- Math Article
- Pictorial Representation Of Data

Pictorial Representation Of Data - Bar Graphs

Pictorial representation of data is called pictograph. As humanity flourished and the population increased, so did the amount of trade and transaction in the world. Ultimately, the amount of data is also increased. The merchants found it harder to keep track of the money flowing in and out of their coffers. When the population was little, trade was fairly simple but keeping track of who owes whom how much (data), so on and so forth became extremely tedious. To this end, the merchants created a bar graph with which they were able to depict a wide variety of information pictorially which not only helped understanding but also made it easier from a merchant’s point of view. What is the Bar Graph? Let’s find out.
Pictorial Representation Using Bar Graph
A bar graph also known as a bar chart is a chart that presents data that is grouped into rectangular bars. Here the length of the bar is directly proportional to the values they represent. The bar graph can be drawn vertically or horizontally. A vertical bar graph is known as a Column Bar Graph . Since one bar graph can be used to display multiple groups of data on the same graph, bar graphs can also be used as comparative tools where the length of the rectangular bar represents the value of each category. Since the rectangular bars are proportional, their differences can be spotted much more easily, visually than through words. Let’s take a closer look at bar graphs.
Say you have pocket money of 100 rupees every week. You are allowed to spend this amount any which way you want to. You use this money to buy chocolate, beverages, food and other miscellaneous toys and stuff. What you notice is that every week, the money just seems to disappear. You ask your father for a little more money but he instead suggests that you see where the money is going so that you can learn the value of money. To this end, you grudgingly make a bar chart. But to create a bar chart, you need to have data. You need to note down the things you are spending money on and how much. After a week you have the details of this week’s expenditure and they look something like this
| Items | Week 1 |
| Chocolate | 25 |
| Beverages | 20 |
| Food | 40 |
| Misc | 15 |
The first thing to observe is how the data is grouped. It is the first step to creating a bar graph. Similar expenses such as chocolates, candies, chewing gums are all grouped together. The same applies to the variety of soft drinks you consume. While discussing a bar graph, it was mentioned that the values are represented as a rectangular bar where the length of the rectangular bar is proportional to the value of the data. Here is where another characteristic of a bar graph comes into play.
A Bar Graph needs to have a uniform scale. The scale dictates the conversion of the data in number into the rectangular format. A bar graph is the representation of numbers using bars of uniform width and length dependent on the number.

For example, if you represent the money you spent on chocolate using a 25 cm long rectangular bar then the scale is 1 rupee is equal to one unit on the graph i.e. one rupee is represented by one centimeter. But you can clearly see that for this type of representation you will need a massive graph. The thing about scale is that it is completely under our control. So instead of 25 cm, you can represent the same quantity with a rectangular bar of length 25 millimeters and here the scale is 10 rupees is equal to the same one unit i.e. 10 rupees is represented by the same one centimeter.
The interpretation of data is heavily reliant on accurate information about the scale, therefore, it is extremely important to mention the scale of your graph along both the x-axis and y-axis. Using the latter scale i.e. 10 rupees is equal to one centimeter. It is important to remember that the same scale is applied to all the groups of data in the bar graph.
Properties of Bar Graph
- The width of each bar or column in a bar graph must be equal
- The base of the bars is common in a bar graph
- The height of bars represent the data in the bar graph, proportionally
- The bars can be drawn horizontally or vertically based on the given data
Types of Bar Graphs
In pictorial representation of data, the data is represented using a bar graph. There are three types of bar graphs that can be used for pictorial representation.
- Vertical bar graph
- Horizontal bar graph
- Double bar graph
Pictorial Representation of Data using Vertical Bar Graph
Vertical bar graphs are commonly used pictorial representations to express the given data using vertical bars. Here, the horizontal axis represents the categories and the vertical bars represent the corresponding data for each category. The horizontal axis is the x-axis and the vertical axis is the y-axis.

The vertical bar graphs are also used to represent the series of data and its variation over a period of time. All the vertical bars goes from the bottom of the x-axis to the top.
Pictorial Representation of Data Using Horizontal Bar graph
The horizontal bar graph represents the data using the bars that are parallel to the x-axis. The categories are defined along the y-axis and the respective data are represented using horizontal bars. The bars in the horizontal graph go from left to side along the x-axis.

Pictorial Representation of Data Using Double Bar Graph
You have seen what the bar graph of your expenses for the first week looks like. Say you continue this habit of tracking where you spent the money for some more time. You find that your week two expenses are slightly different from your first week. The details of the second-week expenses are;
| Items | Week 1 | Week 2 |
| Chocolate | 25 | 20 |
| Beverages | 20 | 35 |
| Food | 40 | 40 |
| Misc | 15 | 5 |
Since they all belong to the same group, they can be charted on the same bar graph. Remember that the same scale applies to all the data in the graph. Instead of charting them individually, you can place similar groups next to each other to compare the changes over a larger time span or over a larger range of data. Now plotting this together, we are better poised to see the differences between the weekly expenditure.

This process can also help you control your expenditure because you now know what you are spending the most on. Through this, you can judge whether your expenses are necessary.
Related Articles
- Pictograph and Interpretation of a Pictograph
- Box and Whisker Plot
Frequently Asked Questions on Pictorial representation of data
What do you mean by pictograph, what are the different ways of pictorial representation of data, is a chart also a pictorial representation of data.
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Pictorial Representation
Some basic ideas of pictorial representation or pictograph, often related types of symbols or pictures are used to represent a specific number of objects.
For example, a symbol may represent 1 or 10 or 100 or 1000 or any other number of related objects. The symbol/picture used is very simple, clear and self explanatory. The quantity that each symbol represents is indicated clearly in the representation, i.e. the scale is mentioned clearly.
1. Examples of objects whose pictures or symbols are used are: different kinds of animals like birds, insects, men, women, boys, girls, fruits like mangoes, grapes, oranges, apples, trees, cars, scooters, bicycles, plants, etc.
2. The symbol or pictures may be colored. So such colors should be used which are very common, like red, blue, green, yellow, etc.
3. Only the pictures of common fruits are used such as banana, apples, guava, orange, grapes, mangoes, etc.
4. Sometimes the names of the month of a year, or the days of a week need to be mentioned. The names of the months and days may be written vertically and in front of each we may write the roll numbers of the students according to their birthday and birth month. This way we may show the number of students who are born in the month or day concerned.
5. Sometimes, data on yearly production such as the yearly production of wheat or rice in a state, of steel in a factory, etc., may have to be represented. Thus, we must be acquainted with the numbers used to describe the years 2007, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, etc.
So, pictures of different objects are used as a symbol to give information regarding mathematical data.
In short, the information presented through pictures or symbol of different objects is called pictorial representation of data. The pictures of different objects are used to represent different information, so such pictorial data are called pictographs .
Pictographs
The students of Class 2 were asked to choose their favourite colour from the colours of the rainbow. The teacher then collected their response and made a chart to show the information.
My Colour of the Rainbow
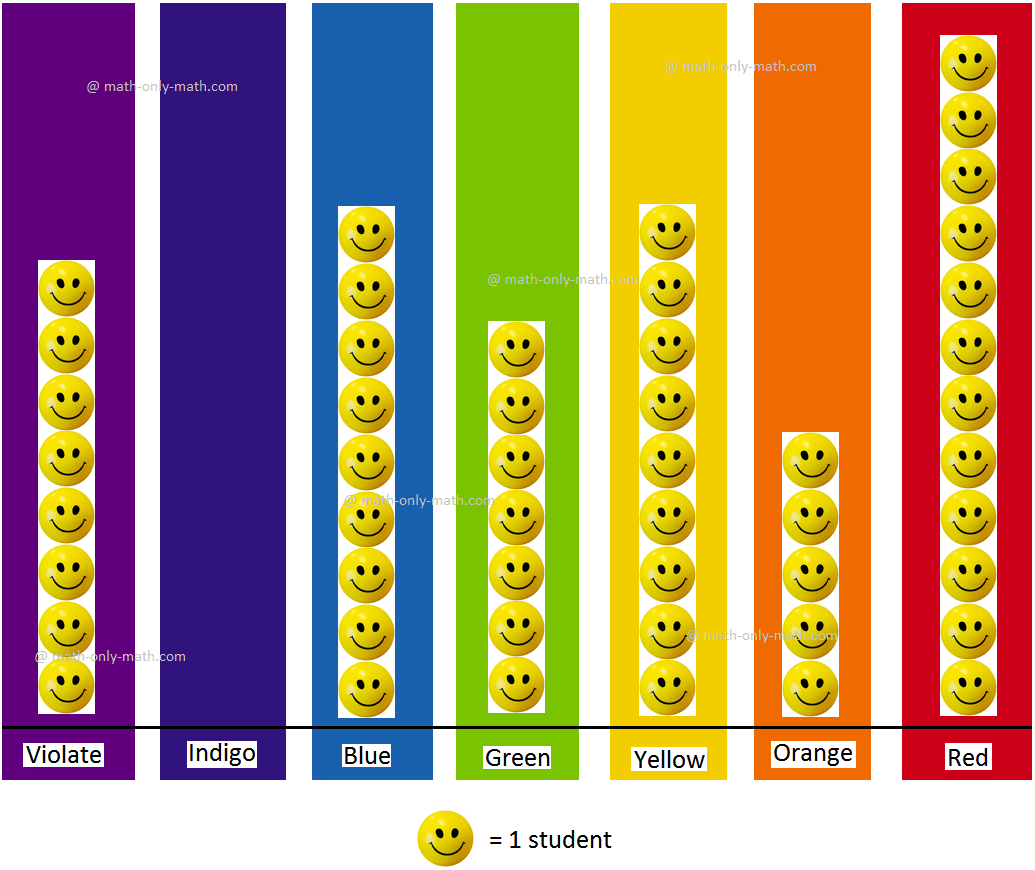
In the chart, each smiling face represents a student. Such a chart that displays information using pictures is known as a pictograph .
Let us see what information we can gather from this pictograph.
Some information can be directly read from the pictograph.
1. The pictograph is titled 'My colour of the rainbow' and it shows us the favourite colour chosen by the students of Class 2.
2. Violet is the favourite colour of 8 students.
3. Indigo is the favourite colour of 0 students.
4. Blue is the favourite colour of 9 students. 5. Green is the favourite colour of 7 students.
6. Yellow is the favourite colour of 9 students.
7. Orange is the favourite colour of 5 students.
8. Red is the favourite colour of 12 students.
Some information can be understood after studying the pictograph.
1. Red is the most popular colour choice of the students.
2. Indigo is the least popular colour choice of the students.
3. An equal number of students chose yellow and blue as their favourite colours.
4. Between violet, green and orange, violet is the most popular colour.
5. Three more students chose violet than those who chose orange as their favourite colour.
Sometimes, when the scores are high, it is not possible to draw so many pictures in a pictograph. In such pictographs one picture can be made to represent a score of more than one. This can be explained better using the example that follows.
Reading Pictograph:
1. Five friends participated in an apple-picking competition. The result of the competition held in an orchard is shown in the pictograph below. Study the pictograph and answer the questions that follow.
Apple Picking Score
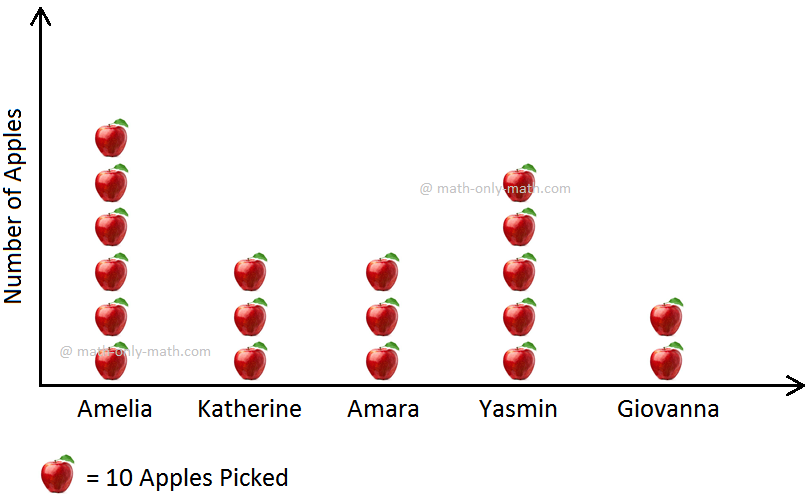
(i) Who picked the most number of apples?
Answer: The most number of apple pictures can be seen in Amelia's column. Thus, Amelia picked the most number of apples.
(ii) Who picked the least number of apples?
Answer: The least number of apple pictures can be seen in Giovanna's column. Thus, Giovanna picked the least number of apples.
(ii) Who picked an equal number of apples?
Answer: An equal number of apple pictures can be seen in Katherine and Amara's columns. Thus, Katherine and Amara picked an equal number of apples.
(iv) How many apples did Yasmin pick?
Answer: Five apple pictures can be seen in Yasmin 's column. It is given in the pictograph that each apple picture stands for 10 apples picked.
Thus, Yasmin picked 5 × 10 = 50 apples.
(v) How many more apples did Katherine pick than Giovanna ?
Answer: Compared to the two apple pictures in Giovanna 's column, Katherine has three or one more picture. Thus, Katherine picked 1 × 10 = 10 more apples than Giovanna .
(vi) How many apples did Amelia pick?
Answer: Amelia picked 6 × 10 = 60 apples.
(vii) How many apples were picked in all by the five friends?
Answer: There are a total of 19 apple pictures against all the five friends. Thus, a total of 19 × 10 = 190 apples got picked by all the five friends.
(viii) How many apples did Amara and Giovanna pick together?
Answer: Amara picked 3 × 10 = 30 apples while Giovanna picked 2 × 10 = 20 apples. Together they picked 30 + 20 = 50 apples.
2. In the month of March Seema bought different types of fruits every week. Read the I pictograph and answer:
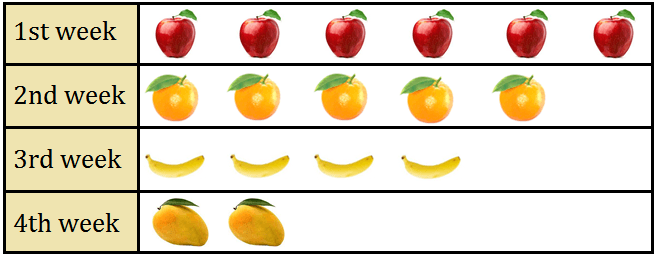
(i) Which week did she buy maximum fruits?
(ii) Which week did she buy 5 fruits?
(iii) How many weeks did she buy fruit?
(iv) Which week did she buy least fruits?
3. Read the pictograph given below and answer the question. (Here 1 picture represents 5 animals.)
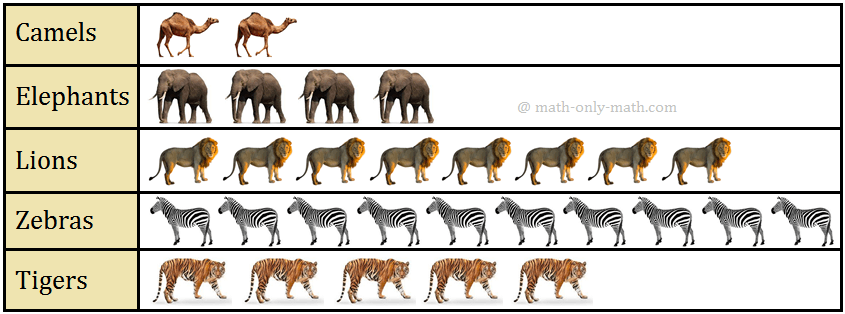
(i) What is the total number of animals?
(ii) Which kind of animal is least in number?
(iii) How many tigers are there?
(iv) How many herbivorous animals are there?
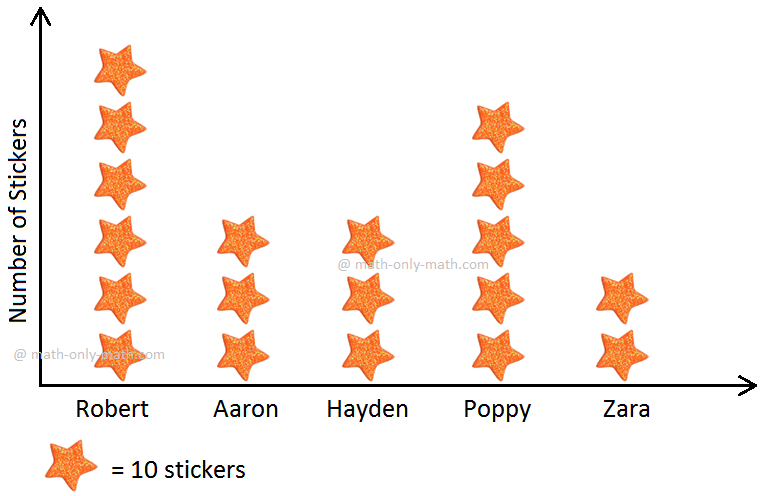
4. Make a pictograph to show the number of star stickers owned by five
| Robert Aaron Hayden Poppy Zara | 40 50 50 30 60 |
It would be very hard to show so many stickers against each friend. So, we can show one picture for every 10 stickers owned.
Star Stickers Owned by Five Friends
5. The mode of transport availed by the students of a preparatory school is put up in a chart on the wall as a pictograph. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Mode of Transport Availed by the Students
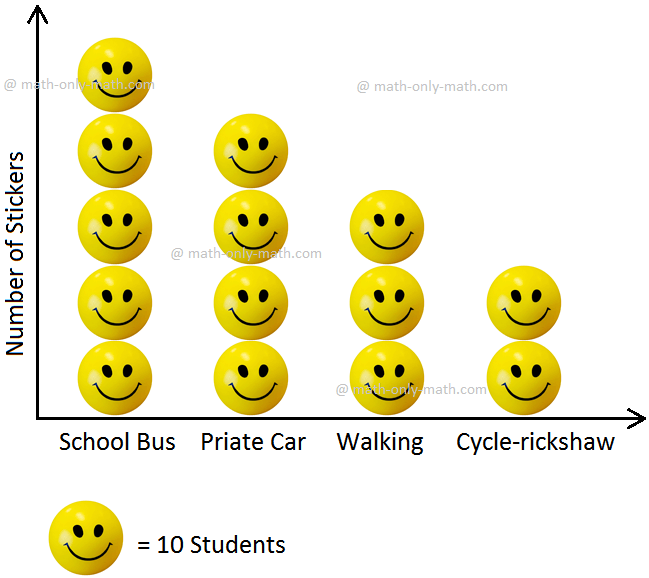
(i) What is the title of this pictograph? (ii) What does one smiling face represent?
(iii) Which is the most popular mode of transport for the students?
(iv) Which is the least popular mode of transport for the students?
(v) How many students travel by private cars?
(vi) How many students travel by a mode of transport that gives out no smoke and consumes no fuel?
(vii) How many students travel to school by a mode of transport that has an engine and consumes fuel?
6. Standing at the bus stop waiting for his school bus, Robert counted all the vehicles that went past him in 10 minutes. He recorded his observations in the following pictograph. Answer the questions that follow .
Vehicles that Went Past in 10 Minutes
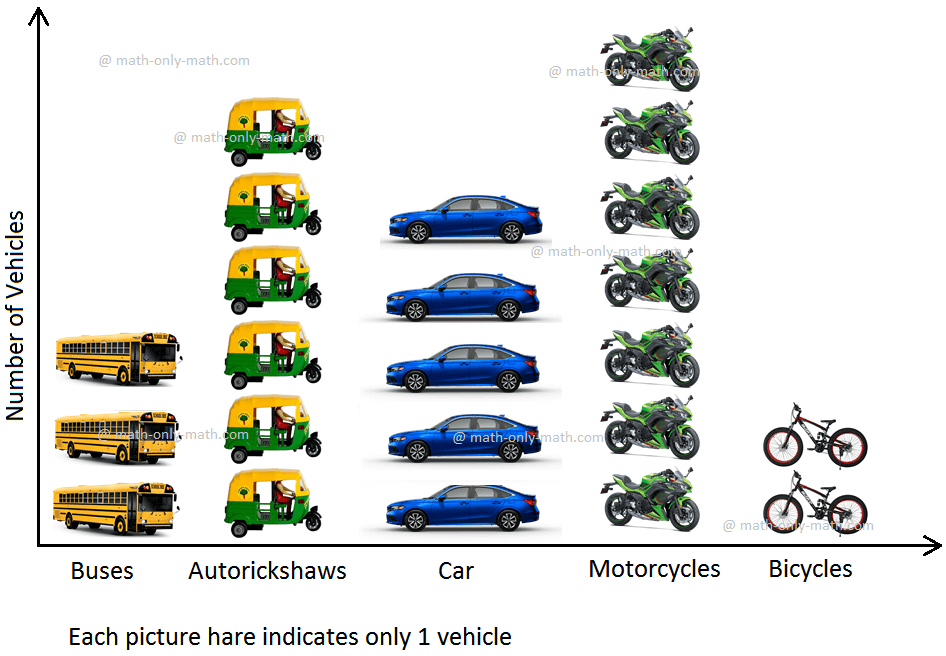
(i) How many different kinds of vehicles went past Robert?
(ii) Out of all the vehicles that went past Robert, which was the most in number?
(iii) Out of all the vehicles that went past Robert, which was the least in number?
(iv) How many buses went past Robert in 10 minutes?
(v) How many cars and bicycles went past Robert ?
(vi) Which were most in number - two wheelers (motorcycles and bicycles), three wheelers (autorickshaws) or four wheelers (cars and buses)?
(vii) How many more cars than bicycles went past Robert?
(viii) How many vehicles in all went past Robert in 10 minutes?
Related Concepts
● Examples of Pictographs
● Problems on Pictographs
3rd Grade Math Worksheets
3rd Grade Math Lessons
From Pictorial Representation to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
New! Comments
|
What’s this? | Facebook X Pinterest WhatsApp Messenger |
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy
| E-mail Address | |
| First Name | |
| to send you Math Only Math. |
Recent Articles
Absolute value of an integer | absolute value | solved examples.
Jun 10, 24 10:14 AM

Ordering Integers | Integers from Greater to Lesser, Lesser to Greater
Jun 08, 24 01:46 PM
Representation of Integers on a Number Line | Integers on Number Line
Jun 08, 24 12:58 PM
What are integers? | Negative and Positive Integers | Natural Numbers
Jun 07, 24 04:42 PM

5th Grade Factors and Multiples Worksheets | L.C.M. | H.C.F. | Answers
Jun 07, 24 02:06 PM

© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

Data Visualization: How to Present Your Research Data Visually
The academic and scientific community produces large amounts of data through their research, and data visualization is a key skill for researchers across all disciplines. Presenting qualitative data visually from one’s research can transform the final output, and one does not have to spend enormous amount of time to accomplish this. Researchers who need to communicate quantitative data have several options to present it visually through bar graphs, pie charts, histograms and even infographics. However, communicating research findings based on complex datasets is not always easy. This is where effective data visualization can greatly help readers. Data visualization is the representation of information and data in a pictorial or graphical format highlighting the trends and outliers and making it easier to understand. Effective use of data visualization techniques helps to focus readers’ attention on critical information, in a way is both simple and engaging.

Many researchers are often under the false impression that presenting qualitative data visually is a complex exercise, but it is not. Today, there are numerous qualitative data visualization tools and techniques that can be used by both beginners and experts alike. Using data visualization to communicate important data can enhance the impact of the researcher’s work thereby making it more meaningful and engaging to potential readers. Adding visuals like graphs and charts can make it easier for not just for researchers to communicate experimental results and share details of interesting new discoveries but also allows readers to analyze and understand complicated data sets and concepts. A study in The Economist revealed the number of citations jumped 120% when a research paper included infographics. 1
Let us look at some ways to make the best use of data visualization techniques that will help present your qualitative research data and information effectively.
Table of Contents
Pair the right kind of visuals to convey specific data sets
The human brain is wired to quickly analyze and understand visual cues which is why it is important to add visual elements in your research paper. Plotting data using charts, graphs and infographics allows readers to quickly identify underlying patterns of data that would otherwise be difficult to comprehend when reading through paragraphs of text. However, using the wrong kind of visuals can be misleading, and reduce readability and comprehension.
Today, with more and more scientific knowledge being conveyed visually via social media, researchers are experimenting with communicating research through different types of visuals. However, using the right kind of visuals is imperative to ease the public understanding of science.
In fact, an interesting study in the Journal of the American Statistical Association by William Cleveland and Robert McGill sheds light on how human perception affects how we decipher graphic displays of data; this made some kinds of charts easier to understand than others. The statisticians were able to prove that charts based on the lengths of bars or lines, such as in a standard bar chart were the easiest to read – especially, when trying to discern small differences between values. Pie charts on the other hand were acceptable only in limited contexts so were rarely the right choice. 2
Focus on balancing form and function
There are several data visualization software and programs available to researchers today that simplify the process of presenting data visually. What needs to be kept in mind, however, is that quantitative data visualization is not just about beautifying graphs to make them look better. Neither is it about heaping information into an infographic to communicate different aspects of research. Researchers must understand that to be effective, data visualization must be a delicate balance between form and function. While a plain graph could be too boring to attract and hold reader attention a beautiful visual could also fail in its endeavor to communicate the right message if it is not presented properly. The data and the visuals need to work together to create a compelling narrative that combines research analysis with storytelling.
Be aware of the use of colors and shapes
While incorporating quantitative data visualization techniques it is recommended not to rely only on the default templates available within software and programs but instead customize and define the layout according to your specific needs. Choosing the right colors and shapes to indicate various categories is very important. For example, it would be appropriate to use light colored text on a darker background to enhance readability. Researchers can also choose to use different shapes to indicate separate data sets and categories of information and use varying sizes to stress the frequency of data. One can also use similar vectors to add a touch of ingenuity to the visuals being used. It is best to avoid using vivid effects and abstract images for denoting differences in data as they can distract readers from key information points being conveyed. Most importantly, avoid adding too many visuals or graphics. Researchers must use visuals only where necessary and align them with the information provided.
While many early career researchers and academics might find it challenging to visualize qualitative data and present it in a manner that is easily understood by an audience, this is an art that should be cultivated and can be mastered. This is where Mind The Graph comes in help researchers get more creative with science communication by offering them a simple way to present data visually. A powerful AI tool for scientists, Mind The Graph is home to the world’s largest scientifically accurate illustrations gallery with over 40,000 illustrations across more than 80 research fields. Choose a format to communicate your research and use one of the 200+ pre-made templates to create powerful scientific infographics, posters, graphical abstracts, and presentations for your own research. It’s a quick, effective, and powerful way to communicate your science to the world. And the best part is that you can now get Mind The Graph at a steal by subscribing to Researcher.Life , which unlocks access to this data visualization tool as well as other premium AI tools and services designed to help you succeed.
References:
- Graphic Details, The Economist, June 2016. Available at https://www.economist.com/science-and-technology/2016/06/16/graphic-details
- Mason, B. Why scientists need to be better at data visualization. Knowable Magazine, 2019. Available at https://knowablemagazine.org/article/mind/2019/science-data-visualization
Related Posts

Tips on Writing the Acknowledgments Section

What is Confidence Interval and How to Calculate it (with Examples)
Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website: https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > Principles of Statistical Techniques
- > The Pictorial Representation of Data

Book contents
- Frontmatter
- 1 The Scope of Statistics
- 2 The Collection of Data
- 3 The Tabulation of Data
- 4 The Pictorial Representation of Data
- 5 Frequency Distributions
- 7 Measures of Dispersion
- 8 Probability and Sampling
- 9 The Binomial Theorem
- 10 Further Probability Concepts
- 11 Tests of Significance
- 12 Further Tests of Significance
- 13 Sampling Techniques
- 14 Simulation
- 15 Time Series
- 16 Pairs of Characters
- Solutions to Exercises
- Bibliography
4 - The Pictorial Representation of Data
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 03 February 2010
The last chapter has shown how tables can facilitate the reduction of the observer's raw data and material to a form which enables the reader to grasp the essential features portrayed. In this chapter a further stage in this reduction is dealt with in the construction of charts and diagrams, which enable the salient features of a set of data to be picked out and vividly portrayed so that the reader can spot, without detailed study of the individual figures, the features of particular interest. The primary consideration to be borne in mind in the construction of any chart or diagram is clarity, since a confused diagram is of little help and it is probably better to have no diagram at all, than one that is virtually impossible to understand without a great deal of effort on the part of the viewer. To achieve this standard it is essential to decide at the outset on the purpose of the diagram and to exclude all irrelevant matter from consideration.
Broadly speaking, different considerations are involved according to whether the data are concerned with qualitative or quantitative characters. In the former case the study is of some characteristic such as hair colouring, for which it is difficult to have a numerical scale, whereas for quantitative characters, such as the height of schoolboys, it is possible to have a continuous numerical scale whose accuracy is limited only by the inability of the measuring apparatus to record heights to an accuracy of less than about, say ⅛ in.
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- The Pictorial Representation of Data
- P. G. Moore
- Book: Principles of Statistical Techniques
- Online publication: 03 February 2010
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511569685.005
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save book to Google Drive
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

2: Graphical Representations of Data
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 22222

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
In this chapter, you will study numerical and graphical ways to describe and display your data. This area of statistics is called "Descriptive Statistics." You will learn how to calculate, and even more importantly, how to interpret these measurements and graphs.
- 2.1: Introduction In this chapter, you will study numerical and graphical ways to describe and display your data. This area of statistics is called "Descriptive Statistics." You will learn how to calculate, and even more importantly, how to interpret these measurements and graphs. In this chapter, we will briefly look at stem-and-leaf plots, line graphs, and bar graphs, as well as frequency polygons, and time series graphs. Our emphasis will be on histograms and box plots.
- 2.2: Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots), Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs A stem-and-leaf plot is a way to plot data and look at the distribution, where all data values within a class are visible. The advantage in a stem-and-leaf plot is that all values are listed, unlike a histogram, which gives classes of data values. A line graph is often used to represent a set of data values in which a quantity varies with time. These graphs are useful for finding trends. A bar graph is a chart that uses either horizontal or vertical bars to show comparisons among categories.
- 2.3: Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Time Series Graphs A histogram is a graphic version of a frequency distribution. The graph consists of bars of equal width drawn adjacent to each other. The horizontal scale represents classes of quantitative data values and the vertical scale represents frequencies. The heights of the bars correspond to frequency values. Histograms are typically used for large, continuous, quantitative data sets. A frequency polygon can also be used when graphing large data sets with data points that repeat.
- 2.4: Using Excel to Create Graphs Using technology to create graphs will make the graphs faster to create, more precise, and give the ability to use larger amounts of data. This section focuses on using Excel to create graphs.
- 2.5: Graphs that Deceive It's common to see graphs displayed in a misleading manner in social media and other instances. This could be done purposefully to make a point, or it could be accidental. Either way, it's important to recognize these instances to ensure you are not misled.
- 2.E: Graphical Representations of Data (Exercises) These are homework exercises to accompany the Textmap created for "Introductory Statistics" by OpenStax.
Contributors and Attributions
Barbara Illowsky and Susan Dean (De Anza College) with many other contributing authors. Content produced by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 license. Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] .
Pictorial Representation of Data
Cite this chapter.

- Arthur H. Hall
245 Accesses
Data often need to be displayed pictorially since extended figures can be difficult to digest and interpret. In order to make them more digestible, to bring out comparisons as well as trends — even for the expert — a suitable form of display has to be chosen. For the mass media, and the public, it is necessary to select a presentation with the greatest impact.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Copyright information
© 1978 Marjorie H. Hall
About this chapter
Hall, A.H. (1978). Pictorial Representation of Data. In: An Introduction to Statistics. Palgrave, London. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-03146-7_18
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-349-03146-7_18
Publisher Name : Palgrave, London
Print ISBN : 978-1-349-03148-1
Online ISBN : 978-1-349-03146-7
eBook Packages : Mathematics and Statistics Mathematics and Statistics (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Praxis Core Math
Course: praxis core math > unit 1, data representations | lesson.
- Data representations | Worked example
- Center and spread | Lesson
- Center and spread | Worked example
- Random sampling | Lesson
- Random sampling | Worked example
- Scatterplots | Lesson
- Scatterplots | Worked example
- Interpreting linear models | Lesson
- Interpreting linear models | Worked example
- Correlation and Causation | Lesson
- Correlation and causation | Worked example
- Probability | Lesson
- Probability | Worked example
What are data representations?
- How much of the data falls within a specified category or range of values?
- What is a typical value of the data?
- How much spread is in the data?
- Is there a trend in the data over time?
- Is there a relationship between two variables?
What skills are tested?
- Matching a data set to its graphical representation
- Matching a graphical representation to a description
- Using data representations to solve problems
How are qualitative data displayed?
| Language | Number of Students |
|---|---|
| Spanish | |
| French | |
| Mandarin | |
| Latin | |
- A vertical bar chart lists the categories of the qualitative variable along a horizontal axis and uses the heights of the bars on the vertical axis to show the values of the quantitative variable. A horizontal bar chart lists the categories along the vertical axis and uses the lengths of the bars on the horizontal axis to show the values of the quantitative variable. This display draws attention to how the categories rank according to the amount of data within each. Example The heights of the bars show the number of students who want to study each language. Using the bar chart, we can conclude that the greatest number of students want to study Mandarin and the least number of students want to study Latin.
- A pictograph is like a horizontal bar chart but uses pictures instead of the lengths of bars to represent the values of the quantitative variable. Each picture represents a certain quantity, and each category can have multiple pictures. Pictographs are visually interesting, but require us to use the legend to convert the number of pictures to quantitative values. Example Each represents 40 students. The number of pictures shows the number of students who want to study each language. Using the pictograph, we can conclude that twice as many students want to study French as want to study Latin.
- A circle graph (or pie chart) is a circle that is divided into as many sections as there are categories of the qualitative variable. The area of each section represents, for each category, the value of the quantitative data as a fraction of the sum of values. The fractions sum to 1 . Sometimes the section labels include both the category and the associated value or percent value for that category. Example The area of each section represents the fraction of students who want to study that language. Using the circle graph, we can conclude that just under 1 2 the students want to study Mandarin and about 1 3 want to study Spanish.
How are quantitative data displayed?
- Dotplots use one dot for each data point. The dots are plotted above their corresponding values on a number line. The number of dots above each specific value represents the count of that value. Dotplots show the value of each data point and are practical for small data sets. Example Each dot represents the typical travel time to school for one student. Using the dotplot, we can conclude that the most common travel time is 10 minutes. We can also see that the values for travel time range from 5 to 35 minutes.
- Histograms divide the horizontal axis into equal-sized intervals and use the heights of the bars to show the count or percent of data within each interval. By convention, each interval includes the lower boundary but not the upper one. Histograms show only totals for the intervals, not specific data points. Example The height of each bar represents the number of students having a typical travel time within the corresponding interval. Using the histogram, we can conclude that the most common travel time is between 10 and 15 minutes and that all typical travel times are between 5 and 40 minutes.
How are trends over time displayed?
How are relationships between variables displayed.
| Grade | Number of Students |
|---|---|
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
- (Choice A) A
- (Choice B) B
- (Choice C) C
- (Choice D) D
- (Choice E) E
- Your answer should be
- an integer, like 6
- a simplified proper fraction, like 3 / 5
- a simplified improper fraction, like 7 / 4
- a mixed number, like 1 3 / 4
- an exact decimal, like 0.75
- a multiple of pi, like 12 pi or 2 / 3 pi
- a proper fraction, like 1 / 2 or 6 / 10
- an improper fraction, like 10 / 7 or 14 / 8
Things to remember
- When matching data to a representation, check that the values are graphed accurately for all categories.
- When reporting data counts or fractions, be clear whether a question asks about data within a single category or a comparison between categories.
- When finding the number or fraction of the data meeting a criteria, watch for key words such as or , and , less than , and more than .
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Guide To What Is The Pictorial Representation Of Worksheet Data
Introduction.
When dealing with a large amount of data, it can be overwhelming to make sense of it all. This is where the pictorial representation of worksheet data comes into play. It is a visual way of representing data using graphs, charts, and other visual elements. This method helps in presenting complex data in a simplified and easy-to-understand format, making it easier for anyone to analyze and interpret the information.
Using pictorial representation in data analysis is crucial as it allows for quick and easy identification of patterns, trends, and outliers at a glance. This visual aid helps in making informed decisions and presenting findings effectively to stakeholders.
Key Takeaways
- Pictorial representation of worksheet data uses graphs, charts, and visual elements to simplify complex data and make it easier to analyze.
- Using pictorial representation allows for quick identification of patterns, trends, and outliers, aiding in making informed decisions.
- When choosing the right pictorial representation, consider the type of data, the message you want to convey, and the audience's familiarity with different types of graphs.
- Best practices for creating pictorial representation include using appropriate scaling, labeling axes, using consistent colors and symbols, and avoiding data distortion.
- Benefits of using pictorial representation include making data easier to understand, highlighting trends and patterns, simplifying complex information, and engaging the audience.
Types of Pictorial Representation
When it comes to representing worksheet data in a visual format, there are several types of pictorial representations to choose from. Each type has its own unique characteristics and is best suited for displaying specific types of data. Let's take a closer look at some of the most commonly used types of pictorial representation:
Bar graphs are one of the most popular and widely used forms of pictorial representation. They are ideal for comparing the values of different categories or groups. The length of the bars represents the value of each category, making it easy to visualize and compare the data.
Pie charts are circular graphs that are divided into slices to represent the proportion of each category within the data set. They are useful for illustrating the breakdown of a whole into its constituent parts and are particularly effective for showing percentages.
- Line graphs
Line graphs are used to display data points connected by straight lines, making it easy to see trends and patterns over time. They are especially useful for showing changes and fluctuations in data over a continuous period.
- Scatter plots
Scatter plots are used to display the relationship between two variables. Each data point is represented by a dot on the graph, and the pattern of the dots can reveal the nature of the relationship between the variables, such as correlation or clustering.
How to Choose the Right Pictorial Representation
When it comes to representing worksheet data visually, selecting the right pictorial representation is essential for effectively communicating information. Here are some key factors to consider when making this decision:
A. Consider the type of data being represented
- 1. Numerical data: If your data consists of numerical values, bar graphs, line graphs, and pie charts are commonly used to depict this type of information. Bar graphs are ideal for comparing values across different categories, while line graphs show trends over time. Pie charts can be used to illustrate the proportion of each category within a whole.
- 2. Categorical data: When dealing with categorical data, bar graphs, pie charts, and stacked bar graphs can effectively showcase this type of information. Bar graphs and stacked bar graphs can compare values within categories, while pie charts display the distribution of each category.
- 3. Relationships between variables: For showing relationships between variables, scatter plots and line graphs are often utilized. These types of graphs can reveal patterns and correlations within the data.
B. Determine the message you want to convey
- 1. Trends: If the goal is to highlight trends or patterns within the data, a line graph or scatter plot may be the most suitable choice. These representations can effectively showcase changes over time or relationships between variables.
- 2. Comparisons: When the objective is to compare different categories or values, bar graphs and pie charts can clearly illustrate these comparisons. Stacked bar graphs are particularly useful for simultaneously comparing subcategories within larger categories.
- 3. Distribution: If you need to display the distribution of categorical data, a pie chart or stacked bar graph can visually represent the proportions of each category within the dataset.
C. Assess the audience's familiarity with different types of graphs
- 1. General audience: If the intended audience is not familiar with complex data representations, it may be best to opt for simpler graphs such as bar graphs and pie charts. These are commonly understood and can effectively convey the information to a broad audience.
- 2. Data-savvy audience: For an audience well-versed in data analysis, more advanced representations like scatter plots and stacked bar graphs may be appropriate. These individuals can interpret and derive insights from more intricate visualizations.
Best Practices for Creating Pictorial Representation
When creating pictorial representations of worksheet data, it's important to follow best practices to ensure that the visualizations accurately and effectively communicate the information. The following are some key best practices to keep in mind:
- Use appropriate scaling
It's important to choose the right scale for your pictorial representation to ensure that the data is accurately represented. Be mindful of the range of the data and choose a scale that effectively captures the variations without distorting the overall picture.
- Label axes and provide a clear title
Labeling the axes and providing a clear title for your pictorial representation is essential for helping the audience understand the context and meaning of the data. Make sure the labels and title are clear, concise, and informative.
- Use consistent colors and symbols
Consistency in the use of colors and symbols in your pictorial representation is crucial for clarity and coherence. Choose a color palette and set of symbols that are easily distinguishable and use them consistently throughout the visualization.
- Avoid distorting the data
It's important to avoid distorting the data in your pictorial representation. Be cautious of various visual techniques such as skewed scales, exaggerated proportions, and manipulated axes that can misrepresent the data.
Tools for Creating Pictorial Representation
When it comes to visualizing data from a worksheet, there are several tools available that can help you create pictorial representations. Here are some of the most popular ones:
Excel is a widely used spreadsheet software that offers various chart and graph options to visually represent data. You can easily create bar graphs, pie charts, line graphs, and more to effectively showcase your worksheet data.
Google Sheets also provides a range of chart types to visually depict your data. With its intuitive interface and built-in chart tools, you can quickly create appealing visual representations of your worksheet data.
Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that allows you to create interactive and dynamic visualizations. It offers advanced features for creating dashboards, maps, and other complex visual representations of worksheet data.
Infogram is a user-friendly tool for creating infographics, charts, and maps. It provides a range of templates and customization options to easily transform your worksheet data into engaging visual content.
Benefits of Using Pictorial Representation
When it comes to presenting worksheet data, using pictorial representation can offer several benefits that can enhance understanding, highlight key trends, simplify complex information, and engage the audience.
Pictorial representation such as graphs, charts, and diagrams can make it easier for individuals to comprehend the data presented. Visualizing the data can help in clarifying the information and making it more accessible.
By using visual representations, it becomes easier to identify trends and patterns within the data. Whether it's a fluctuation in sales over time or a correlation between different variables, pictorial representation can make these insights more apparent.
For datasets that contain complex information, using visuals can simplify the presentation of the data. Instead of overwhelming the audience with raw numbers and figures, creating a visual representation can simplify the message and make it more digestible.
Visuals are inherently more engaging than plain text or tables of data. Pictorial representation can capture the audience's attention and make the information more memorable. This can be particularly effective when presenting to a diverse audience with varying levels of data literacy.
As we wrap up this discussion on the pictorial representation of worksheet data, it's important to emphasize the significance of using graphs and charts to visually represent data. Not only do they make complex data more understandable, but they also facilitate quick and easy analysis. I encourage all readers to incorporate various types of graphs, such as bar graphs, pie charts, and line graphs, in their data analysis to gain deeper insights into their data.

Immediate Download
MAC & PC Compatible
Free Email Support
Related aticles

The Benefits of Excel Dashboards for Data Analysts

Unlock the Power of Real-Time Data Visualization with Excel Dashboards

Unlocking the Potential of Excel's Data Dashboard

Unleashing the Benefits of a Dashboard with Maximum Impact in Excel

Exploring Data Easily and Securely: Essential Features for Excel Dashboards

Unlock the Benefits of Real-Time Dashboard Updates in Excel

Unleashing the Power of Excel Dashboards

Understanding the Benefits and Challenges of Excel Dashboard Design and Development

Leverage Your Data with Excel Dashboards

Crafting the Perfect Dashboard for Excel

An Introduction to Excel Dashboards

How to Create an Effective Excel Dashboard
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
Create a pictorial chart and discover important patterns and trends
A pictorial chart is a visual representation of data that uses icons. Learn how to create an effective pictorial chart quickly with Infogram's free chart maker.

A pictorial chart (also called a pictogram, a pictograph, or a picture chart) is a visual representation of data that uses pictograms – icons or pictures in relative sizes – to highlight data patterns and trends. Pictorial charts are common in business communication or news articles to visually compare data .
With Infogram, you can quickly create professional pictorial charts for your business or personal use. It's easy to get started. Just choose pictorial chart templates created by our designers. Add icons, text, adjust colors, and visualize your data to engage your audience from the first glance.
Read on to learn more how to create a pictorial chart online using our easy-to-use pictorial chart maker. Don't worry, we're handling the complicated pieces, allowing you to focus on making engaging, interactive, and educational content that makes an impact.
Everybody Infogram
Many of our clients are excited by the service that we deliver. read about what some have said about us..

“ With Infogram we turned our service reporting into the cutting-edge category and receive amazing feedback from the user community. ”

Andreas Igler Director of IT & Operations

“ I’m a data nerd, so I love tools that help readers better visualize information. We use a tool called Infogram at TechCrunch for data visualization. It’s super-easy to use, and you don’t have to be a data analyst or graphic designer to use it. ”

Travis Bernard Director of Audience Development

“ Infogram has taken our stats to the next level. It's great to be able to upload a spreadsheet and turn it into a beautiful interactive piece for our clients to enjoy. ”

Kris Carpenter Director of Marketing
Browse all pictorial chart templates
Want to get started right away and create a pictorial chart choose our ready-made chart templates to stand out from the sea of “meh” content. keep it simple and create a professional-looking pictorial chart in seconds..
Get inspired by pictorial chart examples
Trying to find inspiration for creative new ideas check out our wonderful collection of pictorial charts created right here on infogram..

Frequently asked questions
1. Click on the Get started button in the top right corner of the homepage.
2. Sign up with Google, Facebook, or email. If you choose to sign up with Google or Facebook , simply login to your account when asked to do so. If you wish to sign up with your email address , enter the email and your desired password, then hit the Signup button .
3. Provide some basic information about yourself. Enter your first and last name, indicate what kind of organization you belong to, and specify your role. You will then be able to continue with the Basic plan or choose from any of the available paid plans . View more
Pictorial charts are often used to compare the number of units , size , or progress . A pictorial chart is a great choice when comparing a few categories with clear differences. Pictorial charts are very common in business communication and media (for example, in news articles or infographics ).
Pictorial charts are a great pick whenever you want to make your data stand out and become more memorable . When designed effectively, pictorial charts will make a great addition for:
1. News articles
3. Infographics
4. Presentations
Infogram's chart creator allows you to quickly make a pictorial chart in just 5 steps:
1. Log in to Infogram
2. Select the pictorial chart type (the classic pictorial chart , size comparison , or pictorial bar )
3. Upload or copy and paste your data
4. Customize the labels and icons, then adjust the design by changing the background , colors , and fonts
5. Download your pictorial chart , add it to your report , infographic , embed it on your website , or share it on social media
Infogram is super easy to use and made with non-designers in mind. Even if you don't have any programming , coding , or design experience , you'll be able to make pictorial charts in just a couple of steps.
We did all the technical work for you. Now, all that's left to do is start creating.
Here are some general tips to keep in mind to make a pictorial chart like a superstar:
1. Find the right icon. The power of pictorials is in their familiar shapes , so try to find icons that represent your categories.
2. Avoid using very detailed icons. That way, the reader will be able to understand your chart at a glance. Try to think of the simplest picture that represents the data.
3. A void large data sets. Using a pictorial chart for large data sets will make it hard to count the values.
The origins of the pictorial chart can be traced back to the history of civilization. Early written symbols were based on pictographs (pictures that resemble what they signify) and ideograms (symbols which represent ideas). Ancient Sumerian , Egyptian , and Chinese civilizations began to adapt such symbols to represent concepts, developing them into logographic writing systems .
The idea of the universal language of pictorials was best developed by an Austrian social scientist Otto Neurath and a German designer Gerd Arntz in the late 1920s. Together, they were the perfect fit to develop an ISOTYPE (International System Of Typographic Picture Education) – a set of 4,000 pictograms that could express almost anything.
Learn more about the history of the pictorial chart here .
You can customize any pictorial chart to your liking. Pick the right color palette and font , adjust the labels and icons , and even add animations . To edit your chart , click on it, then go to Settings and make the necessary changes.
All rights reserved © 2024 Infogram. Terms & Privacy Infogram and Infogr.am are registered trademarks of Prezi, Inc.

- Infographics
- Facebook posts
- Single chart
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Marketing 10+ Pictograph Examples and How To Make Them
10+ Pictograph Examples and How To Make Them
Written by: Daleska Pedriquez Dec 02, 2021

We’re all used to seeing bar charts , line charts , and pie charts in business settings, but not pictographs. But pictographs can also be a powerful form of data visualization .
How do pictographs work in a business setting and as a visual marketing tool? This guide will share examples of pictographs and show you how to make one yourself.
Haven’t had experience creating pictograms? With the Venngage Chart Maker , you can create pictographs easily.
Click to jump ahead:
- What is a pictograph?
What is the importance of using pictographs?
What are the parts of a pictograph, 5 steps for creating a pictograph, are pictographs and pictograms the same , best venngage pictograph templates, faqs about creating a pictograph, what is a pictograph .
A pictograph is a pictorial representation of data that uses icons, images, or symbols related to the central topic. A key is often included in the chart to indicate what word or numerical data group each icon represents.
The size of your icons must be the same except when you need to show a fraction relative to the amount per key.
Take a look at the pictograph example below. While the numerical values are bold and clear, you appreciate the data more because of the supplemental icons. It emphasizes the point of the pictograph.

This is an excellent design for the type of advocacy where you want to highlight statistics. Or you can use it in a pitch deck to show how many students are using your product.
Another good pictograph design can be found below. As we all know, infographics have been an effective tool to inform and educate the market. This pictograph represents how many children are using social media channels as well as their usage behavior.

And by using pictographs, you get to send your message across clearly. In this specific example, the infographic uses both icons and real photos, making the data easy to understand.
The Venngage library offers a variety of icon and image options. Choose from 40,000+ icons from a variety of styles for your pictogram. Replace them in the editor with the click of a button.
Want to add or swap out images from the template? Venngage’s library includes integration with Pexels and Pixabay, giving you access to 4 million free stock photos .
Related: 9 Best Infographic Makers for Businesses in 2021
Return to Table of Contents
Pictographs are commonly used in mathematics and in data handling. This type of pictorial representation is ideal for early learners because it’s visually appealing and easier to understand compared to other types of charts .
But pictographs have plenty of uses for the corporate world. They can be used in business settings where large amounts of data need to be presented in a by-the-numbers infographic .
Nonprofit organizations can benefit from using pictographs, like in the below pictogram example.

To highlight the percentage of refugee children who are orphaned, the template uses a broken heart icon that. This strengthens the message of the infographic.
Here’s a statistical infographic on a similar central topic that has also used pictographs.

The template uses immediately recognizable and relevant icons for wastewater and highlights the given data by adjusting the transparency. This is a great technique if you want your pictograph to follow a minimalist approach while still breaking down complex data.

Visualizing data is easy with Venngage’s import data function. Import your information from a Google sheet or CSV into the Venngage editor and the charts automatically populate the data.
Related: How to Choose the Best Types of Charts For Your Data
Most of the examples of pictographs in this post are contained within infographics. However, for a standard pictograph, these are the essential elements that you need to include:
- Graph title
- Categories
You can see these elements in action in the following pictograph. Note each symbol is the same size and the difference in numbers is only depicted through a change in color hue.

The above pictograph shows how many students have access to phones. These statistics could have been shown as raw numbers, but a pictograph can visualize numbers so the audience understands them at a glance.
Related: Pie Charts and Other Ways to Show Percentages in Infographics
Now that you know the parts of a picture graph, how can you create one:
- Collect the data – Identify the data for the different categories to create the best chart . From there, create a list or table so you can easily plot it into a pictogram once you have all the other elements.
- Choose a symbol – Think about the most relevant icons or symbols you can use to depict the given data in your pictograph. If you are talking about time, you can use a watch or even an hourglass.
- Include the key – Assign a numerical value per icon. For example, an hourglass could represent five hours. Make sure to include the key in your graph so that your audience will be able to translate your data properly.
- Lay out your pictograph – Create two columns where you can place your categories and data. Add the icons based on your key.
- Review the design – Check all your labels and review to make sure you haven’t missed anything from your report. You can also ask the opinion of others so you can improve your design.
If you don’t want to start from scratch or aren’t sure of your design abilities, use Venngage’s templates to depict your pictograph. With over a thousand free templates, you can depict any type of data.
With Venngage for business , you can add your brand kit to all designs with a single click. Use the My Brand Kit feature to automatically import your logo, colors, and fonts.
Many people confuse pictographs and pictograms . They are actually the same. However, do not confuse them with ideograms that use geometric shapes and lines to represent ideas.
Pictographs and pictograms use pictures, icons, and symbols to depict a topic. For example, you can use the sun to indicate summer, clouds for a windy day, flame for fire, ice cream for desserts, or waves for oceans.
The infographic below uses icons that are universally acknowledged as figures for males and females.

Ideograms are more complex to understand than the above table because they represent abstract ideas.
Related: How to Create a Stunning Pyramid Chart in 5 Steps
Venngage has several templates for pictographs and infographics. We’ve shared a few examples, but here are a few more.
Population growth infographic template
Using different colors for your pictographs is a great strategy if you want to make your design interesting. This can be seen in the picture graph template below.

Apart from making your chart visually appealing, it makes your data stand out. Numbers become clearer and your audience is better able to understand the information right away.
Kubler Ross change management template
If you want to add more information about your pictograph, you can see how the change management communication template below is organized for inspiration.

The categories in the pictograph are straightforward. However, before you present this information to management, you will want to give more details, especially because the subject is related to your employees.
In other words, when you create pictographs, always consider your audience. Ask yourself, what do they need to know and what details can improve your pictogram?
How NPS works infographic template
You can also get creative with your pictographs similar to what you can get from our next example. Instead of using similar graphics, this template uses a variety of styles to represent different categories.

You can follow this style for your own pictogram design. Your audience will be more engaged and interested if your pictograph is unique.
What are the common mistakes in pictograph designs?
Creating a pictograph can be exciting. But that’s also the reason why most people make mistakes with their designs. These are the errors to avoid while making a pictogram.
First, don’t forget to add the title for your pictograph. No matter how good your charts and symbols are, not having a title can confuse your audience. Do not expect that people will understand your graph with that. Highlight your title and use larger fonts.
Since we’re talking about text, always check that you have labeled your graph properly. This includes the categories and the definitions in your key.
Another mistake is using complex icons. The goal is to design a pictogram that everyone can understand at a glance. Use symbols and icons that are universally known.
If you aren’t sure about creating pictographs, using an online design platform like Venngage will make the process easier.
How do you use a pictograph maker?
In today’s digital age, we all need to be efficient. If you can automate tasks, you can get more work done. The same goes for creating graphs .
It’s fine if you aren’t comfortable designing infographics or pictograms. With the Venngage chart maker, creating a pictograph is a breeze.
Sign-up is free and you can start creating immediately. Choose a template, edit the data and swap out icons. It takes little time to work with the intuitive editor before your design is complete.
Use pictogram design to represent data in a visually-appealing way
The examples above prove that pictorial representation can be a powerful tool for sharing complex data with a wider audience.
With Venngage’s simple design solution, you can create a memorable pictogram for marketing and business materials and make an impact on your customers.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

- Study Abroad Get upto 50% discount on Visa Fees
- Top Universities & Colleges
- Abroad Exams
- Top Courses
- Read College Reviews
- Admission Alerts 2024
- Education Loan
- Institute (Counselling, Coaching and More)
- Ask a Question
- College Predictor
- Test Series
- Practice Questions
- Course Finder
- Scholarship
- All Courses
- B.Sc (Nursing)
Pictorial Representation Of Data: Bar Graph, Properties, Types & Examples

Collegedunia Team
Content Curator
Pictograph is a term for a visual or pictorial representation of data . For example, a bar graph allows data stakeholders to visually show a wide range of data, which not only improves understanding but also makes things easier for the merchant. The difference between realistic and logical visuals is a common one in graphical representations. Paintings, Photographs and drawings that are realistic have solid qualities & structures in common with the items they describe. A bar graph, often known as a bar chart, is the most basic visual data representation.
Read Also: Class 8 Introduction to Graph
|
|
Key terms: Bar Graph, Pictorial, Group, Rectangular, Expenditure, Representation,data
Pictorial Representation Using Bar Graph
[Click Here for Sample Questions]
A bar graph , also referred to as a bar chart, is a graph that displays data in the form of rectangular bars. The length of the bar is proportionate to the values it represents in this case. The bar graph can be formed both ways: vertical and horizontal orientation. The term “column bar graph” refers to a vertical bar graph.
Bar graphs are used as comparative tools because they can display multiple groups of data on the same graph. The length of the rectangular bar refers to the value of each category. As these rectangular bars are proportional, the disparities between them may be seen much more easily than with words. Let’s look at bar graphs in more detail.
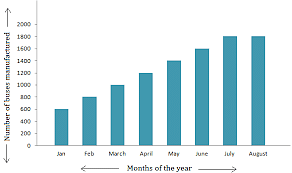
Assume your monthly salary is 15k, and You are free to spend this money in any way you see fit. You spend this money on Groceries, entertainment, electricity bill and all. What you observe is that the money appears to vanish very soon. So, you reluctantly create a bar chart to know about where you are actually spending your money so that you can balance your expenditure accordingly. However, you'll need data to make a bar chart. You should keep track of what you spend money on and how much you spend it on. After a month, you have the details of this months’ expenditure, and they look something like this.
| Expenditure | 1 Month |
|---|---|
| Groceries | 4000 |
| Electricity Bill | 2000 |
| Entertainment | 1500 |
| Outdoors | 4000 |
| Savings | 2500 |
The first thing to notice is how the information is organized. It is the first step in the process of making a bar graph. All the expenditures are all classed together. The same can be said for other things as well. When talking about a bar graph, it was noted that the values are represented by a rectangular bar, the length of which is proportional to the data value. Another feature of a bar graph comes into play at this point. Let’s look at an example,
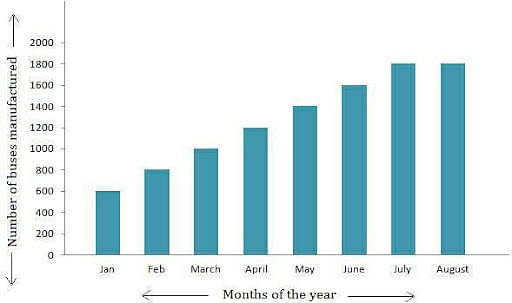
A uniform scale is required for a bar graph. The scale determines how the numerical data is converted into a rectangular representation. A bar graph is a visual depiction of numbers made up of bars of varying widths and lengths that are proportional to the number.
For example, if you use a 25 cm long rectangular bar to symbolize the money you spent on chocolate, the scale is 1 rupee equals one unit on the graph, i.e. one rupee equals one centimeter. However, it is evident that a large graph is required for this form of representation. The problem with scale is that we have complete control over it. So, instead of 25 cm, a rectangular bar of length 25 millimeters can be used to indicate the same number, and here the scale is 10 rupees equals one unit, i.e. 10 rupees equals one centimeter.
As clear information about the scale is critical for data interpretation, it is critical to state the scale of your graph on both the x-axis and the y-axis. Using the latter scale, one centimeter equals ten rupees. It’s vital to remember that all of the data groups in the bar graph have the same scale.
Properties of Bar Graph
Here are some important properties of Bar Graph:
- Each bar or column in a bar graph must have the same width.
- All rectangular bars must have equal space between them.
- The base of the bars is common in a bar graph.
- The height of the bars proportionally represents the data in the bar graph.
- Depending on the data, the bars can be drawn horizontally or vertically.
Check More: Graphical Representation of Data
Types of Bar Graphs
A bar graph is used to show data in a graphical representation. Here are some different types of Bar graphs:
- Vertical bar graph
Vertical bar graphs are graphs or charts in which the given data is shown vertically in a graph or chart with the use of rectangular bars that display the data measure. The y-axis indicates the value of the height of the rectangular bars, which reflects the quantity of the variables stated on the x-axis, and the x-axis shows the vertically drawn rectangular bars.
- Horizontal bar graph
Horizontal bar graphs are graphs in which the provided data is displayed horizontally by rectangular bars that display the data measure. The variables or classifications of the data must be written, and then rectangular bars must be constructed horizontally on the y-axis, with the length of the bars equivalent to the values of the various variables present in the data on the x-axis.
- Stacked Bar Graph
The composite bar graph is another name for the stacked bar graph. It separates the entire bar into sections. Each segment of a bar is represented by a different colour to make it easier to distinguish between the many categories. It necessitates appropriate labelling to distinguish the various portions of the bar. In a stacked bar graph, each rectangular bar represents the entire graph, and each segment in the rectangular bar represents the various components of the entire graph. It can be displayed horizontally or vertically.
- Grouped Bar Graph
The clustered bar graph is another name for the grouped bar graph. It's used to represent the discrete value of two or more categorical data sets. Rectangular bars are clustered by position for levels of one categorical variable, with the secondary category level in each group shown in the same colour. It can be displayed in both vertical and horizontal orientations.
Pictorial Representation of Data using Vertical Bar Graph
Vertical bar graphs are frequent visual representations that employ vertical bars to communicate data. The categories are represented by the horizontal axis, while the data for each category is represented by the vertical bars. The x-axis is the horizontal axis, while the y-axis is the vertical axis.
Vertical bar graphs can also be used to depict a sequence of data and how it changes over time. All of the vertical bars run from the x-bottom axis to its top.
Pictorial Representation of Data Using Horizontal Bar graph
The data is represented in the horizontal bar graph by bars that are parallel to the x-axis. The types are defined on the y-axis, and the data is represented by horizontal bars. The horizontal graph's bars run from left to right along the x-axis.
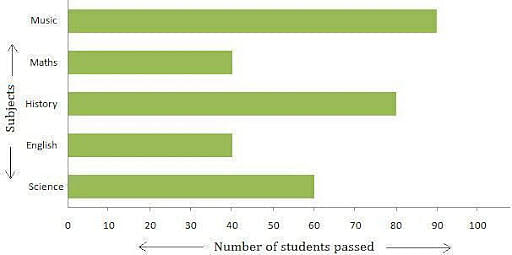
For example, A class teacher of Grade 5 made a note of the students who passed in every subject in the class. She represented the data in the form of a horizontal bar graph to know the passing students in every subject.
You've seen how the bar graph of your first week's expenses looks. Assume you keep track of where you spent your money for a while longer. You discover that your expenses for week two differ slightly from those for week one. The second-week expenses are as follows:
| Expenditure | 1st Month | 2nd Month |
|---|---|---|
| Groceries | 4000 | 4000 |
| Electricity Bill | 2000 | 1500 |
| Entertainment | 1500 | 1500 |
| Outdoors | 4000 | 6000 |
| Savings | 2500 | 2000 |
They can all be plotted on the same bar graph because they are all part of the same group. Remember that the scale is the same for all the data in the graph. Rather than charting them independently, you can compare the changes over a longer time span or across a wider range of data by grouping them together. Now that we've plotted everything together, we'll be able to see the differences in weekly spending.
This process also allows you to control your spending because you now know where your money is going. This allows you to determine whether your expenses are necessary.
Read More: Class 8 Introduction to Graph MCQ’s
Things to remember
- A bar graph, often referred as a bar chart, is a graph that displays data in the form of rectangular bars.
- A bar graph is used to show data in a graphical representation.
- For pictorial representation, there are 3 kinds of bar graphs to choose from: Vertical bar graph, horizontal bar graph and Double bar graph.
- The bar graph can be formed both ways: vertical and horizontal orientation. The term “column bar graph” refers to a vertical bar graph.
- Bar graphs are used as comparative tools because they can display multiple groups of data on the same graph.
Sample Questions
Ans. We can plainly see from the graph above that the fewest number of cakes were prepared on Tuesday because Tuesday is the smallest bar. Following this bar, we can see that 10 cakes were produced on this particular day.
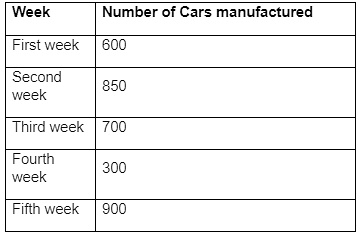
- The data represented by the bar graph is as follows:

- The total number of cars made in the fourth week = 300, as can be seen in the graph above.
As a result, the total number of cars produced during the fourth week was 300.

Ans. The quantity of shirts sold on Thursday is 3535 units, as seen in the bar graph.
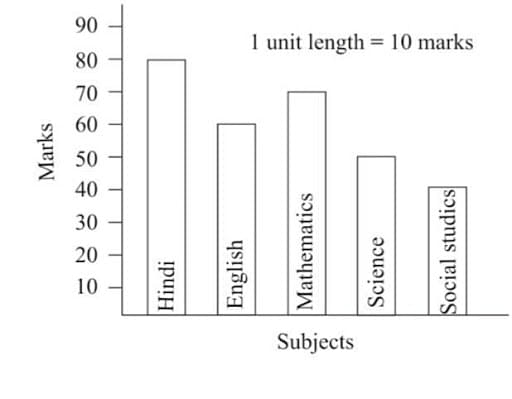
Ans. The minimum mark for Social Studies is 4040, as shown in the bar graph.
As a result, Ajay received the lowest possible grade in Social Studies.

Ans. A bar graph is a visual representation of data that uses vertical or horizontal bars of consistent width to represent data. They can be drawn on the horizontal axis (say, the X-axis) with equal spacing between them to represent the variable. The variable’s values are displayed on the vertical axis (say, the Y-axis), and the heights of the bars are determined by the variable’s values.
As a result, rather than playing, most students prefer to read storybooks.

Ans. It is obvious that wheat output in 1998 was at a minimum, which was 15.
Ans. The data can be represented by the following double bar graph:

Ques. Differentiate between a bar graph and a histogram. (3 Marks)
Ans. A bar graph and a histogram are differentiated as follows:
| Bar Graph | Histogram |
|---|---|
| Bar graphs help in the pictorial representation of categorical data in the form of rectangular bars (as heights or lengths) and compare it. | Histograms help in the frequency distribution of the quantitative data with continuous class intervals. |
| The data provided is represented pictorially. | The data provided is represented graphically |
| Discrete variables are distributed | Non-discrete variables are distributed. |
| Equal spacing between each solid bar and they do not touch each other. | No equal spacing between each solid bar and they touch each other. |
| The data used is categorical | The data used is quantitative |

Ans. The variable shown on the X-axis in the given bar graph is 'Months of Birth,' while the value of the variable plotted on the Y-axis is 'Number of Students.'
By looking at the graph, one can see that there are four individuals born in November.
By looking at the graph, it can be seen that the most individuals were born in August.

CBSE X Related Questions
1. sides ab and bc and median ad of a triangle abc are respectively proportional to sides pq and qr and median pm of ∆pqr (see the given figure). show that ∆abc ∼ ∆pqr., 2. a chord of a circle of radius 15 cm subtends an angle of 60° at the centre. find the areas of the corresponding minor and major segments of the circle. (use \(\pi = 3.14\) and \(\sqrt3 = 1.73\) ), 3. if 3 cot a = 4, check whether \(\frac{(1-\text{tan}^2 a)}{(1+\text{tan}^2 a)}\) = cos 2 a – sin 2 a or not, 4. draw the graphs of the equations \(x – y + 1 = 0 \) and \(3x + 2y – 12 = 0\) . determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and the \(x\) -axis, and shade the triangular region., 5. an umbrella has 8 ribs which are equally spaced (see fig. 11.10). assuming umbrella to be a flat circle of radius 45 cm, find the area between the two consecutive ribs of the umbrella., 6. if the median of the distribution given below is 28.5, find the values of x and y. class interval frequency 0 - 10 5 10 - 20 x 20 - 30 20 30 - 40 15 40 - 50 y 50 - 60 5 total 60, subscribe to our news letter.

Reference.com
What's Your Question?
- History & Geography
- Science & Technology
- Business & Finance
- Pets & Animals
What Is a Pictorial Representation of Data?
A chart or a graph is a pictorial representation of data. Charts and graphs are used to display detailed information and relationships between quantitative data. Examples of charts include bar graphs, pie charts, histograms and time-series graphs.
Charts are often found alongside tables that contain the same data, because people can sometimes make observations and draw conclusions faster through graphical representations than through text. Although charts vary in form, they share common features such as titles, axes for dimensions, grids, labels and legends.
Choosing the correct type of chart helps in presenting data clearly. A bar graph, which consists of rectangular bars whose lengths reflect the values they represent, is appropriate for comparing frequencies of categorical data. A pie chart presents each item as a slice of a circular pie to make composition analysis. A histogram looks similar to a bar graph, but it displays data at the ordinal level of measurement. A time-series graph show changes in data over time.
Charts are more effective when they have accompanying descriptive texts, labels and tips on how to interpret the data. Arranging data in order also helps in finding patterns and trends. Office suite programs, such as word processors, spreadsheets and presentation software, typically offer comprehensive tools for creating charts. Chart and graph generators also are available online.
MORE FROM REFERENCE.COM

- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Class 8 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 11 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
- IBPS Clerk Syllabus of Quantitative Aptitude
Ratio & Proportion, Percentage
- Ratios and Percentages
- Ratio and Proportion
- Tricks To Solve Ratio and Proportion
- Tips & Tricks To Solve Ratio & Proportion - Advance Level
- Basic Concept of Percentage
- Percentages
- Average in Maths
- Tricks To Solve Questions On Average
- Time and Work - Aptitude Questions and Answers
Time Speed, and Distance
- Time Speed Distance
- Speed and Distance Advance Level
Mixtures & Allegations
- Alligation or Mixture - Aptitude Questions and Answers
- Tricks To Solve Mixture and Alligation
- Mixtures and Alligation
- Mixture and Alligation | Set 2
Partnership
- Introduction to Accounting for Partnership
- Partnership : Definition, Concepts, Types of Partnership
- Partnership | Meaning and Features of Partnership
- Types of Partnership
- Tricks To Solve Partnership Problems
- Surface Areas and Volumes
Bar Graphs, Linear Graphs and Pie Charts
- Bar Graphs and Histograms
- What is Linear Graph? Definition, Equation, Examples
Trigonometry, Height and Distances
- Trigonometry & Height and Distances
- Practice Set For Height & Distance
- Height and Distance | Applications of Trigonometry
- Trigonometric Ratios
- Trigonometry in Maths: Table, Formulas, Identities and Ratios
- Laws of Logarithms
- Logarithm Formula
- Permutation and Combination
- Permutations and Combinations
- Combinations Formula with Examples
- Permutation
- Linear Equations Formula
- Linear Equations in One Variable
- Linear Equation in Two Variables
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Relationship Between Two Variables
- Algebraic Methods of Solving Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Linear Function
- Solve the Linear Equation using Substitution Method
- Quadratic Equations: Formula, Method and Examples
- Solving Quadratic Equations
- Quadratic Formula
- Roots of Quadratic Equation

Profit, Loss, and Discount
- Practice Set For Profit and Loss
- Profit and Loss
- Mensuration 2D
- Mensuration in Maths | Formulas for 2D and 3D Shapes, Examples
- Practice Question On Area And Perimeter Of All Shapes
- Algebra in Math: Definition, Branches, Basics and Examples
- Data Interpretation
- Cumulative DI For Bank PO Exam
- DI Table Graph and Chart Questions For Bank PO Exams
Miscellaneous
- Approximation - Aptitude Question and Answers
- Arithmetic Progression
- Number Series Reasoning Questions and Answers
- Important Formulas of Interest, Mensuration, Permutation & Combination and Probability
- Basic Concept Of Number System
- Basic Concepts Of Whole Numbers
A Pie Chart is a pictorial representation of the data. It uses a circle to represent the data and is called a Circle Graph. In a Pie Chart, we present the data by dividing the whole circle into smaller slices or sectors, and each slice or sector represents specific data.
In this article, we will learn about Pie Charts, Steps to Create Pie Charts, Examples, and Others in detail. The image added below shows a pie chart.

Table of Content
What is Pie Chart?
Pie chart definition, types of pie chart, pie chart examples, pie chart formula, how to make pie chart, how to read pie chart, pie chart vs bar graph, pie chart advantages, pie chart disadvantages, uses of pie chart.
- What is Population Pie chart?
Pie Charts Questions
A pie chart is a pictorial or graphical representation of data in chart format. A pie chart uses a circle or sphere to represent the data, where the circle represents the entire data, and the slices represent the data in parts.
Pie chart is one of the easiest ways to present and understand the given data, and pie charts are used very commonly. For example, pie charts are used in Excel very often.
There are different ways of data representation . A pie chart is one of the types of charts in which the data is represented in a circular shape. The pie chart circle is further divided into multiple sectors/slices; those sectors show the different parts of the data from the whole.
Pie charts, also known as circle graphs or pie diagrams, are very useful in representing and interpreting data. The data can be compared easily with the help of a pie chart. Below is an example of a pie chart explained in detail.
There are various variation or types of pie chart, some of the common types include:
- 3D Pie Chart: A 3D pie chart adds depth to the traditional two-dimensional pie chart by rendering it in three dimensions.
- Doughnut Chart: A doughnut chart is similar to a pie chart but with a hole in the center.
- Exploded Pie Chart: In an exploded pie chart, one or more slices are separated from the rest of the pie to emphasize their importance or to make them stand out.
- Nested Pie Chart: Also known as a multi-level pie chart or hierarchical pie chart, this type of chart consists of multiple rings of pie charts, with each ring representing a different level of data hierarchy.
- Ring Chart: A ring chart is similar to a doughnut chart but consists of multiple rings instead of just one. Each ring represents a different category of data, with the size of each segment within the ring corresponding to its proportion of the whole.
Also Check : Pie Chart in MATLAB
Let’s take a look at an example for a better understanding of pie charts. In a class of 200 students, a survey was done to collect each student’s favorite sports. The pie chart of the data is given below:

Since the pie chart is provided and the total number of students is given, we can easily take the original data out for each sport.
- Cricket = 17/100 × 200 = 34 students
- Football = 25/100 × 200 = 50 students
- Badminton = 12/100 × 200 = 24 students
- Hockey = 5/100 × 200 = 10 students
- Other = 41/100 × 200 = 82 students
The original data for the pie chart shown above is given below:
| Sport | Number of Students |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The total value or percentage of the pie is 100% always. Here it contains different sectors and segments in which each sector or segment of the chart corresponds to a certain portion of the net or total percentage (or data). The total or sum of all the data can be summed up to 360 degrees.
- Converting the data into degrees on a pie chart. The formula for a pie chart can be summed up as:
(Given Data / Total Value of Data) × 360°
- Calculating the percentage of each sector from degrees in a pie chart.
To work out with degrees in a pie chart, we need to follow the following steps:
- First, we need to measure every slice of the chart.
- Then we need to divide it by 360°.
- Finally, multiply the obtained result by 100.
The pie chart formula is given below:
(Frequency)/(Total Frequency) × 100
Calculating Number of Sectors on a Pie Chart
To calculate the total number of slices or sectors on a pie chart, we need to multiply the sector’s percentage by the total value of the data and finally divide the result by 100.
We will learn how to create a pie chart step by step with the help of an example. A teacher surveyed a group of students to see what their favorite hobby of each student is. Let’s take a look at the pie chart example with an explanation. The data collected is listed as follows:
| Hobbies | Number of students |
|---|---|
| Singing | 16 |
| Reading books | 20 |
| Dancing | 10 |
| Painting | 30 |
| Others | 24 |
Now we will see how to construct a pie chart step by step.
Step 1: The first step requires us to write down the available data in tabular form as follows:
| Singing | Reading Books | Dancing | Painting | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 20 | 10 | 30 | 24 |
Step 2: Now find the sum of all the given data. Here, the Sum of All Data = (16 + 20 + 10 + 30 + 24) = 100
Step 3: Now, calculate the percentage of each sector. We need to divide each sector value by the sum or total and then multiply it by 100.
| Singing | Reading Books | Dancing | Painting | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (16/100) × 100 = 16% | (20/100) × 100 = 20% | (10/100) × 100 = 10% | (30/100) × 100 = 30% | (24/100) × 100 = 24% |
Step 4: Next step is to calculate the degrees corresponding to each slice. The values can be calculated as:
Central Angle of Each Component = (Given Data / Total Value of Data) × 360
Hence, The values are as follows:
| Singing | Reading Books | Dancing | Painting | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (16/100) × 360 = 57.6 | (20/100) × 360 = 72 | (10/100) × 360 = 36 | (30/100) × 360 = 108 | (24/100) × 360 = 86.4 |
Step 5: Now, with the help of a protractor, we will measure each angle from a single point or central point and draw the circle’s sectors. The resultant pie chart will be:
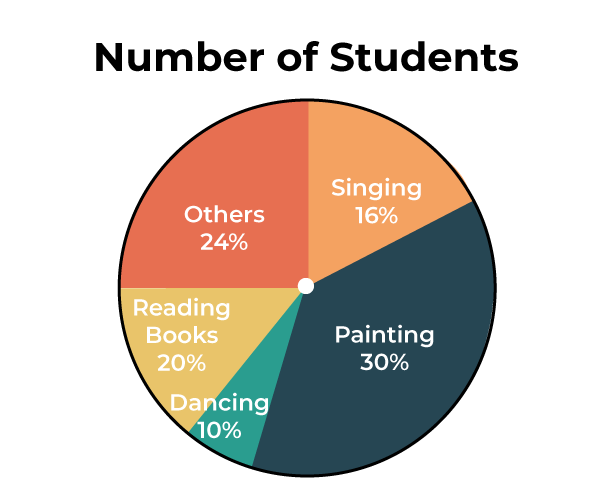
In order to read a pie chart, the first thing to notice is the data presented in the pie chart. If the data is given in percentage, it should be converted accordingly in order to analyze and interpret the data. Let’s take a look at an example in order to learn how to interpret pie charts.
Example: In a survey done among 300 people, it was observed which type of genre each person prefers. The pie chart of the same is mentioned below. Analyze and interpret the pie chart accordingly to find the original data.

While observing the pie chart, it came to notice that the data is present in percentage. Let’s convert the data to obtain the original value. Number of people who like comedy = 20/100 × 300 = 60 people. Number of people who like action = 25/100 × 300 = 75 people. Number of people who like romance = 30/100 × 300 = 90 people. Number of people who like drama = 5/100 × 300 = 15 people. Number of people who like sci-fi = 20/100 × 300 = 60 people.
The key difference between pie chart and bar graph are listed in the following table:
| Aspect | Pie Chart | Bar Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Representation | Circular display of data | rectangular display of data |
| Purpose | Shows parts of a whole | Compares discrete categories |
| Data presentation | Depicts percentages or proportions | Shows exact values or quantities. |
| Number of variables | Typically one variable | Can represent multiple variables. |
| Visualization | Easily shows relative proportions | Effective for comparing quantities. |
| Comparison | Might be difficult to compare precise values | Allows for easy comparison between categories. |
| Data complexity | Works well with simple datasets | Suitable for complex datasets |
| Interpretation | Provides a holistic view | Allows for detailed analysis. |
| Space efficiency | Not efficient with large datasets | Efficient for displaying large datasets |
Pie Chart is very useful for finding and representing data. Various advantages of the pie chart are,
- Pie chart is easily understood and comprehended.
- Visual representation of data in a pie chart is done as a fractional part of a whole.
- Pie chart provides an effective mode of communication to all types of audiences.
- Pie chart provides a better comparison of data for the audience.
There are some disadvantages also of using pie charts and some of them are added below,
- In the case of too much data, this presentation becomes less effective using a pie chart.
- For multiple data sets, we need a series to compare them.
- For analyzing and Assimilating the data in a pie chart, it is difficult for readers to comprehend.
Whenever a fraction or fractions are represented as a part of the whole, pie charts are used. Pie charts are used to compare the data and to analyze which data is bigger or smaller. Hence, while dealing with discrete data, pie charts are preferred. Let’s take a look at the uses of the pie chart:
- Pie charts are used to compare the profit and loss in businesses.
- In schools, the grades can be easily compared using a pie chart.
- The relative sizes of data can be compared using a pie chart.
- The marketing and sales data can be compared using a pie chart.
Measurement of Angles Bar Graph and Histogram
Example 1: The given pie chart shows the subject of interest of each student in a class.

Answer the following question concerning the given pie diagram.
- If 30 students’ subjects of interest are history, how many total students were surveyed?
- Which subject is liked the most?
- Which subject is disliked the most?
1. According to the given question, 8% of the total number of students is 30. i.e. (8/100) x Total = 30 Therefore, Total = 30 x (100/8) = 375 Hence 375 students were surveyed. 2. According to the given pie chart, science is liked the most. 3. According to the given pie chart, history is disliked the most.
Example 2: For a science camp, students from different states have enrolled. Construct a pie chart for the given table:
| States | Number of students |
|---|---|
| West Bengal | 10 |
| Assam | 5 |
| Tamil Nadu | 5 |
| Gujarat | 10 |
| Karnataka | 10 |
Step 1: The first step requires us to jot down the available data into tabular form as follows: West Bengal Assam Tamil Nadu Gujarat Karnataka 10 5 5 10 10 Step 2: The next task is to calculate the sum of all the given data. Here, the Sum of All Data = (10 + 5 + 5 + 10 + 10) = 40 Step 3: Now, the next task is to calculate the percentage of each sector. We need to divide each sector value by the sum or total and then multiply it by 100. West Bengal Assam Tamil Nadu Gujarat Karnataka (10/40) × 100 = 25% (5/40) × 100 = 12.5% (5/40) × 100 = 12.5% (10/40) × 100 = 25% (10/40) × 100 = 25% Step 4: Next step is to calculate the degrees corresponding to each slice. The values can be calculated as: West Bengal Assam Tamil Nadu Gujarat Karnataka (10/40) × 360 = 90 (5/40) × 360 = 45 (5/40) × 360 = 45 (10/40) × 360 = 90 (10/40) × 360 = 90 Step 5: Now, with a protractor’s help, we will measure each angle from a single point or central point and draw the circle’s sectors. The resultant pie chart will be:
Example 3: A pie chart is divided into four parts, and the values are given as x, 3x, 4x, and 4x. Find the value of x in degrees.
As it is known that a pie chart has 360°. Therefore, if all the angles are added, it will give 360°. x + 3x + 4x + 4x = 360° 12x = 360° x = 30°
What i s Population Pie chart?
The population pie chart is the pie chart that represent the population of any area and the population pie chart of the world is shown in the image added below,

Q1. Students selected for ISRO visit from various states are given in the table below. Represent them in a pie chart.
| States | Number of students |
|---|---|
| West Bengal | 7 |
| Assam | 6 |
| Tamil Nadu | 3 |
| Gujarat | 10 |
| Karnataka | 4 |
Q2. Marks scored by Kabir in an exam in various subject is shown in the table below show a pie chart representing the same.
| Subjects | Marks |
|---|---|
| Mathematics | 99 |
| Physics | 98 |
| Chemistry | 98 |
| English | 95 |
| Computers | 97 |
Articles related to Pie Chart:
- Plot a pie chart in Python using Matplotlib
- Pie Diagrams | Meaning, Example and Steps to Construct
- How to create a Pie Chart using HTML & CSS
- How to Make a Pie Chart in Excel
- R – Pie Charts
- Real Life Applications of Pie Chart
- Chart.js Doughnut and Pie Charts
- How to add a Pie Chart into an Android Application
Conclusion – Pie Chart
Pie charts are useful graphical tools for showing data distribution in an understandable way. These are circular diagrams that have been segmented into sectors, each of which represents a percentage or fraction of the entire dataset. Pie charts help viewers rapidly understand distribution patterns by effectively communicating the relative sizes of various categories or components within a dataset. They are frequently used in publications, reports, and presentations in a variety of sectors, including business, finance, statistics, and education
FAQs on Pie Chart
Define pie chart..
Pie chart is the visual representation in which a circle graph is used to represent the values according to numbers, percentages, and degrees.
What is the Formula for Pie Chart?
To calculate the percentage of the given data, the formula used: (Frequency ÷ Total Frequency) × 100 Converting data into degrees: (Given Data ÷ Total Data) × 100
What are Examples of Pie Chart?
There are many examples of pie chart as pie chart is often used for visual representation. Following are some of the real-life examples: Representation of marks obtained by students. The marketing and sales data is obtained by using a pie chart. The profit and loss endured by a business can be represented by a pie chart.
What are the Uses of Pie Graph?
Pie charts are used for various purposes and various uses of pie chart are, It is used to represent various types of data. It is used to show data of various demographics. It is used to represent various objects of sales, marketing, and others, etc.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Data Handling
- Maths-Class-8
- School Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
In Statistics, pictographs are charts that are used to represent data using icons and images relevant to the data. A key is often included in a pictograph that indicates what each icon or image represents. All icons in the pictogram must be of the same size, but we can use the fraction of an icon to show the respective fraction of that amount. Let us understand the concept of pictographs using examples.
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. |
What is Pictograph?
In mathematics, a pictograph, also known as a pictogram, is the pictorial representation of data using images, icons, or symbols. We can represent the frequency of data while using symbols or images that are relevant using a pictograph. Pictographs are one of the simplest ways of representing data.
Pictograph Definition
"A pictograph is a representation of data using images or symbols." Pictographs in maths are typically used in concepts like data handling. They help in laying the foundation for data interpretation based on pictorial information. Now after knowing the pictograph definition, let us understand pictographs using a scenario.
Pictograph Example
A survey was conducted for 40 children by a fast food junction to understand the demand for different flavors of pizza available in their outlet. The results were as follows:

Can you identify the most loved flavor by observing the above table? If 1 full pizza represents 4 children, then what would a quarter slice represent? The scenario that we discussed above represents information in a pictographic manner. Here, the symbol for a full pizza is used to represent data (i.e. the number of students). We need to do simple math to understand how many children voted for each of the flavors. Multiply the number of symbols for the given flavor with the value of each symbol.
For example, the number of children who liked Pepperoni = 2 \(\frac{1}{4}\) × 4 = 2 × 4 + (1/4) × 4 = 8 + 1 = 9
Key to a Pictograph
We use a key to denote the value of the symbol. In the above example, the key was 1 icon of the pizza representing 4 children.
Important Notes on Pictograph:
- All the symbols/icons must be of the same size.
- A fraction of an icon can also be used to show data.
Thus, after going through the above pictograph example , we come to the basic formula which is used to find the value of the data of the categories given in the chart/table.
Value of a category = Product of the number of times the symbol is used and the value of each symbol. If we denote the number of times by 'N', and the value of each symbol by 'S', we get:
Value of a category = N × S
How to Make a Pictograph?
Let us take an example. We will represent the average hours spent by students on different activities.
The following table gives this data:
| Online Classes | 4 hours |
| Gadgets | 4 hours |
| Self Study | 1 hour |
| Sleep | 10 hours |
| Others | 5 hours |
The below-given steps can be followed to represent the data given in the table in the form of a pictograph.
- Collect Data: Firstly, we need to collect the data of the different categories we want to represent. We then form a table or list. In the above example, the data is already provided in the form of a table.
- Review the data and Pick a symbol: Review the collected data and based on it pick a symbol or picture that accurately represents the data. For drawing a pictograph to represent the number of hours spent on a particular activity, we can use an hourglass as a symbol.
- Assign a Key: Based on the frequency of the data, decide the frequency for one symbol. This can be done by setting a numerical value that one symbol will represent. This key or numerical value must be written along with the pictograph. Example one icon of an hourglass represents. This is the key to the pictograph.
- Draw the pictograph: Finally, drawing the pictograph by initially drawing two columns that represent the category and the data. Then, draw the actual symbols representing the frequencies. These symbols can be drawn as fractions as well if the frequency is not a whole number or based on the key.
- Review Pictograph: Check the labeling and review your pictograph and make sure it correctly represents the data.

Reading Pictograph
Let us understand how to read a pictograph based on the pictograph we created above by answering few questions.
Example: Based on the observations from the above pictograph, answer the following questions.
1. What is the average time spent by a child on gadgets?
2. How many hours on average does a child sleep during the lockdown on a weekday?
3. What is the total average time spent by a child on academics?
4. How many hours are spent on other activities?
2. An average child sleeps for 5 × 2 = 10 hours on a weekday during the lockdown.
3. Total time taken for academics = 2 × 2 + (1/2) × 2 = 4 + 1 = 5 hours.
4. Time spent on other activities = 2 × 2 + (1)(2) × 2 = 4 + 1 = 5 hours.
Advantages of Pictograph
Pictographs are widely used in maths. There are several advantages to using pictographs in maths. These are some of the advantages.
- They can be used primarily for making early learners associate objects with numbers.
- They help in visually formatting statistics.
- They make data visually interesting and easy to understand.
- Representing data pictographic way can be useful for representing a large amount of data.
Challenging Question on Pictograph:
Four friends are playing with 44 pieces of the puzzle. The number of pieces that each of them has is recorded in the form of a pictograph below. But there is some information missing. Can you find the missing entries using the given hints?

- 1 icon (1 puzzle piece) = ________.
- How many pieces do Tom and Jerry have, if they both have an equal number of pieces?
Related Articles:
Check out these interesting articles to know more about pictographs and its related topics.
- Data Handling
- Line Graphs
- Stem and Leaf Plot
Pictograph Examples
Example 1: The table below is in the form of a pictorial graph. It shows the number of apples of different varieties (in Kilogram) being sold at a store in a given month.

Based on the pictograph, answer the following questions.
(a) Which variety of apple is the best seller?
(b) How many more kilograms of Fuji apples were sold compared to Ambrosia?
(c) What is the total quantity of apples sold by the store?
(a) Red Delicious is the best seller.
(b) Quantity of Fuji = 3 × 4 = 12 kg
Quantity of Ambrosia = 2 (1/2) × 4 = 2 × 4 + (1/2) × 4 = 8 + 2 = 10 kg Difference = 12 - 10 = 2 kg
(c) Total quantity of apples sold by the store = 16 × 4 = 64 kg.
Example 2: The following table shows information about the modes of transport used by students to commute to school.

Answer the following questions based on the information given above.
1. How many students commute by car?
2. Which is the most commonly used mode of transport?
3. Which is the least preferred mode to reach school?
Answer 1 : No. of students who commute by car = 4 × 4 = 16.
Answer 3 : The least preferred mode to reach school is a bicycle.
Example 3: The following pictograph shows the number of bananas and oranges consumed by students of three schools in a locality.

Based on the above information, answer the following questions.
1. In which school the total number of bananas consumed is more than oranges?
Answer: In school A, the total number of bananas consumed is more than oranges.
2. What is the difference between the number of oranges consumed by students of schools A and C?
Answer: Number of oranges consumed in school A = 4 × 50 = 200
Number of oranges consumed in school C = 6 × 50 = 300
Difference = 300 - 200 = 100
3. In which school the number of bananas and oranges consumed is the same?
Answer: In school B, the number of bananas and oranges consumed is the same.
4. How many fruits were consumed by children of school C?
Answer: Number of fruits consumed by children of school C = No. of bananas + No. of oranges.
= 3 × 50 + 6 × 50 = 150 + 300 = 450
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Pictograph
go to slide go to slide
FAQs on Pictograph
What is a pictograph give examples..
A pictograph is a representation of data using images or symbols. We see these pictographs in many real-life situations. A simple example is the star rating that is given by customers for items purchased. Consider a case when out of 5 stars, there are 3.5 stars highlighted. If it is given that 1 star = 20 points, then the rating by the customer will be 20 × 3.5 = 70 out of 20 × 5 = 100.
What is a Pictograph Chart?
A pictograph chart is a chart that uses icons or symbols to represent information or data. Each icon represents a certain frequency based on the key.
What is a Pictograph Used for?
A pictograph is used to represent data in the form of pictures or icons which makes the presentation more interesting and easier to understand.
What is Used in Pictograph?
In pictographs, we use icons and images to represent the data. These images or icons have a key, where 1 icon represents a certain frequency. Using this key, data can be represented in a tabular form in a pictograph.
What are the Advantages of a Pictograph?
There are many advantages of using a pictograph as a method to represent the given data.
- Pictographs can be used primarily for making early learners associate objects with numbers.
- They help in visually formatting statistical data.
- They help in representing the data visually interesting and easy to understand.
- They can be useful for representing a large amount of data.
What is Key in a Pictograph?
In a pictograph, we use a key to denote the value of the symbol. This key is used in representing the frequency of any category in a pictograph.
How to Draw a Pictograph?
We can draw a pictograph using simple steps,
- Collect and review the data
- Pick a symbol to represent the frequency of the category based on the given data.
- Analyze the collected data and assign a key
- Draw the pictograph in a tabular format
- Finally, review the pictograph.
How do you Find the Key to a Pictograph?
The key to a pictograph is used to find the frequency of the information the graph depicts for a particular category. We can choose a suitable key for a pictograph depending upon the values in the data set.
Who Discovered Pictograph?
Pictographs were used as the earliest known form of writing and are believed to have been discovered in Egypt and Mesopotamia from before 3000 BC.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Published: 02 December 1933
Pictorial Representation of Data
Nature volume 132 , page 849 ( 1933 ) Cite this article
4109 Accesses
Metrics details
ONE of the characteristics of scientific management in modern industry is the use which is made of graphical methods. The importance of the pictorial representation of facts and data has also been widely realised by the various movements aiming at the prevention of accidents whether in industry or in the streets. It is, however, only within the last ten years that pictorial representations have been fashioned on definite scientific principles, and the value of the pioneer work of the Mundaneum Institute, Vienna, is now becoming widely recognised. During the last decade, under the leadership of Dr. Otto Neurath, basic principles for visual presentation have been developed. Charts or illustrations constructed on these lines reveal what is most essential at a first glance; the important details stand out on a second glance and more exact details are evident to a third glance. The method has been applied with conspicuous success to technical and to social facts and data, and the work of the Mundaneum has become known through a series of publications such as Gesellschaft und Wirtschaft, Technik und Menschhiet, Die Bunte Welt and Bildstatistik. Branches have now been established in Amsterdam and London (c/o World Association for Adult Education, 16, Russell Square, W.C.I) through which the services offered, including the preparation of charts, the loan of exhibits, issue of publications and provision of material, and advice on principles of visual presentation may be more accessible. The new technique provides an international cultural factor of high importance, but if its full advantages are to be reaped, its introduction into different countries should proceed on uniform lines under the guidance of the Mundaneum itself.
Article PDF
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Pictorial Representation of Data. Nature 132 , 849 (1933). https://doi.org/10.1038/132849b0
Download citation
Issue Date : 02 December 1933
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/132849b0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Table of Contents
What is data visualization, the importance of data visualization, categories of big data visualization, a look at some data visualization techniques, how is data visualization used, data visualization: why it is one of the top data skills for 2024.

Data analysts and other researchers may compile the most valuable and relevant information available, but it's useless if it isn't accessible and comprehensible to clients and users. That's where data visualization comes into play, guided by the principle that "a picture is worth a thousand words." This method helps transform complex data into clear, intuitive visuals that enhance understanding.
In today's discussion, we delve into data visualization . We'll define it, explore various types, discuss its significance, and examine how different industries and sectors apply these methods. We will also look at a range of data visualization techniques.
Learn how to tell compelling stories with data and significantly impact your organization through Simplilearn's data visualization courses .
Data visualization is the process of communicating and translating data and information in a visual context, usually employing a graph, chart, bar, or other visual aid. Visualization also uses images to communicate the relationships between various sets of data.
Data visualization is also called information visualization, information graphics, and statistical graphics. It is a step in the process of data science , which tells us that after all data has been collected, processed, and modeled, the information must be visualized so that users can use it to draw conclusions.
Also, data visualization is part of the broader discipline of data presentation architecture (DPA), whose purpose is to identify, find, manipulate, format, and deliver data in the best way possible.
Enroll in the Post Graduate Program in Data Analytics to learn over a dozen of data analytics tools and skills, and gain access to masterclasses by Purdue faculty and IBM experts, exclusive hackathons, Ask Me Anything sessions by IBM.
Visually representing insights derived from data provides a means for people to see and understand data patterns, trends, and outliers. Consider the rejoinder “Do I have to draw a picture for you?” aimed at someone who’s not grasping the speaker’s point. Well, data visualization draws us that picture, presenting facts and figures in a clear, visually appealing manner.
More importantly, it is a valuable tool in the ongoing process of mastering the vast volumes of information created by big data. It’s challenging enough to sift through the floods of big data to find relevant, useful information, let alone looking for patterns and trends. That’s why data visualization is critical for today’s data analysts and other users—it helps the data collectors communicate results easier and enables readers to see the trends and patterns easily.
Our brains are wired to respond to visual stimuli and look for patterns in everything we see. Data visualization takes advantage of this human instinct and offers an easier way for people to see the information clearer and draw more accurate conclusions faster.
The benefits of data visualization include:
- Gives the reader the means to quickly absorb information, improve insights and make faster decisions
- Provides an easy means of distributing information that offers users more opportunities to share their insights with everyone involved in the project
- Imparts an increased understanding of what steps an organization must take to improve itself
- Offers the ability to attract and maintain the audience's interest by giving them the information they can understand
- Gives the decision-makers the means to quickly act on findings, deliver successful outcomes faster, and have fewer errors
- Eliminates the need to excessively rely on data scientists because it is more accessible and easily understood
Big data visualization refers to visually presenting large, complex datasets to uncover patterns, correlations, and insights. Given the scale and complexity of the data, different categories of visualization techniques are applied to make the information comprehensible and actionable. Here’s a breakdown of the key categories:
1. Standard Reporting
- Line Graphs
These traditional forms of visualization are best for static reporting and straightforward presentations where the objective is to convey clear, concise, and familiar visualizations to all levels of users.
2. Multidimensional Visualization
- Bubble Charts
These visualizations allow data to be represented across multiple variables simultaneously, providing a deeper understanding of the relationships within the data.
3. Temporal Data Visualization
- Time Series Graphs
- Cohort Analysis
This category focuses on data that changes over time, helping to track trends, patterns, and fluctuations across a timeline.
4. Geospatial Data Visualization
- Geographic Maps
- Choropleth Maps
Visualizing data according to geographical or spatial contexts can reveal disparities, distributions, and trends tied to physical locations.
5. Network and Relationship Data Visualization
- Network Diagrams
- Node-Link Diagrams
- Matrix Charts
These techniques are crucial for understanding and navigating relationships and interactions within data, such as social networks or connectivity maps.
Become a Data Science & Business Analytics Professional
- 11.5 M Expected New Jobs For Data Science And Analytics
- 28% Annual Job Growth By 2026
- $46K-$100K Average Annual Salary
Post Graduate Program in Data Analytics
- Post Graduate Program certificate and Alumni Association membership
- Exclusive hackathons and Ask me Anything sessions by IBM
Data Analyst
- Industry-recognized Data Analyst Master’s certificate from Simplilearn
- Dedicated live sessions by faculty of industry experts
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Felix Chong
Project manage , codethink.
After completing this course, I landed a new job & a salary hike of 30%. I now work with Zuhlke Group as a Project Manager.
Gayathri Ramesh
Associate data engineer , publicis sapient.
The course was well structured and curated. The live classes were extremely helpful. They made learning more productive and interactive. The program helped me change my domain from a data analyst to an Associate Data Engineer.
6. Hierarchical Data Visualization
- Tree Diagrams
- Sunburst Charts
- Dendrograms
Visualizations in this category illustrate data with inherent hierarchical relationships, which can be important for revealing structures from high-level overviews to detailed specifics.
7. Statistical Data Visualization
- Scatter Plots
Focused on statistical analysis, these visualizations help identify distributions, correlations, and outliers in the data.
8. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Parallel Coordinates
- Crossfilter Charts
- Brushing Techniques
EDA tools dynamically explore large datasets and uncover underlying structures to inform more complex analyses.
9. Real-time Data Visualization
- Live Dashboards
- Streaming Charts
- Dynamic Updates
For continuously updated datasets, real-time visualizations provide immediate insights into current conditions and emerging trends.
10. Interactive Data Visualization
- Drill-down Capabilities
- Interactive Reports
- Dynamic Filters
These visualizations allow users to manipulate the data presentation dynamically, fostering a deeper, user-driven exploration of the data.
Scatter Plot
A scatter plot exhibits the values of two variables within a dataset. Each data point is represented as a dot, with one variable determining its placement along the horizontal axis and the other variable determining its position along the vertical axis. These plots are employed to visualize the relationships and correlations between variables.
A heat map is a graphical data representation in which individual values in a matrix are represented as colors. Heat maps are useful for visualizing the magnitude of phenomena in two dimensions, such as color, which can help identify patterns, variances, and outliers.
A bar chart visually illustrates data by using rectangular bars, where the lengths correspond to the values they represent. It stands as one of the most prevalent methods of data visualization, particularly effective for comparing data across various categories.
A histogram is a bar chart representing a frequency distribution by the frequency of data points within certain ranges, called bins. It is particularly useful for understanding the distribution and dispersion of the dataset.
A pie chart visually represents proportions and percentages among categories by partitioning a circle into proportional segments. Each segment's arc length corresponds to its proportion, collectively totaling 100%.
Bullet Graph
A bullet graph is a variation of a bar graph developed to replace dashboard gauges and meters. It displays performance data more compactly while still showing the context, which can benefit dashboard designs.
A line graph is a chart that shows information that changes over time. We plot a series of points connected by straight lines to show how something increases or decreases in value.
A box plot provides a standardized presentation of data distribution using key summary statistics: minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, and maximum. It aids in identifying outliers and grasping the data's dispersion.
Density Plot
A density plot is a smoothed version of a histogram used to show the distribution of a continuous variable. It can help to see the shape of the distribution, particularly when plotting large amounts of data.
In data visualization, a matrix can refer to a grid of colors coded to represent values within a dataset , similar to a heat map but typically without the gradient color scales.
Maps in data visualization represent geographical data. They can vary from simple geographic maps to complex representations overlaying varying data types (like demographic or economic data) onto geography.
Timelines are graphical representations of a period on which important events are marked chronologically. They are used to visualize sequences of events and trends over time.
Computer Network
In data visualization, diagrams of computer networks can show how devices like routers, switches, and endpoints connect within the network. It helps manage, troubleshoot, and design networks.
Diagrams are simplified drawings that show the important parts of something to explain how it works. They can be used in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and education.
Word Clouds and Network Diagrams
Word clouds are visual representations of word frequency that give greater prominence to words that appear more frequently in a source text. Network diagrams visualize interconnections between a set of entities. Both are useful for analyzing relational data and text.
In data visualization, circles can be used to create bubble charts, where the size of the circle represents a value, making it easy to compare different entities.
Nothing speaks more effectively about data visualization’s versatility than real-world examples, and there are plenty to be found. Such as:
- Determining correlations. The best way to determine the relationship and correlations between two variables is to compare them visually.
- Network examination. In this context, “network” refers to the whole market audience. By examining the network, analysts can spot audience clusters, including any influencing factors and the bridges between them, and statistical outliers.
- Tracking changes over time. This use is a simple yet essential data visualization function. Visualization helps people see and analyze how data trends change over a given period.
- Frequency determination. Frequency is related to tracking changes but differs because it examines how often a given event happens.
- Timeline scheduling. Using a resource like a Gantt chart , project leaders can illustrate each assignment within the project and how long the tasks will take.
Our Data Analyst Master's Program will help you learn analytics tools and techniques to become a Data Analyst expert! It's the pefect course for you to jumpstart your career. Enroll now!
Also, many fields benefit from data visualization, including:
- Data Science/Research. Data visualization helps data scientists perform complex data analysis , recognizing patterns, and understanding datasets. Data scientists have many data visualization tools to choose from to help them complete their tasks, including using programming languages such as Python. You can learn more about how to accomplish this through this data visualization in Python tutorial.
- Finance. Data visualization is a handy tool for the investment world, showing how commodities, bonds, and stocks perform over time.
- Healthcare. Choropleth maps show different geographical areas in different colors to illustrate numeric values. They are a good resource for physicians and epidemiologists who track health hazards such as pandemics or heart disease.
- Logistics. Data visualization aids shipping companies in determining the best shipping routes.
- Politics. Pollsters and campaign workers can get a clear picture of who voted for a specific candidate in each region.
- The Sciences. SciVis, or Scientific Visualization, makes it easy for researchers to better understand their experimental data.
Would You Like a Career in Data Analytics?
Today’s society increasingly depends on data to help make life run smoother and develop sounder strategies for tackling the commercial sector’s numerous challenges. Consequently, data analysts are among the most sought-after professionals in today’s business world. They are skilled IT data smiths who know how to take the mountains of information generated by big data and turn it into actionable, useful information.
Simplilearn can help you get your data analytics career started with this popular Data Analytics certification program . This post graduate program gives you broad exposure to key technologies and skills currently used in data analytics and data science , including statistics, Python, R, Tableau, SQL, and Power BI. When you finish this comprehensive Data Analytics course, you will be ready to take on a data analytics professional's exciting role.
According to Salary.com , a data analyst in the US earns an average annual salary of USD 77,025, ranging from USD 67,837 to 86,195. Glassdoor.com reports that data analysts in India make an average of ₹500,000.
Let Simplilearn help you get that started on a rewarding, challenging, and in-demand career in the world of data analysis. You can learn about data analytics, then branch out into another of the many offered bootcamps and other learning resources. Check out Simplilearn’s courses today!
1. What is data visualization and why is it important?
Data visualization involves representing data graphically to help people understand its significance more effectively. It is important because it enables users to see trends, patterns, and outliers in data, facilitating quicker and more informed decision-making than reviewing raw data alone.
2. How does data visualization enhance data analysis?
Data visualization enhances data analysis by making complex data more accessible and digestible. It allows analysts to perceive developments and correlations that might be missed in text-based data, leading to faster insights and better analysis.
3. What are the best practices for creating effective data visualizations?
Best practices for effective data visualizations include keeping designs simple and focused, choosing the right type of chart for the data, using consistent and appropriate scales, and ensuring the visualization is accessible to all audience members, including those with color vision deficiencies.
4. What are some common mistakes to avoid in data visualization?
Common mistakes in data visualization include overcomplicating the graphic, using inappropriate chart types, ignoring the scale and proportions, overusing colors and fonts, and neglecting to label axes or provide a legend when necessary.
5. How do data visualizations support big data analysis?
Data visualizations support big data analysis by providing a means to observe large volumes of data simultaneously in a comprehensible format. They help highlight trends, patterns, and anomalies, making conducting analyses easier and deriving actionable insights from massive datasets.
Data Science & Business Analytics Courses Duration and Fees
Data Science & Business Analytics programs typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 11 Months | € 2,290 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 2,790 |
| Cohort Starts: | 11 Months | € 3,790 |
| Cohort Starts: | 3 Months | € 1,999 |
| Cohort Starts: | 11 Months | € 2,790 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 1,790 |
| 11 Months | € 1,299 | |
| 11 Months | € 1,299 |
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Data science & business analytics.
How Can You Master the Art of Data Analysis: Uncover the Path to Career Advancement
Develop Your Career in Data Analytics with Purdue University Professional Certificate
Career Masterclass: How to Get Qualified for a Data Analytics Career
Recommended Reads
The Rise of the Data-Driven Professional: 6 Non-Data Roles That Need Data Analytics Skills
The Value of Mastering Data Visualization & Storytelling for Data Scientists
The Complete Guide to Data Visualization in Python
Data Analyst Resume Guide
The Best Tools for Visualizing AI Data
An Interesting Guide to Visualizing Data Using Python Seaborn
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Trends and Technological Advancements in the Possible Food Applications of Spirulina and Their Health Benefits: A Review
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Food Science, College of Agriculture, University of Basrah, Basrah 61004, Iraq.
- 2 College of Medicine, University of Warith Al-Anbiyaa, Karbala 56001, Iraq.
- 3 Agricultural and Food Engineering Department, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Kharagpur 721302, West Bengal, India.
- 4 Department of Biomedical, Dental, Morphological and Functional Imaging Sciences, University of Messina, 98125 Messina, Italy.
- 5 Division of Cell and Molecular Biology, PG and Research Department of Zoology, St. Joseph's College (Autonomous), Devagiri, Calicut 673008, Kerala, India.
- PMID: 36080350
- PMCID: PMC9458102
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27175584
Spirulina is a kind of blue-green algae (BGA) that is multicellular, filamentous, and prokaryotic. It is also known as a cyanobacterium. It is classified within the phylum known as blue-green algae. Despite the fact that it includes a high concentration of nutrients, such as proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids-in particular, the necessary omega-3 fatty acids and omega-6 fatty acids-the percentage of total fat and cholesterol that can be found in these algae is substantially lower when compared to other food sources. This is the case even if the percentage of total fat that can be found in these algae is also significantly lower. In addition to this, spirulina has a high concentration of bioactive compounds, such as phenols, phycocyanin pigment, and polysaccharides, which all take part in a number of biological activities, such as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity. As a result of this, spirulina has found its way into the formulation of a great number of medicinal foods, functional foods, and nutritional supplements. Therefore, this article makes an effort to shed light on spirulina, its nutritional value as a result of its chemical composition, and its applications to some food product formulations, such as dairy products, snacks, cookies, and pasta, that are necessary at an industrial level in the food industry all over the world. In addition, this article supports the idea of incorporating it into the food sector, both from a nutritional and health perspective, as it offers numerous advantages.
Keywords: biological activity; chemical composition; food formulation; functional foods; health and nutritional value; spirulina algae.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
( A ) Nutritional composition…
( A ) Nutritional composition and ( B ) biochemical components of spirulina…
A diagrammatic explanation of the…
A diagrammatic explanation of the therapeutic value conferred by spirulina algae.
A pictorial representation of the…
A pictorial representation of the numerous beneficial health effects that have been derived…
Similar articles
- Spirulina, an FDA-Approved Functional Food: Worth the Hype? Ahmad AMR, Intikhab A, Zafar S, Farooq U, Shah HBU, Akram S, Abid J, Parveen Z, Iqbal S. Ahmad AMR, et al. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2023 Jan 31;69(1):137-144. doi: 10.14715/cmb/2022.69.1.24. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2023. PMID: 37213142 Review.
- FUNCTIONAL CHARACTERS EVALUATION OF BISCUITS SUBLIMATED WITH PURE PHYCOCYANIN ISOLATED FROM SPIRULINA AND SPIRULINA BIOMASS. Abd El Baky HH, El Baroty GS, Ibrahem EA. Abd El Baky HH, et al. Nutr Hosp. 2015 Jul 1;32(1):231-41. doi: 10.3305/nh.2015.32.1.8804. Nutr Hosp. 2015. PMID: 26262722
- Food Matrices Affect the Peptides Produced during the Digestion of Arthrospira platensis -Based Functional Aliments. Donadio G, Santoro V, Dal Piaz F, De Tommasi N. Donadio G, et al. Nutrients. 2021 Nov 1;13(11):3919. doi: 10.3390/nu13113919. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34836173 Free PMC article.
- Food and drug industry applications of microalgae Spirulina platensis: A review. Maddiboyina B, Vanamamalai HK, Roy H, Ramaiah, Gandhi S, Kavisri M, Moovendhan M. Maddiboyina B, et al. J Basic Microbiol. 2023 Jun;63(6):573-583. doi: 10.1002/jobm.202200704. Epub 2023 Jan 31. J Basic Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36720046 Review.
- Spirulina- An Edible Cyanobacterium with Potential Therapeutic Health Benefits and Toxicological Consequences. Gogna S, Kaur J, Sharma K, Prasad R, Singh J, Bhadariya V, Kumar P, Jarial S. Gogna S, et al. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023 Aug;42(6):559-572. doi: 10.1080/27697061.2022.2103852. Epub 2022 Aug 2. J Am Nutr Assoc. 2023. PMID: 35916491 Review.
- Determinants of Consumers' Acceptance and Adoption of Novel Food in View of More Resilient and Sustainable Food Systems in the EU: A Systematic Literature Review. Laureati M, De Boni A, Saba A, Lamy E, Minervini F, Delgado AM, Sinesio F. Laureati M, et al. Foods. 2024 May 15;13(10):1534. doi: 10.3390/foods13101534. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38790835 Free PMC article. Review.
- Comprehensive understanding of the mutant 'giant' Arthrospira platensis developed via ultraviolet mutagenesis. Lee C, Han SI, Na H, Kim Z, Ahn JW, Oh B, Kim HS. Lee C, et al. Front Plant Sci. 2024 Mar 19;15:1369976. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1369976. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38567133 Free PMC article.
- Optimization of an Alternative Culture Medium for Phycocyanin Production from Arthrospira platensis under Laboratory Conditions. Freire Balseca DA, Castro Reyes KS, Maldonado Rodríguez ME. Freire Balseca DA, et al. Microorganisms. 2024 Feb 10;12(2):363. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020363. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399769 Free PMC article.
- Anti-Glycation Properties of Zinc-Enriched Arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) Contribute to Prevention of Metaflammation in a Diet-Induced Obese Mouse Model. Aimaretti E, Porchietto E, Mantegazza G, Gargari G, Collotta D, Einaudi G, Ferreira Alves G, Marzani E, Algeri A, Dal Bello F, Aragno M, Cifani C, Guglielmetti S, Mastrocola R, Collino M. Aimaretti E, et al. Nutrients. 2024 Feb 17;16(4):552. doi: 10.3390/nu16040552. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398877 Free PMC article.
- The utility of algae as sources of high value nutritional ingredients, particularly for alternative/complementary proteins to improve human health. Wu JY, Tso R, Teo HS, Haldar S. Wu JY, et al. Front Nutr. 2023 Oct 13;10:1277343. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1277343. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37904788 Free PMC article. Review.
- Carlson S. Spirulina platensis (Conventional and Organic), Spirulina, Organic Spirulina, or Arthrospira Platensis. Division of Biotechnology and Gras Notice Review, Office of Food Additive Safety-CFSAN; Dauphin Island, AL, USA: 2011. p. 36.
- Haoujar I., Haoujar M., Altemimi A.B., Essafi A., Cacciola F. Nutritional, sustainable source of aqua feed and food from microalgae: A mini review. Int. Aquat. Res. 2022;14:1–9.
- Singh S., Verma D.K., Thakur M., Tripathy S., Patel A.R., Shah N., Utama G.L., Srivastav P.P., Benavente-Valdés J.R., Chávez-González M.L., et al. Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SCFE) as Green Extraction Technology for High-value Metabolites of Algae, Its Potential Trends in Food and Human Health. Food Res. Int. 2021;150 Pt A:110746. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110746. - DOI - PubMed
- Nascimento R.Q., Deamici K.M., Tavares P.P.L.G., de Andrade R.B., Guimarães L.C., Costa J.A.V., Guedes K.M., Druzian J.I., de Souza C.O. Improving water kefir nutritional quality via addition of viable Spirulina biomass. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022;17:100914. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100914. - DOI
- Trotta T., Porro C., Cianciulli A., Panaro M.A. Beneficial Effects of Spirulina Consumption on Brain Health. Nutrients. 2022;14:676. doi: 10.3390/nu14030676. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
Related information
Grants and funding, linkout - more resources, full text sources.
- Europe PubMed Central
- PubMed Central
Research Materials
- NCI CPTC Antibody Characterization Program

- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

7 Types of Logos to Inspire Your Next Design (Examples Included)
Logos are everywhere. Many of them are surrounding us, and most of the time, we don’t even notice them, but they are surely part of our daily lives.
I have four brands with their unique logo design on my desk right now.
We probably don’t give a lot of thought to logos if we don’t have to think about creating a design ourselves.
But what if you do have to come up with a logo for a brand? What type of logo design you choose?
It’s an important question to answer because the first thing customers will notice is the logo.
Moreover, a good logo can have a powerful visual impact on potential customers, helping your brand stand out through its uniqueness—on ads, marketing campaigns, brochures, etc. A well-designed logo is a crucial part of your brand identity , fostering connection, engagement, and positive emotional responses.
There are seven different types of logos, and we’re going to discuss all of them in this article. I’ll pinpoint the pros and cons, so you can make the best decision when creating a logo design.
Table of contents
- Emblem logos
- Pictorial mark logos
- Lettermark logos
- Abstract logos
- Mascot logo
- Combination logo marks
What Are the 7 Types of Logos?
The different kinds of logos can be placed into seven categories: emblems, pictorial marks, logotypes, lettermarks, abstract logos, mascot logos, and combination logos.
Let’s analyze each category.
1. Emblem logos

Emblems are the oldest types of logo design. Think of seals, crests, stamps, prestigious school logos, or government agencies.
An emblem is a logo type that features text, a symbol, or imagery inside a geometric shape . It has the power to give a traditional feel to your brand.
They are often richer in detail than other types of logos giving an official look to your brand.
Pros : Once you come up with a good emblem logo, your brand will surely stand the test of time. Moreover, the chances to find another brand with a logo similar to yours are significantly smaller.
They’re memorable, professional, and give a powerful feel to your brand.
Cons : Probably, the only disadvantage to the emblem logo is the scalability. Since they’re detailed, they may not look so good when resized to a smaller resolution or not so readable when placed on a billboard.
Harley Davidson’s “Bar and Shield” logo is recognized worldwide. Its symbol has the shape of a black shield with the word Motorcycles in orange, and over the shield comes a horizontal black bar with Harley Davidson written in white.
Some of the most popular and prestigious universities have an emblem logo, Stella Artois beer, or DC’s Superman.
2. Pictorial mark logos

A pictorial mark logo (or a brandmark) is imagery reduced to its symbolistic meaning. This is why, if you’re leaning towards this type of logo design, it has to be extremely representative, containing elements that will make your audience associate it with your brand. A logo symbol plays a crucial role in brand recognition, as it can convey meaning or emotion through a standalone image or symbol, often representing real-life objects or abstract shapes.
Some huge names, like Starbucks, had two kinds of logos: it changed from an emblem to a symbol over time, only after the company became established on the market.

Image Source
If you’ve just started your business and want to adopt this type of logo, you can still go for a brand mark. Just keep in mind that for a while, you’ll have to use a wordmark associated with the symbol until people get acquainted with your products or services.
Pros : Maybe your brand can be represented through a simple image/symbol. Think of Apple. Its name is also its symbol, and it works perfectly, as their name is drawn literally from the brand mark.
Another great way to use this type of logo is to convey a meaningful idea through a symbol, where the words can’t express it well enough.
Cons: If your business is still fresh and you didn’t manage yet to have a solid base and a stable target audience, it’s better to start with something more explicit for your brand’s logo and adapt it as a brandmark later.
As I said, Apple can use this simple logo without any additional text because their brand name is the symbol’s name.
Other pictorial mark logos are the ones for Twitter and Target. They can now be used without any text, but this is due to their popularity. At first, the brand’s name appeared in the logo as well.
3. Logotypes

Among the most powerful types of logo design out there, we have the logotypes, also known as the wordmark logos. Wordmark logos are significant in brand identity as they are based solely on stylized text, usually the brand’s name, and reflect the brand’s personality through the choice of font.
The logotype definition is simple . They’re composed entirely of the company’s name. On a logotype design, you won’t find symbols, graphic patterns, or emblems.
Since the main feature of the logotype design is typography , the best choice is to have a font specially designed for your logo.
The fonts’ style and color will create the whole identity of your brand.
By doing so, you’ll create uniqueness through your font and brand’s name. What’s even more remarkable about a logotype design is that you’ll help people make the connection between the logo and the brand in an instant.
Pros: It’s a simple yet impactful way to get your brand’s name out there. Once you have the font and your logo’s style, you can mix it with other elements and create logo variations.
The logotypes also help new businesses that need fast recognition, or if your personal name gives your brand’s name.
Cons: The logotype won’t work if your brand has a long name. Also, in time you may have to change the fonts to keep up with font design trends.
The logotype examples above need no further introduction. They are definitely the most famous logotypes in the world.
4. Lettermark logos

Lettermarks (or monograms) are a cool way to reduce your brand’s name to an acronym. Take the initials from each word of your brand’s name, and you’ve got yourself a logo.
The only part left is to think of typography. You have to come up with an eye-catching and unique font since the lettermark logo design uses just a few letters.
Pros: If your brand’s name has several words, then this logo kind is perfect for you, especially if you don’t want to use only a visual symbol.
Cons: If you’re a new company on the market using a lettermark logo, it may confuse your audience. But this situation has an easy solution. At first, you can use your lettermark logo, and underneath it, place the full name.

HBO (Home Box Office) boldly uses the lettermark logo, with the letter “O” that looks like a camera lens. Other examples are the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which also uses an acronym written in a futuristic and unique font, and famous clothing brands like Louis Vuitton.
5. Abstract logos

Next on the logo types list is the abstract logo, or abstract logo marks, which are made of an image without any letters. These marks are significant in conveying a brand’s core values, providing room for creativity and flexibility, and aligning the design with the brand’s identity.
It can be a bit risky to use when you’re new on the market, as not everyone interprets an abstract representation the same way. Still, with a good strategy behind it, your brand’s logo will differentiate you from all the competitors out there.
Pros: With an abstract logo that still manages to showcase your brand’s identity, you’ll create something unique and instantly recognizable on the market.
Another reason can be the versatility of using it in advertising campaigns and on branded merchandise .
Cons: If you’re a new brand making a name for itself, you may have to put some extra effort in helping people know your brand’s reputation. The solution here is to create an abstract logo that conveys the specific feeling you’re aiming for, and maybe join in with the brand’s name for a while, just until people get to know you.
Nike’s abstract logo, the famous swoosh, can work alone because the brand is highly popular, but you can still see it sometimes together with the brand’s name.
Its abstract logo perfectly represents the idea of movement. Just do it and check it on the list as done.
Other notorious examples are Airbnb and Pepsi, which are sometimes accompanied by their brand names, but even without them, you recognize them immediately.
Airbnb actually transitioned to an abstract logo that brings together its core values.

Image source
6. Mascot logo

A mascot logo is a drawing of a person or a non-human entity that received human form or human attributes.
This type of logo creates a friendly and positive feeling towards your audience. You can use a mascot logo and give it different expressions and representations, depending on the message you’re trying to convey.
Mascot logos are used for sports teams, food brands, or service companies.
Pros: If your brand targets families and children, the mascot logo is a great way to go. It will help you establish a fun and friendly approach.
Cons: You definitely can’t use a mascot logo when your brand wants to send a serious, professional message.
The mascot logos used in the image above are sincere and happy, inviting their audiences to try the brands.
7. Combination logo marks

This one is a mix of multiple different types of logo design.
If you can’t decide on a kind of logo from the ones mentioned above, just combine them.
Combination mark logos, which combine a visual element like a pictorial or abstract mark with a wordmark or lettermark, are significant in building visual identity and brand name recognition. Place lettering near symbols, abstract forms, mascots, or create a fusion between a monogram and an abstract logo. Whatever works for you.
You just need to pay attention to the message you’re trying to send through your logo and remember that it is part of your brand’s identity.
So, if you want to include imagery into your logo but feel like you need words to make sure people get exactly what you’re saying, then this is a safe bet.
The great thing about this kind of logo is that once people know about you, it’s easier to be flexible on the logo and use it in various ways. In some situations, you can use just the text. In others, just the imagery.
Pros : This is an excellent option if you want your future logo to be adaptable to changes.
Cons: If you’re aiming for minimalism and simplicity, this type of logo may overload your visual branding.
If you want the best of both worlds, look at these examples of logos above to see how they’re using a symbol together with a perfectly blended text.
Designing your brand’s logo is a creative and fun process that sets the foundation of your business identity.
When you start brainstorming ideas for your logo design, think of your brand’s core values and how you’ll want to present them to the world—this is how your brand will be remembered, after all.
Based on these logo types, try to design multiple options for your brand’s logo, show them to a few people, and see how they respond to them. This should be the test you need to perform.
I hope this article with the seven different types of logo design was helpful and gave you some ideas about which type of logo design would best fit your business.
And remember: with design, it’s all in the details.
18 Comments
Thanks for sharing this info, it helped me a lot. I am avid reader of your blog and always look for the wonderful content you upload. Keep up doing the good work.
Thanks of Sharing.
Great content.!
Finally, found a good piece of content. Amazing work Amalia it really helps me a lot! Thanks for sahring!
Very informative. thank you
Thanks for sharing this useful content
I was looking for such technical information since a long time about Logo design services, thanks for sharing valuable information in this article. Keep coming up with posts like this
Thank you so much for your sharing.This article help self-study way to Graphic Design.
What I have seen mostly is mascot logos are the ones which are selling like hot cakes, just a piece of advice to all that always opt for the mascot business, this works.
Really loved the way she drives this whole article amazingly well.
Im new to graphic design field, and was looking about logo design I had some doubts now it’s very clear thanks for you sharing
Thank you for sharing the information. Indeed mascot logos are the ones which are selling like hot cakes and very popular today. The mascot business work.
burger king have changed logo
Hi. Yes, we are aware of that, but we have used it only to exemplify that type of logo.
Thank you for sharing this detailed information. Learned a lot, I really appreciate your effort.
Thanks very much for sharing, it’s really helpful for newbies.
It helps us to identify the differences in logotypes.
Leave a reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
You may also like

What is Financial Advertising: Benefits, Trends, Strategy, Examples
18 Most Common Advertising Techniques That Work

30 Charming Google Font Pairings That Go Hand in Hand in 2024
More in branding.

Everything You Need to Include in Your Brand Kit

Top 10 Tips to Ensure Your Branding Is Consistent Across Touchpoints

How to Create the Brand Style Guide That Will Help You Keep Brand Consistency
- Inspiration
- – Display ads
- – Social media ads
- – Video ads
- – Automation
- – Collaboration
- – Animation
- Product updates
- Start free trial
Latest Posts
How to write effective ad copy ad copywriting guide for 2024, what are video banner ads: types, benefits and how to make them.

COMMENTS
Pictorial representation of data is called pictograph. As humanity flourished and the population increased, so did the amount of trade and transaction in the world. Ultimately, the amount of data is also increased. The merchants found it harder to keep track of the money flowing in and out of their coffers. When the population was little, trade ...
A bar chart or bar graph is the simplest form of pictorial representation of data with single bars of various heights. Bar graphs are a great tool to be used for representing data that don't need to be in any specific order while being represented and that are independent of one another. Learn more about the pictorial representation of data through bar graphs and double bar graphs.
Graphical representation of data is an attractive method of showcasing numerical data that help in analyzing and representing quantitative data visually. A graph is a kind of a chart where data are plotted as variables across the coordinate. ... Pictorial symbols for words, objects, or phrases can be represented with different numbers. Histogram.
Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data in a pictorial or graphical format (Visualization of Data could be: charts, graphs, and maps). Data visualization tools provide an accessible way to see and understand trends, patterns in data, and outliers. Data visualization tools and technologies are essential to ...
Graphical Representation of Data: Graphical Representation of Data," where numbers and facts become lively pictures and colorful diagrams. Instead of staring at boring lists of numbers, ... There are two ways of representing data, Tables; Pictorial Representation through graphs. They say, "A picture is worth a thousand words". ...
Pictorial Representation. Some basic ideas of pictorial representation or pictograph, often related types of symbols or pictures are used to represent a specific number of objects. For example, a symbol may represent 1 or 10 or 100 or 1000 or any other number of related objects. The symbol/picture used is very simple, clear and self explanatory.
In statistics, a bar chart (or bar graph) is a pictorial representation of data in quantities. It is the most common statistical approach used for data categorization. The data is represented using vertical or horizontal bars that are plotted in accordance with the given value. The length of each rectangular bar horizontal (or vertical) is ...
Bar graph is the pictorial representation of the data present. It is a way to analyse the data in a pictorial format. Bar graphs are represented in Vertical or Horizontal rectangular bars, where the bars' length represents the data's growth. What are the different types of Bar Graph?
Data visualization is the representation of information and data in a pictorial or graphical format highlighting the trends and outliers and making it easier to understand. Effective use of data visualization techniques helps to focus readers' attention on critical information, in a way is both simple and engaging. ...
> The Pictorial Representation of Data; Principles of Statistical Techniques. A First Course from the Beginnings, for Schools and Universities, with Many Examples and Solutions. Buy print or eBook [Opens in a new window] Book contents. Frontmatter. Contents. Preface. 1. The Scope of Statistics. 2.
2.3: Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Time Series Graphs. A histogram is a graphic version of a frequency distribution. The graph consists of bars of equal width drawn adjacent to each other. The horizontal scale represents classes of quantitative data values and the vertical scale represents frequencies. The heights of the bars correspond ...
Data often need to be displayed pictorially since extended figures can be difficult to digest and interpret. In order to make them more digestible, to bring out comparisons as well as trends — even for the expert — a suitable form of display has to be chosen. For the mass media, and the public, it is necessary to select a presentation with ...
Data representations are useful for interpreting data and identifying trends and relationships. When working with data representations, pay close attention to both the data values and the key words in the question. When matching data to a representation, check that the values are graphed accurately for all categories.
This is where the pictorial representation of worksheet data comes into play. It is a visual way of representing data using graphs, charts, and other visual elements. This method helps in presenting complex data in a simplified and easy-to-understand format, making it easier for anyone to analyze and interpret the information.
4.5. 140 reviews. A pictorial chart (also called a pictogram, a pictograph, or a picture chart) is a visual representation of data that uses pictograms - icons or pictures in relative sizes - to highlight data patterns and trends. Pictorial charts are common in business communication or news articles to visually compare data.
What is pictorial representation of data? Flexi Says: Visual representation of the relationship of data may include line chart, Column chart, Bar chart, Pie chart, Area chart and etc. A Venn diagram is a diagram that visually displays all the possible logical relationships between a collection of sets. Each set is typically represented with a ...
A pictograph is a pictorial representation of data that uses icons, images, or symbols related to the central topic. A key is often included in the chart to indicate what word or numerical data group each icon represents. The size of your icons must be the same except when you need to show a fraction relative to the amount per key.
Pictorial Representation Using Bar Graph [Click Here for Sample Questions] A bar graph, also referred to as a bar chart, is a graph that displays data in the form of rectangular bars. The length of the bar is proportionate to the values it represents in this case.
A chart or a graph is a pictorial representation of data. Charts and graphs are used to display detailed information and relationships between quantitative data. Examples of charts include bar graphs, pie charts, histograms and time-series graphs. Charts are often found alongside tables that contain the same data, because people can sometimes ...
A pie chart is a pictorial or graphical representation of data in chart format. A pie chart uses a circle or sphere to represent the data, where the circle represents the entire data, and the slices represent the data in parts. Pie chart is one of the easiest ways to present and understand the given data, and pie charts are used very commonly.
Data visualization is the graphic or pictorial representation of data. This common data analytics practice seeks to convey findings through easily understood visual representation. Complex event processing (CEP) is a method that tracks and analyzes data in real-time in order to derive actionable conclusions.
In mathematics, a pictograph, also known as a pictogram, is the pictorial representation of data using images, icons, or symbols. We can represent the frequency of data while using symbols or images that are relevant using a pictograph. Pictographs are one of the simplest ways of representing data. Pictograph Definition
The importance of the pictorial representation of facts and data has also been widely realised by the various movements aiming at the prevention of accidents whether in industry or in the streets ...
Data visualization is the process of communicating and translating data and information in a visual context, usually employing a graph, chart, bar, or other visual aid. Visualization also uses images to communicate the relationships between various sets of data. Data visualization is also called information visualization, information graphics ...
MeSH and other data. Send email Cancel Add to Collections Create a new collection; Add to an existing collection; Name your collection: ... A pictorial representation of the… Figure 3 . A pictorial representation of the numerous beneficial health effects that have been derived…
The different kinds of logos can be placed into seven categories: emblems, pictorial marks, logotypes, lettermarks, abstract logos, mascot logos, and combination logos. Let's analyze each category. 1. Emblem logos. Emblems are the oldest types of logo design. Think of seals, crests, stamps, prestigious school logos, or government agencies.