behaviors and preferences
- Market segmentation is the process of dividing a target market into distinct groups of consumers; each group of people shares similar characteristics or needs
- Data mining is the process of analyzing large datasets to identify patterns, relevant trends, and valuable marketing insights; data mining for marketing insights is used to influence strategizing and decision-making
- Competitive analysis: By analyzing competitors to understand their strategies, strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning, businesses become able to identify opportunities and threats
- Market trend analysis is the examination of historic and current market data to identify patterns and emerging trends
Primary and Secondary Research in Marketing: What’s the Difference?
To conduct thorough, effective marketing research and analysis, you need both primary and secondary data.
Primary research involves original data collected directly from targeted sources. This is typically done through in-person or online surveys, focus group studies, observations, or experiments.
Primary research offers several distinct advantages. It’s highly relevant due to its freshness and the researchers’ ability to customize the surveys or studies they administer. It also allows analysts to hone in on the specific market they're trying to understand, which leads to sharper data precision and accuracy.
Secondary research, on the other hand, uses existing information that others have previously collected in the form of published reports, articles, academic papers, market research reports, government publications, industry databases, or historical data.
Secondary research is more cost-effective and saves time because it doesn’t require data collection. It also provides a broader perspective by offering a comprehensive view of trends and historical information.
How to Conduct Quantitative and Qualitative Marketing Research
Quantitative marketing research is a structured process that involves gathering, processing, and interpreting numerical data.
- The process begins with defining specific research objectives and selecting an appropriate quantitative research method, such as experiments or customer surveys
- Researchers then develop a structured instrument, like a questionnaire, to collect numerical data from a representative sample
- After data collection, meticulous data entry is essential for ensuring accuracy
- Analysts then employ statistical analysis methods, such as descriptive and inferential statistics, to interpret the data
Qualitative research delves more into the motivations behind consumer behavior by analyzing non-numerical information. By its nature, qualitative data can be ephemeral—hard to quantify. The research process can involve listening to recordings from focus group studies, reading social media comments and reviews, and understanding subtext from customers based on visual and other non-verbal cues.
- Similar to quantitative marketing research, qualitative research begins by selecting a research method, such as individual interviews or focus groups, and defining research objectives
- Researchers then carefully recruit a diverse set of participants that represent a target audience
- During data collection, the use of open-ended discussions and follow-up questions can uncover meaningful insights that might not be readily apparent at the outset
- Afterward, transcribing the data and looking for recurring themes and patterns can allow researchers to interpret the findings within the context of the research objectives
How To Present Market Research and Analysis
Once you’ve completed marketing research and analysis, you’ll likely be called upon to present your findings. If market research techniques come easily to you but presenting before other people seems daunting, a few simple strategies can streamline the process:
Focus on Key Insights
Highlight the most important findings to avoid overwhelming your audience with too much data. They don’t need or want to know every fact that your research turned up, so stick to the information that addresses their priorities. Be ready to answer questions with contextual, detailed information if people ask for it, but keep the structure of your presentation focused on the big-ticket items.
Use Data Visualization
Data visualization involves using software to display substantial amounts of information in a graphic format: as dashboards, pie charts, graphs, and so on. By presenting your findings visually, you can share them with diverse audiences—company leadership, clients, and other stakeholders—in engaging, relatable ways.
Tell a Story
Frame your presentation as a narrative—that is, tell a story—to engage your audience even more and make your findings memorable. Encourage your audience to ask questions. This turns your presentation into a collaborative dialogue, keeps them involved, and helps you shine as you present direct answers to address their needs.
Add Marketing Research and Analysis to Your Expertise
The world of marketing is constantly changing, so up-to-the-moment expertise is essential for a successful career . The comprehensive curriculum in SCU's Online Master of Science in Marketing program will hone your expertise in marketing strategy, marketing technology , social media marketing, search engine optimization, email marketing, marketing analytics, and more.
Built to accommodate the schedules of working professionals and led by a faculty of industry experts , the program provides networking opportunities that will help you gain insights into industry trends and best practices.
Don’t delay your career ascent . Schedule a call with one of our admissions outreach advisors today.
1. Retrieved on September 21, 2023, from statista.com/topics/1293/market-research/#topicOverview 2. Retrieved on September 21, 2023, from bls.gov/ooh/business-and-financial/market-research-analysts.htm 3. Retrieved on September 21, 2023, from keydifferences.com/difference-between-market-research-and-marketing-research.html 4. Retrieved on September 21, 2023, from coursera.org/articles/market-analysis
Return to Media
Santa Clara University has engaged Everspring , a leading provider of education and technology services, to support select aspects of program delivery.
Interested in one of our online programs? Receive a program brochure.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

How Quickly Do Prices Respond to Monetary Policy?

Download PDF (238 KB)
FRBSF Economic Letter 2024-10 | April 8, 2024
With inflation still above the Federal Reserve’s 2% objective, there is renewed interest in understanding how quickly federal funds rate hikes typically affect inflation. Beyond monetary policy’s well-known lagged effect on the economy overall, new analysis highlights that not all prices respond with the same strength or speed. Results suggest that inflation for the most responsive categories of goods and services has come down substantially from recent highs, likely due in part to more restrictive monetary policy. As a result, the contributions of these categories to overall inflation have fallen.
Monetary policy affects inflation with a lag. This means that, although interest rates react quickly when the Federal Reserve raises the federal funds rate, the effects on inflation are slower and indirect. Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, slowing investment and overall demand, which ultimately eases the pressure on prices. Understanding the timing and strength of this mechanism is key for policymakers.
Many researchers have estimated the speed and strength of the economy’s response to monetary policy, notably Romer and Romer (2004). The focus is typically a broader measure of inflation, such as headline or core, which reflects an average across many goods and services. However, not all prices of the component goods and services react to monetary policy in the same way. For example, food and energy prices, which are excluded from core but included in headline inflation, often move more in response to global market fluctuations, such as changes in international oil prices, rather than to changes in domestic monetary policy.
In this Economic Letter , we estimate how prices of different goods and services respond to changes in the federal funds rate and use those estimates to build a monetary policy-responsive inflation index. We find substantial variation in how prices react to monetary policy, which suggests that understanding the makeup of overall inflation can provide insights into the transmission of monetary policy to inflation. The extent to which categories that are more responsive to the federal funds rate contribute to inflation affects how much slowing in economic activity is needed to reduce overall inflation. Our analysis indicates that recent ups and downs of inflation have been focused in categories that are most sensitive to monetary policy. Inflation rates for the most sensitive categories—and their contributions to headline inflation—rose from the first half of 2020 through mid-2022, reaching a higher peak than headline inflation, and then began to decline. The inflation rate for this most responsive group of goods and services categories is now close to its pre-2020 rate. Our findings suggest that the Fed’s rate hikes that began in March 2022 are exerting downward pressure on prices and will continue to do so in the near term. Our estimated lags are consistent with the view that the full effects of past policy tightening are still working their way through the economy.
Measuring how prices react to monetary policy
To understand which goods and services are most responsive to monetary policy, we need to determine how their prices react to changes in the federal funds rate, the Federal Reserve’s main policy rate. Because the Federal Reserve adjusts the federal funds rate target in response to macroeconomic developments, including inflation, we use a transformation of the federal funds rate in our estimation. This transformed series, developed by Romer and Romer (2004) and updated by Wieland and Yang (2020), captures the differences between Federal Reserve staff forecasts and the chosen target rate, leaving only policy shocks, or movements in the federal funds rate that are not driven by actual or anticipated changes in economic conditions. We use this series as a so-called instrument for the federal funds rate, such that our results can account for how the federal funds rate itself, rather than its transformation, affects inflation.
We use an approach developed by Jordà (2005) that compares two forecasts—with and without rate shocks—to estimate how the federal funds rate affects price movements over time. Specifically, we estimate the relationship between the federal funds rate and the cumulative percent change in prices, controlling for recent trends in the federal funds rate, inflation, and economic activity. Repeating this estimation over multiple horizons produces a forecast comparison, or impulse response function, that gives us an estimate of the expected percent change in prices following a rate increase. For example, applying this method to the headline personal consumption expenditures (PCE) price index indicates that four years after a 1 percentage point increase in the federal funds rate, overall prices are typically about 2.5% below what they would have been without the rate increase.
Creating a policy-responsive inflation index
We estimate impulse response functions separately for the 136 goods and services categories that collectively make up headline PCE inflation. Figure 1 shows examples of the largest cumulative percent price declines over a four-year period in response to a 1 percentage point increase in the federal funds rate. The goods and services categories selected as examples account for large shares of total expenditures in headline PCE inflation. We also include one example of the few categories where prices do not decline, higher education, shown as a small positive value.
Figure 1 Reaction to a policy rate increase: Selected PCE categories
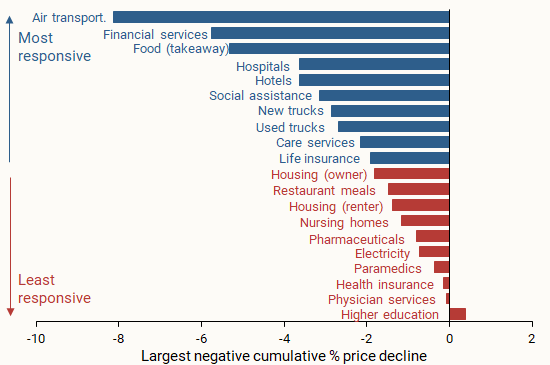
The takeaway from Figure 1 is that headline PCE inflation is made up of categories that differ in their responsiveness to increases in the federal funds rate. Some respond more strongly, such as those with larger typical cumulative price declines, while others respond less strongly, such as those with smaller typical price declines. Focusing on the most responsive categories can shed light on how monetary policy has influenced the path of inflation over the post-pandemic period. We use our results to divide the categories into two groups of goods and services. The most responsive group (blue bars) contains goods and services whose largest cumulative percent price decline over a four-year window is in the top 50% of all such declines. The least responsive group (red bars) contains goods and services in the bottom 50%.
Following the methods in Shapiro (2022), we use these two groups, along with the share of total expenditures for each good or service, to create two new aggregate PCE inflation measures. Figure 2 shows their 12-month percent changes over time. The blue shading marks the period from mid-2019 until early 2020 when the Federal Reserve lowered the federal funds rate. The vertical yellow line marks the start of the most recent tightening cycle in March 2022. Inflation in the most responsive categories (blue line) is more volatile than overall headline PCE inflation (green line) from the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA), and inflation in the least responsive categories is less volatile (red line).
Figure 2 Most and least responsive inflation rates
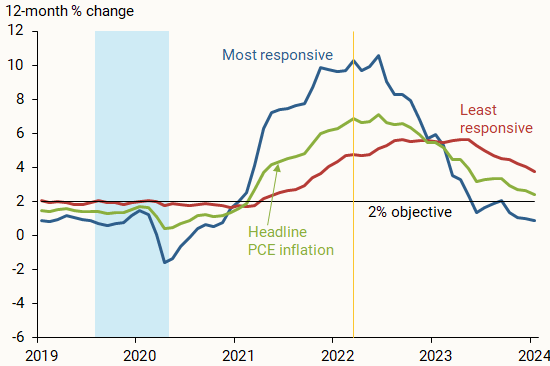
After the start of the 2020 recession, inflation rates for both categories rose but have since come down from their recent peaks. This pattern is particularly pronounced for the most responsive inflation group, for which inflation peaked at 10.5% in mid-2022 and has fallen to 0.9% as of January 2024; this is just under its average of 1% from 2012, when the Federal Reserve officially adopted a numerical inflation objective, to 2019. Inflation in the least responsive group peaked later, in early 2023, and has fallen only slightly to 3.8% as of January 2024; it remains well above its 2012–2019 average of 1.8%.
How does policy-responsive inflation react to rate increases?
The inflation rates of categories in the most and least responsive groups can move for reasons beyond changes in the federal funds rate, such as global or national macroeconomic developments. To assess the specific role of policy rate increases, we use the methodology described earlier to estimate how the most and least responsive inflation groups tend to react to rate hikes.
The results in Figure 3 suggest that an increase in the federal funds rate typically starts exerting downward pressure on the most responsive prices after about 18 months, when the line showing the impulse response function falls below zero. Month-to-month price changes start falling after a little over a year, depicted when the slope drops below zero and stays negative. This is quicker than the response of overall headline prices from the BEA (not shown), which becomes negative after a little over 24 months and shows month-to-month declines after about 18 months.
Figure 3 Reaction of most and least responsive prices to rate hikes
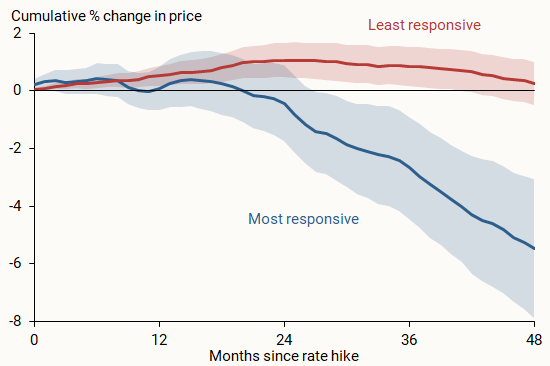
Because we grouped inflation categories based on the size of their response, there is not necessarily a tie-in to the speed of each categories’ change. However, our results suggest that looking at the most responsive goods and services may also be a useful way of assessing how quickly monetary policy affects inflation.
Applying the typical impact timing of the most responsive group of goods and services to the most recent tightening cycle, shown by the federal funds rate line in Figure 4, leads to several conclusions. First, rate cuts from 2019 to early 2020 could have contributed upward price pressures starting in mid- to late 2020 and thus could explain some of the rise in inflation over this period. Second, the tightening cycle that began in March 2022 likely started putting downward pressure on prices in mid-2023 and will continue to do so in the near term. This is consistent with the view that the full effects of monetary policy tightening have yet to be felt. Finally, though inflation for the most responsive categories has been falling since mid-2022, the early part of this decline was likely to have been driven more by changes in prevailing economic conditions than by policy tightening, given estimated policy lags. Some research has considered whether policy lags have shortened (see, for example, Doh and Foerster 2021); however, because inflation began falling mere months after the first rate hike, the drop in inflation may have been too soon to be caused by policy action.
Figure 4 Headline inflation contributions and the federal funds rate
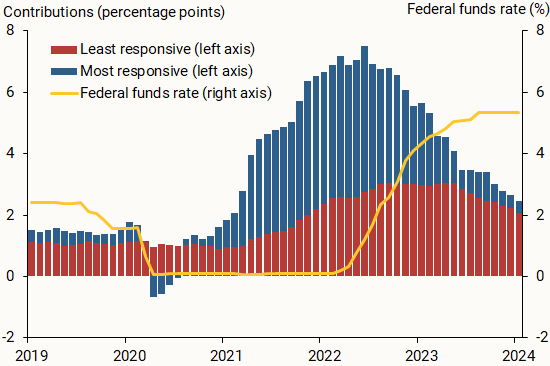
Our findings in this Letter are useful for broadening our understanding of how monetary policy affects inflation. For example, if inflation and the contributions to overall headline inflation are high in a set of categories that are more responsive to monetary policy, as was the case in early 2022, then rate hikes during the most recent tightening cycle are likely to continue to reduce inflation due to policy lags. On the other hand, though inflation in the least responsive categories may come down because of other economic forces, less inflation is currently coming from categories that are most responsive to monetary policy, perhaps limiting policy impacts going forward.
Doh, Taeyoung, and Andrew T. Foerster. 2022. “ Have Lags in Monetary Policy Transmission Shortened? ” FRB Kansas City Economic Bulletin (December 21).
Jordà, Òscar. 2005. “Estimation and Inference of Impulse Responses by Local Projections.” American Economic Review 95(1), pp. 161–182.
Romer, Christina, and David Romer. 2004. “A New Measure of Monetary Shocks: Derivation and Implications.” American Economic Review 94(4), pp. 1,055–1,084.
Shapiro, Adam. 2022. “ A Simple Framework to Monitor Inflation .” FRB San Francisco Working Paper 2020-29.
Wieland, Johannes, and Mu‐Jeung Yang. 2020. “Financial Dampening.” Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 52(1), pp. 79–113.
Opinions expressed in FRBSF Economic Letter do not necessarily reflect the views of the management of the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco or of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. This publication is edited by Anita Todd and Karen Barnes. Permission to reprint portions of articles or whole articles must be obtained in writing. Please send editorial comments and requests for reprint permission to [email protected]
Economic conditions outlook, March 2024
Executives’ latest views on the global economy and their countries’ economies lean much more positive than they did at the end of 2023.
In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on economic conditions, 1 The online survey was in the field from March 4 to March 8, 2024, and garnered responses from 957 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. To adjust for differences in response rates, the data are weighted by the contribution of each respondent’s nation to global GDP. the outlook on domestic conditions in most regions has become more hopeful, despite ongoing shared concerns about geopolitical instability and conflicts. In a year brimming with national elections, 2 Katharina Buchholz, “2024: The super election year,” Statista, January 19, 2024. respondents increasingly see transitions of political leadership as a primary hazard to the global economy, particularly in Asia–Pacific, Europe, and North America.
Furthermore, respondents now view policy and regulatory changes as a top threat to their companies’ performance, and they offer more muted optimism than in December about their companies’ prospects.
Optimism builds over global and domestic conditions
Respondents share much brighter assessments of the global economy and conditions in their countries than they did at the end of 2023, and views of the global economy are the most positive they’ve been since March 2022 (Exhibit 1). In the December survey, respondents were equally likely to say the global economy had improved and worsened. Today, respondents are twice as likely to report improving rather than deteriorating conditions. Looking ahead to the next six months, respondents are also more optimistic than they were last quarter. Forty-six percent expect the global economy to improve—nearly double the share expecting worsening conditions—while 37 percent expected improvement in the previous survey.
Likewise, respondents offer hopeful views when asked about the most likely near-term scenario for the global economy, suggesting confidence in central banks. They are more likely to expect a soft landing overall—with either slowing or accelerating growth compared with 2023—than a recession (Exhibit 2). The largest share of respondents expect a soft landing, with slowing growth relative to 2023.
Respondents’ views on their own economies have also become more upbeat. Nearly half of respondents say economic conditions at home are better now than they were six months ago, up from 41 percent in December, while just 22 percent say conditions have gotten worse. Respondents in Europe—who offered the most negative assessments of any respondents in September and December—are now nearly twice as likely as in December to say conditions have improved in the past six months, though it is unclear what has prompted that change and whether it is a durable finding.

McKinsey’s original survey research
More than half of respondents expect their economies to improve over the next six months. It’s the first time in two years that a majority of respondents have said that. In most regions, larger shares of respondents express optimism about economic conditions at home now than in December (Exhibit 3).
Geopolitical instability remains top of mind as concerns over political transitions rise
Geopolitical instability and conflict continues to be the most cited risk to global growth, selected by two-thirds of respondents for the second quarter in a row (Exhibit 4). Yet in this first quarterly survey of 2024—a year in which more than 60 countries will hold national elections 3 Katharina Buchholz, “2024: The super election year,” Statista, January 19, 2024. —transitions of political leadership have jumped from the fifth-most-cited to the second-most-cited threat to the world economy. The share of respondents in Europe reporting political transitions as a top threat is 2.4 times the share in December, while the shares in North America and Asia–Pacific have nearly doubled. 4 Prior to the latest survey, respondents in Mexico were included in Latin America in analyses but are now included in North America. We see a smaller uptick in concern about supply chain disruptions, which is cited as a threat by the largest share of respondents since December 2022.
Looking at risks to growth in respondents’ countries, geopolitical instability and conflict remains the top perceived threat, cited by a larger share than in any quarter since March 2022. Uneasiness about domestic political conflicts and transitions of political leadership, now the second- and third-most-cited risks, have overtaken concerns about inflation, which was the second-most-cited risk in December. Among respondents in North America, transitions of political leadership are cited nearly twice as often as in December (Exhibit 5). In Greater China, multiple risks now appear to carry equal weight, whereas in December, inflation was the top concern.
Policy and regulatory changes top the list of cited threats to companies’ growth
As respondents’ concerns about inflation as a domestic threat wane, the survey results suggest that companies are holding off on price increases. For the first time since we began asking about companies’ prices in September 2022, less than half of private-sector respondents in the latest survey—45 percent—say their companies increased the price of their goods or services over the past six months, down from 56 percent in December.
For five quarters, respondents’ most cited risk to their companies’ performance in the next 12 months was weak customer demand. Now, they most often point to policy and regulatory changes as a threat. In December 2023, policy and regulatory changes weren’t even one of the top five perceived risks. This increased wariness of policy changes cuts across most regions, though we see the largest increase in Europe.
Even though weak demand is no longer the most cited risk for companies, optimism over expected demand has tapered since December. Fifty-one percent of respondents expect an increase in customer demand over the next six months, down from 57 percent in December. Yet expectations about profits remain upbeat: about six in ten respondents expect increasing profits in the months ahead, in line with expectations in much of 2023.
The survey content and analysis were developed by Jeffrey Condon , a senior knowledge expert in McKinsey’s Atlanta office; Krzysztof Kwiatkowski , a capabilities and insights expert in the Boston office; and Sven Smit , chair of insights and ecosystems, chair of the McKinsey Global Institute, and a senior partner in the Amsterdam office.
They wish to thank Jan Mischke for his contributions to this work.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, a senior editor in the Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Geopolitics and the geometry of global trade

Survey results: Expectations for company performance, by industry

Global Economics Intelligence executive summary, February 2024
- Online Degree Explore Bachelor’s & Master’s degrees
- MasterTrack™ Earn credit towards a Master’s degree
- University Certificates Advance your career with graduate-level learning
- Top Courses
- Join for Free
What Is a Market Research Analyst? 2024 Guide
Market research analysts pore over trending keywords, survey responses, social media mentions, and more to understand markets, customers, and competitors. Learn more about this high-demand role.
![research article market analysis [Featured image] Staff reviews marketing data](https://d3njjcbhbojbot.cloudfront.net/api/utilities/v1/imageproxy/https://images.ctfassets.net/wp1lcwdav1p1/6U4dHHZv6Lj7S8RaAClVHa/1264ed1ba82975ba94f3fb2a59a18d9d/GettyImages-1143029488.jpg?w=1500&h=680&q=60&fit=fill&f=faces&fm=jpg&fl=progressive&auto=format%2Ccompress&dpr=1&w=1000)
Market research analysts—sometimes called market researchers—help companies develop or maintain a competitive edge by finding and delivering data-backed insights into potential markets, competitors, and even customer behaviour.
They’re an integral part of a company’s overall marketing strategy and are in demand across multiple industries. Look at the role of a market research analyst and what you can expect working in the field.
What does a market research analyst do?
Market research analysts pore over trending keywords, survey responses, social media mentions, and other data to find answers. Essentially, they transform information into actionable insights that will help companies develop everything from competitive product launches to effective marketing campaigns.
Each company’s needs differ, but your responsibilities as a market research analyst may include:
Developing data collection tools and techniques
Using data modelling tools
Analysing data sets and communicating findings
Contributing data-backed insights to marketing strategy
Conducting product testing and brand research
What type of research does a market research analyst conduct?
A market research analyst conducts qualitative and quantitative research. In other words, they gather statistical data and solicit responses about people’s beliefs, opinions, and experiences.
An analyst’s research can span multiple areas, including:
Primary and secondary customer research—everything from demographics to opinions—helps a company develop more targeted marketing and align its products and services with customers’ differing needs. Market research analysts may also identify how companies find, acquire, and retain customers while avoiding churn—or customer loss.
Primary vs. secondary research: What's the difference?
Primary research is research you conduct yourself, building original tools or techniques to help you collect new information. Research someone else has done, like a government agency or research think tank, is considered secondary research.
As a company develops new offerings—like products, services, or ideas—market research about competitors, similar products, and potential sales can help successfully position each launch. Market research analysts investigate new and existing markets, learning as much as possible so they can deliver precise suggestions.
Both new and established companies rely on brand research to strengthen their position in the market. Conducting a competitive analysis to see how a company’s brand fares against competitors and researching customers’ brand awareness and perception helps them remain competitive. Those findings can also yield insights into customer acquisition, retention, and loyalty.
Understanding how a company’s customers feel about advertising at all phases of a marketing campaign can produce specific messaging and, in turn, more impactful campaigns. Whilst this type of research typically falls under a marketing analyst role, market research analysts at smaller companies may sometimes analyse a company’s marketing strategy.
Market research analyst job description
Qualifications.
Market research analyst jobs typically require a bachelor’s degree in business or a related field to qualify for an entry-level role. More senior-level market research analyst jobs may require a master’s degree or several years of experience.
Subjects and coursework that can prepare you for a job as a market research analyst:
Business administration
Sociology
Market research analyst technical skills
Data collection tools : Market research analysts gather data from various sources, including surveys, social media platforms, keyword trends, and audience insights. Market research analysts use Qualtrics, SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Google Trends, and SEMrush, among many other tools, to learn more about customers, markets, and competitors.
Statistical analysis : Because market research involves working with quantitative data, it’s important to understand how to apply statistical techniques to group your data into relevant, actionable findings. Whilst many programs, like the data visualisation tools below, offer a statistical analysis feature, they shouldn’t replace a more foundational knowledge.
Data visualisation : Once a market research analyst has collected relevant data, they must structure their findings comprehensively. Using data dashboards or data analytics suites can help convey essential findings to other teams. Market research analysts use data visualisation tools like Tableau, Qlikview, and Plotly.
Programming languages : Although not always necessary, some companies do require market research analysts to know a programming language, such as R, SQL, SAS, or SPSS, which feeds into their data gathering and data interpretation efforts. Make sure to read over job descriptions to learn which language, if any, a company prefers.
Market researcher workplace skills
Interpretation : Parsing data is critical to a market research analyst’s role. After gathering the necessary data, you must interpret those findings in light of a company’s product and marketing needs.
Critical thinking : Conducting market research means asking the right questions to find the best data, extracting meaning from collected data, and then applying those insights to a company’s marketing strategy.
Communication : Translating insights into recommendations that other teams can act upon will help in a marketing research analyst's line of work. A strong ability to speak and write clearly and constructively is an asset.
Interviewing : Many market research analysts rely on digital surveys to glean customer responses, but the role can also involve conducting customer interviews or focus groups. Being comfortable speaking with strangers and getting them to open up about their experiences is a key skill.
What are the benefits of being a market research analyst?
Job prospects.
As companies need insight into customer behaviour to keep their competitive edge, market research analysts will continue to serve an integral role. In 2021, revenue in the Asian Pacific market research industry grew more than 10 per cent year over year [ 1 ]. This trend should continue, as experts expect the global market to exceed $83 billion by 2025 [ 2 ].
Market research analyst salary
According to Glassdoor, the median salary for a market research analyst in India is ₹5,15,767, though salary can differ depending on the industry [ 3 ].
Market research analyst vs. similar roles
Market research analysts share much in common with roles that also parse data and deliver strategic insights.
Marketing analyst
Although market research analysts are sometimes confused—and even called—marketing analysts, the two roles differ slightly. Marketing analysts focus internally on a company’s marketing efforts rather than externally on markets, but both roles use data to inform their recommendations.
Business analyst
Another role that relies heavily on data, a business analyst analyses large data sets to make recommendations that will strengthen a business’ processes and help it run more efficiently.
Data analyst
With a much broader role than the three previously described, a data analyst typically works with large, raw data sets that must first be cleaned to yield important insights. Data analysts apply their findings to an array of organisational and business needs.
How to become a market research analyst
1. look for a related entry-level role.
Whilst some entry-level market research analyst roles exist, most employers prefer at least two years of experience. If you’re interested in becoming a market research analyst, consider a related role to help you gain experience and grow more competitive. Working as a marketing assistant or data analyst can provide you with the experience necessary to move into market research analysis.
2. Brush up on related technical skills
Knowing that market research analysts use specific tools to gather and assess customer, market, and competitor data, it’s a good idea to research the most popular programs and refine your knowledge of them. Watch tutorials, use free trials, and familiarise yourself with the tools of the trade.
3. Take a course
Taking courses that expose you to critical strategies of market research can help introduce you to the work of a market research analyst. You can start with the Google Digital Marketing & E-commerce Professional Certificate offered on Coursera. You’ll learn how to manage digital marketing campaigns, attract and engage customers, and prepare for media planner and marketing coordinator jobs.
Article sources
Statista. " Annual Growth in Market Research Revenue Worldwide by Region 2021 , https://www.statista.com/statistics/378039/annual-change-in-market-research-revenue-by-region/." Accessed July 27, 2023.
PRNewswire. " Global Marketing Research and Analysis Services Market Report 2021: Market is Expected to Reach $83.39 Billion in 2025 - Forecasts to 2030 , https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/global-marketing-research-and-analysis-services-market-report-2021-market-is-expected-to-reach-83-39-billion-in-2025---forecasts-to-2030--301338542.html." Accessed July 27, 2023.
Glassdoor. “ Research Analyst Salaries , https://www.glassdoor.co.in/Salaries/market-research-analyst-salary-SRCH_KO0,23.htm.” Accessed July 27, 2023.
Keep reading
Coursera staff.
Editorial Team
Coursera’s editorial team is comprised of highly experienced professional editors, writers, and fact...
This content has been made available for informational purposes only. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 10 April 2024
The impact of environmental regulation on green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises in China-based on a three-stage exogenous variable model
- Fang-rong Ren 1 ,
- Tao-feng Wu 1 ,
- Yang-jun Ren 2 ,
- Xiao-yan Liu 1 &
- Xiaomei Yuan 3
Scientific Reports volume 14 , Article number: 8400 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Energy and society
- Environmental economics
- Sustainability
Due to the increased frequency of extreme weather events and the implementation of the China’s dual-carbon target, thermal power companies have been under pressure to construct green infrastructure and to actively pursue low-carbon transformation in response to stricter environmental regulations. This research thus selects 30 listed thermal power enterprises in China as study objects and assesses their green investment efficiency in the low-carbon transition process using three-stage DEA evaluation model with environmental regulation as an exogenous variable. Based on this, a benchmark regression model is used to corroborate the relationship between environmental regulation and green investment. Simultaneously, we carry out analysis to compare the correlation between thermal power firms’ green investment efficiency and their focus on green investments. The results show in terms of total efficiency that environmental regulation significantly improves the total efficiency of 80% of thermal power enterprises compared to the absence of this exogenous variable. With the addition of environmental regulation, firms’ total efficiency declines gradually in general from 2018 to 2022, with the mean value of efficiency falling by 0.068. In terms of stage-specific efficiency, the efficiency of the green investment stage of the majority of firms is between 0.3 and 0.6, which is much lower than that of the operational stage and the market performance stage. In terms of sub-indicator efficiency, both green investment efficiency and social donation efficiency among thermal power enterprises show obvious polarization, with 30% of them having an efficiency of 1 and 30% less than 0.1. In terms of green investment focus, thermal power unit renovation has a more obvious role in boosting the green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises than do wind power and photovoltaic projects. Therefore, both governmental departments and thermal power enterprises need to take active measures in order to achieve green transformation from the perspective of green investment efficiency. Through the segmentation of important projects of green investment, this paper provides a reasonable investment direction reference for the sustainable transformation of China’s thermal power industry. It also provides a rich and novel theoretical basis for the Chinese government to further improve the relevant environmental protection laws and regulations of thermal power industry.
Introduction
With environmental degradation and resource depletion becoming key impediments to global economic development, the green transformation of energy firms is on the horizon. According to the Energy Institute of the United Kingdom’s 2023 Statistical Yearbook of World Energy, worldwide energy demand increased by 1% in 2022. The historic increase of renewable energy has not altered the dominance of fossil fuels, which continue to supply 82% of global energy. Governments and other international organizations, such as the World Health Organization and the United Nations Environment Programme, have been actively encouraging research into environmental pollution and its effects on development in this respect. With coordinated efforts, the share of renewable energy in the world’s energy consumption from 2021 to 2022 would be 7.5%, or up around 1% from the year before. Indeed, 84% of the increase in net electricity consumption is met by a record 12% rise in wind and solar power generation.
Thermal power generation in China has accounted for 66.6% of total power generation in 2022, or growing 1.4% year on year. As a key energy supplier, thermal power firms must undergo green transformation in order to achieve sustainable development, and achieving this goal necessitates significant green investments. Global green investment increased from US$7 billion in 2000 to US$154 billion in 2010 1 , with the majority of that growth occurring in China. According to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCC), by 2050, $125 trillion in green investments will be needed to achieve carbon neutrality. According to the United Nations climate change annual report 2021, China is the largest contributor to green investment, particularly in the energy sector, valued at $266 billion. Among them, China's thermal power industry has also made large breakthroughs in the field of green investment. For example, according to the latest analysis of the China Electricity Council, the installed non-fossil energy generation capacity of the thermal power industry exceeded the size of the installed thermal power capacity for the first time in 2023, accounting for the first time for the proportion of the total installed capacity to exceed 50%.
To promote green investment, the China government has also continued to improve the environmental regulatory system by levying environmental protection taxes and opening up the carbon emissions trading market and green subsidy system. China is gradually forming a comprehensive environmental regulatory system combining command and control, market-led, and public participation 2 , 3 . According to the China Electricity Council, between 2016 and 2021 the power industry has already reduced carbon dioxide emissions by approximately 21.51 billion tons through non-fossil energy sources, reduced coal usage in power supply, and lower line-loss rate. China has now constructed the world’s largest ultra-low emission thermal power plant cluster.
As thermal power firms are critical to energy savings and emission reduction, green investment can help drive their sustainable development and also meet market and government requirements by enhancing energy cleanliness and low carbon. Thermal power companies typically boost their green investments in the early stages of tighter environmental rules in order to enhance their brand value and company image. However, because pollution control costs are rising and profit margins are narrowing due to stricter environmental restrictions, green investments have decreased rather than increased (Fig. 1 ). Therefore, it is necessary for this study to dig deeper into the reasons behind the phenomenon—that is, the trade-off between costs and benefits of green investment in thermal power enterprises as well as the relationship between enterprise green investment efficiency and the choice of green investment focus.
China’s thermal power industry annual green investment.
Summarizing the research conducted by scholars at home and abroad in this field, there are three main limitations. First, the analysis of existing research in this field mainly focuses on developed regions or areas, and lacks research on developing countries 1 , 4 . However, the impact of environmental regulation on green investment has a strong geographical nature, and the differences in policies across countries can lead to different implementation strengths of environmental regulation by local governments. Second, due to the difficulty of obtaining data on corporate green investment, scholars' studies on green investment have mainly focused on the national or city cluster level, and lacked analysis on the corporate level 5 , 6 . Even the studies on corporate green investment are too broad in terms of industries, ignoring the fact that the impact of environmental regulations on green investment is limited by industry attributes 3 , 7 . Third, most of the existing literature uses the amount of green investments made by firms or cities, which is rather one-sided 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 . The input–output indicator system constructed with multiple variables is more comprehensive to measure the efficiency of green investment.
Therefore, this study overcomes the above shortcomings with the following three main contributions. First, it considers that changes in both the ESG index and media attention affect the financial support received by enterprises, which in turn influences the size of the funds used by enterprises for green investment projects. Therefore, this study incorporates the enterprise ESG index and media attention into the index system for assessing the green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises.
Second, there are fewer studies on the green investment efficiency of energy enterprises in developing countries, especially Chinese thermal power enterprises. This study analyzes the impact of environmental regulations on the green investment efficiency of Chinese thermal power enterprises in the context of the country’s social system, taking into account the reality of its economic development.
Third, other studies have analyzed the efficiency of green investment using mainly econometric models, which can only deal with a single efficiency assessment. This study adopts the DEA model, which is not only able to deal with multiple inputs and multiple outputs, but also avoids subjectivity due to the assignment of weights.
Literature review
Impact of green investment.
The literature on the impact of green investment of thermal power companies on their market value is divided into two main views: the promotion theory and the inhibition theory. Green investment is a form of resource allocation in thermal power companies, which can improve their environmental quality and corporate reputation by reducing the necessary investment in generating pollutants in their operations 1 . Taking listed energy companies in China as an example, some scholars have found that green investment improves their environmental performance through the reduction of environmental violations. This enhances the impact of green investment on the long-term market value of energy companies 12 . In addition, incorporating green investments into energy business strategy formulation helps reduce corporate environmental risks and prompts companies to create value in terms of social sustainability, ultimately leading to an increase in their market value 7 , 13 , 14 .
Some scholars have put forward opposite views on the impact of green investment on firm value, arguing that green investment has a negative or zero impact on firm performance. This is because green investment is relatively costly, takes away resources that companies use for normal production and operations, and usually requires a long payback period. Therefore, when enterprises conduct green investment operations, they incur a certain negative impact on cash flow and financial performance 15 . In short, green investment may have a certain inhibitory effect on the financial performance of enterprises. However, in the long term, green investments can help improve the environmental performance of energy companies, which in turn contributes to financial performance. Therefore, energy companies need to weigh inputs and outputs when making green investments as part of a long-term development strategy to achieve sustainable development.
Factors affecting green investment
The literature on green investment has a variety of research angles. Some scholars have studied the influencing factors and development trends of green investment in the energy industry in developed countries by using econometric models from the perspective of macroeconomics 5 , 9 . The results show that green investment is influenced by economic growth, interest rates, and fuel prices 1 . At the same time, policy intervention of the national government, such as an environmental tax burden, also has a positive impact on green investment 10 , 11 . In view of the impact of an environmental tax burden, some scholars have used a variety of advanced panel data methods to conduct more detailed research. The results show although taxes have a weak catalytic effect compared to other factors that well-structured environmental regulation can still significantly promote green investment by firms 6 . Therefore, governments can provide tax incentives for companies to undergo green innovation, so that companies can get help with innovative projects.
Some scholars have studied the relationship between corporate ESG ratings and green investment using linear mixed models. The results show that there is a positive correlation between green investment and corporate ESG ratings, which has a significant impact on corporate sustainable operations 8 . In addition, some studies start from the perspective of public attention. Through the use of panel data and econometric models, research has found that strict environmental regulations prompt enterprises to increase green investment 5 . Given the high energy intensity of countries in the Asia–Pacific region, some economists have examined the relationship between green investment and renewable energy deployment from a renewable energy perspective. Using Panel Pooled Mean Group (PMG) technique, the study found that green investment potential positively affects renewable energy deployment 16 . Finally, from the perspective of R&D and innovation, some scholars use multiple regression models to conduct empirical analyses, and the results show that environmental regulation, by increasing green investment, not only benefits green innovation in the region, but also contributes to the neighboring region's 17 .
No matter from which viewpoint, scholars’ analysis of green investment mainly focuses on the motivation, and the conclusions are controversial. Therefore, the reasons for the dispute need to be further analyzed. Moreover, research has mainly focused on the green investment of enterprises, lacking any analysis and evaluation on green investment efficiency.
Influence of environmental regulation on green investments
As an important means to coordinate social development and environmental protection, environmental regulation has played an important role in environmental governance in recent years by effectively guiding the environmental behavior of enterprises and individuals. Studies mainly measure environmental regulation by the cost of pollution control, capital expenditure on pollution reduction 18 , pollutant discharge 19 , environmental tax burden 6 , 20 , 21 , and so on. Based on the differences in the above measurement standards, the impact of environmental regulations on green investment can be divided into three perspectives.
Traditional economists have argued that environmental regulations inhibit firms' green investments. They believe that environmental regulation inhibits firms' green investment. This group of scholars argues that environmental regulation can inhibit green investment by imposing unnecessary costs on firms and having a crowding-out effect on investment in innovation, which reduces the productivity of firms 22 , 23 , 24 . However, some scholars, led by Porter, have challenged that view. Porter believes that environmental regulation can bring “innovation compensation effect”, which is conducive to the realization of the enterprise's environmental performance and economic performance of the joint improvement 25 . Therefore, this group of economists point out that environmental regulation will stimulate enterprises to break the inherent business model and product structure, and put pressure on enterprises to consider environmental issues, so as to realize energy saving and emission reduction 26 , 27 . In addition, a small number of scholars, based on the “factor endowment hypothesis”, believes in a non-linear relationship between environmental regulation and corporate green investment.
No matter using regression analysis or the SBM-DDF model, studies have shown an inverted U-type non-linear relationship between environmental regulation and corporate green investment 3 , 28 . In the early stage of strengthening environmental regulations, enterprises increase green investment and change production methods due to legal requirements. However, with increasing environmental regulation, there will be an inflection point in the factor endowment advantage, when the costs of green investment outweigh the benefits of complying with environmental regulations. This is also contrary to the Poter hypothesis, where high pollution control costs lead to "crowding out" of R&D investment 29 , and firms prefer to accept penalties for non-compliance rather than make more green investments.
Most of the literature acknowledges the significant impact of environmental regulation on enterprises’ green investment, but due to differences in indicators and methods adopted by each research institute, the conclusions are inconsistent. A higher level of environmental tax burden closely relates to strict environmental regulations 30 . As an economic means, an environmental tax burden can regulate the environmental behavior of thermal power enterprises by directly affecting their production and operation. Therefore, this study uses environmental tax burden to measure environmental regulation and studies its impact on the green investment efficiency of China’s thermal power enterprises. Doing so provides a theoretical basis for the government to formulate relevant policies for the sustainable development of thermal power enterprises.
- Green investment efficiency
As green investment efficiency has gradually become a crucial factor affecting the sustainable development of energy enterprises, empirical research based on DEA theory has also been widely used by scholars. Some scholars have analyzed the relationship between enterprise green investment and performance by the DEA method and panel vector autoregression method (VAR). Findings show that enterprises’ green investment inhibits productivity improvement 31 . From the perspective of environmental regulation, some scholars have introduced the learning curve theory into the traditional DEA model to describe the dynamic changes of power enterprises under different policy scenarios. The results show an interactive relationship between environmental regulation, environmental protection investment, and the sustainable development of power enterprises 32 . Environmental regulation motivates enterprises to pay attention to environmental performance, thus improving the efficiency of their green investment 33 .
Some scholars hold a different view, with some quantifying the green investment efficiency of heavy polluting enterprises through the SBM-DEA model. The results show an inverted U-shape non-linear relationship between environmental regulation and green investment efficiency of Chinese polluting enterprises 34 . Some scholars have also utilized the Tobit model and found a double effect of environmental regulation on the green efficiency of thermal power enterprises. It is specifically manifested as a U-shape non-linear relationship of first inhibition and then promotion 35 . Therefore, local governments must pay attention to the differentiation of environmental regulations in order to encourage energy enterprises to improve green investment efficiency.
From the perspective of digital empowerment, some scholars have used the SBM-DEA method to conduct quantitative analysis of the green investment efficiency of heavy polluting enterprises. Research has found that digital empowerment promotes green efficiency through increased analyst attention and greater R&D investment 36 .
In short, the green investment efficiency evaluation method based on DEA has wide application prospects in the current global low-carbon environmental protection era. These theories also provide a theoretical basis for government departments to guide the environmental management of energy enterprises.
Although there is a growing body of literature on the relationship between environmental regulation, green investment efficiency, and firm performance, there are still some limitations in this research field. In fact, most studies admit under strict environmental regulations that green investment of enterprises positively impacts their performance. However, the existing studies on the relationship between green investment and environmental regulation are relatively broad, mostly focusing on city clusters or all enterprises, and rarely focusing on a particular industry, especially the thermal power industry. As a result, the conclusions and policy recommendations are not fully applicable to all industries, and it is difficult for the government to improve environmental policies accordingly. In addition, the existing literature on green investment at the enterprise level is mainly limited to econometric methods, and there is less literature on the use of DEA models to study the efficiency of green investment in energy enterprises.
Research method
Based on the fact that the evaluation performance of the DDF non-ray distance function is better and provides more accurate estimation results, this study amends the traditional DDF model, combines the dynamic DEA model of Tone and Tsutsui 37 , and considers the exogenous problem, so as to solve the deficiencies of one-, two-, and three-stage Dynamic DDF under an exogenous DEA model. The formula runs as follows.
Assume that a decision-making unit ( \({DMU}_{j},j=1,\dots ,J\) ) has \(t (t=1,\dots ,T)\) time periods. Within each time period there are three stages: Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3.
In the first stage, there are D inputs \({x}_{ij}^{t}\left(i=1,\dots ,m\right)\) that produce P intermediate products \({z}_{Pj}^{t}\left(p=1,\dots ,P\right)\) and Q desired outputs \({o}_{qj}^{t}\left(q=1,\dots ,Q\right)\) .
The second stage uses P intermediate products \({z}_{Pj}^{t}\left(p=1,\dots ,P\right)\) and F inputs \({a}_{fj}^{t}\left(f=1,\dots ,F\right)\) to create R desired outputs \({y}_{rj}^{t}\left(r=1,\dots ,R\right)\) and S intermediate products \({u}_{sj}^{t}\left(s=1,\dots ,S\right)\) .
The third stage uses S intermediate products \({u}_{sj}^{t}\left(s=1,\dots ,S\right)\) and G inputs \({f}_{gj}^{t}\left(g=1,\dots ,G\right)\) to create L desired outputs \({n}_{lj}^{t}\left(l=1,\dots ,L\right)\) .
Stage 1 (operation stage) inputs are number of employees and thermal power installed capacity. Output is operating revenue. Stage 1 links to Stage 2 via R&D expenses.
Stage 2 (green investment stage) inputs are green investment, proportion of installed renewable energy capacity, and social donation. Output is the ESG index. Stage 2 links to stage 3 via media attention.
Stage 3 (market performance stage) input is operating costs. Outputs are enterprise market value and market share. Exogenous variable \(={A}_{vj}\left(v=1\dots V\right)\) is environmental regulation, and carry-over \({= c}_{hj}^{t}\left(h=1,\dots ,H\right)\) is fixed assets.
Here, \(j\) represents the number of each DMU, i.e., the 30 thermal power enterprises in this paper, \(t\) represents the stage, and \(i,p,q,f,r,s,g,v,h,l\) represent the order of each variable. For example, \({x}_{ij}^{t}\) stands for the i ’th input of enterprise \(j\) in stage \(t\) .
Objective function
If there is an n dimension \(DMU\) set denoted as j , where \({DMU}_{o}\) represents the \(DMU\) under evaluation and \({DMU}_{o}\in j,\) then the mathematical model is formulated as follows.
Formula ( 1 ) calculates the efficiency of \({DMU}_{o}\) . Of these, formula ( 1 ) is primarily referenced to Chiu et al 38 .
If there is an n dimension \(DMU\) set denoted as \(j\) , where \({DMU}_{o}\) represents the \(DMU\) under evaluation and \({DMU}_{o}\in j.\)
Here, GFE represents Global-Factor Efficiency. \({\gamma }_{t}\) is the weight assigned to period t, and \({w}_{1}^{t}\) , \({w}_{2}^{t}\) , and \({w}_{3}^{t}\) are the weights assigned to Stage 1 efficiency, Stage 2 efficiency, and Stage 3 efficiency, respectively. Therefore, \({w}_{1}^{t}\) , \({w}_{2}^{t}\) , and \({w}_{3}^{t}\) and \(\sum_{t=1}^{T}{\gamma }_{t}=1\) .
Exogenous variable and links of stages
The exogenous variable is formula ( 2 ). Of these, formula ( 2 ) is primarily referenced to Li et al 39 .
Here, \( \lambda_{j}^{t} ,\;\mu_{j}^{t} ,\;\rho_{j}^{t}\) denote the weights of the benchmarking for \({DMU}_{o}\) in the first, second and three stages, respectively.
Stage 1 and Stage 2 links are formula ( 3 ). Stage 2 and Stage 3 links are formula ( 4 ). The two periods of links are formula ( 5 ). Of these, formula ( 3 ), (4), (5) is primarily referenced to Lu et al 40 .
Overall efficiency, period efficiency, stage efficiency, and period stage efficiency can be obtained from the above results.
Sub-efficiency values
The sub-efficiency values of the variables in this study are calculated in accordance with the Total-Factor Efficiency (TFE) indicator published by Hu and Wang 41 via the following equation.
Input variables and good output variables are formulae (6) and (7), respectively.
If the value of total factor efficiency is 1, then the efficiency target has been achieved; conversely, it means that there is an excess of inputs or a shortage of outputs, indicating that there is room for improvement.
Empirical analysis
Data description.
This paper selects data from 30 listed thermal power companies in China from 2018 to 2022. The selection is based on thermal power listed companies that are ranked among the top 30 in market capitalization on the Flush Financial Data Platform as of the end of 2022 and have been listed for more than five years. The abbreviations of the sample companies are in “ Appendix A ”. Since the green investment path of listed thermal power companies is not unique, different companies illustrate differentiated transformation by combining their own advantages.
Studies vary in their division of green investments. According to the green financial products invested, they can be divided into green credit, green securities, and green insurance 42 . According to the use of green investment project funds, they can be divided into expenditures for environmental pollution control and expenditures for environmental infrastructure construction 43 . As the research object of this paper is thermal power listed enterprises, power generation projects are the key aspects of their main business and green investments. Therefore, this paper classifies the green investments of enterprises into three types according to the energy type of the project by analyzing the important ongoing projects of thermal power enterprises: the transformation of thermal power units, photovoltaic projects and wind power projects (Table 1 ).
A new energy project is a national key support project that can effectively reduce the carbon emissions of enterprises. From the viewpoint of power generation cost, the cost of photovoltaic power generation has been reduced to parity and even lower than the cost of thermal power. From the viewpoint of geographical adaptability, wind power projects can be built in cities, suburbs, villages, and coastal areas with strong geographical adaptability. However, the instability of a wind project determines that thermal power units need to be used as a peaking power source to ensure stable operation of the grid. A new energy project construction cycle is longer, and it is difficult to achieve results in the short term. Therefore, thermal power companies still carry out thermal power unit renovation to maintain their stable operation.
Among the enterprises in the sample of this study, there are 25, 18, and 11 carrying out thermal power unit renovation, Photovoltaic projects, and wind power projects, respectively. There are 5 enterprises carrying out all three types of projects at the same time. Finally, 13 enterprises carry out both types of projects at the same time.
This study evaluates the number of employees, installed thermal power capacity, operating revenue, R&D expenses, green investment, proportion of installed renewable energy capacity, social donations, ESG index, media attention, operating costs, enterprise market value, market share, fixed assets, and environmental regulation of the sample companies from 2018 to 2022. Among them, Min–Max normalization is performed on the raw data of the proportion of installed renewable energy capacity and market share. The research framework based on the three-stage parallel DEA model with relevant indicators is given in Fig. 2 .
Research framework based on three-stage parallel DEA modeling.
The main design ideas of the three-stage DEA model in this paper are as follows. First, the process of assessing the green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises is divided into operation stage (Stage 1), green investment stage (Stage 2), and market performance stage (Stage 3). The first stage is operation. Thermal power enterprises through the normal operation and profitability in this stage lay a good foundation for subsequent green investment. Thermal power installed capacity and the number of employees is mainly selected as inputs, and operating revenue and R&D expenses are outputs. The R&D expenses are continuously invested into the second stage as supportive funds for green investment.
Second, the second stage is green investment. Green investment, the proportion of installed renewable energy capacity, and social donations are taken as inputs. The ESG index and media attention are taken as outputs.
Finally, the third stage is market performance. Media attention is used as an input in the third stage to characterize its important role in a firm’s market performance. Operating costs are an input. Market value and market share are outputs. The T and T + 1 stages are connected through the carry-over variable of fixed assets. Table 2 below specifically explains each indicator.
Descriptive statistics
Due to space limitation, only major variables are selected for statistical description in this paper. Green investment stage is a key turning point for thermal power enterprises to achieve sustainable development and plays an important role in the steady operation of enterprises. Therefore, the selected indicators are categorized into two types for statistical description herein: operation and market indicators and sustainability indicators. Their mean, maximum, and standard deviation are calculated respectively, and the results are rounded to two decimal places. Figures 3 and 4 show the statistical description of the two categories of variables by year.
( a – d ) Descriptive statistics of operating and marketability variables.
( a – d ) Descriptive statistics of sustainability variables.
In terms of the operation and market performance of thermal power enterprises, their installed capacity (Fig. 3 a) has been relatively stable in recent years. R&D expenses (Fig. 3 b) have increased year by year, and the growth rate is also increasing year by year. By raising R&D expenses, thermal power enterprises can carry out technological innovation to develop new products or new energy technologies, thus improving their production and operational efficiency. In addition, although the market value of enterprises (Fig. 3 c) has obvious fluctuations, the market share (Fig. 3 d) is generally stable and does not show large changes.
Looking at the sustainability of thermal power firms, first, social donation (Fig. 4 a) is far more volatile than the other variables, with 2019 leading the five-year period in terms of this factor. Second, green investment (Fig. 4 b), which had been trending upward in the previous four years, suddenly declined in 2022, possibly due to increased environmental regulations. Finally, the steady growth trend in the proportion of installed renewable energy capacity (Fig. 4 c) and the high level of the ESG index (Fig. 4 d) reflect that companies are actively pursuing a green and low-carbon transition.
Empirical result analysis
Total efficiency analysis.
This study considers the inclusion of exogenous variables and the absence of exogenous variables separately when assessing each DMU. According to the empirical results of this paper, after adding exogenous variables, the green investment efficiencies of 24 out of 30 firms significantly improve. Without considering exogenous factors, the average value of the overall efficiency of enterprises is 0.553, and 10 enterprises have total efficiency greater than 0.6. After considering exogenous factors, the mean value of overall efficiency is 0.591, and 13 thermal power enterprises have total efficiency greater than 0.6. Obviously, environmental regulation as an exogenous variable in the model significantly improves the underestimation of enterprises’ green investment efficiency.
As can be seen from Fig. 5 , the green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises was at its lowest in 2019 at 0.501 and hit its peak in 2021 at 0.590. The overall trend is that it first declines, then improves, and finally declines again. In 2018–2019, at the beginning of the strengthening of environmental regulations, the increased cost of thermal power enterprises for pollution control had a crowding out effect on innovation investment. This also led to a decline in the green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises, from 0.553 to 0.501. With the implementation of environmental policies, enterprises are forced to develop cleaner and more environmentally friendly production methods due to pressure from the environmental tax burden. For example, the renovation of thermal power units and the development of new energy projects spurred the green investment efficiency of enterprises to increase by 8.9% in two years. However, as the proportion of new energy connected to the grid increases, the power system is not flexible enough, and the problem of consumption gradually emerges. The green investment efficiency of enterprises thus exhibits a significant decrease.
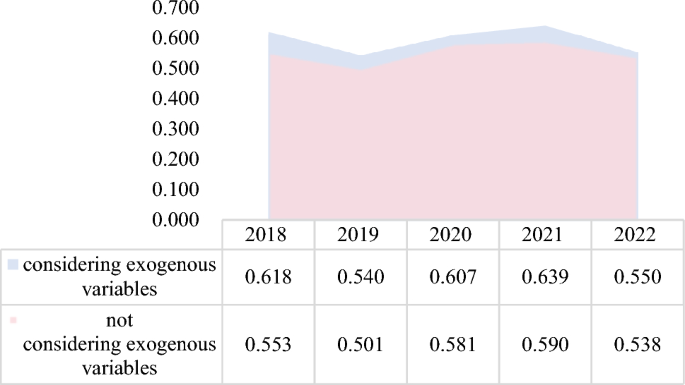
Average green investment efficiency (2018–2022).
Of the 24 thermal power companies that have improved after adhering to the environmental regulation, 18 companies are carrying out retrofitting of thermal power units and 15 are carrying out photovoltaic projects. Relatively fewer firms, less than half, are targeting the construction of wind power projects. Among the top 10 enterprises with the strongest improvement effect, 80% of them have carried out thermal power unit renovation. Obviously, enterprises prefer to realize the improvement of their green investment efficiency by retrofitting thermal power units. On the one hand, retrofitting thermal power units is flexible and has a low cost compared to new energy construction. Thermal power units can operate stably for a long period of time and adjust their output according to power demand. On the other hand, photovoltaic projects and wind power projects have strong volatility, homogeneity and require flexible resource packages to solve the consumption problem. In the case of a significant increase in electricity load, wind and solar clean resources are difficult to provide enough controllable power.
In China there are still provinces with a significant problem of abandoned wind or abandoned light. They include Inner Mongolia, Qinghai, Gansu, and other wind power provinces. Some areas of wind power or photovoltaic power only have a utilization rate of 90%. Therefore, compared with Photovoltaic projects and wind power projects, companies can more feasibly improve their total efficiency through the renovation of thermal power units.
By comparing the green investment efficiency of the top 5 and bottom 5 thermal power enterprises, this paper finds that efficiency significantly improves after considering exogenous variables. As seen from Fig. 6 , the green investment efficiency value of each thermal power enterprise varies greatly. Among them, DHEP has the lowest green investment efficiency value of 0.341, which is only 1% higher than the case without considering environmental regulation. DLPC has the highest efficiency value of 0.960, which is an increase of nearly 10% over the case without taking into account exogenous factors. The improvement is significant. Therefore, the impact of environmental regulations on DLPC is much greater than that on DHEP. This may be due to the fact that DHEP is higher than DLPC in terms of enterprise size, capital cost, and technical feasibility. Its investment in green innovation has already reached a high level, and so the improvement rate is not as high as DLPC. In addition, DHEP’s fuel costs increased by U$$2.953 billion year-over-year in 2021 due to the increase in the unit price of standard coal used for power generation. The significant increase in operating costs leads to a company’s lower gross margin and continued losses. In turn, the focus on green investments continues to diminish, and the efficiency of green investments is bound to decrease.
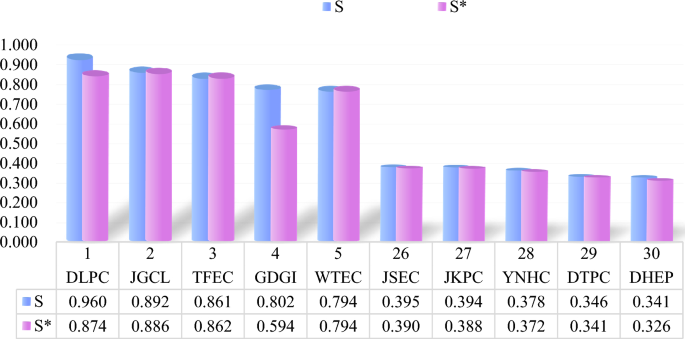
Total efficiency values of thermal power enterprises (top and bottom 5). Notes : The ranking is based on the efficiency value after adding exogenous variables. S means considering exogenous variables. S* means not considering exogenous variables.
In terms of the magnitude of improvement, the impact of environmental regulation on GDGI ranks first among the sample firms, with a 20.8% improvement in green investment efficiency. On the one hand, GDGI's earnings continue to be high, and there is enough capital to build on green investments. On the other hand, environmental regulations have been strengthened, and significant results have been achieved in green investments. Therefore, a company can decide to continue to invest in green investments in the future and continue to invest in research and development. From thermal power generation to multiple energy sources, GDGI has always adhered to the direction of clean energy development. The improvement of its green investment efficiency is also an inevitable trend.
In conclusion, environmental regulations have a more significant impact on the green investment efficiency of Chinese thermal power companies. During the period from 2018 to 2022, the average value of the environmental tax burden paid by enterprises is generally increasing. Environmental regulations force thermal power enterprises to improve their production and operation methods by increasing their environmental management costs. Moreover, thermal power enterprises combine their own advantages to carry out green transformation of industrial structure. While realizing green and high-quality development, they also promote the improvement of green investment efficiency.
Stage efficiency analysis
Efficiency analysis of operation stage (stage 1).
In the operation stage, this study includes the number of employees, installed thermal power capacity, and operating revenue in the input–output index system of this stage. According to the empirical results of this paper, during the period from 2018 to 2022 the efficiency of thermal power enterprises in the operation stage performs well with an overall mean value of 0.613. However, there are still some enterprises with low efficiency in this stage, such as DTPC, whose efficiency value fluctuates around 0.2 or less than one-third of the average value.
As seen from Fig. 7 , the inclusion of environmental regulation can significantly increase the efficiency of thermal power enterprises in the operation stage. The collection of environmental taxes raises the production costs of highly polluting enterprises, thus promoting the optimal allocation of resources and industrial restructuring. For thermal power enterprises, the collection of environmental taxes pushes them to pay more attention to the development of clean energy and to increase investment in renewable energy. By optimizing the industrial structure, the energy efficiency of thermal power enterprises will improve. In response to the role of exogenous variables in this stage, BNEC is most strongly affected, mainly because BNEC is driven by environmental regulations and focuses on the level of cost optimization and energy savings. It is a commitment to operational efficiency improvement whose improvement effect is as high as 0.462 in 2019.
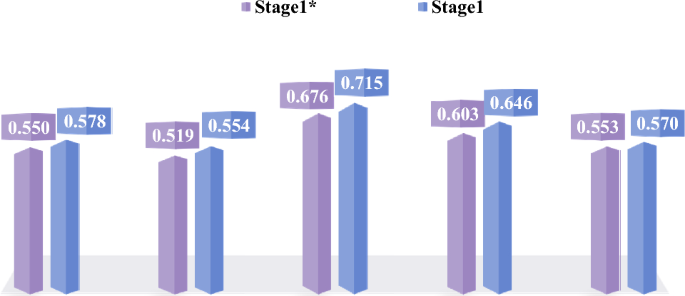
Average value of efficiency in operation stage (2018–2022). Notes : Stage1 means considering exogenous variables. Stage1* means not considering exogenous variables.
After 2020 in the late period of strengthening environmental regulations, the operational efficiency of thermal power enterprises has significantly weakened. The average efficiency fell by 14.5% in two years, perhaps due to the need for thermal power companies to invest more resources and funds in technology upgrades in order to meet more stringent environmental requirements. Therefore, for improving energy efficiency and reducing pollutant emissions, there will be some technical or economic restrictions that result in the decline of efficiency at this stage. In summary, environmental regulations can, to some extent, lead to higher efficiency values by inducing improvements in energy use efficiency and reductions in pollutant emissions during the operational stage of an enterprise. However, with increased pressure on profitability, thermal power companies may encounter some constraints in this regard, leading to a slowdown or decline in the rate of improvement of efficiency values.
Efficiency analysis of green investment stage (Stage 2)
The green investment stage is an indispensable part of thermal power enterprises to realize sustainable development. This study includes green investment, the proportion of installed renewable energy capacity, social donations, and the ESG index into the input–output index system of this stage. Table 3 shows the efficiency value of green investment stage of thermal power enterprises selected by this paper with more typical performance in this stage.
The inclusion of environmental regulations has somewhat increased the efficiency value of the green investment stage of thermal power companies during the period from 2018 to 2022. This may be due to the fact that environmental regulation incentivizes firms to approach the green investment business in a more prudent and proactive manner, which in turn promotes green investment efficiency. However, nearly one-third of the thermal power firms, such as HDEC and TFEC (Table 3 ), have reached the optimal efficiency value before the addition of the exogenous variables, and thus there is no significant improvement.
With the increase of environmental regulation pressure, the efficiency value of thermal power companies in the green investment stage shows a large decline. It falls from 0.566 in 2018 to 0.307 in 2022 or a drop of 25.9% (Fig. 8 ). Even though there is a slight rebound during the period, it again shows a more substantial fall in the following year. This is mainly due to the thermal power enterprises in the process of accelerating the development and utilization of clean energy illustrating that new energy generation will have difficulties in sending out and consuming. The wind turbines and photovoltaic equipment in many areas have been left idle for a long time.
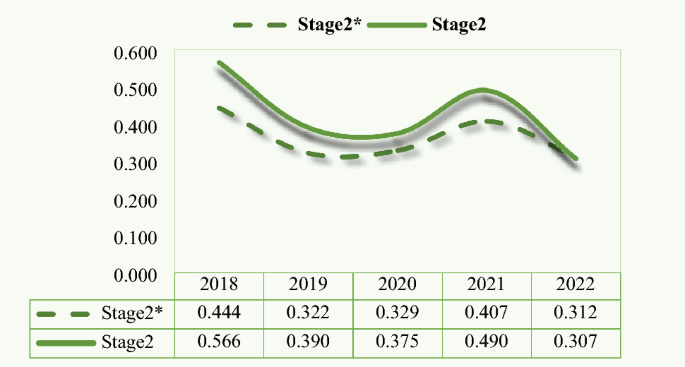
Average efficiency of green investment stage (2018–2022). Notes : Stage2 means considering exogenous variables. Stage2* means not considering exogenous variables.
The phenomenon of abandoning light and wind is serious. Moreover, supply chain issues and downward economic pressure due to COVID-19 could have also hindered green investments by thermal power companies between 2021 and 2022. However, some companies have bucked the trend. For example, GEPC’s green investment stage efficiency grew from 0.047 to 0.112, or an improvement of nearly three times.
Compared with the other two stages, the green investment stage has the lowest average efficiency value, between 0.3 and 0.6, and the largest difference in efficiency between enterprises. This is reflected in the serious bifurcation of the efficiency values of the sample enterprises in this stage. The difference between high-efficiency and low-efficiency enterprises is even close to 100%, which is also directly linked to the green investment focus of thermal power companies. Retrofitting thermal power units not only has greater potential and lower investment costs, but also smoothes out the impact of new energy power on the grid.
Thermal power units have a stronger role in improving the efficiency of the green investment stage. For example, JGCL’s green investment projects during this five-year period were dominated by the renovation of thermal power units and supplemented by the construction of new energy projects (Table 3 ). Thus, JGCL has always maintained a high level of efficiency in the green investment stage. By contrast, HDPC focuses on the construction of new energy projects, such as photovoltaic projects and wind power projects. Therefore, its efficiency in this stage is lower (Table 3 ).
Efficiency analysis of market performance stage (Stage 3)
Thermal power firms have the highest efficiency values in the market performance stage compared to the efficiency values in the other two stages. There is also not much difference in the efficiency values among the firms. Except for a few firms such as JNPC, NMHD, and SNPC, most of the other firms have efficiency values fluctuating around 0.7 in this stage. At this stage, the inclusion of environmental regulations had a relatively small effect on improving efficiency, with most firms improving by less than 5%. Overall, the market performance stage efficiency increased year-on-year with the strengthening of environmental regulations and rose much higher than the operational stage (Fig. 9 ). The unusual performance in 2018 was due to the multiple adjustments in the domestic refined petroleum product market along with the increase in coal prices during the year. They had a dampening effect on the efficiency of most thermal power companies, especially JGCL, in the market performance stage.
Average efficiency of market performance stage (2018–2022). Notes : Stage3 means considering exogenous variables. Stage3* means not considering exogenous variables.
The collection of environmental taxes will prompt thermal power enterprises to increase their investment in and development of clean energy. Thus, it will guide enterprises toward restructuring, transformation, and upgrading. For example, GDGI has not only raised its R&D investment year by year, but also continued to increase mergers and acquisitions of high-quality assets and clean energy to optimize its industrial layout.
There are some firms that are not sensitive to environmental regulation. For example, DTPC and HNPC, whose efficiency values in the market performance stage did not improve more significantly from the environmental tax burden (Table 4 ). The pressure of environmental regulations burden increases the cost of highly polluting and inefficient thermal power firms. For firms adopting clean energy and high efficiency technologies, their costs will be relatively lower. This leads to the exit of inefficient thermal power firms from the market. In turn, high-efficiency firms have the opportunity to expand their market share and increase their efficiency value in the market performance stage.
Sub-index efficiency analysis
Due to space limitations, only the main indicators are selected for sub-indicator efficiency analysis in this paper. Table 5 reflects the average values of the efficiency of the main indicators of Chinese thermal power enterprises from 2018 to 2022 with and without considering exogenous variables.
First, the efficiency of installed thermal power capacity directly affects the power generation capacity and capacity level of the enterprise. Hence, it is an important factor for thermal power enterprises to maintain normal business management. After considering the exogenous variable of environmental regulation, the average value of thermal power firms’ installed capacity efficiency increases in most years and peaks at 0.730 in 2020 (Table 5 ). A few firms are insensitive to the role of environmental regulation, such as JKPC and JNPC. Most companies show a very clustered thermal power installed capacity efficiency of 0.5 or more from 2018 to 2022. For highly polluting and inefficient thermal power units, environmental regulation will increase the operating costs of thermal power enterprises. Therefore, companies will actively adopt energy saving and emission reduction measures and emphasize technological innovation, such as vigorously renovating thermal power units and developing clean energy projects. For example, SNCL has invested in a number of hydrogen energy projects, driven by environmental regulation.
Second, enterprises’ market value efficiency stays at a high level from 2018 to 2021, yet declines substantially in 2022, as in the case of AHWC and GEPC. The inclusion of environmental regulations improves the average market value efficiency of thermal power firms in all years except 2022. In particular, in 2018 the average market value efficiency improves by as much as 15.9%. Environmental regulations can incentivize firms to adopt more environmental protection measures to reduce pollutant emissions, such as ultra-low emissions and desulfurization and denitrification technologies. However, in the late stage of environmental regulation strengthening, the obstruction of new energy construction and excessive cost burden can inhibit the market value efficiency of enterprises. Their average value of efficiency decreases by two-thirds from 0.931 in 2018 to 0.619 in 2022 (Table 5 ). For example, in 2018 to 2021, DTPC and DLPC have reached the optimal point of their enterprises’ market value indicator efficiency in yearly increments under the pressure of the environmental regulation. In 2022, however, excessive cost burdens led to a significant decline in firm market efficiency, or far less than half of what it was in 2021.
Third, with the strengthening of environmental regulations, the average green investment efficiency value of thermal power enterprises has been declining in fluctuation over the five-year period. The average green investment efficiency value is the highest in 2018 at 0.595, while 2022 has the lowest efficiency at 0.274 or less than half of that in 2018 (Table 5 ). Green investment efficiency rebounds considerably in 2021, but then deteriorates sharply in the following year, going from 54.2 to 27.4%. SEPC and GDGI have seen a typical plunge in the efficiency of their green investments, with a decline of almost 100%. This is mainly due to the fact that companies pay more attention to compliance in order to avoid being fined or facing other legal risks. This ultimately results in companies not being able to fully utilize the benefits of green investment.
After adding exogenous variables, the average green investment efficiency of the 30 thermal power companies has improved in the previous four years. Especially for BNEC, the addition of environmental regulation directly doubles its efficiency value several times to reach optimal efficiency. During this period, the average social donation efficiency value has fluctuated slightly, but overall, it is still slowly decreasing. The average social donation efficiency value in 2018 ranked first among the five years at 0.520 (Table 5 ). It is worth noting that both green investment efficiency and social donation efficiency of thermal power enterprises are bifurcated. High-efficiency enterprises, such as DLPC and HDEC, achieve an optimal efficiency of 1 for both green investment efficiency and social donation efficiency. However, more than half of the enterprises have both efficiencies of almost 0. This phenomenon may relate more to the enterprises’ view of social responsibility and their own operation situation.
Finally, the ESG index efficiency of most thermal power companies is decreasing year by year, from 0.907 to 0.486. This is mainly due to the fact that companies will reduce the financial pressure from an environmental tax burden by lowering environmental protection investment, which leads to the inability to fully utilize the benefits of ESG index efficiency. In the first two years, the inclusion of exogenous variables can improve the average ESG index efficiency of thermal power enterprises. However, in the latter three years, environmental regulation shows an inhibitory effect on it, and the inhibitory impact increases year by year. In 2022 the inhibitory effect of environmental regulations on the ESG index efficiency of thermal power companies hit 22.8%. This causes the average ESG index efficiency of firms to fall from 0.714 to 0.486 (Table 5 ). However, there are also firms that show an abnormal rise. For example, CEPC’s ESG index efficiency has been positively affected by environmental regulation with a small increase in efficiency values.
Regression analysis
where i denotes the individual company, t denotes the year, \({Green investment}_{it}\) denotes the amount of green investment of the thermal power enterprise, \({Environmental\; regulation}_{it}\) denotes the environmental tax burden paid by the thermal power enterprise, \({\gamma }_{t}\) denotes the time fixed effect, and \({\varepsilon }_{it}\) is the random perturbation term.
In order to further verify the impact of environmental regulation on green investment, this paper carries out a benchmark regression for formula ( 8 ). The regression results show that environmental regulation is significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that environmental regulation can promote the green investment of thermal power enterprises. On the one hand, under the pressure of environmental regulation, thermal power enterprises will actively make green investment for tax incentives. On the other hand, environmental regulation will increase the cost pressure on thermal power enterprises, which will encourage them to make green investment to reduce their pollutant emissions. This result further confirms the accuracy of the above DEA model evaluation (Table 6 ).
Conclusions and suggestions
The above analysis shows that environmental regulation improves the green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises. This is similar to the view of some scholars 26 , 27 , 33 , 44 . Environmental regulation improves the green investment efficiency of enterprises by encouraging them to use low-carbon technologies, which have a positive effect in promoting the sustainable development of enterprises. Some studies have also suggested that the relationship between environmental regulation and green investment is nonlinear 45 , 46 , 47 , mainly because the relationship is affected by industry and regional differences. Most thermal power enterprises are polluting enterprises, which are more sensitive to the role of environmental regulation and also bear a higher degree of pressure to spend on environmental protection compared to their own environmental pollution.
With the continuous strengthening of environmental regulation, the green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises will gradually decrease. This is slightly different from some of the scholars’ research on heavily polluting enterprises 4 , 34 , 48 . It may be due to the fact that our study just selects the relevant data of thermal power enterprises within 5 years. Only some of the old power plants in thermal power enterprises are heavy polluters, and so there is some difference for the future trend of green investment efficiency.
Although the results of this study show a correlation between the green investment focus of thermal power enterprises and their green investment efficiency, there may still be some errors. Future research should explore the specific reasons for the changes in green investment efficiency in depth, taking into account the geographical location of thermal power enterprises and the impact of the policy environment. This will provide a more comprehensive analysis for the literature on green investment efficiency.
Conclusions
This paper draws the following conclusions by evaluating the operational, green investment and market performance efficiencies of 30 listed thermal power companies from 2018 to 2022, and regressing environmental regulation on green investment.
In terms of total efficiency, 80% of the sample firms show a significant improvement in total efficiency with the addition of environmental regulations compared to without exogenous variables. Among them, the improvement of GDGI is the most prominent. The addition of environmental regulations can force high-polluting enterprises to emphasize green innovation through the R&D mechanism, which turn plays a positive role in promoting the total efficiency of thermal power enterprises. However, with the addition of environmental regulations, the total efficiency of thermal power firms exhibits a slight decreasing trend between 2018 and 2022. This is associated with cost pressures on firms and the long-term nature of the reduction in green investments.
In terms of stage-specific efficiency, more than 60% of thermal power firms’ green investment stages are less efficient as a result of stronger environmental regulations. Compared with the operation and market performance stages, the green investment stage has the lowest efficiency at an overall average value between 0.3 and 0.6. This suggests that the green investment stage is a more difficult stage in the development process of thermal power enterprises and needs to be emphasized by enterprises.
In terms of indicative efficiency, there is a serious bifurcation in the green investment efficiency and social donation efficiency of thermal power enterprises. The difference between high-efficiency enterprises and low-efficiency enterprises even reaches 100%. This is strongly linked to the low-carbon transition strategy and operational financial status among thermal power enterprises.
In the benchmark regression analysis, environmental regulation is significantly positive at the 1% level, indicating that environmental regulation promotes green investment in electric utilities. This further confirms the accuracy of the DEA assessment.
In terms of the green investment focus of thermal power companies, compared to new energy construction, such as photovoltaic and wind power projects, thermal power unit retrofits are more effective in improving green investments in terms of economics and dexterity. Among the top 10 thermal power companies with the strongest improvement effect, eight of them have undertaken thermal power unit retrofits. Thermal unit retrofits are not only cheaper, but can also promote coal power and renewable energy interconnections. Therefore, their effect on energy utilization efficiency and green investment efficiency is more obvious.
Suggestions
Suggestions for thermal power enterprises.
First, thermal power enterprises should pay particular attention to green investment in the process of low-carbon transformation. Enterprises should not only target the expansion and upgrading of thermal power units, but also promote mature energy and low-carbon technologies.
Second, thermal power enterprises should achieve differentiated transformation according to their own situation. Due to wind power, photovoltaic and other new energy generation efficiencies are not high, and in the short term they cannot provide reliable power support. Thus, coal power installed capacity also needs to maintain reasonable growth.
Finally, thermal power companies should strengthen information disclosure. Through open and transparent information, investors can understand the enterprise’s green investment situation and the progress of low-carbon transformation as well as enhance investor confidence. In addition, through information disclosure, thermal power enterprises can also learn from the successful experience and lessons of other enterprises in order to improve their own green investment efficiency.
Suggestions for government departments
First, government departments should formulate medium- and long-term plans for the transformation of the thermal power industry as early as possible. The formulation of environmental regulations should be coordinated with market operation mechanisms. They can guide thermal power enterprises to form a market competition pattern for green investment. Governments can also provide policy preferences to enterprises that meet environmental protection standards and formulate and implement further incentive policies.
Second, in view of the phenomenon of increasing wind and solar curtailment in some local areas, government departments should coordinate solutions to the large-scale development and high-level consumption of new energy. When implementing unified dispatch across the entire grid, the State Grid Corporation should break through inter-provincial barriers, accelerate the construction of a new power system, and minimize the start-up period of thermal power as much as possible. At the same time, it can implement mandatory consumption of new energy across the entire grid. When wind and solar energy are curtailed, it can obligatorily reduce the output of matched thermal power and prioritize the transmission of new energy.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Eyraud, L., Clements, B. & Wane, A. Green investment: Trends and determinants. Energy Pol. 60 , 852–865 (2013).
Article Google Scholar
Zhang, J. X., Cai, N. & Yang, C. Impact of environmental regulation on green growth index of industry in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 25 (1), 24–31 (2015).
CAS Google Scholar
Huang, L. & Lei, Z. How environmental regulation affect corporate green investment: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 279 , 123560 (2021).
Leiter, A. M., Parolini, A. & Winner, H. Environmental regulation and investment: Evidence from European industry data. Ecol. Econ. 70 (4), 759–770 (2011).
Liao, X. Public appeal, environmental regulation and green investment: Evidence from China. Energy Pol. 119 , 554–562 (2018).
Sharif, A., Kocak, S., Khan, H. H. A., Uzuner, G. & Tiwari, S. Demystifying the links between green technology innovation, economic growth, and environmental tax in ASEAN-6 countries: The dynamic role of green energy and green investment. Gondwana Res. 115 , 98–106 (2023).
Article ADS Google Scholar
Zhang, D. & Kong, Q. Renewable energy policy, green investment, and sustainability of energy firms. Renew. Eng. 192 , 118–133 (2022).
Cao, M., Duan, K. & Ibrahim, H. Green investments and their impact on ESG ratings: An evidence from China. Econ. Lett. 232 , 111365 (2023).
Zhang, H., Shao, Y., Han, X. & Chang, H. L. A road towards ecological development in China: The nexus between green investment, natural resources, green technology innovation, and economic growth. Res. Pol. 77 , 102746 (2022).
Shen, F. et al. The effect of economic growth target constraints on green technology innovation. J. Environ. Manag. 292 , 112765 (2021).
Ramanathan, R., He, Q., Black, A., Ghobadian, A. & Gallear, D. Environmental regulations, innovation and firm performance: A revisit of the Porter hypothesis. J. Clean. Prod. 155 , 79–92 (2017).
Chen, Y. & Ma, Y. Does green investment improve energy firm performance?. Energy Pol. 153 , 112252 (2021).
Tang, M., Walsh, G., Lerner, D., Fitza, M. A. & Li, Q. Green innovation, managerial concern and firm performance: An empirical study. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 27 (1), 39–51 (2018).
Saunila, M., Ukko, J. & Rantala, T. Sustainability as a driver of green innovation investment and exploitation. J. Clean. Prod. 179 , 631–641 (2018).
Wu, W., Liu, Y., Wu, C. H. & Tsai, S. B. An empirical study on government direct environmental regulation and heterogeneous innovation investment. J. Clean. Prod. 254 , 120079 (2020).
Wang, Y. & Xu, A. Green investments and development of renewable energy projects: Evidence from 15 RCEP member countries. Renew. Eng. 211 , 1045–1050 (2023).
Li, C. J., Razzaq, A., Irfan, M. & Luqman, A. Green innovation, environmental governance and green investment in China: Exploring the intrinsic mechanisms under the framework of COP26. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 194 , 122708 (2023).
Gray, W. B., Shadbegian, R. J., Wang, C. & Meral, M. Do EPA regulations affect labor demand? Evidence from the pulp and paper industry. J. Environ. Econ. Manag. 68 (1), 188–202 (2014).
Xing, Y. & Kolstad, C. D. Do lax environmental regulations attract foreign investment?. Environ. Resour. Econ. 21 , 1–22 (2002).
Krass, D., Nedorezov, T. & Ovchinnikov, A. Environmental taxes and the choice of green technology. Prod. Oper. Manag. 22 (5), 1035–1055 (2013).
Hieu, V. M. Influence of green investment, environmental tax and sustainable environment: Evidence from ASEAN countries. Int. J. Energy Econ. Policy 12 (3), 227–235 (2022).
Yuan, B. & Xiang, Q. Environmental regulation, industrial innovation and green development of Chinese manufacturing: Based on an extended CDM model. J. Clean. Prod. 176 , 895–908 (2018).
Orsato, R. J. Competitive environmental strategies: When does it pay to be green?. Calif. Manag. Renew. 48 (2), 127–143 (2006).
Arouri, M. E. H., Caporale, G. M., Rault, C., Sova, R. & Sova, A. Environmental regulation and competitiveness: Evidence from Romania. Ecol Econ. 81 , 130–139 (2012).
Porter, M. E. & Linde, C. V. D. Toward a new conception of the environment-competitiveness relationship. J. Econ. Perspect. 9 (4), 97–118 (1995).
Lv, C., Shao, C. & Lee, C. C. Green technology innovation and financial development: Do environmental regulation and innovation output matter?. Energy Econ. 98 , 105237 (2021).
Zhao, L., Zhang, Y., Sadiq, M., Hieu, V. M. & Ngo, T. Q. Testing green fiscal policies for green investment, innovation and green productivity amid the COVID-19 era. Econ. Change Restruct. 56 (5), 2943–2964 (2023).
Zhang, J. et al. The impact of environmental regulations on urban Green innovation efficiency: The case of Xi’an. Sust. Cities Soc. 57 , 102123 (2020).
Ouyang, X., Li, Q. & Du, K. How does environmental regulation promote technological innovations in the industrial sector? Evidence from Chinese provincial panel data. Energy Pol. 139 , 111310 (2020).
Dean, J. M., Lovely, M. E. & Wang, H. Are foreign investors attracted to weak environmental regulations? Evaluating the evidence from China. J. Dev. Econ. 90 (1), 1–13 (2009).
Lundgren, T. & Zhou, W. Firm performance and the role of environmental management. J. Environ. Manag. 203 , 330–341 (2017).
Ji, X., Li, G. & Wang, Z. Impact of emission regulation policies on Chinese power firms’ reusable environmental investments and sustainable operations. Energy Pol. 108 , 163–177 (2017).
Iyer, G. C., Clarke, L. E., Edmonds, J. A., Hultman, N. E. & McJeon, H. C. Long-term payoffs of near-term low-carbon deployment policies. Energy Pol. 86 , 493–505 (2015).
Chen, Y. & Feng, J. Do corporate green investments improve environmental performance? Evidence from the perspective of efficiency. China J. Account. Stud. 7 (1), 62–92 (2019).
Bai, Y., Hua, C., Jiao, J., Yang, M. & Li, F. Green efficiency and environmental subsidy: Evidence from thermal power firms in China. J. Clean. Prod. 188 , 49–61 (2018).
Liao, F., Hu, Y., Sun, Y. & Ye, S. Does digital empowerment affect corporate green investment efficiency?. Environ. Dev. Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-023-03591-5 (2023).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Tone, K. & Tsutsui, M. Network DEA: A slacks-based measure approach. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 197 (1), 243–252 (2009).
Chiu, Y. H., Huang, C. W. & Ma, C. M. Assessment of China transit and economic efficiencies in a modified value-chains DEA model. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 209 (2), 95–103 (2011).
Li, L. B., Liu, B. L., Liu, W. L. & Chiu, Y. H. Efficiency evaluation of the regional high-tech industry in China: A new framework based on meta-frontier dynamic DEA analysis. Socio-Econ-Plan-Sci. 60 , 24–33 (2017).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Lu, L. C., Chiu, S. Y., Chiu, Y. H. & Chang, T. H. Three-stage circular efficiency evaluation of agricultural food production, food consumption, and food waste recycling in EU countries. J. Clean. Prod. 343 , 130870 (2022).
Hu, J. L. & Wang, S. C. Total-factor energy efficiency of regions in China. Energy pol. 34 (17), 3206–3217 (2006).
He, L. Y., Zang, L. H., Zhong, Z. Q., Wang, D. Q. & Wang, F. Green credit, renewable energy investment and green economy development: Empirical analysis based on 150 listed companies of China. J. Clean. Prod. 208 , 363–372 (2019).
Han, Y. Impact of environmental regulation policy on environmental regulation level: A quasi-natural experiment based on carbon emission trading pilot. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 , 23602–23615 (2020).
Kesidou, E. & Demirel, P. On the drivers of eco-innovations: Empirical evidence from the UK. Res. Pol. 41 (5), 862–870 (2012).
Ai, Y. H., Peng, D. Y. & Xiong, H. H. Impact of environmental regulation intensity on green technology innovation: From the perspective of political and business connections. Sustainability. 13 (9), 4862 (2021).
Perino, G. & Requate, T. Does more stringent environmental regulation induce or reduce technology adoption? When the rate of technology adoption is inverted U-shaped. J. Environ. Econ. 64 (3), 456–467 (2012).
Google Scholar
Wang, Y. & Yu, L. Can the current environmental tax rate promote green technology innovation? Evidence from China’s resource-based industries. J. Clean. Prod. 278 , 123443 (2021).
Oggioni, G., Riccardi, R. & Toninelli, R. Eco-efficiency of the world cement industry: A data envelopment analysis. Energy Pol. 39 (5), 2842–2854 (2011).
Download references
This study was supported by Jiangsu Province Social Science Foundation Project (22GLD019), Major Project of Philosophy and Social Science Research in Universities of Jiangsu Province (2022SJZD053).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Economics and Management, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, 210037, People’s Republic of China
Fang-rong Ren, Tao-feng Wu & Xiao-yan Liu
Changzhou Vocational Institute of Textile and Garment, Changzhou, 213164, People’s Republic of China
Yang-jun Ren
Shaanxi Rural Revitalization Institute, Xi’an Innovation College of Yan’an University, Xi’an, 710100, People’s Republic of China
Xiaomei Yuan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
F.-rR.: conceptualization, methodology and software resources. T.-fW.: formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation. Y.-jR.: visualization and investigation. X.-yL.: data curation, writing—review and editing. X.-mY.: project administration. All authors read and contributed to the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Xiaomei Yuan .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information., supplementary information 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ren, Fr., Wu, Tf., Ren, Yj. et al. The impact of environmental regulation on green investment efficiency of thermal power enterprises in China-based on a three-stage exogenous variable model. Sci Rep 14 , 8400 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58396-x
Download citation
Received : 16 January 2024
Accepted : 28 March 2024
Published : 10 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58396-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Environmental regulation
- Thermal power enterprises
- Three-stage model
- Exogenous variable
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- Data library
2024 Housing Market Forecast and Predictions: Housing Affordability Finally Begins to Turnaround

As we look ahead to 2024 , we see a mix of continuity and change in both the housing market and economy. Against a backdrop of modest economic growth, slightly higher unemployment, and easing inflation longer term interest rates including mortgage rates begin a slow retreat. The shift from climbing to falling mortgage rates improves housing affordability, but saps some of the urgency home shoppers had previously sensed. Less frenzied housing demand and plenty of rental home options keep home sales relatively stable at low levels in 2024, helping home prices to adjust slightly lower even as the number of for-sale homes continues to dwindle.
Realtor.com ® 2024 Forecast for Key Housing Indicators

Home Prices Dip, Improving Affordability
Home prices grew at a double-digit annual clip for the better part of two years spanning the second half of 2020 through 2022, a notable burst following a growing streak that spanned back to 2012. As mortgage rates climbed, home price growth flatlined, actually declining on an annual basis in early 2023 before an early-year dip in mortgage rates spurred enough buyer demand to reignite competition for still-limited inventory. Home prices began to climb again, and while they did not reach a new monthly peak, on average for the year we expect that the 2023 median home price will slightly exceed the 2022 annual median.
Nevertheless, even during the brief period when prices eased, using a mortgage to buy a home remained expensive. Since May 2022, purchasing the typical for-sale home listing at the prevailing rate for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage with a 20% down payment meant forking over a quarter or more of the typical household paycheck. In fact, in October 2023, it required 39% of the typical household income and this share is expected to average 36.7% for the full calendar year in 2023. This figure has typically ranged around 21%, so it is well above historical average. We expect that the return to pricing in line with financing costs will begin in 2024, and home prices, mortgage rates, and income growth will each contribute to the improvement. Home prices are expected to ease slightly, dropping less than 2% for the year on average. Combined with lower mortgage rates and income growth this will improve the home purchase mortgage payment share relative to median income to an average 34.9% in 2024, with the share slipping under 30% by the end of the year.

Home Sales Barely Budge Above 2023’s Likely Record Low
After soaring during the pandemic, existing home sales were weighed down in the latter half of 2022 as mortgage rates took off, climbing from just over 3% at the start of the year to a peak of more than 7% in the fourth quarter. The reprieve in mortgage rates in early 2023, when they dipped to around 6%, brought some life to home sales, but the renewed climb of mortgage rates has again exerted significant pressure on home sales that is exacerbated by the fact that a greater than usual number of households bought homes over the past few years, and despite stories of pandemic purchase regret , for the most part, these homeowners continue to be happy in their homes.
This is consistent with what visitors to Realtor.com report when asked why they are not planning to sell their homes. The number one reason homeowners aren’t trying to sell is that they just don’t need to; concern about losing an existing low-rate mortgage is the top financial concern cited. Our current projection is for 2023 home sales to tally just over 4 million, a dip of 19% over the 2022 5 million total.

With many of the same forces at play heading into 2024, the housing chill will continue, with sales expected to remain essentially unchanged at just over 4 million. Although mortgage rates are expected to ease throughout the course of the year, the continuation of high costs will mean that existing homeowners will have a very high threshold for deciding to move, with many likely choosing to stay in place. Moves of necessity–for job changes, family situation changes, and downsizing to a more affordable market–are likely to drive home sales in 2024.

Shoppers Find Even Fewer Existing Homes For Sale
Even before the pandemic, housing inventory was on a long, slow downward trajectory. Insufficient building meant that the supply of houses did not keep up with household formation and left little slack in the housing market. Both homeowner and rental vacancy remain below historic averages . In contrast with the existing home market, which remains sluggish, builders have been catching up, with construction remaining near pre-pandemic highs for single-family and hitting record levels for multi-family .

Despite this, the lack of excess capacity in housing has been painfully obvious in the for-sale home market. The number of existing homes on the market has dwindled. With home sales activity to continue at a relatively low pace, the number of unsold homes on the market is also expected to remain low. Although mortgage rates are expected to begin to ease, they are expected to exceed 6.5% for the calendar year. This means that the lock-in effect, in which the gap between market mortgage rates and the mortgage rates existing homeowners enjoy on their outstanding mortgage, will remain a factor. Roughly two-thirds of outstanding mortgages have a rate under 4% and more than 90% have a rate less than 6%.

Rental Supply Outpaces Demand to Drive Mild Further Decline in Rents
After almost a full year of double-digit rent growth between mid-2021 and mid-2022, the rental market has finally cooled down, as evidenced by the year-over-year decline that started in May 2023 . In 2024, we expect the rental market will closely resemble the dynamics witnessed in 2023, as the tug of war between supply and demand results in a mild annual decline of -0.2% in the median asking rent.

New multi-family supply will continue to be a key element shaping the 2024 rental market. In the third quarter of 2023, the annual pace of newly completed multi-family homes stood at 385,000 units. Although absorption rates remained elevated in the second quarter, especially at lower price points, the rental vacancy rate ticked up to 6.6% in the third quarter. This uptick in rental vacancy suggests the recent supply has outpaced demand, but context is important. After recent gains, the rental vacancy rate is on par with its level right before the onset of the pandemic in early 2020, still below its 7.2% average from the 2013 to 2019 period. Looking ahead, the strong construction pipeline– which hit a record high for units under construction this summer –is expected to continue fueling rental supply growth in 2024 pushing rental vacancy back toward its long-run average.
While the surge in new multi-family supply gives renters options, the sheer number of renters will minimize the potential price impact. The median asking rent in 2024 is expected to drop only slightly below its 2023 level. Renting is expected to continue to be a more budget friendly option than buying in the vast majority of markets, even though home prices and mortgage rates are both expected to dip, helping pull the purchase market down slightly from record unaffordability.
Young adult renters who lack the benefit of historically high home equity to tap into for a home purchase will continue to find the housing market challenging. Specifically, as many Millennials age past first-time home buying age and more Gen Z approach these years, the current housing landscape is likely to keep these households in the rental market for a longer period as they work to save up more money for the growing down payment needed to buy a first home. This trend is expected to sustain robust demand for rental properties. Consequently, we anticipate that rental markets favored by young adults , a list which includes a mix of affordable areas and tech-heavy job markets in the South, Midwest, and West, will be rental markets to watch in 2024.
Key Wildcards:
- Wildcard 1: Mortgage Rates With both mortgage rates and home prices expected to turn the corner in 2024, record high unaffordability will become a thing of the past, though as noted above, the return to normal won’t be accomplished within the year. This prediction hinges on the expectation that inflation will continue to subside, enabling the recent declines in longer-term interest rates to continue. If inflation were to instead see a surprise resurgence, this aspect of the forecast would change, and home sales could slip lower instead of steadying.
- Wildcard 2: Geopolitics In our forecast for 2023 , we cited the risk of geopolitical instability on trade and energy costs as something to watch. In addition to Russia’s ongoing war in Ukraine, instability in the Middle East has not only had a catastrophic human toll, both conflicts have the potential to impact the economic outlook in ways that cannot be fully anticipated.
- Wildcard 3: Domestic Politics: 2024 Elections In 2020, amid the upheaval of pandemic-era adaptations, many Americans were on the move. We noted that Realtor.com traffic patterns indicated that home shoppers in very traditionally ‘blue’ or Democratic areas were tending to look for homes in markets where voters have more typically voted ‘red’ or Republican. While consumers also reported preferring to live in locations where their political views align with the majority , few actually reported wanting to move for this reason alone.
Housing Perspectives:
What will the market be like for homebuyers, especially first-time homebuyers.
First-time homebuyers will continue to face a challenging housing market in 2024, but there are some green shoots. The record-high share of income required to purchase the median priced home is expected to begin to decline as mortgage rates ease, home prices soften, and incomes grow. In 2023 we expect that for the year as a whole, the monthly cost of financing the typical for-sale home will average more than $2,240, a nearly 20% increase over the mortgage payment in 2022, and roughly double the typical payment for buyers in 2020. This amounted to a whopping nearly 37% of the typical household income. In 2024 as modest price declines take hold and mortgage rates dip, the typical purchase cost is expected to slip just under $2,200 which would amount to nearly 35% of income. While far higher than historically average, this is a significant first step in a buyer-friendly direction.
How can homebuyers prepare?
Homebuyers can prepare for this year’s housing market by getting financially ready. Buyers can use a home affordability calculator , like this one at Realtor.com to translate their income and savings into a home price range. And shoppers can pressure test the results by using a mortgage calculator to consider different down payment, price, and loan scenarios to see how their monthly costs would be impacted. Working with a lender can help potential buyers explore different loan products such as FHA or VA loans that may offer lower mortgage interest rates or more flexible credit criteria.
Although prices are anticipated to fall in 2024, housing costs remain high, and a down payment can be a big obstacle for buyers. Recent research shows that the typical down payment on a home reached a record high of $30,000 . To make it easier to cobble together a down payment, shoppers can access information about down payment assistance options at Realtor.com/fairhousing and in the monthly payment section of home listing pages. Furthermore, home shoppers can explore loan products geared toward helping families access homeownership by enabling down payments as low as 3.5% in the case of FHA loans and 0% in the case of VA loans .
What will the market be like for home sellers?
Home sellers are likely to face more competition from builders than from other sellers in 2024. Because builders are continuing to maintain supply and increasingly adapting to market conditions, they are increasingly focused on lower-priced homes and willing to make price adjustments when needed. As a result, potential sellers will want to consider the landscape for new construction housing in their markets and any implications for pricing and marketing before listing their home for sale.
What will the market be like for renters?
In 2024, renting is expected to continue to be a more cost-effective option than buying in the short term even though we anticipate the advantage for renting to diminish as home prices and mortgage rates decline.
However, for those considering the pursuit of long-term equity through homeownership, it’s essential to not only stay alert about market trends but also to carefully consider the intended duration of residence in their next home. When home prices rise rapidly, like they did during the pandemic, the higher cost of purchasing a home may break even with the cost of renting in as little as 3 years. Generally, it takes longer to reach the breakeven point, typically within a 5 to 7-year timeframe. Importantly, when home prices are falling and rents are also declining, as is expected to be the case in 2024, it can take longer to recoup some of the higher costs of buying a home. Individuals using Realtor.com’s Rent vs. Buy Calculator can thoroughly evaluate the costs and benefits associated with renting versus buying over time and how many years current market trends suggest it will take before buying is the better financial decision. This comprehensive tool can provide insights tailored to a household’s specific rent versus buying decision and empowers consumers to consider not only the optimal choice for the current month but also how the trade-offs evolve over several years.
Local Market Predictions:
All real estate is local and while the national trends are instructive, what matters most is what’s expected in your local market.
Sign up for updates
Join our mailing list to receive the latest data and research.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Market Analysis - Science topic. Feb 2024. Farai Chigora. Joram Ndlovu. Brighton Nyagadza. Christopher Buschow. Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints ...
Traditionally, market research's role was to focus on task execution (i.e. collection and analysis of market data by means of varied research methodologies). Nowadays, stakeholder demands include the need for interpretation of research that creates a distinct value proposition for the client organisation ( Di Fiore, 2012 ; Handley, 2016 ).
1. Research your industry. Gain a holistic understanding of everything happening in your industry and prepare to navigate it. 2. Investigate competitors. Know who the big players are and how you can differentiate your brand. 3. Identify market gaps. Find unsolved problems and unmet desires in your market.
Market analysis seeks to understand the dynamics of markets, with the goal of informing business strategies. For example, analysis of the current and potential future markets for drugs to treat ...
June 3, 2021 28 min read. Market research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a given market. It takes into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic data about past, current, and potential customers, as well as competitive analysis to evaluate the viability of a product offer.
To conduct an effective comparative analysis: Collect Data: Gather data on your business, competitors, and the market as a whole. Use Key Metrics: Focus on key performance metrics relevant to your industry. Benchmark Against Competitors: Compare your performance against that of your direct competitors.
Market Research Analysis Steps. Market research analysis involves a series of systematic steps to gather, process, and interpret data to gain insights into a specific market or industry. These steps are crucial for making informed business decisions and developing effective strategies. Here are the key steps in the market research analysis process:
The basic methods of market research include surveys, personal interviews, customer observation, and the review of secondary research. In addition to these basic methods, a forward-thinking market research approach incorporates data from the digital landscape like social media analysis, SEO research, gathering feedback via forums, and more.
The International Journal of Market Research (IJMR) publishes original research addressing key challenges in market research and insight. Since its founding in 1958 IJMR has been at the forefront of the development of new research methods, … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
Market research is the process of assessing the viability of a new good or service through research conducted directly with the consumer which allows a company to ...
The short answer is, attitudes have improved, but not as much as men seem to think. In the July-August 1965 issue of HBR, Garda W. Bowman, N. Beatrice Worthy, and Stephen A. Greyser examined the ...
Step 1 - Market segmentation. What: Whether you want to enter a new market, launch a new product, or simply assess opportunities for an existing business, this first step in the market analysis process is crucial yet often overlooked. Why: Market segmentation helps you identify the core segments of a market to target.
Senior Lecturer Jill Avery and The YES co-founder and CEO Julie Bornstein discuss this make-or-break dilemma in the case, The YES: Reimagining the Future of e-Commerce with Artificial Intelligence (AI). This episode was recorded live at Harvard Business School on March 30, 2022 as part of our Case Method 100 celebration.
The median salary for a market research analyst in the US is $63,920, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), though salary can differ depending on the industry . Market research analyst vs. similar roles. Market research analysts share much in common with roles that also parse data and deliver strategic insights. Marketing analyst
As part of that process, one of the very first steps is market research and market analysis. Well-executed market analysis will give you a clear indication of how successful the right product can be when introduced to the right target market for the right price. In this article, we'll talk about market analysis and how to do it effectively ...
The three terms, market analysis, market research, and industry analysis, are related but differ in focus and scope. Market research focuses on a specific market segment and its customers, while market analysis studies the entire market. Industry analysis examines the whole industry, including its components and players, and can be conducted ...
The papers in this special issue focus on the emerging phenomenon of cryptocurrencies. Cryptocurrencies are digital financial assets, for which ownership and transfers of ownership are guaranteed by a cryptographic decentralized technology. The rise of cryptocurrencies' value on the market and the growing popularity around the world open a number of challenges and concerns for business and ...
Modern market research means you can track consumer behavior across diverse segments, benchmark your company versus competitors, conduct complex academic research, and capture the insights you need to move the needle. Today's market research is predictive and collaborative so everyone in your organization has the same information to drive the ...
Market research: A study done to collect statistics on a given market within a specific industry. Market analysis: Interpretation of market information to determine a market's size, growth potential, audience, and competitive landscape 4. Marketing research: The process of collecting data to understand consumer behaviors, preferences, and ...
1. Research your industry. Gain a holistic understanding of everything happening in your industry and prepare to navigate it. 2. Investigate competitors. Know who your main competitors are and how you can differentiate your brand. 3. Identify market gaps. Find unsolved problems and unmet needs in your market.
Step 4: Calculate market value. You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value. A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the ...
With inflation still above the Federal Reserve's 2% objective, there is renewed interest in understanding how quickly federal funds rate hikes typically affect inflation. Beyond monetary policy's well-known lagged effect on the economy overall, new analysis highlights that not all prices respond with the same strength or speed. Results suggest that inflation for the most responsive ...
Executives' latest views on the global economy and their countries' economies lean much more positive than they did at the end of 2023.. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on economic conditions, 1 The online survey was in the field from March 4 to March 8, 2024, and garnered responses from 957 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional ...
Market research analysts—sometimes called market researchers—help companies develop or maintain a competitive edge by finding and delivering data-backed insights into potential markets, competitors, and even customer behaviour. They're an integral part of a company's overall marketing strategy and are in demand across multiple industries.
Identifying these effects would enable candidates to improve their email text and increase their donations by 9% on average. This research provides a practical and flexible roadmap for automated text analysis in situations where political campaigns do not have clear a priori hypotheses about which textual characteristics will be effective for them.
First, the analysis of existing research in this field mainly focuses on developed regions or areas, and lacks research on developing countries 1,4. However, the impact of environmental regulation ...
The website of the studied higher education institution (University of Customs and Finance) has 64 points according to experts. In general, it has convenient navigation, simple design, textual ...
In 2023 we expect that for the year as a whole, the monthly cost of financing the typical for-sale home will average more than $2,240, a nearly 20% increase over the mortgage payment in 2022, and ...
The Texas Real Estate Research Center at Texas A&M University (TRERC) is the nation's largest publicly funded organization devoted to real estate research. TRERC was created by the state legislature in 1971 to meet the needs of many audiences, including the real estate industry, instructors, researchers, legislators, and the public.
Low-cost ETFs lost US$469mn in March: North American inflows (+US$128m) were outpaced by European outflows (-US$594mn). During the first quarter global gold ETF outflows piled up to US$6.5bn, led by North America and Europe while Asia attracted the largest inflows. Low-cost funds saw outflows of US$893mn in Q1, mainly driven by Europe (-US$728mn).