Hungarian Method
The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term “Hungarian method” to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let’s go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.

Hungarian Method to Solve Assignment Problems
The Hungarian method is a simple way to solve assignment problems. Let us first discuss the assignment problems before moving on to learning the Hungarian method.
What is an Assignment Problem?
A transportation problem is a type of assignment problem. The goal is to allocate an equal amount of resources to the same number of activities. As a result, the overall cost of allocation is minimised or the total profit is maximised.
Because available resources such as workers, machines, and other resources have varying degrees of efficiency for executing different activities, and hence the cost, profit, or loss of conducting such activities varies.
Assume we have ‘n’ jobs to do on ‘m’ machines (i.e., one job to one machine). Our goal is to assign jobs to machines for the least amount of money possible (or maximum profit). Based on the notion that each machine can accomplish each task, but at variable levels of efficiency.
Hungarian Method Steps
Check to see if the number of rows and columns are equal; if they are, the assignment problem is considered to be balanced. Then go to step 1. If it is not balanced, it should be balanced before the algorithm is applied.
Step 1 – In the given cost matrix, subtract the least cost element of each row from all the entries in that row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
Step 2 – In the resultant cost matrix produced in step 1, subtract the least cost element in each column from all the components in that column, ensuring that each column contains at least one zero.
Step 3 – Assign zeros
- Analyse the rows one by one until you find a row with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this lonely unmarked zero and assign it a task. All other zeros in the column of this circular zero should be crossed out because they will not be used in any future assignments. Continue in this manner until you’ve gone through all of the rows.
- Examine the columns one by one until you find one with precisely one unmarked zero. Encircle this single unmarked zero and cross any other zero in its row to make an assignment to it. Continue until you’ve gone through all of the columns.
Step 4 – Perform the Optimal Test
- The present assignment is optimal if each row and column has exactly one encircled zero.
- The present assignment is not optimal if at least one row or column is missing an assignment (i.e., if at least one row or column is missing one encircled zero). Continue to step 5. Subtract the least cost element from all the entries in each column of the final cost matrix created in step 1 and ensure that each column has at least one zero.
Step 5 – Draw the least number of straight lines to cover all of the zeros as follows:
(a) Highlight the rows that aren’t assigned.
(b) Label the columns with zeros in marked rows (if they haven’t already been marked).
(c) Highlight the rows that have assignments in indicated columns (if they haven’t previously been marked).
(d) Continue with (b) and (c) until no further marking is needed.
(f) Simply draw the lines through all rows and columns that are not marked. If the number of these lines equals the order of the matrix, then the solution is optimal; otherwise, it is not.
Step 6 – Find the lowest cost factor that is not covered by the straight lines. Subtract this least-cost component from all the uncovered elements and add it to all the elements that are at the intersection of these straight lines, but leave the rest of the elements alone.
Step 7 – Continue with steps 1 – 6 until you’ve found the highest suitable assignment.
Hungarian Method Example
Use the Hungarian method to solve the given assignment problem stated in the table. The entries in the matrix represent each man’s processing time in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix} & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\2 & 18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\3 & 21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\4 & 17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\5 & 18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
With 5 jobs and 5 men, the stated problem is balanced.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}20 & 15 & 18 & 20 & 25 \\18 & 20 & 12 & 14 & 15 \\21 & 23 & 25 & 27 & 25 \\17 & 18 & 21 & 23 & 20 \\18 & 18 & 16 & 19 & 20 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the lowest cost element in each row from all of the elements in the given cost matrix’s row. Make sure that each row has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 5 & 10 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 2 & 3 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 6 & 4 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 6 & 3 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 3 & 4 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Subtract the least cost element in each Column from all of the components in the given cost matrix’s Column. Check to see if each column has at least one zero.
\(\begin{array}{l}A = \begin{bmatrix}5 & 0 & 3 & 3 & 7 \\6 & 8 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 2 & 4 & 4 & 1 \\0 & 1 & 4 & 4 & 0 \\2 & 2 & 0 & 1 & 1 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
When the zeros are assigned, we get the following:
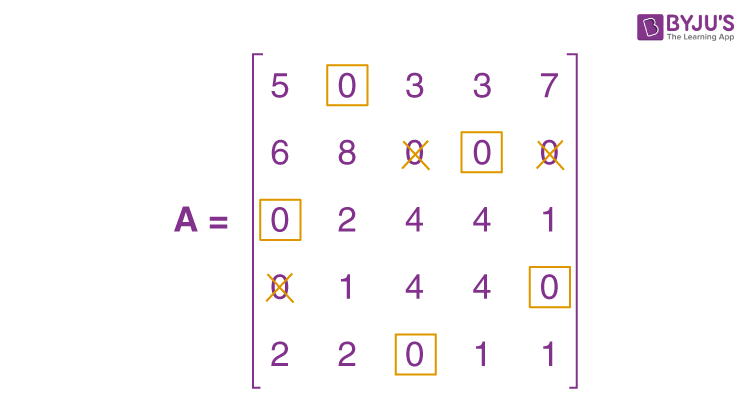
The present assignment is optimal because each row and column contain precisely one encircled zero.
Where 1 to II, 2 to IV, 3 to I, 4 to V, and 5 to III are the best assignments.
Hence, z = 15 + 14 + 21 + 20 + 16 = 86 hours is the optimal time.
Practice Question on Hungarian Method
Use the Hungarian method to solve the following assignment problem shown in table. The matrix entries represent the time it takes for each job to be processed by each machine in hours.
\(\begin{array}{l}\begin{bmatrix}J/M & I & II & III & IV & V \\1 & 9 & 22 & 58 & 11 & 19 \\2 & 43 & 78 & 72 & 50 & 63 \\3 & 41 & 28 & 91 & 37 & 45 \\4 & 74 & 42 & 27 & 49 & 39 \\5 & 36 & 11 & 57 & 22 & 25 \\\end{bmatrix}\end{array} \)
Stay tuned to BYJU’S – The Learning App and download the app to explore all Maths-related topics.
Frequently Asked Questions on Hungarian Method
What is hungarian method.
The Hungarian method is defined as a combinatorial optimization technique that solves the assignment problems in polynomial time and foreshadowed subsequent primal–dual approaches.
What are the steps involved in Hungarian method?
The following is a quick overview of the Hungarian method: Step 1: Subtract the row minima. Step 2: Subtract the column minimums. Step 3: Use a limited number of lines to cover all zeros. Step 4: Add some more zeros to the equation.
What is the purpose of the Hungarian method?
When workers are assigned to certain activities based on cost, the Hungarian method is beneficial for identifying minimum costs.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Procedure, Example Solved Problem | Operations Research - Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method) | 12th Business Maths and Statistics : Chapter 10 : Operations Research
Chapter: 12th business maths and statistics : chapter 10 : operations research.
Solution of assignment problems (Hungarian Method)
First check whether the number of rows is equal to the numbers of columns, if it is so, the assignment problem is said to be balanced.
Step :1 Choose the least element in each row and subtract it from all the elements of that row.
Step :2 Choose the least element in each column and subtract it from all the elements of that column. Step 2 has to be performed from the table obtained in step 1.
Step:3 Check whether there is atleast one zero in each row and each column and make an assignment as follows.
Step :4 If each row and each column contains exactly one assignment, then the solution is optimal.
Example 10.7
Solve the following assignment problem. Cell values represent cost of assigning job A, B, C and D to the machines I, II, III and IV.
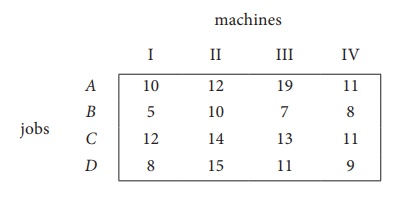
Here the number of rows and columns are equal.
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced. Now let us find the solution.
Step 1: Select a smallest element in each row and subtract this from all the elements in its row.
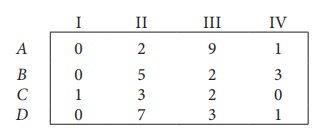
Look for atleast one zero in each row and each column.Otherwise go to step 2.
Step 2: Select the smallest element in each column and subtract this from all the elements in its column.
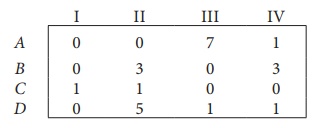
Since each row and column contains atleast one zero, assignments can be made.
Step 3 (Assignment):
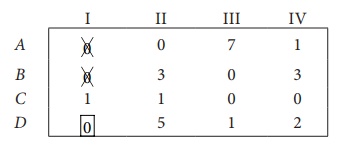
Thus all the four assignments have been made. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
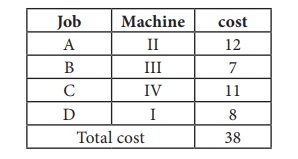
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost
Example 10.8
Consider the problem of assigning five jobs to five persons. The assignment costs are given as follows. Determine the optimum assignment schedule.
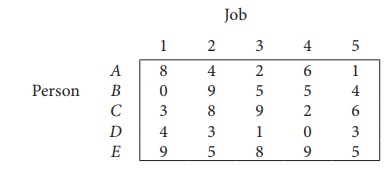
∴ The given assignment problem is balanced.
Now let us find the solution.
The cost matrix of the given assignment problem is
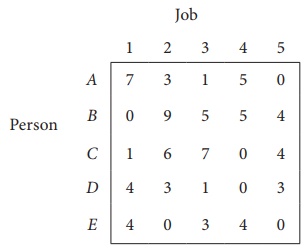
Column 3 contains no zero. Go to Step 2.
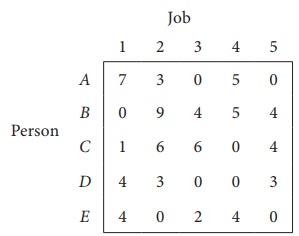
Thus all the five assignments have been made. The Optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
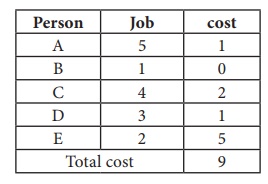
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ` 9
Example 10.9
Solve the following assignment problem.
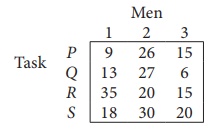
Since the number of columns is less than the number of rows, given assignment problem is unbalanced one. To balance it , introduce a dummy column with all the entries zero. The revised assignment problem is
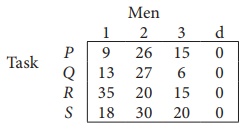
Here only 3 tasks can be assigned to 3 men.
Step 1: is not necessary, since each row contains zero entry. Go to Step 2.
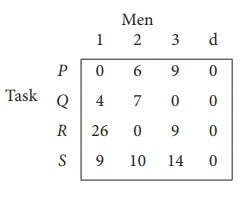
Step 3 (Assignment) :
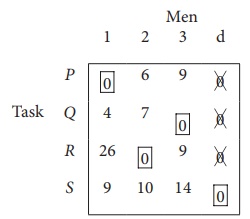
Since each row and each columncontains exactly one assignment,all the three men have been assigned a task. But task S is not assigned to any Man. The optimal assignment schedule and total cost is
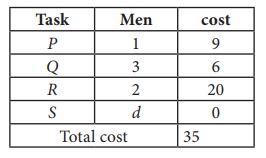
The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ₹ 35
Related Topics
Privacy Policy , Terms and Conditions , DMCA Policy and Compliant
Copyright © 2018-2024 BrainKart.com; All Rights Reserved. Developed by Therithal info, Chennai.
- Data Structures
- Linked List
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- Segment Tree
- Disjoint Set Union
- Fenwick Tree
- Red-Black Tree
- Advanced Data Structures
Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 2 (Implementation)
- Introduction to Exact Cover Problem and Algorithm X
- Greedy Approximate Algorithm for Set Cover Problem
- Job Assignment Problem using Branch And Bound
- Implementation of Exhaustive Search Algorithm for Set Packing
- Channel Assignment Problem
- Chocolate Distribution Problem | Set 2
- Transportation Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- OLA Interview Experience | Set 11 ( For Internship)
- Top 20 Greedy Algorithms Interview Questions
- Job Sequencing Problem - Loss Minimization
- Prim's Algorithm (Simple Implementation for Adjacency Matrix Representation)
- Data Structures and Algorithms | Set 21
- Adobe Interview Experience | Set 55 (On-Campus Full Time for MTS profile)
- Amazon Interview Experience | Set 211 (On-Campus for Internship)
- OYO Rooms Interview Experience | Set 3 (For SDE-II, Gurgaon)
- C# Program for Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm | Greedy Algo-7
- Algorithms | Dynamic Programming | Question 7
- Amazon Interview | Set 46 (On-campus for Internship)
- For each row of the matrix, find the smallest element and subtract it from every element in its row.
- Do the same (as step 1) for all columns.
- Cover all zeros in the matrix using minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.
- Test for Optimality: If the minimum number of covering lines is n, an optimal assignment is possible and we are finished. Else if lines are lesser than n, we haven’t found the optimal assignment, and must proceed to step 5.
- Determine the smallest entry not covered by any line. Subtract this entry from each uncovered row, and then add it to each covered column. Return to step 3.
Try it before moving to see the solution
Explanation for above simple example:
An example that doesn’t lead to optimal value in first attempt: In the above example, the first check for optimality did give us solution. What if we the number covering lines is less than n.
Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3).
Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional arrays of size n to store the labels, matches, and auxiliary information needed for the algorithm.
In the next post, we will be discussing implementation of the above algorithm. The implementation requires more steps as we need to find minimum number of lines to cover all 0’s using a program. References: http://www.math.harvard.edu/archive/20_spring_05/handouts/assignment_overheads.pdf https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQDZNHwuuOY
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Mathematical
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Business Essentials
Assignment Method: Examples of How Resources Are Allocated
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
What Is the Assignment Method?
The assignment method is a way of allocating organizational resources in which each resource is assigned to a particular task. The resource could be monetary, personnel , or technological.
Understanding the Assignment Method
The assignment method is used to determine what resources are assigned to which department, machine, or center of operation in the production process. The goal is to assign resources in such a way to enhance production efficiency, control costs, and maximize profits.
The assignment method has various applications in maximizing resources, including:
- Allocating the proper number of employees to a machine or task
- Allocating a machine or a manufacturing plant and the number of jobs that a given machine or factory can produce
- Assigning a number of salespersons to a given territory or territories
- Assigning new computers, laptops, and other expensive high-tech devices to the areas that need them the most while lower priority departments would get the older models
Companies can make budgeting decisions using the assignment method since it can help determine the amount of capital or money needed for each area of the company. Allocating money or resources can be done by analyzing the past performance of an employee, project, or department to determine the most efficient approach.
Regardless of the resource being allocated or the task to be accomplished, the goal is to assign resources to maximize the profit produced by the task or project.
Example of Assignment Method
A bank is allocating its sales force to grow its mortgage lending business. The bank has over 50 branches in New York but only ten in Chicago. Each branch has a staff that is used to bring in new clients.
The bank's management team decides to perform an analysis using the assignment method to determine where their newly-hired salespeople should be allocated. Given the past performance results in the Chicago area, the bank has produced fewer new clients than in New York. The fewer new clients are the result of having a small market presence in Chicago.
As a result, the management decides to allocate the new hires to the New York region, where it has a greater market share to maximize new client growth and, ultimately, revenue.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Human-Resources-2ad3f1b88ed448b193e82c9fed171fcd.png)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Index Assignment problem Hungarian algorithm Solve online
The Hungarian algorithm: An example
We consider an example where four jobs (J1, J2, J3, and J4) need to be executed by four workers (W1, W2, W3, and W4), one job per worker. The matrix below shows the cost of assigning a certain worker to a certain job. The objective is to minimize the total cost of the assignment.
Below we will explain the Hungarian algorithm using this example. Note that a general description of the algorithm can be found here .
Step 1: Subtract row minima
We start with subtracting the row minimum from each row. The smallest element in the first row is, for example, 69. Therefore, we substract 69 from each element in the first row. The resulting matrix is:
Step 2: Subtract column minima
Similarly, we subtract the column minimum from each column, giving the following matrix:
Step 3: Cover all zeros with a minimum number of lines
We will now determine the minimum number of lines (horizontal or vertical) that are required to cover all zeros in the matrix. All zeros can be covered using 3 lines:
Step 4: Create additional zeros
First, we find that the smallest uncovered number is 6. We subtract this number from all uncovered elements and add it to all elements that are covered twice. This results in the following matrix:
Now we return to Step 3.
Again, We determine the minimum number of lines required to cover all zeros in the matrix. Now there are 4 lines required:
Because the number of lines required (4) equals the size of the matrix ( n =4), an optimal assignment exists among the zeros in the matrix. Therefore, the algorithm stops.
The optimal assignment
The following zeros cover an optimal assignment:
This corresponds to the following optimal assignment in the original cost matrix:
Thus, worker 1 should perform job 3, worker 2 job 2, worker 3 job 1, and worker 4 should perform job 4. The total cost of this optimal assignment is to 69 + 37 + 11 + 23 = 140.
Solve your own problem online
HungarianAlgorithm.com © 2013-2024
Assignment Problem: Meaning, Methods and Variations | Operations Research
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations.
Meaning of Assignment Problem:
An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total cost or maximize total profit of allocation.
The problem of assignment arises because available resources such as men, machines etc. have varying degrees of efficiency for performing different activities, therefore, cost, profit or loss of performing the different activities is different.
Thus, the problem is “How should the assignments be made so as to optimize the given objective”. Some of the problem where the assignment technique may be useful are assignment of workers to machines, salesman to different sales areas.
Definition of Assignment Problem:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Suppose there are n jobs to be performed and n persons are available for doing these jobs. Assume that each person can do each job at a term, though with varying degree of efficiency, let c ij be the cost if the i-th person is assigned to the j-th job. The problem is to find an assignment (which job should be assigned to which person one on-one basis) So that the total cost of performing all jobs is minimum, problem of this kind are known as assignment problem.
The assignment problem can be stated in the form of n x n cost matrix C real members as given in the following table:
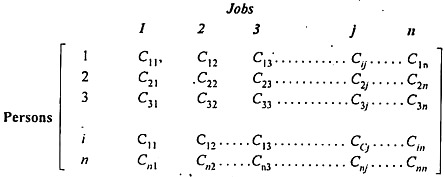
Solving Assignment Problem using Linear Programming in Python
Learn how to use Python PuLP to solve Assignment problems using Linear Programming.
In earlier articles, we have seen various applications of Linear programming such as transportation, transshipment problem, Cargo Loading problem, and shift-scheduling problem. Now In this tutorial, we will focus on another model that comes under the class of linear programming model known as the Assignment problem. Its objective function is similar to transportation problems. Here we minimize the objective function time or cost of manufacturing the products by allocating one job to one machine.
If we want to solve the maximization problem assignment problem then we subtract all the elements of the matrix from the highest element in the matrix or multiply the entire matrix by –1 and continue with the procedure. For solving the assignment problem, we use the Assignment technique or Hungarian method, or Flood’s technique.
The transportation problem is a special case of the linear programming model and the assignment problem is a special case of transportation problem, therefore it is also a special case of the linear programming problem.
In this tutorial, we are going to cover the following topics:
Assignment Problem
A problem that requires pairing two sets of items given a set of paired costs or profit in such a way that the total cost of the pairings is minimized or maximized. The assignment problem is a special case of linear programming.
For example, an operation manager needs to assign four jobs to four machines. The project manager needs to assign four projects to four staff members. Similarly, the marketing manager needs to assign the 4 salespersons to 4 territories. The manager’s goal is to minimize the total time or cost.
Problem Formulation
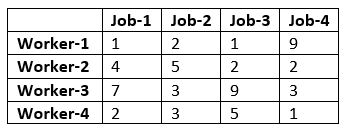
A manager has prepared a table that shows the cost of performing each of four jobs by each of four employees. The manager has stated his goal is to develop a set of job assignments that will minimize the total cost of getting all 4 jobs.
Initialize LP Model
In this step, we will import all the classes and functions of pulp module and create a Minimization LP problem using LpProblem class.
Define Decision Variable
In this step, we will define the decision variables. In our problem, we have two variable lists: workers and jobs. Let’s create them using LpVariable.dicts() class. LpVariable.dicts() used with Python’s list comprehension. LpVariable.dicts() will take the following four values:
- First, prefix name of what this variable represents.
- Second is the list of all the variables.
- Third is the lower bound on this variable.
- Fourth variable is the upper bound.
- Fourth is essentially the type of data (discrete or continuous). The options for the fourth parameter are LpContinuous or LpInteger .
Let’s first create a list route for the route between warehouse and project site and create the decision variables using LpVariable.dicts() the method.
Define Objective Function
In this step, we will define the minimum objective function by adding it to the LpProblem object. lpSum(vector)is used here to define multiple linear expressions. It also used list comprehension to add multiple variables.
Define the Constraints
Here, we are adding two types of constraints: Each job can be assigned to only one employee constraint and Each employee can be assigned to only one job. We have added the 2 constraints defined in the problem by adding them to the LpProblem object.
Solve Model
In this step, we will solve the LP problem by calling solve() method. We can print the final value by using the following for loop.
From the above results, we can infer that Worker-1 will be assigned to Job-1, Worker-2 will be assigned to job-3, Worker-3 will be assigned to Job-2, and Worker-4 will assign with job-4.
In this article, we have learned about Assignment problems, Problem Formulation, and implementation using the python PuLp library. We have solved the Assignment problem using a Linear programming problem in Python. Of course, this is just a simple case study, we can add more constraints to it and make it more complicated. You can also run other case studies on Cargo Loading problems , Staff scheduling problems . In upcoming articles, we will write more on different optimization problems such as transshipment problem, balanced diet problem. You can revise the basics of mathematical concepts in this article and learn about Linear Programming in this article .
- Solving Blending Problem in Python using Gurobi
- Transshipment Problem in Python Using PuLP

You May Also Like
Sensitivity Analysis in Python
Iterating over rows and columns in Pandas DataFrame

Cross-Validation in scikit-learn

How to Solve the Assignment Problem: A Complete Guide
Table of Contents
Assignment problem is a special type of linear programming problem that deals with assigning a number of resources to an equal number of tasks in the most efficient way. The goal is to minimize the total cost of assignments while ensuring that each task is assigned to only one resource and each resource is assigned to only one task. In this blog, we will discuss the solution of the assignment problem using the Hungarian method, which is a popular algorithm for solving the problem.
Understanding the Assignment Problem
Before we dive into the solution, it is important to understand the problem itself. In the assignment problem, we have a matrix of costs, where each row represents a resource and each column represents a task. The objective is to assign each resource to a task in such a way that the total cost of assignments is minimized. However, there are certain constraints that need to be satisfied – each resource can be assigned to only one task and each task can be assigned to only one resource.
Solving the Assignment Problem
There are various methods for solving the assignment problem, including the Hungarian method, the brute force method, and the auction algorithm. Here, we will focus on the steps involved in solving the assignment problem using the Hungarian method, which is the most commonly used and efficient method.
Step 1: Set up the cost matrix
The first step in solving the assignment problem is to set up the cost matrix, which represents the cost of assigning a task to an agent. The matrix should be square and have the same number of rows and columns as the number of tasks and agents, respectively.
Step 2: Subtract the smallest element from each row and column
To simplify the calculations, we need to reduce the size of the cost matrix by subtracting the smallest element from each row and column. This step is called matrix reduction.
Step 3: Cover all zeros with the minimum number of lines
The next step is to cover all zeros in the matrix with the minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines. This step is called matrix covering.
Step 4: Test for optimality and adjust the matrix
To test for optimality, we need to calculate the minimum number of lines required to cover all zeros in the matrix. If the number of lines equals the number of rows or columns, the solution is optimal. If not, we need to adjust the matrix and repeat steps 3 and 4 until we get an optimal solution.
Step 5: Assign the tasks to the agents
The final step is to assign the tasks to the agents based on the optimal solution obtained in step 4. This will give us the most cost-effective or profit-maximizing assignment.
Solution of the Assignment Problem using the Hungarian Method
The Hungarian method is an algorithm that uses a step-by-step approach to find the optimal assignment. The algorithm consists of the following steps:
- Subtract the smallest entry in each row from all the entries of the row.
- Subtract the smallest entry in each column from all the entries of the column.
- Draw the minimum number of lines to cover all zeros in the matrix. If the number of lines drawn is equal to the number of rows, we have an optimal solution. If not, go to step 4.
- Determine the smallest entry not covered by any line. Subtract it from all uncovered entries and add it to all entries covered by two lines. Go to step 3.
The above steps are repeated until an optimal solution is obtained. The optimal solution will have all zeros covered by the minimum number of lines. The assignments can be made by selecting the rows and columns with a single zero in the final matrix.
Applications of the Assignment Problem
The assignment problem has various applications in different fields, including computer science, economics, logistics, and management. In this section, we will provide some examples of how the assignment problem is used in real-life situations.
Applications in Computer Science
The assignment problem can be used in computer science to allocate resources to different tasks, such as allocating memory to processes or assigning threads to processors.
Applications in Economics
The assignment problem can be used in economics to allocate resources to different agents, such as allocating workers to jobs or assigning projects to contractors.
Applications in Logistics
The assignment problem can be used in logistics to allocate resources to different activities, such as allocating vehicles to routes or assigning warehouses to customers.
Applications in Management
The assignment problem can be used in management to allocate resources to different projects, such as allocating employees to tasks or assigning budgets to departments.
Let’s consider the following scenario: a manager needs to assign three employees to three different tasks. Each employee has different skills, and each task requires specific skills. The manager wants to minimize the total time it takes to complete all the tasks. The skills and the time required for each task are given in the table below:
The assignment problem is to determine which employee should be assigned to which task to minimize the total time required. To solve this problem, we can use the Hungarian method, which we discussed in the previous blog.
Using the Hungarian method, we first subtract the smallest entry in each row from all the entries of the row:
Next, we subtract the smallest entry in each column from all the entries of the column:
We draw the minimum number of lines to cover all the zeros in the matrix, which in this case is three:
Since the number of lines is equal to the number of rows, we have an optimal solution. The assignments can be made by selecting the rows and columns with a single zero in the final matrix. In this case, the optimal assignments are:
- Emp 1 to Task 3
- Emp 2 to Task 2
- Emp 3 to Task 1
This assignment results in a total time of 9 units.
I hope this example helps you better understand the assignment problem and how to solve it using the Hungarian method.
Solving the assignment problem may seem daunting, but with the right approach, it can be a straightforward process. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently tackle any assignment problem that comes your way.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you! 😔
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Operations Research
1 Operations Research-An Overview
- History of O.R.
- Approach, Techniques and Tools
- Phases and Processes of O.R. Study
- Typical Applications of O.R
- Limitations of Operations Research
- Models in Operations Research
- O.R. in real world
2 Linear Programming: Formulation and Graphical Method
- General formulation of Linear Programming Problem
- Optimisation Models
- Basics of Graphic Method
- Important steps to draw graph
- Multiple, Unbounded Solution and Infeasible Problems
- Solving Linear Programming Graphically Using Computer
- Application of Linear Programming in Business and Industry
3 Linear Programming-Simplex Method
- Principle of Simplex Method
- Computational aspect of Simplex Method
- Simplex Method with several Decision Variables
- Two Phase and M-method
- Multiple Solution, Unbounded Solution and Infeasible Problem
- Sensitivity Analysis
- Dual Linear Programming Problem
4 Transportation Problem
- Basic Feasible Solution of a Transportation Problem
- Modified Distribution Method
- Stepping Stone Method
- Unbalanced Transportation Problem
- Degenerate Transportation Problem
- Transhipment Problem
- Maximisation in a Transportation Problem
5 Assignment Problem
- Solution of the Assignment Problem
- Unbalanced Assignment Problem
- Problem with some Infeasible Assignments
- Maximisation in an Assignment Problem
- Crew Assignment Problem
6 Application of Excel Solver to Solve LPP
- Building Excel model for solving LP: An Illustrative Example
7 Goal Programming
- Concepts of goal programming
- Goal programming model formulation
- Graphical method of goal programming
- The simplex method of goal programming
- Using Excel Solver to Solve Goal Programming Models
- Application areas of goal programming
8 Integer Programming
- Some Integer Programming Formulation Techniques
- Binary Representation of General Integer Variables
- Unimodularity
- Cutting Plane Method
- Branch and Bound Method
- Solver Solution
9 Dynamic Programming
- Dynamic Programming Methodology: An Example
- Definitions and Notations
- Dynamic Programming Applications
10 Non-Linear Programming
- Solution of a Non-linear Programming Problem
- Convex and Concave Functions
- Kuhn-Tucker Conditions for Constrained Optimisation
- Quadratic Programming
- Separable Programming
- NLP Models with Solver
11 Introduction to game theory and its Applications
- Important terms in Game Theory
- Saddle points
- Mixed strategies: Games without saddle points
- 2 x n games
- Exploiting an opponent’s mistakes
12 Monte Carlo Simulation
- Reasons for using simulation
- Monte Carlo simulation
- Limitations of simulation
- Steps in the simulation process
- Some practical applications of simulation
- Two typical examples of hand-computed simulation
- Computer simulation
13 Queueing Models
- Characteristics of a queueing model
- Notations and Symbols
- Statistical methods in queueing
- The M/M/I System
- The M/M/C System
- The M/Ek/I System
- Decision problems in queueing
Assignment Problem: Maximization
There are problems where certain facilities have to be assigned to a number of jobs, so as to maximize the overall performance of the assignment.
The Hungarian Method can also solve such assignment problems , as it is easy to obtain an equivalent minimization problem by converting every number in the matrix to an opportunity loss.
The conversion is accomplished by subtracting all the elements of the given matrix from the highest element. It turns out that minimizing opportunity loss produces the same assignment solution as the original maximization problem.
- Unbalanced Assignment Problem
- Multiple Optimal Solutions
Example: Maximization In An Assignment Problem
At the head office of www.universalteacherpublications.com there are five registration counters. Five persons are available for service.
How should the counters be assigned to persons so as to maximize the profit ?
Here, the highest value is 62. So we subtract each value from 62. The conversion is shown in the following table.
On small screens, scroll horizontally to view full calculation
Now the above problem can be easily solved by Hungarian method . After applying steps 1 to 3 of the Hungarian method, we get the following matrix.
Draw the minimum number of vertical and horizontal lines necessary to cover all the zeros in the reduced matrix.
Select the smallest element from all the uncovered elements, i.e., 4. Subtract this element from all the uncovered elements and add it to the elements, which lie at the intersection of two lines. Thus, we obtain another reduced matrix for fresh assignment. Repeating step 3, we obtain a solution which is shown in the following table.
Final Table: Maximization Problem
Use Horizontal Scrollbar to View Full Table Calculation
The total cost of assignment = 1C + 2E + 3A + 4D + 5B
Substituting values from original table: 40 + 36 + 40 + 36 + 62 = 214.
Share This Article
Operations Research Simplified Back Next
Goal programming Linear programming Simplex Method Transportation Problem

- Google OR-Tools
- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
- Tiếng Việt
Solving an Assignment Problem
This section presents an example that shows how to solve an assignment problem using both the MIP solver and the CP-SAT solver.
In the example there are five workers (numbered 0-4) and four tasks (numbered 0-3). Note that there is one more worker than in the example in the Overview .
The costs of assigning workers to tasks are shown in the following table.
The problem is to assign each worker to at most one task, with no two workers performing the same task, while minimizing the total cost. Since there are more workers than tasks, one worker will not be assigned a task.
MIP solution
The following sections describe how to solve the problem using the MPSolver wrapper .
Import the libraries
The following code imports the required libraries.
Create the data
The following code creates the data for the problem.
The costs array corresponds to the table of costs for assigning workers to tasks, shown above.
Declare the MIP solver
The following code declares the MIP solver.
Create the variables
The following code creates binary integer variables for the problem.
Create the constraints
Create the objective function.
The following code creates the objective function for the problem.
The value of the objective function is the total cost over all variables that are assigned the value 1 by the solver.
Invoke the solver
The following code invokes the solver.
Print the solution
The following code prints the solution to the problem.
Here is the output of the program.
Complete programs
Here are the complete programs for the MIP solution.
CP SAT solution
The following sections describe how to solve the problem using the CP-SAT solver.
Declare the model
The following code declares the CP-SAT model.
The following code sets up the data for the problem.
The following code creates the constraints for the problem.
Here are the complete programs for the CP-SAT solution.
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License , and code samples are licensed under the Apache 2.0 License . For details, see the Google Developers Site Policies . Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2023-01-02 UTC.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Assignment Method Explained. The assignment method in operation research is a strategy for allocating organizational resources to tasks to increase profit via efficiency gains, cost reductions, and improved handling of operations that might create bottlenecks.It is an operations management tool that, by allocating jobs to the appropriate individual, minimizes expenses, time, and effort.
The Hungarian method is a computational optimization technique that addresses the assignment problem in polynomial time and foreshadows following primal-dual alternatives. In 1955, Harold Kuhn used the term "Hungarian method" to honour two Hungarian mathematicians, Dénes Kőnig and Jenő Egerváry. Let's go through the steps of the Hungarian method with the help of a solved example.
There is an assignment in Column 3 and column 4. Go to Column 5. There is exactly one zero. Mark that zero by . Mark other zeros in its row by × . Thus all the five assignments have been made. The Optimal assignment schedule and total cost is. The optimal assignment (minimum) cost = ` 9. Example 10.9. Solve the following assignment problem ...
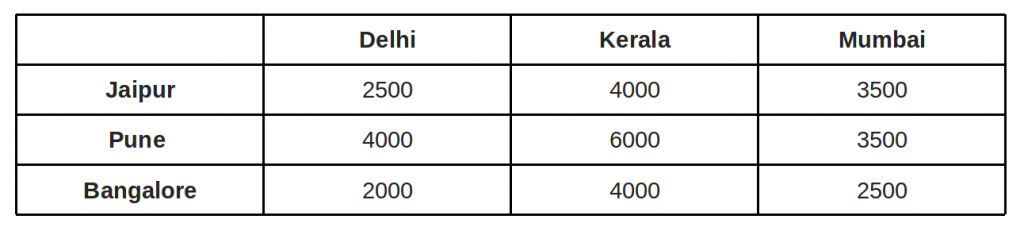
Explanation for above simple example: Below is the cost matrix of example given in above diagrams. 2500 4000 3500 4000 6000 3500 2000 4000 2500 Step 1: Subtract minimum of every row. 2500, 3500 and 2000 are subtracted from rows 1, 2 and 3 respectively. 0 1500 1000 500 2500 0 0 2000 500 Step 2: Subtract minimum of every column. 0, 1500 and 0 are subtracted from columns 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
Example 1: Hungarian Method. The Funny Toys Company has four men available for work on four separate jobs. Only one man can work on any one job. The cost of assigning each man to each job is given in the following table. The objective is to assign men to jobs in such a way that the total cost of assignment is minimum. Job.
Worked example of assigning tasks to an unequal number of workers using the Hungarian method. The assignment problem is a fundamental combinatorial optimization problem. In its most general form, the problem is as follows: The problem instance has a number of agents and a number of tasks.Any agent can be assigned to perform any task, incurring some cost that may vary depending on the agent ...
Hungarian method for assignment problem Step 1. Subtract the entries of each row by the row minimum. Step 2. Subtract the entries of each column by the column minimum. Step 3. Make an assignment to the zero entries in the resulting matrix. A = M 17 10 15 17 18 M 6 10 20 12 5 M 14 19 12 11 15 M 7 16 21 18 6 M −10
In this lesson we learn what is an assignment problem and how we can solve it using the Hungarian method.
The Hungarian Method: The following algorithm applies the above theorem to a given n × n cost matrix to find an optimal assignment. Step 1. Subtract the smallest entry in each row from all the entries of its row. Step 2. Subtract the smallest entry in each column from all the entries of its column. Step 3.
Assignment Method: A method of allocating organizational resources. The assignment method is used to determine what resources are assigned to which department, machine or center of operation in ...
The matrix below shows the cost of assigning a certain worker to a certain job. The objective is to minimize the total cost of the assignment. Below we will explain the Hungarian algorithm using this example. Note that a general description of the algorithm can be found here. Step 1: Subtract row minima.
Small example just to make things clearer: General description of the algorithm. This problem is known as the assignment problem. The assignment problem is a special case of the transportation problem, which in turn is a special case of the min-cost flow problem, so it can be solved using algorithms that solve the more general cases. Also, our ...
Step 1: For each row, subtract the minimum number in that row from all numbers in that row. Step 2: For each column, subtract the minimum number in that column from all numbers in that column. Step 3: Draw the minimum number of lines to cover all zeroes. If this number = n, Done — an assignment can be made.
The Hungarian algorithm is useful to identify minimum costs when people are assigned to specific activities based on cost. Practice using this algorithm in example equations of real-world scenarios.
After reading this article you will learn about:- 1. Meaning of Assignment Problem 2. Definition of Assignment Problem 3. Mathematical Formulation 4. Hungarian Method 5. Variations. Meaning of Assignment Problem: An assignment problem is a particular case of transportation problem where the objective is to assign a number of resources to an equal number of activities so as to minimise total ...
Assignment Problem. A problem that requires pairing two sets of items given a set of paired costs or profit in such a way that the total cost of the pairings is minimized or maximized. The assignment problem is a special case of linear programming. For example, an operation manager needs to assign four jobs to four machines.
The Assignment Problem: An Example A company has 4 machines available for assignment to 4 tasks. Any machine can be assigned ... Using the least-cost method, an initial basic feasible solution can be easily obtained; this is ... in an assignment problem is that it is degenerate. Next, we will use the u-v method to conduct the optimality test ...
The Hungarian method is an algorithm that uses a step-by-step approach to find the optimal assignment. The algorithm consists of the following steps: Subtract the smallest entry in each row from all the entries of the row. Subtract the smallest entry in each column from all the entries of the column. Draw the minimum number of lines to cover ...
The Hungarian Method can also solve such assignment problems, as it is easy to obtain an equivalent minimization problem by converting every number in the matrix to an opportunity loss. The conversion is accomplished by subtracting all the elements of the given matrix from the highest element. It turns out that minimizing opportunity loss ...
This section presents an example that shows how to solve an assignment problem using both the MIP solver and the CP-SAT solver. Example. In the example there are five workers (numbered 0-4) and four tasks (numbered 0-3). Note that there is one more worker than in the example in the Overview.
Some examples of teaching methods and strategies include: lectures, seminars, project-based instruction, dictation, and assignments. ... Assignment: An assignment is a task, often a written task ...
Assignment is a task given to students by a teacher or professor, usually as a means of assessing their understanding and application of course material. Assignments can take various forms, including essays, research papers, presentations, problem sets, lab reports, and more. Assignments are typically designed to be completed outside of class ...
Example: Non-random assignment In your clinical study, you recruit participants using flyers. at gyms, cafes, and local community centers. You use a haphazard method to assign participants to groups based on the recruitment location: participants recruited from cafes are placed in the control group,