- Wealth Management
- IT Services
- Client Login
- (847) 247-8959


February 27, 2024
How to create a business budget: 8 simple steps.

No matter the size of your business, a business budget is vital to planning and guiding your business’s growth. By understanding the fixed expenses of a company and accounting for the ebb and flow of work, a proper business budget can help your business maintain itself through the year and create protection around unplanned expenses through well allocated funds. In this guide, we'll walk you through the process of creating a business budget, outlining essential steps to help you manage your finances effectively.
What Is a Business Budget?
A business budget is a financial plan outlining projected revenues and expenses for a business during a specific period of time (most typically a year, though there are often monthly or quarterly reexaminations). Although there are variables throughout the year, a complete and accurate budget will serve as a blueprint for businesses in managing income and expenditures, guiding decision-making processes, and ensuring financial stability.
What Should a Business Budget Include?
A comprehensive business budget’s purpose is to provide a business a holistic view of their financial health. When looking through bank statements, take note of those expenses that reoccur throughout the year and note those—as well as those unexpected expenses your company should instead anticipate. Key components to include are:
- Revenue Forecast: Anticipated income from sales, services, or other sources after deducting costs, taxes, and other fees.
- Fixed Operating Expenses: Costs associated with running the business, such as rent, utilities, salaries, and supplies.
- Capital Expenditures: Investments in assets like equipment, machinery, or property.
- Debt Service: Payments towards loans, credit lines, or other forms of debt.
- Taxes: Estimated tax liabilities, including income tax, sales tax, and payroll taxes.
- Contingency Funds: Reserves set aside for unexpected expenses or emergencies.
- Profit Targets: Desired levels of profitability, indicating the financial performance you aim to achieve.
Why Is Budgeting Important to a Business?
Budgeting plays a crucial role in the financial management of a business for several reasons:
- Resource Allocation: Helps allocate resources efficiently to prioritize essential activities and investments.
- Financial Control: Provides a framework for monitoring and controlling expenses to prevent overspending.
- Performance Evaluation: Facilitates performance measurement against predetermined targets, enabling timely corrective actions.
- Decision Making: Guides decision-making processes by providing insights into the financial implications of various options.
- Risk Management: Identifies potential risks and allows for proactive mitigation strategies to safeguard financial stability.

How Does Budgeting Help a Business?
Effective budgeting contributes to the success and sustainability of a business in numerous ways:
- Improved Cash Flow Management: Helps maintain adequate cash reserves to meet financial obligations and fund growth initiatives.
- Enhanced Profitability: Enables businesses to identify opportunities for revenue growth and cost optimization, leading to higher profitability.
- Better Resource Utilization: Ensures optimal utilization of resources by aligning expenditures with strategic priorities and operational needs.
- Increased Financial Transparency: Provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of the company's financial health and performance.
- Long-term Planning: Facilitates long-term planning by forecasting future financial requirements and setting achievable goals.
How to Create a Business Budget
Now that we’ve gone over the importance of a business budget, it’s time to understand the steps you need to take in order to create a comprehensive plan.
Gather Financial Information
Start by compiling relevant financial data, including past income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. Analyze historical trends to identify patterns and make informed projections for the upcoming period.
Determine Your Financial Goals
Define clear, measurable financial goals aligned with your business objectives. Whether it's increasing revenue, reducing costs, or improving profitability, setting specific targets will provide a roadmap for your budgeting process.
Identify Revenue Sources
Identify all potential sources of revenue, including sales, services, investments, and other income streams. Estimate the expected revenue for each source based on market trends, historical data, and sales forecasts.
Estimate Expenses
Next, list all anticipated expenses, categorizing them into fixed and variable costs. Fixed expenses, such as rent and salaries, remain constant regardless of business activity, while variable expenses, like supplies and utilities, fluctuate based on demand.
Factor in Contingencies & Emergency Funds
Allocate a portion of your budget for contingencies and emergency funds to cover unforeseen expenses or revenue shortfalls. Building a financial cushion will provide stability and resilience during challenging times.
Balance Your Budget
Balance your budget by ensuring that projected revenues exceed estimated expenses. If there's a deficit, identify areas where you can reduce costs or increase revenue to achieve equilibrium.
Monitor & Track Your Budget
Regularly monitor and track your budget against actual financial performance to identify variances and deviations. Use accounting software or spreadsheets to update your budget and make adjustments as needed to stay on course.
Review & Adjust Budget Regularly
Review your budget periodically, ideally on a quarterly or annual basis, to assess its effectiveness and relevance. Adjust your budget as necessary based on changing market conditions, business priorities, and performance trends.
Contact Mowery & Schoenfeld for Help with Business Budgeting
Creating and managing a business budget requires expertise and strategic planning. At Mowery & Schoenfeld, we specialize in helping businesses develop robust financial strategies to achieve their financial goals. Contact us today to learn how our team of experienced professionals can assist you with business budgeting and financial management.
How to Write a Small Business Financial Plan

Noah Parsons
4 min. read
Updated April 22, 2024
Creating a financial plan is often the most intimidating part of writing a business plan.
It’s also one of the most vital. Businesses with well-structured and accurate financial statements are more prepared to pitch to investors, receive funding, and achieve long-term success.
Thankfully, you don’t need an accounting degree to successfully create your budget and forecasts.
Here is everything you need to include in your financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid , and free templates.
- Key components of a financial plan
A sound financial plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
Sales forecast
What do you expect to sell in a given period? Segment and organize your sales projections with a personalized sales forecast based on your business type.
Subscription sales forecast
While not too different from traditional sales forecasts—there are a few specific terms and calculations you’ll need to know when forecasting sales for a subscription-based business.
Expense budget
Create, review, and revise your expense budget to keep your business on track and more easily predict future expenses.
How to forecast personnel costs
How much do your current, and future, employees’ pay, taxes, and benefits cost your business? Find out by forecasting your personnel costs.
Profit and loss forecast
Track how you make money and how much you spend by listing all of your revenue streams and expenses in your profit and loss statement.
Cash flow forecast
Manage and create projections for the inflow and outflow of cash by building a cash flow statement and forecast.
Balance sheet
Need a snapshot of your business’s financial position? Keep an eye on your assets, liabilities, and equity within the balance sheet.
What to include if you plan to pursue funding
Do you plan to pursue any form of funding or financing? If the answer is yes, then there are a few additional pieces of information that you’ll need to include as part of your financial plan.
Highlight any risks and assumptions
Every entrepreneur takes risks with the biggest being assumptions and guesses about the future. Just be sure to track and address these unknowns in your plan early on.
Plan your exit strategy
Investors will want to know your long-term plans as a business owner. While you don’t need to have all the details, it’s worth taking the time to think through how you eventually plan to leave your business.
- Financial ratios and metrics
With your financial statements and forecasts in place, you have all the numbers needed to calculate insightful financial ratios.
While including these metrics in your plan is entirely optional, having them easily accessible can be valuable for tracking your performance and overall financial situation.
Key financial terms you should know
It’s not hard. Anybody who can run a business can understand these key financial terms. And every business owner and entrepreneur should know them.
Common business ratios
Unsure of which business ratios you should be using? Check out this list of key financial ratios that bankers, financial analysts, and investors will want to see.
Break-even analysis
Do you want to know when you’ll become profitable? Find out how much you need to sell to offset your production costs by conducting a break-even analysis.
How to calculate ROI
How much could a business decision be worth? Evaluate the efficiency or profitability by calculating the potential return on investment (ROI).
- How to improve your financial plan
Your financial statements are the core part of your business plan that you’ll revisit most often. Instead of worrying about getting it perfect the first time, check out the following resources to learn how to improve your projections over time.
Common mistakes with business forecasts
I was glad to be asked about common mistakes with startup financial projections. I read about 100 business plans per year, and I have this list of mistakes.
How to improve your financial projections
Learn how to improve your business financial projections by following these five basic guidelines.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- Financial plan templates and tools
Download and use these free financial templates and calculators to easily create your own financial plan.

Sales forecast template
Download a free detailed sales forecast spreadsheet, with built-in formulas, to easily estimate your first full year of monthly sales.
Download Template

Accurate and easy financial forecasting
Get a full financial picture of your business with LivePlan's simple financial management tools.
Get Started
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
- What to include for funding
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Write Your Business Plan Cover Page + Template

10 Min. Read
How to Write a Competitive Analysis for Your Business Plan

How to Set and Use Milestones in Your Business Plan

24 Min. Read
The 10 AI Prompts You Need to Write a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
How to create a business budget
Advertiser disclosure.
We are an independent, advertising-supported comparison service. Our goal is to help you make smarter financial decisions by providing you with interactive tools and financial calculators, publishing original and objective content, by enabling you to conduct research and compare information for free - so that you can make financial decisions with confidence.
Bankrate has partnerships with issuers including, but not limited to, American Express, Bank of America, Capital One, Chase, Citi and Discover.
How We Make Money
The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. This compensation may impact how and where products appear on this site, including, for example, the order in which they may appear within the listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site. We do not include the universe of companies or financial offers that may be available to you.
- Share this article on Facebook Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter Twitter
- Share this article on LinkedIn Linkedin
- Share this article via email Email

- • Small business loans
- • Bad credit loans

- • Funding inequality
- Connect with Emily Maracle on LinkedIn Linkedin
The Bankrate promise
At Bankrate we strive to help you make smarter financial decisions. While we adhere to strict editorial integrity , this post may contain references to products from our partners. Here's an explanation for how we make money .
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. We’ve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts , who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our banking reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most — the best banks, latest rates, different types of accounts, money-saving tips and more — so you can feel confident as you’re managing your money.
Editorial integrity
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that we’re putting your interests first. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions.
Key Principles
We value your trust. Our mission is to provide readers with accurate and unbiased information, and we have editorial standards in place to ensure that happens. Our editors and reporters thoroughly fact-check editorial content to ensure the information you’re reading is accurate. We maintain a firewall between our advertisers and our editorial team. Our editorial team does not receive direct compensation from our advertisers.
Editorial Independence
Bankrate’s editorial team writes on behalf of YOU – the reader. Our goal is to give you the best advice to help you make smart personal finance decisions. We follow strict guidelines to ensure that our editorial content is not influenced by advertisers. Our editorial team receives no direct compensation from advertisers, and our content is thoroughly fact-checked to ensure accuracy. So, whether you’re reading an article or a review, you can trust that you’re getting credible and dependable information.
How we make money
You have money questions. Bankrate has answers. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades. We continually strive to provide consumers with the expert advice and tools needed to succeed throughout life’s financial journey.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy , so you can trust that our content is honest and accurate. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. The content created by our editorial staff is objective, factual, and not influenced by our advertisers.
We’re transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money.
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and, services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
Our writers and editors used an in-house natural language generation platform to assist with portions of this article, allowing them to focus on adding information that is uniquely helpful. The article was reviewed, fact-checked and edited by our editorial staff prior to publication.
Key takeaways
- A business budget is a financial plan that helps estimate a company's revenue and expenses, making it an essential tool for small businesses
- The steps to creating a business budget include choosing budget and accounting software, listing expenses and forecasting revenue
- If a business finds itself in a budget deficit, strategies such as cutting costs, negotiating with suppliers and diversifying revenue streams can help
As a small business owner, keeping your finances organized through a business budget is crucial to running a successful company.
Business budgeting involves creating a financial plan that estimates future revenue and expenses to make informed financial decisions, which can ultimately move the needle on your business’s financial goals and help it grow in profitability.
What is a business budget?
A business budget is a financial plan that outlines the company’s current revenue and expenses. The budget also forecasts expected revenue that can be used for future business activities, such as purchasing equipment. It sets targets for your business’s revenue, expenses and profit and helps you determine if you’ll have more money coming in than you pay out.
A business budget is an essential tool that helps you make wise business decisions. Without it, it’s difficult to gauge your business’s financial health.
What is the difference between a cash flow statement and a business budget?
A cash flow statement (CFS) is a financial document that summarizes the movement of cash coming in and going out of a company. The CFS gauges how effectively a company manages its finances, including how it manages debt responsibilities and funds day-to-day operations.
It’s similar to a business budget in that you can see expenses and revenue. But while a budget gives a moment-in-time snapshot of your business’s financial performance compared to forecasts, the cash flow statement focuses on the actual inflows and outflows of money through your business.
Follow these steps to ensure a well-developed budget, from understanding your expenses to generating revenue and adjusting expenses to balance the budget.
1. Choose a budget and accounting software
First, you’ll want to store your expense and revenue information with accounting software to help you track your numbers and generate reports. Some software may also help you assign categories to the transactions, identify tax deductions and file taxes. Quickbooks is an example of accounting software.
Some business bank accounts also have accounting software built in, helping you stay organized by keeping your accounting and banking in one place.
2. List your business expenses
The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget:
- Fixed expenses: Fixed expenses cost a fixed amount monthly or within the assessed period. Those costs include rent, insurance, salaries and loan payments.
- Variable expenses: Variable expenses can change monthly or over time, making them trickier to budget. This might include materials, direct labor, utility bills or marketing expenses.
- Annual or one-time costs: Some costs only occur a few times per year, while others you’ll only pay for as needed, such as buying new equipment. You still want to budget for these expenses by allocating a portion of your weekly or monthly budget toward one-time expenses.
- Contingency funds: Unexpected business costs can throw a wrench in your budget if not planned for. Such costs could include emergency repairs, necessary equipment purchases, sudden tax increases or unforeseen legal fees. To plan for these costs, you can create a contingency or emergency fund that’s separate from your operational budget.
- Maintenance costs: To allocate funds for maintenance costs, begin by including regular inspections and maintenance in your budget. Then, make sure to leave room for changes and unexpected maintenance costs.
3. Forecast your revenue
To estimate your future revenue, start by deciding on a timeline for your forecast. A good place to start is the previous 12 months. Your accounting software may also include revenue forecasting as one of its features, which can automate this step for you.
The timeline and your recent past growth can help you understand how much revenue you’ll generate in the future. Consider external factors that could drive revenue growth, such as planned business activities like expansion, marketing campaigns or new product launches.
You’ll also want to think about anything that might slow your growth. Many businesses experience seasonal fluctuations, which can impact your budget if you don’t plan for it. To account for these changes, list the minimum expenses required to keep your business running. Use your financial statements to understand these costs, and consider averaging out irregular expenses over the year to avoid surprises.
Ideally, your business should build a cash reserve during profitable periods to cover expenses during slower seasons. If necessary, consider various financing options, such as a business credit card or line of credit, that you can draw from to manage cash flow during peak or off times.
4. Calculate your profits
The next step in creating a business budget is to calculate your business profits. You can look at your total profits by calculating revenue minus expenses. That way, you see how much money you have to work with, called your working capital .
You should also understand your profit margins for each of your products and services, which can help you set prices or decide whether to offer a new product or service.
How to calculate your profit margins
To find out your gross profit margin, you’ll first need to calculate the gross profit. To calculate your business’s gross profit, subtract the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your total revenue. COGS includes all the expenses related to producing your products and services.
Once you have the gross profit, use the gross profit margin formula: (Revenue – COGS) / Revenue x 100. This will give you a percentage that shows how much profit you gain from that particular product after accounting for the product’s costs.
5. Make a strategy for your working capital
Knowing what to do with extra revenue, which is your working capital, is crucial for managing your business finances and growth. Here’s how to get started with a financial strategy that propels your business goals forward:
- Set spending limits for different categories in your budget. When listing your expenses, you should have set a dollar amount for each category. You can estimate this by a monthly average or a general forecasted amount.
- Set realistic short- and long-term goals. These goals will motivate you to stick to your budget and guide your spending decisions.
- Compare your actual spending with your net income and priorities. Look at the areas you’re spending and consider whether you need to reallocate money to different categories. Consider separating expenses into business needs and extras.
- Adjust your budget and actual spending. Adjust your spending to ensure you do not overspend and can allocate money towards your goals. If you need to cut spending, consider the categories that are extras, such as types of marketing that you don’t know will generate a return on investment.
6. Review your budget and forecasts regularly
Finally, review your budget regularly. By frequently checking in on your budget, you can identify any discrepancies between your planned and actual expenses and adjust accordingly. This allows you to proactively handle any financial issues that may arise rather than reacting to them after they’ve become a problem.
Regular reviews also allow you to refine your budgeting process and improve its accuracy over time. Keep in mind that your budget is not set in stone but rather a tool to guide your financial decisions and help you achieve your business goals.
What to do if you have a deficit in your business budget
Finding a deficit in your small business budget can be alarming, but there are several strategies you can employ to handle this situation.
- Do a cash flow analysis. Begin by doing a cash flow analysis to review what your business is earning and spending money on. Identify potential problems and adjust the budget as needed to prevent overspending.
- Cut nonessential business costs. Cutting spending may involve eliminating nonessential costs and transferring funds from other categories to overspent categories. Your goal is a balanced or profitable budget.
- Negotiate with suppliers. Be transparent in your communications with suppliers and explain your quality standards and why you’re seeking cost reduction. Explore options for cost reduction that do not compromise quality, such as process improvements or ordering in larger quantities.
- Create a lean business model. By removing anything that doesn’t benefit your customer, your business can potentially save time and resources. Lean business models focus on continually improving processes and customer experience without adding additional resources, time or funds.
- Add revenue and diversify revenue streams. Raising revenue requires a realistic plan with measurable goals to increase sales and overall business income. You can also consider other products and services you could offer that would make your business profitable.
- Use financing to cover temporary gaps. Applying for a small business loan can help pay bills during an unplanned shortfall. Since this will add an expense to your budget, make sure you can handle the loan repayments and your regular expenses.
- Plan for a deficit. In some cases, a planned budget deficit might be a strategic decision, such as investing in new opportunities that promise long-term benefits.
Bottom line
Having a well-developed business budget is crucial for making informed decisions. You can effectively manage your small business’s finances by tracking and analyzing your business’s inflows and outflows, forecasting your expected revenue and adjusting your budget to stay balanced.
Even in the face of a budget deficit, there are various strategies you can use to keep your business profitable, including negotiating costs with your suppliers, assessing your business operations and offering new products and services.
With a solid business budget in place, you can confidently navigate financial challenges and drive long-term success for your small business.
Frequently asked questions
What are the benefits of a business budget, what are the components of a business budget, how do you calculate fixed and variable costs in a business budget.

Related Articles

How to get an equipment loan

How to finance a small business for the holidays

How to start a small business

How to build business credit: 7 steps
- Building Your Site
- Promote Your Site
- Entrepreneurship
- Design & Inspiration
- Tips & Tricks
Step-by-Step Guide to Creating a Business Budget Plan
A well-structured business budget plan is crucial for success. It serves as a financial stability and growth roadmap, allowing companies to allocate resources wisely and make informed decisions. Understanding the basics of business budgeting is essential for any entrepreneur or business owner looking to create a solid financial plan to help them achieve their goals.
The Importance of Business Budget Planning
Business budget planning is not just about crunching numbers; it's about setting clear financial goals and outlining strategies to achieve them. It provides a framework for managing expenses, maximizing revenue , and ensuring the long-term sustainability of a company. Without a well-thought-out budget plan, businesses may struggle to stay afloat in today's competitive market.
Understanding the Basics of Business Budget
At its core, a business budget is an estimate of future income and expenses based on historical data and current trends. It involves identifying all sources of revenue and categorizing various types of expenses, including fixed costs (rent, salaries) and variable costs (utilities, marketing). Understanding these fundamental concepts is essential for creating an effective budget plan.
Benefits of Creating a Business Budget Plan
The benefits of creating a business budget plan are manifold. It clarifies where money is being spent and helps identify areas where costs can be reduced or investments can be made to drive growth. Additionally, having a well-structured budget plan can instill confidence in stakeholders, such as investors or lenders who want to see evidence of sound financial management .
Now that we've laid the groundwork for understanding the importance of business budget planning and its basics, let's delve deeper into the process by assessing your financial situation and setting achievable goals.
Assessing Your Financial Situation

Sarah Horsman Template from Strikingly
Now that you understand the importance of business budget planning, it's time to assess your financial situation. This involves analyzing your current revenue and expenses, identifying fixed and variable costs, and projecting future income and expenses.
Analyzing Current Revenue and Expenses
You must clearly understand your current revenue and expenses to create a business budget plan that works for your company . This involves looking at your sales figures, incoming cash flow, and all the money going out of your business. By analyzing these numbers, you can gain valuable insights into where your money is coming from and where it's going.
Identifying Fixed and Variable Costs
When creating a business budget plan, it's crucial to distinguish between fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs, such as rent or salaries, remain constant regardless of your level of production or sales. Variable costs, like raw materials or shipping expenses, fluctuate with production levels or sales volume. Identifying these costs will help you make more accurate financial projections.
Projecting Future Income and Expenses
Looking ahead is an essential part of business budget planning. You can anticipate potential financial challenges or opportunities by projecting future income and expenses based on historical data and market trends. This will enable you to make informed decisions about resource allocation and strategic investments.
Remember that creating a business budget plan is not just about crunching numbers; it's about setting the stage for sustainable growth and success in the long run.
Setting Financial Goals
Now that you understand the basics of business budget planning, it's time to set your financial goals . Establishing short-term and long-term objectives can create a roadmap for your business's financial success. Whether increasing revenue or reducing expenses, having clear goals will guide your budgeting decisions.
Establishing Short-term and Long-term Objectives
To effectively create a business budget plan, it's crucial to establish both short-term and long-term financial objectives. Short-term goals could include reducing overhead costs by a certain percentage within six months, while long-term goals might involve doubling your annual revenue within three years. These objectives provide direction for allocating funds and making strategic financial decisions.
Allocating Funds for Growth and Expansion
One of the key benefits of creating a business budget plan is the ability to allocate funds for growth and expansion. Whether you're looking to invest in new equipment, expand your product line, or open additional locations, setting aside funds in your budget allows you to pursue these opportunities without compromising your financial stability .
Planning for Contingencies and Emergencies
In business, unexpected events can have a significant impact on your finances. Planning for contingencies and emergencies is essential when creating a business budget plan. You can protect your business from potential financial hardships by setting aside a portion of your budget for unforeseen circumstances, such as economic downturns or equipment breakdowns.
Creating the Budget Plan
Now that you understand the importance of business budget planning, it's time to create a solid business budget plan. When choosing the right budgeting method, consider your company's size, industry, and financial goals. Whether it's zero- or activity-based budgeting, select a method that aligns with your business objectives and ensures accurate financial management .
Choosing the Right Budgeting Method
Selecting the right budgeting method is crucial for effective business budget planning. Zero-based budgeting involves justifying every expense from scratch, while activity-based budgeting focuses on cost allocation based on activities. Whichever method you choose, ensure it aligns with your company's financial objectives and provides a clear resource allocation roadmap.
Allocating Funds to Different Departments
When creating a business budget plan, allocating funds to different departments is essential based on their specific needs and priorities. Consider departmental goals, operational requirements, and revenue generation potential when distributing financial resources. This approach ensures each department has the necessary funds to function effectively within the business framework.
Monitoring and Adjusting the Budget as Needed
Once you've allocated funds to different departments in your business budget plan, monitoring and adjusting the budget as needed is essential. Regularly review your financial performance against the set targets and adjust based on changing market conditions or internal dynamics. Flexibility ensures that your business remains agile and responsive to evolving economic landscapes.
By carefully choosing the right budgeting method, allocating funds to different departments thoughtfully, and monitoring and adjusting the budget as needed, you can create a robust business budget plan that sets your company up for long-term success in managing its finances effectively.
Implementing the Budget Plan

Quantum Template from Strikingly
Now that you have created a solid business budget plan, it's time to implement it. This step involves communicating the budget to key stakeholders, training employees on budgetary guidelines, and integrating the budget into daily operations.
Communicating the Budget to Key Stakeholders
It is crucial to inform all relevant stakeholders about the business budget plan. This includes shareholders, managers, and other decision-makers who must know the financial goals and constraints. Clear communication will ensure everyone is on the same page and can work towards common objectives.
Training Employees on Budgetary Guidelines
Employees play a vital role in adhering to the budget plan. Providing them with comprehensive training on budgetary guidelines will help them understand their responsibilities in managing costs and staying within allocated funds. This will empower them to make informed decisions that align with the company's financial objectives.
Integrating the Budget into Daily Operations
Incorporating the business budget plan into daily operations requires a strategic approach. It involves aligning all activities with the financial goals outlined in the budget, ensuring that resources are utilized efficiently, and making adjustments as needed to stay within budgetary limits. This integration fosters a culture of financial responsibility throughout the organization.
By effectively implementing your business budget plan through clear communication, employee training, and seamless integration into daily operations, you can set your company up for financial success while achieving your long-term objectives.
Tracking and Evaluating Performance

Monitoring Budget Variance and Deviations
Once you have implemented your business budget plan, it's crucial to regularly monitor the budget variance and identify any deviations from the projected expenses and revenue. This will help you understand where adjustments need to be made and where you may exceed or fall short of your financial goals.
Conducting Regular Financial Reviews
Regular financial reviews are essential for evaluating the performance of your business budget plan. By conducting these reviews, you can assess whether your actual income and expenses align with what was projected in the budget. This will allow you to make informed decisions on where to allocate funds or where to cut back to stay on track with your financial objectives.
Making Informed Decisions Based on Budget Analysis
Analyzing the data from your business budget plan is key to making informed decisions for your company's future. By understanding how well your budget is performing, you can strategically plan for growth, expansion, and any potential contingencies or emergencies that may arise.
Continuously tracking and evaluating the performance of your business budget plan is vital for maintaining financial stability and achieving long-term success. By closely monitoring variance, conducting regular reviews, and making informed decisions based on budget analysis, you can ensure that your business stays on track toward its financial goals.
Tips for Successfully Implementing Your Business Budget Plan: Striking a Balance Between Dreams and Dollars
Every business owner knows the importance of a budget—it's the roadmap to financial stability and growth. But crafting a brilliant budget is only half the battle. The real test lies in implementation. How do you translate those meticulously planned numbers into tangible results? Here are some key tips to ensure your business budget plan becomes a reality, not just a document gathering dust on a shelf:
1. Set SMART Goals
Your budget shouldn't exist in a vacuum. It should be tightly woven into your business goals. But instead of vague aspirations, set SMART goals: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound . This clarity provides a clear direction for allocating resources and tracking progress.
2. Foster Collaboration
Budgeting isn't a solo act. Involve key stakeholders in the process, from department heads to team members. This collaborative approach fosters buy-in, ensures everyone understands their role in achieving financial goals, and harnesses diverse perspectives for smarter decision-making.
3. Embrace Transparency
Open communication is crucial. Share the budget with relevant team members, not just financial experts. This transparency builds trust, empowers employees to make informed decisions, and encourages a culture of financial responsibility.
4. Track and Monitor
Don't let your budget become a static document. Regularly track actual spending against the planned figures. Identify any discrepancies, analyze the causes, and make adjustments as needed. This active monitoring allows you to course-correct before small deviations snowball into major issues.
5. Leverage Technology

Strikingly Landing Page
- Easy to use. Strikingly is a user-friendly platform that is easy to use, even for those without experience in website design .
- Affordable. Strikingly offers a variety of affordable plans to fit any budget.
- Mobile-friendly. Strikingly's websites are mobile-friendly, so you can reach your customers wherever they are.

Strikingly Website on a Mobile Device
- SEO-friendly. Strikingly's websites are SEO-friendly so that you can improve your website's ranking in search results.
Strikingly is a valuable tool to help businesses create and manage their online presence . Strikingly's features can also be helpful for businesses when creating a business budget plan.
6. Review and Adapt
The business landscape is dynamic. Be prepared to adapt your budget as circumstances change. Regularly review your plan, considering market shifts, new opportunities, and unforeseen challenges. A flexible approach ensures your budget remains relevant and responsive to the ever-evolving environment.
7. Celebrate Successes
Don't forget to celebrate your wins! Recognizing positive financial milestones and acknowledging the collective effort motivates everyone and reinforces the importance of adhering to the budget plan.
8. Build a Culture of Accountability
Create a culture where all share financial responsibility. Hold yourself and your team accountable for staying within budget limits. This fosters a sense of ownership and promotes responsible financial behavior across the organization.
9. Communicate Effectively
Regularly communicate budget updates, performance metrics, and any necessary adjustments to the team. This transparency keeps everyone informed, engaged, and empowered to contribute to the business's financial success.
10. Continuously Improve
Never stop learning and evolving. Regularly evaluate your budgeting process, identify areas for improvement, and implement new strategies to optimize your financial management. Remember, a successful budget is a living document, constantly adapting and growing alongside your business.
By following these tips and embracing tools like Strikingly , you can transform your business budget plan from a theoretical framework into a powerful tool for driving growth and achieving your financial aspirations. Remember, successful budgeting is a journey, not a destination. It requires ongoing commitment, collaboration, and a continuous focus on improvement. So, embark on your financial journey confidently and watch your business reach new heights of success.
A well-structured business budget plan can lead to long-term financial stability and growth. It helps identify areas for cost savings, allocate funds for expansion, and plan for contingencies, ultimately leading to improved profitability and sustainability for your business.
Remember that creating a well-structured business budget plan is crucial for the success and sustainability of your business. By following these steps and incorporating these tips into your planning process, you can ensure that your business is on the path to financial success and growth.
Trusted by millions of entrepreneurs & creatives.
How to Create a Small Business Budget in 5 Simple Steps
Want to protect the financial health of your small business? You need a business budget. Here's how to create one.

When you build a business, there are a lot of things to stay on top of, from marketing and finding new clients to building a website and establishing your digital presence. But there’s one element that you want to stay on top of from the very beginning—and that’s your business budget.
Having a detailed and accurate budget is a must if you want to build a thriving, sustainable business. But how, exactly, do you create one? What are the steps for business budget planning?
As a small business owner, let’s take a look at how to create a business budget in five simple, straightforward steps.
What’s a Business Budget—and Why Is It Important?
Before we jump into creating a business budget, let’s quickly cover what a business budget is—and why it’s so important for small businesses.
A business budget is an overview of your business funds. It outlines key information on both the current state of your finances (including income and expenses) and your long-term financial goals. Because your budget will play a key role in making sound financial decisions for your business, it should be one of the first tasks you tackle to improve business success.
And, as a financially savvy owners, you’ll also want to have a budget in place to help you:
- Make sound financial decisions. In many ways, your business budgets are like a financial road map. It helps you evaluate where your business finances currently stand—and what you need to do to hit your financial goals in the future for business growth.
- Identify where to cut spending or grow revenue. Your business budgets can help you identify areas to decrease your spending or increase your revenue, which will increase your profitability in the process, outline unexpected costs, and help your sustain your business goals.
- Land funding to grow your business. If you’re planning to apply for a business loan or raise funding from investors, you’ll need to provide a detailed budget that outlines your income and expenses.
Now that you understand why budget creation is so important to your business decisions, let’s jump into how to do it.
Business Budget Step 1: Tally Your Income Sources

First things first. When building a small business budget, you need to figure out how much money your business is bringing in each month and where that money is coming from – this will hep create an operating budget based on your business income.
Your sales figures (which you can access using the Profit & Loss report function in FreshBooks) are a great place to start. From there, you can add any other sources of income for your business throughout the month.
Your total number of income sources will depend on your business model.
For example, if you run a freelance writing business, you might have multiple sources of income from:
- Freelance writing projects
- A writing course you sell on your website
- Consulting with other writers who are starting small businesses
Or, if you run a brick-and-mortar retail business, you may only have one source of income from your store sales.
However many income sources you have, make sure to account for any and all income that’s flowing into your business—then tally all those sources to get a clear picture of your total monthly income to build your master business budget template.
Business Budget Step 2: Determine Fixed Costs
Once you’ve got a handle on your income, it’s time to get a handle of your costs—starting with fixed costs.
Your fixed costs are any expenses that stay the same from month to month. This can include expenses like rent, certain utilities (like internet or phone plans), website hosting, and payroll costs.
Review your expenses (either via your bank statements or through your FreshBooks reports) and see which costs have stayed the same from month to month. These are the expenses you’re going to categorize as fixed costs.
Once these costs are determined, add them together to get your total fixed and variable costs expense for the month.
TIP: If you’re just starting your business and don’t have financial data to review, make sure to use projected costs. For example, if you’ve signed a lease for office space, use the monthly rent you will pay moving forward.
Business Budget Step 3: Include Variable Expenses
Related articles.

Variable costs don’t come with a fixed price tag—and will vary each month based on your business performance and activity. These can include things like usage-based utilities (like electricity or gas), shipping costs, sales commissions, or travel costs.
Variable expenses will, by definition, change from month to month. When your profits are higher than expected, you can spend more on the variables that will help your business scale faster. But when your profits are lower than expected, consider cutting these variable costs until you can get your profits up.
At the end of each month, tally these expenses. Over time, you’ll get a sense of how these expenses fluctuate with your business performance or during certain months, which can help you make more accurate financial projections and budget accordingly.
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends
Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they’re fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don’t forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
If you know you have one-time spends on the horizon (for example, an upcoming business course or a new laptop), adding them to your budget can help you set aside the financial resources necessary to cover those expenses—and protect your business from unexpected costs in the form of a sudden or large financial burden.
On top of adding planned one-time spends to your budget, you should also add a buffer to cover any unplanned purchases or expenses, like fixing a damaged cell phone or hiring an IT consultant to deal with a security breach. That way, when an unexpected expense pops up (and they always do), you’re prepared!
Business Budget Step 5: Pull It All Together
You’ve gathered all of your income sources and all of your revenue and expenses. What’s next? Pulling it all together to get a comprehensive view of your financial standing for the month.
On your businesses master budget, you’ll want to tally your total income and your total expenses (i.e., adding your total fixed costs, variable expenses, cost of goods, and one-time spends)—then compare cash flow in (income) to cash flow out (expenses) to determine your overall profitability.
Having a hard time visualizing what a business budget looks like in action? Here’s an operating budget example to give you an idea of what your new business budget might look like each month:
A Client Hourly Earnings: $5,000 B Client Hourly Earnings: $4,500 C Client Hourly Earnings: $6,000 Product Sales: $1,500 Loans: $1,000 Savings: $1,000 Investment Income: $500
Total Income: $19,500
Fixed Costs
Rent: $1,000 Internet: $50 Payroll costs: $5,000 Website hosting: $50 Insurance: $50 Government and bank fees: $25 Cell phone: $50 Accounting services : $100 Legal services: $100
Total Fixed Costs: $6,425
Variable Expenses
Sales commissions: $2,000 Contractor wages: $500 Electricity bill: $125 Gas bill: $75 Water bill: $125 Printing services: $300 Raw materials: $200 Digital advertising costs: $750 Travel and events: $0 Transportation: $50
Total Variable Expenses: $4,125
One-Time Spends
Office furniture: $450 Office supplies for new location: $300 December business retreat: $1,000 New time tracking software: $500 Client gifts : $100
One-Time Spends: $2,350
Expenses: $12,900
Total Income ($19,500) – Total Expenses ($12,900) = Total Net Income ($6,600)
Above all, once you have a clear sense of your profitability for the month, you can use it to make the right financial decisions for your small business moving forward.

For example, if you realize you’re in the red and spending more than you earn, you might cut your spending and focus on finding new clients . Alternatively, if your income is significantly higher than your expenses, you might consider investing your profits back into your business (like investing in new software or equipment).
Use Your Business Budget to Stay on Track
Putting in the work to create a budget for your small business may seem like a hassle. But while it takes a bit of time and energy, it’s worth the extra effort. Thorough business budgeting gives you the financial insights you need to make the right decisions for your business to grow, scale, and prosper in the future.
This post was updated in October 2023

Written by Deanna deBara , Freelance Contributor
Posted on June 20, 2017
Freshly picked for you

Thanks for subscribing to the FreshBooks Blog Newsletter.
Expect the first one to arrive in your inbox in the next two weeks. Happy reading!
Free Business Budget Templates for Any Company
By Andy Marker | February 23, 2017
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Creating a budget is always a good idea, but it’s even more crucial when you run a business. Failure to properly budget can seriously impact your bottom line, and even jeopardize the success of your enterprise. By making and following a budget, you can better control costs, avoid overspending, and plan to meet financial goals.
Of course, you’ll also need to document and track your budget. Using business budgeting worksheets for this purpose can help you:
- Set and achieve profit goals
- Track revenue, expenses, and cash flow
- Cut unnecessary spending
- Properly allocate revenue to other areas of the business
- Prepare for busy seasons and slowdowns
- Plan for required purchases, such as equipment and materials
- Gauge the positive impact of budget changes
- Secure funding from current and potential investors or financial institutions
- Keep colleagues and coworkers informed on the financial health of the business
- Project startup costs, monthly operational expenses, and revenue needed to break even
To help you get started, we’ve created a variety of business budget templates for Excel that you can use for any organization - from startup companies to established enterprises. Download the template that best fits your needs, and start planning for financial success.
Business Budget Template
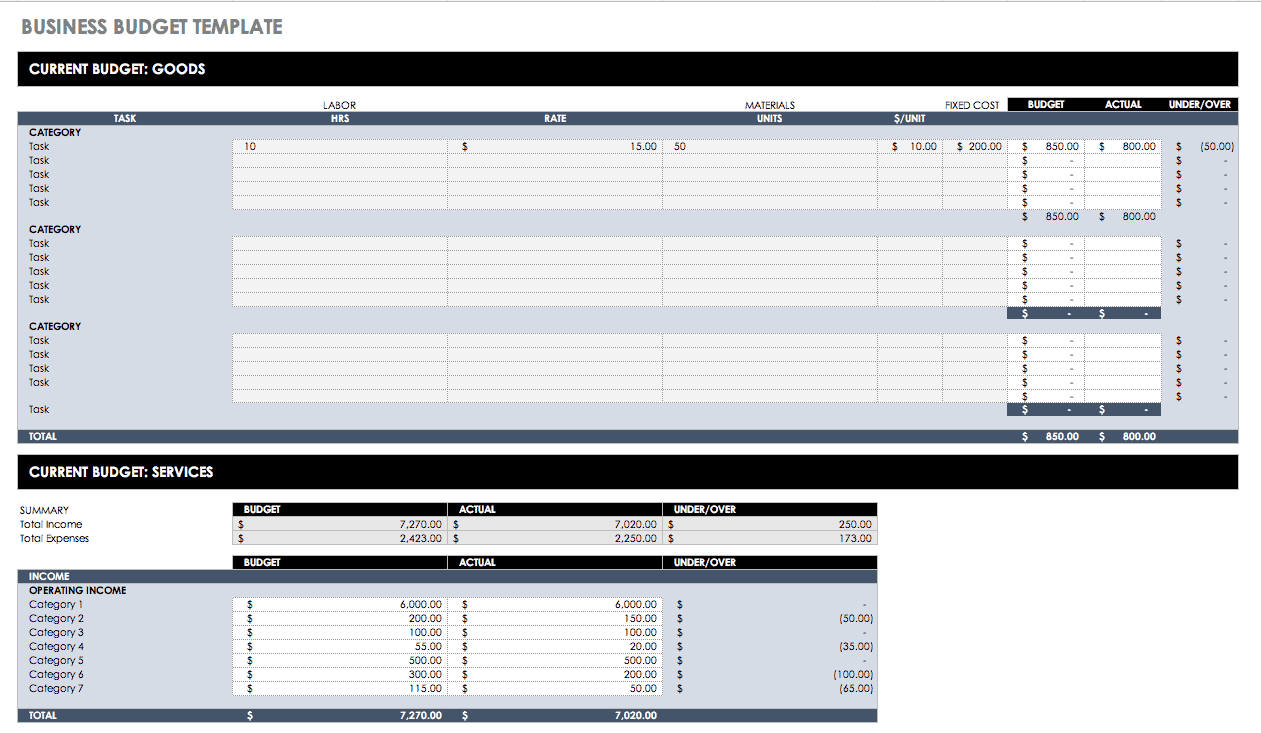
Download Excel Template
Try Smartsheet Template
Use this basic business budgeting template to track monthly income and expenses for companies of any size. This template has separate sheets to create budgets for either services- or goods-based businesses. Income and expenses are also broken down by category to provide a closer look at where company funds are made and spent.
12-Month Business Budget Template
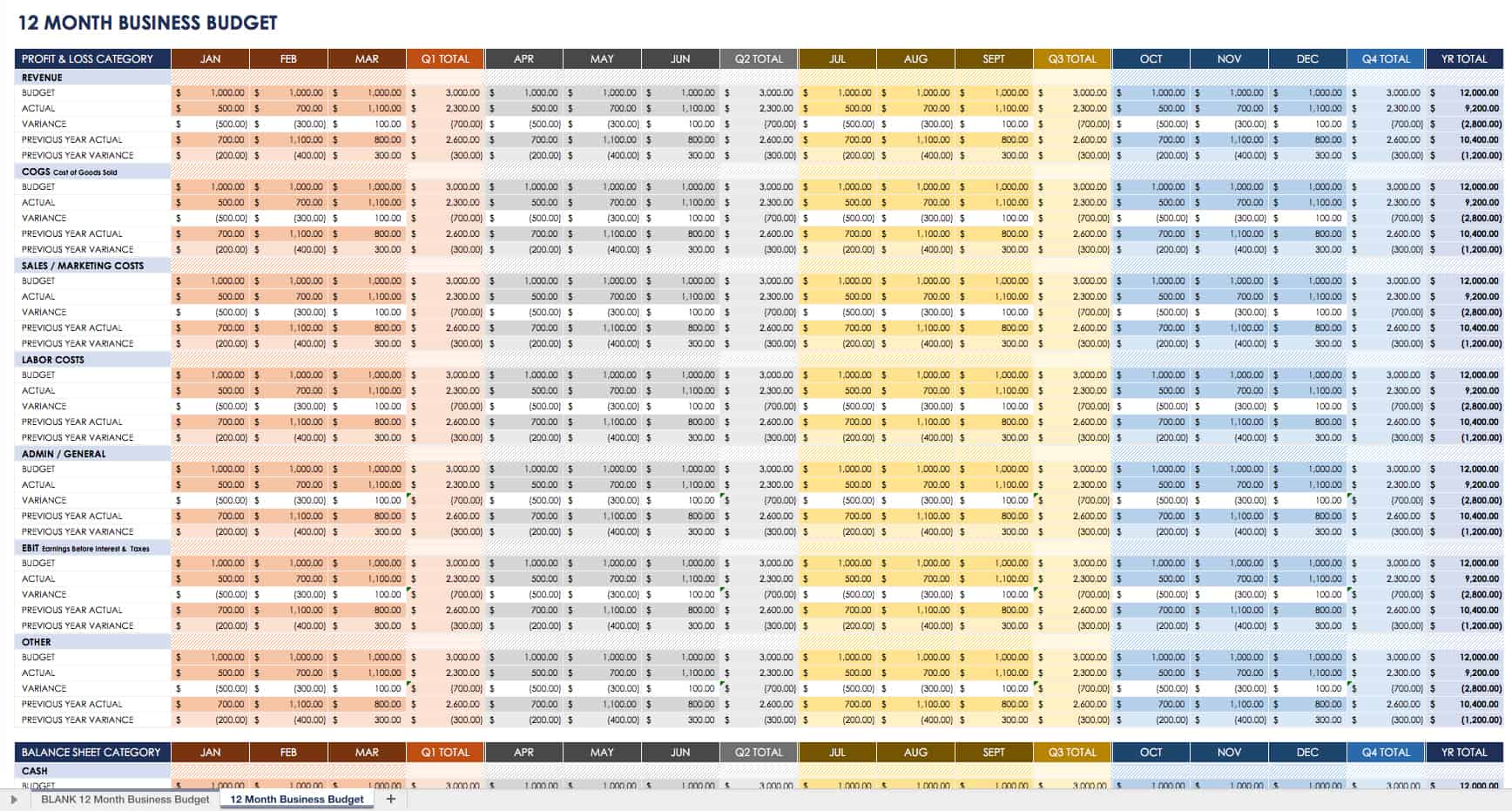
For a more detailed view of your company’s financials over time, use this business budgeting spreadsheet. Enter your revenue and expense estimations for each month and the entire year. Then, add your actual income and expenditures month by month to see how closely you’re meeting your budget (the accuracy of your estimates). Income and expense categories are broken out, so you can clearly see where funds are going to and coming from.
Department Budget
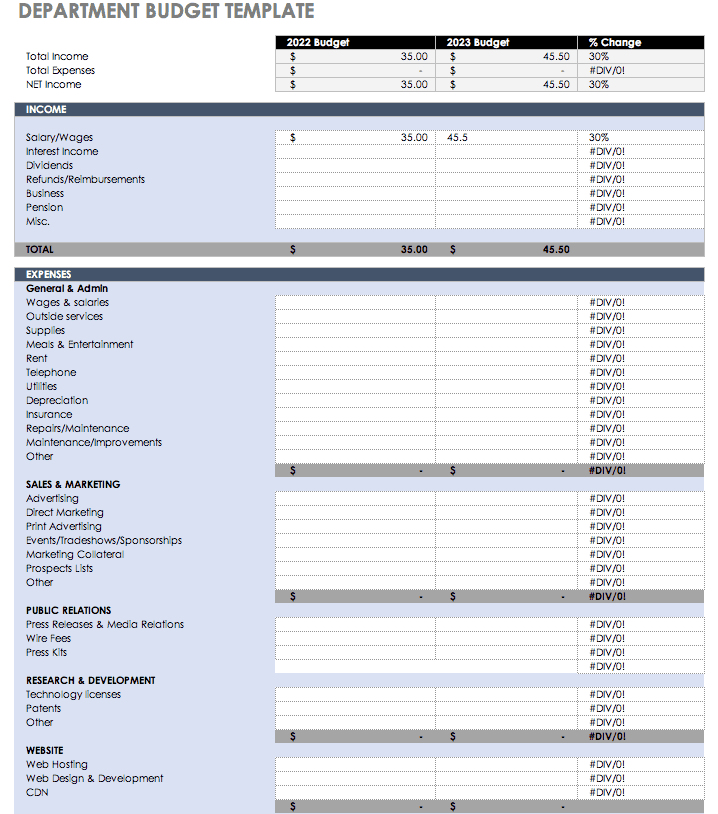
To make sure your department is staying within its allotted budget, use this Excel business budget template. It allows you to plot yearly income and expenses for a company or academic department, and compare the percentage change year over year. View revenue and expense subtotals by category to see where you can make cuts, and identify any surpluses.
Detailed Financial Projections Spreadsheet
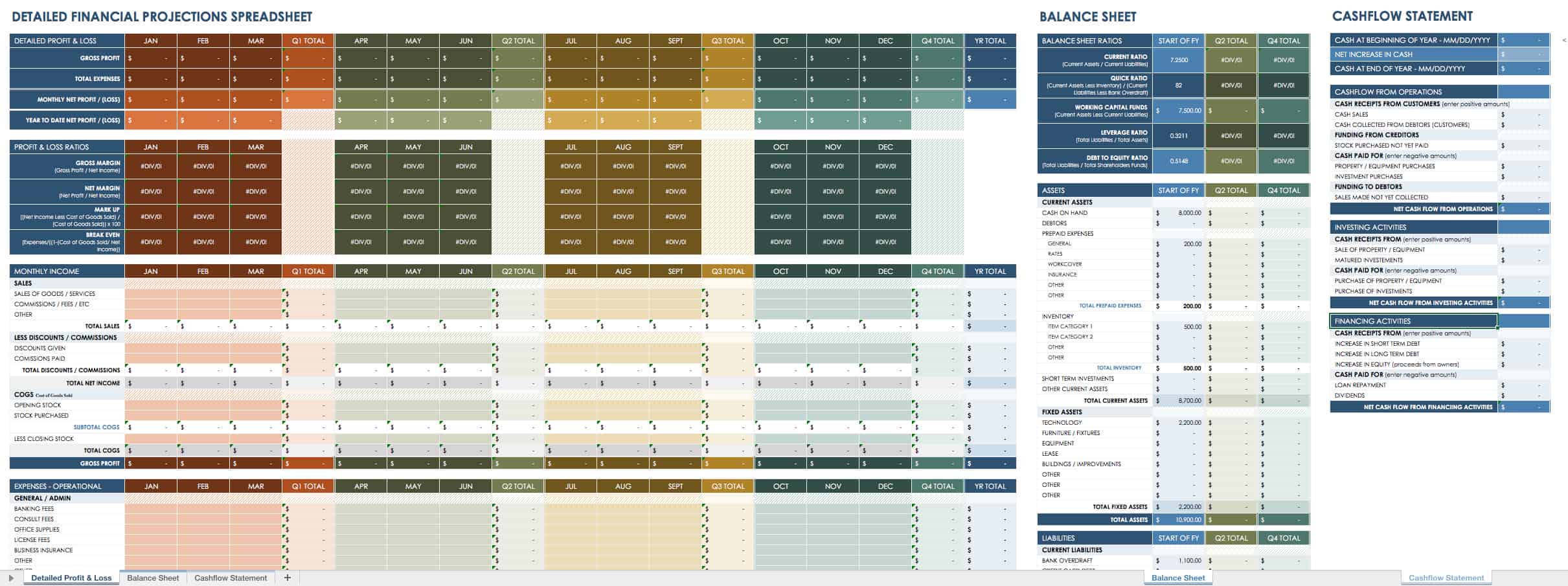
For larger, more complex businesses, you need more comprehensive business budget plans. This detailed spreadsheet tracks all the information you need to make important financial decisions — from startup costs to sales and operating expense forecasts. Estimate and track payroll costs, accounts payable and receivable, the cost of goods sold, lines of credit, and monthly fixed costs. You can also compare year-end totals against one another.
First-Year Budget Calculator
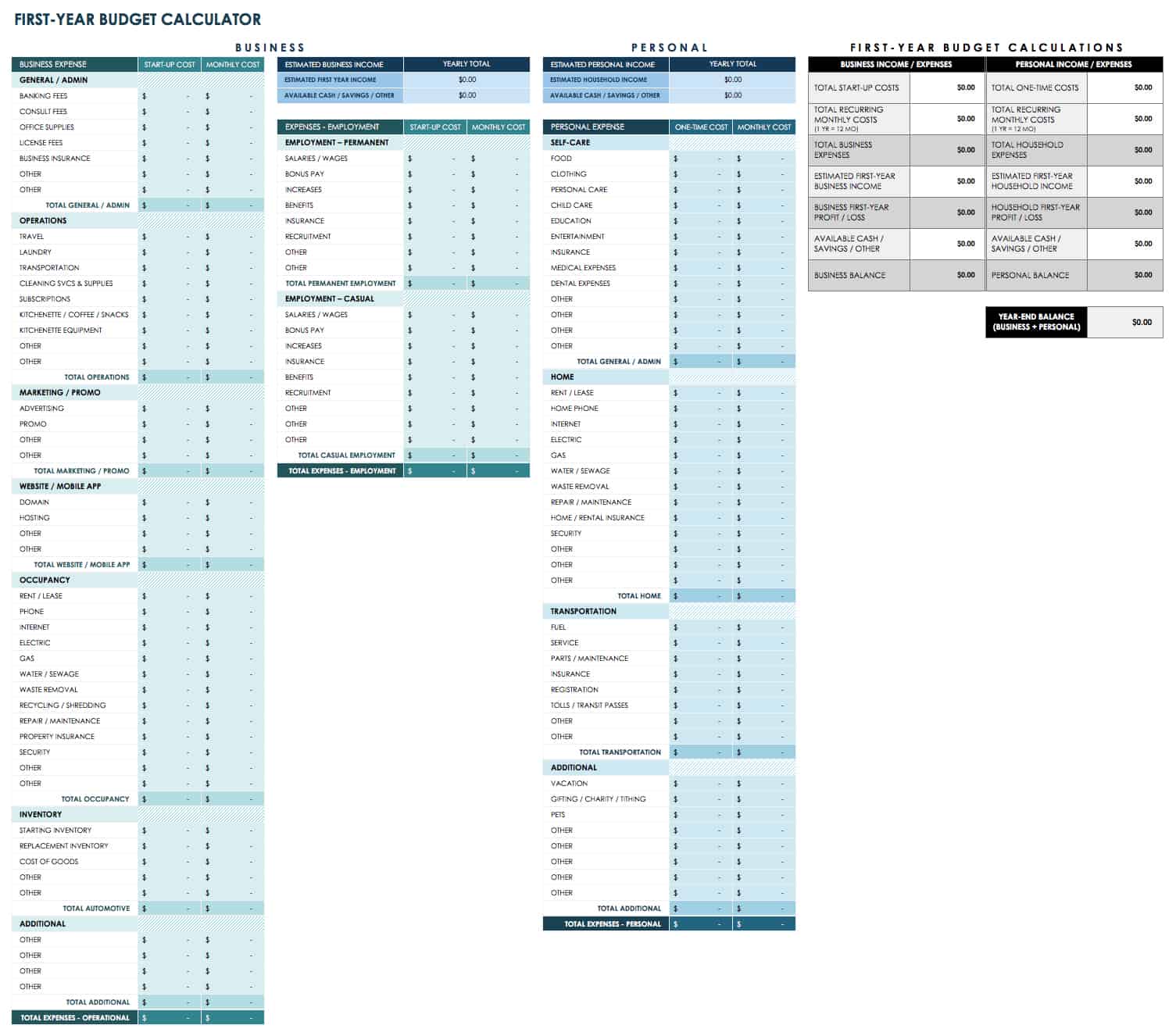
If you’re getting ready to launch a startup, a small business budget template can be a useful tool. This basic calculator can help you quickly gauge costs for your new venture and estimate your first-year business income. It also includes a column for plotting monthly personal expenses, along with available cash from savings and other sources. This way, you can estimate the amount you’ll need to get your new business off the ground.
Professional Business Budget Template

Download Professional Business Budget Template
Excel | Smartsheet
This comprehensive budget template is ideal for larger, more established businesses: it offers one sheet for estimated expenditures (labor costs, office expenses, marketing spending, travel fees, etc.), and another sheet to plot expenses that accrue. It also allows you to track expense variances and offers charts for analyzing how closely your business is adhering to its budget.
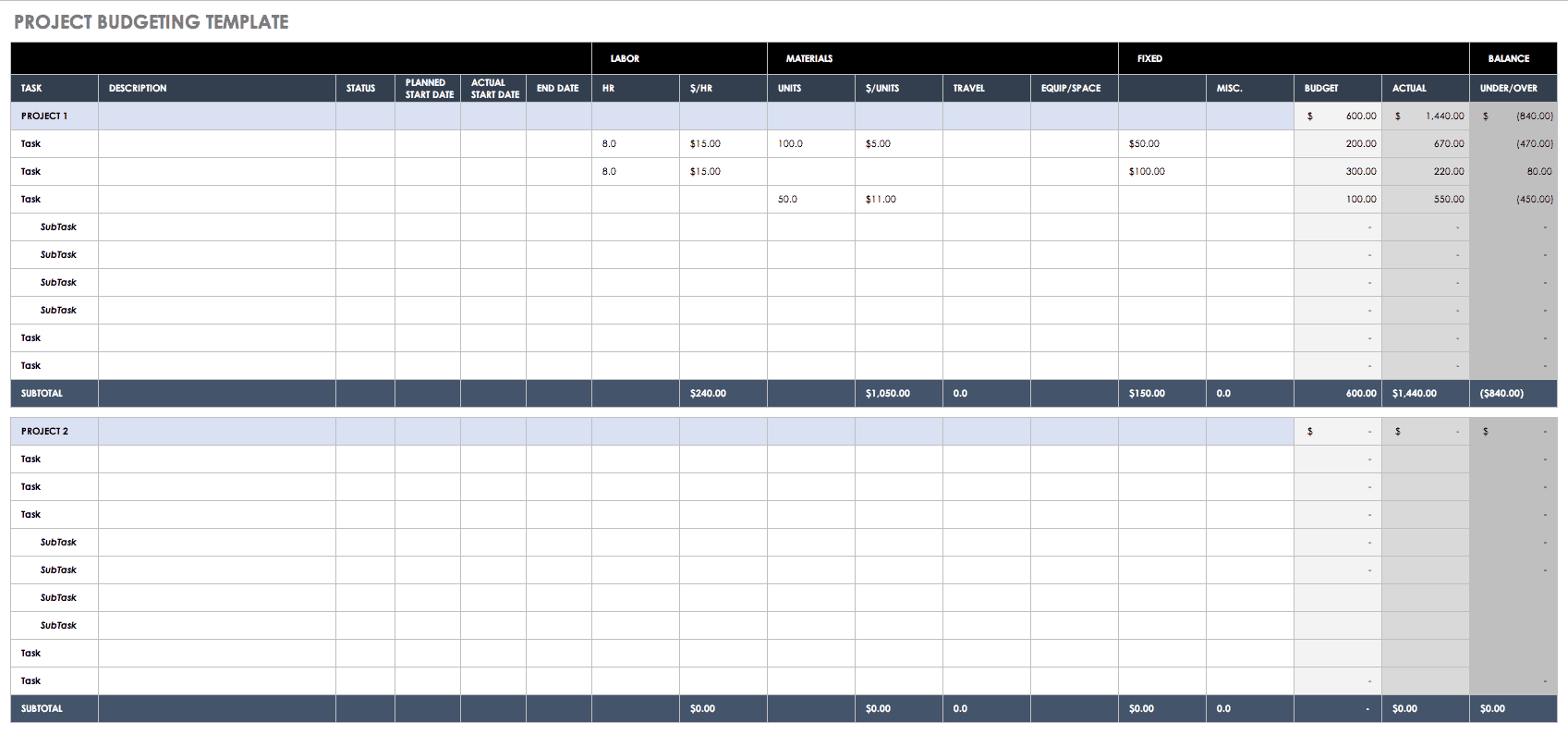
Project Budget Template
Download Excel Template
Need to create a specific, detailed budget for a particular job? This business budget worksheet can help you track income and expenses at the individual project level. Calculate labor, materials, and fixed costs for individual tasks across different categories, and compare estimated against actual expenses and revenues. Keep per-project spending under control with this business budget spreadsheet.
Small Business Budget Template
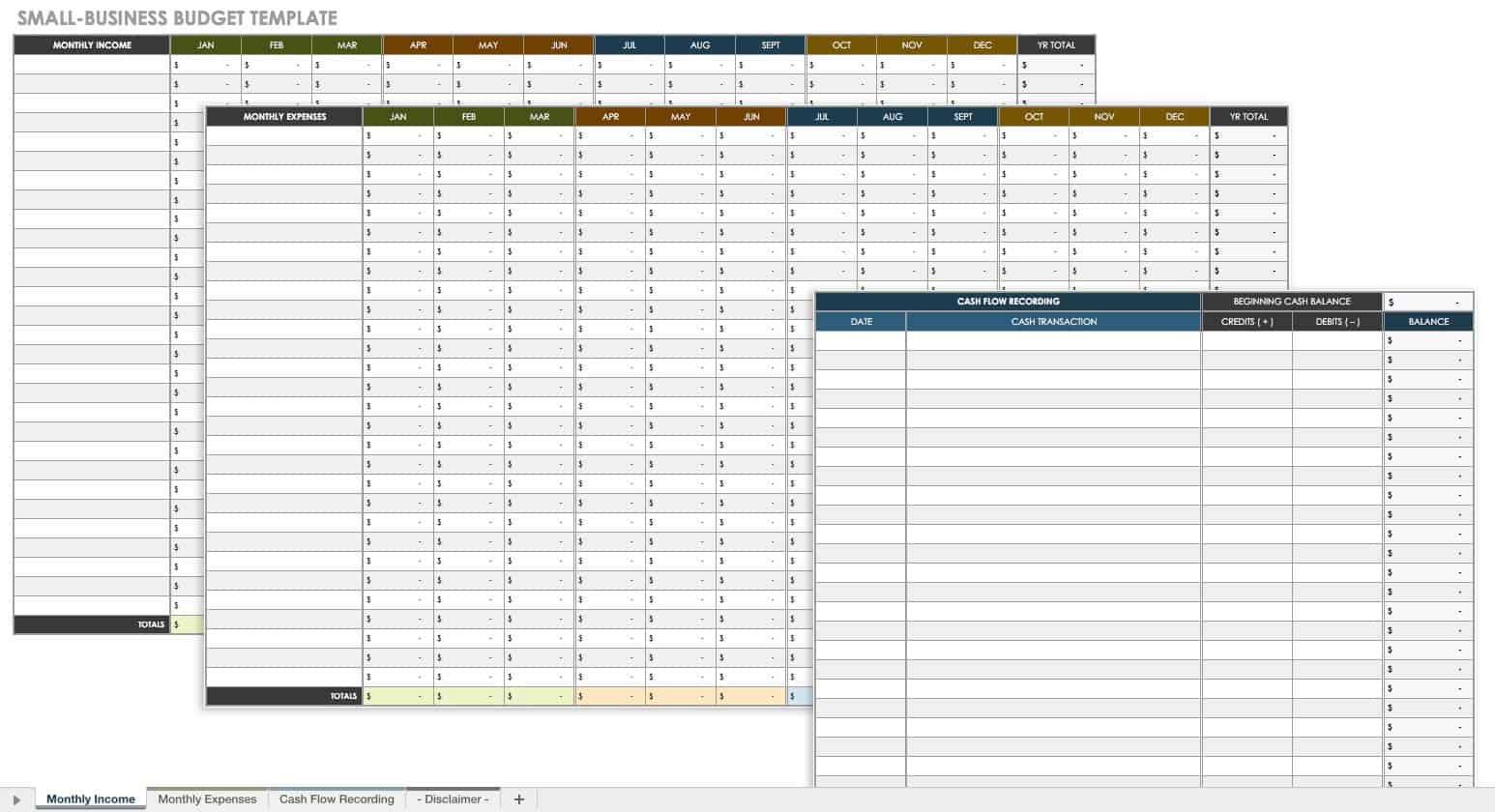
If you run a small business or are self-employed, use this small business budget template to track and manage your finances. This basic budget planner has one sheet for tracking income sources, one for expense types, and another for cash transactions. Easily track monthly income and expenses and calculate total profits.
Start-up Budget Template
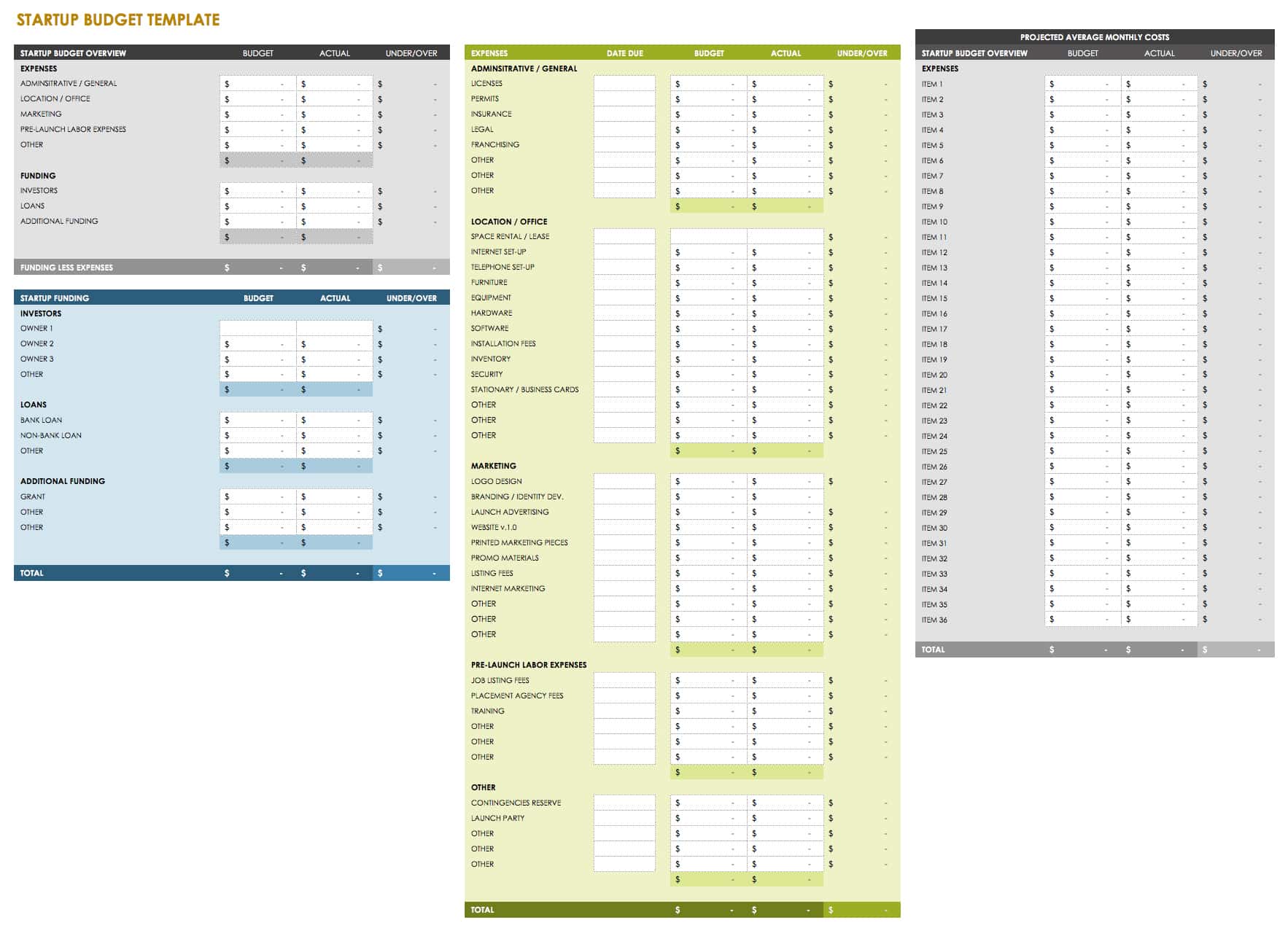
Download Start-up Budget Template
Are you opening a new business? Using small business budgeting templates can help you manage finances properly from day one. If you plan effectively, you’ll lay a strong economic foundation for your company as it grows. This small business budget template allows you to track estimated versus actual funding sources and amounts, determine pre-opening costs, and calculate ongoing expenses so you’ll know how much income you need to come out ahead.
What’s in a Business Budget?
According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA), a business budget should contain the following information:
- Expected sales and revenues
- Fixed costs (those that don’t depend on sales, such as rent and business license expenses)
- Variable costs (items related to sales, such as materials and production expenses)
- Semi-variable costs (those that may or may not change depending on sales, such as wages and marketing fees)
- Profits (expected sales and income minus costs)
You may also choose to include additional information in your budget, depending on your business size and the level of financial information you want to track. For example, if you run a startup, you may want to include data on the total cost of getting your business up and running, as well as the amounts and sources of investor funding. If you have a large enterprise with multiple branch offices, you may want to create separate sheets for each location, as well as for the company’s overall budget.
How to Create a Business Budget Plan
When creating your initial budget, you can use a business budget template to help calculate revenues, expenses, and profits. You may also choose to purchase business budget software to create a more detailed plan. Whatever method you choose, follow these basic steps when forming a budget:
- Gather historical information: If you have an established business, collect historical data on operating expenses, salaries, sales, and revenues over time. If you’re starting a new business, look for financial information on a business similar to yours (in size and type) and use it as a benchmark.
- Estimate sales and set profit goals: Calculate the sales you expect to make during different times of the year, factoring in holidays, office or plant closures, and seasonal booms and lulls. Set profit goals, and make realistic revenue projections for the year and into the future.
- Determine fixed and variable costs: Calculate all the fixed costs involved in operating your business such as rent, insurance, and business licenses. Also determine estimates for your variable costs, including materials and equipment, labor, salaries for company executives, employee benefits, and training and travel expenditures.
- Calculate your profit margin: To determine how much profit you expect the business to make, subtract your expenses from estimated sales and revenues. Include the total cost of goods sold (the total amount it costs to produce your product or service), and factor in other costs like shipping, equipment, and materials for your office or production facility.
- Adjust your budget over time: Continually update your budget over time to see how your estimates compare with actual sales and expenses. If you’re not making a profit, try adjusting your budget to increase revenues and decrease overhead costs.
Discover a Better Way to Manage Business Expenses and Finance Operations
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Business Budget: What is it & Why is it important?

According to a survey conducted by Clutch , 61 percent of small businesses have not created a formal budget. Without a budget, you may not understand how your business is performing.
Creating a budget helps you understand how much money you have, how much you have spent, and how much money you will need in the future. A budget can drive important business decisions like cutting down on unwanted expenses, increasing staff, or purchasing new equipment. If you end up with insufficient money, the budget can guide you in altering your business plan or prioritizing your spending on activities.
With the right budgeting plan, you can keep your business out of debt or find ways to reduce the debt it is currently facing. A comprehensive budget can even be used for obtaining business loans from banks or other financial institutions.
In this guide, you will learn about the importance of a business budget, the components of a good budget, and the different types of budgets.
So, what exactly is a business budget?
A business budget is a spending plan for your business based on your income and expenses. It identifies your available capital, estimates your spending, and helps you predict revenue.
A budget can help you plan your business activities and can act as a yardstick for setting up financial goals. It can help you tackle both short-term obstacles and long-term planning.
Different types of budgets
Your final budget is usually a combination of inputs from several other budgets that are prepared at a departmental level. Let’s look at the different types of budget and how they contribute to drafting a business plan.
1. Master budget
A master budget is an aggregation of lower-level budgets created by the different functional areas in an organization. It uses inputs from financial statements, the cash forecast, and the financial plan. Management teams use master budgets to plan the activities they need to achieve their business goals. In larger organizations, the senior management is responsible for creating several iterations of the master budget before it is finalized. Once it has been reviewed for the final time, funds can be allocated for specific business activities.
Smaller businesses often use spreadsheets to create their master budgets, but replacing the spreadsheets with efficient budgeting software typically reduces errors.
2. Operating budget
An operating budget shows a business’s projected revenue and the expenses associated with it for a period of time. It’s very similar to a profit and loss report. It includes fixed cost, variable cost, capital costs, and non-operating expenses. Although this budget is a high-level summary report, each line item is backed up with relevant details. This information is useful for checking whether the business is spending according to its plans.
In most organizations, the management prepares this budget at the beginning of each year. The document is updated throughout the year, either monthly or quarterly, and can be used as a forecast for consecutive years.
3. Cash budget
A cash flow budget gives you an estimate of the money that comes in or goes out of a business for a specific period in time. Organizations create cash budgets using inferences from sales forecasts and production, and by estimating the payables and receivables.
The information in this budget can help you evaluate whether you have enough liquid cash for operating, whether your money is being used productively, and whether there is and whether you are on track to earn a profit .
4. Financial budget
Businesses draft this budget to understand how much capital they’ll need and at what times for fulfilling short-term and long-term needs. It factors in assets, liabilities, and stakeholder’s equity—the important components of a balance sheet , which give you an overall idea of your business health.
5. Labor budget
For any business that is planning on hiring employees to achieve its goals, a labor budget will be important. It helps you determine the workforce you will require to achieve your goals so you can plan the payroll for all of those employees. In addition to planning regular staffing, it also helps you allocate expenses for seasonal workers.
6. Static budget
As the name suggests, this budget is an estimate of revenue and expenses that will remain fixed throughout the year. The line items in this budget can be used as goals to meet regardless of any increases or decreases in sales. Static budgets are usually prepared by nonprofits, educational institutions, or government bodies that have been allocated a fixed amount to use for their activities in each area.
Components of a budget
If you are starting a new business, the first budget you create might be a challenge, but it is a good learning experience and a good way to understand what works best for your business. The best place to start is getting to know your budget components. Initially you may need to make several assumptions to get your budget started.
1. Estimated revenue
This is the money you expect your business to make from the sale of goods and services. There are two main components of estimated revenue: sales forecast and estimated cost of goods sold or services rendered. If your business is more than a year old, then your experience will guide you in estimating these components. If your business is new, you can check the revenue of similar local businesses and use those figures to conservatively create some estimated revenue numbers. But whether your business is new or old, it is important to stay realistic to avoid over-estimating.
2. Fixed cost
When your business pays the same amount regularly for a particular expense, that is classified as a fixed cost . Some examples of fixed costs include building rent, mortgage/utility payments, employee salaries, internet service, accounting services, and insurance premiums. Factoring these expenses into the budget is important so that you can set aside the exact amount of money required to cover these expenses. They can also be a good reference point to check for problems if your business finances aren’t going as planned.
3. Variable costs
This category includes the cost of goods or services that can fluctuate based on your business success. For example, let us assume you have a product in the market that is gaining popularity. The next thing you would like to do is manufacture more of that product. The costs of the raw materials required for production, the distribution channels used for supplying the product, and the production labor will all change when you increase production, so they will all be considered variable expenses.
4. One-time expenses
These are one-off, unexpected costs that your business might incur in any given year. Some examples of these costs include replacing broken furniture or purchasing a laptop.
Since it is difficult to predict these expenses, there is no certain way to estimate for them. But it’s wise to set aside some cash for this category to stay prepared.
5. Cash flow
This is the money that travels in and out of the business. You can get an idea of it from your previous financial records and use that information to forecast your earnings for the year you’re budgeting for. You’ll want to pay attention not only to how much money is coming in, but also when. If your business has a peak season and a dry season, knowing when your cash flow is highest will help you plan when to make large purchases or investments.
The final budget component is profit, which is a number you arrive at by subtracting your estimated cost from revenue. An increase in profit means your business is growing, which is a good sign. Once you have projected how much profit you are likely to make in a year, you’ll be able to decide how much to invest in each functional area of your organization. For example, will you use your profit to invest in advertising or marketing to drive more sales?
A budget is a road map for your business. It helps you predict cash flow, identify functional areas that need improvement, and run your operations smoothly. Successful businesses invest a lot of time and effort into creating realistic budgets, because they’re an efficient way of tracking the extent to which the business has achieved its goals. Creating a budget can get a bit overwhelming for new businesses as there are no previous figures to guide their budget estimates, but with some estimates based on the performance of competitors and an understanding of the components of a budget, you can complete your first budget and have a good road map for future budgets.
Related Posts
- Cash Flow Statement - Definition and Importance
- How to Create a Business Budget for Your Small Business
- Income statement - Definition, Importance and Example
Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
may I have more materials for budgeting?
Hey Patricia,
While we appreciate suggestions from our readers, we just wanted to let you know there’s more coming up on budgeting. However, besides this article, there’s another one on – How to create a business budget for your small business. Hope it’s insightful.
Has helped me learn a few things about types of budgets
I love this article. It is very helpful. I am interested in knowing which budgeting softwares are efficient when you say,” Smaller businesses often use spreadsheets to create their master budgets, but replacing the spreadsheets with efficient budgeting software typically reduces errors.” I am looking for one software for my company!
Thank you. Respectfully,
Hi Nilamba!
Budgeting is one of the important features in Zoho Books.
A few key highlights of Zoho Books include: 1. Management of vendors and customers. 2. Creating Estimates, Sales orders and Invoices. 3. Managing your Expenses, Bills, Purchase Orders. 4. Collaborative Client Portal through which your clients can easily view all their transactions and also make payments. 5. Integrations with other Zoho apps. 6. Integrations with Online payment gateways 7. Automated Bank feeds. 8. Exhaustive Reports and much more… It is available as a mobile app on Android, iOS and Windows as well. Please do write to us at [email protected] and we will be happy to explain how Zoho Books will be a great fit for your business.
Thanks you for the level of understanding on this topic but I need new materials as technology advance.
Thank you for the information, it’s great help.
Excellent and easily elaborated..
You might also like
Switch to smart accounting. try zoho books today.
Business growth
Business tips
7 free small business budget templates for future-proofing your finances

As a small business owner, you're likely balling with a lot more than your personal checking account. If you don't properly manage your business finances, there's more on the line than an overdraft fee—you now have an entire organization to account for.
Small business budgets are necessary to balance revenue, estimate how much you'll spend, and project financial forecasts, so you can stay out of the red and keep your business afloat.
But creating a small business budget template isn't a small task. Since I don't have a business to run, I did the heavy lifting for you—check out these free, downloadable templates for your small business budgeting.
Table of contents:
2. Overhead budget template
3. multiple-project budget template.
4. Startup budget template
5. Labor budget template
6. cash flow budget template, 7. administrative budget template, periodic budget reviews, how to design your small business budget plan, small business budget faq, 1. static budget template.
Best for: Multiple departments or revenue streams; Industries with complex operations
A static budget combines all the function-specific budgets a business uses into one. Typically, a static budget includes the following items (plus any other budgets your business might use):
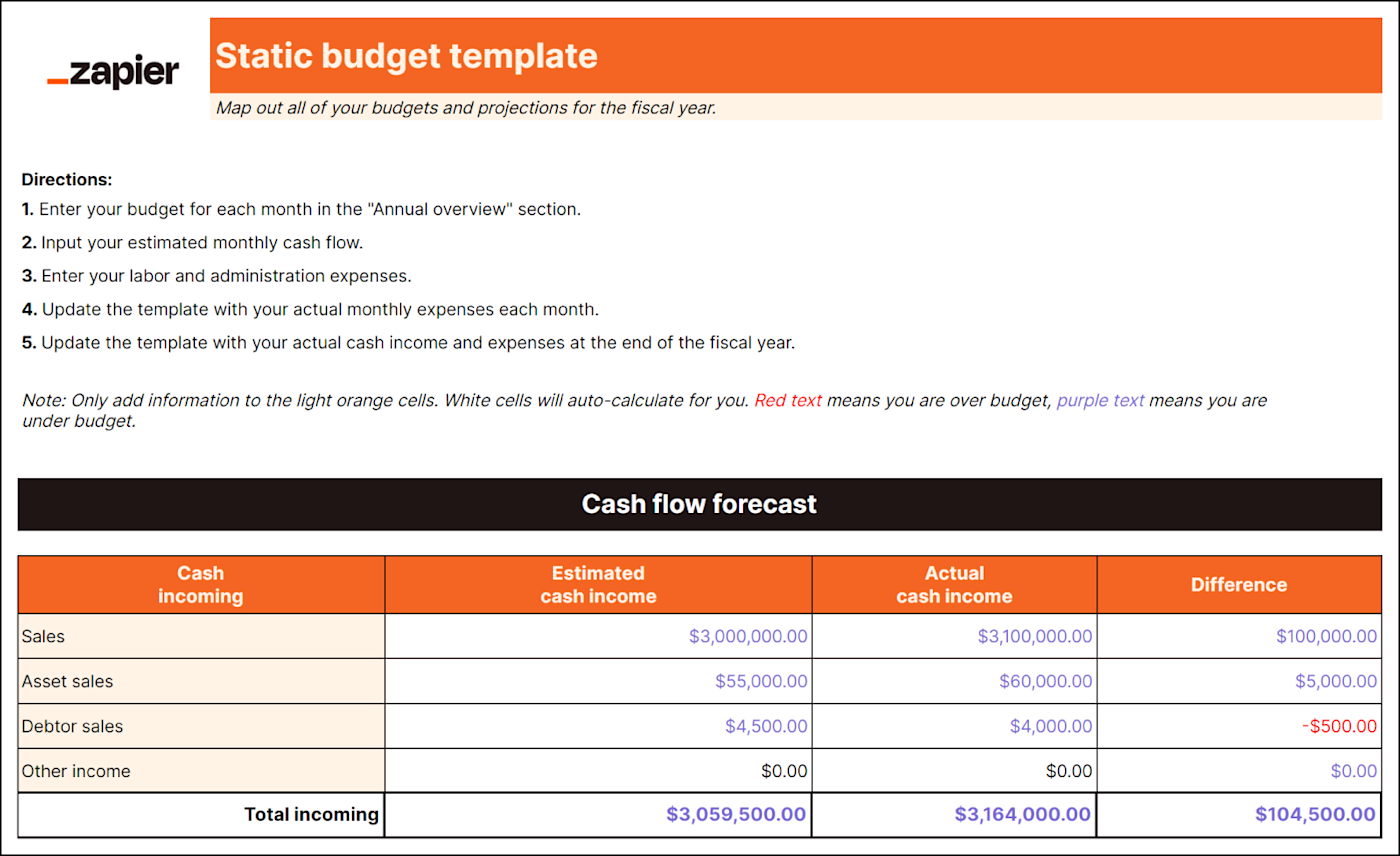
Cash flow projections: Estimations of how much money will flow into and out of your business. They also help you decide when, how, and what you should spend money on.
Total expected spending: All estimated expenses, including labor and administrative costs.
By integrating all of your budgets and projections, the static budget provides a full picture of your business's estimated expenses and financial strategy for the upcoming fiscal year.
Best for: Service-based businesses
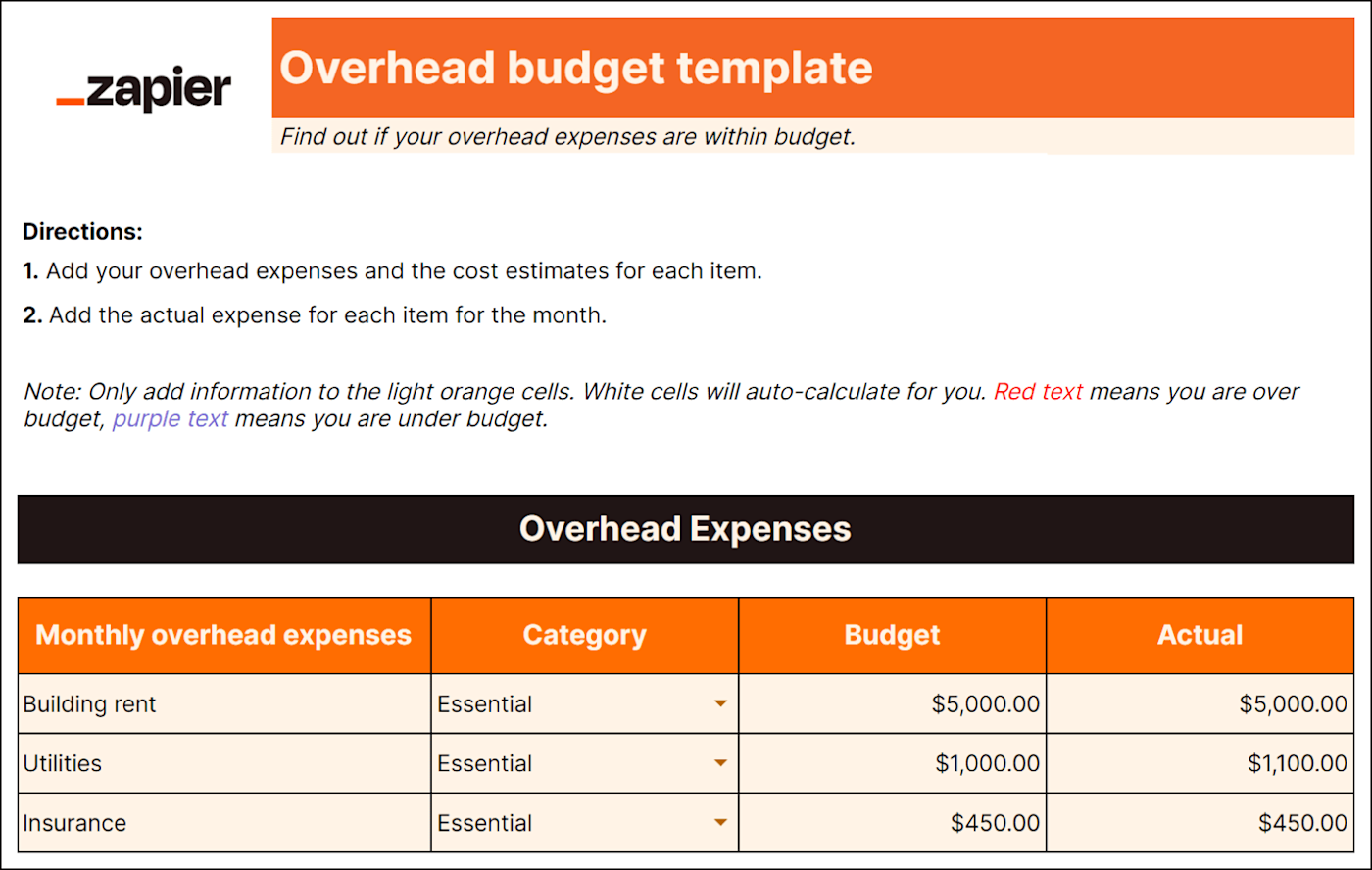
It's easy to forget about expenses that aren't directly tied to production, like delivery charges or utilities. But these costs exist (and can add up quickly), so you need an overhead budget. A detailed overhead budget template will include:
Administration expenses
It compares your budgeted amount to actual figures (warning: it may be a rude awakening) and can help improve accuracy for future financial planning.
Predicting overhead spending helps you plan how to use other funds more practically too—if you know how much you'll spend on overhead, you can make better business decisions. For example, you'd know whether you can afford to invest money into other initiatives like adding a delivery service or upgrading equipment.
Best for: Project-based industries
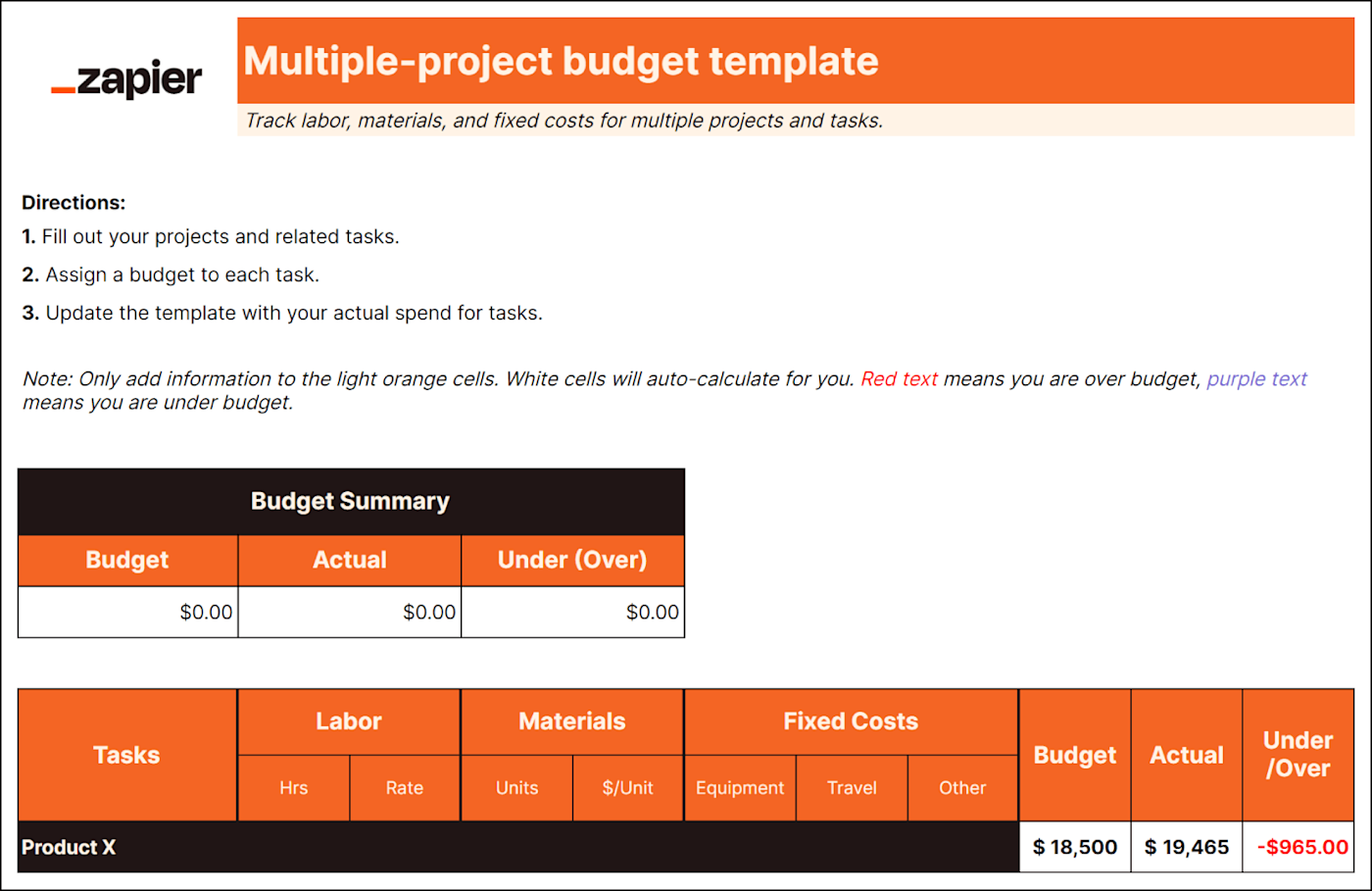
If you're managing multiple projects like website development or event planning, each with its own budget and expenses, you need a multiple-project budget to help keep your head on straight. This type of budget will help you track the following items per project:
Product-by-product COGS (cost of goods sold)
Labor costs
Equipment and resource costs
Indirect project expenses like travel
A multiple-projects budget establishes estimates for everything you need to get projects across the finish line. It also lets you track costs to ensure you're not spending more than you accounted for in the budget.
4. Startup budget template
Best for: New small businesses and startups
Startups need to ensure financial success from the get-go, so they can reinvest profit into the business and potentially attract more investors.
But unlike established small businesses, you don't have past financial data to base expenses on. That's why you need a startup budget to focus on expenses for your first year of business, including items like:
Funding from investors and loans
Licensing and permits
Logo and website design
Website domain
Business software
Security installation
Overhead expenses
Capital expenses
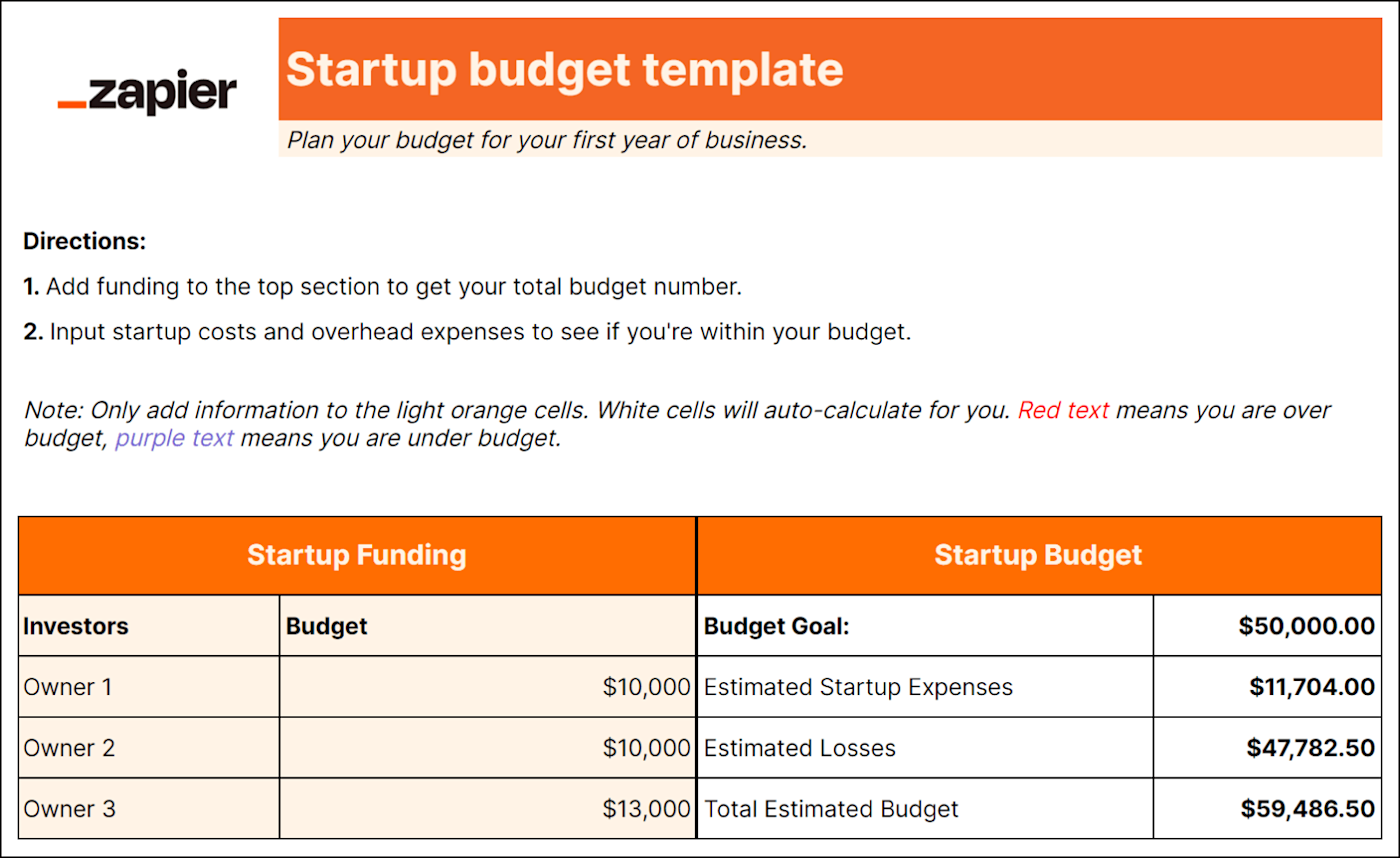
Best for: Larger businesses with lots of employees
Unless you're a one-person show, you'll need a labor budget. And even if you are a one-person show, it's good to know if you can afford to pay yourself. A labor budget breaks down all employee-related costs like:
Payroll taxes
Contract labor
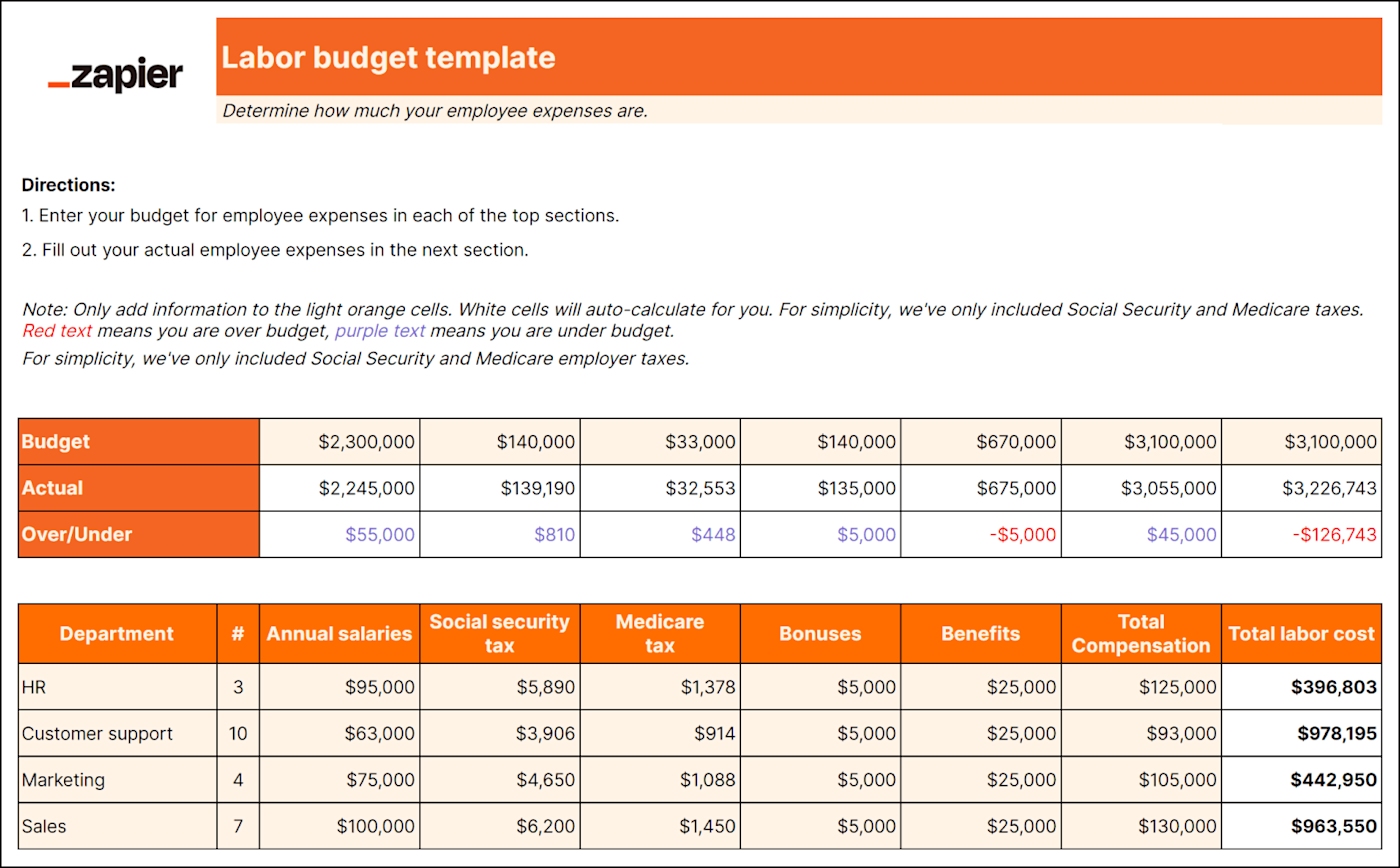
Break down employee costs into direct, indirect, fixed, and variable categories to clarify how your company allocates its resources. You can also consider different scenarios more easily when you understand the breakdown of labor costs.
For example, you can simulate the impact of adding or reducing staff in specific departments or assess the effects of different compensation structures on different teams.
An accurate forecast of labor costs ensures you can sustainably meet your staffing needs and can help you make informed hiring decisions. Down the road, it can also help you determine if you can afford to give your staff raises, bonuses, or additional benefits.
Best for: Businesses with fluctuating income and expenses; Seasonal businesses; Retail
As important as it is to be mindful of how much money you're spending, you should also track how much money you're making . A cash flow budget helps estimate how money is flowing in and out of your business. It includes:
Starting balance (set at the beginning of the month, quarter, or year)
Projected cash inflow from all revenue streams
Estimated cash expenditures
Ending balance (calculated at the end of the month, quarter, or year)
This type of budget lets you proactively manage your resources, anticipate potential cash shortages, and strategize for growth. For instance, if you know you're only going to break even this year, you may wait on expanding or making a large investment.
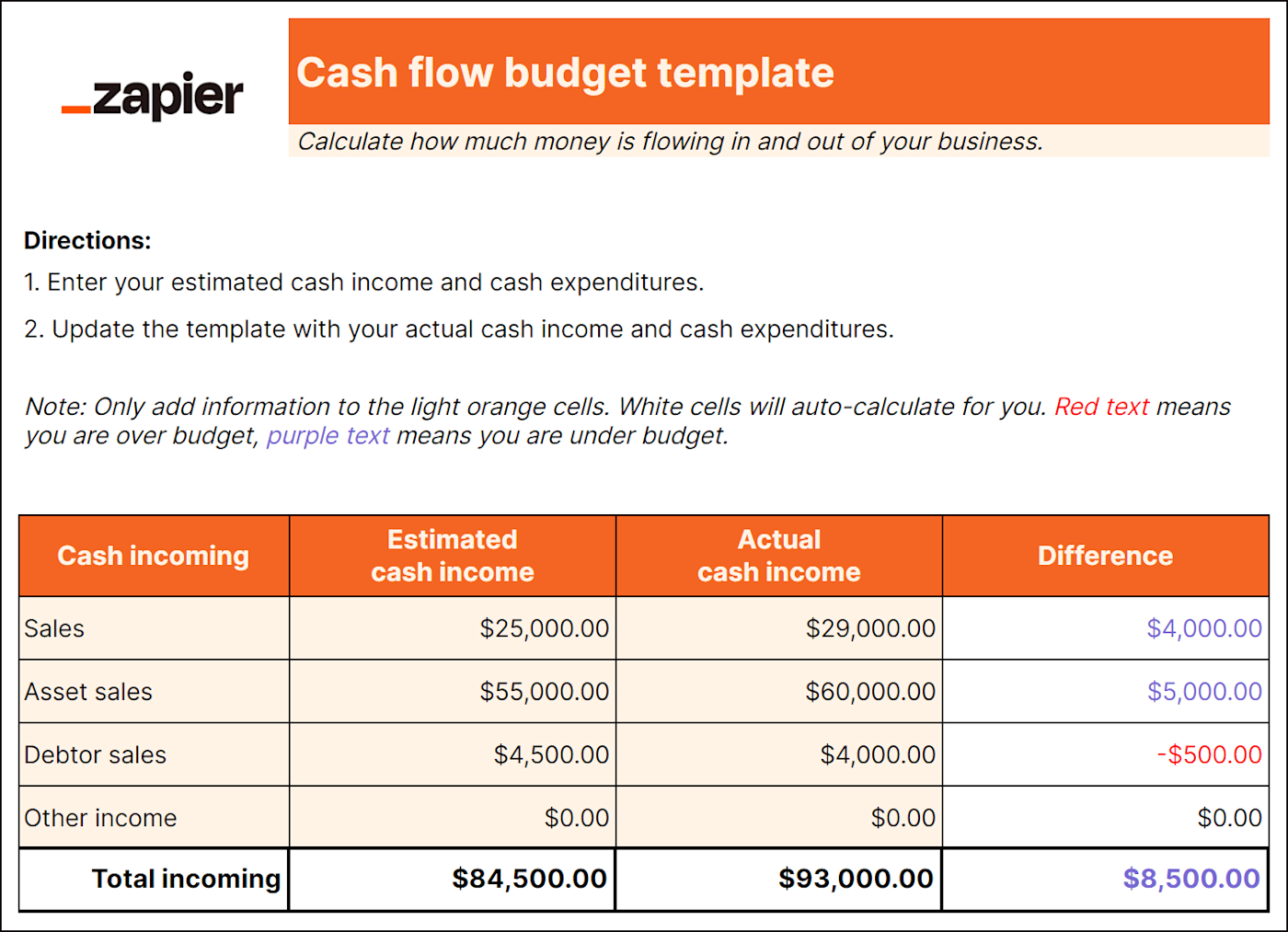
Best for: Businesses focused on streamlining operations
An administrative budget includes all those general expenses that the company as a whole needs to function. This type of budget accounts for:
Depreciation expenses
Training and development
Communication expenses
Accounting fees
While you could technically include administrative expenses in an overhead budget and call it a day, a separate administrative budget gives more of an eagle-eye view of how well your business is operating.
Without an eye on administrative costs, you may be spending unnecessarily or lose focus on areas where it'd be wiser to invest your money. In other words, you could be spending way too much on fancy pens when you should be saving up to upgrade your cash register.

A budget isn't a "set it and forget it" deal. Regular budget reviews can help you stay on track with your financial goals and respond proactively to changing market conditions.
You should compare your estimated budget to actual spending. Then you can see where you went over and where you can splurge more. Try to review your budget monthly, quarterly, and yearly.
Monthly: Compare actual performance against your budgeted figures for the month. Identify any deviations and look for insights into cash flow, sales trends, and expense management.
Quarterly: Dive deeper into performance over the last three months. Use trends to project revenue and expenses for the upcoming quarter and identify areas for improvement.
Yearly: Reflect on your long-term financial objectives for the fiscal year. Assess the effectiveness of your budgeting strategies, and set new budget targets for the upcoming year.
It's cliched but true: you gotta spend money to make money. But that's no excuse to start throwing cash at your business willy-nilly.
Budgeting forces you to prioritize your objectives, so you spend money on the things that matter most. Here's how to create a small business budget in four steps:
Identify your working capital for the budgeting period. Add up your current assets like cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. Then subtract current liabilities like accounts payable and short-term debt. The remaining amount is what you have left to cover your operational expenses during the budgeting period.
Separate business and personal expenses. If you haven't already, open a dedicated business bank account. This makes it easier to track, categorize, and analyze your finances.
Determine your fixed and variable costs. Make a list of costs that stay the same every month (fixed costs) and what changes (variable costs). These will change based on the purpose of the budget. For instance, a labor budget will only consider employee-related costs.
Calculate your total expenses. Add up all the costs for your business, including fixed costs, variable costs, labor, and any other applicable expenses. This total is how much your business needs to run. Any leftover money from your working capital can be allocated toward other business investments.
Budgeting methods
If you've budgeted before and hated it, you may just have been using an ineffective budgeting method for your preferences. Here are a few budgeting methods to try instead:
Traditional: This budget is set for a determined amount of time and uses last year's numbers as a benchmark. Once you set your budget, you don't change it unless you get approval for an adjustment.
Rolling: This dynamic approach spans a continuous time frame instead of a fixed time period. As each month or quarter passes, you add a new budget period and drop the oldest period. This lets businesses adjust projections based on real-time performance and market conditions.
Flexible: This budget changes along with your sales forecast. As real-time sales activity deviates from budgeted amounts, you recalculate the budget to reflect the new data.
Still don't know where to start with your small business budget? Check out the answers to these common questions before you open a new Google Sheet.
What should a business budget include?
A business budget should include all income sources and expenses. Income sources could include projected revenue from sales, loans, or potential investor funding. Expenses may include items like office space rent, employee salaries, insurance, and marketing. Add anything that helps paint a full picture of your finances.
How much does the average small business startup cost?
The average small business startup costs $40,000 in its first year of business. But this will absolutely vary depending on your type of business, unique expenses, and cash income. For instance, there are multiple types of businesses you can start with $10,000 or less.
What is the best free business budgeting software?
The best free budgeting business software will depend on what your business needs, but you can try apps like Mint or Wave. Or you can use a spreadsheet—scroll up for some free small business budget templates.
Automate your small business
Knowing when or where to invest money into your business is just one of the many tasks you have on your plate as a small business owner. Learn how automation for small businesses can help take some of those recurring tasks off your hands, so you can focus on growing your business.
Related reading:
The best free small business software
The best CRMs for small businesses
How to create effective document templates
21 free Google Sheets templates to boost productivity
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Cecilia Gillen
Cecilia is a content marketer with a degree in Media and Journalism from the University of South Dakota. After graduating, Cecilia moved to Omaha, Nebraska where she enjoys reading (almost as much as book buying), decor hunting at garage sales, and spending time with her two cats.
- Small business
- Finance & accounting
Related articles
Keep your company adaptable with automation
How to enrich lead data for personalized outreach
How to enrich lead data for personalized...
What is a proof of concept? And how to write one (with template)
What is a proof of concept? And how to write...
How to choose the best automation software
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.

Please note that the contents of this site are not being updated since October 1, 2023.
As of October 2, 2023, Acclr Business Information Services (Info entrepreneurs) will be delivered directly by CED’s Business Information Services . To find out more about CCMM’s other Acclr services, please visit this page: Acclr – Business Services | CCMM.

- Advice and guidance
- Starting a business
- Personalized Guidance
- Seminars on Business Opportunities
- Certification of Export Documents
- Market Studies
- Export Financing
- International Trade Training
- Connection with the World Bank
- Trade Missions
- SME Passport
- Export Resources
- Import Resources
- Networking Activities
- Networking Training
- CCMM Member Directory
- Market Studies and Research Services
- Business plan
- Registration and legal structures
- Guidance for Drafting a Business Plan
- Help in Seeking Funding
- News, Grants, and Competitions
- Funding Meet-and-Greet
- Resources for Drafting a Business Plan
- Regulations / Permits / Licences
- Personalized Market Information Research
- Personalized Meetings with Guest Experts
- Government Subsidies and Programs
- Training for your employees
- Employee Management
- Interconnection Program
- Wage Subsidies
- French courses
- Merchant-Student Pairing
- Intellectual property
- Marketing and sales
- Operations management
- Hiring and managing human resources
- Growth and innovation
- Importing and exporting
- Calls for tenders
- Support organizations
- Sale / Closure / Bankruptcy
- Business intelligence
- Business lists and profiles
- Market data
- Market trends
- Business advice
- Business plan management consultant
- Legal structures consultant
- Accounting consultant
- Legal consultant
- Export certification
- Resource centre
Budgeting and business planning
Once your business is operational, it's essential to plan and tightly manage its financial performance. Creating a budgeting process is the most effective way to keep your business - and its finances - on track.
This guide outlines the advantages of business planning and budgeting and explains how to go about it. It suggests action points to help you manage your business' financial position more effectively and ensure your plans are practical.
Planning for business success
The benefits, what to include in your annual plan, a typical business planning cycle, budgets and business planning, benefits of a business budget, creating a budget, key steps in drawing up a budget, what your budget should cover, what your budget will need to include, use your budget to measure performance, review your budget regularly.
When you're running a business, it's easy to get bogged down in day-to-day problems and forget the bigger picture. However, successful businesses invest time to create and manage budgets, prepare and review business plans and regularly monitor finance and performance.
Structured planning can make all the difference to the growth of your business. It will enable you to concentrate resources on improving profits, reducing costs and increasing returns on investment.
In fact, even without a formal process, many businesses carry out the majority of the activities associated with business planning, such as thinking about growth areas, competitors, cashflow and profit.
Converting this into a cohesive process to manage your business' development doesn't have to be difficult or time-consuming. The most important thing is that plans are made, they are dynamic and are communicated to everyone involved. See the page in this guide on what to include in your annual plan.
The key benefit of business planning is that it allows you to create a focus for the direction of your business and provides targets that will help your business grow. It will also give you the opportunity to stand back and review your performance and the factors affecting your business. Business planning can give you:
- a greater ability to make continuous improvements and anticipate problems
- sound financial information on which to base decisions
- improved clarity and focus
- a greater confidence in your decision-making
The main aim of your annual business plan is to set out the strategy and action plan for your business. This should include a clear financial picture of where you stand - and expect to stand - over the coming year. Your annual business plan should include:
- an outline of changes that you want to make to your business
- potential changes to your market, customers and competition
- your objectives and goals for the year
- your key performance indicators
- any issues or problems
- any operational changes
- information about your management and people
- your financial performance and forecasts
- details of investment in the business
Business planning is most effective when it's an ongoing process. This allows you to act quickly where necessary, rather than simply reacting to events after they've happened.
- Review your current performance against last year/current year targets.
- Work out your opportunities and threats.
- Analyse your successes and failures during the previous year.
- Look at your key objectives for the coming year and change or re-establish your longer-term planning.
- Identify and refine the resource implications of your review and build a budget.
- Define the new financial year's profit-and-loss and balance-sheet targets.
- Conclude the plan.
- Review it regularly - for example, on a monthly basis - by monitoring performance, reviewing progress and achieving objectives.
- Go back to 1.
New small business owners may run their businesses in a relaxed way and may not see the need to budget. However, if you are planning for your business' future, you will need to fund your plans. Budgeting is the most effective way to control your cashflow, allowing you to invest in new opportunities at the appropriate time.
If your business is growing, you may not always be able to be hands-on with every part of it. You may have to split your budget up between different areas such as sales, production, marketing etc. You'll find that money starts to move in many different directions through your organisation - budgets are a vital tool in ensuring that you stay in control of expenditure.
A budget is a plan to:
- control your finances
- ensure you can continue to fund your current commitments
- enable you to make confident financial decisions and meet your objectives
- ensure you have enough money for your future projects
It outlines what you will spend your money on and how that spending will be financed. However, it is not a forecast. A forecast is a prediction of the future whereas a budget is a planned outcome of the future - defined by your plan that your business wants to achieve.
There are a number of benefits of drawing up a business budget, including being better able to:
- manage your money effectively
- allocate appropriate resources to projects
- monitor performance
- meet your objectives
- improve decision-making
- identify problems before they occur - such as the need to raise finance or cash flow difficulties
- plan for the future
- increase staff motivation
Creating, monitoring and managing a budget is key to business success. It should help you allocate resources where they are needed, so that your business remains profitable and successful. It need not be complicated. You simply need to work out what you are likely to earn and spend in the budget period.
Begin by asking these questions:
- What are the projected sales for the budget period? Be realistic - if you overestimate, it will cause you problems in the future.
- What are the direct costs of sales – i.e. costs of materials, components or subcontractors to make the product or supply the service?
- What are the fixed costs or overheads?
You should break down the fixed costs and overheads by type, e.g.:
- cost of premises, including rent, municipal taxes and service charges
- staff costs –e.g. wages, benefits, Québec Parental Insurance Plan (QPIP) premiums, contributions to the Québec Pension Plan (QPP) and to the financing of the Commission des normes du travail (CNT)
- utilities – e.g. heating, lighting, telephone
- printing, postage and stationery
- vehicle expenses
- equipment costs
- advertising and promotion
- travel and subsistence expenses
- legal and professional costs, including insurance
Your business may have different types of expenses, and you may need to divide up the budget by department. Don't forget to add in how much you need to pay yourself, and include an allowance for tax.
Your business plan should help in establishing projected sales, cost of sales, fixed costs and overheads, so it would be worthwhile preparing this first. See the page in this guide on planning for business success.
Once you've got figures for income and expenditure, you can work out how much money you're making. You can look at costs and work out ways to reduce them. You can see if you are likely to have cash flow problems, giving yourself time to do something about them.
When you've made a budget, you should stick to it as far as possible, but review and revise it as needed. Successful businesses often have a rolling budget, so that they are continually budgeting, e.g. for a year in advance.
There are a number of key steps you should follow to make sure your budgets and plans are as realistic and useful as possible.
Make time for budgeting
If you invest some time in creating a comprehensive and realistic budget, it will be easier to manage and ultimately more effective.
Use last year's figures - but only as a guide
Collect historical information on sales and costs if they are available - these could give you a good indication of likely sales and costs. But it's also essential to consider what your sales plans are, how your sales resources will be used and any changes in the competitive environment.
Create realistic budgets
Use historical information, your business plan and any changes in operations or priorities to budget for overheads and other fixed costs.
It's useful to work out the relationship between variable costs and sales and then use your sales forecast to project variable costs. For example, if your unit costs reduce by 10 per cent for each additional 20 per cent of sales, how much will your unit costs decrease if you have a 33 per cent rise in sales?
Make sure your budgets contain enough information for you to easily monitor the key drivers of your business such as sales, costs and working capital. Accounting software can help you manage your accounts.
Involve the right people
It's best to ask staff with financial responsibilities to provide you with estimates of figures for your budget - for example, sales targets, production costs or specific project control. If you balance their estimates against your own, you will achieve a more realistic budget. This involvement will also give them greater commitment to meeting the budget.
Decide how many budgets you really need. Many small businesses have one overall operating budget which sets out how much money is needed to run the business over the coming period - usually a year. As your business grows, your total operating budget is likely to be made up of several individual budgets such as your marketing or sales budgets.
Projected cash flow -your cash budget projects your future cash position on a month-by-month basis. Budgeting in this way is vital for small businesses as it can pinpoint any difficulties you might be having. It should be reviewed at least monthly.
Costs - typically, your business will have three kinds of costs:
- fixed costs - items such as rent, salaries and financing costs
- variable costs - including raw materials and overtime
- one-off capital costs - purchases of computer equipment or premises, for example
To forecast your costs, it can help to look at last year's records and contact your suppliers for quotes.
Revenues - sales or revenue forecasts are typically based on a combination of your sales history and how effective you expect your future efforts to be.
Using your sales and expenditure forecasts, you can prepare projected profits for the next 12 months. This will enable you to analyse your margins and other key ratios such as your return on investment.
If you base your budget on your business plan, you will be creating a financial action plan. This can serve several useful functions, particularly if you review your budgets regularly as part of your annual planning cycle.
Your budget can serve as:
- an indicator of the costs and revenues linked to each of your activities
- a way of providing information and supporting management decisions throughout the year
- a means of monitoring and controlling your business, particularly if you analyse the differences between your actual and budgeted income
Benchmarking performance
Comparing your budget year on year can be an excellent way of benchmarking your business' performance - you can compare your projected figures, for example, with previous years to measure your performance.
You can also compare your figures for projected margins and growth with those of other companies in the same sector, or across different parts of your business.
Key performance indicators
To boost your business' performance you need to understand and monitor the key "drivers" of your business - a driver is something that has a major impact on your business. There are many factors affecting every business' performance, so it is vital to focus on a handful of these and monitor them carefully.
The three key drivers for most businesses are:
- working capital
Any trends towards cash flow problems or falling profitability will show up in these figures when measured against your budgets and forecasts. They can help you spot problems early on if they are calculated on a consistent basis.
To use your budgets effectively, you will need to review and revise them frequently. This is particularly true if your business is growing and you are planning to move into new areas.
Using up to date budgets enables you to be flexible and also lets you manage your cash flow and identify what needs to be achieved in the next budgeting period.
Two main areas to consider
Your actual income - each month compare your actual income with your sales budget, by:
- analysing the reasons for any shortfall - for example lower sales volumes, flat markets, underperforming products
- considering the reasons for a particularly high turnover - for example whether your targets were too low
- comparing the timing of your income with your projections and checking that they fit
Analysing these variations will help you to set future budgets more accurately and also allow you to take action where needed.
Your actual expenditure - regularly review your actual expenditure against your budget. This will help you to predict future costs with better reliability. You should:
- look at how your fixed costs differed from your budget
- check that your variable costs were in line with your budget - normally variable costs adjust in line with your sales volume
- analyse any reasons for changes in the relationship between costs and turnover
- analyse any differences in the timing of your expenditure, for example by checking suppliers' payment terms
Original document, Budgeting and business planning , © Crown copyright 2009 Source: Business Link UK (now GOV.UK/Business ) Adapted for Québec by Info entrepreneurs
Our information is provided free of charge and is intended to be helpful to a large range of UK-based (gov.uk/business) and Québec-based (infoentrepreneurs.org) businesses. Because of its general nature the information cannot be taken as comprehensive and should never be used as a substitute for legal or professional advice. We cannot guarantee that the information applies to the individual circumstances of your business. Despite our best efforts it is possible that some information may be out of date.
- The websites operators cannot take any responsibility for the consequences of errors or omissions.
- You should always follow the links to more detailed information from the relevant government department or agency.
- Any reliance you place on our information or linked to on other websites will be at your own risk. You should consider seeking the advice of independent advisors, and should always check your decisions against your normal business methods and best practice in your field of business.
- The websites operators, their agents and employees, are not liable for any losses or damages arising from your use of our websites, other than in respect of death or personal injury caused by their negligence or in respect of fraud.
Need help? Our qualified agents can help you. Contact us!
- Create my account

The address of this page is: https://www.infoentrepreneurs.org/en/guides/budgeting-and-business-planning/
INFO ENTREPRENEURS
380 St-Antoine West Suite W204 (mezzanine level) Montréal, Québec, Canada H2Y 3X7
www.infoentrepreneurs.org
514-496-4636 | 888-576-4444 [email protected]

Consent to Cookies
This website uses necessary cookies to ensure its proper functioning and security. Other cookies and optional technologies make it possible to facilitate, improve or personalize your navigation on our website. If you click "Refuse", some portions of our website may not function properly. Learn more about our privacy policy.
Click on one of the two buttons to access the content you wish to view.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Prepare a Budget for an Organization: 4 Steps

- 16 Nov 2021
An organization’s budget dictates how it leverages capital to work toward goals. For this reason, the ability to prepare a budget is one of the most crucial skills for any business leader —whether a current or aspiring entrepreneur, executive, functional lead, or manager.
Before preparing your first organizational budget, it’s important to understand what goes into a budget and the key steps involved in creating one.
What Is a Budget?
A budget is a document businesses use to track income and expenses in a detailed enough way to make operational decisions.
Budgets are typically forward-looking in nature. Income is based on projections and estimates for the periods they cover, as are expenses. For this reason, organizations often create both short- (monthly or quarterly) and long-term (annual) budgets, where the short-term budget is regularly adjusted to ensure the long-term budget stays on track.
Access your free e-book today.
Most organizations also prepare what’s known as an “actual budget” or “actual report” to compare estimates against reality following the period covered by the budget. This allows an organization to understand where it went wrong in the budgeting process and adjust estimates moving forward.
Budget vs. Cash Flow Statement
If the definition above sounds similar to a cash flow statement , you’re right: Your organization’s budget and cash flow statement are similar in that they both monitor the flow of money into and out of your business. Yet, they differ in key ways.
First, a budget typically offers more granular details about how money is spent than a cash flow statement does. This provides greater context for making tactical business decisions, such as considering where to trim business expenses.
Related: The Beginner’s Guide to Reading & Understanding Financial Statements
Second, a budget is, quite literally, a tool used to direct work done within an organization. The cash flow statement plays a different role by offering a higher-level overview of how money moves into, throughout, and out of an organization.
Instead of thinking of the two documents as competing, view them as complementary, with each playing a role in driving your business’s performance.
Steps to Prepare a Budget for Your Organization
The steps below can be followed whether creating a budget for a project, initiative, department, or entire organization.
1. Understand Your Organization’s Goals
Before you compile your budget, it’s important to have a firm understanding of the goals your organization is working toward in the period covered by it. By understanding those goals, you can prepare a budget that aligns with and facilitates them.
Related: The Advantages of Data-Driven Decision-Making
For example, consider a business that regularly experiences year-over-year revenue growth that’s offset by rising expenses. That organization might benefit from focusing efforts on better controlling expenses during the budgeting process.
Alternatively, consider a company launching a new product or service. The company may invest more heavily in the fledgling business line to grow it. With this goal, the company may need to trim expenses or growth initiatives elsewhere in its budget.
2. Estimate Your Income for the Period Covered by the Budget
To allocate funds for business expenses, you first need to determine your income and cash flow for the period to the best of your ability.
Depending on the nature of your organization, this can be a simple or complicated process. For example, a business that sells products or services to known clients locked in with contracts will likely have an easier time estimating income than a business that depends on active sales activity. In the second case, it would be important to reference historical sales and marketing data to understand whether the market is changing in a way that might cause you to miss or exceed historical trends.
Related: How to Read & Understand an Income Statement
Beyond income from sales activity, you should include other income sources, such as returns on investments, asset sales, and bond or share offerings.

3. Identify Your Expenses
Once you understand your projected income for the period, you need to estimate your expenses. This process involves three main categories: fixed costs, variable expenses, and one-time expenses.
Fixed costs are any expenses that remain constant over time and don’t dramatically vary from week to week or month to month. In many cases, those expenses are locked in by some form of contract, making it easy to anticipate and account for them. This category usually includes expenses related to overhead, such as rent payments and utilities. Phone, data, and software subscriptions can also fall into this category, along with debt payments. Any expense that’s regular and expected should be included.
Related: 6 Budgeting Tips for Managers
Variable expenses are those your business incurs, which vary over time depending on several factors, including sales activities. Your shipping and distribution costs, for example, are likely to be higher during a period when you sell more product than one when you sell less product. Likewise, utilities such as water, gas, and electricity will be higher during periods of increased use. This is especially true for businesses that manufacture their own products. Sales commissions, materials costs, and labor costs are other examples of variable expenses.
Both fixed expenses and variable expenses are recurring in nature, making it easy to account for them (even if variable expenses must be projected). One-time expenses , also called “one-time spends,” don’t recur and happen more rarely. Purchasing equipment or facilities, developing a new product or service, hiring a consultant, and handling a security breach are all examples of one-time expenses. Understanding major initiatives—and what it will take to accomplish them—and what you’ve spent in previous years on similar expenses can help account for them in your budget, even if you’re unsure of their exact values.
4. Determine Your Budget Surplus or Deficit
After you’ve accounted for all your income and expenses, you can apply them to your budget. This is where you determine whether you have enough projected income to cover all your expenses.
If you have more than enough income to cover your expenses, you have a budget surplus. Knowing this, you should determine how to use additional funds best. You may, for example, move the money into a rainy day fund you can access should your actual income fall short of projections. Alternatively, you may deploy the funds to grow your business.
On the other hand, if your expenses exceed your income, you have a budget deficit. At this point, you must identify the best path forward to close the gap. Can you bring in additional funds by selling more aggressively? Can you lower your fixed or variable expenses? Would you consider selling bonds or shares of company stock to infuse the business with additional capital?

An Important Financial Statement
The person responsible for generating a budget varies depending on an organization’s nature and its budgetary goals. An entrepreneur or small business owner, for example, is likely to prepare an organizational budget on their own. Meanwhile, a larger organization may rely on a member of the accounting department to generate a budget for the entire business. Individual department heads or functional leads might also be called on to submit budget proposals for their teams.
With this in mind, anyone who aspires to start their own business or move into an organizational leadership position can benefit from learning how to prepare a budget.
Do you want to take your career to the next level? Consider enrolling in our eight-week Financial Accounting course or three-course Credential of Readiness (CORe) program to learn financial concepts that can enable you to unlock critical insights into business performance and potential. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author

- Creating a Small Business Financial Plan

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on September 02, 2023
Get Any Financial Question Answered
Table of contents, financial plan overview.
A financial plan is a comprehensive document that charts a business's monetary objectives and the strategies to achieve them. It encapsulates everything from budgeting and forecasting to investments and resource allocation.
For small businesses, a solid financial plan provides direction, helping them navigate economic challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and ensure sustainable growth.
The strength of a financial plan lies in its ability to offer a clear roadmap for businesses.
Especially for small businesses that may not have a vast reserve of resources, prioritizing financial goals and understanding where every dollar goes can be the difference between growth and stagnation.
It lends clarity, ensures informed decision-making, and sets the stage for profitability and success.
Understanding the Basics of Financial Planning for Small Businesses
Role of financial planning in business success.
Financial planning is the backbone of any successful business endeavor. It serves as a compass, guiding businesses toward profitability, stability, and growth.
With proper financial planning, businesses can anticipate potential cash shortfalls, make informed investment decisions, and ensure they have the capital needed to seize new opportunities.
For small businesses, in particular, tight financial planning can mean the difference between thriving and shuttering. Given the limited resources, it's vital to maximize every dollar and anticipate financial challenges.
Through diligent planning, small businesses can position themselves competitively, adapt to market changes, and drive consistent growth.
Core Components of a Financial Plan for Small Businesses
Every financial plan comprises several core components that, together, provide a holistic view of a business's financial health and direction. These include setting clear objectives, estimating costs , preparing financial statements , and considering sources of financing.
Each component plays a pivotal role in ensuring a thorough and actionable financial strategy .
For small businesses, these components often need a more granular approach. Given the scale of operations, even minor financial missteps can have significant repercussions.
As such, it's essential to tailor each component, ensuring they address specific challenges and opportunities that small businesses face, from initial startup costs to revenue forecasting and budgetary constraints.
Setting Clear Small Business Financial Objectives
Identifying business's short-term and long-term financial goals.
Every business venture starts with a vision. Translating this vision into actionable financial goals is the essence of effective planning.
Short-term goals could range from securing initial funding and achieving a set monthly revenue to covering startup costs. These targets, usually spanning a year or less, set the immediate direction for the business.
On the other hand, long-term financial goals delve into the broader horizon. They might encompass aspirations like expanding to new locations, diversifying product lines, or achieving a specific market share within a decade.
By segmenting goals into short-term and long-term, businesses can craft a step-by-step strategy, making the larger vision more attainable and manageable.
Understanding the Difference Between Profitability and Cash Flow
Profitability and cash flow, while closely linked, are distinct concepts in the financial realm. Profitability pertains to the ability of a business to generate a surplus after deducting all expenses.
It's a metric of success and indicates the viability of a business model . Simply put, it answers whether a business is making more than it spends.
In contrast, cash flow represents the inflow and outflow of cash within a business. A company might be profitable on paper yet struggle with cash flow if, for instance, clients delay payments or unexpected expenses arise.
For small businesses, maintaining positive cash flow is paramount. It ensures that they can cover operational costs, pay employees, and reinvest in growth, even if they're awaiting payments or navigating financial hiccups.
Estimating Small Business Startup Costs (for New Businesses)
Fixed vs variable costs.
When embarking on a new business venture, understanding costs is paramount. Fixed costs remain consistent regardless of production levels. They include expenses like rent, salaries, and insurance . These are predictable outlays that don't fluctuate with business performance.
Variable costs , conversely, change in direct proportion to production or business activity. Think of costs associated with materials for manufacturing or commission for sales .
For a startup, delineating between fixed and variable costs aids in crafting a more dynamic budget, allowing for adaptability as the business scales and evolves.
One-Time Expenditures vs Ongoing Expenses
Startups often grapple with numerous upfront costs. From purchasing equipment and setting up a workspace to initial marketing campaigns, these one-time expenditures lay the foundation for business operations.
They differ from ongoing expenses like utility bills, raw materials, or employee wages that recur monthly or annually.
For a small business owner, distinguishing between these costs is critical. One-time expenditures often demand a larger chunk of initial capital, while ongoing expenses shape the monthly and annual budget.
By categorizing them separately, businesses can strategize funding needs more effectively, ensuring they're equipped to meet both immediate and recurrent financial obligations.
Funding Sources for Small Businesses
Personal savings.
This is often the most straightforward way to fund a startup. Entrepreneurs tap into their personal savings accounts to jumpstart their business.
While this method has the benefit of not incurring debt or diluting company ownership, it intertwines the individual's personal financial security with the business's fate.
The entrepreneur must be prepared for potential losses, and there's the evident psychological strain of putting one's hard-earned money on the line.
Loans can be sourced from various institutions, from traditional banks to credit unions . They offer a substantial sum of money that can be paid back over time, usually with interest .
The main advantage of taking a loan is that the entrepreneur retains full ownership and control of the business.
However, there's the obligation of monthly repayments, which can strain a business's cash flow, especially in its early days. Additionally, securing a loan often requires collateral and a sound credit history.
Investors, including angel investors and venture capitalists , offer capital in exchange for equity or a stake in the company.
Angel investors are typically high-net-worth individuals who provide funding in the initial stages, while venture capitalists come in when there's proven business potential, often injecting larger sums. The advantage is substantial funding without the immediate pressure of repayments.
However, in exchange for their investment, they often seek a say in business decisions, which might mean compromising on some aspects of the original business vision.
Grants are essentially 'free money' often provided by government programs, non-profit organizations, or corporations to promote innovation and support businesses in specific sectors.
The primary advantage of grants is that they don't need to be repaid, nor do they dilute company ownership. However, they can be highly competitive and might come with stipulations on how the funds should be used.
Moreover, the application process can be lengthy and requires showcasing the business's potential or alignment with the specific goals or missions of the granting institution.

Preparing Key Financial Statements for Small Businesses
Income statement (profit & loss).
An Income Statement , often termed as the Profit & Loss statement , showcases a business's financial performance over a specific time frame. It details revenues , expenses, and ultimately, profits or losses.
By analyzing this statement, business owners can pinpoint revenue drivers, identify exorbitant costs, and understand the net result of their operations.
For small businesses, this document is instrumental in making informed decisions. For instance, if a certain product line is consistently unprofitable, it might be prudent to discontinue it. Conversely, if another segment is thriving, it might warrant further investment.
The Income Statement, thus, serves as a financial mirror, reflecting the outcomes of business strategies and decisions.
Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet offers a snapshot of a company's assets , liabilities , and equity at a specific point in time.
Assets include everything the business owns, from physical items like equipment to intangible assets like patents .
Liabilities, on the other hand, encompass what the company owes, be it bank loans or unpaid bills.
Equity represents the owner's stake in the business, calculated as assets minus liabilities.
This statement is crucial for small businesses as it offers insights into their financial health. A robust asset base, minimal liabilities, and growing equity signify a thriving enterprise.
In contrast, mounting liabilities or dwindling assets could be red flags, signaling the need for intervention and strategy recalibration.
Cash Flow Statement
While the Income Statement reveals profitability, the Cash Flow Statement tracks the actual movement of money.
It categorizes cash flows into operating (day-to-day business), investing (buying/selling assets), and financing (loans or equity transactions) activities. This statement unveils the liquidity of a business, indicating whether it has sufficient cash to meet immediate obligations.
For small businesses, maintaining positive cash flow is often more vital than showcasing profitability.
After all, a business might be profitable on paper yet struggle if clients delay payments or unforeseen expenses emerge.
By regularly reviewing the Cash Flow Statement, small business owners can anticipate cash crunches and strategize accordingly, ensuring seamless operations irrespective of revenue cycles.

Small Business Budgeting and Expense Management
Importance of budgeting for a small business.
Budgeting is the financial blueprint for any business, detailing anticipated revenues and expenses for a forthcoming period. It's a proactive approach, enabling businesses to allocate resources efficiently, plan for investments, and prepare for potential financial challenges.
For small businesses, a meticulous budget is often the linchpin of stability, ensuring they operate within their means and avoid financial pitfalls.
Having a well-defined budget also fosters discipline. It curtails frivolous spending, emphasizes cost-efficiency, and sets clear financial boundaries.
For small businesses, where every dollar counts, a stringent budget is the gateway to financial prudence, ensuring that funds are utilized judiciously, fostering growth, and minimizing wastage.
Strategies for Reducing Costs and Optimizing Expenses
Bulk purchasing.
When businesses buy supplies in large quantities, they often benefit from discounts due to economies of scale . This can significantly reduce per-unit costs.
However, while bulk purchasing leads to immediate savings, businesses must ensure they have adequate storage and that the products won't expire or become obsolete before they're used.
Renegotiating Vendor Contracts
Regularly reviewing and renegotiating contracts with suppliers or service providers can lead to better terms and lower costs. This might involve exploring volume discounts, longer payment terms, or even bartering services.
Building strong relationships with vendors often paves the way for such negotiations.
Adopting Energy-Saving Measures
Simple changes, like switching to LED lighting or investing in energy-efficient appliances, can lead to long-term savings in utility bills. Moreover, energy conservation not only reduces costs but also minimizes the environmental footprint, which can enhance the business's reputation.
Embracing Technology
Modern software and technology can streamline business processes. Automation tools can handle repetitive tasks, reducing labor costs.
Meanwhile, data analytics tools can provide insights into customer preferences and behavior, ensuring that marketing budgets are used effectively and target the right audience.
Streamlining Operations
Regularly reviewing and refining business processes can eliminate redundancies and improve efficiency. This might mean merging roles, cutting down on unnecessary meetings, or simplifying supply chains. A leaner operation often translates to reduced expenses.

Outsourcing Non-core Tasks
Instead of maintaining an in-house team for every function, businesses can outsource tasks that aren't central to their operations.
For instance, functions like accounting , IT support, or digital marketing can be outsourced to specialized agencies, often leading to cost savings and access to expert skills.
Cultivating a Culture of Frugality
Encouraging employees to adopt a cost-conscious mindset can lead to collective savings. This can be fostered through incentives, regular training, or even simple practices like recycling and reusing office supplies.
When everyone in the organization is attuned to the importance of cost savings, the cumulative effect can be substantial.

Forecasting Small Business Revenue and Cash Flow
Techniques for predicting future sales in a small business, past sales data analysis.
Historical sales data is a foundational element in any forecasting effort. By reviewing previous sales figures, businesses can identify patterns, understand seasonal fluctuations, and recognize the effects of past initiatives.
This information offers a baseline upon which to build future projections, accounting for known recurring variables in the business cycle .
Market Research
Understanding the larger market dynamics is crucial for accurate forecasting. This involves tracking industry trends, monitoring shifts in consumer behavior, and being aware of potential market disruptions.
For instance, a sudden technological advancement can change consumer preferences or regulatory changes might impact an industry.
Local Trend Analysis
For small businesses, localized insights can be especially impactful. Observing local competitors, understanding regional consumer preferences, or noting shifts in the local economy can offer precise data points.
These granular details, when integrated into a larger forecasting model, can enhance prediction accuracy.
Customer Feedback
Direct feedback from customers is an invaluable source of insights. Surveys, focus groups, or even informal chats can reveal customer sentiments, preferences, and potential future purchasing behavior.
For instance, if a majority of loyal customers express interest in a new product or service, it can be indicative of future sales potential.
Moving Averages
This technique involves analyzing a series of data points (like monthly sales) by creating averages from different subsets of the full data set.
For yearly forecasting, a 12-month moving average can be used to smooth out short-term fluctuations and highlight longer-term trends or cycles.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical tool used to identify relationships between variables. In sales forecasting, it can help understand how different factors (like marketing spend, seasonal variations, or competitor actions) relate to sales figures.
Once these relationships are understood, businesses can predict future sales based on planned actions or expected external events.

Understanding the Cash Cycle of Business
The cash cycle encompasses the time it takes for a business to convert resource investments, often in the form of inventory, back into cash.
This involves the processes of purchasing inventory, selling it, and subsequently collecting payment. A shorter cycle implies quicker cash turnarounds, which are vital for liquidity.
For small businesses, a firm grasp of the cash cycle can aid in managing cash flow more effectively.
By identifying bottlenecks or delays, businesses can strategize to expedite processes. This might involve renegotiating payment terms with suppliers, offering discounts for prompt customer payments, or optimizing inventory levels to prevent overstocking.
Ultimately, understanding and optimizing the cash cycle ensures that a business remains liquid and agile.
Preparing for Seasonality and Unexpected Changes
Seasonality affects many businesses, from the ice cream vendor witnessing summer surges to the retailer bracing for holiday shopping frenzies.
By analyzing historical data and market trends, businesses can prepare for these cyclical shifts, ensuring they stock up, staff appropriately, and market effectively.
Small businesses, often operating on tighter margins , need to be especially vigilant. Beyond seasonality, they must also brace for unexpected changes – a local construction project obstructing store access, a sudden competitor emergence, or unforeseen regulatory changes.
Building a financial buffer, diversifying product or service lines, and maintaining flexible operational strategies can equip small businesses to weather these unforeseen challenges with resilience.
Securing Small Business Financing and Capital
Role of debt and equity financing.
When businesses seek external funding, they often grapple with the debt vs. equity conundrum. Debt financing involves borrowing money, typically via loans. While it doesn't dilute ownership, it necessitates regular interest payments, potentially impacting cash flow.
Equity financing, on the other hand, entails selling a stake in the business to investors. It might not demand regular repayments, but it dilutes ownership and might influence business decisions.
Small businesses must weigh these options carefully. While loans offer a structured repayment plan and retained control, they might strain finances if the business hits a rough patch.
Equity financing, although relinquishing some control, might bring aboard strategic partners, offering expertise and networks in addition to funds.
The optimal choice hinges on the business's financial health, growth aspirations, and the founder's comfort with sharing control.
Choosing Between Different Types of Loans
A staple in the lending arena, term loans offer businesses a fixed amount of capital that is paid back over a specified period with interest. They're often used for significant one-time expenses, such as purchasing machinery, real estate , or even business expansion.
With predictable monthly payments, businesses can plan their budgets accordingly. However, they might require collateral and a robust credit history for approval.
Lines of Credit
Unlike term loans that provide funds in a lump sum, a line of credit grants businesses access to a pool of funds up to a certain limit.
Businesses can draw from this line as needed, only paying interest on the amount they use. This makes it a versatile tool, especially for managing cash flow fluctuations or unexpected expenses. It serves as a financial safety net, ready for use whenever required.
As the name suggests, microloans are smaller loans designed to cater to businesses that might not need substantial amounts of capital. They're particularly beneficial for startups, businesses with limited credit histories, or those in need of a quick, small financial boost.
Since they are of a smaller denomination, the approval process might be more lenient than traditional loans.
Peer-To-Peer Lending
A contemporary twist to the traditional lending model, peer-to-peer (P2P) platforms connect borrowers directly with individual lenders or investor groups.
This direct model often translates to quicker approvals and competitive interest rates as the overheads of traditional banking structures are removed. With technology at its core, P2P lending can offer a more user-friendly, streamlined process.
However, creditworthiness still plays a pivotal role in determining interest rates and loan amounts.
Crowdfunding and Alternative Financing Options
In an increasingly digital age, crowdfunding platforms like Kickstarter or Indiegogo have emerged as viable financing avenues.
These platforms enable businesses to raise small amounts from a large number of people, often in exchange for product discounts, early access, or other perks. This not only secures funds but also validates the business idea and fosters a community of supporters.
Other alternatives include invoice financing, where businesses get an advance on pending invoices, or merchant cash advances tailored for businesses with significant credit card sales.
Each financing mode offers unique advantages and constraints. Small businesses must meticulously evaluate their financial landscape, growth trajectories, and risk appetite to harness the most suitable option.
Small Business Tax Planning and Management
Basic tax obligations for small businesses.
Navigating the maze of taxation can be daunting, especially for small businesses. Yet, understanding and fulfilling tax obligations is crucial.
Depending on the business structure—whether sole proprietorship , partnership , LLC , or corporation—different tax rules apply. For instance, while corporations are taxed on their earnings, sole proprietors report business income and expenses on their personal tax returns.
In addition to income taxes, small businesses may also be responsible for employment taxes if they have employees. This covers Social Security , Medicare , federal unemployment, and sometimes state-specific taxes.
There might also be sales taxes, property taxes, or special state-specific levies to consider.
Consistently maintaining accurate financial records, being aware of filing deadlines, and setting aside funds for tax obligations are essential practices to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Advantages of Tax Planning and Potential Deductions
Tax planning is the strategic approach to minimizing tax liability through the best use of available allowances, deductions, exclusions, and breaks.
For small businesses, effective tax planning can lead to significant savings.
This might involve strategies like deferring income to a later tax year, choosing the optimal time to purchase equipment, or taking advantage of specific credits available to businesses in certain sectors or regions.
Several potential deductions can reduce taxable income for small businesses. These include expenses like rent, utilities, business travel, employee wages, and even certain meals.
By keeping abreast of tax law changes and actively seeking out eligible deductions, small businesses can optimize their financial landscape, ensuring they're not paying more in taxes than necessary.
Importance of Hiring a Tax Professional or Accountant
While it's feasible for small business owners to manage their taxes, the intricate nuances of tax laws make it beneficial to consult professionals.
An experienced accountant or tax consultant can not only ensure compliance but can proactively recommend strategies to reduce tax liability.
They can guide businesses on issues like whether to classify someone as an employee or a contractor, how to structure the business for optimal taxation, or when to make certain capital investments.
Beyond just annual tax filing, these professionals offer year-round counsel, helping businesses maintain clean financial records, stay updated on tax law changes, and plan for future financial moves.
The investment in professional advice often pays dividends , saving businesses from costly mistakes, penalties, or missed financial opportunities.
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting the Small Business Financial Plan
Setting checkpoints and milestones.
Like any strategic blueprint, a financial plan isn't static. It serves as a guiding framework but should be flexible enough to adapt to evolving business realities.
Setting regular checkpoints— quarterly , half-yearly, or annually—can help businesses assess whether they're on track to meet their financial objectives.
Milestones, such as reaching a specific sales target, launching a new product, or expanding into a new market, offer tangible markers of progress. Celebrating these victories can bolster morale, while any shortfalls can serve as lessons, prompting strategy tweaks. F
or small businesses, where agility is an asset, regularly revisiting the financial plan ensures that the business remains aligned with its overarching financial goals while being responsive to the dynamic marketplace.
Using Financial Ratios to Monitor Business Health
Financial ratios offer a distilled snapshot of a business's health. Ratios like the current ratio ( current assets divided by current liabilities ) can shed light on liquidity, indicating whether a business can meet short-term obligations.
The debt-to-equity ratio , contrasting borrowed funds with owner's equity, offers insights into the business's leverage and potential financial risk.
Profit margin , depicting profitability relative to sales, can highlight operational efficiency. By consistently monitoring these and other pertinent ratios, small businesses can glean actionable insights, understanding their financial strengths and areas needing attention.
In a realm where early intervention can stave off major financial setbacks, these ratios serve as vital diagnostic tools, guiding informed decision-making.
Pivoting Strategies Based on Financial Performance
In the ever-evolving world of business, flexibility is paramount. If financial reviews indicate that certain strategies aren't yielding anticipated results, it might be time to pivot.
This could involve tweaking product offerings, revising pricing strategies, targeting a different customer segment, or even overhauling the business model.
For small businesses, the ability to pivot can be a lifeline. It allows them to respond swiftly to market changes, customer feedback, or internal challenges.
A robust financial plan, while offering direction, should also be pliable, accommodating shifts in strategy based on real-world performance. After all, in the business arena, adaptability often spells the difference between stagnation and growth.

Bottom Line
Financial foresight is integral for the stability and growth of small businesses. Effective revenue and cash flow forecasting, anchored by historical sales data and enhanced by market research, local trends, and customer feedback, ensures businesses are prepared for future demands.
With the unpredictability of the business environment, understanding the cash cycle and preparing for unforeseen challenges is essential.
As businesses contemplate external financing, the decision between debt and equity and the myriad of loan types, should be made judiciously, keeping in mind the business's health, growth aspirations, and risk appetite.
Furthermore, diligent tax planning, with professional guidance, can lead to significant financial benefits. Regular reviews using financial ratios allow businesses to gauge their performance, adapt strategies, and pivot when necessary.
Ultimately, the agility to adapt, guided by a well-structured financial plan, is pivotal for businesses to thrive in a dynamic marketplace.
Creating a Small Business Financial Plan FAQs
What is the importance of a financial plan for small businesses.
A financial plan offers a structured roadmap, guiding businesses in making informed decisions, ensuring growth, and navigating financial challenges.
How do forecasting revenue and understanding cash cycles aid in financial planning?
Forecasting provides insights into expected income, aiding in budget allocation, while understanding cash cycles ensures effective liquidity management.
What are the core components of a financial plan for small businesses?
Core components include setting objectives, estimating startup costs, preparing financial statements, budgeting, forecasting, securing financing, and tax management.
Why is tax planning vital for small businesses?
Tax planning ensures compliance, optimizes tax liabilities through available deductions, and helps businesses save money and avoid penalties.
How often should a small business review its financial plan?
Regular reviews, ideally quarterly or half-yearly, ensure alignment with business goals and allow for strategy adjustments based on real-world performance.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Average Cost of a Certified Financial Planner
- Benefits of Having a Financial Planner
- Cash Flow Management
- Cash Flow-Based Financial Planning
- Components of a Good Financial Plan
- Debt Reduction Strategies
- Divorce Financial Planning
- Education Planning
- Fee-Only Financial Planning
- Financial Contingency Planning
- Financial Planner for Retirement
- Financial Planning Career Pathway
- Financial Planning Pyramid
- Financial Planning Tips
- Financial Planning Trends
- Financial Planning and Analysis
- Financial Planning for Allied Health Professionals
- Financial Planning for Married Couples
- Financial Planning for Military Families
- Financial Planning for Retirement
- Financial Planning for Startups
- Financial Planning vs Budgeting
- Financial Tips for Young Adults
- How to Become a Chartered Financial Planner
- How to Build a 5-Year Financial Plan
- Limitations of Financial Planning
- Military Spouse Financial Planning
- The Function of a Financial Planner
- When Do You Need a Financial Planner?
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Meet top certified financial advisors near you, find advisor near you, our recommended advisors.

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation

Claudia Valladares
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.
Get Started
Hey, did we answer your financial question.
We want to make sure that all of our readers get their questions answered.
Great, Want to Test Your Knowledge of This Lesson?
Create an Account to Test Your Knowledge of This Topic and Thousands of Others.
Get Your Question Answered by a Financial Professional
Create a free account and submit your question. We'll make sure a financial professional gets back to you shortly.
To Ensure One Vote Per Person, Please Include the Following Info
Great thank you for voting..
Unlock peak financial performance at Perform24
Financial Budgeting
Financial budgeting definition.
Financial budgeting is the process of planning company expenses and revenues for a time period. Budgets set forth the plans of management in financial terms. This includes allocating financial resources and identifying available cash flows for required spending.
A budget and financial planning strategy detail a company’s expectations for what it aims to achieve for the current, upcoming year or another timeframe. For example:
- Expense and revenue estimates
- Cash flows expected
- Debt reduction expected
- Comparison of actual versus projected business financial budget, calculation of variances between them
Financial budgeting represents the overall financial position, goals, and cash flow of an organization. This regular practice of timely operational and financial budgeting creates a baseline for comparison to see how actual results vary from expected performance.
Basic corporate financial budgeting process steps for an annual budget usually take between three to six months to complete. The components of this process, which remains confidential, might include:
- Establish and communicate management targets and goals
- Develop the detailed, final budget to directly support those targets and goals, and attach financial documents such as the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement
- Finalize employee compensation plans (usually this is part of the process)
- Compile and adjust budget model and measurement metrics so management can assess progress
- Review and make final changes
- Disseminate subordinate and/or line of business budgets across the organization
Financial budgeting enables a team to implement a business plan tactically to achieve corporate goals based on a detailed and descriptive roadmap using set metrics. This allows for careful monitoring of performance over time and the ability to make changes while in progress to eventually achieve the desired goals.
Financial Budgeting FAQs
What is financial budgeting and forecasting.
Financial budgeting and financial forecasting help organizations plan where and how to evolve. The financial budget helps the business with the plan itself and the financial forecasting helps the team assess the current financial situation and whether the organization is moving in the right direction financially. The two tools are used in tandem, but they are distinct.
Budgeting quantifies the projected finances a business will be working with during a period. It sets the company’s financial direction for that period and sets expectations for income and revenue.
In contrast, financial forecasting estimates how much income or revenue will be achieved in a future period. This projection helps determine whether the company is meeting goals, allocating funds properly, and going in the right direction.
Budgeting serves as a baseline for comparison; this way management can see how expectations differ from actual performance. Management uses financial forecasting to analyze historical trends and company data to determine how to allocate the budget for the future.
In brief, financial forecasting:
- Does not engage in the historical analysis of the difference between actual performance and past forecasts like budgeting
- This is the future-facing assessment of how to allocate the budget for a future period
- Updated regularly, periodically, month-to-month or quarterly, as inventory, operations, or the financial budgeting plan change
- Can be short-term and/or long-term and can be updated with new data; for example, quarterly revenue forecasts might need to be updated based on changes to customer roll-up
- With forecasted data, a management team can take immediate action
Why is Budgeting Important for Financial Planning?
There are several reasons why financial management is important:
Greater resource availability. The primary function of financial budgeting is to ensure core resources are available as needed to implement plans and achieve business goals. Advance planning of financials allows leadership to determine which initiatives and teams require more or fewer resources.
Inform financial goals. Financial planning and budgeting can help set metrics for internal financial goals and record progress against them. Budgeting for any given period involves assessing how much revenue is needed to meet company-wide and team financial goals, not just allocating spend. Financial goals should be evidence-based and achievable enough that they inform other budget allocations.
Prioritize projects and initiatives. The value proposition of financial budgeting techniques is that prioritizing projects and initiatives is a natural byproduct of the process. When prioritizing each project, consider how it aligns with company values, the potential return on investment (ROI), and the extent it might affect broader financial goals. Determine each line item’s value to the organization and compare them.
Optimize financing opportunities. Documented budgetary information is particularly important for anyone potentially seeking funding or financing, such as a startup seeking outside investors, or an existing company needing a loan. Investors value detailed information about past, current, and predicted financial performance highly. Offering budgeting and financial reporting documents for previous periods demonstrates the ability to manage the finances of a business and allocate funds, and in some cases is required.
Achieve optimal flexibility. Ideally, everything goes to plan and all predictions are accurate. But as things like the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic in 2020 show us, this is rarely the case for organizations in the real world. Executives must often rework budgets thoughtfully and rapidly to account for safety concerns, major losses, and potential reputation damage. A budget is a plan to start with, and an agile mindset and the right tools enable leadership to adjust the plan as needed.
Business financial management is important because it helps organizations improve their profitability, extend their mission, save money, remain economically stable, and increase in value over the long haul.
Types of Financial Budgets
There are several types of financial budgets. Each approaches financial planning prioritizing different factors. Here are some common types:
Zero-based budgeting. At the start of each planning period, each item is set at zero dollars before reallocating. This approach is often used by organizations in financial distress, allowing them to start over each period.
Activity-based budgeting. Works backward from the company’s goals to determine the cost of achieving them and can be used to improve efficiencies and cut costs, especially in a large business.
Static budgeting/Incremental-based budgeting. Creates the budget for the upcoming period by adding or subtracting a percentage from the previous period using historical data. This model is usually best for businesses with highly predictable revenue and expenses that don’t fluctuate much.
Performance-based budgeting. Performance-based budgeting focuses on cash flow per unit toward programmatic results. It is often used by governments and nonprofits that need to keep an overall focus on their mission.
Value proposition budgeting. Assumes only line items that directly provide value to the organization should be included in the budget. This is another approach to government spending and sometimes to larger businesses taking an aggressive approach to spending.
Trialing various financial budgeting and forecasting techniques is one way to determine which is best suited to your organization; the right type of financial budget varies by situation and company.
What is the Financial Budgeting Process?
There are multiple steps in the process of creating a budget. Keep budgets as detailed and thorough as possible. Typically, a financial budget should include:
- All predicted revenue—including the value, types of revenue, and when it is expected
- Fixed expenses for the organization (employee salaries, insurance, property taxes, rent, utilities, etc.)
- Variable costs (maintenance, professional services, supplies, vehicle and travel expenses, etc.)
To create a budget, consider these financial budgeting tips:
- Review, collect, and comprehend all of the required budgetary inputs
- Analyze historical data, including previous budgets, to determine revenue and expense expectations by each fiscal period and year
- Collaborate with a cross-functional team of stakeholders, including budget owners, C-suite executives, and sales leaders to formulate the plan
- Identify any required capital expenditures such as infrastructure, equipment, or property that are required during the period
- Prepare financial statements with budgeted numbers including balance sheet, cash flow, and income statement
- Identify KPIs to measure progress
- Review the final budget for strategic growth opportunities such as adding equity or reducing debt, or other investment and divestment opportunities
Always monitor progress throughout the budgeted period, based on performance against budgeted goals, and update forecasts periodically.
Generate reliable financial forecasts as follows:
- Identify key metrics to focus the forecast such as marketing expenses or sales volume
- Input the latest actuals into the forecast template
- Determine the forecast time frame, typically to the end of the budgeted period
- Calculate trends based on year-to-date and historical actuals
- Apply trend calculations to real-time numbers and forecast results
- When updating the forecast, consider any variables such as geopolitical conditions or business situations, like a merger, that could skew the forecast
Periodic forecasts typically only project to the end of the current fiscal year. Instead of projecting to the end of the fiscal year, rolling forecasts are generated monthly, quarterly or weekly to help plan for a specific period beyond the annual budget—the coming six quarters, for instance. The forecast actualizes a unit, whether it’s a fiscal month or quarter, and then “rolls” to the next period. This enables the leadership to keep sight of long-term business strategies.

What is Included in a Financial Budget?
A financial budget offers a strategic overview of how a business manages cash flow, assets, expenses, and income. It establishes a comprehensive overview of revenue from core operations relative to spending via a comprehensive documentary picture of a company’s financial health. Financial budgets typically include a balance sheet, budgeted income statement, capital expenditures budget, and cash budget.
Benefits of Financial Budgeting
Financial budgeting enables an organization to chart its path and empowers the management team to engage in strategic enterprise budgeting and planning . The financial budgeting process delivers a clearly defined plan that reflects organizational goals for operations and finances. Financial budgets offer critical guidance for the year’s goals.
Other key benefits of financial budgeting include:
- Close examination of financial activities
- Expenses are more likely to be assessed for viability
- Detailed documentation of all the uses and sources of cash is required, ultimately allowing for accurate anticipation of cash flows by management
- Cross-functional stakeholders involved in budgeting create a sense of ownership and motivate team to achieve budgeted goals
- Budget, forecasts, and up-to-date financial results can always be compared for real-time insights into performance, and offer a chance to adapt
- Clarifies internal hierarchies and individual responsibilities
- Clarifies where and when financial resources are allocated and needed
Remember, budgets can become outdated as they are prepared in advance and based on a number of assumptions, so forecasting is also important—especially when questions are time-sensitive.
Other benefits to forecasting include:
- Forecasting identifies trends that may require a strategic adjustment
- A well-informed prediction of how, when, and why future costs may fluctuate enables simpler management of capital requirements and cash flows
- Reliable forecasts may open up more opportunities for financing with investors
- Forecasted numbers offer a logical starting point for the next budget
- Forecasting offers smart short-term focus for managers
Who is Responsible for Enterprise Financial Budgeting?
The budget owner is the person who is ultimately responsible for ensuring that the budget is followed. Budget owners are usually the operational directors and managers of companies who must ensure that the company follows whatever budget is laid out for them. The shareholders, owners, or the board of directors tasks the budget owner with this one, overarching duty.
Many large companies employ a committee of multiple budget owners charged with ensuring that the budget is followed. Typically, the committee consists of directors and managers from various divisions and departments of the company. This is a more democratic but less efficient approach that can lead to indecisiveness and even infighting.
However, even a single budget owner does not work alone and instead has consultants, financial experts, lawyers, industry experts, and others working under them. The budget owner is ultimately accountable to the shareholders or owners.
Typically on the budget owner team:
Department managers. Mid-level department managers provide information to the finance and accounting department throughout the budgeting process, reporting revenue contributions and departmental expenses and providing the details needed to project future income and expenses.
Finance and Accounting team. Corporate finance and accounting teams manage accounts receivable, accounts payable, bookkeeping, and payroll. Senior associates might create sales and payroll reports, analyze input-cost trends, audit expense reports, or engage in other tasks as part of the budgeting process.
Corporate executives. Corporate executives at the top management level are directly accountable to the board of directors, manage the company’s finances, and present final budget proposals to the board. The chief financial officer (CFO) or equivalent executive is responsible for top-level budgets based on the finance or accounting team’s input. Sales directors forecast the next year’s sales trends. Chief operating officers (COOs) forecast future payroll and operating costs. Chief marketing officers (CMOs) forecast the next year’s expected market-share increase and marketing expenses, while chief technology officers (CTOs) forecast technology expenses.
Board of Directors. Corporate executives report directly to the board of directors who serve as the stockholders’ chosen representatives, and offer the final vote on proposed budgets. Board members answer directly to shareholders and company owners.
What are Financial Budgeting Tools?
There are a number of challenges that impede financial budgeting and forecasting efforts. Financial planning & budgeting software tools are commonly used to deal with these issues—because nearly all of them have to do with coping with data.
Disparate, wide-ranging sources of disconnected data collected. Data silos are a tremendous problem for finance and budgeting teams. Trying to extract data from siloed sources reduces the time spent on real analysis. It slows down the financial budgeting and forecasting cycle and makes it tougher to adapt to rapidly changing market conditions.
Manual processes and inaccurate data. While many finance teams still use offline spreadsheets and similar analog tools for financial budgeting and other core FP&A activities, they are slow, labor intensive, and impossible to manage across large businesses. Something like an Excel spreadsheet lacks the version control and data integrity solutions of corporate financial budgeting software with database capabilities.
Time-consuming data collection and input automated. Many contributors spending time editing many spreadsheets means that aggregation and data entry will be lengthy, error-ridden tasks. Finance automation tools render this manual sorting of budgeting data unnecessary.
Difficult collaboration simplified. The old-fashioned way of collecting data for the budgeting process from various departments is difficult. Spreadsheets are inflexible, and it’s not easy to aggregate, manipulate, retroactively change, and/or share budgeting data. An FP&A platform such as Planful makes data sharing and work between cross-functional teams simpler, and lends visibility to processes with current, accurate data.
Insights made relevant. Real-time tracking of forecasting and financial budgeting KPIs are the key to regulating the financial health of a business. This kind of agile budgeting and financial planning process keeps companies profitable and competitive.
The role of data-driven platforms is to remain responsive, and rapidly help the user share insights. They can generate accurate sales forecasts based on historical data, create projections for future sales, and predict fluctuations to help develop accurate budget plans.
Does Planful Help With Financial Budgeting?
How does Planful financial budgeting and forecasting software help with financial budgeting?
Planful financial budgeting and forecasting software helps by providing teams with audit trails, workflows, and data validation measures all in one place for confident financial budgeting and forecasting.
There are many reasons to automate data entries for financial budgeting and forecasting:
- Reduce budgeting and forecasting cycle times by up to 50% or more
- View forecasts, budgets, and actuals from the same template so you can more easily identify trends and variances
- Drill down into transaction-level details right from your budget and forecast templates
- Complete planning solutions don’t usually require maintenance or management from IT
- Cross-functional stakeholders can all work from the same connected template. Audit trails allow users to track, validate, and approve changes and add commentary
- Scenario modeling features make it simple to test forecasts and budgets against an unlimited number of potential future business scenarios
- Customizable workflows let you supplement the budgeting process with an additional executive review step
- Data visualization dashboarding helps stakeholders visualize where the business is headed
Curious to learn what else Planful can do to help your team learn how to do financial budgeting more effectively? Contact us for a demo of our automated financial budgeting services.
Get Started with Planful
Small Business Resources is now the Center for Business Empowerment.
Suggested Keywords
Center for Business Empowerment
How to create a budget for your business
January 16, 2024 | 7 minute read
If you want to increase the odds of having a successful small business, start by creating a budget. A budget is a powerful tool. It helps you understand how much money you have and what you’ve spent where — and provides clues about how much money you’ll need in the short and long term. It can also help shape key business decisions like whether to add staff and equipment or where to cut expenses to avoid cash flow issues .
A budget is critical, particularly at a time when companies are coping with rising costs. Seventy-nine percent of small business owners polled in Bank of America’s 2023 Small Business Owner Report said they are concerned about inflation and 68% said they are worried about commodity prices. Here’s how to create a budget and use it to make the best decisions today, tomorrow and in the future.
What is a business budget?
Simply put, a budget is a spending plan based on your business’ income and expenses. It shows your available capital, estimates spending and assists in predicting revenue. The information in your budget can help you plan your company’s next moves. A budget looks at activities for a specified time. Think of it as a tool to help you allocate resources toward the strategic priorities in your business plan.
What are the benefits of creating a business budget?
Budgeting enables you to allocate financial resources more effectively, track variances and make changes to your spending plan as needed. A budget provides a much-needed assist in maintaining daily operations, giving you the intel to deploy your cash more strategically so you don’t face a cash flow crunch. It can identify when you need to raise financing. Debt is a fact of life in many businesses. A budget can help you manage debts with controlled and planned financial activities.
A budget can also help you stay ready for the unexpected. Staying within your budget and creating a safety net for emergencies will give you a firmer financial foundation.
Types of business budgets
When it comes to business budgets, it’s not one and done. There are several types that may be helpful in your business.
Master budget
This type of budget uses inputs from financial statements, your cash forecast and your financial plan to create a single document you can use to keep your finger on the pulse of your business. Your management team can use it to plan the activities needed to reach business goals. Typically, small businesses use spreadsheets to create their master budgets or consider using budgeting software too, as it may help minimize mistakes.
Operating budget
This budget shows your projected revenue and expenses for a given period. Think of it as a profit and loss report , but for the future. The operating budget includes fixed and variable costs, as well as non-operating expenses. Capital expenditures are usually excluded from an operating budget. Each line item should be backed up with key details.
Fixed costs occur monthly.
Variable costs, like utilities , change depending on factors like usage.
Capital costs are one-time expenses, such as the purchase of a building.
The operating budget gives you a reality check on whether you’re spending according to plan. While this budget is often prepared at the start of each year, don’t set it and forget it. Update it throughout the year, be it monthly or quarterly, so you always know where your business stands.
Capital budget
Companies sometimes create a capital budget when they are looking to make a large purchase, such as a large piece of factory equipment or a new technology system that will require a substantial investment. This allows the finance team to determine the impact on cash flow and plan accordingly.
Cash budget or cash flow budget
This document will give you an estimate of how money comes in and goes out during a certain time horizon. You create a cash budget using the conclusions you draw from sales forecasts and production, and by estimating payables and receivables.
Labor budget
If you will hire employees , this type of budget is helpful in planning for the money you’ll need to meet payroll, not only for regular employees, but also for any temporary and seasonal staff.
Budgeting methods you can use
There’s more than one way to budget. Here are some common methods:
An incremental budget
This takes the current period’s budget or actual performance, uses it as a base and then adjusts it in incremental amounts to account for any increases in costs. Typically, when you put together an incremental budget, you use the rate of inflation as a guide for fine-tuning the amounts. One plus of budgeting this way is that it is relatively easy to do.
Zero-based budgeting
Here, you’re budgeting from scratch. You must scrutinize every expense or potential expense before deciding to add it to your budget. This helps you align your business goals with your expenses. Unlike other types of budgeting, it doesn’t focus on historical results. A zero-based budget is ideal when you’re looking to reduce expenses.
Activity-based budgeting
Actions speak louder than words. This type of budgeting looks at the inputs required to reach the targets or outputs set by the company. Say your business wants to achieve $5 million in revenue. First, you need to figure out the activities that need to happen to make that revenue a reality and then determine the costs of carrying out those activities.
Participative budgeting
There are more cooks in the kitchen with participative budgeting, which is often used by larger small businesses. Both middle management and lower levels of management share in the responsibility of putting together the budget. The budget begins with lower management then moves to middle managers before top management weighs in and signs off. An upside of this type of budgeting is that information is shared, and when management and staff are on the same page in terms of goals, they’re more likely to achieve those goals.
How to create a business budget
Creating a business budget takes several steps:
- Calculate your revenue . Include all your revenue streams, preferably over at least the last 12 months, to determine your monthly income. If your business is new, you can research what’s typical in your industry and use that as a guide to come up with estimates.
- Add up your fixed costs . Fixed costs are things like rent, payroll and debt repayment.
- Determine variable costs . In addition to utilities, these may include billable labor, materials, transaction fees and commissions.
Using a budget to make better decisions
If you make your budget a regular resource, you’ll be rewarded for your budgeting efforts. As you make spending decisions, consult your budget frequently and use it as a reality check. If you have budgeted for X amount and go beyond it, you’ll have some explaining to do, even if you’re only answering to yourself. Being disciplined can be challenging, but ultimately it will position your business for growth , both today and in the future.
Explore more

How to create a sales forecast

Understanding free cash flow
Important Disclosures and Information
QuickBooks is registered trademark of Intuit, Inc., used under license. Bank of America does not deliver and is not responsible for the products, services or performance of Intuit, Inc. You are responsible for separately purchasing QuickBooks, QuickBooks Online, or QuickBooks Online Payroll, and Bank of America makes no warranties nor accepts any liability for such software.
Internet access may be required. Internet service provider fees may apply. Other bank fees may apply. See the Business Schedule of Fees available at bankofamerica.com/businessfeesataglance for details.
Bank of America and/or its affiliates or service providers may receive compensation from third parties for clients' use of their services.
Bank of America, Merrill, their affiliates and advisors do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice. Consult your own legal and/or tax advisors before making any financial decisions. Any informational materials provided are for your discussion or review purposes only. The content on the Center for Business Empowerment (including, without limitations, third party and any Bank of America content) is provided “as is” and carries no express or implied warranties, or promise or guaranty of success. Bank of America does not warrant or guarantee the accuracy, reliability, completeness, usefulness, non-infringement of intellectual property rights, or quality of any content, regardless of who originates that content, and disclaims the same to the extent allowable by law. All third party trademarks, service marks, trade names and logos referenced in this material are the property of their respective owners. Bank of America does not deliver and is not responsible for the products, services or performance of any third party.
Not all materials on the Center for Business Empowerment will be available in Spanish.
Certain links may direct you away from Bank of America to unaffiliated sites. Bank of America has not been involved in the preparation of the content supplied at unaffiliated sites and does not guarantee or assume any responsibility for their content. When you visit these sites, you are agreeing to all of their terms of use, including their privacy and security policies.
Credit cards, credit lines and loans are subject to credit approval and creditworthiness. Some restrictions may apply.
Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated (also referred to as “MLPF&S" or “Merrill") makes available certain investment products sponsored, managed, distributed or provided by companies that are affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“BofA Corp."). MLPF&S is a registered broker-dealer, registered investment adviser, Member SIPC , and a wholly owned subsidiary of BofA Corp.
Banking products are provided by Bank of America, N.A., and affiliated banks, Members FDIC, and wholly owned subsidiaries of BofA Corp.
“Bank of America” and “BofA Securities” are the marketing names used by the Global Banking and Global Markets division of Bank of America Corporation. Lending, derivatives, other commercial banking activities, and trading in certain financial instruments are performed globally by banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation, including Bank of America, N.A., Member FDIC. Trading in securities and financial instruments, and strategic advisory, and other investment banking activities, are performed globally by investment banking affiliates of Bank of America Corporation (“Investment Banking Affiliates”), including, in the United States, BofA Securities, Inc., which is a registered broker-dealer and Member of SIPC , and, in other jurisdictions, by locally registered entities. BofA Securities, Inc. is a registered futures commission merchant with the CFTC and a member of the NFA.
Investment products:
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Operations & Success
How to Create A Financial Budget for a Small Business
The Cash Budget, Capital Budget, and Budgeted Balance Sheet
- Purpose of Financial Budget
Capital Expenditures Budget
Cash budget, budgeted balance sheet.
The financial budget is one part of a business's master budget. The second part of the firm’s master budget is the operating budget. The master budget is the financial portion of the business's strategic plan for the near future. The strategic plan for the business maps out the firm's planned financial activities for the next five years.
Purpose of the Financial Budget
The purpose of the financial budget is to estimate the firm’s cash budget , capital expenditures , and balance sheet line items like assets, liabilities, and owner’s investment. The financial budget is the last budget to be developed by the firm every year since all other budgets, like the individual budgets in the operating budget, are necessary first. The financial budget helps the firm by allowing it to calculate net profit when the budget process is complete.
The capital expenditures budget is the first budget of these three budgets to be prepared within the framework of the financial budget. The information from this budget is needed for both the cash budget and the budgeted balance sheet.
Capital expenditures are fixed asset expenditures. Fixed assets are equipment or facilities needed for a business to operate. These expenditures also include maintenance for these items. While there are businesses that purchase larger amounts of fixed assets, most smaller businesses do not.
Small businesses tend to be more conservative in their capital expenditures since these types of purchases can be very costly. Many do not own the facilities they operate in, reducing capital expenditures.
While an expenditures plan for maintenance of the equipment is likely, a smaller business may lease, rather than own, their equipment. Consider depreciation and standard lifetimes of your equipment when designing your capital budget if you own your plant and equipment.
Here is an example of a simple capital expenditures budget for a small business:
The cash budget is a short-term, internal-only financial document usually prepared on a monthly basis. It is a tool that helps the business manage its net working capital .
Business firms, especially small ones, cannot operate without cash. Cash is king in the small business firm. The cash budget is a very important tool that a business firm should rely on.
The cash budget shows the firm how much cash is either available to the firm at the end of each month or how much the firm will have to borrow. The cash budget accomplishes this by comparing the cash receipts the firm takes in each month against the cash purchases it makes.
Firms will usually develop a forecasted monthly cash budget for a one-year time period. If the cash budget shows an increase in net working capital, the firm may use that increase to reduce operating costs; by repaying borrowed money, for example. If the cash budget shows a decrease in net working capital, you may need to find some way of increasing available cash; by drawing on a line of credit, taking out a bank loan or by factoring .
Here is an example of a simple cash budget:
In this example, the ending available cash ($20,000) exceeds the ending cash used ($18,000) by $2,000, which represents the net cash available and the beginning cash position for the following month.
Both the capital expenditures budget and the cash budget must be completed before the budgeted balance sheet can be developed. The budgeted balance sheet begins with the current balance sheet. It then takes the data from the other budgets that have been developed, such as the cash budget and the capital expenditures budget. It also takes the data from the firm’s operating budget .
That data includes the firm’s sales forecast—the production budget which includes the direct materials purchased budget, the direct labor budget, and the overhead budget; the ending finished goods inventory budget; the cost of goods sold budget; and the selling and administrative budget. After you combine this information and the information from the financial budget, you can develop the budgeted balance sheet.
Quickbooks Canada. " Formulating and Forecasting a Yearly Budget ." Accessed Jan. 14, 2020.
Lumen Managerial Accounting. " 11.5 Controlling Capital Investment Expenditures ." Accessed Jan. 15, 2020.
Lumen Learning. " Cash Budgeting ." Accessed Jan. 16, 2020.
PrinciplesofAccounting.com. " Components of the Budget ." Accessed Jan. 16, 2020.
PrinciplesofAccounting.com. " Components of the Budget ." Accessed Jan. 17, 2020.
Create Your Business Plan in Minutes
Type your business idea below.

What Our Users Say

Zakariya A.

How it Works
Questionnaire
Respond to a series of targeted questions about your business goals and objectives.
AI Business Plan Generator
The engine analyzes your responses and generates a business plan tailored to your vision.
SBA Approved Business Plan
Receive a detailed, tailored business plan that aligns with your requirements. Ready for funding.
WHO BENEFITS FROM Plannit?

Aspiring Entrepreneurs
Analyze your ventures through extensive business plans aligned with your vision and goals.

Business Owners
Back your business with a solid plan that aligns with your vision and goals. Perfect for startups and small businesses.

Educational Institutions
Develop your business understanding and vocabulary by analyzing your business idea and creating a plan.

Startups Accelerators
Work alongside your founders as they build their plan to ensure they have a solid roadmap for growth and scalability.
Try Plannit AI For Free
Funding ready business plan, executive summary, company overview.
Problem Statement
Business Description
Mission Statement
Business Model
Products and Services
Additional Features
Revenue Model
Market Analysis
Target Market
Market Size and Segments
Unique Value Proposition
Risks and Mitigations
Identified Risks
Mitigation Strategies
Financial Overview
Income Statement
Marketing and Sales Plan
Focus On Your Vision
Key features & benefits, ai editing companion.
Modify and regenerate sections of your business plan using premade or custom prompts. Our AI will help you refine your plan to perfection.
Multi-User Collaboration
Invite team members with easy sharing to collaborate on your business plan in real-time. Communicate and make changes together. Collaborate with your partners in real-time as you perfect your plan.
Education Center
Immerse yourself in a rich library of articles, tools, templates, webinars and resources for continuous business and professional growth. Learn all about the key aspects of starting, running and growing a business.
Powered by Chat GPT
Our algorithms are powered the latest in AI technology to ensure the most accurate and relevant output. We use OpenAI's GPT 4 and 3.5 engines for the perfect blend of accuracy and speed.
Business Resources
We recommend a variety of useful tools and resurces that help sustain your growth. We only recommend the best in the business. Filter your needs and equip yourself with the best tools.
Plan Samples
Explore a library of sample business plans we generated to get the idea of what to expect. Currently able to generate viable plans for 50+ industries.
Financial Projections
Take an additional questionnaire about your financial trajectory and get a detailed financial projection + 3 year income statement for your business.
Tools and Templates
Plannit's comprehensive suite that accompany business planning. From pitch decks to financial models, we have you covered.
Plan Export
Download your business plan in an editable .docx format. Fully edit & share your plan with investors, partners, and stakeholders.
Privacy & Security
Rest assured, your privacy is our top priority, and we're committed to keeping your information safe and confidential.
PLANNIT BUSINESS ECOSYSTEM

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Initiate with Your Business Concept: Lay the Groundwork: Start by introducing your business idea into Plannit AI's Business Plan Generator. This first step is crucial, as it sets the tone for a tailored, insightful business plan that truly resonates with your vision. Capture the Essence: Our platform is designed to grasp the nuances of your concept, ensuring that the generated plan accurately reflects the core and potential of your business.
- Navigate Through the AI-Guided Questionnaire: Tailored Interactive Experience: Plannit AI’s AI-guided questionnaire is your interactive guide through the planning process. It meticulously gathers information about your business's objectives, strategies, and market positioning, ensuring a comprehensive and reflective plan. Intelligent Feedback and Suggestions: As you progress through the questionnaire, benefit from smart prompts and suggestions, ensuring that your plan is not just detailed but also strategically sound and aligned with industry standards.
- Generate Your Plan with Advanced AI: Intuitive Plan Creation: With the questionnaire complete, Plannit AI's advanced algorithms intelligently analyze your responses. They then craft a detailed, customizable, and strategically aligned business plan, providing you with a structured, coherent, and actionable format. Benefit from AI-Powered Insights: Plannit AI offers AI-driven insights and suggestions, ensuring your plan is not just a document but a strategic tool equipped with tailored AI prompts and an in-app plan editor. Get inspired by browsing through our sample business plans, a collection of successful strategies across various industries.
- Finalize Your Plan with Confidence: Dynamic Adaptation and Refinement: Plannit AI recognizes that a business plan is a living document. Our platform allows for continuous adaptation and refinement, ensuring your strategy remains agile, relevant, and aligned with your evolving business goals. Professional Presentation and Sharing: Once your plan meets your standards, utilize Plannit AI's export features to present your plan professionally. Choose between various formats for exporting your business plan, ready to impress stakeholders, attract investors, or guide your team. Review and Adapt: Ensure your business plan is a living document, ready to evolve with your growing business. Plannit AI's dynamic platform allows you to adapt your strategy as new opportunities or challenges arise.
- Roadmap for Success: At its core, a business plan acts as a strategic guide, providing detailed steps on how your business will achieve its objectives. It helps you navigate the startup phase, manage growth effectively, and tackle unforeseen challenges with a well-thought-out strategy.
- Securing Funding: For startups and businesses looking to expand, a business plan is crucial for securing loans or attracting investors. It demonstrates to potential financial backers that your business has a clear vision, a solid strategy for profitability, and a plan for delivering returns on their investment.
- Informed Decision-Making: A well-prepared business plan offers valuable insights into your market, competition, and potential challenges. This information is vital for making informed decisions, from day-to-day operations to long-term strategic shifts.
- Market Analysis and Strategy: It allows you to conduct an in-depth analysis of your target market, understand customer needs, and position your product or service effectively. The marketing strategy outlined in your business plan helps in identifying the best channels and tactics to reach your audience and achieve market penetration.
- Financial Planning: One of the most critical components of a business plan is the financial forecast. It outlines your funding requirements, expected revenue, profit margins, and cash flow projections. This section is essential for budgeting, financial management, and ensuring the financial viability of your business.
- Goal Setting and Performance Measurement: A business plan sets clear, measurable goals and objectives. It provides a framework for monitoring performance, measuring success, and making necessary adjustments to stay on track.
- Aspiring Entrepreneurs: If you're at the idea stage, looking to transform your vision into a viable business, Plannit AI offers the tools and guidance to bring your concept to life. Our platform helps you articulate your business idea, define your target market, and develop a solid plan to turn your dream into reality.
- Students and Educators: For students delving into the intricacies of business planning and educators teaching the fundamentals of entrepreneurship, Plannit AI serves as an invaluable resource. It provides a practical, hands-on tool for learning and teaching how to create detailed business plans, analyze markets, and understand financials in a real-world context.
- Startup Founders: In the dynamic startup environment, Plannit AI is the ideal partner for founders looking to pivot quickly, secure funding, or understand their competitive landscape. With our AI-driven insights and market analysis tools, startups can make informed decisions and adapt their strategies to thrive in competitive markets.
- Small Business Owners: For small business owners seeking to optimize their operations, expand their customer base, or explore new markets, Plannit AI offers targeted solutions. Our platform simplifies the planning process, enabling owners to focus on growth while managing the day-to-day challenges of running their business.
- Consultants and Freelancers: Consultants and freelancers specializing in business development, strategic planning, or financial advising will find Plannit AI a powerful addition to their toolkit. It allows them to provide clients with comprehensive, data-driven business plans and strategies, enhancing the value of their services.
- Non-Profit Organizations: Leaders of non-profit organizations can leverage Plannit AI to plan initiatives, secure funding, and manage resources more efficiently. Our platform helps non-profits articulate their mission, set achievable goals, and measure their impact, ensuring they can make a difference in their communities.
- Innovators and Inventors: Individuals looking to commercialize innovative products or technologies can use Plannit AI to navigate the complexities of bringing new ideas to market. From patent strategies to go-to-market plans, our platform covers all bases, ensuring innovators can focus on what they do best.
- Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs) and Government Agencies: Government and SBA backed entities can greatly benefit from integrating Plannit AI into their services, enhancing their ability to support a larger number of clients more efficiently. By facilitating quicker, more in-depth business plan development, these organizations can spend more time assisting with plan execution and less time on creation, ultimately serving their communities more effectively.
- Anyone with a Business Idea: Ultimately, Plannit AI is for anyone with a business idea, regardless of industry, experience, or stage of business development. Our mission is to democratize business planning, making it accessible, understandable, and actionable for everyone.
- Interactive Questionnaire and ChatGPT Integration: Plannit AI transforms the business planning process into an engaging conversation. Through our advanced ChatGPT integration, we offer a questionnaire that dynamically adapts to your responses, ensuring your plan is personalized, comprehensive, and aligned with your business goals.
- Dynamic Planning Environment: Unlike static templates provided by many, Plannit AI introduces a living platform that grows with your business. It features real-time updates, strategic insights, and a feedback mechanism that keeps your business plan current and actionable.
- Extensive Educational Resources: Our Education Center is packed with articles, guides, and sample plans to bolster your planning process. It's designed to arm you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of your industry confidently.
- Enhanced Collaboration and Customization: Recognizing the collaborative essence of business planning, Plannit AI supports team efforts with multi-user editing, annotations, and feedback features, ensuring a comprehensive approach to your strategy.
- Customer Success Stories: Our users' achievements are a testament to Plannit AI's effectiveness. These success stories illustrate how diverse businesses have utilized our platform for strategic planning and growth.
- Tailored Business Plan Creation: Our platform stands out with its tailored approach, featuring customizable templates that directly cater to your business type and industry, making plan creation straightforward and relevant.
- Content Generation:: ChatGPT helps draft various sections of a business plan, from executive summaries to marketing strategies, by providing structured and coherent text based on the prompts given.
- Strategic Insights: It can offer suggestions on business strategies by analyzing trends and providing examples from a wide range of industries.
- Financial Planning: While it can't replace professional financial advice, ChatGPT can guide the structure of financial projections and statements, helping you consider important financial aspects of your plan.
Take The First Step Towards Success With our AI-Generated Business Plans
Customer login
Tax Pro login
Business tips
Learn How to Craft a Successful Business Plan (Even with No Experience)
10 Minute Read
Copy Article URL
Take the First Step in Learning How to Write a Business Plan, Even with No Experience
Antonio Del Cueto, CPA
May 8, 2024

Imagine your business as a spaceship blasting off into uncharted territory. It may sound exciting, but without a precise flight plan, that thrilling journey could end in a fiery crash. Similarly, most businesses don't fail because of bad ideas. They fail because they lack a clear roadmap.
This article will guide you through the process of crafting a business plan that's more than just numbers on a page. Learn the secret formulas that propel businesses from mere concepts to thriving realities.

Reimagining Traditional Business Plan Components
Executive summary with interactive elements.
Transform the executive summary into a dynamic experience using multimedia elements such as videos and interactive timelines. These components help demonstrate the business’s mission and goals, making it more attractive to would-be investors and potential customers.
Flexible Organizational Structures
Suggest designing an adaptable organizational framework that evolves according to strategic business needs and operational demands. This is especially beneficial for entrepreneurs who might need to navigate changes without a background in HR or traditional management.
Navigating Financial Management Without a Background
Simplified accounting tools.
For many new entrepreneurs, managing finances can feel overwhelming. Leveraging simplified digital accounting tools can significantly reduce this stress by automating most of the routine bookkeeping tasks. These tools are particularly beneficial for those without a financial background, making it easier to focus on other aspects of entrepreneurship.
- Automation : Choose tools that automate entries for sales, purchases, and payroll transactions, ensuring accuracy and saving time.
- User-Friendly Dashboard : Opt for software with an intuitive interface that simplifies financial tracking and report generation. This feature is essential for entrepreneurs who need to quickly access financial data without navigating complex menus.
- Integration Capabilities : It’s important to invest in software that integrates with other business tools (e.g., inventory management systems, e-commerce platforms) to streamline all financial processes.
- Scalability : As your business grows, you’ll need accounting software that can adapt to more complex financial demands without requiring a complete overhaul.
Further reading: Mastering Accounting for Tech Companies: The Ultimate Guide to Industry Accounting in the Technology Sector
Understanding business taxes.
A basic understanding of business taxes is essential for any entrepreneur, including those running a nonprofit or other types of organizations. Here are key elements your business plan should focus on:
- Fundamental Tax Responsibilities : Clearly outline what taxes the business is liable for, such as income, payroll, and sales taxes. This information should be specific to your business's location and structure.
- Maximizing Deductions : Include information on how to identify and claim relevant deductions to minimize tax liability. For example, if your business has significant equipment expenses or if you’re renting office space, you should know how these affect your taxes.
- Seeking Professional Advice : While basic tax guides are helpful, consulting with a tax advisor or strategist can provide tailored advice that ensures compliance and optimizes tax benefits. This step is integral for complex situations or where the tax implications could significantly impact business finances.
Further reading: Maximizing Your Small Business Tax Benefits: 2023 Tax Year Strategies & New Reporting Changes
Budgeting made easy.
Budgeting effectively is a core skill every business owner should develop to ensure financial stability and facilitate growth. Here’s how to incorporate straightforward budgeting strategies into your business operations:
- Expense Tracking : Start by categorizing expenses to track where every dollar is going. Categories might include rent, salaries, marketing, and web design. This clarity helps in making informed spending decisions.
- Financial Forecasting : Use historical data to predict future spending needs and income . This is especially important for planning major investments or when scaling operations.
- Regular Financial Reviews : Conducting regular reviews of your budget will help you stay on track and make necessary adjustments in response to financial performance or changing market conditions.
- Budgeting Tools : Recommend specific budgeting tools that are designed for small business needs. These tools should provide visual representations of financial data, making it easier to digest and act upon.
Each of these sections should be detailed in the business plan to demonstrate a thorough understanding and proactive management of financial aspects. This approach not only helps in securing funding (e.g., from banks or venture capital) but also in managing day-to-day financial operations efficiently.
Building Strategic Partnerships and Collaborative Networks
Cross-industry alliances.
Engaging in cross-industry alliances is a strategic move that can drive substantial business growth and innovation. These partnerships leverage complementary strengths and resources, offering a multitude of benefits:
- Innovation through Diverse Expertise : Combining knowledge and resources from different sectors can catalyze innovative solutions that neither partner could develop alone. For instance, a tech startup could collaborate with an established manufacturing firm to optimize production processes using advanced technology, resulting in a competitive edge in the market.
- Access to New Markets : Each industry has its unique customer base. By forming alliances, businesses can bridge their offerings to new audiences. A successful example could involve a collaboration between a software development company and a telecommunications firm to introduce a new tech product to a broader audience, utilizing the telecom firm's extensive customer network.
- Resource Sharing : Strategic partnerships allow for the sharing of critical assets such as technology, marketing channels, and expertise, leading to cost savings and enhanced product offerings. This might involve sharing R&D facilities or co-branding efforts for joint marketing campaigns.
- Enhanced Credibility and Brand Perception : Partnering with reputable firms in other sectors can significantly boost a company's credibility and strengthen its brand image, attracting more customers and potential investors.
Documenting cross-industry alliances in a business plan must specify the objectives, expected outcomes, and the nature of the collaboration. Include specific information on how these alliances align with the business’ strategy and how they contribute to achieving the company’s goals.
Customer Involvement in Product Development
Integrate customer feedback into the product development process for aligning products with market needs and enhancing customer satisfaction. This strategy not only improves product-market fit but also fosters customer loyalty:
- Direct Feedback for Better Products : Involving customers early in the development process ensures that the final product meets actual user needs and solves relevant problems. This can be achieved through methods like crowdsourcing ideas, beta testing new products, and incorporating user-generated content and suggestions into product design.
- Build Customer Loyalty : Customers who participate in the product development lifecycle are more likely to develop a deeper connection with the brand, increasing their likelihood of becoming repeat buyers and brand advocates.
- Agile Feedback Loops : Utilizing customer feedback during product testing phases allows for quick iterations and adjustments, greatly enhancing the product’s relevance and appeal upon launch.
- Unlocking New Ideas : Customers often see different uses for a product or identify missing features that can lead to significant innovations, helping a company stay ahead of competitors.
The business plan must include a dedicated section outlining how customer feedback will be integrated into product development processes. This section should also include pricing strategies informed by customer input to ensure market competitiveness.
For businesses seeking funding or partnership, a well-crafted business plan is essential. Including sections like Cross-Industry Alliances and Customer Involvement showcases a comprehensive approach to strategic planning and market engagement.
For simplicity and clarity, especially when presenting to potential investors, consider summarizing key strategies in a one-page overview within the larger business plan. This not only highlights the strategic vision but also ensures that readers can quickly grasp the core elements of your plan.
Key Takeaways
- Clarity is Key : Craft a clear, concise business plan to create financial projections and ensure a solid foundation.
- Know Your Audience : Tailor your plan to engage stakeholders, addressing related topics like brand awareness.
- Research Matters : Thorough market research strengthens your plan, supporting its solidity.
- Financial Focus : Develop realistic projections for revenue and expenses to fortify your business plan.
- Stay Adaptable : Flexibility is key to evolve strategies, including those for brand awareness, to maintain relevance.
How can Taxfyle help?
Finding an accountant to manage your bookkeeping and file taxes is a big decision. Luckily, you don't have to handle the search on your own.
At Taxfyle , we connect small businesses with licensed, experienced CPAs or EAs in the US. We handle the hard part of finding the right tax professional by matching you with a Pro who has the right experience to meet your unique needs and will manage your bookkeeping and file taxes for you.
Legal Disclaimer
Tickmark, Inc. and its affiliates do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice. The information provided on this website does not, and is not intended to, constitute legal, tax or accounting advice or recommendations. All information prepared on this site is for informational purposes only, and should not be relied on for legal, tax or accounting advice. You should consult your own legal, tax or accounting advisors before engaging in any transaction. The content on this website is provided “as is;” no representations are made that the content is error-free.

Was this post helpful?
Did you know business owners can spend over 100 hours filing taxes, it’s time to focus on what matters..
With Taxfyle, the work is done for you. You can connect with a licensed CPA or EA who can file your business tax returns. Get $30 off off today.
Want to put your taxes in an expert’s hands?
Taxes are best done by an expert. Here’s a $30 coupon to access to a licensed CPA or EA who can do all the work for you.
Is this article answering your questions?
Thanks for letting us know.
Whatever your questions are, Taxfyle’s got you covered. If you have any further questions, why not talk to a Pro? Get $30 off today.
Our apologies.
Taxes are incredibly complex, so we may not have been able to answer your question in the article. Fortunately, the Pros do have answers. Get $30 off a tax consultation with a licensed CPA or EA, and we’ll be sure to provide you with a robust, bespoke answer to whatever tax problems you may have.
Do you do your own bookkeeping?
There’s an easier way to do bookkeeping..
Taxfyle connects you to a licensed CPA or EA who can take time-consuming bookkeeping work off your hands. Get $30 off today.
Why not upgrade to a licensed, vetted Professional?
When you use Taxfyle, you’re guaranteed an affordable, licensed Professional. With a more secure, easy-to-use platform and an average Pro experience of 12 years, there’s no beating Taxfyle. Get $30 off today.
Are you filing your own taxes?
Do you know if you’re missing out on ways to reduce your tax liability.
Knowing the right forms and documents to claim each credit and deduction is daunting. Luckily, you can get $30 off your tax job.
Get $30 off your tax filing job today and access an affordable, licensed Tax Professional. With a more secure, easy-to-use platform and an average Pro experience of 12 years, there’s no beating Taxfyle.
How is your work-life balance?
Why not spend some of that free time with taxfyle.
When you’re a Pro, you’re able to pick up tax filing, consultation, and bookkeeping jobs on our platform while maintaining your flexibility.
Why not try something new?
Increase your desired income on your desired schedule by using Taxfyle’s platform to pick up tax filing, consultation, and bookkeeping jobs.
Is your firm falling behind during the busy season?
Need an extra hand.
With Taxfyle, your firm can access licensed CPAs and EAs who can prepare and review tax returns for your clients.
Perhaps it’s time to scale up.
We love to hear from firms that have made the busy season work for them–why not use this opportunity to scale up your business and take on more returns using Taxfyle’s network?

by this author
Share this article
Subscribe to taxfyle.
Sign up to hear Taxfye's latest tips.
By clicking subscribe, I agree to Taxfyle's Terms of Service , Privacy Policy , and am opting in to receive marketing emails.
Get our FREE Tax Guide for Individuals
Looking for something else? Check out our other guides here .
By clicking download, I agree to Taxfyle's Terms of Service , Privacy Policy , and am opting in to receive marketing emails.
File simpler.
File smarter., file with taxfyle..
2899 Grand Avenue, Coconut Grove, FL 33133
Copyright © 2024 Tickmark, Inc.
34 episodes
Welcome to Freelancing Your Way to Financial Freedom, the podcast that empowers women and moms to take control of their financial futures. Join Megan as she guides you through the journey of building both personal and business foundations. Whether you're seeking to supplement your income, transition away from the 9-5 grind, or achieve financial freedom, this podcast provides practical advice, inspiring stories, and actionable strategies to help you thrive in the world of freelancing. Get ready to unlock the doors to financial security and step into a brighter future filled with possibilities. Connect with Megan: Follow on Instagram - @meganmendez__ Website - meganmendez.com Email - [email protected]
Freelancing Your Way to Financial Freedom Megan Mendez
- 4.0 • 6 Ratings
- MAY 6, 2024
Welcome to Freelancing Your Way to Financial Freedom
Welcome to Freelancing Your Way to Financial Freedom, the podcast that's changing lives one freelance gig at a time. Hey friends, I'm Megan, your host, and I'm so excited to welcome you to our community of women and moms on a mission to achieve financial freedom. Whether you're juggling parenthood, seeking to escape the confines of a traditional job, or dreaming of building your business empire, this podcast is for you. In this podcast, you'll hear about how to build personal and business foundations. I'll help you manage the application of your business so that you can achieve financial security, leave the classroom and get out of debt. If that's what you want. It is my goal to see every mom and business owner achieve their definition of true financial freedom in their life. Because let's be honest, it really does look different for everyone. And that is okay. You will walk away from this podcast, learning more about freelancing, how to leverage your freelancing income in your finances, and how to use this business to become financially free. If you're ready to get started, let's get started.
- APR 22, 2024
31. Finding Fulfillment in Business and Life with Cassandra Rosa
In this episode of The Debt-Free CEO Podcast, I chat with Cassandra Rosa, a certified coach, healer, and intuitive business coach. Cassandra shares her journey from feeling unfulfilled in a traditional career to finding her passion in the personal development world. She discusses the financial challenges she faced when starting her business and how she overcame them by tapping into her intuitive guidance system. Cassandra also delves into her approach to helping clients find fulfillment in their lives and businesses, emphasizing the importance of clarity, mindset, and celebrating small wins. In this episode I share:Transition from traditional schooling to the personal development worldFinancial challenges in businessThe importance of finding a balance in financial decision-makingHelping clients achieve fulfillment in businessTechniques for seeking clarity in business decisions Visit the Show Notes:31. Finding Fulfillment in Business and Life with Cassandra Rosa Resources:Ditch the 9-5 and Go Debt-FreeFree Budget TemplateFree Training: How to Start Your Freelancing Business to go Debt-FreePassion to Profit and On to Debt-Free Workbook Connect with Cassandra: Instagram - @cassandrarosaaWebsite - cassandrarosa.comPodcast - The Fulfilled Female EntrepreneurBook - Now What? Create the Clarity to Achieve Your Dreams Connect with Megan:Instagram - @thedebtfreeceoWebsite - meganmendez.comJoin The Debt-Free CEO FB Community - The Debt-Free CEO CommunityEmail - [email protected] - pinterest.com/meganmendez__/
- APR 8, 2024
30. The Power of Budgeting As a Business Owner with Melissa from Not Another VA
In this episode of the Debt-Free CEO Podcast, Melissa, the founder of Not Another VA, discusses her journey from a history teacher to a successful virtual assistant business owner specializing in email marketing. She shares insights on managing finances, transitioning to full-time entrepreneurship, and the importance of budgeting. Melissa highlights budgeting strategies for personal and business expenses, investing in education accounts, and achieving financial goals. She emphasizes the benefits of early budgeting to reduce financial stress, strengthen relationships, and secure a better financial future. In this episode we share:Transitioning from Overspending to BudgetingImplementing Budgeting in BusinessUsing Unexpected Money WiselyAdvice on Setting Goals and Budgeting Visit the Show Notes:30. The Power of Budgeting As a Business Owner with Melissa from Not Another VA Resources:Ditch the 9-5 and Go Debt-FreeFree Budget TemplateFree Training: How to Start Your Freelancing Business to go Debt-FreePassion to Profit and On to Debt-Free Workbook Connect with Melissa:Instagram - @notanothervaWebsite - notanothervirtualassistant.comYNAB budgeting app Connect with Megan:Follow on Instagram @thedebtfreeceoWebsite - meganmendez.comJoin The Debt-Free CEO FB Community - The Debt-Free CEO CommunityEmail - [email protected] - pinterest.com/meganmendez__/
- MAR 25, 2024
29. How to Quarterly Plan Your Finances
In this episode, I dive into the importance of quarterly planning for both your business and personal finances. The significance of understanding your numbers helps you make informed decisions and achieve your financial goals. From calculating profit percentages to projecting future earnings, I provide valuable insights and actionable steps to empower you in managing your finances effectively. Tune in as I share practical tips and encourage you to take control of their financial well-being. In this episode I share:The concept of quarterly financial planning for both personal and business financesThe value of mapping out 12 weeks to achieve what could be done in 12 monthsThe significance of knowing where money is being spent and how much is coming inThe benefits of planning for future business and personal expensesInsight into profit percentage and its significance in financial planning and goal setting Visit the Show Notes:29. How to Quarterly Plan Your Finances Related Episodes:21. Reflecting on 2023: Lessons Learned and How to Plan for 2024 The 12 Week Year by Brian Moran Resources:Ditch the 9-5 and Go Debt-FreeFree Budget TemplateFree Training: How to Start Your Freelancing Business to go Debt-FreePassion to Profit and On to Debt-Free Workbook Connect with Megan:Follow on Instagram @thedebtfreeceoWebsite - meganmendez.comJoin The Debt-Free CEO FB Community - The Debt-Free CEO CommunityEmail - [email protected] - pinterest.com/meganmendez__/
- MAR 11, 2024
28. Achieving Financial Stability through Multiple Income Streams with Jamie Rohrbaugh
Welcome back to The Debt-Free CEO Podcast. In this episode, we're joined by the incredible Jamie Rohrbaugh, a corporate leader, entrepreneur, and multi-passionate woman who truly embodies the principles we celebrate here on the show. Jamie is not just an accounting analyst for a global company; she's a wellness consultant, co-founder of a networking organization, and a talented social media content creator and graphic designer. She joins us to discuss her journey from a negative bank account to paying for college in cash, building a house, and creating a diverse portfolio of multiple income streams that have allowed her to live debt-free. In this episode we share:Jamie's starting point with a negative bank account and self-funding collegeemergency expenses and strategies for paying off debtLeveraging Multiple Income StreamsFinancial Management and InvestmentsJamie's belief in the necessity of balancing work with personal passionsThe importance of being proactive rather than waiting for a perfect time to secure one's financial future Visit the Show Notes:28. Achieving Financial Stability through Multiple Income Streams with Jamie Rohrbaugh Resources:Ditch the 9-5 and Go Debt-FreeFree Budget TemplateFree Training: How to Start Your Freelancing Business to go Debt-FreePassion to Profit and On to Debt-Free Workbook Connect with Jamie: Follow on Instagram @jamrohr93 Connect with Megan:Follow on Instagram @thedebtfreeceoWebsite - meganmendez.comJoin The Debt-Free CEO FB Community - The Debt-Free CEO CommunityEmail - [email protected] - pinterest.com/meganmendez__/
- FEB 26, 2024
27. Learn How to Make $2K by Spring Break!
In this episode of The Debt-Free CEO Podcast, I share valuable insights on how to generate an extra $2,000 by spring break. I outline practical steps for finding freelance opportunities and setting your rates, emphasizing the importance of choosing services that align with your skills and passions. My approach offers a way to increase your income without relying on MLM or direct sales. Tune in for actionable strategies and check the show notes for a free training on freelancing to kickstart your journey to financial freedom. In this episode I share:How to evaluating your existing skills and interestsDetermine appropriate rates for different types of servicesCreating package prices to offer clientsBreaking down the earning goal into manageable client targets Visit the Show Notes:27. Learn How to Make $2K by Spring Break! Resources:Ditch the 9-5 and Go Debt-FreeFree Budget TemplateFree Training: How to Start Your Freelancing Business to go Debt-FreePassion to Profit and On to Debt-Free Workbook Don’t Miss Last Week’s Post:26. From Education to Entrepreneurship: Sadie Snedeker's Virtual Assisting Story Connect with Megan:Follow on Instagram @thedebtfreeceoWebsite - meganmendez.comJoin The Debt-Free CEO FB Community - The Debt-Free CEO CommunityEmail - [email protected] - pinterest.com/meganmendez__/
- © Copyright 2024 Megan Mendez
Customer Reviews
Megan provides such a wealth of knowledge and information when it comes to saving money and going debt-free. Each episode provides tips and advice on how to best go about tackling your finances and debt!!
Holy husband
Entire first episode is just rambling. Could get seriously drunk taking a shot every time she brings up “my husband.”
Digestible and valuable
Megan has done the work, studied up, and has LIVED EXPERIENCES to share in the realm of financial success and independence. When listening to her speak and provide tips and tricks regarding finances, you KNOW that she is a master of her craft. As someone who’s always been very overwhelmed with money (and frankly avoided anything relating to the health of my own finances out of straight fear), she has made tackling debt and finding financial freedom so much more approachable. I cannot wait to see how this podcast grows and what other nuggets of wisdom she'll be providing. highly recomment!
Top Podcasts In Business
You might also like.

Governor Newsom Unveils Revised State Budget, Prioritizing Balanced Solutions for a Leaner, More Efficient Government
Published: May 10, 2024
The Budget Proposal — Covering Two Years — Cuts Spending, Makes Government Leaner, and Preserves Core Services Without New Taxes on Hardworking Californians
Watch Governor Newsom’s May Revise presentation here
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: The Governor’s revised budget proposal closes both this year’s remaining $27.6 billion budget shortfall and next year’s projected $28.4 billion deficit while preserving many key services that Californians rely on — including education, housing, health care, and food assistance.
SACRAMENTO – Governor Gavin Newsom today released a May Revision proposal for the 2024-25 fiscal year that ensures the budget is balanced over the next two fiscal years by tightening the state’s belt and stabilizing spending following the tumultuous COVID-19 pandemic, all while preserving key ongoing investments.
Under the Governor’s proposal, the state is projected to achieve a positive operating reserve balance not only in this budget year but also in the next. This “budget year, plus one” proposal is designed to bring longer-term stability to state finances without delay and create an operating surplus in the 2025-26 budget year.
In the years leading up to this May Revision, the Newsom Administration recognized the threats of an uncertain stock market and federal tax deadline delays – setting aside $38 billion in reserves that could be utilized for shortfalls. That has put California in a strong position to maintain fiscal stability.
“Even when revenues were booming, we were preparing for possible downturns by investing in reserves and paying down debts – that’s put us in a position to close budget gaps while protecting core services that Californians depend on. Without raising taxes on Californians, we’re delivering a balanced budget over two years that continues the progress we’ve fought so hard to achieve, from getting folks off the streets to addressing the climate crisis to keeping our communities safe.” – Governor Gavin Newsom
Below are the key takeaways from Governor Newsom’s proposed budget:
A BALANCED BUDGET OVER TWO YEARS. The Governor is solving two years of budget problems in a single budget, tightening the state’s belt to get the budget back to normal after the tumultuous years of the COVID-19 pandemic. By addressing the shortfall for this budget year — and next year — the Governor is eliminating the 2024-25 deficit and eliminating a projected deficit for the 2025-26 budget year that is $27.6 billion (after taking an early budget action) and $28.4 billion respectively.
CUTTING SPENDING, MAKING GOVERNMENT LEANER. Governor Newsom’s revised balanced state budget cuts one-time spending by $19.1 billion and ongoing spending by $13.7 billion through 2025-26. This includes a nearly 8% cut to state operations and a targeted elimination of 10,000 unfilled state positions, improving government efficiency and reducing non-essential spending — without raising taxes on individuals or proposing state worker furloughs. The budget makes California government more efficient, leaner, and modern — saving costs by streamlining procurement, cutting bureaucratic red tape, and reducing redundancies.
PRESERVING CORE SERVICES & SAFETY NETS. The budget maintains service levels for key housing, food, health care, and other assistance programs that Californians rely on while addressing the deficit by pausing the expansion of certain programs and decreasing numerous recent one-time and ongoing investments.
NO NEW TAXES & MORE RAINY DAY SAVINGS. Governor Newsom is balancing the budget by getting state spending under control — cutting costs, not proposing new taxes on hardworking Californians and small businesses — and reducing the reliance on the state’s “Rainy Day” reserves this year.
HOW WE GOT HERE: California’s budget shortfall is rooted in two separate but related developments over the past two years.
- First, the state’s revenue, heavily reliant on personal income taxes including capital gains, surged in 2021 due to a robust stock market but plummeted in 2022 following a market downturn. While the market bounced back by late 2023, the state continued to collect less tax revenue than projected in part due to something called “capital loss carryover,” which allows losses from previous years to reduce how much an individual is taxed.
- Second, the IRS extended the tax filing deadline for most California taxpayers in 2023 following severe winter storms, delaying the revelation of reduced tax receipts. When these receipts were able to eventually be processed, they were 22% below expectations. Without the filing delay, the revenue drop would have been incorporated into last year’s budget and the shortfall this year would be significantly smaller.
CALIFORNIA’S ECONOMY REMAINS STRONG: The Governor’s revised balanced budget sets the state up for continued economic success. California’s economy remains the 5th largest economy in the world and for the first time in years, the state’s population is increasing and tourism spending recently experienced a record high. California is #1 in the nation for new business starts , #1 for access to venture capital funding , and the #1 state for manufacturing , high-tech , and agriculture .
Additional details on the May Revise proposal can be found in this fact sheet and at www.ebudget.ca.gov .
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How Participating in Campus Protests Could Affect Your Financial Aid

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Nationwide, students have organized protests over the Israel and Gaza conflict, urging their colleges to divest holdings of Israeli-connected investments. But participation in a protest could lead to steep — and long-lasting — consequences, including criminal charges and loss of financial aid.
Though free speech is a protected right, protestors can be arrested. The Appeal, a nonprofit news organization, estimates nearly 2,500 campus protestors have been arrested nationwide since April 17.
But arrest isn’t the only potential consequence. For example, Washington University temporarily suspended 23 students after they set up an encampment and were arrested for trespassing. Three Vanderbilt University students were expelled after their involvement in a campus sit-in. In Florida, Gov. Ron DeSantis warned students they could be expelled for protesting.
“While the First Amendment guarantees students the right to speak and even to protest on those campuses, the colleges may maintain reasonable 'time, place, and manner' restrictions on student speech in public areas of campus," says Amanda Nordstrom, a program officer for campus rights advocacy with the Foundation for Individual Rights and Expression.
Student financial aid could also be on the line. Review your college's code of conduct and financial aid agreements to understand what’s at stake. Here’s what you might face.
Lost institutional or state aid
Schools set their own policies regarding institutional financial aid, such as school scholarships or grants. Joseph Lento, an attorney specializing in student discipline defense and the founder of the Lento Law Group, says institutional aid can generally be canceled or denied at the school's discretion if you violate the university's code of conduct — even if you don't violate the law.
"Accepting financial aid and scholarships forms a contractual agreement between the student and the granting institution," Lento says. "As such, violating laws or campus policies can risk the continuation of a student’s financial aid."
States have their own policies, too.
"If a scholarship recipient is disciplined by the school as a result of a protest, they may lose their [state] scholarship as a result," says Lori Wurtzel, a Florida-based attorney and founder of the firm Wurtzel Law. This is especially the case if that discipline is part of an arrest and criminal charge. "For example," says Wurtzel, "Florida's Bright Futures Scholarship is not available to students who enter a plea to a felony charge."
Unsatisfactory academic progress
You must meet standards for satisfactory academic progress to maintain eligibility for financial aid. These standards are determined by benchmarks your college sets for grades and credits. If you don't pass enough classes or earn enough credits, you could lose financial aid eligibility .
The satisfactory academic progress requirement could pose a surprise to protestors, says Jill Desjean, senior policy analyst with the National Association of Student Financial Aid Administrators, as schools like Columbia University warned student protestors they could lose credit for the current semester.
"If [the colleges] say they're doing away with this term, now you could be potentially bumping up against the [financial aid] eligibility in terms of not progressing towards your degree," Desjean says. You may be ineligible for financial aid as a result.
Federal aid limits
There are strict annual and aggregate loan limits on how much you can receive in Pell Grants and federal student loans , particularly for undergraduate students. If you’re suspended or lose credit for the semester, you could reach your limits before you finish your education.
For example, the aggregate limit for dependent undergraduate students is $31,000. If you need to retake a semester or transfer to another school, you may need to find other sources of financing, such as parent student loans or private student loans.
Student loan repayment
You still have to repay your loans if you’re not allowed to attend school. Federal student loans enter repayment six months after you leave school or drop below half-time status, so you may have to start making payments even if you haven't completed your degree.
Difficult and expensive college transfer
If you're expelled, you may be able to transfer to another college or university to finish your education. However, it's unlikely that all of your credits would transfer, says Desjean.
"Transferring credits isn't a seamless process," she says. "A lot of schools don't accept transfer credits from other colleges, so there's the disruption of trying to find another school to transfer to."
According to the news and analysis website Inside Higher Ed, nationally, students lose 43% of their credits when transferring. This could cause you to lose a lot of progress, leading to thousands of dollars in additional costs to finish your degree.
New legislation that affects your future aid eligibility
Individuals who have been convicted of crimes, incarcerated, and are now on probation or parole are still eligible for federal financial aid, including Pell Grants and federal loans. However, some lawmakers in states including California, Texas and Iowa have introduced legislation to change that. Under the proposed legislation, those who are convicted of crimes related to the protests would be ineligible for aid.
If you want to protest anyway
"It’s important for students interested in engaging in peaceful protest to familiarize themselves with the rules on their campus, as well as educate themselves on the legal basics so they can insist their rights are respected by college administrators and police," Nordstrom says.
You may be able to appeal if you’re involved in a protest and are suspended or lose your financial aid.
"Most university discipline codes allow a student to continue attending classes while a disciplinary decision is being appealed," Wurtzel says. "Conscious timing of appeals may help a student to finish a semester."
Every school has its own process for filing appeals, so consult with your college to learn about next steps. In some cases, a lawyer may help you appeal your case or have your financial aid reinstated on legal grounds.
On a similar note...
Gov. Gavin Newsom Proposes Painful Cuts to Close California's Growing Budget Deficit
California Gov. Gavin Newsom has proposed a series of painful budget cuts to close the state's growing deficit
Gov. Gavin Newsom Proposes Painful Cuts to Close California's Growing Budget Deficit

Rich Pedroncelli
California Gov. Gavin Newsom unveils his revised 2024-25 state budget during a news conference in Sacramento, Calif., Friday, May 10, 2024. (AP Photo/Rich Pedroncelli)
SACRAMENTO, Calif. (AP) — California 's budget deficit is at least $45 billion, a shortfall so large it prompted Gov. Gavin Newsom on Friday to propose painful spending cuts impacting immigrants, kindergarteners and low-income parents seeking child care in a state often lauded for having the world's fifth-largest economy.
Officially, Newsom said the state's deficit is $27.6 billion. But really, it's closer to $45 billion when including previous spending reductions that Newsom and the state Legislature agreed to in March. Including reductions in public education spending, which Newsom has not included, the deficit would be even billions of dollars more, according to recent analysis by the nonpartisan Legislative Analyst's Office.
The size of the deficit is important as it will shape the national perspectives of Newsom, who is a top surrogate for President Joe Biden's reelection campaign and who is widely believed to harbor presidential aspirations of his own. Newsom has spent much of his time in office basking in the glow of historic budget surpluses that allowed him to greatly expand state spending. But back-to-back budget deficits — with more on the horizon — are testing California's commitment to those increases.
So far, Newsom has not gutted some of his splashiest policy advancements, including free kindergarten for all 4-year-olds and free health insurance for all low-income adults regardless of their immigration status. But as Friday's proposal showed, Newsom is willing to chip away at some of those promises to balance the budget.
While Newsom has not taken away health insurance from anyone, he proposed the state stop paying for health care workers to care for some 14,000 disabled immigrants in their home. That would save the state $94.7 million. While he hasn't pulled back the state's commitment to expanded kindergarten, he proposed eliminating $550 million that would have helped school districts build the facilities they need to teach all of those extra students.
After promising to pay for child care for another 146,000 children from low-income families, Newsom on Friday proposed pausing that expansion at 119,000. And after promising to boost how much money doctor's get to treat Medicaid patients , Newsom on Friday proposed canceling $6.7 billion that had been set aside to do that.
The cuts prompted outrage from across the political and ideological spectrum. Anthony Wright, executive director of the consumer advocacy group Health Access California, said the removal of in-home care for immigrants with disabilities would result in those people becoming “further impoverished or end up in much more expensive nursing home care.”
Yolanda Thomas, a member of the Child Care Providers United negotiations team, said cutting the child care slots means “we cannot build a stronger economy when our lowest paid workers ... don't have somewhere safe to send their children during their shifts.”
For every question on Friday, Newsom had a similar response.
“I prefer not to make this cut. These are programs, propositions that I have long advanced, many of them,” he said. “But you've got to do it. You have to be responsible.”
Before the coronavirus pandemic, California's revenues were growing at about 5% per year. From 2019-20 through 2021-22, revenues grew an astounding 55%. That's because California got a lot of money from the federal government to blunt the impact of the pandemic. And it's because the stock market had historic increases, fueling a rapid expansion of wealth among California's richest residents — generating a tax windfall for the state .
State budgeting is a guessing game, where governors and lawmakers have to predict how much money they will have and plan to spend it. Following the bountiful years of the pandemic, California's guesses have been way off. The Newsom administration now predicts state revenues will be $83.1 billion lower than they thought for the 2022-23 and 2023-24 fiscal years.
“If you knew that those were unrealistically high and totally unsustainable revenue levels, why wouldn't you put a little bit more in the reserves,” said state Sen. Roger Niello, a Republican and vice chair of the Senate Budget and Fiscal Review Committee. “If that's the case, you know it's going to come crashing down and you are going to have a big deficit to cover.”
Newsom defended California's previous budget actions, noting the state Constitution required the state to return a big chunk of that surplus to taxpayers in the form of rebates. Newsom said it “provided a lot of support at the time to people who needed money.”
“I feel like we were doing the best we could under that circumstance,” he said.
Newsom on Friday repeatedly vowed he would not sign a sweeping tax increase on individuals. But he did propose suspending a popular tax deduction for businesses, which many see as a tax increase.
In total, Newsom is proposing $32.8 billion in cuts over two years, including eliminating 10,000 unfilled state jobs and an 8% cut to state operations — including things like eliminating landlines. He promised there would be no layoffs, furloughs or salary cuts for the state's more than 221,000 state workers.
Democratic legislators applauded Newsom’s effort to deal with multiple years of deficits and vowed to protect spending for social safety net fundings and classrooms.
“Nobody knows what challenges California may face, so we must always stay prepared,” Assembly Speaker Robert Rivas and Assembly Budget Chair Jesse Gabriel said in a joint statement. ___ This story has been corrected to show that Newsom proposed eliminating $550 million for school facilities, not $500 million.
Copyright 2024 The Associated Press . All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
Photos You Should See - May 2024

Join the Conversation
Tags: Associated Press , business , politics , taxes , California
Related Articles
Best states.

America 2024

Best States Rankings
- # 2 New Hampshire
- # 3 Nebraska
- # 4 Minnesota
Health News Bulletin
Stay informed on the latest news on health and COVID-19 from the editors at U.S. News & World Report.
Sign in to manage your newsletters »
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
You May Also Like
The 10 best states in america.
Elliott Davis Jr. May 7, 2024

Why Utah Is the Best State
Elliott Davis Jr. and Julia Haines May 7, 2024

Why Florida Is No. 1 in Education
Tim Smart May 7, 2024

They Made One-Of-A-Kind Quilts That Captured the Public's Imagination. Then Target Came Along
Associated Press May 11, 2024

Red, Yellow, Green ... and White? Smarter Vehicles Could Mean Big Changes for the Traffic Light

Trump Heading to Jersey Shore to Rally 'Mega Crowd' in Weekend Break From Hush Money Trial

Honolulu Agrees to 4-Month Window to Grant or Deny Gun Carrying Licenses After Lawsuit Over Delays
Associated Press May 10, 2024

Thomas Says Critics Are Pushing 'Nastiness' and Calls Washington a 'Hideous Place'

Sean 'Diddy' Combs Asks Judge to Dismiss 'False' Claim That He, Others Raped 17-Year-Old Girl

Amid GOP Focus on Elections, Georgia Republicans Remove Officer Found to Have Voted Illegally


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Profit is what remains after expenses are deducted. 2. Subtract fixed costs. The second step for creating a business budget involves adding up all of your historic fixed costs and using them to ...
Budgeting plays a crucial role in the financial management of a business for several reasons: Resource Allocation: Helps allocate resources efficiently to prioritize essential activities and investments. Financial Control: Provides a framework for monitoring and controlling expenses to prevent overspending. Performance Evaluation: Facilitates ...
Here is everything you need to include in your financial plan, along with optional performance metrics, funding specifics, mistakes to avoid, and free templates. Key components of a financial plan. A sound financial plan is made up of six key components that help you easily track and forecast your business financials. They include your:
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business. . Download Startup Financial Projections Template.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Use the numbers that you put in your sales forecast, expense projections, and cash flow statement. "Sales, lest cost of sales, is gross margin," Berry says. "Gross margin, less expenses, interest ...
2. List your business expenses. The next step in creating a small business budget is to list all your business expenses. Here are the types of expenses you want to include in your budget: Fixed ...
A small business financial plan is an outline of the financial status of your business, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow information. A financial plan can help guide a small business toward sustainable growth. Financial plans can aid in business goal setting and metrics tracking, as well as provide proof of profitable ...
Goals of the Budgeting Process. Budgeting is a critical process for any business in several ways. 1. Aids in the planning of actual operations. The process gets managers to consider how conditions may change and what steps they need to take, while also allowing managers to understand how to address problems when they arise. 2.
To effectively create a business budget plan, it's crucial to establish both short-term and long-term financial objectives. Short-term goals could include reducing overhead costs by a certain percentage within six months, while long-term goals might involve doubling your annual revenue within three years. These objectives provide direction for ...
Business Budget Step 4: Predict One-Time Spends. Many of your business expenses will be regular expenses that you pay for each month, whether they're fixed or variable costs. But there are also costs that will happen far less frequently. Just don't forget to factor those expenses when you create a budget as well.
By making and following a budget, you can better control costs, avoid overspending, and plan to meet financial goals. Of course, you'll also need to document and track your budget. Using business budgeting worksheets for this purpose can help you: Set and achieve profit goals; Track revenue, expenses, and cash flow; Cut unnecessary spending
Let's look at the different types of budget and how they contribute to drafting a business plan. 1. Master budget. A master budget is an aggregation of lower-level budgets created by the different functional areas in an organization. It uses inputs from financial statements, the cash forecast, and the financial plan.
1. Static budget template. Best for: Multiple departments or revenue streams; Industries with complex operations A static budget combines all the function-specific budgets a business uses into one. Typically, a static budget includes the following items (plus any other budgets your business might use):
Budgeting and business planning. Once your business is operational, it's essential to plan and tightly manage its financial performance. Creating a budgeting process is the most effective way to keep your business - and its finances - on track. This guide outlines the advantages of business planning and budgeting and explains how to go about it.
The steps below can be followed whether creating a budget for a project, initiative, department, or entire organization. 1. Understand Your Organization's Goals. Before you compile your budget, it's important to have a firm understanding of the goals your organization is working toward in the period covered by it.
Financial Plan Overview. A financial plan is a comprehensive document that charts a business's monetary objectives and the strategies to achieve them. It encapsulates everything from budgeting and forecasting to investments and resource allocation.. For small businesses, a solid financial plan provides direction, helping them navigate economic challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and ...
Financial budgeting is the process of planning company expenses and revenues for a time period. Budgets set forth the plans of management in financial terms. This includes allocating financial resources and identifying available cash flows for required spending. A budget and financial planning strategy detail a company's expectations for what ...
What is a business budget? Simply put, a budget is a spending plan based on your business' income and expenses. It shows your available capital, estimates spending and assists in predicting revenue. The information in your budget can help you plan your company's next moves. A budget looks at activities for a specified time.
The financial budget is one part of a business's master budget. The second part of the firm's master budget is the operating budget. The master budget is the financial portion of the business's strategic plan for the near future. The strategic plan for the business maps out the firm's planned financial activities for the next five years.
Financial Planning: One of the most critical components of a business plan is the financial forecast. It outlines your funding requirements, expected revenue, profit margins, and cash flow projections. This section is essential for budgeting, financial management, and ensuring the financial viability of your business.
Why you need a budget for your business. Budgets are essential for tracking the financial health of your business. Your budget is your planned income and spending. It helps you to allocate funds for particular items and activities. Your budget also helps you to: set business goals. make good business decisions. get finance.
The business plan must include a dedicated section outlining how customer feedback will be integrated into product development processes. This section should also include pricing strategies informed by customer input to ensure market competitiveness. For businesses seeking funding or partnership, a well-crafted business plan is essential.
A financial plan may address budgeting, debt management, ... Long-term goals may encompass objectives such as saving for a child's college education, buying a home, starting a business, or accumulating a substantial retirement nest egg. 2. Make a Budget That You Can Follow.
Melissa highlights budgeting strategies for personal and business expenses, investing in education accounts, and achieving financial goals. She emphasizes the benefits of early budgeting to reduce financial stress, strengthen relationships, and secure a better financial future.
The Governor is solving two years of budget problems in a single budget, tightening the state's belt to get the budget back to normal after the tumultuous years of the COVID-19 pandemic. By addressing the shortfall for this budget year — and next year — the Governor is eliminating the 2024-25 deficit and eliminating a projected deficit ...
Funding your business Small-business loans SBA loans Business credit cards Business grants Managing business finances Business bank accounts Accounting Payroll & HR Business taxes
Due to the high spending requests of the ministries for the 2025 budget, current plans must be internally discussed within the government, a spokesperson of the finance ministry said.
Lawmakers still had to pass a budget by June, despite not knowing how much money they had. This January, Newsom said the state's revenues for 2022-23 to 2024-25 have been coming in $42.9 billion ...