An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health


Work–Life Balance: Weighing the Importance of Work–Family and Work–Health Balance
Associated data.
To date, research directed at the work–life balance (WLB) has focused mainly on the work and family domains. However, the current labor force is heterogeneous, and workers may also value other nonworking domains besides the family. The aim of this study was to investigate the importance of other nonworking domains in the WLB with a particular focus on health. Moreover, the importance of the effects of the work–family balance (WFB) and the work–health balance (WHB) on job satisfaction was investigated. Finally, we explored how the effects of the WFB and the WHB on job satisfaction change according to worker characteristics (age, gender, parental status, and work ability). This study involved 318 workers who completed an online questionnaire. The importance of the nonworking domains was compared with a t -test. The effect of the WFB and the WHB on job satisfaction was investigated with multiple and moderated regression analyses. The results show that workers considered health as important as family in the WLB. The WHB explained more of the variance in job satisfaction than the WFB. Age, gender and parental status moderated the effect of the WFB on job satisfaction, and work ability moderated the effect of the WHB on job satisfaction. This study highlights the importance of the health domain in the WLB and stresses that it is crucial to consider the specificity of different groups of workers when considering the WLB.
1. Introduction
The term work–life balance (WLB) has gained increasing popularity in the public discourse [ 1 ]. It is a term that is commonly used in companies, especially large ones, and it is often said to be at the core of their corporate welfare, e.g., [ 2 , 3 , 4 ]. However, academic knowledge around the WLB concept is not as solid and extensive as the widespread use of the term would suggest [ 1 ]. Researchers have argued that WLB theoretical development has not kept pace with the popularity of the concept [ 5 , 6 ]. Among the many issues raised by recent critical reviews [ 1 , 7 , 8 , 9 ], the present study focuses on the limited consideration that has been given to the heterogeneity of the contemporary labor force in the WLB literature [ 8 ]. The extant research has largely assumed that the WLB is a concern mainly for working parents, where caring for dependent children is the relevant load in the life part of the WLB [ 1 ]. This became clear when we realized that the majority of the studies about the WLB actually only considered the family in the “life” part of the balance; that is, they considered the work–family balance (WFB) [ 6 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
Currently, in addition to the massive presence of women in the labor market, which has fostered the literature about work–family balance, there is a highly increasing rate of active elderly workers, workers with a long-standing health problem or disability (LSHPD), single workers, and childless couples [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. These workers have different needs and interests outside work. This situation places renewed importance on a key feature of the WLB: The importance that is attached to the many different life role changes from person to person [ 9 ]. Therefore, even if the family role remains central in nonworking life, it is important to recognize the value of other roles when conceptualizing and measuring the WLB [ 11 ]. The family may not be the most important part of the WLB in determining the positive outcomes of, for example, workers with chronic diseases for whom the management of health has great influence. From this perspective, Gragnano et al. [ 15 ] recently developed the concept and measure of the work–health balance (WHB), which is particularly relevant for elderly workers and workers with a LSHPD.
This study aims to contribute to the WLB research by comparing the relevance of other nonwork domains beyond family and considering the heterogeneity of the current labor force in studying the WLB. Specifically, we (a) investigate the perceived importance of other nonwork life domains beyond family, with a focus on health; (b) compare the influence of the WFB and the WHB on job satisfaction; and (c) examine how the effects of the WFB and the WHB on job satisfaction change according to different worker characteristics.
In subsequent sections of this article, we discuss the relationship between the WLB and the WFB, also considering different worker characteristics. We then introduce the concept of the WHB.
2. Theoretical Background and Hypotheses
2.1. specific nonwork life domains: family and health.
The field of study about the work–life balance has had difficulty in establishing a commonly agreed-upon definition of the WLB [ 16 ]. A plethora of different conceptualizations exist in the literature, and many researchers have tried to summarize them [ 9 , 10 , 16 ]. After a review of the conceptualizations of the WLB in the literature, Kalliath and Brough [ 16 ] proposed a definition of the WLB that we endorse. “Work–life balance is the individual perception that work and nonwork activities are compatible and promote growth in accordance with an individual’s current life priorities” (p.326). A recent review indicated that a better work–life balance fosters not only job satisfaction, job performance, and organizational commitment but also life and family satisfaction [ 10 ]. The work–life balance also reduces stress-related outcomes such as psychological distress, emotional exhaustion, anxiety, and depression [ 10 ].
Research on work and nonwork interactions dates back to the mid-twentieth century, e.g., [ 17 ], and the issue has gained increasing importance in the popular press since the 1990s [ 16 ]. Today, there exists an extensive and growing body of research about the work–life balance [ 18 ], and the topic is of even more concern than in the past considering the new flexible ways of managing work (e.g., agile working, smart working, activity-based working, and flexible working).
Researchers have highlighted that the field of research about the work–life balance is itself “unbalanced.” The majority of studies on the work–life balance have focused only on work and family roles, that is, on the work–family balance [ 6 , 9 , 10 , 11 ]. For example, Casper et al. [ 9 ] reviewed the conceptual definition of the balance in the academic literature and found that 66% of the definitions focused only on work and family. In their review, Chang et al. [ 7 ] found that the WLB was studied specifically, not in the form of the WFB, in only 9% and 26% of the quantitative and qualitative studies reviewed, respectively. As a result, the knowledge acquired over time about the predictors and consequences of the balance with work is based mainly on the work–family balance [ 1 , 10 ].
Different types of the work–family balance have been studied in the literature. A general classification distinguished four types of influence that can occur between work and family based on their direction and valence [ 19 ]. When the effect is negative from the family domain to the work domain, it is called the family-to-work conflict. When the effect is still negative but from the work domain to the family domain, it is called work-to-family conflict. When the effect is positive, it is called enrichment and can have the same two directions; therefore, there is family-to-work enrichment and work-to-family enrichment. The work–family balance has been extensively studied in its negative form, work–family conflict [ 19 ]. However, since the 2000s, the scientific community has begun to focus on its positive form, work–family enrichment [ 20 ].
Many researchers have called for a real expansion of the WLB concept, such that the second arm of the balance—life—is not confined to the family role [ 6 , 9 , 19 ]. The call for an expansion of the concept is not only theoretically grounded but also related to recent changes in the labor market. The identification of the WFB as an indicator of the WLB was relatively effective and useful in recent decades, when the greatest change in workplace demographics was the increase in the participation of women, and the management of family and work roles for working women and dual-earner couples, especially those with children, became a central issue within organizations. Currently, workplace demographics are more heterogeneous. In addition to the massive presence of woman in the labor market, we are also seeing an increase in the rate of active elderly workers, workers with an LSHPD, single workers, and childless couples [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. It is clear that an exclusive focus on family has become at least reductive when considering the WLB [ 1 , 21 ].
The majority of the studies that have investigated the work–nonwork balance without an exclusive focus on the family domain have considered nonwork to be unspecific, i.e., they have considered nonworking life in general, including nonfamily and family domains [ 19 ]. However, the consideration of the specific nonwork domains is essential to a full comprehension of the dynamics that influence the work–life balance in the heterogeneous working population, that is, the different, specific nonwork domains will have different levels of importance and different effects in the determination of the work–life balance among workers with diverse characteristics and needs outside work [ 11 ].
Based on the quality of life literature [ 22 ], the multiple identity perspective [ 23 ], and Super’s [ 24 ] life-space theory of career development, Keeney et al. [ 11 ] identified eight nonwork domains of relevance in the WLB: education, health, leisure, friendships, romantic relationships, family, household management, and community involvement. The importance that individuals give to the different domains varies from person to person [ 11 ]. Moreover, the relative importance of these life domains is likely to change over time within the same person because of changes in interests and life circumstances [ 24 ]. Thus, it is crucial to understand whether the other nonwork domains are as important as family and under which circumstances the priorities change. Among the domains that were detected by Keeney et al. [ 11 ], there was health. This is relevant because to our knowledge, for the first time in work–life balance literature, it has been recognized that health management can conflict with work activity.
As stated, the relevance of health to the work life derives from an increase in the rate of workers with an LSHPD and elderly workers, both with a higher incidence of health problems. In 2017, 27.8% of the European Union (EU) workers reported an LSHPD, and 19% of the employed persons in the EU were 55 years of age or older [ 25 , 26 ]. There is, however, another reason that makes the health domain relevant even for “healthy” workers. A paradigm shift has occurred in the planning and delivery of healthcare. People are now expected to actively manage their healthcare. Theorizations in the field of public health and in medicine have indicated that it is strategic for healthcare systems to have informed patients who are more directly responsible for their health and care management [ 27 ]. This has been paired with an increasing focus on health promotion that is based, partly but strongly, on good individual healthy behaviors [ 28 ]. Therefore, the workers, not just the sick ones, must take on a somewhat active role in the health domain of life, which may be more or less compatible with the working role.
In light of this literature and considering the life domains defined by Keeney et al. [ 11 ], we hypothesized that family is still central in the WLB of workers but that the health domain also has an equally important role. Therefore, if the workers were asked directly:
Workers will indicate that the family and health domains are more important than the other life domains in the WLB process .
2.2. Consequences of Work–Family Balance: Job Satisfaction
Many studies have analyzed individual consequences of the different types of the work–life balance, and several meta-analyses have summarized the literature about the correlates of work–family conflict [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 ] and work–family enrichment [ 20 ]. Work–family conflict, in both directions, has been consistently found to be associated with work-related, family-related, and domain-unspecific outcomes. Specifically, among the many outcomes that are associated with work–family conflict in a statistically significant manner, the ones that were more strongly associated were organizational citizenship behavior, work-related and general stress, burnout and exhaustion, and job, marital and life satisfaction [ 29 ]. Far fewer studies exist for work–family enrichment, but by comparing the two extant bodies of literature, it is possible to note that the effect sizes of work–family enrichment are comparable to those of work–family conflict [ 20 , 29 ]. For simplicity and because more studies are needed about the relationship between work–family enrichment and conflict [ 33 ], which goes beyond the objectives of this research, we considered only the conflict, in both directions, in our study.
Among the literature considering work-related outcomes, job satisfaction has been the most studied variable [ 29 ]. Job satisfaction represents the extent to which workers like or dislike their job [ 34 ]. Job satisfaction is a central variable in organizational behavior research. Spector [ 34 ] ascribed its importance to three main reasons. Job satisfaction is an indicator of well-being and psychological health, it is related to many behaviors of the worker that are positive for the organization, and finally, it is a very useful indicator of organizational problems when its level is low. In fact, job satisfaction is highly related to burn-out, self-esteem, depression, anxiety and, to a lower extent, perceived physical illness [ 35 ]. It is consistently correlated with job performance [ 36 ] and with four dispositional traits predictive of job performance: self-esteem, generalized self-efficacy, locus of control, and emotional stability [ 37 ]. Job satisfaction has also been found to be a significant predictor of turnover and turnover intention [ 38 , 39 ].
Job satisfaction is also related to the work–family balance. The meta-analysis conducted by Amstad et al. [ 29 ] reported that the correlation with job satisfaction was stronger for work-to-family conflict (weighted mean correlation = −0.26) than for family-to-work conflict (weighted mean correlation = −0.13). Theoretically, the work–family balance affects job satisfaction because an incompatibility between two personally relevant roles creates negative states and feelings. Following the principle that when something threatens something else personally relevant, the first is appraised negatively with negative emotion [ 40 ], and a role that interferes with the fulfilment of another personally relevant role is negatively evaluated. Specifically, a negative evaluation of an individual’s job is formed (i.e., low job satisfaction) depending on the extent to which the job threatens the fulfillment of the family role [ 41 ]. This explanation justifies why family-to-work conflict has been found to have a lower correlation with job satisfaction than work-to-family conflict. In fact, provided that both conflict directions may generate a strain in both domains, the family-to-work conflict will generate a low family satisfaction—instead of a low job satisfaction—because the family role interferes with the work role, and the negative evaluation will be toward the source of the interference [ 41 ]. This was supported by the meta-analysis conducted by Amstad et al. [ 29 ], who found that work-to-family conflict was more strongly correlated with work-related outcomes than family-related ones and that the opposite was true for family-to-work conflict. Based on these premises, we hypothesized that:
Work-to-family and family-to-work conflict will be significantly and negatively related to job satisfaction.
The relationship between work-to-family conflict and job satisfaction will be greater than the relationship between family-to-work conflict and job satisfaction.
2.3. Consequences of Work–Health Balance
The present study aimed to expand the knowledge about the nonwork life domain other than family, specifically the health domain. Despite the importance of the life domain of health, the literature has not offered many studies that consider health in the WLB process or measurement instruments that are specifically designed for the purpose [ 42 ]. Considering the literature about job retention and the quality of working life among workers with an LSHPD [ 43 , 44 ], Gragnano et al. [ 15 ] conceptualized the work–health balance (WHB) as a state in which the worker feels able to effectively balance health and work needs, arising from the perception of how much the characteristics of one’s work are a barrier to health needs and counterbalanced by the evaluation of the helpfulness of the working environment to meet health needs.
Health needs are understood here in a broad sense, covering not only the care needs of workers with chronic illnesses or conditions but all the needs that a worker considers necessary to adequately care for his or her health. From the definition, a measure of the WHB has been developed. The WHB questionnaire measures three distinct constructs: work–health incompatibility, health climate and external support [ 15 ]. The first construct measures how much work commitments hamper the desired management of health. The last two constructs measure the helpfulness of the working environment for health needs. The health climate detects the extent to which workers perceive that management is truly interested in their employees’ health, whereas external support identifies the perception of the level of help available for health problems in the workplace in the form of support from the supervisor and work flexibility.
Studies have shown that elderly workers and workers with an LSHPD have more difficulties in reaching a good WHB [ 45 , 46 ]. In addition, it has been shown that among workers who stop working for cardiovascular diseases, the process of returning to work is faster for those who have a good WHB [ 47 ]. With low levels of the WHB, the rates of presenteeism, emotional exhaustion, workaholism and general psychological distress (GHQ) increase [ 15 , 48 ]. In contrast, a good WHB is associated with greater work autonomy, job engagement, and job satisfaction [ 15 , 49 , 50 , 51 ].
In the WHB, a good balance generates job satisfaction because the work role is not a threat to the management of health. A low level of work-to-family conflict generates job satisfaction because the work role is not a threat to the family domain. Because the two domains at risk are different, the proportion of the job satisfaction variance that is explained by the WHB is expected to not overlap, to a great extent, with the proportion that is explained by the work-to-family conflict. Moreover, in the current working context, characterized by a great heterogeneity of the contemporary labor force with a substantial proportion of elderly workers and workers with an LSHPD, as well as with the increasing spread of a health care system that is based on the active and informed role of patients, we expect the WHB to be as important as work-to-family conflict in shaping attitudes toward job and job satisfaction. Therefore, we hypothesized that:
The WHB will have a significant positive effect on job satisfaction.
The effect size of the WHB on job satisfaction will be at least as large as that of work-to-family conflict.
2.4. The Heterogeneity of the Labor Force and WLB
As stated before, the present study focuses on the problem of the limited consideration that has been given in the WLB literature to the heterogeneity of the contemporary labor force [ 8 ]. The current labor force is characterized not only by a greater female presence but also by an increasing rate of elderly workers, workers with an LSHPD, single workers, and childless couples [ 12 , 13 , 14 ], all with different needs and with a different levels of importance that are given to their various nonworking roles [ 1 ].
This last consideration is particularly relevant in the context of the WLB because the balance is not absolute; rather, it depends on the importance that is given by the worker to the various roles. Therefore, when studying the effect of the WLB on outcomes by using concepts and measures such as work-to-family conflict or the WHB, which measure the balance between a specific nonwork role and work, it is theoretically appropriate to expect that the studied effect will vary based on the importance that is given by the worker to the nonwork role under consideration. In other words, the perception of an imbalance between a specific nonworking role and work will have a negative effect on the outcome to the extent that the nonworking role in question is important for the worker.
Despite the centrality of individual priorities in the definition of the WLB [ 9 , 10 , 16 ], surprisingly few studies have explored how individual priorities moderate the effect of the WLB on outcomes [ 6 , 29 , 52 ], which is a symptom of the limited consideration of diversity in the labor force by the WLB literature [ 1 , 8 ]. Individual differences have been considered as predictors of differences in the level of balance [ 10 , 53 ] instead of as moderators of the effects of the balance on the outcomes. Crooker et al. [ 21 ] developed a theoretical framework that extensively considered differences in individual value systems as moderators, but this study was focused on the genesis of the WLB instead of its consequences.
In the present study, we considered four variables (i.e., age, gender, parental status, and work ability) that, according to the literature, moderate the relationship between the WFB and job satisfaction or, alternatively, the relationship between the WHB and job satisfaction. The hypothesis is that individual conditions and characteristics that increase (or decrease) the importance that is given by the worker to the family or health domain will increase (or decrease) the effect that the work–family balance or the WHB has on job satisfaction.
Gender has been studied in the WLB literature as a possible predictor of different levels of the work–family balance. The hypothesis has been that, since family responsibilities usually pertain more to women, women have worse levels of the work–family balance, but these studies have not consistently supported this hypothesis [ 54 ]. However, research has still indicated that there are significant disparities between men and women pertaining to the work–family balance [ 55 ]. There have also been studies that have indicated that women do value family more than men, and the opposite has been shown to be true for work [ 56 , 57 ]. This is consistent with other studies that have indicated a stronger effect of the work–family balance on job satisfaction [ 58 , 59 ] and negative emotional responses [ 60 ] for women. Based on these premises, we hypothesized that:
The negative effect of work–family conflict (work-to-family and family-to work) on job satisfaction will be stronger for women than for men.
Similarly, there is evidence that parents experience more problems with the work–family balance than workers without children (for a meta-analysis, see [ 61 ]). This is often because family-related demands are higher for parents [ 62 ]. However, we also sustain that the importance that is given to the family domain is higher for workers with children than for those without. Thus, we hypothesized that:
The negative effect of work–family conflict (work-to-family and family-to work) on job satisfaction will be stronger for workers with children than for those without.
Socioemotional selectivity theory (SST) [ 63 ] sustains that individuals have an intrinsic perception of the time left in their life—the future time perspective—and based on that, they adjust their preferences and behavior. A shortened future time perspective promotes the pursuit of short-term emotion-related goals, such as positive emotional and psychological well-being, and it devaluates long-term goals, such as the development of skills or career advancements [ 63 ]. In the WLB literature, SST implies that elderly workers, who have a shorter future time perspective, should consider family relationships more important than work [ 64 ]. Therefore, a high level of work-to-family conflict will affect elderly workers and their evaluation of job satisfaction more than younger worker. In line with this, Treadway et al. [ 65 ] found that, in the presence of a high work-to-family conflict, workers with a more constrained future time perspective experienced a lower continuance commitment than employees with a less shallow future time perspective.
The negative effect of work–family conflict (work-to-family and family-to-work) on job satisfaction will be stronger for elderly workers than for younger workers.
Because increasing age is associated with higher morbidity, (multiple) chronic conditions, and higher use of health services [ 66 ], the importance of the health domain is expected to be higher among elderly workers than younger workers. Therefore, we hypothesized that:
The positive effect of the WHB on job satisfaction will be stronger for elderly workers than for younger workers.
Finally, work ability is expected to play a role in association with the WHB. Work ability represents the perceived ability to do one’s job effectively and to continue to do so in the near future when considering personal health problems and resources [ 66 ]. Thus, in the life of workers with a low work ability, the health domain generally has more importance than workers with a high work ability because health is a current problem. Considering this, we hypothesized that:
The positive effect of the WHB on job satisfaction will be stronger for workers with a low work ability than for those with a high work ability.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. sample and procedure.
The study involved workers of full age under an employment contract. Entrepreneurs and self-employed workers were excluded. We distributed the link to the online questionnaire with a brief description of the research through social networks (i.e., Facebook and LinkedIn), messaging applications, and email. To begin the assessment, the participants had to read and approve an informed consent form to freely decide whether to participate in the research. The informed consent provided informed about the aim of the study and the procedures to collect the data, and it ensured that there were no potential risks or costs involved. The research team assured the anonymity and confidentiality of the participants’ responses throughout the entire study process. The contact details of the researcher in charge were provided in the event of any further questions. The study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards set by the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Milano-Bicocca (Prot.160-2014). The number of subjects that started the questionnaire was 350. However, the dataset used in the analyses contained 318 responses after excluding 32 questionnaires because they were substantially incomplete; that is, the subjects opened the online page of the questionnaire but did not answer any questions. These values represent a completion rate of 91%. All participants lived in Italy; 90% lived in northern Italy. Overall, 37%, 28%, and 35% of the respondents were between 20 and 30, 31 and 44, and 45 and 60 years old, respectively. The proportion of men and women, as well as people with and without children, was balanced in the sample (56% women and 58% with children). Among the 134 workers with children, 49%, 43%, and 8% of the respondents had one, two, and three or more children, respectively. The workers with one or more children under the age of twelve were 51%. Most of the respondents had a partner (76%) and at least an upper secondary school diploma (93%). Most of the participants worked full-time (85%) with an open-ended contract (79%) as a white-collar worker (72%). Table 1 presents detailed descriptive statistics of the sample.
Descriptive statistics of the sample (N = 318).
3.2. Measures
The sociodemographic information described above was provided by the respondents at the beginning of the online questionnaire.
Based on the instrument developed by Keeney et al. [ 11 ] to evaluate the importance in the WLB attached to the different life domains (family, health, household management, friendship, training activities, favorite leisure activities, and community involvement), respondents were asked “How important is it in your life to reconcile work with …? ”. The question was asked, changing the final part, for all of the seven domains of life considered. The response scale was a 10-point scale from 1 (not at all important) to 10 (extremely important).
Two forms of the WLB were measured: the work–family balance and the work–health balance. The work–family balance was measured in the form of the work-to-family conflict (WFC—three items, α = 0.79) and family-to-work conflict (FWC—three items, α = 0.72) with the abbreviated version of the measure of work–family conflict [ 67 ]. Answers were given with a five-point Likert scale, from 1 (completely disagree) to 5 (completely agree). The work–health balance was measured with the Work–Health Balance Questionnaire [ 15 ], which was composed of three subscales: work–health incompatibility (WH—six items, α = 0.84), health climate (HC—five items, α = 0.92), and external support (ES—six items, α = 0.81). The total WHB score was calculated by subtracting WHI from the mean of HC and ES. Answers were given according to a five-point rating scale from 1 (completely disagree) to 5 (completely agree) for WHI and from 1 (never) to 5 (always) for HC and ES.
Work ability, the perceived ability to do one’s job effectively and to continue to do so in the near future when considering personal health problems and resources, was measured with the Work Ability Index (WAI) [ 68 ]. The index was calculated from seven factors (α = 0.79) for a total of 10 items with different rating scales.
Job satisfaction was measured with a single item that asked respondents to rate their overall satisfaction with their job on a 5-point scale from 1 (not at all satisfied) to 5 (fully satisfied). The reliability and validity of the single-item measure to assess job satisfaction has been established [ 69 ].
Harman’s single-factor test was adopted to check for a common method bias. The first factor explained 27% of the variance. Given that this fell below the threshold of 50%, the common method bias does not appear to have been a significant factor in this study. The results of the explorative factor analysis performed for the Harman single-factor test are available in the online Supplementary Materials of this article.
3.3. Data Analysis
All data analyses were performed by using R [ 70 ]. The different life domains were ordered according to the mean importance to the WLB that was attached to them by the respondents. Mean and standard deviations were provided for all the life domains. To test whether family and health domains were considered more important than the other life domains in the WLB (H1), the mean of the importance that was attached to health and family were compared to the mean of the importance that was attached to all the other life domains with a paired t-test. Even if no hypothesis was formulated specifically on this point, we explored whether the family and health domain were considered equally important. A paired t-test between the importance ascribed to family and to health was performed.
The hypotheses about the direction and effect size of work-to-family conflict, family-to-work conflict, and the WHB on job satisfaction (H2a,b and H3a,b) were tested with a multiple linear regression with job satisfaction as the dependent variable and work-to-family conflict, family-to-work conflict and the WHB as independent variables. To evaluate the relative importance of these predictors to the multiple regression model just described, we used the Lindeman, Merenda, and Gold’s metric (LMG) and reported the standardized β . The LMG expresses the squared semipartial correlation that was averaged across all possible ordering of the predictors. Since each order of predictors yields a different decomposition of the model sum of squares, the variance of the dependent variable that is explained by a predictor in a multiple regression varies according to the sequential order in which a predictor is entered into the model in relation to the other predictors. LMG averaged this value for all the possible orders of entry [ 71 ]. As a result, LMG considers both the predictor’s direct effect and its effect when combined with other predictors. Conversely, the standardized β represents only the incremental contribution of each predictor when combined with all remaining predictors [ 71 , 72 ].
This model, as well as the other following models, was controlled for age, marital status, and parental status. The control variables to be included were chosen with a backward model selection by the Akaike information criterion (AIC) from an initial model that included age, gender, education level, marital and parental status, job role, type of contract, and working hours. These preliminary analyses are available in the online Supplementary Material of this article.
Finally, the hypotheses about the moderation of the relation between the work–family balance and/or the WHB with job satisfaction (H4a–e) by individual characteristics (age, gender, parental status, and work ability) were tested with several models—one per moderator—with interaction effects. Continuous variables involved in the interaction were centered on the mean.
4.1. Perceived Importance of Family and Health Domain
The mean and standard deviation of the importance that is attached to the different life domains, ordered by their importance, are listed in Figure 1 .

Mean importance and standard deviation of the seven life domains.
The first paired t-test resulted in a significant difference in the mean of the importance that was attached to health and family (M = 9.27 and SD = 1.04) and those ascribed to the other life domains (M = 7.3 and SD = 1.32); t (317) = 25.7 and p < 0.001. This result supported H1a, that is, the health and family domains were considered to be more important than the other domains in the WLB.
Moreover, the second paired t-test resulted in a nonsignificant difference in the importance that is attached to health (M = 9.29 and SD = 1.18) and those attached to family (M = 9.25 and SD = 1.3); t (317) = 0.57 and p = 0.57. This exploratory analysis showed that health and family are life domains considered of equivalent importance in the WLB.
4.2. Consequences of Work–Family and Work–Health Balance on Job Satisfaction
Table 2 presents the result of the first model that tested the effects of work-to-family conflict, family-to-work conflict, and the WHB on job satisfaction (R 2 = 0.28, F (6/308) = 20.24, and p < 0.001).
Adjusted effects of work-to-family conflict, family-to-work conflict, and the work–health balance (WHB) on job satisfaction.
*** = p < 0.001; ** = p < 0.01; * = p < 0.05; 1 se = standard error.
The model resulted in a significant negative effect of work-to-family conflict and a nonsignificant effect of family-to-work conflict, thus partially supporting H2a. The LMG of work-to-family conflict on job satisfaction (LMG = 0.08) was eight times greater than that of family-to-work conflict (LMG = 0.01). Moreover, the former was statistically significant, while the other was not. These results fully supported H2b. Considering the effect of the WHB on job satisfaction, the model estimated a significant positive effect, supporting H3a. Moreover, the variance that was explained by the WHB (LMG = 0.16) was twice as much as the variance that was explained by work-to-family conflict (LMG = 0.08), supporting H3b.
4.3. Moderators of the Effects of Work–Family and Work–Health Balance
Table 3 reports models 1 and 2, which tested the moderating effect of gender and parental status, respectively.
Adjusted effects of work-to-family conflict, family-to-work conflict, and the WHB on job satisfaction.
*** = p < 0.001; ** = p < 0.01; * = p < 0.05; 1 In model 1, the moderator is gender (female); in model 2, the moderator is parental status (no children). Continuous variables in the interactions have been centered on the mean.
Model 1 (R 2 = 0.30, F (9/305) = 14.54, and p < 0.001) in Table 3 showed a significant negative interaction of gender with work-to-family conflict but no interaction with family-to-work conflict. The interaction indicates that the negative effect of work-to-family conflict on job satisfaction was stronger among women than among men. To facilitate the interpretation, the interaction effect is depicted in Figure 2 . This result partially supported H4a: The effect of the work–family balance, specifically of work-to-family conflict, on job satisfaction was stronger among women than among men.

Moderating effect of gender on the relationship between work-to-family conflict and job satisfaction.
Model 2 (R 2 = 0.31, F (8/306) = 17.46, and p < 0.001) in Table 3 again showed a significant interaction of work-to-family conflict with the moderator (i.e., parental support) but no interaction of the moderator with family-to-work conflict. The interaction indicates that the negative effect of work-to-family conflict on job satisfaction was stronger among workers with children than among those without. This interaction effect is depicted in Figure 3 . This result partially supported H4b: The effect of the work–family balance on job satisfaction, specifically of work-to-family conflict, is stronger among workers with children than among those without.

Moderating effect of parental status on the relationship between work-to-family conflict and job satisfaction.
Table 4 reports models 3 and 4, which tested the effects of two moderators—age and work ability, respectively. Model 3 (R 2 = 0.31, F (9/305) = 15.28, and p < 0.001) in Table 4 showed a significant interaction of age with work-to-family and family-to-work conflict but no interaction with the WHB.
*** = p < 0.001; ** = p < 0.01; * = p < 0.05; 1 In model 3, the moderator is age; in model 4, the moderator is work ability. Continuous variables in the interactions have been centered on the mean.
The interactions showed that the negative effect of work-to-family conflict on job satisfaction increased with age ( Figure 4 a), whereas family-to-work conflict appeared to have a positive effect for older workers ( Figure 4 b). These results again supported H4c only for work-to-family conflict, whereas they showed an unexpected positive effect of family-to-work conflict on job satisfaction among the elderly. In contrast, the results did not support H4d because the effect of the WHB on job satisfaction did not seem to increase with age.

( a ) Moderating effect of age on the relationship between work-to-family conflict and job satisfaction. ( b ) Moderating effect of age on the relationship between family-to-work conflict and job satisfaction.
Model 4 (R 2 = 0.33, F (8/306) = 18.18, and p < 0.001) in Table 4 showed a significant negative interaction between the WHB and work ability. The interaction showed that the positive effect of the WHB on job satisfaction decreased with the increase in work ability ( Figure 5 ). This result supported H4e: The positive effect of the WHB on job satisfaction increased with the decline in work ability.

Moderating effect of work ability on the relationship between the work–health balance and job satisfaction.
5. Discussion
This study aimed to verify the importance of different, specific nonwork domains in the work–life balance process, with a focus on family and health. We also investigated the impact of the work–family balance (in both directions) and the work–health balance on job satisfaction and how the heterogeneity of the current workforce modifies these relationships.
The results supported the first hypothesis. As hypothesized, when considering their work–life balance, the workers attached more importance to the health and family domains than to the other nonwork domains. A further analysis showed that the health and family domains were given similar importance. This result was the starting point of the entire study and justified the inclusion of the concept of the work–health balance. The workers rated family and health as 25% more important than the other nonwork life domain in their work–life balance. The fact that health was important as family is a relevant result, and it was found to be even more important when we analyzed the sample. Indeed, there were no apparent sample characteristics that made this sample more exposed to health issues than the general population. This fact suggests that researchers and companies should pay more attention to the health domain even for workers that are not affected by severe or chronic health conditions.
The second hypothesis concerned the effect of the work–family balance on job satisfaction. The work–family balance was supposed to affect job satisfaction, and work-to-family conflict was supposed to be more important than family-to-work conflict. The results supported this hypothesis and, consistent with other studies, the effect of family-to-work conflict on job satisfaction was smaller than that of work-to-family conflict and was statistically not significant [ 73 ]. This result can be explained in light of the appraisal theory [ 40 ]: If work threatens family life (work–life conflict), work will be negatively appraised; if family issues threaten work participation (family–work conflict), family, not the work, will be negatively appraised [ 41 ]. Consistent with a prior meta-analysis [ 29 ], these results support the “matching-hypothesis” (work-to-family conflict affects the work domain more, whereas family-to-work conflict affects the family domain more) as opposed to the “cross-domain hypothesis” (work-to-family conflict affects the family domain more, whereas family-to-work conflict affects the work domain more). Our study provides new evidence in this sense because the regression model was controlled for the work–health balance and because of the adoption of the LMG metric.
The third hypothesis investigated the effect of the WHB on job satisfaction and its importance relative to work–family conflict. As hypothesized, the WHB had a positive and statistically significant relationship with job satisfaction, and its importance was two times greater than that of work-to-family conflict. This result supports the usefulness of the specific instrument, the WHB questionnaire, and confirms the importance of filling the gap in the literature [ 42 ] by introducing the health domain into the concept of the work–life balance. Even if our results cannot be considered definitive in saying that the health domain is more important than the family domain in the genesis of job satisfaction, they clearly indicate that, when investigating or promoting work–life balance, considering the WHB is at least as important as considering the work–family balance. The common practice of considering the work–life balance as an issue that is related only to family is wrong and limits the possibility to explain work phenomena through the lens of the work–life balance.
The fourth hypothesis was related to the moderation of the effects of work–family conflict and the WHB by specific work characteristics (i.e., gender, parental status, age, and work ability) on job satisfaction. All three hypothesized moderators of the effect of work-to-family conflict on job satisfaction (i.e., gender, parental status, and age) were supported, whereas only one moderator of the family-to-work conflict effect (i.e., age) was sustained. Of the two hypothesized moderators (age and work ability) of the WHB effect on job satisfaction, only the interaction with work ability was supported.
In particular, the impact of work-to-family conflict on job satisfaction was greater for women (H4a), parent workers (H4b), and elderly workers (H4c). The reason for this moderation effect is likely due to the difference in salience of the family domain attached by the groups of workers. Women are likely to evaluate family as more central in their lives than men because of widespread cultural norms and gender-differentiated values [ 56 , 57 ]. Likewise, parents are likely to give more salience to family than people with no children because of cultural norms and, possibly, because of a “self-selection process” that brings people with a high salience of family to be more prone to parenthood than people with a low salience [ 62 , 74 ]. Given such result, it is possible, and should be tested in future studies, that being responsible for eldercare, beyond generally increasing the level of work-to-family conflict, also increases the impact of work-to-family conflict on job satisfaction. Finally, as implied by the socioemotional selectivity theory, elderly workers are likely to consider family relationships more important than younger workers because of a shorter future time perspective [ 64 ].
Given the theoretically coherent nonsignificant main effect of family-to-work conflict on job satisfaction, it was not surprising that the hypothesized moderators of its effects were not relevant. However, the moderation of the effect of family-to-work conflict on job satisfaction by age was significant and indicated that among older workers, a higher level of family-to-work conflict was related to higher job satisfaction. A further analyses showed that the effect of family-to-work conflict was nonsignificant among workers of 27 (the first quartile) and 38 years of age (the mean age), but this effect was statistically significant among workers of 49 years of age (the third quartile). The interpretation of this effect is hazardous with the data at hand. Further studies should investigate this effect while also considering the cross-sectional nature of our study. In fact, it is not possible to exclude that the found relationship was inverse. That is, older workers with higher job satisfaction perceived a higher family-to-work conflict because of a greater importance that is attached to the work domain than other elderly workers with lower job satisfaction.
Concerning the WHB, we hypothesized that its effect on job satisfaction was stronger among older workers (H4d) and workers with a lower WAI score (H4e). Since the interaction term was not significant in the case of age, H4d was not supported. Our results showed that a good WHB was associated with an equally high job satisfaction among all ages. We believe this is simply because, in our sample, the importance that was given to the health domain was not associated with age. This idea was supported by post hoc analyses that correlated the importance that was given by the workers to the health domain with their age, which resulted in a nonsignificant correlation ( r = −0.09, t = −1.62, and p = 0.11). We believe this result indicates that the health domain is crucial for both younger and older workers. There is the possibility that the WHB is a very important dimension at all ages—not only for elderly workers as originally intended [ 15 ]. In contrast, our results supported H4e. With the decline of the WAI, that is, with more health problems affecting job activity, the importance of the positive effect of the WHB on job satisfaction was increased. As proposed elsewhere [ 15 ], workers who are more vulnerable to health problems had a greater gain from their work situation with a good balance between health needs and work demands than healthy workers.
Overall, the results regarding the hypothesized moderators indicate that it is crucial to take into account the heterogeneity of the current workforce and to consider the specificity of different groups of workers when considering the WLB. From the outset, most definitions of the work–life balance have stressed the fact that it is not possible to identify an absolute optimal balance because it depends on the importance that the worker gives to the different domains of life [ 1 , 9 , 10 , 16 ]. Despite being theoretically clear, individual differences have been mainly overlooked in the WLB literature. Our study presents strong evidence that the issue must be considered, especially in light of the large presence of women, elderly individuals, people with an LSHPD, singles, and childless couples in the labor force [ 12 , 13 , 14 ].
The current study presents some limitations to consider when interpreting the results. First, the study design was cross-sectional. This limits our confidence in determining the cause and effect in the relationships between the considered variables. We based our considerations on a strong theoretical basis [ 10 , 29 ], but longitudinal studies are needed to replicate our findings.
Second, we adopted an online recruitment procedure that has the problem of a participant selection bias because of the self-selection of participants [ 75 ]. The online recruitment made our sample not representative of the entire working population, but this was beyond our intent. As explained by Landers and Behrend [ 76 ], when the aim is to test theoretically relevant hypotheses, as in our study, sample representativeness is less crucial than when a study aims to estimate the presence and the level of one or more variables in the workers’ population. Of course, our results must be replicated in other samples to increase their generalizability. By comparing our sample characteristics with data representative of the employees in north Italy [ 77 ] (data shown in the online Supplementary Material of this article), it is possible to note some differences in the proportions of job roles, type of occupations, and levels of education that are worth being mentioned. Specifically, like many studies in the WLB literature [ 7 ], in our sample, there was an over-representation of white-collar workers and an under-representation of blue-collar workers. There was an over-representation of clerical support workers and an under-representation of factory workers, skilled laborers, building workers, elementary occupations, and services and sale workers. Finally, the level of education of the sample was higher than in the general population of employees in north Italy. Given these specificities, it will be necessary to test whether the same results hold across samples with an appropriate representation of factory workers, skilled laborers, building workers, elementary occupations, and services and sale workers, as well as employees with a lower level of education.
Third, the measure of the importance that workers gave to the different life domains was based on the instrument of Keeney et al. [ 11 ], but the final instrument was created ad hoc for this study. Therefore, the measurement instrument may have biased the results regarding the importance of the different life domains. However, it should be considered that the questions that were posed to the participants were quite straightforward, and the values obtained for each domain were plausible and not extreme. Even if the instrument was not fine-tuned for exact comparisons, we believe it was appropriate for the aim of the study. The cited limitations warn against an unconditional generalization of the results of this study that, instead, have to be replicated with stronger research designs and other samples of workers.
6. Conclusions
The health issue has emerged in the organizational literature as a central topic. It no longer pertains to only small groups of workers with severe health problems. The changes in the labor force and of the patient’s role in the health system have made it impossible to consider the management of health as an exclusively nonworking activity. This study shows that workers are aware of the importance of the health domain for achieving a good work–life balance. Our results indicate health as a fundamental domain in the work–life balance dynamic that is as important as the family domain, if not more so. Researchers and practitioners should therefore consider the health domain in addition to the family domain when investigating the work–life balance.
By showing the differences in the effects of the work–family balance and the work–health balance on job satisfaction for different categories of workers, the present study demonstrates the importance of individual differences in the work–life balance process. That is, the balance between work and life is not absolute, but it is related to the importance that is given by the worker to the various domains. This relationship is of prominent importance in the current heterogeneous labor force.
Finally, our results provide evidence, to be replicated, that the importance of the work–health balance is not related to age, as previously believed; but only with the health condition.
Overall, this study is relevant for the work–life balance literature because, to the best of our knowledge, it is the first to consider the work–health balance. Moreover, it is one of the few studies that, through moderation analyses, investigates how the effect of the work–life balance on a relevant outcome changes according to workers’ characteristics.
Acknowledgments
We thank Martina Raimondi for her valuable assistance during the process of data collection and Zavagno D. for his help in proofreading the final changes made to the manuscript.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/17/3/907/s1 , Table S1: Factor Loadings of the EFA performed for the Harman’s single factor test, Table S2: Percentage of variance explained by the factors, Table S3: Comparison of the characteristics of the sample with those of the population of employees in north Italy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G. and M.M.; Methodology, A.G. and S.S.; Formal analysis, A.G.; Investigation, A.G. and M.M.; Data curation, A.G., M.M.; Writing—original draft preparation, A.G.; Writing—review and editing, S.S., M.M. and A.G.; Visualization, A.G. and S.S.; Supervision, M.M.; Project administration, M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This research received no external funding. The APC was funded by the “Fondo di Ateneo” grant, from the University of Milano-Bicocca to M.M.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Work-life balance -a systematic review
Vilakshan - XIMB Journal of Management
ISSN : 0973-1954
Article publication date: 15 December 2021
Issue publication date: 31 July 2023
This study aims to systematically review the existing literature and develop an understanding of work-life balance (WLB) and its relationship with other forms of work-related behavior and unearth research gaps to recommend future research possibilities and priorities.
Design/methodology/approach
The current study attempts to make a detailed survey of the research work done by the pioneers in the domain WLB and its related aspects. A total of 99 research work has been included in this systematic review. The research works have been classified based on the year of publication, geographical distribution, the methodology used and the sector. The various concepts and components that have made significant contributions, factors that influence WLB, importance and implications are discussed.
The paper points to the research gaps and scope for future research in the area of WLB.
Originality/value
The current study uncovered the research gaps regarding the systematic review and classifications based on demography, year of publication, the research method used and sector being studied.
- Work-life balance
- Flexibility
- Individual’s ability to balance work-life
- Support system
- WLB policy utilization
- Societal culture
S., T. and S.N., G. (2023), "Work-life balance -a systematic review", Vilakshan - XIMB Journal of Management , Vol. 20 No. 2, pp. 258-276. https://doi.org/10.1108/XJM-10-2020-0186
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Thilagavathy S. and Geetha S.N.
Published in Vilakshan – XIMB Journal of Management . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence maybe seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
In this technological era, work is becoming demanding with changing nature of work and working patterns (Thilagavathy and Geetha, 2020 ). The proactive, aggressive and demanding nature of business with the intention of reaching the top requires active involvement and comprehensive devotion from the employees, thereby compromising their work-life balance (WLB) (Turanlıgil and Farooq, 2019 ). Research concerning the work-life interface has exploded over the past five decades because of the changing trends in the nature of gender roles, families, work and careers (Powell et al. , 2019 ). Researchers in this domain has published many literature reviews with regard to WLB. It is argued that the study of WLB remains snowed under by a lack of conceptual clarity (Perrigino et al. , 2018 ). Thus, research and theory only partially view the employees’ work-life needs and experiences.
How WLB is conceptualized in the past?
What are the factors that significantly influenced WLB?
In which geographical areas were the WLB studies undertaken?
Which sectors remain unstudied or understudied with regard to WLB?
Methodology
We systematically conducted the literature review with the following five steps, as shown in Figure 1 . The first step was to review the abstracts from the database like EBSCO, Science Direct, Proquest and JSTOR. The articles from publishers like ELSEVIER, Emerald insight, Springer, Taylor and Francis and Sage were considered. The literature survey was conducted using the search terms WLB, balancing work and family responsibility and domains of work and life between the period 1990 to 2019. This search process led to the identification of 1,230 relevant papers. Inclusion criteria: The scholarly articles concerning WLB published in the English language in journals listed in Scopus, web of science or Australian business deans council (ABDC) were included in this review. Exclusion criteria: The scholarly articles concerning WLB published in languages other than English were not taken into consideration. Similarly, unpublished papers and articles published in journals not listed in Scopus, web of science or ABDC were excluded.
In the second step, we identified the duplicates and removed them. Thus, the total number of papers got reduced to 960. Following this, many papers relating to work-life spillover and work-life conflict were removed, resulting in further reduction of the papers to 416. Subsequently, in the third step, the papers were further filtered based on the language. The paper in the English language from journals listed in Scopus, web of science or ABDC were only considered. This search process resulted in the reduction of related papers to 93. The fourth step in the search process was further supplemented with the organic search for the related articles, leading to 99 papers illustrated in Appendix Table 1 . In the fifth step, an Excel sheet was created to review the paper under different headings and the results are as follows.
Literature review
Evolution and conceptualization of work-life balance.
WLB concern was raised earlier by the working mothers of the 1960s and 1970s in the UK. Later the issue was given due consideration by the US Government during the mid of 1980. During the 1990s WLB gained adequate recognition as the issue of human resource management in other parts of the world (Bird, 2006 ). The scholarly works concerning WLB have increased, mainly because of the increasing strength of the women workforce, technological innovations, cultural shifts in attitudes toward the relationship between the work and the family and the diversity of family structures (Greenhaus and Kossek, 2014 ). The research works on WLB include several theoretical work-family models. Though the research on WLB has expanded to a greater extend, there are considerable gaps in our knowledge concerning work-family issues (Powell et al. , 2019 ).
Moreover, in studies where WLB and related aspects are explored, researchers have used different operational definitions and measurements for the construct. Kalliath and Brough (2008) have defined WLB as “The individual’s perception that work and non-work activities are compatible and promote growth in accordance with an individual’s current life priorities.” WLB is “a self-defined, self-determined state of well being that a person can reach, or can set as a goal, that allows them to manage effectively multiple responsibilities at work, at home and in their community; it supports physical, emotional, family, and community health, and does so without grief, stress or negative impact” (Canadian Department of Labor, as cited in Waters and Bardoel, 2006 ).
Figure 2 depicts the flowchart of the framework for the literature survey. It clearly shows the factors that have been surveyed in this research article.
Individual factors
The individual factors of WLB include demographic variables, personal demands, family demands, family support and individual ability.
Work-life balance and demography.
WLB has significant variations with demographic variables (Waters and Bardoel, 2006 ). A significant difference was found between age (Powell et al. , 2019 ), gender (Thilagavathy and Geetha, 2020 ) and marital status (Powell et al. , 2019 ) regarding WLB. There is a significant rise in women’s participation in the workforce (Jenkins and Harvey, 2019 ). WLB issues are higher for dual-career couples (Crawford et al. , 2019 ).
Many studies were conducted on WLB with reference to sectors like information technology (IT), information technology enabled services, Banking, Teaching, Academics and Women Employment. A few WLB studies are conducted among services sector employees, hotel and catering services, nurses, doctors, middle-level managers and entrepreneurs. Only very scarce research has been found concerning police, defense, chief executive officers, researchers, lawyers, journalists and road transport.
Work-life balance and personal demands.
High work pressure and high family demand lead to poor physical, psychological and emotional well-being (Jensen and Knudsen, 2017 ), causing concern to employers as this leads to reduced productivity and increased absenteeism (Jackson and Fransman, 2018 ).
Work-life balance and family demands.
An employee spends most of the time commuting (Denstadli et al. , 2017 ) or meeting their work and family responsibilities. Dual career couple in the nuclear family finds it difficult to balance work and life without domestic help (Dumas and Perry-Smith, 2018 ; Srinivasan and Sulur Nachimuthu, 2021 ). Difficulty in a joint family is elderly care (Powell et al. , 2019 ). Thus, family demands negatively predict WLB (Haar et al. , 2019 ).
Work-life balance and family support.
Spouse support enables better WLB (Dumas and Perry-Smith, 2018 ). Family support positively impacted WLB, especially for dual-career couples, with dependent responsibilities (Groysberg and Abrahams, 2014 ).
Work-life balance and individual’s ability.
Though the organizations implement many WLB policies, employees still face the problems of WLB (Dave and Purohit, 2016 ). Employees achieve better well-being through individual coping strategies (Zheng et al. , 2016 ). Individual resources such as stress coping strategy, mindfulness emotional intelligence positively predicted WLB (Kiburz et al. , 2017 ). This indicates the imperative need to improve the individual’s ability to manage work and life.
Organizational factor
Organizational factors are those relating to organization design in terms of framing policies, rules and regulations for administering employees and dealing with their various activities regarding WLB ( Kar and Misra, 2013 ). In this review, organizational factors and their impact on the WLB of the employee have been dealt with in detail.
Work-life balance and organizational work-life policies.
The organization provides a variety of WLB policies (Jenkins and Harvey, 2019 ). Employee-friendly policies positively influenced WLB ( Berg et al. , 2003 ). Further, only a few IT industries provided Flexi timing, work from home and crèches facilities (Downes and Koekemoer, 2012 ). According to Galea et al. (2014) , industry-specific nuance exists.
Work-life balance and organizational demands.
Organizations expect employees to multi-task, causing role overload (Bacharach et al. , 1991 ). The increasing intensity of work and tight deadlines negatively influenced WLB (Allan et al. , 1999 ). The shorter time boundaries make it challenging to balance professional and family life (Jenkins and Harvey, 2019 ). Job demands negatively predicted WLB (Haar et al. , 2019 ).
Work-life balance and working hours.
Work does vacuum up a greater portion of the personal hours (Haar et al. , 2019 ). This causes some important aspects of their lives to be depleted, undernourished or ignored (Hughes et al. , 2018 ). Thus, employees find less time for “quality” family life (Jenkins and Harvey, 2019 ).
Work-life balance and productivity.
Organizational productivity is enhanced by the synergies of work-family practices and work-team design (Johari et al. , 2018 ). Enhanced WLB leads to increased employee productivity (Jackson and Fransman, 2018 ).
Work-life balance and burnout.
WLB is significantly influenced by work exhaustion (burnout). Negative psychological experience arising from job stress is defined as burnout (Ratlif, 1988). Increased work and non-work demands contribute to occupational burnout and, in turn, negatively predict WLB and employee well-being (Jones et al. , 2019 ).
Work-life balance and support system.
Support from Colleagues, supervisors and the head of institutions positively predicted WLB (Ehrhardt and Ragins, 2019 ; Yadav and Sharma, 2021 ). Family-supportive organization policy positively influenced WLB (Haar and Roche, 2010 ).
Work-life balance and employee perception.
The employee’s perception regarding their job, work environment, supervision and organization positively influenced WLB (Fontinha et al. , 2019 ). Employees’ awareness concerning the existence of WLB policies is necessary to appreciate it (Matthews et al. , 2014). The employee’s perception of the need for WLB policies differs with respect to their background (Kiburz et al. , 2017 ).
Work-life balance and job autonomy.
Job autonomy is expressed as the extent of freedom the employee has in their work and working pattern ( Bailey, 1993 ). According to Ahuja and Thatcher (2005) , autonomy and flexibility enable employees to balance competing demands of work-life. Job autonomy will enhance WLB (Johari et al. , 2018 ).
Work-life balance and job satisfaction.
Job satisfaction is the driving force for task accomplishment and employees’ intention to stay (Brough et al. , 2014 ). Employees’ positive perception concerning their job enhances job satisfaction (Singh et al. , 2020 ; Yadav and Sharma, 2021 ). WLB and job satisfaction are positively correlated (Jackson and Fransman, 2018 ).
Work-life balance and organizational commitment.
Alvesson (2002) describes organizational commitment as a mutual and fair social exchange. WLB positively predicted organizational commitment (Emre and De Spiegeleare, 2019 ). Work-life policies offered by an organization lead to increased loyalty and commitment (Callan, 2008 ).
Work-life balance and work-life balance policy utilization.
The utilization of WLB policies (Adame-Sánchez et al. , 2018 ) helps meet job and family demands. Despite the availability of WLB policies, their actual adoption is rather small (Waters and Bardoel, 2006 ) and often lag behind implementation (Adame-Sánchez et al. , 2018 ).
Work-life balance and organizational culture.
Employees perceive WLB policy utilization may badly reflect their performance appraisal and promotion (Bourdeau et al. , 2019 ). Hence, seldom use the WLB policies (Dave and Purohit, 2016 ). The perception of the organization culture as isolated, unfriendly and unaccommodating (Fontinha et al. , 2017 ); a lack of supervisor and manager support and a lack of communication and education about WLB strategies (Jenkins and Harvey, 2019 ). This leads to counterproductive work behavior and work-family backlash (Alexandra, 2014 ). As a result, growing evidence suggests a dark side to WLB policies, but these findings remain scattered and unorganized (Perrigino et al. , 2018 ). Organizational culture significantly affects WLB policy utilization (Callan, 2008 ; Dave and Purohit, 2016 ).
Societal factors
Societal changes that have taken place globally and locally have impacted the individual’s lifestyle. In this modern techno world, a diversified workforce resulting from demographic shifts and communication technology results in blurring of boundaries between work and personal life (Kalliath and Brough, 2008 ).
Work-life balance and societal demands.
Being members of society, mandates employee’s participation in social events. But in the current scenario, this is witnessing a downward trend. The employee often comes across issues of inability to meet the expectation of friends, relatives and society because of increased work pressure. Societal demands significantly predicted WLB (Mushfiqur et al. , 2018 ).
Work-life balance and societal culture.
Societal culture has a strong influence on WLB policy utilization and work and non-work self-efficacy. Specifically, collectivism, power distance and gendered norms had a strong and consistent impact on WLB Policy utilization by employees (Brown et al. , 2019 ). Women’s aspiration to achieve WLB is frequently frustrated by patriarchal norms deep-rooted in the culture (Mushfiqur et al. , 2018 ).
Work-life balance and societal support.
WLB was significantly predicted by support from neighbors, friends and community members (Mushfiqur et al. , 2018 ). Sometimes employees need friend’s viewpoints to get a new perspective on a problem or make a tough decision (Dhanya and Kinslin, 2016 ). Community support is an imperative indicator of WLB ( Phillips et al. , 2016 ).
Analyzes and results
Article distribution based on year of publication.
The WLB studies included for this review were between the periods of 1990–2019. Only a few studies were published in the initial period. A maximum of 44 papers was published during 2016–2019. Out of which, 17 studies were published during the year 2019. In the years 2018, 2017 and 2016 a total of 12, 7 and 8 studies were published, respectively. The details of the article distribution over the years illustrate a rising trend, as shown in Figure 3 .
Geographical distribution
Papers considered for this review were taken globally, including the research works from 26 countries. American and European countries contributed to a maximum of 60% of the publications regarding WLB research. Figure 4 illustrates the contribution of different countries toward the WLB research.
Basic classification
The review included 99 indexed research work contributed by more than 70 authors published in 69 journals. The contribution worth mentioning was from authors like Allen T.D, Biron M, Greenhaus J. H, Haar J.M, Jensen M.T, Kalliath T and Mc Carthy A. The basic categorization revealed that the geographical distribution considered for this review was from 26 different countries, as shown in Figure 4 . The research was conducted in (but not limited to) countries like Africa, Australia, Canada, China, India, Israel, The Netherlands, Norway, New Zealand, Pakistan, Singapore, Sweden, Turkey, the USA and the UK. American and European countries together contributed to the maximum of 60% of publications. Further, the categorization uncovered that 7 out of the 99 journals contributed to 30% of the WLB papers considered for this review, clearly illustrated in Table 1 .
Methodology-based categorization of papers
The basic information like research methods, sources of data, the proportion of papers using specific methodologies were considered for methodology-based categorization. The categorization revealed that 27 out of 99 papers reviewed were conceptual and the remaining 72 papers were empirical. The empirical papers used descriptive, exploratory, explanatory or experimental research designs. Further, categorization based on the data collection method revealed that 69 papers used the primary data collection method. Additionally, classification uncovered that 57 papers used the quantitative method, whereas 11 papers used the qualitative approach and four used the mixed method. The most prominent primary method used for data collection was the questionnaire method with 58 papers, while the remaining 20 papers used interview (10), case study (5), experimental studies (3), daily dairy (1) or panel discussion (1).
Sector-based categorization of papers
The sector-based categorization of papers revealed that 41.6% (30 papers) of research work was carried out in service sectors. This is followed by 40.2% (29 papers) research in the general public. While one paper was found in the manufacturing sector, the remaining nine papers focused on managers, women, the defense sector, police and the public sector, the details of which are showcased in Table 2 .
Research gap
Individual factor.
The literature survey results demonstrated that the impact of employee education and experience on their WLB had not been examined.
The literature survey has uncovered that the relationship between income and WLB has not been explored.
The influence of domestic help on WLB has not been investigated.
Much of the research work has been carried out in developed countries like the US, UK, European countries and Australia. In contrast, very scarce research works have been found in developing countries and underdeveloped countries.
Not much work has been done in WLB regarding service sectors like fire-fighters, transport services like drivers, railway employees, pilots, air hostesses, power supply department and unorganized sectors.
A review of the relevant literature uncovered that studies concerning the individual’s ability to balance work and life are limited. The individual’s ability, along with WLB policies, considerably improved WLB. Individual strategies are the important ones that need investigation rather than workplace practices.
Kibur z et al . (2017) addressed the ongoing need for experimental, intervention-based design in work-family research. There are so far very scares experimental studies conducted with regard to WLB.
Organizational factor.
A very few studies explored the impact of the WLB policies after the implementation.
Studies concerning the organizational culture, psychological climate and WLB policy utilizations require investigation.
Organizational climates influence on the various factors that predict WLB needs exploration.
Societal factor.
The impact of the societal factors on WLB is not explored much.
Similarly, the influence of societal culture (societal beliefs, societal norms and values systems) on WLB is not investigated.
Discussion and conclusion
The current research work aspires to conduct a systematic review to unearth the research gaps, and propose direction for future studies. For this purpose, literature with regard to WLB was systematically surveyed from 1990 to 2019. This led to identifying 99 scientific research papers from index journals listed in Scopus, the web of science or the ABDC list. Only papers in the English language were considered. The review section elaborated on the evolution and conceptualization of WLB. Moreover, the literature review discussed in detail the relationship between WLB and other related variables. Further, the research works were classified based on the fundamental information revealed that a maximum of 44 papers was published during the year 2016–2019. The geographical distribution revealed that a maximum of research publications concerning WLB was from American and European countries. Further, the basic classification revealed that 7 out of the 69 journals contributed to 30% of the WLB papers considered for this review. The methodology-based classification unearthed the fact that 73% of the papers were empirical studies. Additionally, the categorization uncovered that 79% ( n = 57) of papers used quantitative methods dominated by survey method of data collection. Sector-based categorization made known the fact that a maximum of 41.6% of research work was carried out in the service sector. The research gaps were uncovered based on the systematic literature review and classifications and proposed future research directions.
Limitations
We acknowledge that there is a possibility of missing out a few papers unintentionally, which may not be included in this review. Further, papers in the English language were only considered. Thus, the papers in other languages were not included in this systematic review which is one of the limitations of this research work.

Implications
The discussion reveals the importance and essentiality of the individual’s ability to balance work and life. Consequently, the researchers have proposed future research directions exploring the relationship between the variables. WLB is an important area of research; thus, the proposed research directions are of importance to academicians. The review’s finding demonstrates that there are very scarce studies on the individual’s ability to balance work and life. This leaves a lot of scopes for researchers to do continuous investigation in this area. Hence, it is essential to conduct more research on developing individuals’ ability to balance work and life. There are a few experimental studies conducted so far in WLB. Future experimental studies can be undertaken to enhance the individual’s ability to balance work and life.
Flow chart of the steps in systematic review process
Framework for the literature review
Distribution of papers based on year of publication
Geographical distribution of papers across countries
Journals details
Table 1 List of papers included in the review
Adame-Sánchez , C. , Caplliure , E.M. and Miquel-Romero , M.J. ( 2018 ), “ Paving the way for competition: drivers for work-life balance policy implementation ”, Review of Managerial Science , Vol. 12 No. 2 , pp. 519 - 533 , doi: 10.1007/s11846-017-0271-y .
Ahuja , M. and Thatcher , J. ( 2005 ), “ Moving beyond intentions and towards the theory of trying: effects of work environment and gender on post-adoption information technology use ”, MIS Quarterly , Vol. 29 No. 3 , pp. 427 - 459 .
Allan , C. , O'Donnell , M. and Peetz , D. ( 1999 ), “ More tasks, less secure, working harder: three dimensions of labour utilization ”, Journal of Industrial Relations , Vol. 41 No. 4 , pp. 519 - 535 , doi: 10.1177/002218569904100403 .
Alvesson ( 2002 ), Understanding Organizational Culture , Sage Publications , London . 10.4135/9781446280072
Bacharach , S.B. , Bamberger , R. and Conely , S. ( 1991 ), “ Work-home conflict among nurses and engineers: mediating the impact of stress on burnout and satisfaction at work ”, Journal of Organizational Behavior , Vol. 12 No. 1 , pp. 39 - 63 , doi: 10.1002/job.4030120104 .
Bailey , T.R. ( 1993 ), “ Discretionary effort and the organization of work: employee participation and work reform since Hawthorne ”, Teachers College and Conservation of Human Resources , Columbia University .
Bardoel , E.A. ( 2006 ), “ Work-life balance and human resource development ”, Holland , P. and De Cieri , H. (Eds), Contemporary Issues in Human Resource Development: An Australian Perspective , Pearson Education , Frenchs Forest, NSW , pp. 237 - 259 .
Berg , P. , Kalleberg , A.L. and Appelbaum , E. ( 2003 ), “ Balancing work and family: the role of high - commitment environments ”, Industrial Relations , Vol. 42 No. 2 , pp. 168 - 188 , doi: 10.1111/1468-232X.00286 .
Bird , J. ( 2006 ), “ Work-life balance: doing it right and avoiding the pitfalls ”, Employment Relations Today , Vol. 33 No. 3 , pp. 21 - 30 , doi: 10.1002/ert.20114 .
Bourdeau , S. , Ollier-Malaterre , A. and Houlfort , N. ( 2019 ), “ Not all work-life policies are created equal: career consequences of using enabling versus enclosing work-life policies ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 172 - 193 , doi: 10.5465/amr.2016.0429 .
Brough , P. , Timm , C. , Driscoll , M.P.O. , Kalliath , T. , Siu , O.L. , Sit , C. and Lo , D. ( 2014 ), “ Work-life balance: a longitudinal evaluation of a new measure across Australia and New Zealand workers ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 25 No. 19 , pp. 2724 - 2744 , doi: 10.1080/09585192.2014.899262 .
Callan , S.J. ( 2008 ), “ Cultural revitalization: the importance of acknowledging the values of an organization's ‘golden era’ when promoting work-life balance ”, Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal , Vol. 3 No. 1 , pp. 78 - 97 , doi: 10.1108/17465640810870409 .
Crawford , W.S. , Thompson , M.J. and Ashforth , B.E. ( 2019 ), “ Work-life events theory: making sense of shock events in dual-earner couples ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 194 - 212 , doi: 10.5465/amr.2016.0432 .
Dave , J. and Purohit , H. ( 2016 ), “ Work-life balance and perception: a conceptual framework ”, The Clarion- International Multidisciplinary Journal , Vol. 5 No. 1 , pp. 98 - 104 .
Denstadli , J.M. , Julsrud , T.E. and Christiansen , P. ( 2017 ), “ Urban commuting – a threat to the work-family balance? ”, Journal of Transport Geography , Vol. 61 , pp. 87 - 94 , doi: 10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2017.04.011 .
Downes , C. and Koekemoer , E. ( 2012 ), “ Work-life balance policies: the use of flexitime ”, Journal of Psychology in Africa , Vol. 22 No. 2 , pp. 201 - 208 , doi: 10.1080/14330237.2012.10820518 .
Dumas , T.L. and Perry-Smith , J.E. ( 2018 ), “ The paradox of family structure and plans after work: why single childless employees may be the least absorbed at work ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 61 No. 4 , pp. 1231 - 1252 , doi: 10.5465/amj.2016.0086 .
Ehrhardt , K. and Ragins , B.R. ( 2019 ), “ Relational attachment at work: a complimentary fit perspective on the role of relationships in organizational life ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 62 No. 1 , pp. 248 - 282 , doi: 10.5465/amj.2016.0245 .
Emre , O. and De Spiegeleare , S. ( 2019 ), “ The role of work-life balance and autonomy in the relationship between commuting, employee commitment, and well-being ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 32 No. 11 , pp. 1 - 25 , doi: 10.1080/09585192.2019.1583270 .
Fontinha , R. , Easton , S. and Van Laar , D. ( 2017 ), “ Overtime and quality of working life in academics and non-academics: the role of perceived work-life balance ”, International Journal of Stress Management , ( in Press ).
Fontinha , R. , Easton , S. and Van Laar , D. ( 2019 ), “ Overtime and quality of working life in academics and non-academics: the role of perceived work-life balance ”, International Journal of Stress Management , Vol. 26 No. 2 , pp. 173 , doi: 10.1037/str0000067 .
Galea , C. , Houkes , I. and Rijk , A.D. ( 2014 ), “ An insider’s point of view: how a system of flexible working hours helps employees to strike a proper balance between work and personal life ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 25 No. 8 , pp. 1090 - 1111 , doi: 10.1080/09585192.2013.816862 .
Greenhaus , J.H. and Kossek , E.E. ( 2014 ), “ The contemporary career: a work–home perspective ”, Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior , Vol. 1 No. 1 , pp. 361 - 388 , doi: 10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091324 .
Groysberg , B. and Abrahams , R. ( 2014 ), “ Manage your work, manage your life ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 92 No. 3 , pp. 58 - 66 , available at: https://hbr.org/2014/03/manage-your-work-manage-your-life
Haar , J.M. and Roche , M. ( 2010 ), “ Family-supportive organization perceptions and employee outcomes: the mediating effects of life satisfaction ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 21 No. 7 , pp. 999 - 1014 , doi: 10.1080/09585191003783462 .
Haar , J.M. , Sune , A. , Russo , M. and Ollier-Malaterre , A. ( 2019 ), “ A cross-national study on the antecedents of work-life balance from the fit and balance perspective ”, Social Indicators Research , Vol. 142 No. 1 , pp. 261 - 282 , doi: 10.1007/s11205-018-1875-6 .
Hughes , R. , Kinder , A. and Cooper , C.L. ( 2018 ), “ Work-life balance ”, The Wellbeing Workout , pp. 249 - 253 , doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-92552-3_42 .
Jackson , L.T. and Fransman , E.I. ( 2018 ), “ Flexi work, financial well-being, work-life balance and their effects on subjective experiences of productivity and job satisfaction of females in an institution of higher learning ”, South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences , Vol. 21 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 13 , doi: 10.4102/sajems.v21i1.1487 .
Jenkins , K. and Harvey , S.B. ( 2019 ), “ Australian experiences ”, Mental Health in the Workplace , pp. 49 - 66 . Springer , Cham .
Jensen , M.T. and Knudsen , K. ( 2017 ), “ A two-wave cross-lagged study of business travel, work-family conflict, emotional exhaustion, and psychological health complaints ”, European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology , Vol. 26 No. 1 , pp. 30 - 41 , doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2016.1197206 .
Johari , J. , Yean Tan , F. and TjikZulkarnain , Z.I. ( 2018 ), “ Autonomy, workload, work-life balance, and job performance among teachers ”, International Journal of Educational Management , Vol. 32 No. 1 , pp. 107 - 120 , doi: 10.1108/IJEM-10-2016-0226 .
Jones , R. , Cleveland , M. and Uther , M. ( 2019 ), “ State and trait neural correlates of the balance between work-non work roles ”, Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging , Vol. 287 , pp. 19 - 30 , doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2019.03.009 .
Kalliath , T. and Brough , P. ( 2008 ), “ Work-life balance: a review of the meaning of the balance construct ”, Journal of Management & Organization , Vol. 14 No. 3 , pp. 323 - 327 , doi: 10.1017/S1833367200003308 .
Kar , S. and Misra , K.C. ( 2013 ), “ Nexus between work life balance practices and employee retention-the mediating effect of a supportive culture ”, Asian Social Science , Vol. 9 No. 11 , p. 63 , doi: 10.1016/j.soscij.2019.03.008 , doi: 10.5539/ass.v9n11p63 .
Kiburz , K.M. , Allen , T.D. and French , K.A. ( 2017 ), “ Work-family conflict and mindfulness: investigating the effectiveness of a brief training intervention ”, Journal of Organizational Behavior , Vol. 38 No. 7 , pp. 1016 - 1037 , doi: 10.1002/job.2181 .
Mushfiqur , R. , Mordi , C. , Oruh , E.S. , Nwagbara , U. , Mordi , T. and Turner , I.M. ( 2018 ), “ The impacts of work-life balance (WLB) challenges on social sustainability: the experience of nigerian female medical doctors ”, Employee Relations , Vol. 40 No. 5 , pp. 868 - 888 , doi: 10.1108/ER-06-2017-0131 .
Perrigino , M.B. , Dunford , B.B. and Wilson , K.S. ( 2018 ), “ Work-family backlash: the ‘dark side’ of work-life balance (WLB) policies ”, Academy of Management Annals , Vol. 12 No. 2 , pp. 600 - 630 , doi: 10.5465/annals.2016.0077 .
Phillips , J. , Hustedde , C. , Bjorkman , S. , Prasad , R. , Sola , O. , Wendling , A. and Paladine , H. ( 2016 ), “ Rural women family physicians: strategies for successful work-life balance ”, The Annals of Family Medicine , Vol. 14 No. 3 , pp. 244 - 251 .
Powell , G.N. , Greenhaus , J.H. , Allen , T.D. and Johnson , R.E. ( 2019 ), “ Introduction to special topic forum: advancing and expanding work-life theory from multiple perspectives ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 54 - 71 , doi: 10.5465/amr.2018.0310 .
Ratliff , N. ( 1988 ), “ Stress and burnout in the helping professions ”, Social Casework , Vol. 69 No. 1 , pp. 147 - 154 .
Singh , S. , Singh , S.K. and Srivastava , S. ( 2020 ), “ Relational exploration of the effect of the work-related scheme on job satisfaction ”, Vilakshan – XIMB Journal of Management , Vol. 17 Nos 1/2 , pp. 111 - 128 , doi: 10.1108/XJM-07-2020-0019 .
Srinivasan , T. and Sulur Nachimuthu , G. ( 2021 ), “ COVID-19 impact on employee flourishing: parental stress as mediator ”, Psychological Trauma: Theory, Research, Practice, and Policy. Advance Online Publication , doi: 10.1037/tra0001037 .
Thilagavathy , S. and Geetha , S.N. ( 2020 ), “ A morphological analyses of the literature on employee work-life balance ”, Current Psychology , pp. 1 - 26 , doi: 10.1007/s12144-020-00968-x .
Turanlıgil , F.G. and Farooq , M. ( 2019 ), “ Work-Life balance in tourism industry ”, in Contemporary Human Resources Management in the Tourism Industry , pp. 237 - 274 , IGI Global .
Waters , M.A. and Bardoel , E.A. ( 2006 ), “ Work-family policies in the context of higher education: useful or symbolic? ”, Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 67 - 82 , doi: 10.1177/1038411106061510 .
Yadav , V. and Sharma , H. ( 2021 ), “ Family-friendly policies, supervisor support, and job satisfaction: mediating effect of work-family conflict ”, Vilakshan - XIMB Journal of Management , doi: 10.1108/XJM-02-2021-0050 .
Zheng , C. , Kashi , K. , Fan , D. , Molineux , J. and Ee , M.S. ( 2016 ), “ Impact of individual coping strategies and organizational work-life balance programmes on australian employee well-being ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 27 No. 5 , pp. 501 - 526 , doi: 10.1080/09585192.2015.1020447 .
Further reading
Allen , T.D. ( 2012 ), “ The work and family interface ”, in Kozlowski , S.W.J. (Ed.), The Oxford Handbook of Organizational Psychology , Vol. 2 , Oxford University Press , New York, NY , pp. 1163 - 1198 .
Bell , A.S. , Rajendran , D. and Theiler , S. ( 2012 ), “ Job stress, wellbeing, work-life balance and work-life conflict among Australian academics ”, Electronic Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 8 No. 1 , pp. 25 - 37 .
Biron , M. ( 2013 ), “ Effective and ineffective support: how different sources of support buffer the short–and long–term effects of a working day ”, European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology , Vol. 22 No. 2 , pp. 150 - 164 , doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2011.640772 .
Carlson , D.S. and Kacmar , K.M. ( 2000 ), “ Work-family conflict in the organization: do life role values make a difference? ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 26 No. 5 , pp. 1031 - 1054 , doi: 10.1177/014920630002600502 .
Clark , S.C. ( 2000 ), “ Work/family border theory: a new theory of work/family balance ”, Human Relations , Vol. 53 No. 6 , pp. 747 - 770 , doi: 10.1177/0018726700536001 .
Daipuria , P. and Kakar , D. ( 2013 ), “ Work-Life balance for working parents: perspectives and strategies ”, Journal of Strategic Human Resource Management , Vol. 2 No. 1 , pp. 45 - 52 .
Gregory , A. and Milner , S. ( 2009 ), “ Editorial: work-life balance: a matter of choice? ”, Gender, Work & Organization , Vol. 16 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 13 , doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0432.2008.00429.x .
Hirschi , A. , Shockley , K.M. and Zacher , H. ( 2019 ), “ Achieving work-family balance: an action regulation model ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 150 - 171 , doi: 10.5465/amr.2016.0409 .
Adame-Sánchez , C. , Caplliure , E.M. and Miquel-Romero , M.J. ( 2018 ), “ Paving the way for coopetition: drivers for work–life balance policy implementation ”, Review of Managerial Science , Vol. 12 No. 2 , pp. 519 - 533 , doi: 10.1007/s11846-017-0271-y .
Adame , C. , Caplliure , E.M. and Miquel , M.J. ( 2016 ), “ Work–life balance and firms: a matter of women? ”, Journal of Business Research , Vol. 69 No. 4 , pp. 1379 - 1383 , doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2015.10.111 .
Adame-Sánchez , C. , González-Cruz , T.F. and Martínez-Fuentes , C. ( 2016 ), “ Do firms implement work–life balance policies to benefit their workers or themselves? ”, Journal of Business Research , Vol. 69 No. 11 , pp. 5519 - 5523 , doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.164 .
Ahuja , M. and Thatcher , J. ( 2005 ), “ Moving beyond intentions and towards the theory of trying: effects of work environment and gender on post-adoption information technology use ”, MIS Quarterly , Vol. 29 , pp. 427 - 459 .
Alam , M. , Ezzedeen , S.R. and Latham , S.D. ( 2018 ), “ Managing work-generated emotions at home: an exploration of the ‘bright side’ of emotion regulation ”, Human Resource Management Review , Vol. 29 No. 4 , doi: 10.1016/j.hrmr.2018.12.002 .
Alexandra , B.T. ( 2014 ), “ Fairness perceptions of work−life balance initiatives: effects on counterproductive work behaviour ”, British Journal of Management , Vol. 25 , pp. 772 - 789 .
Allan , C. , O'Donnell . M. and Peetz , D. ( 1999 ), “ More tasks, less secure, working harder: three dimensions of labour utilization ”, Journal of Industrial Relations , Vol. 41 No. 4 , pp. 519 - 535 .
Allen , T.D. ( 2001 ), “ Family-Supportive work environments: the role of organisational perceptions ”, Journal of Vocational Behavior , Vol. 58 No. 3 , pp. 414 - 435 .
Antonoff , M.B. and Brown , L.M. ( 2015 ), “ Work–life balance: the female cardiothoracic surgeons perspective ”, The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery , Vol. 150 No. 6 , pp. 1416 - 1421 , doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2015.09.057 .
Barber , L.K. , Conlin , A.L. and Santuzzi , A.M. ( 2019 ), “ Workplace telepressure and work life balance outcomes: the role of work recovery experiences ”, Stress and Health , Vol. 35 No. 3 , doi: 10.1002/smi.2864 .
Beckman , C.M. and Stanko , T.L. ( 2019 ), “ It takes three: relational boundary work, resilience, and commitment among navy couples ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 63 No. 2 , doi: 10.5465/amj.2017.0653 .
Bell , A.S. , Rajendran , D. and Theiler , S. ( 2012 ), “ Job stress, wellbeing, work-life balance and work-life conflict among Australian academics ”, Electronic Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 8 , pp. 25 - 37 .
Bird , J. ( 2006 ), “ Work life balance: doing it right and avoiding the pitfalls ”, Employment Relations Today , Vol. 33 No. 3 , pp. 21 - 30 .
Boiarintseva , G. and Richardson , J. ( 2019 ), “ Work-life balance and male lawyers: a socially constructed and dynamic process ”, Personnel Review , Vol. 48 No. 4 , pp. 866 - 879 , doi: 10.1108/PR-02-2017-0038 .
Brescoll , V.L. , Glass , J. and Sedlovskaya , A. ( 2013 ), “ Ask and ye shall receive? The dynamics of employer‐provided flexible work options and the need for public policy ”, Journal of Social Issues , Vol. 69 No. 2 , pp. 367 - 388 , doi: 10.1111/josi.12019 .
Brough , P. , Timm , C. , Driscoll , M.P.O. , Kalliath , T. , Siu , O.L. , Sit , C. and Lo , D. ( 2014 ), “ Work-life balance: a longitudinal evaluation of a new measure across Australia and New Zealand workers ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 25 No. 19 , pp. 2724 - 2744 .
Brown , H. , Kim , J.S. and Faerman , S.R. ( 2019 ), “ The influence of societal and organizational culture on the use of work-life balance programs: a comparative analysis of the United States and the Republic of Korea ”, The Social Science Journal , doi: 10.1016/j.soscij.2019.03.008 .
Buffardi , L.C. , Smith , J.S. , O’Brien , A.S. and Erdwins , C.J. ( 1999 ), “ The impact of dependent-care responsibility and gender on work attitudes ”, Journal of Occupational Health Psychology , Vol. 4 No. 4 , pp. 356 - 367 .
Callan , S.J. ( 2008 ), “ Cultural revitalisation: the importance of acknowledging the values of an organization’s ‘golden era’ when promoting work-life balance ”, Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal , Vol. 3 No. 1 , pp. 78 - 97 .
Cannizzo , F. , Mauri , C. and Osbaldiston , N. ( 2019 ), “ Moral barriers between work/life balance policy and practice in academia ”, Journal of Cultural Economy , Vol. 12 No. 4 , pp. 1 - 14 , doi: 10.1080/17530350.2019.1605400 .
Chernyak-Hai , L. and Tziner , A. ( 2016 ), “ The ‘I believe’ and the ‘I invest’ of work-family balance: the indirect influences of personal values and work engagement via perceived organizational climate and workplace burnout ”, Revista de Psicología Del Trabajo y de Las Organizaciones , Vol. 32 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 10 , doi: 10.1016/j.rpto.2015.11.004 .
Cho , E. and Allen , T.D. ( 2019 ), “ The transnational family: a typology and implications for work-family balance ”, Human Resource Management Review , Vol. 29 No. 1 , pp. 76 - 86 .
Clark , S.C. ( 2000 ), “ Work/family border theory: a new theory of work/family balance ”, Human Relations , Vol. 53 No. 6 , pp. 747 - 770 .
Crawford , W.S. , Thompson , M.J. and Ashforth , B.E. ( 2019 ), “ Work-life events theory: making sense of shock events in dual-earner couples ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 194 - 212 .
Daipuria , P. and Kakar , D. ( 2013 ), “ Work-Life balance for working parents: perspectives and strategies ”, Journal of Strategic Human Resource Management , Vol. 2 , pp. 45 - 52 .
Dave , J. and Purohit , H. ( 2016 ), “ Work life balance and perception: a conceptual framework ”, The Clarion- International Multidisciplinary Journal , Vol. 5 No. 1 , pp. 98 - 104 .
Dhanya , J.S.1. and Kinslin , D. ( 2016 ), “ A study on work life balance of teachers in engineering colleges in Kerala ”, Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Sciences , Vol. 9 No. 4 , pp. 2098 - 2104 .
Divine , L.M. , Perez , M.J. , Binder , P.S. , Kuroki , L.M. , Lange , S.S. , Palisoul , M. and Hagemann , A.R. ( 2017 ), “ Improving work-life balance: a pilot program of workplace yoga for physician wellness ”, Gynecologic Oncology , Vol. 145 , p. 170 , doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2017.03.389 .
Downes , C. and Koekemoer , E. ( 2012 ), “ Work-life balance policies: the use of flexitime ”, Journal of Psychology in Africa , Vol. 22 No. 2 , pp. 201 - 208 .
Eagle , B.W. , Miles , E.W. and Icenogle , M.L. ( 1997 ), “ Inter-role conflicts and the permeability of work and family domains: are there gender differences? ”, Journal of Vocational Behavior , Vol. 50 No. 2 , pp. 168 - 184 .
Ehrhardt , K. and Ragins , B.R. ( 2019 ), “ Relational attachment at work: a complementary fit perspective on the role of relationships in organizational life ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 62 No. 1 , pp. 248 - 282 , doi: 10.5465/amj.2016.0245 .
Emre , O. and De Spiegeleare , S. ( 2019 ), “ The role of work–life balance and autonomy in the relationship between commuting, employee commitment and well-being ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 32 No. 11 , pp. 1 - 25 , doi: 10.1080/09585192.2019.1583270 .
Feldman , D.C. ( 2002 ), “ Managers' propensity to work longer hours: a multilevel analysis ”, Human Resource Management Review , Vol. 12 No. 3 , pp. 339 - 357 , doi: 10.1016/S1053-4822(02)00064-5 .
Forsyth , S. and Debruyne , P.A. ( 2007 ), “ The organisational pay-offs for perceived work-life balance support ”, Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources , Vol. 45 No. 1 , pp. 113 - 123 , doi: 10.1177/1038411107073610 .
Galea , C. , Houkes , I. and Rijk , A.D. ( 2014 ), “ An insider’s point of view: how a system of flexible working hours helps employees to strike a proper balance between work and personal life ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 25 No. 8 , pp. 1090 - 1111 .
Greenhaus , J.H. , Collins , K.M. and Shaw , J.D. ( 2003 ), “ The relation between work–family balance and quality of life ”, Journal of Vocational Behavior , Vol. 63 No. 3 , pp. 510 - 531 .
Gregory , A. and Milner , S. ( 2009 ), “ Editorial: work–life balance: a matter of choice? ”, Gender, Work & Organization , Vol. 16 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 13 .
Groysberg , B. and Abrahams , R. ( 2014 ), “ Manage your work, manage your life ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 92 No. 3 , pp. 58 - 66 .
Gumani , M.A. , Fourie , M.E. and Blanch , M.J.T. ( 2013 ), “ Inner strategies of coping with operational work amongst SAPS officers ”, SA Journal of Industrial Psychology , Vol. 39 No. 2 , pp. 1151 - 1161 , doi: 10.4102/sajip. v39i2.1151 .
Haar , J. and Roche , M. ( 2010 ), “ Family-Supportive organization perceptions and employee outcomes: the mediating effects of life satisfaction ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 21 No. 7 , pp. 999 - 1014 .
Haar , J.M. , Sune , A. , Russo , M. and Ollier-Malaterre , A. ( 2019 ), “ A cross-national study on the antecedents of work–life balance from the fit and balance perspective ”, Social Indicators Research , Vol. 142 No. 1 , pp. 261 - 282 , doi: 10.1007/s11205-018-1875-6 .
Haider , S. , Jabeen , S. and Ahmad , J. ( 2018 ), “ Moderated mediation between work life balance and employee job performance: the role of psychological wellbeing and satisfaction with co-workers ”, Revista de Psicología Del Trabajo y de Las Organizaciones , Vol. 34 No. 1 , pp. 29 - 37 , doi: 10.5093/jwop2018a4 .
Hill , E.J. , Hawkins , A.J. , Ferris , M. and Weitzman , M. ( 2001 ), “ Finding an extra day a week: the positive influence of perceived job flexibility on work and family life balance ”, Family Relations , Vol. 50 No. 1 , pp. 49 - 65 .
Hirschi , A. , Shockley , K.M. and Zacher , H. ( 2019 ), “ Achieving work-family balance: an action regulation model ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 150 - 171 .
Hofmann , V. and Stokburger-Sauer , N.E. ( 2017 ), “ The impact of emotional labor on employees’ work-life balance perception and commitment: a study in the hospitality industry ”, International Journal of Hospitality Management , Vol. 65 , pp. 47 - 58 , doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2017.06.003 .
Hughes , D.L. and Galinsky , E. ( 1994 ), “ Gender, job and family conditions, and psychological symptoms ”, Psychology of Women Quarterly , Vol. 18 No. 2 , pp. 251 - 270 .
Jensen , M.T. ( 2014 ), “ Exploring business travel with work–family conflict and the emotional exhaustion component of burnout as outcome variables: the job demands–resources perspective ”, European Journal of Work and Organizational Psychology , Vol. 23 No. 4 , pp. 497 - 510 , doi: 10.1080/1359432X.2013.787183 .
Jiang , H. and Shen , H. ( 2018 ), “ Supportive organizational environment, work-life enrichment, trust and turnover intention: a national survey of PRSA membership ”, Public Relations Review , Vol. 44 No. 5 , pp. 681 - 689 , doi: 10.1016/j.pubrev.2018.08.007 .
Johari , J. , Yean Tan , F. and TjikZulkarnain , Z.I. ( 2018 ), “ Autonomy, workload, work-life balance and job performance among teachers ”, International Journal of Educational Management , Vol. 32 No. 1 , pp. 107 - 120 , doi: 10.1108/IJEM-10-2016-0226 .
Johnston , D.D. and Swanson , D.H. ( 2007 ), “ Cognitive acrobatics in the construction of worker–mother identity ”, Sex Roles , Vol. 57 Nos 5/6 , pp. 447 - 459 , doi: 10.1007/s11199-007-9267-4 .
Kalliath , P. , Kalliath , T. , Chan , X.W. and Chan , C. ( 2018 ), “ Linking work–family enrichment to job satisfaction through job Well-Being and family support: a moderated mediation analysis of social workers across India ”, The British Journal of Social Work , Vol. 49 No. 1 , pp. 234 - 255 .
Kalliath , T. and Brough , P. ( 2008 ), “ Work–life balance: a review of the meaning of the balance construct ”, Journal of Management & Organization , Vol. 14 No. 3 , pp. 323 - 327 .
Kim , H.K. ( 2014 ), “ Work-life balance and employees’ performance: the mediating role of affective commitment ”, Global Business and Management Research: An International Journal , Vol. 6 , pp. 37 - 51 .
Kowitlawkul , Y. , Yap , S.F. , Makabe , S. , Chan , S. , Takagai , J. , Tam , W.W.S. and Nurumal , M.S. ( 2019 ), “ Investigating nurses’ quality of life and work‐life balance statuses in Singapore ”, International Nursing Review , Vol. 66 No. 1 , pp. 61 - 69 , doi: 10.1111/inr.12457 .
Li , A. , McCauley , K.D. and Shaffer , J.A. ( 2017 ), “ The influence of leadership behavior on employee work-family outcomes: a review and research agenda ”, Human Resource Management Review , Vol. 27 No. 3 , pp. 458 - 472 , doi: 10.1016/j.hrmr.2017.02.003 .
Lingard , H. , Brown , K. , Bradley , L. , Bailey , C. and Townsend , K. ( 2007 ), “ Improving employees’ work-life balance in the construction industry: project alliance case study ”, Journal of Construction Engineering and Management , Vol. 133 No. 10 , pp. 807 - 815 .
Liu , N.C. and Wang , C.Y. ( 2011 ), “ Searching for a balance: work–family practices, work–team design, and organizational performance ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 22 No. 10 , pp. 2071 - 2085 .
Lundberg , U. , Mardberg , B. and Frankenhaeuser , M. ( 1994 ), “ The total workload of male and female white collar workers as related to age, occupational level, and number of children ”, Scandinavian Journal of Psychology , Vol. 35 No. 4 , pp. 315 - 327 .
Lyness , K.S. and Judiesch , M.K. ( 2014 ), “ Gender egalitarianism and work–life balance for managers: multisource perspectives in 36 countries ”, Applied Psychology , Vol. 63 No. 1 , pp. 96 - 129 .
McCarthy , A. , Darcy , C. and Grady , G. ( 2010 ), “ Work-life balance policy and practice: understanding line manager attitudes and behaviors ”, Human Resource Management Review , Vol. 20 No. 2 , pp. 158 - 167 , doi: 10.1016/j.hrmr.2009.12.001 .
McCarthy , A. , Cleveland , J.N. , Hunter , S. , Darcy , C. and Grady , G. ( 2013 ), “ Employee work–life balance outcomes in Ireland: a multilevel investigation of supervisory support and perceived organizational support ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 24 No. 6 , pp. 1257 - 1276 .
McDonald , P. , Brown , K. and Bradley , L. ( 2005 ), “ Explanations for the provision-utilisation gap in work-life policy ”, Women in Management Review , Vol. 20 No. 1 , pp. 37 - 55 .
Matteson , M.T. and Ivancevich , J.M. ( 1987 ), “ Individual stress management intervention: evaluation of techniques ”, Journal of Managerial Psychology , Vol. 2 No. 1 , pp. 24 - 31 .
Mattessich , S. , Shea , K. and Whitaker-Worth , D. ( 2017 ), “ Parenting and female dermatologists’ perceptions of work-life balance ”, International Journal of Women's Dermatology , Vol. 3 No. 3 , pp. 127 - 130 , doi: 10.1016/j.ijwd.2017.04.001 .
Matthews , R.A. , Mills , M.J. , Trout , R.C. and English , L. ( 2014 ), “ Family-supportive supervisor behaviors, work engagement, and subjective well-being: a contextually dependent mediated process ”, Journal of Occupational Health Psychology , Vol. 19 No. 2 , p. 168 , doi: 10.1037/a0036012 .
Maura , M.S. , Russell , J. , Matthews , A. , Henning , J.B. and Woo , V.A. ( 2014 ), “ Family-supportive organizations and supervisors: how do they influence employee outcomes and for whom? ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 25 No. 12 , pp. 1763 - 1785 .
Michel , A. , Bosch , C. and Rexroth , M. ( 2014 ), “ Mindfulness as a cognitive–emotional segmentation strategy: an intervention promoting work–life balance ”, Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology , Vol. 87 No. 4 , pp. 733 - 754 .
Moore , J.E. ( 2000 ), “ One road to turnover: an examination of work exhaustion in technology professionals ”, MIS Quarterly , Vol. 24 No. 1 , pp. 141 - 168 .
Muna , F.A. and Mansour , N. ( 2009 ), “ Balancing work and personal life: the leader as ACROBAT ”, Journal of Management Development , Vol. 28 No. 2 , pp. 121 - 133 , doi: 10.1108/02621710910932089 .
Mushfiqur , R. , Mordi , C. , Oruh , E.S. , Nwagbara , U. , Mordi , T. and Turner , I.M. ( 2018 ), “ The impacts of work-life-balance (WLB) challenges on social sustainability: the experience of Nigerian female medical doctors ”, Employee Relations , Vol. 40 No. 5 , pp. 868 - 888 , doi: 10.1108/ER-06-2017-0131 .
Onyishi , L.A. ( 2016 ), “ Stress coping strategies, perceived organizational support, and marital status as predictors of work-life balance among Nigerian bank employees ”, Social Indicators Research , Vol. 128 No. 1 , pp. 147 - 159 .
Potgieter , S.C. and Barnard , A. ( 2010 ), “ The construction of work-life balance: the experience of black employees in a call-centre ”, SA Journal of Industrial Psychology , Vol. 36 No. 1 , pp. 8 .
Rudman , L.A. and Mescher , K. ( 2013 ), “ Penalizing men who request a family leave: is flexibility stigma a femininity stigma? ”, Journal of Social Issues , Vol. 69 No. 2 , pp. 322 - 340 , doi: 10.1111/josi.12017 .
Russo , M. , Shteigman , A. and Carmeli , A. ( 2016 ), “ Workplace and family support and work–life balance: implications for individual psychological availability and energy at work ”, The Journal of Positive Psychology , Vol. 11 No. 2 , pp. 173 - 188 , doi: 10.1080/17439760.2015.1025424 .
Sandow , E. ( 2019 ), “ Til work do us part: the social fallacy of long-distance commuting ”, Integrating Gender into Transport Planning , 121 - 144 . Palgrave Macmillan , Cham , doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-05042-9_6
Sigroha , A. ( 2014 ), “ Impact of work life balance on working women: a comparative analysis ”, The Business and Management Review , Vol. 5 , pp. 22 - 30 .
Spector , P.E. ( 1997 ), Job Satisfaction: Application, Assessment, Causes, and Consequences , Sage , Thousand Oaks. CA .
Swanson , V. , Power , K.G. and Simpson , R.J. ( 1998 ), “ Occupational stress and family life: a comparison of male and female doctors ”, Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology , Vol. 71 No. 3 , pp. 237 - 260 .
Tammy , D.A. and Kaitlin , M.K. ( 2012 ), “ Trait mindfulness and work–family balance among working parents: the mediating effects of vitality and sleep quality ”, Journal of Vocational Behaviour , Vol. 80 No. 2 , pp. 372 - 379 , doi: 10.1016/j.jvb.2011.09.002 .
Talukder , A.K.M. , Vickers , M. and Khan , A. ( 2018 ), “ Supervisor support and work-life balance: impacts on job performance in the Australian financial sector ”, Personnel Review , Vol. 47 No. 3 , pp. 727 - 744 , doi: 10.1108/PR-12-2016-0314 .
Tenney , E.R. , Poole , J.M. and Diener , E. ( 2016 ), “ Does positivity enhance work performance? Why, when, and what we don’t know ”, Research in Organizational Behavior , Vol. 36 , pp. 27 - 46 .
Theorell , T. and Karasek , R.A. ( 1996 ), “ Current issues relating to psychosocial job strain and CV disease research ”, Journal of Occupational Health Psychology , Vol. 1 No. 1 , pp. 9 - 26 .
Turanlıgil , F.G. and Farooq , M. ( 2019 ), “ Work-life balance in tourism industry ”, in Contemporary Human Resources Management in the Tourism Industry , IGI Global , pp. 237 - 274 .
Waters , M.A. and Bardoel , E.A. ( 2006 ), “ Work – family policies in the context of higher education: useful or symbolic? ”, Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources , Vol. 44 No. 1 , pp. 67 - 82 .
Wayne , J. , Randel , A. and Stevens , J. ( 2006 ), “ The role of identity and work family support in WFE and work-related consequences ”, Journal of Vocational Behavior , Vol. 69 No. 3 , pp. 445 - 461 .
Whitehouse , G. , Hosking , A. and Baird , M. ( 2008 ), “ Returning too soon? Australian mothers' satisfaction with maternity leave duration ”, Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources , Vol. 46 No. 3 , pp. 188 - 302 .
Yadav , R.K. and Dabhade , N. ( 2013 ), “ Work life balance amongst the working women – a case study of SBI ”, International Letters of Social and Humanistic Sciences , Vol. 7 , pp. 1 - 22 .
Yu , H.H. ( 2019 ), “ Work-life balance: an exploratory analysis of family-friendly policies for reducing turnover intentions among women in U.S. Federal law enforcement ”, International Journal of Public Administration , Vol. 42 No. 4 , pp. 345 - 357 , doi: 10.1080/01900692.2018.1463541 .
Zheng , C. , Kashi , K. , Fan , D. , Molineux , J. and Ee , M.S. ( 2016 ), “ Impact of individual coping strategies and organisational work–life balance programmes on Australian employee well-being ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 27 No. 5 , pp. 501 - 526 .
Zucker , R. ( 2017 ), “ Help your team achieve work-life balance – even when you can’t ”, Harvard Business Review , available at: https://hbr.org/2017/08/help-your-team-achieve-work-life-balance-even-when-you-cant
Acknowledgements
Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Data availability: The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Compliance of ethical standard statement: The results reported in this manuscript were conducted in accordance with general ethical guidelines in psychology.
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Work-Life Balance and Well-Being at Work
Employees’ Perspective to Promote a Psychologically Healthy Workplace
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 17 July 2020
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Nicole Cvenkel 3
87 Accesses
1 Citations
Work-life balance is growing to be an issue of focus for organizational leaders, employees, HR professionals, and wellness coordinators as individuals and the organization benefit from having health and well-being when work-life balance is embraced strategically, which in turn impacts on productivity and performance. The purpose of this chapter and empirical research study is to explore managerial and nonmanagerial employees’ perspectives that relate to work-life balance from the perspective of work-family conflicts, health and well-being initiatives to promote work-life balance satisfaction, and the organization’s implementation of work-life balance (aka family supportive or family-friendly policies) to promote a more psychologically healthy workplace. A qualitative methodological approach was adopted, and data was collected through 36 semi-structured interviews and 2 focus groups with managerial and nonmanagerial employees from diverse occupational groups. The research found that work-life conflicts that affect employees work-life balance includes limited resources, workplace stress, poor relationships, substance abuse, and other external factors. Organizational family-friendly work-life balance initiatives that were found to help employee health and well-being include fun and family-friendly activities, counselling, periodic breaks, trust, and confidentiality. Organizational health and well-being policy initiatives that promote work-life balance satisfaction consist of company group health plan, employee assistance program (EAP), gym membership, flexible working arrangements, wellness strategies, and fairness at work. The originality and value of this research reveal an important interface with employees’ work-life balance strategies and organizational work-life balance policies and programs in addressing overall employee health and well-being. The results have implications for organizational delivery of work-life balance policies and practices, corporate social responsibility, and other human resource management practices to support employees’ work-life balance, health, and well-being.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Akintayo DI (2010) Work-family conflict and organization commitment among industrial workers in Nigeria. Journal of Psychology and Counseling 2:1), 1–1), 8
Google Scholar
Allen TD (2001) Family-supportive work environments: the role of organizational perceptions. Journal of Vocational Behaviour 58:414–435
Antai D, Oke A, Braithwaite, Anthony DS (2015) A ‘balanced’ life: work-life balance and sickness absence in four Nordic countries. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine 6(4):205–222
Article Google Scholar
Beauregard TA, Henry LC (2009) Making the link between work-life balance practices and organizational performance. Human Resource Management Review 19(1):9–22
Beauregard TA, Lesley HC (2009) Making the link between work-life balance practices and organizational performance. Human Resource Management Review 19:9–22
Boamah SA, Laschinger H (2015) The influence of areas of worklife fit and work-life interference on burnout and turnover intentions among new graduate nurses. Journal of Nursing Management, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.12318
Bond JT, Galinsky E, Kim SS, Brownfield E (2005) National study of employers. Families and Work Institute, New York
Bosch G (2004) Towards a new standard employment relationship in Western Europe. British Journal of Industrial Relations 42:617–636
Bratberg E, Dahl SÅ, Risa AE (2002) The double burden. Do combinations of career and family obligations increase sickness absence among women? European Sociological Review 18:233–249
Burke RJ, Greenglass ER (2001) Hospital restructuring, work-family conflict and psychological burnout among nursing staff. Psychological Health 16:583–594
Chen PY, Cooper CL (2014) Wellbeing: a complete reference guide, work and wellbeing. Wiley, Oxford
Cho J, Laschinger HKS, Wong C (2006) Workplace empowerment, work engagement and organizational commitment of new graduate nurses. Nursing Leadership 19(3):43–60
CIPD (2006). http://www.cipd.co.uk/subjects/wrkgtime/wrktmewrklfbal/worklifeba.htm?IsSrchRes=1 . Available February
CIPD (2020) Working time and time off work: understand the basics of the working time regulations in the UK, working hours trends, holidays and special leave. https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/working-time/factsheet . Accessed 25 Mar 2020
Clutterbuck D (2003) Managing Work-Life Balance: A Guide for HR in Achieving Organisational and Individual Change. Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development, CIPD House, London
Crompton R (2002) Employment, flexible working and the family. British of Journal Sociology 53(4):537–338
Crompton R, Lyonette C (2006) Work-life ‘balance’ in Europe. Acta Social 49:379–393
Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) (2003) Flexible working: the right to request and the duty to consider. Department of Trade & Industry, London
Estes SB, Michael J (2005) Work-Family Practices and Gender Inequality at Work: A Sloan Work and Family Encyclopedia Entry. http://wfnetwork.bc.edu/encylopedia_entry.php?id=1230&area=All (accessed November 12th, 2020)
Fleetwood S (2006) Why work-life balance now? Lancaster university management school working paper 2006/041 . The Department of Organisation, Work and Technology, Lancaster
Frone MR (2003) Work-family balance. In: Quick JC, Tetrick LE (eds) Handbook of occupational health psychology. American Psychological Association, Washington, DC, pp 13–162
Frone MR, Yardley JK, Markel KS (1997) Developing and testing an integrative model of the work-family interface. Journal of Vocational Behaviour 50:145–167
Gray A (2005) Unsocial Europe: social protection or flexploitation. Pluto, London
Greenhaus JH, Collins KM, Shaw JD (2003) The relation between work-family balance and quality of life. Journal Vocational Behavior 63:510–531
Greenhaus JH, Allen TD, Spector PE (2006) Health consequences of work-family conflict: the dark side of the work family interface. Research in Occupational Stress and Wellbeing 5:61–98
Grzywacz JG, Carlson DS (2007) Conceptualizing work– family balance: implications for practice and research. Advances Developing Human Resources 9:455–471
Hayes LJ, O’Brien-Pallas L, Duffield C et al (2006) Nurse turnover: a literature review. Int Journal Nursing Studies 43:237–263
Hyman J, Baldry C, Scholarios D, Bunzel D (2002) Work-life imbalance in call centres and software development. British Journal of Industrial Relations 41(2):215–239
Jacobs JA, Gerson K (2004) The time divide: work, family, and gender inequality. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Jansen NW, Kant IJ, van Amelsvoort LG et al (2006) Work-family conflict as a risk factor for sickness absence. Occupational Environment Medicine 63:488–494
Kossek EE, Pichler S, Bodner T et al (2011) Workplace social support and work – family conflict: a meta-analysis clarifying the influence of general and work-family specific supervisor and organisation support. Personnel Psycholgy 64:289–313
Lambert SJ, Waxman E (2005) Organizational stratification: distributing opportunities for work-life integration. In: Kossek EE, Lambert SJ (eds) Work and life integration: organizational, cultural and individual perspectives. Lawrence Erlbaum, Mahwah, pp 103–126
Leiter MP, Maslach C (2004) Areas of worklife: a structured approach to organizational predictors of job burn-out. In: Perrewe PI, Ganster DC (eds) Research in occupational stress and well-being. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 91–134
Lewis S (2003) The integration of paid work and the rest of life. Is post-leisure work the new leisure? Leis Stud 22:343–355
Maslach C, Leiter MP (1997) The truth about burnout. Jossey-Bass, San Francisco
Michel JS, Kotrba LM, Mitchelson JK et al (2011) Antecedents of work-family conflict: a meta-analytic review. Journal Organization Behaviour 32:689–725
Miles MB, Huberman AM (1994) Qualitative data analysis: an expanded sourcebook, 2nd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Nielsen ML, Kristensen TS, Smith-Hansen L (2002) The intervention project on absence and well-being (IPAW): design and results from the baseline of a 5-year study. Work Stress 16:191–206
Parasuraman S, Greenhaus JH (1997) The changing world of work and family. In: Parasuraman S, Greenhaus JH (eds) Integrating work and family: challenges & choices for a changing world. Quorum Books, Westport, pp 3–14
Patton MQ (2002) Qualitative research and evaluation methods, 3rd edn. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Saltzstein AL, Ting Y, Saltzstein GH (2001) Work-family balance and job satisfaction: the impact of family-friendly policies on attitudes of federal government employees. Public Adminstrative Review 61(4):452–467
Saunders M, Lewis P, Thornhill A (2009) Research methods for business students, 5th edn. Pearson Education, Financial Times, Prentice Hall, London
Serena Y (2014) Work-life balance – work intensification and job insecurity as job stressors. Labour & Industry 24:203–216
Simon M, Kummerling A, Hasselhorn HM (2004) Work home conflict in the European nursing profession. International Journal of Occupational Environmental Health 10:384–391
Van Maanen M (1994) Researching lived experience: human science for an action sensitive pedagogy. Althouse, Michigan
Virtanen M, Kivimäki M, Elovainio M et al (2003) From insecure to secure employment: changes in work, health, health related behaviours, and sickness absence. Occupation Environment Medicine 60:948–953
Voydanoff P (2004) The effects of work demands and resources on work-to-family conflict. Journal of Marriage Families 66:398–412
Williams ML, Ford LR, Dohring PL, Lee MD, MacDermid SM (2000) Outcomes of reduced load work arrangements at managerial and professional levels: perspectives from multiple stakeholders. In: Paper presented at the annual meeting of the academy of management, Toronto
Wood SJ, de Menezes L (2008) Family-friendly management, organizational performance and social legitimacy. Institute of Work Psychology, University of Sheffield, Mimeo
Yeandle S, Crompton R, Wigfield A, Dennett J (2002) Employed carers and family-friendly employment policies. Joseph Rowntree Foundation Policy Press, London
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
My Work & Well-Being Consulting Inc, Prince George, British Columbia, Canada
Nicole Cvenkel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nicole Cvenkel .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
De Montfort University, Leicester, UK
David Crowther
Social Responsibility Research Network, Derby, UK
Shahla Seifi
Section Editor information
University of Derby, Derby, UK
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Cvenkel, N. (2020). Work-Life Balance and Well-Being at Work. In: Crowther, D., Seifi, S. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Corporate Social Responsibility . Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-22438-7_19-1
Sustaining the nursing workforce - exploring enabling and motivating factors for the retention of returning nurses: a qualitative descriptive design
- Kumiko Yamamoto 1 ,
- Katsumi Nasu 1 ,
- Yoko Nakayoshi 1 &
- Miyuki Takase 1
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 248 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
260 Accesses
Metrics details
The nursing shortage represents a persistent and urgent challenge within the healthcare industry. One of the most cost-effective and time-efficient solutions to address this issue is the recruitment of inactive nurses to rejoin the nursing workforce, while simultaneously ensuring the long-term sustainability of their careers following their return to work. The aim of this study is to explore the factors that facilitate the retention of nurses who have returned to work, from their perspective.
To achieve this aim, a qualitative descriptive design was employed. A total of 15 registered nurses who had not practiced nursing for a minimum of three years prior to their return to work, and had been working as nurses for at least three months following their return, were selected from seven healthcare institutions using convenience sampling. Face-to-face or online semi-structured interviews were conducted, and qualitative inductive analysis was employed to analyze the collected data.
The analysis revealed five key themes, two of which were related to the enabling factors making it possible for the nurses to continue their work, while the remaining three pertained to the motivating factors driving the pursuit of professional careers. The two themes associated with enabling factors were identified as “Conditions and support that sustain work-life balance” and “A workplace that acknowledges my career, and encourages my growth as an experienced nurse”. The three themes related to motivating factors were entitled “Pride in reconnecting with and contributing to society,” “Cultivating confidence through incremental professional development and future envisioning,” and “Enrichment of my own and my family’s life”.
Conclusions
Returning nurses constitute a valuable asset for healthcare institutions. To effectively retain these nurses, it is crucial to implement multi-dimensional approaches that enable and motivate them to sustain and enrich their professional and personal lives while continuing their work in the nursing field.
Peer Review reports
Nurses constitute a vital cornerstone of the healthcare system, assuming a foundational role in providing patient care, and notably representing over half of the entire healthcare workforce [ 1 ]. The global nurse population was estimated at 27.9 million in 2018 [ 1 ], and there was a notable growth of 4.7 million nurses between 2013 and 2018 [ 1 ]. Simultaneously, the WHO [ 1 ] reported a deficit of 5.9 million nurses in 2018, with the shortfall in the number of nurses expected to reach 10.6 million by 2030 [ 2 ]. This trend is primarily driven by the mounting demand for nursing services stemming from population aging dynamics. Moreover, the aging composition of the nursing workforce exacerbates the existing shortage of nurses. Currently, 17% of the global nursing population is aged 55 years or over [ 2 ], and projections indicate that within the upcoming decade, approximately 4.7 million nurses are expected to retire [ 3 ]. This means that an estimated annual influx of 47,000 new nurses is required just to sustain the current nursing workforce. Failure to meet this demand will probably intensify the nursing shortage at an accelerating pace. There is an immediate need for cost-effective measures aimed at mitigating the shortage of nurses.
Numerous policies have been implemented on a global scale to address the persistent shortage of nursing professionals. These policy measures encompass creating new registered nurses through education; facilitating re-entry into the nursing workforce for currently inactive registered nurses, and recruiting nurses from other countries [ 4 ]. Among the aforementioned strategies, one particularly promising approach to overcoming the nursing shortage involves the recruitment of inactive nurses, which has been implemented in many countries [ 4 , 5 ]. The reintegration of inactive nurses into the labor force is advantageous in terms of cost and time, as it obviates the need to invest social capital and years of resources in educating and nurturing new nursing students. Countries have implemented Return to Practice Programs designed for inactive nurses, each varying in educational content and duration [e.g., 6 , 7 ], and these initiatives have demonstrated notable success in augmenting the nursing labor force [ 8 , 9 , 10 , 11 ].
The reintegration of these nurses into the labor force holds significant importance in addressing the nursing shortage in Japan in particular. Japan is currently facing the challenge of a super-aging population, with 29.0% of its total population being 65 years and older [ 12 ]. This demographic shift has imposed increasing demands on nursing professionals, as older people often experience multiple chronic illnesses that result in physical and cognitive decline [ 13 ], necessitating substantial medical support and assistance in daily activities. In response to this demand, the Japanese government has actively pursued strategies to increase enrollment in nursing schools, reduce attrition rates, promote the retention of currently practicing nurses, and encourage inactive nurses to return to nursing practice [ 14 ]. However, the declining birth rate in Japan has led to a decrease in the number of students enrolling in nursing schools since 2018 [ 15 ]. Although the improvement in the workplace environment has contributed to a reduction in the turnover rate of full-time nursing personnel from 11.0% in 2013 to 10.6% in 2021, which is slightly lower than the average turnover rate across all occupations (i.e., 11.3%) [ 16 ], this alone cannot address the issue of the nursing shortage. Consequently, an inevitable imbalance between demand and supply persists. The Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare in Japan [ 14 ] projected a demand for 1.88–2.02 million nurses by 2025, when the baby boomer generation reaches 75 years old or older, while the projected supply would be 1.75–1.82 million nurses, resulting in a shortage of 60,000 to 250,000 nurses. Therefore, the recruitment of inactive nurses has emerged as a pivotal measure to rectify this imbalance promptly.
Available statistics show that there is an estimated population of approximately 700,000–860,000 inactive nurses in Japan [ 17 ], the United States [ 18 ] and Germany [ 19 ]. Several studies have demonstrated that a significant proportion of surveyed inactive nurses, ranging from 43 to 85%, expressed a desire to return to nursing practice [ 20 , 21 ]. The motivations behind their return or desire to return to nursing practice encompass factors such as no longer having childcare responsibilities [ 22 ], a yearning for nursing practice [ 22 ], seeking a renewed purpose in life after completing child-rearing [ 23 ], financial incentives [ 10 , 22 , 23 ], and a desire to update skills and knowledge in acute care nursing [ 24 ]. Similarly, a more recent study conducted in Taiwan reported that incentives for returning to practice included the improvement of the nurse staffing level, and the provision of a safer working environment and re-entry preparation programs [ 20 ].
However, it should be noted that despite the expressed intentions, many inactive nurses have faced challenges in returning to practice as well as in sustaining their employment [ 25 ]. These challenges related to returning to work include difficulties in balancing work with childcare and household responsibilities, anxiety arising from a perceived lack of competency, concern about heavy work responsibilities, and fears of committing medical errors [ 15 ]. Consequently, previous research findings have indicated that only 57–69% of nurses who completed the Return to Practice Program were able to successfully re-enter the nursing workforce [ 26 ]. These challenges persist even after returning to work, as reported in subsequent studies [ 27 , 28 , 29 ], exacerbated by the absence of family-friendly working conditions, inadequate on-the-job training opportunities, and insufficient ongoing education and mental support to overcome anxiety and regain confidence [ 30 ]. As a consequence, nurses who have returned to work experience a sense of guilt toward both their colleagues and patients for perceived inadequacies in care provision, as well as feelings of guilt toward their families due to the sacrifices necessitated by their work obligations [ 31 ], all of which contribute to higher attrition rates among returners. In fact, the findings from a small-scale survey conducted in Japan revealed that 25% of nurses who participated in refresher programs and returned to work were unable to sustain their employment [ 32 ]. This retention rate is significantly higher compared to the turnover rates observed among newly graduated nurses (7.8%) and nurses with prior experience (17.7%) [ 16 ].
While it is crucial to address the barriers encountered by nurses who wish to return to practice and have successfully done so, it is equally imperative to ensure the long-term sustainability of their careers following their return to work. However, the factors that contribute to the retention of these returners have not been thoroughly investigated. For instance, Barriball et al. [ 33 ] and Elwin [ 27 ] investigated the experiences of nurses returning to practice, although their focus was primarily on the experiences within the Return to Practice Program, rather than the process of returning to the workplace itself. Conversely, Durand and Randhawa [ 34 ], Hammer and Craig [ 23 ] and Costantini, et al. [ 35 ] explored the experiences of nurses returning to work; however, they did not focus on the specific factors that facilitate retention. In fact, only a limited number of studies have endeavored to identify factors that facilitate the retention of inactive nurses. The key findings facilitating their retention were preceptors fulfilling their learning needs [ 28 , 31 ], support on nursing units [ 31 ], flexible working atmosphere [ 28 ], and re-building a new family life [ 28 ] or re-negotiation with both work and home life [ 36 ]. Nevertheless, these studies are based on a relatively small sample of five to eight nurses who have returned to practice, thus leaving the possibility that some factors remain undiscovered. A comprehensive understanding of the factors that not only prompt nurses to leave their positions but also motivate them to remain is crucial for the development of strategies that ensure a sufficient nursing workforce and the provision of high-quality nursing care in countries grappling with nursing shortages.
Therefore, the aim of this study is to explore the factors that facilitate the retention of nurses who have returned to work, from their perspectives.
Methodology
This study employed a qualitative descriptive design [ 37 ]. The qualitative descriptive approach produces “findings closer to the data as given, or data-near” [ 38 , p. 78], without commitment to any theoretical views and without being bounded by preconceptions [ 38 ]. As such, this approach provides straightforward and comprehensive descriptive summaries of participants’ experiences and perceptions [ 39 , 40 ], thus it is suitable for areas where little is known about the topic under investigation [ 39 ]. We applied this approach to investigate the factors that contributed to the retention of these returners.
Participants
The participants were selected from seven healthcare institutions located in the southwestern region of Japan, and using convenience sampling and snowball sampling. The participants comprised re-entry nurses employed in five community hospitals and two long-term care facilities situated across metropolitan, urban, and rural areas of Japan with populations ranging from 0.4 million to 2.7 million. Inclusion criteria for the nurses were that they (1) had not practiced nursing for a minimum of three years prior to returning to work (based on the Japanese childcare policy allowing a maximum three-year leave), (2) had been working as nurses for a minimum of three months after returning to work, and (3) were able to participate in interviews conducted in Japanese. Exclusion criteria included: (1) working as nursing managers after returning to work, and (2) being without prior experience of working in Japanese healthcare institutions (i.e., those who only had overseas experience). Participants were recruited until saturation was reached, i.e., no further new information emerged during the interviews. A total of 15 participants were recruited as a result.
Data collection
The research team approached the Directors of Nursing and obtained permission to recruit potential participants. Written statements were distributed to the potential participants to explain the purpose and methods of the study.
Semi-structured interviews (see Table 1 for the interview guide) were conducted face-to-face or online, between November 2021 and July 2022. The interview guide was developed based on the research purpose and the review of existing literature. The first author conducted all interviews because her 16-year career hiatus from nursing for child-rearing would help her establish a mutually respectful relationship with the participants and foster an environment free from intimidation. These conditions are crucial for eliciting participants’ genuine sentiments. Throughout the interviews, the author demonstrated respect and empathy toward the participants by openly sharing her own feelings. Additionally, she skilfully guided the discussions to extract the participants’ experiences, concurrently undergoing a process of reintegration in tandem with them. Conversely, the dynamic between the interviewer and participants could be impacted by the assumptions and biases inherent in the interviewer’s background. To mitigate this potential influence, data analysis was performed independently by two researchers (refer to the Data Analysis section).
The interviews were conducted in private rooms, and all sessions were audio-recorded. Nonverbal data, such as the participants’ posture during the interviews, were recorded in an observation notebook. Each participant underwent a single interview session and received a book voucher valued at ¥2500 as a token of appreciation. The interviews lasted between 18 and 49 min (Mean = 39.2 min). Audio-recorded data were transcribed verbatim.
Data analysis
Qualitative inductive analysis [ 41 ] was conducted. Verbatim transcripts were thoroughly reviewed to develop an overall understanding of the participants’ statements. Meaningful words and paragraphs related to the factors that had facilitated the retention of these re-entry nurses were extracted, and codes were assigned to represent the symbolic meanings of the data segments (first-cycle coding). Subsequently, the codes were compared and contrasted to group them into categories based on their similarities in meaning. These categories were further integrated into themes that captured the essence of the factors facilitating the retention of nurses who returned to the nursing workforce (second cycle coding). The first-cycle coding was conducted by the first author (KY) by utilizing her understandings of the participants’ context and their experiences. In the second cycle of coding, the first (KY)and second (KN) authors independently categorized the codes, and the congruencies or discrepancies between them were discussed among all the research team members (KY, KN, YN, and MT), who possessed nursing backgrounds and qualitative research experience. Discussion continued until consensus was reached among all the research members. NVivo12 (QSR International, Melbourne, Australia) software was used for data management.
The trustworthiness of the study
Ensuring credibility, confirmability, transferability and dependability contributes to the trustworthiness of the study [ 42 ]. To enhance the credibility, we applied method triangulation. The interviewer (i.e., the first author) took notes on the participants’ facial expressions and eye movements during the interview, which were included in the analysis along with the verbatim transcripts of the interview data. During the analysis process, the first author repeatedly read the transcripts and observational notes to code the data. For confirmability, two researchers independently categorized the codes, and discussions among the research team took place repeatedly to ensure the elimination of any preconceptions or biases. Any disagreements that arose during this process were resolved through discussions among the research team. To enhance the transferability of the findings, participants were recruited from diverse practice areas and various regions. Furthermore, detailed information was provided regarding the participants’ characteristics and their practicing contexts. In addition, the dependability of the findings was assured by providing detailed descriptions of the data collection and analysis process.
Ethical considerations
This study was approved by the Review Board of Yasuda Women’s University (approval number: 210007), and ethical approval was waived by the participating institutions. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The participants were fully informed about the study’s purpose, methods, potential risks, and benefits of participation as well as their right to decline participation or withdraw from the study. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant before the data collection. The interview schedule and location were prioritized according to the preferences of the participants, as many were balancing work and childcare responsibilities. Participants were assured that they could refrain from answering any questions that made them feel uncomfortable. Additionally, they were informed that they could end the interview session at any time if they experienced emotional distress. The collected data were securely stored in a locked cabinet, and pseudonyms were used to maintain the participants’ anonymity and protect their privacy.
All 15 eligible participants were female. The reasons cited for leaving employment were childbirth/child-rearing in 11 cases, caring for older family members in three cases, and pursuing a postgraduate degree in one case. The range of length of clinical experience before leaving employment was 3–20 (Mean = 8.2, SD = 4.2) years, that of career breaks was 3–19 (Mean = 6.6, SD = 4.0) years, and that of work after returning was 7 months to 8 years (Mean = 2.6 years, SD = 1.7 years). During the period of data collection, only two participants worked full-time, and 13 worked part-time. The areas of practice encompassed outpatient departments in hospitals ( n = 8), hospital wards ( n = 4), and long-term care facilities ( n = 3) (see Table 2 ).
The data analysis revealed five themes that facilitated the continuation of work for these participants. These themes include “Conditions and support that sustain work-life balance,” “A workplace that acknowledges my career, and encourages my growth as an experienced nurse,” “Pride in reconnecting with and contributing to society,” “Cultivating confidence through incremental professional development and future envisioning,” and “Enrichment of my own and family’s life.” The first two themes represent conditions that enabled the participants to continue their work. Thus, these conditions are referred to as “enablers”. The latter three themes describe factors that motivated the participants to pursue their professional careers. Thus, these factors are referred to as “motivators”.
Theme 1: conditions and support that sustain work-life balance
The participants identified support systems at home, in the workplace, and within society as prerequisites for maintaining a work-life balance, essential for sustaining their employment. This theme encompasses crucial elements that allow nurses to balance their work and family responsibilities, such as work conditions that consider their family circumstances, and support from family and friends. The theme consists of three categories: “Work (i.e., hours and location) and childcare conditions that meet my preferences,” “A family-friendly work environment,” and “Instrumental and emotional support from family and friends.”
Most participants juggled work, household, and childcare responsibilities. Therefore, effectively managing childcare duties while fulfilling work roles became a priority in their lives. Access to childcare facilities was deemed a basic requirement for them to work, as well as conditions such as workplaces located close to their homes and offering flexible working hours to address child-related matters promptly.
“When I was contemplating returning to work, one requirement was that I should be able to look after my two children, so it was important for me that all the conditions related to my children were in place, such as time restrictions and being able to go home immediately if something happens to them.” (ID 10) .
The participants also emphasized the need for a family-friendly work environment, where colleagues and supervisors understood their family circumstances and provided support in balancing work and family duties.
“When I returned to work, I wondered if I would be allowed to take a sudden leave if my child was ill. And they told me, ‘We take turns (taking a leave) so you can do it now, it’s fine,’ as well as ‘We can’t do it for you (take care of your child) but we can do the work in your place.’ Here at my current workplace, we can say such things to each other.” (ID 06) .
Given that most participants were engaged in multiple tasks both at home and work, they experienced physical and mental fatigue and strain. However, they managed to overcome these challenges by receiving instrumental and emotional support from their families and friends. Examples of such assistance included husbands and children sharing household chores and friends providing emotional support during conflicts arising from the intersection of family and work responsibilities.
“Regarding my husband, yes. When I started working, I was no longer a full-time housewife. But I’ve been working alongside him, and he’s been supporting me a lot, such as by taking the kids to school and picking them up after, things like that.” (ID 13) .
Ensuring the effective management of household responsibilities, particularly childcare, was a fundamental prerequisite for the participants to continue their employment. Consequently, the provision of “Conditions and support that sustain work-life balance” acted as an enabler, facilitating their continued engagement in work by sustaining their personal lives.
Theme 2: a workplace that acknowledges my career, and encourages my growth as an experienced nurse
The participants asserted that receiving support to cultivate their professional competencies within their work environment facilitated their transition through a process of reorientation. The participants were returners who had prior nursing experience and possessed a certain level of nursing competence required for professional practice. Initially apprehensive about their competence level, they desired recognition and appreciation for their previous experience and expertise from their supervisors and colleagues. They also expressed a preference for on-the-job refresher training that helped them regain necessary knowledge and skills. This training differed from that provided to newly graduated nurses. This theme represents the importance of receiving educational support to function as a nurse and opportunities for further growth, both of which facilitated the continuation of their work. The theme comprises three categories: “Supervisors and colleagues who appreciate and accept me,” “Support for myself as both a beginner and someone with experience,” and “Comprehensive manual and training.”
The participants emphasized the significance of being recognized and accepted by their colleagues and supervisors. The acknowledgment of their efforts by supervisors and the understanding of their hard work by colleagues served as encouragement to sustain their work. Furthermore, perceiving themselves as individuals who were relied upon by others and striving to meet those expectations facilitated their professional growth and their desire to contribute to the workplace.
“One thing is that um, I also discussed this with the Head Nurse, regarding training, that maybe we should improve the training even more, and the Head Nurse feels the same way, and so, she said I can go ahead and think about a program or something. When I’m entrusted with making these kinds of decisions, the work becomes fulfilling.” (ID 09) .
The participants also expressed the importance of receiving support from their colleagues as newcomers while appreciating their prior experience. The participants were often perceived as fully capable individuals and were assigned a workload equivalent to that of experienced nurses. However, the participants stressed the need for support from their colleagues during the initial phase of readjustment to their duties. Simultaneously, they sought appropriate levels of support while valuing their previous work experience and expertise. They felt reassured when their supervisors or colleagues offered support, recognizing them as both a beginner but also as someone with experience.
“From the day after I started working, I had my own room, and on that day, someone from the day shift always made it a point to talk to me and support me, and it felt like fate. I thought if I were being supported this much, I should do the same, and well, everyone in the ward helped me understand the patients within the week, so much that I thought I already remember them. I felt that I should make an effort to do so, since they supported me so much.” (ID 06) .
Additionally, they desired to receive training and manuals tailored to their skill set, enabling them to effectively perform their roles as staff members.
“Although it was only 3 years, I did have a work gap, so I was thinking that my skills and knowledge might be obsolete and that I might have forgotten some things, but this hospital has a very detailed manual.” (ID 06) .
Acceptance and support from both managers and colleagues, coupled with access to on-the-job training and manuals, emerged as crucial resources enabling participants to realign with their work responsibilities, especially in cases where they lacked up-to-date knowledge and skills. Additionally, feeling valued and trusted by colleagues played a pivotal role in bolstering their confidence, an essential attribute for navigating through challenging periods. Consequently, the provision of “A workplace that acknowledges my career, and encourages my growth as an experienced nurse” served as the pivotal enabler that sustained their professional life though continued commitment to their careers.
Theme 3: pride in reconnecting with and contributing to society
The participants described working as nurses as giving them a sense of pride and of being valuable to society, which motivated them to continue their work. Prior to returning to work, the participants experienced social isolation due to their engagement in various household responsibilities. However, returning to the nursing profession allows the participants to reclaim their roles as active members of society and regain confidence in their contribution to society. The theme comprises three categories: “Desire to contribute as a nurse,” “Expansion of relationships resulting from stepping out of the home,” and “My children feeling proud of me for being an active nurse.”
The participants maintained a strong sense of pride in their profession and were motivated by the desire to contribute to society as nurses, utilizing their nursing qualifications. As the demand for nurses increased during the COVID-19 pandemic, their determination to support patients as nurses grew even stronger. They also expressed a desire to share their expertise with younger nurses and provide guidance to other inactive nurses who were considering returning to work.
“Nurses are needed in situations like COVID-19, and I had gone through the trouble of getting my license, and all that.” (ID 03) . “Well, I’d like to be in a position where people feel they can ask me and maybe find a bit of a solution. I work with the mindset that someone a bit older, like me, should take a role of listening to and giving advice to younger colleagues.” (ID 8) .
Moreover, returning to work reaffirmed their sense of belonging to society not only as mothers but also as nurses. When they were solely focused on child-rearing, their social interactions were limited to those associated with their children. However, by returning to work and establishing their own place in the workplace, their social connections expanded beyond the confines of their homes. The opportunity to reconnect with broader society and experience personal freedom outside of their domestic responsibilities served as a motivation for the participants to continue their work.
“It definitely connects me to society. Until now, my connections with society were through my child. I think I couldn’t have had that without my child, and now it feels like I have a separate community of my own. I feel like that.” (ID 08) .
Furthermore, their pride in being nurses was reinforced by the admiration of their children, who proudly spoke of their mothers’ profession, especially during the challenging times of the pandemic. This alleviated any guilt associated with not having enough time to devote to their children and not fulfilling their maternal roles to the same extent as before. On the contrary, their professional engagement enhanced their self-esteem as proud mothers to their children.
“When I think of these moments, it makes me really happy. Like those moments when I feel that my children have become interested in me (omitted). For example, when they say things like, ‘Nurses are really cool,’ or ‘My mom works in a hospital.’ They’ve even written about me in their diaries.” (ID 01) .
Reclaiming a sense of pride and expanding their professional network through contributions to society represented profoundly fulfilling experiences for the participants. These experiences not only brought them joy in their work but also transcended the mere facilitation of work continuation. Consequently, “Pride in reconnecting with and contributing to society” operated as a potent motivator, driving their commitment to pursue their professional careers and advance, thus enriching their professional life.
Theme 4: cultivating confidence through incremental professional development and future envisioning
The participants were motivated to continue their work by their passion for professional growth and self-actualization. The participants engaged in introspection regarding their journey from the moment they returned to work up until the present. Despite encountering challenging circumstances, they swiftly reacquired previously possessed skills and knowledge, thus restoring their self-assurance in the practice of nursing. This newfound confidence propelled them to envision their future career paths. The following three categories encompass this overarching theme: “Confidence arising from successfully surmounting challenges upon restarting,” “Realization that I have finally made my comeback as a nurse,” and “Personal aspirations for the future.”
According to the participants, they encountered arduous situations upon re-entering the workforce, as they were frequently required to perform tasks that exceeded their current skill sets. Irrespective of their absence from work, their colleagues often regarded them as seasoned nurses. Struggling to fulfill assigned responsibilities, they engaged in negotiations with colleagues and supervisors, asserting their capabilities and limitations. These challenging experiences facilitated the recovery and enhancement of the necessary skills and knowledge, bolstering their confidence, and motivating them to persevere in their work.
“After returning to work, for about half a year, I struggled for a while before getting used to it again. It took me more than six months to understand why I was struggling. But when I got used to the working life, I was able to gain self-confidence.” (ID 04) .
Through introspection and self-comparison between the time of restarting and the present, the participants recognized their continuous development as nursing professionals, observing their ability to provide a sufficient level of patient care.
“In the sense that my intuition has returned, um, it was definitely the fact that before I started working, all I had was anxiety, but when I was actually able to perform my work by myself again, I think that was when I became confident.” (ID 10) .
This developmental process stimulated their anticipation of future career prospects. Some participants expressed aspirations to acquire advanced qualifications and pursue managerial positions, thus making career advancement their future objective.
“There was definitely something different about me, internally, before and after returning to work. It seems like I was lively, like I was going to set my goals, and that I was doing my best. There was a sense of certainty (omitted) and I was able to find what I wanted to do, too.” (ID 11) .
The successful completion of the readjustment journey played a pivotal role in bolstering the participants’ confidence, and encouraged them to envisage future professional goals. The process of “Cultivating confidence through incremental professional development and future envisioning” emerged as a critical motivating factor (i.e., motivator), propelling the participants towards continued professional growth, and thereafter enriching their professional life.
Theme 5. Enrichment of my own and my family’s life
The participants perceived added value when their own lives and their families were enriched by their work, which encouraged them to continue their jobs. The participants acknowledged the positive transformations in their physical and emotional well-being, as well as in the lives of their families, following their return to work. They perceived an overall improvement in their daily lives. This theme encompasses three categories: “A healthy mind and body attained by adding variety to life,” “Positive influence on family dynamics,” and “Income that enriches my life.”
The participants said that resuming employment contributed to a well-rounded lifestyle and positively impacted their physical and mental health. Specifically, those who were responsible for raising children noted that having time away from their children reduced feelings of irritability and enabled them to engage with their children in a more compassionate and nurturing manner upon returning home from work.
“I feel like my day has become balanced. I do feel a little sad that I’m spending a lot more time away from my children (omitted). I make up for it when I see them, and I think I’ve become a little less irritable.” (ID 10) .
Furthermore, having a job established a consistent rhythm to their lives and facilitated physical fitness, thus promoting a balanced existence. They also perceived the involvement of others in caring for their children as an opportunity for their children to interact with a broader network of individuals, fostering their growth and healthy development. Moreover, the up-to-date medical knowledge gained through their work served to safeguard the health of their families.
“Because I want to know about cutting-edge technology. You know, if I quit this job, it will affect my life directly, because it’s a job that involves the body after all. I think it’s always gonna be useful (in my life).” (ID 13) .
By earning their own income, they were able to provide economic security to their families, which was closely linked to their mental well-being.
“Before I was reinstated, we were living on my husband’s salary alone. I felt bad about it, but now we have some financial leeway, so that definitely was a benefit for me.” (ID 11) .
Resuming employment engendered an ‘Enrichment of my own and my family’s life,’ demonstrated by enhancements in physical and mental well-being, the wholesome development of children, and economic incentives. Consequently, this theme illustrates the enrichment of the participants’ personal lives as a result of having fulfilling professional lives, and emerged as an additional motivator.
This study explored factors contributing to the retention of nurses re-entering the workforce after a career break, resulting in the identification of five themes. The first two, “Conditions and support that sustain work-life balance” and “A workplace that acknowledges my career, and encourages my growth as an experienced nurse,” were identified as enablers, sustaining the participants’ continued engagement in work. The next three themes, “Pride in reconnecting with and contributing to society,” “Cultivating confidence through incremental professional development and future envisioning,” and “Enrichment of my own and family’s life,” served as motivators, propelling them toward a professional career.
The concept of enablers and motivators parallels Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory of Motivation [ 43 ], where hygiene factors, including salary and work conditions, are essential but their absence leads to dissatisfaction, while motivation factors, like achievement and recognition, promote job satisfaction and enhanced performance [ 43 ]. Similarly, enablers such as family-friendly work conditions, peer support, and on-the-job training played pivotal roles in the participants’ job continuity, and their absence could result in dissatisfaction or job exit. Likewise, motivators such as pride and confidence yielded personal fulfillment, motivating participants to pursue their professional goals. However, distinctions arise. While the Two-Factor Theory focuses on work components, our study contends that healthcare institutions must address both professional and personal factors for nurse retention. This is critical, particularly for returning nurses, often with caregiving responsibilities, necessitating a balance between sustaining and enriching their professional and personal lives. Another distinction lies in the relationship between the enablers and motivators. According to the Two-Factor Theory, hygiene and motivation factors exist independently, while motivators do not exist without the presence of enablers. For example, without adequate support for nurses to achieve work-life balance, they are unable to enhance their own or their family’s quality of life. Similarly, lacking encouragement in professional development, nurses are unable to cultivate pride or confidence, or envision their future. These relationships are depicted in Fig. 1 . The subsequent sections provide a detailed explanation of each of these factors.
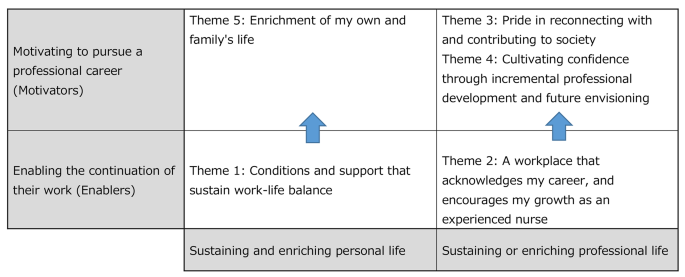
Framework for the sustainability of career for returners
The first theme, “Conditions and support that sustain work-life balance,” functions as an enabler that sustains nurses’ personal life. Nurses are prominent double-duty caregivers, tending to family and patients [ 44 ]. The majority of our participants had children, reflecting the fact that in Japan, 55–66% of nurses are parents [ 16 , 45 ]. Therefore, balancing family and work is crucial, regardless of career breaks. Specifically, nurses who temporarily left their employment due to childcare responsibilities had various reasons such as the absence of available childcare support. Especially in Japan, women often prioritize their childcare responsibilities over work commitments, or may feel societal pressure to remain at home and care for their children [ 46 ]. These cultural practices and norms could potentially elucidate their career hiatus. Therefore, family-friendly working conditions (e.g., flexible hours, location, childcare support) are vital for returning and sustaining work. This finding is consistent with previous studies indicating that workplace flexibility, which helps alleviate childcare concerns, is crucial for enabling nurses to sustain their work [ 28 , 30 , 35 , 36 ]. Furthermore, nurses who juggle dual caregiving roles often experience fatigue and stress [ 44 ]. Therefore, receiving instrumental and emotional support from their spouses is essential for maintaining a healthy work-life balance. In fact, recent studies have highlighted that support from their families enables nurses to effectively manage the demands of both their family and work spheres, facilitating their re-entry into professional practice [ 28 , 35 ]. The successful sharing of household responsibilities and childcare is indispensable for returners who aspire to continue their professional work, particularly those with young children.
The second theme, “A workplace that acknowledges my career, and encourages my growth as an experienced nurse,” serves as an enabler that sustains the professional practice of returners. This finding is also in line with previous studies that have highlighted the significance of a supportive work environment in aiding individuals to manage their jobs and regain confidence [ 28 , 35 ]. Although returners are often perceived as experienced nurses capable of functioning independently, the literature indicates that they encounter significant challenges in reacquiring their previous knowledge and skills, while also adapting to the rapidly advancing field of medical technology [ 21 , 33 , 35 ]. Reintegrating into the nursing workforce is arduous, and returners often experience anxiety and confidence issues [ 27 , 31 ]. This was also evident among our participants. Consequently, receiving appropriate initial training and access to manuals are critical factors enabling returners to fulfill their duties and sustain their professional work [ 30 ]. On the other hand, the majority of the participants had achieved an expert nurse level, possessing more than five years of previous clinical experience [ 47 ], thus they desired recognition and acceptance of this. The need for acceptance and respect was also identified in previous studies on returning nurses [ 27 , 30 ]. Appreciating their skills, efforts, and contributions while identifying areas for professional development represents the ideal “just-right preceptorship” for returners. Organizational support of this nature promotes work engagement [ 48 ], thus sustaining their professional practice.
While the existing literature commonly highlights the enablers necessary for nurses to return to work and continue their professional roles, previous studies have overlooked the motivating factors that drive them to work. Merely creating a sustainable environment for their return is insufficient. Internal drivers are essential to maintain their motivation to work, especially during challenging times. The following three themes describe the motivators that encourage nurses to pursue their professional careers, thus enriching their professional life.
“Pride in reconnecting with and contributing to society” stimulates nurses’ work motivation and enriches their professional lives. Previous studies have demonstrated that returning to work helps them regain self-esteem through their contribution to society, increasing pride as valuable society members [ 35 , 36 ]. This study contributed new knowledge by highlighting how this sense of pride motivates returning nurses to pursue their professional careers. Nurses who had previously been inactive cited the desire to utilize their qualifications and contribute to the welfare of society as the main reason for returning to work [ 16 ]. They took pride in being nurses and were eager to apply their professional knowledge and skills, supported by their abundant clinical experience. This aligns with previous studies emphasizing their high levels of clinical and leadership skills [ 20 , 28 ] and the enthusiasm exhibited by returners [ 30 ]. While initially struggling to adjust, their experience enables them to quickly adapt [ 33 ]. Once they regain competence, they contribute to healthcare and society by providing competent nursing care, educating colleagues, and serving as successful examples for potential returners. These experiences may instill a career calling characterized by self-actualization, personal fulfillment, and passion for their work [ 49 ], which promote job satisfaction [ 50 ] and engagement [ 51 ]. Returning to work also allows them to establish their societal position and expand their network, which is limited when solely fulfilling household responsibilities. According to the Self-Determination Theory [ 52 ], relating to others by engaging in employment outside the home not only alleviates isolation but also enhances their motivation. Additionally, contributing to society as valued members of the healthcare profession enhances their self-esteem [ 36 ] and allows them to cultivate a professional identity. If their children or significant others take pride in the nursing profession, their identification with nursing becomes stronger. During the COVID-19 pandemic, nurses were portrayed as heroes combating the crisis, which enhanced their professional identity and the pride their families had in them. Professional identity is known to enhance individual motivation to remain in the profession [ 53 , 54 ]. Therefore, reconnecting with and making contributions to society enrich nurses’ professional lives.
“Cultivating confidence through incremental professional development and future envisioning” represents another motivator that enriches the professional lives of returners. Previous studies have shown the struggles and challenges that returning nurses faced in their journey towards reintegration, and in reaffirming their identity as nursing professionals [ 28 , 31 , 35 ]. When restarting their careers, returning nurses often experience anxiety due to changes within healthcare institutions, such as the introduction of new medical equipment and technology, shifts in insurance policies, increased demands for high-level physical assessment skills, and the expanded scope of responsibilities they now carry [ 55 ]. Nevertheless, the participants in this study successfully overcame numerous challenges and navigated the journey of reintegration. This experience of triumph and the acquisition of new knowledge and skills enabled them to regain the confidence they had in their previous career. Reflecting on their hard work and learning trajectory also instilled a sense of professional growth. Possessing confidence and a sense of self-worth has enhanced their self-efficacy, which, in turn, has promoted affective organizational commitment [ 56 ] and work engagement [ 57 ]. Furthermore, a successful reintegration fulfills their need for competence, thereby bolstering their motivation [ 52 ]. In addition. their learning achievements foster expectations for their future career goals. Having a clear goal enhances their professional development and further enriches their professional life. This study contributes new insights by demonstrating that perceiving their own professional development and embracing future goals motivates them to continue their work.
The final theme, “Enrichment of my own and family’s life,” highlights the reciprocity between personal and professional aspects for returners. Returning to work enables a balanced lifestyle, which improves mental and physical health and reduces strain and fatigue for double-duty caregivers. Employment also provides financial stability and enriches personal life, aligning with the previous findings [ 35 ]. Financial incentives are often cited as reasons for nurses to consider returning [ 23 , 33 ]. While extrinsic, these incentives improve individuals’ quality of life, enriching their minds and energizing their work. Furthermore, work positively influences family dynamics, countering feelings of guilt at leaving children, often portrayed as a negative consequence of returning to work [ 31 ]. The participants in this study recognized the benefits, such as positive effects on their children’s healthy development, and how it led to an improved relationship with their children. Another study also observes a positive reciprocal relationship between work and family [ 35 ]. The theory of work-family enrichment asserts that " experiences in one role improve the quality of life in the other role” [ 58 ]. Work enriches personal life, while fulfillment in personal life motivates job continuation. Positive family experiences also enhance work performance [ 59 ]. Enrichment of personal life forms the foundation for individual professional life, and vice versa. This study reveals a new insight: returning to work can yield positive outcomes for nurses’ own lives and those of their families, particularly concerning child development.
Implications for nursing management
The findings of this study suggest that in order to retain returners in the current nursing force, it is imperative to maximize both the enablers and motivators that contribute to the sustainability and enrichment of their personal and professional lives. In order to maximize the enablers, the establishment of a family-friendly environment is crucial. Nurse managers should strive to comprehend the personal and professional lifestyles that returners desire and should provide support accordingly. Furthermore, the formation of a mutual support group among returners can facilitate the exchange of experiences and encouragement, as well as make it possible to accommodate shift changes when family-related issues arise. The provision of adequate training is also of paramount importance. Unlike new graduate nurses, returning nurses possess diverse nursing skills and experience, necessitating a comprehensive evaluation by managers and colleagues to determine their competencies, while simultaneously providing them with the necessary knowledge and skills required for current clinical practice.
To enhance motivators, nursing managers should actively encourage returners to revive their professional pride and sense of fulfillment as nurses. One effective approach involves providing positive and constructive feedback on their contributions to the well-being of patients, thereby bolstering their pride. Additionally, managers need to assist returners in regaining their confidence and should support their progress toward achieving personal goals. Encouraging self-reflection on their clinical experiences can serve as a powerful means to help them realize the extent of their growth and subsequently enhance their confidence [ 31 ]. Assisting them in setting future professional goals represents another important strategy. Finally, managers should help returners recognize the positive changes that have occurred in their family dynamics as a result of their return to work. Engaging in discussions about personal life with managers or other returners may prove beneficial in this regard.
Limitations
Efforts were made to enhance the transferability of the findings, by recruiting a heterogeneous sample of returning nurses, considering factors such as the duration of their career breaks, the length of clinical experience after returning, their employment status, and their area of practice. However, it cannot be assured that our sample is truly representative of Japanese returning nurses due to the relatively limited number of participants in this study. To enhance the transferability of the results, future studies should aim to replicate this research by encompassing diverse characteristics of returning nurses from various geographical locations. This approach would facilitate the aggregation of findings and the formulation of more robust programs designed to promote the retention of re-entering nurses.
The nursing shortage is a persistent issue that is anticipated to worsen in the foreseeable future. The available solutions to alleviate this problem are limited, and a cost-effective approach involves incentivizing inactive nurses to rejoin the nursing workforce [ 60 ]. Returning nurses constitute a valuable asset for hospitals, as they possess a renewed professional commitment and can quickly regain nursing competence. Furthermore, their diverse experience in various clinical areas and organizations has the potential to introduce innovative clinical and managerial solutions within the current healthcare setting, thereby enhancing clinical outcomes and improving patient satisfaction. Therefore, it is imperative to implement multi-dimensional approaches aimed at retaining and harnessing the potential of these valuable human resources.
Data availability
The data are not publicly available because they contain information that could compromise the privacy of the research participants.
World Health Organization, State of the world’s nursing 2020: investing in education, jobs and leadership. 2020. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240003279 .
International Council of Nurses. Ageing well? Policies to support older nurses at work. 2020. https://www.icn.ch/sites/default/files/inline-files/Ageing%20ICNM%20Report%20December%209%202020.pdf .
International Council of Nurses. The Global Nursing shortage and Nurse Retention. 2022. https://www.icn.ch/sites/default/files/inline-files/ICN%20Policy%20Brief_Nurse%20Shortage%20and%20Retention_0.pdf .
Foundation TH. T.H., REAL Centre Workforce Pressure points: Building the NHS nursing workforce in England 2020. https://www.health.org.uk/sites/default/files/upload/publications/2020/NursingReport_WEB.pdf .
Lucker P, Henning E, Hoffmann W. To come back or not to come back during the coronavirus crisis-A cross-sectional online survey of inactive nurses. J Adv Nurs. 2022;78(11):3687–95.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Australian College of Nursing. (n.d.). Graduate Certificate in Nursing (Bridging and Re-entry). Accessed Nov 10th, 2023. https://www.acn.edu.au/education/postgraduate-course/nursing-re-entry?gclid=EAIaIQobChMInsvp8qy4ggMV0WgPAh1_yw4WEAAYASAAEgJjh_D_BwE .
National Health Service. (n.d.). The return to nursing practice programme. Accessed Nov 10th, 2023. https://www.healthcareers.nhs.uk/explore-roles/nursing/returning-nursing/returning-nursing/return-nursing-practice-programme/return-nursing-practice-programme .
Borgfeld JK. A registered nurse refresher course: serving the community. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2014;45(2):77–82.
Davidhizar RE, Bartlett D. Re-entry into the registered nursing work force: we did it! J Contin Educ Nurs. 2006;37(4):185–90.
McLean T, Anema M. Reduce the nursing shortage: help inactive nurses return to work. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2004;35(5):211–5.
Department of Health and Social Care. How the NHS is supporting nurses to return to practice. DHSC Healthcare leaders. 2022. https://healthcareleaders.blog.gov.uk/2022/03/21/how-the-nhs-is-supporting-nurses-to-return-to-practice/ .
Cabinet Office Japan. White Paper on the Ageing Society 2023. 2023. https://www8.cao.go.jp/kourei/whitepaper/w-2023/zenbun/pdf/1s1s_01.pdf (in Japanese).
American Association of Colleges of Nursing. Fact Sheet: Nursing Shortage. 2022; https://www.aacnnursing.org/Portals/0/PDFs/Fact-Sheets/Nursing-Shortage-Factsheet.pdf .
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. 11th Subcommittee on Nursing Staff Supply and Demand. 2019. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/newpage_07019.html (in Japanese).
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Survey of enrollment and employment of graduates of nursing and other training schools. 2022. https://www.e-stat.go.jp/index.php/stat-search/files?toukei=00450141&tstat=000001022606&cycle=8&tclass1=000001168648&tclass2=000001168649&layout=datalist&page=1&tclass3val=0 (in Japanese).
Japanese Nursing Association. Hospital Nursing and Outpatient Nursing Fact-Finding Survey Report 2021. 2022; https://www.nurse.or.jp/nursing/home/publication/pdf/research/97.pdf . (in Japanese).
Kobayashi M, Igarashi A, Ikeda S. A study on the factors affecting the estimation of nursing staff supply amd demand and the verification of evidence in response to new nursing staff workforce styles. Report for Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research by the Ministry of Heath, Labour and Welfare . 2020. (in Japanese).
Castner J, et al. National Estimates of the Reserve Capacity of Registered nurses not currently employed in nursing and emergency nursing job mobility in the United States. Ann Emerg Med. 2021;78(2):201–11.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Auffenberg J, Becka D, Evans M, Kokott N, Schleicher S, Braun E. Ich pflege wieder, wenn… Potenzialanalyse zur Berufsrückkehr und Arbeitszeitaufstockung von Pflegefachkräften. 2022. Available from https://arbei tnehm erkam mer.de/filea dmin/user_uploa d/Downl oads/Polit ik/Rente_ Gesun dheit_Pfleg e/Bunde sweite_Studie_Ich_pflege_wieder_wenn_Langf assung.pdf.
Yu HY, et al. Nurse administrators’ intentions and considerations in recruiting inactive nurses. J Nurs Manag. 2016;24(5):589–97.
Reed JM. Learning from non-practicing registered nurses. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2022;53(11):486–90.
Jamieson I, Taua C. Leaving from and returning to nursing practice: contributing factors. Nurs Prax N Z. 2009;25(2):15–27.
PubMed Google Scholar
Hammer VR, Craig GP. The experiences of inactive nurses returned to nursing after completing a refresher course. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2008;39(8):358–67.
Curtis P, Schneidenbach L. Brief: successful strategies for a reentry program–one example. J Contin Educ Nurs. 1991;22(1):36–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Japanese Nursing Association. Report for a survey on the employment intentions of inactive and retired nursing staff. 2007. https://www.nurse-center.net/nccs/scontents/sm01/SM010801_S1801.html (in Japanese).
Tanaka S, Serizawa T, Sakaguchi C. Career redevelopment programmes for inactive nurses in Japan. J Clin Nurs. 2008;17(24):3296–305.
Elwin C. Returning to nursing practice: a learning journey. Contemp Nurse. 2007;24(2):203–11.
Mohammadi N, et al. Struggle turning back to professional nursing practice in Iran: a qualitative study. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2021;26(1):75–80.
Chen K, et al. Work stress in nurses returning to tertiary a general hospitals in China after the delivery of their second child: a cross-sectional study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):492.
Long J, West S. Returning to nursing after a career break: elements of successful re-entry. Australian J Adv Nurs. 2007;25(1):49–55.
Google Scholar
Asselin M, Osterman P, Cullen HA. In their own words: the experience of returning to acute care practice. J Nurses Staff Dev. 2006;22(3):104–11. quiz 112-3.
Tomita M, et al. Issues and curriculum development from the implementation of a support course for inactive nurses returning to the workforce. Kangokanri. 2008;18(2):118–24. (in Japanese).
Barriball KL, et al. Evaluation of return to practice: the views of nurse returnees from three NHS hospital trusts. J Nurs Manag. 2007;15(4):433–41.
Durand MA, Randhawa G. Nurses’ views about returning to practice after a career break. Br J Nurs. 2002;11(7):477–85.
Costantini A, et al. Return to work after prolonged maternity leave. An interpretative description. Women’s Studies International Forum; 2022. p. 90.
Khalil A, Davies N. The experience of nurses returning to work after childbirth: ‘making a difference’. J Nurs Adm Manag. 2000;8(6):337–44.
Article Google Scholar
Sandelowski M. Whatever happened to qualitative description? Res Nurs Health. 2000;23(4):334–40.
Sandelowski M. What’s in a name? Qualitative description revisited. Res Nurs Health. 2010;33(1):77–84.
Doyle L, et al. An overview of the qualitative descriptive design within nursing research. J Res Nurs. 2020;25(5):443–55.
Kim H, Sefcik JS, Bradway C. Characteristics of qualitative descriptive studies: a systematic review. Res Nurs Health. 2017;40(1):23–42.
Miles MB, Huberman AM, Saldana J. Qualitative data analysis: a methods Source Book Fourth Edition. SAGE; 2020.
Lincoln YS, Guba EG. Naturalistic inquiry.1985. CA: Sage.
Herzberg F, Mausner B, Snyderman B. The motivation to work. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley; 1959.
Detaille SI, et al. Supporting double Duty Caregiving and Good Employment practices in Health Care within an Aging Society. Front Psychol. 2020;11:535353.
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Results of the Survey on the Employment Situation of Nursing Staff. 2011. https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/houdou/2r98520000017cjh.html (in Japanese).
Cabinet Office Japan. The White Paper on Gender Equality 2023. 2023. https://www.gender.go.jp/about_danjo/whitepaper/r04/gaiyou/pdf/r04_gaiyou_en.pdf .
Benner P. From novice to expert: excellence and power in clinical nursing practice, 1984. Menlo Park, CA, Addison-Wesley.
Al-Hamdan Z, Bani H, Issa. The role of organizational support and self-efficacy on work engagement among registered nurses in Jordan: a descriptive study. J Nurs Manag. 2022;30(7):2154–64.
Zhang L, Guo X. Social Support on calling: mediating role of work engagement and professional identity. Career Dev Quartely. 2023;71:97–110.
Huang X, et al. Career calling as the Mediator and Moderator of Job demands and Job resources for job satisfaction in Health workers: a cross-sectional study. Front Psychol. 2022;13:856997.
Erum H, Abid G, Contreras F. THE CALLING OF EMPLOYEES AND WORK ENGAGEMENT: THE ROLE OF FLOURISHING AT WORK. Bus Manage Educ. 2020;18(1):14–32.
Reeve J, Deci E, Ryan R. Self-determination theory: a dialectical framework for understanding sociocultural influences on student motivation. In: McInerney D, Van Etten S, editors. Research on sociocultural influences on motivation and learning: big theories revisited. Greewich, CT: Information Age; 2004. pp. 31–59.
Hanum AL, et al. Professional identity, job satisfaction, and intention to stay among clinical nurses during the prolonged COVID-19 pandemic: a mediation analysis. Jpn J Nurs Sci. 2023;20(2):e12515.
Jiang H, et al. Professional identity and turnover intentions of social workers in Beijing, China: the roles of job satisfaction and agency type. Int Social Work. 2019;62:146–60.
Burns HK, et al. Returning nurses to the workforce: developing a fast track back program. Nurs Forum. 2006;41(3):125–32.
Orgambídez A, Borrego Y, Vázquez-Aguado O. Self-efficacy and organizational commitment among Spanish nurses: the role of work engagement. Int Nurs Rev. 2019;66(3):381–8.
Heng Q, Chu L. Self-efficacy, reflection, and resilience as predictors of work engagement among English teachers. Front Psychol. 2023;14:1160681.
Greenhaus JH, Powell GN. When work and family are allies: a theory of work-family enrichment. Acad Manage Rev. 2006;31(1):72–92.
Savard YP. Work-family spillover of daily positive affect onto performance: the moderating role of domain identity salience. Eur Rev Appl Psychology-Revue Europeenne De Psychologie Appliquee, 2023. 73(2).
Randolph P. Employment patterns in RN refresher graduates: a 4-year follow-up. J Nurs Regul. 2013;3(4):60–1.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the participants for participating in the study and for sharing their experiences.
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 22K10697. The funder had no role in the conceptualization, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Nursing, Yasuda Women’s University, 6-13-1, Yasuhigashi, Asaminami-ku, 731-0153, Hiroshima, Japan
Kumiko Yamamoto, Katsumi Nasu, Yoko Nakayoshi & Miyuki Takase
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KY designed this study under the supervision of MT. KY performed the data collection and the initial data analysis. KY, KN, YN and MT contributed to the data analysis. KY, KN and MT wrote the manuscript. All co-authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Miyuki Takase .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Review Board of Yasuda Women’s University (approval number: 210007). This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The participants were fully informed about the study’s purpose, methods, potential risks, and benefits of participation as well as their right to decline participation or withdraw from the study. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant before the data collection. The collected data were securely stored in a locked cabinet, and pseudonyms were used throughout the paper to maintain the participants’ anonymity and protect their privacy.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Yamamoto, K., Nasu, K., Nakayoshi, Y. et al. Sustaining the nursing workforce - exploring enabling and motivating factors for the retention of returning nurses: a qualitative descriptive design. BMC Nurs 23 , 248 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01900-5
Download citation
Received : 16 October 2023
Accepted : 29 March 2024
Published : 17 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01900-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Returning nurses
- Enabling factors
- Motivating factors
- Qualitative descriptive design
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Edinburgh Research Archive

- ERA Home
- Business School
- Business and Management thesis and dissertation collection
Systematic approach to work-life balance research: theoretical development and empirical examination
Collections.
- Help & FAQ
Wellbeing, Work-Life Balance and the Quality of Working Life in the New World of Hybrid Work
- Business School
- Organisation Studies
- Leadership, Organisations and Society
Research output : Contribution to conference › Abstract › peer-review
Abstract / Description of output
Other files and links.
- https://britsoc.co.uk/media/25566/wes2021_abstract_book.pdf
Fingerprint
- Work-Family Conflict Social Sciences 100%
- Quality of Working Life Social Sciences 100%
- Work Social Sciences 100%
- Work-Life Balance Psychology 100%
- Wellbeing Psychology 100%
- Workers Social Sciences 36%
- Home-Based Work Social Sciences 32%
- Support Social Sciences 20%
T1 - Wellbeing, Work-Life Balance and the Quality of Working Life in the New World of Hybrid Work
AU - Skountridaki, Lila
AU - Marks, Abigail
AU - Mallett, Oliver
PY - 2021/8/25
Y1 - 2021/8/25
N2 - Real wage suppression and underemployment are persisting trends in the UK labour market for over a decade (Blanchflower 2019). The COVID-19 pandemic one year long home-based work experience for a large portion of the UK workforce (ONS 2020) has made home-based work an appealing work arrangement to both employers and employees: from a largely ‘on-papers-only’ option until the pandemic, hybrid work now features as the ‘future’ of (desk-based) work (Walker 2021). How can the quality of working life (Warhurst and Knox 2020), however, be best promoted in the new world of hybrid work? Our UKRI/ESRC funded working@home study highlights that the majority of workers wish to partially continue working from home. Yet, it also suggests that organisational support is crucial for workers’ wellbeing and work-life balance when working at home. Repeated qualitative interviews with 80 home-workers and data from nearly 2800 responses to two UK-wide surveys, suggest that those workers who are very satisfied with the organisational IT support and support to adjust their work station at home, report higher levels of wellbeing and work-life balance. Simultaneously, our findings show that the majority of home-workers have invested in equipment, furniture, and the physical space to improve the quality of their home office (e.g. light, heating, sound and audio/visual distractions, view etc.) and, thus, the quality of their working life. These findings coupled with the potential savings that organisations will make from increased home-based work due to the reduced use of office space and increased productivity, suggest that employers have a responsibility and duty to support workers who will engage in hybrid work patterns. At the same time, our study participants’ experience of home-based work largely depends on the local infrastructure. For example, the perceived quality of the internet (a good internet connection improves the experience of home-based work) and that of transportation (expensive and unreliable transport is linked to an increased desire to work from home) are crucial factors in workers’ desire and ability to engage in remote / home-based work. These findings highlight the necessity of state intervention to improve the experience of home-based work. Warhurst and Knox (2020) in their manifesto for the quality of working life make a compelling argument for establishing and monitoring minimum job quality standards overseen by a regulatory governmental authority. In the aftermath of the pandemic, which has arguably redefined the locus of work for a large portion of the workforce, there is a real danger that employers will internalise benefits of home-based work (such as increased productivity), externalise operational costs to workers (such as utility bills), and neglect the new types of support needed for wellbeing and work-life balance in hybrid work arrangements. This paper echoes Warhurst and Knox’s (2020) call for minimum standards to ensure the quality of working life and suggests that the new locus of work implies that new understandings of the quality of work are necessary, if workers are to meaningfully enjoy a share in the benefits of hybrid work patterns.
AB - Real wage suppression and underemployment are persisting trends in the UK labour market for over a decade (Blanchflower 2019). The COVID-19 pandemic one year long home-based work experience for a large portion of the UK workforce (ONS 2020) has made home-based work an appealing work arrangement to both employers and employees: from a largely ‘on-papers-only’ option until the pandemic, hybrid work now features as the ‘future’ of (desk-based) work (Walker 2021). How can the quality of working life (Warhurst and Knox 2020), however, be best promoted in the new world of hybrid work? Our UKRI/ESRC funded working@home study highlights that the majority of workers wish to partially continue working from home. Yet, it also suggests that organisational support is crucial for workers’ wellbeing and work-life balance when working at home. Repeated qualitative interviews with 80 home-workers and data from nearly 2800 responses to two UK-wide surveys, suggest that those workers who are very satisfied with the organisational IT support and support to adjust their work station at home, report higher levels of wellbeing and work-life balance. Simultaneously, our findings show that the majority of home-workers have invested in equipment, furniture, and the physical space to improve the quality of their home office (e.g. light, heating, sound and audio/visual distractions, view etc.) and, thus, the quality of their working life. These findings coupled with the potential savings that organisations will make from increased home-based work due to the reduced use of office space and increased productivity, suggest that employers have a responsibility and duty to support workers who will engage in hybrid work patterns. At the same time, our study participants’ experience of home-based work largely depends on the local infrastructure. For example, the perceived quality of the internet (a good internet connection improves the experience of home-based work) and that of transportation (expensive and unreliable transport is linked to an increased desire to work from home) are crucial factors in workers’ desire and ability to engage in remote / home-based work. These findings highlight the necessity of state intervention to improve the experience of home-based work. Warhurst and Knox (2020) in their manifesto for the quality of working life make a compelling argument for establishing and monitoring minimum job quality standards overseen by a regulatory governmental authority. In the aftermath of the pandemic, which has arguably redefined the locus of work for a large portion of the workforce, there is a real danger that employers will internalise benefits of home-based work (such as increased productivity), externalise operational costs to workers (such as utility bills), and neglect the new types of support needed for wellbeing and work-life balance in hybrid work arrangements. This paper echoes Warhurst and Knox’s (2020) call for minimum standards to ensure the quality of working life and suggests that the new locus of work implies that new understandings of the quality of work are necessary, if workers are to meaningfully enjoy a share in the benefits of hybrid work patterns.
UR - https://britsoc.co.uk/media/25566/wes2021_abstract_book.pdf
M3 - Abstract
T2 - BSA Work, Employment and Society Conference 2021
Y2 - 25 August 2021 through 27 August 2021
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
This article is part of the research topic.
Women and Mental Health in Education and Leadership
Work-life integration among nurse educators: A meta-synthesis Provisionally Accepted

- 1 University of Johannesburg, South Africa
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Background: Work-life integration has been extensively researched in various contexts.Women dominate the nursing profession, but work-life integration is essential for men and women since both are expected to focus equally on their families and careers. The nursing faculty perceives nurse educators' work environment as undervalued, lacking support, and limited time to grow and carry the heavy workload.Method: A qualitative meta-synthesis of studies between 2013 and 2023 was conducted using ScienceDirect, EBSCO Host, Sage and Sabinet databases. Seven articles related to the research phenomenon were retrieved.The resulting themes revolved around two central aspects: nurse educators' work and life integration. Nurse educators face various challenges with work-life integration and often view their failure as a personal rather than a societal issue. However, as much as achieving work-life integration is personal, there is a call for employers in academic environments to improve workplace policies, like better-paid maternity leave, affordable quality childcare, and social support. Furthermore, nurse educators' line managers should display warmth and encouragement about personal challenges affecting nurse educators.
Keywords: work-life balance, Nurse educator, Systematic review, Faculty (MeSH), nurse academic
Received: 01 Sep 2023; Accepted: 25 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Erasmus, Downing and Ntshingila. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Prof. Charlene Downing, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, 2092, Gauteng, South Africa
People also looked at
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
About a third of U.S. workers who can work from home now do so all the time

Roughly three years after the COVID-19 pandemic upended U.S. workplaces, about a third (35%) of workers with jobs that can be done remotely are working from home all of the time, according to a new Pew Research Center survey. This is down from 43% in January 2022 and 55% in October 2020 – but up from only 7% before the pandemic.
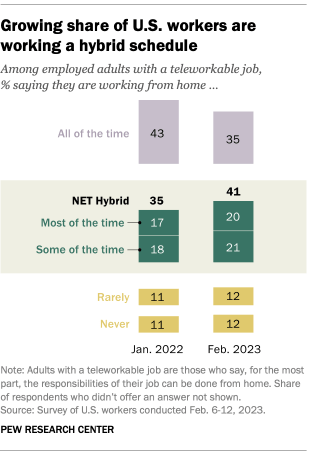
While the share working from home all the time has fallen off somewhat as the pandemic has gone on, many workers have settled into hybrid work. The new survey finds that 41% of those with jobs that can be done remotely are working a hybrid schedule – that is, working from home some days and from the office, workplace or job site other days. This is up from 35% in January 2022.
Among hybrid workers who are not self-employed, most (63%) say their employer requires them to work in person a certain number of days per week or month. About six-in-ten hybrid workers (59%) say they work from home three or more days in a typical week, while 41% say they do so two days or fewer.
Related: How Americans View Their Jobs
Many hybrid workers would prefer to spend more time working from home than they currently do. About a third (34%) of those who are currently working from home most of the time say, if they had the choice, they’d like to work from home all the time. And among those who are working from home some of the time, half say they’d like to do so all (18%) or most (32%) of the time.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to study how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected the workplace and specifically how workers with jobs that can be done from home have adapted their work schedules. To do this, we surveyed 5,775 U.S. adults who are working part time or full time and who have only one job or who have more than one job but consider one of them to be their primary job. All the workers who took part are members of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses.
Address-based sampling ensures that nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and the survey’s methodology .
The majority of U.S. workers overall (61%) do not have jobs that can be done from home. Workers with lower incomes and those without a four-year college degree are more likely to fall into this category. Among those who do have teleworkable jobs, Hispanic adults and those without a college degree are among the most likely to say they rarely or never work from home.
When looking at all employed adults ages 18 and older in the United States, Pew Research Center estimates that about 14% – or roughly 22 million people – are currently working from home all the time.
The advantages and disadvantages of working from home
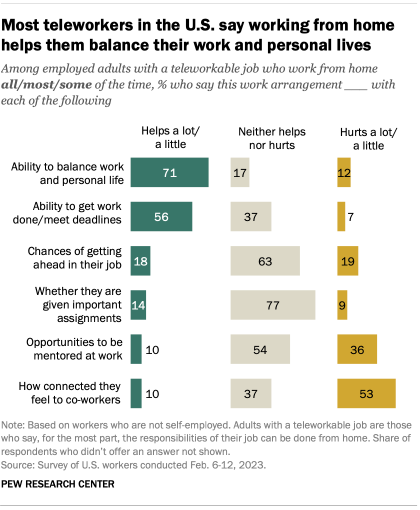
Workers who are not self-employed and who are teleworking at least some of the time see one clear advantage – and relatively few downsides – to working from home. By far the biggest perceived upside to working from home is the balance it provides: 71% of those who work from home all, most or some of the time say doing so helps them balance their work and personal lives. That includes 52% who say it helps them a lot with this.
About one-in-ten (12%) of those who are at least occasionally working from home say it hurts their ability to strike the right work-life balance, and 17% say it neither helps nor hurts. There is no significant gender difference in these views. However, parents with children younger than 18 are somewhat more likely than workers without children in that age range to say working from home is helpful in this regard (76% vs. 69%).
A majority of those who are working from home at least some of the time (56%) say this arrangement helps them get their work done and meet deadlines. Only 7% say working from home hurts their ability to do these things, and 37% say it neither helps nor hurts.
There are other aspects of work – some of them related to career advancement – where the impact of working from home seems minimal:
- When asked how working from home affects whether they are given important assignments, 77% of those who are at least sometimes working from home say it neither helps nor hurts, while 14% say it helps and 9% say it hurts.
- When it comes to their chances of getting ahead at work, 63% of teleworkers say working from home neither helps or hurts, while 18% say it helps and 19% say it hurts.
- A narrow majority of teleworkers (54%) say working from home neither helps nor hurts with opportunities to be mentored at work. Among those who do see an impact, it’s perceived to be more negative than positive: 36% say working from home hurts opportunities to be mentored and 10% say it helps.
One aspect of work that many remote workers say working from home makes more challenging is connecting with co-workers: 53% of those who work from home at least some of the time say working from home hurts their ability to feel connected with co-workers, while 37% say it neither helps nor hurts. Only 10% say it helps them feel connected.
In spite of this, those who work from home all the time or occasionally are no less satisfied with their relationship with co-workers than those who never work from home. Roughly two-thirds of workers – whether they are working exclusively from home, follow a hybrid schedule or don’t work from home at all – say they are extremely or very satisfied with these relationships. In addition, among those with teleworkable jobs, employed adults who work from home all the time are about as likely as hybrid workers to say they have at least one close friend at work.
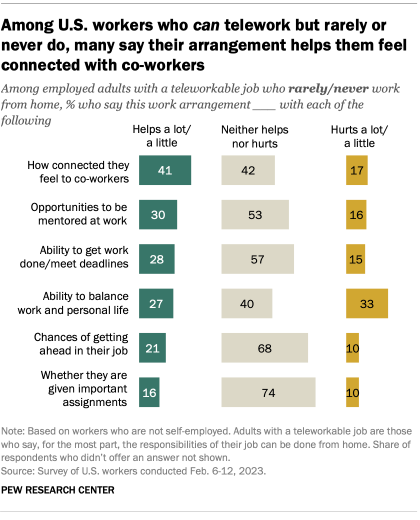
Feeling connected with co-workers is one area where many workers who rarely or never work from home see an advantage in their setup. About four-in-ten of these workers (41%) say the fact that they rarely or never work from home helps in how connected they feel to their co-workers. A similar share (42%) say it neither helps nor hurts, and 17% say it hurts.
At the same time, those who rarely or never work from home are less likely than teleworkers to say their current arrangement helps them achieve work-life balance. A third of these workers say the fact that they rarely or never work from home hurts their ability to balance their work and personal lives, while 40% say it neither helps nor hurts and 27% say it helps.
When it comes to other aspects of work, many of those who rarely or never work from home say their arrangement is neither helpful nor hurtful. This is true when it comes to opportunities to be mentored (53% say this), their ability to get work done and meet deadlines (57%), their chances of getting ahead in their job (68%) and whether they are given important assignments (74%).
Most adults with teleworkable jobs who work from home at least some of the time (71%) say their manager or supervisor trusts them a great deal to get their work done when they’re doing so. Those who work from home all the time are the most likely to feel trusted: 79% of these workers say their manager trusts them a great deal, compared with 64% of hybrid workers.
Hybrid workers feel about as trusted when they’re not working from home: 68% say their manager or supervisor trusts them a great deal to get their work done when they’re not teleworking.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis, along with responses, and the survey’s methodology .
- Business & Workplace
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)

Kim Parker is director of social trends research at Pew Research Center
A look at small businesses in the U.S.
Majorities of adults see decline of union membership as bad for the u.s. and working people, a look at black-owned businesses in the u.s., from businesses and banks to colleges and churches: americans’ views of u.s. institutions, 2023 saw some of the biggest, hardest-fought labor disputes in recent decades, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To date, research directed at the work-life balance (WLB) has focused mainly on the work and family domains. However, the current labor force is heterogeneous, and workers may also value other nonworking domains besides the family. The aim of this study was to investigate the importance of other nonworking domains in the WLB with a particular ...
Abstract. Work-life balance is considered to be important for both, business practice and academic research. The literature shows that work-life balance is a central issue affecting wellbeing, as ...
This study systematically synthesizes the existing literature on work-life balance ... Qualitative Research Journal, 14(3), 289-306. Crossref. ... Perceptions of academic administrators of the effect of involvement in doctoral programs on faculty members' research and work-life balance. Nursing Outlook, 65(6), 753-760. Crossref. PubMed.
Most research on work-life balance concentrates on the experiences of the mothers of young children. However, lack of work-life balance is a problem for men as well as women, and for the parents of older, as well as preschool, children (Chandola et al., 2004; Emslie et al., 2004a). Our research contributes to the literature in exploring the ...
Work-life balance is a contemporary and interdisciplinary issue that has received immense attention in scholarly work, social circles and media (Brough et al., 2020; Muasya, 2021).Task forces in various sectors have sought to find solutions to work-life balance issues, eliciting many suggestions, contradictions and dilemmas on the appropriate way forwards (Mokomane et al., 2017; Poelmans et al ...
Introduction. In this technological era, work is becoming demanding with changing nature of work and working patterns (Thilagavathy and Geetha, 2020).The proactive, aggressive and demanding nature of business with the intention of reaching the top requires active involvement and comprehensive devotion from the employees, thereby compromising their work-life balance (WLB) (Turanlıgil and ...
Research conducted during the pandemic suggests that adequate workspace at home - characterized as good physical conditions, free from distraction and noise - was a key to employees' successful adjustment to remote work and to their work-life balance (Akuoko, Aggrey, and Dokbila Mengba Citation 2021; Carillo et al. Citation 2021; Craig ...
Abstract and Figures. Purpose The purpose of this paper is to provide a clear view of current dynamics and research diversification of extant literature in the field of work-life balance (WLB ...
A qualitative methodological approach was adopted, and data was collected through 36 semi-structured interviews and 2 focus groups with managerial and nonmanagerial employees from diverse occupational groups. The research found that work-life conflicts that affect employees work-life balance includes limited resources, workplace stress, poor ...
Within the last decade, changes in individuals' needs and work conditions have altered what constitutes a satisfactory work-life balance and how individuals manage their engagement in various life activities. In response to these changes, this paper presents a conceptual framework that integrates three established theories to develop a better understanding of what and how individuals are ...
The ability to reconcile work and private life is a pressing social issue - one driving a large body of academic research as well as government policy, employment legislation and organizational policy and practice (Abendroth and Den Dulk, 2011; Booney, 2005; Gerstal and Clawson, 2014; Kelly et al., 2014; Warren et al., 2009).The most familiar term, work-life balance, can be defined as a ...
Work-life balance (WLB) is a central concern in daily work and life discourse (Greenhaus et al., 2012). The definition of "work" is often straightforward while the concept of "life" is more diffuse. ... We employed an exploratory qualitative research approach due to the emphasis on how individuals interpret their social world (Bryman ...
This innovative and thought-provoking Research Handbook explores the theoretical debate surrounding work-life balance, and provides a reflection on the opportunity to adopt multilevel research approaches and perspectives, along gender and temporal axes. The Research Handbook is an international overview of current research on work-life balance, considered in macro, meso and micro perspectives.
The data analysis revealed five themes that facilitated the continuation of work for these participants. These themes include "Conditions and support that sustain work-life balance," "A workplace that acknowledges my career, and encourages my growth as an experienced nurse," "Pride in reconnecting with and contributing to society," "Cultivating confidence through incremental ...
1.1 Defining Work Life Balance Work life is a serious question in the modern age. Many books and research articles have been published on this topic. Work affects personal life and personal life affects working life. Work is important for the survival of human beings to satisfy basic needs, and work may also give a deeper meaning to people's ...
Women and work-life balance: a phenomenological qualitative analysis of identity, relational style, adaptive style, and drive and motivation, and the role of faith from the narrative life-story framework Elizabeth Krymis Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.pepperdine.edu/etd Recommended Citation
Work-life balance research has been extensively studied in Western contexts with a focus on high-income and industrialized societies. ... (see CHAPTER 5) is an exploratory qualitative study which advances a holistic perspective of work-life balance and offers a systematic analytical framework for explicating the contextualized relationships ...
The impacts of the work-life balance arrangement on organisational performance is a growing concern amongst researchers and practitioners. This study synthesised 202 records from 58 published ...
Cite this article: Liswandi. (2020). A Qualitative Exploration of Work-Life Balance: Experiences of Millennial Married Women Workers. International Journal of Management, Accounting and Economics, 7(3), 134-148. Introduction Work life balance is a topic of great interest and a matter of high priority these days
Repeated qualitative interviews with 80 home-workers and data from nearly 2800 responses to two UK-wide surveys, suggest that those workers who are very satisfied with the organisational IT support and support to adjust their work station at home, report higher levels of wellbeing and work-life balance. ... Dive into the research topics of ...
The purpose of this article is to unearth the dimensions of quality of work life and work-life balance and to find the impact of the quality of work life on work-life balance. Data have been gathered from 89 managers of public and private sector banks in India using a convenience sampling method and analysed using principal component ...
This paper is based on an understanding of work-life balance in which working life and private life are in a balanced ratio that corresponds to subjective needs. In the research to date on the factors influencing work-life balance, the relationship between work and family is examined bi-directionally.
Background: Work-life integration has been extensively researched in various contexts.Women dominate the nursing profession, but work-life integration is essential for men and women since both are expected to focus equally on their families and careers. The nursing faculty perceives nurse educators' work environment as undervalued, lacking support, and limited time to grow and carry the heavy ...
Finding a healthy work-life balance has always been a challenge. At one point, we thought tools like email, smartphones and AI would tip the scales, freeing up time people used to spend in the office.
Our five key findings are: (1) it is possible to balance work, studies and private life, (2) work-study balance (WSB) is critical for achieving WSLB, (3) all subgroups of students based on their ...
At the same time, those who rarely or never work from home are less likely than teleworkers to say their current arrangement helps them achieve work-life balance. A third of these workers say the fact that they rarely or never work from home hurts their ability to balance their work and personal lives, while 40% say it neither helps nor hurts ...