The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example
Negative effects of fast food: essay introduction, negative effects of fast food: essay body, negative effects of fast food: essay conclusion, works cited.
Consumption of fast food is believed to have negative impact on physical and psychological health. Fast food is rich in glycemic load and energy densities. When consumed in excessive portions it contributes to the escalation of obesity, digestive problems, and depression. Obesity and depression have become an epidemic in countries like the US and UK due to increased consumption of fast food.
Fast food is defined as food purchased from outlets that are self-service or take-out restaurants. A few well-known leaders in the fast food industry are MacDonald, KFC, Pepsi, etc. In the US, fast food outlets increased from 30,000 in 1970 to more than 233000 locations in 2004 (Rosenheck 535). I believe fast food negatively affects physical and emotional health of consumers.
A typical portion of fast food meal is usually very large and exceeds the average calories intake of home made food for an adult. Fast food contains more fats than can be burnt during our daily activities. Hence, regular consumption of fast food increases the chances of gaining excessive weight.
Further, fast food restaurants sell pre-specified portions which are higher than the average calorie intake of an adult. For instance, sandwiches in fast food outlets have two specific sizes – 12 and 6 inches. Research has shown that women consume 31% and men 56% more energy when they eat a 6-inch or 12-inch sandwich respectively (Ledikwe, Ello-Martin and Rolls 906).
Research on fast food snacks served to men and women has shown that women consumed 18% and men 37% more calorie than their usual energy intake (Ledikwe, Ello-Martin and Rolls 907). Fast food has high energy density as the fat content in it is very high. One can definitely state that portion size has a positive influence on the energy density of fast food, thus, increasing the calorie intake of consumers.
Fast food has high fat content. Fat, when consumed from natural sources, plays a vital role in digestion, absorption, and transportation of vitamins and fat-soluble essentials. However, fats contained in fast food are mostly saturated fats and trans fats. An adult male should not consume more than 30g and woman 20g of saturated fats, and less than 5g of trans fat in order to remain healthy (Rosenheck 536).
However, every bite of a burger consumed at a restaurant contains almost 10g of saturated fats. This is higher than what an adult male should consume. The high content of fat, salt, and sugar in fast food increases harmful bacteria content that causes indigestion. Fast foods like french fries, fried chicken, and bread use hydrogenated oil that is not good for digestion.
Depression has become an epidemic problem. Researchers believe that food which is rich in certain substances like vitamin B, omega 3 fatty acids, and olive oil, help reduce depression (Robson par. 1), consequently, researches have connected dietary habit and nutrition to occurrence of depression. Trans fats and saturated fats in fast food increase the risk of depression among consumers.
To sum up it all, excessive intake of fast food may increase the risk of deterioration of physical and mental well-being. Health issues related to obesity or indigestion are common problems faced by consumers of fast food. Due to the lack of certain ingredients that prevent depression, fast food adversely affects mental health. Thus, over-consumption of fast food leads to physical and emotional problems.
Ledikwe, Jenny H., Julia A. Ello-Martin and Barbara J. Rolls. “Portion Sizes and the Obesity Epidemic.” The Journal of Nutrition 135.4 (2005): 905-909. Print.
Robson, David. “ Is fast food making us depressed ?” 14 August 2014.
Rosenheck, R. “Fast food consumption and increased caloric intake: a systematic review of a trajectory towards weight gain and obesity risk.” Obesity Reviews 9.6 (2008): 535-547. Print.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, January 9). The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example. https://studycorgi.com/the-negative-effects-of-fast-food/
"The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." StudyCorgi , 9 Jan. 2020, studycorgi.com/the-negative-effects-of-fast-food/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example'. 9 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." January 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-negative-effects-of-fast-food/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." January 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-negative-effects-of-fast-food/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example." January 9, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/the-negative-effects-of-fast-food/.
This paper, “The Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Example”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: November 8, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Am J Lifestyle Med
- v.12(5); Sep-Oct 2018

The Hidden Dangers of Fast and Processed Food *
The fundamental concern as we look to reform health in America is the known reality that most chronic diseases that afflict Americans are predominantly lifestyle induced; and the belief is that the vast majority of heart attacks and strokes could be prevented if people were willing to adopt healthy lifestyle behaviors. In addition, healthy lifestyles would impact a significant number of cancers which are also believed to be related to lifestyle exposures, especially to obesity, cigarettes, and other toxins.
Over the past 50 years, the health of Americans has gotten worse, and now 71% of Americans are overweight or obese—not 66%, which was reported 5 years ago. 1 That means a staggering 100 million people in America are obese. Today, eating processed foods and fast foods may kill more people prematurely than cigarette smoking. 2
Authorities determined the 71% figure by classifying people with a body mass index (BMI) over 25 kg/m 2 as overweight or obese. Yet in long-lived societies such as in the “Blue Zones” (Ikaria, Greece; Sardinia, Italy; Okinawa, Japan; the Nicoya Peninsula of Costa Rica; and Loma, Linda California) and wherever we find groups of centenarians, we observe a healthy BMI below 23 kg/m 2 , not 25 kg/m 2 . If we use above 23 kg/m 2 as the demarcation for overweight or obesity, then we find that 88% of Americans are overweight. And out of the approximately 10% that are of normal weight, the majority of those so-called “normal weight individuals” are either cigarette smokers, or suffer from alcoholism, drug addiction or dependency, autoimmune disease, occult cancers, inflammatory disorders, autoimmune conditions, digestive disorders, irritable bowel syndrome, and other illnesses that lower their body weight. Therefore, perhaps that only about 5% of the American population is at a normal weight as a result of eating healthy and living a healthy life. A recent study documented that only 2.7% of Americans adopt a relatively healthy lifestyle by combining exercise with healthy eating. 3 The Standard American Diet (SAD) is clearly not a healthy diet.
I use the term “Fast Food Genocide” because most don’t understand the depth and breadth of the harm as a large segment of our society eats a diet worse than the dangerous SAD. Many people recognize that junk food, fast food, processed food, white flour, sugar, maple syrup, honey, agave nectar, and all the junk people are eating contribute to in obesity, diabetes, heart attacks, strokes, dementia and cancer, but many don’t realize the strong causative role an unhealthy diet may have in mental illness. Currently, 1 in 5 Americans suffers from a psychiatric disorder. And many people don’t realize the harm that processed foods have on Americans living in urban areas where they don’t have easy access to whole, fresh foods.
These unfortunate folks live in what we call “food deserts,” with reduced availability to fresh fruits and vegetables. Because of the limited access to supermarkets, they eat more unhealthy fast and processed foods and end up having 7 times the risk of early-life stroke (before age 45), putting people in nursing homes in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. 4 - 7
The vulnerable poor in these areas also have double the risk of heart attack, double the risk of diabetes, and 4 times the risk of renal failure 8 - 10 ; Unfortunately, the decrease in life span due to food inequality is shocking but rarely discussed. A substantial proportion of people in these urban environments are overweight, prediabetic, or fully diabetic. Researchers determined that compared with other areas in America with easy access to supermarket food, that the YPLL (Years of Potential Life Lost) for an overweight diabetic living in a zone classified as a food desert was a shocking 45 years! 11 , 12
A link may even exist between fast food, processed food, commercial baked goods, and sweets and destruction of brain cell and a lowering of intelligence. Candy and sweetened baked goods may even stimulate the brain in an addictive fashion, which can lead to more serious illnesses.
The nutritional fundamentals accepted by the World Health Organization and most nutritional authorities today include vegetables, beans, nuts, seeds, and fruit as healthy foods; and salt, saturated fat, and excess sugar as disease causing. Excessive amounts of animal products may lead to premature aging, increased risk of chronic disease and higher all-cause mortality. Multiple studies have been published on hundreds of thousands of people, followed for decades showing that the objective endpoint of death is increased with higher amounts of animal product consumption. 13 - 17 Furthermore, refined carbohydrates may not just lead to being overweight and diabetic but also contribute to dementia, mental illness, and cancer. 18 - 21 There is considerable evidence today that heart disease is not only promoted by saturated fat and increased animal products but also by refined carbohydrates, including white rice, white bread, sugar, honey, maple syrup, and agave nectar. 22 - 25
Research has shown that excess calories shorten lifespan, whereas moderate caloric restriction slows the aging process and protects the body and brain. Americans consume more calories than any other population; and they consume foods, many of which have minimal or no nutritional value (soda and alcohol as examples). So let’s consider the individual who is consuming 50 excess calories per day. What will be the short- and long-term result? Fifty excess calories per day, over and above your basic metabolic needs, over a 10-year period, adds about 50 pounds of extra body weight. The excess weight increases the risk of multiple chronic illnesses, cancers, and also takes many years of life away from the individual simply as a result of consuming only 50 calories a day too many.
Conversely, if an individual consumed 50 calories a day less that their metabolic requirements what would happen then? Would he or she become too thin, anorexic, and unhealthy? Would their bones fall apart? Obviously not! When you moderately caloric-restrict, even a small amount such as 50 to 100 calories a day, weight remains about the same, the person is slim, not too thin, and healthy. He or she will have a lower body fat percentage, and the skeletal mass, bones, and muscle mass are strong. In this scenario, the metabolic rate would slow down accordingly. The respiratory quotient, (the number of calories lost through respiration) would decrease, the body temperature would lower, and thyroid function would decrease slightly, all lowering the metabolic rate, which overall may result in a slowing of the aging process. The secret to a long life and freedom from chronic disease may be simply to moderately reduce calories in order to slow down our metabolic rate. The only behavior proven scientifically to dramatically increase life span in every species of animals, including primates, is to lower caloric intake while maintaining an environment of micronutrient adequacy, assuring that we have exposure to every micronutrient humans need. The American diet is also deficient in antioxidants and phytochemicals that are needed for normal immune function, for maximizing brain health, protecting against dementia, chronic illness, cancer, and premature aging.
A nutritarian diet is designed to establish excellent micronutrient intake without excess calories . A nutritarian diet is designed to help prolong human life span, decrease the risk of cancer, and keep the brain functioning well for many years. This principle is represented by the equation I use: H = N /C, which means your healthy life expectancy (H) is proportional to the micronutrient (N) per calorie intake (C) over your life span. This means that we are encouraged to seek out foods that are rich in nutrients. We should try to limit or exclude empty-calorie foods and drinks. We should also limit or avoid calorically dense foods, and not eat for recreation or when we are not hungry.
A nutritarian diet is rich in phytochemicals and antioxidants. It is a vegetable-based, utilizing a wide assortment of colorful vegetables, root vegetables, green vegetables, peas, beans, mushrooms, onions, nuts, seeds, and some intact whole grains. While the standard American diet and most traditional diets are grain-based and lack sufficient exposure to the broad spectrum of antioxidants and phytochemicals (with their anticancer effects), it is important to note that not all plant-based diets are equally cancer-protective. As an example, a rice-heavy, macrobiotic diet limits phytochemical diversity, and brown rice produced in this country is contaminated with arsenic, extensively documented by Consumer Reports and white rice is refined, high glycemic food, and therefore not a healthy starch.
In comparison, the SAD is almost the opposite of a nutritarian diet. Over 55% of the SAD’s calories are processed foods, and about 33% of calories come from animal products. If we are looking at the amount of fresh produce (fruits and vegetables) consumed in America, the food consumption data reports about 10%; but in actuality, it is less than 5%, because they include French fries and ketchup in the definition of “produce!” The point here is that processed foods such as bread, pasta, salad oil, mayonnaise, doughnuts, cookies, rice cakes, breakfast bars, chips, soda, candy, and popcorn do not contain a significant micronutrient benefit. A piece of chicken is like a bagel, because they are both rich sources of macronutrients (calories), but neither one contains the necessary amounts of micronutrients, especially the antioxidants and phytochemicals only found in plants.
The high glycemic white flour products with added sweetening agents, flood the bloodstream with glucose without fiber, nutrients, or phytochemicals; and these baked goods are also high in acrylamides and advanced glycation end-products, further increasing the glycoproteins in our tissues. The resulting spike in glucose leads to abnormally high amounts of insulin, which will also promote angiogenesis, which fuels the growth of fat cells, increases cellular replication and tumor growth. The liberal amount of animal protein (including chicken which many incorrectly believe is the more healthy meat) consumed by most Americans promotes excessive insulin-like growth factor–1 (IGF-1), making a synergistic “sandwich” of insulin and IGF-1, which may accelerate aging of the brain, interfere with cellular detoxification and repair, and promote cancer. 26 The SAD has created a nutritional disaster and a significant health crisis that will not be solved by governmental “health care reform.”
Now when we think about “fast food” we’re not just referring to the food in fast food restaurants. Fast foods include chips, soda, cookies, candy, breakfast cereals, bars, French fries, burgers, pizza, white flour baked goods, and all other high-calorie, low-nutrient foods that people often eat multiple times per day. These are processed foods and for many, are the primary source of calories. These fast foods have certain characteristics: They can be accessed easily and quickly; they don’t need to be prepared; they come out of a bag or box ready to go right into your mouth. You can eat them rapidly and they’re absorbed very quickly into the bloodstream. These fast foods typically contain multiple chemicals and synthetic ingredients. They are calorically dense, highly flavored, and nutritionally barren. Fast foods typically contain extra corn syrup, sugar, artificial sweeteners, salt, coloring agents, and other potentially disease promoting chemicals.
When calories flood the bloodstream rapidly they have dramatic biological effects. Let’s compare 200 calories of white bread to 200 calories of beans. The white bread would be metabolized into simple sugars (glucose) which enters the bloodstream in 5 to 10 minutes. This requires a rapid increase in insulin; and the rapid insulin response will remain for hours. On the other hand, the carbohydrates from beans will take much more time to be digested and, as a result these calories enter the bloodstream slowly. Essentially, the calories will trickle in over hours. When eating beans, a small amount of glucose enters the blood each minute and therefore you won’t need much of an insulin response to deal with this amount of sugar. As mentioned above, the buildup of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) accelerates aging and chronic disease. 27 , 28 When a diabetic suffers from kidney failure, blindness, or a leg amputation, a major causative factor is the buildup of AGEs in the tissues. Interestingly, these same glycated end-products and glycoproteins build up in the tissues of people who are not diabetic but who continually expose themselves to excess sugar and white flour products.
Next, it is important to understand that oils are also processed foods. When consumed, oil enters the bloodstream rapidly similar to high glycemic carbohydrates. Anything cooked in oil should be considered a fast food. Beans, nuts, and seeds are whole foods whose calories are absorbed gradually over hours. In contrast, the calories from oil are absorbed rapidly, and are largely empty calories (with insignificant micronutrients and no fiber)—a combination that leads to obesity, disease, and premature aging.
If I set up a buffet dinner and I asked all the guests to form 2 lines and then gave everyone on the right side a tablespoon of olive oil, and each of those on the left side an apple to consume while they were waiting in line, those who ate the 65-calorie apple will generally eat 65 less calories from the buffet. But those who had the 120-calorie tablespoon of oil will not usually consume 120 calories less. The oil contains neither fiber, nor micronutrients and contains nothing to decrease the appestat. A matter of fact, if you put oil on food, it may actually increase one’s appetite. Not only will these individuals not eat fewer calories—they will eat even more than the 120 calories from the oil. 29 When added or mixed into food, oil drives overeating behavior.
Nutrients and fiber are needed to control the appestat, so you consume a healthy amount of calories. My experience has demonstrated with thousands of patients, the more nutrient and fiber dense your diet becomes the lower your drive to overeat. 30 This is extremely important, because even a moderate amount of extra fat on the body induces more rapid aging and increases the risk of diabetes, heart disease and cancer. A mild degree of caloric restriction becomes comfortable and achievable when the diet is high in micronutrients and fiber. When you have enough micronutrients and fiber in your diet, you don’t feel driven to overeat. But when you don’t have enough micronutrients and fiber in your diet, you become a food-craving, overeating machine.
Even worse is what happens when you eat food fried in oil because fried food may create carcinogenic and mutagenic aldehydes. 31 Food that is fried such as in a fast food restaurant is usually cooked in oil that has been heated and used multiple times. One serving of French fries or fried chicken that is cooked in a fast food restaurant has 100 times the level of aldehydes designated as safe by the World Health Organization. Even the fumes are so toxic they increase the risk of cancer. People working in restaurants that fry the food, or those working in a movie theater making popcorn, have a heighted risk of lung and other cancers, even if they don’t eat any of the fried foods. 32
The explosion of fast food restaurants has significantly increased the intake of fried foods, and people are now eating 1000 times the amount of soybean oil compared with the early 1900s. 33 Humans never ate 400 calories of oil a day the way people do in America, especially in the Southern states—which are known for the highest stroke and heart attack rates in the world. 34 When you use nuts and seeds as your source of fat as opposed to oil, we see the opposite effect.
The Physician’s Health Study, the Nurses’ Health Study, Iowa Women’s Health Study, the Adventist Health Study—any study with large numbers of people followed for decades—demonstrates the relationship between nut and seed consumption and longer life span. We always have to give more credence to clinical research studies that involve large numbers of people followed over decades using objective endpoints such as mortality. When you do that, you find that people who consume nuts and seeds regularly have lower cancer rates, lower cardiovascular death rates, lower sudden cardiac death, less irregular heartbeats, and an increase in life span.
A 2015 meta-analysis that included over 44 000 deaths demonstrated an almost 40% decrease in cardiovascular mortality for people eating nuts and seeds regularly (one serving a day). The European PreviMed study, which randomized 7216 individuals to nuts or olive oil as part of a Mediterranean diet showed a 39% decrease in all-cause mortality in the nut eaters. 35
When we look at the health implications of animal protein we should compare this type of nutrition with plant-based proteins, especially when an individual has cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, or even cancer. When your protein comes from beans, nuts, seeds, and greens, the body more gradually assimilates a complete array of amino acids to make functional proteins and hormones, keeping IGF-1 production much lower. Adequate amounts of plant protein keep IGF-1 in that moderate range, between 100 and 175, which is where it should be. The average American’s IGF-1 level is around 225, which is a level which has been linked to cancer promotion. When we eat a variety of plants, we get a full balance of amino acids, which slowly enter the blood—and we also digest some of the bacteria in the digestive track and some of the cells that slough off of the villi endothelium, enabling the utilization of partially incomplete plant proteins, now made complete. Conversely, when you eat large portions of meat, eggs, or cheese, the amino acid mix enters the bloodstream faster and because it is already biologically complete, it stimulates excessive amounts of IGF-1, again increasing the risk of cancer. 36 - 43
The average American consumes 10 to 20 ounces a day of animal products, whereas the safe level of consumption is likely less than 10 ounces per week . My estimate of 10% of calories as an upper limit of safe consumption is for a person with favorable genetics and is still likely more animal products than ideal for the nonelderly adults. It may be the case that under 5% of calories from animal products would be more ideal for life span and for facilitating disease reversal. Of course, any diet designed to optimize health should include a broad array of colorful plants with phytochemicals and antioxidants, which have been shown to increase life span and prevent cancer.
The animal products served at fast food restaurants are making the health of the population much worse, creating dangerous carcinogens from the food being grilled, barbecued, and fried at high temperatures. The World Health Organization has classified processed meats (hot dogs, sausage, bacon, and lunch meats) a class 1 carcinogen. AGEs are also highest in barbecued and fried animal products which also contain cancer-causing chemicals such as heterocyclic amines, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and lipid peroxidases, which are mutagenic.
There are 2 phases of the digestive cycle: the anabolic phase, when you are eating and digesting, and the catabolic phase, when digestion has ceased. When you are eating and digesting food, the body turns those calories into stored glycogen, increasing fat storage and the storage of waste. During this phase of the digestive cycle, growth hormones and fat storage hormones are activated.
When your body is finished digesting, you enter the catabolic phase, where the stored glycogen and fat are utilized for energy. This is the phase when your body can most effectively detoxify and enhance cellular repair. It is the time when the liver and kidneys work together to remove aldehydes, AGEs, and other toxic metabolites. Repair and healing is enhanced during the catabolic phase when you are not eating food.
Most Americans have made their bodies so toxic, that when they enter the catabolic phase of the digestive cycle, they feel uncomfortable. That means they feel fatigue, headache, stomach cramping or fluttering, anxiety, or other uncomfortable symptoms when they stop digesting food and the body starts to mobilize waste and repair the damage. They typically interpret these symptoms as hunger or low blood sugar, because they feel better if they eat again—even though there is no biological need for calories at this time; and so they just get fatter and sicker. Every addiction has a “high” during the caloric rush and a “low” during withdrawal and repair from the disease-causing diet and resultant metabolic wastes and toxins that accrue from it. The American diet results in withdrawal symptoms and discomfort which promotes overeating and too-frequent eating. The lower the quality of the food consumed, the more discomfort felt when not eating and digesting, which makes it very difficult to maintain a healthy body weight.
If you’re healthy and eating nutritious food, you feel nothing when you enter the catabolic phase, with no desire to eat again until glycogen stores are nearly exhausted. True hunger is a mild sensation felt in the throat and base of the neck. True hunger heightens taste sensitivity too, making eating more pleasurable. True hunger directs when you should eat and therefore it’s more difficult to become overweight if you pay attention to the signs your body sends to your brain. Being overweight requires eating outside of the demands of true hunger, either recreationally or because of withdrawal symptoms from improper eating, stimulating the overconsumption of calories.
Enhanced detoxification—reduction of metabolic waste, aldehydes, and AGEs—occurs most effectively in the catabolic phase. That means the longer you live in the catabolic phase of the digestive cycle, the longer you live. If you finish dinner earlier or have a lighter dinner, and you have a 13-hour window between the end of dinner and the start of breakfast, you are going to live longer. A recent study had women with breast cancer followed for 10 years and found that those who finished dinner earlier and had a 13-hour window before the start of breakfast had a 26% reduction in the risk of death or recurrence from breast cancer. 44 , 45 The increased nighttime window was also linked to improved glycemic control and a lower HbA1c (glycated hemoglobin). They had no better diet, no different number of calories, no better food; they just finished dinner earlier.
The goal for excellent health is to eat as infrequently as possible. Many people believe just the opposite and eat frequent small meals that increase endothelial dysfunction leading to an increased risk for arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. In addition, all the fad diets encourage people to make the wrong choices about what and when to eat. Many suggest the use of frequent high-protein meals so as not to feel the effects of normal detoxification. When the digestive track is continually busy, it results in accelerated aging.
Processed and fast foods are also high in salt. The fast and processed food manufacturers don’t just put salt on the French fries and on the meat, they also put salt in the French fry batter and inside the chopped meat. They also include high fructose corn syrup in most foods. The added fat, sugar, and salt create a taste that makes people crave these foods, a sensation that many describe as an addiction. Both sugar and salt intake increase stroke risk, especially when consumed daily for years. Additionally, what is generally not appreciated is that the regular consumption of artificially sweetened soda creates more of a stroke risk. 46 High salt does not merely raise blood pressure; it also causes microvascular hemorrhaging, which damages the interior walls of the blood vessels in the brain and increases permeability and the propensity for hemorrhagic stroke. 47 , 48
Over the past 30 years, we’ve also seen an explosion of diabetes in Japan, Korea, and China, occurring at a lower body weight than we typically see in America, likely because the cumulative effects of eating more fast food, more oil and sugar, along with all of the white rice (a refined, high glycemic food), which they already had in their diet.
We know that people have the power to change when significant effort and attention is directed to the problems at hand. With good information, emotional support, increased food availability and food preparation instruction, we have found people enthused and willing to work together for change. They don’t have to be convinced of the tragic dangers of fast food; they see the obesity, diabetes, leg amputations, strokes, and blindness all around them. But if people don’t have good information, then they don’t have a choice. If they don’t have access to healthy, affordable food, and they don’t know how to make it taste good, then they are not given a chance to change.
The goal for physicians and other health care professionals is to work to transform America’s inner cities into zones of nutritional excellence. Our nation’s pride and heritage are based on the equal opportunity to achieve the American dream of prosperity and happiness. This critical information needs to be spread and put into action by community activists, teachers, educators, celebrities, health professionals, athletes, and politicians. The more people who know the critical importance of eating healthfully, and the more they take a stand, the greater the effect will be on transforming the health of all in America. By working together, we can save millions of lives.
Acknowledgments
This work was presented at Lifestyle Medicine 2017, October 22-25; Tucson, AZ.
Authors’ Note: The opinions presented in this article are those of the author and may not represent those of the Guest Editor, Editor, or the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethical Approval: Not applicable, because this article does not contain anystudies with human or animal subjects.
Informed Consent: Not applicable, because this article does not contain anystudies with human or animal subjects.
Trial Registration: Not applicable, because this article does not contain anyclinical trials.
Search form
An opinion essay about fast food.
Look at the exam question and essay and do the exercises to improve your writing skills.
Instructions
Do the preparation exercise first. Then read the text and do the other exercises.
Preparation

Check your understanding: matching
Check your vocabulary: gap fill, check your writing: multiple choice, worksheets and downloads.
Is fast food popular in your country? Do you think it causes health problems or any other kinds of problems?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Food Fast Food
Cause and Effect of Fast Food: the Impact on Health and Society
Table of contents, causes of fast food consumption, effects on physical well-being, cultural and societal impact, economic considerations, promoting healthier lifestyles, conclusion: balancing convenience and health.
- Ludwig, D. S., Peterson, K. E., & Gortmaker, S. L. (2001). Relation between consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks and childhood obesity: a prospective, observational analysis. The Lancet, 357(9255), 505-508.
- Malik, V. S., Pan, A., Willett, W. C., & Hu, F. B. (2013). Sugar-sweetened beverages and weight gain in children and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 98(4), 1084-1102.
- Story, M., Kaphingst, K. M., Robinson-O'Brien, R., & Glanz, K. (2008). Creating healthy food and eating environments: policy and environmental approaches. Annual Review of Public Health, 29, 253-272.
- Stuckler, D., McKee, M., Ebrahim, S., & Basu, S. (2012). Manufacturing epidemics: the role of global producers in increased consumption of unhealthy commodities including processed foods, alcohol, and tobacco. PLOS Medicine, 9(6), e1001235.
- World Health Organization. (2016). Report of the Commission on Ending Childhood Obesity. WHO Press.
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Japanese Food Culture
- Importance of Food
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
Frontiers for Young Minds
- Download PDF
The Impacts of Junk Food on Health
Energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods, otherwise known as junk foods, have never been more accessible and available. Young people are bombarded with unhealthy junk-food choices daily, and this can lead to life-long dietary habits that are difficult to undo. In this article, we explore the scientific evidence behind both the short-term and long-term impacts of junk food consumption on our health.
Introduction
The world is currently facing an obesity epidemic, which puts people at risk for chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes. Junk food can contribute to obesity and yet it is becoming a part of our everyday lives because of our fast-paced lifestyles. Life can be jam-packed when you are juggling school, sport, and hanging with friends and family! Junk food companies make food convenient, tasty, and affordable, so it has largely replaced preparing and eating healthy homemade meals. Junk foods include foods like burgers, fried chicken, and pizza from fast-food restaurants, as well as packaged foods like chips, biscuits, and ice-cream, sugar-sweetened beverages like soda, fatty meats like bacon, sugary cereals, and frozen ready meals like lasagne. These are typically highly processed foods , meaning several steps were involved in making the food, with a focus on making them tasty and thus easy to overeat. Unfortunately, junk foods provide lots of calories and energy, but little of the vital nutrients our bodies need to grow and be healthy, like proteins, vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Australian teenagers aged 14–18 years get more than 40% of their daily energy from these types of foods, which is concerning [ 1 ]. Junk foods are also known as discretionary foods , which means they are “not needed to meet nutrient requirements and do not belong to the five food groups” [ 2 ]. According to the dietary guidelines of Australian and many other countries, these five food groups are grains and cereals, vegetables and legumes, fruits, dairy and dairy alternatives, and meat and meat alternatives.
Young people are often the targets of sneaky advertising tactics by junk food companies, which show our heroes and icons promoting junk foods. In Australia, cricket, one of our favorite sports, is sponsored by a big fast-food brand. Elite athletes like cricket players are not fuelling their bodies with fried chicken, burgers, and fries! A study showed that adolescents aged 12–17 years view over 14.4 million food advertisements in a single year on popular websites, with cakes, cookies, and ice cream being the most frequently advertised products [ 3 ]. Another study examining YouTube videos popular amongst children reported that 38% of all ads involved a food or beverage and 56% of those food ads were for junk foods [ 4 ].
What Happens to Our Bodies Shortly After We Eat Junk Foods?
Food is made up of three major nutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. There are also vitamins and minerals in food that support good health, growth, and development. Getting the proper nutrition is very important during our teenage years. However, when we eat junk foods, we are consuming high amounts of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, which are quickly absorbed by the body.
Let us take the example of eating a hamburger. A burger typically contains carbohydrates from the bun, proteins and fats from the beef patty, and fats from the cheese and sauce. On average, a burger from a fast-food chain contains 36–40% of your daily energy needs and this does not account for any chips or drinks consumed with it ( Figure 1 ). This is a large amount of food for the body to digest—not good if you are about to hit the cricket pitch!
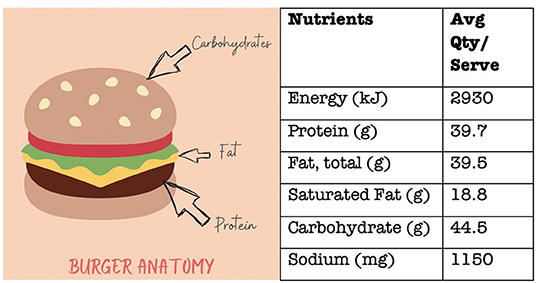
- Figure 1 - The nutritional composition of a popular burger from a famous fast-food restaurant, detailing the average quantity per serving and per 100 g.
- The carbohydrates of a burger are mainly from the bun, while the protein comes from the beef patty. Large amounts of fat come from the cheese and sauce. Based on the Australian dietary guidelines, just one burger can be 36% of the recommended daily energy intake for teenage boys aged 12–15 years and 40% of the recommendations for teenage girls 12–15 years.
A few hours to a few days after eating rich, heavy foods such as a burger, unpleasant symptoms like tiredness, poor sleep, and even hunger can result ( Figure 2 ). Rather than providing an energy boost, junk foods can lead to a lack of energy. For a short time, sugar (a type of carbohydrate) makes people feel energized, happy, and upbeat as it is used by the body for energy. However, refined sugar , which is the type of sugar commonly found in junk foods, leads to a quick drop in blood sugar levels because it is digested quickly by the body. This can lead tiredness and cravings [ 5 ].
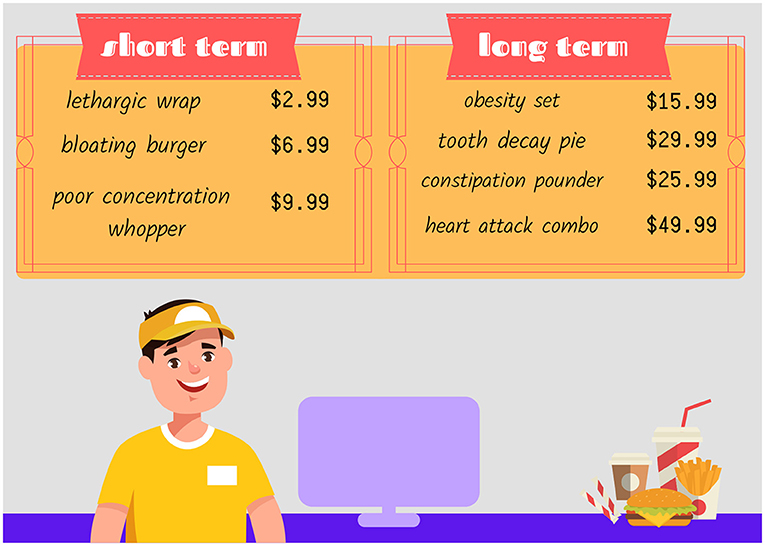
- Figure 2 - The short- and long-term impacts of junk food consumption.
- In the short-term, junk foods can make you feel tired, bloated, and unable to concentrate. Long-term, junk foods can lead to tooth decay and poor bowel habits. Junk foods can also lead to obesity and associated diseases such as heart disease. When junk foods are regularly consumed over long periods of time, the damages and complications to health are increasingly costly.
Fiber is a good carbohydrate commonly found in vegetables, fruits, barley, legumes, nuts, and seeds—foods from the five food groups. Fiber not only keeps the digestive system healthy, but also slows the stomach’s emptying process, keeping us feeling full for longer. Junk foods tend to lack fiber, so when we eat them, we notice decreasing energy and increasing hunger sooner.
Foods such as walnuts, berries, tuna, and green veggies can boost concentration levels. This is particularly important for young minds who are doing lots of schoolwork. These foods are what most elite athletes are eating! On the other hand, eating junk foods can lead to poor concentration. Eating junk foods can lead to swelling in the part of the brain that has a major role in memory. A study performed in humans showed that eating an unhealthy breakfast high in fat and sugar for 4 days in a row caused disruptions to the learning and memory parts of the brain [ 6 ].
Long-Term Impacts of Junk Foods
If we eat mostly junk foods over many weeks, months, or years, there can be several long-term impacts on health ( Figure 2 ). For example, high saturated fat intake is strongly linked with high levels of bad cholesterol in the blood, which can be a sign of heart disease. Respected research studies found that young people who eat only small amounts of saturated fat have lower total cholesterol levels [ 7 ].
Frequent consumption of junk foods can also increase the risk of diseases such as hypertension and stroke. Hypertension is also known as high blood pressure and a stroke is damage to the brain from reduced blood supply, which prevents the brain from receiving the oxygen and nutrients it needs to survive. Hypertension and stroke can occur because of the high amounts of cholesterol and salt in junk foods.
Furthermore, junk foods can trigger the “happy hormone,” dopamine , to be released in the brain, making us feel good when we eat these foods. This can lead us to wanting more junk food to get that same happy feeling again [ 8 ]. Other long-term effects of eating too much junk food include tooth decay and constipation. Soft drinks, for instance, can cause tooth decay due to high amounts of sugar and acid that can wear down the protective tooth enamel. Junk foods are typically low in fiber too, which has negative consequences for gut health in the long term. Fiber forms the bulk of our poop and without it, it can be hard to poop!
Tips for Being Healthy
One way to figure out whether a food is a junk food is to think about how processed it is. When we think of foods in their whole and original forms, like a fresh tomato, a grain of rice, or milk squeezed from a cow, we can then start to imagine how many steps are involved to transform that whole food into something that is ready-to-eat, tasty, convenient, and has a long shelf life.
For teenagers 13–14 years old, the recommended daily energy intake is 8,200–9,900 kJ/day or 1,960 kcal-2,370 kcal/day for boys and 7,400–8,200 kJ/day or 1,770–1,960 kcal for girls, according to the Australian dietary guidelines. Of course, the more physically active you are, the higher your energy needs. Remember that junk foods are okay to eat occasionally, but they should not make up more than 10% of your daily energy intake. In a day, this may be a simple treat such as a small muffin or a few squares of chocolate. On a weekly basis, this might mean no more than two fast-food meals per week. The remaining 90% of food eaten should be from the five food groups.
In conclusion, we know that junk foods are tasty, affordable, and convenient. This makes it hard to limit the amount of junk food we eat. However, if junk foods become a staple of our diets, there can be negative impacts on our health. We should aim for high-fiber foods such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits; meals that have moderate amounts of sugar and salt; and calcium-rich and iron-rich foods. Healthy foods help to build strong bodies and brains. Limiting junk food intake can happen on an individual level, based on our food choices, or through government policies and health-promotion strategies. We need governments to stop junk food companies from advertising to young people, and we need their help to replace junk food restaurants with more healthy options. Researchers can focus on education and health promotion around healthy food options and can work with young people to develop solutions. If we all work together, we can help young people across the world to make food choices that will improve their short and long-term health.
Obesity : ↑ A disorder where too much body fat increases the risk of health problems.
Processed Food : ↑ A raw agricultural food that has undergone processes to be washed, ground, cleaned and/or cooked further.
Discretionary Food : ↑ Foods and drinks not necessary to provide the nutrients the body needs but that may add variety to a person’s diet (according to the Australian dietary guidelines).
Refined Sugar : ↑ Sugar that has been processed from raw sources such as sugar cane, sugar beets or corn.
Saturated Fat : ↑ A type of fat commonly eaten from animal sources such as beef, chicken and pork, which typically promotes the production of “bad” cholesterol in the body.
Dopamine : ↑ A hormone that is released when the brain is expecting a reward and is associated with activities that generate pleasure, such as eating or shopping.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
[1] ↑ Australian Bureau of Statistics. 2013. 4324.0.55.002 - Microdata: Australian Health Survey: Nutrition and Physical Activity, 2011-12 . Australian Bureau of Statistics. Available online at: http://bit.ly/2jkRRZO (accessed December 13, 2019).
[2] ↑ National Health and Medical Research Council. 2013. Australian Dietary Guidelines Summary . Canberra, ACT: National Health and Medical Research Council.
[3] ↑ Potvin Kent, M., and Pauzé, E. 2018. The frequency and healthfulness of food and beverages advertised on adolescents’ preferred web sites in Canada. J. Adolesc. Health. 63:102–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2018.01.007
[4] ↑ Tan, L., Ng, S. H., Omar, A., and Karupaiah, T. 2018. What’s on YouTube? A case study on food and beverage advertising in videos targeted at children on social media. Child Obes. 14:280–90. doi: 10.1089/chi.2018.0037
[5] ↑ Gómez-Pinilla, F. 2008. Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 568–78. doi: 10.1038/nrn2421
[6] ↑ Attuquayefio, T., Stevenson, R. J., Oaten, M. J., and Francis, H. M. 2017. A four-day western-style dietary intervention causes reductions in hippocampal-dependent learning and memory and interoceptive sensitivity. PLoS ONE . 12:e0172645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172645
[7] ↑ Te Morenga, L., and Montez, J. 2017. Health effects of saturated and trans-fatty acid intake in children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 12:e0186672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186672
[8] ↑ Reichelt, A. C. 2016. Adolescent maturational transitions in the prefrontal cortex and dopamine signaling as a risk factor for the development of obesity and high fat/high sugar diet induced cognitive deficits. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2016.00189
Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects Essay
According to Schlosser, the expansion of the fast-food industry is influenced by major adjustments in American culture. This resulted from the lowering of the hourly wage of most US workers from 1970. This made many mothers seek other jobs where most of them work outside their homes. This led to a trend where many of them rely on fast foods for their daily meal instead of preparing their own meals at home. In addition, most mothers tend to buy and stock these fast foods in their homes for their family’s daily consumption creating more demand for these foods at home.
The dependency of most mothers on fast foods rendered their families no other option other than following the same trend. In terms of businesses, the fast-food industries seem to replace small businesses as more American civilians tend to prefer these fast foods other than a home-prepared meal. According to Schlosser, companies like McDonald’s corporation seem to dominate the food industry as their target children and their parents. They deal with beef, pork, chicken, and potatoes that in most cases tend to add the amount of cholesterol to the body. Cholesterol is vital to patients suffering from diabetes or even obesity. However, many Americans do not seem to be alarmed rather they seem to opt and appreciate the fast-food culture.
In addition, he observed that technology changes have made many people be workaholics leaving little time for preparing meals at home as well as paying very little attention to the kind of food they eat i.e. whether it is balanced or not. Further, he argues that the growth of the fast-food industry over the years was triggered by their exclusive advertisements that seem to convince many Americans that fast foods are the best. They appeal to the civilians by convincing them that it is the American culture and it’s unique, hence many Americans have come to appreciate and respect it blindly.
More so, most of the fast foods target schools for their businesses by offering sponsorships that tend to be conditional i.e. if they donate books they tend to promote their products in these schools, contrary to adhering to these terms and conditions they stand to lose the sponsorship. Others have opted for the high schools to sell fast foods to students in their cafeterias; this contributed to the expansion of these corporations’ profits at the expense of young Americans. The extensive opening of kiosks in high schools that sell exclusively fast foods has led to the expansion of the fast-food industry as many students have been accustomed to the daily consumption of these foods.
Further, Schlosser observed that the meat industry has been exploiting workers who happen to be immigrants in their efforts to make big profits. They normally do not mind the health of these workers yet they understand the dangers prone to these workers. The appraisal of fast foods has made the health of many Americans deteriorate from good to worse, just in the name of making money. The extensive use of very sharp equipment to slaughter makes the workers prone to cumulative trauma disorders (CTO).
These chronic injuries such as tendonitis and tenosynovitis destroy the soft cells, nervous system, and tissues that may cause crippling and organ mutilation or dysfunction. Most of the researches carried out reveals that many of these factory workers suffer from musculoskeletal disorders. These are mainly caused by the vibrating knives and other equipment applied for meat extraction and processing.
According to pollan, the farm bill has been in the forefront to promote the consumption of fast foods with most of them being processed hence not appropriate for consumption in large amounts in a society where diabetes and obesity seem to be prevalent. The bill tends to promote the usage of hydrogenated oils and corn syrup that contain a large amount of fructose by subsidizing the farmers of the corns yet the government understands the hazards associated with these foods. In addition, the bill endorses factory farming by grants and subsidies despite these companies polluting the environment with their wastes. Further, the bill seems to favor the consumption of soft drinks like coca-cola instead of water where these soft drinks enjoy the tax cut by the government compared to water industries.
On the international front, the effects of the bill have prevalent in other countries that produce these crops that include cotton, corn, wheat, and Soya beans, which tend to be favored by the bill where many of these countries tend to be encouraged by being offered grants and subsidies to produce more of this products. The production of more wheat tends to make fast foods easier to produce compared to other more nutritious and healthier foods that are never favored by the bill in terms of their production costs, distribution, and marketing.
However, the reformation would greatly change the fast-food culture adopted as the bill exclusively seems to promote the consumption of processed foods and soft drinks, rather than naturally produced foods without chemicals. The subsidies offered tend to lower the prices of these foods in the market making them affordable by many Americans at the expense of their health. On the other hand, the prices of agricultural foods tend to soar high rendering them unaffordable. Therefore, reforming the farm bill would greatly influence the preference of fast foods, as it would make naturally produced foods affordable.
The excessive consumption of fast foods is injuries and hazardous to human health due to the fact that many of these foods contain high levels of cholesterol and fats that tend to various kinds of diseases such as heart diseases and dysfunctional of other body organs as they t5end to block the veins and arteries. The major causes of these food’s consumption are their easy accessibility, change in culture, and the policy changes that tend to favor the production and consumption of fast foods at the expense of other agriculturally produced foods. These agricultural foods tend to be nutritious, less hazardous but they have been rendered expensive as the farm bill does not support their production at all rather promotes the production and consumption of fast foods. In addition, they have been attributed to the increase in diabetes and obesity cases in America and other developed countries due to their high levels of fats and cholesterol.
References:
Schlosser, E. Fast food nation, Houghton Mifflin publishers, New York 2001.
Bonnie RJ, Fulco CE& Liver man CT (1999) Reducing the burden of injury: advancing prevention and treatment. National Academy Press, Washington, DC: Institute of Medicine.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, August 14). Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fast-foods-popularity-causes-and-effects/
"Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects." IvyPanda , 14 Aug. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/fast-foods-popularity-causes-and-effects/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects'. 14 August.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects." August 14, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fast-foods-popularity-causes-and-effects/.
1. IvyPanda . "Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects." August 14, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fast-foods-popularity-causes-and-effects/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects." August 14, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/fast-foods-popularity-causes-and-effects/.
- Analysis of a Look at the Fast-Food Industry by Eric Schlosser
- “The Most Dangerous Job” by Schlosser
- Behind the Counter: Falling Behind the Trend
- Fast Food Restaurants and Buyers' Responsibility
- Fast Food, Fat Profits: Obesity in America
- Fast Food in Campus: Advantages and Disadvantages
- Fast-Food Marketing and Childhood Obesity in the USA
- Fast Food History and Global Presence

Essay on Effects of Fast Food on Health
Students are often asked to write an essay on Effects of Fast Food on Health in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Effects of Fast Food on Health
Introduction.
Fast food is popular because it’s convenient and tasty. But, it’s often unhealthy.
Nutritional Content
Fast food is high in calories, salt, and unhealthy fats. It lacks important nutrients like vitamins and fiber.
Obesity Risk
Eating too much fast food can lead to weight gain. This increases the risk of obesity, a serious health problem.

Heart Problems
Fast food’s high fat and salt content can contribute to heart problems, like high blood pressure and heart disease.
While fast food is convenient, it’s important to eat it in moderation due to its negative health effects.
250 Words Essay on Effects of Fast Food on Health
Fast food, a staple in today’s hurried society, is often blamed for a variety of health issues. Its impact on health is multifaceted, affecting not only physical well-being but also mental health.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Fast foods are typically high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium while being low in essential nutrients. These nutritional imbalances can lead to deficiencies, which manifest as fatigue, poor concentration, and weakened immune system.
Obesity and Related Diseases
The high calorie content of fast food contributes to obesity, a global health crisis. Obesity, in turn, increases the risk of serious diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Mental Health Implications
Recent research suggests a link between fast food consumption and mental health issues. High sugar and fat content may contribute to depression, while the lack of essential nutrients can exacerbate anxiety and mood disorders.
While fast food offers convenience, its health effects are far-reaching. As consumers, we must make informed choices about our dietary habits, balancing convenience with health. As a society, we must advocate for healthier fast food options and improved nutritional education.
500 Words Essay on Effects of Fast Food on Health
Fast food has become a staple in the diet of many, primarily due to its convenience and accessibility. However, this shift in dietary habits has profound implications on health.
The Nutritional Profile of Fast Food
Fast food is notorious for its high caloric content, saturated and trans fats, sodium, and sugar, while being low in essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber. This skewed nutritional profile contributes to the onset of various health issues.
Obesity and Fast Food
One of the most visible effects of fast food consumption is the rise in obesity rates. The high energy density of fast food, combined with its palatability, promotes overeating. This chronic energy surplus leads to weight gain and obesity. Obesity, in turn, is a risk factor for numerous health conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Fast Food and Cardiovascular Health
Fast food’s high sodium and saturated fat content contribute to elevated blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which are precursors to heart disease. Furthermore, trans fats found in fast food have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, as they raise bad cholesterol levels and lower good cholesterol levels.
Impact on Digestive and Metabolic Health
Fast food’s low fiber content affects digestive health, leading to conditions like constipation and diverticular disease. Also, the high sugar content can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Studies have shown a direct correlation between the frequency of fast food consumption and the risk of developing these metabolic disorders.
Effects on Mental Health
Emerging research suggests that fast food may also affect mental health. Diets high in fat and sugar can cause alterations in brain chemistry that lead to symptoms of depression and anxiety. Additionally, the blood sugar spikes and crashes associated with high-sugar fast foods can cause mood swings and impair cognitive function.
Fast food, while convenient, has a detrimental impact on health, contributing to obesity, heart disease, digestive issues, metabolic disorders, and potentially, mental health problems. It is crucial to raise awareness about these health risks and promote healthier dietary choices among the public. The fast-food industry also has a role to play in this, by reformulating their products to be healthier and offering a wider range of nutritious options. The effects of fast food on health are a pressing issue that requires collective action from individuals, communities, and policymakers alike.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Nutritious Food
- Essay on Disadvantages of Fast Food
- Essay on Healthy and Unhealthy
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Home — Essay Samples — Nursing & Health — Fast Food — Negative Effects of Fast Foods
Negative Effects of Fast Foods
- Categories: Fast Food Junk Food
About this sample

Words: 399 |
Published: Feb 12, 2019
Words: 399 | Page: 1 | 2 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Nursing & Health

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 642 words
6 pages / 2633 words
2 pages / 716 words
2 pages / 1118 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Fast Food
As childhood obesity rates continue to rise, the debate over whether schools should offer fast food options has become increasingly contentious. On one hand, fast food is often seen as a convenient and affordable choice for busy [...]
In a world filled with fast food chains and processed snacks, the importance of eating healthy cannot be overstated. As we navigate our daily lives, it's easy to prioritize convenience over nutrition, leading to a myriad of [...]
Consuming fast food has been linked to negative effects on both physical and psychological health. Fast food is characterized by high glycemic load and energy densities, which can lead to obesity, digestive problems, and [...]
He argues that fast food has become a significant aspect of social culture, affecting how people understand and navigate the world. Schlosser views fast food as both a commodity and a metaphor, allowing him to analyze and reveal [...]
Are fast food companies the only reason for America being the fattest nation in the world? This question is challenged in the documentary ‘Supersize Me’ (2004). Director Morgan Spurlock attempts a social experiment to prove that [...]
In conclusion, Chipotle and Chick-fil-A are two fast food giants that have carved out their own niches in the industry. While both emphasize food quality and customer satisfaction, they differ significantly in their sourcing [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
IELTS Practice.Org
IELTS Practice Tests and Preparation Tips
- Sample Essays
IELTS essay sample | Fast foods are bad. Do you agree?
by Manjusha Nambiar · Published March 22, 2016 · Updated April 23, 2024
Essay topic
The fast food industry has negative effects on our health, the environment and family eating habits. Do you agree or disagree?
Sample essay
Fast foods have invaded our kitchen and living room. They have changed our eating habits and made us prone to developing several health problems. I certainly agree with the argument that fast foods have a negative impact on our health and on the environment.
To start with, fast foods cause several health problems. They are rich in calories and make us obese. Regular consumption of fast foods leads to several health problems including diabetes, heart trouble and liver damage.
Most people who consume packaged food products are actually aware of their health consequences; still they can’t resist the temptation to eat them. There are several reasons to this. First, fast foods taste better. They use several ingredients that make us addicted to them. Second, fast foods are readily available. It takes hours to cook a meal. Today, most of us lead busy lives that leave us with little time to cook or clean. As a result, we are often compelled to buy fast foods even though we are aware of their health consequences.
Fast foods have a negative impact on the environment as well. The junk food industry uses plastic for packaging. The environmental consequences of plastic are well-known. Each year tons of plastic end up in landfills. It spoils the soil and clogs the drains.
Eating habits of families have also changed due to the adoption of fast foods. Parents and children munching on packaged foods sitting in front of a television is now a common sight. Gone are the days when families used to sit around a table to enjoy a meal.
To conclude, fast foods have a negative impact on almost all aspects of our life and the environment. In my opinion, it is high time we expelled them from our lives.
Tags: ielts essay sample
Manjusha Nambiar
Hi, I'm Manjusha. This is my blog where I give IELTS preparation tips.
- Next story IELTS speaking test in India | Sample questions and answers
- Previous story Sample letter | An apology
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Academic Writing Task 1
- Agree Or Disagree
- Band 7 essay samples
- Band 8 Essay Samples
- Band 8 letter samples
- Band 9 IELTS Essays
- Discuss Both Views
- Grammar exercises
- IELTS Writing
- Learn English
- OET Letters
- Sample Letters
- Writing Tips
Enter your email address:
Delivered by FeedBurner
IELTS Practice


COMMENTS
Negative Effects of Fast Food: Essay Body. Fast food is defined as food purchased from outlets that are self-service or take-out restaurants. A few well-known leaders in the fast food industry are MacDonald, KFC, Pepsi, etc. In the US, fast food outlets increased from 30,000 in 1970 to more than 233000 locations in 2004 (Rosenheck 535).
Fast food tends to be high in salt, sugar, saturated fats, trans fats, calories, and processed preservatives and ingredients. A wealth of well-conducted research has proven the negative health ...
Because of the limited access to supermarkets, they eat more unhealthy fast and processed foods and end up having 7 times the risk of early-life stroke (before age 45), putting people in nursing homes in their 30s, 40s, and 50s. 4 - 7. The vulnerable poor in these areas also have double the risk of heart attack, double the risk of diabetes, and ...
Look at the exam question and essay and do the exercises to improve your writing skills. Reading. Check your understanding: matching. Check your vocabulary: gap fill. Check your writing: multiple choice. Check your vocabulary: gap fill. Worksheets and downloads. An opinion essay about fast food - exercises 860.68 KB.
Fast food poses a profound negative impact on health due to the dynamic preparation means and the reliance on carbohydrates. Apart from the reuse of oils, a significant percentage of junk lacks a balanced diet for consumers. The phenomenon results in the ideological perspectives of increased obesity and the emergence of lifestyle diseases.
Fast food has become a significant portion of the world's diet. For example, Table 1 shows the rapid increase in consumption in the United States across all age groups. In the 1970s, an average US adult (aged 18-65 y) consumed fast food on <10% of days, but this had risen to 40.7% of days in 2017-2018. Among US survey participants aged 12 ...
Fast food has been a staple of the American diet since the early 1900s, and it has rapidly expanded over the past few decades. While fast food restaurants offer affordable and convenient meals, their impact on public health and society has been a subject of debate. This essay investigates the history and growth of the fast food industry, its impact on public health and society, the ...
Fast foods should be discouraged at all costs and if it requires the use of laws to enforce this, so be it because the benefits a person reaps from eating healthily far outweigh the burden brought about by indulging in fast foods. Works Cited. Facts. Fast Food Facts. Vivavegie. Web. Freiboth, Glenn. 6 Negative Effects of Eating Fast Food.
Arguments for the Fast Food Industry. According to Smith (2006, p. 55), fast food industry is one of the fastest developing industries not only in the developed nations but also in the developing world. This scholar argues that for the last one decade, there has been over 70% growth of this industry worldwide.
One of the most obvious threats to excessive eating fast food is obesity, which, in turn, leads to a number of diseases, creating an unnecessary burden on vital organs. Such food also has a negative effect on bones. This is mainly due to the fact that they contain sodium and other additives, which weakens bones.
The researchers acknowledge that the two essential nutrients — which play key roles in bone and blood health — are much more present in fast food now than they were 30 years ago. Specifically ...
Get original essay. One of the most significant drawbacks of fast food is its detrimental effect on our health. Fast food is often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and sugar, leading to an increased risk of obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. Studies have shown that regular consumption of fast food is associated with higher body mass index ...
Fast Food Causes and Effects: Conclusion. In conclusion, the rise of fast food is a direct consequence of the modern lifestyle prevalent in our societies. Unfortunately, its effects on human health and well-being are overwhelmingly negative. Additionally, it disrupts important family traditions and imposes financial burdens on households.
Fast food, a convenient and readily available option, has significant effects on individuals' health and the broader society. This cause and effect essay delves into the reasons why people consume fast food and examines its far-reaching consequences on physical well-being, cultural practices, and the economy.
Figure 2 - The short- and long-term impacts of junk food consumption. In the short-term, junk foods can make you feel tired, bloated, and unable to concentrate. Long-term, junk foods can lead to tooth decay and poor bowel habits. Junk foods can also lead to obesity and associated diseases such as heart disease.
Consumption of fast foods t wo times or more per. week has been associa ted with 31% highe r. prevalen ce of moderate abdominal obesity in men. and 25% higher preval ence in women 70. Obesity is ...
Explain your main idea. Develop your main idea with specific support. Continue to develop the idea. This question asks for advantages/disadvantages so make sure that you switch to a second main idea. Develop the second main idea as fully as possible. 1. Nonetheless, fast food has a huge impact in the health sector. 2.
Short Essay on Fast Food 400 Words in English. Life today has become quick and way of life changes have made individuals dependent on food and eatables that can be promptly made. Fast food is the name authored for such food things which are either pre-cooked or can be cooked in lesser time than ordinary food. ... Terrible Effects of Junk food ...
Fast Foods Popularity: Causes and Effects Essay. According to Schlosser, the expansion of the fast-food industry is influenced by major adjustments in American culture. This resulted from the lowering of the hourly wage of most US workers from 1970. This made many mothers seek other jobs where most of them work outside their homes.
One of the most visible effects of fast food consumption is the rise in obesity rates. The high energy density of fast food, combined with its palatability, promotes overeating. This chronic energy surplus leads to weight gain and obesity. Obesity, in turn, is a risk factor for numerous health conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes ...
Rapid food charges exceedingly little and tastes correct, however the negative consequences on bodily health final an awful lot longer than those immediately issues. With the high-calorie food come greater fat, cholesterol, salt and sugar -- and consequently fewer nutrients, minerals and different vitamins -- than in more healthy ingredients.
The fast food industry has negative effects on our health, the environment and family eating habits. Do you agree or disagree? Sample essay. Fast foods have invaded our kitchen and living room. They have changed our eating habits and made us prone to developing several health problems. I certainly agree with the argument that fast foods have a ...