- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

A Guide to Rebuttals in Argumentative Essays

4-minute read
- 27th May 2023
Rebuttals are an essential part of a strong argument. But what are they, exactly, and how can you use them effectively? Read on to find out.
What Is a Rebuttal?
When writing an argumentative essay , there’s always an opposing point of view. You can’t present an argument without the possibility of someone disagreeing.
Sure, you could just focus on your argument and ignore the other perspective, but that weakens your essay. Coming up with possible alternative points of view, or counterarguments, and being prepared to address them, gives you an edge. A rebuttal is your response to these opposing viewpoints.
How Do Rebuttals Work?
With a rebuttal, you can take the fighting power away from any opposition to your idea before they have a chance to attack. For a rebuttal to work, it needs to follow the same formula as the other key points in your essay: it should be researched, developed, and presented with evidence.
Rebuttals in Action
Suppose you’re writing an essay arguing that strawberries are the best fruit. A potential counterargument could be that strawberries don’t work as well in baked goods as other berries do, as they can get soggy and lose some of their flavor. Your rebuttal would state this point and then explain why it’s not valid:
Read on for a few simple steps to formulating an effective rebuttal.
Step 1. Come up with a Counterargument
A strong rebuttal is only possible when there’s a strong counterargument. You may be convinced of your idea but try to place yourself on the other side. Rather than addressing weak opposing views that are easy to fend off, try to come up with the strongest claims that could be made.
In your essay, explain the counterargument and agree with it. That’s right, agree with it – to an extent. State why there’s some truth to it and validate the concerns it presents.
Step 2. Point Out Its Flaws
Now that you’ve presented a counterargument, poke holes in it . To do so, analyze the argument carefully and notice if there are any biases or caveats that weaken it. Looking at the claim that strawberries don’t work well in baked goods, a weakness could be that this argument only applies when strawberries are baked in a pie.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Step 3. Present New Points
Once you reveal the counterargument’s weakness, present a new perspective, and provide supporting evidence to show that your argument is still the correct one. This means providing new points that the opposer may not have considered when presenting their claim.
Offering new ideas that weaken a counterargument makes you come off as authoritative and informed, which will make your readers more likely to agree with you.
Summary: Rebuttals
Rebuttals are essential when presenting an argument. Even if a counterargument is stronger than your point, you can construct an effective rebuttal that stands a chance against it.
We hope this guide helps you to structure and format your argumentative essay . And once you’ve finished writing, send a copy to our expert editors. We’ll ensure perfect grammar, spelling, punctuation, referencing, and more. Try it out for free today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a rebuttal in an essay.
A rebuttal is a response to a counterargument. It presents the potential counterclaim, discusses why it could be valid, and then explains why the original argument is still correct.
How do you form an effective rebuttal?
To use rebuttals effectively, come up with a strong counterclaim and respectfully point out its weaknesses. Then present new ideas that fill those gaps and strengthen your point.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- Learning Tips
- Exam Guides
- School Life
How to write a Counterclaim Paragraph, Sentence or Rebuttal
- by Joseph Kenas
- January 18, 2024

If you are writing an argumentative essay, you will find yourself including counterclaims. In this guide, we guide you on how to write a good counterclaim in an essay and how to frame your counterclaim sentence and paragraph in rebuttal.
Counterclaims are mostly included in an argumentative essay where you are required to convince your readers to agree with your arguments and point of view concerning the topic in question.
What is a Counterclaim in an Essay?
A counterclaim can be regarded as the argument or arguments that oppose the thesis statement in your essay. Within the introduction, you introduce the topic and create a thesis statement in the last sentence that makes it clear to your audience the point(s) you want to prove and the strategy you will use to prove it.
The counterclaim demonstrates to the reader that you have put into consideration the perspectives of the opposing side and you find such perspectives to be weak.
As such, a counterclaim will allow you to respond to the potential arguments of your readers before they complete reading the essay.
Additionally, a counterclaim demonstrates that both sides of the debate have been put into consideration, hence strengthening your position.
Difference Between a Claim and a Counterclaim
There is a big difference between a claim and a counterclaim. When writing essays, one may need to include both in the same essay, especially when presenting an argumentative topic.
The difference between a claim and a counterclaim lies in their assertion. A claim is a statement that demonstrates the position of argument or the assertion of a fact or a truth. On the other hand, a counterclaim is an argument that negates a specific claim by rebutting it. While a claim asserts the writer’s argument, a counterclaim rebuts.
When writing an essay, particularly an argumentative essay, you will have a topic and a thesis statement that will show the readers the points you are going to prove and how you will prove them.

Most of your paper will be dedicated to proving your claim to the reader so that they can agree with your point of view.
A good claim should be arguable and at times controversial to allow the readers to think otherwise about your perspectives as the writer.
It can also come up with their interpretations concerning the topic.
Because of this, the essay will be based on the claim and you will demonstrate why your claim is accepted. On the other hand, a counterclaim is a statement of opposition that will allow the readers to perceive the whole picture of the arguments.
Though this is the case, the counterclaim demonstrates that the writer has anticipated arguments against their claim and has provided proof, through the counterclaim, that the readers’ perspectives are false or weak.
As such, when the counterclaim is stated, it is addressed concerning its weaknesses or limitations. This enhances the claim’s strength.
How to Write a Good Counterclaim in an Essay
If you wish to write a good counterclaim, make sure that it takes the form of two stages.

The first stage is where you go against your claim or argument so that you can challenge it and the second stage is where you turn back to your claim or argument to re-affirm it.
When writing a good counterclaim, you imagine that some of your readers will be skeptical and you have to make them agree with you.
For example, if you want to present a counterclaim showing that there was a problem with how you demonstrated your claims, like an unwarranted assumption, certain evidence was played down or ignored, and so on, you can support the counterclaim by presenting the disadvantages or drawbacks of the issues with the presentation. Then, give an alternative proposal or alternative that would make more sense to the readers.
To refute the counterclaim, you announce with words like ‘yet’, ‘but’, ‘however’, ‘still’, or ‘nevertheless’ to indicate that you are about to show why the counterclaim is wrong. Acknowledge that it is a good claim but demonstrate that yours might help the argument more.
Where to Write a Counterclaim in an Essay
A counterclaim can be included anywhere within the body of the essay except the conclusion. There are some cases where you can write a counterclaim at the second last sentence of the introduction paragraph followed by the thesis statement which acts as the refutation.
You can also write a counterargument after the introduction to show the anticipated reaction to your point of view before moving forward with writing your actual claims.
Moving forward, the reason why you cannot place the counterclaim within the conclusion is that you have to include a rebuttal paragraph or statements after you have written the counterclaim. Therefore, a counterclaim located at the conclusion will miss the rebuttal paragraph or statements.
However, argumentative essays can take different structures. Even though such essays will have a basic structure of an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, the differences will occur within the body paragraphs. Such differences dictate where the counterclaim(s) are located.
There is a structure where the counterclaims are located within all the body paragraphs. In this case, you will write your claim, followed by a counterclaim, and then a rebuttal. This means that for every claim you present to support your thesis, there will be a counterclaim and a rebuttal.
The most common structure is where you present your claims and present the counterclaim(s) before the conclusion. The counterclaim is immediately followed by a rebuttal.
Dos and Don’ts of Writing a Counterclaim
When it comes to the dos of writing a counterclaim, always ensure that it is followed by a rebuttal to demonstrate that your claims are superior to it. Secondly, courteously present your counterclaims to avoid upsetting the reader.

Acknowledge the anticipated arguments from the readers.
Demonstrate that the readers’ points of view are valid but your perspective makes more sense.
Finally, appeal to the logic of the readers through the use of valid evidence.
Concerning the don’ts when writing a counterclaim, do not include a counterargument just for the sake of it.
Make sure that the counterargument is valid in its own right and it is verifiable through evidence.
This is because your readers will also use logic and evidence when thinking about your claims. Secondly, do not use a disrespectful or uncourteous tone when addressing the other side of the argument.
Examples of Counterclaims
A counterclaim in a separate paragraph.
Counterclaim: “Opponents argue that after-school sports can increase the likelihood of sports-related injuries (Bancroft, 2018). Even minor injuries sustained from participation in after-school sports increase absent rates and the expense of creating injury reports for students (Sizemore, 2019)” .
Refutation: “Although students do suffer both serious and minor injuries in after-school sports, these injuries are quite rare (Kinney, 2016) .
Embedded Within a Paragraph
“Without free after-school sports programs, many students would still play sports without adult supervision and even more injuries would result”. Counterclaim : “However, some people would argue that after-school sports can increase the likelihood of sports-related injuries (Sizemore 2019)”. Refutation: “Although students do suffer both serious and minor injuries in after-school sports, without school-sponsored sports, the likelihood of more injuries from less supervised recreational leagues or privately sponsored leagues with fewer safety regulations would be much worse” .
How Long Should a Counterclaim Be?
A counterclaim can be as long as a paragraph if it appears after the introduction paragraph or at the end of the body before the conclusion. However, if a counterclaim is located within a paragraph, it can be a few sentences long (2-3).
However, the length of a counterclaim depends on the length of a claim in general. You can learn more about how to write a claim paragraph in that guide so that you can learn the two in general.
How many Counterclaims can you Put?
This depends on the structure of the essay. If the counterclaim appears after the introduction or before the conclusion, then it will only be one. However, if it is embedded within paragraphs, then they will be as many as the supportive augments.
This is because they will be used to refute every claim made within the body paragraph. If your supporting claims are 5 then the counterclaims will be 5 and so on.
Check out how to write college essays in our guide that we hope will lead you to score well.

Joseph is a freelance journalist and a part-time writer with a particular interest in the gig economy. He writes about schooling, college life, and changing trends in education. When not writing, Joseph is hiking or playing chess.
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
A Student's Guide: Crafting an Effective Rebuttal in Argumentative Essays
Table of contents
Picture this – you're in the middle of a heated debate with your classmate. You've spent minutes passionately laying out your argument, backing it up with well-researched facts and statistics, and you think you've got it in the bag. But then, your classmate fires back with a rebuttal that leaves you stumped, and you realize your argument wasn't as bulletproof as you thought.
This scenario could easily translate to the world of writing – specifically, to argumentative essays. Just as in a real-life debate, your arguments in an essay need to stand up to scrutiny, and that's where the concept of a rebuttal comes into play.
In this blog post, we will unpack the notion of a rebuttal in an argumentative essay, delve into its importance, and show you how to write one effectively. We will provide you with step-by-step guidance, illustrate with examples, and give you expert tips to enhance your essay writing skills. So, get ready to strengthen your arguments and make your essays more compelling than ever before!
Understanding the Concept of a Rebuttal
In the world of debates and argumentative essays, a rebuttal is your opportunity to counter an opposing argument. It's your chance to present evidence and reasoning that discredits the counter-argument, thereby strengthening your stance.
Let's simplify this with an example . Imagine you're writing an argumentative essay on why school uniforms should be mandatory. One common opposing argument could be that uniforms curb individuality. Your rebuttal to this could argue that uniforms do not stifle individuality but promote equality, and help reduce distractions, thus creating a better learning environment.
Understanding rebuttals and their structure is the first step towards integrating them into your argumentative essays effectively. This process will add depth to your argument and demonstrate your ability to consider different perspectives, making your essay robust and thought-provoking.
Let's get into the nitty-gritty of how to structure your rebuttals and make them as effective as possible in the following sections.
The Structural Anatomy of a Rebuttal: How It Fits into Your Argumentative Essay
The potency of an argumentative essay lies in its structure, and a rebuttal is an integral part of this structure. It ensures that your argument remains balanced and considers opposing viewpoints. So, how does a rebuttal fit into an argumentative essay? Where does it go?
In a traditional argumentative essay structure, the rebuttal generally follows your argument and precedes the conclusion. Here's a simple breakdown:
Introduction : The opening segment where you introduce the topic and your thesis statement.
Your Argument : The body of your essay where you present your arguments in support of your thesis.
Rebuttal or Counterargument : Here's where you present the opposing arguments and your rebuttals against them.
Conclusion : The final segment where you wrap up your argument, reaffirming your thesis statement.
Understanding the placement of the rebuttal within your essay will help you maintain a logical flow in your writing, ensuring that your readers can follow your arguments and counterarguments seamlessly. Let's delve deeper into the construction of a rebuttal in the next section.
Components of a Persuasive Rebuttal: Breaking It Down
A well-crafted rebuttal can significantly fortify your argumentative essay. However, the key to a persuasive rebuttal lies in its construction. Let's break down the components of an effective rebuttal:
Recognize the Opposing Argument : Begin by acknowledging the opposing point of view. This helps you establish credibility with your readers and shows them that you're not dismissing other perspectives.
Refute the Opposing Argument : Now, address why you believe the opposing viewpoint is incorrect or flawed. Use facts, logic, or reasoning to dismantle the counter-argument.
Support Your Rebuttal : Provide evidence, examples, or facts that support your rebuttal. This not only strengthens your argument but also adds credibility to your stance.
Transition to the Next Point : Finally, provide a smooth transition to the next part of your essay. This could be another argument in favor of your thesis or your conclusion, depending on the structure of your essay.
Each of these components is a crucial building block for a persuasive rebuttal. By structuring your rebuttal correctly, you can effectively refute opposing arguments and fortify your own stance. Let's move to some practical applications of these components in the next section.
Building Your Rebuttal: A Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a persuasive rebuttal may seem challenging, especially if you're new to argumentative essays. However, it's less daunting when broken down into smaller steps. Here's a practical step-by-step guide on how to construct your rebuttal:
Step 1: Identify the Counter-Arguments
The first step is to identify the potential counter-arguments that could be made against your thesis. This requires you to put yourself in your opposition's shoes and think critically about your own arguments.
Step 2: Choose the Strongest Counter-Argument
It's not practical or necessary to respond to every potential counter-argument. Instead, choose the most significant one(s) that, if left unaddressed, could undermine your argument.
Step 3: Research and Collect Evidence
Once you've chosen a counter-argument to rebut, it's time to research. Find facts, statistics, or examples that clearly refute the counter-argument. Remember, the stronger your evidence, the more persuasive your rebuttal will be.
Step 4: Write the Rebuttal
Using the components we outlined earlier, write your rebuttal. Begin by acknowledging the opposing argument, refute it using your evidence, and then transition smoothly to your next point.
Step 5: Review and Refine
Finally, review your rebuttal. Check for logical consistency, clarity, and strength of evidence. Refine as necessary to ensure your rebuttal is as persuasive and robust as possible.
Remember, practice makes perfect. The more you practice writing rebuttals, the more comfortable you'll become at identifying strong counter-arguments and refuting them effectively. Let's illustrate these steps with a practical example in the next section.
Practical Example: Constructing a Rebuttal
In this section, we'll apply the steps discussed above to construct a rebuttal. We'll use a hypothetical argumentative essay topic: "Should schools switch to a four-day school week?"
Thesis Statement : You are arguing in favor of a four-day school week, citing reasons such as improved student mental health, reduced operational costs for schools, and enhanced quality of education due to extended hours.
Identify Counter-Arguments : The opposition could argue that a four-day school week might lead to childcare issues for working parents or that the extended hours each day could lead to student burnout.
Choose the Strongest Counter-Argument : The point about childcare issues for working parents is potentially a significant concern that needs addressing.
Research and Collect Evidence : Research reveals that many community organizations offer affordable after-school programs. Additionally, some schools adopting a four-day week have offered optional fifth-day enrichment programs.
Write the Rebuttal : "While it's valid to consider the childcare challenges a four-day school week could impose on working parents, many community organizations provide affordable after-school programs. Moreover, some schools that have already adopted the four-day week offer an optional fifth-day enrichment program, demonstrating that viable solutions exist."
Review and Refine: Re-read your rebuttal, refine for clarity and impact, and ensure it integrates smoothly into your argument.
This is a simplified example, but it serves to illustrate the process of crafting a rebuttal. Let's move on to look at two full-length examples to further demonstrate effective rebuttals.
Case Study: Effective vs. Ineffective Rebuttal
Now that we've covered the theoretical and practical aspects, let's delve into two case studies. These examples will compare an effective rebuttal versus an ineffective one, so you can better understand what separates a compelling argument from a weak one.
Example 1: "Homework is unnecessary."
Ineffective Rebuttal : "I don't agree with you. Homework is important because it's part of the curriculum and it helps students study."
Effective Rebuttal : "Your concern about the overuse of homework is valid, considering the amount of stress students face today. However, research shows that homework, when thoughtfully assigned and not overused, can reinforce classroom learning, provide students with valuable time management skills, and help teachers evaluate student understanding."
The effective rebuttal acknowledges the opposing argument, uses evidence-backed reasoning, and strengthens the argument by showing the value of homework in the larger context of learning.
Example 2: "Standardized testing doesn't accurately measure student intelligence."
Ineffective Rebuttal : "I think you're wrong. Standardized tests have been around for a long time, and they wouldn't use them if they didn't work."
Effective Rebuttal : "Indeed, the limitations of standardized testing, such as potential cultural bias or the inability to measure creativity, are recognized issues. However, these tests are a tool—albeit an imperfect one—for comparing student achievement across regions and identifying areas where curriculum and teaching methods might need improvement. More comprehensive methods, blending standardized testing with other assessment forms, are promising approaches for future development."
The effective rebuttal in this instance acknowledges the flaws in standardized testing but highlights its role as a tool for larger educational system assessments and improvements.
Remember, an effective rebuttal is respectful, acknowledges the opposing viewpoint, provides strong counter-arguments, and integrates evidence. With practice, you will get better at crafting compelling rebuttals. In the next section, we will discuss some additional strategies to improve your rebuttal skills.
Final Thoughts
The art of constructing a compelling rebuttal is a crucial skill in argumentative essay writing. It's not just about presenting your own views but also about understanding, acknowledging, and effectively countering the opposing viewpoint. This makes your argument more robust and balanced, increasing its persuasive power.
However, developing this skill requires patience, practice, and a thoughtful approach. The techniques we've discussed in this guide can serve as a starting point, but remember that every argument is unique, and flexibility is key.
Always be ready to adapt and refine your rebuttal strategy based on the particular argument and evidence you're dealing with. And don't shy away from seeking feedback and learning from others - this is how we grow as writers and thinkers.
But remember, you're not alone on this journey. If you're ever struggling with writing your argumentative essay or crafting that perfect rebuttal, we're here to help. Our experienced writers at Writers Per Hour are well-versed in the nuances of argumentative writing and can assist you in achieving your academic goals.
So don't stress - embrace the challenge of argumentative writing, keep refining your skills, and remember that help is just a click away! In the next section, you'll find additional resources to continue learning and growing in your argumentative writing journey.
Additional Resources
As you continue to learn and develop your argumentative writing skills, having access to additional resources can be immensely beneficial. Here are some that you might find helpful:
Posts from Writers Per Hour Blog :
- How Significant Are Opposing Points of View in an Argument
- Writing a Hook for an Argumentative Essay
- Strong Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas
- Writing an Introduction for Your Argumentative Essay
External Resources :
- University of California Berkeley Student Learning Center: Writing Argumentative Essays
- Stanford Online Writing Center: Techniques of Persuasive Argument
Remember, mastery in argumentative writing doesn't happen overnight – it's a journey that requires patience, practice, and persistence. But with the right guidance and resources, you're already on the right path. And, of course, if you ever need assistance, our argumentative essay writing service services are always ready to help you reach your academic goals. Happy writing!
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
What is Rebuttal in an Argumentative Essay? (How to Write It)
by Antony W
April 7, 2022

Even if you have the most convincing evidence and reasons to explain your position on an issue, there will still be people in your audience who will not agree with you.
Usually, this creates an opportunity for counterclaims, which requires a response through rebuttal. So what exactly is rebuttal in an argumentative essay?
A rebuttal in an argumentative essay is a response you give to your opponent’s argument to show that the position they currently hold on an issue is wrong. While you agree with their counterargument, you point out the flaws using the strongest piece of evidence to strengthen your position.
To be clear, it’s hard to write an argument on an issue without considering counterclaim and rebuttals in the first place.
If you think about it, debatable topics require a consideration of both sides of an issue, which is why it’s important to learn about counterclaims and rebuttals in argumentative writing.
What is a Counterclaim in an Argument?
To understand why rebuttal comes into play in an argumentative essay, you first have to know what a counterclaim is and why it’s important in writing.
A counterclaim is an argument that an opponent makes to weaken your thesis. In particular, counterarguments try to show why your argument’s claim is wrong and try to propose an alternative to what you stand for.
From a writing standpoint, you have to recognize the counterclaims presented by the opposing side.
In fact, argumentative writing requires you to look at the two sides of an issue even if you’ve already taken a strong stance on it.
There are a number of benefits of including counterarguments in your argumentative essay:
- It shows your instructor that you’ve looked into both sides of the argument and recognize that some readers may not share your views initially.
- You create an opportunity to provide a strong rebuttal to the counterclaims, so readers see them before they finish reading the essay.
- You end up strengthening your writing because the essay turns out more objective than it would without recognizing the counterclaims from the opposing side.
What is Rebuttal in Argumentative Essay?
Your opponent will always look for weaknesses in your argument and try the best they can to show that you’re wrong.
Since you have solid grounds that your stance on an issue is reasonable, truthful, or more meaningful, you have to give a solid response to the opposition.
This is where rebuttal comes in.
In argumentative writing, rebuttal refers to the answer you give directly to an opponent in response to their counterargument. The answer should be a convincing explanation that shows an opponent why and/or how they’re wrong on an issue.
How to Write a Rebuttal Paragraph in Argumentative Essay
Now that you understand the connection between a counterclaim and rebuttal in an argumentative writing, let’s look at some approaches that you can use to refute your opponent’s arguments.
1. Point Out the Errors in the Counterargument
You’ve taken a stance on an issue for a reason, and mostly it’s because you believe yours is the most reasonable position based on the data, statistics, and the information you’ve collected.
Now that there’s a counterargument that tries to challenge your position, you can refute it by mentioning the flaws in it.
It’s best to analyze the counterargument carefully. Doing so will make it easy for you to identify the weaknesses, which you can point out and use the strongest points for rebuttal
2. Give New Points that Contradict the Counterclaims
Imagine yourself in a hall full of debaters. On your left side is an audience that agrees with your arguable claim and on your left is a group of listeners who don’t buy into your argument.
Your opponents in the room are not holding back, especially because they’re constantly raising their hands to question your information.
To win them over in such a situation, you have to play smart by recognizing their stance on the issue but then explaining why they’re wrong.
Now, take a closer look at the structure of an argument . You’ll notice that it features a section for counterclaims, which means you have to address them if your essay must stand out.
Here, it’s ideal to recognize and agree with the counterargument that the opposing side presents. Then, present a new point of view or facts that contradict the arguments.
Doing so will get the opposing side to consider your stance, even if they don’t agree with you entirely.
3. Twist Facts in Favor of Your Argument
Sometimes the other side of the argument may make more sense than yours does. However, that doesn’t mean you have to concede entirely.
You can agree with the other side of the argument, but then twist facts and provide solid evidence to suit your argument.
This strategy can work for just about any topic, including the most complicated or controversial ones that you have never dealt with before.
4. Making an Emotional Plea
Making an emotional plea isn’t a powerful rebuttal strategy, but it can also be a good option to consider.
It’s important to make sure that the emotional appeal you make outweighs the argument that your opponent brings forth.
Given that it’s often the least effective option in most arguments, making an emotional appeal should be a last resort if all the other options fail.
Final Thoughts
As you can see, counterclaims are important in an argumentative essay and there’s more than one way to give your rebuttal.
Whichever approach you use, make sure you use the strongest facts, stats, evidence, or argument to prove that your position on an issue makes more sense that what your opponents currently hold.
Lastly, if you feel like your essay topic is complicated and you have only a few hours to complete the assignment, you can get in touch with Help for Assessment and we’ll point you in the right direction so you get your essay done right.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Rebuttal Sections

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
In order to present a fair and convincing message, you may need to anticipate, research, and outline some of the common positions (arguments) that dispute your thesis. If the situation (purpose) calls for you to do this, you will present and then refute these other positions in the rebuttal section of your essay.
It is important to consider other positions because in most cases, your primary audience will be fence-sitters. Fence-sitters are people who have not decided which side of the argument to support.
People who are on your side of the argument will not need a lot of information to align with your position. People who are completely against your argument—perhaps for ethical or religious reasons—will probably never align with your position no matter how much information you provide. Therefore, the audience you should consider most important are those people who haven't decided which side of the argument they will support—the fence-sitters.
In many cases, these fence-sitters have not decided which side to align with because they see value in both positions. Therefore, to not consider opposing positions to your own in a fair manner may alienate fence-sitters when they see that you are not addressing their concerns or discussion opposing positions at all.
Organizing your rebuttal section
Following the TTEB method outlined in the Body Paragraph section, forecast all the information that will follow in the rebuttal section and then move point by point through the other positions addressing each one as you go. The outline below, adapted from Seyler's Understanding Argument , is an example of a rebuttal section from a thesis essay.
When you rebut or refute an opposing position, use the following three-part organization:
The opponent’s argument : Usually, you should not assume that your reader has read or remembered the argument you are refuting. Thus, at the beginning of your paragraph, you need to state, accurately and fairly, the main points of the argument you will refute.
Your position : Next, make clear the nature of your disagreement with the argument or position you are refuting. Your position might assert, for example, that a writer has not proved his assertion because he has provided evidence that is outdated, or that the argument is filled with fallacies.
Your refutation : The specifics of your counterargument will depend upon the nature of your disagreement. If you challenge the writer’s evidence, then you must present the more recent evidence. If you challenge assumptions, then you must explain why they do not hold up. If your position is that the piece is filled with fallacies, then you must present and explain each fallacy.
Counterargument
Argument: your position/opinion about the topic (usually stated in the thesis and then supported with main points throughout the essay)
Counterargument: a section in your essay that describes the other side of the issue (what would someone say who disagrees with your position?)
Rebuttal (or Refutation): a section where you respond to the counterargument in a way that shows your position is the stronger one (what would you say to defeat their point?)
Why would I want to include a counterargument in my essay?
- It gives you the opportunity to anticipate your reader’s concerns or objections to your viewpoint and address them head-on.
- It improves your credibility by showing your reader you are a reasonable, fair, and informed person who has considered all sides of the issue.
- Part of being a strong critical thinker and communicator is examining a subject from all sides and angles.
What do I do after I explain the other side's position?
- Defeat it with a rebuttal.
- How you do this depends on what you perceive as weaknesses in the opposing argument. There may be any number of faults you find with the other side's position (it uses outdated information; it relies on perception or opinion rather than facts; it is based on false assumptions).
- After you identify weaknesses, point those out to your reader, and present your response to them. For example, if you feel that the other side's position is based on outdated information, you’ll have to present more current research to support your point.
- In some cases, you might think that the other side makes a good point. In that instance, you can acknowledge that and establish common ground with the other side, but then describe why even though their reasons have validity, your reasons outweigh theirs on this particular issue.
Where does the counterargument go in the paper?
Counterarguments are often placed toward the end of the essay after the author has argued all their points supporting their position. You might decide to tackle both the counterargument and rebuttal in one paragraph, or you may decide to break them up into separate paragraphs, as seen in the example outline below:
- Introduction and thesis
- Supporting point #1
- Supporting point #2 (there can be any number of supporting points)
- Counterargument
- Rebuttal/Refutation
- Conclusion
Example of a counterargument and rebuttal in the same paragraph; common words/phrases used in a counterargument are in bold:
Supporters of spanking as a means to punish children claim that it is the most effective method of discipline. Parents might feel that it’s the only punishment their children take seriously, and it teaches their children that there are real and immediate consequences to their actions. They believe that this lesson far outweighs the small and momentary pain of the actual spanking. Although this may be a popular position and spanking might seem to be an effective method of discipline in the short term, studies have shown that children who are spanked actually act out more than children who are not (Adams 12). In fact, according to child psychologist Lucille Murray, when alternate forms of discipline are used (time-outs, confiscating toys, etc.), children still learn about consequences but without the pain and humiliation that comes with spanking.
Suggested phrases to help you start the counterargument and rebuttal
How can I start the counterargument?
- Some people believe/argue/feel/think that…
- It is true that…
- Opposing views claim…
- One common concern about (the issue) is…
- Supporters of….
How can I start my rebuttal?
- What this argument overlooks…
- This view seems convincing/plausible/persuasive at first, but…
- While this position is popular, it is not supported by the facts…
- Although part of this claim is valid, it suffers from a flaw…
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, counterarguments – rebuttal – refutation.
- © 2023 by Roberto León - Georgia College & State University
Ignoring what your target audience thinks and feels about your argument isn't a recipe for success. Instead, engage in audience analysis : ask yourself, "How is your target audience likely to respond to your propositions? What counterarguments -- arguments about your argument -- will your target audience likely raise before considering your propositions?"

Counterargument Definition
C ounterargument refers to an argument given in response to another argument that takes an alternative approach to the issue at hand.
C ounterargument may also be known as rebuttal or refutation .
Related Concepts
Audience Awareness ; Authority (in Speech and Writing) ; Critical Literacy ; Ethos ; Openness ; Researching Your Audience

Guide to Counterarguments in Writing Studies
Counterarguments are a topic of study in Writing Studies as
- Rhetors engage in rhetorical reasoning : They analyze the rebuttals their target audiences may have to their claims , interpretations , propositions, and proposals
- Rhetors may develop counterarguments by questioning a rhetor’s backing , data , qualifiers, and/or warrants
- Rhetors begin arguments with sincere summaries of counterarguments
- a strategy of Organization .
Learning about the placement of counterarguments in Toulmin Argument , Arisotelian Argument , and Rogerian Argument will help you understand when you need to introduce counterarguments and how thoroughly you need to address them.
Why Do Counterarguments Matter?
If your goal is clarity and persuasion, you cannot ignore what your target audience thinks, feels, and does about the argument. To communicate successfully with audiences, rhetors need to engage in audience analysis : they need to understand the arguments against their argument that the audience may hold.
Imagine that you are scrolling through your social media feed when you see a post from an old friend. As you read, you immediately feel that your friend’s post doesn’t make sense. “They can’t possibly believe that!” you tell yourself. You quickly reply “I’m not sure I agree. Why do you believe that?” Your friend then posts a link to an article and tells you to see for yourself.
There are many ways to analyze your friend’s social media post or the professor’s article your friend shared. You might, for example, evaluate the professor’s article by using the CRAAP Test or by conducting a rhetorical analysis of their aims and ethos . After engaging in these prewriting heuristics to get a better sense of what your friend knows and feels about the topic at hand, you may feel more prepared to respond to their arguments and also sense how they might react to your post.
Toulmin Counterarguments
There’s more than one way to counter an argument.
In Toulmin Argument , a counterargument can be made against the writer’s claim by questioning their backing , data , qualifiers, and/or warrants . For example, let’s say we wrote the following argument:
“Social media is bad for you (claim) because it always (qualifier) promotes an unrealistic standard of beauty (backing). In this article, researchers found that most images were photoshopped (data). Standards should be realistic; if they are not, those standards are bad (warrant).”
Besides noting we might have a series of logical fallacies here, counterarguments and dissociations can be made against each of these parts:
- Against the qualifier: Social media does not always promote unrealistic standards.
- Against the backing : Social media presents but does not promote unrealistic standards.
- Against the data : This article focuses on Instagram; these findings are not applicable to Twitter.
- Against the warrant : How we approach standards matters more than the standards themselves; standards do not need to be realistic, but rather we need to be realistic about how we approach standards.
In generating and considering counterarguments and conditions of rebuttal, it is important to consider how we approach alternative views. Alternative viewpoints are opportunities not only to strengthen and contrast our own arguments with those of others; alternative viewpoints are also opportunities to nuance and develop our own arguments.
Let us continue to look at our social media argument and potential counterarguments. We might prepare responses to each of these potential counterarguments, anticipating the ways in which our audience might try to shift how we frame this situation. However, we might also concede that some of these counterarguments actually have good points.
For example, we might still believe that social media is bad, but perhaps we also need to consider more about
- What factors make it worse (nuance the qualifier)?
- Whether or not social media is a neutral tool or whether algorithms take advantage of our baser instincts (nuance the backing )
- Whether this applies to all social media or whether we want to focus on just one social media platform (nuance the data )
- How should we approach social standards (nuance the warrant )?
Identifying counterarguments can help us strengthen our arguments by helping us recognize the complexity of the issue at hand.
Neoclassical Argument – Aristotelian Argument
Learn how to compose a counterargument passage or section.
While Toulmin Argument focuses on the nuts and bolts of argumentation, a counterargument can also act as an entire section of an Aristotelian Argument . This section typically comes after you have presented your own lines of argument and evidence .
This section typically consists of two rhetorical moves :
Examples of Counterarguments
By introducing counterarguments, we show we are aware of alternative viewpoints— other definitions, explanations, meanings, solutions, etc. We want to show that we are good listeners and aren’t committing the strawman fallacy . We also concede some of the alternative viewpoints that we find most persuasive. By making concessions, we can show that we are reasonable ( ethos ) and that we are listening . Rogerian Argument is an example of building listening more fully into our writing.
Using our social media example, we might write:
I recognize that in many ways social media is only as good as the content that people upload to it. As Professor X argues, social media amplifies both the good and the bad of human nature.
Once we’ve shown that we understand and recognize good arguments when we see them, we put forward our response to the counterclaim. In our response, we do not simply dismiss alternative viewpoints, but provide our own backing, data, and warrants to show that we, in fact, have the more compelling position.
To counter Professor X’s argument, we might write:
At the same time, there are clear instances where social media amplifies the bad over the good by design. While content matters, the design of social media is only as good as the people who created it.
Through conceding and countering, we can show that we recognize others’ good points and clarify where we stand in relation to others’ arguments.
Counterarguments and Organization
Learn when and how to weave counterarguments into your texts.
As we write, it is also important to consider the extent to which we will respond to counterarguments. If we focus too much on counterarguments, we run the risk of downplaying our own contributions. If we focus too little on counterarguments, we run the risk of seeming aloof and unaware of reality. Ideally, we will be somewhere in between these two extremes.
There are many places to respond to counterarguments in our writing. Where you place your counterarguments will depend on the rhetorical situation (ex: audience , purpose, subject ), your rhetorical stance (how you want to present yourself), and your sense of kairos . Here are some common choices based on a combination of these rhetorical situation factors:
- If a counterargument is well-established for your audience, you may want to respond to that counterargument earlier in your essay, clearing the field and creating space for you to make your own arguments. An essay about gun rights, for example, would need to make it clear very quickly that it is adding something new to this old debate. Doing so shows your audience that you are very aware of their needs.
- If a counterargument is especially well-established for your audience and you simply want to prove that it is incorrect rather than discuss another solution, you might respond to it point by point, structuring your whole essay as an extended refutation. Fact-checking and commentary articles often make this move. Responding point by point shows that you take the other’s point of view seriously.
- If you are discussing something relatively unknown or new to your audience (such as a problem with black mold in your dormitory), you might save your response for after you have made your points. Including alternative viewpoints even here shows that you are aware of the situation and have nothing to hide.
Whichever you choose, remember that counterarguments are opportunities to ethically engage with alternative viewpoints and your audience.
The following questions can guide you as you begin to think about counterarguments:
- What is your argument ? What alternative positions might exist as counterarguments to your argument?
- How can considering counterarguments strengthen your argument?
- Given possible counterarguments, what points might you reconsider or concede?
- To what extent might you respond to counterarguments in your essay so that they can create and respond to the rhetorical situation ?
- Where might you place your counterarguments in your essay?
- What might including counterarguments do for your ethos ?
Recommended Resources
- Sweetland Center for Writing (n.d.). “ How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument? ” University of Michigan.
- The Writing Center (n.d.) “ All About Counterarguments .” George Mason University.
- Lachner, N. (n.d.). “ Counterarguments .” University of Nevada Reno, University Writing and Speaking Center.
- Jeffrey, R. (n.d.). “ Questions for Thinking about Counterarguments .” In M. Gagich and E. Zickel, A Guide to Rhetoric, Genre, and Success in First-Year Writing.
- Kause, S. (2011). “ On the Other Hand: The Role of Antithetical Writing in First Year Composition Courses .” Writing Spaces Vol. 2.
- Burton, G. “ Refutatio .” Silvae Rhetoricae.
Toulmin, S. (1958). The Uses of Argument. Cambridge University Press.
Perelman, C. and Olbrechts-Tyteca, L. (1971). “The Dissociation of Concepts”; “The Interaction of Arguments,” in The New Rhetoric: A Treatise on Argumentation (pp. 411-459, 460-508), University of Notre Dame Press.
Mozafari, C. (2018). “Crafting Counterarguments,” in Fearless Writing: Rhetoric, Inquiry, Argument (pp. 333-337), MacMillian Learning

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
When you write an academic essay, you make an argument: you propose a thesis and offer some reasoning, using evidence, that suggests why the thesis is true. When you counter-argue, you consider a possible argument against your thesis or some aspect of your reasoning. This is a good way to test your ideas when drafting, while you still have time to revise them. And in the finished essay, it can be a persuasive and (in both senses of the word) disarming tactic. It allows you to anticipate doubts and pre-empt objections that a skeptical reader might have; it presents you as the kind of person who weighs alternatives before arguing for one, who confronts difficulties instead of sweeping them under the rug, who is more interested in discovering the truth than winning a point.
Not every objection is worth entertaining, of course, and you shouldn't include one just to include one. But some imagining of other views, or of resistance to one's own, occurs in most good essays. And instructors are glad to encounter counterargument in student papers, even if they haven't specifically asked for it.
The Turn Against
Counterargument in an essay has two stages: you turn against your argument to challenge it and then you turn back to re-affirm it. You first imagine a skeptical reader, or cite an actual source, who might resist your argument by pointing out
- a problem with your demonstration, e.g., that a different conclusion could be drawn from the same facts, a key assumption is unwarranted, a key term is used unfairly, certain evidence is ignored or played down;
- one or more disadvantages or practical drawbacks to what you propose;
- an alternative explanation or proposal that makes more sense.
You introduce this turn against with a phrase like One might object here that... or It might seem that... or It's true that... or Admittedly,... or Of course,... or with an anticipated challenging question: But how...? or But why...? or But isn't this just...? or But if this is so, what about...? Then you state the case against yourself as briefly but as clearly and forcefully as you can, pointing to evidence where possible. (An obviously feeble or perfunctory counterargument does more harm than good.)
The Turn Back
Your return to your own argument—which you announce with a but, yet, however, nevertheless or still —must likewise involve careful reasoning, not a flippant (or nervous) dismissal. In reasoning about the proposed counterargument, you may
- refute it, showing why it is mistaken—an apparent but not real problem;
- acknowledge its validity or plausibility, but suggest why on balance it's relatively less important or less likely than what you propose, and thus doesn't overturn it;
- concede its force and complicate your idea accordingly—restate your thesis in a more exact, qualified, or nuanced way that takes account of the objection, or start a new section in which you consider your topic in light of it. This will work if the counterargument concerns only an aspect of your argument; if it undermines your whole case, you need a new thesis.
Where to Put a Counterargument
Counterargument can appear anywhere in the essay, but it most commonly appears
- as part of your introduction—before you propose your thesis—where the existence of a different view is the motive for your essay, the reason it needs writing;
- as a section or paragraph just after your introduction, in which you lay out the expected reaction or standard position before turning away to develop your own;
- as a quick move within a paragraph, where you imagine a counterargument not to your main idea but to the sub-idea that the paragraph is arguing or is about to argue;
- as a section or paragraph just before the conclusion of your essay, in which you imagine what someone might object to what you have argued.
But watch that you don't overdo it. A turn into counterargument here and there will sharpen and energize your essay, but too many such turns will have the reverse effect by obscuring your main idea or suggesting that you're ambivalent.
Counterargument in Pre-Writing and Revising
Good thinking constantly questions itself, as Socrates observed long ago. But at some point in the process of composing an essay, you need to switch off the questioning in your head and make a case. Having such an inner conversation during the drafting stage, however, can help you settle on a case worth making. As you consider possible theses and begin to work on your draft, ask yourself how an intelligent person might plausibly disagree with you or see matters differently. When you can imagine an intelligent disagreement, you have an arguable idea.
And, of course, the disagreeing reader doesn't need to be in your head: if, as you're starting work on an essay, you ask a few people around you what they think of topic X (or of your idea about X) and keep alert for uncongenial remarks in class discussion and in assigned readings, you'll encounter a useful disagreement somewhere. Awareness of this disagreement, however you use it in your essay, will force you to sharpen your own thinking as you compose. If you come to find the counterargument truer than your thesis, consider making it your thesis and turning your original thesis into a counterargument. If you manage to draft an essay without imagining a counterargument, make yourself imagine one before you revise and see if you can integrate it.
Gordon Harvey (adapted from The Academic Essay: A Brief Anatomy), for the Writing Center at Harvard University

Counterarguments and Rebuttals – Learning to Disagree and Defend Your Case
All of us have had points of disagreement with others, and these are part and parcel of daily life. Sometimes we argue our way out and try to convince the other party to our point of view, at other times we just agree to disagree.
But what do you do when you strongly disagree with someone in a public setting and have to reason your way out?
SPH CEO Ng Yat Chung recently found himself in a spot when he took offence at a reporter’s question and shot back with the now-iconic “I take umbrage at your comment.” Little was said to explain himself and Ng subsequently found himself the subject of online memes, criticising his unbecoming behaviour. How then should he — and in fact, we —refute and defend ourselves in a calm, civil and persuasive way?
This post will cover the topics of counterarguments and rebuttals —what each of them mean; and how you can structure a rebuttal paragraph (which includes the counterargument) in your argumentative essay .
Note that a rebuttal is required only in an argumentative essay since you need to convince the reader towards your stand/point of view. (A discursive essay does not require one as its purpose is to throw up reasons for both sides of the issue without compelling the reader to take a side.)
What is a counterargument?
A counterargument(CA) is an argument from the opposing point of view. In the context of an argumentative essay, it should oppose the stand that you made in the introduction.
Let’s take this essay question for example:
The COVID-19 circuit breaker has been detrimental for families. Do you agree?
Your stand:
No , the COVID-19 circuit breaker has not been detrimental for families.
Counterargument
On the other hand , [signal CA] there are families who are unable to provide adequate support for their children’s home-based learning (HBL) needs. [opposing point] These parents could be working outside and are unable to care for their children at home, with the latter gradually becoming disengaged from the challenges of HBL. [brief explanation of why it matters/its severity]
The CA highlights a group of families who are adversely affected by the circuit breaker and explains why it is a valid point of concern. This anticipates what people on the opposing side might disagree about, giving you an opportunity to convince them that their concerns are probably unfounded. This is when you can defend your stand.
Note: When you surface a CA, you need to ensure that you are able to refute it well. Otherwise, you’d very well be shooting yourself in the foot and weaken your stand.
There are also other ways to signal your CA: – Some may claim that… – Some people believe that… – However, others might argue that…
What is a rebuttal?
After you have raised a point of concern, the rebuttal comes after the counterargument and disputes/refutes it.
It should show why the counterargument given is: – False — explain why it is invalid – Weak — acknowledge that the CA is true, but has its loopholes – A problem that can be easily solved — acknowledge that the CA is true, but there are solutions to address it
Admittedly , there are families who are at a disadvantage because parents are unable to provide care and support for their children over a prolonged time indoors. [acknowledge that CA is true] However, [signal rebuttal] schools do provide support for students who may not have a conducive learning environment and resources at home. These students can use a school laptop, enjoy a quiet environment and consult a teacher on duty when in doubt. (P1) Moreover, even though parents may not be around at home, there are opportunities for children to take up household responsibilities. They can help with the chores, look after their siblings and learn to work independently. (P2) [offer solutions to address the problems] As such, a prolonged stay-in period may not be all that undesirable as arrangements can be in place to support both parents and children. [reiterate that your argument still stands]
In this rebuttal, two solutions are offered to resolve two potential problems faced by low-income families (which were raised in the CA). This is then followed by a concluding statement that the situation is not all that bleak for this group of families and that support is available and opportunities for growth can be seized amidst such challenges.
There are also other ways to signal your rebuttal: – There is some truth to this claim, but… – Perhaps, to a certain extent, it may be true that…, but… – While this may be true in certain cases,… – While we acknowledge that…, but nevertheless,…
Note that the CA and rebuttal come together in one paragraph.
We have learnt what a CA and rebuttal are, and how to structure them in a paragraph. They provide meaningful ways of engaging your “critics” (those who oppose your stand) and showing why they should buy your point of view. This brings your argumentative essay to another level where you are not only arguing for your case, but persuading people to join your camp, so to speak. Beyond taking umbrage, there is always a place for winsome argumentation. How do you think SPH CEO Ng could have responded in a more persuasive way?
Check the other articles from this section
- Writing Expository Essays: Grabbing Your Readers’ Attention and Leaving a Lasting Impression
- Sec 4 Continuous Writing (P1SC): Planning to Write the Essay
- Writing Narratives: Starting with a Splash and Ending with a Bang
- How to use persuasive techniques in speech (part 1)
- How to use persuasive techniques in speech writing (part 2 – advanced)
Don’t Miss Any Future Post!
2024 Bukit Timah Branch Secondary English Tuition Timetable
How To Write A Rebuttal In An Essay
What is a rebuttal in writing.
When writing an essay, rebutting is one way to argue points or facts that have been stated. It will directly oppose any view and will include reasons for your claims being valid. When including this in an essay, you will be acknowledging what the opposition is saying, but will continue to argue your own points. Here, you can see how to write a good rebuttal that will be easy to understand while getting your point across.
Why Are Rebuttal Paragraphs Important?
When planning to include a rebuttal in an argumentative essay, it is essential to know how to write a rebuttal paragraph. Students should plan an outline for an argumentative essay and know where to place these paragraphs. These are used for arguing points that have been made. They will appear after the main argument in an essay. When working on these paragraphs, it is important for there to be evidence that supports your arguments.
These paragraphs will introduce your opposing argument and will also acknowledge that some parts of the opposition are valid points. It will also be used for introducing the conclusion of the essay. Learning how to include these paragraphs is not always an easy task. If you need help with your essay, you can hire an argumentative essay writer that has experience including counterarguments. With professional help, students can create a powerful argument that will attract the attention of the reader and be backed with evidence.
How to Start Refuting
To get started, a three-part organization process should be used. You must have a complete understanding of the opposing viewpoint. Know who the intended audience is, what message is being sent, and what points you agree with. You will then analyze the argument and determine your position. The argument may contain untrue statements or claims that cannot be verified.
Additional research will then have to be performed. You need to back up your statements with facts and evidence when you write a counterargument. It will be important to fact-check any of the opposition’s arguments and collect reliable data that can disprove these.
Using Effective Transition Words

Transition words and phrases are key things that one should consider when writing an argumentative paper. They act as bridges and will connect your ideas and arguments. Transition words will help your reader identify the counter argument and rebuttal you are writing. It is an effective way of making the argument clearer. When you are creating a refutation essay, it is important you include these words. Some common transition phrases that can be used when writing include:
- However
- Instead of
- On the other hand
- In contrast
- It can be argued that
- The problem with that
As you write a rebuttal in a sentence, be sure you use words that will easily connect the two things being compared or contrasted. These words will show a relationship between arguments and will link one idea to the next being presented.
Rebuttal Examples In an Argumentative Essay
You will have to make your arguments in essays on various topics. It is important to know the proper argumentative essay structure before getting started. Once this has been addressed, you can start to work on the counter-argument. For example, let’s say that the essay focuses on the violence children learn from video games. The objection being made is that these games cause children to use guns and shoot people.
You would then assert that violence in media existed long before the creation of video games. You would then make a counterargument that may state:
“Some may argue that certain video games include violent scenes that cause children to use guns. Youth violence does appear to be on the rise. However, before video games, there were other courses of violence that children had been exposed to. To blame video games, one would have to ignore the effect of movies, books, music, and other forms of media.”
In this example, the counter-argument addresses the initial point and acknowledges validity. It then makes use of transition words to present a different view, backed by research stating that other types of media have also had an impact on the rise of violence.
Being able to make a concise counter-argument is not always easy. It should be short and to the point. With a custom argumentative essay writing service , you can get help from experienced writers who know how to generate an effective counter-argument.
Common Mistakes To Avoid While Writing Refutation Sentences
There are some common mistakes that are often made by students when writing essays. This is why using a custom essay writing service can be beneficial. The professionals with these services will know how to properly structure an essay and know how to do a rebuttal in an essay. Here, you can learn about the mistakes that should be avoided when writing sentences and paragraphs.
- Irrelevant counter-argument
- Single sentence refutations
- Repeating points already made
- Not using transition words
- Lack of research
- Not citing sources and references
- Being emotional
- Relying on fallacies
- Failure to fact-check
- Poor structure and grammar
Avoiding these will ensure that any arguments made against an oppositional point will be effective.
Know that you know how to refute the points of the opposition and have this be an effective piece of an essay, you can create a paper that presents your view and supporting facts. While these essays can be difficult to structure, there are many resources online and services that can be of use. With the help me do my assignment service, you can gain access to expert advice that can help you with your essay structure and make sure that you avoid any common mistakes. Additionally, experienced professionals can provide guidance on how to effectively use transition words and how to start your essay. Knowing that you have this kind of assistance can make the essay writing process much less daunting.
Do you need a rebuttal in a synthesis essay?
This is not needed in a synthesis essay. These essays have an intro that provides the topic, a body that offers an objective two-sided interpretation, info from multiple sources, as well as citations, and a conclusion.
Which rebuttal would be ineffective in an argumentative essay?
If it takes the opposition’s point, acknowledges it, and then uses words to insult that point, it would be considered to be ineffective when drafting an argumentative essay.
Does a persuasive essay have a refutation?
Refutations are not used in persuasive essays. They are found in argumentative essays, where the writer is arguing a point and proving it is false by providing their own ideas and facts.
Related posts:
- How To Write A Good Compare And Contrast Essay: Topics, Examples And Step-by-step Guide
How to Write a Scholarship Essay
- The Best Online AP Courses For High School Students [Full Guide]
- Explaining Appeal to Ignorance Fallacy with Demonstrative Examples
Improve your writing with our guides

Definition Essay: The Complete Guide with Essay Topics and Examples

Critical Essay: The Complete Guide. Essay Topics, Examples and Outlines
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.


Home » Writers-House Blog » A Rebuttal: What It Is and How to Write One
A Rebuttal: What It Is and How to Write One
Students write thousands of essays in their academic career, and they often need to address counterarguments. However, what rebuttals are? Are they the same thing as counterarguments or should students approach them differently? Writers-house.com is here with some helpful tips.
First, a rebuttal isn’t a necessary part of an academic paper. A rebuttal is just a part of an argument. For example, when a student struggles to meet the word count, they can include a rebuttal that will both make the paper longer and strengthen the argument. Let’s consider rebuttals in more details so that everyone can figure out what a rebuttal should look like.
What Is a Rebuttal?
To understand the concept of a rebuttal, students should know how to include it in their argument. Therefore, it makes sense to consider arguments and counterarguments.
- The Argument The first part of the general argument is the author’s point. The author should have a strong opinion on an arguable topic, and the audience should be able to either agree or disagree with it.
- The Counterargument This is the opposing viewpoint. It’s what people who don’t agree with the author would say about the subject matter. The counterargument is also important because it makes the argument stronger, proving that the author has done their research and considered different opinions.
- The Rebuttal The rebuttal connects the argument and the counterargument, explaining why the former is correct and the latter is wrong. When writing a rebuttal, students can acknowledge the opposite opinion why also standing their ground.
For example, when choosing a restaurant, one may come up with an argument that a certain restaurant has great food and a nice atmosphere. A counterargument may state that the atmosphere isn’t good at all because the place is dark and the music is too loud. A possible rebuttal is that the dark atmosphere and loud music are not bad, and everything depends on a particular visitor’s preferences.
A rebuttal is a simple concept. First, the author presents their argument, then they address the counterargument, and then explain why they’re still right. Now let’s consider a rebuttal in an argumentative essay.
An Effective Rebuttal: Writing Strategies
An effective rebuttal shouldn’t just state that an argument is right and the counterargument is wrong. Academic writing requires students to use formal language and to create the right structure
1. Addressing the weaknesses of the counterargument
If a writer acknowledges the counterargument while also addressing its weaknesses, such an approach also helps to strengthen the argument. This way, the writer can demonstrate that they’ve studied the issue and considered different perspectives. Including a rebuttal allows for explaining why the argument is still valid and stronger than the counterargument.
2. Agreeing with the opposite opinion but providing additional information that weakens it
Sometimes, writers might partially agree with a counterargument, because the opposite opinion cannot be always wrong. In this case, the author should provide more information to explain why their point is still stronger, despite the validity of the counterargument. For example, there may be a piece of evidence that weakens the opposite point or illustrates very important exceptions.
Transitions and Their Importance
The argument, counterargument, and rebuttal should be connected so that the paper can be easy to comprehend. Transitions provide such connection, explaining how the author has switched from the argument to the counterargument to avoid possible confusion.
Transitions must help readers identify both the argument and counterargument, briefly explaining how the rebuttal supports the former and disproves or weakens the latter.
Final Thoughts
When writing an academic paper, one shouldn’t forget that both the counterargument and rebuttal should appear at the end of the paper. They must be followed by a strong conclusion that will help readers focus on the author’s point. It’s also important to check the required citation format and to make sure that all the sections of the paper are logically connected.
Leave a Reply
Be the First to Comment!
Place your order
- Essay Writer
- Essay Writing Service
- Term Paper Writing
- Research Paper Writing
- Assignment Writing Service
- Cover Letter Writing
- CV Writing Service
- Resume Writing Service
- 5-Paragraph Essays
- Paper By Subjects
- Affordable Papers
- Prime quality of each and every paper
- Everything written per your instructions
- Native-speaking expert writers
- 100% authenticity guaranteed
- Timely delivery
- Attentive 24/7 customer care team
- Benefits for return customers
- Affordable pricing

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

10.13: Formula for Refutation and Rebuttal
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 59932
Learning Objective
- Recognize strategies for rebuttal and refutation of counterargument
Though writers may handle rebuttal and refutation in different ways, there is a formula for success in academic argument. Here are the key parts of that formula:
Accurately represent opposing viewpoints
If you don’t accurately and thoroughly represent opposing viewpoints in your own writing, some of your potential audience will automatically be turned off. Good rebuttal and refutation begins with a solid understanding of all possible points of view on your topic. That may mean you even need to acknowledge and accommodate opposing points of view. Acknowledging other views shows you are aware of ideas that run counter to your claims. You will almost always be expected to at least acknowledge such views in your work. You may also, though, need to accommodate opposing views, especially if many people see them as reasonable. If, for example, you were writing a piece arguing that students should take a gap year between high school and college, it would benefit your work to acknowledge that a gap year isn’t realistic for or even desired by all students. You may further accommodate this other view by explaining how some students may thrive in the structure that school provides and would gain by going directly from high school to college. Remember that even if you cannot prove positions that counter your own are wrong, you can still use rebuttal and refutation to show why they might be problematic, flawed, or just not as good as another possible position for some people.
Use a respectful, non-incendiary tone
It doesn’t help the writer’s cause to offend, upset, or alienate potential readers, even those who hold differing views. Treating all potential readers with respect and avoiding words or phrases that belittle people and/or their views will help you get your points across more effectively. For example, if you are writing a paper on why America would benefit from a third viable major political party, it will not help your cause to write that “Republicans are dumb, and Democrats are whiny.” First, those claims are too general. But even if they weren’t, they won’t help your cause. If you choose to break down the perceived problems with members of political parties, you must do so in a way that is as respectful as possible. Calling someone a name or insulting them (directly or indirectly) is very rarely a successful strategy in argument.
Use reliable information in your rebuttal/refutation
Always be sure to carefully check the ideas or claims you make in rebutting a counterargument. The brain is not an infallible computer, and there are instances when we think we know information is accurate but it isn’t. Sometimes we know a lot about a particular subject but we get information confused or time has changed things a bit. Additionally, we may be tempted to use a source that backs up our ideas perfectly, but it might not be the most reputable, credible, or up-to-date place for information. Don’t assume you just have all of the information to shoot down counterarguments. Use your knowledge, but also do thorough research, double- and triple-check information, and look for sources that are likely to carry weight with readers. For example, it is widely assumed that bulls are attracted to the color red; however, in reality, bulls are colorblind, so what many people assume as fact is incorrect. Be thorough so you have confidence in your claims when you are rebutting/refuting and likewise when you are attempting to prevent yourself from being open to rebuttal/refutation.
Use qualifying words when applicable to help you be more accurate and to avoid locking you into an absolute claim
Qualifying words are terms such as “many,” “most,” “some,” “might,” “rarely,” “doubtful,” “often,” etc. You get the point. These are words that don’t lock you into a claim that could be easily refuted and that can help you more easily rebut counterarguments. For example, if someone says “Nobody dies of tuberculosis anymore” we might get the point that it isn’t as common as it used to be. Still, it isn’t an accurate statement, and a more precise way to phrase such a claim would be to qualify it: “Not many people die each year in America from tuberculosis.” You might not always need to use qualifying terms. If you are making a point that is absolute, feel free to make it strongly; however, if there is a need to give your claim more flexibility, use qualifying words to help you.
- Rebuttal and Refutation. Provided by : University of Mississippi. Project : PLATO Project. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Key Concept
Rebuttal Argument : argues against an existing argument; seeks to poke holes in or dismantle another argument; can offer a counterargument to the original, but doesn’t have to.
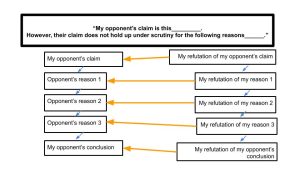
As we know, arguments don’t exist in a vacuum, and discourse is highly based on context. When we make an argument, we’re often doing so in response to other things that have been said and done. For example, an arguer rarely forwards their positions on things like gun laws or the importance of mental health initiatives without being prompted; however, when a national tragedy–like a devastating school shooting–occurs, then it compels stakeholders who are concerned about these issues or those who are directly impacted by them to articulate their views and to share those views with a wider audience.
In rhetoric, the initial event that has created the opportunity for stakeholders to offer their views on certain issues is called a kairos , which means “an opening.” The idea is that the event (the kairos ) has created an opening for those who are impacted by or concerned about something to voice their positions.
However, as we all know, rarely if ever does one person voice a position without that position being critiqued or questioned by others. In fact, more often than not, when one stakeholder voices a position, another stakeholder will critique or challenge their ideas.
And that is exactly what a rebuttal argument is: an argument that argues against an existing claim.
Or, here’s another way to think about rebuttal arguments: imagine a group of three friends are driving home from the movies. One by one, everyone begins discussing the movie, and the friends all gradually learn that they all had differing opinions on it. Their conversation might look like this:
- Friend #1: “That movie was so awesome! I loved everything about it. The acting was so great; the movie was perfectly cast, and the chase scene at the end was so intense!”
- Friend #2: “Yeah, I dunno. I thought it was pretty good. I was really into the acting, for sure.”
- Friend #3: “I agree, the acting was really good, but the special effects were super weak in my opinion–so weak, in fact, that I had a hard time getting past how bad they were. It really took me out of the film in a bad way. All I could think about was how silly the special effects were.”
Notice in the above interaction, the fact that all three friends just saw the same movie presents a kairos (an opening, or opportunity) for them to discuss it and forward their opinions about it. Equally, after Friend #1 voices their stance (they really liked the movie) and their rationale for that stance (the acting and cast were good, and specific scenes were particularly riveting), Friends #2 and #3 respond to –and offer a rebuttal to–Friend #1’s stance by critiquing certain elements of the film and, thereby, Friend #1’s stance.
One final thing to note in the above interaction is that while Friends #2 and #3 critique or pick apart Friend #1’s argument that the film is good, they can still find common ground in appreciating the acting, so while a rebuttal reacts to and picks apart an existing argument, it doesn’t have to completely shut that argument down. In fact, some of the most effective rebuttal arguments seek to acknowledge the partial value of the argument they’re critiquing. This is called making a concession , when we identify the value of an opponent’s stance in the pursuit of forwarding our own position. Doing this allows us to build our credibility with our audience by helping them see that we are capable of rationally considering what someone who we disagree with is saying.
For our purposes, however, here is how we can think about making rebuttal arguments :
Rebuttal arguments involve refutation (identifying where the argument is wrong, flawed, or not complete) and/or offer counter arguments (offering argumentative points that differ from the original argument). To make a rebuttal argument, choose one of your text/sources you have found on your issue for the rebuttal argument. This will be your primary text, and you’ll seek to represent that argument fully and fairly so that you can refute it. Then, you must use your other sources to support your rebuttal claims that are picking apart the argument from your primary text. Remember, the goal of a rebuttal argument is to dismiss or weaken an argument so that it become irrelevant or questionable to an audience who might be or has been persuaded to accept it.
Recapping the main ideas behind rebuttal arguments:
● Rebuttal arguments argue that another argument doesn’t hold up under scrutiny
● Rebuttal arguments pick apart and critique an existing argument
● In order to preserve their own credibility, rebuttal arguments should fully and fairly represent the positions of the argument they’re critiquing
● In all arguments, but especially so in rebuttal arguments, concessions (acknowledging the value of an opponent’s position) can be really useful for building our credibility by helping our audience see that we’re capable of rationally considering conflicting stances
College Comp II Copyright © 2019 by Jude Miller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write a Rebuttal Essay — An Easy Guide to Follow
Ever wondered how to write a rebuttal essay? Face this academic assignment for the first time and can’t find an understandable guide to follow? Don’t worry because here you’ll find a detailed guideline allowing you to set the record straight and understand what tips to follow while writing. We’ll take a look at all the aspects of writing, check what rebuttal in an essay is and list all tips to follow.
What Is a Rebuttal in an Essay — Simple Explanation
Academicians also call this form of writing a counter-argument essay. Its principal mission is to respond to some points made by a person. If you render a decision to answer one or another argument, you should present a rebuttal which is also known as a counter-argument. Otherwise stated, it is a simple attempt to disprove some statements by suggesting a counter-argument.
At a glance, this task seems to be quite challenging. However, rebuttal argument essay writing doesn’t take a massive amount of time. You just need to air your personal opinion on one or another situation.
Related essays:
- Economic recession essay
- Hamlet & formal structure
- The counter revolution and the 1960s essay
- Viacom Strategic Analysis essay
Nevertheless, your viewpoint should be based on your research and comprise a strong thesis statement. An excellent essay can even change the opinion of the intended audience. Thus, you need to be very attentive while writing and use only strong and double-checked arguments.
How to Do a Rebuttal in an Essay — Useful Tutorial
Firstly, you should conduct simple research before you start expressing your ideas. Don’t tend to procrastinate this task because it is tough to organize your thoughts when your deadline is dangerously close. If you don’t have a desire to spend the whole night poring over the books, it is better to start processing the literature as soon as possible. It would be great if you subdivide this task into a few sections. As a result, it will be easier to work!
The majority of academicians have not the slightest idea how to answer the question of how to start a rebuttal in an essay. In sober fact, you need to start with a strong introduction, comprising a thesis statement. Besides, your introductory part should explain what particular situation you are going to discuss. Your core audience should look it through and immediately understand what position you desire to explore.
You should create a list of claims and build your essay structure in the way allowing you to explain each claim one by one. Writing a rebuttal essay, you should follow a pre-written outline. As a result, you won’t face difficulties with the structure.
For instance, there is a particular situation, and you don’t agree with it. You wish to prove the targeted audience that your idea is correct. In this scenario, you need to state your opinion in a thesis statement and list all counter-arguments one by one.
Each rebuttal paragraph should be short and complete. Besides, you should avoid making too general statements because your targeted audience won’t understand what you mean. If you wish to air your proof-point, you should try to make more precise arguments. As a result, your readers won’t face difficulties trying to understand what you mean.
Rebuttal Essay Outline — Why Should You Create It
As well as any other academic paper, this one also should have a plan to follow. Your rebuttal essay outline is a sterling opportunity to organize your thoughts and create an approximate plan to follow. Commonly, your outline should look like this:
- Short but informative introduction with a thesis statement (just a few sentences).
- 3 or 5 body paragraphs presenting all counter-arguments.
- Strong conclusion where you should repeat your opinion once again.
For you not to forget some ideas, we highly recommend writing a list of all claims you wish to discuss in all paragraphs. Even if you are a seasoned writer who is engaged in this area and deals with creative assignments on a rolling basis, you won’t regret it. You’ll spend a few minutes creating the outline, but the general content of your essay will be considerably better.
Top-7 Rebuttal Essay Topics for Students
If you really can’t render a correct decision and pick a worthy topic, look through the rebuttal essay ideas published below. You can’t go wrong if you choose one of the below-listed ideas:
- Is it necessary to sentence juveniles to life imprisonment?
- Why are electro cars better for the environment?
- Distance learning is more effective than the traditional approach to education.
- Why should animal testing be forbidden?
- Modern drones can help police solve the crimes faster.
- Why should smoking marijuana be prohibited?
- Why should the screentime of kids be limited?
We hope our tips will help you catch the inspiration and create a compelling essay which will make your audience think of the discussed problem and even change their minds.
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
How To Write A Counterclaim For A Successful Result

You might have probably heard about a counterclaim or written one that did not go well with you, which is why you are here. We understand your frustrations and anxiety about writing counterclaims, which is why we developed this comprehensive article.
Here is what to expect:
An in-depth explanation of what a counterclaim is The necessity of a counterclaim How to write a good counterclaim Characteristics of an excellent counterclaim Structure and formatting of counterclaims
After reading this post, you will have all the information you need to craft an award-winning paper. We will not leave anything to chance until you know how to write a counterclaim like a top-class student!
Table of Contents
What is a counterclaim in writing, why is a counterclaim necessary, how to write a counterclaim from scratch, detailed guide on how to start a counterclaim paragraph, how to write rebuttal, characteristics of a good counterclaim, example of a good counterclaim.
A counterclaim refers to an argument that opposes the author’s claim. The writer presents the claim and then refutes it, giving reasons why others should not take up the contrary view and agree with their initial stand.
The counterclaim opposes the thesis statement in your essay. So, this is how a counterclaim comes about:
- You first introduce the topic in the introductory paragraph
- Create a thesis statement in the last sentence
- Write a counterclaim that rebuts the initial argument
Many students fail to appreciate the fact that there is a difference between a claim and a counterclaim. The claim demonstrates your position of argument or the assertion of a fact, whereas a counterclaim negates a specific claim by refuting it.
Any top-rated argumentative will always have a counterclaim which disagrees with and disapproves of a claim. Such a claim also provides reasoning that further clarifies a particular argument. The two main purposes of a counterclaim are as follows:
It enhances the credibility of the author: A strong argumentative essay will utilize the rhetorical appeal of ethos. With a counterclaim, a writer will prove that they researched extensively on the topic and are not trying to hide possible information from the audience. It also allows the writer to provide a rebuttal to the essay. The rebuttal is used to disprove the counterclaim within the writer’s argument.
For instance, if the claim is that the government should ban gun use, the counterclaim would be that it should not ban it because it infringes on human rights. There should always be reasons and evidence for you to have a successful counterclaim.
In the next few lines, we will provide all you need to know about starting a counterclaim and delivering the best! So stay tuned.
Every successful essay begins with thorough background research on the topic of discussion. Exploring all possible angles of your essay before embarking on the writing process is recommended—those who end up with a good counterclaim put in extra hours in research and extensive consultation.
You can read thousands of articles on how to write a counterclaim, but without the right background research strategies, that great essay might amount to nothing. So, if you want to crack your counterclaim paragraph like a guru, here are excellent tips for you:
Understand your topic Explore what previous authors have done on it Identify the knowledge gaps Seek facts to defend your claim
Once you have all the information needed for your topic, nothing will stand in the way of you writing a top-notch paper that will impress your professor. When you have factual proof of every statement you make in your essay, you will have a non-biased and credible paper. That means that the sources you use should always be credible and directly relevant to the topic of your essay.
After stating all the base knowledge you need about counterclaims, we now want to dive into the practical part of writing a counterclaim argument. Let’s explore how to write counterclaims by looking at the elements needed:
- The main counterclaim: It states an opposing argument to the claim.
- The evidence includes a previous position to show that others welcome the view.
- An explanation entails providing reasons why people hold the particular view you presented.
- A rebuttal: Here, you will explain the weakness of the counterclaim and present show why your original position is correct.
The process might be challenging initially, but with the right tools and expert advice, you will be up and running in minutes. A counterclaim is included in argumentative writing to address the opposite side of the argument and provide a rebuttal.
The process of writing an outstanding counterclaim in an argumentative essay is as follows:
Where do you put a counterclaim in an essay? Every top-ranking essay begins with a catchy intro comprising statistics or a rather dramatic intro to a particular problem. The thesis statement follows, and the then claim comes on stage. Therefore, the counterclaim comes after you have backed up your claims with evidence and further arguments. How long is the counterclaim? It depends on the number of counterclaims and the overall length of your essay. A typical counterclaim should be at least one paragraph long. Remember that you are not just stating it but explaining why it is so. That is why most guides on writing a counterclaim and rebuttal will recommend either writing them in one paragraph or separately. What different points of view do others hold? You should always understand all the possible points that may arise to counter your claim. Researching why people oppose your claim will give you room for a balanced and reliable paper. It requires a creative mind to determine how your claim goes against the common view. How to introduce a counterclaim now: The general rule is that you should present the contrary opinion fairly. You will only be ready to craft a brilliant counterclaim once you dive into the possible arguments that others who oppose your thesis make. Sincerely present the contrary opinion fairly.
Always remember to use transitions when moving on to present your counterclaim. Just like in a debate, the contrary side will come after the proposers have made their submissions. Therefore, you can begin your counterclaim paragraphs with the following:
- On the contrary, side
- Critics say that
Having presented the other side, you will detail why people also hold that view. It is where the evidence comes in to solidify your counterclaim.
It is advisable to have it in a similar paragraph where your counterclaim is, but if that is not possible, begin it in a new paragraph. However, always remember to keep it short while bringing out the following:
- How the contrary position in your counterclaim is false or weak.
- Presenting the advantages in the counterclaim but giving reasons why the opposite view may not hold water.
- Describe how your main argument outweighs the risks in the counterclaim.
After introducing the counterclaim, you have to discuss why the counterclaim is incorrect. You can start the rebuttal in several ways, such as:
Despite this information Nevertheless However
It is your opportunity to prove why the contrary view is wrong.
You cannot achieve this milestone without considering all sides of the argument first. That is why most researchers in college and university take their time before beginning the writing process. It provides a base for the facts and opinions and saves the time one will spend completing the argumentative essay.
Acknowledging the valid points of the other side is necessary for any form of argumentative writing. This practice eliminates the thought of narrow-mindedness from the reader’s point of view, which may make your essay less effective.
Instead of making your argument look weak, a counterclaim will strengthen your essay by proving that you thoughtfully considered all possible angles before writing your essay. Nobody will accuse you of bias or inadequate research when you have a formulated counterclaim.
A good counterclaim, therefore:
Acknowledges what the opposing side says Provides evidence from the opposing side Refutes the point of view and evidence
It is also crucial to state that when you have more than one claim in your paper, there is always an option of writing a counterclaim for each. You are not limited to presenting the different counterclaims in the same essay. However, follow the structure outline above in terms of length and format.
Additional characteristics of a world-class essay include:
- Objectivity in the language use
- Fairness in the diction
- Evidence to back up the counterclaim
- Fairness in the rebuttal
By validating any underlying concerns, you eliminate room for doubt or error. Remember also to explain why your argument works in that context.
Below is a brief example of what a good counterclaim can look like, from professional dissertation writers :
“On the other hand, some students say homework presents unnecessary stress and pressure. This point of view makes sense because the article states that too much homework may be overwhelming for students, which is why most of them do not complete it. However, homework does not harm the student because the article also says that homework is necessary to test students’ understanding after classroom learning. Therefore, even though homework may cause stress and pressure on the student, it does not harm the student in any way.”
From the example, you can note the following:
Phrases that can begin a counterclaim:
On the other hand, some people say Admittedly, some people say Certainly, some people say
Phrases to refer to the initial claim:
However Nevertheless On the other hand
Phrases to bring paragraph to a conclusion:
Thus Therefore As a result
A good counterclaim will always give you an edge over your competitors in any case.
Writing A Counterclaim Can Be Very Easy
Writing an all-inclusive counterclaim is not a big deal if you have all the facts rights – our writing service and master thesis help offers top-notch assistance with an incredible team of writers and research gurus. We will help you identify winning arguments and provide you with the best rebuttals.
Do not second guess what you will score in your counterclaim essay when you can try out our custom thesis writing service today. Make your pick today and improve your score effortlessly.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Step 1. Come up with a Counterargument. A strong rebuttal is only possible when there's a strong counterargument. You may be convinced of your idea but try to place yourself on the other side. Rather than addressing weak opposing views that are easy to fend off, try to come up with the strongest claims that could be made.
Such differences dictate where the counterclaim (s) are located. There is a structure where the counterclaims are located within all the body paragraphs. In this case, you will write your claim, followed by a counterclaim, and then a rebuttal. This means that for every claim you present to support your thesis, there will be a counterclaim and a ...
A counter-argument can appear anywhere in your essay, but it most commonly appears: As part of your introduction—before you propose your thesis—where the existence of a different view is the motive for your essay, the reason it needs writing. As a section or paragraph just after your introduction, in which you lay
The most common spots are the following: Before your conclusion. This is a common and effective spot for a counterargument because it's a chance to address anything that you think a reader might still be concerned about after you've made your main argument. Don't put a counterargument in your conclusion, however.
Rebuttal: In this section, you incorporate your own evidence that disagrees with the counterclaim. It is essential to include a thorough warrant or bridge to strengthen your essay's argument. If you present data to your audience without explaining how it supports your thesis, your readers may not make a connection between the two, or they may ...
In a traditional argumentative essay structure, the rebuttal generally follows your argument and precedes the conclusion. Here's a simple breakdown: Introduction: The opening segment where you introduce the topic and your thesis statement. Your Argument: The body of your essay where you present your arguments in support of your thesis.
Rebuttal and refutation are common in all types of argument, including academic argument. As you complete more advanced work in college, you will be expected to address counterargument often. And while you might not always need to or be able to prove that other points of view are wrong, you may at least need to try to argue against them. ...
Rebuttal and refutation are common in all types of argument, including academic argument. As you complete more advanced work in college, you will be expected to address counterargument often. And while you might not always need to or be able to prove that other points of view are wrong, you may at least need to try to argue against them. ...
A rebuttal in an argumentative essay is a response you give to your opponent's argument to show that the position they currently hold on an issue is wrong. While you agree with their counterargument, you point out the flaws using the strongest piece of evidence to strengthen your position. To be clear, it's hard to write an argument on an ...
Now let's take a look at examples of rebuttal and refutation and consider how students follow these guidelines to approach counterarguments to their viewpoints: They accurately represent opposing viewpoints. They use a respectful, non-incendiary tone. They use reliable information. They use qualifying words. Felix is writing his argument ...
Rebuttal Sections. In order to present a fair and convincing message, you may need to anticipate, research, and outline some of the common positions (arguments) that dispute your thesis. If the situation (purpose) calls for you to do this, you will present and then refute these other positions in the rebuttal section of your essay.
Rebuttal (or Refutation): a ... Counterarguments are often placed toward the end of the essay after the author has argued all their points supporting their position. You might decide to tackle both the counterargument and rebuttal in one paragraph, or you may decide to break them up into separate paragraphs, as seen in the example outline below ...
This section typically comes after you have presented your own lines of argument and evidence. This section typically consists of two rhetorical moves: concession; counter. Examples of Counterarguments. By introducing counterarguments, we show we are aware of alternative viewpoints— other definitions, explanations, meanings, solutions, etc.
Writing an effective rebuttal means more than saying, "I'm right, and you're wrong.". Essentially, that is the gist of what you're saying, but remember, you're writing an academic essay. That means you'll use formal language and sentence structure, use a few of those 10-dollar words, and show that you know your stuff.
Counterargument. When you write an academic essay, you make an argument: you propose a thesis and offer some reasoning, using evidence, that suggests why the thesis is true. When you counter-argue, you consider a possible argument against your thesis or some aspect of your reasoning. This is a good way to test your ideas when drafting, while ...
After you have raised a point of concern, the rebuttal comes after the counterargument and disputes/refutes it. It should show why the counterargument given is: - False — explain why it is invalid. - Weak — acknowledge that the CA is true, but has its loopholes. - A problem that can be easily solved — acknowledge that the CA is true ...
Transition words will help your reader identify the counter argument and rebuttal you are writing. It is an effective way of making the argument clearer. When you are creating a refutation essay, it is important you include these words. Some common transition phrases that can be used when writing include: But. However.
Here are rebuttal examples for debate & essays. Learn to convince others to agree with you with our explanation of good rebuttals & famous rebuttal examples.
A possible rebuttal is that the dark atmosphere and loud music are not bad, and everything depends on a particular visitor's preferences. A rebuttal is a simple concept. First, the author presents their argument, then they address the counterargument, and then explain why they're still right. Now let's consider a rebuttal in an ...
Good rebuttal and refutation begins with a solid understanding of all possible points of view on your topic. That may mean you even need to acknowledge and accommodate opposing points of view. Acknowledging other views shows you are aware of ideas that run counter to your claims. You will almost always be expected to at least acknowledge such ...
15. Key Concept. Rebuttal Argument: argues against an existing argument; seeks to poke holes in or dismantle another argument; can offer a counterargument to the original, but doesn't have to. As we know, arguments don't exist in a vacuum, and discourse is highly based on context. When we make an argument, we're often doing so in response ...
Your rebuttal essay outline is a sterling opportunity to organize your thoughts and create an approximate plan to follow. Commonly, your outline should look like this: Short but informative introduction with a thesis statement (just a few sentences). 3 or 5 body paragraphs presenting all counter-arguments.
So, this is how a counterclaim comes about: You first introduce the topic in the introductory paragraph. Create a thesis statement in the last sentence. Write a counterclaim that rebuts the initial argument. Many students fail to appreciate the fact that there is a difference between a claim and a counterclaim.