The 10 Most Important Lab Safety Rules
ThoughtCo / Nusha Ashjaee
- Chemical Laws
- Periodic Table
- Projects & Experiments
- Scientific Method
- Biochemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Medical Chemistry
- Chemistry In Everyday Life
- Famous Chemists
- Activities for Kids
- Abbreviations & Acronyms
- Weather & Climate
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
The science lab is an inherently dangerous place, with fire hazards, dangerous chemicals, and risky procedures. No one wants to have an accident in the lab, so it's imperative to follow lab safety rules.
Key rules include following all instructions carefully, knowing the location and proper use of safety equipment, and dressing appropriately for lab work. These precautions help ensure a safer environment and minimize the risk of accidents. Here are the most important lab safety rules and why you must follow them.

The Most Important Lab Safety Rule
Follow the instructions. Whether it's listening to your instructor or lab supervisor or following a procedure in a book, it's critical to listen, pay attention, and be familiar with all the steps, from start to finish, before you begin. If you are unclear about any point or have questions, get them answered before starting, even if it's a question about a step later on in the protocol. Know how to use all of the lab equipment before you begin.
Why is this the most important rule? If you don't follow it:
- You endanger yourself and others in the lab.
- You could easily ruin your experiment.
- You put the lab at risk of an accident, which could damage equipment as well as harm people.
- You could get suspended (if you're a student) or fired (if you're a researcher).
Know the Location of Safety Equipment
In the event something goes wrong, it's important to know the location of the safety equipment and how to use it. It's a good idea to periodically check equipment to make sure it is in working order. For example, does water actually come out of the safety shower? Does the water in the eye wash look clean?
Not sure where safety equipment is located? Review lab safety signs and look for them before starting an experiment.
Dress for the Lab
Dress for the lab. This is a safety rule because your clothing is one of your best forms of protection against an accident. For any science lab, wear covered shoes and long pants, and keep your hair up so it can't fall into your experiment or a flame.
Make sure you wear protective gear , as needed. Basics include a lab coat and safety goggles. You may also need gloves, hearing protection, and other items, depending on the nature of the experiment.
Don't Eat or Drink in the Laboratory
Save your snacking for the office, not the lab. Don't eat or drink in the science laboratory. Don't store your food or beverages in the same refrigerator that contains experiments, chemicals, or cultures.
- There is too much risk of contaminating your food. You could touch it with a hand that is coated with chemicals or pathogens or set it down on a lab bench that has residue from past experiments.
- Having drinks in the lab risks your experiment, too. You could spill a drink on your research or lab notebook.
- Eating and drinking in the lab is a form of distraction. If you are eating, you aren't concentrating on your work.
- If you're used to drinking liquids in the lab, you might accidentally reach for and drink the wrong liquid. This is especially true if you did not label your glassware or used lab glassware as dishes.
Don't Taste or Sniff Chemicals
Not only should you not bring in food or drinks, but you shouldn't taste or smell chemicals or biological cultures already in the lab. Tasting or smelling some chemicals can be dangerous or even deadly. The best way to know what's in a container is to label it, so get in the habit of making a label for glassware before adding the chemical.
Don't Play Mad Scientist in the Laboratory
Another important safety rule is to act responsibly in the lab; don't play Mad Scientist, randomly mixing chemicals to see what happens. The result could be an explosion, fire, or release of toxic gases .
Similarly, the laboratory is not the place for horseplay. You could break glassware, annoy others, and potentially cause an accident.
Dispose of Lab Waste Properly
Matthias Tunger/Getty Images
Another important laboratory safety rule is to know what to do with your experiment when it's over. Before you start an experiment, you should know what to do at the end. Don't leave your mess for the next person to clean up.
Here are some questions to consider:
- Are the chemicals safe to dump down the drain? If not, what do you do with them?
- If you have biological cultures, is it safe to clean up with soap and water or do you need an autoclave to kill dangerous organisms?
- Do you have broken glass or needles? Know the protocol for disposing of chemical sharps.
Know What to Do With Lab Accidents
Getty Images/Oliver Sun Kim
Accidents happen, but you can do your best to prevent them and have a plan to follow when they occur. Most laboratories have a plan to follow in the event of an accident.
One particularly important safety rule is to tell a supervisor if and when an accident occurs . Don't lie about it or try to cover it up. If you get cut, exposed to a chemical, or bitten by a lab animal, or if you spill something, there could be consequences, and the danger isn't necessarily only to you. If you don't get the proper care, sometimes you could expose others to a toxin or pathogen. Also, if you don't admit to an accident, you could get your lab in a lot of trouble.
Leave Experiments at the Lab
Getty Images/G Robert Bishop
It's important, for your safety and the safety of others, to leave your experiment at the lab. Don't take it home with you. You could cause a spill, lose a specimen, or have an accident. This is how science fiction movies start. In real life, you can hurt someone, cause a fire, or lose your lab privileges.
While you should leave lab experiments at the lab, if you want to do science at home, there are many safe science experiments you can try.
Don't Experiment on Yourself
The premise of many a science fiction movie starts with a scientist conducting an experiment on him or herself. However, you won't gain superpowers or discover the secret to eternal youth. More than likely, whatever you accomplish will be at great personal risk.
Science means using the scientific method . You need data on multiple subjects to draw conclusions, but using yourself as a subject and self-experimenting is dangerous, not to mention bad science.
- Have You Touched Liquid Mercury?
- Chemistry Laboratory Safety Rules
- Chemistry Pick Up Lines to Try on Your Crush
- Chemistry Glassware Types, Names and Uses
- Biology Lab Safety Rules
- Examples of Independent and Dependent Variables
- The Most Common Injuries in a Chemistry Lab
- Science Projects for Every Subject
- Pre-Lab Prep for Chemistry Lab
- Setting Up a Home Chemistry Lab
- Printable Lab Safety Sign Quiz
- Thames & Kosmos Chem 3000 Chemistry Kit Review
- 10 Things You Need To Know About Chemistry
- Mad Scientist Party Theme
- Top Tips for Observing Mitosis Lab
- How to Format a Biology Lab Report
- Lab Manager Academy
- Subscribe Today!
- Safety Culture & Compliance

Lab Safety Rules and Guidelines
A comprehensive round-up of common lab safety rules as well as frquently asked questions about lab safety to help you develop or update a set of policies for your own lab.

Jonathan Klane, M.S.Ed., CIH, CSP, CHMM, CIT, is senior safety editor for Lab Manager . His EHS and risk career spans more than three decades in various roles as a...
Rules, rules, rules. Labs need rules to operate well. Below, we focus on the rules specific to safety, hazards, and risks in labs. There are so many that you need to sort them by hazard types (like chemical hygiene, laser safety, or dress codes, for example).
Guidelines are also in plentiful supply when it comes to lab safety. But what’s the difference between a rule and a guideline? A rule is a mandatory must and a guideline is a voluntary should. Rules are often based on external regulatory requirements or internal policies. Guidelines are often in addition to the requirements and promote best practices . When it comes to lab risks, survival is usually based on those best practices.
This comprehensive list can be used as an informative resource for your lab teams. So, review these lab safety rules and guidelines and share them with your lab folks. They just might save a life.
General lab safety rules
The following are rules that relate to almost every laboratory and should be included in most safety policies. They cover what you should know in the event of an emergency, proper signage , lab safety equipment, safely using laboratory equipment, and basic common-sense rules.
- Be sure to read all fire alarm and lab safety symbols and signs and follow the instructions in the event of an accident or emergency.
- Ensure you are fully aware of your facility's/building's evacuation procedures.
- Make sure you know where your lab's safety equipment—including first aid kit(s), fire extinguishers, eye wash stations, and safety showers—is located and how to properly use it.
- Know emergency phone numbers to use to call for help in case of an emergency.
- Lab areas containing carcinogens, radioisotopes, biohazards, and lasers should be properly marked with the appropriate warning signs.
- Open flames should never be used in the laboratory unless you have permission from a qualified supervisor.
- Make sure you are aware of where your lab's exits and fire alarms are located.
- An area of 36" diameter must be kept clear at all times around all fire sprinkler heads.
- If there is a fire drill, be sure to turn off all electrical equipment and close all containers.
- Always work in properly-ventilated areas.
- Do not chew gum, drink, eat, or apply lip balm or cosmetics while working in the lab.
- Laboratory glassware should never be used as food or beverage containers.
- Each time you use glassware, be sure to check it for chips and cracks. Notify your lab supervisor of any damaged glassware so it can be properly disposed of or recycled.
- Never use lab equipment that you are not approved or trained by your supervisor to operate.
- If an instrument or piece of equipment fails during use, or isn't operating properly, report the issue to a technician right away. Never try to repair an equipment problem on your own.
- If you are the last person to leave the lab, make sure to lock all the doors and turn off all ignition sources.
- Do not work alone in the lab.
- Never leave an ongoing experiment unattended.
- Never lift any glassware, solutions, or other types of apparatus above eye level.
- Never purposefully smell or taste chemicals.
- Do not pipette by mouth.
- Make sure you always follow the proper lab safety procedures for disposing of lab waste.
- Report all injuries, accidents, and broken equipment or glass right away, even if the incident seems small or unimportant.
- If you have been injured, yell out immediately and as loud as you can to ensure you get help.
- In the event of a chemical splashing into your eye(s) or on your skin, immediately flush the affected area(s) with running water for at least 20 minutes.
- If you notice any unsafe lab conditions , let your supervisor know as soon as possible.
Housekeeping safety rules

Laboratory housekeeping rules also apply to most facilities and deal with the basic upkeep, tidiness, and maintenance of a safe laboratory.
- Always keep your work area(s) tidy and clean.
- Make sure that all lab safety equipment , like eyewash stations, emergency showers, fire extinguishers, and exits are always unobstructed and accessible.
- Only materials you require for your work should be kept in your work area. Everything else should be stored safely out of the way.
- Only lightweight items should be stored on top of cabinets; heavier items should always be kept at waist height to avoid bending and lifting.
- Solids should always be kept out of the laboratory sink.
- Any equipment that requires air flow or ventilation to prevent overheating should always be kept clear.
Dress code safety rules

As you’d expect, laboratory dress codes set a clear policy for the clothing employees should avoid wearing to prevent accidents or injuries in the lab. For example, skirts and shorts might be nice for enjoying the warm weather outside, but quickly become a liability in the lab where skin can be exposed to heat or dangerous chemicals.

- Always tie back hair that is chin-length or longer and as needed.
- Make sure that loose clothing or dangling jewelry is removed, or avoid wearing it in the first place.
- Never wear sandals or other open-toed shoes in the lab. Footwear must always cover the foot completely.
- Never wear shorts or skirts in the lab.
- When working with Bunsen burners, lighted splints, matches, etc., acrylic nails are not allowed.
Personal protection safety rules

Unlike laboratory dress code policies, rules for personal protection cover what employees must be wearing in the lab to protect themselves from various lab hazards, as well as basic hygiene rules to follow to avoid any sort of contamination.
- When working with equipment, hazardous materials, glassware, heat, and/or chemicals, always wear safety glasses or goggles, and additionally use a face shield as needed.
- When handling any toxic or hazardous agent, always wear the appropriate gloves that resist the specific chemicals you’re working with.
- When performing laboratory experiments, you must always wear a lab coat.
- Before leaving the lab or eating, always wash your hands.
- After performing an experiment, you should always wash your hands with soap and water.
- When using lab equipment and chemicals, be sure to keep your hands away from your body, mouth, eyes, face, and items you’ll handle after removing your gloves (e.g., your phone, laptop).
Chemical safety rules

Since almost every lab uses chemicals of some sort, chemical lab safety rules are a must. Following these policies helps employees avoid spills and other accidents, as well as damage to the environment outside of the lab. These rules also set a clear procedure for employees to follow in the event that a spill does occur to ensure it is cleaned up properly and injuries are avoided.
- Every chemical should be treated as though it were dangerous.
- Do not allow any solvent to come into contact with your skin.
- All chemicals should always be clearly labeled with the name of the substance, its concentration, the date it was received, and the name of the person responsible for it.
- Before removing any of the contents from a chemical bottle, read the label twice.
- Never take more chemicals from a bottle than you need for your work.
- Do not put unused chemicals back into their original container.
- Chemicals or other materials should never be taken out of the laboratory.
- Chemicals should never be mixed in sink drains.
- Flammable and volatile chemicals should only be used in a fume hood.
- If a chemical spill occurs, clean it up right away.
- Ensure that all chemical waste is disposed of properly.
Chemistry lab safety rules
As chemistry labs are one of the most common types, these basic chemistry lab safety rules are relevant to many scientists, dealing with the safe performance of common activities and tasks in the average chemistry lab:
- Before you start an experiment, make sure you are fully aware of the hazards of the materials you'll be using.
- When refluxing, distilling, or transferring volatile liquids, always exercise extreme caution.
- Use smaller amounts and containers as able. When transferring a solvent, ensure proper bonding and grounding. Make sure that containers are always labeled appropriately.
- Never pour chemicals that have been used back into the stock container.
- Never tap flasks that are under vacuum.
- Chemicals should never be mixed, measured, or heated in front of your face.
- Water should not be poured into concentrated acid. Instead, pour acid slowly into water while stirring constantly. In many cases, mixing acid with water is exothermic. Remember the saying, “Add acid to water, just like you oughta.”
Electrical safety rules

Like almost every other workplace, laboratories contain electronic equipment. Electrical lab safety rules help prevent the misuse of electronic instruments, electric shocks, and other injuries, and ensure that any damaged equipment, cords, or plugs are reported to the appropriate authorities so they can be repaired or replaced.
- Before using any high voltage equipment (voltages above 50Vrms ac and 50V dc) or high amperage current, make sure you get permission from your lab supervisor.
- High voltage equipment should never be changed or modified in any way.
- Always turn off a high voltage power supply when you are attaching it.
- Use only one hand if you need to adjust any high voltage equipment. It's safest to place your other hand either behind your back or in a pocket.
- Make sure all electrical panels are unobstructed and easily accessible.
- Whenever you can, avoid using extension cords.
Laser safety rules

Perhaps not as common as some of the other lab safety rules listed here, many laboratories do use lasers and it’s important to follow some key rules of thumb to prevent injuries. In particular, lab safety accidents due to reflection are something that many employees may not think about. A clear set of lab safety rules for the use of lasers is essential to ensure that everyone is aware of all hazards and that the appropriate personal protective equipment is worn at all times.
- Even if you are certain that a laser beam is "eye" safe or low power, you should never look into it.
- Always wear the appropriate goggles in areas of the lab where lasers are present. The most common laser injuries are those caused by scattered laser light reflecting either off the shiny surface of optical tables, the sides of mirrors, or off of mountings. Use laser curtains and signs. Goggles rated for that laser and frequency will help you avoid damage from such scattered light.
- You should never keep your head at the same level as the laser beam.
- Always keep the laser beam at or below chest level.
- Laser beams should never be allowed to spread into the lab. Beam stops should always be used to intercept laser beams.
- Do not walk through laser beams.
Lab safety: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the most important lab safety rule?
A: The most important lab safety rule is “Always perform a risk assessment”—it trumps all other science safety rules. Risk assessing is the key to all aspects of lab rules and safety. If you always assess risk, you should be successful in minimizing or even eliminating any bad or unexpected outcomes.
Q: What PPE is needed in the laboratory?
A: PPE in science labs should always include safety glasses or goggles, chemical-resistant gloves, and a lab coat. Other PPE may be needed depending on the hazards and risks in the lab. With PPE, you also need proper lab safety attire—covered from the neck down—no bare arms, legs, or toes.
Q: What is the first step in lab safety?
A: The first step in lab safety is to recognize and respect the hazards and risks. Once you accept the realities of the safety issues, the rest should come naturally. You start to look at the chemicals, equipment, processes, experiments, and controls in a new and more productive way. Open your eyes, then open your mind.
Q: Who is responsible for lab safety?
A: You are, the PI or teacher is, your classmates or other researchers are, EHS is, risk management is, institutional or organizational leadership is, and I am. We all are. It must be a group ethos, part of a true culture of lab safety, where we all care about each other’s safety and openly discuss risk. Without positive group norms and behaviors, we are lost, and risk is ever-present.
Q: What are the legal aspects for consideration when it comes to lab safety?
A: In the US, the standard is “do what a reasonable and prudent person would do to not cause harm.” That is the standard language for negligence, and no one wants to be negligent and cause harm. It’s purposefully an open-ended, performance-based standard of care. As part of this, we have a “duty to warn”—thus the need for signs, labels, training, and effective risk communication.
Our focused blog section talks about immersive technology developments, industry applications of simulation and much more.
The essential lab safety rules every student should know.

Science is an exciting journey of exploration. However, as scientific exploration and discovery continue to advance, laboratories have become intriguing fields where students engage in hands-on experiments and research.
It is fun but we need to be careful because there are some potential dangers in the lab. That's why lab rules are important!
In this blog, we'll talk about the most crucial lab safety rules for students should know. We'll learn how to spot potential dangers, be careful in our actions, and follow safety rules to make the lab a safe and awesome place for learning and discovery.
So, Let's dive in and explore the secrets to staying safe in the lab!
Lab Safety Rules for Students
Laboratories are hubs of hands-on experiments and research, where students explore the wonders of science. However, the potential hazards that accompany such experiences demand a cautious and responsible approach.
Laboratory Safety Introduction
When it comes to working in a lab, safety should always be the number one priority.
Laboratories are unique environments where students engage in hands-on experiments and research, but they can also present potential hazards that must be understood and mitigated.
Laboratory safety introduction is the foundation upon which fruitful scientific exploration is built.
By understanding potential hazards, emphasizing cautious behavior, and acknowledging the consequences of disregarding safety protocols, students can create a secure and conducive environment for learning and discovery in the chemistry and science lab.
1. Potential Hazards in a Lab
Laboratories house various chemicals, equipment, and procedures that can pose risks if not handled properly. Chemical spills, fires, explosions, and exposure to toxic substances are some of the potential hazards students may encounter.
By recognizing these risks, students become aware of the necessity for taking necessary precautions and adopting a safety-first mindset.
2. Need for a Cautious and Responsible Behavior
In any laboratory setting, cautious and responsible behavior is non-negotiable. Students must follow instructions meticulously, be attentive, and avoid any shortcuts.
Complacency or carelessness can lead to serious accidents that may not only harm the individual but also jeopardize the safety of others in the vicinity.
3. Consequences of Neglecting Safety Protocols
Neglecting safety protocols can result in dire consequences. Accidents may lead to injuries, property damage, and even legal repercussions.
Additionally, neglecting safety can hinder the learning process, as students may be hesitant to engage fully in experiments if they feel unsafe.
Also Read: 5 Creative Ways to Teach Turbofan Jet Engine
Why Is Lab Safety Important
The integrity of the experiments being carried out and the safety of those working in laboratories are both guaranteed by lab safety. Accidents, injuries, and exposure to dangerous chemicals are all prevented. Following lab safety regulations also protects the validity and dependability of experimental findings, increasing research and supporting scientific correctness.
Safe Lab Practices

In the laboratory, practicing safety goes hand in hand with scientific exploration. Adopting safe lab practices ensures that students can conduct experiments and research with confidence while minimizing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Adhering to safe lab practices not only safeguards the well-being of students but also enhances the accuracy and reliability of experimental results.
By establishing a culture of safety, educators instill valuable habits that students can carry forward into their future scientific endeavors.
1. Proper Handling and Storage of Chemicals
Chemicals are an integral part of laboratory work, but they can be hazardous if mishandled. It is crucial for students to be well-informed about the properties of each chemical they are working with and to follow precise procedures for their handling and storage.
This includes using the correct labeling, storing chemicals in designated areas, and avoiding incompatible combinations that could lead to reactions.
2. Wearing Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is the first line of defense against potential hazards in the lab. Students should wear the necessary gear, such as lab coats, safety goggles, gloves, and closed-toe shoes, to protect themselves from chemical spills, splashes, and other accidents.
Properly fitted PPE can significantly reduce the risk of exposure and injury.
3. Preventing accidents with good lab hygiene
Maintaining good lab hygiene and organization is essential for accident prevention. Keeping the workspace clean and uncluttered reduces the likelihood of accidental spills or tripping hazards.
Properly disposing of waste materials and cleaning up after experiments are equally important. Additionally, students should be aware of emergency exits and safety equipment locations in the lab.
Science Lab Safety Rules
Laboratory safety rules are the backbone of a secure and conducive learning environment in science labs.
By providing students with detailed explanations of essential science lab safety rules, emphasizing proper handling of chemicals and equipment, educating them about fire safety and emergency procedures, stressing the importance of waste disposal, and instructing them on dealing with accidents and injuries, educators can foster a culture of safety that empowers students to explore the wonders of science with confidence and responsibility.
Detailed Explanation of the Most Crucial Science Lab Safety Rules
A comprehensive understanding of the most crucial lab safety rules is the foundation of a safe laboratory experience.
These rules encompass various aspects of safety, including personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements, specific protocols for different experiments, and guidelines for handling emergencies.
Educators should thoroughly explain and emphasize these rules to students before they commence any lab work.
☑️ Handling of Chemicals and Equipment
Proper handling of chemicals and lab equipment is a cornerstone of lab safety.
Students must be educated on how to measure, mix, and use chemicals safely. This includes understanding chemical compatibility, avoiding cross-contamination, and following precise instructions for experiments.
Mishandling chemicals and equipment can lead to hazardous situations, making this rule of paramount importance.
☑️ Fire Safety and Emergency Procedures
In any lab setting, the risk of fire and other emergencies cannot be overlooked. Students should be acquainted with the location and operation of fire extinguishers, emergency showers, and eyewash stations.
Furthermore, they must know how to respond to fire incidents and other emergencies, such as chemical spills or injuries, swiftly and calmly.
☑️ Proper Disposal of Waste Materials
The proper disposal of waste materials is an essential aspect of lab safety and environmental responsibility. Students should be aware of the designated waste disposal areas and the specific requirements for each type of waste.
Incorrect disposal could lead to chemical reactions, environmental contamination, or potential harm to lab staff.
☑️ Dealing with Accidents and Injuries
Despite all precautions, accidents can still occur in the lab. In the event of an accident or injury, students should know the appropriate procedures to follow.
This includes seeking immediate medical attention for injuries, reporting incidents to the lab supervisor, and documenting the details of the accident for future reference and improvement.
Also Read: A Guide to Virtual College Tours: Exploring Campuses from Anywhere
Lab Safety Guidelines

Lab safety guidelines serve as a vital complement to general safety rules, providing students and researchers with a comprehensive approach to safety.
By offering specific safety guidelines for experiments and activities and addressing the safety concerns inherent in different lab setups, educators create a safer and more enriching laboratory environment for scientific exploration and discovery.
☑️ Additional Guidelines for Specific Experiments and Activities
Different experiments and activities require tailored safety guidelines to mitigate specific hazards.
For instance, experiments involving volatile substances may demand additional ventilation measures to prevent the buildup of harmful fumes.
Similarly, procedures that produce aerosols might necessitate the use of specialized respiratory protection.
By outlining these specific guidelines, students can approach each experiment with a deeper understanding of the associated risks and appropriate safety measures.
☑️ Addressing Safety Concerns for Different Lab Setups
Laboratories come in various setups and configurations, each presenting its unique safety considerations. For instance, chemistry labs, biology labs, and physics labs may have distinct safety requirements based on the nature of their experiments.
Additionally, university research labs and K-12 educational labs may differ in the level of expertise and supervision, leading to variations in safety protocols.
Addressing these differences through tailored safety guidelines ensures that all labs, regardless of their setup, uphold the highest safety standards.
By incorporating additional guidelines for specific experiments and addressing safety concerns for different lab setups, educators can empower students to conduct experiments with a heightened awareness of safety.
It encourages a proactive approach to safety and reinforces the idea that safety measures should be customized to suit the unique demands of each scientific endeavor.
Safe Laboratory Procedures
When conducting experiments in the laboratory, following safe laboratory procedures is paramount to safeguarding the well-being of students and researchers.
A step-by-step guide to maintaining safety during experiments, along with effective communication and teamwork, forms the backbone of a secure and productive lab environment.
☑️ Step-By-Step Guide to Maintaining Safety During Experiments
Measure 1: Preparation and Planning: Before commencing any experiment, students should thoroughly read and understand the procedure. This includes identifying potential hazards and ensuring the availability of necessary safety equipment and personal protective gear.
Measure 2: Workspace Setup: Organize the workspace to minimize clutter and create clear pathways. Ensure all necessary equipment and chemicals are within reach to avoid unnecessary movements during the experiment.
Measure 3: Handling Chemicals: Follow precise instructions for the handling and storage of chemicals. Be mindful of chemical compatibility and potential reactions, and always use appropriate safety labels.
Measure 4: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear the necessary PPE, such as lab coats, safety goggles, gloves, and closed-toe shoes, to protect against chemical splashes, spills, and potential injuries.
Measure 5: Ventilation and Fume Hoods: When working with volatile substances, use fume hoods to prevent the buildup of harmful vapors. Ensure proper ventilation in the lab at all times.
Measure 6: Equipment Inspection: Before using lab equipment, inspect it for any damages or malfunctions. Report any issues to the lab supervisor or technician immediately.
Measure 7: Proper Measurements: Use calibrated instruments for accurate measurements, and double-check measurements before proceeding with the experiment.
Measure 8: No Eating or Drinking: Emphasize the importance of not consuming food or beverages in the lab to avoid accidental ingestion of hazardous substances.
Measure 9: Communication: Establish clear communication channels among lab members. Inform team members about the experiment's progress, any observations of concern, and any deviations from the expected outcomes.
Role of Communication and Teamwork in Lab Safety
Effective communication and teamwork are vital components of lab safety. Students should feel comfortable discussing safety concerns with their peers and lab instructors. Open dialogue encourages a proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential hazards.
Teamwork also plays a critical role in lab safety. In a collaborative environment, students can watch out for each other and assist when needed.
Team members can share responsibilities, such as monitoring experiments and ensuring that safety protocols are followed diligently.
Encouraging a culture of safety-conscious communication and teamwork fosters a sense of responsibility and accountability among lab participants.
By working together, students can create a safer and more supportive laboratory environment, leading to enhanced scientific learning and discovery.
Also Read: The Future of Healthcare: Transforming the Patient Experience with Immersive Technologies
Introducing the Concept of Virtual Reality (VR) Labs
In this era of rapid advancement, technology is permeating various aspects of our lives. Embracing progress has become crucial across diverse fields, and education, especially in the world of science, stands to benefit immensely from technological integration.
As technology continues to evolve, traditional teaching methods are proving insufficient to fully engage and prepare today's students for the challenges of tomorrow.

Science education must adapt to equip students with the necessary skills and knowledge in a world shaped by science and technology.
The introduction of Virtual Reality (VR) labs represents a significant transformation in science education.
Leveraging VR technology, educational institutions can create immersive and interactive learning experiences that transcend the limitations of traditional classrooms and laboratories.
VR Labs increase students' engagement . Through VR labs, students can explore complex scientific concepts through simulated experiments and real-life scenarios within a safe and controlled environment.
By embracing VR labs in science education, institutions can not only enhance student engagement and motivation but also find cost-effective solutions.
Reducing reliance on expensive laboratory equipment and materials makes science education more accessible and scalable, empowering students from diverse backgrounds to experience cutting-edge learning opportunities.
Moreover, integrating VR labs in the metaverse adds a thrilling dimension to science education.
The metaverse, a shared virtual space where real-time interactions occur, fosters collaborative learning opportunities beyond geographical boundaries.
In this interconnected global learning community, students can engage in group projects, knowledge-sharing, and interactive discussions with peers and educators from around the globe.
Also Read: How to set up VR lab in universities and colleges?
Why Engineering Colleges Should Consider VR Labs?

Well, the adoption of VR labs in engineering colleges brings a myriad of benefits, catering to the specific needs of engineering students, preparing them for the modern workplace, and offering cost-effective scalability.
By integrating VR technology, engineering colleges can elevate the learning experience, empowering students with the skills they need to thrive in a technology-driven world.
"Unlock the potential of tomorrow's engineers today with VR Labs, where hands-on experience meets digital innovation for unparalleled learning."
Book A Demo 1. Specific Benefits for Engineering Students
The benefits of VR labs are endless. It offers engineering students a highly interactive and immersive learning experience.
They can engage in realistic simulations of complex engineering processes and experiments, allowing them to grasp intricate concepts with greater clarity.
Additionally, VR labs enable students to practice problem-solving skills in a risk-free environment, building their confidence and proficiency.
2. Prepare Students for Modern Workplace Requirements
In today's technologically driven workplace, proficiency in virtual environments is increasingly essential. By utilizing VR labs, engineering colleges equip their students with practical skills that align with modern industry demands.
Graduates who have experienced VR labs are better prepared to adapt to cutting-edge technologies and excel in their careers.
3. Cost-effectiveness and Scalability of VR Labs in Colleges
Compared to traditional physical labs, VR labs offer significant cost savings in terms of equipment, maintenance, and consumables.
Moreover, they can be easily scaled to accommodate more students without incurring additional costs.
This makes VR labs a cost-effective solution, particularly for colleges with limited resources and space constraints.
In conclusion, lab safety rules remain of utmost importance for every student engaged in scientific exploration.
By adhering to these guidelines, we ensure a secure and conducive learning environment, fostering a culture of responsibility and care.
However, the adoption of VR labs represents a transformative step in enhancing science education. The immersive and interactive experiences provided by VR technology open new horizons for students, boosting their engagement, motivation, and understanding of complex scientific concepts.
Why are lab rules important, you might wonder? Well, lab rules are crucial to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these virtual laboratories, making it imperative for students to learn and adhere to them.
While VR labs offer unprecedented advantages, we also recognize the value of traditional labs in fostering hands-on experiences and practical skills.
The synergy between traditional and virtual labs holds the key to the future of learning, where students can access a diverse range of learning environments tailored to their needs.
At iXR Labs, We at iXR Labs, tailor unique and futuristic VR Content for Engineering, Medical, and Sciences Students and help institutes build VR Labs to change the way students interact and experience reality.
If you are interested in giving this technical edge to your college/ university or wish to know more about how to set up VR Labs in your institutions, you can visit www.ixrlabs.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some science lab safety rules.
Handling of Chemicals and Equipment, Fire Safety and Emergency Procedures and Proper Disposal of Waste Materials are some science lab safety rules.
Why are lab rules important ?
Lab rules are crucial to ensure the safety and effectiveness of these virtual laboratories, making it imperative for students to learn and adhere to them.
Recent Posts .

Revolutionizing Electromagnetic Education with VR Technology

Virtual reality for Robotics Engineering Education

Applications of VR in Telecommunication Engineering


5 Creative Ways to Teach Stepper Motor

Understanding Cardio-Respiratory Physiology through Virtual Models
Categories ..
- AI and Machine Learning
- Augmented Reality
- Engineering
- Online Assessment
- Teaching in VR
- Virtual Reality
5 Creative Ways to Teach Turbofan Jet Engine
Virtual reality training in higher education: exploring its transformative impact.

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Lab Safety Rules and Guidelines

It’s important to follow lab safety rules to avoid accidents and be prepared in case of an emergency. Follow these 10 rules to protect yourself and others and get the most from your lab experience.
Follow the Instructions
The most important lab safety rule is to follow the instructions. Read or listen to instructions and get answers to questions before you start lab work. This is the most important rule because if you don’t follow it:
- You could endanger yourself and others.
- You could ruin your experiment.
- You could cause an accident.
- You could get suspended or fired.
Know the Location of Safety Equipment and How to Use It
It’s important to know the location of safety equipment and how to use it. Be familiar with key safety signs and know the location of the emergency exit. Make sure equipment is in working order.
Wear Appropriate Clothing and Gear
Wear shoes with covered toes and long pants. Tie back long hair and secure dangling jewelry. Avoid acrylic nails when working with flames. You shouldn’t wear contact lenses in chemical labs (and some biological labs). Once you get to the lab, wear appropriate safety gear. You may need goggles, a lab coat, gloves , hearing protection, or other gear.
Don’t Eat or Drink in the Lab
Don’t eat or drink in the lab. Similarly, don’t store food or beverages in a refrigerator that contains chemicals, cultures, or other experimental material. Don’t use lab glassware as cooking utensils. Even if it looks clean, it could retain chemical or biological residues from experiments.
Don’t Taste or Sniff Experiments
Tasting or smelling chemicals or biological cultures can be dangerous or possibly deadly. Use labels to identify samples. If you must sniff an experiment as part of a protocol, use your hand to waft the scent over toward your nose.
Don’t Play Mad Scientist
Be responsible in the lab. Don’t randomly mix chemicals or deviate from the lab protocol. You could cause a fire or explosion or produce toxic fumes. Similarly, don’t engage in horseplay in the lab. You could distract others, break glassware, or cause an accident.
Know What to Do in an Emergency
You can prevent most lab accidents, but should know what to do when one happens. Immediately report an accident when it occurs. Don’t lie about it or try to cover it up because there could be consequences for you, other people, or the facility.
Dispose of Waste Properly
Clean up after yourself and know what to do with an experiment once it’s completed.
- Know where to dispose of “sharps” such as broken glass and needles.
- Know whether chemicals can be poured down the drain. If not, learn how to neutralize or store them.
- Know whether biological cultures can be cleaned with soap and water or require an autoclave.
Leave Experiments in the Lab
Don’t take experiment materials or specimens home with you. In some cases, lab notebooks must stay in the lab, too.
Treat Everything Like It’s Hazardous
Always label containers, even if they only contain water. Remember hot glass looks just like cool glass. If there’s heat in the lab, assume a container could be hot. Assume biological agents are infectious and treat them with respect. Basically, use caution with all lab equipment, chemicals, and specimens.
More Lab Safety Rules
- Don’t experiment on yourself.
- Don’t leave experiments unattended.
- Don’t work alone in the lab.
- Report unsafe conditions as soon as possible.
- Never pipette by mouth. Always use a pipette bulb.
- Don’t set hot glass directly on a lab bench. It will shatter.
- Know emergency phone numbers in case you need to call for help.
- Work using appropriate ventilation. If an experiment requires a fume hood, don’t perform it out in the open.
- Check glassware for chips and cracks. Damaged glassware is harder to clean, more susceptible to breakage, and more likely to cut you.
- Don’t use equipment until you have been trained in its proper usage.
- Wash your hands with soap and water before leaving the lab.
- Don’t put unused chemicals back in their original container.
- Don’t mix chemicals in sink drains.
Related Posts
Professional writing services chosen by demanding students

Stop stressing over papers due – have them written today!
We work for you, and only you.

Our most requested types of work and disciplines
- Research paper
- Research proposal
- And lots of other tasks
- Business & Management
- Criminal Justice
- English, Literature & Philology
- Health Sciences & Nursing
- Social & Political Sciences
- And 40 more

How it works
What you can obtain with us.

What clients say about our custom essay writing service
We are in media
How we achieve outstanding quality.

What else our professional essay writing service can do for you

- 714-258-7535
Why Is Lab Safety Important?
Jan 4, 2023 8:31:11 AM / by WSI Team
Explosive chemicals. High-pressure gasses. Flammable liquids. Toxic substances. Dangerous projectiles.
Why is lab safety important? Because each of the potential risks outlined above can lead to laboratory mishaps, or worse, catastrophic consequences.
It’s unclear exactly how many accidents occur in laboratories each year. An Occupational Safety and Health Research Institute study found that among 220 participants, 45% had experienced accidents in the lab. About 74% reported exposure to chemicals, while about 45% of respondents reported inhalation specifically.
A survey published in the journal, Nature , also found that 25 to 38% of academic lab personnel who had been involved in an accident or injury in the lab never reported it to a supervisor or investigator.
Let’s face it. Laboratory work can be dangerous. Yet it can be incredibly rewarding as well, and with the right guidelines put into place, the work performed in labs can be safe. Let’s explore some of the greatest hazards found in the lab, and what you can do to ensure your employees remain safe.
Electrical Components
Electrical cords, outlets and equipment like oscilloscopes, power supplies and soldering irons are often found in laboratories. Misuse or simply poor layouts of these items can result in tripping hazards, accidental shocks or fires.
Tips to improve lab safety:
Never leave power cords near heat sources
Do not run extension cords across or near doorways
Do not connect power strips together
Label high voltage equipment with signs warning of danger
Before inspecting power equipment, turn power and circuit breakers off
Only use equipment with non-conducting handles when working with electrical devices
When examining an operating circuit, avoid making your body a closed circuit by keeping one hand in your pocket or behind your back
Keep work areas near electrical devices and outlets clear of paper, books and other clutter
Avoid using electrical equipment around any water sources unless the equipment is designed for that use
Do not use flammable substances near electrical equipment
Keep electrical panels unobstructed
Avoid creating sparks where static electricity is a concern
One of the ways you can help minimize electrostatic discharges in a lab is by choosing lab clothing and furniture that helps protect against ESD. Spark sources can be a major concern in laboratories. If ESD, or electrostatic discharge, is a concern in your lab, you will want to ensure your technicians wear PPE or clothing that is made of static dissipative fabric.
A laboratory fume hood removes substances that may cause harm, such as fumes, aerosol, gasses, vapors and dust. They also create a barrier between the lab when a chemical reaction occurs.

While this important piece of lab equipment is rooted in safety, it’s important to follow a separate set of guidelines to ensure the fume hood is operating efficiently and safely.
In 2008, a UCLA research assistant died after a reagent she was using ignited spontaneously in the air. As she was transferring a tert -butyllithium ( t -BuLi) solution using a plastic syringe, the plunger came out of the syringe barrel and the reagent was exposed to the air. The t -BuLi solution and the research assistant’s clothing ignited.
To help avoid a scenario like the one above, your fume hood safety checklist should include these tips to improve lab safety:
Know the chemicals that are being worked with and any potential reactions of those chemicals
Ensure the hood sash is opened to the proper height to provide the proper level of protection.
Check the air gauge to ensure the airflow is within the required range.
Make sure the exhaust fan is working so that hazardous chemical fumes can escape.
Check the baffles in the exhaust fan since these keep airflow uniform.
Double check there are no spark sources nearby that can cause a fire or explosion.
Examine the air filters to ensure they are not clogged.
Ensure anyone operating under a fume hood is wearing the proper PPE, or personal protective equipment ( Clean room garments like lab coats, coveralls and full body suits; eye protection like goggles and face shields; gloves and more)
All new employees should also be up-to-date on proper use of fume hood equipment. Current workers should regularly undergo refresher training as well, especially if a new chemical is being used under the hood.
When handling any type of laboratory glassware, such as beakers, funnels and burettes, there are several steps lab technicians can take to protect themselves.
Inspect all glassware before use for chips or cracks
Move slowly and steadily when transferring chemicals from one glassware to another
Keep glassware from edges when working
Stir gently during the heating of a solution in a glass container
Avoid heating liquids on a direct flame
Wear the proper protection, including lab coats, chemically-resistant gloves and protective eyewear
When choosing the proper eyewear, you typically have three choices: Lab safety glasses, goggles and face shields.
Lab safety glasses , goggles and face shields all provide different levels of protection. Lab safety glasses often have shatter-resistant lenses and are designed to stop large objects from injuring eyes. Lab safety goggles may be a better fit if your lab workers regularly deal with chemicals, bloodborne pathogens or other substances that produce mists, vapors or fumes.
Face shields are not designed to be the only appropriate eye protection a lab worker should wear. Instead, they can help provide additional protection when worn over eye protection glasses or goggles. Face shields also help protect the entire face, rather than only eyes.

Every employee should be trained according to the types of chemicals and substances used in your lab. In fact, OSHA requires that laboratories identify possible hazards and develop a Chemical Hygiene Plan (CHP). This plan is a written program that states specific policies, procedures and responsibilities that labs have in protecting workers from health hazards associated with any chemical used in a workplace.
In addition to creating a Chemical Hygiene Plan, lab managers can take other actions to protect employees from chemical hazards.
Ensure any fabric a technician is wearing is resistant to chemicals (such as polypropylene, which allows moisture to evaporate more quickly and is resistant to many acids and alkalis)
Never leave containers of chemicals open and unattended
Do not consume beverages and food where hazardous chemicals are used or stored
Never pour chemicals down drains, and instead according to chemical waste disposal regulations
Do not store chemicals inside a fume hood, but rather in the proper laboratory cabinets
While selecting the right laboratory cabinets for your workspace can be challenging, one of the best and most commonly used materials today is steel. Variations of steel, such as stainless steel, are some of the most common materials used to construct lab cabinetry because steel components are heavy duty and provide maximum strength and rigidity. Steel is also an effective material choice for labs that require a sterile or hygienic environment.
Make sure the laboratory cabinets you consider can safely store the chemicals you use. Locks can also add an additional layer of protection if substances should be secured.
Physical Hazards
Finally, one of the most common yet overlooked hazards present in labs today are physical injuries sustained.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that sprains, strains and tears collectively are the leading type of injury in manufacturing. While at first glance these seem like minor injuries, they can still impact time on the job, worker efficiency and overall productivity.
Ergonomically-designed pieces of furniture, from the industrial workstation itself to the lab chairs employees sit in, focus on keeping the body in its natural position. Alternatively, when employees must continuously bend, twist and turn, they are more prone to painful injuries.
Consider benches that easily raise and lower, such as ergonomically adjustable hydraulic benches
Don’t forget industrial chairs that feature sturdy frames, adjustable heights and comfortable backrests and seats
Don’t overlook other workbench features that can impact the physical health of a worker, such as the placement of drawers and utility features so that employees do not have to extend in an unnatural position to reach them
Lab managers often worry about hazardous conditions that can quickly develop, but sometimes the most costly injuries can happen over time. A lab that is designed ergonomically-friendly can help ensure a healthy, productive employee in the long run.

Topics: Laboratory

Written by WSI Team
Employees of Workstation Industries who write on different topics to inform and educate.
- Laboratory Furniture (38)
- Laboratory (29)
- Work Surfaces (20)
- workbench (15)
- Workstations (14)
- Portable Clean Rooms (11)
- American Made (7)
Subscribe to Email Updates
Follow wsi.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Lab Safety Essay | Safety in The Lab, Importance of Lab Safety Essay in English
December 27, 2021 by Prasanna
Lab Safety Essay: If you’re an aspiring chemist or lab technician, then this essay is for you! There are many dangers that surround the lab, and you must be aware of them if you want to prevent injury or even death. This essay explores the safest and most effective methods of keeping yourself and your coworkers safe while in a lab.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
Safety In The Lab
Laboratory safety is a broad term that refers to the safe use of a lab and its associated equipment. There are many different aspects to laboratory safety, including chemical hygiene, hazard identification and risk assessment, as well as work-place injury prevention. Laboratory accidents can occur at any time and could result in serious injury or even death. One of the most common accidents in the lab are chemical fires. Chemical fires can occur when flammable materials are exposed to an open flame or spark. They result in burns, blindness, and death if left untreated.
The majority of chemical fires are caused due to careless handling and human errors – such as the storage of combustible materials near the ceiling or in inaccessible areas. If a fire occurs, it can spread rapidly and cause large amounts of damage to the lab and other areas in the building. Some examples of flammable materials include: alcohol, butane, gasoline, gasoline vapors, acetone, benzene, ethyl acetate, acetic acid, hydrogen cyanide, kerosene, lacquer thinner, propane, methane, etc. Following are a few important rules to be followed when working in a lab
- Use gloves when handling chemicals. Whenever you are handling chemicals, it is important to use gloves. Since the skin has the potential to absorb chemicals into the body, gloves should be worn to avoid contact with harmful substances.
- Open chemicals in a well-ventilated area. Prior to beginning an experiment, make sure the laboratory is well-ventilated and all chemicals and equipment are in good working order.
- Use the appropriate sized container for the chemical being handled. Chemical containers are marked with various sizes to show the volume of liquid that the container is capable of holding. These markings are in liters or milliliters and help identify the best container for the chemical being handled.
- Clean up spills immediately, using the appropriate solvent or solids. It’s important to use the appropriate solvent to avoid damage, and to do it as soon as possible.
- Do not eat or drink in the lab. Eating or drinking in the lab is not allowed because it can lead to contamination.
- Before starting any experiment, it is important to have the appropriate safety equipment. The most important safety equipment is a lab coat. Protective goggles are also recommended.
What To Do If You Come Into Contact With Hazardous Substances?
The most important thing you can do is be aware of your surroundings. If you see something, say something immediately to someone else in the lab or a supervisor. If you need to work with hazardous substances, remember to put on protective gear. If you come into contact with a hazardous substance, then follow these steps:
- Evacuate the lab if it is safe to do so. Sometimes, it is necessary to evacuate the lab for safety reasons. If there is a fire, chemical spill or other emergency that requires evacuation, all employees should evacuate the building immediately.
- Get medical attention if needed. Injuries sustained in the lab must be treated. Rinse the wound with saline or clean water and cover it with a sterile dressing if available. If exposed to dangerous substances, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. The risk of infection increases dramatically after the first few hours. If left untreated, an infection can lead to life-threatening problems such as sepsis or gangrene.
- Report the spill to your supervisor. When a spill occurs, it is important to report it to your supervisor. The spill should be cleaned up quickly and everyone in the area must be notified.
- Wash your hands, face, and other parts of the body. Chemical exposure can cause skin irritation, allergic reactions, and other health problems. Washing exposed areas after handling chemicals is the best way to protect yourself and avoid potential hazards.
- Change or dispose of your clothes if exposed to ionizing radiation. The most important thing to do in case of nuclear radiation exposure is to change or dispose of your clothes and shoes. Even if you haven’t been exposed to any radiation, it’s important to take precautions and securely dispose of your clothes as soon as possible.
Prudent Practices in Educational Institutions
Chemical safety is an important issue for labs, and many chemistry labs will have a designated chemical safety officer. When working with chemicals, it’s important to know how to handle them safely and how to store them safely as well. It is also important to understand how to properly dispose of hazardous chemicals, and to know who is responsible for their disposal. The lab management team should make sure that all members are on board with the lab’s policies and procedures. Safety glasses, dust masks, and gloves should be worn when handling potentially dangerous chemicals.
All chemical containers should have labels with the name and appropriate chemical hazards noted. For example, if a lab uses solutions or solutions containing acids, then the labels should have a warning statement of what to do if the solution gets in the eyes, and how to wash off acid spills. Laboratory glassware should be labeled with identification as to what it contains, including name and chemical hazards. Volatile chemicals should not be stored in the same container as other chemicals. If a container is punctured, it should be immediately contained. If a chemical spills, it should be cleaned up immediately by rinsing with appropriate chemicals. Also, never eat, drink or smoke in a lab setting.

Key Takeaways of Lab Safety
Laboratory safety is a significant concern. In order to keep your laboratory as safe as possible, it’s important to follow some general lab safety rules. Every lab should have a fire alarm and evacuation plan. Some labs even have smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors. Also, ask your facility manager or staff if they have a safety committee that oversees the safety practices for your lab. The following are rules that relate to almost every laboratory, which is the focus of this essay.
- Pipettes, thermometers and other lab tools should be cleaned after use.
- Glassware and other materials may need to be well rinsed with relevant solutions or other disinfectants before reuse.
- Properly sterilize all equipment to minimize cross contamination. For example, all pipettes should be thoroughly cleaned in an autoclave before use. Disposable glassware should be cleaned with a hot, soapy water solution. The dishwasher is not suitable for glassware, because the heating elements can break bits off the dishes as they are being washed.
- Laboratory waste should be handled and disposed of in a proper manner. It should never be thrown away with the regular weekly garbage. The waste should be carefully removed from the laboratory and deposited in a designated place. Most labs will set aside a small waste container for different types of wastes.
- Be sure to read all safety signs on your lab’s bulletin boards.
- Also, beware of any safety violations your lab may have.
- Safety rules and protocols are designed to keep you safe, hence follow them strictly.
- If chemicals must be disposed of, try to dispose of them correctly. For instance, some chemicals should never be poured down the drain or thrown away in the trash. Chemicals that are dangerous should be taken to the hazardous waste site.
- Proper disposal of chemicals will help prevent accidents and unnecessary exposures to people and the environment.
- Moreover, be aware of how hazardous chemicals can affect your body. For instance, acetone is very flammable. Acetone will burn your eyes and skin if you breathe it in, but once it comes into contact with the air or skin, it will burn. The fumes are also irritating, and chronic exposure can cause respiratory problems. Rubber gloves will protect your skin from chemical burns. Acidic liquids are corrosive and can damage metals, wood, and synthetic materials. Acids can also react with bases to produce dangerous fumes. Some acid spills are not easily cleaned up and tend to leave behind corrosive residue. Acid spills can also cause damage to sensitive electronic or metal equipment. Also, try to use bunds, spill kits, and spill pallets to contain acid spills.
Conclusion on Lab Safety Essay
There are many factors to consider when making laboratory safety plans. The most important factor is having a plan for all of the chemicals in your lab. You should also have a plan for emergency situations that involve spills or fires as well as how you will respond to emergency situations.
FAQ’s on Lab Safety Essay
Question 1. How do you stay safe in a lab?
Answer: In a lab, safety is of the utmost importance. There are many types of hazards in a lab, so take the time to learn about the risks and how to protect yourself against them.
Question 2. What is the first rule of lab safety?
Answer: The first rule of lab safety is to never work alone. This rule is especially important when working with hazardous substances.
Question 3. What are some Do and Don’ts in the laboratory?
Answer: Do:
- Wear safety glasses and protective clothing
- Wipe spills and prevent contamination
- Wash hands before working
Don’t:
- Eat-in the lab
- Touch volatile or dangerous chemicals
- Touch lab equipment without washing hands
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
Essay Service Examples Business Safety
Why Is Lab Safety Important Essay
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee

Our writers will provide you with an essay sample written from scratch: any topic, any deadline, any instructions.
Cite this paper
Related essay topics.
Get your paper done in as fast as 3 hours, 24/7.
Related articles

Most popular essays
- College Students
- Student Life
In this carefully demonstrated article, Marci Nathai-Balkissoon, analysis the impact of the taught...
- Biotechnology
Biotechnology consists of various techniques that helps in improving and providing better life to...
- School Violence
School safety is a complex problem without a one size fits all solution. Trauma associated with...
Medication errors is still the most common cause of unintentional harm to patients (Cloete 2015)....
- Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is a advanced technology, which drivevariationof economy and society...
In Australia, the importance of sun safety should be extremely high as Australia has one of the...
Laboratory safety training in educators has become an increasingly studied issue. Although there...
The occupational health and safety is a multidisciplinary field which is concerned with the health...
Due to the rapid expansion of the middle class throughout Southeast Asia, the aviation industry...
Join our 150k of happy users
- Get original paper written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most
Fair Use Policy
EduBirdie considers academic integrity to be the essential part of the learning process and does not support any violation of the academic standards. Should you have any questions regarding our Fair Use Policy or become aware of any violations, please do not hesitate to contact us via [email protected].
We are here 24/7 to write your paper in as fast as 3 hours.
Provide your email, and we'll send you this sample!
By providing your email, you agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy .
Say goodbye to copy-pasting!
Get custom-crafted papers for you.
Enter your email, and we'll promptly send you the full essay. No need to copy piece by piece. It's in your inbox!
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 26 June 2024
The strategy behind one of the most successful labs in the world
- Luka Gebel 0 ,
- Chander Velu 1 &
- Antonio Vidal-Puig 2
Luka Gebel is a PhD candidate at King’s College London and incoming assistant professor of strategy and entrepreneurship at the Global Business School for Health, University College London.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Chander Velu is professor of innovation and economics at the Institute for Manufacturing, Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
Antonio Vidal-Puig is professor of molecular nutrition and metabolism at the Institute of Metabolic Science, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
Biochemist John Kendrew working on a structural model of a protein at the Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, UK, in the 1960s. Credit: MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
You have full access to this article via your institution.
The Medical Research Council’s Laboratory of Molecular Biology (LMB) in Cambridge, UK, is a world leader in basic biology research. The lab’s list of breakthroughs is enviable, from the structure of DNA and proteins to genetic sequencing. Since its origins in the late 1940s, the institute — currently with around 700 staff members — has produced a dozen Nobel prizewinners, including DNA decipherers James Watson, Francis Crick and Fred Sanger. Four LMB scientists received their awards in the past 15 years: Venkatraman Ramakrishnan for determining the structure of ribosomes, Michael Levitt for computer models of chemical reactions, Richard Henderson for cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and Gregory Winter for work on the evolution of antibodies (see Figure S1 in Supplementary information; SI). Between 2015 and 2019, more than one-third (36%) of the LMB’s output was in the top 10% of the world’s most-cited papers 1 .
What is the secret of the LMB’s success? Many researchers and historians have pointed to its origins in the Cavendish Laboratory, the physics department of the University of Cambridge, UK, where researchers brought techniques such as X-ray crystallography to bear in the messy world of biology. Its pool of exceptional talent, coupled with generous and stable funding from the Medical Research Council (MRC), undoubtedly played a part. However, there is much more to it. None of these discoveries was serendipitous: the lab is organized in a way that increases the likelihood of discoveries (see ‘New questions, new technologies’).
To find out how, we conducted 12 interviews with senior LMB and external scientists to provide insights into the organization. We also analysed 60 years’ worth of archival documents from the lab, including research publications, meeting minutes, external assessments and internal management reports (see SI for methods).
New questions, new technologies
The LMB’s approach is to identify new and important scientific questions in uncrowded fields that require pioneering technologies to answer them. The lab develops that technology to open up the field; continual improvements bring more breakthroughs, which can be scaled up to enter markets. Here are three examples.
DNA sequencing. In the 1940s and 1950s, biochemists Max Perutz and John Kendrew sought a way to discriminate between normal and pathological haemoglobins and myoglobin. The LMB developed molecular fingerprinting and chromatography technologies 11 that allowed various biological questions to be addressed, such as how genes are regulated or how molecular programming is involved in cell death. Protein and DNA sequencing also enabled the study of molecular mechanisms of viruses and organ development. Transferring these discoveries into clinical and industrial settings changed drug discovery from a process of screening compounds to one of active design.
Antibodies. At the LMB in 1975, biologist George Köhler and biochemist César Milstein discovered a method to isolate and reproduce individual (monoclonal) antibodies from the many proteins that the immune system makes. This breakthrough enabled the characterization of antibodies, and sparked inquiries into gene regulation and programmed cell death. Monoclonal antibodies now account for one-third of new treatments that reach the clinic.
Cryogenic electron microscopy. The LMB has a long-standing history in the development of electron microscopy, with Aaron Klug’s group using it in the 1960s to elucidate the structure of viruses. Cryo-EM visualizes atoms in biological molecules in 3D. It was developed on the back of three decades of the LMB’s accumulated expertise in areas from optimizing cooling and vacuum technology to microscopy, computing-based imaging and electron detectors. The method has revolutionized protein research and many other areas.
We identify the LMB’s management model as the key — it sets a culture with incentives and provides oversight to optimize the interplay between science and technology. By integrating high-risk basic science with innovative technology, the LMB facilitates a knowledge feedback loop that helps the institute to identify promising questions and continuously push scientific boundaries (see SI, quote 1). In the context of economics and management theory, the LMB behaves as a ‘complex adaptive system’.
Here, we outline our findings and encourage research organizations, funding bodies and policymakers to consider adopting a similarly holistic and coherent approach to managing basic scientific research. In short, they should prioritize long-term scientific goals and effectively manage scarce resources; foster economies of scale and scope by promoting complementarities between different areas of scientific research; and create value by establishing synergies and feedback between scientific questions and engineering-based technology solutions.
Integrated management
The LMB’s management strategy prioritizes three elements — culture, incentives and management oversight — that sustain a feedback loop between science and technology development (see SI, Figure S2).
Culture. The LMB sets a coherent culture by promoting scientific diversity among its staff, encouraging the exchange of knowledge and ideas and valuing scientific synergies between different areas of research. Senior managers view this culture as central to an evolutionary process in which a broad and diverse talent pool helps the organization to be flexible and to adapt and survive. Scientific discovery emerges from it in a sustainable but unpredictable way.
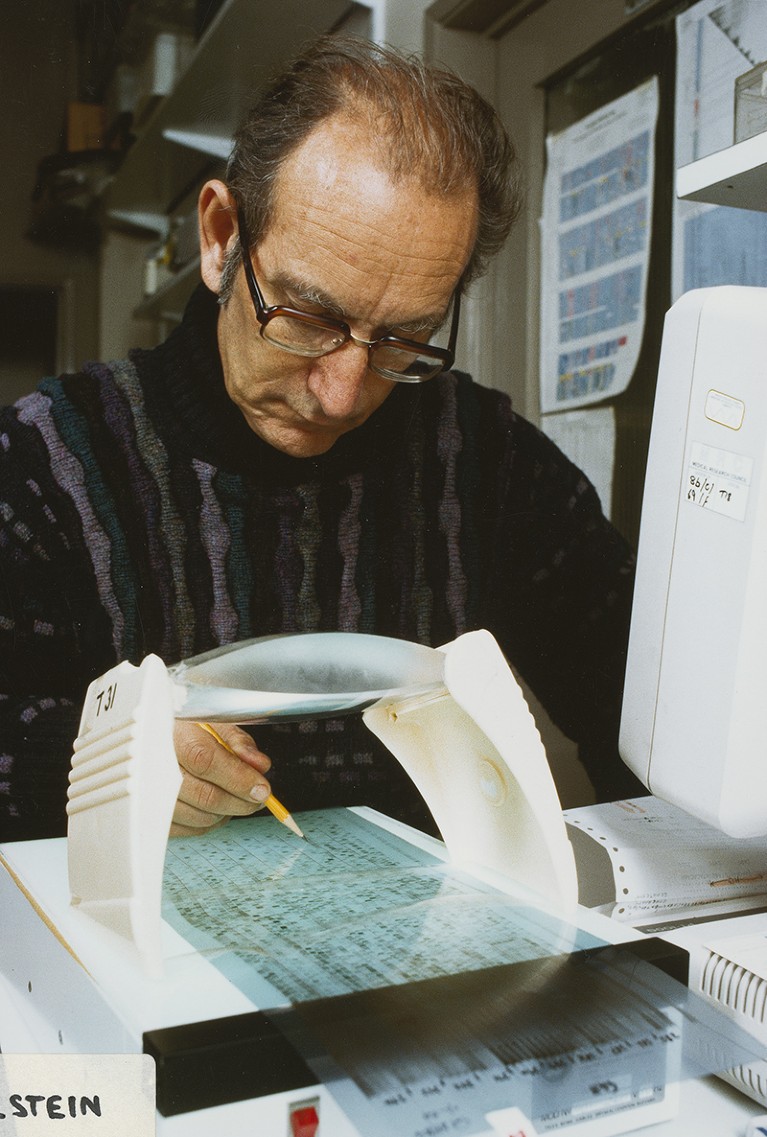

César Milstein analysing DNA. Credit: MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
The LMB recognizes the importance of having a defined, yet broad and open, institutional research direction. It encourages the recruitment of groups with diverse but aligned interests that are complementary (see SI quote 2). This approach has ensured that the LMB can achieve a critical mass of expertise in specific research areas. It enables economies of scale while retaining the flexibility to innovate by pioneering new avenues and emerging fields. It also recognizes that not every promising direction can be followed.
Scientific diversity has been a trait from the start. Although the lab was founded by physicists and chemists, its researchers today include mathematicians, engineers and zoologists (see SI quote 3). Yet too much variety is to be avoided in case it dilutes the culture. Minutes of an executive committee meeting from 1997 reveal the reticence of lab heads to appoint purely clinical researchers on the grounds that this might alter the lab’s culture and its focus (see SI quote 4).

We can make the UK a science superpower — with a radical political manifesto
A diverse portfolio of related and aligned themes makes it easier to share techniques and methods between projects and inspires programmes to aim at bolder goals (see SI quote 5). For example, the development of cryo-EM to examine macromolecules benefited both the structural-studies division and the neurobiology division, and led to a better understanding of molecular pathways in neurodegeneration.
Incentives. The LMB uses an incentive structure to align the organization’s culture with the goals of its people. Actively promoting shared values and common aims helps researchers to feel part of the LMB community and proud to belong to it, fostering long-term loyalty. “The LMB has always had a non-hierarchical structure — one in which emphasis lies in the quality of the argument, rather than in the status of the proponent,” a 2001 external review of the LMB noted (see SI quote 6).
Unlike many labs, the LMB focuses on investing in and promoting junior members rather than bringing in external talent. This is reflected in the high standards of its junior scientific recruitment. Many of its Nobel prizewinners, including Richard Henderson and Gregory Winter, began their careers at the lab and were promoted internally.
Prioritizing small teams also optimizes the sharing of technologies and budgets and incentivizes scientists from different fields to converge on the same projects. Although the LMB is structured in divisions, almost all career scientists have independent but aligned scientific programmes. This connectivity often leads to rapid and creative combinations of ideas between teams. It also allows for the sharing of failure and resilience to it, which is inevitable in high-risk, high-stakes innovative research (see SI quote 7).

Structural biologist Daniela Rhodes studies chromatin structure and regulation at the LMB. Credit: MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
LMB resources are allocated in ways that encourage innovative collaboration between internal teams and divisions. For example, limits are set for research groups to bid for external grants, because these tend to have short-term, results-oriented requirements that might not align with the LMB’s longer-term ambitions.
Furthermore, the LMB’s director can flexibly allocate funds to promote innovative collaborations and initiatives. Recent examples include forays into synthetic biology (using engineering to develop or redesign biological systems) and connectomics (the study of the connections in the brain and nervous system).
Management oversight. The LMB uses a management oversight system that resolves tensions between technology and science priorities, which would otherwise affect productivity. Technologists aim to develop and improve tools to match the best specifications for as many potential users as possible. Scientists help to define technology specifications that are based on their aims and data, which are usually on the cutting edge of existing capabilities.

Want to speed up scientific progress? First understand how science policy works
Tensions are present in the differences between how technology developers and scientists speak, define problems, operate and organize their project milestones and risk assessments. Technologists often focus on developing solutions for relatively well-defined practical problems that are amenable to rigorous project-management techniques, whereas scientists tend to work on uncertain, ambiguous questions and problems that require flexibility in experimental processes and resource allocation 2 .
To address these issues, the LMB uses a mixture of interventions and a robust process for selecting which scientific questions it focuses on. For example, technology developers with distinct specialisms operate in a dedicated workshop unit to develop prototypes. Experienced principal investigators act as go-betweens, translating scientific terms into technical engineering requirements and vice versa. Decisions around scientific resources are delegated to the divisions; money for major technology development is allocated centrally through the lab’s executive committee. Thus, the feedback loop between science and technology that facilitates innovation is enhanced (see SI quote 8).
Long-term potential
Because the LMB’s strategy focuses on long-term, transformational goals rather than short-term incremental gains, its internal evaluation system for researchers is more concerned with the potential of the overall scientific programme 3 than with standard individual performance metrics, such as the number of journal publications and citations, personal impact factors, grant funding, awards and collaborations. Scientists must openly assess which questions hold the highest value according to the LMB’s focus areas, and balance that with the cost of technology development and risks of failure while sustaining diversity in their research portfolio.
To manage these competing demands, the LMB integrates internal expertise and external reviews. The quinquennial external review process by the MRC is a strategic approach to innovation that anticipates future trends and brings fairness to decision-making. In our interviews, managers articulated the importance of quinquennial reviews to inform and stress-test the scientific direction of the organization. These reviews include visits from a committee of reviewers who are aware of the lab’s culture and who score a group leader’s scientific productivity and originality on the basis of reports, internal reviews and interviews.
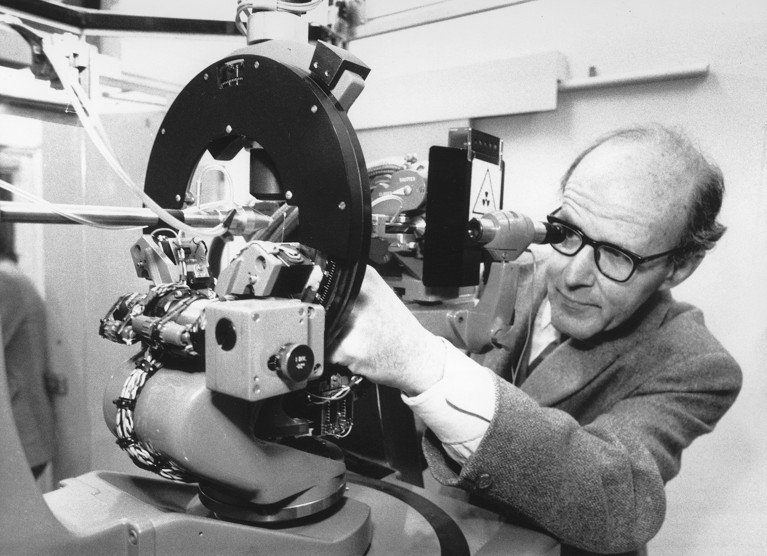

Biochemist Max Perutz preparing a sample for examination using X-ray crystallography. Credit: MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
Individual labs are evaluated on the usual metrics, such as results from past research, but more emphasis is placed on the future outlook. As a result, a young investigator’s potential and the impact of their research might result in tenure, even if they have a limited number of publications. Marks below a certain point mean the research group will be closed within a year. But this remains an exception so that the long-term nature of programmes is not lost.
The review process also plays a crucial part in identifying emerging scientific trends and opportunities. For example, in 2005, the visiting review committee identified the need for a new animal facility that would highlight the potential of mammalian biology — a concept that had not been prioritized previously (see SI quote 5).

US agency launches experiments to find innovative ways to fund research
Indeed, the LMB generally declines projects that require scaling up technology and large physical spaces, in case they come to dominate the lab’s work and space requirements beyond the financial income that the project can generate. In 1996, for example, the lab decided to forgo projects that involved scaling up its profitable protein and antibody engineering successes (see SI quote 9).
The LMB could be seen as a high-quality incubator for early-stage innovative projects, with a high turnover of research projects. This turnover does not compromise the viability of the research, because the small group structure allows for flexibility of research projects and mobility of staff. The LMB focuses on projects until they become successful, fundable and scalable by having access to funding opportunities closer to later stages of scientific development and translational research.
A complex adaptive system
Although these rules govern the LMB, the outcomes are more than the sum of their parts. The organization’s management strategy gives rise to emergent behaviours and deliverables that align with its long-term research goals. The management model has emerged from a set of actions taken by management over time that collectively result in a coherent approach to achieving the overall aim of the LMB 4 . In management theory terms, the LMB is a complex adaptive system, similar to an ecosystem.
A complex adaptive system is a self-organizing system with distinctive behaviour that emerges from interactions between its components in a manner that is usually not easy to predict 5 . Components might include individuals and their activities; material parts, such as technologies; and the ideas generated from these interactions 6 .
Effective management of this complex adaptive system is fundamental to the LMB’s success. Through continual adaptation and evolution, the LMB can generate new knowledge more effectively than most other institutions can.
For example, the LMB helped to develop cryo-EM for application in the biological sciences through collaborative efforts involving scientists and engineers and the integration of software and advanced cooling techniques. Rather than one individual orchestrating and coordinating all the steps, this multidisciplinary team exhibited self-organization and iterative adjustments, bound by its shared culture. This allowed the emergence of new solutions, mirroring the adaptability seen in ecosystems.
Lessons and challenges ahead
In our view, the LMB system should be considered a framework for how funding is allocated to basic science more widely. Looking to the future, however, we see three challenges that the LMB and the life-sciences community will need to overcome.
First, scientific questions in the basic biosciences are becoming more complex, requiring ever more sophisticated and expensive equipment 7 . Developing such tools might be beyond the capability of one lab, and wider institutional collaborations will be required.

The Medical Research Council’s Laboratory of Molecular Biology in 2021. Credit: MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
Second, institutions dedicated to basic life sciences are increasingly urged by funders and society to transition quickly into clinical applications, which risks undermining the quality and competitive edge of their fundamental research 8 . The gap between fundamental bioscience and clinical translation is notoriously hard to bridge 9 (see also Nature 453 , 830–831; 2008 ). It is also high risk.
In recent years, some funders have pulled out of basic bioscience. For example, more of the US National Institutes of Health’s extramural funding over the past decade has gone to translational and applied research than to basic science (see Science 382 , 863; 2023 ). Some highly reputable basic-science research institutions have suffered as a result and have even been dissolved, such as the Skirball Institute in New York City 10 . However, it is crucial to resist the temptation of dismantling basic science research, considering the complexity and difficulty of re-establishing it.
In response, a lab such as the LMB might enhance the translation of its discoveries by strengthening connections with the clinical academic sciences and private-sector industries. Leveraging strengths in the pharmaceutical industry — in areas such as artificial intelligence and in silico modelling — can bolster basic science without compromising a research lab’s focus. The LMB’s Blue Sky collaboration with the biopharmaceutical firm AstraZeneca is a step in this direction (see go.nature.com/3rnsvyu ).
Third, it is becoming increasingly challenging for basic science labs to recruit and retain the best scientific minds. Translational research institutes are proliferating globally. Biotechnology and pharma firms can pay higher salaries to leading researchers. And researchers might be put off by the large failure rates for high-risk projects in fundamental research, as well as by the difficulties of getting tenure in a competitive lab such as the LMB.
As a first step, governments must recognize these issues and continue to fund high-quality, high-impact fundamental science discoveries. The use of effective research-management strategies such as the LMB’s will make such investments a better bet, de-risking discovery for the long-term benefit of society.
Nature 630 , 813-816 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-02085-2
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology. Quinquennial Review 2021 (MRC LMB, 2021).
Google Scholar
Nightingale, P. Res. Policy 27 , 689–709 (1998).
Article Google Scholar
Tansey, E. M. & Catterall, P. P. Contemporary Record 9 , 409–444 (1995).
Mintzberg, H. & Waters, J. A. Strat . Mgmt J. 6 , 257–272 (1985).
Markose, S. M. Econ. J. 115 , F159–F192 (2005).
Velu, C. Business Model Innovation: A Blueprint for Strategic Change (Cambridge Univ. Press, 2024).
Park, M., Leahey, E. & Funk, R. J. Nature 613 , 138–144 (2023).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Kupferschmidt, K. Science 370 , 392 (2020).
Spector, J. M., Harrison, R. S. & Fishman, M. C. Sci. Transl. Med. 10 , eaaq1787 (2018).
Sfeir, A. et al. Cell 185 , 755–758 (2022).
Perutz, M. F., Kendrew, J. C. & Watson, H. C. J. Mol. Biol. 13 , 669–678 (1965).
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Supplementary Information
- Supplementary figures, methodology, quotes and acknowledgements
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Related Articles

- Research management
- Molecular biology
- Scientific community

What it means to be a successful male academic
Career Column 26 JUN 24

How I’m using AI tools to help universities maximize research impacts
World View 26 JUN 24

Is science’s dominant funding model broken?
Editorial 26 JUN 24

How researchers navigate a PhD later in life
Career Feature 25 JUN 24
Mechanism for the initiation of spliceosome disassembly
Article 26 JUN 24
Programmable RNA-guided enzymes for next-generation genome editing
News & Views 26 JUN 24

Bridge RNAs direct programmable recombination of target and donor DNA
Postdoctoral Associate- Statistical Genetics
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Senior Research Associate (Single Cell/Transcriptomics Senior Bioinformatician)
Metabolic Research Laboratories at the Clinical School, University of Cambridge are recruiting 3 senior bioinformatician specialists to create a dynam
Cambridge, Cambridgeshire (GB)
University of Cambridge
Cancer Biology Postdoctoral Fellow
Tampa, Florida
Moffitt Cancer Center
Postdoctoral Scholar - Physiology
Postdoctoral Scholar - Physiology-Epigenetic and Exosomal regulation of cardiovascular and renal function
Memphis, Tennessee
The University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC)
Postdoctoral fellow – iPSC generation for modeling genetic disorders
Postdoctoral fellow – iPSC generation for modeling genetic disorders – Mayo Clinic
Rochester, Minnesota (US)
Mayo Clinic
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Snapsolve any problem by taking a picture. Try it in the Numerade app?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A laboratory has rules that the employees have to follow so that they don't find themselves being harmed during their time of practice, these rules include: (1). No eating and drinking in the lab. (2). No use of cell phones in the lab. (3). No smelling or inhaling anything in the lab. (4).
You should never enter a lab just in your everyday clothes. The most important parts of your body should be covered - your eyes, hands, hair, and shoes. This helps minimize exposure to any toxic or dangerous fluids, even hot surfaces. Never play with open flames, even if you have done this outside the laboratory area.
Conclusion. The adherence to laboratory safety rules and guidelines cannot be overemphasized and with reports of a continually high number of accidents in academic and research laboratories, a culture of safety has to be ingrained in every staff, student, or researcher working in these spaces.
Don't Eat or Drink in the Laboratory. Save your snacking for the office, not the lab. Don't eat or drink in the science laboratory. Don't store your food or beverages in the same refrigerator that contains experiments, chemicals, or cultures. There is too much risk of contaminating your food.
If you are the last person to leave the lab, make sure to lock all the doors and turn off all ignition sources. Do not work alone in the lab. Never leave an ongoing experiment unattended. Never lift any glassware, solutions, or other types of apparatus above eye level. Never purposefully smell or taste chemicals.
Introduction. What Is Lab Safety And Why Is It Important. It protects you from unnecessary injury and prevents loss of life. It teaches you how to conduct yourself professionally. It promotes a spirit of teamwork and accountability. It educates people on potential hazards in the lab. It brings peace of mind to teachers.
Preventing Accidents. Lab safety rules are designed to mitigate the risk of accidents and mishaps that could have severe consequences. Accidental spills, fires, explosions, or chemical reactions gone awry can lead to injuries, property damage, and even loss of life.
Students should wear the necessary gear, such as lab coats, safety goggles, gloves, and closed-toe shoes, to protect themselves from chemical spills, splashes, and other accidents. Properly fitted PPE can significantly reduce the risk of exposure and injury. 3. Preventing accidents with good lab hygiene.
Lab rules play a vital role in promoting ethical conduct within the scientific community. Here are several reasons why lab rules are crucial for upholding ethical standards: 2.1. Preventing Plagiarism and Data Manipulation. Lab rules often include guidelines on authorship, data handling, and reporting.
Follow these 10 rules to protect yourself and others and get the most from your lab experience. Follow the Instructions. The most important lab safety rule is to follow the instructions. Read or listen to instructions and get answers to questions before you start lab work. This is the most important rule because if you don't follow it: You ...
1219 Words5 Pages. Laboratory is one of the chief causes of accidents and, because it involves the human element, is one of the most difficult to cope with. The purpose of this is to help the lab students to understand proper laboratory safety, to increase their awareness of the possible risks or hazards involved with laboratory work and to ...
Title: The Paramount Significance of Lab Safety: Protecting Lives and Advancing Science Introduction Laboratories are the heart of scientific exploration and discovery, where groundbreaking research and experiments take place daily. They are the birthplace of innovations that revolutionize industries and improve our quality of life. However, amidst the excitement of scientific pursuits, it is ...
Why are lab rules important essay - Intro. If we solely focused on our desired results without considering the moral dilemma that may sometimes accompany them, then it would be close to impossible to maintain order. As a way of maintaining these policies, many countries have decided to turn them into laws because they maintain the safety of ...
Lab safety glasses often have shatter-resistant lenses and are designed to stop large objects from injuring eyes. Lab safety goggles may be a better fit if your lab workers regularly deal with chemicals, bloodborne pathogens or other substances that produce mists, vapors or fumes.
There are many different aspects to laboratory safety, including chemical hygiene, hazard identification and risk assessment, as well as work-place injury prevention. Laboratory accidents can occur at any time and could result in serious injury or even death. One of the most common accidents in the lab are chemical fires.
Lab safety is important because it keeps people from getting severely injured. Proper lab rules are important because they keep people from getting hurt. Lab safety is rules that are used in every lab to keep everyone safe. If you do not follow the lab safety rules then you could get hurt. Proper lab safety prevents cross contamination.
Why Is Lab Safety Important Essay. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. HACCP is a systematic preventive approach to food safety from chemical and physical hazards in the production process that can cause the unfinished product to be unsafe.
First, goggles must be worn always while working in the lab. The eyes are most vulnerable of endangerment because they are usually the first ones to be affected. While doing a lab fumes are always around in the air that can burn the eyes, sharp objects can become projectiles, and chemicals can splash which can then get in the eyes.
The two things to always remember when working in a lab is safety and that lab is a privilege. The Lab is a privilege each student is lucky to have, without it the students would not be able to conduct experiments in the laboratory. One of the most important reasons why students should always be safe is because many things in the lab can be ...
why rules are important. Rules are very important. Rules help our country function and without rules we would fall into chaos. It keeps boundaries on what we can and cannot do. Rules help keep peace and order‚ keep things fair and keep people safe. First rules keep peace and order. Without rules people would be out of control.
Explanation: Lab rules are important in ensuring safety, accuracy, and consistency during scientific experiments. They provide guidelines for handling equipment and chemicals, as well as maintaining a controlled environment. For example, wearing safety goggles and lab coats can protect eyes and skin from hazardous substances.
The Medical Research Council's Laboratory of Molecular Biology (LMB) in Cambridge, UK, is a world leader in basic biology research. The lab's list of breakthroughs is enviable, from the ...
why rules are important. Rules are very important. Rules help our country function and without rules we would fall into chaos. It keeps boundaries on what we can and cannot do. Rules help keep peace and order‚ keep things fair and keep people safe. First rules keep peace and order. Without rules people would be out of control.
Hi in this question, we need to discuss about the lap safety rules, so you aid in preventing you aid in preventing or eliminating his arts by being familiar with the laboratory. You are working with working in and by constantly gathering to the correct safety protocol safety protocol. So, additionally, you will be aware of what to do in thin the…