When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods


Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Methods Section for a Psychology Paper
Tips and Examples of an APA Methods Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
The methods section of an APA format psychology paper provides the methods and procedures used in a research study or experiment . This part of an APA paper is critical because it allows other researchers to see exactly how you conducted your research.
Method refers to the procedure that was used in a research study. It included a precise description of how the experiments were performed and why particular procedures were selected. While the APA technically refers to this section as the 'method section,' it is also often known as a 'methods section.'
The methods section ensures the experiment's reproducibility and the assessment of alternative methods that might produce different results. It also allows researchers to replicate the experiment and judge the study's validity.
This article discusses how to write a methods section for a psychology paper, including important elements to include and tips that can help.
What to Include in a Method Section
So what exactly do you need to include when writing your method section? You should provide detailed information on the following:
- Research design
- Participants
- Participant behavior
The method section should provide enough information to allow other researchers to replicate your experiment or study.
Components of a Method Section
The method section should utilize subheadings to divide up different subsections. These subsections typically include participants, materials, design, and procedure.
Participants
In this part of the method section, you should describe the participants in your experiment, including who they were (and any unique features that set them apart from the general population), how many there were, and how they were selected. If you utilized random selection to choose your participants, it should be noted here.
For example: "We randomly selected 100 children from elementary schools near the University of Arizona."
At the very minimum, this part of your method section must convey:
- Basic demographic characteristics of your participants (such as sex, age, ethnicity, or religion)
- The population from which your participants were drawn
- Any restrictions on your pool of participants
- How many participants were assigned to each condition and how they were assigned to each group (i.e., randomly assignment , another selection method, etc.)
- Why participants took part in your research (i.e., the study was advertised at a college or hospital, they received some type of incentive, etc.)
Information about participants helps other researchers understand how your study was performed, how generalizable the result might be, and allows other researchers to replicate the experiment with other populations to see if they might obtain the same results.
In this part of the method section, you should describe the materials, measures, equipment, or stimuli used in the experiment. This may include:
- Testing instruments
- Technical equipment
- Any psychological assessments that were used
- Any special equipment that was used
For example: "Two stories from Sullivan et al.'s (1994) second-order false belief attribution tasks were used to assess children's understanding of second-order beliefs."
For standard equipment such as computers, televisions, and videos, you can simply name the device and not provide further explanation.
Specialized equipment should be given greater detail, especially if it is complex or created for a niche purpose. In some instances, such as if you created a special material or apparatus for your study, you might need to include an illustration of the item in the appendix of your paper.
In this part of your method section, describe the type of design used in the experiment. Specify the variables as well as the levels of these variables. Identify:
- The independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Control variables
- Any extraneous variables that might influence your results.
Also, explain whether your experiment uses a within-groups or between-groups design.
For example: "The experiment used a 3x2 between-subjects design. The independent variables were age and understanding of second-order beliefs."
The next part of your method section should detail the procedures used in your experiment. Your procedures should explain:
- What the participants did
- How data was collected
- The order in which steps occurred
For example: "An examiner interviewed children individually at their school in one session that lasted 20 minutes on average. The examiner explained to each child that he or she would be told two short stories and that some questions would be asked after each story. All sessions were videotaped so the data could later be coded."
Keep this subsection concise yet detailed. Explain what you did and how you did it, but do not overwhelm your readers with too much information.
Tips for How to Write a Methods Section
In addition to following the basic structure of an APA method section, there are also certain things you should remember when writing this section of your paper. Consider the following tips when writing this section:
- Use the past tense : Always write the method section in the past tense.
- Be descriptive : Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your experiment, but focus on brevity. Avoid unnecessary detail that is not relevant to the outcome of the experiment.
- Use an academic tone : Use formal language and avoid slang or colloquial expressions. Word choice is also important. Refer to the people in your experiment or study as "participants" rather than "subjects."
- Use APA format : Keep a style guide on hand as you write your method section. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Make connections : Read through each section of your paper for agreement with other sections. If you mention procedures in the method section, these elements should be discussed in the results and discussion sections.
- Proofread : Check your paper for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.. typos, grammar problems, and spelling errors. Although a spell checker is a handy tool, there are some errors only you can catch.
After writing a draft of your method section, be sure to get a second opinion. You can often become too close to your work to see errors or lack of clarity. Take a rough draft of your method section to your university's writing lab for additional assistance.
A Word From Verywell
The method section is one of the most important components of your APA format paper. The goal of your paper should be to clearly detail what you did in your experiment. Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your study if they wanted.
Finally, if you are writing your paper for a class or for a specific publication, be sure to keep in mind any specific instructions provided by your instructor or by the journal editor. Your instructor may have certain requirements that you need to follow while writing your method section.
Frequently Asked Questions
While the subsections can vary, the three components that should be included are sections on the participants, the materials, and the procedures.
- Describe who the participants were in the study and how they were selected.
- Define and describe the materials that were used including any equipment, tests, or assessments
- Describe how the data was collected
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded, left-aligned and in title case.
The purpose of the methods section is to describe what you did in your experiment. It should be brief, but include enough detail that someone could replicate your experiment based on this information. Your methods section should detail what you did to answer your research question. Describe how the study was conducted, the study design that was used and why it was chosen, and how you collected the data and analyzed the results.
Erdemir F. How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):10-5. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.047
Kallet RH. How to write the methods section of a research paper . Respir Care . 2004;49(10):1229-32. PMID: 15447808.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write the Methods Section of an APA Paper

3-minute read
- 23rd December 2021
If you’re a researcher writing an APA paper , you’ll need to include a Methods section. This part explains the methods you used to conduct your experiment or research study and is always written in the past tense.
It’s crucial that you include all the relevant information here because other researchers will use this section to recreate your study, as well as judge how valid and accurate your results are.
In this guide, we’ll show you how to write a clear and comprehensive Methods section for your research paper.
Structuring the Methods Section
This section of an APA paper is typically split into three subsections under the following subheadings:
- Participants —who took part in the experiment and why?
- Materials —what tools did you use to conduct the experiment?
- Procedure —what steps were involved in the experiment?
If necessary, you may add further subsections. Different institutions have specific rules on what subsections should be included (for example, some universities require a “Design” subsection), so make sure to check your institution’s requirements before you start writing your Methods section.
Writing the Participants Subsection
In this first subsection, you will need to identify the participants of your experiment or study. You should include:
● How many people took part, and how many were assigned to the experimental condition
● How they were selected for participation
● Any relevant demographic information (e.g., age, sex, ethnicity)
You’ll also need to address whether any restrictions were placed on who was selected and if any incentives were offered to encourage participants to take part.
Writing the Materials Subsection
In this subsection, you should address the materials, equipment, measures, and stimuli used in the study. These might include technology and computer software, tools such as questionnaires and psychological assessments, and, if relevant, the physical setting where the study took place.
You’ll need to describe specialist equipment in detail, especially if it has a niche purpose. However, you don’t need to provide specific information about common or standard equipment (e.g., the type of computer on which participants completed a survey) unless it’s relevant to the experiment.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
In addition, you don’t need to explain a material in depth if it’s well known within your field, such as a famous psychological assessment. Instead, you can provide a citation referring to that material.
If any materials were designed specifically for the experiment, such as a questionnaire, you’ll need to provide such materials in the appendix .
Writing the Procedure Subsection
The procedure subsection should describe what you had participants do in a step-by-step format. It should be detailed but concise and will typically include:
● A summary of the instructions given to participants (as well as any information that was intentionally withheld)
● A description of how participants in different conditions were treated
● How long each step of the process took
● How participants were debriefed or dismissed at the end of the experiment
After detailing the steps of the experiment, you should then address the methods you used to collect and analyze data.
Proofreading Your Methods Section
Because the Methods section of your paper will help other researchers understand and recreate your experiment, you’ll want your writing to be at its best.
Our expert research paper proofreaders can help your research get the recognition it deserves by making sure your work is clear, concise, and error-free. Why not try our services for free by submitting a trial document ?
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
Published on August 25, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 20, 2023.
Your research methodology discusses and explains the data collection and analysis methods you used in your research. A key part of your thesis, dissertation , or research paper , the methodology chapter explains what you did and how you did it, allowing readers to evaluate the reliability and validity of your research and your dissertation topic .
It should include:
- The type of research you conducted
- How you collected and analyzed your data
- Any tools or materials you used in the research
- How you mitigated or avoided research biases
- Why you chose these methods
- Your methodology section should generally be written in the past tense .
- Academic style guides in your field may provide detailed guidelines on what to include for different types of studies.
- Your citation style might provide guidelines for your methodology section (e.g., an APA Style methods section ).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a research methodology, why is a methods section important, step 1: explain your methodological approach, step 2: describe your data collection methods, step 3: describe your analysis method, step 4: evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made, tips for writing a strong methodology chapter, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about methodology.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Your methods section is your opportunity to share how you conducted your research and why you chose the methods you chose. It’s also the place to show that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated .
It gives your research legitimacy and situates it within your field, and also gives your readers a place to refer to if they have any questions or critiques in other sections.
You can start by introducing your overall approach to your research. You have two options here.
Option 1: Start with your “what”
What research problem or question did you investigate?
- Aim to describe the characteristics of something?
- Explore an under-researched topic?
- Establish a causal relationship?
And what type of data did you need to achieve this aim?
- Quantitative data , qualitative data , or a mix of both?
- Primary data collected yourself, or secondary data collected by someone else?
- Experimental data gathered by controlling and manipulating variables, or descriptive data gathered via observations?
Option 2: Start with your “why”
Depending on your discipline, you can also start with a discussion of the rationale and assumptions underpinning your methodology. In other words, why did you choose these methods for your study?
- Why is this the best way to answer your research question?
- Is this a standard methodology in your field, or does it require justification?
- Were there any ethical considerations involved in your choices?
- What are the criteria for validity and reliability in this type of research ? How did you prevent bias from affecting your data?
Once you have introduced your reader to your methodological approach, you should share full details about your data collection methods .
Quantitative methods
In order to be considered generalizable, you should describe quantitative research methods in enough detail for another researcher to replicate your study.
Here, explain how you operationalized your concepts and measured your variables. Discuss your sampling method or inclusion and exclusion criteria , as well as any tools, procedures, and materials you used to gather your data.
Surveys Describe where, when, and how the survey was conducted.
- How did you design the questionnaire?
- What form did your questions take (e.g., multiple choice, Likert scale )?
- Were your surveys conducted in-person or virtually?
- What sampling method did you use to select participants?
- What was your sample size and response rate?
Experiments Share full details of the tools, techniques, and procedures you used to conduct your experiment.
- How did you design the experiment ?
- How did you recruit participants?
- How did you manipulate and measure the variables ?
- What tools did you use?
Existing data Explain how you gathered and selected the material (such as datasets or archival data) that you used in your analysis.
- Where did you source the material?
- How was the data originally produced?
- What criteria did you use to select material (e.g., date range)?
The survey consisted of 5 multiple-choice questions and 10 questions measured on a 7-point Likert scale.
The goal was to collect survey responses from 350 customers visiting the fitness apparel company’s brick-and-mortar location in Boston on July 4–8, 2022, between 11:00 and 15:00.
Here, a customer was defined as a person who had purchased a product from the company on the day they took the survey. Participants were given 5 minutes to fill in the survey anonymously. In total, 408 customers responded, but not all surveys were fully completed. Due to this, 371 survey results were included in the analysis.
- Information bias
- Omitted variable bias
- Regression to the mean
- Survivorship bias
- Undercoverage bias
- Sampling bias
Qualitative methods
In qualitative research , methods are often more flexible and subjective. For this reason, it’s crucial to robustly explain the methodology choices you made.
Be sure to discuss the criteria you used to select your data, the context in which your research was conducted, and the role you played in collecting your data (e.g., were you an active participant, or a passive observer?)
Interviews or focus groups Describe where, when, and how the interviews were conducted.
- How did you find and select participants?
- How many participants took part?
- What form did the interviews take ( structured , semi-structured , or unstructured )?
- How long were the interviews?
- How were they recorded?
Participant observation Describe where, when, and how you conducted the observation or ethnography .
- What group or community did you observe? How long did you spend there?
- How did you gain access to this group? What role did you play in the community?
- How long did you spend conducting the research? Where was it located?
- How did you record your data (e.g., audiovisual recordings, note-taking)?
Existing data Explain how you selected case study materials for your analysis.
- What type of materials did you analyze?
- How did you select them?
In order to gain better insight into possibilities for future improvement of the fitness store’s product range, semi-structured interviews were conducted with 8 returning customers.
Here, a returning customer was defined as someone who usually bought products at least twice a week from the store.
Surveys were used to select participants. Interviews were conducted in a small office next to the cash register and lasted approximately 20 minutes each. Answers were recorded by note-taking, and seven interviews were also filmed with consent. One interviewee preferred not to be filmed.
- The Hawthorne effect
- Observer bias
- The placebo effect
- Response bias and Nonresponse bias
- The Pygmalion effect
- Recall bias
- Social desirability bias
- Self-selection bias
Mixed methods
Mixed methods research combines quantitative and qualitative approaches. If a standalone quantitative or qualitative study is insufficient to answer your research question, mixed methods may be a good fit for you.
Mixed methods are less common than standalone analyses, largely because they require a great deal of effort to pull off successfully. If you choose to pursue mixed methods, it’s especially important to robustly justify your methods.
Next, you should indicate how you processed and analyzed your data. Avoid going into too much detail: you should not start introducing or discussing any of your results at this stage.
In quantitative research , your analysis will be based on numbers. In your methods section, you can include:
- How you prepared the data before analyzing it (e.g., checking for missing data , removing outliers , transforming variables)
- Which software you used (e.g., SPSS, Stata or R)
- Which statistical tests you used (e.g., two-tailed t test , simple linear regression )
In qualitative research, your analysis will be based on language, images, and observations (often involving some form of textual analysis ).
Specific methods might include:
- Content analysis : Categorizing and discussing the meaning of words, phrases and sentences
- Thematic analysis : Coding and closely examining the data to identify broad themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying communication and meaning in relation to their social context
Mixed methods combine the above two research methods, integrating both qualitative and quantitative approaches into one coherent analytical process.
Above all, your methodology section should clearly make the case for why you chose the methods you did. This is especially true if you did not take the most standard approach to your topic. In this case, discuss why other methods were not suitable for your objectives, and show how this approach contributes new knowledge or understanding.
In any case, it should be overwhelmingly clear to your reader that you set yourself up for success in terms of your methodology’s design. Show how your methods should lead to results that are valid and reliable, while leaving the analysis of the meaning, importance, and relevance of your results for your discussion section .
- Quantitative: Lab-based experiments cannot always accurately simulate real-life situations and behaviors, but they are effective for testing causal relationships between variables .
- Qualitative: Unstructured interviews usually produce results that cannot be generalized beyond the sample group , but they provide a more in-depth understanding of participants’ perceptions, motivations, and emotions.
- Mixed methods: Despite issues systematically comparing differing types of data, a solely quantitative study would not sufficiently incorporate the lived experience of each participant, while a solely qualitative study would be insufficiently generalizable.
Remember that your aim is not just to describe your methods, but to show how and why you applied them. Again, it’s critical to demonstrate that your research was rigorously conducted and can be replicated.
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions
The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions .
2. Cite relevant sources
Your methodology can be strengthened by referencing existing research in your field. This can help you to:
- Show that you followed established practice for your type of research
- Discuss how you decided on your approach by evaluating existing research
- Present a novel methodological approach to address a gap in the literature
3. Write for your audience
Consider how much information you need to give, and avoid getting too lengthy. If you are using methods that are standard for your discipline, you probably don’t need to give a lot of background or justification.
Regardless, your methodology should be a clear, well-structured text that makes an argument for your approach, not just a list of technical details and procedures.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Thematic analysis
- Cohort study
- Peer review
- Ethnography
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Conformity bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Availability heuristic
- Attrition bias
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
In a scientific paper, the methodology always comes after the introduction and before the results , discussion and conclusion . The same basic structure also applies to a thesis, dissertation , or research proposal .
Depending on the length and type of document, you might also include a literature review or theoretical framework before the methodology.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
Reliability and validity are both about how well a method measures something:
- Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure (whether the results can be reproduced under the same conditions).
- Validity refers to the accuracy of a measure (whether the results really do represent what they are supposed to measure).
If you are doing experimental research, you also have to consider the internal and external validity of your experiment.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved July 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/methodology/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research design | types, guide & examples, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, what is your plagiarism score.

How to Write the Methods Section of a Scientific Paper
Full guide and template.

The methods section is one of the most important parts of a s cientific pape r; writing one is a cornerstone of Academic writing and medical research. This section describes the procedures and processes used to conduct the study and collect the data. Writing a clear and comprehensive methods section is critical for allowing other researchers to evaluate, reproduce, and build upon the research. Three questions must be answered in this section.
How was the experiment conducted?
What details are necessary for replication?
What are the expected outputs from the experiment?
In this blog post, we provide a step-by-step guide to writing an effective methods section for a scientific paper and a comprehensive template to supercharge your academic writing .
Thanks for reading DrAiMD’s Substack! Subscribe for free to receive new posts and support my work.
Organizing the Methods Section
The methods section should be divided into logical subsections to improve flow and readability. Common subsection headers include:
Participants
Materials/Instruments
Research Design
Describe the Study Participants
The participant’s subsection should provide relevant details about the subjects, including:
The total number of participants
Key eligibility criteria and demographic details
How participants were recruited/selected
Any grouping or assignment of participants to conditions
Thoroughly List Research Instruments and Materials
The materials subsection should include a detailed list of instruments, tools, and materials central to data collection and analysis. For specialized or custom equipment, include schematics or technical specifications. For clinical research based on data analysis, the statistical software used and the methods to procure the data or database must be outlined.
Explain the Research Design
Clearly describe the study design and define all variables. Explain how variables were measured and manipulated. Identify controls, interventions, comparison groups, etc.
Provide a Step-by-Step Procedure
The procedure subsection should provide an exact, step-by-step description of how the study was conducted and data was collected. Be precise and detailed enough to enable replication. Reference appendices and citations where applicable.
Emphasize Transparency
Strive for complete transparency regarding all instruments, measurements, data processing/analysis, subject selection criteria, and limitations. Thoroughly describe any custom tools or analysis code.
Use Concise, Technical Language
The methods section calls for clear, clinical writing absent of interpretation or opinion. Use precise terminology and active technical language. Provide specifics - do not overgeneralize processes.
Enable Replication
The end goal is to allow other researchers in the field to replicate experiments and verify analyses accurately. The ideal methods section leaves no relevant procedural uncertainties. It is usually about 2-3 pages (possibly higher in experiments resorting to innovative methods or plenty of techniques or sophisticated statistics) - and does not normally exceed 750 words over 6 9 paragraphs; 5-15 references is an average and is about 20% of the paper.
Clinical Research Methods Section Template
Introduction to Methods
Overview : Begin with a brief introduction summarizing the purpose of the study and the overarching research question. This section sets the stage for the detailed methodology that follows.
Subsection Division
Subsection Overview : Divide the methods section into clear, distinct subsections. Each subsection should correspond to a specific aspect of your experimental process, including data collection, data analysis, and any other critical steps.
Subsection 1: [Title e.g., Participant Selection]
Purpose : Explain why this part of the experiment was conducted. Connect it to the overall research question.
Process Description : Detail the specific procedures followed, including participant selection criteria, settings, and timelines.
Replication Details : Provide information necessary for replication, such as selection tools, questionnaires, or screening methods used.
Subsection 2: [Title e.g., Data Collection]
Purpose : Describe the significance of this data collection method in the context of your research.
Process Description : Elaborate on how data was gathered, mentioning any instruments or equipment used.
Replication Details : Include detailed parameters, settings, and protocols to enable accurate replication.
Subsection 3: [Title e.g., Data Analysis]
Purpose : Clarify the role of this analysis in answering your research question.
Process Description : Describe the analysis methods, including any statistical tests or software used.
Replication Details : Detail the software settings, versions, and specific statistical methods, ensuring clarity for replication.
Subsection 4: [Additional Subsections as Required]
Purpose : Relate each subsection to the overarching research aim.
Process Description : Offer a clear, step-by-step description of the procedures.
Replication Details : Provide exhaustive details for others to replicate the experiment accurately.
Expected Outcomes
For Each Subsection : Discuss what outcomes you expect from each part of the experiment. This might include expected data trends, anticipated findings, or potential impacts on the research question.
Anticipation of Challenges
Address Potential Criticisms : Use this section to pre-emptively address potential criticisms of your methodology. Explain your choices and how they strengthen the study's validity.
By following these key guidelines, you can write a clear, replicable methods section that bolsters the impact and legitimacy of your scientific paper. Let us know in the comments if you have any other methods of writing tips!
Ready for more?

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
- INTRODUCTION
Writing a "good" methods section
"methods checklist" from: how to write a good scientific paper. chris a. mack. spie. 2018..
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
The purpose is to provide enough detail that a competent worker could repeat the experiment. Many of your readers will skip this section because they already know from the Introduction the general methods you used. However careful writing of this section is important because for your results to be of scientific merit they must be reproducible. Otherwise your paper does not represent good science.
- Exact technical specifications and quantities and source or method of preparation
- Describe equipment used and provide illustrations where relevant.
- Chronological presentation (but related methods described together)
- Questions about "how" and "how much" are answered for the reader and not left for them to puzzle over
- Discuss statistical methods only if unusual or advanced
- When a large number of components are used prepare tables for the benefit of the reader
- Do not state the action without stating the agent of the action
- Describe how the results were generated with sufficient detail so that an independent researcher (working in the same field) could reproduce the results sufficiently to allow validation of the conclusions.
- Can the reader assess internal validity (conclusions are supported by the results presented)?
- Can the reader assess external validity (conclusions are properly generalized beyond these specific results)?
- Has the chosen method been justified?
- Are data analysis and statistical approaches justified, with assumptions and biases considered?
- Avoid: including results in the Method section; including extraneous details (unnecessary to enable reproducibility or judge validity); treating the method as a chronological history of events; unneeded references to commercial products; references to “proprietary” products or processes unavailable to the reader.
- << Previous: INTRODUCTION
- Next: RESULTS >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
How to Write a Methods Section for a Research Paper
- Purpose of methods section
- Key components
- How to describe
- Step-by-step guide
- Methods section formats
- Additional elements

Purpose of the Methods section
What key components must be included in the methods section.
- Research design. This is the most important section to help your audience see the methods used. Make sure to structure your research methodology correctly and follow the rules of the scientific field. Depending on your work type, the research design of a methods section should represent an outline with the basic introduction, set objectives, a lab/field environment, and other related elements.
- Participants. When dealing with a sample group or a case study, you must discuss the research participants. Always narrow things down to why a specific group of participants have been chosen and talk about how it will be helpful to stay objective and unbiased.
- Equipment. This part describes the set of tools that have been used. Writing a methods section can include software, hardware, voice recorders, chemical equipment, special labs, and more.
- Materials. Describe what materials have been used for your studies. Talk about the studies and procedures used based on the available data.
- Variables. Talk about independent and dependent variables. The independent variables are related to those elements of your research that can be changed, like the amount of water or the use of certain colors to replicate a process. As for dependent variables, these are those affected by specific changes. In other words, variables in a methods section can change during the process of studies, like the experiment outcome or exceptions in the sample group.
- Participant behavior . This is where you talk about what has been experienced by the participants (if relevant). A methods section example may include a description of actions taken, processes experienced, and the environment used to conduct the research.
How to describe your research design and procedures?
- Reflect on your hypothesis . Talk about variables or aspects you should research. This is a procedure section of a research paper where you describe the type of information you must collect as you work on your main arguments. Narrow down the scope of data that has to be evaluated.
- Define your research approach . In most cases, it can be either qualitative or quantitative. While you can choose a mixture of both for your paper, focusing on one to clarify a relevant section is recommended.
- Choose your research design type . If you are dealing with quantitative research, it’s possible to use experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, or descriptive design methods. Suppose you are choosing a qualitative design methodology. In that case, you may approach ethnography (a method based on cultural immersion, inside research), phenomenology (research based on the perspective of an individual, an intuitive analytical variable), or a grounded method (social-based research).
- Define your research sampling method . The risk here is to generate excessive data, making it extremely challenging to see things to include and avoid. You can choose a probabilistic sampling method or a deterministic sampling approach, also known as non-random selection. Certain methods can fit better depending on the materials section of the research paper. If you still choose a non-random design, the only challenge is that the latter sampling method is more biased.
- Evaluate the best data collection method . Start your Methodology section by marking the difference between your primary (surveys, interviews) and secondary data (references that have already been published) sources.
- Choose an approach to data analysis . You can alternate between qualitative and quantitative data analysis methods section approaches.
Step-by-step guide on how to compose your Methods section
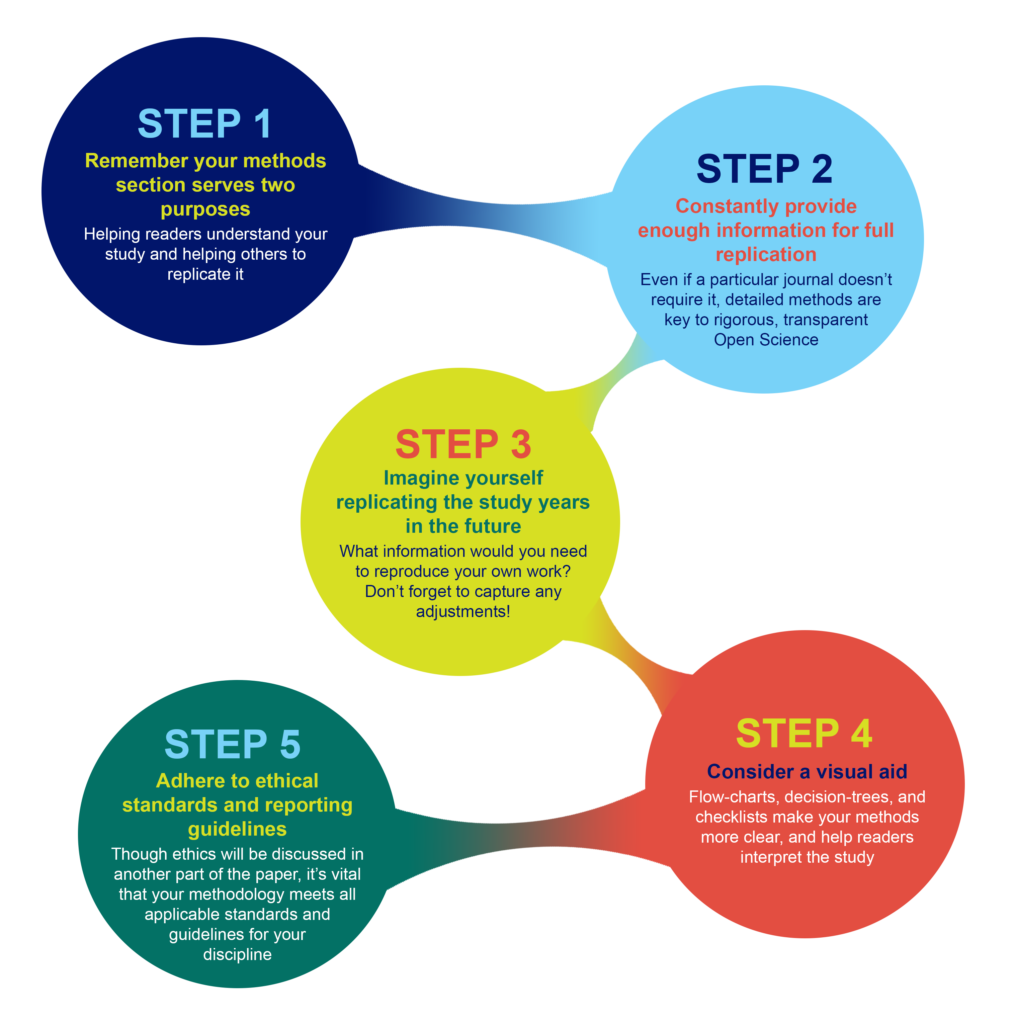
- Step 1: Focus on two main purposes of your Methods section. You should help your target audience understand your research project easier and make it possible to replicate all the vital processes.
- Step 2: Offer sufficient information to make replication unbiased and complete. While you may have your research project ready for publishing, providing overly detailed information is only sometimes necessary. Always check things twice to learn the requirements. Most importantly, keep your research transparent, provide a clear methodology, and keep every step easy to replicate.
- Step 3: To make things easier, imagine you are an individual in your target audience. Think about how you would replicate your study and what scientific paper methods you would find accessible. Ask yourself about what information you would require. Take notes and create 2-3 outlines for additional clarity.
- Step 4: Consider adding visual aid elements. It may include relevant flow charts, mind maps, checklists, or statistical data for your methodology. It will help your readers interpret the study and avoid unnecessary steps.
- Step 5: Always adhere to strict ethical standards and scientific guidelines. Even though the “Ethical Guidelines” section will be presented in another research paper part, you must show the main arguments and thesis concerning ethical rules. It will show that you are using strict standards and following the rules related to your discipline.
Methods section checklist
- Is your logic consistent in every section?
- Does your introduction provide sufficient background information?
- Does your methodology structure sound clear and follows a chronology of the research?
- Do you provide the results of your research in the same format?
- Can you replicate your study based on a given methodology?
- Do your readers have all the necessary objectives mentioned?
- Are the tools used mentioned?

Methods section formats and features
Additional elements to consider.
- Location specifics. This is where the location and research environment can make a major difference for replication purposes.
- Limitations of the research. Talk about the limitations and specifics of the tools and methods being used.
- Writing style and tone. Remember to write in the past tense and keep the same tone throughout your research paper.
- Ethical considerations. Clarify and specify all the ethical guidelines for your institution, a scientific journal methodology, and a field of science.
- Data analysis methodology.
- Participants and subjects.
- Data collection methodology.
- Things required to replicate the research.
- Addressing the research objectives.
- Basic research question.

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research
Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
How to Master the Methods Section of Your Research Paper

The Methods section is a fundamental component of any research paper, playing a crucial role in establishing the validity and reliability of your study. It serves as a detailed roadmap of the research process that you undertook, providing sufficient information for the replication of the study. An effectively written Methods section can enhance the impact and credibility of your research, giving your readers a clear understanding of how your findings were achieved.
The methods section essentially answers the questions:
- What did you do?
- How did you do it?
- What tools and procedures did you use?
- And how did you analyze the data you collected?
Providing thorough responses to these questions, it typically includes detailed descriptions of your research design , participants or subjects of study, equipment or materials used, the procedures you followed, and the statistical methods applied for data analysis.
In the following sections, we'll delve into each of these elements, providing you with a comprehensive guide on how to craft a compelling, informative, and rigorous Methods section for your research paper.
Understanding the purpose of the methods section
Adding validity and credibility to the research.
The Methods section plays a pivotal role in adding validity and credibility to your research. By detailing the procedures you used, it allows readers to evaluate the soundness of your methodology. A well-written Methods section makes your research transparent, enabling others to understand exactly what you did and how you did it. This transparency not only adds to the credibility of your work but also allows for an accurate evaluation of the results. The Methods section is where you demonstrate that your research has been conducted in a rigorous, systematic, and ethical manner.

Enabling replication of the study
Perhaps one of the most crucial roles of the Methods section is to allow other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is a key aspect of scientific research - it's how we ensure that findings are not mere flukes or products of bias. By providing a clear and detailed description of your methodology, others can repeat your study under the same conditions to see if they achieve similar results. This not only reinforces the robustness of your own research but also contributes to the collective knowledge in your field. Consequently, the Methods section must be thorough and precise, ensuring that every step of your process can be duplicated accurately.
Deciding what to include in your methods section
Elements to include in the methods section.
The Methods section should provide a clear and comprehensive account of how you conducted your study. The content can vary depending on your field of study and the nature of your research, but typically, you should include the following elements:
- Participants: Describe who took part in your study. This might include details about their demographics (age, gender, etc.), how they were selected, and how they were assigned to groups in the case of experimental research.
- Materials and Equipment: Detail the materials or equipment you used during your study. This can range from lab equipment in a scientific study, surveys or tests in a social science study, to software and data sources in a computational study.
- Procedure: Give a step-by-step account of what you did during your study. This should be detailed enough to enable another researcher to replicate your study exactly.
- Data Analysis Methods: Explain how you analyzed your data. This might include statistical analysis methods, coding procedures for qualitative data , or computational algorithms.
Balancing detail and brevity
While it's important to provide enough detail in your Methods section to allow for replication, it's also crucial to avoid including unnecessary or irrelevant information. Striking a balance between detail and brevity is key. You should aim to provide a complete account of your methodology without getting lost in minute details that don't significantly impact the understanding or replication of your research.
Ask yourself, "Would including this detail enhance the understanding of my study or the ability to replicate it?" If the answer is no, you can likely leave that detail out. Remember, the goal is to provide a thorough, yet concise and readable account of your research methods .
Writing the participants section
Describing the participants.
In describing your participants, or subjects, it's essential to provide clear demographic information. This includes, but is not limited to, aspects like age, sex, ethnicity, occupation, education level, or any other characteristic relevant to your study. These details help provide context and allow readers to understand who your research is applicable to. For instance, a study involving only teenagers will have different implications than one involving adults.
Discussing selection and assignment to groups
The process of participant selection and assignment to groups is fundamental to many research studies, especially those involving experimental design. You should describe how you recruited your participants (e.g., through random sampling, convenience sampling, etc. ), and how they were assigned to different conditions or treatment groups if applicable. This might include a description of any randomization or matching procedures used. Clarity in this section bolsters the transparency and replicability of your study.
Ethical considerations in participant selection and treatment
It's also vital to discuss any ethical considerations related to your participants. This includes obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy and confidentiality, and minimizing potential harm. If your study was reviewed and approved by an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or Ethics Committee, mention this in your Methods section. It's also appropriate to detail any steps you took to minimize potential bias or discrimination in participant selection. This not only demonstrates your commitment to ethical research practices but also contributes to the credibility of your study.
Writing the materials and equipment section
Detailing materials and equipment used in the study.
When detailing the materials and equipment used in your study, it's important to be as specific and precise as possible. This might include the make and model of equipment, the type and source of materials, and even the versions of software packages used. These specifics enable replication and also allow other researchers to understand the tools that contributed to your findings. This part of the Methods section might vary significantly depending on your field of research. For example, a biology study might detail the type of microscopes used, whereas a psychology study could discuss specific psychometric tests.
Providing information about unique or unusually used tools
If you used special or unique tools, or if you used standard tools in an unusual way, this should be clearly specified in the Materials and Equipment section. Describe these tools or methods in detail, and explain why they were necessary for your study. If a tool is rare or specialized, consider providing a citation or source where readers can learn more about it. If a standard tool was used in a novel or unconventional way, explain what you did and why. This not only adds interest to your paper, but also contributes to the complete understanding and potential replication of your research. Remember, transparency is key in this section, as it helps enhance the credibility of your study and its findings.
Writing the procedure section
Importance of including each step taken during the study.
The Procedure section serves as a step-by-step guide to your study, detailing each phase from start to finish. The significance of this section cannot be overstated, as it offers a comprehensive look at the "how" of your research. Each step you took, every decision you made, and all procedures you followed should be recorded in this section. This level of detail not only supports your study's validity but also enables others to replicate your study accurately, fostering scientific transparency.
Tips for writing clearly and concisely, yet with enough detail for replication
When detailing your procedures, clarity and conciseness are key. Strive to describe your methods in a way that's straightforward and easy to follow. Avoid jargon where possible, and when it's unavoidable, make sure to provide clear definitions.
Remember, while conciseness is important, so too is the inclusion of sufficient detail to allow for replication. One approach to ensuring the right level of detail is to write as though you are explaining your study to another researcher in your field. They should be able to read your Procedure section and know exactly how to carry out your study.
Considerations for describing experimental and control conditions
If your study involved experimental and control conditions, these should be described with particular care. Detail the experimental procedures, clearly stating what distinguishes the experimental group from the control group. This includes any stimuli or treatments that were administered, as well as how, when, and where they were delivered. In addition, it's essential to articulate any measures that were taken to minimize the effects of confounding variables. This precise detailing underscores the reliability of your research and enhances the likelihood of accurate replication.
Writing the data analysis section
Describing the statistical or other methods used to analyze the data.
In the Data Analysis section, your aim should be to clearly describe the statistical or other methods you used to analyze your data. Include specifics about the tests used, the software employed, and the reasoning behind choosing these particular methods. For statistical tests, mention the test name, the variables it was used for, and any specific variations of the test that were applied. If you conducted qualitative analysis, explain the coding process, thematic analysis, or other methods used. Providing this level of detail allows other researchers to assess the appropriateness and rigor of your data analysis.
Importance of including all steps of the analysis, not just the final results
Remember that the Data Analysis section is not just about presenting the final results, but also about revealing the process you used to get there. Including each step of your analysis provides a complete picture of your research journey and ensures that your methodology can be accurately replicated and evaluated by others. Whether it involves data cleaning, variable coding, preliminary analyses, or specific sequences of statistical tests, all these details contribute to the overall transparency of your research.
Explaining any adjustments for potential biases or confounds
Lastly, be sure to explain any adjustments or corrections you made to account for potential biases or confounding variables in your data. This may include controlling for certain variables, dealing with missing data, or using specific statistical techniques to address these issues. Clearly articulating these adjustments enhances the reliability and validity of your findings, and also provides a more comprehensive understanding of your research approach. This is also where you can discuss the limitations of your study and how you accounted for them in your analysis.
Common mistakes and how to avoid them
Typical errors in the methods section.
One common mistake in writing the Methods section is providing too little detail. A lack of specificity can make it difficult for others to replicate your study or fully understand your process. On the other hand, including too much detail, particularly irrelevant information, can dilute the focus of your Methods section and confuse your readers.
Another common error is forgetting to include important steps, such as the processes for data cleaning, preprocessing, or certain aspects of participant recruitment and management. Also, failing to adequately discuss ethical considerations, when relevant, can negatively impact the perceived credibility of your research.
Tips and strategies for avoiding these mistakes
In order to effectively avoid common errors when writing the Methods section of your research paper, consider implementing the following strategies:
- Create a Detailed Outline: Begin by outlining your Methods section in detail. This will help you ensure that all important elements of your research process are captured and not forgotten in the final write-up.
- Strive for Balance: Aim for a balance between brevity and comprehensiveness. Remember, your primary objective is to provide enough information so that someone else can replicate your study.
- Review for Relevance: After drafting your section, review it to ensure that all included information is relevant and necessary. If certain details do not directly contribute to understanding your method or facilitating replication, consider removing them.
- Include Ethical Considerations: Ethics are a crucial aspect of any research. Therefore, remember to discuss any ethical considerations and approvals related to your study.
- Get Feedback: Have colleagues or mentors review your Methods section. They can offer valuable feedback and catch any errors or omissions you may have overlooked. It's always beneficial to have another pair of eyes on your work.
Sample methods sections and analysis
Consider the following examples of well-written methods sections from different fields of study. These fictional examples illustrate the important elements discussed above:
Psychology study example
In this study, 100 undergraduate students (50 males and 50 females, aged 18-25) were randomly selected from XYZ University. The selection criteria included full-time enrollment status and willingness to participate in the study. All participants provided informed consent prior to participation, and the study received ethical approval from the University's Institutional Review Board.
The instruments used included a demographic questionnaire, the Big Five Personality Test, and an academic performance survey. The demographic questionnaire gathered data on participants' age, gender, major, and year in college. The Big Five Personality Test, a validated and reliable instrument, was used to assess participants' personality traits. Academic performance was gauged through self-reported grade point averages (GPAs).
The experiment was conducted in a quiet and well-lit room. Participants first completed the demographic questionnaire, followed by the personality test. Afterward, they reported their GPAs on the academic performance survey. All responses were recorded anonymously to protect participant confidentiality.
The data were analyzed using SPSS software, version 24. Pearson's correlation coefficient was used to assess the relationship between personality traits and academic performance.
Psychology study example analysis
The above example illustrates several good practices in writing a methods section.
- Clear description of participants: The researcher clearly stated the number, gender distribution, and age range of the participants, and also mentioned the selection criteria.
- Detailed information about materials: The researcher named the tests and surveys used and briefly described what they measure.
- Transparent procedure: The researcher provided a step-by-step guide to how the experiment was conducted, ensuring that it could be replicated by others.
- Explanation of data analysis: The researcher stated which software was used and what statistical tests were performed.
Environmental science study example
For this study, soil samples were collected from 10 different locations within the ABC National Park. The locations were chosen to represent a variety of habitats within the park, including grassland, wetland, and forest areas. The study was conducted in the spring season to ensure consistency in environmental conditions.
At each location, five soil samples were taken using a standard soil corer. The samples were taken from the top 10 cm of the soil, as this is where the majority of biological activity typically occurs. Each sample was immediately sealed in a sterile container to prevent contamination.
Back in the lab, the soil samples were analyzed for nutrient content and microbial diversity. Nutrient content, including levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, was measured using a soil nutrient testing kit from XYZ Company. Microbial diversity was assessed through DNA extraction and sequencing, using the DEF DNA extraction kit and the GHI sequencing platform.
The collected data were then analyzed using the JKL statistical software package. A one-way ANOVA was used to compare nutrient levels between the different habitats, while microbial diversity was evaluated using a diversity index.
In all cases, appropriate precautions were taken to minimize potential contamination and to ensure the accuracy of our measurements. This study was approved by the ABC National Park's Research Review Board.
Environmental science study example analysis
This example effectively demonstrates the correct structure and content for a methods section in environmental science.
- Clear explanation of sample collection: The researcher has detailed where, when, and how the soil samples were collected.
- Transparent process of sample analysis: The specific procedures and equipment used for analyzing the samples are clearly outlined, providing potential for replication.
- Methodical data analysis: The use of specific software and statistical tests is mentioned, providing clarity on how results were derived.
Linguistics study example
For this study, the use of passive voice in academic writing across disciplines was investigated. A corpus of 500 peer-reviewed journal articles was created, comprising 100 articles from each of the following disciplines: Social Sciences, Humanities, Natural Sciences, Applied Sciences, and Formal Sciences. Articles were selected randomly from journals indexed in the ABC Database from the year 2022.
The data collection tool was a script written in Python, utilizing the Natural Language Toolkit (NLTK) for text processing and analysis. The script identified and counted instances of passive voice in each article.
The articles were processed one by one, first being converted into plain text files to allow for easy processing. The Python script then ran on each text file, analyzing and storing the data on passive voice usage. This process was automated to minimize errors and ensure consistency.
For data analysis, the counts of passive voice instances were normalized by the total word count of each article to account for variations in article length. The differences in passive voice usage across disciplines were then statistically analyzed using a Chi-square test in the R software environment.
All procedures in this study were designed with consideration to copyright and fair use policies. The Python script used for this study is openly available for other researchers to use and modify.
Linguistics study example analysis
This example demonstrates effective writing of a methods section in a Linguistics study.
- Detailed description of the corpus: The researcher clearly defined the source and composition of the corpus, including the number of texts and their disciplinary distribution.
- Explanation of data collection tool and process: The researcher explained the software and process used for text analysis, providing enough detail for replication.
- Transparent data analysis: The researcher mentioned how they accounted for variations in article length and which statistical test was used for analysis.
Remember, although methods sections will differ across disciplines, they all should provide a clear, concise, and replicable roadmap of the research process.
The methods section of a research paper is a critical component that adds credibility to your research and allows others to replicate and verify your study. It involves providing detailed descriptions of the participants, materials and equipment used, the procedures followed, and the methods of data analysis.
While the exact content may vary depending on your research design and field of study, a well-crafted methods section will always focus on clarity, comprehensiveness, and transparency. The examples provided in this post illustrate good practices in diverse fields and can serve as a guide for you to construct your own.
Avoid common errors by creating a detailed outline, striving for balance in information, reviewing for relevance, including ethical considerations, and getting feedback from colleagues or mentors.
With these steps, you'll be well on your way to writing a high-quality methods section that bolsters your research paper's integrity and contributes meaningfully to your field.
Header image by Cytonn Photography .
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Elevate your research paper with expert editing services
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Methods Section for a Research Paper
A common piece of advice for authors preparing their first journal article for publication is to start with the methods section: just list everything that was done and go from there. While that might seem like a very practical approach to a first draft, if you do this without a clear outline and a story in mind, you can easily end up with journal manuscript sections that are not logically related to each other.
Since the methods section constitutes the core of your paper, no matter when you write it, you need to use it to guide the reader carefully through your story from beginning to end without leaving questions unanswered. Missing or confusing details in this section will likely lead to early rejection of your manuscript or unnecessary back-and-forth with the reviewers until eventual publication. Here, you will find some useful tips on how to make your methods section the logical foundation of your research paper.
Not just a list of experiments and methods
While your introduction section provides the reader with the necessary background to understand your rationale and research question (and, depending on journal format and your personal preference, might already summarize the results), the methods section explains what exactly you did and how you did it. The point of this section is not to list all the boring details just for the sake of completeness. The purpose of the methods sections is to enable the reader to replicate exactly what you did, verify or corroborate your results, or maybe find that there are factors you did not consider or that are more relevant than expected.
To make this section as easy to read as possible, you must clearly connect it to the information you provide in the introduction section before and the results section after, it needs to have a clear structure (chronologically or according to topics), and you need to present your results according to the same structure or topics later in the manuscript. There are also official guidelines and journal instructions to follow and ethical issues to avoid to ensure that your manuscript can quickly reach the publication stage.
Table of Contents:
- General Methods Structure: What is Your Story?
- What Methods Should You Report (and Leave Out)?
- Details Frequently Missing from the Methods Section
More Journal Guidelines to Consider
- Accurate and Appropriate Language in the Methods
General Methods Section Structure: What Is Your Story?
You might have conducted a number of experiments, maybe also a pilot before the main study to determine some specific factors or a follow-up experiment to clarify unclear details later in the process. Throwing all of these into your methods section, however, might not help the reader understand how everything is connected and how useful and appropriate your methodological approach is to investigate your specific research question. You therefore need to first come up with a clear outline and decide what to report and how to present that to the reader.
The first (and very important) decision to make is whether you present your experiments chronologically (e.g., Experiment 1, Experiment 2, Experiment 3… ), and guide the reader through every step of the process, or if you organize everything according to subtopics (e.g., Behavioral measures, Structural imaging markers, Functional imaging markers… ). In both cases, you need to use clear subheaders for the different subsections of your methods, and, very importantly, follow the same structure or focus on the same topics/measures in the results section so that the reader can easily follow along (see the two examples below).
If you are in doubt which way of organizing your experiments is better for your study, just ask yourself the following questions:
- Does the reader need to know the timeline of your study?
- Is it relevant that one experiment was conducted first, because the outcome of this experiment determined the stimuli or factors that went into the next?
- Did the results of your first experiment leave important questions open that you addressed in an additional experiment (that was maybe not planned initially)?
- Is the answer to all of these questions “no”? Then organizing your methods section according to topics of interest might be the more logical choice.
If you think your timeline, protocol, or setup might be confusing or difficult for the reader to grasp, consider adding a graphic, flow diagram, decision tree, or table as a visual aid.
What Methods Should You Report (and Leave Out)?
The answer to this question is quite simple–you need to report everything that another researcher needs to know to be able to replicate your study. Just imagine yourself reading your methods section in the future and trying to set up the same experiments again without prior knowledge. You would probably need to ask questions such as:
- Where did you conduct your experiments (e.g., in what kind of room, under what lighting or temperature conditions, if those are relevant)?
- What devices did you use? Are there specific settings to report?
- What specific software (and version of that software) did you use?
- How did you find and select your participants?
- How did you assign participants into groups?
- Did you exclude participants from the analysis? Why and how?
- Where did your reagents or antibodies come from? Can you provide a Research Resource Identifier (RRID) ?
- Did you make your stimuli yourself or did you get them from somewhere?
- Are the stimuli you used available for other researchers?
- What kind of questionnaires did you use? Have they been validated?
- How did you analyze your data? What level of significance did you use?
- Were there any technical issues and did you have to adjust protocols?
Note that for every experimental detail you provide, you need to tell the reader (briefly) why you used this type of stimulus/this group of participants/these specific amounts of reagents. If there is earlier published research reporting the same methods, cite those studies. If you did pilot experiments to determine those details, describe the procedures and the outcomes of these experiments. If you made assumptions about the suitability of something based on the literature and common practice at your institution, then explain that to the reader.
In a nutshell, established methods need to be cited, and new methods need to be clearly described and briefly justified. However, if the fact that you use a new approach or a method that is not traditionally used for the data or phenomenon you study is one of the main points of your study (and maybe already reflected in the title of your article), then you need to explain your rationale for doing so in the introduction already and discuss it in more detail in the discussion section .
Note that you also need to explain your statistical analyses at the end of your methods section. You present the results of these analyses later, in the results section of your paper, but you need to show the reader in the methods section already that your approach is either well-established or valid, even if it is new or unusual.
When it comes to the question of what details you should leave out, the answer is equally simple ‒ everything that you would not need to replicate your study in the future. If the educational background of your participants is listed in your institutional database but is not relevant to your study outcome, then don’t include that. Other things you should not include in the methods section:
- Background information that you already presented in the introduction section.
- In-depth comparisons of different methods ‒ these belong in the discussion section.
- Results, unless you summarize outcomes of pilot experiments that helped you determine factors for your main experiment.
Also, make sure your subheadings are as clear as possible, suit the structure you chose for your methods section, and are in line with the target journal guidelines. If you studied a disease intervention in human participants, then your methods section could look similar to this:
Since the main point of interest here are your patient-centered outcome variables, you would center your results section on these as well and choose your headers accordingly (e.g., Patient characteristics, Baseline evaluation, Outcome variable 1, Outcome variable 2, Drop-out rate ).
If, instead, you did a series of visual experiments investigating the perception of faces including a pilot experiment to create the stimuli for your actual study, you would need to structure your methods section in a very different way, maybe like this:
Since here the analysis and outcome of the pilot experiment are already described in the methods section (as the basis for the main experimental setup and procedure), you do not have to mention it again in the results section. Instead, you could choose the two main experiments to structure your results section ( Discrimination and classification, Familiarization and adaptation ), or divide the results into all your test measures and/or potential interactions you described in the methods section (e.g., Discrimination performance, Classification performance, Adaptation aftereffects, Correlation analysis ).
Details Commonly Missing from the Methods Section
Manufacturer information.
For laboratory or technical equipment, you need to provide the model, name of the manufacturer, and company’s location. The usual format for these details is the product name (company name, city, state) for US-based manufacturers and the product name (company name, city/town, country) for companies outside the US.
Sample size and power estimation
Power and sample size estimations are measures for how many patients or participants are needed in a study in order to detect statistical significance and draw meaningful conclusions from the results. Outside of the medical field, studies are sometimes still conducted with a “the more the better” approach in mind, but since many journals now ask for those details, it is better to not skip this important step.
Ethical guidelines and approval
In addition to describing what you did, you also need to assure the editor and reviewers that your methods and protocols followed all relevant ethical standards and guidelines. This includes applying for approval at your local or national ethics committee, providing the name or location of that committee as well as the approval reference number you received, and, if you studied human participants, a statement that participants were informed about all relevant experimental details in advance and signed consent forms before the start of the study. For animal studies, you usually need to provide a statement that all procedures included in your research were in line with the Declaration of Helsinki. Make sure you check the target journal guidelines carefully, as these statements sometimes need to be placed at the end of the main article text rather than in the method section.
Structure & word limitations
While many journals simply follow the usual style guidelines (e.g., APA for the social sciences and psychology, AMA for medical research) and let you choose the headers of your method section according to your preferred structure and focus, some have precise guidelines and strict limitations, for example, on manuscript length and the maximum number of subsections or header levels. Make sure you read the instructions of your target journal carefully and restructure your method section if necessary before submission. If the journal does not give you enough space to include all the details that you deem necessary, then you can usually submit additional details as “supplemental” files and refer to those in the main text where necessary.
Standardized checklists
In addition to ethical guidelines and approval, journals also often ask you to submit one of the official standardized checklists for different study types to ensure all essential details are included in your manuscript. For example, there are checklists for randomized clinical trials, CONSORT (Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials) , cohort, case-control, cross‐sectional studies, STROBE (STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology ), diagnostic accuracy, STARD (STAndards for the Reporting of Diagnostic accuracy studies) , systematic reviews and meta‐analyses PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta‐Analyses) , and Case reports, CARE (CAse REport) .
Make sure you check if the manuscript uses a single- or double-blind review procedure , and delete all information that might allow a reviewer to guess where the authors are located from the manuscript text if necessary. This means that your method section cannot list the name and location of your institution, the names of researchers who conducted specific tests, or the name of your institutional ethics committee.

Accurate and Appropriate Language in the Methods Section
Like all sections of your research paper, your method section needs to be written in an academic tone . That means it should be formal, vague expressions and colloquial language need to be avoided, and you need to correctly cite all your sources. If you describe human participants in your method section then you should be especially careful about your choice of words. For example, “participants” sounds more respectful than “subjects,” and patient-first language, that is, “patients with cancer,” is considered more appropriate than “cancer patients” by many journals.
Passive voice is often considered the standard for research papers, but it is completely fine to mix passive and active voice, even in the method section, to make your text as clear and concise as possible. Use the simple past tense to describe what you did, and the present tense when you refer to diagrams or tables. Have a look at this article if you need more general input on which verb tenses to use in a research paper .
Lastly, make sure you label all the standard tests and questionnaires you use correctly (look up the original publication when in doubt) and spell genes and proteins according to the common databases for the species you studied, such as the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee database for human studies .
Visit Wordvice AI’s AI Text Editor to receive a free grammar check and English editing services (including manuscript editing , paper editing , and dissertation editing ) before submitting your manuscript to journal editors.
A Scholar’s Guide to Writing the Methods Section of a Research Paper
Table of contents
- 1 What Is the Methods Section of a Research Paper
- 2 Methodology vs. Methods
- 3.1 Participants
- 3.2 Apparatus
- 3.3 Procedure
- 4.1 Methods and Results Should Match
- 4.2 Preparing the Statistical Methods Subsection
- 4.3 The Style of the Methodology
- 5 Key Information to Include in Methodology
- 6 Helping Hand in Writing Methodology Chapter
- 7.1 Which information is not included in the methodology section of a research article?
- 7.2 Where does the research methodology section go in a research paper?
- 7.3 What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative methods?
In the vast realm of academic writing, the research paper stands as a testament to a scholar’s systematic exploration of a particular subject. Each section of the paper plays a pivotal role, knitting together the fabric of the study. While the introduction sets the stage and the results showcase the findings, it is the Methods section that forms the backbone, providing a clear roadmap for any reader or researcher wishing to replicate or understand the study’s inner workings. As pivotal as it is, crafting an impeccable Methods section often poses challenges for researchers. This article aims to elucidate the intricacies of constructing a robust Methodology section in a research paper.
After reading our guide, you will:
- Get a clear understanding of the importance and purpose of the Methods in a research paper.
- Discover in details what should contain a comprehensive Methods section.
- Learn essentials on writing a Methodology in a research paper.
Now, let’s take a detailed look at these points!
What Is the Methods Section of a Research Paper
Do you have any questions about how to write the Methodology? Firstly, let’s define this section for research. The Methods or Methodology section of the research paper gives the road map for how the research was conducted. A well-crafted Methods section not only guides the researcher but also helps other scholars understand, replicate your study.
In other words, it’s like a recipe in a cookbook. If you want others to recreate your experiment or study, this section tells them exactly how you did it. It includes details about the steps you took, the tools or ingredients you used, and how you measured your results. This way, others can see if they get the same outcome when they follow your “recipe” or if they can trust your findings.
This means that the Methodology should be thoughtfully planned, executed, and reported. The reader should understand the basic research structure and the steps taken to conduct the study, including the research design, methods, gathered data, and data analysis techniques used.
The Methodology of a research study is essential for several reasons:
Validity and Reliability: A well-defined Methodology provides the foundation for the criteria and reliability of the study, particularly in addressing the research question for research. It helps to ensure that the research is conducted in a systematic and controlled manner and that the results are accurate and trustworthy.
Replicability: It allows other researchers to understand and replicate the study, which is important for building on existing knowledge and advancing the field.
Clarity and Transparency: A clear and concise Methods part makes it easier for readers to understand the research process and evaluate the results. This helps to increase transparency and build trust in the findings.
Justification of Approach: The research methodology provides a rationale for the approach taken, including why certain methods and techniques were chosen and how they relate to the question for research.
Evidence of Rigor: A well-executed research methodology demonstrates the rigor and thoroughness of the study, which is important for establishing the credibility of the results.
Methodology vs. Methods
In rigorous academic and research contexts, there is a distinction between “methods” and “methodology.” However, outside of strict scholarly circles or in more informal discussions, there might be some overlapping use. The “methods” generally refer to the specific techniques or procedures, while “methodology” dives into the theoretical framework and rationale behind those techniques. It’s essential to use the terms correctly in formal academic and research writings to maintain clarity and precision.
Nevertheless, in many research papers, the specifics of the methods (the “how”) are the primary focus, and the theoretical rationale (the “why”) might be briefly touched upon within the same section.
Structure of the Methodology In A Research Paper
The Methods section typically begins with a brief overview of its contents and a reiteration of the research question. This is followed by a description of the participants, detailing their demographics, and how they were recruited. The materials or apparatus used are then specified, from tools to equipment, with any unique specifications highlighted.
The core of the Methods section is the procedure, a step-by-step account of the study, from experimental tasks to the sequence of operations. This is complemented by an explanation of the experimental design, where the type of research design is described, along with the variables involved. Detailed accounts of how data was gathered, whether through surveys, interviews, or other methods, are provided, ensuring the reader understands the data collection nuances.
Critical to the credibility of the study is the section on statistical analysis, which reveals how data was processed, what statistical tests were used, and the software or tools employed. If the research involved humans or animals, the ethical considerations section becomes pivotal. Here, measures taken to ensure participants’ rights, confidentiality, and informed consent are documented. Towards the end, the limitations of the study are discussed, providing insights into potential biases or constraints faced during the research process. The section wraps up with a brief recap, emphasizing the methods’ role in ensuring the study’s integrity and reproducibility.
According to APA style , there are three major subsections to report here: participants, apparatus, and procedure.
Participants
This segment reports the characteristics of the participants involved in the experiment, the method of sampling, and the sample size.
- Characteristics
This details the demography of the respondents that may be relevant to the experiment. This includes but is not limited to age, gender, ethnicity or race, religion, level of education, socioeconomic status, origin of the population, and any restrictions.
✏️Example:
Fifty female undergraduate students between the ages of 19 and 23 participated in the experiment. All were sophomores in the Faculty of Engineering and native English speakers who lived on the university campus. The participants were separated into two groups of 25 students, each without any determining criteria. This study was conducted at the University of Alabama, USA .
- Sampling Strategy
Identify the selection criteria and whether the sample was random or not. Include it if you have access to data informing the percentage of people invited to participate and how many agreed. You should also report the selection mode; was it voluntary, or were the participants assigned to the study? Additionally, identify any compensation that was provided to participants.
The ethics board was petitioned, and approval was granted before the recruitment of participants commenced. All the female sophomores from the faculty of Engineering at the University of Alabama, USA, were invited to participate, and those who did were self-selected. In liaison with department heads, the students were offered additional credits in a faculty-wide course as compensation for their time.
- Sample Size
Identify the sample size per group, the statistical power you aimed to attain, whether you could attain it, and the analyses you used to determine the figures you arrived at. You should also include whether the final sample you got was what you initially required.
The required power for this experiment to detect a 15% effect at a significance level of .08 was 75%. To achieve this, we needed 25 participants in each group. The final sample met these conditions.
This subsection describes the materials and apparatus used in the experiment. It calls for detailed information on all devices and techniques used to collate data, measure suitable variables, and reach analysis, including tests and surveys. You must include a proper count of the number of apparatus used, their names, model number, manufacturer, reliability, and validity. For surveys, including the meaning of the formats used and the number of questions asked.
A survey that consisted of 15 multiple-choice questions was carried out to determine the safety of female students on the school campus. The participants were asked to answer the questions using a 5-point grading system (1 = Extremely True and 5 = Extremely False).
This includes the conditions in which data was collated, instructions given to the participants, and data analysis methods.
The two groups of participants were placed in two different classrooms at individual desks and given 10 minutes to answer the questions. They were instructed to give the first answers they thought of without thinking too deeply. Each group had a supervisor attached to it.
Writing a research paper requires a great deal of skill and knowledge, so if you need help compiling the Methods section of your paper, consider using a professional coursework writing service to help you.
Advice On How to Write the Methods Section
You already know the relevance of the Methods part to your research paper. Additionally, you must adhere to formatting guidelines specific for your field.
If you cannot write according to standards, you can use a research paper writing service to get good results. Go for one with good reviews and a super online reputation.
Here are some more tips for a concise and meticulously written Methodology:
- Method Introduction: Begin the section on methodology by introducing the methods used in the research. Provide a brief overview of the research design and the data collection and analysis techniques used.
- Methodological Connection: Establish the connection between the methodology and the research query.
- Instrument Introduction: Introduce the instruments used to assemble data, such as surveys, interviews, or observation. Provide a brief description of each instrument and how it will be used in the study.
- Analysis Discussion: Discuss the analysis techniques used to analyze the data collected. Explain how the data will be organized, coded, and analyzed to address the research query.
- Background Information: Provide background information about the methodology and the relevant literature. Explain how the methodology fits into the broader context of the research area and what it contributes to the current understanding of the topic.
- Sampling Process: Discuss the sampling process used in the study. Explain how the sample was selected, what criteria were used, and how the samples taken were determined.
- Limitations: It was required to discuss any research constraints in the past tense, such as limited sample sizes, issues with the data collection process, or issues with the analysis methods employed. Researchers had to explain how these constraints might have affected the study’s findings and conclusions.
Methods and Results Should Match
In the Methods section, the results obtained should be discussed based on the experimental procedures used. Explain the methodology behind the techniques used to acquire all the observations and results of the experiment in the right order. You can create a detailed flowchart or block flow diagram (BFD) to easily describe the complexities of the study and its procedures to the reader.
Preparing the Statistical Methods Subsection
The statistical analysis subsection comes at the end of the Methods section. It includes a thorough description of the analyzed data to arrive at the results and conclusion. Due to its technicality, it might be a little difficult and daunting to write. If this is the case, you can get the statistician who participated in the study to write it.
Here, you must indicate all the data variables, including the control variables, dependent and independent variables, and any potentially irrelevant variables that could affect your results and conclusion. Specify the exact tests carried out on the different types of data you have, the requirements you tested, like distribution normality, and all assumptions you initially applied.
You should also include all data alterations, possible mix-ups, confidence intervals or significance levels used, techniques for data analysis, and ensuing statistical tests that were employed. Furthermore, specify any criteria particular to the experiment, like set baselines and any specific software used to conduct the statistical analysis.
The Style of the Methodology
As mentioned earlier, it aims to explain how and why the experiment was carried out so that readers can understand it and possibly repeat the procedure.
Therefore, it is essential to be aware of your audience so you can modify your writing based on what they know and explain technical terms where necessary. If you are finding it difficult to write in the appropriate style, you can buy a research paper written by writers. You can find these writers on several platforms for college essays.
The methodology should read as though you describe the experiment to your reader. For this reason, it should be worded in third-person constructs and a passive voice. For example, you should use “We carried out a survey” and not “I carried out a survey.” Since the experiment has already been carried out, you must write the entire section in the past tense.
Key Information to Include in Methodology
Now you know what the Methods section is, what information must be included in this segment of your paper? Here’s a summary of the things you need to include:
- Literature review . The sources that helped in the methods are cited under this heading.
- Research participants. This includes all information about the study participants, including compensations, mode of selection, and demographics.
- Criteria for inclusion or exclusion include the factors determining what participants were eliminated and why.
- Grouping conditions are the factors determining the subgrouping of the chosen participants.
- Procedures. These are the conditions under which the experiment was carried out.
- Materials and apparatus. These include all devices, equipment, reliability, and validity.
- Statistical analysis. This is detailed information about the data, measured and analyzed, and the tests carried out.
Helping Hand in Writing Methodology Chapter
It can be challenging for researchers to adequately describe their study methodologies and strategies when writing the methodology chapter of a research report. Organizing and presenting complex material, retaining clarity and conciseness, and describing technical processes or approaches are among the usual difficulties.
To overcome these challenges, researchers can consider seeking feedback from peers, utilizing a https://papersowl.com/ or editor, and thoroughly reviewing and revising their methodology chapter multiple times. With the help of an essay writing service, you can ensure that your research paper is accurate and successful.
Which information is not included in the methodology section of a research article?
Where does the research methodology section go in a research paper, what is the difference between qualitative and quantitative methods, readers also enjoyed.

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article?
In contrast to past centuries, scientific researchers have been currently conducted systematically in all countries as part of an education strategy. As a consequence, scientists have published thousands of reports. Writing an effective article is generally a significant problem for researchers. All parts of an article, specifically the abstract, material and methods, results, discussion and references sections should contain certain features that should always be considered before sending a manuscript to a journal for publication. It is generally known that the material and methods section is a relatively easy section of an article to write. Therefore, it is often a good idea to begin by writing the materials and methods section, which is also a crucial part of an article. Because “reproducible results” are very important in science, a detailed account of the study should be given in this section. If the authors provide sufficient detail, other scientists can repeat their experiments to verify their findings. It is generally recommended that the materials and methods should be written in the past tense, either in active or passive voice. In this section, ethical approval, study dates, number of subjects, groups, evaluation criteria, exclusion criteria and statistical methods should be described sequentially. It should be noted that a well-written materials and methods section markedly enhances the chances of an article being published.
How to Write a Materials and Methods Section of a Scientific Article?
Up to the 18 th Century scientific researches were performed on a voluntary basis by certain scientists. However from the second half of the 19 th century, scientific development has gained momentum with the contributions of numerous scientists including Edison, Fleming, and Koch. In parallel with these developments, apparently each scientific field, and even their branches made, and still making magnificent progressions from the end of the 18 th century. Secondary to these developments, scientific researches have been implemented systematically by universities, and various institutions in every part of the world as an integral component of national strategies. Naturally, the number of researchers who performed scientific investigations or sponsored by various institutions increased considerably. Also, as is known very well, all over the world scientists, and researchers move from one place to another to disseminate scientific knowledge. All of these scientific efforts, and activities reflect on clinical practice, and hundreds of thousands, and millions scientific articles which we can currently gain access into all of them online. As indicated by the investigator Gerard Piel, “Without publication, science is dead” which explains the importance of publication. In other words, if you don’t share your investigation and knowledge, they don’t mean anything by themselves. Although sharing the knowledge is essential for writing a scientific paper, nowadays writing a scientific article is mostly learnt as a master-apprentice relationship, and therefore certain standards have not been established. This phenomenon creates serious stress especially for young investigators in their early stage of writing scientific papers. Indeed investigators receiving their residency training confront this reality finally during writing of their dissertations. Though sharing knowledge is known as a fundamental principle in writing a scientific paper, it creates difficulties in the whole world. Relevant to this issue, in the whole world investigations have been performed, and books have been written on the subject of how to write a scientific paper. Accordingly, in our country mostly local meetings, and courses have been organized. These organizations, and investigations should be performed. Indeed, nowadays, in the first assessments, the rejection rate of the journals by internationally acknowledged scientific indexes as “Science Citation İndex (SCI)” and “Science Citation İndex Expanded (SCI-extended” which have certain scientific standards, increases to 62 percent. As a matter of fact only 25% of Class A journals have been included in the lists of SCI, and SCI-extended.
As we all know very well, scientific articles consist of sections of summary, introduction, material, and methods, discussion, and references. Among them, conventionally Materials and Methods section has been reported as the most easily written or will be written section. Although it is known as the most easily written section, nearly 30% of the reasons for rejection are related to this section per se. Therefore due care, and attention should be given to the writing of this section. In the writing process of the ‘Material and Methods’ section, all achievements performed throughout the study period should be dealt with in consideration of certain criteria in a specific sequence. Since as a globally anticipated viewpoint, ‘Materials and Methods’ section can be written quite easily, it has been indicated that if difficulties are encountered in writing a manuscript, then one should start writing from this section. In writing this section, study design describing the type of the article, study subjects to be investigated, methods, and procedures of measurements should be provided under four main headings. [ 1 , 2 ] Accordingly, in brief, we can emphasize the importance of providing clear-cut, adequate, and detailed information in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section to the scientists who will read this scientific article. Meeting these criteria carries great importance with respect to the evaluation of reliability of the investigation by the readers, and reviewers, and also informing them about procedural method, design, data collection, and assessment methods of the investigation, Priorly, as is the case in all scientific investigations, one should be reminded about the importance, and indispensability of compliance with certain standard writing rules. Accordingly, rules of grammar should be obeyed, and if possible passive voice of simple past tense should be used. Related to these rules, use of verbs ‘investigated’, ‘evaluated’ or ‘performed’ will be appropriate. Recently, expressions showing the ownership of the investigation as ‘we performed’, ‘we evaluated’, ‘we implemented’ have taken priority. Since the important point is communication of the message contained in the scientific study, the message should be clearly comprehensible. While ensuring clarity of the message, use of flourishing, and irrelevant sentences should be avoided. [ 1 , 3 ] According to another approach, since our article will be read by professionals of other disciplines, it is important to comply with certain rules of writing. To that end, standard units of measurements, and international abbreviations should be used. Abbreviations should be explained within parentheses at their first mention in the manuscript. For instance let’s analyze the following sentence” The patients were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, complete urinalysis, PSA, and urinary system ultrasound” The abbreviation PSA is very well known by the urologist. However we shouldn’t forget that this article will be read by the professionals in other medical disciplines. Similarly this sentence should not be written as: “The patients were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, complete urinalysis PSA (prostate-specific antigen), and urinary system ultrasound.” Indeed the abbreviation should follow the explanation of this abbreviation. Then the appropriate expression of the sentence should be. “The patients were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, complete urinalysis, prostate-specific antigen (PSA), and urinary system ultrasound.”
In addition to the abovementioned information, in the beginning paragraphs of ‘Materials and Methods’ section of a clinical study the answers to the following questions should be absolutely provided:
- The beginning, and termination dates of the study period.
- Number of subjects/patients/experimental animals etc. enrolled in the study,
- Has the approval of the ethics committee been obtained?
- Study design (prospective, retrospective or other). [ 1 , 2 , 4 – 7 ]
Still additional features of the study design (cross-sectional) should be indicated. Apart from this, other types of study designs (randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled or double-blind, parallel control etc.) should be revealed.
The heading of the section “Materials and Methods” can be changed to “Patients and the Method” in accordance with writing rules of the journal in question. Indication of starting, and termination dates of a clinical study will facilitate scientific interpretation of the article. Accordingly, outcomes obtained during development phase of a newly implemented method might be considered differently from those acquired during conventional use of this method. Besides, incidence of the diseases, and number of affected people might vary under the impact of social fluctuations, and environmental factors. Therefore with this justification study period should be specified. Number of cases included in the study should be absolutely indicated in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section. It will be appropriate to determine study population after consultation to a statistician-and if required-following “power analysis” Accordingly, the need for a control group will be indicated based on the study design. Nowadays, as a requirement of patient rights, obtainment of approval from ethics committee should be indicated with its registration number. In addition, acquirement of informed consent forms from patients should be indicated. Ethics Committee approval should be obtained in prospective studies performed with study drugs. Otherwise in case of occurrence of adverse effects, it should be acknowledged that in compliance with Article #90 of the Turkish Criminal Law, a 3-year prison sentence is given to the guilty parties. [ 8 ] Since issues related to the Ethics Committee are the subject of another manuscript, they won’t be handled herein.
The following paragraph exemplifies clearly the aforementioned arguments: “After approval of the local ethics committee (BADK-22), informed consent forms from the patients were obtained, and a total of 176 cases with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) were retrospectively evaluated between January 2011, and December 2012.” In a prospectively designed study, methods used to communicate with the cases including face-to-face interviews, phone calls and/or e-mail should be indicated. [ 1 , 2 ] Each paragraph or subheading in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section should be in accordance with the related ones in the ‘Results’ section. In other words, the sequence of paragraphs, and subheadings in the ‘Results’ section should be the same in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section.
As a next step, names of the groups, and distribution of the cases in these groups should be indicated. For instance: the statement “Cases were divided into 3 groups based on their LUTS scores as. Groups 1 (0–9; n=91), 2 (10–18; n=66), and 3 (≥19; n=20)” clearly delineates the scope of the study at baseline.. In the ‘Materials and Methods’ section the number of study subjects should be absolutely documented. Herein, after assignment of names to groups, in the rest of the manuscript, these names should be used. For example instead of saying: “Mean ages of the cases with LUTS scores between 0–9, 10–18, and ≥19 were determined to be 63.2±2.1, 62.8±4.5, and 65.7±3.9 years, respectively” it will be more comprehensible to use the expression: “Mean ages of the Groups 1, 2, and 3 were specified as 63.2±2.1, 62.8±4.5, and 65.7±3.9 years.” (p=0.478). Expressions indicated in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section should not be repeated in the “Results” section. Thus, errors of repetition will be precluded. Following the abovementioned information, the evaluation method of the cases enrolled in the study should be indicated. Hence, results of medical history, physical examination, and if performed laboratory or radiological evaluations-in that order-should be indicated. The application of survey study-if any-should be investigated, and documented. Therefore, the following sentences encompass all the information stated above: “The cases were evaluated with detailed medical history, physical examination, measurements of serum follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone (T) levels, complete urinalysis, urinary flow rate, direct urinary system roentgenograms, urinary system ultrasound, and if required cyctoscopy. Lower urinary system complaints, and erectile dysfunction were evaluated using International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and International Erectile Function Scale (IIEF), respectively.” Apparently, questionnaire forms were used in the above-cited study. However, methods used for the evaluation of questionnaire forms, and significance of the results obtained, and if possible, the first performer of this survey should be written with accompanying references. In relation to the abovementioned questionnaires the following statements constitute standard expressions for the ‘Materials and Methods’ section: “International Prostate Symptom Score (IPPS) was used in the determination of the severity of prostatic symptoms. IPSS used to determine the severity of the disease, evaluate treatment response, and ascertain the symptomatic progression, is the most optimal scoring system recommended by European Association of Urology (EAU) which classifies the severity of the disease based on IPSS scores as mild (0–7), moderate (8–19), and severe symptomatic (20–35) disease. In the evaluation of sexual function International Erectile Function Scale (IIEF) was used. IIEF is one of the most prevalently used form for the patients who consulted for the complaints of sexual dysfunction Based on IIEF scores, the severity of the disease was classified as severe (1–10), moderate (11–16), mild to moderate (17–21), mild (22–25), and no ED (26–30).”
Whether the institutions of the authors working for should be written in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section can be a subject of debate, generally viewpoints favour provision of this information. However, in compliance with their writing rules, some journals do not favour open-label studies where name of the study site is indicated, and this principle is communicated to the author during editorial evaluation Besides, in the ‘Materials and Methods’ section, the brand of the study object, and its country of origin should be indicated. (ie. if radiological methods are used, then the brand of radiological equipment, and its manufacturing country should be specified. In a study entitled ‘The Impact of Computed Tomography in the Prediction of Post-Radical Nephrectomy Stage in Renal Tumours’ since the main topic of the study is computed tomography, the specifications of the equipment used should be explicitely indicated. On the other hand, the details of the medical method which can effect the outcomes of the study should be also recorded. Accordingly, the methods applied for percutaneous nephrolithotomy, ureterorenoscopy, varicocelectomy, transurethral prostatectomy, radical prostatectomy (perineal, open, laparoscopic or robotic should be absolutely indicated. Then inclusion, and exclusion criteria, and if used control group, and its characteristics should be documented. Thus the following paragraph about exclusion criteria will be appropriate: Patients with a history of neurogenic bladder, prostatic or abdominal operation, and transrectal ultrasound guided prostate biopsy (within the previous 6 months), those aged <40 or >70 years, individuals with a peak urine flow rate below 10 ml/sec, and residual urine more than 150 cc were not included in the study.” [ 1 – 3 , 9 ]
Some diseases mentioned in the “Materials and Methods” section require special monitorization procedures. In these cases the procedure of monitorization should be documented for the sake of the validity of the study in question. Accordingly, in conditions such as “nephrectomy, prostatectomy, orchidectomy, pyeloplasty, varicocelectomy, drug therapies, penile prosthesis, and urethral stricture” clinical follow-up protocols should be provided.
The abovementioned rules, and recommendations are most frequently valid for a clinical study, and some points indicated in experimental studies should be also considered. Types, weights, gender, and number of the animals used in animal studies should be absolutely specified. Besides condition of evaluation of experimental animals should be noted. Then as is the case with clinical studies, approval of the ethics committee should be obtained, and documented. Accordingly, the beginning paragraphs of the ‘Materials and Methods’ can be expressed as follows:
“In the study, 40 Wistar-Albino 6-month-old rats each weighing 350–400 g were used. After approval of the ethics committee (HADYEK-41) the study was performed within the frame of rules specified by the National Institute for animal experiments. The rats were divided into 3 groups. Hence, Group 1 (n=7) was accepted as the control group. The rats subjected to partial ureteral obstruction with or without oral carvedilol therapy at daily doses of 2 mg/kg maintained for 7 days constituted Groups 3 (n=8), and 2 (n=8), respectively. Each group of 4 rats was housed in standard cages with an area of 40×60 cm. The animals were fed with standard 8 mm food pellets, and fresh daily tap water. The rats were kept in the cages under 12 hours of light, and 12 hours of dark. Ambient temperature, and humidity were set at 22±2°C, and 50±10%, respectively.”
Herein, the method, and agent of anesthesia used (local or general anesthesia) in surgical procedures, and then the experimental method applied should be clearly indicated. For example the following sentences explain our abovementioned arguments; “All surgical procedures were performed under xylazine-ketamine anesthesia. In all groups, ureters were approached through midline abdominal incision. In Group 1, ureters were manipulated without causing obstruction. Results of biochemical, and pathological evaluations performed in Group 1 were considered as baseline values.”
“Through a midline abdominal incision partial ureteral obstruction was achieved by embedding two-thirds of the distal part of the left ureter into psoas muscle using 4/0 silk sutures as described formerly by Wen et al. [ 10 ] ( Figure 1 ). [ 11 ] All rats were subjected to left nephrectomies at the end of the experimental study.” As formulated by the above paragraph, if the method used is not widely utilized, then the first researcher who describes the method should be indicated with relevant references. One or more than one figures with a good resolution, and easily comprehensible legends should be also included in the explanation of the experimental model. For very prevalently used experimental models as torsion models cited in the “Materials and Methods” section, there is no need to include figures in the manuscript.

Partial ureteral obstruction model [ 11 ]
Appropriate signs, and marks placed on the figure will facilitate comprehension of the legends ( Figure 2 ).

Ureteral segments (black arrows) seen in a rat partial ureteral obstruction model [ 11 ]
The signs used will also improve intelligibility of the target. The figures should be indicated within parentheses in their first mention in the “Materials and Methods” section. Headings and as a prevalent convention legends of the figures should be indicated at the end of the manuscript.
If a different method is used in the study, this should be explained in detail. For instance, in a study where the effect of smoking on testes was investigated, the method, and the applicator used to expose rats to cigarette smoke should be indicated in the ‘Methods’ section following classical description. Relevant to the study in question, the following paragraph explaining the study method should be written: “A glass chamber with dimensions of 75 × 50 × 50 cm was prepared, and divided into 4 compartments with wire fences. The rats in the 2., and 4. cages were placed in these compartments. Each compartment contained 4 rats. Cigarette smoke was produced using one cigarette per hour, and smoke coming from the tip, and the filter of the lighted cigarette was pumped into the gas chamber with a pneumatic motor. The rats were exposed to smoke of 6 cigarettes for 6 hours. The compartments of the rats were changed every day so as to achieve balanced exposure of the rats to cigarette smoke.” [ 12 ]
Meanwhile, chemical names, doses, and routes of administration of the substances used in experimental studies should be indicated. If the substance used is a solution or an antibody, then manufacturing firm, and its country should be indicated in parenthesis. This approach can be exemplified as “Animals used in experiments were randomized into 4 groups of 8 animals. Each group was housed in 2 cages each containing 4 animals. The first group did not undergo any additional procedure (Group 1). The second group was exposed to cigarette smoke (Group 2). The third (Group 3), and the fourth (Group 4) groups received daily intraperitoneal injectable doses of 10 mg/kg resveratrol (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). The Group 4 was also exposed to cigarette smoke. [ 12 ]
After all of these procedures, method, and analytical procedure of histopathological examination used should be described-if possible-by a pathologist Similarly, biochemical method used should be referenced, and written by the department of clinical chemistry. It can be inferred that each division should describe its own method. In other words, histopathological, microbiological, and pharmacological method should be described in detail by respective divisions.
If we summarize all the information stated above, understandably sharing of the scientific knowledge is essential.. Since reproducibility of a study demonstrates the robustness of a study, with the detailed approaches indicated above, reproducibility of our study is provided, and the relevant questions of “How?”, and “How much?” are answered. Besides, since ‘Materials, and Methods’, and ‘Results’ sections will constitute a meaningful whole, explanations of all information related to the data mentioned in the ‘Results’ section should be provided. As an important point not to be forgotten, evaluation or measurement method used for each parameter indicated in the ‘Results’ section should be expounded in the “Materials and Methods” section. For example if you used an expression in the” Results” section like “median body mass index (BMI) of the patients was 27.42 kg/m 2 ”, then you should beforehand indicate that comparative evaluation of BMIs will be done in the “Materials and Methods” section. In addition, the description, and significance of the values expressed in the “Results” section should be indicated in the “Materials and Methods” section. In other words, it should be stated that the patients were evaluated based on their BMIs as normal (18–24.9 kg/m 2 ), overweight (25 kg/m 2 –40 kg/m 2 ), and morbid obesity (>40 kg/m 2 ). If you encounter difficulties in writing “Materials and Methods” section, also a valid approach for other sections, firstly simple headings can be written, then you can go into details. In brief, for every parameter, the reader should get clear-cut answers to the questions such as “How did they evaluate this parameter, and which criteria were used?”. [ 1 , 3 , 13 – 15 ]
The last paragraph of the ‘Materials, and Methods’ section should naturally involve statistical evaluations. This section should be written by statisticians. Accordingly, the preferred statistical method, and the justifications for this preference should be indicated. In conventional statistical evaluations, provision of details is not required. In information indicated above, the statement “For statistical analysis, ANOVA test, chi-square test, T test, Kruskal-Wallis test have been used.” is not required very much. Instead, more appropriate expression will be a statement indicating that recommendations of a knowledgeable, and an experienced statistician were taken into consideration or advanced statistical information was reflected on the statistical evaluations as follows: “Chi-square tests were used in intergroup comparisons of categorical variables, and categorical variables were expressed as numbers, and percentages. In comparisons between LUTS, and ED as for age, independent two samples t-test was used. In the evaluation of the factors effective on erectile dysfunction multivariate logistic regresssion test was used. P values lower than 0.05 were considered as statistically significant The calculations were performed using a statistical package program (PASW v18, SPSS Inc, Chicago, IL).” Herein, the type of statistical package used for statistical methods should be emphasized.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Manuscript
Affiliation.
- 1 Respiratory Care Services, Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, Arkansas. [email protected].
- PMID: 37643870
- PMCID: PMC10676260 (available on 2024-12-01 )
- DOI: 10.4187/respcare.11437
The methods section of a manuscript is one of the most important parts of a research paper because it provides information on the validity of the study and credibility of the results. Inadequate description of the methods has been reported as one of the main reasons for manuscript rejection. The methods section must include sufficient detail so that others could repeat the study and reproduce the results. The structure of the methods section should flow logically and chronologically. There are multiple components of methods sections, including study design, materials used, study procedures, and data analysis. Each element must be adequately described and thoroughly detailed to provide an understanding of how the results were obtained and how to interpret the findings. Studies that involved humans or animals must include an ethics statement of approval from the appropriate governing body. The methods section should explain how subjects were identified and should state inclusion and exclusion criteria. All materials used to complete the study should be described in detail, including equipment, drugs, gases, chemicals, treatments, interventions, or other items. Study procedures should outline all steps taken to obtain the results and clearly state the outcome measures. Subheadings might be helpful for organizing the methods section into subsections when there is a considerable amount of information to report. A well-written methods section will guide the reader through the research process and provide adequate information to evaluate study validity and reproduce the work. The purpose of this paper is to provide guidance for writing the methods section of a manuscript.
Keywords: manuscript; methods; publication; research; research paper; science writing; study protocol.
Copyright © 2023 by Daedalus Enterprises.
PubMed Disclaimer
Conflict of interest statement
Ms Willis is a Section Editor for Respiratory Care.
Similar articles
- Publishing particulars: Part 2. Tips for effective manuscript development. Seals DR. Seals DR. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2023 Mar 1;324(3):R393-R408. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00267.2022. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36749294 Review.
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, Moraleda C, Rogers L, Daniels K, Green P. Crider K, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
- The Principles of Biomedical Scientific Writing: Materials and Methods. Ghasemi A, Bahadoran Z, Zadeh-Vakili A, Montazeri SA, Hosseinpanah F. Ghasemi A, et al. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Jan 28;17(1):e88155. doi: 10.5812/ijem.88155. eCollection 2019 Jan. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 30881471 Free PMC article. Review.
- How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article? Erdemir F. Erdemir F. Turk J Urol. 2013 Sep;39(Suppl 1):10-5. doi: 10.5152/tud.2013.047. Turk J Urol. 2013. PMID: 26328129 Free PMC article.
- How to write the methods section of a research paper. Kallet RH. Kallet RH. Respir Care. 2004 Oct;49(10):1229-32. Respir Care. 2004. PMID: 15447808
- Statistics for the Non-Statistician: How to Read the Respiratory Care Literature. Hess DR. Hess DR. Respir Care. 2024 Mar 27;69(4):500-515. doi: 10.4187/respcare.11860. Respir Care. 2024. PMID: 38538021 Review.
- The Peer Review Process. Willis LD. Willis LD. Respir Care. 2024 Mar 27;69(4):492-499. doi: 10.4187/respcare.11838. Respir Care. 2024. PMID: 38538018
- Miller AG. How to write an abstract for presentation at a scientific meeting. Respir Care 2023;68(11):1569-1575. - PMC - PubMed
- Willis LD. How to present your research findings at a scientific meeting. Respir Care 2023;68(11):1598-1605. - PMC - PubMed
- Miller AG. Moving from abstract to manuscript. Respir Care 2023. [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.4187/respcare.11370. - PMC - PubMed
- Branson RD. Anatomy of a research paper. Respir Care 2004;49(10):1222-1228. - PubMed
- Hess DR. Research and publication in respiratory care. Respir Care 2023;68(8):1171-1173. - PMC - PubMed
- Search in MeSH
Related information
Linkout - more resources, full text sources.
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Courses in spotlight
LEARNING PATH
Research Writing Courses
Masterclasses and webinars.
MASTERCLASS
Essential thinking strategies for researchers - By Dr. David Eagleman
Know your data: decoding the art of statistical analysis - by dr. jo roislien.
Popular Topics
- Editage One platform for all researcher needs
- Paperpal AI-powered academic writing assistant
- R Discovery Your #1 AI companion for literature search
- Mind the Graph AI tool for graphics, illustrations, and artwork
- [email protected]
- Request a callback
Methods Section In Research Paper: Writing The Best Research Methodology
Course in Journal Publication
Gareth Dyke Paleontologist, Editor-in-Chief, Historical Biology, Taylor & Francis
Get a comprehensive guide with expert advice, practical tips and a reliable checklist to showcase and explain the robust methods used to conduct your research study.
719 Enrolled
1 Checklist
video + text
Certificate on completion
Online, On-demand learning
Access on any device
4 modules each
What you learn
The importance of a well-written methods section
The basic flow when planning the methods section
How to structure individual elements in the methods section
Main techniques to write an effective methods section
How to avoid making critical errors in the methods section
How to use a checklist and apply your learnings to showcase your methods
Description
A well-scripted methods sections lays the foundation for your research by outlining the different methods you used to derive your brilliant results. Your peers look for essential details on how to replicate the experiments of your study in this section, which is also what readers use to understand your research better.
This structured course covers all the basics of writing and structuring the methods section, including advice on common errors that most authors make and how to avoid them. Great for authors looking to enhance their technical writing skills, this comprehensive guide includes an assortment of interactive quizzes, easy-to-follow tips to structure and describe your methods effectively, and a handy checklist to ensure that your methods section is accurate and detailed.
Featured in
LECTURE 1 | Video
Let's start with the basics!
LECTURE 2 | Video
Structuring the methods section: What you should know
LECTURE 3 | Video
Writing the methods section: Tips and guidelines
LECTURE 4 | Video
Let’s do a quick recap!
Instructor (1)

Gareth Dyke
Paleontologist, Editor-in-Chief, Historical Biology, Taylor & Francis
Gareth Dyke manages the Taylor & Francis journal Historical Biology as Editor-in-Chief. His research has been widely covered in the media and he is often invited to present talks and lead workshops around the world, most recently in Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, China, Colombia, Spain, Hungary, Romania, and Slovakia.
A regular contributor to The Conversation, he has also written numerous news…
Helen Palik
Very interesting and I learnt more in detail about writing the methods section of my paper.
Related courses
- Journal Publication
Methods Section
From this instructor

Statistical and research design problems to avoid in manuscripts

How to avoid rejections in publishing research papers

Wiley experts share getting published in international journals –…

Preparing a professional submission package and getting published in…

Wolters Kluwer EIC shares pet peeves that lead to manuscript…

How to write an article in the IMRaD format: A section-by-section…

Predatory Publishing
Copyright 2024 Cactus Communications. All rights reserved.
Human Subjects Office
Medical terms in lay language.
Please use these descriptions in place of medical jargon in consent documents, recruitment materials and other study documents. Note: These terms are not the only acceptable plain language alternatives for these vocabulary words.
This glossary of terms is derived from a list copyrighted by the University of Kentucky, Office of Research Integrity (1990).
For clinical research-specific definitions, see also the Clinical Research Glossary developed by the Multi-Regional Clinical Trials (MRCT) Center of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard and the Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC) .
Alternative Lay Language for Medical Terms for use in Informed Consent Documents
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
ABDOMEN/ABDOMINAL body cavity below diaphragm that contains stomach, intestines, liver and other organs ABSORB take up fluids, take in ACIDOSIS condition when blood contains more acid than normal ACUITY clearness, keenness, esp. of vision and airways ACUTE new, recent, sudden, urgent ADENOPATHY swollen lymph nodes (glands) ADJUVANT helpful, assisting, aiding, supportive ADJUVANT TREATMENT added treatment (usually to a standard treatment) ANTIBIOTIC drug that kills bacteria and other germs ANTIMICROBIAL drug that kills bacteria and other germs ANTIRETROVIRAL drug that works against the growth of certain viruses ADVERSE EFFECT side effect, bad reaction, unwanted response ALLERGIC REACTION rash, hives, swelling, trouble breathing AMBULATE/AMBULATION/AMBULATORY walk, able to walk ANAPHYLAXIS serious, potentially life-threatening allergic reaction ANEMIA decreased red blood cells; low red cell blood count ANESTHETIC a drug or agent used to decrease the feeling of pain, or eliminate the feeling of pain by putting you to sleep ANGINA pain resulting from not enough blood flowing to the heart ANGINA PECTORIS pain resulting from not enough blood flowing to the heart ANOREXIA disorder in which person will not eat; lack of appetite ANTECUBITAL related to the inner side of the forearm ANTIBODY protein made in the body in response to foreign substance ANTICONVULSANT drug used to prevent seizures ANTILIPEMIC a drug that lowers fat levels in the blood ANTITUSSIVE a drug used to relieve coughing ARRHYTHMIA abnormal heartbeat; any change from the normal heartbeat ASPIRATION fluid entering the lungs, such as after vomiting ASSAY lab test ASSESS to learn about, measure, evaluate, look at ASTHMA lung disease associated with tightening of air passages, making breathing difficult ASYMPTOMATIC without symptoms AXILLA armpit
BENIGN not malignant, without serious consequences BID twice a day BINDING/BOUND carried by, to make stick together, transported BIOAVAILABILITY the extent to which a drug or other substance becomes available to the body BLOOD PROFILE series of blood tests BOLUS a large amount given all at once BONE MASS the amount of calcium and other minerals in a given amount of bone BRADYARRHYTHMIAS slow, irregular heartbeats BRADYCARDIA slow heartbeat BRONCHOSPASM breathing distress caused by narrowing of the airways
CARCINOGENIC cancer-causing CARCINOMA type of cancer CARDIAC related to the heart CARDIOVERSION return to normal heartbeat by electric shock CATHETER a tube for withdrawing or giving fluids CATHETER a tube placed near the spinal cord and used for anesthesia (indwelling epidural) during surgery CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) brain and spinal cord CEREBRAL TRAUMA damage to the brain CESSATION stopping CHD coronary heart disease CHEMOTHERAPY treatment of disease, usually cancer, by chemical agents CHRONIC continuing for a long time, ongoing CLINICAL pertaining to medical care CLINICAL TRIAL an experiment involving human subjects COMA unconscious state COMPLETE RESPONSE total disappearance of disease CONGENITAL present before birth CONJUNCTIVITIS redness and irritation of the thin membrane that covers the eye CONSOLIDATION PHASE treatment phase intended to make a remission permanent (follows induction phase) CONTROLLED TRIAL research study in which the experimental treatment or procedure is compared to a standard (control) treatment or procedure COOPERATIVE GROUP association of multiple institutions to perform clinical trials CORONARY related to the blood vessels that supply the heart, or to the heart itself CT SCAN (CAT) computerized series of x-rays (computerized tomography) CULTURE test for infection, or for organisms that could cause infection CUMULATIVE added together from the beginning CUTANEOUS relating to the skin CVA stroke (cerebrovascular accident)
DERMATOLOGIC pertaining to the skin DIASTOLIC lower number in a blood pressure reading DISTAL toward the end, away from the center of the body DIURETIC "water pill" or drug that causes increase in urination DOPPLER device using sound waves to diagnose or test DOUBLE BLIND study in which neither investigators nor subjects know what drug or treatment the subject is receiving DYSFUNCTION state of improper function DYSPLASIA abnormal cells
ECHOCARDIOGRAM sound wave test of the heart EDEMA excess fluid collecting in tissue EEG electric brain wave tracing (electroencephalogram) EFFICACY effectiveness ELECTROCARDIOGRAM electrical tracing of the heartbeat (ECG or EKG) ELECTROLYTE IMBALANCE an imbalance of minerals in the blood EMESIS vomiting EMPIRIC based on experience ENDOSCOPIC EXAMINATION viewing an internal part of the body with a lighted tube ENTERAL by way of the intestines EPIDURAL outside the spinal cord ERADICATE get rid of (such as disease) Page 2 of 7 EVALUATED, ASSESSED examined for a medical condition EXPEDITED REVIEW rapid review of a protocol by the IRB Chair without full committee approval, permitted with certain low-risk research studies EXTERNAL outside the body EXTRAVASATE to leak outside of a planned area, such as out of a blood vessel
FDA U.S. Food and Drug Administration, the branch of federal government that approves new drugs FIBROUS having many fibers, such as scar tissue FIBRILLATION irregular beat of the heart or other muscle
GENERAL ANESTHESIA pain prevention by giving drugs to cause loss of consciousness, as during surgery GESTATIONAL pertaining to pregnancy
HEMATOCRIT amount of red blood cells in the blood HEMATOMA a bruise, a black and blue mark HEMODYNAMIC MEASURING blood flow HEMOLYSIS breakdown in red blood cells HEPARIN LOCK needle placed in the arm with blood thinner to keep the blood from clotting HEPATOMA cancer or tumor of the liver HERITABLE DISEASE can be transmitted to one’s offspring, resulting in damage to future children HISTOPATHOLOGIC pertaining to the disease status of body tissues or cells HOLTER MONITOR a portable machine for recording heart beats HYPERCALCEMIA high blood calcium level HYPERKALEMIA high blood potassium level HYPERNATREMIA high blood sodium level HYPERTENSION high blood pressure HYPOCALCEMIA low blood calcium level HYPOKALEMIA low blood potassium level HYPONATREMIA low blood sodium level HYPOTENSION low blood pressure HYPOXEMIA a decrease of oxygen in the blood HYPOXIA a decrease of oxygen reaching body tissues HYSTERECTOMY surgical removal of the uterus, ovaries (female sex glands), or both uterus and ovaries
IATROGENIC caused by a physician or by treatment IDE investigational device exemption, the license to test an unapproved new medical device IDIOPATHIC of unknown cause IMMUNITY defense against, protection from IMMUNOGLOBIN a protein that makes antibodies IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE drug which works against the body's immune (protective) response, often used in transplantation and diseases caused by immune system malfunction IMMUNOTHERAPY giving of drugs to help the body's immune (protective) system; usually used to destroy cancer cells IMPAIRED FUNCTION abnormal function IMPLANTED placed in the body IND investigational new drug, the license to test an unapproved new drug INDUCTION PHASE beginning phase or stage of a treatment INDURATION hardening INDWELLING remaining in a given location, such as a catheter INFARCT death of tissue due to lack of blood supply INFECTIOUS DISEASE transmitted from one person to the next INFLAMMATION swelling that is generally painful, red, and warm INFUSION slow injection of a substance into the body, usually into the blood by means of a catheter INGESTION eating; taking by mouth INTERFERON drug which acts against viruses; antiviral agent INTERMITTENT occurring (regularly or irregularly) between two time points; repeatedly stopping, then starting again INTERNAL within the body INTERIOR inside of the body INTRAMUSCULAR into the muscle; within the muscle INTRAPERITONEAL into the abdominal cavity INTRATHECAL into the spinal fluid INTRAVENOUS (IV) through the vein INTRAVESICAL in the bladder INTUBATE the placement of a tube into the airway INVASIVE PROCEDURE puncturing, opening, or cutting the skin INVESTIGATIONAL NEW DRUG (IND) a new drug that has not been approved by the FDA INVESTIGATIONAL METHOD a treatment method which has not been proven to be beneficial or has not been accepted as standard care ISCHEMIA decreased oxygen in a tissue (usually because of decreased blood flow)
LAPAROTOMY surgical procedure in which an incision is made in the abdominal wall to enable a doctor to look at the organs inside LESION wound or injury; a diseased patch of skin LETHARGY sleepiness, tiredness LEUKOPENIA low white blood cell count LIPID fat LIPID CONTENT fat content in the blood LIPID PROFILE (PANEL) fat and cholesterol levels in the blood LOCAL ANESTHESIA creation of insensitivity to pain in a small, local area of the body, usually by injection of numbing drugs LOCALIZED restricted to one area, limited to one area LUMEN the cavity of an organ or tube (e.g., blood vessel) LYMPHANGIOGRAPHY an x-ray of the lymph nodes or tissues after injecting dye into lymph vessels (e.g., in feet) LYMPHOCYTE a type of white blood cell important in immunity (protection) against infection LYMPHOMA a cancer of the lymph nodes (or tissues)
MALAISE a vague feeling of bodily discomfort, feeling badly MALFUNCTION condition in which something is not functioning properly MALIGNANCY cancer or other progressively enlarging and spreading tumor, usually fatal if not successfully treated MEDULLABLASTOMA a type of brain tumor MEGALOBLASTOSIS change in red blood cells METABOLIZE process of breaking down substances in the cells to obtain energy METASTASIS spread of cancer cells from one part of the body to another METRONIDAZOLE drug used to treat infections caused by parasites (invading organisms that take up living in the body) or other causes of anaerobic infection (not requiring oxygen to survive) MI myocardial infarction, heart attack MINIMAL slight MINIMIZE reduce as much as possible Page 4 of 7 MONITOR check on; keep track of; watch carefully MOBILITY ease of movement MORBIDITY undesired result or complication MORTALITY death MOTILITY the ability to move MRI magnetic resonance imaging, diagnostic pictures of the inside of the body, created using magnetic rather than x-ray energy MUCOSA, MUCOUS MEMBRANE moist lining of digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary tracts MYALGIA muscle aches MYOCARDIAL pertaining to the heart muscle MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION heart attack
NASOGASTRIC TUBE placed in the nose, reaching to the stomach NCI the National Cancer Institute NECROSIS death of tissue NEOPLASIA/NEOPLASM tumor, may be benign or malignant NEUROBLASTOMA a cancer of nerve tissue NEUROLOGICAL pertaining to the nervous system NEUTROPENIA decrease in the main part of the white blood cells NIH the National Institutes of Health NONINVASIVE not breaking, cutting, or entering the skin NOSOCOMIAL acquired in the hospital
OCCLUSION closing; blockage; obstruction ONCOLOGY the study of tumors or cancer OPHTHALMIC pertaining to the eye OPTIMAL best, most favorable or desirable ORAL ADMINISTRATION by mouth ORTHOPEDIC pertaining to the bones OSTEOPETROSIS rare bone disorder characterized by dense bone OSTEOPOROSIS softening of the bones OVARIES female sex glands
PARENTERAL given by injection PATENCY condition of being open PATHOGENESIS development of a disease or unhealthy condition PERCUTANEOUS through the skin PERIPHERAL not central PER OS (PO) by mouth PHARMACOKINETICS the study of the way the body absorbs, distributes, and gets rid of a drug PHASE I first phase of study of a new drug in humans to determine action, safety, and proper dosing PHASE II second phase of study of a new drug in humans, intended to gather information about safety and effectiveness of the drug for certain uses PHASE III large-scale studies to confirm and expand information on safety and effectiveness of new drug for certain uses, and to study common side effects PHASE IV studies done after the drug is approved by the FDA, especially to compare it to standard care or to try it for new uses PHLEBITIS irritation or inflammation of the vein PLACEBO an inactive substance; a pill/liquid that contains no medicine PLACEBO EFFECT improvement seen with giving subjects a placebo, though it contains no active drug/treatment PLATELETS small particles in the blood that help with clotting POTENTIAL possible POTENTIATE increase or multiply the effect of a drug or toxin (poison) by giving another drug or toxin at the same time (sometimes an unintentional result) POTENTIATOR an agent that helps another agent work better PRENATAL before birth PROPHYLAXIS a drug given to prevent disease or infection PER OS (PO) by mouth PRN as needed PROGNOSIS outlook, probable outcomes PRONE lying on the stomach PROSPECTIVE STUDY following patients forward in time PROSTHESIS artificial part, most often limbs, such as arms or legs PROTOCOL plan of study PROXIMAL closer to the center of the body, away from the end PULMONARY pertaining to the lungs
QD every day; daily QID four times a day
RADIATION THERAPY x-ray or cobalt treatment RANDOM by chance (like the flip of a coin) RANDOMIZATION chance selection RBC red blood cell RECOMBINANT formation of new combinations of genes RECONSTITUTION putting back together the original parts or elements RECUR happen again REFRACTORY not responding to treatment REGENERATION re-growth of a structure or of lost tissue REGIMEN pattern of giving treatment RELAPSE the return of a disease REMISSION disappearance of evidence of cancer or other disease RENAL pertaining to the kidneys REPLICABLE possible to duplicate RESECT remove or cut out surgically RETROSPECTIVE STUDY looking back over past experience
SARCOMA a type of cancer SEDATIVE a drug to calm or make less anxious SEMINOMA a type of testicular cancer (found in the male sex glands) SEQUENTIALLY in a row, in order SOMNOLENCE sleepiness SPIROMETER an instrument to measure the amount of air taken into and exhaled from the lungs STAGING an evaluation of the extent of the disease STANDARD OF CARE a treatment plan that the majority of the medical community would accept as appropriate STENOSIS narrowing of a duct, tube, or one of the blood vessels in the heart STOMATITIS mouth sores, inflammation of the mouth STRATIFY arrange in groups for analysis of results (e.g., stratify by age, sex, etc.) STUPOR stunned state in which it is difficult to get a response or the attention of the subject SUBCLAVIAN under the collarbone SUBCUTANEOUS under the skin SUPINE lying on the back SUPPORTIVE CARE general medical care aimed at symptoms, not intended to improve or cure underlying disease SYMPTOMATIC having symptoms SYNDROME a condition characterized by a set of symptoms SYSTOLIC top number in blood pressure; pressure during active contraction of the heart
TERATOGENIC capable of causing malformations in a fetus (developing baby still inside the mother’s body) TESTES/TESTICLES male sex glands THROMBOSIS clotting THROMBUS blood clot TID three times a day TITRATION a method for deciding on the strength of a drug or solution; gradually increasing the dose T-LYMPHOCYTES type of white blood cells TOPICAL on the surface TOPICAL ANESTHETIC applied to a certain area of the skin and reducing pain only in the area to which applied TOXICITY side effects or undesirable effects of a drug or treatment TRANSDERMAL through the skin TRANSIENTLY temporarily TRAUMA injury; wound TREADMILL walking machine used to test heart function
UPTAKE absorbing and taking in of a substance by living tissue
VALVULOPLASTY plastic repair of a valve, especially a heart valve VARICES enlarged veins VASOSPASM narrowing of the blood vessels VECTOR a carrier that can transmit disease-causing microorganisms (germs and viruses) VENIPUNCTURE needle stick, blood draw, entering the skin with a needle VERTICAL TRANSMISSION spread of disease
WBC white blood cell

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research papers in the social and natural sciences often follow APA style. This article focuses on reporting quantitative research methods. In your APA methods section, you should report enough information to understand and replicate your study, including detailed information on the sample, measures, and procedures used.
The methods section is a fundamental section of any paper since it typically discusses the 'what', 'how', 'which', and 'why' of the study, which is necessary to arrive at the final conclusions. In a research article, the introduction, which serves to set the foundation for comprehending the background and results is usually ...
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail ...
4. Use subheadings: Dividing the Methods section in terms of the experiments helps the reader to follow the section better. You may write the specific objective of each experiment as a subheading. Alternatively, if applicable, the name of each experiment can also be used as subheading. 5.
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded ...
The methods section should describe what was done to answer the research question, describe how it was done, justify the experimental design, and explain how the results were analyzed. Scientific writing is direct and orderly. Therefore, the methods section structure should: describe the materials used in the study, explain how the materials ...
Writing* / standards. The methods section of a research paper provides the information by which a study's validity is judged. Therefore, it requires a clear and precise description of how an experiment was done, and the rationale for why specific experimental procedures were chosen. The methods section should describe wh ….
The methodology section of your paper describes how your research was conducted. This information allows readers to check whether your approach is accurate and dependable. A good methodology can help increase the reader's trust in your findings. First, we will define and differentiate quantitative and qualitative research.
Methods section is the easiest part of the scientific paper and you can start writing it down even when the research is unfinished. It has to be written in the past tense because you have already written the proposal and either you have started or have conducted the study. The basic elements of the methods section are study design, setting and ...
In this first subsection, you will need to identify the participants of your experiment or study. You should include: How many people took part, and how many were assigned to the experimental condition. How they were selected for participation. Any relevant demographic information (e.g., age, sex, ethnicity) You'll also need to address ...
1. Focus on your objectives and research questions. The methodology section should clearly show why your methods suit your objectives and convince the reader that you chose the best possible approach to answering your problem statement and research questions. 2.
The writing of the Methods section should be clear and orderly to avoid confusion and ambiguity. The methods section should ideally be structured in a set of subsections describing its main content. 13, 14, 15 A possible structure is proposed along this paper including the following subsections 13, 14, 15: 1. 2.
Introduction to Methods. Overview: Begin with a brief introduction summarizing the purpose of the study and the overarching research question.This section sets the stage for the detailed methodology that follows. Subsection Division. Subsection Overview: Divide the methods section into clear, distinct subsections.Each subsection should correspond to a specific aspect of your experimental ...
The section should provide readers with enough detail to replicate the study. It should also give readers a "feel for what it was like to be a participant," as Daryl Bem stated in his instructions for writing journal articles. Typical structure of a Method section in an empirical research paper: Most Method sections are organized ...
However careful writing of this section is important because for your results to be of scientific merit they must be reproducible. Otherwise your paper does not represent good science. Goals: Describe equipment used and provide illustrations where relevant. "Methods Checklist" from: How to Write a Good Scientific Paper. Chris A. Mack. SPIE. 2018.
The main heading of the methods section should be written in bold and capitalized. Centering must be used. As for the methodology in research paper subheadings, they should be aligned to the left and done in bold. Chicago. Your Methods section must have 1′ margins on all sides, top and bottom. Times New Roman or Times pt. 12 font must be used.
4 Extra Tips. Before we part for today, here are a few more tips that will help you make your methods section the best it can be: Write in the past tense ("I collected my data…") If relevant, reference other credible sources that help show your knowledge of the field (but don't go into too much detail - that's what your literature ...
The Methods section is a fundamental component of any research paper, playing a crucial role in establishing the validity and reliability of your study. It serves as a detailed roadmap of the research process that you undertook, providing sufficient information for the replication of the study. An effectively written Methods section can enhance the impact and credibility of your research ...
Wordvice How to Write a Methods Section for a Research Paper. Oct 25, 2022. 75,068. ... If you describe human participants in your method section then you should be especially careful about your choice of words. For example, "participants" sounds more respectful than "subjects," and patient-first language, that is, "patients with ...
Method Introduction: Begin the section on methodology by introducing the methods used in the research. Provide a brief overview of the research design and the data collection and analysis techniques used. Methodological Connection: Establish the connection between the methodology and the research query.
The figures should be indicated within parentheses in their first mention in the "Materials and Methods" section. Headings and as a prevalent convention legends of the figures should be indicated at the end of the manuscript. If a different method is used in the study, this should be explained in detail.
The methods section should explain how subjects were identified and should state inclusion and exclusion criteria. All materials used to complete the study should be described in detail, including equipment, drugs, gases, chemicals, treatments, interventions, or other items. Study procedures should outline all steps taken to obtain the results ...
Methods Section In Research Paper: Writing The Best Research Methodology. Gareth Dyke Paleontologist, Editor-in-Chief, Historical Biology, Taylor & Francis. Get a comprehensive guide with expert advice, practical tips and a reliable checklist to showcase and explain the robust methods used to conduct your research study. Popular.
How long should a research paper introduction be? It depends on the overall length of your paper, but the intro is typically one of the shortest sections. For example, in a short paper like an essay, you can complete each of the steps above in just a sentence or two.
Human Subjects Office / IRB Hardin Library, Suite 105A 600 Newton Rd Iowa City, IA 52242-1098. Voice: 319-335-6564 Fax: 319-335-7310