Save £500 when you enrol by 30th September! T&C’s apply
- 40 Useful Words and Phrases for Top-Notch Essays

To be truly brilliant, an essay needs to utilise the right language. You could make a great point, but if it’s not intelligently articulated, you almost needn’t have bothered.
Developing the language skills to build an argument and to write persuasively is crucial if you’re to write outstanding essays every time. In this article, we’re going to equip you with the words and phrases you need to write a top-notch essay, along with examples of how to utilise them.
It’s by no means an exhaustive list, and there will often be other ways of using the words and phrases we describe that we won’t have room to include, but there should be more than enough below to help you make an instant improvement to your essay-writing skills.
If you’re interested in developing your language and persuasive skills, Oxford Royale offers summer courses at its Oxford Summer School , Cambridge Summer School , London Summer School , San Francisco Summer School and Yale Summer School . You can study courses to learn english , prepare for careers in law , medicine , business , engineering and leadership.

General explaining
Let’s start by looking at language for general explanations of complex points.
1. In order to
Usage: “In order to” can be used to introduce an explanation for the purpose of an argument. Example: “In order to understand X, we need first to understand Y.”
2. In other words
Usage: Use “in other words” when you want to express something in a different way (more simply), to make it easier to understand, or to emphasise or expand on a point. Example: “Frogs are amphibians. In other words, they live on the land and in the water.”
3. To put it another way
Usage: This phrase is another way of saying “in other words”, and can be used in particularly complex points, when you feel that an alternative way of wording a problem may help the reader achieve a better understanding of its significance. Example: “Plants rely on photosynthesis. To put it another way, they will die without the sun.”
4. That is to say
Usage: “That is” and “that is to say” can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: “Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.”
5. To that end
Usage: Use “to that end” or “to this end” in a similar way to “in order to” or “so”. Example: “Zoologists have long sought to understand how animals communicate with each other. To that end, a new study has been launched that looks at elephant sounds and their possible meanings.”
Adding additional information to support a point
Students often make the mistake of using synonyms of “and” each time they want to add further information in support of a point they’re making, or to build an argument. Here are some cleverer ways of doing this.
6. Moreover
Usage: Employ “moreover” at the start of a sentence to add extra information in support of a point you’re making. Example: “Moreover, the results of a recent piece of research provide compelling evidence in support of…”
7. Furthermore
Usage:This is also generally used at the start of a sentence, to add extra information. Example: “Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that…”
8. What’s more
Usage: This is used in the same way as “moreover” and “furthermore”. Example: “What’s more, this isn’t the only evidence that supports this hypothesis.”
9. Likewise
Usage: Use “likewise” when you want to talk about something that agrees with what you’ve just mentioned. Example: “Scholar A believes X. Likewise, Scholar B argues compellingly in favour of this point of view.”
10. Similarly
Usage: Use “similarly” in the same way as “likewise”. Example: “Audiences at the time reacted with shock to Beethoven’s new work, because it was very different to what they were used to. Similarly, we have a tendency to react with surprise to the unfamiliar.”
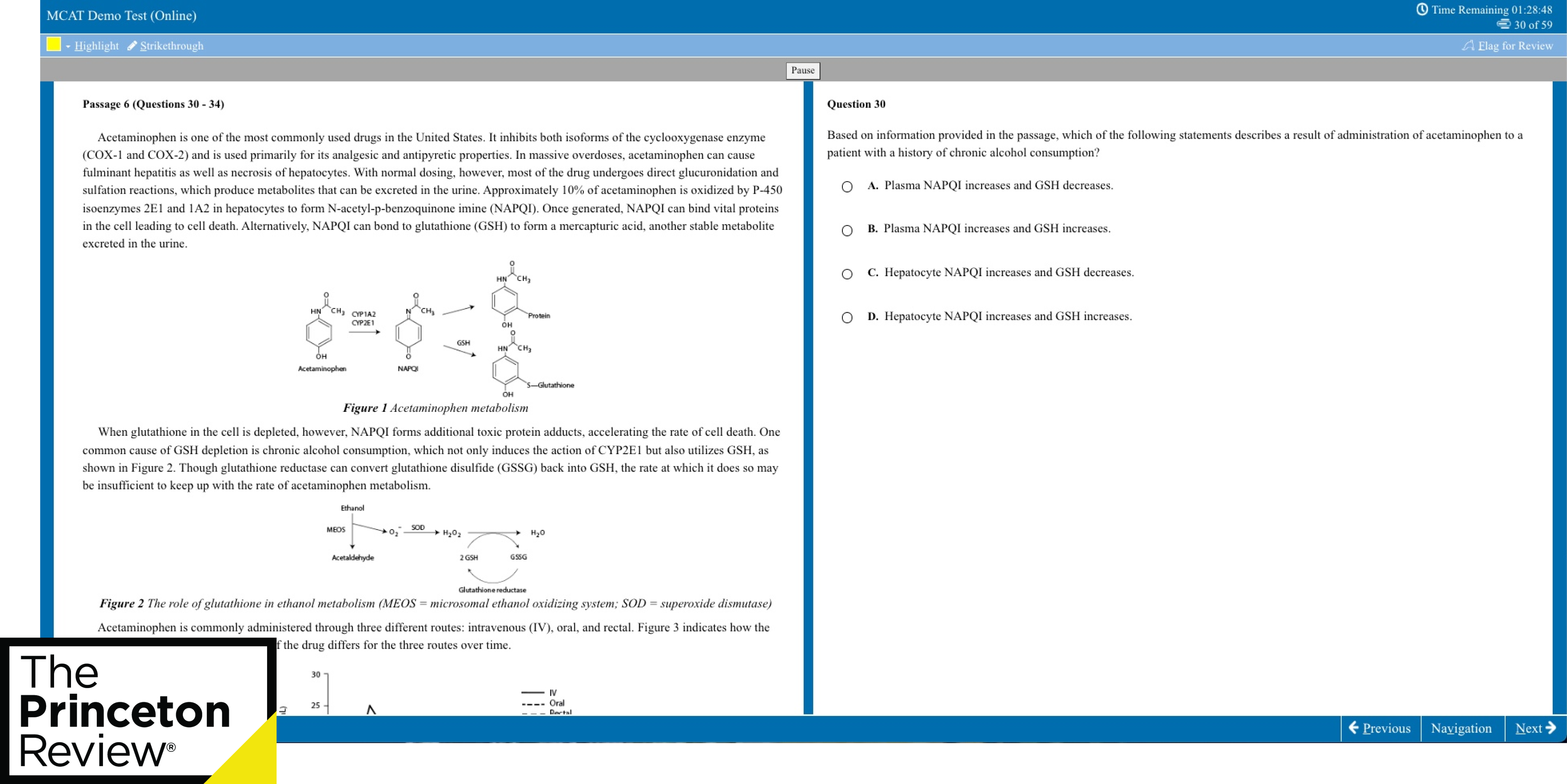
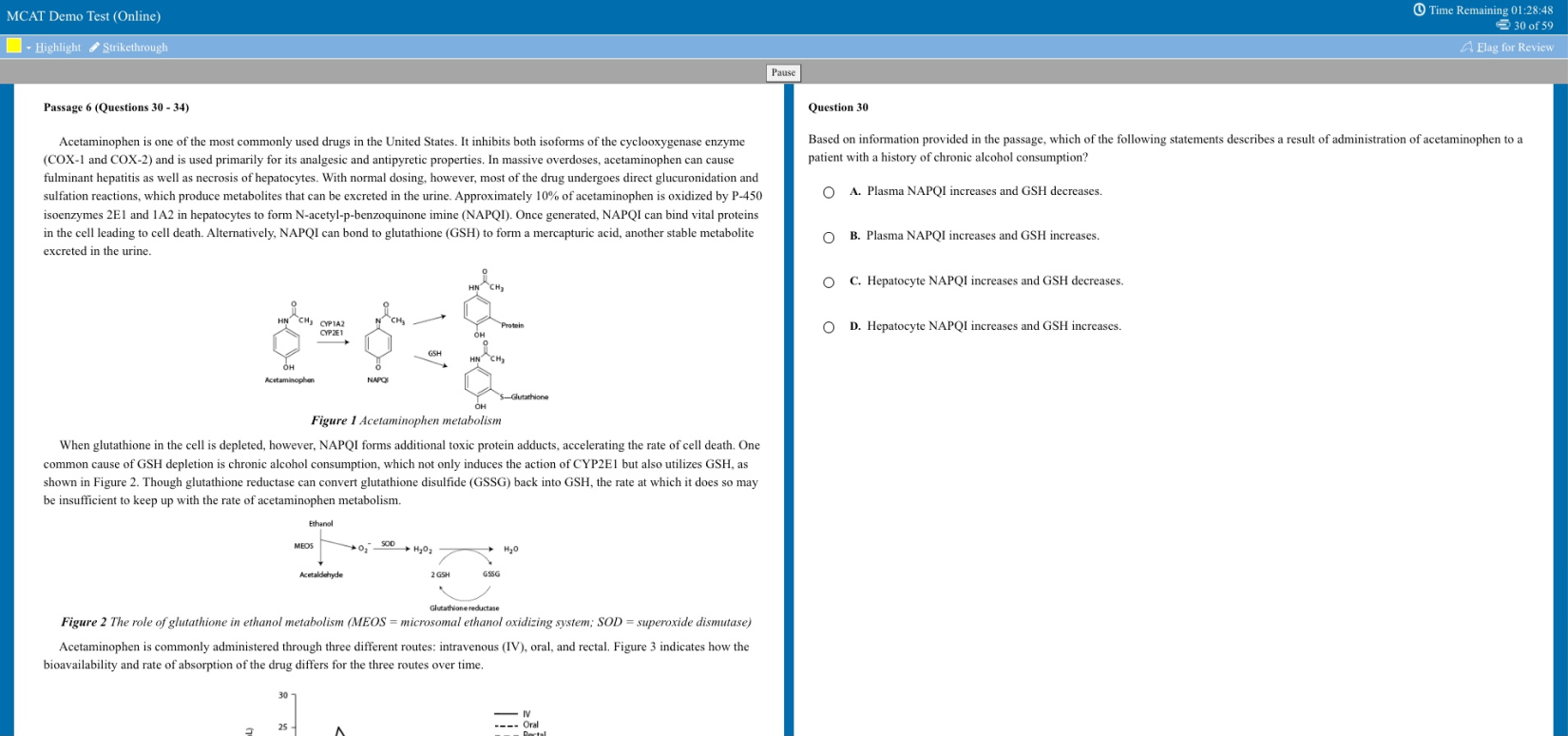
11. Another key thing to remember
Usage: Use the phrase “another key point to remember” or “another key fact to remember” to introduce additional facts without using the word “also”. Example: “As a Romantic, Blake was a proponent of a closer relationship between humans and nature. Another key point to remember is that Blake was writing during the Industrial Revolution, which had a major impact on the world around him.”
12. As well as
Usage: Use “as well as” instead of “also” or “and”. Example: “Scholar A argued that this was due to X, as well as Y.”
13. Not only… but also
Usage: This wording is used to add an extra piece of information, often something that’s in some way more surprising or unexpected than the first piece of information. Example: “Not only did Edmund Hillary have the honour of being the first to reach the summit of Everest, but he was also appointed Knight Commander of the Order of the British Empire.”
14. Coupled with
Usage: Used when considering two or more arguments at a time. Example: “Coupled with the literary evidence, the statistics paint a compelling view of…”
15. Firstly, secondly, thirdly…
Usage: This can be used to structure an argument, presenting facts clearly one after the other. Example: “There are many points in support of this view. Firstly, X. Secondly, Y. And thirdly, Z.
16. Not to mention/to say nothing of
Usage: “Not to mention” and “to say nothing of” can be used to add extra information with a bit of emphasis. Example: “The war caused unprecedented suffering to millions of people, not to mention its impact on the country’s economy.”
Words and phrases for demonstrating contrast
When you’re developing an argument, you will often need to present contrasting or opposing opinions or evidence – “it could show this, but it could also show this”, or “X says this, but Y disagrees”. This section covers words you can use instead of the “but” in these examples, to make your writing sound more intelligent and interesting.
17. However
Usage: Use “however” to introduce a point that disagrees with what you’ve just said. Example: “Scholar A thinks this. However, Scholar B reached a different conclusion.”
18. On the other hand
Usage: Usage of this phrase includes introducing a contrasting interpretation of the same piece of evidence, a different piece of evidence that suggests something else, or an opposing opinion. Example: “The historical evidence appears to suggest a clear-cut situation. On the other hand, the archaeological evidence presents a somewhat less straightforward picture of what happened that day.”
19. Having said that
Usage: Used in a similar manner to “on the other hand” or “but”. Example: “The historians are unanimous in telling us X, an agreement that suggests that this version of events must be an accurate account. Having said that, the archaeology tells a different story.”
20. By contrast/in comparison
Usage: Use “by contrast” or “in comparison” when you’re comparing and contrasting pieces of evidence. Example: “Scholar A’s opinion, then, is based on insufficient evidence. By contrast, Scholar B’s opinion seems more plausible.”
21. Then again
Usage: Use this to cast doubt on an assertion. Example: “Writer A asserts that this was the reason for what happened. Then again, it’s possible that he was being paid to say this.”
22. That said
Usage: This is used in the same way as “then again”. Example: “The evidence ostensibly appears to point to this conclusion. That said, much of the evidence is unreliable at best.”
Usage: Use this when you want to introduce a contrasting idea. Example: “Much of scholarship has focused on this evidence. Yet not everyone agrees that this is the most important aspect of the situation.”
Adding a proviso or acknowledging reservations
Sometimes, you may need to acknowledge a shortfalling in a piece of evidence, or add a proviso. Here are some ways of doing so.
24. Despite this
Usage: Use “despite this” or “in spite of this” when you want to outline a point that stands regardless of a shortfalling in the evidence. Example: “The sample size was small, but the results were important despite this.”
25. With this in mind
Usage: Use this when you want your reader to consider a point in the knowledge of something else. Example: “We’ve seen that the methods used in the 19th century study did not always live up to the rigorous standards expected in scientific research today, which makes it difficult to draw definite conclusions. With this in mind, let’s look at a more recent study to see how the results compare.”
26. Provided that
Usage: This means “on condition that”. You can also say “providing that” or just “providing” to mean the same thing. Example: “We may use this as evidence to support our argument, provided that we bear in mind the limitations of the methods used to obtain it.”
27. In view of/in light of
Usage: These phrases are used when something has shed light on something else. Example: “In light of the evidence from the 2013 study, we have a better understanding of…”
28. Nonetheless
Usage: This is similar to “despite this”. Example: “The study had its limitations, but it was nonetheless groundbreaking for its day.”
29. Nevertheless
Usage: This is the same as “nonetheless”. Example: “The study was flawed, but it was important nevertheless.”
30. Notwithstanding
Usage: This is another way of saying “nonetheless”. Example: “Notwithstanding the limitations of the methodology used, it was an important study in the development of how we view the workings of the human mind.”
Giving examples
Good essays always back up points with examples, but it’s going to get boring if you use the expression “for example” every time. Here are a couple of other ways of saying the same thing.
31. For instance
Example: “Some birds migrate to avoid harsher winter climates. Swallows, for instance, leave the UK in early winter and fly south…”
32. To give an illustration
Example: “To give an illustration of what I mean, let’s look at the case of…”
Signifying importance
When you want to demonstrate that a point is particularly important, there are several ways of highlighting it as such.
33. Significantly
Usage: Used to introduce a point that is loaded with meaning that might not be immediately apparent. Example: “Significantly, Tacitus omits to tell us the kind of gossip prevalent in Suetonius’ accounts of the same period.”
34. Notably
Usage: This can be used to mean “significantly” (as above), and it can also be used interchangeably with “in particular” (the example below demonstrates the first of these ways of using it). Example: “Actual figures are notably absent from Scholar A’s analysis.”
35. Importantly
Usage: Use “importantly” interchangeably with “significantly”. Example: “Importantly, Scholar A was being employed by X when he wrote this work, and was presumably therefore under pressure to portray the situation more favourably than he perhaps might otherwise have done.”
Summarising
You’ve almost made it to the end of the essay, but your work isn’t over yet. You need to end by wrapping up everything you’ve talked about, showing that you’ve considered the arguments on both sides and reached the most likely conclusion. Here are some words and phrases to help you.
36. In conclusion
Usage: Typically used to introduce the concluding paragraph or sentence of an essay, summarising what you’ve discussed in a broad overview. Example: “In conclusion, the evidence points almost exclusively to Argument A.”
37. Above all
Usage: Used to signify what you believe to be the most significant point, and the main takeaway from the essay. Example: “Above all, it seems pertinent to remember that…”
38. Persuasive
Usage: This is a useful word to use when summarising which argument you find most convincing. Example: “Scholar A’s point – that Constanze Mozart was motivated by financial gain – seems to me to be the most persuasive argument for her actions following Mozart’s death.”
39. Compelling
Usage: Use in the same way as “persuasive” above. Example: “The most compelling argument is presented by Scholar A.”
40. All things considered
Usage: This means “taking everything into account”. Example: “All things considered, it seems reasonable to assume that…”
How many of these words and phrases will you get into your next essay? And are any of your favourite essay terms missing from our list? Let us know in the comments below, or get in touch here to find out more about courses that can help you with your essays.
At Oxford Royale Academy, we offer a number of summer school courses for young people who are keen to improve their essay writing skills. Click here to apply for one of our courses today, including law , business , medicine and engineering .
Comments are closed.

100+ Useful Words and Phrases to Write a Great Essay
By: Author Sophia
Posted on Last updated: October 25, 2023
Sharing is caring!
How to Write a Great Essay in English! This lesson provides 100+ useful words, transition words and expressions used in writing an essay. Let’s take a look!
The secret to a successful essay doesn’t just lie in the clever things you talk about and the way you structure your points.
Useful Words and Phrases to Write a Great Essay
Overview of an essay.

Useful Phrases for Proficiency Essays
Developing the argument
- The first aspect to point out is that…
- Let us start by considering the facts.
- The novel portrays, deals with, revolves around…
- Central to the novel is…
- The character of xxx embodies/ epitomizes…
The other side of the argument
- It would also be interesting to see…
- One should, nevertheless, consider the problem from another angle.
- Equally relevant to the issue are the questions of…
- The arguments we have presented… suggest that…/ prove that…/ would indicate that…
- From these arguments one must…/ could…/ might… conclude that…
- All of this points to the conclusion that…
- To conclude…
Ordering elements
- Firstly,…/ Secondly,…/ Finally,… (note the comma after all these introductory words.)
- As a final point…
- On the one hand, …. on the other hand…
- If on the one hand it can be said that… the same is not true for…
- The first argument suggests that… whilst the second suggests that…
- There are at least xxx points to highlight.
Adding elements
- Furthermore, one should not forget that…
- In addition to…
- Moreover…
- It is important to add that…
Accepting other points of view
- Nevertheless, one should accept that…
- However, we also agree that…
Personal opinion
- We/I personally believe that…
- Our/My own point of view is that…
- It is my contention that…
- I am convinced that…
- My own opinion is…
Others’ opinions
- According to some critics… Critics:
- believe that
- suggest that
- are convinced that
- point out that
- emphasize that
- contend that
- go as far as to say that
- argue for this
Introducing examples
- For example…
- For instance…
- To illustrate this point…
Introducing facts
- It is… true that…/ clear that…/ noticeable that…
- One should note here that…
Saying what you think is true
- This leads us to believe that…
- It is very possible that…
- In view of these facts, it is quite likely that…
- Doubtless,…
- One cannot deny that…
- It is (very) clear from these observations that…
- All the same, it is possible that…
- It is difficult to believe that…
Accepting other points to a certain degree
- One can agree up to a certain point with…
- Certainly,… However,…
- It cannot be denied that…
Emphasizing particular points
- The last example highlights the fact that…
- Not only… but also…
- We would even go so far as to say that…
Moderating, agreeing, disagreeing
- By and large…
- Perhaps we should also point out the fact that…
- It would be unfair not to mention the fact that…
- One must admit that…
- We cannot ignore the fact that…
- One cannot possibly accept the fact that…
Consequences
- From these facts, one may conclude that…
- That is why, in our opinion, …
- Which seems to confirm the idea that…
- Thus,…/ Therefore,…
- Some critics suggest…, whereas others…
- Compared to…
- On the one hand, there is the firm belief that… On the other hand, many people are convinced that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 1

How to Write a Great Essay | Image 2

Phrases For Balanced Arguments
Introduction
- It is often said that…
- It is undeniable that…
- It is a well-known fact that…
- One of the most striking features of this text is…
- The first thing that needs to be said is…
- First of all, let us try to analyze…
- One argument in support of…
- We must distinguish carefully between…
- The second reason for…
- An important aspect of the text is…
- It is worth stating at this point that…
- On the other hand, we can observe that…
- The other side of the coin is, however, that…
- Another way of looking at this question is to…
- What conclusions can be drawn from all this?
- The most satisfactory conclusion that we can come to is…
- To sum up… we are convinced that…/ …we believe that…/ …we have to accept that…
How to Write a Great Essay | Image 3

- Recent Posts
- Plural of Process in the English Grammar - October 3, 2023
- Best Kahoot Names: Get Creative with These Fun Ideas! - October 2, 2023
- List of Homophones for English Learners - September 30, 2023
Related posts:
- How to Write a Letter: A Guide to Informal and Formal English
- How to Write Informal Letters in English (with Examples)
- Most Commonly Used English Phrases on the Phone
- Asking for Help, Asking for Opinions and Asking for Approval
Nur Syuhadah Zainuddin
Friday 19th of August 2022
thank u so much its really usefull
12thSeahorse
Wednesday 3rd of August 2022
He or she who masters the English language rules the world!
Friday 25th of March 2022
Thank you so so much, this helped me in my essays with A+
Theophilus Muzvidziwa
Friday 11th of March 2022
Monday 21st of February 2022
Celebrating 150 years of Harvard Summer School. Learn about our history.
12 Strategies to Writing the Perfect College Essay
College admission committees sift through thousands of college essays each year. Here’s how to make yours stand out.
Pamela Reynolds
When it comes to deciding who they will admit into their programs, colleges consider many criteria, including high school grades, extracurricular activities, and ACT and SAT scores. But in recent years, more colleges are no longer considering test scores.
Instead, many (including Harvard through 2026) are opting for “test-blind” admission policies that give more weight to other elements in a college application. This policy change is seen as fairer to students who don’t have the means or access to testing, or who suffer from test anxiety.
So, what does this mean for you?
Simply that your college essay, traditionally a requirement of any college application, is more important than ever.
A college essay is your unique opportunity to introduce yourself to admissions committees who must comb through thousands of applications each year. It is your chance to stand out as someone worthy of a seat in that classroom.
A well-written and thoughtful essay—reflecting who you are and what you believe—can go a long way to separating your application from the slew of forgettable ones that admissions officers read. Indeed, officers may rely on them even more now that many colleges are not considering test scores.
Below we’ll discuss a few strategies you can use to help your essay stand out from the pack. We’ll touch on how to start your essay, what you should write for your college essay, and elements that make for a great college essay.
Be Authentic
More than any other consideration, you should choose a topic or point of view that is consistent with who you truly are.
Readers can sense when writers are inauthentic.
Inauthenticity could mean the use of overly flowery language that no one would ever use in conversation, or it could mean choosing an inconsequential topic that reveals very little about who you are.
Use your own voice, sense of humor, and a natural way of speaking.
Whatever subject you choose, make sure it’s something that’s genuinely important to you and not a subject you’ve chosen just to impress. You can write about a specific experience, hobby, or personality quirk that illustrates your strengths, but also feel free to write about your weaknesses.
Honesty about traits, situations, or a childhood background that you are working to improve may resonate with the reader more strongly than a glib victory speech.
Grab the Reader From the Start
You’ll be competing with so many other applicants for an admission officer’s attention.
Therefore, start your essay with an opening sentence or paragraph that immediately seizes the imagination. This might be a bold statement, a thoughtful quote, a question you pose, or a descriptive scene.
Starting your essay in a powerful way with a clear thesis statement can often help you along in the writing process. If your task is to tell a good story, a bold beginning can be a natural prelude to getting there, serving as a roadmap, engaging the reader from the start, and presenting the purpose of your writing.
Focus on Deeper Themes
Some essay writers think they will impress committees by loading an essay with facts, figures, and descriptions of activities, like wins in sports or descriptions of volunteer work. But that’s not the point.
College admissions officers are interested in learning more about who you are as a person and what makes you tick.
They want to know what has brought you to this stage in life. They want to read about realizations you may have come to through adversity as well as your successes, not just about how many games you won while on the soccer team or how many people you served at a soup kitchen.
Let the reader know how winning the soccer game helped you develop as a person, friend, family member, or leader. Make a connection with your soup kitchen volunteerism and how it may have inspired your educational journey and future aspirations. What did you discover about yourself?
Show Don’t Tell
As you expand on whatever theme you’ve decided to explore in your essay, remember to show, don’t tell.
The most engaging writing “shows” by setting scenes and providing anecdotes, rather than just providing a list of accomplishments and activities.
Reciting a list of activities is also boring. An admissions officer will want to know about the arc of your emotional journey too.
Try Doing Something Different
If you want your essay to stand out, think about approaching your subject from an entirely new perspective. While many students might choose to write about their wins, for instance, what if you wrote an essay about what you learned from all your losses?
If you are an especially talented writer, you might play with the element of surprise by crafting an essay that leaves the response to a question to the very last sentence.
You may want to stay away from well-worn themes entirely, like a sports-related obstacle or success, volunteer stories, immigration stories, moving, a summary of personal achievements or overcoming obstacles.
However, such themes are popular for a reason. They represent the totality of most people’s lives coming out of high school. Therefore, it may be less important to stay away from these topics than to take a fresh approach.
Explore Harvard Summer School’s College Programs for High School Students
Write With the Reader in Mind
Writing for the reader means building a clear and logical argument in which one thought flows naturally from another.
Use transitions between paragraphs.
Think about any information you may have left out that the reader may need to know. Are there ideas you have included that do not help illustrate your theme?
Be sure you can answer questions such as: Does what you have written make sense? Is the essay organized? Does the opening grab the reader? Is there a strong ending? Have you given enough background information? Is it wordy?
Write Several Drafts
Set your essay aside for a few days and come back to it after you’ve had some time to forget what you’ve written. Often, you’ll discover you have a whole new perspective that enhances your ability to make revisions.
Start writing months before your essay is due to give yourself enough time to write multiple drafts. A good time to start could be as early as the summer before your senior year when homework and extracurricular activities take up less time.
Read It Aloud
Writer’s tip : Reading your essay aloud can instantly uncover passages that sound clumsy, long-winded, or false.
Don’t Repeat
If you’ve mentioned an activity, story, or anecdote in some other part of your application, don’t repeat it again in your essay.
Your essay should tell college admissions officers something new. Whatever you write in your essay should be in philosophical alignment with the rest of your application.
Also, be sure you’ve answered whatever question or prompt may have been posed to you at the outset.
Ask Others to Read Your Essay
Be sure the people you ask to read your essay represent different demographic groups—a teacher, a parent, even a younger sister or brother.
Ask each reader what they took from the essay and listen closely to what they have to say. If anyone expresses confusion, revise until the confusion is cleared up.
Pay Attention to Form
Although there are often no strict word limits for college essays, most essays are shorter rather than longer. Common App, which students can use to submit to multiple colleges, suggests that essays stay at about 650 words.
“While we won’t as a rule stop reading after 650 words, we cannot promise that an overly wordy essay will hold our attention for as long as you’d hoped it would,” the Common App website states.
In reviewing other technical aspects of your essay, be sure that the font is readable, that the margins are properly spaced, that any dialogue is set off properly, and that there is enough spacing at the top. Your essay should look clean and inviting to readers.
End Your Essay With a “Kicker”
In journalism, a kicker is the last punchy line, paragraph, or section that brings everything together.
It provides a lasting impression that leaves the reader satisfied and impressed by the points you have artfully woven throughout your piece.
So, here’s our kicker: Be concise and coherent, engage in honest self-reflection, and include vivid details and anecdotes that deftly illustrate your point.
While writing a fantastic essay may not guarantee you get selected, it can tip the balance in your favor if admissions officers are considering a candidate with a similar GPA and background.
Write, revise, revise again, and good luck!
Experience life on a college campus. Spend your summer at Harvard.
Explore Harvard Summer School’s College Programs for High School Students.
About the Author
Pamela Reynolds is a Boston-area feature writer and editor whose work appears in numerous publications. She is the author of “Revamp: A Memoir of Travel and Obsessive Renovation.”
How Involved Should Parents and Guardians Be in High School Student College Applications and Admissions?
There are several ways parents can lend support to their children during the college application process. Here's how to get the ball rolling.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an sat or act program, by submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., crafting an unforgettable college essay.
Most selective colleges require you to submit an essay or personal statement as part of your application.

It may sound like a chore, and it will certainly take a substantial amount of work. But it's also a unique opportunity that can make a difference at decision time. Admissions committees put the most weight on your high school grades and your test scores . However, selective colleges receive applications from many worthy students with similar scores and grades—too many to admit. So they use your essay, along with your letters of recommendation and extracurricular activities , to find out what sets you apart from the other talented candidates.
Telling Your Story to Colleges
So what does set you apart?
You have a unique background, interests and personality. This is your chance to tell your story (or at least part of it). The best way to tell your story is to write a personal, thoughtful essay about something that has meaning for you. Be honest and genuine, and your unique qualities will shine through.
Admissions officers have to read an unbelievable number of college essays, most of which are forgettable. Many students try to sound smart rather than sounding like themselves. Others write about a subject that they don't care about, but that they think will impress admissions officers.
You don't need to have started your own business or have spent the summer hiking the Appalachian Trail. Colleges are simply looking for thoughtful, motivated students who will add something to the first-year class.
Tips for a Stellar College Application Essay
1. write about something that's important to you..
It could be an experience, a person, a book—anything that has had an impact on your life.
2. Don't just recount—reflect!
Anyone can write about how they won the big game or the summer they spent in Rome. When recalling these events, you need to give more than the play-by-play or itinerary. Describe what you learned from the experience and how it changed you.
Free SAT Practice Tests & Events
Evaluate and improve your SAT score.
3. Being funny is tough.
A student who can make an admissions officer laugh never gets lost in the shuffle. But beware. What you think is funny and what an adult working in a college thinks is funny are probably different. We caution against one-liners, limericks and anything off–color.
4. Start early and write several drafts.
Set it aside for a few days and read it again. Put yourself in the shoes of an admissions officer: Is the essay interesting? Do the ideas flow logically? Does it reveal something about the applicant? Is it written in the applicant’s own voice?

5. No repeats.
What you write in your application essay or personal statement should not contradict any other part of your application–nor should it repeat it. This isn't the place to list your awards or discuss your grades or test scores.
6. Answer the question being asked.
Don't reuse an answer to a similar question from another application.
7. Have at least one other person edit your essay.
A teacher or college counselor is your best resource. And before you send it off, check, check again, and then triple check to make sure your essay is free of spelling or grammar errors.
Read More: 2018-2019 Common Application Essay Prompts (and How to Answer Them)
Test Your College Knowledge
How well do you understand the college admissions process? Find out with our quiz.
Take the Quiz

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 17, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
How to Write the Perfect Essay
06 Feb, 2024 | Blog Articles , English Language Articles , Get the Edge , Humanities Articles , Writing Articles

You can keep adding to this plan, crossing bits out and linking the different bubbles when you spot connections between them. Even though you won’t have time to make a detailed plan under exam conditions, it can be helpful to draft a brief one, including a few key words, so that you don’t panic and go off topic when writing your essay.
If you don’t like the mind map format, there are plenty of others to choose from: you could make a table, a flowchart, or simply a list of bullet points.
Discover More
Thanks for signing up, step 2: have a clear structure.
Think about this while you’re planning: your essay is like an argument or a speech. It needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question.
Start with the basics! It’s best to choose a few major points which will become your main paragraphs. Three main paragraphs is a good number for an exam essay, since you’ll be under time pressure.
If you agree with the question overall, it can be helpful to organise your points in the following pattern:
- YES (agreement with the question)
- AND (another YES point)
- BUT (disagreement or complication)
If you disagree with the question overall, try:
- AND (another BUT point)
For example, you could structure the Of Mice and Men sample question, “To what extent is Curley’s wife portrayed as a victim in Of Mice and Men ?”, as follows:
- YES (descriptions of her appearance)
- AND (other people’s attitudes towards her)
- BUT (her position as the only woman on the ranch gives her power as she uses her femininity to her advantage)
If you wanted to write a longer essay, you could include additional paragraphs under the YES/AND categories, perhaps discussing the ways in which Curley’s wife reveals her vulnerability and insecurities, and shares her dreams with the other characters. Alternatively, you could also lengthen your essay by including another BUT paragraph about her cruel and manipulative streak.
Of course, this is not necessarily the only right way to answer this essay question – as long as you back up your points with evidence from the text, you can take any standpoint that makes sense.

Step 3: Back up your points with well-analysed quotations
You wouldn’t write a scientific report without including evidence to support your findings, so why should it be any different with an essay? Even though you aren’t strictly required to substantiate every single point you make with a quotation, there’s no harm in trying.
A close reading of your quotations can enrich your appreciation of the question and will be sure to impress examiners. When selecting the best quotations to use in your essay, keep an eye out for specific literary techniques. For example, you could highlight Curley’s wife’s use of a rhetorical question when she says, a”n’ what am I doin’? Standin’ here talking to a bunch of bindle stiffs.” This might look like:
The rhetorical question “an’ what am I doin’?” signifies that Curley’s wife is very insecure; she seems to be questioning her own life choices. Moreover, she does not expect anyone to respond to her question, highlighting her loneliness and isolation on the ranch.
Other literary techniques to look out for include:
- Tricolon – a group of three words or phrases placed close together for emphasis
- Tautology – using different words that mean the same thing: e.g. “frightening” and “terrifying”
- Parallelism – ABAB structure, often signifying movement from one concept to another
- Chiasmus – ABBA structure, drawing attention to a phrase
- Polysyndeton – many conjunctions in a sentence
- Asyndeton – lack of conjunctions, which can speed up the pace of a sentence
- Polyptoton – using the same word in different forms for emphasis: e.g. “done” and “doing”
- Alliteration – repetition of the same sound, including assonance (similar vowel sounds), plosive alliteration (“b”, “d” and “p” sounds) and sibilance (“s” sounds)
- Anaphora – repetition of words, often used to emphasise a particular point
Don’t worry if you can’t locate all of these literary devices in the work you’re analysing. You can also discuss more obvious techniques, like metaphor, simile and onomatopoeia. It’s not a problem if you can’t remember all the long names; it’s far more important to be able to confidently explain the effects of each technique and highlight its relevance to the question.

Step 4: Be creative and original throughout
Anyone can write an essay using the tips above, but the thing that really makes it “perfect” is your own unique take on the topic. If you’ve noticed something intriguing or unusual in your reading, point it out – if you find it interesting, chances are the examiner will too!
Creative writing and essay writing are more closely linked than you might imagine. Keep the idea that you’re writing a speech or argument in mind, and you’re guaranteed to grab your reader’s attention.
It’s important to set out your line of argument in your introduction, introducing your main points and the general direction your essay will take, but don’t forget to keep something back for the conclusion, too. Yes, you need to summarise your main points, but if you’re just repeating the things you said in your introduction, the body of the essay is rendered pointless.
Think of your conclusion as the climax of your speech, the bit everything else has been leading up to, rather than the boring plenary at the end of the interesting stuff.
To return to Of Mice and Men once more, here’s an example of the ideal difference between an introduction and a conclusion:
Introduction
In John Steinbeck’s Of Mice and Men , Curley’s wife is portrayed as an ambiguous character. She could be viewed either as a cruel, seductive temptress or a lonely woman who is a victim of her society’s attitudes. Though she does seem to wield a form of sexual power, it is clear that Curley’s wife is largely a victim. This interpretation is supported by Steinbeck’s description of her appearance, other people’s attitudes, her dreams, and her evident loneliness and insecurity.
Overall, it is clear that Curley’s wife is a victim and is portrayed as such throughout the novel in the descriptions of her appearance, her dreams, other people’s judgemental attitudes, and her loneliness and insecurities. However, a character who was a victim and nothing else would be one-dimensional and Curley’s wife is not. Although she suffers in many ways, she is shown to assert herself through the manipulation of her femininity – a small rebellion against the victimisation she experiences.
Both refer back consistently to the question and summarise the essay’s main points. However, the conclusion adds something new which has been established in the main body of the essay and complicates the simple summary which is found in the introduction.

Hannah is an undergraduate English student at Somerville College, University of Oxford, and has a particular interest in postcolonial literature and the Gothic. She thinks literature is a crucial way of developing empathy and learning about the wider world. When she isn’t writing about 17th-century court masques, she enjoys acting, travelling and creative writing.
Recommended articles
Best Universities to Study Medicine in the World
A degree in Medicine spans many years, so it’s important to make a good choice when committing yourself to your studies. This guide is designed to help you figure out where you'd like to study and practise medicine. For those interested in getting a head start, the...

What Is A Year Abroad?
One of the great opportunities offered to UK university students is taking a year abroad. But what does this involve? Who can do it? What are some of the pros and cons? In our year abroad guide, we’ll explain some of the things to bear in mind when considering this...

The Ultimate Guide To Summer Internships
Are you eager to make the most of your summer break and jumpstart your career? There are so many productive things students can do in the summer or with their school holidays, and an internship is one of the most valuable! A summer internship could be the perfect...
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Personal Statement That Wows Colleges
← What Is an Application Theme and Why Is It Important?
10 Personal Statement Examples That Work →

Most of the college applications process is fairly cut and dry. You’ll submit information about your classes and grades, standardized test scores, and various other accomplishments and honors. On much of the application, your accomplishments must speak for themselves.
The personal statement is different though, and it’s your chance to let your voice be heard. To learn more about the personal statement, how to choose a topic, and how to write one that wows colleges, don’t miss this post.
What is the Personal Statement?
Personal statements are used in both undergraduate and graduate admissions. For undergrad admissions, personal statements are any essays students must write to submit their main application. For example, the Common App Essay and Coalition Application Essay are examples of personal statements. Similarly, the ApplyTexas Essays and University of California Essays are also good examples .
Personal statements in college admissions are generally not school-specific (those are called “supplemental essays”). Instead, they’re sent to a wide range of schools, usually every school you apply to.
What is the Purpose of the Personal Statement?
The personal statement is generally your opportunity to speak to your unique experiences, qualities, or beliefs that aren’t elsewhere represented on the application. It is a chance to break away from the data that defines you on paper, and provide a glimpse into who you really are. In short, it’s the admissions committee’s chance to get to know the real you.
So, what are colleges looking for in your personal statement? They are looking for something that sets you apart. They are asking themselves: do you write about something truly unique? Do you write about something common, in a new and interesting way? Do you write about an aspect of your application that needed further explanation? All of these are great ways to impress with your personal statement.
Beyond getting to know you, admissions committees are also evaluating your writing skills. Are you able to write clearly and succinctly? Can you tell an engaging story? Writing effectively is an important skill in both college and life, so be sure to also fine-tune your actual writing (grammar and syntax), not just the content of your essay.
Is your personal statement strong enough? Get a free review of your personal statement with CollegeVine’s Peer Essay Review.
How To a Choose A Topic For Your Personal Statement
Most of the time, you’re given a handful of prompts to choose from. Common personal statement prompts include:
- Central aspect of your identity (activity, interest, talent, background)
- Overcoming a failure
- Time you rose to a challenge or showed leadership
- Experience that changed your beliefs
- Problem you’d like to solve
- Subject or idea that captivates you
One of the questions that we hear most often about the personal statement is, “How do I choose what to write about?” For some students, the personal statement prompt triggers an immediate and strong idea. For many more, there is at least initially some uncertainty.
We often encourage students to think less about the exact prompt and more about what aspects of themselves they think are most worthy of highlighting. This is especially helpful if you’re offered a “topic of your choice” prompt, as the best essay topic for you might actually be one you make up!
For students with an interesting story or a defining background, these can serve as the perfect catalyst to shape your approach. For students with a unique voice or different perspective, simple topics written in a new way can be engaging and insightful.
Finally, you need to consider the rest of your application when you choose a topic for your personal statement. If you are returning from a gap year, failed a single class during sophomore year, or participated extensively in something you’re passionate about that isn’t elsewhere on your application, you might attempt to address one of these topics in your statement. After all, the admissions committee wants to get to know you and understand who you really are, and these are all things that will give them a deeper understanding of that.
Still, tons of students have a decent amount of writer’s block when it comes to choosing a topic. This is understandable since the personal statement tends to be considered rather high stakes. To help you get the ball rolling, we recommend the post What If I Don’t Have Anything Interesting To Write About In My College Essay?
Tips for Writing a Personal Statement for College
1. approach this as a creative writing assignment..
Personal statements are difficult for many students because they’ve never had to do this type of writing. High schoolers are used to writing academic reports or analytical papers, but not creative storytelling pieces.
The point of creative writing is to have fun with it, and to share a meaningful story. Choose a topic that inspires you so that you’ll enjoy writing your essay. It doesn’t have to be intellectual or impressive at all. You have your transcript and test scores to prove your academic skills, so the point of the personal statement is to give you free rein to showcase your personality. This will result in a more engaging essay and reading experience for admissions officers.
As you’re writing, there’s no need to follow the traditional five-paragraph format with an explicit thesis. Your story should have an overarching message, but it doesn’t need to be explicitly stated—it should shine through organically.
Your writing should also feel natural. While it will be more refined than a conversation with your best friend, it shouldn’t feel stuffy or contrived when it comes off your tongue. This balance can be difficult to strike, but a tone that would feel natural when talking with an admired teacher or a longtime mentor is usually a good fit.
2. Show, don’t tell.
One of the biggest mistakes students make is to simply state everything that happened, instead of actually bringing the reader to the moment it happened, and telling a story. It’s boring to read: “I was overjoyed and felt empowered when I finished my first half marathon.” It’s much more interesting when the writing actually shows you what happened and what the writer felt in that moment: “As I rounded the final bend before the finish line, my heart fluttered in excitement. The adrenaline drowned out my burning legs and gasping lungs. I was going to finish my first half marathon! This was almost incomprehensible to me, as someone who could barely run a mile just a year ago.”
If you find yourself starting to write your essay like a report, and are having trouble going beyond “telling,” envision yourself in the moment you want to write about. What did you feel, emotionally and physically? Why was this moment meaningful? What did you see or hear? What were your thoughts?
For inspiration, read some memoirs or personal essays, like The New York Times Modern Love Column . You could also listen to podcasts of personal stories, like The Moth . What do these writers and storytellers do that make their stories engaging? If you didn’t enjoy a particular story, what was it that you didn’t like? Analyzing real stories can help you identify techniques that you personally resonate with.
3. Use dialogue.
A great way to keep your writing engaging is to include some dialogue. Instead of writing: “My brothers taunted me,” consider sharing what they actually said. It’s more powerful to read something like:
“Where’s the fire, Princess Clara?” they taunted. “Having some trouble?” They prodded me with the ends of the chewed branches and, with a few effortless scrapes of wood on rock, sparked a red and roaring flame. My face burned long after I left the fire pit. The camp stank of salmon and shame.
Having dialogue can break up longer paragraphs of text, and bring some action and immediacy to your story. That being said, don’t overdo it. It’s important to strike a balance between relying too much on dialogue, and using it occasionally as an effective writing tool. You don’t want your essay to read like a script for a movie (unless, of course, that’s intentional and you want to showcase your screenwriting skills!).
Want free essay feedback? Submit your essay to CollegeVine’s Peer Essay Review and get fast, actionable edits on your essay.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Personal Statements
1. giving a recap or report of all the events..
Your essay isn’t a play-by-play of everything that happened in that time frame. Only include relevant details that enrich the story, instead of making your personal statement a report of the events. Remember that the goal is to share your voice, what’s important to you, and who you are.
2. Writing about too many events or experiences.
Similarly, another common mistake is to make your personal statement a resume or recap of all your high school accomplishments. The Activities Section of the Common App is the place for listing out your achievements, not your personal statement. Focus on one specific experience or a few related experiences, and go into detail on those.
3. Using cliche language.
Try to avoid overdone quotes from famous people like Gandhi or Thoreau. Better yet, try to avoid quotes from other people in general, unless it’s a message from someone you personally know. Adding these famous quotes won’t make your essay unique, and it takes up valuable space for you to share your voice.
You should also steer away from broad language or lavish claims like “It was the best day of my life.” Since they’re so cliche, these statements also obscure your message, and it’s hard to understand what you actually mean. If it was actually the best day of your life, show us why, rather than just telling us.
If you want to learn more about personal statements, see our post of 11 Common App Essay Examples .
Want help with your college essays to improve your admissions chances? Sign up for your free CollegeVine account and get access to our essay guides and courses. You can also get your essay peer-reviewed and improve your own writing skills by reviewing other students’ essays.
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

How To Start a College Essay: 9 Effective Techniques

This post was co-written by me (Ethan) and Luci Jones (Brown University, CO ‘23).
How to start a college essay TABLE OF CONTENTS
The full hemingway, the mini hemingway, the philosophical question, the confession, the trailer thesis, the fascinating concept, the random personal fun fact, the shocking image.
In anything you do, there’s a special, pivotal moment.
I don’t mean the moment when inspiration strikes or the last brushstroke is painted or the audience oohs and ahs over the final product. The point in time we’re talking about here is the Moment When You Do The Darn Thing (DTDT for short). It’s when you get off the couch, stop binging Netflix , and take action. It’s when you put pencil to paper, fingers to keyboard, or *insert whatever other analogy feels applicable here.*
For many, getting started is the hardest part of anything. And that’s understandable. First, because it turns whatever you’re doing into a reality, which raises the stakes. Second, because where you start can easily dictate the quality of where you end up.
College essays have their own special brand of DTDT. Knowing how to begin a college essay is daunting. It can be hard to write an engaging, authentic opener. But without an interesting hook, you risk getting lost in a vast sea of applications. To this end, we’ve put together some techniques about how to start a college essay to make your DTDT moment a little smoother and a little less stressful.
I say “probably” because I’m about to share a few overused techniques that I don’t recommend. Having said that, it is possible to pull them off—they’re just really hard to do well.
The Overly Grand Ambiguous Statement: From a distance, it might seem nice to talk about why all of humankind has felt some type of way for as long as history has existed. (Examples: “Many great thinkers have existed in our nation’s history” or “The key to a successful endeavor is perseverance.”) But these kinds of overly generalized or impersonal grand statements get lost easily in the crowd because they don’t tell the reader much about you. And without a connection to you, there’s not much reason for them to continue reading.
Going Meta: As cool as it may seem to demonstrate to your audience that you are aware of how you’re writing your essay in the moment you’re writing it, it’s less cool to college admissions officers who read meta stuff like that all the time. There are other, more subtle ways to demonstrate self-awareness in your intro rather than to open your essay with some variation of, “I stare at the blank screen...” or, worse, “When I was asked to write this personal statement, at first I wasn’t sure how to begin.” Note that the meta essay can sometimes work (you’ll see a couple examples below), but has a higher degree of difficulty.
The Quote: While quoting famous people who have said something cool in the past may seem like an appealing way to start your essay, remember that colleges want to hear YOUR thoughts. Don’t use the words of another person to stand in for your own opinions or insights. You have cool things to say. It may just take a little while to discover what those things are.
The Too-Obvious Thesis That Spoils the Ending of the Movie (i.e. Your Essay): What if Avengers: Infinity War had opened with a voiceover from the director saying, “This is a film about how Thanos collects all the infinity stones and destroys half the population.” (Aaaaaand this is your too-late spoiler alert. Sorry. But don’t worry, they go back in time and undo it in Endgame . Oh, also spoiler.) That would’ve sucked. That’s what it feels like, though, if you start your essay with something like, “I want to be a veterinarian because I care about animals and the environment.” I read a sentence like that and I go, “Cool, thanks, now I can save myself the three minutes it would’ve taken to read the essay. Thank you, next.” While you may want to have that sentence in mind so you know what you’re trying to get across (this is called a logline), just don’t give away the whole thing. Instead, start your essay with something to pique our interest. How? We’re about to share 9 ways.
Want to read a few more college essay tips? Check out this huge list from admissions experts.
9 WAYS TO START A COLLEGE ESSAY:
An image-based description that focuses on a particular moment and doesn’t explain much—at least not right away. This technique lets dialogue, actions, or details speak for themselves.
(Note that there are many other authors that do this — it’s part of great writing — but my little brother suggested Hemingway and I kinda’ liked the sound of it.)
Example:
Every Saturday morning, I’d awaken to the smell of crushed garlic and piquant pepper. I would stumble into the kitchen to find my grandma squatting over a large silver bowl, mixing fat lips of fresh cabbages with garlic, salt, and red pepper.
Why It Works: In this intro, the author paints a very visceral picture of waking up in the morning to the smell of her grandmother’s traditional Korean cooking. Through the careful word choice (“piquant pepper,” “fat lips of fresh cabbages,” etc.), we get a sense that something important is happening, even if we don’t know what it is yet. But this one can be difficult to pull off if you don’t help the reader understand why you’ve described what you’ve described. Read the rest of the essay here .
Which brings us to...
An image-based description, perhaps 1-3 sentences in length, that focuses on a particular moment and then follows up with a sentence that explains, comments on, or somehow provides context for what is being described.
Take a look at how this can happen by just adding one sentence to the example above (see bolded line below):
Every Saturday morning, I’d awaken to the smell of crushed garlic and piquant pepper. I would stumble into the kitchen to find my grandma squatting over a large silver bowl, mixing fat lips of fresh cabbages with garlic, salt, and red pepper. That was how the delectable Korean dish, kimchi, was born every weekend at my home.
Why it Works: This single sentence hints at some of the author’s core values—culture, ritual, family—without giving too much away about where the essay is headed. Like any good intro, this one creates more questions that answers. (Read the rest of the essay here .)
Another example:
They covered the precious mahogany coffin with a brown amalgam of rocks, decomposed organisms, and weeds. It was my turn to take the shovel, but I felt too ashamed to dutifully send her off when I had not properly said goodbye. I refused to throw dirt on her. I refused to let go of my grandmother, to accept a death I had not seen coming, to believe that an illness could not only interrupt, but steal a beloved life.
Why It Works: The author drops us right into the middle of something we know nothing about, yet it invites us to care. How? The specifics. The details she notices and the resistance she’s feeling help to put us in her shoes. This means we don’t just feel sympathy, we feel empathy . And that empathetic connection heightens the stakes for us by raising questions: How did her grandmother die? Why can’t the author let her go? Why is she angry? (Spoiler: It turns out she’s more angry at herself than anyone else. Read the rest of the essay here .)
The author begins with information that creates certain expectations about them before taking us in a surprising direction.
Growing up, my world was basketball. My summers were spent between the two solid black lines. My skin was consistently tan in splotches and ridden with random scratches. My wardrobe consisted mainly of track shorts, Nike shoes, and tournament t-shirts. Gatorade and Fun Dip were my pre-game snacks. The cacophony of rowdy crowds, ref whistles, squeaky shoes, and scoreboard buzzers was a familiar sound. I was the team captain of almost every team I played on—familiar with the Xs and Os of plays, commander of the court, and the coach’s right hand girl. But that was only me on the surface. Deep down I was an East-Asian influenced bibliophile and a Young Adult fiction writer.
Why It Works: We’re introduced to the author as a basketball superstar, the queen of the court, a sports fanatic—and at this point the reader may even be making assumptions about this author’s identity based on her initial description of herself. However, in one sentence, the writer takes us in a completely unexpected direction. This plays with audience expectations and demonstrates that she has a good degree of self awareness about the layers of her identity. After having our expectations thrown for a loop, we can’t help but wonder more about who exactly this person is (and if you want to know like I did, read the rest of this essay here ).
Another example:
I am on Oxford Academy’s Speech and Debate Team, in both the Parliamentary Debate division and the Lincoln-Douglass debate division. I write screenplays, short stories, and opinionated blogs and am a regular contributor to my school literary magazine, The Gluestick. I have accumulated over 300 community service hours that includes work at homeless shelters, libraries, and special education youth camps. I have been evaluated by the College Board and have placed within the top percentile. But I am not any of these things. I am not a test score, nor a debater, nor a writer. I am an anti-nihilist punk rock philosopher. And I became so when I realized three things:
Why It Works: He basically tears up his (impressive) resume in the first few sentences and says, “That’s not me! Here’s the real me…” and as a result we wonder, “How does one become an anti-nihilist punk rock philosopher? And what are the three things??” (Read the rest here .)
Ask a question that you won’t (and probably can’t) answer in your essay. This gives you a chance to show how your brilliant brain works, plus keeps us hooked as you explore possible answers/solutions.
Does every life matter? Because it seems like certain lives matter more than others, especially when it comes to money.
Why it Works: It raises a complex, interesting question and poses a controversial idea: that we treat some lives as though they matter more than others. We wonder: “Is that true? Could it be? Say more…” Heads-up: This one can veer into the “Overly Grand Ambiguous Statement” opening if you’re not careful. Click here to read the rest of the essay mentioned above, which by the way took him a long time to refine—as this approach is not easy to pull off.
Begin by admitting something you might be judged (or judge yourself) for.
Example:
I have been pooped on many times. I mean this in the most literal sense possible. I have been pooped on by pigeons and possums, house finches and hawks, egrets and eastern grays. (Read the rest here .)
Why it Works: Shows vulnerability, but also in many cases intrigues us to learn more.
Here is a secret that no one in my family knows: I shot my brother when I was six. Luckily, it was a BB gun. But to this day, my older brother Jonathan does not know who shot him. And I have finally promised myself to confess this eleven year old secret to him after I write this essay.
Why It Works: This is a super vulnerable to admit and raises all sorts of questions for us: Why did he shoot his brother? Why hasn’t he confessed it to him? What will his brother say once he tells him? (Fun fact: This essay actually breaks the “don’t start with a quote” rule. Here’s the rest if you wanna’ read it.)
A contextualizing 1-2-sentences (often at the end of the first paragraph) to ground the essay by giving us a sneak peek at what’s to come in the essay—but that do NOT give away the ending.
Example (I’ve marked it in bold below at the end of the first paragraph):
Six years ago, a scrawny twelve year old kid took his first steps into Home Depot: the epitome of manliness. As he marched through the wood section, his eyes scrolled past the options. Red Oak? No, too ubiquitous. Pine? No, too banal. Mahogany? Perfect, it would nicely complement his walls. As days went on, the final product was almost ready. 91 degree angles had been perfected to 90. Drawer slides had been lubricated ten times over. Finally, the masterpiece was finished, and the little boy couldn’t help but smile. A scrawny 12-year-old kid had become a scrawny 12-year-old man. This desk I sit at has not only seen me through the last six years, but its story and the story of the objects I keep on it provide a foundation for my future pursuits.
Why It Works: As we read the first few sentences of this paragraph we might wonder, “Where is this going?” But this sentence sets us at ease and—again, without giving too much away—gives us a sense of what’s to come. We know that we’re going to learn about the author and his future through the objects on his desk. Great! It also signals to the reader “Don’t worry, you’re in good hands. I’m still aware of the task at hand.”
Begin with a concept that’s unusual, paradoxical, and/or marked a turning point in your thinking. This is often followed up with context explaining where the concept came from and why the author is considering it.
Crayfish can turn their red blood cells into precursor neuronal cells, I read in shock. The scientific paper, published in Cell 2014, outlined the process where crayfish could regenerate lost eyestalks or olfactory (smell and odor) nerves with their blood – they could see and smell again! It seemed unfair from an evolutionary standpoint. Humans, who were so much larger than a 7-ounce crayfish, couldn’t use their abundant blood to fix their brain damage.
Why It Works: This opening signals to the reader that the author is: a) someone who has read quite a bit, b) curious, and c) knows, as I like to say, “some stuff about some stuff.” In this case, she knows some science stuff.
Do you know some stuff about some stuff? If so, a little geeky language can help signal this to the reader. Don’t overdo it, though, or it can seem showy.
FYI: I see this more often at the start of great essays than personal statements, as this can often lead to an essay that’s more heady/intellectual and less vulnerable/personal. A variation on this that’s a bit more personal is the...
Begin with a strange fact about yourself to grab our attention. Then go on to say why it’s meaningful. Example:
I subscribe to what the New York Times dubs “the most welcomed piece of daily e-mail in cyberspace.” Cat pictures? Kardashian updates? Nope: A Word A Day.
(Read the rest here .)
Why It Works: It pulls us in by making us think, “Oh, that’s cool!” and then wondering, “Okay, where is this going?”
Grab our attention with an incredibly specific and arresting image or sentence. Then tell us why it matters.
Smeared blood, shredded feathers. Clearly, the bird was dead. But wait, the slight fluctuation of its chest, the slow blinking of its shiny black eyes. No, it was alive.
Why It Works: This style subtly highlights the writing talent of the author without drawing attention away from the content of the story. In this example, the staccatoed sentence fragments convey a sense of halting anxiety and also mimic the movement of the bird’s chest as it struggles to breathe. All sorts of questions come up: What happened to the bird? What will the author do? (Read the rest of the essay here .)
February 2011– My brothers and I were showing off our soccer dribbling skills in my grandfather’s yard when we heard gunshots and screaming in the distance. We paused and listened, confused by sounds we had only ever heard on the news or in movies. My mother rushed out of the house and ordered us inside. The Arab Spring had come to Bahrain.
(Read the rest of the essay here .)
Bowing down to the porcelain god, I emptied the contents of my stomach. Foaming at the mouth, I was ready to pass out. My body couldn’t stop shaking as I gasped for air, and the room started spinning. (Read the rest of the essay here .)
There are, of course, many more kinds of openings—and I’ll add to this post as I discover new ones.
We get it, writing a standout introduction is easier said than done. Hopefully though, after seeing some examples of dynamic and thoughtful intros that used our techniques, you’re inspired to brainstorm some of your own . You’ve got this. DTDT has never looked so good.
Have a great college essay opening or a new type of opening you’d like to suggest? Share it in the comments below!
This post was co-written by me (Ethan) and Luci Jones (Brown University, CO ‘23). Luci took my How to Write a Personal Statement course last year. The essay that she produced was so good and her writing was so beautiful, I’ve asked her to help me co-write this blog post with me, create a few techniques for writing a great introduction, and analyze why they work so well.


Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
The 7 Things That Really Look Good on a College Application
College Admissions , College Info

What looks good on a college application? It's the question nearly every high school student will ask at some point while applying to college. But is there a clear answer?
Fortunately, the answer is yes! Read on to learn what colleges look for in applicants, what looks really good on a college application, and what kinds of myths there are about good things to put on a college application.

What Are Colleges Looking for in Applicants?
Everyone applying to college has wondered, "What exactly are colleges looking for in applicants?" In other words, what looks good on a college application?
While all colleges are different, of course, with some valuing certain qualities or skills more or less than other schools, all colleges generally look for smart, studious, ambitious, and passionate students.
Therefore, your college application should emphasize your best, most impressive qualities. For example, if you play the violin and want to study music in college, you'll want to touch on this interest you have in different areas of your application.
A good college application will also showcase your sincere interest in the school. You wouldn't be applying to a college unless you had a reason to want to go there, right? Make sure to explain (especially if you need to write a "Why This College" essay ) exactly how you became interested in the school and why you think it's a good fit for you and your goals.
You don't need to be the next Marie Curie or Stephen Hawking, but you should be open to new opportunities and willing to challenge yourself.
Overall, the basic point of a college application is to make you stand out from other applicants in a positive, memorable, and unique way.
This fact is especially important in light of how many first-year applications colleges receive each year. According to the 2019 report by the National Association for College Admission Counseling (NACAC) , the number of first-year applications received by US colleges increased by 6% from fall 2017 to fall 2018.
The report found that "the average number of applications for each admission office staff member (excluding administrative staff) for the Fall 2017 admission cycle was 1,035 for public institutions and 461 for private institutions."
These trends indicate that your application will definitely need to leave a lasting impression on the admissions committee if you hope to get into that school.
The degree by which you must stand out from other applicants will depend on how selective a particular school is. In general, the more selective a college is, the more impressive and unique your application will have to be.
Finally, what looks good on an application will vary depending on the college and what the college values. For instance, at colleges that don't place a big emphasis on standardized tests, a high SAT score likely won't be much of a factor in admissions.
This is just a general overview of what colleges look for in applicants. So what looks really good on a college application? Up next, we look at the specific qualities you should strive to include on your application so you can raise your chances of getting accepted.

What Looks Good on a College Application? 7 Key Elements
In addition to key personality traits, such as ambition, passion, genuine interest, and academic curiosity, what looks really good on a college application?
In general, a great application will have most or all of the following elements:
- A high GPA (relative to what admitted students have) and a rigorous curriculum
- Strong test scores (relative to what admitted students have)
- A specific, honest, and well-written personal statement and/or essays
- A unique extracurricular interest or passion (a "spike," as we like to call it)
- Volunteering experience with measurable impact
- Compelling letters of recommendation written on your behalf
- Work experience, particularly jobs related to your academic or professional interests
It's OK if you don't have every single quality listed above, but if you do, your chances of getting accepted to the college of your dreams will go way up!
Now then, let's take a look at each of these qualities in more detail.
#1: Excellent Grades in Challenging Courses
The first important part of the college application is the transcript, which consists of your GPA and the names and types of classes you've taken in high school.
Most people believe a high GPA (the definition of which can vary at different colleges) will make an application stronger. And this is true!
According to NACAC, 75% of colleges ranked grades in high school classes considerably important. In fact, this factor was ranked the most important of any in the report.
What's truly important, though, isn't that you simply have a high GPA overall but rather that you have a GPA that's higher than the average GPA of admitted students at the college you're applying to.
To find a college's average GPA, search "[School Name] PrepScholar admission requirements" on Google and then click our database link to that school. This page will show you what the school's average GPA is, in addition to other admission requirements.
For example, if you want to apply to Notre Dame, you would search for "Notre Dame PrepScholar admission requirements" and click the link to our Notre Dame admission reqs page , which looks like this:
As you can see, Notre Dame's average (weighted) GPA for admitted applicants is 4.06. As a result, if you're applying here, you'll want to have a GPA of at least 4.06, preferably higher so you will be an above-average applicant.
It's not just about getting a high GPA, though; you must also take a range of challenging courses throughout high school if you really wish to impress an admissions committee. According to the NACAC report, 73 percent of colleges rated grades in college prep courses as considerably important. This means you'll want to take not just basic-level classes but also some AP, honors, and/or IB courses, particularly in subjects you are good at and might want to continue to study in college or major in.
The 2019 NACAC report found that a whopping 84% of colleges ranked an applicant's rigor of curriculum moderately or considerably important.
Think about it: though a perfect 4.0 might look great at an initial glance, if you got this high GPA by only taking the easiest classes available and didn't challenge yourself with higher-level coursework, your transcripts aren't likely to impress college admissions officers that much.
Even if you started high school with lower grades, an upward grade trend is a great point to emphasize on your application. This suggests that you're capable of bouncing back from any difficulties you might face and are willing to put in the work necessary for excelling in college.

#2: High Test Scores
Test scores, mainly SAT/ACT scores, are another key part of college applications (unless, of course, you're applying to colleges that don't require test scores ).
On the NACAC report, 83% of colleges believe admission test scores are at least moderately important. This is why it's vital that you try to get as high an SAT/ACT score as you can, ideally one in at least the 75th percentile for your colleges.
The 75th percentile means that 75% of admitted students at a particular school achieved this score or lower. Reaching (or surpassing) this threshold means that you're scoring higher than most other admitted applicants are—and well above that college's average score.
To find the middle 50% (that is, the 25th and 75th percentile SAT/ACT scores) for a school, search on Google for "[School Name] PrepScholar admission requirements." Click the link to our page for the school to see its requirements, including its average SAT/ACT scores.
For example, say you're planning to apply to NYU. Here's what the SAT scores section on NYU's PrepScholar admission reqs page looks like:
Here, we can see the average SAT score for NYU is 1440—that's pretty high, in the 95th percentile nationally !
To really stand out as an applicant, though, you'll want to aim for at least the 75th percentile. For NYU, that's 1510, which corresponds to the 98th percentile, or the top 1% of test takers.
Since you're likely applying to more than just one school, you'll need to set an SAT / ACT goal score , that is, a score high enough to get you into all the colleges you're applying to.
To set a goal score, start by making a chart of all the schools you're applying to. You can make your own chart or download a blank template .
Below is a sample SAT goal score chart:
|
|
|
|
| Marquette University | ||
| University of Wisconsin—Madison | ||
| Michigan State University | ||
| University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign |
Next, look up the 25th and 75th percentile SAT scores for each of the schools you're applying to using our PrepScholar admission requirements pages. (Follow the steps above for NYU to learn how to do this.)
Once you've got these scores, write them in your chart as so:
|
|
|
|
| 1150 | 1320 | |
| 1300 | 1480 | |
| 1120 | 1310 | |
| 1220 | 1480 |
Now, look at all the 75th percentile scores in your chart. The highest score will be your goal score, as this is the one most likely to get you into all the schools you're applying to.
With our example chart, the highest score is 1480, or the 75th percentile score for the University of Illinois and UW Wisconsin. By getting a 1480 or higher, you'll be getting an impressive score not just for these two schools, school but also for Marquette and MSU, thereby raising your chances of getting into all colleges you're applying to.

#3: Sincere, Specific, and Well-Written Essays
The personal statement is an important part of your college application as it's one of the only areas where you can really showcase your personality.
According to the 2019 NACAC survey, 56% of schools consider application essays moderately or considerably important. While some colleges don't require essays , those that do usually place at least moderate importance on them.
So how can you ensure your essay will impress the admissions committee? Generally, colleges are looking for three main qualities in a personal essay:
- Honesty: What you write about should have actually happened to you and should be how you actually feel. Exaggerating details and outright lying are big no-nos here!
- Specificity: Using concrete details to effectively convey your thoughts, views, and experiences will make your essay a lot more memorable, personable, and—most importantly—unique.
- Eloquence: Don't expect to get accepted anywhere if your essay is poorly written and full of grammar and spelling errors. A great personal statement has a sensible organization, tells a compelling story, and is completely free of technical errors.
Below are some steps you can take to guarantee that your essay will have all three qualities.
Step 1: Brainstorm Significant Moments From Your Life
What you write about for your college essay will vary depending on the prompt(s) you're given from your school or the prompt you choose (for example, the Common App and Coalition App allow you to choose from among several prompts for your essay).
In general, you'll want to pick a topic that meets the following criteria:
- It really happened and was significant to you: If you're writing about a specific incident, it should be something that actually happened and that had a large impact on how you define yourself, your goals, and/or your interests.
- It's specific and interesting: Don't write about a broad, universal topic that can apply to tons of other applicants as well. Instead, focus on an event, issue, person, or struggle that's unique to you and your life.
- It reveals something important about you: The essay is meant to highlight something you think the admissions committee should know about you, such as a personality trait you have, how you overcame some sort of challenge, or how you became interested in a field of study.
- It has a positive lean: While you don't need to pick a topic that's overly light or cheery, it should still have an ultimately positive lean that reveals something good about you rather than something bad, controversial, or immoral.
Step 2: Write Your Essay
The next step is to actually begin writing your essay. Don't worry too much about grammar and flow at this point; just get down your ideas and start deciding which details and examples might work well in your essay.
As you write, remember to channel your inner voice. This essay should sound like the real you, not an imitation of what you think colleges want to hear. So if you're the sarcastic type, you might want to include a joke or two, for instance. Don't forget that the essay is a way for the admissions committee to learn more about you, so don't shy away from your true self!
On that same note, it's OK to get creative here. The essay isn't an academic essay you'd write for English class—it's a story. Feel free to inject your writing with various literary techniques , such as a non-chronological organization, realistic dialogue, and memorable imagery.
Lastly, make sure you're sufficiently answering the prompt and are abiding by all technical requirements (such as length). You can check a college's essay requirements by referring to its application requirements page or by reading the instructions on the Common App, Coalition App, or Universal College App websites (if submitting your application through one of these platforms).
An essay that's too long might get cut off when you submit it electronically, so be sure it adheres to all the requirements.
Step 3: Edit and Proofread Several Times
Once you have a rough draft of your college essay, it's time to polish it up for submission.
The best way to edit is to put your essay away for a few days. This will give you some distance away from your writing, allowing you to look back at your essay later with a fresher perspective.
As you reread your essay, mark any areas in it that are unclear, awkward, or irrelevant to the main point you're trying to make with it. You should also correct any obvious typos or errors, such as mistakes in grammar, spelling, or punctuation.
Once you've done this process a few times, give your essay to someone to read. Ideally, this will be a person you trust, such as a parent, teacher, counselor, or tutor. Have the person you choose offer clear feedback on your essay and check that you've met all requirements. Edit your essay as needed in accordance with the comments you get.
After you've finished all of this, you should now have a perfect college essay to submit with your application!

#4: A Spike in Your Extracurriculars
Almost every college will want to know what kinds of extracurricular activities you do or have done in your spare time.
Indeed, 49% of colleges surveyed regard students' extracurricular activities moderately or considerably important. Ask yourself: what are your interests outside of school and how do you engage in them?
The trick here is to provide not a list of all the random activities you've done but rather a detailed overview of one to two of your most passionate interests and any big achievements you've made in them.
In other words, you need to figure out what your "spike" is, a concept which PrepScholar co-founder and Harvard alum Allen Cheng describes in his expert guide on how to get into the Ivy League .
To put it simply, a spike is deep accomplishment in and knowledge of a particular field.
As an example, say you plan to major in biology. You'll stand out as an applicant if you have tons of biology- or science-related experiences under your belt. Maybe you're part of your school's biology club, or maybe you volunteered at a local research lab, which taught you the basics of handling lab equipment.
In addition to having a variety of experiences and sufficient background knowledge in the field, you want to highlight any relevant major accomplishments you have. For instance, maybe you won a science fair your sophomore year of high school; most recently, you submitted an award-winning invention idea to a national science contest. All of these accomplishments illustrate your deep accomplishment and knowledge in the field of science!
As you can see, this concept of the spike is the opposite of being well rounded, which most students assume they need to be (read the next section to learn more about this myth).
If you're not sure what your spike is just yet, take some time to try out new activities and explore any interests you have, both in and outside of school. Over time you should start to get a feel for what you're passionate about and what you can see yourself committing to in the future.

#5: Compelling Letters of Recommendation
Most colleges require at least one letter of recommendation from either your high school counselor or a high school teacher (or both).
The 2019 NACAC survey indicates that 54% of colleges consider teacher recommendations at least moderately important, while a higher 55% consider counselor recommendations the same. Therefore, we can say it's pretty important to secure great recommendation letters for your application.
If you're asking for a letter from a teacher , make sure to choose someone whose class you got a high grade in (ideally an A) and who is familiar with your abilities, ambitions, and interests. Typically, you'll need to submit at least one letter from a teacher who taught a core class (so math, English, science, or social studies/history).
It's a good idea to also get a letter from a teacher who works in the field you plan to major in. So if you got an A in AP English and plan to major in English, asking that teacher for a recommendation letter would give a great boost to your application.
While you don't have to be best buddies with the teacher you ask, they should definitely know you well , beyond the classroom, so they can effectively explain to admissions committees what makes you special, that is, what makes you worth admitting.
For example, if you did research with a particular teacher, are part of a club this teacher coaches or leads, or helped out this teacher with a project, this would be a good person to ask to write a letter for you.
Once you've secured a recommendation letter writer, be sure to provide them with any materials or information they might need to help them craft a compelling letter .
#6: Volunteering Experience With Measurable Impact
Colleges love it when an applicant has not simply volunteered but has also made a measurable impact with their volunteering efforts. What does this mean exactly? If you have volunteered somewhere or for an organization, your assistance should have resulted in a noticeable, positive change to the group, community, or area you were aiming to help.
For instance, say you volunteered at a local library. Maybe the library was struggling to get funds to continue operating, and you came up with the idea to hold a 24-hour reading marathon in order to raise money. The fundraiser ended up making more than $5,000, a figure that would be a concrete indicator of the positive impact your service had on the library. With your college application, then, you could specifically mention how your initiative allowed the library to remain open.
Note that you don't need to have assumed a leadership role in order to have made a positive impact through your service. That said, college admissions committees are often very big fans of students who show evidence of their budding leadership skills.

#7: (Relevant) Work Experience
Although you're certainly not required to work a part-time job in high school, having some work experience on your college applications, especially any jobs that are related to what you want to study or do professionally, will help you stand out in a positive way.
Even if your job isn't connected to a long-term academic or career goal you have, any (part-time) work experience you have will be great to put down on your application because it emphasizes your sense of responsibility, maturity, and willingness to work for your goals, key qualities that are usually considered important for success in college.
Also, if you have any room on the application to elaborate on your job, I suggest explaining why you initially took the job and what values or skills it's taught you, such as the importance of responsibility or how to work with certain equipment that you'll likely use again in the future.
4 Myths About What Looks Good on a College Application
What looks really good on a college application? Many students think they know, but the truth is that there are a lot of myths out there about what you should include on your application.
Below, we introduce to you the top four myths about what looks good on college applications.
Myth 1: Being Well Rounded Is Critical for Success
One of the most pervasive myths out there about what looks good on a college application is the idea of being well rounded.
Many students assume they'll need to have tons of extracurricular activities on their applications; this, they believe, will emphasize their array of interests as well as their knowledge of a variety of fields. But all this really tells admissions committees is that you're stretching yourself too thin and (most likely) lack focus on a specific endeavor in your life.
What colleges actually want to see is a spike, that is, a single passion. This allows colleges to get a clearer feel for who you are, what you're interested in, and what your goals are. Having a spike lets you stand out in a truly meaningful way, whereas being well rounded will make you forgettable and seem too similar to other applicants.
Spikes are especially important at highly selective colleges and universities , such as Harvard, Yale, and other Ivy League-level schools . You can read more about how to develop a spike in our guide to getting into the Ivy League . Alternatively, if you're interested in pursuing education at a liberal arts school , check out our article on how to figure out what to go to college for .

Myth 2: Essays Aren't That Important
After Time published a 2014 article on why college application essays don't actually matter all that much , students began to fear that all their hard work on their statements wouldn't mean much in the end, if at all.
But while some colleges don't require personal essays , most colleges do require at least one or two essays—and will place a decent amount of emphasis on it, especially if it is being used as a deciding factor between two otherwise equally qualified applicants.
Even though you should approach the essay seriously, it's still generally rare for an exceptionally well-written essay to make up for tons of low grades and poor test scores. On the flip side, if you have a great application but a badly written essay, that essay alone could get you rejected!
Therefore, make sure that you are following all the steps listed above so you can craft the perfect statement for your application.
Myth 3: An A in an Easy Class Is Better Than a B in a Hard Class
Many students believe it's better to stick to the classes you know you'll get As in, but this piece of advice is misguided when it comes to college applications.
In general, colleges prefer students who challenge themselves by taking an array of difficult classes, such as AP and honors classes. And you don't have to get perfect grades in them. If you get a B in a tough AP class, for example, this will emphasize to the admissions committee that you are willing to take on new challenges and test your limits, traits that are necessary for succeeding in and after college.
On the other hand, getting As in all easy classes, though not totally unimpressive, is not nearly as interesting to colleges, as it suggests you're unwilling to push yourself and further hone your higher-level critical thinking skills.
All of this being said, try to avoid getting very low grades in any classes you take (regular or honors/AP). C and D grades obviously won't look great to an admissions committee, even if you got these grades while challenging yourself in AP classes.
If you can't get at least a B or B+ in a difficult class, it'll probably be better for you to drop it and switch to either the regular version of that class or an entirely different class altogether.
Myth 4: Only Perfect Applicants Get Admitted
Many students assume that if they have one little flaw in their application, such as a below-average test score or slightly low grade in a class, their chances of getting admitted to college will be slim to none.
This just isn't true.
Yes, a very low test score or a very poor transcript may cause you to get rejected from a college, but many colleges use a holistic admission process, meaning they look at and consider each individual applicant as a whole. So even if your application has a not-so-stellar component on it, this doesn't necessarily mean you'll be a reject.
In fact, at particularly selective colleges, such as the Ivy League , you'll often hear of cases in which ostensibly "perfect" applicants got rejected. This is most likely because they didn't have a spike in their applications (i.e., something that made them stand out).
Overall, just try your best to produce the best application you can, and then hope for a good result!

Takeaways: What Looks Good on a College Application
Applying to college is tough, and knowing what to put on your applications to make yourself stand out is even tougher. What looks really good on a college application?
Generally speaking, colleges want to see your passion, intellectual curiosity, willingness to challenge yourself, and academic accomplishments.
More specifically, though, colleges typically prefer applicants who have most or all of the following characteristics:
- Good grades and a challenging course load
- Strong test scores
- Honest, specific, and eloquent essays
- A spike in your extracurricular activities
- Compelling letters of recommendation
- Volunteer experience with clear impact on the groups or places you've helped
- Any relevant or impactful work experience
Finally, as you apply to college and try to think of good things to put on a college application, make sure you're aware of the following truths about the application process:
- It's better to have a spike than to be well rounded
- Essays are important!
- A B in a hard course is more impressive than an A in an easy course
- You can still get into your dream school even if your application isn't perfect
What's Next?
A great college application will get you admitted. Use our college acceptance calculator to get an estimated percentage of your chance of getting into your dream school, based on your SAT or ACT score and GPA.
One thing a great college application can have is a high SAT or ACT score. Get expert tips in our guides on how to get a perfect 36 on the ACT and how to get a perfect 1600 on the SAT .
Need help figuring out which colleges to apply to? Our guide teaches you how to narrow down your college choices so that you're applying to the best schools for you.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Hannah received her MA in Japanese Studies from the University of Michigan and holds a bachelor's degree from the University of Southern California. From 2013 to 2015, she taught English in Japan via the JET Program. She is passionate about education, writing, and travel.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Things to Include in Your College Application Essay
Deciding which colleges to apply to is difficult enough, but you add to that the stress of writing a personal essay for each of your applications. Your personal essay is supposed to give college admissions teams a snapshot of who you are as a person and who you hope to become but you don’t have to spill your guts or transcribe your whole life story. To increase your chances of getting accepted, first learn just how important your essay is, and then take the time to learn the Dos and Don’ts of college application essays.
How Important is Your Application Essay?
Every year, colleges and universities receive hundreds or even thousands of applications. Many of those applications are virtually identical in terms of GPA, class load, and test scores – so how do you make yourself stand out in a crowd? The college application essay is designed to give you a chance to speak directly to the admissions committee, to tell them who you are and why you want to go to their school. But is your application essay more important than the rest of your application or is it just one factor that admissions committees weigh evenly with your GPA and test scores?
According to an article published on Time.com, college application essays aren’t as important as they are cracked up to be. In fact, Stanford sociologist Mitchell Stevens worked alongside admissions officers at numerous top-tier liberal arts schools for 18 months and he discovered that in cases where students met the minimum requirements for GPA and test scores, the personal essay was rarely used as a deciding factor for admission. According to Stevens, there are too many other factors to consider such as previous offers of admission from the student’s zip code, special endorsements from a faculty member or alumnus, the likelihood of the student accepting an offer of admission, and whether the admissions office owes a favor to the student’s guidance counselor.
This video explains the importance of your college admissions essay.
On the other side of the issue, a report sponsored by the National Association for College Admission Counseling suggests that while grades, test scores, and curriculum are the top deciding factors for admission, a majority of universities and colleges believe that the essay is of moderate to considerable importance. To put it another way, in a world where everything else is equal between the applicants, a good essay can make a difference. There are, however, different ways to write college essays that can increase your chance of an admission offer and things you can do that may hurt your chances.
What Should You Include in Your Essay?
Basically, what colleges are looking for in an application essay is evidence that the applicant has strong writing skills and the ability to support ideas with logical arguments. Schools also want to get a glimpse of the student’s personality and what makes him or her different. Of course, some colleges weigh the essay more heavily than others so it never hurts to talk to your admissions counselor about the role the college essay plays in admission to a particular school. Here are some things you should definitely include in your college essay :
- Why you want to attend this school – admissions committees want to know why you are interested in their program and what makes you a good fit.
- Specific details about what interests you about the program and why you are a good fit.
- Information about your past accomplishments that have led you to choose this program.
- Your plan for the future – how you plan to succeed in the program and what you see in your future after completing the program.
- Supplemental stories and anecdotes to help drive your point home and to help you stand out.
This video shows you how to write an effective college admissions essay.
In addition to making sure that all of these things are included, you should also be aware of HOW you write your essay. Admissions committees want essays to be concise – you want to make your point in about 700 words or less. You should also make sure that your essay is coherent – that your ideas flow and your arguments make sense. Don’t be afraid to show off your writing skills, but don’t do anything that takes away from your core message.
What Should You Leave Out of Your Essay?
When preparing to write their college application essays, many students obsess about what they SHOULD do, forgetting to think at all about the things they shouldn’t do. Even if your essay is a work of art – the best thing you’ve ever written – it won’t matter if you don’t address the prompt or if your essay doesn’t paint a picture of who you are as a person. Here are some common mistakes students make with their essays that you should avoid:
- If a school offers multiple prompt options for the essay, don’t choose too quickly – think about how you would answer each prompt and choose the strongest option.
- Be sure to address the question, especially if it is a two-part question – admission essays are just as much about showing who you are as they are about proving your writing skills.
- Don’t be too general – college admissions committees want to see specifics. Don’t be afraid to go into detail to make your point!
- Don’t ignore guidelines – if there is a minimum or maximum word count, stick to it! Longer is not always better when it comes to college essays either, so don’t feel like you have to hit the maximum word limit
- Keep an eye on your tone throughout the essay – this will help to shape the committee’s impression of you. You don’t want to come off as lazy, prejudiced, or cynical.
- Don’t forget to proofread! Your computer’s spell check option may not catch every little mistake you make so you should plan to read back through your essay a few times on your own and have as many other people go over it as you can.
Other College Essay Writing Tips
Once you have written your college application essay, your job isn’t done – you need to keep working on it to improve it until you can improve it no further. It is a great idea to have someone else read your essay to provide feedback. In fact, the more people who read your essay, the better. Ask your readers whether the essay provides an accurate depiction of who you are and ask whether it is clear, concise, and easy to read. If you were given a prompt by a certain school, make sure that your essay actually addresses the prompt. Even if you don’t have anyone else who can read your essay, you can review it yourself – just take a day or two off after writing it before you read it back so you can view it with fresh eyes.
Writing an essay is something students learn to do in school from a fairly young age, but it is a skill that must be perfected over a number of years. The college application essay is the true test of those skills and of your ability to present an accurate picture of who you are. There is some controversy regarding the importance of the college essay but, for now, it is a mandatory inclusion for most applications so you should take the time to learn what you should and should not include in your essay for the best results.
Questions? Contact us on Facebook. @communitycollegereview
Get Your Degree!
Find schools and get information on the program that’s right for you.
Powered by Campus Explorer
More Articles

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. That is to say. Usage: "That is" and "that is to say" can be used to add further detail to your explanation, or to be more precise. Example: "Whales are mammals. That is to say, they must breathe air.". 5. To that end. Usage: Use "to that end" or "to this end" in a similar way to "in order to" or "so".
This college essay tip is by Abigail McFee, Admissions Counselor for Tufts University and Tufts '17 graduate. 2. Write like a journalist. "Don't bury the lede!" The first few sentences must capture the reader's attention, provide a gist of the story, and give a sense of where the essay is heading.
Sharing is caring! How to Write a Great Essay in English! This lesson provides 100+ useful words, transition words and expressions used in writing an essay. Let's take a look! The secret to a successful essay doesn't just lie in the clever things you talk about and the way you structure your points.
Use your essays to empower your chances of acceptance, merit money, and scholarships.". This college essay tip is by Dr. Rebecca Joseph, professor at California State University and founder of All College Application Essays, develops tools for making the college essay process faster and easier. 15. Get personal.
Step 0: choose a structure. By "structure," we mean what you'll use to organize your essay's content in a way that helps your reader understand clearly and easily. We'll talk through two structural options below: "montage" and "narrative.". Some quick definitions:
Smith College. Each year, Smith asks its applicants to answer a different prompt with a 200-word essay. Here are six of these short essays answering the 2014 prompt: "Tell us about the best gift you've ever given or received." 6 "best gift" essays from the class of 2018. You really can find everything at the library.
Come up with a thesis. Create an essay outline. Write the introduction. Write the main body, organized into paragraphs. Write the conclusion. Evaluate the overall organization. Revise the content of each paragraph. Proofread your essay or use a Grammar Checker for language errors. Use a plagiarism checker.
Starting your essay in a powerful way with a clear thesis statement can often help you along in the writing process. If your task is to tell a good story, a bold beginning can be a natural prelude to getting there, serving as a roadmap, engaging the reader from the start, and presenting the purpose of your writing. Focus on Deeper Themes
Tips for a Stellar College Application Essay. 1. Write about something that's important to you. It could be an experience, a person, a book—anything that has had an impact on your life. 2. Don't just recount—reflect! Anyone can write about how they won the big game or the summer they spent in Rome.
Table of contents. Step 1: Hook your reader. Step 2: Give background information. Step 3: Present your thesis statement. Step 4: Map your essay's structure. Step 5: Check and revise. More examples of essay introductions. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about the essay introduction.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Here's a list of essay topics and ideas that worked for my one-on-one students: Essay Topic: My Allergies Inspired Me. After nearly dying from anaphylactic shock at five years old, I began a journey healing my anxiety and understanding the PTSD around my allergies. This created a passion for medicine and immunology, and now I want to become ...
Step 2: Have a clear structure. Think about this while you're planning: your essay is like an argument or a speech. It needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question. Start with the basics! It's best to choose a few major points which will become your main paragraphs.
Awesome College Essay Topics + Sample Essays. The truth is that a "good" college essay topic varies by individual, as it really depends on your life experiences. That being said, there are some topics that should work well for most people, and they are: 1. A unique extracurricular activity or passion.
Applying for scholarships means starting early and writing strong essays. Key Takeaways. Start writing essays early to allow time for research and editing. Grab the reader's attention immediately ...
In this section, we give you a list of 53 examples of college essay topics. Use these as jumping-off points to help you get started on your college essay and to ensure that you're on track to coming up with a relevant and effective topic. All college application essay topics below are categorized by essay prompt type.
Tips for Writing a Personal Statement for College. 1. Approach this as a creative writing assignment. Personal statements are difficult for many students because they've never had to do this type of writing. High schoolers are used to writing academic reports or analytical papers, but not creative storytelling pieces.
How to start a college essayTABLE OF CONTENTS. (click to scroll) How You Probably Shouldn't Start Your College Essay. 9 Ways to Start a College Essay. The Full Hemingway. The Mini Hemingway. The Twist. The Philosophical Question. The Confession.
Strong test scores (relative to what admitted students have) A specific, honest, and well-written personal statement and/or essays. A unique extracurricular interest or passion (a "spike," as we like to call it) Volunteering experience with measurable impact. Compelling letters of recommendation written on your behalf.
To put it another way, in a world where everything else is equal between the applicants, a good essay can make a difference. There are, however, different ways to write college essays that can increase your chance of an admission offer and things you can do that may hurt your chances. ... 5 Things to Include in the Personal Essay." College View.