- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes

You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
A lot of preparation goes into starting a business before you can open your doors to the public or launch your online store. One of your first steps should be to write a business plan . A business plan will serve as your roadmap when building your business.
Within your business plan, there’s an important section you should pay careful attention to: your market analysis. Your market analysis helps you understand your target market and how you can thrive within it.
Simply put, your market analysis shows that you’ve done your research. It also contributes to your marketing strategy by defining your target customer and researching their buying habits. Overall, a market analysis will yield invaluable data if you have limited knowledge about your market, the market has fierce competition, and if you require a business loan. In this guide, we'll explore how to conduct your own market analysis.
How to conduct a market analysis: A step-by-step guide
In your market analysis, you can expect to cover the following:
Industry outlook
Target market
Market value
Competition
Barriers to entry
Let’s dive into an in-depth look into each section:
Step 1: Define your objective
Before you begin your market analysis, it’s important to define your objective for writing a market analysis. Are you writing it for internal purposes or for external purposes?
If you were doing a market analysis for internal purposes, you might be brainstorming new products to launch or adjusting your marketing tactics. An example of an external purpose might be that you need a market analysis to get approved for a business loan .
The comprehensiveness of your market analysis will depend on your objective. If you’re preparing for a new product launch, you might focus more heavily on researching the competition. A market analysis for a loan approval would require heavy data and research into market size and growth, share potential, and pricing.
Step 2: Provide an industry outlook
An industry outlook is a general direction of where your industry is heading. Lenders want to know whether you’re targeting a growing industry or declining industry. For example, if you’re looking to sell VCRs in 2020, it’s unlikely that your business will succeed.
Starting your market analysis with an industry outlook offers a preliminary view of the market and what to expect in your market analysis. When writing this section, you'll want to include:
Market size
Are you chasing big markets or are you targeting very niche markets? If you’re targeting a niche market, are there enough customers to support your business and buy your product?
Product life cycle
If you develop a product, what will its life cycle look like? Lenders want an overview of how your product will come into fruition after it’s developed and launched. In this section, you can discuss your product’s:
Research and development
Projected growth
How do you see your company performing over time? Calculating your year-over-year growth will help you and lenders see how your business has grown thus far. Calculating your projected growth shows how your business will fare in future projected market conditions.
Step 3: Determine your target market
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential customer. Who is your ideal target customer? How can you cater your product to serve them specifically?
Don’t make the mistake of wanting to sell your product to everybody. Your target customer should be specific. For example, if you’re selling mittens, you wouldn’t want to market to warmer climates like Hawaii. You should target customers who live in colder regions. The more nuanced your target market is, the more information you’ll have to inform your business and marketing strategy.
With that in mind, your target market section should include the following points:
Demographics
This is where you leave nothing to mystery about your ideal customer. You want to know every aspect of your customer so you can best serve them. Dedicate time to researching the following demographics:
Income level
Create a customer persona
Creating a customer persona can help you better understand your customer. It can be easier to market to a person than data on paper. You can give this persona a name, background, and job. Mold this persona into your target customer.
What are your customer’s pain points? How do these pain points influence how they buy products? What matters most to them? Why do they choose one brand over another?
Research and supporting material
Information without data are just claims. To add credibility to your market analysis, you need to include data. Some methods for collecting data include:
Target group surveys
Focus groups
Reading reviews
Feedback surveys
You can also consult resources online. For example, the U.S. Census Bureau can help you find demographics in calculating your market share. The U.S. Department of Commerce and the U.S. Small Business Administration also offer general data that can help you research your target industry.
Step 4: Calculate market value
You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value.
A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the two. It requires for you to calculate the entire market and then estimate how much of a share you expect your business to get. For example, let’s assume your target market consists of 100,000 people. If you’re optimistic and manage to get 1% of that market, you can expect to make 1,000 sales.
A bottom-up analysis is more data-driven and requires more research. You calculate the individual factors of your business and then estimate how high you can scale them to arrive at a projected market share. Some factors to consider when doing a bottom-up analysis include:
Where products are sold
Who your competition is
The price per unit
How many consumers you expect to reach
The average amount a customer would buy over time
While a bottom-up analysis requires more data than a top-down analysis, you can usually arrive at a more accurate calculation.
Step 5: Get to know your competition
Before you start a business, you need to research the level of competition within your market. Are there certain companies getting the lion’s share of the market? How can you position yourself to stand out from the competition?
There are two types of competitors that you should be aware of: direct competitors and indirect competitors.
Direct competitors are other businesses who sell the same product as you. If you and the company across town both sell apples, you are direct competitors.
An indirect competitor sells a different but similar product to yours. If that company across town sells oranges instead, they are an indirect competitor. Apples and oranges are different but they still target a similar market: people who eat fruits.
Also, here are some questions you want to answer when writing this section of your market analysis:
What are your competitor’s strengths?
What are your competitor’s weaknesses?
How can you cover your competitor’s weaknesses in your own business?
How can you solve the same problems better or differently than your competitors?
How can you leverage technology to better serve your customers?
How big of a threat are your competitors if you open your business?
Step 6: Identify your barriers
Writing a market analysis can help you identify some glaring barriers to starting your business. Researching these barriers will help you avoid any costly legal or business mistakes down the line. Some entry barriers to address in your marketing analysis include:
Technology: How rapid is technology advancing and can it render your product obsolete within the next five years?
Branding: You need to establish your brand identity to stand out in a saturated market.
Cost of entry: Startup costs, like renting a space and hiring employees, are expensive. Also, specialty equipment often comes with hefty price tags. (Consider researching equipment financing to help finance these purchases.)
Location: You need to secure a prime location if you’re opening a physical store.
Competition: A market with fierce competition can be a steep uphill battle (like attempting to go toe-to-toe with Apple or Amazon).
Step 7: Know the regulations
When starting a business, it’s your responsibility to research governmental and state business regulations within your market. Some regulations to keep in mind include (but aren’t limited to):
Employment and labor laws
Advertising
Environmental regulations
If you’re a newer entrepreneur and this is your first business, this part can be daunting so you might want to consult with a business attorney. A legal professional will help you identify the legal requirements specific to your business. You can also check online legal help sites like LegalZoom or Rocket Lawyer.
Tips when writing your market analysis
We wouldn’t be surprised if you feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information needed in a market analysis. Keep in mind, though, this research is key to launching a successful business. You don’t want to cut corners, but here are a few tips to help you out when writing your market analysis:
Use visual aids
Nobody likes 30 pages of nothing but text. Using visual aids can break up those text blocks, making your market analysis more visually appealing. When discussing statistics and metrics, charts and graphs will help you better communicate your data.
Include a summary
If you’ve ever read an article from an academic journal, you’ll notice that writers include an abstract that offers the reader a preview.
Use this same tactic when writing your market analysis. It will prime the reader of your market highlights before they dive into the hard data.
Get to the point
It’s better to keep your market analysis concise than to stuff it with fluff and repetition. You’ll want to present your data, analyze it, and then tie it back into how your business can thrive within your target market.
Revisit your market analysis regularly
Markets are always changing and it's important that your business changes with your target market. Revisiting your market analysis ensures that your business operations align with changing market conditions. The best businesses are the ones that can adapt.
Why should you write a market analysis?
Your market analysis helps you look at factors within your market to determine if it’s a good fit for your business model. A market analysis will help you:
1. Learn how to analyze the market need
Markets are always shifting and it’s a good idea to identify current and projected market conditions. These trends will help you understand the size of your market and whether there are paying customers waiting for you. Doing a market analysis helps you confirm that your target market is a lucrative market.
2. Learn about your customers
The best way to serve your customer is to understand them. A market analysis will examine your customer’s buying habits, pain points, and desires. This information will aid you in developing a business that addresses those points.
3. Get approved for a business loan
Starting a business, especially if it’s your first one, requires startup funding. A good first step is to apply for a business loan with your bank or other financial institution.
A thorough market analysis shows that you’re professional, prepared, and worth the investment from lenders. This preparation inspires confidence within the lender that you can build a business and repay the loan.
4. Beat the competition
Your research will offer valuable insight and certain advantages that the competition might not have. For example, thoroughly understanding your customer’s pain points and desires will help you develop a superior product or service than your competitors. If your business is already up and running, an updated market analysis can upgrade your marketing strategy or help you launch a new product.
Final thoughts
There is a saying that the first step to cutting down a tree is to sharpen an axe. In other words, preparation is the key to success. In business, preparation increases the chances that your business will succeed, even in a competitive market.
The market analysis section of your business plan separates the entrepreneurs who have done their homework from those who haven’t. Now that you’ve learned how to write a market analysis, it’s time for you to sharpen your axe and grow a successful business. And keep in mind, if you need help crafting your business plan, you can always turn to business plan software or a free template to help you stay organized.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...


Business Plan Market Analysis - Your Road Map to Success
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the business plan market analysis section of a business plan. Market Analysis is a key part of any good business plan, which will help you better assess and understand your market. The business plan market analysis section is the heart and soul of your strategy, impacting everything from marketing to operations to the financial forecast. The market analysis helps you understand your position within the industry, the potential size of your market, the competitive landscape, and most importantly, it assists in identifying your target customers. In this blog post, we'll take you through the essentials of market analysis: what it is, why it's crucial, and the components it comprises.
Table of Contents
Business Plan Market Analysis - What Is It?
- Key Components
- How To Implement
Tips and Best Practices
- Market Analysis Case Study
Wrapping It All Up
Market analysis is a comprehensive examination of the dynamics, trends, and competitive landscape of the business environment within which a company operates. It is a vital component of a business plan as it allows entrepreneurs and business owners to understand their industry and market better, enabling them to make well-informed decisions. The business plan market analysis section has two main benefits. Firstly, it Allows you to Identify key opportunities in the market. By studying the market, a business can identify gaps, trends, or customer needs that aren't currently being met and then plan to cater to them effectively. Secondly, it also allows you to recognise potential threats and competition. By understanding your competitors, their offerings, strategies, strengths, and weaknesses, you can position yourself better against their position in the marketplace. Overall the role of market analysis in a business plan cannot be understated. It serves as the foundation upon which the marketing and sales strategies are built. In the following sections, we will take a deep dive into the key components of market analysis and how to conduct it effectively.
Remember, the opening of your Executive Summary sets the tone for the entire document. Make it memorable and compelling to encourage the reader to continue exploring.

What Are The Key Components of Market Analysis?
Understanding the key components of a market analysis is crucial to conducting one effectively. Each element contributes a unique insight into your market, providing a comprehensive overview of the environment in which your business will operate. Here are the key components:
- Industry Description and Outlook: This involves describing the industry within which your business will operate. Look to identify the key trends influencing it and the outlook of the future of the industry based on reliable industry forecasts.
- Target Market: It's vital to identify and understand your ideal customers. This involves defining the demographics (age, gender, income, etc.), psychographics (interests, values, behaviours, etc.), and geographic location of the customers your business aims to target. Furthermore, it's important to understand their needs, preferences, and buying habits.
- Market Size and Trends: Here, you need to determine the total size of your target market. This involves quantifying the number of potential customers, the total sales volume, or the total market value. Furthermore, it's crucial to identify key market trends, which may include changes in customer behaviour, new technologies, or shifting regulatory environments.
- Market Segmentation: This involves dividing your target market into distinct groups (segments) based on certain characteristics. These might include age, location, buying habits, or customer needs. By taking the time to segment your customers you can develop better targeting strategies for your marketing campaigns.
- Competitive Analysis: This component involves identifying your key competitors and analysing their products, sales strategies, market share, strengths, and weaknesses. A competitive analysis will help your business identify its unique selling proposition (USP) and differentiate itself from competitors.
- SWOT Analysis: Finally, conducting a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis will allow your business to identify its internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats in the market. This can help your business leverage its strengths, address its weaknesses, capitalise on opportunities, and prepare for potential threats.
Business Plan Market Analysis - How to Implement
Conducting a business plan market analysis might seem like a daunting task, but you can make it more achievable by breaking it down into key tasks.
- Industry Description and Outlook: Start by gathering data on your industry. This can include industry reports, market research data, news articles, and government statistics. Remember to cite your sources to add credibility to your analysis.
- Target Market: Identifying your target market requires an understanding of who is most likely to buy your product or service. You can conduct surveys, interviews, or focus groups to gather data on potential customers. If you already have a customer database, try to delve into this further by conducting post-purchase interviews with customers. Try to identify demographic, geographic, and psychographic characteristics, as well as buying habits and needs. The aim is to create a clear and specific profile of your ideal customer. You will aim to use this data to generate customer segments to target with your marketing campaigns.
- Market Size and Trends: Estimating market size can be challenging but can be done by looking at industry reports, government data, and market research studies. You can also look at the sales of competitors or analogous products. Identify key market trends by examining changes in customer behaviour, technological advances, and regulatory changes.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify your key competitors and analyse their offerings. Look at their products, pricing, marketing strategies, and market share. Try to understand their strengths and weaknesses. You can gather this information from their websites, customer reviews, and industry reports. Use this analysis to identify opportunities for your business to differentiate itself.
- SWOT Analysis: You can consolidate all of your initial research into a SWOT analysis which will help synthesise your learning and make it easier to develop strategies from your research.
Remember, conducting a market analysis isn't a one-time task. Markets are dynamic, with customer preferences, competition, and external factors continually changing. Your aim should be to continually update your business plan market analysis periodically. Here at Action Planr we have a full guide on how to conduct a SWOT Analysis for more detailed information on the full process.

Successfully conducting a market analysis involves more than just understanding its components and knowing where to find the necessary data. Here are some tips and best practices to help make your market analysis more robust, reliable, and useful for decision-making:
- Using Reliable Data Sources for Market Research: The quality of your analysis is directly tied to the quality of your data. Therefore, it's important to use reliable sources such as government databases, industry reports, reputable market research firms, and academic studies. Be wary of data that doesn't come from reliable sources.
- Understanding the Importance of Both Quantitative and Qualitative Research: Quantitative data, like statistics and numerical facts, provides a solid base for your analysis. But don't underestimate the power of qualitative data—opinions, anecdotes, and experiences—which can provide deeper insight into customer behaviours and preferences.
- Keeping the Analysis Current and Updated: Markets change rapidly. What was true last year—or even last month—may not hold today. Regularly updating your market analysis can help you keep up with changes and adjust your business strategies accordingly.
- Ensuring Your Analysis is Relevant to Your Specific Business Model: The insights you need depend on your business model. A B2B company will need a different kind of analysis than a B2C company. Tailor your market analysis to your specific business needs and objectives.
- Importance of Validating Assumptions: In the course of conducting a market analysis, you'll likely make assumptions. Be sure to validate these assumptions with solid data whenever possible.
- Keep your Audience in Mind: If your business plan is read by investors, they'll be interested in market size, growth opportunities, and competitive landscape. Make sure your market analysis addresses these topics and is presented in a clear, easy-to-understand format.

Business Plan Market Analysis - Case Study
To understand how the principles and processes of market analysis work in a real-world context, let's look at a case study of an innovative tech startup, "Techie Toys." Techie Toys is a company that produces educational toys based on augmented reality technology, targeting children aged 6 to 12. Their goal is to make learning fun and interactive.
- Industry Description and Outlook: Techie Toys reviewed multiple industry reports and found that the educational toy market has seen substantial growth over recent years, and this growth is expected to continue due to increasing focus on interactive learning methods. The integration of technology into educational toys, specifically augmented reality, is a significant trend shaping the industry.
- Target Market: Through surveys and focus groups, Techie Toys identified their target customers as parents of children aged 6 to 12 who value educational development and are comfortable with technology integration in toys. These parents have middle to upper-middle income, are mostly city dwellers, and are willing to invest in their children's education.
- Market Size and Trends: By analysing industry reports and sales of similar products, Techie Toys estimated a sizable target market for their augmented reality educational toys. The trend of "edutainment" was identified as a key market trend, with technology-based educational toys gaining popularity.
- Market Segmentation: Techie Toys segmented their market based on age (6-8, 9-12), type of toy preferred (science, math, language arts), and parents' willingness to spend on educational toys. They plan to tailor their products and marketing strategies according to these segments.
- Competitive Analysis: Techie Toys identified several key competitors offering educational toys but found a gap in those providing augmented reality-based learning. They also discovered that their unique selling proposition – interactive learning through augmented reality – is an aspect where they outshine their competitors.
- SWOT Analysis: Strengths identified included a strong development team, unique product offering, and alignment with market trends. Weaknesses involved a higher price point and lack of brand recognition. Opportunities included a growing market and a trend toward edutainment, while threats were potential competitors and rapid technological change.
By conducting this detailed market analysis, Techie Toys was able to effectively position itself within the market, identify its unique selling proposition, and tailor their product development and marketing strategy to their target audience. This comprehensive understanding of their market greatly contributed to their success.
The business plan market analysis section of a business plan is one of its most critical components. Conducting a detailed and accurate market analysis can be a challenging process, but as we've seen in our guide, the benefits are large. Business is all about planning and conducting an in-depth market analysis process, It will allow your business to navigate its environment with knowledge and foresight. The insight gained can help you identify growth opportunities and provide a strong basis for the development of effective marketing and sales strategies. Keep these insights, steps, and tips in mind as you work on your market analysis and remember markets are continually changing so don't make this a one-and-done exercise. If you are looking for help with other sections of the business plan, please check out our Learning Zone homepage.
Analyze your market like a pro with this step-by-step guide + insider tips
Don’t fall into the trap of assuming that you already know enough about your market.
No matter how fantastic your product or service is, your business cannot succeed without sufficient market demand .
You need a clear understanding of who will buy your product or service and why .
You want to know if there is a clear market gap and a market large enough to support the survival and growth of your business.
Industry research and market analysis will help make sure that you are on the right track .
It takes time , but it is time well spent . Thank me later.
WHAT is Market Analysis?
The Market Analysis section of a business plan is also sometimes called:
- Market Demand, Market Trends, Target Market, The Market
- Industry Analysis & Trends, Industry & Market Analysis, Industry and Market Research
WHY Should You Do Market Analysis?
First and foremost, you need to demonstrate beyond any reasonable doubt that there is real need and sufficient demand for your product or service in the market, now and going forward.
- What makes you think that people will buy your products or services?
- Can you prove it?
Your due diligence on the market opportunity and validating the problem and solution described in the Product and Service section of your business plan are crucial for the success of your venture.
Also, no company operates in a vacuum. Every business is part of a larger overall industry, the forces that affect your industry as a whole will inevitably affect your business as well.
Evaluating your industry and market increases your own knowledge of the factors that contribute to your company’s success and shows the readers of your business plan that you understand the external business conditions.
External Support
In fact, if you are seeking outside financing, potential backers will most definitely be interested in industry and market conditions and trends.
You will make a positive impression and have a better chance of getting their support if you show market analysis that strengthens your business case, combining relevant and reliable data with sound judgement.
Let’s break down how to do exactly that, step by step:
HOW To Do Market Analysis: Step-by-Step
So, let’s break up how market analysis is done into three steps:
- Industry: the total market
- Target Market: specific segments of the industry that you will target
- Target Customer: characteristics of the customers that you will focus on
Step 1: Industry Analysis
How do you define an industry.
For example, the fashion industry includes fabric suppliers, designers, companies making finished clothing, distributors, sales representatives, trade publications, retail outlets online and on the high street.
How Do You Analyze an Industry?
Briefly describe your industry, including the following considerations:
1.1. Economic Conditions
Outline the current and projected economic conditions that influence the industry your business operates in, such as:
- Official economic indicators like GDP or inflation
- Labour market statistics
- Foreign trade (e.g., import and export statistics)
1.2. Industry Description
Highlight the distinct characteristic of your industry, including:
- Market leaders , major customer groups and customer loyalty
- Supply chain and distribution channels
- Profitability (e.g., pricing, cost structure, margins), financials
- Key success factors
- Barriers to entry preventing new companies from competing in the industry
1.3. Industry Size and Growth
Estimate the size of your industry and analyze how industry growth affects your company’s prospects:
- Current size (e.g., revenues, units sold, employment)
- Historic and projected industry growth rate (low/medium/high)
- Life-cycle stage /maturity (emerging/expanding/ mature/declining)
1.4. Industry Trends
- Industry Trends: Describe the key industry trends and evaluate the potential impact of PESTEL (political / economic / social / technological / environmental / legal) changes on the industry, including the level of sensitivity to:
- Seasonality
- Economic cycles
- Government regulation (e.g. environment, health and safety, international trade, performance standards, licensing/certification/fair trade/deregulation, product claims) Technological change
- Global Trends: Outline global trends affecting your industry
- Identify global industry concerns and opportunities
- International markets that could help to grow your business
- Strategic Opportunity: Highlight the strategic opportunities that exist in your industry
Step 2: Target Customer Identification
Who is a target customer.
One business can have–and often does have–more than one target customer group.
The success of your business depends on your ability to meet the needs and wants of your customers. So, in a business plan, your aim is to assure readers that:
- Your customers actually exist
- You know exactly who they are and what they want
- They are ready for what you have to offer and are likely to actually buy
How Do You Identify an Ideal Target Customer?
2.1. target customer.
- Identify the customer, remembering that the decision-maker who makes the purchase can be a different person or entity than the end-user.
2.2. Demographics
- For consumers ( demographics ): Age, gender, income, occupation, education, family status, home ownership, lifestyle (e.g., work and leisure activities)
- For businesses ( firmographic ): Industry, sector, years in business, ownership, size (e.g., sales, revenues, budget, employees, branches, sq footage)
2.3. Geographic Location
- Where are your customers based, where do they buy their products/services and where do they actually use them
2.4 Purchasing Patterns
- Identify customer behaviors, i.e., what actions they take
- how frequently
- and how quickly they buy
2.5. Psychographics
- Identify customer attitudes, i.e., how they think or feel
- Urgency, price, quality, reputation, image, convenience, availability, features, brand, customer service, return policy, sustainability, eco-friendliness, supporting local business
- Necessity/luxury, high involvement bit ticket item / low involvement consumable
Step 3: Target Market Analysis
What is a target market.
Target market, or 'target audience', is a group of people that a business has identified as the most likely to purchase its offering, defined by demographic, psychographic, geographic and other characteristics. Target market may be broken down to target customers to customize marketing efforts.
How Do You Analyze a Target Market?
So, how many people are likely to become your customers?
To get an answer to this questions, narrow the industry into your target market with a manageable size, and identify its key characteristics, size and trends:
3.1. Target Market Description
Define your target market by:
- Type: B2C, B2B, government, non-profits
- Geographic reach: Specify the geographic location and reach of your target market
3.2. Market Size and Share
Estimate how large is the market for your product or service (e.g., number of customers, annual purchases in sales units and $ revenues). Explain the logic behind your calculation:
- TAM (Total Available/Addressable/Attainable Market) is the total maximum demand for a product or service that could theoretically be generated by selling to everyone in the world who could possibly buy from you, regardless of competition and any other considerations and restrictions.
- SAM (Serviceable Available Market) is the portion of the TAM that you could potentially address in a specific market. For example, if your product/service is only available in one country or language.
- SOM (Service Obtainable Market / Share of Market) is the share of the SAM that you can realistically carve out for your product or service. This the target market that you will be going after and can reasonably expect to convert into a customer base.
3.3. Market Trends
Illustrate the most important themes, changes and developments happening in your market. Explain the reasons behind these trends and how they will favor your business.
3.4. Demand Growth Opportunity
Estimate future demand for your offering by translating past, current and future market demand trends and drivers into forecasts:
- Historic growth: Check how your target market has grown in the past.
- Drivers past: Identify what has been driving that growth in the past.
- Drivers future: Assess whether there will be any change in influence of these and other drivers in the future.
How Big Should My Target Market Be?
Well, if the market opportunity is small, it will limit how big and successful your business can become. In fact, it may even be too small to support a successful business at all.
On the other hand, many businesses make the mistake of trying to appeal to too many target markets, which also limits their success by distracting their focus.
What If My Stats Look Bad?
Large and growing market suggests promising demand for your offering now and into the future. Nevertheless, your business can still thrive in a smaller or contracting market.
Instead of hiding from unfavorable stats, acknowledge that you are swimming against the tide and devise strategies to cope with whatever lies ahead.
Step 4: Industry and Market Analysis Research
The market analysis section of your business plan should illustrate your own industry and market knowledge as well as the key findings and conclusions from your research.
Back up your findings with external research sources (= secondary research) and results of internal market research and testing (= primary research).
What is Primary and Secondary Market Research?
Yes, there are two main types of market research – primary and secondary – and you should do both to adequately cover the market analysis section of your business plan:
- Primary market research is original data you gather yourself, for example in the form of active fieldwork collecting specific information in your market.
- Secondary market research involves collating information from existing data, which has been researched and shared by reliable outside sources . This is essentially passive desk research of information already published .
Unless you are working for a corporation, this exercise is not about your ability to do professional-level market research.
Instead, you just need to demonstrate fundamental understanding of your business environment and where you fit in within the market and broader industry.
Why Do You Need To Do Primary & Secondary Market Research?
There are countless ways you could go collecting industry and market research data, depending on the type of your business, what your business plan is for, and what your needs, resources and circumstances are.
For tried and tested tips on how to properly conduct your market research, read the next section of this guide that is dedicated to primary and secondary market research methods.
In any case, tell the reader how you carried out your market research. Prove what the facts are and where you got your data. Be as specific as possible. Provide statistics, numbers, and sources.
When doing secondary research, always make sure that all stats, facts and figures are from reputable sources and properly referenced in both the main text and the Appendix of your business plan. This gives more credibility to your business case as the reader has more confidence in the information provided.
Go to the Primary and Secondary Market Research post for my best tips on industry, market and competitor research.
7 TOP TIPS For Writing Market Analysis
1. realistic projections.
Above all, make sure that you are realistic in your projections about how your product or service is going to be accepted in the market, otherwise you are going to seriously undermine the credibility of your entire business case.
2. Laser Focus
Discuss only characteristic of your target market and customers that are observable, factual and meaningful, i.e. directly relate to your customers’ decision to purchase.
Always relate the data back to your business. Market statistics are meaningless until you explain where and how your company fits in.
For example, as you write about the market gap and the needs of your target customers, highlight how you are uniquely positioned to fill them.
In other words, your goal is to:
- Present your data
- Analyze the data
- Tie the data back to how your business can thrive within your target market
3. Target Audience
On a similar note, tailor the market analysis to your target audience and the specific purpose at hand.
For example, if your business plan is for internal use, you may not have to go into as much detail about the market as you would have for external financiers, since your team is likely already very familiar with the business environment your company operates in.
4. Story Time
Make sure that there is a compelling storyline and logical flow to the market information presented.
The saying “a picture is worth a thousand words” certainly applies here. Industry and market statistics are easier to understand and more impactful if presented as a chart or graph.
6. Information Overload
Keep your market analysis concise by only including pertinent information. No fluff, no repetition, no drowning the reader in a sea of redundant facts.
While you should not assume that the reader knows anything about your market, do not elaborate on unnecessary basic facts either.
Do not overload the reader in the main body of the business plan. Move everything that is not essential to telling the story into the Appendix. For example, summarize the results of market testing survey in the main body of the business plan document, but move the list of the actual survey questions into the appendix.
7. Marketing Plan
Note that market analysis and marketing plan are two different things, with two distinct chapters in a business plan.
As the name suggests, market analysis examines where you fit in within your desired industry and market. As you work thorugh this section, jot down your ideas for the marketing and strategy section of your business plan.
Final Thoughts
Remember that the very act of doing the research and analysis is a great opportunity to learn things that affect your business that you did not know before, so take your time doing the work.
Related Questions
What is the purpose of industry & market research and analysis.
The purpose of industry and market research and analysis is to qualitatively and quantitatively assess the environment of a business and to confirm that the market opportunity is sufficient for sustainable success of that business.
Why are Industry & Market Research and Analysis IMPORTANT?
Industry and market research and analysis are important because they allow you to gain knowledge of the industry, the target market you are planning to sell to, and your competition, so you can make informed strategic decisions on how to make your business succeed.
How Can Industry & Market Research and Analysis BENEFIT a Business?
Industry and market research and analysis benefit a business by uncovering opportunities and threats within its environment, including attainable market size, ideal target customers, competition and any potential difficulties on the company’s journey to success.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts

How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

What is the Market Analysis in a Business Plan?
The market analysis section of your business plan is where you discuss the size of the market in which you’re competing and market trends that might affect your future potential such as economic, political, social and/or technological shifts.
This helps you and readers understand if your market is big enough to support your business’ growth, and whether future conditions will help or hurt your business. For example, stating that your market size is $56 billion, has been growing by 10% for the last 10 years, and that trends are expected to further increase the market size bodes well for your company’s success.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
What Should a Market Analysis Include?
You’ll want to address these issues in your market analysis:
- Size of Industry – How big is the overall industry?
- Projected Growth Rate of Industry – Is the industry growing or shrinking? How fast?
- Target Market – Who are you targeting with this product or service?
- Competition – How many businesses are currently in the same industry?
Learn how to write the full market analysis below.
How to Write a Market Analysis
Here’s how to write the market analysis section of a business plan.
- Describe each industry that you are competing in or will be targeting.
- Identify direct competition, but don’t forget about indirect competition – this may include companies selling different products to the same potential customer segments.
- Highlight strengths and weaknesses for both direct and indirect competitors, along with how your company stacks up against them based on what makes your company uniquely positioned to succeed.
- Include specific data, statistics, graphs, or charts if possible to make the market analysis more convincing to investors or lenders.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Industry overview.
In your industry overview, you will define the market in which you are competing (e.g., restaurant, medical devices, etc.).
You will then detail the sub-segment or niche of that market if applicable (e.g., within restaurants there are fast food restaurants, fine dining, etc.).
Next, you will describe the key characteristics of your industry. For example, discuss how big the market is in terms of units and revenues. Let the reader know if the market is growing or declining (and at what rate), and what key industry trends are facing your market.
Use third-party market research as much as possible to validate the discussion of your industry.
Here is a list of additional items you may analyze for a complete industry overview:
- An overview of the current state of the industry . How big is it, how much does it produce or sell? What are its key differentiators from competitors? What is its target customer base like – demographic information and psychographics? How has the industry performed over time (global, domestic)?
- Analyze the macro-economic factors impacting your industry . This includes items such as economic growth opportunities, inflation, exchange rates, interest rates, labor market trends, and technological improvements. You want to make sure that all of these are trending in a positive direction for you while also being realistic about them. For example, if the economy is in shambles you might want to wait before entering the particular market.
- Analyze the political factors impacting your industry . This is an often-overlooked section of any business plan, but it can be important depending on what type of company you are starting. If you’re in a highly regulated industry (such as medical devices), this is something that you’ll want to include.
- Analyze the social factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing society’s interest in your product or service, historical trends in buying patterns in your industry, and any effects on the industry due to changes in culture. For example, if there is a growing counter-culture trend against big oil companies you might want to position yourself differently than a company in this industry.
- Analyze the technological factors impacting your industry . This includes analyzing new technologies being developed in software, hardware, or applications that can be used to improve your product or service. It also includes emerging consumer trends and will be highly dependent on your business type. In a technology-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting consumers. For an educational-related venture, you would analyze how these changes are impacting students, teachers, and/or administrators.
For each of these items, you want to provide some detail about them including their current state as well as what external factors have played a role in the recent past. You can also include many other important factors if they apply to your business including demographic trends, legal issues, environmental concerns, and sustainability issues.
When you are done analyzing all of these factors, wrap it up by summing them up in a statement that includes your view on the future of the industry. This should be positive to attract investors, potential customers, and partners.
If you’re having trouble thinking about all of these factors then it might be helpful to first develop a SWOT analysis for your business.
Once you have an understanding of the market, you’ll need to think about how you will position yourself within that potential market.
Picking Your Niche
You want to think about how large your market is for this venture. You also want to consider whether you’d like to pick a niche within the overall industry or launch yourself into the mainstream.
If you have an innovative product it can be easier to enter the mainstream market – but at the same time, you might face some additional competition if there are similar products available.
You can choose to specialize in a niche market where you’ll face less competition – but might be able to sell your services at a higher price point (this could make it easier for you to get potential customers).
Of course, if your product or service is unique then there should be no competition. But, what happens if it isn’t unique? Will you be able to differentiate yourself enough to create a competitive advantage or edge?
If you are planning on entering the mainstream market, think about whether there are different sub-niches within your specific market. For example, within the technology industry, you can choose to specialize in laptops or smartphones or tablets, or other categories. While it will be more difficult to be unique in a mainstream market, you will still be able to focus on one type or category of products.
How Will You Stand Out?
Many companies are able to stand out – whether by offering a product that is unique or by marketing their products in a way that consumers notice. For example, Steve Jobs was able to take a business idea like the iPhone and make it into something that people talked about (while competitors struggled to play catch up).
You want your venture to stand out – whether with an innovative product or service or through marketing strategies. This might include a unique brand, name, or logo. It might also include packaging that stands out from competitors.
Write down how you will achieve this goal of standing out in the marketplace. If it’s a product, then what features do you have that other products don’t? If it’s a service, then what is it about this service that will make people want to use your company rather than your competition?
You also need to think about marketing. How are you going to promote yourself or sell your product or service? You’ll need a marketing plan for this – which might include writing copy, creating an advertisement, setting up a website, and several other activities. This should include a description of each of these strategies.
If you’re struggling with the details of any of these sections, it might be helpful to research what other companies in your market are doing and how they’ve been successful. You can use this business information to inform your own strategies and plans.
Relevant Market Size & Competition
In the second stage of your analysis, you must determine the size and competition in your specific market.
Target Market Section
Your company’s relevant market size is the amount of money it could make each year if it owned a complete market share.
It’s simple.
To begin, estimate how many consumers you expect to be interested in purchasing your products or services each year.
To generate a more precise estimate, enter the monetary amount these potential customers may be ready to spend on your goods or services each year.
The size of your market is the product of these two figures. Calculate this market value here so that your readers can see how big your market opportunity is (particularly if you are seeking debt or equity funding).
You’ll also want to include an analysis of your market conditions. Is this a growing or declining market? How fast is it growing (or declining)? What are the general trends in the market? How has your market shifted over time?
Include all of this information in your own business plan to give your readers a clear understanding of the market landscape you’re competing in.
The Competition
Next, you’ll need to create a comprehensive list of the competitors in your market. This competitive analysis includes:
- Direct Competitors – Companies that offer a similar product or service
- Indirect Competitors – Companies that sell products or services that are complementary to yours but not directly related
To show how large each competitor is, you can use metrics such as revenue, employees, number of locations, etc. If you have limited information about the company on hand then you may want to do some additional research or contact them directly for more information. You should also include their website so readers can learn more if they desire (along with social media profiles).
Once you complete this list, take a step back and try to determine how much market share each competitor has. You can use different methods to do this such as market research, surveys, or conduct focus groups or interviews with target customers.
You should also take into account the barriers to entry that exist in your market. What would it take for a new company to enter the market and start competing with you? This could be anything from capital requirements to licensing and permits.
When you have all of this information, you’ll want to create a table like the one below:
Once you have this data, you can start developing strategies to compete with the other companies which will be used again later to help you develop your marketing strategy and plan.
Writing a Market Analysis Tips
- Include an explanation of how you determined the size of the market and how much share competitors have.
- Include tables like the one above that show competitor size, barriers to entry, etc.
- Decide where you’re going to place this section in your business plan – before or after your SWOT analysis. You can use other sections as well such as your company summary or product/service description. Make sure you consider which information should come first for the reader to make the most sense.
- Brainstorm how you’re going to stand out in this competitive market.
Formatting the Market Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
Now that you understand the different components of the market analysis, let’s take a look at how you should structure this section in your business plan.
Your market analysis should be divided into two sections: the industry overview and market size & competition.
Each section should include detailed information about the topic and supporting evidence to back up your claims.
You’ll also want to make sure that all of your data is up-to-date. Be sure to include the date of the analysis in your business plan so readers know when it was conducted and if there have been any major changes since then.
In addition, you should also provide a short summary of what this section covers at the beginning of each paragraph or page. You can do this by using a title such as “Industry Overview” or another descriptive phrase that is easy to follow.
As with all sections in a business plan, make sure your market analysis is concise and includes only the most relevant information to keep your audience engaged until they reach your conclusion.
A strong market analysis can give your company a competitive edge over other businesses in its industry, which is why it’s essential to include this section in your business plan. By providing detailed information about the market you’re competing in, you can show your readers that you understand the industry and know how to capitalize on current and future trends.
Business Plan Market Analysis Examples
The following are examples of how to write the market analysis section of a business plan:
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #1 – Hosmer Sunglasses, a sunglasses manufacturer based in California
According to the Sunglass Association of America, the retail sales volume of Plano (non-prescription) sunglasses, clip-on sunglasses, and children’s sunglasses (hereinafter collectively referred to as “Sunwear”) totaled $2.9 billion last year. Premium-priced sunglasses are driving the Plano Sunwear market. Plano sunglasses priced at $100 or more accounted for more than 49% of all Sunwear sales among independent retail locations last year.
The Sunglass Association of America has projected that the dollar volume for retail sales of Plano Sunwear will grow 1.7% next year. Plano sunglass vendors are also bullish about sales in this year and beyond as a result of the growth of technology, particularly the growth of laser surgery and e-commerce.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #2 – Nailed It!, a family-owned restaurant in Omaha, NE
According to the Nebraska Restaurant Association, last year total restaurant sales in Nebraska grew by 4.3%, reaching a record high of $2.8 billion. Sales at full-service restaurants were particularly strong, growing 7% over 2012 figures. This steady increase is being driven by population growth throughout the state. The Average Annual Growth Rate (AGR) since 2009 is 2.89%.
This fast growth has also encouraged the opening of new restaurants, with 3,035 operating statewide as of this year. The restaurant industry employs more than 41,000 workers in Nebraska and contributes nearly $3 billion to the state economy every year.
Nebraska’s population continues to increase – reaching 1.9 million in 2012, a 1.5% growth rate. In addition to population, the state has experienced record low unemployment every year since 2009 – with an average of 4.7% in 2013 and 2014.
Business Plan Market Analysis Example #3 – American Insurance Company (AIC), a chain of insurance agencies in Maine
American Insurance Company (AIC) offers high-quality insurance at low prices through its chain of retail outlets in the state of Maine. Since its inception, AIC has created an extensive network of agents and brokers across the country with expanding online, call center and retail business operations.
AIC is entering a market that will more than double in size over the next 50 years according to some industry forecasts. The insurance industry is enjoying low inflation rates, steady income growth, and improving standards of living for most Americans during what has been a difficult period for much of American business. This makes this a good time to enter the insurance industry as it enjoys higher margins because customers are purchasing more coverage due to increased costs from medical care and higher liability claims.
American Insurance Company provides affordable homeowners, auto, and business insurance through high-quality fulfillment centers across America that have earned a reputation for top-notch customer service.
AIC will face significant competition from both direct and indirect competitors. The indirect competition will come from a variety of businesses, including banks, other insurance companies, and online retailers. The direct competition will come from other well-funded start-ups as well as incumbents in the industry. AIC’s competitive advantages include its low prices, high quality, and excellent customer service.
AIC plans to grow at a rate that is above average for the industry as a whole. The company has identified a market that is expected to grow by more than 100% in the next decade. This growth is due to several factors: the increase in the number of two-income households, the aging population, and the impending retirement of many baby boomers will lead to an increase in the number of people who are purchasing insurance.
AIC projects revenues of $20M in year one, which is equivalent to 100% growth over the previous year. AIC forecasts revenue growth of 40%-60% each year on average for 10 years. After that, revenue growth is expected to slow down significantly due to market saturation.
The following table illustrates these projections:
Competitive Landscape
Direct Competition: P&C Insurance Market Leaders
Indirect Competition: Banks, Other Insurance Companies, Retailers
Market Analysis Conclusion
When writing the market analysis section, it is important to provide specific data and forecasts about the industry that your company operates in. This information can help make your business plan more convincing to potential investors.
If it’s helpful, you should also discuss how your company stacks up against its competitors based on what makes it unique. In addition, you can identify any strengths or weaknesses that your company has compared to its competitors.
Based on this data, provide projections for how much revenue your company expects to generate over the next few years. Providing this information early on in the business plan will help convince investors that you know what you are talking about and your company is well-positioned to succeed.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
How to Write a Great Business Plan Executive Summary How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan The Management Team Section of Your Business Plan Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix Best Business Plan Software Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Planning Articles & Templates

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
Alyssa Gregory is an entrepreneur, writer, and marketer with 20 years of experience in the business world. She is the founder of the Small Business Bonfire, a community for entrepreneurs, and has authored more than 2,500 articles for The Balance and other popular small business websites.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/alyssa-headshot-2018-5b73ee0046e0fb002531cb50.png)
The market analysis section of your business plan comes after the products or services section and should provide a detailed overview of the industry you intend to sell your product or service in, including statistics to support your claims.
In general, the market analysis section should include information about the industry, your target market, your competition, and how you intend to make a place for your own product and service. Extensive data for this section should be added to the end of the business plan as appendices, with only the most important statistics included in the market analysis section itself.
What Should a Market Analysis Include?
The market analysis section of your small business plan should include the following:
- Industry Description and Outlook : Describe your industry both qualitatively and quantitatively by laying out the factors that make your industry an attractive place to start and grow a business. Be sure to include detailed statistics that define the industry including size, growth rate , trends, and outlook.
- Target Market : Who is your ideal client/customer? This data should include demographics on the group you are targeting including age, gender, income level, and lifestyle preferences. This section should also include data on the size of the target market, the purchase potential and motivations of the audience, and how you intend to reach the market.
- Market Test Results : This is where you include the results of the market research you conducted as part of your initial investigation into the market. Details about your testing process and supporting statistics should be included in the appendix.
- Lead Time : Lead time is the amount of time it takes for an order to be fulfilled once a customer makes a purchase. This is where you provide information on the research you've completed on how long it will take to handle individual orders and large volume purchases, if applicable.
- Competitive Analysis : Who is your competition? What are the strengths and weaknesses of the competition? What are the potential roadblocks preventing you from entering the market?
7 Tips for Writing a Market Analysis
Here is a collection of tips to help you write an effective and well-rounded market analysis for your small business plan.
- Use the Internet : Since much of the market analysis section relies on raw data, the Internet is a great place to start. Demographic data can be gathered from the U.S. Census Bureau. A series of searches can uncover information on your competition, and you can conduct a portion of your market research online.
- Be the Customer : One of the most effective ways to gauge opportunity among your target market is to look at your products and services through the eyes of a purchaser. What is the problem that needs to be solved? How does the competition solve that problem? How will you solve the problem better or differently?
- Cut to the Chase : It can be helpful to your business plan audience if you include a summary of the market analysis section before diving into the details. This gives the reader an idea about what's to come and helps them zero in on the most important details quickly.
- Conduct Thorough Market Research : Put in the necessary time during the initial exploration phase to research the market and gather as much information as you can. Send out surveys, conduct focus groups, and ask for feedback when you have an opportunity. Then use the data gathered as supporting materials for your market analysis.
- Use Visual Aids : Information that is highly number-driven, such as statistics and metrics included in the market analysis, is typically easier to grasp when it's presented visually. Use charts and graphs to illustrate the most important numbers.
- Be Concise : In most cases, those reading your business plan already have some understanding of the market. Include the most important data and results in the market analysis section and move the support documentation and statistics to the appendix.
- Relate Back to Your Business : All of the statistics and data you incorporate in your market analysis should be related back to your company and your products and services. When you outline the target market's needs, put the focus on how you are uniquely positioned to fulfill those needs.
- 400+ Sample Business Plans
- WHY UPMETRICS?
Customer Success Stories
Business Plan Course
Strategic Planning Templates
E-books, Guides & More
Entrepreneurs & Small Business
Accelerators & Incubators
Business Consultants & Advisors
Educators & Business Schools
Students & Scholars
AI Business Plan Generator
Financial Forecasting
AI Assistance
Ai Pitch Deck Generator
Strategic Planning
See How Upmetrics Works →
- Sample Plans
Small Business Tools
How to Write a Market Analysis for a Business Plan?

Free Market Analysis Kit
- April 11, 2024
13 Min Read

Market analysis is the foundation upon which the success of your business relies.
Whether you are a seasoned entrepreneur planning to enter a new geographical market or an emerging startup struggling to place together your business plan—a thorough understanding of the market, customers, and competitors is essential for a business to thrive successfully.
Now, writing a market analysis for your business plan is quite a challenge. But with this step-by-step guide, we have made the entire process quite simple and easy to follow.
Also, get tips to write this section and our curated market analysis example for a business plan.
Ready to dive in? Let’s get started.
What is Market Analysis?
Market analysis is a detailed analysis of your business’s target market and the competitive landscape within a specific industry. It is an important section of your business plan offering a thorough insight into the state of the industry, the potential target market, and your business’s competition.
A well-targeted market analysis forms the base upon which the foundation of your business relies. It assures the readers that you have a thorough understanding of the market you are about to enter.

Why should you Conduct Market Research?
Wondering how market analysis will contribute to the success of your business? Well, check these benefits of conducting a comprehensive market analysis for your business:
1. Reduces the risk
Instead of operating on instincts and gut feelings, market research enables you to make decisions based on data and analysis. When you know with surety what works and what doesn’t, you will make decisions that are more likely to succeed than fail.
To summarize, having an in-depth market analysis will reduce the risks associated with starting a business in a thriving marketplace.
2. Identifies emerging trends
A market analysis identifies emerging market trends and patterns and thereby helps you stay at the top of the competition. Not only the trends, but you can also identify challenges that may potentially arise in your business and design a pivot plan.
3. Assist in product development
A detailed analysis of the target market, industry, and competitors helps you create the product that the customer will be willing to buy. The analysis will not only assist in product development, but also with pricing, marketing, and sales strategies to ensure thriving business conditions.
4. Optimize your target market
Your business is not for everyone and the sooner you realize this the better. A target market analysis helps in understanding who your potential customers are and accordingly strategize your marketing efforts to attract them.
5. Establishes evaluation benchmarks
Market analysis benefits your business by offering evaluation metrics and KPIs. Such metrics help in measuring a company’s performance and its edge over the competitors.
Lastly, a thorough market analysis is quintessential if you are planning to secure funds. As a matter of fact, it is non-negotiable.
Now that you know how important having a market analysis section is, let’s learn a detailed way of conducting such analysis.
How to Simplify Your Market Analysis?
Market analysis is a broad concept covering a wide range of details. There’s no denying that it is a tiring task requiring extremely dedicated efforts.
From understanding the purpose of research to undertaking surveys, gathering data, and converting it into worthy analysis—the research itself is a lot for an individual to cover.
Upmetrics market analysis tool kit includes a variety of guidebooks and templates that will help you with target customer analysis , surveys, and competitor surveys.
The documents will guide you in a strategic direction to conduct qualitative research and analysis. They are well-crafted and quite simple to follow even for someone with no prior experience at market analysis.
Got it? No more side talking, let’s get straight to what you are here for.
How to Conduct a Market Analysis?
Conducting thorough market research and analysis could be a hassle, but not with this easy-to-follow 7-step guide. Let’s get over it.
1. Determine your objective
When you write a business plan , market analysis is going to be one prominent component.
However, it is important to know the clear objective of conducting such analysis before you kickstart.
For instance, are you planning to acquire funding from investors or are you conducting this research to test the viability of your business idea? Are you looking to add a new product segment to your business or are you looking to expand in other states and countries?
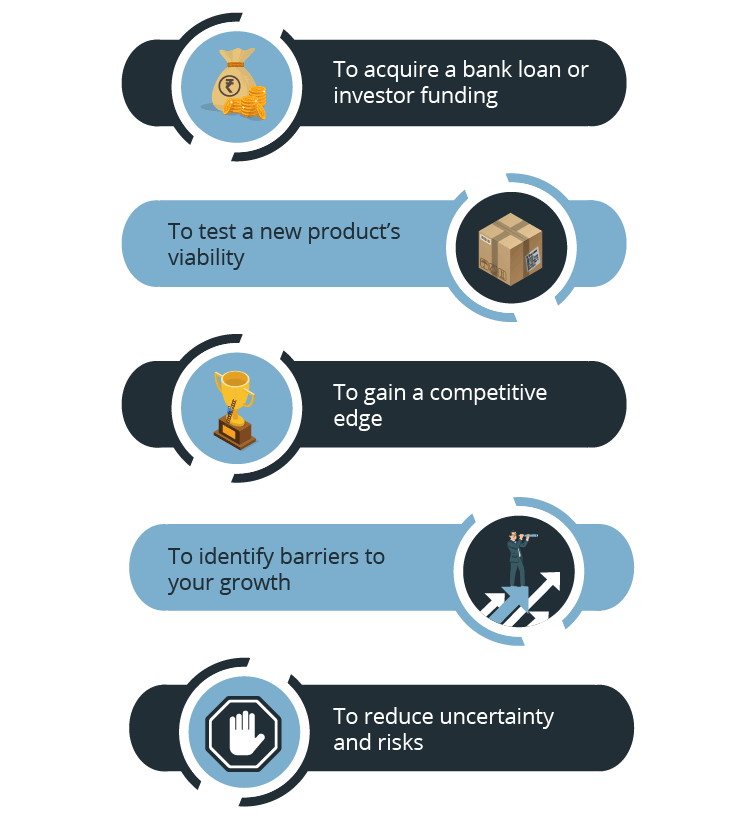
That being said, the purpose of your market analysis will determine the extent and scope of research essential for your business.
Spend more time researching, less writing
Make business plans in minutes with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Conduct an Industry Analysis
In this part of your analysis, you will highlight the state of the current industry and show where it seems to be moving. Investors would want to know if the industry is growing or declining, so present accordingly.
This section should include metrics for market size, projected growth, average market growth rate, product life cycle, and market trends.
Ensure that you gather data from highly authoritative sites like the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), Bureau of Economic Analysis, and industry publications to make your analysis.
To make this section enriching and meaningful, begin with a macro industry overview and then drill down to your specific market and business offering as thorough details as possible.
3. Identify your target audience
This section of your market analysis is dedicated to your potential target customers.
And, although your product might be suitable for everyone, there is a high possibility that not all of them will be your customers due to many reasons.
It is therefore better to target a specific category of customers to grow your business effectively and efficiently.
Now, you can begin by creating a buyer’s persona of your ideal customer describing their demographic and psychographic details. This includes talking about the age, gender, location, income, occupation, needs, pain points, problems, and spending capacity of your target customer.
You can conduct surveys, interviews, and focus groups, and gather data from high-end sources to get essential details for a customer profile.
However, make sure that you dig into details to make this section resourceful for business planning and strategizing.
4. Analyze your competitors
Competitive analysis is the most important aspect of your market analysis highlighting the state of the competitive landscape, potential business competitors, and your competitive edge in the market.
Now, a business may have direct as well as indirect competitors. And while indirect competition won’t affect your business directly, it definitely would have an impact on your market share.
To begin this section, identify your top competitors and list them down.
Conduct a SWOT analysis of your top competitors and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses against your business.
Identify their USPs, study their market strategies, understand how they pose a threat to your business, and ideate strategies to leverage their weaknesses.
Don’t undervalue or overestimate your competitors. Instead, focus on offering a realistic state of competition to the readers.
Additionally, readers also want to know your strengths and how you will leverage a competitive edge over your competitors. Ensure that this section highlights your edge in terms of pricing, product, market share, target customer, or anything else.
Want to create a SWOT analysis for your business?
Craft a powerful SWOT Analysis in just minutes using our user-friendly and free online SWOT Analysis Generator Tool!
5. Calculate your market share
The analysis section of your business plan must also include details of your market share.
If your estimated market share is not big enough, chances are your business idea might not be profitable enough to pursue further.
Now, you can use these proven metrics to forecast your market share:
TAM (Total available market)
It represents the total demand available in the market. In other words, it is the maximum amount of sales or revenue the market has to offer.
SAM (Serviceable available market)
It represents the segment of TAM that you can obtain with your solution within your limitations. These limitations can be geographical location, business model, type of product, etc.
SOM (Serviceable obtainable market)
It represents the segment of SAM that you can realistically capture after considering your competitors, customer preferences, production capabilities, etc.
SOM is your estimated market share. Once you have calculated it, you can actualize it via suitable pricing strategies.Apart from this method, you can also use other approaches like top-down, bottom-up, and triangulation to estimate your market share.
However, whatever method you use, ensure that the projections are realistic and attainable.
6. Know the regulations and restrictions
Before entering a new market or starting a new business , you need to know the regulations and restrictions in your industry.
Understanding these can help you stay out of legal pitfalls and inspire confidence in prospective investors.
Some of the regulations you need to know are:
- Government policies
- Tax regulations
- Trade policies
- Employment laws
- Environmental regulations
- Security and privacy
- Protection of intellectual properties
Include these details in your market analysis section to help readers understand the risk value and federal regulations associated with your business.
7. Organize and implement the data
After completing your research, it’s now time to make sense of all the data you’ve gathered.
There is no strict structure when it comes to organizing your market analysis. However, ensure that your analysis includes specific sections for objective, target market, and competition.
Focus on creating an easy-to-digest and visually appealing analysis section to help the readers gather essential essence.
Now, it’s a waste if you are not putting all this research to some use. Identify the business areas where you can implement your research be it product development, exploring the new market, or business operations, and develop strategies accordingly.
All in all lay the foundation of a successful business with a thorough and insightful market analysis. And, you can do it by having an organized market analysis section in your business plan.
Create visually appealing business plan with our
Tips to Write Your Market Analysis
After conducting thorough market research, it is important to present that information strategically in a business plan to help the readers get meaningful insights.
Well, here are a few tips to help you write the market analysis for a business plan.
1. Stay in context
Remember the objective of your market analysis and stick to it. Keeping the context in mind, identify what essential information to present and back them up with high-end sources.
Also, tie your data with essential analysis to show how your business would survive and thrive in the market.
2. Add visual graphics
No one prefers shifting through pages of pure text content. Graphics and visuals make your market analysis easy to absorb and understand. You are more likely to capture readers with visual attractiveness rather than risk their attention with pure textual content.
3. Offer an engaging summary
Offer readers a quick overview of your detailed market analysis by including a summarizing text. A summary will help readers gather a macro perspective before diving deep into hard facts and figures.
4. Avoid fluff and repetition
Ensure that everything you present in your market analysis section holds a meaning. Avoid adding inessential and fluff information.
To best identify whether or not the information is essential for the reader, ask this simple question: Will the reader learn something about my business’s market or its customers from this information?
If not, the information is most likely inessential. And, those were some quick tips to ensure effective market analysis for your business plan.
Market Analysis in a Business Plan Example
Before we conclude, check out this market analysis example from Upmetrics’ sample yoga studio business plan.
Business Name: Lotus Harmony
Location: Green Valley
Core Objective for Market Analysis
Our goal for the market analysis at Lotus Harmony is straightforward: to deeply understand what the Green Valley community seeks in yoga and wellness. We’ll closely look at local demand and the competitive scene, shaping our services to precisely meet community needs. This approach promises to make Lotus Harmony a distinct and beloved wellness destination in our neighborhood.
Industry Overview of the Green Valley Yoga Market
Market Size:
Green Valley is home to nearly 1M yoga enthusiasts, predominantly aged 25-45. This demographic suggests a robust market for yoga and wellness, ripe for a studio that offers diverse and inclusive programs.
Projected Growth:
The yoga community is expected to grow by 5% annually over the next five years. This growth is driven by an increasing interest in holistic health, presenting a fertile ground for a new yoga studio to thrive.
Market Trends:
A rising trend is the demand for comprehensive wellness services, including mindfulness and nutrition, alongside traditional yoga. Specialized classes like prenatal yoga are also gaining popularity, signaling opportunities for niche offerings.
By tapping into these insights, a new yoga studio in Green Valley can strategically position itself as a premier wellness destination, catering to the evolving needs of the community.
Target Market Analysis for Lotus Harmony
Lotus Harmony Yoga Studio’s ideal customers are mainly Urban Millennials and Gen Z (ages 18-35) who prioritize:
- Wellness and mindfulness as part of their lifestyle.
- Affordable, holistic health experiences blending physical and mental well-being.
- Convenience with flexible class schedules and online access.
- Community and sustainability, preferring spaces that offer personal growth and eco-consciousness.
- A welcoming atmosphere that supports inclusivity and connection.
Competitive Landscape for Lotus Harmony
Lotus Harmony’s success relies on understanding consumer preferences and income, securing prime locations, attracting patrons, and offering quality services. Competing with gyms, wellness centers, and home fitness, it positions itself as a holistic wellness choice, aiming to stand out in Green Valley’s wellness scene.
Market Share for Lotus Harmony
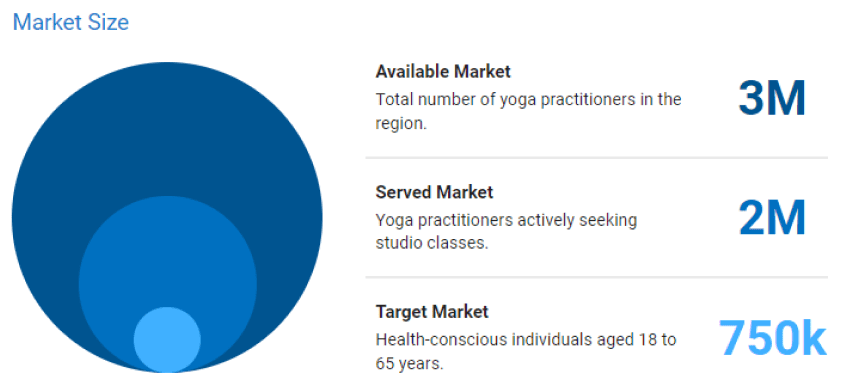
Regulatory Requirements for Lotus Harmony
Here are a few aspects of legal compliance essential for Lotus Harmony:
- Business Registration and Licensing
- Zoning and Land Use Permits
- Health and Safety Compliance
- Professional Liability Insurance
- Instructor Certifications
- Building Safety Certificates
- Accessibility Compliance
- Tax Registration
Final Thoughts
It takes an extremely dedicated effort to undertake market research and craft it into a compelling analysis. However, it’s a worthy business planning effort that will set a cornerstone of success for your business.
Don’t worry. You don’t need to spend days figuring out what and how to write your market analysis. Upmetrics, an AI-powered business planning app , will help you write your overall business plan in less than an hour.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 c's of marketing analysis.
The 4 C’s of marketing analysis are customer, cost, convenience, and communication which would together determine whether the company would succeed or fail in the long run.
Is SWOT analysis a market analysis?
SWOT analysis is a small but important tool for market research that would determine the success of a business or its edge over other businesses based on strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
How long does a market analysis take?
Market analysis can take anywhere from 4 to 8 weeks, given that secondary sources of data are easily available. However, for complex large-scale projects, analysis can take up to months to complete.
What are the three core components of a market analysis?
The three most crucial components of a market analysis are the study of market size and market share, target market determination, and competitor analysis.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Related Articles

How to Write a Customer Analysis Section for Your Business Plan
5 Types Of Competitive Analysis Frameworks

Strategic Marketing Process: A Full Step-by-Step Guide
Reach your goals with accurate planning.
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Popular Templates

How to do a market analysis for a business plan

A key part of any business plan is market analysis. This section needs to demonstrate both your expertise in your particular market and the attractiveness of the market from a financial standpoint.
This article first looks at what we mean exactly by market analysis before looking at how to make a good one for your business plan.
What is a market analysis?
A market analysis is a quantitative and qualitative assessment of a market. It looks into the size of the market both in volume and in value, the various customer segments and buying patterns, the competition, and the economic environment in terms of barriers to entry and regulation.
How to do a market analysis?
The objectives of the market analysis section of a business plan are to show to investors that:
- you know your market
- the market is large enough to build a sustainable business
In order to do that I recommend the following plan:
Demographics and Segmentation
Target market, market need, competition, barriers to entry.
The first step of the analysis consists in assessing the size of the market.
When assessing the size of the market, your approach will depend on the type of business you are selling to investors. If your business plan is for a small shop or a restaurant then you need to take a local approach and try to assess the market around your shop. If you are writing a business plan for a restaurant chain then you need to assess the market a national level.
Depending on your market you might also want to slice it into different segments. This is especially relevant if you or your competitors focus only on certain segments.
Volume & Value
There are two factors you need to look at when assessing the size of a market: the number of potential customers and the value of the market. It is very important to look at both numbers separately, let's take an example to understand why.
Imagine that you have the opportunity to open a shop either in Town A or in Town B:
Although Town B looks more competitive (10 competitors vs. 2 in Town A) and a smaller opportunity (market size of £100m vs. £200 in Town A), with 1,000 potential customers it is actually a more accessible market than Town A where you have only 2 potential customers.
Potential customer?
The definition of a potential customer will depend on your type of business. For example, if you are opening a small shop selling office furniture then your market will be all the companies within your delivery range. As in the example above it is likely that most companies would have only one person in charge of purchasing furniture hence you wouldn't take the size of these businesses in consideration when assessing the number of potential customers. You would however factor it when assessing the value of the market.
Market value
Estimating the market value is often more difficult than assessing the number of potential customers. The first thing to do is to see if the figure is publicly available as either published by a consultancy firm or by a state body. It is very likely that you will find at least a number on a national level.
If not then you can either buy some market research or try to estimate it yourself.
Methods for building an estimate
There are 2 methods that can be used to build estimates: the bottom-up approach or the top-down approach.
The bottom-up approach consists in building a global number starting with unitary values. In our case the number of potential clients multiplied by an average transaction value.
Let's keep our office furniture example and try to estimate the value of the 'desk' segment. We would first factor in the size of the businesses in our delivery range in order to come up with the size of the desks park. Then we would try to estimate the renewal rate of the park to get the volume of annual transactions. Finally, we would apply an average price to the annual volume of transactions to get to the estimated market value.
Here is a summary of the steps including where to find the information:
- Size of desks park = number of businesses in delivery area x number of employees (you might want to refine this number based on the sector as not all employees have desks)
- Renewal rate = 1 / useful life of a desk
- The volume of transactions = size of desks park x renewal rate
- Value of 1 transaction = average price of a desk
- Market value = volume of transactions x value of 1 transaction
You should be able to find most of the information for free in this example. You can get the number and size of businesses in your delivery area from the national statistics. Your accountant should be able to give you the useful life of a desk (but you should know it since it is your market!). You can compare the desk prices of other furniture stores in your area. As a side note here: it is always a good idea to ask your competitors for market data (just don't say you are going to compete with them).
That was the bottom-up approach, now let's look into the top-down approach.
The top-down approach consists of starting with a global number and reducing it pro-rata. In our case, we would start with the value of the UK office furniture market which AMA Research estimates to be around £650m and then do a pro-rata on this number using the number of businesses in our delivery area x their number of employees / total number of people employed in the UK. Once again the number of employees would only be a rough proxy given all business don't have the same furniture requirements.
When coming up with an estimate yourself it is always a good practice to test both the bottom up and top-down approaches and to compare the results. If the numbers are too far away then you probably missed something or used the wrong proxy.
Once you have estimated the market size you need to explain to your reader which segment(s) of the market you view as your target market.
The target market is the type of customers you target within the market. For example, if you are selling jewellery you can either be a generalist or decide to focus on the high end or the lower end of the market. This section is relevant when your market has clear segments with different drivers of demand. In my example of jewels, value for money would be one of the drivers of the lower end market whereas exclusivity and prestige would drive the high end.
Now it is time to focus on the more qualitative side of the market analysis by looking at what drives the demand.
This section is very important as it is where you show your potential investor that you have an intimate knowledge of your market. You know why they buy!
Here you need to get into the details of the drivers of demand for your product or services. One way to look at what a driver is to look at takeaway coffee. One of the drivers for coffee is consistency. The coffee one buys in a chain is not necessarily better than the one from the independent coffee shop next door. But if you are not from the area then you don't know what the independent coffee shop's coffee is worth it. Whereas you know that the coffee from the chain will taste just like in every other shop of this chain. Hence most people on the move buy coffee from chains rather than independent coffee shops.
From a tactical point of view, this section is also where you need to place your competitive edge without mentioning it explicitly. In the following sections of your business plan, you are going to talk about your competition and their strengths, weaknesses and market positioning before reaching the Strategy section in which you'll explain your own market positioning. What you want to do is prepare the reader to embrace your positioning and invest in your company.
To do so you need to highlight in this section some of the drivers that your competition has not been focussing on. A quick example for an independent coffee shop surrounded by coffee chains would be to say that on top of consistency, which is relevant for people on the move, another driver for coffee shop demand is the place itself as what coffee shops sell before most is a place for people to meet. You would then present your competition. And in the Strategy section explain that you will focus on locals looking for a place to meet rather than takeaway coffee and that your differentiating factor will be the authenticity and atmosphere of your local shop.
The aim of this section is to give a fair view of who you are competing against. You need to explain your competitors' positioning and describe their strengths and weaknesses. You should write this part in parallel with the Competitive Edge part of the Strategy section.
The idea here is to analyse your competitor's angle to the market in order to find a weakness that your company will be able to use in its own market positioning.
One way to carry the analysis is to benchmark your competitor against each of the key drivers of demand for your market (price, quality, add-on services, etc.) and present the results in a table.
Below is an example of a furniture shop in France. As you can see from the table all the actors on the market are currently focused on the low medium range of the market leaving the space free for a high end focused new player.
This section is all about answering two questions from your investors:
- what prevents someone from opening a shop in front of yours and take 50% of your business?
- having answered the previous question what makes you think you will be successful in trying to enter this market? (start-up only)
As you would have guess barriers to entry are great. Investors love them and there is one reason for this: it protects your business from new competition!
Here are a few examples of barriers to entry:
- Investment (a project that requires a substantial investment)
- Technology (sophisticated technology a website is not one, knowing how to process uranium is)
- Brand (the huge marketing costs required to get to a certain level of recognition)
- Regulation (licences and concessions in particular)
- Access to resources (exclusivity with suppliers, proprietary resources)
- Access to distribution channels (exclusivity with distributors, proprietary network)
- Location (a shop on Regent's Street)
The answer to the questions above will be highly dependent on your type of business, your management team and any relations it might have. Therefore it is hard for me to give any general tips about it.
If regulation is a barrier at entry in your sector then I would advise you to merge this section with the previous one. Otherwise, this section should be just a tick the box exercise where you explain the main regulations applicable to your business and which steps you are going to take to remain compliant.
Now you know how to do a market analysis for a business plan! I hope you found this article useful. If so please share it, and if not let us know what we need to improve.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- Free business plan template to download
- TAM SAM SOM, what it means and why it matters
- Business model vs business plan
- What is a business plan and how to create one?

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
How to Write a Market Analysis for Your Business Plan
An important part of any good business plan is the Market Analysis. Before you can describe your marketing and sales strategies, you need to figure out what market you serve and what need you fulfill. Then, your Marketing Strategy and Implementation Plan, ideally covered in the next section of your business plan, will fit into a logical flow.
I have read many business plans that make the mistake of starting a Market Analysis section, only to wander off into a description of what the company sells, how it will promote its products, and how its product or service is different. These are all undeniably important points; however, they deserve a their own section and should be addressed in turn.
Let’s start with what a market is. A market, in this instance, refers either to a place where goods can be sold, or to a particular class of buyers. So the market is the “Where?” that your product or service is sold, and the “Who?” you sell it to.
So what should you include in the Market Analysis section of your business plan?
Size of the Market
The first number you need to identify is the total annual sales, in dollars, of the market you serve. If you are selling cars, state the total sales of cars in your geographical area for the most recently ended year. This number will be important later when you forecast your sales because it will enable you to calculate what share of the market you expect to capture.
Besides stating the current size of the market, it is also valuable to include forecasts of the future size of the market. Such market projections should be offered only if they come from acknowledged government or research organizations. Certainly you can make up your own projection, but it will lack the credibility of a recognized authority on the subject and probably will serve only to make you look amateurish.
We hope you find this article helpful. For more great information about writing a quality business plan, check out “How to Write a Shark-Ready Business Plan” by our Founder Al Lierman.
Market Segments
There are several ways that you can break a market down into segments. Doing so will help you and the reader of your plan understand where your specific product fits into the total market, and who the potential customers are.
Geography and Location
It is a good idea to indicate the geographic segments of your product’s market, especially the market in which you sell. If you are an international company, then describe the size and characteristics of the international market. If, on the other extreme, you only sell to customers within 10 miles of your location, then provide information about this local segment.
Customer Segments
On one level, all customers who a buy a particular product make up that product’s market. But, not all buyers of the product buy it for the same reason. For example, buyers of Personal Computers can be segmented into business users and home users. This type of market segmentation is essential because your marketing plan, which you will present later, will describe your strategy for targeting these customers.
Further segmentation might be called for in many cases. To continue with the PC example, if your business is selling servers to corporate clients, it makes sense to identify the portion of the PC market that is businesses that buy network servers. The more detail you can provide about the customer segments that you target, the better.
The level of detail you provide about your market’s customer segments depends on the level of detail in your marketing plan. Any customers you intend to pursue with your marketing strategy should be identified and quantified in the market analysis section.
This section is also an appropriate place to provide a profile of your target customer. This profile should include any demographic or psychographic information relevant to buyers of your product or service. For business customers, provide statistics about the size of the typical client firm, number of employees, location, or industry.
Market Trends and Needs
Once you have described the segments of your product’s market, explain the trends, growth, and needs of the market. Turn your focus especially to the trends in the market segments within which your product fits. In this section you should provide statistics for the growth in the market over the last five to ten years. If you can provide forecasted growth rates from an acknowledged agency or research firm, do it.
If your market segment is growing and is projected to continue to grow, talk about it and back it up with numbers. If the trend is for new products like yours to sell well and replace older models, then say so. Ideally, the trends you identify should support the positioning statement and marketing strategy that you are about to present.
As for market needs, a business plan can make a powerful statement about a company’s chance for success if it can show a need in the market that is unmet or underserved, and then present the company’s product as the perfect solution to that problem.
Venture capitalists and angel investors often refer to products as either painkillers or vitamins. Painkillers tend to get the most funding because they are products that, as soon as they come out, people have to have them. Vitamins are products that are good, useful, and maybe even important, but we can live without them.
The ultimate goal of the Market Analysis is to show where the burning need, the source of the pain, is in the market. In the best business plans, the Marketing Strategy describes how the company will position its product to ease the pain.
Industry Analysis
The final section of the Market Analysis is the Industry Analysis. Where the earlier sections of the Market Analysis dealt with issues of who buys the product and where they are located, the Industry Analysis addresses the making and selling of the product: industry participants, distribution patterns, and competition. A thorough discussion of these aspects of the industry will provide a good overview of the industry to a reader who is otherwise unfamiliar with it.
Industry Participants
Industry participants are those firms and individuals that are involved in at least one aspect of bringing the industry’s product to its customers. Examples include manufacturers, suppliers, service providers, wholesalers, distributors, dealers, and reps.
For example, an analysis of the book publishing industry would identify participants such as authors, agents, publishers, book manufacturers, book wholesalers, bookstores, and book clubs.
Distribution Patterns
If you are dealing with a physical product you will probably want to describe how it is distributed, from the time it is created until it makes its way into a customer’s hands. Explain the various ways that finished products are distributed, whether directly to end users, through wholesalers, from wholesalers to retailers, and so on.
A company can often distinguish itself, even if it does not have a unique product, by providing a new way to sell or distribute the product to its customers. Dell Computer was a great example back in the day. The company was successful not because its PCs were better then any other company’s; it made a fortune because it revolutionized the way computers were manufactured and distributed to consumers. It configured its products to its customers’ specifications and sold them direct rather than prebuilding them and selling them through distributors as its competitors did. In short, it’s success was based on a better business model more than on a better product.
Competition
Once you have identified all of the industry’s participants you are in a better position to explain where your company fits in. Unless you have a completely new concept or product with no competition, your industry analysis should include a thorough discussion of your competitors. I have seen many first-time plan writers gloss over this section or ignore it altogether. Don’t make this mistake.
Any smart venture capitalist, angel investor, or lending officer recognizes that every business has competition. By avoiding this topic in your business plan you will show your reader one of two things: either you are naïve about your competition and have not done your homework, or you are less than forthcoming and are hiding something. Furthermore, you miss an opportunity to show exactly how your proposition is unique and different from your competitors’.
The Market Analysis section of your business plan is a great place to show that you know your business inside and out. Stick to the concept of describing the market and the industry as they exist today, a sort of situation analysis. If you do it right, the stage will be set for you to present your plan for conquering the world in your Marketing Plan and Strategy Implementation section immediately following the Market Analysis.

Performing a Strategic Business Plan Market Analysis

Before getting too far down the road with your business planning process , you will need to complete a thorough market analysis based on the research you did in deciding to launch your business.
Your market analysis not only provides an overview of your industry, but also the conclusions you were able to draw from your market research findings. While there is no absolute method for including a market analysis, under most circumstances you are going to want to include most or all of the following points as you create this valuable section of your plan:
Business Plan Market Analysis
Business plan swot analysis, customizing your business plan, your business plan should communicate to investors, business planning mistakes to avoid, crafting a strategic business plan.
1. Industry description and outlook
Regardless of how you decide to proceed with your market analysis, you will almost certainly want to start this section of your business plan with a description of your company’s industry. Research your industry’s growth and note its current scope. Then, discuss some of the business characteristics of your industry, such as its projected growth rate. Include the major customer segments.
2. Introduce your target market
Once you have described the overall industry and marketplace, next indicate how you have narrowed down your target market to a workable size. One of the biggest errors new business owners make is in keeping their target market too broad, which leaves them in the impossible position of trying to meet the needs of too many diverse customer groups. This obviously runs the risk of stretching limited resources too thin.
3. Distinguish target customer characteristics
Next, describe the critical needs of your targeted customer base and to what extent–and by whom–these needs are currently being met. This is also the place to detail the demographics of your customer group. If there are cyclical purchasing trends, including seasonal buying, this is the place to note them as well.
4. Target market size and growth
You will also want to include additional details about the size of your targeted market. Conduct sufficient research to provide data on total annual purchases within your targeted marketplace. In addition, do sufficient research to create a reasonable forecast of market growth.
5. Market share percentage
Once you have described the size and potential growth for your targeted market, next identify the market share percentage and number of customers you believe you will be able to gain within a defined demographic area. Include justification for the numbers you come up with.
6. Pricing and gross margin targets
Explain your pricing strategy, gross margin levels and any special pricing schemes you plan to use, such as discounts.
7. Competitive analysis
Finally, identify your competitors and their targeted markets. Also, make note of any indirect or secondary competitors impacting your target markets. Include information on their current marketshare as well as what you perceive as their strengths and weaknesses.
8. Barriers and regulatory restrictions
Discuss any barriers to entering the market that you have identified. These might include technology changes, unusually high investment costs, lack of qualified personnel, and other hurdles. In some cases, there may be regulatory restrictions impacting your business. In that case, describe how you plan to comply with these regulations.
Your market analysis forms a key part of your business plan. Interpreting your market research results in a clear and concise manner will provide a strong foundation for your overall plan.
Unfortunately, the SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats) analysis is one of the more cliched components of any business plan. While the cliche exists, the exercise of running through the components of a thorough SWOT is helpful for any business, regardless of its “stage.” Furthermore, including a SWOT (or at least some form of one) in a business plan has become somewhat of an expectation among private equity investors who might fund your business.
Internal Analysis
The S.W. portion of your SWOT encompasses an internal analysis of the strength of the business including the plan itself, the ability of management to execute and the robustness of any intellectual property or tacit knowledge held by the company. It’s a visceral look at the businesses’ ability to succeed. For some individuals, it can be difficult to find personal and business strengths within yourself or your own organization. In the case of entrepreneurs, I’ve always found the opposite to be the case.
In many startup venture, it can be difficult to avoid what could be called “startup bias.” From the founders’ perspective, the bias generally leans toward the “we’ll never fail.” From the perspective of investors a bias will lean more on the side of “you’ll probably fail.”
Like strengths, weaknesses are always internal. Weaknesses can be as simple as understanding a gap in talent to finding highly-deleterious legal blockades to your product or service. Full-fledged analysis is helpful to understand the chinks in the proverbial armor, whether large or small.
An Industry View
The O.T. portion of your business plan comes from the 30,000 foot-level. It represents an industry view, an in-depth look at where the Blue Ocean of opportunity truly exists. In some instances, it a story told about how a product or service provides such an innovative leap that the company can easily capture low-hanging fruit and gain an advantage–some might call it first movers.
But where low-hanging fruit exists, competition is sure to follow. Since the term “first mover’s advantage” has been effectively written-off as a misnomer, threats must remain extremely credible to the livelihood of your organization. Understanding existing and potential threats can also paint a preemptive picture for planning on how to deal with them even before they may arise in the future–an extremely helpful exercise for the entrepreneur.
Not Just for Startups
SWOTs are developed for all types of business plans, not just startups. They are particularly helpful for the company looking to launch a new product or service or seeking of potential opportunities and problems inherent in entering new markets with an existing product. Plans may help to clarify the direction of an existing business or justify lofty future growth assumptions in the case of a merger or acquisition. In short, SWOT is universal in its business application, just be careful not to overuse or abuse it.
My personal suggestion: don’t spell out S, W, O, T in the plan itself, but include the meat and potatoes of a typical SWOT, complete with an in-depth dive into how the company will most-likely succeed and how it will possibly fail. Ultimately, the goal of your analysis is for both internal managers and potential external investors or buyers go gain a deep understanding into the potential risks and rewards inherent in the company.
Developing a business plan is an important part of owning and operating a business, but if you think of the process only as a means of attracting investment or guiding you through startup, you are ignoring the many other ways a business plan becomes essential to the success of your business.
Here are a few examples of business plan needs throughout the life of your business:
When thinking about the need for a business plan, a business launch is usually the first thing that comes to mind. This popular type of business plan differentiates itself from other types due to its focus on describing the company, explaining the products or services your business will provide, marketing analysis and plan and financial projections, including cash flow projections, profit, expenses and income.
Also an internal plan, this type of business plan is often viewed as the natural successor to a business launch plan and includes some of the same components, but updated. Your operations plan should map out company operations for the coming year and include specifics regarding individual employee roles and responsibilities.
Internal project analysis
Unlike the business launch plan, this business plan is narrow in its approach and developed to provide projections for internal business decision-making. Its purpose it to evaluate a proposed project or action. Your financial analysis should include any additional personnel costs, technology needs and operating expenses. Include the project’s capital needs and assumptions for repayment. You will also want to include a marketing plan specifically targeting the proposed project.
The primary function of your strategic business plan is to focus on your company’s vision, mission, goals and action plan for achieving them, including timeline. This plan should also define critical success factor. A hallmark of this type of business plan is that it cuts across all department to provide the big picture for your business. Often, advisory boards are more involved in development of this type of business plan over any other.
Also known as a growth plan, this customized business plan may be written for either internal or external purposes. Whether internal or external, financial projections will be the primary focus. A plan meant to attract outside investors, however, will also need to include background information on the company and its operations to-date to provide potential investors with the details necessary to make a decision. If your expansion does not involve outside capital and will only be used internally, there is no need to include obvious company details.
Feasibility plan
A feasibility plan includes elements of both project analysis plans and expansion plans. However, a feasibility plan’s primary purpose is just as its name implies: to establish the feasibility of a proposed business venture and make recommendations for moving forward (or not). This type of plan focuses on demand for the proposed product or services made possible by the new venture. A feasibility plan will also include capital needs and profit projections in formulating recommendations.
Most small business startups can benefit from outside acquisition financing and most often, at least a portion of that funding will come in the form of business loans. As you ready your business plan for review by a lender, your focus is likely on the financial projections in your plan. But don’t sell other areas short. Your management competency, market outlook and assets are just a few of the other components that will be scrutinized.
Here are some of the factors your lender will consider when making the decision whether to provide you with a business loan.
Management Experience
Your potential lender is going to want assurances you have the necessary expertise onboard. Be sure your plan details your education and experience, as well as that of your management team. In addition, include information on your board officers and advisors, if applicable. Your plan should communicate a high level of both competency and commitment.
Marketing Analysis
Your lender is going to want to understand your business, your competitors, your customers and the industry in which your business will operate. Completing a thorough market analysis as part of your business plan before applying for a loan will provide this necessary information to your lender.
Your lender is going to want collateral in the form of personal and business assets that could be sold for cash if your business does not meet its financial goals. Identifying all your business assets within your business plan provides a listing of potential collateral for your lender to consider. Keep in mind, however, that the value of most of your assets will be discounted from market value when viewed as collateral. The lender will also determine your collateral coverage ratio, calculated by dividing the total discounted collateral value by the amount of your loan request. Both collateral and projected cash flow are taken into account when determining your ability to repay a loan.
Debt-to-Equity Ratio
The more you are able to invest in your business, the easier it will be to obtain financing. New businesses will most often use a combination of equity financing and debt financing. Be sure your business plan describes in detail all anticipated outside funding. Your lender will want to review your plan to determine if your request for debt financing keeps your debt-to-equity ratio within acceptable limits. If your debt-to-equity ratio dictates, seek additional equity investment before requesting a loan.
There are a lot of steps to take when launching a new business or embarking on a new product venture, but writing your business plan is probably one of the most important.
However, there are many common missteps that can occur when putting together a business plan. Number one on the list is the biggest error you can make: thinking you don’t need a formal business plan at all. This is often the mindset when a business owner isn’t seeking outside investment. But a business plan does more than attract investment. The business planning process itself will help you determine if your great idea is truly a viable business . It’s the single most important step you will take in becoming an entrepreneur.
Here are five more typical–but avoidable–errors that harm the process:
1. Failing to acknowledge competition
In your pursuit to show your business idea in the best possible light to investors, it can be easy to gloss over the competition. But that would be doing yourself a disservice. One of the purposes of your business plan is to do the necessary research to determine if your business idea can be transformed into a viable business. Not digging deeply enough when researching competitors will make investors wary of your ability to succeed.
2. Being amateurish
It may sound like one of the least important things to worry about, but how well your plan is written and how it is presented in final printed form are important. You don’t want an important investor to get a few pages into your plan and start to doze off or find it riddled with grammatical errors. Unless you are a professional writer, invest in a professional business plan writer or consultant. Likewise, an eye-catching, well-designed logo for your new business gracing the cover of your business plan will give a professional finish.
3. Being inconsistent
Business plans con be complicated. It is common to rewrite some portions and not others. But be sure to read the final version several times over, enlisting friends or trusted colleagues to review it as well, to avoid any errors or inconsistencies. Don’t make a financial assumption in one section of your plan, then turn around and contradict it later in the document.
4. Too much hype
You might think your business idea is the next great thing, but you need to back up that kind of enthusiasm with hard research, not a bunch of hype and hyperbole. Peppering your business plan with too many meaningless superlatives like “greatest” and “incredible” doesn’t add anything of substance. Instead, rely on the thoroughness of your market research and analysis to “wow” readers.
5. Poor quality research
Doing thorough research and analysis is not something you can fake. An investor will immediately identify “fluff” in place of facts. Again, if this is not your forte, hire a consultant to provide some assistance based on your knowledge and experience.
There are plenty of land mines to avoid as you go through one of the most important steps for launching a business. These are just a few of the mistakes to avoid in bringing your plan to fruition.
These components of your business plan are not the only areas a lender will want to review closely, nor will everything your lender consider be addressed by your business plan. For example, you will also want to check your personal credit report before applying for a loan.
Your business will not have a proven financial track record at its launch, but you can boost a lender’s confidence in its credit worthiness by providing a detailed business plan that uses market analysis, management expertise, assets and financial projections to clearly communicate the ability of your business to repay its loan.
Related posts
10 real estate investment exit strategies to consider, investing in residential vs. commercial real estate: which is better, what is private equity real estate investing.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to footer
Market Analysis
Connecting the Dots, Quantifying Technology Trends & Measuring Disruption
Why is market analysis important?
Market analysis is the process of evaluating the size, competition, and potential profitability of a market. It is an important aspect of business planning and strategy, as it helps a company understand the market in which it operates and identify opportunities and threats.
There are several reasons why market analysis is important:
It helps a company understand its target market: Market analysis helps a company understand the demographics, needs, and preferences of its target customers. This information is crucial for developing marketing strategies and products that will appeal to the target market.
It helps a company identify opportunities: Market analysis helps a company identify new opportunities for growth and expansion. This could include identifying untapped markets, new products or services, or new distribution channels.
It helps a company understand the competition: Market analysis helps a company understand the competitive landscape in which it operates. This includes understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors, as well as identifying potential threats and opportunities.
It helps a company make informed decisions: Market analysis provides a company with valuable information that can be used to make informed decisions about its business. For example, a company may use market analysis to decide whether to enter a new market, launch a new product, or expand into a new distribution channel.
Overall, market analysis is an important tool for businesses to understand and navigate their market, identify opportunities, and make informed decisions about their strategy and operations.
Recent Posts
- Impact of Electric Vehicles on Independent Repair Shops
- RISC-V and Open POWER Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) Fortunes are Rising, Market Analysis
- Resilient Workforce Stokes Inflation Fears: Fed Likely to Keep Foot on the Gas Pedal
- The AI Boom That Propelled the 2023 Market
- Electric Car Industry Charges Ahead: Hong Kong’s Financial Hub Beckons for Expansion
- Fund Managers Exercise Caution Amidst European Stock Market Challenges
- Kenya’s Economic Landscape: Balancing Declining Inflation and Aggressive Interest Rate Hike
- Fueling China’s Coffee Craze: Emerging Markets and the Growing Demand for Beans
- AI reality vs. myth: predictions for 2024
- Cloudflare is introducing the concept of the “connectivity cloud”
Market Research Media
- High Energy Military Laser Market Forecast
- U.S. Federal Cybersecurity Market Forecast
- Adapting to Survive: Analyzing the Evolution of the Social Media Industry Amidst Technological, Regulatory, and User-Driven Shifts
- Social Media Monitoring in PR and Communication
- The Rise of Federation in Social Media
- Navigating the Regulatory Landscape: Deepfakes and Altered Media
- Embracing Universal Benefits: A Case for Fair and Inclusive Welfare Systems
- Beyond Fairytales: The Billion-Dollar Legacy of Disney’s Public Domain Adaptations
- Text-to-Image AI Generators and their Impact on Media Markets
- The Evolution of RSS Feeds: A Media Analyst’s Perspective
Media Partners
- Technology Conferences
- Event Sharing Network
- Defense Market
- Cybersecurity Events
- Event Calendar
- Calendarial
- Venture Capital
- Exclusive Domains
Privacy Overview

The Importance of a Market Analysis

A complete market analysis is a cornerstone of a successful marketing and advertising campaign. All too often companies neglect to perform a thorough market analysis and are left to the bleak alternative of guesswork. Market analysis is a strategic management strategy that provides an analytical approach to answering some of your companies most difficult questions:
- Who are our customers?
- How competitive is the current market landscape?
- How risky is entering this market?
- How efficient are our branding efforts?
Most business plans start on a hunch that a product or service could sell or be beneficial to someone. That may have been enough to launch your idea off the ground, but in order to keep your business plans thriving, it’s important you get accurate and concise answers to these questions and to perform a SWOT analysis.
What is market analysis?
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the external market and your internal resources. Thorough market analysis adequately assesses opportunity, value, risk, customer purchasing behavior, competition, and economic entry barriers and regulations.
3 Reasons Market Analysis is Important
This strategic management strategy does not tell you exactly how you should run your marketing campaign or position your company’s brand. However, it provides analytical insight that allows you to steer your company and brand around barriers or obstacles that could have impeded or completely halted your company’s progression. So, while there are many, let’s focus on the top 3 reasons market analysis is important.
1. Market Analysis Puts Your Customer First
Not long ago, Harvard Business School professor, Clayton Christensen , shook up the marketing world when he asked, “What job are people hiring your product for?” This simple question opened a door for those selling commodities to differentiate themselves from their competition.
The principle at play in Professor Christensen’s idea can be summed up in just one sentence,
“People don’t want to buy a quarter-inch drill; they want a quarter-inch hole.” – Theodore Levitt
Once we discover that people are hiring our services or products we realize that our competitors are not always what we think. A morning bagel’s competition might be a fruit smoothie, or an ice cream sundae’s competition could be a pastry. These things are often competitors to the problem of morning hunger or late-night dessert, yet they are not always sold by the business you would generally consider your “competition.”
Market analysis allows you to optimize your service or product for the job your consumer is hiring it to do.
TAKE A LOOK AT HOW WE INITIATED A REBRAND THAT RESULTED IN 6.5X WEB CONVERSIONS.
2. market analysis forces companies to look inward.

Critically acclaimed author Simon Sinek prompts business owners to think differently in regards to how they sell. He says, “People don’t buy what you do; people buy why you do it.”
He asks us to compare the following sales pitches:
“We make great computers. They’re beautifully designed, simple to use and user-friendly. Want to buy one?”
“Everything we do, we believe in challenging the status quo. We believe in thinking differently. The way we challenge the status quo is by making our products beautifully designed, simple to use and user-friendly . We just happen to make great computers. Want to buy one?”
This principle is especially important when your product or service is tied to the consumer’s self-actualizing vision of themselves. This benchmarking principle is more apparent in the apparel business than any other. Take the members of the surf culture around the North Shore of Hawaii, for example. Do you think they care how breathable the fabric of their t-shirt is? Or the thread-count of their hoodie? No. Their predominant want is to identify with a brand that helps them feel like their best self.
Market analysis forces companies to consider how their product makes their consumer feel and to what degree that feeling is driving the purchase decision.
TAKE A LOOK AT HOW WE TURNED AN INTERNATIONAL LAW FIRM’S BRAND FROM COMMONPLACE TO CONTEMPORARY
3. market analysis helps determine your unique sales proposition.

Though they are not always semantically agreed upon, there are five ways a company can differentiate their product or service in order to make it appealing to customers. Market analysis enables you to determine which of these methods of differentiation would be the most effective way to enter the market through strategic control.
- Brand- Companies differentiate themselves by brand by standing for something or associating their brand with a cause. Ex: TOMS’ slogan is, “One for One.” Their initiative to give shoes to the impoverished and shoeless is built heavily into their branding strategy. This branding strategy seeks to resonate with empathetic people who can turn a common purchase into one that helps others.
- Product- Companies differentiate themselves by product by positioning themselves as the highest quality product on the market. Ex: BMW’s slogan is, “The Ultimate Driving Machine.” Their branding and marketing goals set out to position themselves as the best car someone can own in the minds of their consumers.
- Service- Companies with organizational structure differentiate themselves by service by offering a one-of-a-kind experience for their customer; this is typically done by showing exceptional customer service. Ex: Nordstrom’s mission statement begins with, “To provide outstanding service every day one customer at a time.” Nordstrom’s has been accredited for having an extremely lenient return policy, swift response time to customer inquiry via email and even social media. Their brand is built around treating their customers with care and they are therefore retained.
- Price- Companies differentiate themselves by price by positioning themselves as the most affordable or even the most expensive. Ex: Wal-Mart’s slogan is, “Save money. Live better.” After Wal-Mart introduced their price matching program, they successfully branded themselves as the most affordable grocer by doing just that, literally being the most affordable.
- Audience- Companies differentiate themselves by audience by branding their product or services to specifically aid or benefit a certain group or type of person. Ex: Whole Foods’ brand is reflected in their motto, “Whole Foods, Whole People, Whole Planet.” Because their branding stands for healthy living, it often resonates with healthy people. Because of this people are often willing to pay more for the shopping experience.
Take a look at these two e-commerce Cheerio’s offers. Can you guess which one is from Wal- Mart and which is from Whole Foods?

Marketing analysis is the first step to making data-driven decisions in your business plan. Get in touch with our marketing team to see how we can assist you with finding your brand voice and your audience.
Related Posts:
Launching a Brand New Product: Tricks, Tips, and Traps
Marketing Psychology 101: How to Get Inside the Mind of Your Target Market
Some of Our Recent Work
Feeling ambitious? Read some more:

Navigating the New Digital Era: How Epic Can Help
Over the last few months, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into marketing needs has ushered in a brand new era of technological innovation and strategy, forcing businesses to face the daunting task of keeping up with the …

Scaling Smart: Agency Solutions for Growth
Whether you’re a small startup with big dreams, or a seasoned business ready to take on the world, scaling a business is your secret weapon for turning dreams into reality. Scalability represents a company’s ability to adapt, expand, …

Marketing vs. Advertising
Knowing the Difference How often do you mix up or get confused about the terms “marketing” and “advertising?” No worries, these are often used interchangeably, and while both are vital components of a comprehensive brand strategy, they both …
Ready when you are.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
PESTLE Analysis
Insights and resources on business analysis tools
How to Do Market Analysis for a Business Plan
Last Updated: Sep 11, 2020 by Kiesha Frue Filed Under: Business
A business plan highlights the future objectives of a company, often relating to how the company will sell their product. It also explains proposed strategies to meet sales goals. And market analysis communicates information regarding business.
But market analysis is a broad term . In a business plan, it means you must understand your market/industry and prove to potential investors it’s worth providing funds to your company.
Specifically, you can include:
- Your industry
- Your target market
- The product you intend to sell
- Information about competitors and
- Your marketing plan
This section can appear after introducing your products and/or services. The market analysis section should be fully fleshed out , backed with statistics and reliable data.
A breakdown of market analysis in business plans
You’ll be including the following information:
Your industry: Through data and analytics, this section highlights the trends and buying behavior within your industry. The point is to prove to investors this is a viable market by providing statistics on growth rate and industry size.
Your target market: These are your prospective customers . You tell who they are, their salary, biggest ailments, where to find them, location, and social factors that affect their purchasing decisions.
The product you intend to sell: You’ve mostly explained this in a previous section, but it can be smart to introduce it again, backed with any data collected that proves your product’s worth in the market.
Information about competitors: You’ll explain the strengths and weaknesses of major competitors in your industry. You’ll want to explain how you’ll utilize the weaknesses to market your product. SWOT analysis is perfect for this .
Your marketing plan: The strategies used to market your product should be based on data, research, and competitors. This section will highlight offline, online, digital, and various technologies required to market your product.
The research necessary to complete these sections may be extensive. But there are several avenues you can use to collect it.
Custom surveys: If you’ve ever provided a survey to existing clients from a road test or testimonial phase, you can include their feedback to prove your product is desirable.
Become your customer: Many businesses create a product because it didn’t exist for their problem. If you’re one of them, you’ve already assessed your product through the eyes of a buyer. But if you didn’t, it’s time you sit down and look at it from their point of view. Why would you want your product ? How would you buy it? Does the competitor do it better and if so, how?
Google. Statistics and facts from official publications, such as the government, are often readily available online. These statistics can be inputted to strengthen your points related to demographics, industry research, and the competition. But the stats you choose must be linked to your business and/or product positively. Otherwise, they’re useless.
Chop it down. Your business plan should be concise. Include the most relevant facts, information, and statistics then cut the fat from the rest. Investors don’t want to sift through endless information to get to the conclusion.
In conclusion…
The section about market analysis in your business plan is crucial. It must explain the strengths of your industry, product, and marketing strategies . It requires statistics and data to prove to your investors they will make their money back — meaning your company is a profitable investment.
You can use tools such as SWOT analysis to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats regarding your products, industry, or the competition. And every piece of information, from the analysis to the data, must point back positively to your company.
Image: Rawpixel/ Shutterstock.com
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for April 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- Case Studies
- Flexible Products

- Expert Insights
- Research Studies

- Creativity and Culture
- Management and Leadership
- Business Solutions
- Member Spotlight
- Employee Spotlight
What is a marketing plan and why is it important?
Before you spend a cent on marketing, you first have to understand the market and your customers.

Companies of all sizes have one thing in common: They all began as small businesses. Starting small is the corner for those just getting off the ground. Learn about how to make that first hire, deal with all things administrative, and set yourself up for success.
A marketing plan is a blueprint for launching new products, understanding the intricacies of your market, growing your audience, and promoting your company to customers who want what you’re selling.
With a well-designed marketing plan, you can design more effective promotions and impactful campaigns, reach your customers with targeted advertising, and track your business success with analytics. Without one, you might as well throw your marketing budget down a well and hope for the best.
If you’ve been tasked with creating a marketing plan for your company, there are some basic elements to keep in mind. Though every marketing plan will reflect the specific business and industry it’s been created for, most share a few common features and can be boiled down to just one or two simple objectives. In this article, we’ll outline some of the basic elements of a marketing plan and how to write one.
When you’re ready to put the plan into action, WeWork All Access and WeWork On Demand are there to support you with hundreds of dedicated workspaces around the world, so you can seamlessly collaborate on marketing strategy in a professional and stylish office space.
What is a marketing plan?
A marketing plan is a document outlining a company’s future marketing efforts and goals. It can be as short as a single page or made up of many smaller campaign plans from different marketing teams.
However large and complex those plans are, the idea remains the same: A marketing plan is created to organize, execute, and eventually measure the success of a business’s marketing strategy .
Types of marketing plans
Marketing plans come in as many different shapes and sizes as there are different kinds of business, but they can be broadly placed into one (or more) of a few different categories. Here are some of the most common you’ll encounter.
- Annual marketing plans. These types of marketing plans arrange campaigns according to when they’re expected to launch, rather than the content of the campaigns themselves. It’s a useful way to get an overview of a marketing strategy for the upcoming year, and to measure success continuously as time passes.
- Content marketing plans. This is a more content-focused way of approaching a marketing strategy, and highlights the specific channels and audiences you want to reach. Content marketing plans can look very similar to annual marketing plans, but are less concerned with the “when” and more with the “what” and the “how.”
- Product launch plans. Launching a new product or service requires a specific kind of marketing plan. The main goal is to successfully introduce the new product to the market. But these plans also include the strategies, tactics, and content needed in the buildup to the launch itself.
- Social media marketing plans. Social media channels are such a vital part of a company’s marketing goals that it’s often wise to create a separate social media marketing plan dedicated to creating advertising and promotional content on these platforms.
What is the purpose of a marketing plan?
A marketing plan lays out your business strategy for acquiring new customers and selling more products and services. But it also serves as a way of analyzing exactly how successful your marketing efforts have been so far. Knowing this information helps steer ongoing campaigns in the right direction, aligns your marketing with your company’s values, and ensures that future campaigns are better targeted and more effective.
To understand why a marketing plan is important, just consider what would happen without one. Your advertising budget would be spent based entirely on guesswork about where your potential customers can be found and what they’re looking for. You’d have no idea which of your campaigns contributed to increased sales figures. And you’d have no baselines from which to build more effective campaigns in the future.
How to create a marketing plan
Elements of a marketing plan.
The basic building blocks of any good marketing plan are focused on objectives, research, competitors, and content. These objectives should be clearly defined and easily measurable goals —ideally no more than two or three—and informed by as much consumer research as you can reasonably gather.
Whether your goal is increasing your Instagram followers, driving traffic to your site, or attracting more cheese fans to your cheese store, set a specific target by which to monitor the performance of any campaign. As you develop your marketing plan and learn what’s effective and what’s not, you can set more accurate targets and begin to hone in on the strategies that really work for your company.
A marketing plan should also describe your brand’s biggest competitors and the campaigns they’re running, as well as identify any openings in the market that would allow your company to grab market share. This is where SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis comes into its own, enabling a company to shape its marketing plan around its own strengths and weaknesses.
Lastly, a marketing plan should outline the content of each campaign. Will your pre-roll video content use animation or live actors? Can you offer discounts and voucher codes to new customers? Will you leverage your mailing list to notify existing customers of a new product launch?
Define a marketing plan strategy
If your marketing plan is a roadmap, then your marketing strategy is the road. The strategy describes which tools you’ll use to hit the targets laid out by the main marketing plan document, and how they’ll be applied.
Here’s where you get down to the fundamentals of selling. Depending on who you ask, there are as many as seven P’s of marketing, though most agree on four core elements: price, product, place, and promotion.
What are you selling? How much are you charging? Where will your customers see it? And how will you promote it to them? Marketing gurus will promise you that if you can answer all of these questions correctly, you’ll be guaranteed boundless success.
Of course, in the real world it’s not quite so straightforward. But the four main P’s are an ideal starting point for anyone creating a market plan from scratch.
How to measure the success of a marketing plan
An enormous amount of effort and investment is poured into monitoring the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, but at some level, consumer behavior becomes what’s known as a black box. You can measure what goes into it and what comes out the other end, but what happens inside the mind of a consumer can ultimately only be guessed at based on outcomes. Even the shoppers themselves can’t reliably report on why they choose certain products over others.
That’s why tracking a marketing plan’s performance alongside more specific KPIs (key performance indicators) is crucial. Advertising spend and sales figures aren’t linked in a simple or obvious way, so measuring success on a more granular level—such as increasing conversions or returning customers—helps create a much clearer picture of how well your marketing plan is doing.
Related articles

Final thoughts on creating a marketing plan
Marketing plans need to be squarely outlined and adhered to, but they shouldn’t be set in stone. You need to be able to course-correct when something isn’t landing, or lean more into campaigns when they’re working well.
Quick aside: This is particularly true when it comes to the content of social media marketing plans, which are truly effective only when they’re timely and topical. Memes are a perfect example of this: How often have you seen a promoted tweet deploy some forgotten joke from months ago, presumably because it had been left in somebody’s annual marketing plan?
But while it’s useful to have a flexible approach , it’s important that your marketing plan is resilient and doesn’t flip-flop or bounce wildly between ideas. Move the goalposts too much and your plan will quickly fall apart, leaving your campaign in chaos. Allow your strategies some time to settle in, and even if you don’t reach success, you will gain invaluable performance data for future projects.
Steve Hogarty is a writer and journalist based in London. He is the travel editor of City AM newspaper and the deputy editor of City AM Magazine , where his work focuses on technology, travel, and entertainment.
Rethinking your workspace?

Tom Hewitson, Chief AI Officer at leading AI training company General Purpose , offers tips for small businesses

Learn the differences between Class A, Class B, and Class C buildings based on their visual appeal, location, and amenities to see which of them best suits your business.

Short-term leases can offer startups and established companies some much-needed flexibility
Just in Time for Spring 🌻 50% Off for 3 Months. BUY NOW & SAVE
50% Off for 3 Months Buy Now & Save
Wow clients with professional invoices that take seconds to create
Quick and easy online, recurring, and invoice-free payment options
Automated, to accurately track time and easily log billable hours
Reports and tools to track money in and out, so you know where you stand
Easily log expenses and receipts to ensure your books are always tax-time ready
Tax time and business health reports keep you informed and tax-time ready
Automatically track your mileage and never miss a mileage deduction again
Time-saving all-in-one bookkeeping that your business can count on
Track project status and collaborate with clients and team members
Organized and professional, helping you stand out and win new clients
Set clear expectations with clients and organize your plans for each project
Client management made easy, with client info all in one place
Pay your employees and keep accurate books with Payroll software integrations
- Team Management
FreshBooks integrates with over 100 partners to help you simplify your workflows
Send invoices, track time, manage payments, and more…from anywhere.
- Freelancers
- Self-Employed Professionals
- Businesses With Employees
- Businesses With Contractors
- Marketing & Agencies
- Construction & Trades
- IT & Technology
- Business & Prof. Services
- Accounting Partner Program
- Collaborative Accounting™
- Accountant Hub
- Reports Library
- FreshBooks vs QuickBooks
- FreshBooks vs HoneyBook
- FreshBooks vs Harvest
- FreshBooks vs Wave
- FreshBooks vs Xero
- Free Invoice Generator
- Invoice Templates
- Accounting Templates
- Business Name Generator
- Estimate Templates
- Help Center
- Business Loan Calculator
- Mark Up Calculator
Call Toll Free: 1.866.303.6061
1-888-674-3175
- All Articles
- Productivity
- Project Management
- Bookkeeping
Resources for Your Growing Business
The importance of business plan: 5 key reasons.
A key part of any business is its business plan. They can help define the goals of your business and help it reach success. A good business plan can also help you develop an adequate marketing strategy. There are a number of reasons all business owners need business plans, keep reading to learn more!
Here’s What We’ll Cover:
What Is a Business Plan?
5 reasons you need a well-written business plan, how do i make a business plan, key takeaways.
A business plan contains detailed information that can help determine its success. Some of this information can include the following:
- Market analysis
- Cash flow projection
- Competitive analysis
- Financial statements and financial projections
- An operating plan
A solid business plan is a good way to attract potential investors. It can also help you display to business partners that you have a successful business growing. In a competitive landscape, a formal business plan is your key to success.

Check out all of the biggest reasons you need a good business plan below.
1. To Secure Funding
Whether you’re seeking funding from a venture capitalist or a bank, you’ll need a business plan. Business plans are the foundation of a business. They tell the parties that you’re seeking funding from whether or not you’re worth investing in. If you need any sort of outside financing, you’ll need a good business plan to secure it.
2. Set and Communicate Goals
A business plan gives you a tangible way of reviewing your business goals. Business plans revolve around the present and the future. When you establish your goals and put them in writing, you’re more likely to reach them. A strong business plan includes these goals, and allows you to communicate them to investors and employees alike.
3. Prove Viability in the Market
While many businesses are born from passion, not many will last without an effective business plan. While a business concept may seem sound, things may change once the specifics are written down. Often, people who attempt to start a business without a plan will fail. This is because they don’t take into account all of the planning and funds needed to get a business off of the ground.
Market research is a large part of the business planning process. It lets you review your potential customers, as well as the competition, in your field. By understanding both you can set price points for products or services. Sometimes, it may not make sense to start a business based on the existing competition. Other times, market research can guide you to effective marketing strategies that others lack. To have a successful business, it has to be viable. A business plan will help you determine that.
4. They Help Owners Avoid Failure
Far too often, small businesses fail. Many times, this is due to the lack of a strong business plan. There are many reasons that small businesses fail, most of which can be avoided by developing a business plan. Some of them are listed below, which can be avoided by having a business plan:
- The market doesn’t need the business’s product or service
- The business didn’t take into account the amount of capital needed
- The market is oversaturated
- The prices set by the business are too high, pushing potential customers away
Any good business plan includes information to help business owners avoid these issues.

5. Business Plans Reduce Risk
Related to the last reason, business plans help reduce risk. A well-thought-out business plan helps reduce risky decisions. They help business owners make informed decisions based on the research they conduct. Any business owner can tell you that the most important part of their job is making critical decisions. A business plan that factors in all possible situations helps make those decisions.
Luckily, there are plenty of tools available to help you create a business plan. A simple search can lead you to helpful tools, like a business plan template . These are helpful, as they let you fill in the information as you go. Many of them provide basic instructions on how to create the business plan, as well.
If you plan on starting a business, you’ll need a business plan. They’re good for a vast number of things. Business plans help owners make informed decisions, as well as set goals and secure funding. Don’t put off putting together your business plan!
If you’re in the planning stages of your business, be sure to check out our resource hub . We have plenty of valuable resources and articles for you when you’re just getting started. Check it out today!
RELATED ARTICLES

Save Time Billing and Get Paid 2x Faster With FreshBooks
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
Get more great content in your Inbox.
By subscribing, you agree to receive communications from FreshBooks and acknowledge and agree to FreshBook’s Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time by contacting us at [email protected].
👋 Welcome to FreshBooks
To see our product designed specifically for your country, please visit the United States site.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 4: Calculate market value. You can use either top-down analysis or bottom-up analysis to calculate an estimate of your market value. A top-down analysis tends to be the easier option of the ...
Plan several rounds of edits or have someone else review it. Keep everything in the context of your business. Make sure all the statistics and data you use in your market analysis relate back to your business. Your focus should be on how you are uniquely positioned to meet the needs of the target market.
It is a vital component of a business plan as it allows entrepreneurs and business owners to understand their industry and market better, enabling them to make well-informed decisions. The business plan market analysis section has two main benefits. Firstly, it Allows you to Identify key opportunities in the market.
7 TOP TIPS For Writing Market Analysis. 1. Realistic Projections. Above all, make sure that you are realistic in your projections about how your product or service is going to be accepted in the market, otherwise you are going to seriously undermine the credibility of your entire business case. 2.
Writing a Market Analysis Tips. Include an explanation of how you determined the size of the market and how much share competitors have. Include tables like the one above that show competitor size, barriers to entry, etc. Decide where you're going to place this section in your business plan - before or after your SWOT analysis.
4. Define your target market. Know your customers' unique characteristics and tailor your offers and marketing accordingly. 5. Identify barriers to entry. Know what stands in your way and address challenges head-on. 6. Create a sales forecast. Estimate future sales and make confident business decisions.
The market analysis section of your small business plan should include the following: Industry Description and Outlook: Describe your industry both qualitatively and quantitatively by laying out the factors that make your industry an attractive place to start and grow a business. Be sure to include detailed statistics that define the industry ...
1. Stay in context. Remember the objective of your market analysis and stick to it. Keeping the context in mind, identify what essential information to present and back them up with high-end sources. Also, tie your data with essential analysis to show how your business would survive and thrive in the market. 2.
It involves researching and analyzing the target market, competitors, and industry trends in order to identify opportunities and challenges. Here are the steps you can follow to do a market analysis for a business plan: Define your target market: The first step in a market analysis is to identify the specific group of customers that you will be ...
Renewal rate = 1 / useful life of a desk. The volume of transactions = size of desks park x renewal rate. Value of 1 transaction = average price of a desk. Market value = volume of transactions x value of 1 transaction. You should be able to find most of the information for free in this example.
Market analysis is a comprehensive examination of the market and its components globally or in a specific region. Its main objective is understanding the market's opportunities, strengths, weaknesses, and consumer behavior patterns. The key components include market size, distribution channels, profitability, growth rate, key success factors ...
An important part of any good business plan is the Market Analysis. Before you can describe your marketing and sales strategies, you need to figure out what market you serve and what need you fulfill. Then, your Marketing Strategy and Implementation Plan, ideally covered in the next section of your business plan, will fit into a logical flow.
Peppering your business plan with too many meaningless superlatives like "greatest" and "incredible" doesn't add anything of substance. Instead, rely on the thoroughness of your market research and analysis to "wow" readers. 5. Poor quality research. Doing thorough research and analysis is not something you can fake.
A proper market analysis will include more than just confident declarations. You need statistics that show that there is a market for your business and that it's large enough to allow you to make a profit. You'll need to provide information about your industry, a specific description of your target market and some competitive analysis.
Market analysis is the process of evaluating the size, competition, and potential profitability of a market. It is an important aspect of business planning and strategy, as it helps a company understand the market in which it operates and identify opportunities and threats. There are several reasons why market analysis is important:
Using market analysis to determine your entry point and your unique selling proposition is crucial for creating a sustainable business model. Marketing analysis is the first step to making data-driven decisions in your business plan. Get in touch with our marketing team to see how we can assist you with finding your brand voice and your audience.
Step 5: Analyze your findings and create a plan. Once you've completed your market analysis, it's time to analyze your findings and start planning. You can easily create a cash flow forecast ...
Target market analysis is a necessary step in establishing a successful business. It takes time to gather all of the information you'll need, but it will definitely be worth it, as it will guide you in making the best decisions for your company. If you find yourself struggling with the process, though, consider taking a course in market ...
Specifically, you can include: Your industry. Your target market. The product you intend to sell. Information about competitors and. Your marketing plan. This section can appear after introducing your products and/or services. The market analysis section should be fully fleshed out, backed with statistics and reliable data.
4. Define your target market. Know your customers' unique characteristics and tailor your offers and marketing accordingly. 5. Identify barriers to entry. Know what stands in your way and address challenges head-on. 6. Create a sales forecast. Estimate future sales and make confident business decisions.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A marketing plan is a document outlining a company's future marketing efforts and goals. It can be as short as a single page or made up of many smaller campaign plans from different marketing teams. However large and complex those plans are, the idea remains the same: A marketing plan is created to organize, execute, and eventually measure ...
A business plan contains detailed information that can help determine its success. Some of this information can include the following: Market analysis. Cash flow projection. Competitive analysis. Financial statements and financial projections. An operating plan. A solid business plan is a good way to attract potential investors.