If my paraphrase consists of several sentences, should a citation for the original source appear after each sentence?
Note: This post relates to content in the eighth edition of the MLA Handbook . For up-to-date guidance, see the ninth edition of the MLA Handbook .
No. The citation should appear only after the final sentence of the paraphrase. If, however, it will be unclear to your reader where your source’s idea begins, include the author of the source in your prose rather than in a parenthetical citation.
For example, the following is a paraphrase from an essay by Naomi S. Baron:
Literacy consists of both reading and writing. The writing might take the form of marking up a text or making notes about it (Baron 194).
Here your reader might think that the first sentence is your idea and that Baron’s idea begins in the second sentence. For clarity, you might revise as follows:
Naomi S. Baron argues that literacy consists of both reading and writing. The writing might take the form of marking up a text or making notes about it (194).
Baron, Naomi S. “Redefining Reading: The Impact of Digital Communication Media.” PMLA , vol. 128, no. 1, Jan. 2013, pp. 193-200.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Paraphrase: Write It in Your Own Words

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Paraphrasing is one way to use a text in your own writing without directly quoting source material. Anytime you are taking information from a source that is not your own, you need to specify where you got that information.
A paraphrase is...
- Your own rendition of essential information and ideas expressed by someone else, presented in a new form.
- One legitimate way (when accompanied by accurate documentation) to borrow from a source.
- A more detailed restatement than a summary, which focuses concisely on a single main idea.
Paraphrasing is a valuable skill because...
- It is better than quoting information from an undistinguished passage.
- It helps you control the temptation to quote too much.
- The mental process required for successful paraphrasing helps you to grasp the full meaning of the original.
6 Steps to Effective Paraphrasing
- Reread the original passage until you understand its full meaning.
- Set the original aside, and write your paraphrase on a note card.
- Jot down a few words below your paraphrase to remind you later how you envision using this material. At the top of the note card, write a key word or phrase to indicate the subject of your paraphrase.
- Check your rendition with the original to make sure that your version accurately expresses all the essential information in a new form.
- Use quotation marks to identify any unique term or phraseology you have borrowed exactly from the source.
- Record the source (including the page) on your note card so that you can credit it easily if you decide to incorporate the material into your paper.
Some examples to compare
Note that the examples in this section use MLA style for in-text citation.
The original passage:
Students frequently overuse direct quotation in taking notes, and as a result they overuse quotations in the final [research] paper. Probably only about 10% of your final manuscript should appear as directly quoted matter. Therefore, you should strive to limit the amount of exact transcribing of source materials while taking notes. Lester, James D. Writing Research Papers . 2nd ed., 1976, pp. 46-47.
A legitimate paraphrase:
In research papers, students often quote excessively, failing to keep quoted material down to a desirable level. Since the problem usually originates during note taking, it is essential to minimize the material recorded verbatim (Lester 46-47).
An acceptable summary:
Students should take just a few notes in direct quotation from sources to help minimize the amount of quoted material in a research paper (Lester 46-47).
A plagiarized version:
Students often use too many direct quotations when they take notes, resulting in too many of them in the final research paper. In fact, probably only about 10% of the final copy should consist of directly quoted material. So it is important to limit the amount of source material copied while taking notes.
A note about plagiarism: This example has been classed as plagiarism, in part, because of its failure to deploy any citation. Plagiarism is a serious offense in the academic world. However, we acknowledge that plagiarism is a difficult term to define; that its definition may be contextually sensitive; and that not all instances of plagiarism are created equal—that is, there are varying “degrees of egregiousness” for different cases of plagiarism.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / MLA In-text Citations
MLA In-Text Citations
An in-text citation is a reference to a source that is found within the text of a paper ( Handbook 227). This tells a reader that an idea, quote, or paraphrase originated from a source. MLA in-text citations usually include the last name of the author and the location of cited information.
This guide focuses on how to create MLA in-text citations, such as citations in prose and parenthetical citations in the current MLA style, which is in its 9th edition. This style was created by the Modern Language Association . This guide reviews MLA guidelines but is not related directly to the association.
Table of Contents
Here’s a quick rundown of the contents of this guide on how to use in-text citations.
Fundamentals
- Why in-text citations are important
- Prose vs parenthetical in-text citation differences
- Parenthetical citation reference chart
In-text citation examples
- In-text citation with two authors
- In-text citation with 3+ authors
- In-text citation with no authors
- In-text citation with corporate authors
- In-text citation with edited books and anthologies
- In-text citation with no page numbers and online sources
- Citing the same sources multiple times
- Citing 2+ sources in the same in-text citation
- Citing multiple works by the same author in the same in-text citation
- Abbreviating titles
- Citing religious works and scriptures
- Citing long or block quotes
Why are in-text citations important?
In-text citations
- Give full credit to sources that are quoted and paraphrased in a work/paper.
- Help the writer avoid plagiarism.
- Are a signal that the information came from another source.
- Tell the reader where the information came from.
In-text citation vs. in-prose vs. parenthetical
An in-text citation is a general citation of where presented information came from. In MLA, an in-text citation can be displayed in two different ways:
- In the prose
- As a parenthetical citation
While the two ways are similar, there are slight differences. However, for both ways, you’ll need to know how to format page numbers in MLA .
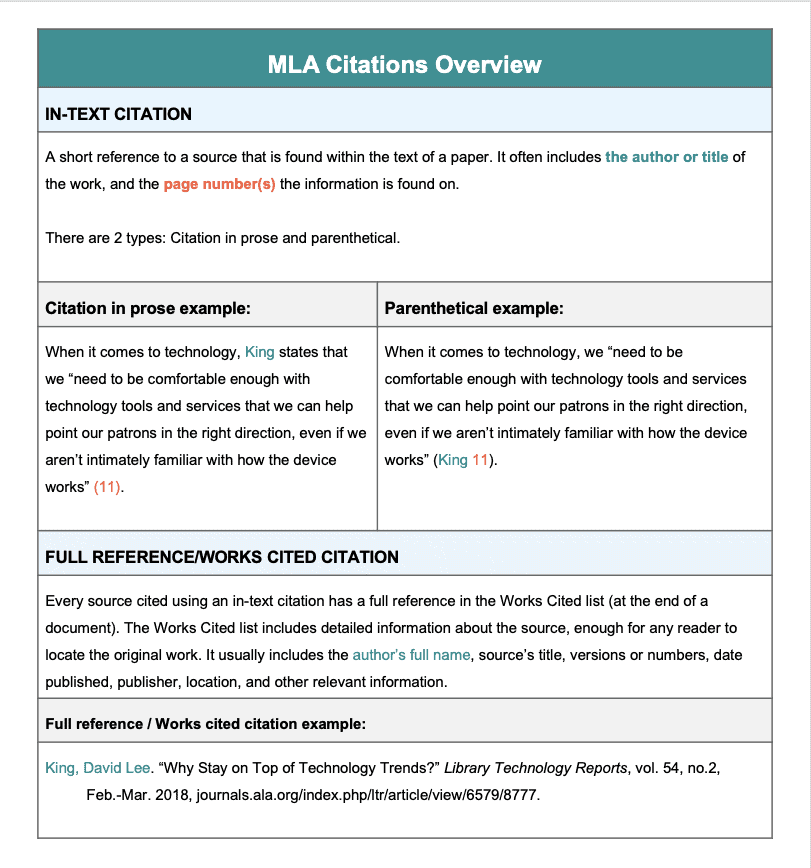
Citation in prose
An MLA citation in prose is when the author’s name is used in the text of the sentence. At the end of the sentence, in parentheses, is the page number where the information was found.
Here is an example
When it comes to technology, King states that we “need to be comfortable enough with technology tools and services that we can help point our patrons in the right direction, even if we aren’t intimately familiar with how the device works” (11).
This MLA citation in prose includes King’s name in the sentence itself, and this specific line of text was taken from page 11 of the journal it was found in.
Parenthetical citation
An MLA parenthetical citation is created when the author’s name is NOT in the sentence. Instead, the author’s name is in parentheses after the sentence, along with the page number.
Here is an MLA parenthetical citation example
When it comes to technology, we “need to be comfortable enough with technology tools and services that we can help point our patrons in the right direction, even if we aren’t intimately familiar with how the device works” (King 11).
In the above example, King’s name is not included in the sentence itself, so his name is in parentheses after the sentence, with 11 for the page number. The 11 indicates that the quote is found on page 11 in the journal.
Full reference
For every source that is cited using an in-text citation, there is a corresponding full reference. This allows readers to track down the original source.
At the end of the assignment, on the MLA works cited page , is the full reference. The full reference includes the full name of the author, the title of the article, the title of the journal, the volume and issue number, the date the journal was published, and the URL where the article was found.
Here is the full reference for King’s quote
King, David Lee. “Why Stay on Top of Technology Trends?” Library Technology Reports , vol. 54, no. 2, Feb.-Mar. 2018, ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=//search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/2008817033?accountid=35635.
Readers can locate the article online via the information included above.
Citation overview
The next section of this guide focuses on how to structure an MLA in-text citation and reference in parentheses in various situations.
A narrative APA in-text citation and APA parenthetical citation are somewhat similar but have some minor differences. Check out our helpful guides, and others, on EasyBib.com!
Wondering how to handle these types of references in other styles? Check out our page on APA format , or choose from more styles .
Parenthetical Citation Reference Chart
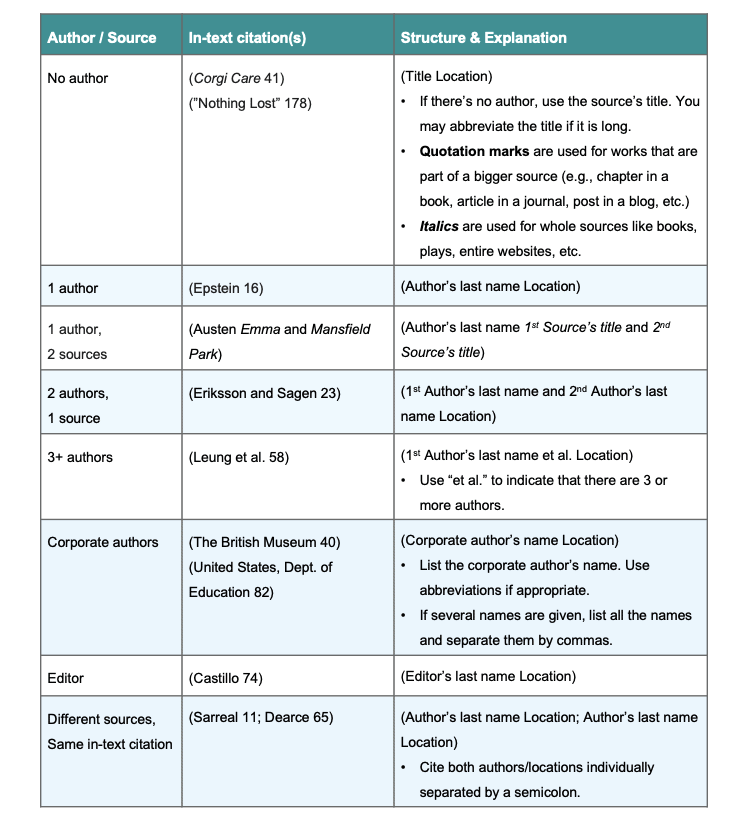
| Author/Sources | In-text citation | Structure & Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 41 (“Nothing Lost” 178) | (Title Location) Use the title. Use an abbreviated version if it’s long. Format the title like you do in the reference. “Quotation marks” = Work that’s part of a bigger source (e.g., book chapter, journal article, blog post, etc.) = Book, play, entire website, etc. | |
| One author | (Epstein 161) | (Author’s last name Location) |
| (Austen and ) | (Last name and ) | |
| (Eriksson and Sagen 23) | From one source – list both authors separated by , followed by the page number. | |
| (Leung et al. 58) | Use et al. to indicate that there are 3 or more authors. | |
| (The British Museum) (United States, Dept. of Education 82) | List the corporation or organization’s name. Use abbreviations as appropriate. If several names are given, list all the names and separate them by a comma. | |
| (Castillo 74) | Use the editor’s name instead of the author’s name. | |
| (Sarreal 11; DeArce 65) | Cite both authors/locations individually separated by a semicolon. |
Sources with Two Authors
There are many books, journal articles, magazine articles, reports, and other source types written or created by two authors.
When a source has two authors, place both authors’ last names in the body of your work ( Handbook 232). The last names do not need to be listed in alphabetical order. Instead, follow the same order as shown on the source.
In an MLA in-text citation, separate the two last names with the word “and.” After both authors’ names, add a space and the page number where the original quote or information is found on.
Here is an example of an MLA citation in prose for a book with two authors
Gaiman and Pratchett further elaborate by sharing their creepy reminder that “just because it’s a mild night doesn’t mean that dark forces aren’t abroad. They’re abroad all of the time. They’re everywhere” (15).
Here is an example of an MLA parenthetical citation for a book with two authors
Don’t forget that “just because it’s a mild night doesn’t mean that dark forces aren’t abroad. They’re abroad all of the time. They’re everywhere” (Gaiman and Pratchett 15).
If you’re still confused, check out EasyBib.com’s MLA in-text citation generator, which allows you to create MLA in-text citations and other types of references in just a few clicks!
If it’s an APA book citation you’re looking to create, we have a helpful guide on EasyBib.com. While you’re at it, check out our APA journal guide!
Sources With Three or More Authors
There are a number of sources written or created by three or more authors. Many research studies and reports, scholarly journal articles, and government publications are developed by three or more individuals.
If you included the last names of all individuals in your MLA in-text citations or in parentheses, it would be too distracting to the reader. It may also cause the reader to lose sight of the overall message of the paper or assignment. Instead of including all last names, only include the last name of the first individual shown on the source. Follow the first author’s last name with the Latin phrase, “et al.” This Latin phrase translates to “and others.” Add the page number after et al.
Here’s an example of an MLA parenthetical citation for multiple authors
“School library programs in Croatia and Hong Kong are mainly focused on two major educational tasks. One task is enhancing students’ general literacy and developing reading habits, whereas the other task is developing students’ information literacy and research abilities” (Tam et al. 299).
The example above only includes the first listed author’s last name. All other authors are credited when “et al.” is used. If the reader wants to see the other authors’ full names, the reader can refer to the final references at the end of the assignment or to the full source.
The abbreviation et al. is used with references in parentheses, as well as in full references. To include the authors’ names in prose, you can either write each name out individually or, you can type out the meaning of et al., which is “and others.”
Here is an acceptable MLA citation in prose example for sources with more than three authors
School library programming in Croatia and Hong Kong is somewhat similar to programming in the United States. Tam, Choi, Tkalcevic, Dukic, and Zheng share that “school library programs in Croatia and Hong Kong are mainly focused on two major educational tasks. One task is enhancing students’ general literacy and developing reading habits, whereas the other task is developing students’ information literacy and research abilities” (299).
If your instructor’s examples of how to do MLA in-text citations for three or more authors looks different than the example here, your instructor may be using an older edition of this style. To discover more about previous editions, learn more here .
Need some inspiration for your research project? Trying to figure out the perfect topic? Check out our Dr. Seuss , Marilyn Monroe , and Malcolm X topic guides!
Sources Without an Author
It may seem unlikely, but there are times when an author’s name isn’t included on a source. Many digital images, films and videos, encyclopedia articles, dictionary entries, web pages, and more do not have author names listed.
If the source you’re attempting to cite does not have an author’s name listed, the MLA in-text citation or parenthetical citation should display the title. If the title is rather long, it is acceptable to shorten it in the body of your assignment. If you choose to shorten the title, make sure the first word in the full citation is also the first word used in the citation in prose or parenthetical citation. This is done to allow the reader to easily locate the full citation that corresponds with the reference in the text.
If, in the Works Cited list, the full reference has the title within quotation marks, include those quotation marks in the in-text citation or reference in parentheses. If the title is written in italics in the full reference, use italics for the title in the in-text citation or reference in parentheses as well.
Parenthetical Citations MLA Examples
The example below is from a poem found online, titled “the last time.” the poem’s author is unknown..
“From the moment you hold your baby in your arms you will never be the same. You might long for the person you were before, when you had freedom and time and nothing in particular to worry about” (“The Last Time”).
The example below is from the movie, The Englishman Who Went Up a Hill But Came Down a Mountain .
“Perhaps it would have been different if there hadn’t been a war, but this was 1917, and people were exhausted by loss. Those that were allowed to stay manned the pits, mining the coal that would fuel the ships. Twenty-four hours a day they labored” ( Englishman ).
Notice the shortened title in the above reference. This allows the reader to spend more time focusing on the content of your project, rather than the sources.
If you’re looking for an MLA in-text citation website to help you with your references, check out EasyBib Plus on EasyBib.com! EasyBib Plus can help you determine how to do in-text citations MLA and many other types of references!
Corporate Authors
Numerous government publications, research reports, and brochures state the name of the organization as the author responsible for publishing it.
When the author is a corporate entity or organization, this information is included in the MLA citation in prose or parenthetical citation.
“One project became the first to evaluate how e-prescribing standards work in certain long-term care settings and assessed the impact of e-prescribing on the workflow among prescribers, nurses, the pharmacies, and payers” (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 2).
If the full name of the organization or governmental agency is long in length, it is acceptable to abbreviate some words, as long as they are considered common abbreviations. These abbreviations should only be in the references with parentheses. They should not be used in citations in prose.
Here is a list of words that can be abbreviated in parentheses:
- Department = Dept.
- Government = Govt.
- Corporation = Corp.
- Incorporated = Inc.
- Company = Co.
- United States = US
Example of a shortened corporate author name in an MLA parenthetical citation
“Based on our analysis of available data provided by selected states’ departments of corrections, the most common crimes committed by inmates with serious mental illness varied from state to state” (US Govt. Accountability Office 14).
Here is how the same corporate author name would look in an MLA citation in prose
The United States Government Accountability Office states, “Based on our analysis of available data provided by selected states’ departments of corrections, the most common crimes committed by inmates with serious mental illness varied from state to state” (14).
Remember, citations in prose should not have abbreviations; other types of references can.
Looking for more information on abbreviations? Check out our page on MLA format.
Edited Books and Anthologies
Edited books and anthologies often include chapters or sections, each written by an individual author or a small group of authors. These compilations are placed together by an editor or a group of editors. There are tons of edited books and anthologies available today, ranging from ones showcasing Black history facts and literature to those focusing on notable individuals such as scientists like Albert Eintein and politicians such as Winston Churchill .
If you’re using information from an edited book or an anthology, include the chapter author’s name in your MLA citation in prose or reference in parentheses. Do not use the name(s) of the editor(s). Remember, the purpose of these references is to provide the reader with some insight as to where the information originated. If, after reading your project, the reader would like more information on the sources used, the reader can use the information provided in the full reference, at the very end of the assignment. With that in mind, since the full reference begins with the author of the individual chapter or section, that same information is what should be included in any citations in prose or references in parentheses.
Here is an example of an MLA citation in prose for a book with an editor
Weinstein further states that “one implication of this widespread adaptation of anthropological methods to historical research was the eclipse of the longstanding concern with “change over time,” and the emergence of a preference for synchronic, rather than diachronic, themes” (195).
Full reference at the end of the assignment
Weinstein, Barbara. “History Without a Cause? Grand Narratives, World History, and the Postcolonial Dilemma.” Postcolonial Studies: An Anthology , edited by Pramod K. Nayar, Wiley-Blackwell, 2015, p. 196. Wiley , www.wiley.com/en-us/Postcolonial+Studies%3A+An+Anthology-p-9781118780985.
Once you’re through with writing and citing, run your paper through our innovative plagiarism checker ! It’s the editor of your dreams and provides suggestions for improvement.
Sources Without Page Numbers and Online Sources
When a source has no page numbers, which is often the case with long web page articles, e-books, and numerous other source types, do not include any page number information in the body of the project. Do not estimate or invent your own page numbering system for the source. If there aren’t any page numbers, omit this information from the MLA in-text citation. There may, however, be paragraph numbers included in some sources. If there are distinct and clear paragraph numbers directly on the source, replace the page number with this information. Make it clear to the reader that the source is organized by paragraphs by using “par.” before the paragraph number, or use “pars.” if the information is from more than one paragraph.
Here is an example of how to create an MLA parenthetical citation for a website
“She ran through the field with the wind blowing in her hair and a song through the breeze” (Jackson par. 5).
Here’s an example of an MLA citation in prose for a website
In Brenner’s meeting notes, he further shared his motivation to actively seek out and secure self help resources when he announced, “When we looked at statistical evidence, the most commonly checked out section of the library was self-help. This proves that patrons consistently seek out help for personal issues and wish to solve them with the help of the community’s resources” (pars. 2-3).
Here’s another MLA in-text citation example for a website
Holson writes about a new mindful app, which provides listeners with the soothing sound of not only Bob Ross’ voice, but also the “soothing swish of his painter’s brush on canvas.”
In above example, the information normally found in the parentheses is omitted since there aren’t any page, parentheses, or chapter numbers on the website article.
Looking for APA citation website examples? We have what you need on EasyBib.com!
Need an in-text or parenthetical citation MLA website? Check out EasyBib Plus on EasyBib.com! Also, check out MLA Citation Website , which explains how to create references for websites.
Citing the Same Source Multiple Times
It may seem redundant to constantly include an author’s name in the body of a research project or paper. If you use an author’s work in one section of your project, and the next piece of information included is by the same individual(s), then it is not necessary to share in-text, whether in prose or in parentheses, that both items are from the same author. It is acceptable to include the last name of the author in the first use, and in the second usage, only a page number needs to be included.
Here is an example of how to cite the same source multiple times
“One of the major tests is the Project for Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills. This measurement was developed over four years as a joint partnership between the Association of Research Libraries and Kent State University” (Tong and Moran 290). This exam is just one of many available to measure students’ information literacy skills. It is fee-based, so it is not free, but the results can provide stakeholders, professors, curriculum developers, and even librarians and library service team members with an understanding of students’ abilities and misconceptions. It is not surprising to read the results, which stated that “upper-level undergraduate students generally lack information literacy skills as evidenced by the results on this specific iteration of the Standardized Assessment of Information Literacy Skills test” (295).
The reader can assume that the information in the second quote is from the same article as the first quote. If, in between the two quotes, a different source is included, Tong and Moran’s names would need to be added again in the last quote.
Here is the full reference at the end of the project:
Tong, Min, and Carrie Moran. “Are Transfer Students Lagging Behind in Information Literacy?” Reference Services Review , vol. 45, no. 2, 2017, pp. 286-297. ProQuest , ezproxy.nypl.org/login?url=//search-proquest-com.i.ezproxy.nypl.org/docview/1917280148?accountid=35635.
Citing Two or More Sources in the Same In-text Citation
According to section 6.30 of the Handbook , parenthetical citations containing multiple sources in a single parenthesis should be separated by semicolons.
(Granger 5; Tsun 77) (Ruiz 212; Diego 149)
Citing Multiple Works by the Same Author in One In-text Citation
Just as you might want to cite two different sources at the same time, it can also be useful to cite different works by the same author all at once.
Section 6.30 of the Handbook specifies that “citations of different locations in a single source are separated by commas” (251).
(Maeda 59, 174-76, 24) (Kauffman 7, 234, 299)
Furthermore, if you are citing multiple works by the same author, the titles should be joined by and if there are only two. Otherwise, use commas and and .
(Murakami, Wild Sheep Chase and Norwegian Wood ) (Murakami, Wild Sheep Chase , Norwegian Wood , and “With the Beatles”)
Abbreviating Titles
When listing the titles, be aware that long titles in parenthetical citations can distract the reader and cause confusion. It will be necessary to shorten the titles appropriately for in-text citations. According to the Handbook , “shorten the title if it is longer than a noun phrase” (237). The abbreviated title should begin with the word by which the title is alphabetized.
Best practice is to give the first word the reference is listed by so the source is easily found in the works cited. Omit articles that start a title: a, an, the. When possible, use the first noun (and any adjectives before it). For more on titles and their abbreviations, head to section 6.10 of the Handbook .
- Full title : The Curious Incident of the Dog in the Night-Time
- Abbreviated: Curious
- Full title: The Disreputable History of Frankie Landau-Banks
- Abbreviated: Disreputable History
Religious Works and Scriptures
There are instances when religious works are italicized in the text of a project, and times when it is not necessary to italicize the title.
If you’re referring to the general religious text, such as the Bible, Torah, or Qur’an, it is not necessary to italicize the name of the scripture in the body of the project. If you’re referring to a specific edition of a religious text, then it is necessary to italicize it, both in text and in the full reference.
Here are some commonly used editions:
- King James Bible
- The Orthodox Jewish Bible
- American Standard Bible
- The Steinsaltz Talmud
- The Babylonian Talmud
- New International Bible
When including a reference, do not use page numbers from the scripture. Instead, use the designated chapter numbers and verse numbers.
MLA example of an in-text citation for a religious scripture
While, unacceptable in today’s society, the Bible is riddled with individuals who have two, three, and sometimes four or more spouses. One example in the King James Bible , states that an individual “had two wives, the name of the one was Hannah, and the name of the other Peninnah. Peninnah had children, but Hannah had no children” (1 Sam. 1.2)
The only religious scripture that is allowed to be in the text of a project, but not in the Works Cited list, is the Qur’an. There is only one version of the Qur’an. It is acceptable to include the name of the Qur’an in the text, along with the specific chapter and verse numbers.
If you’re attempting to create a reference for a religious work, but it’s not considered a “classic” religious book, such as a biography about Mother Teresa , or a book about Muhammed Ali’s conversion, then a reference in the text and also on the final page of the project is necessary.
If you’re creating an APA bibliography , you do not need to create a full reference for classic religious works on an APA reference page .
For another MLA in-text citation website and for more on the Bible and other source types, click here .
Long or Block Quotes
Quotes longer than four lines are called, “block quotes.” Block quotes are sometimes necessary when you’re adding a lengthy piece of information into your project. If you’d like to add a large portion of Martin Luther King ’s “I Have a Dream” speech, a lengthy amount of text from a Mark Twain book, or multiple lines from Abraham Lincoln ’s Gettysburg Address, a block quote is needed.
MLA block quotes are formatted differently than shorter quotes in the body of a project. Why? The unique formatting signals to the reader that they’re about to read a lengthy quote.
Block quotes are called block quotes because they form their own block of text. They are set apart from the body of a project with different spacing and margins.
Begin the block quote on a new line. The body of the full project should run along the one inch margin, but the block quote should be set in an inch and a half. The entire quote should be along the inch and a half margin.
If there aren’t any quotation marks in the text itself, do not include any in the block quote. This is very different than standard reference rules. In most cases, quotation marks are added around quoted material. For block quotes, since the reader can see that the quoted material sits in its own block, it is not necessary to place quotation marks around it.
Here is an MLA citation in prose example of a block quote
Despite Bruchac’s consistent difficult situations at home, basketball kept his mind busy and focused:
When I got off the late bus that afternoon, my grandparents weren’t home. The store was locked and there was a note from Grama on the house door. Doc Magovern had come to the house because Grampa was “having trouble with his blood.” Now they were off to the hospital and I “wasn’t to worry.” This had happened before. Grampa had pernicious anemia and sometimes was very sick. So, naturally, it worried the pants off me. I actually thought about taking my bike down the dreaded 9N the three miles to the Saratoga Hospital. Instead, I did as I knew they wanted. I opened the store and waited for customers. None came, though, and my eye was caught by the basketball stowed away as usual behind the door. I had to do something to take my mind off what was happening to Grampa. I took out the ball and went around the side. (13)
Notice the use of the colon prior to the start of the block quote. Do not use a colon if the block quote is part of the sentence above it.
Here is an example of the same block quote, without the use of the colon:
Despite Bruchac’s consistent difficult situations at home, it was clear that basketball kept his mind busy and focused when he states
When I get off the late bus that afternoon, my grandparents weren’t home…
If two or more paragraphs are included in your block quote, start each paragraph on a new line.
Looking for additional helpful websites? Need another MLA in-text citation website? Check out the style in the news . We also have other handy articles, guides, and posts to help you with your research needs. Here’s one on how to write an MLA annotated bibliography .
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
If you’re looking for information on styling an APA citation , EasyBib.com has the guides you need!
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Published October 31, 2011. Updated July 5, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
In MLA style, if multiple sources have the same author , the titles should be joined by and if there are only two. Otherwise, use commas and and .
- In-text citation: (Austen Emma and Mansfield Park )
- Structure: (Last name 1st Source’s title and 2nd Source’s title )
- In-text citation: (Leung et al. 58)
If the author is a corporate entity or organization, included the name of the corporate entity or organization in the in-text citation.
- In-text citation: (Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality 2)
Yes, there’s an option to download source citations as a Word Doc or a Google Doc. You may also copy citations from the EasyBib Citation Generator and paste them into your paper.
Yes! Whether you’d like to learn how to construct citations on your own, our Autocite tool isn’t able to gather the metadata you need, or anything in between, manual citations are always an option. Click here for directions on using creating manual citations.
An in-text citation is a shortened version of the source being referred to in the paper. As the name implies, it appears in the text of the paper. A works cited list entry, on the other hand, details the complete information of the source being cited and is listed within the works cited list at the end of the paper after the main text. The in-text citation is designed to direct the reader to the full works cited list entry. An example of an in-text citation and the corresponding works cited list entry for a journal article with one author is listed below:
In-text citation template and example:
Only the author surname (or the title of the work if there is no author) is used in in-text citations to direct the reader to the corresponding reference list entry. For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author for the first occurrence. In subsequent citations, use only the surname. In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author. If you are directly quoting the source, the page number should also be included in the in-text citation.
Citation in prose:
First mention: Christopher Collins ….
Subsequent occurrences: Collins ….
Parenthetical:
….(Collins)
….(Collins 5)
Works cited list entry template and example:
The title of the article is in plain text and title case and is placed inside quotation marks. The title of the journal is set in italics.
Surname, F. “Title of the Article.” Journal Title , vol. #, no. #, Publication Date, page range.
Collins, Christopher. “On Posthuman Materiality: Art-Making as Rhizomatic Rehearsal.” Text and Performance Quarterly , vol. 39, no. 2, 2019, pp. 153–59.
Note that because the author’s surname (Collins) was included in the in-text citation, the reader would then be able to easily locate the works cited list entry since the entry begins with the author’s surname.
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when text is quoted from the source being cited. In-text citations are mentioned in the text in two ways: as a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
Citations in prose are incorporated into the text and act as a part of the sentence. Usually, citations in prose use the author’s full name when cited the first time in the text. Thereafter, only the surname is used. Avoid including the middle initial even if it is present in the works-cited-list entry.
Parenthetical
Parenthetical citations add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses.
Examples of in-text citations
Here are a few tips to create in-text citations for sources with various numbers and types of authors:
Use both the first name and surname of the author if you are mentioning the author for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the author’s surname. Always use only the surname of the author in parenthetical citations.
First mention: Sheele John asserts …. (7).
Subsequent occurrences: John argues …. (7).
…. (John 7).
Two authors
Use the first name and surname of both authors if you are mentioning the work for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the surnames of the two authors. Always use only the authors’ surnames in parenthetical citations. Use “and” to separate the two authors in parenthetical citations.
First mention: Katie Longman and Clara Sullivan ….
Subsequent occurrences: Longman and Sullivan ….
…. ( Longman and Sullivan).
Three or more authors
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues.” For parenthetical citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
Lincy Mathew and colleagues…. or Lincy Mathew and others ….
…. (Mathew et al.).
Corporate author
For citations in prose, treat the corporate author like you would treat the author’s name. For parenthetical citations, shorten the organization name to the shortest noun phrase. For example, shorten the Modern Language Association of America to Modern Language Association.
The Literary Society of Malaysia….
…. (Literary Society).
If there is no author for the source, use the source’s title in place of the author’s name for both citations in prose and parenthetical citations.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, shorten the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them to Fantastic Beasts .
Knowing Body of Work explains …. (102).
….( Knowing Body 102).
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Find and fix writing mistakes instantly
- Check for unintentional plagiarism
- Get instant grammar and style suggestions
Paraphrasing in MLA
Paraphrasing can be a useful tool to help you avoid relying too heavily on quotes. You should avoid using too many quotes in your writing.
That being said, you still need to cite your sources properly when paraphrasing. You are borrowing other people’s ideas, so it’s important to give credit where it’s due.
If your instructor wants you to use MLA-style citations, it’s important to know how this works in regard to paraphrasing.
What is MLA style?
MLA stands for “Modern Language Association.” This association was founded in 1983, and it’s the leading professional academic organization in the United States. The MLA style is frequently used by schools, instructors, and academic organizations. While many students use the MLA style when writing, it’s especially popular in humanities courses.
What is paraphrasing?
When you paraphrase a passage, you are putting it in your own words. In most cases, the result is that this passage becomes clearer and easier to understand. Paraphrases can be shorter, longer, or the same length as the original passage. Paraphrasing is useful because it shows that you actually understand the key ideas behind the passage.
Paraphrasing & citing in MLA style
Once you understand the system for citing your sources in MLA style, paraphrasing is easy. You can use this process to cite your sources when paraphrasing, summarizing, or using direct quotes.
1. Create a works cited page
Both a works cited page and a bibliography list sources that were used in the making of your paper. The main difference is that a works cited page only includes sources that were referenced in your work (via an in-text citation). On the other hand, a bibliography includes all sources consulted, even if they were not directly referenced in your work. Both are placed at the end of your research paper or essay and follow the same MLA guidelines. It is important to create a works cited page because your in-text citations will help your reader to identify the source you are referencing from that list.
To create a works cited page based on the MLA format, you need to follow a number of guidelines.
This is the basic structure for a book reference in MLA format:
Author Last, Author First, Middle Initial. Title of Work . Publisher, Year.
Here’s an example:
Kafka, Franz. The Metamorphosis . Modern Library, 1915.
For more help creating citations, visit the Citation Machine MLA citation generator .
2. In-text citations
When writing according to the MLA style citation guide, you will use in-text citations. The goal of in-text citations is to direct your reader to the appropriate citation in your works cited list. At the end of your paraphrase, you’ll write the last name of the author and the page number you’re referencing.
This is the basic structure for an in-text citation in MLA format:
(Author Last Name Page number).
For example:
Captain Montgomery forced Pendrick off his ship, claiming that Pendrick was in league with “beasts and cannibals” (Wells 26).
The period is always placed after the parentheses.
If there’s more than one author, you simply use both of their last names, followed by the page number.
(Smith and Jones 77).
If there are three or more authors, you simply use the first author’s last name and then write “et al.”
(Smith et al. 77).
If there is no page number, just use the author’s last name. You’ll likely need to do this if you’re citing a web page or another source where page numbers are not included.
If you’re repeatedly citing the same source, you can simply refer to the page number after the first time. Note that you can only do this if you’re not citing other sources in between and this shouldn’t be used if it will cause confusion.
Captain Montgomery forced Pendrick off his ship, claiming that Pendrick was in league with “beasts and cannibals” (Wells 26). After being stranded on a small dinghy, Pendrick begs God to end his suffering (30).
You can also use only the page number if you have included the author’s name within the test itself. This is called a narrative citation.
Basic structure:
Text that mentions the author’s last name (page number).
Wells writes that Captain Montgomery forced Pendrick off his ship, claiming that Pendrick was in league with “beasts and cannibals” (26).
Key takeaways
- When paraphrasing, you need to put the writing in your own words.
- Citing your sources is important when paraphrasing.
- The MLA style is used for academic writing, especially in the humanities.
- The first step is to create a works cited page.
- Next, you use in-text citations after your paraphrases to direct your reader to the source listed in your works cited page.
- You generally use the last name of the author and the page number in parentheses after your paraphrases.
Published October 29, 2020.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

MLA Citation Guide (9th Edition): In-Text Citation
- What Kind of Source Is This?
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Book Reviews
- Class Handouts, Presentations, and Readings
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Artwork, Charts, Graphs & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Primary Sources
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- In-Text Citation
Works Quoted in Another Source
- No Author, No Date etc.
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Powerpoint Presentations
On This Page
About in-text citations, no known author, quoting directly, paraphrasing, no page numbers, repeated use of sources, in-text citation for more than one source, long quotations, quoting and paraphrasing: what's the difference, signal phrases, avoiding plagiarism when using sources.
T here are two ways to integrate others' research into your assignment: you can paraphrase or you can quote.
Paraphrasing is used to show that you understand what the author wrote. You must restate the meaning of the passage, expressing the ideas in your own words and voice, and not just change a few words here and there. Make sure to also include an in-text citation.
Quoting is copying the wording from someone else's work, keeping it exactly as it was originally written. When quoting, place quotation marks (" ") around the selected passage to show where the quote begins and where it ends. Make sure to include an in-text citation.
If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name again as part of your in-text citation. Instead include the page number (if there is one) at the end of the quotation or paraphrased section.
Hunt explains that mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (358).
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the Works Cited list at the end of the paper.
| Number of Authors/Editors | Format of In-Text Citation |
|---|---|
| One | (Author's Last Name Page Number) Example: (Case 57) |
| Two | (Author's Last Name and Author's Last Name Page Number) Example: (Case and Daristotle 57) |
| Three or more | (Author's Last Name et al. Page Number) Example: (Case et al. 57) |
When a source has no known author, use the first one, two, or three words from the title instead of the author's last name. Don't count initial articles like "A", "An" or "The". You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your Works Cited list.
If the title in the Works Cited list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation.
( Cell Biology 12)
If the title in the Works Cited list is in quotation marks, put quotation marks around the words from the title in the in-text citation.
("Nursing" 12)
When you quote directly from a source, enclose the quoted section in quotation marks. Add an in-text citation at the end of the quote with the author name and page number, like this:
"Here's a direct quote" (Smith 8).
"Here's a direct quote" ("Trouble" 22).
Note: The period goes outside the brackets, at the end of your in-text citation.
Mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (Hunt 358).
When you write information or ideas from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion, like this:
This is a paraphrase (Smith 8).
This is a paraphrase ("Trouble" 22).
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65).
Note: If the paraphrased information/idea summarizes several pages, include all of the page numbers.
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 50, 55, 65-71).
When you quote from electronic sources that do not provide page numbers (like webpages), cite the author name only. If there is no author, cite the first word or words from the title only.
"Three phases of the separation response: protest, despair, and detachment" (Garelli).
"Nutrition is a critical part of health and development" ("Nutrition").
Sources that are paraphrased or quoted in other sources are called indirect sources. MLA recommends you take information from the original source whenever possible.
If you must cite information from an indirect source, mention the author of the original source in the body of your text and place the name of the author of the source you actually consulted in your in-text citation. Begin your in-text citation with 'qtd. in.'
Kumashiro notes that lesbian and bisexual women of colour are often excluded from both queer communities and communities of colour (qtd. in Dua 188).
(You are reading an article by Dua that cites information from Kumashiro (the original source))
Note: In your Works Cited list, you only include a citation for the source you consulted, NOT the original source.
In the above example, your Works Cited list would include a citation for Dua's article, and NOT Kumashiro's.
If you're using information from a single source more than once in a row (with no other sources referred to in between), you can use a simplified in-text citation. The first time you use information from the source, use a full in-text citation. The second time, you only need to give the page number.
Cell biology is an area of science that focuses on the structure and function of cells (Smith 15). It revolves around the idea that the cell is a "fundamental unit of life" (17). Many important scientists have contributed to the evolution of cell biology. Mattias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, for example, were scientists who formulated cell theory in 1838 (20).
Note: If using this simplified in-text citation creates ambiguity regarding the source being referred to, use the full in-text citation format.
If you would like to cite more than one source within the same in-text citation, simply record the in-text citations as normal and separate them with a semi-colon.
(Smith 42; Bennett 71).
( It Takes Two ; Brock 43).
Note: The sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order for MLA style.
What Is a Long Quotation?
If your quotation is longer than four lines, it is a considered a long quotation. This can also be referred to as a block quotation.
Rules for Long Quotations
There are 4 rules that apply to long quotations that are different from regular quotations:
- Place a colon at the end of the line that you write to introduce your long quotation.
- Indent the long quotation 0.5 inches from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- Do not put quotation marks around the quotation.
- Place the period at the end of the quotation before your in-text citation instead of after , as with regular quotations.
Example of a Long Quotation
Vivian Gornick describes the process of maturing as a reader as a reckoning with human limitations:
Suddenly, literature, politics, and analysis came together, and I began to think more inclusively about the emotional
imprisonment of mind and spirit to which all human beings are heir. In the course of analytic time, it became apparent
that—with or without the burden of social justice—the effort required to attain any semblance of inner freedom was
extraordinary. Great literature, I then realized, is a record not of the achievement, but of the effort.
With this insight as my guiding light, I began to interpret the lives and work of women and men alike who had
spent their years making literature. (x-xi)
- << Previous: Websites
- Next: Works Quoted in Another Source >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 11:24 AM
- URL: https://columbiacollege-ca.libguides.com/MLA9

Paraphrasing
What is paraphrasing.
When you paraphrase, you take key ideas from an original source and rewrite them using your own words.
Characteristics of Paraphrasing
- Includes all key points
- Includes all details
- Includes smaller details not just the bigger main idea
- Is accurate
- Is objective/unbiased
- It is about the same length as the original source
- Uses different words than the original source
- Uses different sentence structure than the original source
- Credits original source
- Includes a signal phrase at the beginning to introduce the paraphrase
- For a paraphrase that is multiple sentences long, start each sentence with an indicator that the paraphrase is continuing, such as a signal phrase: The author further explains….. (81).
When to Use Paraphrasing
- When you want to use your own words and keep all of the details from the original source in your writing
- Paraphrase is preferred over direct quotes in academic writing because you are using your own voice as a writer to present others’ ideas.

Test Your Understanding of Paraphrasing:
This article contains the following quotation:
“Student development of 21st-century skills is greatly needed to promote workforce preparedness and long-term success of the U.S. economy. To add to the discussion on which skills are of greatest importance for students to develop before entering the workforce, this study investigated skill demand based on direct communication from employers to potential employees via job advertisements. The four most in-demand 21st-century skills found across roughly 142,000 job advertisements were oral and written communication, collaboration, and problem solving (Rios et al. 80).”
Article: Animal Testing: Is Animal Testing Morally Justified?, Issues & Controversies , 2020
Example: From the article ” Human beings have long used animals as test subjects for a variety of purposes. Every year, tens of millions of animals are used in laboratory settings to gauge the toxicity of newly developed chemicals. If deemed safe, these chemicals find their way into a wide range of consumer goods including cosmetics, household cleaners, pesticides, shampoos, and sunscreens (“Animal Testing”).
MLA in Minutes Copyright © by Sami Lange; Vicki Brandenburg; and Leila Palis is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Citations - MLA: In-Text Citations - Quotations & Paraphrasing
- Advertisements
- Artificial Intelligence: AI
- Books, eBooks, & Pamphlets
- Class Notes & Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries (Reference Works)
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Pesonal Communication (Interviews, Emails, & Telephone)
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- When Creating Digital Assignments
- When Information Is Missing
- Works in a Foreign Language
- Works Quoted in Another Source (Secondary Source)
- In-Text Citations - Quotations & Paraphrasing
- Formatting - Essay, Works Cited, Appendix, & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
On This Page
- About In-text Citations
Paraphrasing
- In-Text Citation for One, Two, or More Authors/Editors
Unknown Author
Repeated use of sources, long quotations.
- In-Text Citation for More Than One Source
Citing a Source that you Found in Another Source (Secondary Source)
Order of authors, physician credentials, about in-text citations.
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to the full citation on the works cited list at the end of the paper.
Create in-text citations for the following:
- Direct quotes
If you're using information from a single source more than once in succession (i.e., no other sources referred to in between), you can use a simplified in-text citation.
Cell biology is an area of science that focuses on the structure and function of cells (Smith 15). It revolves around the idea that the cell is a "fundamental unit of life" (17). Many important scientists have contributed to the evolution of cell biology. Mattias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, for example, were scientists who formulated cell theory in 1838 (20).
Note: If using this simplified in-text citation creates ambiguity regarding the source being referred to, use the full in-text citation format.
What Is a Long Quotation?
If your quotation extends to more than four lines as you're typing your essay, it is a long quotation.
Rules for Long Quotations
There are 4 rules that apply to long quotations that are different from regular quotations:
- The line before your long quotation, when you're introducing the quote, usually ends with a colon.
- The long quotation is indented half an inch from the rest of the text, so it looks like a block of text.
- There are no quotation marks around the quotation.
- The period at the end of the quotation comes before your in-text citation as opposed to after , as it does with regular quotations.
Example of a Long Quotation
At the end of Lord of the Flies the boys are struck with the realization of their behaviour:
The tears began to flow and sobs shook him. He gave himself up to them now for the first time on the island; great, shuddering spasms of grief that seemed to wrench his whole body. His voice rose under the black smoke before the burning wreckage of the island; and infected by that emotion, the other little boys began to shake and sob too . (Golding 186)
Direct Quote - Add an in-text citation at the end of the quote with the author name and page number:
Mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (Hunt 358).
Authors Name in the Sentence & with a Direct Quote - If you refer to the author's name in a sentence you do not have to include the name in the in-text citation, instead include the page number (if there is one) at the end of the quotation or paraphrased section. For example:
Hunt explains that mother-infant attachment has been a leading topic of developmental research since John Bowlby found that "children raised in institutions were deficient in emotional and personality development" (358).
No Page Numbers & with a Direct Quote - When you quote from electronic sources that do not provide page numbers (like Web pages), cite the author name only.
"Three phases of the separation response: protest, despair, and detachment" (Garelli).
Note: The period goes outside the brackets, at the end of your in-text citation.
In-Text Citation For One, Two, or More Authors/Editors
Author Known:
- "Here's a direct quote" (Smith 8).
| Number of Authors/Editors | In-Text Citation Example |
|---|---|
| One | (Author's Last Name Page Number) (Lee 5) |
| Two | (Author's Last Name and Author's Last Name Page Number) Example: (Daristotle and Case 57) |
| Three or more | (Author's Last Name et al. Page Number) Example: (Daristotle et al. 57) |
In-Text Citation For More Than One Source
If you would like to cite more than one source within the same in-text citation, simply record the in-text citations as normal and separate them with a semi-colon.
(Smith 42; Bennett 71).
( It Takes Two ; Brock 43).
Note: The sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order for MLA style.
When creating an in-text citation or full citation, the authors should be listed in the original order displayed on the item (book, article, ...).
Do not include academic credentials (e.g., MD, MPH, PhD,. DDS) when citing doctors in the in-text or full citation.
The writer may refer to the physician by Dr. (name), when writing a paraphrase or inserting a direct quotation, although, it is not required.
Using the medical credential in the sentence:
Dr. Higgins, said the reason behind the complication was "direct quote here" (257).
Dr. Price realized that nutrition was tied to health outcomes and encountered this observation in various regions of the world during his travels (390).
Omitting the medical credential from the sentence:
He sad the reason behind the complication was "direct quote here" (Higgins 257).
Price observed that nutrition was tied to health outcomes and encountered this in various regions of the world during his travels (390).
When you write information or ideas from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion.
Paraphrasing from One Page
Include a full in-text citation with the author name and page number (if there is one). For example:
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65).
Hunt discussed mother-infant attachment becoming a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (65).
Paraphrasing from Multiple Pages
If the paraphrased information/idea is from several pages, include them. For example:
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 50, 55, 65-71).
Author Unknown:
- If the author's name is not given, then use the first word or words of the title. Follow the same formatting that was used in the works cited list, such as quotation marks. This is a paraphrase ("Trouble" 22).
- Where you'd normally put the author's last name, instead use the first one, two, or three words from the title. Don't count initial articles like "A", "An" or "The". You should provide enough words to make it clear which work you're referring to from your Works Cited list.
- If the title in the Works Cited list is in italics, italicize the words from the title in the in-text citation.
- If the title in the Works Cited list is in quotation marks, put quotation marks around the words from the title in the in-text citation.
( Cell Biology 12)
("Nursing" 12)
Sometimes an author of a book, article or website will mention another person’s work by using a quotation or paraphrased idea from that source. ( This may be called a secondary source.)
For example, the Kirkey article you are reading includes a quotation by Smith that you would like to include in your essay.
- The basic rule: in your Works Cited and in-text citation you will still cite Kirkey NOT Smith.
- A dd the words “qtd. in” to your in-text citation.
Examples of in-text citations :
According to a study by Smith (qtd. in Kirkey) 42% of doctors would refuse to perform legal euthanasia.
Smith (qtd. in Kirkey) states that “even if euthanasia was legal, 42% of doctors would be against this method of assisted dying” (A.10).
Example of Works Cited list citation:
Kirkey, Susan. "Euthanasia." The Montreal Gazette , 9 Feb. 2013, p. A.10. Canadian Newsstand Major Dailies.
- << Previous: Works Quoted in Another Source (Secondary Source)
- Next: Formatting - Essay, Works Cited, Appendix, & Sample Paper >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 10:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.lahc.edu/mla

MLA Style: Writing & Citation
- Advertisements
- Books, eBooks & Pamphlets
- Class Notes & Presentations
- Encyclopedias & Dictionaries
- Government Documents
- Images, Charts, Graphs, Maps & Tables
- Interviews and Emails (Personal Communications)
- Journal Articles
- Magazine Articles
- Newspaper Articles
- Religious Texts
- Social Media
- Videos & DVDs
- When Information Is Missing
- Works Quoted in Another Source
- MLA Writing Style
- Unknown or Multiple Authors
Paraphrasing
- Long Quotes
- Repeated Sources
- In-Text Citation For More Than One Source
- Works Cited List & Sample Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
Need Help? Virtual Chat with a Librarian, 24/7
You Can Also:
When you write information or ideas from a source in your own words, cite the source by adding an in-text citation at the end of the paraphrased portion.
Paraphrasing from One Page
Include a full in-text citation with the author name and page number (if there is one). For example:
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65).
Paraphrasing from Multiple Pages
If the paraphrased information/idea is from several pages, include them. For example:
Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 50, 55, 65-71).
- << Previous: Unknown or Multiple Authors
- Next: Long Quotes >>
- Last Updated: Jun 10, 2024 10:58 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gvltec.edu/CiteMLA
In-text citation
- Works Cited
- Artificial intelligence
- Audiovisual
- Encyclopaedias and dictionaries
- Government and organisation publications
- Interviews / speeches
- Journals / periodicals
- Live performances
- Music scores / recordings
- Online communication / social media
- Other sources
- Print this page
- Other styles AGLC4 APA 7th Chicago 17th (A) Notes Chicago 17th (B) Author-Date Harvard MLA 9th Vancouver
- Referencing home
The MLA 9th style uses author-date in-text citations, used when quoting or paraphrasing people’s work.
Two types of in-text citations
1. author prominent format .
Use this format if you want to emphasise the author. Their name becomes part of your sentence.
"It was the best of times, it was the worst of times," wrote Charles Dickens of the eighteenth century (5).
2. Information prominent format
Use this format if you want to emphasise the information. It cites the author’s name, typically at the end of a sentence.
as demonstrated in the opening line, "it was the best of times, it was the worst of times" (Dickens 5).
Examples of in-text citations
Less than four lines of text.
If a prose quotation is no more than four lines and does not require special emphasis, put it in quotation marks and incorporate it into the text. Include the page number(s) in brackets.
"It was the best of times it was the worst of times" wrote Charles Dickens of the eighteenth century (5).
- See Plays and Poetry sections below for how to cite these in-text.
More than three lines of text
If a quotation is longer than three lines, set it off from your text by beginning a new line, indenting half an inch from the left margin. Quotation marks around the text are not required. Introduce the quotation with a colon. Place the parenthetical reference after the last line. For example, the above discusses John Corner in his book, The Art of Record: A Critical Introduction to Documentary , which refers to Brian Winston's revaluation of the documentary tradition in the writings of John Grierson.
Winston's reassessment of Grierson finds the play-off between creativity and realness unconvincing: Grierson's taxonomic triumph was to make his particular species of non-fiction film, the non-fiction genre while at the same time allowing the films to use the significant fictionalising technique of dramatisation. (Winston 103)
This is a usefully provocative point, though agreement with it will largely rest on certain, contestable ideas about 'fictionalisation' and 'dramatisation'. The issue is dealt with directly in Chapter Two, as part of considering the debate around drama-documentary forms, and it occurs in relation to specific works throughout this book.
Two authors
In prose, the first time the two authors are mentioned, use both first and second names. In a parenthetical citation use 'and', not '&' to connect the two surnames.
Others, like Cheryl Brown and Laura Czerniewicz argue that the idea of a generation of ‘digital natives’ is flawed (359). The Brown and Czerniewicz article focuses on…
(Brown and Czerniewicz 359)
Three or more authors
When citing a source with three or more authors in prose you only refer to the first coauthor and can follow the additional authors by “and others“ or “and colleagues.” A parenthetical citation requires the first author's surname, followed by et al.
Laura Czerniewicz and colleagues argue…
(Czerniewicz et al. 53)
Different authors, same surname
If you use works from more than one author with the same last name, eliminate any ambiguity by including the author's first initial as well (or if the initial is also the same, the full first name).
(N. Palmer 45)
(N. Palmer 45; M. Palmer 102)
Citing more than one author
If you are citing more than one source at the same point, place them in the same parentheses, separated by a semi-colon.
(Jackson 41; Smith 150)
Same author, two or more works
If you cite multiple works by the same author, include a shortened title in each in-text citation to establish which work you are referring to. To avoid overly lengthy in-text citations, shorten the title to a simple noun phrase, or a few words.
The first example references Said's book, so the title is italicised. The second example references Said's journal article, so it is in quotation marks.
For more tips on how to abbreviate titles of sources, see 6.10 of the MLA Handbook .
..."the Orient was a scholar's word, signifying what modern Europe had recently made of the still peculiar East" (Said, Orientalism 92).
..."there is something basically unworkable or at least drastically changed about the traditional frameworks in which we study literature" (Said, "Globalizing Literary Study" 64).
Anonymous or no author
For works that are anonymously authored, or have no author, include a shortened version of the title in the in-text citation (do not list the author as "anonymous", nor as "anon.").
It has been argued that the hat symbolised freedom (Wandering Merchant 157).
Corporate author
Abbreviate terms that are commonly abbreviated (e.g. Department becomes Dept.), so as to not disrupt the flow of your text with overly long in-text citations.
If the corporate author is identified in the works-cited list by the names of administrative units separated by commas, give all the names in the parenthetical citation.
The Australian Research Council found that there are limited policies and procedures in place to manage foreign interference (4).
(Monash University 176)
Citing an author within another source
An indirect source is a source that is cited in another source. To quote this second-hand source, use “qtd. in” (quoted in), and then include the information of the source you actually consulted. Similarly, for the reference list use the source that you actually consulted (i.e. the indirect source). Keep in mind that it is good academic practice to seek out and use the original source, rather than the second-hand one, however this is not always possible.
For the below example, the student is using Petrarch's quote which is found in Hui. The page number refers to the source actually consulted (Hui), and the reference list would only list Hui, as shown below:
Hui, Andrew. The Poetics of Ruins in Renaissance Literature. Fordham UP, 2016.
For more information, see section 6.77 of the MLA Handbook .
Petrarch laments that Cicero’s manuscripts are “in such fragmentary and mutilated condition that it would perhaps have been better for them to have perished” (qtd. in Hui 4).
Author in a translation
If you think your audience would require a translation for your quoted material, then provide one. Give the source of the translation, as well as the source of the quote.
If you did the translation yourself, then insert my trans. where you would usually put the translation source, as shown in the example above.
If you're quoting in a language that does not use the Latin alphabet (Arabic, Chinese, Japanese, etc.), then consistently use the original writing system for your quotes or romanisation. Note that proper nouns are usually romanised.
For more information, see 6.75 Translations of Quotations in the MLA Style Guide .
Mme d'Aulnoy's heroine is "la chatte blanche" ("the white cat"; my trans.; 56)

Poetry - Short quotations
Quotations from poetry from part of a line up to three lines in length, which do not need particular emphasis, may be added, placed in quotation marks, within your text as part of a sentence. Use a slash with a space on either side ( / ) to indicate a new line of poetry.
If the poem you are referencing has line numbers, then omit page numbers all-together and cite by line number instead. Do not use the abbreviation l. or ll. , but instead in your first citation, use the word line, or lines as shown in the example below. After the first citation, it can be assumed that the numbers refer to lines, so you can include the numbers alone.
More's distress that she had not written about the problems of the slave trade earlier are expressed in the poem: "Whene'er to Afric's shores I turn my eyes, / Horrors of deepest, deadliest guilt arise" (line 5).
Poetry - Block quotations
When quoting a block of poetry, introduce it in the same manner as a prose block quotation, i.e. begin the quote on a new line and indent each line as below. There is no need to add quotation marks. A reference to the page or line number should be included in parenthesis at the end of the last line. If the original text is creatively spaced or indented, then try to replicate the original as best you can.
Judith Wright 's poetry explores the Australian environment:
And have we eaten in the heart of the yellow wheat the sullen unforgetting seed of fire? And now, set free by the climate of man's hate, that seed sets time ablaze (14)
If you quote the lines of more than one actor or if the piece you are quoting is long, the quotation should not be integrated into your text. The rules in MLA for presenting this text are:
- Leave a line between your text and the quotation
- Begin each part of the dialogue with the character's name, indented half an inch from the margin, in upper case and with a full-stop, e.g. BODYGUARDS.
- Start dialogue after full-stop or match spacing shown in original source
- Indent all dialogue an additional amount, as shown below
- End each piece of dialogue with a full-stop
- End the last line of the quotation with a full-stop and then add the section and line numbers in parentheses.
For more information, see section 6.40 of the MLA 9th Handbook .
TARTUFFE. Yes, my brother, I am a sinner, a guilty man. An unhappy sinner full of iniquity. (III. vi.)
In-text citation general checklist
| Format | Rule |
|---|---|
| Don't include publication year | The citation in the text consists of the . Unlike other referencing styles, the year of publication is not included. |
| Long quotations | Long prose quotations (more than four lines) should be indented. Long verse quotations (more than three lines) should be indented. |
| Citing more than one author | If you are citing more than one author at the same point in a document, separate the names with a semicolon, e.g. (Smith 150; Jackson 41). |
| Authors with same surname | If two authors have the same surname, include their first initial, e.g. (G. Brown 26). |
| Multiple works by same author | If two or more works by the same author appear in the Works Cited list, add a title to your in-text citation, e.g. author mentioned in text: ( 35), author's name and title in text: (35), author's name and title not included in text (Morrison, 35). |
| Where no author, use title | If an entry in the Works Cited list begins with a title, as there is no author, the title can be used in the prose in-text citation or parentheses, e.g. can be styled ( 3). |
| Numbered notes | A numbered note(s) is cited in parentheses by giving the page number(s), followed by the abbreviation (for note) or (for notes), then the note(s) number(s) - use if there is no note number. No spaces are required if you are citing multiple consecutive notes, e.g. - (96n3). If notes are not consecutive or have no number, spaces are required, e.g. - (96 nn 1,3,4). |
- << Previous: Getting started
- Next: Works Cited >>
Did you find this page helpful?
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
progress_activity
Thank you. Your feedback was successfully submitted.
An error has occurred, please try to submit this form again. If the error persists, contact the Library via this link .
- Last Updated: Jun 19, 2024 12:58 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.monash.edu/mla9

MLA Style Guide: 8th Edition: Multiple Authors
- Works Cited examples
- Direct Quote
- Block Quote
- Paraphrase/Summary
- Indirect Quote
Multiple Authors
- In-Text Exceptions
- Personal Communications
- MLA Handbook/Other Resources
- NoodleTools
IN-TEXT CITATIONS FOR A...
See examples below to learn about how multiple authors for one work are handled in MLA parenthetical citations.
Include author's last name and the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses:
(Austen 75)
Two Authors
Include last name of both authors connected by the word ‘and’, followed by the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses.
(Johnson and Tuite 110)
Three or more Authors
Include the first author’s last name followed by ‘et al.’ and the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses.
(Richard et al. 25)
- << Previous: Indirect Quote
- Next: No Author >>
- Last Updated: Jan 5, 2023 1:44 PM
- URL: https://research.wou.edu/mla
MLA 9 Citation Style: Direct Quotes, Paraphrasing, Summarizing
- Textbook With One Author
- Textbook With Two Authors
- Textbook With Three or More Authors
- Textbook as an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook Work Within an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook Two or More from an Anthology or Edited Book
- Textbook with One Author (Mobile)
- Textbook with Two Authors (Mobile)
- Textbook with Three or More Authors (Mobile)
- Textbook as an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Textbook Work Within an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Textbook Two or More from an Anthology or Edited Book (Mobile)
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Anthology or Edited Book
- Work in an Anthology or Edited Book
- Two or More Selections from the Same Anthology or Edited Book
- Journal Article (Print)
- Journal Article (Online)
- Newspaper Articles (Print)
- Newspaper Articles (Online)
- Database Article with One Author
- Database Article with Two Authors
- Database Article with More Than Three Authors
- Database Previously Published Scholarly Article (Blooms, MasterPlots, Literary Reference Center)
- Online Government Publication
- Website with an Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Website with No Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Web Page with Author
- Web Page with No Author’s/Contributor’s Name
- Art – From a Book
- Art – From a Web Page
- Picture/Photo Online -- General
- Motion Picture -- DVD
- Motion Picture -- Streaming
- Video -- Online (YouTube, etc.)
- An Interview You Conducted
- Lecture Notes, PowerPoints, or Handouts from Class
- In-Text Citations
- Works Cited Page
- Popular vs. Scholarly Sources
- Direct Quotes, Paraphrasing, Summarizing
Quoting, Paraphrasing, Summarizing
You already know that you need to use various kinds of resources when you are researching. Now things can get a little more complicated when trying to use those resources in your assignments.
We find that most students accidently plagiarize because they don’t know how to correctly quote, paraphrase, and/or summarize information they are trying to incorporate into their papers. Or how and when to cite things.
So, what's the difference?

(Venn_quote, n.d.)
Direct Quotes
Quotes are the exact words that the author has used, word for word. When quoting, you must use quotation marks and include an in-text citation .
According to the MLA Handbook, quotes should be "used selectively" and should "be as brief as possible" (75).
Rather, most professors prefer you to paraphrase or summarize information from your source because it demonstrates that you really understand what you're writing about.
Paraphrasing
Paraphrasing means putting the information you could have quoted into your own words, but keeping the intention of the original source. Paraphrases do not have quotation marks because you are using your own words, yet still must include an in-text citation at the end of the part you are paraphrasing.
Summarizing
When you summarize information, it's really a shorter version of the original source where you relate the overall meaning from the source. Like when paraphrasing, when you summarize you must still include an in-text citation at the end of the part you are summarizing.
Works Cited
Works Cited
The Modern Language Association of America. MLA Handbook , 8th edition. The Modern Language Association of America, 2016.
"Venn_quote." Dallas Learning Cloud , n.d., dlc.dcccd.edu/embed.php?key=dcccd+1dcccd234+englishcomp1rlc-units/quoting-paraphrasing-and-summarizing. Accessed 9 Sep 2019.
Additional Resources
- When to Summarize, Paraphrase, and Quote (George Mason University's Writing Center)
- Paraphrasing and Quoting 101 (IRSC Libraries)
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Summarizing (Purdue University's Online Writing Lab)
- Quoting and Paraphrasing (University of Wisconsin's Writing Center)
- << Previous: Popular vs. Scholarly Sources
- Last Updated: Mar 7, 2024 10:33 AM
- URL: https://warren.libguides.com/MLA9
Warren County Community College Haytaian & Maier Library 475 Route 57 West Washington, New Jersey 07882 Text: 908-652-4445 [email protected]
Penn State University Libraries
Mla quick citation guide.
- In-text Citation
- Citing Generative AI
- Citing Web Pages and Social Media
- Citing Articles
- Citing Books
- Other formats
- MLA Style Quiz
Using In-text Citation
Include an in-text citation when you refer to, summarize, paraphrase, or quote from another source. For every in-text citation in your paper, there must be a corresponding entry in your reference list.
MLA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the page number from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken, for example: (Smith 163). If the source does not use page numbers, do not include a number in the parenthetical citation: (Smith).
For more information on in-text citation, see the MLA Style Center .
Example paragraph with in-text citation
A few researchers in the linguistics field have developed training programs designed to improve native speakers' ability to understand accented speech (Derwing et al. 246; Thomas 15). Their training techniques are based on the research described above indicating that comprehension improves with exposure to non-native speech. Derwing and others conducted their training with students preparing to be social workers, but note that other professionals who work with non-native speakers could benefit from a similar program (258).
Works Cited List
Derwing, Tracey M., et al. "Teaching Native Speakers to Listen to Foreign-accented Speech." Journal of Multilingual and Multicultural Development, vol. 23, no. 4, 2002, pp. 245-259.
Thomas, Holly K. Training Strategies for Improving Listeners' Comprehension of Foreign-accented Speech. University of Colorado, Boulder, 2004.
Citing Web Pages In Text
Cite web pages in text as you would any other source, using the author if known. If the author is not known, use the title as the in-text citation.
Your in-text citation should lead your reader to the corresponding entry in the reference list. Below are examples of using in-text citation with web pages.
Entire website with author: In-text citation Parents play an important role in helping children learn techniques for coping with bullying (Kraizer).
Works cited entry Kraizer, Sherryll. Safe Child. Coalition for Children, 2011, www.safechild.org.
Web page with no author: In-text citation The term Nittany Lion was coined by Penn State football player Joe Mason in 1904 ("All Things Nittany").
Works cited entry "All Things Nittany." About Penn State. Penn State University, 2006, www.psu.edu/ur/about/nittanymascot.html.
General Guidelines
In MLA style the author's name can be included either in the narrative text of your paper, or in parentheses following the reference to the source.
Author's name part of narrative:
Gass and Varonis found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic (163).
Author's name in parentheses:
One study found that the most important element in comprehending non-native speech is familiarity with the topic (Gass and Varonis 163).
Group as author: (American Psychological Association 123)
Multiple works: (separate each work with semi-colons)
Research shows that listening to a particular accent improves comprehension of accented speech in general (Gass and Varonis 143; Thomas 24).
Direct quote:
One study found that “the listener's familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (Gass and Varonis 85).
Gass and Varonis found that “the listener’s familiarity with the topic of discourse greatly facilitates the interpretation of the entire message” (85).
Note: For quotations that are more than four lines of prose or three lines of verse, display quotations as an indented block of text (one inch from left margin) and omit quotation marks. Place your parenthetical citation at the end of the block of text, after the final punctuation mark.
In addition to awareness-raising, practicing listening to accented speech has been shown to improve listening comprehension. This article recommends developing listening training programs for library faculty and staff, based on research from the linguistics and language teaching fields. Even brief exposure to accented speech can help listeners improve their comprehension, thereby improving the level of service to international patrons. (O'Malley 19)
Works by Multiple Authors
When citing works by multiple authors, always spell out the word "and." When a source has three or more authors, only the first one shown in the source is normally given followed by et al.
One author: (Field 399)
Works Cited entry: Field, John. "Intelligibility and the Listener: The Role of Lexical Stress." TESOL Quarterly , vol. 39, no. 3, 2005, pp. 399-423.
Two authors: (Gass and Varonis 67)
Works Cited entry: Gass, Susan, and Evangeline M. Varonis. "The Effect of Familiarity on the Comprehensibility of Nonnative Speech." Language Learning , vol. 34, no. 1, 1984, pp. 65-89.
Three or more authors: (Munro et al. 70)
Works Cited entry: Munro, Murray J., et al. "Salient Accents, Covert Attitudes: Consciousness-raising for Pre-service Second Language Teachers." Prospect , vol. 21, no. 1, 2006, pp. 67-79.
- << Previous: Overview
- Next: Citing Generative AI >>
- Last Updated: Feb 14, 2024 8:47 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.psu.edu/mlacitation

- [email protected]
- Shapiro Library
- SNHU Library Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: How do I cite a source with multiple authors in MLA Style (in-text)?
- 7 Academic Integrity & Plagiarism
- 64 Academic Support, Writing Help, & Presentation Help
- 28 Access/Remote Access
- 7 Accessibility
- 9 Building/Facilities
- 7 Career/Job Information
- 26 Catalog/Print Books
- 25 Circulation
- 129 Citing Sources
- 14 Copyright
- 310 Databases
- 24 Directions/Location
- 18 Faculty Resources/Needs
- 7 Hours/Contacts
- 2 Innovation Lab & Makerspace/3D Printing
- 25 Interlibrary Loan
- 43 IT/Computer/Printing Support
- 3 Library Instruction
- 38 Library Technology Help
- 6 Multimedia
- 17 Online Programs
- 19 Periodicals
- 24 Policies
- 8 RefWorks/Citation Managers
- 4 Research Guides (LibGuides)
- 216 Research Help
- 23 University Services
Last Updated: Jun 22, 2023 Views: 348595
MLA Style requires an in-text citation to indicate the sources that were consulted and used in your work. The in-text citation must correspond with the entry on the Works Cited page,
MLA in-text citations follow the Author-Page style, meaning the author's last name and the page number(s) of the quotation or paraphrase must appear in the text. Page numbers always appear in the parentheses, not in the text of your sentence.
General Format
Parenthetical Citation
(Author page#)
Citation in Prose
Author stated that ... (page#).
For Example
(Ramugondo 189)
Ramugondo stated that ....... (189).
Two Authors
(Leon and Andrews 250-258)
Javier F. Leon and Ronald Andrews argue that ....... (250-258).
Three or More Authors
(Zhang et al. 11)
Zhang and colleagues concluded from their experiments that ....... (11).
More Information
- MLA Guide (Shapiro Library)
Further Help
This information is intended to be a guideline, not expert advice. Please be sure to speak to your professor about the appropriate way to cite sources in your class assignments and projects.
Campus Students
To access Academic Support, visit your Brightspace course and select “Tutoring and Mentoring” from the Academic Support pulldown menu.
Online Students
To access help with citations and more, visit the Academic Support via modules in Brightspace:
- Academic Support Overview: Getting Help with your Schoolwork This link opens in a new window
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 14 No 35
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a self-serve option for users to search and find answers to their questions.
Use the search box above to type your question to search for an answer or browse existing FAQs by group, topic, etc.
Tell Me More
Link to Question Form
More assistance.
Submit a Question
Related FAQs
Scribbr MLA Citation Generator
Accurate MLA citations, verified by experts, trusted by millions.
Scribbr's MLA Citation Generator for Chrome
Effortlessly cite any page or article directly from your browser with just one click. Our extension simplifies the citation process by automatically retrieving essential details such as the title, author(s), and publication date , ensuring accurate MLA citations in seconds.
| ⚙️ Styles | MLA 9 & MLA 8 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Source types | Websites, books, articles |
| 🔎 Autocite | Search by title, URL, DOI, or ISBN |

Trust in expert-verified MLA citations
Avoid the risk of losing points due to incorrect citations. Our MLA citation experts have meticulously refined our algorithms, ensuring precision and reliability. This dedication has earned us recognition and recommendations from educators worldwide.
Experience distraction-free citation
Focus on your work without interruptions. Our citation generator provides a clean interface, free from distracting video pop-ups and flashing ads. Best of all, it's completely free for everyone.
Features you'll love
Search for your source by title, URL, DOI, ISBN, and more to retrieve the relevant information automatically.
MLA 8th & 9th edition
Scribbr's Citation Generator supports both MLA 8 and MLA 9 (as well as APA and Harvard ). No matter what edition you're using, we’ve got you covered!
Export to Bib(La)TeX
Easily export in BibTeX format and continue working in your favorite LaTeX editor.
Export to Word
Reference list finished? Export to Word with perfect indentation and spacing set up for you.
Sorting, grouping, and filtering
Organize the reference list the way you want: from A to Z, new to old, or grouped by source type.
Save multiple lists
Stay organized by creating a separate reference list for each of your assignments.
Choose between Times New Roman, Arial, Calibri, and more options to match your style.
Industry-standard technology
Scribbr's citation generator is built using the same citation software (CSL) as Mendeley and Zotero, but with an added layer for improved accuracy.
Annotations
Create perfectly formatted MLA Style annotated bibliographies with just a few clicks.
Explanatory tips help you get the details right to ensure accurate citations.
Citation guides
Getting to grips with citation is simple with the help of our highly rated MLA citation guides and videos .
Secure backup
Your work is saved automatically after every change and stored securely in your Scribbr account.
- Introduction
- Missing information
- No page numbers
- Scroll to top
How to cite in MLA format

MLA is one of the most common citation styles used by students and academics. This quick guide explains how to cite sources according to the 9th edition (the most recent) of the MLA Handbook . You can also use Scribbr’s free citation generator to automatically generate references and in-text citations.
An MLA citation has two components:
- In-text citation : Every time you quote or paraphrase a source, you cite the author and the page number in parentheses.
- Works Cited : At the end of your paper, you give a full reference for every source you cited, alphabetized by the author’s last name.
MLA Works Cited list
The list of Works Cited (also known as the bibliography or reference page) gives full details of every source you cited in your text. Each entry is built from nine core elements:
Following this format, you can create a citation for any type of source—for example, a book , journal article , website , or movie . You only include information that’s relevant to the type of source you’re citing.
Missing information in MLA citations
Regardless of the source type, the most important elements of any MLA citation are the author , the source title , and the publication date. If any of these are missing from the source, the Works Cited entry will look slightly different.
| What’s missing? | What to do | Works Cited example |
|---|---|---|
| No author | Start with the source title instead. Alphabetize by the first word (ignoring ). | “Australia fires: ‘Catastrophic’ alerts in South Australia and Victoria.” , 20 Nov. 2019, www.bbc.com/news/world-australia-50483410. |
| No title | Give a brief description of the source. Use sentence case and no italics or quotation marks. | Mackintosh, Charles Rennie. Chair of stained oak. 1897–1900, Victoria and Albert Museum, London. |
| No date | Leave out the publication date. Add the date you accessed the source at the end of the citation. | “Who are Scribbr Editors?” , www.scribbr.com/about-us/editors/. Accessed 10 June 2019. |
MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate MLA citations in seconds
Get started
MLA in-text citations
MLA in-text citations are brief references that direct your reader to the full source entry. You include them every time you quote , block quote , paraphrase or summarize a source.
The in-text citation must match the first word of the Works Cited entry—usually the author’s last name . It also includes a page number or range to help the reader locate the relevant passage.
| Author | What to do | Citation example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | Give the author’s last name. | (Wallace 11–12) |
| 2 authors | Give both author’s last names. | (Wallace and Armstrong 11–12) |
| 3+ authors | Name the first author followed by “et al.” | (Wallace et al. 11–12) |
| Corporate author | If a source was created by an organization other than the publisher, use the organization name as author. | (U.S. Global Change Research Program 22) |
| No author | If the author is the same as the publisher, or if no author is credited, use the source title instead. Format the title the same as in the full Works Cited reference, and shorten if it is more than four words. | (“Australia Fires”) |
| Multiple sources by the same author | Include the title (or a shortened version) after the author’s name in each source citation. | (Morrison, , 73) (Morrison, , 45) |
If you already named the author in your sentence, include only the page number in parentheses:
Sources with no page numbers
If the source has no page numbers, you either use an alternative locator, or leave the page number out of the citation:
| Source type | What to do | Citation example |
|---|---|---|
| Audiovisual source (e.g. a or ) | Give the time range of the relevant section. | (Arnold 03:15–03:21). |
| Source with numbered sections (e.g. an ) | Give a paragraph, section, or chapter number. | (Smith, par. 38) (Rowling, ch. 6) |
| Source with no numbered sections (e.g. a ) | Leave out the page number. | (Barker) |
Tools and resources
Besides the MLA Citation Generator, Scribbr provides many more helpful tools and resources;
- Citation generator : Generate flawless APA , MLA , and Harvard citations in seconds
- Free plagiarism checker : Detect and correct plagiarism with the most accurate plagiarism checker for students
- AI Proofreader : Upload and improve unlimited documents and earn higher grades on your assignments. Try it for free!
- Paraphrasing tool: Avoid accidental plagiarism and make your text sound better.
- Grammar checker : Eliminate pesky spelling and grammar mistakes.
- Summarizer: Read more in less time. Distill lengthy and complex texts down to their key points.
- AI detector: Find out if your text was written with ChatGPT or any other AI writing tool. ChatGPT 2 & ChatGPT 3 supported.
- Proofreading services : Hire a professional editor to improve your writing
- Citation checker : Check your work for citation errors and missing citations.
- Guides and videos : Explore hundreds of articles, bite-sized videos, time-saving templates, and handy checklists that guide you through the process of research, writing, and citation.
- Free Tools for Students
- MLA Citation Generator
Free MLA Citation Generator
Generate accurate citations in MLA format automatically, with MyBib!

😕 What is an MLA Citation Generator?
An MLA citation generator is a software tool designed to automatically create academic citations in the Modern Language Association (MLA) citation format. The generator will take information such as document titles, author, and URLs as in input, and output fully formatted citations that can be inserted into the Works Cited page of an MLA-compliant academic paper.
The citations on a Works Cited page show the external sources that were used to write the main body of the academic paper, either directly as references and quotes, or indirectly as ideas.
👩🎓 Who uses an MLA Citation Generator?
MLA style is most often used by middle school and high school students in preparation for transition to college and further education. Ironically, MLA style is not actually used all that often beyond middle and high school, with APA (American Psychological Association) style being the favored style at colleges across the country.
It is also important at this level to learn why it's critical to cite sources, not just how to cite them.
🙌 Why should I use a Citation Generator?
Writing citations manually is time consuming and error prone. Automating this process with a citation generator is easy, straightforward, and gives accurate results. It's also easier to keep citations organized and in the correct order.
The Works Cited page contributes to the overall grade of a paper, so it is important to produce accurately formatted citations that follow the guidelines in the official MLA Handbook .
⚙️ How do I use MyBib's MLA Citation Generator?
It's super easy to create MLA style citations with our MLA Citation Generator. Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form.
The generator will produce a formatted MLA citation that can be copied and pasted directly into your document, or saved to MyBib as part of your overall Works Cited page (which can be downloaded fully later!).
MyBib supports the following for MLA style:
| ⚙️ Styles | MLA 8 & MLA 9 |
|---|---|
| 📚 Sources | Websites, books, journals, newspapers |
| 🔎 Autocite | Yes |
| 📥 Download to | Microsoft Word, Google Docs |

Daniel is a qualified librarian, former teacher, and citation expert. He has been contributing to MyBib since 2018.

Generative Artificial Intelligence
- A Very Brief Introduction to Generative AI
- Information Discovery with AI
Citation and Attribution with AI Tools
Chicago style.
- Copyright and Scholarly Communication
If you choose to use generative AI tools for course assignments, academic work, or other forms of published writing, you should give special attention to how you acknowledge and cite the output of those tools in your work. You should always check with your instructor before using AI for coursework.
As with all things related to AI, the norms and conventions for citing AI-generated content are likely to evolve over the next few years. For now, some of the major style guides have released preliminary guidelines. Individual publishers may have their own guidance on citing AI-generated content.
Here are some fundamental ideas that hold true for citing AI generated content, no matter which citation style you're using:
- Do cite or acknowledge the outputs of generative AI tools when you use them in your work. This includes direct quotations and paraphrasing, as well as using the tool for tasks like editing, translating, idea generation, and data processing.
- Generative AI tools can create fake citations.
- These tools may cite a real piece of writing, but the cited content may be inaccurate.
Be flexible in your approach to citing AI-generated content, because emerging guidelines will always lag behind the current state of technology, and the way that technology is applied. If you are unsure of how to cite something, include a note in your text that describes how you used a certain tool.
When in doubt, remember that we cite sources for two primary purposes: first, to give credit to the author or creator; and second, to help others locate the sources you used in your research. Use these two concepts to help make decisions about using and citing AI-generated content.
- APA: How to Cite ChatGPT Released April 7, 2023
When you cite AI-generated content using APA style, you should treat that content as the output of an algorithm , with the author of the content being the company or organization that created the model. For example, when citing ChatGPT, the author would be OpenAI, the company that created ChatGPT.
Here are some guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in APA style:
- When you reference this content directly in your text, you should include an in-text citation, and an associated entry in your reference list.
- If you have used AI tools for some part of your research, you should describe that use in your introduction or methods section, and include the prompts that you used.
When referencing shorter passages of text, you can include that text directly in your paper. You might also include an appendix or link to an online supplement that includes the full text of long responses from a generative AI tool.
Author. (Date). Name of tool (Version of tool) [Large language model]. URL
OpenAI. (2023). ChatGPT (Mar 14 version) [Large language model]. https://chat.openai.com/chat
In-Text Citation Example:
(OpenAI, 2023)
- Chicago Manual of Style, Citing Content Developed or Generated by Artificial Intelligence Released in spring 2023
Chicago style requires that you cite AI-generated content in your work by including either a note or a parenthetical citation, but advises you not to include that source in your bibliography or reference list. The reason given for this is that, because you cannot provide a link to the conversation or session with the AI tool, you should tread that content as you would a phone call or private conversation. However, AI tools are starting to introduce functionality that does allow a user to generate a sharable link to a chat conversation, so this guidance from the Chicago Manual of Style may change.
Here are some general guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in Chicago style:
- Treat the AI tool as the author of the content.
- If possible, describe the prompt used to generate the content in the text, but if that approach doesn't work, you can include that information in a footnote or endnote.
- The date used in your citation will be the date the content was generated.
Format: 1. Author, Title, Publisher, Date, url for the tool.
Example (if information about the prompt has been included within the text of your paper):
1. Text generated by ChatGPT, OpenAI, March 7, 2023, https://chat.openai.com/chat.
Example (including information about the prompt):
1. ChatGPT, response to "Explain how to make pizza dough from common household ingredients," OpenAI, March 7, 2023, https://chat.openai.com/chat.
- How Do I Cite Generative AI in MLA Style? Released March 17, 2023
MLA style is generally more flexible that either APA or Chicago style, so while they provide specific examples for citing commonly used AI tools, they encourage writers to adapt those guidelines to fit the situation.
Hare are some other guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in MLA style:
- Cite the AI tool when you incorporate its output into your work. This includes direct quotations, images, and data, as well as paraphrased content.
- If you use an AI tool for some other purpose, such as translating, editing, or generating an outline, include a note about this somewhere in your paper.
- The MLA views AI-generated content as a source with no author, so you'll use the title of the source in your in-text citations, and in your reference list. The title you choose should be a brief description of the AI-generated content, such as an abbreviated version of the prompt you used.
- If you create a shareable link to the chat transcript, include that instead of the tool's URL.
Format: "Description of chat" prompt. Name of AI tool, version of AI tool, Company, Date of chat, URL.
Example:
"Examples of harm reduction initiatives" prompt. ChatGPT, 23 Mar. version, OpenAI, 4 Mar. 2023, chat.openai.com/chat.
("Examples of harm reduction")
- << Previous: Information Discovery with AI
- Next: Copyright and Scholarly Communication >>
- Last Updated: Jan 29, 2024 8:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.brown.edu/AI
Brown University Library | Providence, RI 02912 | (401) 863-2165 | Contact | Comments | Library Feedback | Site Map
Library Intranet
QuillBot AI Review: Everything You Need to Know (2024)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is evolving quickly, and new AI tools and platforms are constantly appearing. In an era where clear, concise writing is highly coveted, AI writing tools are becoming increasingly crucial. One such impressive technology is QuillBot AI . Starting as a simple paraphrasing tool, QuillBot has become a robust AI writing assistant that symbolizes a significant stride in AI content optimization. This review thoroughly explores QuillBot AI, focusing on its key features, pricing structure, and strengths and weaknesses.
- 1 What is QuillBot AI?
- 2 How Quillbot AI Works
- 3.1 1. The Paraphraser
- 3.2 2. The Grammar Checker
- 3.3 3. Summarizer
- 3.4 4. Citation Generator
- 3.5 5. QuillBot Plagiarism Checker
- 3.6 6. The Translator
- 3.7 7. Quillbot Extensions
- 4 QuillBot AI Pricing and Plans Review
- 5.1 Pros of Using QuillBot AI
- 5.2 Cons of Using QuillBot AI
- 6 How QuillBot Compares to Other Similar Tools
- 7 Should You Use QuillBot? (The Verdict)
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is QuillBot AI?

QuillBot AI is a leading AI writing companion and paraphrasing software designed to help anyone elevate the quality of their writing. At its core, it functions as one of the best AI rewriter tools to edit, rephrase, and enhance content like a professional.
It presents various features, including grammar checking, plagiarism detection, and content summarization. As such, QuillBot AI delivers substantial benefits for academics, essayists, and writers. Creating high-quality professional content can be time-consuming, and Quillbot streamlines the process using AI to improve your writing quickly, offering real-time suggestions and one-click solutions. Plus, it is an all-in-one solution that replaces the need to invest in multiple tools, making it cost-effective.
The versatility of the software caters to a diverse audience. While students can utilize its various writing tools, professional writers can efficiently collaborate and summarize lengthy text. If you want to improve your writing process, whether writing an email, an essay, or a long-form blog article, you will find Quillbot AI to be a valuable addition to your writing toolkit. It can revolutionize your writing process to produce surprising results.
How Quillbot AI Works
You can access QuillBot by visiting their online platform on their website . You don’t need to create an account; you can use a free version of QuillBot with limitations. Once you are there, you will see the available tools in the left sidebar. Click any of the tools to launch the user interface for each.
Each tool will have a consistent layout with different features that you can use to start refining your content. For example, when using the Grammar Checker, you can copy and paste your content into the user interface. QuillBot will readily analyze your text, pinpointing broken sentences and grammatical errors you can fix with a single click.
And the other other tools share the same easy-to-use interface and functionality. For instance, the Summarizer makes condensing long-form content or essays easy. Paste your text to generate a summary of key points. Additionally, it features a plagiarism checker, which helps identify and fix plagiarized content to ensure the originality of your content.
QuillBot’s AI functions by learning from datasets. Comprehending grammar, spelling, punctuation, tone, sentence structure, and readability, these datasets serve as knowledge accumulations. So, when users regularly disregard a specific suggestion, the AI adjusts to present more contextually relevant alternatives.
Breaking Down QuillBot AI Features
QuillBot AI offers several features for easy and effective content organization. We’ll delve into these features now.
1. The Paraphraser
QuillBot AI includes a paraphrasing tool. It empowers writers to rephrase text while preserving its central message. It’s an ideal tool for students and aspiring authors, requiring no account signup. Options for ‘Fewer Changes’ or ‘More Changes’ are available, with premium users getting maximum adjustments.
Paraphrase Modes
QuillBot AI assists users in paraphrasing and refining text. It employs seven unique modes, each tailored to specific objectives, to enhance the quality and readability of written content. Whether striving for clarity, professionalism, creativity, or conciseness, QuillBot AI offers a mode to suit your needs.
Here is an example sentence I added to the paraphraser text input area:
“It was a tough match. After three hours of immense struggle, I was able to get the job done.”
1. Standard Mode
Standard Mode serves as the default setting. It balances modifying the text for clarity and fluency while preserving the original meaning. The result is a refined text that maintains its natural flow and readability.
After clicking the Rephrase button, QuillBot swiftly provided a paraphrased output in Standard Mode. It merits noting that the level of paraphrasing hinges on the level of synonyms you set in the Synonyms bar at the right of the Modes bar above the content. The higher the level, the more liberty you give QuillBot to change the words of the original content.
The ensuing result was generated with a low Synonyms bar:
“It was a challenging game. I had to struggle for three hours before I was able to finish the task.”
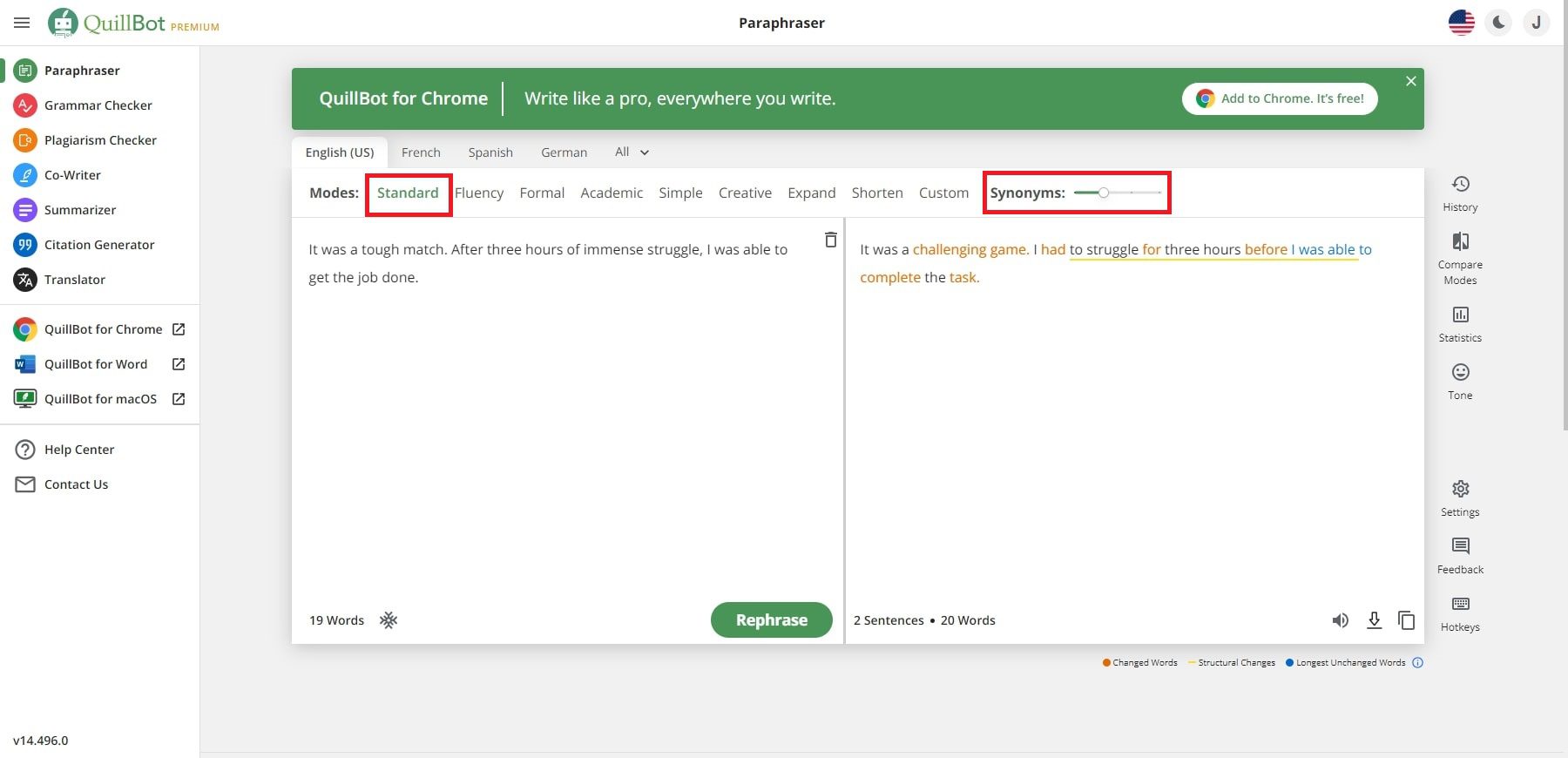
The following result was generated with a maximum level of Synonyms:
“It was a challenging game. I had to battle for three hours before I was able to finish the task.”
With just one sentence, you can see that only one word changed, but with larger blocks of content, you will see that QuillBot will make more word changes with a higher level of synonyms.
2. Fluency Mode
In Fluency Mode, QuillBot AI ensures that the text is grammatically sound and genuinely readable. It makes minimal changes, primarily correcting grammar and providing the text sounds natural. Synonym substitutions are kept to a minimum, preserving the original meaning.
We paraphrased the same content in Fluency mode . It generated the following output:
“It was a difficult match. I completed the task after three hours of intense effort.”
3. Formal Mode
Formal Mode is the ideal choice for those working in academic or professional contexts. It transforms the text to sound more polished and professional, making it suitable for business reports, academic papers, and formal documents.
We paraphrased the same content in Formal Mode . It generated the following output:
“ It was a difficult match. After three hours of arduous effort, I was able to complete the task. ”
4. Academic Mode
Then, we paraphrased the same content in Academic Mode . Unlike the other modes, it doesn’t have any Synonyms bar. Instead, it seemed to give the content more details and wording suitable for academia. It generated the following output:
“ The contest was challenging. Following a prolonged period of three hours, characterized by significant exertion and effort, I successfully completed the task at hand. ”
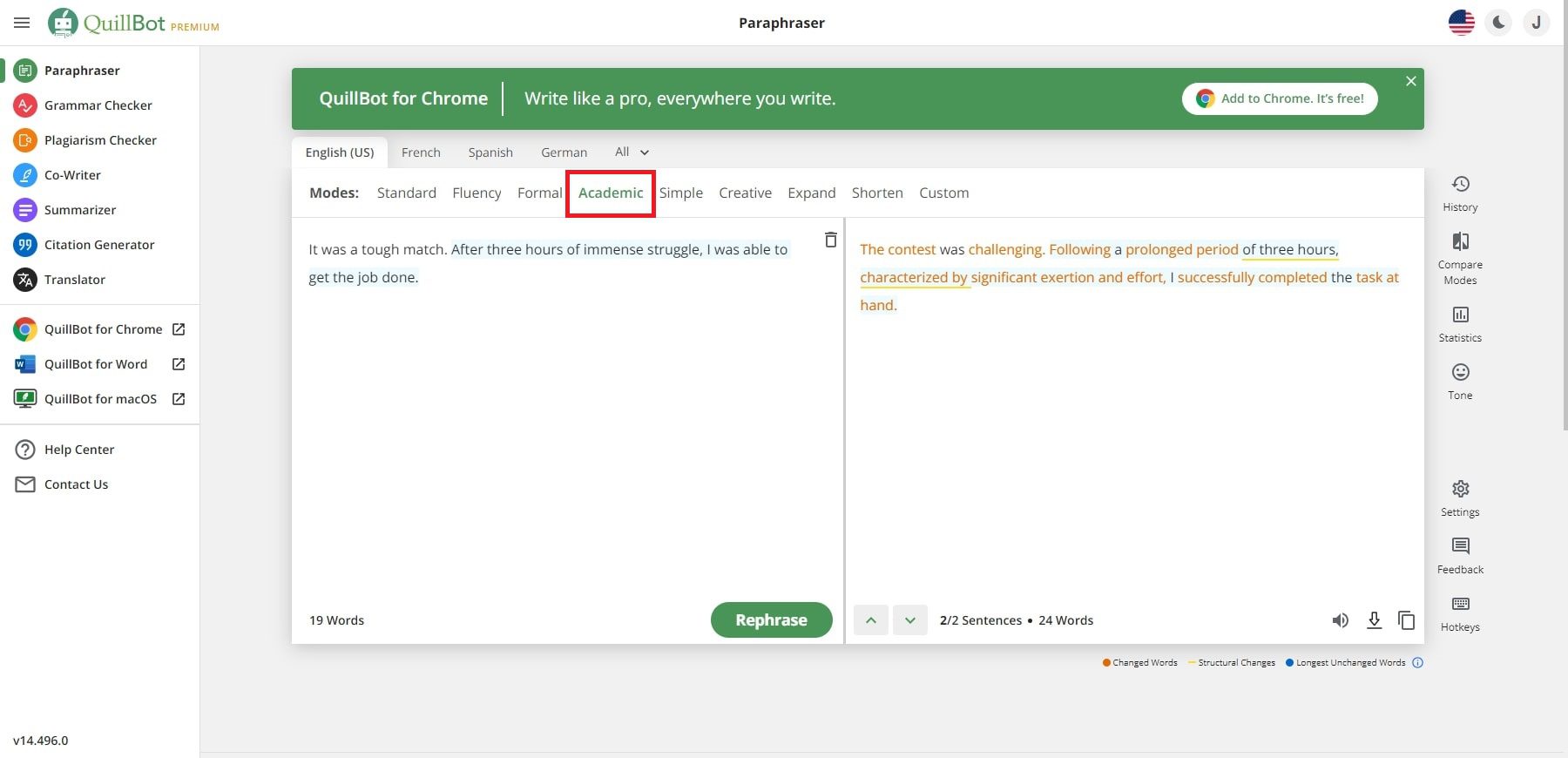
5. Simple Mode
Simple Mode simplifies the text, making it easier to understand and more accessible to a broader audience. It is an excellent choice when clarity and straightforward communication are essential.
We paraphrased the same content in Simple Mode . It generated the following output:
“ It was a hard game. I was able to finish the job after three hours of hard work. ”
6. Creative Mode
Creative Mode is the way to go if you’re looking to unleash your creativity and generate entirely unique content. This Mode substantially changes the text, potentially altering the original meaning. It’s a valuable tool for content creators seeking a fresh spin on their writing.
We paraphrased the same content in Creative Mode . It generated the following output:
“ That was one intense contest. It took me three hours of relentless effort, but I finally completed the task at hand. ”
7. Expand Mode
Expand Mode is perfect for those aiming to increase the length of their text. It adds words and details while retaining the original meaning, making it valuable for projects requiring a higher word count.
We paraphrased the same content in Expand Mode . It generated the following output:
“ It was a difficult match to watch. I had to put in a lot of effort for three hours before I was finally successful in completing the task. ”
Then, we produced an output with a high level of Synonyms as follows:
“The contest was a challenging one. I was able to finish the work, despite the fact that it took me three hours of intense effort.”
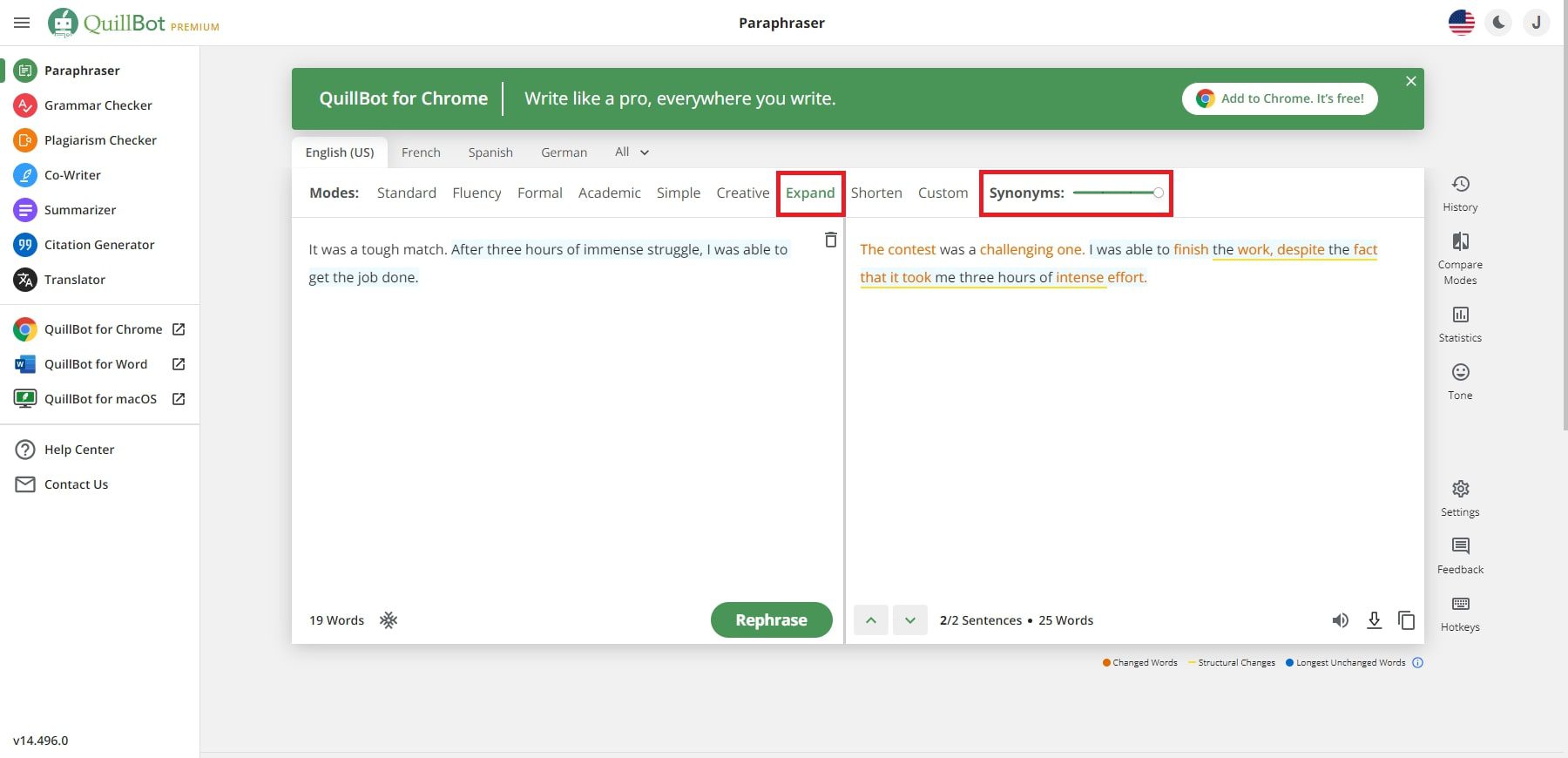
8. Shorten Mode
Shorten Mode comes to the rescue when you need to reduce the overall word count while maintaining the essence of your text. It trims unnecessary words and phrases, delivering a concise version of your content.
Lastly, we paraphrased the same content in Shorten Mode. It generated the following output:
“ The match was hard. I finished after three hours of intense struggle. ”
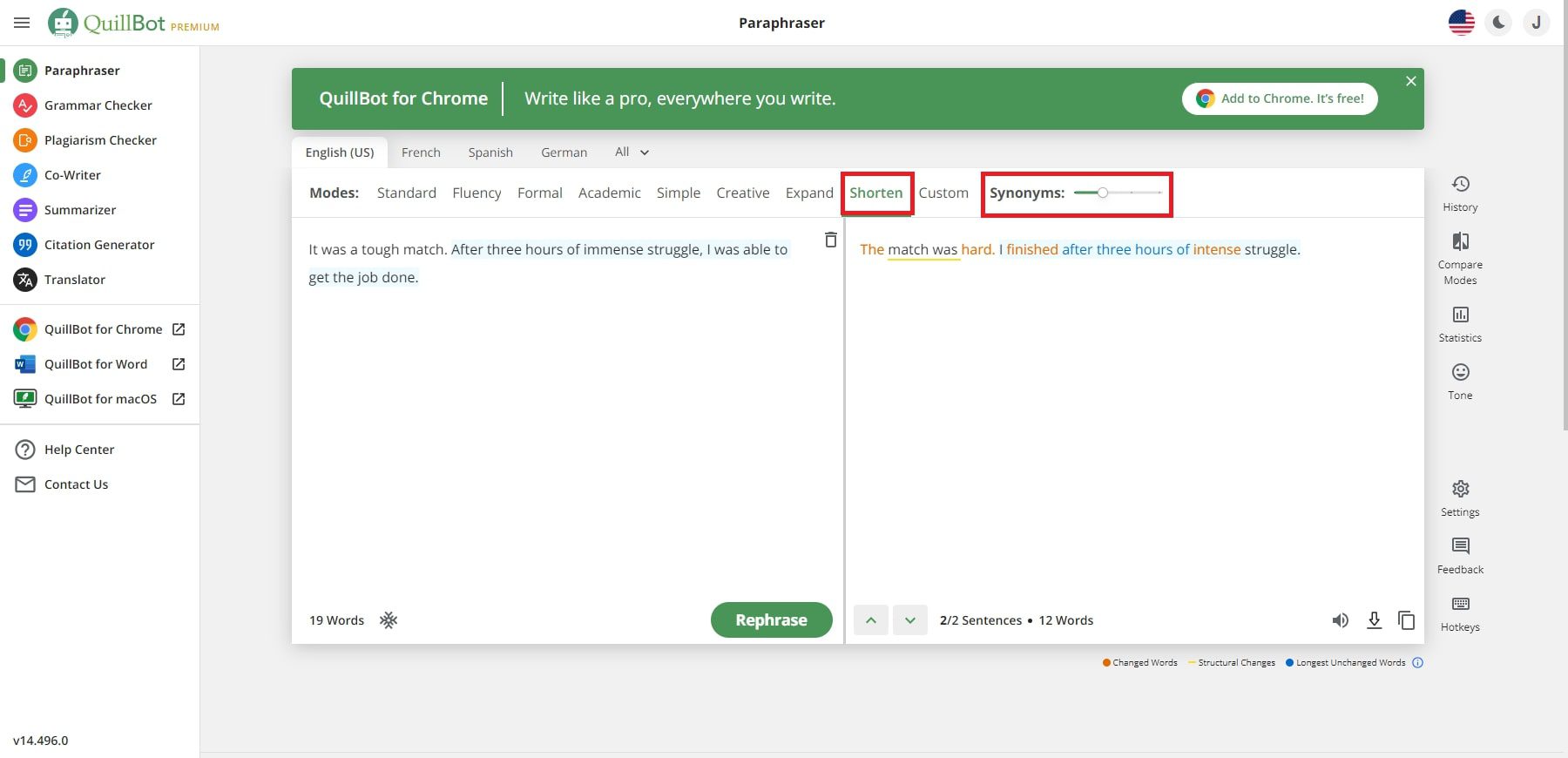
Paraphraser Statistics
The ‘Statistics’ feature offers insights into text complexity and readability. It aids writers in adjusting their style to the desired tone and audience. Premium subscribers unlock tonality analysis, which assesses reader perceptions to enhance persuasive writing.
I have used the same content as the previous one in the “Fluency” mode. It has generated the following statistics.
The Statistics of the generated content are based on the following aspects:
- Average words in a sentence
- Average Syllables in a word
- Readability
- Sentence Count
- Character Count
- Percent Change
- Longest Unchanged Words
Paraphraser Settings
The “Settings” feature in the Paraphraser tool provides options to control how you want your content to be paraphrased and how you want the results to be displayed on the interface. In terms of paraphrasing the content, you choose the following:
- Paraphrase quotations
- Use contractions
- Prefer active voice
Under the Interface options, you can select the following:
- Use yellow highlight
- Show tooltips
- Show legend
- Show changed words
- Show structural changes
- Show the longest unchanged words
Overall, these settings do seem to give users more control and help them identify changes to their content much easier.
Paraphraser Compare Modes
Compare Modes is a valuable feature exclusively available to premium users, offering a comprehensive view of how a sentence is transformed across different modes within the platform. This feature enables users to evaluate and choose the most suitable rendition for their content by comparing various paraphrased versions. To access Compare Modes, locate and click on the dedicated icon in the settings bar on the right side of the page.
Once activated, Compare Modes opens a sidebar on the right-hand side of the screen, displaying the original sentence before paraphrasing and the results generated by all available modes simultaneously. The system defaults to the effect produced by the Mode in which the sentence was paraphrased. You can easily click the “Select” button next to the desired text to select your preferred sentence, seamlessly replacing the paraphrased sentence in your results. Additionally, you can further modify individual sentence results by clicking on circular arrow icons or making copies of them with a simple click on the copy icon. This powerful feature empowers users to fine-tune their content according to their specific needs and preferences, streamlining the content creation process.
Paraphraser History
By accessing the history feature, you can go through all the previous content you have modified. In my case, I checked my history, and it showed the last text paraphrased. It also shares the date and time when the content was modified.
The “Tone” feature in QuillBot AI paraphraser allows users to control and tailor the emotional and stylistic tone of their paraphrased content. With this feature, users can choose from various preset tones, such as casual , unfriendly , wordy , complex , and unclear . It ensures that the paraphrased text aligns perfectly with the desired style and intent. Whether you need your content to sound professional and academic or friendly and conversational, the Tone feature empowers you to achieve the right mood for your writing.
Paraphrasing for Different Languages
Quillbot AI supports 23 different languages for paraphrasing purposes. Not only does this make the tool more accessible, but it also comes in handy for making tweaks to the content generator by Quillbot’s translator tool.
2. The Grammar Checker
Quillbot AI offers a user-friendly and free Grammar-checking feature that doesn’t require signing up. When you paste your text into Quillbot’s editor, it identifies and highlights grammatical errors, including punctuation and spelling. With a convenient Fix All Errors option, you can swiftly correct multiple issues simultaneously. This Grammar Checker enhances writing precision and consistency. It quickly pinpoints potential errors in red, simplifying the editing process. This real-time underlining and instant correction feature saves writers time and improves productivity.
For instance, here is an example sentence I added to the grammar checker text input area:
“ Manchester United signed Sofyan Amrabat on a season-long loan move from Fiorentina. The Morocco midfielder has been desperate to join Erik ten Hag’s team since getting linked to the Red Devils in June. However, Manchester United’s plans differed on Deadline Day as they wanted to sign Fulham’s Joao Palhinha instead. ”
After copy-pasting the text into the Grammar Check, it will detect all the potential errors within the content. By putting your cursor on the underlined words, it will show you the errors individually.
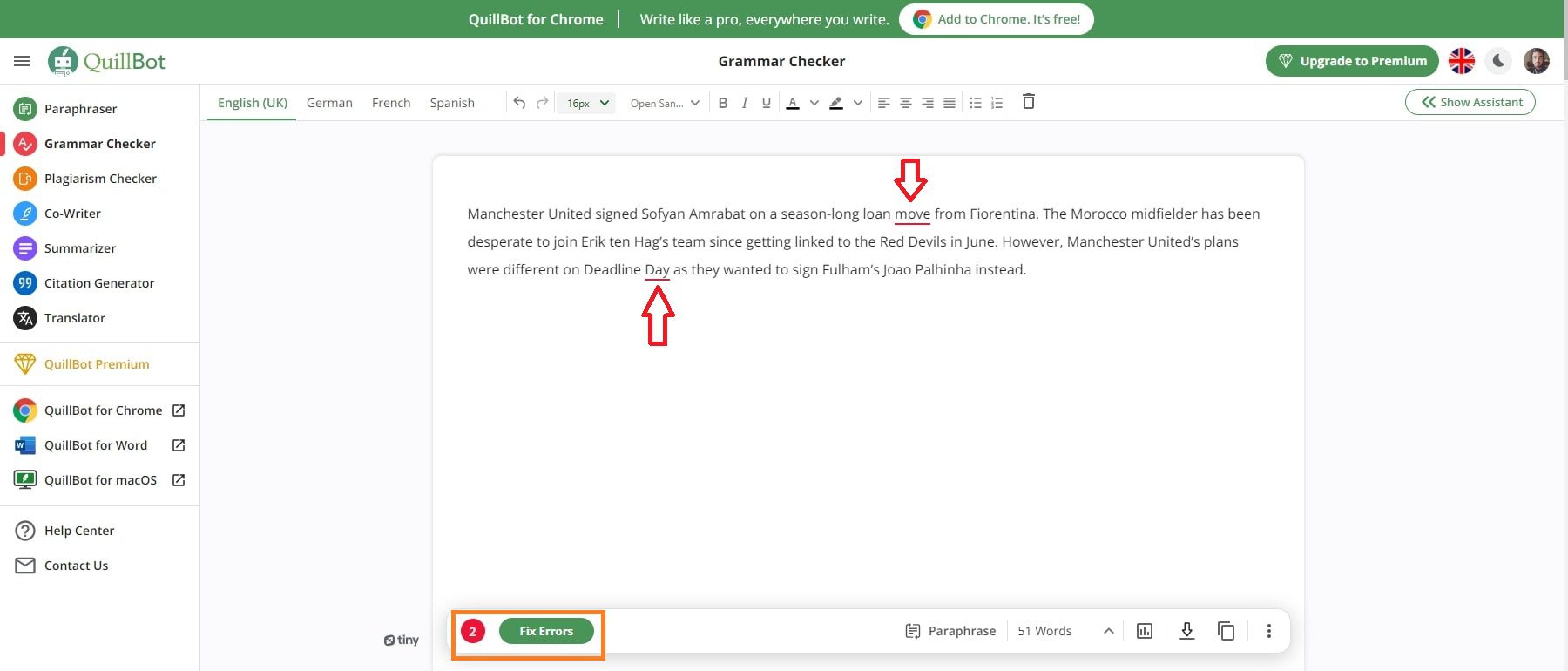
Once you remove all the errors, it will provide you with the correct grammatical content. It will generate the following content.
“ Manchester United signed Sofyan Amrabat on a season-long loan deal from Fiorentina. The Morocco midfielder has been desperate to join Erik ten Hag’s team since getting linked to the Red Devils in June. However, Manchester United’s plans were different on Deadline Day, as they wanted to sign Fulham’s Joao Palhinha instead. ”
Furthermore, it seamlessly integrates with Quillbot’s Paraphrase tool, offering a comprehensive writing experience without needing an account. Its grammar-checking feature is valuable for writers seeking error-free, professional content.
3. Summarizer
Quillbot AI provides a Summarizer tool that condenses lengthy texts or articles into concise summaries, making it invaluable for students, researchers, and professionals.
Users can choose between Short and Long summarization options to control the level of detail. The Short summarization offers a brief overview, ideal for quickly grasping the central ideas or skimming through multiple articles. In contrast, the Long outline provides a more comprehensive summary, suitable for in-depth analysis or a deeper understanding of the text.
Quillbot AI’s Summarizer utilizes natural language processing to extract critical information while preserving the original context. It offers two summarization types: Key Sentences and Paragraph modes.
For instance, I added a block of content to the summarizer text input area. Using the Key Sentences feature, the tool has created five articulate points that summarize the content.
Changing the Summary Length can increase or decrease the depth of those points.
Selecting the Paragraph mode will provide a summary of the content in paragraph form.
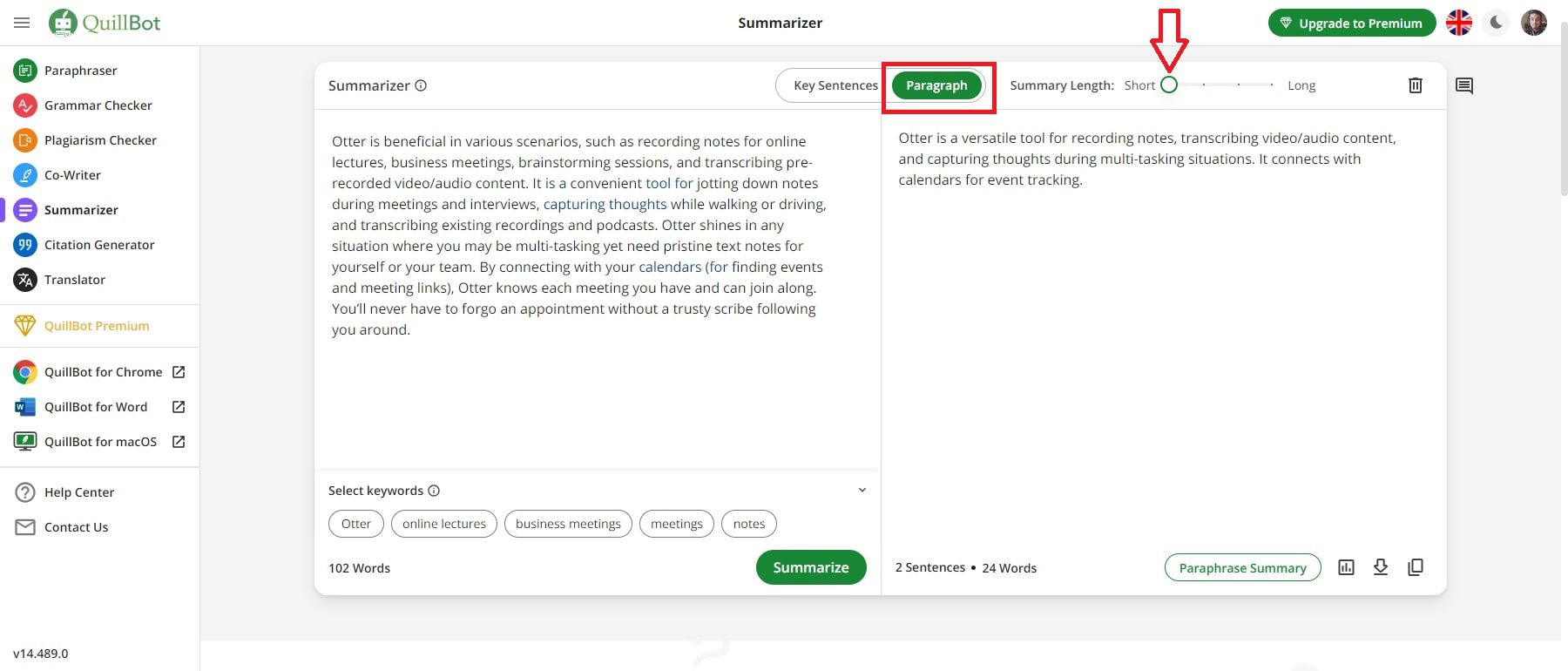
Like the Key Sentences mode, the length of the summary can be changed by adjusting the Summary Length .
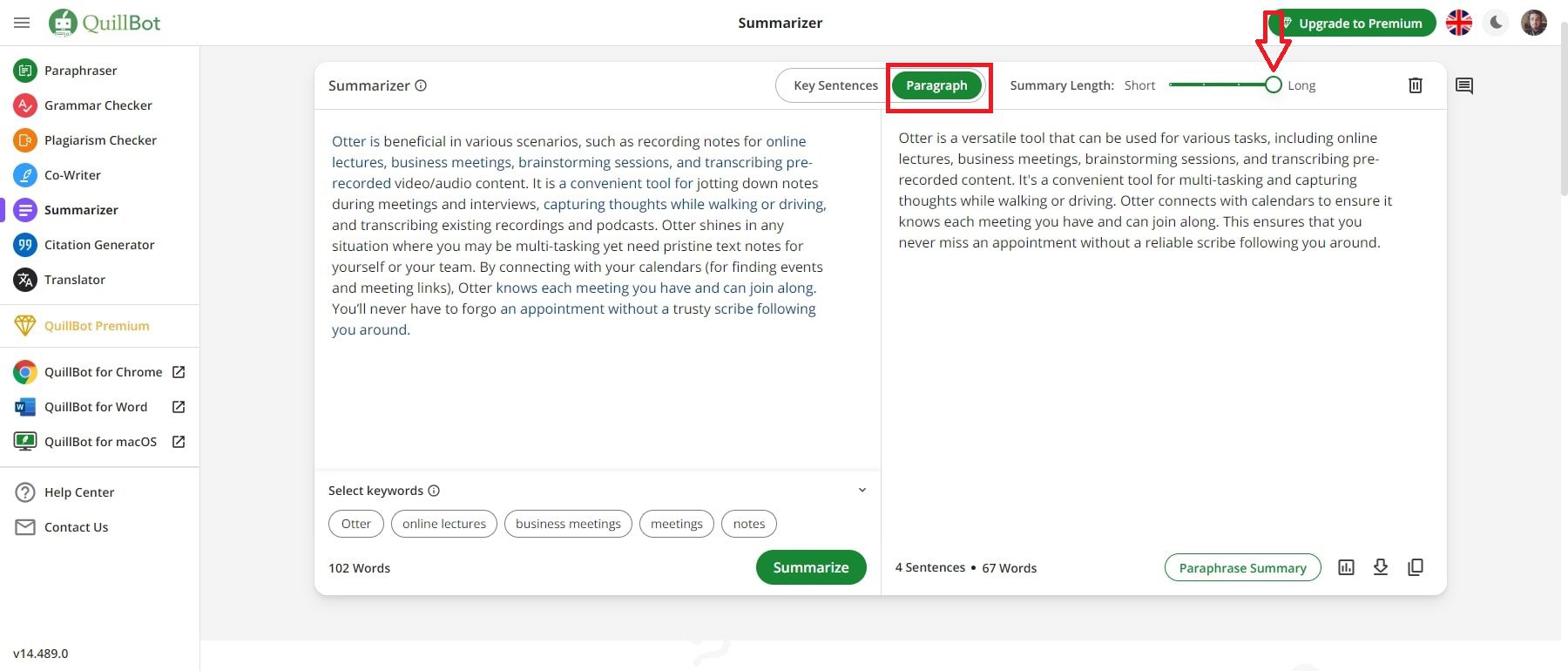
This feature streamlines research, study, and content review processes, enhancing productivity and comprehension for users across various fields.
4. Citation Generator
QuillBot’s Citation Generator is a valuable tool that simplifies the often complex process of citing sources in academic and professional writing. It allows users to choose from various citation styles and formats, ensuring compliance with specific guidelines and educational requirements. This feature dramatically reduces the potential headache associated with accurate source attribution.
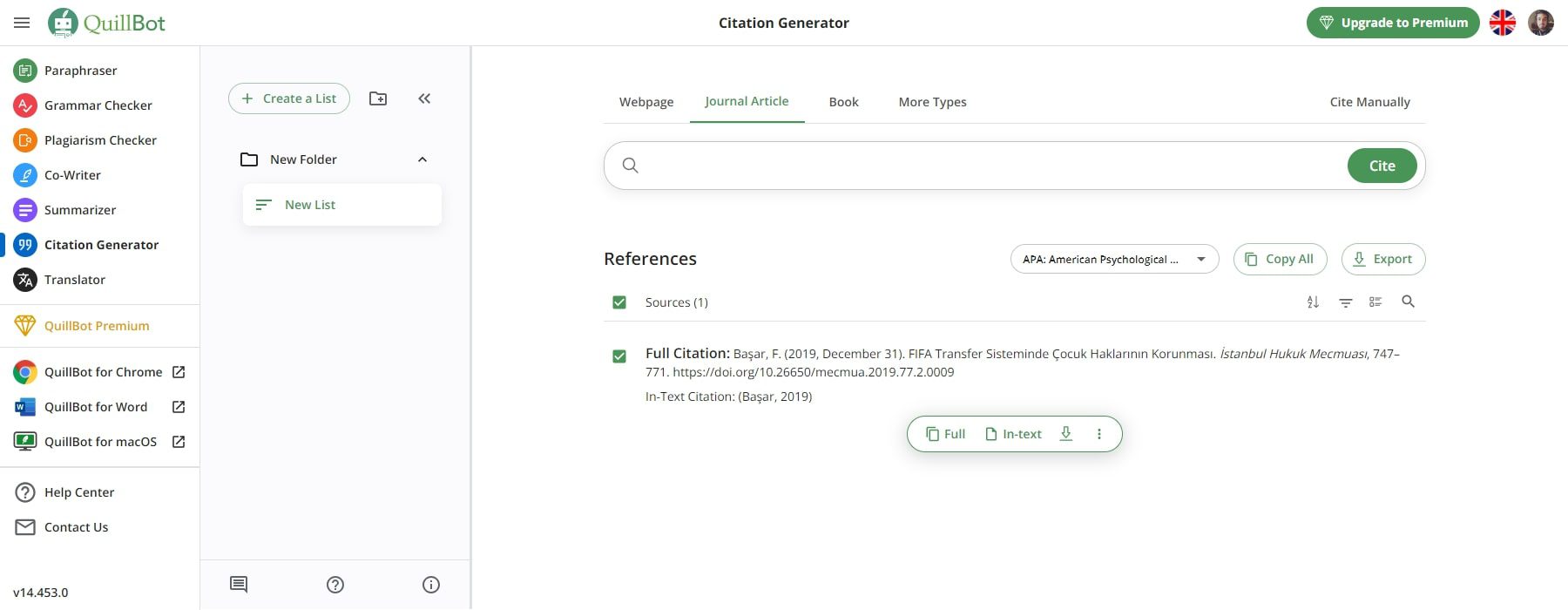
It supports common APA, MLA, and Chicago styles, covering reference types like books and websites. With an intuitive interface, it swiftly generates in-text and complete citations, labeled and exportable to Microsoft Word. By automating this process, QuillBot’s Citation Generator saves users time and ensures proper crediting of sources, benefiting those involved in research and academic writing projects.
5. QuillBot Plagiarism Checker
Quillbot AI provides a plagiarism checker, which is a premium feature. It eliminates the need for external tools to verify content originality. Premium users can paste their content into the checker, receiving results within minutes, indicating if the content is unique or plagiarized. Premium members can scan up to 20 pages per month with this tool, making it suitable for various types of content, including research papers.
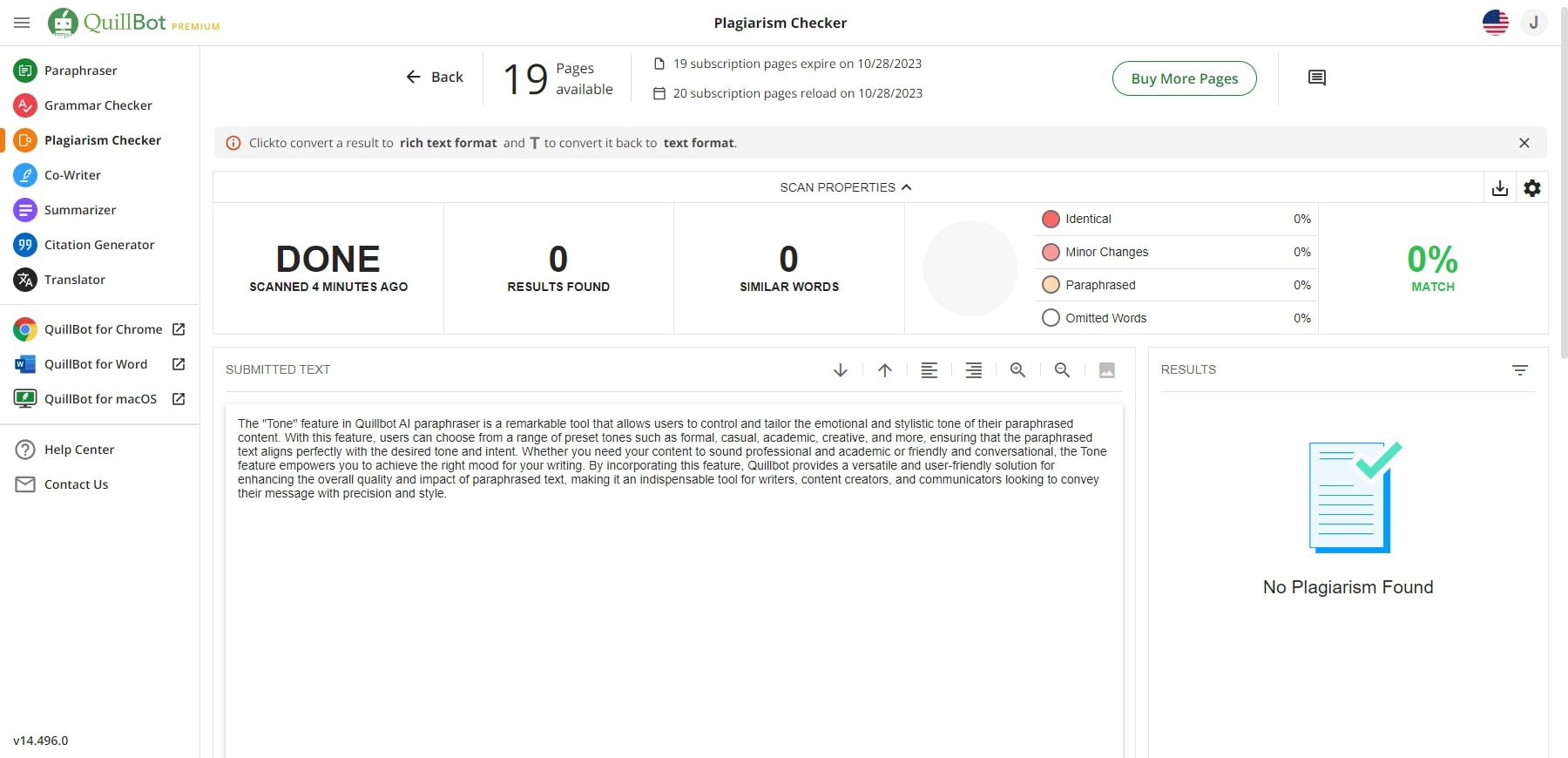
Its plagiarism checker stands out by accommodating research paper plagiarism checks, scanning up to 20 pages (approximately 5000 words) monthly. Consequently, it proves to be a valuable resource for essayists and academic writers, ensuring the integrity of their work.
Plagiarism detection is based on identical words , minor changes , paraphrased words , and omitted words .
6. The Translator
QuillBot AI provides its users with a Translation feature, allowing them to translate text into over 30 languages, making research and writing accessible across language barriers. It offers ad-free translation of up to 5,000 characters at once, includes integrated writing tools, and provides quick and accurate translations. The best part is that it’s free, enhancing convenience and accessibility for writers and researchers.
As a test, I added a block of content in the German language. The translator automatically detected it as German.
Then all you need to do is select the language you want it translated to on the right and click the Translate button.
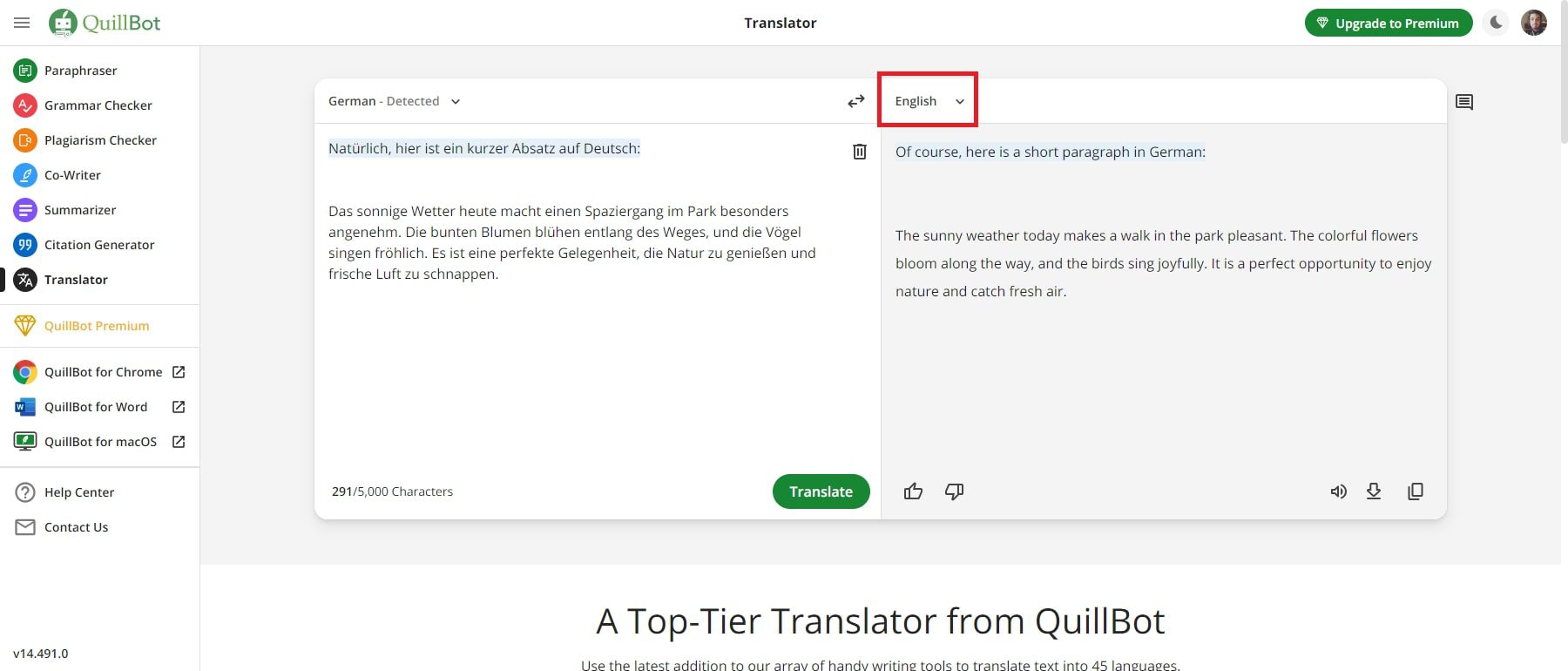
7. Quillbot Extensions
The tool offers three convenient extensions and applications to enhance your writing experience across different platforms.
QuillBot Chrome Extension
The QuillBot Google Chrome extension is a valuable tool for online writing. It seamlessly integrates with your web browsing, allowing you to check grammar, paraphrase, and summarize online documents (Google Docs), emails, and social media posts. Moreover, it ensures your writing is polished and error-free across the internet.
QuillBot for Word
If you’re working offline in Microsoft Word, this extension empowers you to access the full capabilities of QuillBot. It assists you in crafting high-quality documents, reports, and essays, ensuring your writing is clear and concise, even when you’re not connected to the internet.
QuillBot for macOS
For Mac users, QuillBot offers a browser-free desktop application. This standalone tool simplifies the writing process, providing a smooth and efficient writing experience on your macOS device. Moreover, it’s perfect for those who prefer a dedicated desktop application for their writing needs.
QuillBot AI Pricing and Plans Review
QuillBot AI provides three different pricing options to suit different needs and budgets.
The Basic (Free) Plan allows you to experiment with the tool before attaining its subscription. With it, you can paraphrase 125 words. It provides Standard and Fluency modes with limited use of the Synonym Slider. Moreover, you can summarize up to 1,200 words through the Summarizer mode.
The premium version of QuillBot AI allows unlimited words for the Parphraser, more writing style modes, and up to 6,000 words in the Summarizer. It also provides access to Plagiarism Checker, Paraphraser History, and Compare Modes.
You have the choice of three different payment plans for premium. The Annual Plan costs $8.33 monthly, with $99.95 billed every 12 months. The Semi-Annual Plan costs $13.33 monthly, with $79.95 billed every six months. The Monthly Plan costs $19.95 per month. By subscribing to either of these premium subscriptions, you can paraphrase unlimited words in Paraphraser. The Summarizer will allow you to summarize up to 6,000 words, and you can fully use the Synonym Slider.
Pros and Cons of QuillBot AI
As we delve deeper into our comprehensive review of QuillBot AI, it becomes imperative to assess the advantages and disadvantages of this sophisticated language processing tool. While this tool boasts various features and capabilities, no technology is without its strengths and weaknesses.
Pros of Using QuillBot AI
- A free plan is available, and there’s no need to sign up.
- There is a refund policy in place.
- Extensions for Microsoft Word, Google Chrome, and macOS are readily available.
- You can access a free Language Translator.
- The option to upgrade makes it very affordable to access additional features.
- An app for content summarization is available for free.
- Additionally, there is a free Grammar Checker app provided.
Cons of Using QuillBot AI
- Only two writing modes are available for free.
- OpenAI GPT AI writing is unavailable.
- There is no AI content detection feature.
- Manual intervention is usually required.
- Both free and paid plans have character limitations in place
How QuillBot Compares to Other Similar Tools
QuillBot AI offers valuable features for text enhancement, including effective paraphrasing and translation. Its free plan is a budget-friendly option, making it accessible to a broad audience. When compared to Grammarly , QuillBot outshines Grammarly’s ability to rephrase content. However, Quillbot’s grammar-checking capabilities fall short of Grammarly’s robust editing features.
Tools like Copy.ai and Rytr AI may offer more comprehensive solutions for advanced AI content generation than QuillBot. These alternatives excel in generating content from scratch, making them suitable for various writing needs.
Regarding accessibility, QuillBot stands out with extensions for Microsoft Word, Google Chrome, and macOS. This enhances its usability and integration into daily writing tasks. It also eliminates the language barrier, whereas Grammarly, Copy.ai, and Rytr AI primarily focus on English.
Ultimately, choosing these tools depends on your specific requirements and budget. QuillBot is a reliable option for text enhancement, while other tools may be better suited for advanced AI content generation and comprehensive grammar checking.
Should You Use QuillBot? (The Verdict)
QuillBot AI offers undeniable value as an AI writing assistant for various teams and individuals. Need an alternative version of your original article? QuillBot can generate a new and improved version swiftly. It is handy for optimizing blog posts and other content, outperforming many free and paid AI rewriter tools . Its ability to paraphrase content significantly reduces plagiarism risks for academic assignments and research papers. Although some detectors, like Originality.ai , may still recognize QuillBot paraphrased content in some cases. No AI content generator is 100% human. That said, thanks to its versatility and proficiency, QuillBot is a worthwhile asset for writers, students, and content creators.
Looking for more? Check out our list of top AI writing tools . And for all aspiring writers, check out these AI story generators . You can also explore more of the best overall AI tools you can use to boost your productivity in various ways .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Here are some common questions that may help you decide if QuillBot is right for you.
What is QuillBot?
Can quillbot be detected, how much does quillbot premium cost, how can quillbot be used as a paraphrasing tool, how can quillbot be used as a summarizer.

Get Started With QuillBot AI!
Explore plans, pricing and features. Click here to get started. 👇
Explore plans, pricing and features here. 👇
By fahad hamid.
Fahad enjoys writing about a diverse range of topics, from business and marketing to design. Alongside this, he balances his love for tennis, showing skill both on the page and on the court.
Explore Divi, The Most Popular WordPress Theme In The World And The Ultimate Page Builder
Check Out These Related Posts

- 6 Easiest Website Builders for Beginners in 2024 (Compared)
Posted on June 27, 2024 in Business
These days, having an online presence is a must. Without a website, you might as well be invisible on the internet. But if you’re not tech-savvy, the thought of creating and designing a website can be pretty intimidating. CSS, HTML, and coding can seem like a foreign language. You’ve...

- Divi vs. GeneratePress: Which WordPress Theme Wins in 2024?
Posted on June 26, 2024 in WordPress
As website owners and developers strive to create visually appealing and high-performing websites, two themes have become prominent: Divi and GeneratePress. These themes offer top-notch features and customization options. This post compares Divi vs. GeneratePress in a head-to-head battle of two of...

BigCommerce vs. Shopify for Online Stores: Who Wins in 2024?
Posted on June 13, 2024 in Business
Are you excited to launch your business venture to the online world but are struggling to identify the best eCommerce platforms? You may have heard of Shopify and Bigcommerce and want to see which better suits your needs. They are two of the most prominent names in the eCommerce industry. With...
Where did you get that annual price? I would love to get it. When I visited the site the price was twice as much ($99.95) if I paid the full year in advance.
Hi, Carlos. The pricing must have changed since writing the post. I have updated the article. Thanks for bringing it to our attention.
Carlos – for me, it’s showing as: USD Annual Save 58% $4.17 USD per month $49.95 billed every 12 months
Leave A Reply Cancel reply
- Recent Posts
- How to Make a Directory Website with WordPress (2024)
- Get a Free Eatery Layout Pack For Divi
- How to Choose a WordPress Theme in 2024 (9 Key Factors)
- Divi Resources
- Theme Releases
- Tips & Tricks
974,872 Customers Are Already Building Amazing Websites With Divi. Join The Most Empowered WordPress Community On The Web
We offer a 30 Day Money Back Guarantee, so joining is Risk-Free!
Divi Features
- All Features Explore Divi
- Divi Modules
- Divi Layouts
- No-Code Builder
- Ecommerce Websites
- Theme Builder
- Marketing Platform
- Speed & Performance
- Premium Support
- Divi Marketplace
- Divi AI Brand New!
- Divi Hosting
- Extra Theme
- Bloom Plugin
- Monarch Plugin
- Plans & Pricing Get Divi Today
- Documentation
- Help Articles & FAQ
- 24/7 Support
- Developer Docs
- System Status
- Product Updates
- Best Plugins
- Best Hosting
- Divi Meetups
- Divi Facebook Group
- Divi Examples
- Divi Integrations
- Divi Reviews
- Community Forum
- Affiliate Program
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Elegant Themes ®

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An MLA in-text citation can be done in two ways: Parenthetical; In prose; Both approaches require you to know the following: Last name of the author; ... Paraphrase (Author Last Name Page #) Parenthetical example: I kept pounding on the doors 'til my hands hurt and I woke up the dogs (Bronte 12).
No. The citation should appear only after the final sentence of the paraphrase. If, however, it will be unclear to your reader where your source's idea begins, include the author of the source in your prose rather than in a parenthetical citation. For example, the following is a paraphrase from an essay by Naomi S. …
In-text citations: Author-page style. MLA format follows the author-page method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the page number (s) from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken must appear in the text, and a complete reference should appear on your Works Cited page. The author's name may appear either in the ...
6 Steps to Effective Paraphrasing. Reread the original passage until you understand its full meaning. Set the original aside, and write your paraphrase on a note card. Jot down a few words below your paraphrase to remind you later how you envision using this material. At the top of the note card, write a key word or phrase to indicate the ...
Revised on March 5, 2024. An MLA in-text citation provides the author's last name and a page number in parentheses. If a source has two authors, name both. If a source has more than two authors, name only the first author, followed by " et al. ". If the part you're citing spans multiple pages, include the full page range.
3.4. ( 145) An in-text citation is a reference to a source that is found within the text of a paper ( Handbook 227). This tells a reader that an idea, quote, or paraphrase originated from a source. MLA in-text citations usually include the last name of the author and the location of cited information. This guide focuses on how to create MLA in ...
If a source has no author, start the MLA Works Cited entry with the source title.Use a shortened version of the title in your MLA in-text citation.. If a source has no page numbers, you can use an alternative locator (e.g. a chapter number, or a timestamp for a video or audio source) to identify the relevant passage in your in-text citation. If the source has no numbered divisions, cite only ...
The first step is to create a works cited page. Next, you use in-text citations after your paraphrases to direct your reader to the source listed in your works cited page. You generally use the last name of the author and the page number in parentheses after your paraphrases. Published October 29, 2020.
MLA In-Text Citations. MLA style uses in-text citations to give credit to authors when paraphrasing or quoting their ideas. In-text citations include two parts, the lead-in (or signal) phrase and the parenthetical citation. The lead-in phrase is an important element of the in-text citation to include when integrating sources into your own writing.
Paraphrasing . Quoting Directly . Long Quotations ... More Than One Source. In-Text Citation For Two or More Authors/Editors. Number of Authors/Editors In-Text Citation Example; Two (Author's Last Name and Author's Last Name Page Number) ... The sources within the in-text citation do not need to be in alphabetical order for MLA style ...
In MLA, in-text citations are inserted in the body of your research paper to briefly document the source of your information. Brief in-text citations point the reader to more complete information in the Works Cited list at the end of the paper. Number of Authors/Editors. Format of In-Text Citation. One.
Includes a signal phrase at the beginning to introduce the paraphrase; For a paraphrase that is multiple sentences long, start each sentence with an indicator that the paraphrase is continuing, such as a signal phrase: The author further explains….. (81). When to Use Paraphrasing
Author Unknown: If the author's name is not given, then use the first word or words of the title. Follow the same formatting that was used in the works cited list, such as quotation marks. This is a paraphrase ("Trouble" 22). Where you'd normally put the author's last name, instead use the first one, two, or three words from the title.
Include a full in-text citation with the author name and page number (if there is one). For example: Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65). Paraphrasing from Multiple Pages. If the paraphrased information/idea is from several pages, include them.
Paraphrasing from One Page. Include a full in-text citation with the author name and page number (if there is one). For example: Mother-infant attachment became a leading topic of developmental research following the publication of John Bowlby's studies (Hunt 65). Paraphrasing from Multiple Pages
The MLA 9th style uses author-date in-text citations, used when quoting or paraphrasing people's work. Two types of in-text citations 1. Author prominent format . Use this format if you want to emphasise the author. Their name becomes part of your sentence.
QuillBot's AI-powered paraphrasing tool will enhance your writing. Try for free. ... For sources with two authors, the citation should include both authors' names connected with "and." ... MLA multiple source in-text citation examples Children's stories have a long history as cautionary tales (Polk 85-89; Eqqa 102).
Multiple Authors. See examples below to learn about how multiple authors for one work are handled in MLA parenthetical citations. One Author. Include author's last name and the page number (no comma before the page number) in parentheses: (Austen 75) Two Authors. Include last name of both authors connected by the word 'and', followed by the ...
Paraphrasing means putting the information you could have quoted into your own words, but keeping the intention of the original source. Paraphrases do not have quotation marks because you are using your own words, yet still must include an in-text citation at the end of the part you are paraphrasing.
MLA in-text citation style uses the author's last name and the page number from which the quotation or paraphrase is taken, for example: (Smith 163). If the source does not use page numbers, do not include a number in the parenthetical citation: (Smith). For more information on in-text citation, see the MLA Style Center.
MLA Style requires an in-text citation to indicate the sources that were consulted and used in your work. The in-text citation must correspond with the entry on the Works Cited page, MLA in-text citations follow the Author-Page style, meaning the author's last name and the page number(s) of the quotation or paraphrase must appear in the text.
An MLA citation has two components: In-text citation: Every time you quote or paraphrase a source, you cite the author and the page number in parentheses. Works Cited: At the end of your paper, you give a full reference for every source you cited, alphabetized by the author's last name. MLA Works Cited list
Scroll back up to the generator at the top of the page and select the type of source you're citing. Books, journal articles, and webpages are all examples of the types of sources our generator can cite automatically. Then either search for the source, or enter the details manually in the citation form. The generator will produce a formatted MLA ...
MLA style is generally more flexible that either APA or Chicago style, so while they provide specific examples for citing commonly used AI tools, they encourage writers to adapt those guidelines to fit the situation.. Hare are some other guidelines for referencing AI-generated content in MLA style: Cite the AI tool when you incorporate its output into your work.
Yes. There is a chance that QuillBot-generated content can be detected as AI. There are several AI Content Detectors available for this purpose. Plagiarism and AI detectors like Originality.AI and Turnitin have developed innovative AI to identify content that QuillBot or similar AI writing tools have altered. These detectors have been trained extensively to recognize AI paraphrased content ...