- Strategic Planning
- Strategy Communication
- Strategy Execution
- Strategy Workshops
- Tools & Templates


What Comes First: Objective, Goals Or Strategy?
In business, objectives, goals and strategies are often used interchangeably when describing a company’s direction. Yet they are very different. Which one comes first – and does it really matter?
When developing a business strategy, first decide your objective, i.e. where you are going. Translate your objective into measurable goals that define success. Then develop your strategies which determine how you are going to achieve your objective and reach your goals.
Or said differently, if business strategy was a road trip, then your objective would be your destination and your strategies your means to reach it. Unless you are a happy-go-lucky vacationeer for whom the journey is the destination, you decide on your destination first and then determine how to get there. Let’s explore further why this order is important.
Begin with the end in mind
One of the books that has been most influential in my career is The 7 Habits Of Highly Effective People by Stephen Covey. One specific quote left a particular impression on me which I have since applied to almost every endeavor in my business life including strategy: begin with the end in mind.
“To begin with the end in mind means to start with a clear understanding of your destination. It means to know where you’re going so that you better understand where you are now and so that the steps you take are always in the right direction.” Stephen Covey
It is this quote that convinced me that strategy must begin with the destination . What do I aim to achieve? What dream or vision do I have for my business? Where do I want to be in e.g. five years? Painting this vision in as concrete terms as possible makes it tangible – not only for myself but also for my team. And a concrete, tangible vision inspires action. Turning the description of my destination into an objective statement and clearly defined goals make them tangible .
What is a strategic objective?
The objective is a qualitative statement about what a business aims to achieve over a specified timeframe . The chosen timeframe of a strategic plan is typically 3-5 years and for an annual operating plan 1 year.
The goals are the quantifiable targets or intended results to be accomplished. These typically are financial figures or other measurable metrics. In strategy, goals are the quantification of the objective to judge its achievement over the chosen timeframe.
It is best to describe the goals as SMART goals . SMART stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Thereby each goal is clear and unambiguous.
Once I have defined my destination, then I can decide how I will get there. As Stephen said, only then do I know that “the steps [I] take are always in the right direction.” And these steps are my strategies.
Should small businesses do strategic planning?
What is the difference between goals and strategies?
Strategies are the plan of action to achieve a long-term vision or objective. Strategies describe the choices a business makes about resource allocation to accomplish its objective and goals .
When designing my strategic plans, I aim to choose 3-5 strategies to give the business sufficient focus without putting all my eggs in one basket. Once I have made those choices, I develop an implementation plan that turns the strategies into action. This ensures that I move my business towards the destination.
So what is the difference between goals and strategies? The goals are part of the description of the destination while the strategies describe the way to reach it.
What are objective and goal examples?
When writing my objective statement, I use the ‘what-by-how’ method described by van Eck and Leenhouts in their excellent book “ The 1 Page Business Strategy ”. The ‘what-by-how’ method divides the objective statement into a ‘what’-part which describes what I aim to achieve and a ‘how’-part which already gives a sneak-preview on how I am going to achieve it. In the objective statement, I already build-in a lead to my strategy! This makes the objective statement clear and actionable. Consider the following simple examples:
- “Go to Berlin by bus”
- “Learn to master the guitar by practicing every day”
- “Drive rapid business growth by launching a new product line”
Goals then are the quantification of these objective statements. Goals are facts and figures that turn objectives into measurable results. I define 1-2 goals each for the ‘what’-part and the ‘how’-part of the objective. Referring to previous examples:
- Reach Berlin-Mitte by 4pm . Pay less than $20 for the ticket. Less than 2 hours journey time.
- Master “Sultans of Swing” by Dire Straits within 2 years . Practice 1 hour daily.
- Grow 15% CAGR over 3 years . $5MM annual sales from new product line by year 2 .
By setting concrete goals for both the ‘what’-part and the ‘how’-part of the objective statement, the objective becomes clear and measurable and you can track that you stay on course.
Read more about how to create clear goals for your business strategy here.
So does it matter whether objective or strategies come first?
In my experience it does matter whether objective or strategies come first. Strategies describe how I aim to achieve an objective. I would therefore define my objective first and then only after I am clear about my objective and my goals would I define my strategies.
Having said that, the objective is not the very first item I discuss in my strategic planning process. Before looking into the future and developing my objective, I analyze where I am today . I want to be clear about my business’ current situation. What is the purpose of my business? What kind of business am I running? What mission am I on? What success have I had so far? Only when I know where I am today, can I look to the future.
Let’s come back to Stephen Covey. He said, beginning with the end in mind “means to know where you’re going so that you better understand where you are now […] so that the steps you take are always in the right direction.” So knowing where you are starting from is just as important as knowing where you are headed.
So know where you are today, define where you are headed and then choose how you will get there.
A great way to define your strategic plan starting with a clear objective statement is the OGSM methodology. Read on about the OGSM approach to strategy here .
When developing a strategy, always start with the end in mind. Once you define your destination, you know that the steps you take are always in the right direction.
Therefore, first define your objective statement and your goals. Then develop your strategies that help you reach your destination and avoid the 7 deadly sins of business strategy .
If this article was helpful or if you have any questions or comments, feel free to leave us a reply below. We would love to hear from you.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Discover more from Rock Your Strategy
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
More Like this
What is the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan.
It is not uncommon that the terms ‘strategic plan’ and ‘business plan’ get confused in the business world. While a strategic plan is a type of business plan, there are several important distinctions between the two types that are worth noting. Before beginning your strategic planning process or strategy implementation, look at the article below to learn the key difference between a business vs strategic plan and how each are important to your organization.
Definition of a business plan vs. a strategic plan
A strategic plan is essential for already established organizations looking for a way to manage and implement their strategic direction and future growth. Strategic planning is future-focused and serves as a roadmap to outline where the organization is going over the next 3-5 years (or more) and the steps it will take to get there.
Get the Free Guide for Setting OKRs that Work (with 100 examples!)
A strategic plan serves 6 functions for an organization that is striving to reach the next level of their growth:.
- Defines the purpose of the organization.
- Builds on an organization’s competitive advantages.
- Communicates the strategy to the staff.
- Prioritizes the financial needs of the organization.
- Directs the team to move from plan to action.
- Creates long-term sustainability and growth impact
Alternatively, a business plan is used by new businesses or organizations trying to get off the ground. The fundamentals of a business plan focus on setting the foundation for the business or organization. While it looks towards the future, the focus is set more on the immediate future (>1 year). Some of the functions of a business plan may overlap with a strategic plan. However, the focus and intentions diverge in a few key areas.
A business plan for new businesses, projects, or organizations serves these 5 functions:
- Simplifies or explains the objectives and goals of your organization.
- Coordinates human resource management and determines operational requirements.
- Secures funding for your organization.
- Evaluates potential business prospects.
- Creates a framework for conceptualizing ideas.
In other words, a strategic plan is utilized to direct the momentum and growth of an established company or organization. In contrast, a business plan is meant to set the foundation of a newly (or not quite) developed company by setting up its operational teams, strategizing ways to enter a new market, and obtaining funding.
A strategic plan focuses on long-term growth and the organization’s impact on the market and its customers. Meanwhile, a business plan must focus more on the short-term, day-to-day operational functions. Often, new businesses don’t have the capacity or resources to create a strategic plan, though developing a business plan with strategy elements is never a bad idea.
Business and strategic plans ultimately differ in several key areas–timeframe, target audience, focus, resource allocation, nature, and scalability.
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take now to succeed.
A strategic plan generally covers the organizational plan over 3 to 5+ years. It is set with future expansion and development in mind and sets up roadmaps for how the organization will reach its desired future state.
Pro Tip: While a vision statement could benefit a business plan, it is essential to a strategic plan.
Target Audience
A strategic plan is for established companies, businesses, organizations, and owners serious about growing their organizations. A strategic plan communicates the organization’s direction to the staff and stakeholders. The strategic plan is communicated to the essential change makers in the organization who will have a hand in making the progress happen.
A business plan could be for new businesses and entrepreneurs who are start-ups. The target audience for the business plan could also be stakeholders, partners, or investors. However, a business plan generally presents the entrepreneur’s ideas to a bank. It is meant to get the necessary people onboard to obtain the funding needed for the project.
A strategic plan provides focus, direction, and action to move the organization from where they are now to where they want to go. A strategic plan may consist of several months of studies, analyses, and other processes to gauge an organization’s current state. The strategy officers may conduct an internal and external analysis, determine competitive advantages, and create a strategy roadmap. They may take the time to redefine their mission, vision, and values statements.
Alternatively, a business plan provides a structure for ideas to define the business initially. It maps out the more tactical beginning stages of the plan.
Pro Tip: A mission statement is useful for business and strategic plans as it helps further define the enterprise’s value and purpose. If an organization never set its mission statement at the beginning stages of its business plan, it can create one for its strategic plan.
A strategic plan is critical to prioritizing resources (time, money, and people) to grow the revenue and increase the return on investment. The strategic plan may start with reallocating current financial resources already being utilized more strategically.
A business plan will focus on the resources the business still needs to obtain, such as vendors, investors, staff, and funding. A business plan is critical if new companies seek funding from banks or investors. It will add accountability and transparency for the organization and tell the funding channels how they plan to grow their business operations and ROI in the first year of the business.
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan
Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in ‘scale’ between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan. It is often followed by departmental and marketing plans that work from the Strategic Plan.
Smaller and start-up companies typically use only a business plan to develop all aspects of operations of the business on paper, obtain funding and then start the business.
Why understanding the differences between a business plan vs a strategic plan matters
It is important to know the key differences between the two terms, despite often being used interchangeably. But here’s a simple final explanation:
A business plan explains how a new business will get off the ground. A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state.
A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
10 Comments
I agree with your analysis about small companies, but they should do a strategic plan. Just check out how many of the INC 500 companies have an active strategic planning process and they started small. Its about 78%,
Strategic management is a key role of any organization even if belong to small business. it help in growth and also to steam line your values. im agree with kristin.
I agree with what you said, without strategic planning no organization can survive whether it is big or small. Without a clear strategic plan, it is like walking in the darkness.. Best Regards..
Vision, Mission in Business Plan VS Strategic Plan ?
you made a good analysis on strategic plan and Business plan the difference is quite clear now. But on the other hand, it seems that strategic plan and strategic management are similar which I think not correct. Please can you tell us the difference between these two?. Thanks
Thank you. I get points to work on it
super answer Thanking you
Hi. I went through all the discussions, comments and replies. Thanks! I got a very preliminary idea about functions and necessity of Strategic Planning in Business. But currently I am looking for a brief nice, flowery, juicy definition of “Business Strategic Planning” as a whole, which will give anyone a fun and interesting way to understand. Can anyone help me out please? Awaiting replies…… 🙂
that was easy to understand,
Developing a strategic plan either big or small company or organization mostly can’t achieve its goal. A strategic plan or formulation is the first stage of the strategic management plan, therefore, we should be encouraged to develop a strategic management plan. We can develop the best strategic plan but without a clear plan of implementation and evaluation, it will be difficult to achieve goals.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.

- Certifications
- Associate Business Strategy Professional
- Senior Business Strategy Professional
- Examination
- Partnership
- For Academic Affiliation
- For Training Companies
- For Corporates
- Help Center
- Associate Business Strategy Professional (ABSP™)
- Senior Business Strategy Professional (SBSP™)
- Certification Process
- TSI Certification Examination
- Get your Institution TSI Affiliated
- Become a Corporate Education Partner
- Become a Strategy Educator
- Frequently Asked Questions
Business plan vs Strategic Plan - What You Must Know

Like everything else in life, the nature of business needs a plan in place to follow and measure. Crafting a strategic roadmap isn't just a suggestion—it's a necessity.
This is one of the key elements of a startup or even a business division within an organization that is expanding or diversifying. It has every resource element and needs to be mapped out for the business, including projected milestones for the future.
However, every business strategist needs to know that there are some subtle differences between what constitutes a business plan, and the several differences it has with a strategic plan. Let’s walk through the different elements that comprise each and understand the outcome each aims to achieve.
Introducing The Business Plan
A business plan is exactly what the name suggests— a plan to start and run a business or a new entity of an existing business; usually either an expansion in a newer region or a diversification into a new market. Business plans are mainly created for internal reference purposes or external funding purposes, with the latter being the common usage. They form the basis of all business strategies and decisions made at the ownership level in an organization. The most essential components of a business plan include:
Organizational Plan - This is the core of a business plan, and it includes the mission and vision statement, along with the market in which the company plans to operate. This plan also encompasses thorough market research to gauge the potential of the business, crucial for securing funding or sponsorship. It articulates the rationale behind the business's growth trajectory, outlining clear timelines for achieving milestones along the way.
Financial Plan - A robust financial plan is the bedrock of any successful business venture, where cash flow reigns supreme, and a meticulously crafted balance sheet serves as the ultimate scorecard. A financial plan includes some of the most important elements of the entire business plan and includes elements like projected cash flow statements, capital requirements, a summary of projected overheads, a projected balance sheet including assets and liabilities, and income and expense statements.
Remember to regard this as the central nervous system, for it permeates and influences almost every aspiration the enterprise hopes to attain.
Sales and Marketing Plan - We mentioned “almost” everything above for this very reason. Sales and marketing form the other significant component of the business plan. These include sales forecasts and overheads, marketing and brand management summaries, and market share projections that the business hopes to achieve within a time frame.
Business plans are indeed comprehensive and all-encompassing. They form the basis of the business's existence or the rationale for investments in it. But what about translating these plans into action? How do we ensure that the sky-high goals set forth are actually achievable?
The Actionables- A Strategic Plan
Strategic plans constitute the basis of operations and responsibilities within the business. These plans lay the paths out for each member of the organization to follow and define the functional outline and the key outcomes for every project and process within the business. A strategic plan goes on to define the operations and their outcomes within the organization, its departments, and its employees. The single thread connecting strategic planning with the business plan is the vision of the organization, and for obvious reasons— vision serves as the guiding light for strategy formation, which, in turn, directs the day-to-day operations of the business.
Why A Strategic Plan is Crucial to The Organization
In a word— synchronization. A robust and well-laid-out strategic plan establishes the much-needed sync between teams and their objectives. Not only that, it also provides a guide for daily operations alongside the focus and direction that teams often need to get the job done, on time and within budget. When all these components are integrated into a cohesive network, the true value of a strategic plan emerges—a seamless and grand orchestration of departments, teams, and individuals using the resources allocated to them to achieve the key performance indicator that they are responsible for.
Elements to Consider in a Strategic Plan
When tasked with creating a strategic plan for your business, you will need to incorporate certain components that will ensure that the stakeholders are aligned completely with the organization’s goals and objectives. These include:
Vision and Values - The vision statement is the most important component of the strategic plan and the most overarching. It propels the organization towards established goals and the values that every employee and stakeholder must incorporate.
Goals - These are short, medium, or long-term, depending on the scope of the strategic plan. They provide the much-needed context for the organization to undertake initiatives that meet the vision while maintaining the values.
Guiding Principles - Often, organizations face crossroads where they must decide which steps to take next, to reach their vision. Principles are included in strategic plans to align teams towards the vision when faced with a dilemma and form a critical part of strategic planning.
Action Plans - A sum of key initiatives, processes, and projects that are required to be performed on a pre-determined periodic basis for the goal to be accomplished. These also include the time frames for each stakeholder responsible for each option. They usually follow the DACI format for each action (Driver, Approver, Contributor, Informed)
SWOT Analysis - The quintessential component, the Strength, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats analysis of the strategic plan lends context to all business actions vis-a-vis the external environment. This includes competitors, market forces and conditions, identification of internal and external threats, and several other factors.
Read This - SWOT Analysis: How to Strengthen Your Business Plan
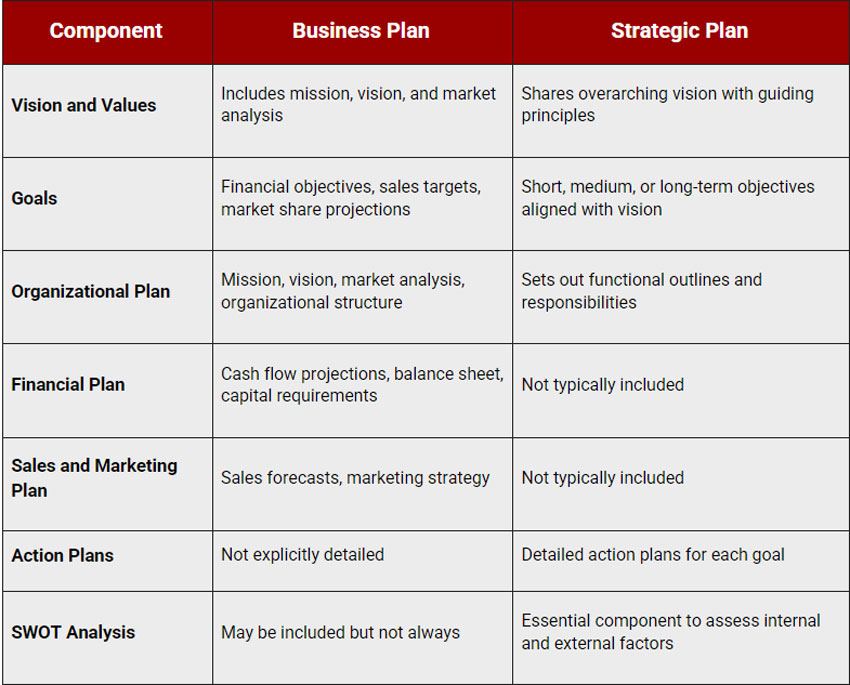
Here’s a table highlighting the main differences between a Business Plan and a Strategic Plan with a focus on the key components of each—
Learning All About Strategic Planning
In all businesses, a strategic plan serves as the foundational blueprint, akin to a meticulously drawn map for a general. It provides the essential guidance and direction needed for the entire organization to navigate toward success. It is crucial, therefore, to acquire the necessary skills and certifications for employment as a business strategist who would be entrusted with creating it. Know more about how to become a successful and sought-after business strategist today!

Recent Posts

How Data Analytics Can Revolutionize Your Business - A Strategist's Guide
Download this Strategist's Guide to empower yourself with resourceful insights:
- Roadblocks to Data Usage
- Advantages that Data Analytics offer for businesses
- Elements of a Data Analytics Strategy
- Top reasons why businesses must adopt a Data Analytics Strategy
- Case studies, Scenarios, and more

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Verify A Credential
Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TSI.
Stay Informed!
Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.
Start Your Journey with The Strategy Institute by Creating Your myTSI Account Today.
- Manage your professional profile conveniently.
- Manage your credentials anytime.
- Share your experiences and ideas with The Strategy Institute.
Account Login
- Remember Password
- Forgot Password?
Forgot Password

How to Write Your First Business Plan
Bryce Warnes
Reviewed by
April 8, 2021
This article is Tax Professional approved
A business plan lays out where your business stands in the present and where it’s headed in the future. If you’re applying for a loan or bringing on investors, your business plan proves that your business is making money, and that you’re well positioned to make more.
I am the text that will be copied.
But even if you aren’t looking for working capital, having a business plan can be a huge benefit. It helps you set future goals, put together strategies to help you reach them, and make decisions along the way.
What a business plan tells you
Every business plan is different. The way you create yours will depend on the nature of your business. However, it should include the following:
- The value you offer customers or clients
- How your business makes money
- The resources you rely on to operate
- New products or services you may provide in the future
- Your position in the market versus competitors
- How you plan for your business to grow
- Current financial report
- Financial projections
There are different ways to communicate this information—we’ll get to those shortly.
Reasons to write a business plan
A business plan is like a Swiss Army knife—it can do a lot of things really well. And once you have one, it soon becomes indispensable.
While each industry’s business plan will look different— an ecommerce business plan will be different than a medical tech company—there are very basic commonalities. Broadly speaking, here are five important goals you can achieve with a business plan.
1. Test out your business idea
Maybe you’re considering turning your side hustle into a full-time gig, or maybe it’s still just a twinkle in your eye. Either way, writing a plan is a good way to see if it’s feasible before you start investing serious time and money.
Working through a business plan can lay bare your idea’s strengths and weaknesses, and flag any roadblocks you may face down the line. Specifically, when you do market and competitor analysis for your prospective business, you should quickly be able to tell whether it will be profitable. Financial projections can help you determine what type of income you’ll be earning, and what you need for funding.
2. Get funding
If you’re applying for a small business loan, having a thorough business plan is essential. Lenders want to be sure you’ll be able to pay off the loan, with interest. A business plan shows them how you’ll do that.
3. Attract investors
Similar to lenders, investors—whether they’re angel investors, venture capital firms, or even friends and family—want to know your business will turn a profit. After all, they’ll want a good return on their investment. Most investors expect to see your business plan before they risk their money.
4. Plan for the future
With financial projections and marketing objectives, your business plan sets a roadmap for the future. That can help you decide what to do in the here and now, and prepare for the years to come.
5. Make decisions more easily
When you’ve got a map guiding you, you spend less time at the crossroads picking a direction to take. As you face decisions during periods of business growth, your business plan acts as a powerful tool.
Should you open a brick-and-mortar location, or offer a wider range of products online? Should you apply for a loan now, or wait until next year? If your business plan is thorough, you already have the answers. That means less time debating, and more time acting.
Steps to writing a business plan
1. Determine its purpose
First, decide what goals you hope your business plan will help you achieve. Your business plan’s purpose will determine how you format it, what type of documentation you need to support it, and the kind of research you’ll need to conduct. For instance, if your aim is to secure financing, your plan will be different than it would be if you were using it internally to make business decisions.
2. Pick your audience
Who will read your business plan? Potential investors, lenders, or buyers? Employees? All of the above? Write your plan, choosing the language you use and the information you present with your specific audience in mind.
3. Do the research
Any claims you make need to be supported by hard facts. Research will take up the bulk of the time you spend creating your business plan. For instance, if your business plan assumes your industry is on the upswing, you should have the numbers to prove it.
Some questions you should be prepared to answer with the support of research:
- Who are your main competitors?
- What services/products are your target clients or customers looking for?
- Where is your industry headed?
- What is the history of your industry or niche?
- What types of roadblocks could you potentially face down the line?
4. Get documentation together
The most important documents in your business plan are your financial records . Past tax returns, financial reports, and comprehensive bookkeeping demonstrate your company’s history and future viability. You’ll use them to create financial projections.
You’ll also need a list of all employees and their positions within the company. And if your business relies on licensing agreements or intellectual property, be prepared to compile those as well.
5. Create a company profile
Your company profile is a public-facing document. For inspiration, make a list of companies you admire and then check their website’s “About” page and their LinkedIn profile.
Your company profile should explain:
- The problems your business solves for customers and clients
- What sets you apart from the competition
- The resources you use to get the job done
- Your company’s history
- What inspired you to go into business
- Your mission statement and vision for the future
This should be a short document, no longer than one page. These topics will be covered in greater detail within the business statement itself, but spelling out all the info now can help you get started and guide you as you write it.
6. Write the business plan
When you’ve decided what you’re aiming to achieve and who you’re addressing, compiled all the information you need, and laid the groundwork with a company profile, you’re ready to write your plan. Don’t start until you’ve covered the previous five steps—it’s better to over prepare for writing your plan rather than scramble for information when you’re in the thick of it.
It’s also best practice to include a cover page . It should be simple and introduce the key information of your business including a logo and legal information.
7. (Optional) Prepare a presentation
If you’re looking for funding or sharing your work with partners and employees, you may want to create a business plan presentation. This can take the form of a speech, slideshow, promotional video, audio track, or any combination of the above.
Think of it as a pitch for your company and your plans for the future. Boil down the information in your business plan into a digestible format, with the goal of getting your audience excited.
Types of business plans: traditional vs. lean
Business plans can be split into two categories: traditional and lean (or “startup”). Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the type that’s relevant to your business will depend on how you intend to use your business plan.
Traditional
A traditional business plan is highly detailed, and relies on plenty of research. This is the type favored by investors and lenders—if you’re seeking out more working capital, it’s a good choice.
The drawback? Traditional plans take longer to research, plan, and write than lean business plans.
A lean business plan is less detailed than a traditional one, relying on less research. Specifically, it doesn’t feature financial projections or detailed competitor and market analysis. It’s relatively quick to write, and leaves you more flexibility—you can write a lean business plan now, and a traditional one later on. That makes it a great choice for startups still sketching out exactly what their business will look like.
Since it’s less detailed than a traditional plan, if you present a lean business plan to lenders or investors, they may ask you for more information. A lean plan is best used as a “rough draft” to help guide you in the early days of your business.
Business plan formats
Even if you’re seeking funding, the traditional format may seem like overkill. But each of the following nine parts plays an important role—feel free to adjust them to suit your needs.
The lean business plan is based on the Lean Business Model Canvas , a classic format for startup business plans. When creating a lean business plan, keep it brief and digestible. It can be as short as one page.
Even if you aren’t using your business plan to seek funding, including financial projections offers major benefits. By looking into the future of your business, you can make plans for growth and set realistic goals to reach along the way. Get started with our guide to financial forecasting .
Join over 140,000 fellow entrepreneurs who receive expert advice for their small business finances
Get a regular dose of educational guides and resources curated from the experts at Bench to help you confidently make the right decisions to grow your business. No spam. Unsubscribe at any time.

How to make a business plan
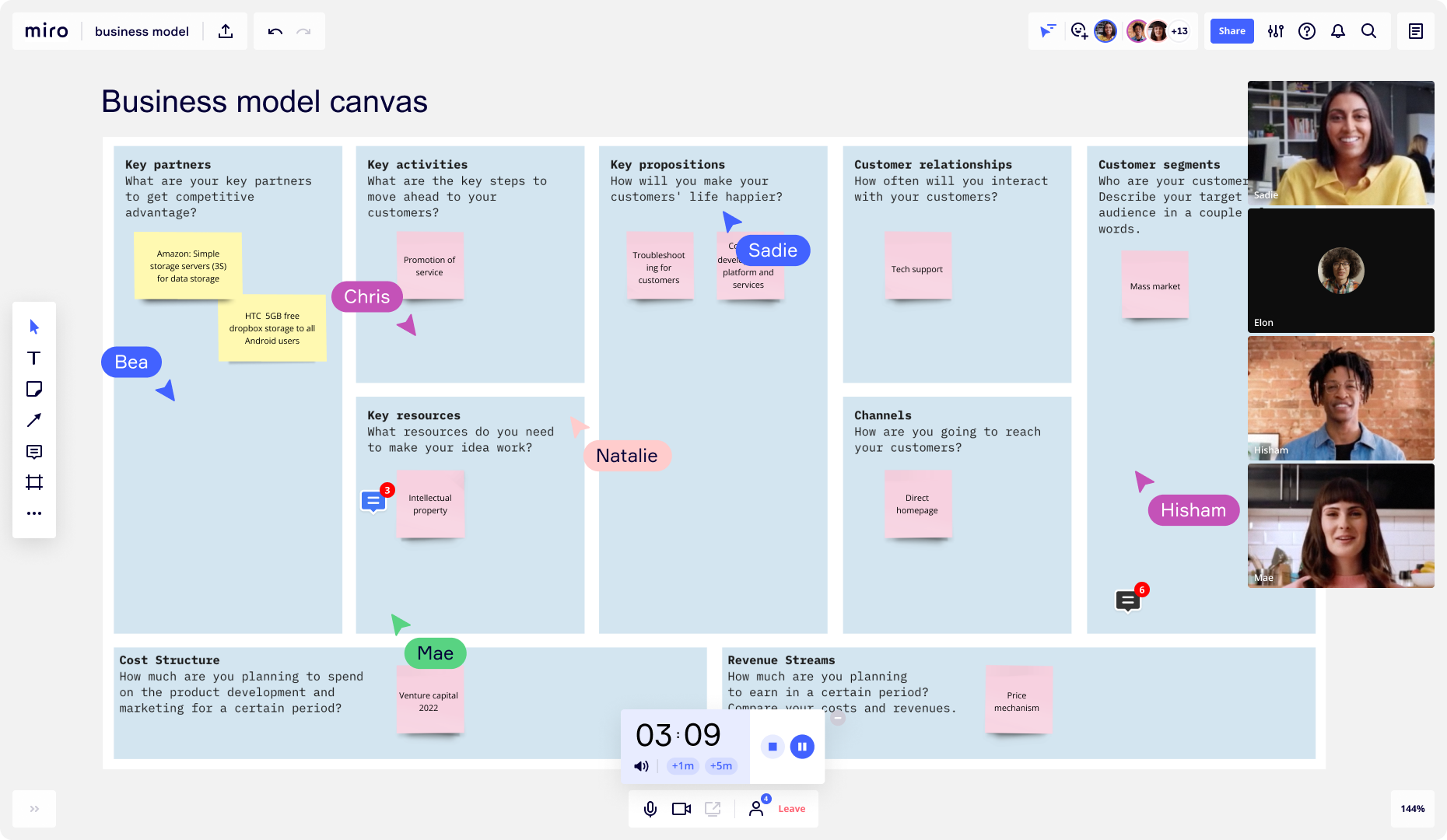
Table of Contents
How to make a good business plan: step-by-step guide.
A business plan is a strategic roadmap used to navigate the challenging journey of entrepreneurship. It's the foundation upon which you build a successful business.
A well-crafted business plan can help you define your vision, clarify your goals, and identify potential problems before they arise.
But where do you start? How do you create a business plan that sets you up for success?
This article will explore the step-by-step process of creating a comprehensive business plan.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a business's objectives, strategies, and operational procedures. It typically includes the following information about a company:
Products or services
Target market
Competitors
Marketing and sales strategies
Financial plan
Management team
A business plan serves as a roadmap for a company's success and provides a blueprint for its growth and development. It helps entrepreneurs and business owners organize their ideas, evaluate the feasibility, and identify potential challenges and opportunities.
As well as serving as a guide for business owners, a business plan can attract investors and secure funding. It demonstrates the company's understanding of the market, its ability to generate revenue and profits, and its strategy for managing risks and achieving success.
Business plan vs. business model canvas
A business plan may seem similar to a business model canvas, but each document serves a different purpose.
A business model canvas is a high-level overview that helps entrepreneurs and business owners quickly test and iterate their ideas. It is often a one-page document that briefly outlines the following:
Key partnerships
Key activities
Key propositions
Customer relationships
Customer segments
Key resources
Cost structure
Revenue streams
On the other hand, a Business Plan Template provides a more in-depth analysis of a company's strategy and operations. It is typically a lengthy document and requires significant time and effort to develop.
A business model shouldn’t replace a business plan, and vice versa. Business owners should lay the foundations and visually capture the most important information with a Business Model Canvas Template . Because this is a fast and efficient way to communicate a business idea, a business model canvas is a good starting point before developing a more comprehensive business plan.
A business plan can aim to secure funding from investors or lenders, while a business model canvas communicates a business idea to potential customers or partners.
Why is a business plan important?
A business plan is crucial for any entrepreneur or business owner wanting to increase their chances of success.
Here are some of the many benefits of having a thorough business plan.
Helps to define the business goals and objectives
A business plan encourages you to think critically about your goals and objectives. Doing so lets you clearly understand what you want to achieve and how you plan to get there.
A well-defined set of goals, objectives, and key results also provides a sense of direction and purpose, which helps keep business owners focused and motivated.
Guides decision-making
A business plan requires you to consider different scenarios and potential problems that may arise in your business. This awareness allows you to devise strategies to deal with these issues and avoid pitfalls.
With a clear plan, entrepreneurs can make informed decisions aligning with their overall business goals and objectives. This helps reduce the risk of making costly mistakes and ensures they make decisions with long-term success in mind.
Attracts investors and secures funding
Investors and lenders often require a business plan before considering investing in your business. A document that outlines the company's goals, objectives, and financial forecasts can help instill confidence in potential investors and lenders.
A well-written business plan demonstrates that you have thoroughly thought through your business idea and have a solid plan for success.
Identifies potential challenges and risks
A business plan requires entrepreneurs to consider potential challenges and risks that could impact their business. For example:
Is there enough demand for my product or service?
Will I have enough capital to start my business?
Is the market oversaturated with too many competitors?
What will happen if my marketing strategy is ineffective?
By identifying these potential challenges, entrepreneurs can develop strategies to mitigate risks and overcome challenges. This can reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes and ensure the business is well-positioned to take on any challenges.
Provides a basis for measuring success
A business plan serves as a framework for measuring success by providing clear goals and financial projections . Entrepreneurs can regularly refer to the original business plan as a benchmark to measure progress. By comparing the current business position to initial forecasts, business owners can answer questions such as:
Are we where we want to be at this point?
Did we achieve our goals?
If not, why not, and what do we need to do?
After assessing whether the business is meeting its objectives or falling short, business owners can adjust their strategies as needed.
How to make a business plan step by step
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include.
1. Create an executive summary
Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Keep your executive summary concise and clear with the Executive Summary Template . The simple design helps readers understand the crux of your business plan without reading the entire document.
2. Write your company description
Provide a detailed explanation of your company. Include information on what your company does, the mission statement, and your vision for the future.
Provide additional background information on the history of your company, the founders, and any notable achievements or milestones.
3. Conduct a market analysis
Conduct an in-depth analysis of your industry, competitors, and target market. This is best done with a SWOT analysis to identify your strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Next, identify your target market's needs, demographics, and behaviors.
Use the Competitive Analysis Template to brainstorm answers to simple questions like:
What does the current market look like?
Who are your competitors?
What are they offering?
What will give you a competitive advantage?
Who is your target market?
What are they looking for and why?
How will your product or service satisfy a need?
These questions should give you valuable insights into the current market and where your business stands.
4. Describe your products and services
Provide detailed information about your products and services. This includes pricing information, product features, and any unique selling points.
Use the Product/Market Fit Template to explain how your products meet the needs of your target market. Describe what sets them apart from the competition.
5. Design a marketing and sales strategy
Outline how you plan to promote and sell your products. Your marketing strategy and sales strategy should include information about your:
Pricing strategy
Advertising and promotional tactics
Sales channels
The Go to Market Strategy Template is a great way to visually map how you plan to launch your product or service in a new or existing market.
6. Determine budget and financial projections
Document detailed information on your business’ finances. Describe the current financial position of the company and how you expect the finances to play out.
Some details to include in this section are:
Startup costs
Revenue projections
Profit and loss statement
Funding you have received or plan to receive
Strategy for raising funds
7. Set the organization and management structure
Define how your company is structured and who will be responsible for each aspect of the business. Use the Business Organizational Chart Template to visually map the company’s teams, roles, and hierarchy.
As well as the organization and management structure, discuss the legal structure of your business. Clarify whether your business is a corporation, partnership, sole proprietorship, or LLC.
8. Make an action plan
At this point in your business plan, you’ve described what you’re aiming for. But how are you going to get there? The Action Plan Template describes the following steps to move your business plan forward. Outline the next steps you plan to take to bring your business plan to fruition.
Types of business plans
Several types of business plans cater to different purposes and stages of a company's lifecycle. Here are some of the most common types of business plans.
Startup business plan
A startup business plan is typically an entrepreneur's first business plan. This document helps entrepreneurs articulate their business idea when starting a new business.
Not sure how to make a business plan for a startup? It’s pretty similar to a regular business plan, except the primary purpose of a startup business plan is to convince investors to provide funding for the business. A startup business plan also outlines the potential target market, product/service offering, marketing plan, and financial projections.
Strategic business plan
A strategic business plan is a long-term plan that outlines a company's overall strategy, objectives, and tactics. This type of strategic plan focuses on the big picture and helps business owners set goals and priorities and measure progress.
The primary purpose of a strategic business plan is to provide direction and guidance to the company's management team and stakeholders. The plan typically covers a period of three to five years.
Operational business plan
An operational business plan is a detailed document that outlines the day-to-day operations of a business. It focuses on the specific activities and processes required to run the business, such as:
Organizational structure
Staffing plan
Production plan
Quality control
Inventory management
Supply chain
The primary purpose of an operational business plan is to ensure that the business runs efficiently and effectively. It helps business owners manage their resources, track their performance, and identify areas for improvement.
Growth-business plan
A growth-business plan is a strategic plan that outlines how a company plans to expand its business. It helps business owners identify new market opportunities and increase revenue and profitability. The primary purpose of a growth-business plan is to provide a roadmap for the company's expansion and growth.
The 3 Horizons of Growth Template is a great tool to identify new areas of growth. This framework categorizes growth opportunities into three categories: Horizon 1 (core business), Horizon 2 (emerging business), and Horizon 3 (potential business).
One-page business plan
A one-page business plan is a condensed version of a full business plan that focuses on the most critical aspects of a business. It’s a great tool for entrepreneurs who want to quickly communicate their business idea to potential investors, partners, or employees.
A one-page business plan typically includes sections such as business concept, value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure.
Best practices for how to make a good business plan
Here are some additional tips for creating a business plan:
Use a template
A template can help you organize your thoughts and effectively communicate your business ideas and strategies. Starting with a template can also save you time and effort when formatting your plan.
Miro’s extensive library of customizable templates includes all the necessary sections for a comprehensive business plan. With our templates, you can confidently present your business plans to stakeholders and investors.
Be practical
Avoid overestimating revenue projections or underestimating expenses. Your business plan should be grounded in practical realities like your budget, resources, and capabilities.
Be specific
Provide as much detail as possible in your business plan. A specific plan is easier to execute because it provides clear guidance on what needs to be done and how. Without specific details, your plan may be too broad or vague, making it difficult to know where to start or how to measure success.
Be thorough with your research
Conduct thorough research to fully understand the market, your competitors, and your target audience . By conducting thorough research, you can identify potential risks and challenges your business may face and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Get input from others
It can be easy to become overly focused on your vision and ideas, leading to tunnel vision and a lack of objectivity. By seeking input from others, you can identify potential opportunities you may have overlooked.
Review and revise regularly
A business plan is a living document. You should update it regularly to reflect market, industry, and business changes. Set aside time for regular reviews and revisions to ensure your plan remains relevant and effective.
Create a winning business plan to chart your path to success
Starting or growing a business can be challenging, but it doesn't have to be. Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting, a well-written business plan can make or break your business’ success.
The purpose of a business plan is more than just to secure funding and attract investors. It also serves as a roadmap for achieving your business goals and realizing your vision. With the right mindset, tools, and strategies, you can develop a visually appealing, persuasive business plan.
Ready to make an effective business plan that works for you? Check out our library of ready-made strategy and planning templates and chart your path to success.
Get on board in seconds
Join thousands of teams using Miro to do their best work yet.
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Write a Business Plan, Step by Step

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
What is a business plan?
1. write an executive summary, 2. describe your company, 3. state your business goals, 4. describe your products and services, 5. do your market research, 6. outline your marketing and sales plan, 7. perform a business financial analysis, 8. make financial projections, 9. summarize how your company operates, 10. add any additional information to an appendix, business plan tips and resources.
A business plan outlines your business’s financial goals and explains how you’ll achieve them over the next three to five years. Here’s a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan that will offer a strong, detailed road map for your business.

ZenBusiness
A business plan is a document that explains what your business does, how it makes money and who its customers are. Internally, writing a business plan should help you clarify your vision and organize your operations. Externally, you can share it with potential lenders and investors to show them you’re on the right track.
Business plans are living documents; it’s OK for them to change over time. Startups may update their business plans often as they figure out who their customers are and what products and services fit them best. Mature companies might only revisit their business plan every few years. Regardless of your business’s age, brush up this document before you apply for a business loan .
» Need help writing? Learn about the best business plan software .
This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your business offers and a broad summary of your financial growth plans.
Though the executive summary is the first thing your investors will read, it can be easier to write it last. That way, you can highlight information you’ve identified while writing other sections that go into more detail.
» MORE: How to write an executive summary in 6 steps
Next up is your company description. This should contain basic information like:
Your business’s registered name.
Address of your business location .
Names of key people in the business. Make sure to highlight unique skills or technical expertise among members of your team.
Your company description should also define your business structure — such as a sole proprietorship, partnership or corporation — and include the percent ownership that each owner has and the extent of each owner’s involvement in the company.
Lastly, write a little about the history of your company and the nature of your business now. This prepares the reader to learn about your goals in the next section.
» MORE: How to write a company overview for a business plan

The third part of a business plan is an objective statement. This section spells out what you’d like to accomplish, both in the near term and over the coming years.
If you’re looking for a business loan or outside investment, you can use this section to explain how the financing will help your business grow and how you plan to achieve those growth targets. The key is to provide a clear explanation of the opportunity your business presents to the lender.
For example, if your business is launching a second product line, you might explain how the loan will help your company launch that new product and how much you think sales will increase over the next three years as a result.
» MORE: How to write a successful business plan for a loan
In this section, go into detail about the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
You should include the following:
An explanation of how your product or service works.
The pricing model for your product or service.
The typical customers you serve.
Your supply chain and order fulfillment strategy.
You can also discuss current or pending trademarks and patents associated with your product or service.
Lenders and investors will want to know what sets your product apart from your competition. In your market analysis section , explain who your competitors are. Discuss what they do well, and point out what you can do better. If you’re serving a different or underserved market, explain that.
Here, you can address how you plan to persuade customers to buy your products or services, or how you will develop customer loyalty that will lead to repeat business.
Include details about your sales and distribution strategies, including the costs involved in selling each product .
» MORE: R e a d our complete guide to small business marketing
If you’re a startup, you may not have much information on your business financials yet. However, if you’re an existing business, you’ll want to include income or profit-and-loss statements, a balance sheet that lists your assets and debts, and a cash flow statement that shows how cash comes into and goes out of the company.
Accounting software may be able to generate these reports for you. It may also help you calculate metrics such as:
Net profit margin: the percentage of revenue you keep as net income.
Current ratio: the measurement of your liquidity and ability to repay debts.
Accounts receivable turnover ratio: a measurement of how frequently you collect on receivables per year.
This is a great place to include charts and graphs that make it easy for those reading your plan to understand the financial health of your business.
This is a critical part of your business plan if you’re seeking financing or investors. It outlines how your business will generate enough profit to repay the loan or how you will earn a decent return for investors.
Here, you’ll provide your business’s monthly or quarterly sales, expenses and profit estimates over at least a three-year period — with the future numbers assuming you’ve obtained a new loan.
Accuracy is key, so carefully analyze your past financial statements before giving projections. Your goals may be aggressive, but they should also be realistic.
NerdWallet’s picks for setting up your business finances:
The best business checking accounts .
The best business credit cards .
The best accounting software .
Before the end of your business plan, summarize how your business is structured and outline each team’s responsibilities. This will help your readers understand who performs each of the functions you’ve described above — making and selling your products or services — and how much each of those functions cost.
If any of your employees have exceptional skills, you may want to include their resumes to help explain the competitive advantage they give you.
Finally, attach any supporting information or additional materials that you couldn’t fit in elsewhere. That might include:
Licenses and permits.
Equipment leases.
Bank statements.
Details of your personal and business credit history, if you’re seeking financing.
If the appendix is long, you may want to consider adding a table of contents at the beginning of this section.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
Here are some tips to write a detailed, convincing business plan:
Avoid over-optimism: If you’re applying for a business bank loan or professional investment, someone will be reading your business plan closely. Providing unreasonable sales estimates can hurt your chances of approval.
Proofread: Spelling, punctuation and grammatical errors can jump off the page and turn off lenders and prospective investors. If writing and editing aren't your strong suit, you may want to hire a professional business plan writer, copy editor or proofreader.
Use free resources: SCORE is a nonprofit association that offers a large network of volunteer business mentors and experts who can help you write or edit your business plan. The U.S. Small Business Administration’s Small Business Development Centers , which provide free business consulting and help with business plan development, can also be a resource.
On a similar note...
Find small-business financing
Compare multiple lenders that fit your business

Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained

Noah Parsons
5 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023
Many business owners know and understand the value of a business plan. The business plan is a key component of the startup and fundraising process and serves as a foundation for your organization. However, it only tells part of the story. To get the whole picture and have a framework on which to build your business you also need a strategic plan and an operational plan.
- What is a business plan?
In its simplest format, a business plan describes the “who” and the “what” of your business. It lays out who is running the business and what the business does. It describes the products and services that your business sells and who the customers are.
- What is a strategic plan?
A strategic plan looks beyond the basics of a business plan to explain the “how”. It explains the long-term goals of the business and how it expects to achieve those goals over the long term. A strategic plan explores future products and services that your business might offer and target markets that you might expand into. The plan explains your strategy for long-term growth and expansion.
- What is an operational plan?
An operation plan zooms into the details of your business to explain how you are going to achieve your short-term goals . It is the “when” and “where” of your planning process. The operational plan covers the details of marketing campaigns, short-term product development, and more immediate goals and projects that will happen within the next year.
- What is the difference between a strategic plan and a business plan?
First, let’s look at the difference between a business and a strategic plan. For review:
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of the business. The strategic plan gives us long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there, providing a long-term view.
In broader terms, the business plan tells us who by showing us:
- Who is running the business? What makes them qualified? What do they bring to the table that adds value?
- Who is the competition? What do they offer and what makes you different?
- Who is your customer? How big is the market? Where are they? What do they want and how will you give it to them? Also, how will you connect with your market?
The business plan answers the “what” by telling us:
- What the business provides and how it’s provided.
- Product, services, and operations are all explained so that readers understand how customer needs are met.
The strategic plan, on the other hand, outlines long term goals and the “how”, focusing on the following:
- Where will the business be in 3, 5, or even 10 years?
- How will you expand to offer different products and services over time?
- Will your market and industry change over time and how will your business react to those changes?
- How will you grow your market and reach new customers?
- What needs to happen so you can achieve your goals? What resources do you need to get there?
- How will you measure success? What metrics matter and how will you track them?
So, your business plan explains what you are doing right now. Your strategic plan explains long-term aspirations and how you plan to transition your business from where it is today to where you want it to be in the future. The strategic plan helps you look more deeply into the future and explains the key moves you have to make to achieve your vision.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What is the difference between strategic planning and operational planning?
While strategic planning looks at the long term and explains your broad strategies for growth, an operational plan looks at the short term. It explains the details of what your business is going to do and when it’s going to do it over the next twelve months or so. An operational plan covers details like:
- What activities need to happen to achieve your business goals?
- When will each activity take place, who will do it, and when do you need to reach specific milestones?
- How will your business operate? What suppliers will you work with? When do you need to have them in place?
- What marketing campaigns will you run and what will they cost?
- What investments will you make in your products and services this year?
The bottom line, your operational plan is the short-term action plan for your business. It’s the tasks, milestones, and steps needed to drive your business forward. Typically an operational plan provides details for a 1-year period, while a strategic plan looks at a 3-5 year timeline , and sometimes even longer. The operational plan is essentially the roadmap for how you will execute your strategic plan.
- How to use your business plan for strategic development and operations
A great business plan can encompass both the basic plans for the business, the long-term strategic plan, and the near-term operational plan. Using a lean planning method, you can tackle all three phases of planning and make the process easy to review and revise as your business grows, changes, and adapts.
Start with a simple plan
The lean planning methodology starts with a simple, 30-minute business plan that outlines the fundamentals of your business: who you are, what you are doing, and who your customers are. It’s a great way to provide a brief overview of your business.
Expand your plan
From there, you can expand your plan to include your longer-term strategy. Adding greater detail to elements of the plan to explain long-term goals, milestones, and how your products and services will change and expand over time to meet changing market conditions.
Finally, your lean plan will cover financial forecasts that include monthly details about the short-term revenue and expenses, as well as longer-term annual summaries of your financial goals, including profitability and potential future loans and investments.
- Use your business plan to manage your business
Regardless of the type of plan, you are working on, you need a team of players on hand to help you plan, develop, and execute both the operational and strategic plans. Remember, your business needs both to give it a clear foundation and a sense of direction. As well as to assist you with identifying the detailed work that has to happen to help you reach your long-term goals.
Learn how LivePlan can help you develop a business plan that defines your business, outlines strategic steps, and tracks ongoing operations. You can easily share it with your team and all of the right stakeholders, explore scenarios and update your plan based on real-world results. Everything you need to turn your business plan into a tool for growth.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.

Table of Contents
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free

12 Min. Read
Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes

3 Min. Read
5 Fundamental Principles of Business Planning

11 Key Components of a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

From template to plan in 30 minutes
- Step-by-step guidance
- Crystal clear financials
- Expert advice at your fingertips
- Funding & lender ready formats
- PLUS all the tools to manage & grow

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, how often should a business plan be updated, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that details a company's goals and how it intends to achieve them. Business plans can be of benefit to both startups and well-established companies. For startups, a business plan can be essential for winning over potential lenders and investors. Established businesses can find one useful for staying on track and not losing sight of their goals. This article explains what an effective business plan needs to include and how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document describing a company's business activities and how it plans to achieve its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to get off the ground and attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan can help keep the executive team focused on and working toward the company's short- and long-term objectives.
- There is no single format that a business plan must follow, but there are certain key elements that most companies will want to include.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place prior to beginning operations. In fact, banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before they'll consider making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a business isn't looking to raise additional money, a business plan can help it focus on its goals. A 2017 Harvard Business Review article reported that, "Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical nonplanning entrepreneurs."
Ideally, a business plan should be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect any goals that have been achieved or that may have changed. An established business that has decided to move in a new direction might create an entirely new business plan for itself.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. These include being able to think through ideas before investing too much money in them and highlighting any potential obstacles to success. A company might also share its business plan with trusted outsiders to get their objective feedback. In addition, a business plan can help keep a company's executive team on the same page about strategic action items and priorities.
Business plans, even among competitors in the same industry, are rarely identical. However, they often have some of the same basic elements, as we describe below.
While it's a good idea to provide as much detail as necessary, it's also important that a business plan be concise enough to hold a reader's attention to the end.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, it's best to fit the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document. Other crucial elements that take up a lot of space—such as applications for patents—can be referenced in the main document and attached as appendices.
These are some of the most common elements in many business plans:
- Executive summary: This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services: Here, the company should describe the products and services it offers or plans to introduce. That might include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other factors that could go into this section include production and manufacturing processes, any relevant patents the company may have, as well as proprietary technology . Information about research and development (R&D) can also be included here.
- Market analysis: A company needs to have a good handle on the current state of its industry and the existing competition. This section should explain where the company fits in, what types of customers it plans to target, and how easy or difficult it may be to take market share from incumbents.
- Marketing strategy: This section can describe how the company plans to attract and keep customers, including any anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. It should also describe the distribution channel or channels it will use to get its products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections: Established businesses can include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses can provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. Your plan might also include any funding requests you're making.
The best business plans aren't generic ones created from easily accessed templates. A company should aim to entice readers with a plan that demonstrates its uniqueness and potential for success.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can take many forms, but they are sometimes divided into two basic categories: traditional and lean startup. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These plans tend to be much longer than lean startup plans and contain considerably more detail. As a result they require more work on the part of the business, but they can also be more persuasive (and reassuring) to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These use an abbreviated structure that highlights key elements. These business plans are short—as short as one page—and provide only the most basic detail. If a company wants to use this kind of plan, it should be prepared to provide more detail if an investor or a lender requests it.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan is not a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections to begin with. Markets and the overall economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All of this calls for building some flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on the nature of the business. A well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary. A new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is an option when a company prefers to give a quick explanation of its business. For example, a brand-new company may feel that it doesn't have a lot of information to provide yet.
Sections can include: a value proposition ; the company's major activities and advantages; resources such as staff, intellectual property, and capital; a list of partnerships; customer segments; and revenue sources.
A business plan can be useful to companies of all kinds. But as a company grows and the world around it changes, so too should its business plan. So don't think of your business plan as carved in granite but as a living document designed to evolve with your business.
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans for May 2024 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How To Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
What Is Business Strategy & Why Is It Important?

- 20 Oct 2022
Every business leader wants their organization to succeed. Turning a profit and satisfying stakeholders are worthy objectives but aren’t feasible without an effective business strategy.
To attain success, leaders must hone their skills and set clear business goals by crafting a strategy that creates value for the firm, customers, suppliers, and employees. Here's an overview of business strategy and why it's essential to your company’s success.
Access your free e-book today.
What’s a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the strategic initiatives a company pursues to create value for the organization and its stakeholders and gain a competitive advantage in the market. This strategy is crucial to a company's success and is needed before any goods or services are produced or delivered.
According to Harvard Business School Online's Business Strategy course, an effective strategy is built around three key questions:
- How can my business create value for customers?
- How can my business create value for employees?
- How can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers?
Many promising business initiatives don’t come to fruition because the company failed to build its strategy around value creation. Creativity is important in business , but a company won't last without prioritizing value.
The Importance of Business Strategy
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including:
- Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials
- Suppliers: Whether to source materials sustainably and from which suppliers
- Employee recruitment: How to attract and maintain talent
- Resource allocation: How to allocate resources effectively
Without a clear business strategy, a company can't create value and is unlikely to succeed.
Creating Value
To craft a successful business strategy, it's necessary to obtain a thorough understanding of value creation. In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee explains that, at its core, value represents a difference. For example, the difference between a customer's willingness to pay for a good or service and its price represents the value the business has created for the customer. This difference can be visualized with a tool known as the value stick.
The value stick has four components, representing the value a strategy can bring different stakeholders.

- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The maximum amount a customer is willing to pay for a company's goods or services
- Price : The actual price of the goods or services
- Cost : The cost of the raw materials required to produce the goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to receive for raw materials, or the minimum employees are willing to earn for their work
The difference between each component represents the value created for each stakeholder. A business strategy seeks to widen these gaps, increasing the value created by the firm’s endeavors.
Increasing Customer Delight
The difference between a customer's WTP and the price is known as customer delight . An effective business strategy creates value for customers by raising their WTP or decreasing the price of the company’s goods or services. The larger the difference between the two, the more value is created for customers.
A company might focus on increasing WTP with its marketing strategy. Effective market research can help a company set its pricing strategy by determining target customers' WTP and finding ways to increase it. For example, a business might differentiate itself and increase customer loyalty by incorporating sustainability into its business strategy. By aligning its values with its target audiences', an organization can effectively raise consumers' WTP.
Increasing Firm Margin
The value created for the firm is the difference between the price of an item and its cost to produce. This difference is known as the firm’s margin and represents the strategy's financial success. One metric used to quantify this margin is return on invested capital (ROIC) . This metric compares a business's operating income with the capital necessary to generate it. The formula for ROIC is:
Return on Invested Capital = Net Operating Cost After Tax (NOCAT) / Invested Capital (IC)
ROIC tells investors how successful a company is at turning its investments into profit. By raising WTP, a company can risk increasing prices, thereby increasing firm margin. Business leaders can also increase this metric by decreasing their costs. For example, sustainability initiatives—in addition to raising WTP—can lower production costs by using fewer or more sustainable resources. By focusing on the triple bottom line , a firm can simultaneously increase customer delight and margin.
Increasing Supplier Surplus & Employee Satisfaction
By decreasing suppliers' WTS, or increasing costs, a company can create value for suppliers—or supplier surplus . Since increasing costs isn't sustainable, an effective business strategy seeks to create value for suppliers by decreasing WTS. How a company accomplishes this varies. For example, a brick-and-mortar company might partner with vendors to showcase its products in exchange for a discount. Suppliers may also be willing to offer a discount in exchange for a long-term contract.
In addition to supplier WTS, companies are also responsible for creating value for another key stakeholder: its employees. The difference between employee compensation and the minimum they're willing to receive is employee satisfaction . There are several ways companies can increase this difference, including:
- Increasing compensation: While most companies hesitate to raise salaries, some have found success in doing so. For example, Dan Price, CEO of Gravity Payments, increased his company's minimum wage to $80,000 per year and enjoyed substantial growth and publicity as a result.
- Increasing benefits: Companies can also decrease WTS by making working conditions more desirable to prospective employees. Some offer remote or hybrid working opportunities to give employees more flexibility. Several have also started offering four-day work weeks , often experiencing increased productivity as a result.
There are several ways to increase supplier surplus and employee satisfaction without hurting the company's bottom line. Unfortunately, most managers only devote seven percent of their time to developing employees and engaging stakeholders. Yet, a successful strategy creates value for every stakeholder—both internal and external.


Strategy Implementation
Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution . Successful implementation includes the following steps :
- Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
- Delegate work and allocate resources effectively
- Put the plan into action and continuously monitor its progress
- Adjust your plan as necessary
- Ensure your team has what they need to succeed and agrees on the desired outcome
- Evaluate the results of the plan
Throughout the process, it's important to remember to adjust your plan throughout its execution but to avoid second-guessing your decisions. Striking this balance is challenging, but crucial to a business strategy's success.

Learn More About Creating a Successful Business Strategy
Business strategy constantly evolves with changing consumer expectations and market conditions. For this reason, business leaders should continuously educate themselves on creating and executing an effective strategy.
One of the best ways to stay up-to-date on best practices is to take an online course, such as HBS Online's Business Strategy program. The course will provide guidance on creating a value-driven strategy for your business.
Do you want to learn how to craft an effective business strategy and create value for your company's stakeholders? Explore our online course Business Strategy , or other strategy courses , to develop your strategic planning skills. To determine which strategy course is right for you, download our free flowchart .

About the Author
Which Comes First: The Goal Or The Strategy?
Table of contents

Enjoy reading this blog post written by our experts or partners.
If you want to see what Databox can do for you, click here .
For most people, the answer is obvious. You define a goal first and then work out a strategy that will help you achieve that goal. Simple, right? Well, things are not quite that clear-cut.
Databox has surveyed 91 companies in various fields, from B2B and B2C Services or Products to Marketing and Digital Media Consultants and Agencies. We’ve discovered that roughly two-thirds of respondents (67.03%) stated they set goals first while just over a quarter (27.47%) said that strategy comes first in their business. The remaining 5.49% were undecided.
What muddies the waters somewhat is the fact that companies tend to focus on strategy more. Over half (57%) of our respondents prioritize strategy over goals (47%).
So what’s really important here? Strategy or goals?
Well, it turns out that people frequently use objectives, goals, and ideas interchangeably, and see no real difference between a strategy and tactics. By necessity, the advice presented seems contradictory.
We’ll do our best to present it clearly and it will be up to you to decide what approach best suits your business.
This article covers:
Strategy vs Tactics
Companies set goals first.
- But Focus on Strategy More
Why You Should Set Strategy First
- Why You Should Define Business Objectives First
The Takeaway
In simple terms, strategy is what defines your long-term goals and lays out a plan to achieve them. It’s the path you follow in order to achieve your mission, vision, or idea. It’s usually defined in broad strokes and it’s more about planning than doing.
Tactics, on the other hand, focus on smaller, more concrete steps you can undertake in the service of your strategy. It’s more focused on the short term and involves specific plans, best practices, and objectives.
A good way to differentiate between them is to think of the maxim “ Think strategically, act tactically. ”
A good strategy should reflect the core values of an organization and clearly align with the priorities of any separate departments, while a good tactic should have a clear purpose that aids your strategy.
Both strategy and tactics need to work together in order to realize the company’s vision. In essence, they’re both necessary.
Reaching strategic goals is impossible without tactics since tactics are the concrete steps you need to take to get where you want to go. Conversely, relying on tactics without a strategy just leads to aimless busywork. Without a unifying vision, you’re at risk of taking random actions with no end in sight.
Related : What Is Strategic Reporting? 4 Report Examples to Get Inspiration From
Here, we have a clear favorite with over two-thirds of respondents saying they set goals first and only 27.47% do the same with strategy.
Most agree it’s hard to build a strategy if you don’t know what you want to accomplish and that strategies without goals tend to be aimless. After all, you have to know where you’re going in order to plan the trip.
Lydia Mwangi of Barbell Jobs compares setting a strategy without a goal to picking a random recipe and hoping to get the cake that you wanted. “You have to know the kind of cake you want first so that you can objectively come up with, or decide on the right ingredients.” Know what you want to do before figuring out how to do it.
Gerrard Lipscombe of Landmark Labs has a slightly different take. In his view, strategy and goals co-evolve with one another through time. The first step is still to ‘set the clearest possible goal you can formulate’ and then go about developing a concrete strategy to reach it.
That doesn’t end the process. “Even in the initial process of strategizing, it’s common to reassess and gather new information that will, in turn, adjust your goals.
Through time this interplay evolves, and eventually, it becomes difficult to say with confidence which is the prime mover: one’s goals, or the strategy to achieve them,” Lipscombe concludes.
Related : Goals vs. KPIs: How to Set KPIs and Targets That Will Help You Reach Your Business Goals
…But Focus on Strategy More
This is not as contradictory as it seems at first. In a way, setting a goal is easy, strategy takes work and refinement. A slight but noticeable majority of our respondents say they spend more time working out their strategies than their goals (57% to 43%).
Information’s Candice Moses emphasizes the importance of strategy. “Strategy is about making decisions, weighing trade-offs, and deciding what type of distinctive value you will offer to particular clients in our cutthroat market. Building a strong presence inside the market is a strategy. It’s important to get and keep focused on business.” Setting goals is all well and good, but it doesn’t mean anything unless you know exactly what you’re giving the customer and what your business needs to concentrate on.
Naturally, some goals arise from strategy and both will evolve and change as time goes on and the market changes. While the maxim “ No plan survives the contact with the enemy ” initially referred to the military, it’s universally applicable.
As your strategy is put into place, you’ll gain more information about its effectiveness and be able to adjust it accordingly.
The goals themselves are less likely to change at an early juncture as you’ll simply use them to gauge the effectiveness of your strategy.
PRO TIP: How Well Are Your Marketing KPIs Performing?
Like most marketers and marketing managers, you want to know how well your efforts are translating into results each month. How much traffic and new contact conversions do you get? How many new contacts do you get from organic sessions? How are your email campaigns performing? How well are your landing pages converting? You might have to scramble to put all of this together in a single report, but now you can have it all at your fingertips in a single Databox dashboard.
Our Marketing Overview Dashboard includes data from Google Analytics 4 and HubSpot Marketing with key performance metrics like:
- Sessions . The number of sessions can tell you how many times people are returning to your website. Obviously, the higher the better.
- New Contacts from Sessions . How well is your campaign driving new contacts and customers?
- Marketing Performance KPIs . Tracking the number of MQLs, SQLs, New Contacts and similar will help you identify how your marketing efforts contribute to sales.
- Email Performance . Measure the success of your email campaigns from HubSpot. Keep an eye on your most important email marketing metrics such as number of sent emails, number of opened emails, open rate, email click-through rate, and more.
- Blog Posts and Landing Pages . How many people have viewed your blog recently? How well are your landing pages performing?
Now you can benefit from the experience of our Google Analytics and HubSpot Marketing experts, who have put together a plug-and-play Databox template that contains all the essential metrics for monitoring your leads. It’s simple to implement and start using as a standalone dashboard or in marketing reports, and best of all, it’s free!
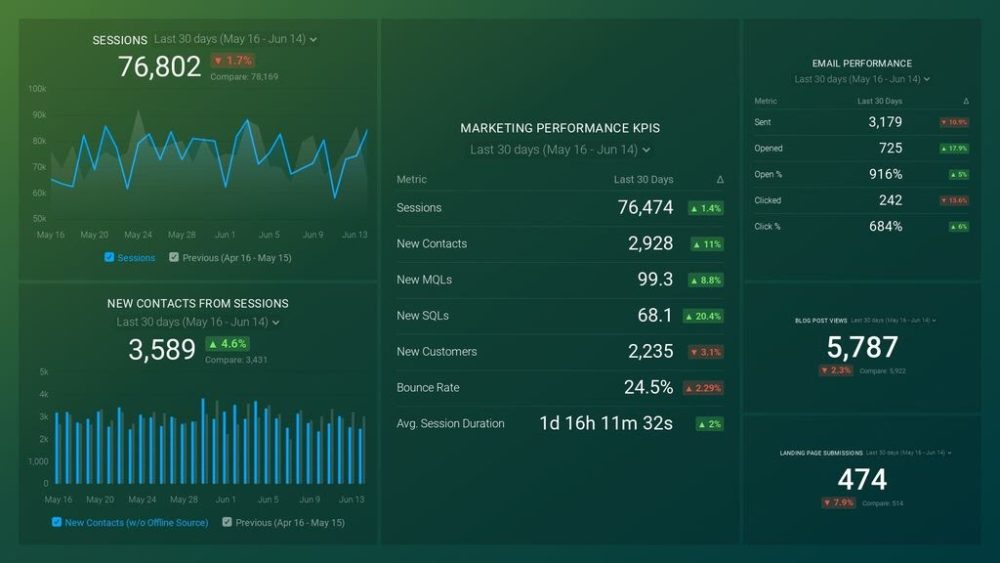
You can easily set it up in just a few clicks – no coding required.
To set up the dashboard, follow these 3 simple steps:
Step 1: Get the template
Step 2: Connect your HubSpot and Google Analytics 4 accounts with Databox.
Step 3: Watch your dashboard populate in seconds.
People who put strategy before goals tend to think of goals as parts of the strategy or milestones that a strategy should achieve. There’s a unifying vision or the main objective that a strategy should achieve, but goals are something different.
Brandconvert’s Andrew Spence firmly believes in getting strategy down first. “This is because without a strategy in place, it is very difficult to know what the goals should be. A clear strategy will help guide the business and ensure that all decisions are in line with the company’s overall vision.”
In addition, a strategy can help set the tone for the company and expectations for employees. If you set goals without having a strategy in place, you risk bouncing around without purpose or direction, which can be demoralizing for employees.
The best way to think of a strategy is as a roadmap for your business. Mark Pierce of Cloud Peak Law Group believes that creating it first can help you set more clearly defined and targeted goals. “That being said, goals and strategy go hand in hand, and one without the other isn’t enough. Once you’ve laid out your strategy, goals help to ensure that steady progress is being made and provides you with something measurable to track,” Pierce concludes.
A good strategy will outline the steps that you need to take to reach your destination. Once it’s in place, you can set goals that align with it. In the opinion of Harry Johns white of NBA Blast , Developing a clear and achievable strategy is the only way you can hope to reach your destination.
Related : How to Write a Marketing Strategy? (5 Ready-to-Use Report Templates Included)
Why You Should Define Business Goals First
A journey starts when you set a destination. This is a common approach to running a business and over 67% of our respondents define goals before setting strategy. The common response is that you simply need to know where you’re going before planning your trip, and it does ring true.
People who want to define goals first tend to think of them as big ideas and endpoints, rather than smaller goals that are a part of the strategy.
C Shakhawat Sultan of WPFunnels says that “A company should know what it wants to achieve. It should have a target vision and goal it wants to reach at the end of the year. Once the goal is clear, then you start devising strategies to achieve that goal.” That way, you’ll have a clear idea of what needs to be achieved with your strategy, which will help you plan for long-term results.
Despite focusing on goals first, Sultan still thinks that both are equally important. “If you do not have a proper visionary goal, your strategies won’t be good enough to help you grow your business. If your strategy is not well-planned, then you might fail to reach your goal. So they both have equal importance in the process.”
This is a recurring theme in all the answers we analyzed. Define the goals in order to build a strategy around achieving them. Goals should be the drivers of strategy and according to Julia Tiedt of SmartBug Media , you should simply ignore strategy ideas that don’t line up with your goals. Getting sales and marketing to align on shared goals and KPIs is the real first step. Only after they’ve agreed on goals can the real strategic planning begin.
Related : Goals Based Reporting: Everything You Need to Know
It’s clear that our respondents are well-aware that both goals and strategies are important. However, they need something to focus on and the goals seem more tangible and easier to pin down. In addition, goal progress is easier to monitor than strategy. After they defined their goals, companies build a strategy around them and focus on fine-tuning it quite a lot.
Of course, some think of different things when they say “strategy” and “goal.” For people who think you have to set the strategy first, goals are simply metrics by which you gauge the effectiveness of your strategy. For those who believe in defining goals, goals are big objectives that shape what the strategy is aiming for and it doesn’t make sense to “plan a road trip without knowing where you’re headed.”
These disparate opinions can lead to somewhat confusing results, but our takeaway is that most people would agree with the sequence of vision > strategy > goals (or objectives).
Ensuring all of these aspects are in sync is paramount and none of them can function in isolation.
Vision is as necessary as strategy and if you don’t set up objectives, you’ll have a hard time tracking the progress of your strategy.
Of course, it’s possible to set up objectives first and then build a strategy around them, this is particularly useful for agencies working with clients who have clearly defined goals they want to achieve. In this case, you have business goals pre-built and focus on figuring out how to best achieve them.
In either case, tracking goals is absolutely essential if you want to know how well you’re doing in the market. With the right dashboard, you’ll be able to visualize performance and analyze your progress. With Databox, you’ll be able to set goals for any metric from literally any data source, visualize your goals against current performance and make adjustments when they matter most. Try out Databox by signing up for a free account today.
Do you want an All-in-One Analytics Platform?
Hey, we’re Databox. Our mission is to help businesses save time and grow faster. Click here to see our platform in action.
- Databox Benchmarks
- Future Value Calculator
- ROI Calculator
- Return On Ads Calculator
- Percentage Growth Rate Calculator
- Report Automation
- Client Reporting
- What is a KPI?
- Google Sheets KPIs
- Sales Analysis Report
- Shopify Reports
- Data Analysis Report
- Google Sheets Dashboard
- Best Dashboard Examples
- Analysing Data
- Marketing Agency KPIs
- Automate Agency Google Ads Report
- Marketing Research Report
- Social Media Dashboard Examples
- Ecom Dashboard Examples

Does Your Performance Stack Up?
Are you maximizing your business potential? Stop guessing and start comparing with companies like yours.

A Message From Our CEO
At Databox, we’re obsessed with helping companies more easily monitor, analyze, and report their results. Whether it’s the resources we put into building and maintaining integrations with 100+ popular marketing tools, enabling customizability of charts, dashboards, and reports, or building functionality to make analysis, benchmarking, and forecasting easier, we’re constantly trying to find ways to help our customers save time and deliver better results.
Davor is an English literature graduate and an avid reader with a passion for languages. Working as a translator, editor, and writer has allowed him to learn about a wide range of topics — making him something of a jack-of-all-trades when it comes to content. In his spare time, he reads, plays video games and boardgames, and runs/plays tabletop RPGs.
Get practical strategies that drive consistent growth
12 Tips for Developing a Successful Data Analytics Strategy

What Is Data Reporting and How to Create Data Reports for Your Business

What Is KPI Reporting? KPI Report Examples, Tips, and Best Practices
Build your first dashboard in 5 minutes or less.
Latest from our blog
- The State of B2B Content Creation: Navigating the Future of In-House Marketing Innovation May 9, 2024
- New in Databox: Analyze the Performance of Any Metric or KPI with Metric Insights April 22, 2024
- Metrics & KPIs
- vs. Tableau
- vs. Looker Studio
- vs. Klipfolio
- vs. Power BI
- vs. Whatagraph
- vs. AgencyAnalytics
- Product & Engineering
- Inside Databox
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Talent Resources
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- API Documentation
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Business strategy |
- What is strategic planning? A 5-step gu ...
What is strategic planning? A 5-step guide

Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. In this article, we'll guide you through the strategic planning process, including why it's important, the benefits and best practices, and five steps to get you from beginning to end.
Strategic planning is a process through which business leaders map out their vision for their organization’s growth and how they’re going to get there. The strategic planning process informs your organization’s decisions, growth, and goals.
Strategic planning helps you clearly define your company’s long-term objectives—and maps how your short-term goals and work will help you achieve them. This, in turn, gives you a clear sense of where your organization is going and allows you to ensure your teams are working on projects that make the most impact. Think of it this way—if your goals and objectives are your destination on a map, your strategic plan is your navigation system.
In this article, we walk you through the 5-step strategic planning process and show you how to get started developing your own strategic plan.
How to build an organizational strategy
Get our free ebook and learn how to bridge the gap between mission, strategic goals, and work at your organization.
What is strategic planning?
Strategic planning is a business process that helps you define and share the direction your company will take in the next three to five years. During the strategic planning process, stakeholders review and define the organization’s mission and goals, conduct competitive assessments, and identify company goals and objectives. The product of the planning cycle is a strategic plan, which is shared throughout the company.
What is a strategic plan?
![what comes first business plan or strategy [inline illustration] Strategic plan elements (infographic)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/7d1f14e4-b008-4ea6-9579-5af6236ce367/inline-business-strategy-strategic-planning-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A strategic plan is the end result of the strategic planning process. At its most basic, it’s a tool used to define your organization’s goals and what actions you’ll take to achieve them.
Typically, your strategic plan should include:
Your company’s mission statement
Your organizational goals, including your long-term goals and short-term, yearly objectives
Any plan of action, tactics, or approaches you plan to take to meet those goals
What are the benefits of strategic planning?
Strategic planning can help with goal setting and decision-making by allowing you to map out how your company will move toward your organization’s vision and mission statements in the next three to five years. Let’s circle back to our map metaphor. If you think of your company trajectory as a line on a map, a strategic plan can help you better quantify how you’ll get from point A (where you are now) to point B (where you want to be in a few years).
When you create and share a clear strategic plan with your team, you can:
Build a strong organizational culture by clearly defining and aligning on your organization’s mission, vision, and goals.
Align everyone around a shared purpose and ensure all departments and teams are working toward a common objective.
Proactively set objectives to help you get where you want to go and achieve desired outcomes.
Promote a long-term vision for your company rather than focusing primarily on short-term gains.
Ensure resources are allocated around the most high-impact priorities.
Define long-term goals and set shorter-term goals to support them.
Assess your current situation and identify any opportunities—or threats—allowing your organization to mitigate potential risks.
Create a proactive business culture that enables your organization to respond more swiftly to emerging market changes and opportunities.
What are the 5 steps in strategic planning?
The strategic planning process involves a structured methodology that guides the organization from vision to implementation. The strategic planning process starts with assembling a small, dedicated team of key strategic planners—typically five to 10 members—who will form the strategic planning, or management, committee. This team is responsible for gathering crucial information, guiding the development of the plan, and overseeing strategy execution.
Once you’ve established your management committee, you can get to work on the planning process.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment
Before you can define where you’re going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
To do this, your management committee should collect a variety of information from additional stakeholders, like employees and customers. In particular, plan to gather:
Relevant industry and market data to inform any market opportunities, as well as any potential upcoming threats in the near future.
Customer insights to understand what your customers want from your company—like product improvements or additional services.
Employee feedback that needs to be addressed—whether about the product, business practices, or the day-to-day company culture.
Consider different types of strategic planning tools and analytical techniques to gather this information, such as:
A balanced scorecard to help you evaluate four major elements of a business: learning and growth, business processes, customer satisfaction, and financial performance.
A SWOT analysis to help you assess both current and future potential for the business (you’ll return to this analysis periodically during the strategic planning process).
To fill out each letter in the SWOT acronym, your management committee will answer a series of questions:
What does your organization currently do well?
What separates you from your competitors?
What are your most valuable internal resources?
What tangible assets do you have?
What is your biggest strength?
Weaknesses:
What does your organization do poorly?
What do you currently lack (whether that’s a product, resource, or process)?
What do your competitors do better than you?
What, if any, limitations are holding your organization back?
What processes or products need improvement?
Opportunities:
What opportunities does your organization have?
How can you leverage your unique company strengths?
Are there any trends that you can take advantage of?
How can you capitalize on marketing or press opportunities?
Is there an emerging need for your product or service?
What emerging competitors should you keep an eye on?
Are there any weaknesses that expose your organization to risk?
Have you or could you experience negative press that could reduce market share?
Is there a chance of changing customer attitudes towards your company?
Step 2: Identify your company’s goals and objectives
To begin strategy development, take into account your current position, which is where you are now. Then, draw inspiration from your vision, mission, and current position to identify and define your goals—these are your final destination.
To develop your strategy, you’re essentially pulling out your compass and asking, “Where are we going next?” “What’s the ideal future state of this company?” This can help you figure out which path you need to take to get there.
During this phase of the planning process, take inspiration from important company documents, such as:
Your mission statement, to understand how you can continue moving towards your organization’s core purpose.
Your vision statement, to clarify how your strategic plan fits into your long-term vision.
Your company values, to guide you towards what matters most towards your company.
Your competitive advantages, to understand what unique benefit you offer to the market.
Your long-term goals, to track where you want to be in five or 10 years.
Your financial forecast and projection, to understand where you expect your financials to be in the next three years, what your expected cash flow is, and what new opportunities you will likely be able to invest in.
Step 3: Develop your strategic plan and determine performance metrics
Now that you understand where you are and where you want to go, it’s time to put pen to paper. Take your current business position and strategy into account, as well as your organization’s goals and objectives, and build out a strategic plan for the next three to five years. Keep in mind that even though you’re creating a long-term plan, parts of your plan should be created or revisited as the quarters and years go on.
As you build your strategic plan, you should define:
Company priorities for the next three to five years, based on your SWOT analysis and strategy.
Yearly objectives for the first year. You don’t need to define your objectives for every year of the strategic plan. As the years go on, create new yearly objectives that connect back to your overall strategic goals .
Related key results and KPIs. Some of these should be set by the management committee, and some should be set by specific teams that are closer to the work. Make sure your key results and KPIs are measurable and actionable. These KPIs will help you track progress and ensure you’re moving in the right direction.
Budget for the next year or few years. This should be based on your financial forecast as well as your direction. Do you need to spend aggressively to develop your product? Build your team? Make a dent with marketing? Clarify your most important initiatives and how you’ll budget for those.
A high-level project roadmap . A project roadmap is a tool in project management that helps you visualize the timeline of a complex initiative, but you can also create a very high-level project roadmap for your strategic plan. Outline what you expect to be working on in certain quarters or years to make the plan more actionable and understandable.
Step 4: Implement and share your plan
Now it’s time to put your plan into action. Strategy implementation involves clear communication across your entire organization to make sure everyone knows their responsibilities and how to measure the plan’s success.
Make sure your team (especially senior leadership) has access to the strategic plan, so they can understand how their work contributes to company priorities and the overall strategy map. We recommend sharing your plan in the same tool you use to manage and track work, so you can more easily connect high-level objectives to daily work. If you don’t already, consider using a work management platform .
A few tips to make sure your plan will be executed without a hitch:
Communicate clearly to your entire organization throughout the implementation process, to ensure all team members understand the strategic plan and how to implement it effectively.
Define what “success” looks like by mapping your strategic plan to key performance indicators.
Ensure that the actions outlined in the strategic plan are integrated into the daily operations of the organization, so that every team member's daily activities are aligned with the broader strategic objectives.
Utilize tools and software—like a work management platform—that can aid in implementing and tracking the progress of your plan.
Regularly monitor and share the progress of the strategic plan with the entire organization, to keep everyone informed and reinforce the importance of the plan.
Establish regular check-ins to monitor the progress of your strategic plan and make adjustments as needed.
Step 5: Revise and restructure as needed
Once you’ve created and implemented your new strategic framework, the final step of the planning process is to monitor and manage your plan.
Remember, your strategic plan isn’t set in stone. You’ll need to revisit and update the plan if your company changes directions or makes new investments. As new market opportunities and threats come up, you’ll likely want to tweak your strategic plan. Make sure to review your plan regularly—meaning quarterly and annually—to ensure it’s still aligned with your organization’s vision and goals.
Keep in mind that your plan won’t last forever, even if you do update it frequently. A successful strategic plan evolves with your company’s long-term goals. When you’ve achieved most of your strategic goals, or if your strategy has evolved significantly since you first made your plan, it might be time to create a new one.
Build a smarter strategic plan with a work management platform
To turn your company strategy into a plan—and ultimately, impact—make sure you’re proactively connecting company objectives to daily work. When you can clarify this connection, you’re giving your team members the context they need to get their best work done.
A work management platform plays a pivotal role in this process. It acts as a central hub for your strategic plan, ensuring that every task and project is directly tied to your broader company goals. This alignment is crucial for visibility and coordination, allowing team members to see how their individual efforts contribute to the company’s success.
By leveraging such a platform, you not only streamline workflow and enhance team productivity but also align every action with your strategic objectives—allowing teams to drive greater impact and helping your company move toward goals more effectively.
Strategic planning FAQs
Still have questions about strategic planning? We have answers.
Why do I need a strategic plan?
A strategic plan is one of many tools you can use to plan and hit your goals. It helps map out strategic objectives and growth metrics that will help your company be successful.
When should I create a strategic plan?
You should aim to create a strategic plan every three to five years, depending on your organization’s growth speed.
Since the point of a strategic plan is to map out your long-term goals and how you’ll get there, you should create a strategic plan when you’ve met most or all of them. You should also create a strategic plan any time you’re going to make a large pivot in your organization’s mission or enter new markets.
What is a strategic planning template?
A strategic planning template is a tool organizations can use to map out their strategic plan and track progress. Typically, a strategic planning template houses all the components needed to build out a strategic plan, including your company’s vision and mission statements, information from any competitive analyses or SWOT assessments, and relevant KPIs.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. business plan?
A business plan can help you document your strategy as you’re getting started so every team member is on the same page about your core business priorities and goals. This tool can help you document and share your strategy with key investors or stakeholders as you get your business up and running.
You should create a business plan when you’re:
Just starting your business
Significantly restructuring your business
If your business is already established, you should create a strategic plan instead of a business plan. Even if you’re working at a relatively young company, your strategic plan can build on your business plan to help you move in the right direction. During the strategic planning process, you’ll draw from a lot of the fundamental business elements you built early on to establish your strategy for the next three to five years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. mission and vision statements?
Your strategic plan, mission statement, and vision statements are all closely connected. In fact, during the strategic planning process, you will take inspiration from your mission and vision statements in order to build out your strategic plan.
Simply put:
A mission statement summarizes your company’s purpose.
A vision statement broadly explains how you’ll reach your company’s purpose.
A strategic plan pulls in inspiration from your mission and vision statements and outlines what actions you’re going to take to move in the right direction.
For example, if your company produces pet safety equipment, here’s how your mission statement, vision statement, and strategic plan might shake out:
Mission statement: “To ensure the safety of the world’s animals.”
Vision statement: “To create pet safety and tracking products that are effortless to use.”
Your strategic plan would outline the steps you’re going to take in the next few years to bring your company closer to your mission and vision. For example, you develop a new pet tracking smart collar or improve the microchipping experience for pet owners.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. company objectives?
Company objectives are broad goals. You should set these on a yearly or quarterly basis (if your organization moves quickly). These objectives give your team a clear sense of what you intend to accomplish for a set period of time.
Your strategic plan is more forward-thinking than your company goals, and it should cover more than one year of work. Think of it this way: your company objectives will move the needle towards your overall strategy—but your strategic plan should be bigger than company objectives because it spans multiple years.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a business case?
A business case is a document to help you pitch a significant investment or initiative for your company. When you create a business case, you’re outlining why this investment is a good idea, and how this large-scale project will positively impact the business.
You might end up building business cases for things on your strategic plan’s roadmap—but your strategic plan should be bigger than that. This tool should encompass multiple years of your roadmap, across your entire company—not just one initiative.
What’s the difference between a strategic plan vs. a project plan?
A strategic plan is a company-wide, multi-year plan of what you want to accomplish in the next three to five years and how you plan to accomplish that. A project plan, on the other hand, outlines how you’re going to accomplish a specific project. This project could be one of many initiatives that contribute to a specific company objective which, in turn, is one of many objectives that contribute to your strategic plan.
What’s the difference between strategic management vs. strategic planning?
A strategic plan is a tool to define where your organization wants to go and what actions you need to take to achieve those goals. Strategic planning is the process of creating a plan in order to hit your strategic objectives.
Strategic management includes the strategic planning process, but also goes beyond it. In addition to planning how you will achieve your big-picture goals, strategic management also helps you organize your resources and figure out the best action plans for success.
Related resources
Grant management: A nonprofit’s guide

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

Solve your tech overload with an intelligent transformation

This is a great place to tell people more about yourself and peak their interest.
For more info, they can follow you on social in a click.

- iota consultants
- Mar 23, 2022
Strategic Plan or Business Plan: What Comes First?
The classic chicken and egg question: what comes first?
We can only speculate to the chicken and egg question, but we do know the answer to the order when it comes to strategic planning and business planning.

In order to answer that question, we first need to understand the difference between a strategic plan and business plan .
What is the difference between a strategic plan and business plan?
We have previously written about this topic in a past blog. Briefly, there is a significant difference in the intent of each plan. A strategic plan is focused on advancing all aspects of a business toward a common goal(s), exploiting opportunities, building market share and engaging with stakeholders. A business plan is focused more on the nuts and bolts, looking at the operational, financial aspects as well as improving performance. The components, functions and reporting structures of each plan are inherently different.
What comes first?
Before a business plan is created, should your organization should develop a strategic plan first? Strategic planning defines the mission, vision, and your organization's values among numerous other things. Without understanding what your organization is trying to achieve, how can you plan the more granular aspects your business and budget? Of course, both of these plans are continuously updated, and referencing each other, likely where much of the chicken-egg confusion comes in. Moreover, there are certain components that may be present in both plans such as vision, mission, values and the fundamentals of your direction and culture, though these can become more specific and change from organizational to department based as your company grows. Regardless, the business plan should contain more detail about the functional, financial and performance management aspects of the business.
A small business, with a team focused on 1-2 key targets should begin with a business plan. A growing or large business, with more goals, departments and customer variation, should look to work toward achieving common goals and how to support each-other, this is where a strategic plan is required.
The vast majority of quality private company investors will request a business plan, that is because they know where the detail should be. A strategic plan presented in its place will paint a nice picture of the business, but will not provide enough confidence to invest, in most circumstances.
So if you are a new business, trying to succeed, create a business plan.
If you are an established business struggling to keep the wheels on, create a strategic plan. These plans should not be seen as separate or similar documents, they are inter-dependant, with their own unique features. Though we have developed Strategic Business Plans for clients that needed to find a healthy balance.
Do I need both a strategic plan and business plan?
In many cases, yes. Both these plans help businesses achieve operational efficiency and organizational alignment. However, with small businesses, there are some instances where developing a strategic plan may not be needed.
Need advice with your strategic or business plan?
Iota consultants can help! Our team of business and strategic consultant can help you develop and audit your strategic and business plans. Feel free to reach out to us today.
- Strategic plan
- Business plan
Recent Posts
Why is Strategic Planning Important?
Why Do Strategic Plans Fail? (And How To Avoid These Mistakes)
Strategic Plan Development
Commentaires
- Services Overview
- The MAP Program
- The MAP Management System ™
- Business Planning
- Onsite Training
- MAP Digital
- Executive Coaching
- Team Building
- MAP Film Series
- Customized Leadership Development
- Workshops Overview
- Workshops Schedule
- Client Video Testimonials
- Financial Services
- Food & Beverage
- Construction
- Public Sector
- Real Estate
- Manufacturing
- Miscellaneous
View Cart Registration Confirmation
- No products in the cart.
Subtotal: $ 0.00
Which Comes First: The Goal or the Strategy?

Most business leaders don’t realize that, to be successful, strategy must come first. Creating a goal is a way to measure what you want to achieve as an organization. Strategy is about choices, trade-offs, and defining what kind of unique value you are going to deliver to specific customers in our competitive landscape. Strategy is creating a powerful position within the marketplace.
In business, it’s about getting focused, and staying focused. You can set all the goals you want, but unless you understand exactly what you’re delivering to the customer, and what your company needs to focus on, goals won’t mean anything. Strategy is critical. You have to make a choice about your most dedicated and profitable customers, and how you deliver what they truly want and need. Who are you as a company? If you don’t measure and aim for that, you’ll just be chasing goals that won’t actually serve to grow and support your company’s profitability.
If you don’t have focus, you’re building a company on “ready-fire-aim.” Remember, the tighter the bulls eye the greater the opportunity.
Don’t create goals without an underlying strategy to direct them. The people in your organization, from the front line to your executive team, must understand the “why” behind those goals. Otherwise, they won’t understand the context that the goals are set in, and can’t operate independently to achieve those goals. They will be unfocused, unaligned, and unable to extemporize. It’s critical that everyone in your organization is focused, and knows how they impact company strategy. That creates alignment, and gets everyone moving in the same direction.
That said, a lot of people throw out goals and just take on the strategy part. That doesn’t work, either! Once you have a focus and a strategy, you do need to set goals in order to measure and support the company’s movement. A goal gives everyone a target; a metric to show how much the company is growing and improving. They provide tangible metrics to see how you’re doing on implementing your strategy.
So, where’s your focus? Do you know where your people are spending most of their time?
Related Articles

Let Us Be Your Guide
Have questions about what program works best for you and your team? We’re here to help. Connect with our expert team members to create the custom roadmap you need.
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

How to Write Your First Business Plan
Planning a business means planning to succeed in business. A business plan helps you define what you do so that you can explain this clearly and succinctly to customers. It helps you see if your plans are going astray so that you can take corrective action. It helps you think about your position in your market and how to be competitive.
It’s worth noting that there are different schools of thought on business planning. Some people argue it’s unnecessary, such as the authors of Rework , Jason Fried and David Heinemeier Hansson, who also founded 37 Signals and created Ruby on Rails. Some say that it’s essential such as Richard Branson, the founder of Virgin. Others, such as the Interaction Design Foundation, try to take a middle path like the one we’ve detailed for you here.
We advocate for a simple plan that helps you towards your goals and keeps you on track without getting you bogged down forever in writing that plan.
Not every business has a business plan, but businesses that do tend to do much better than those that don’t have one. Some very good reasons to have a business plan include:
It helps you to define what your business is (and isn’t) about.
It helps you plan how to sell and market your services.
It can define your current objectives and help you evaluate your progress against them.
It can help to raise funding or with a loan application.
It can help to define relationships between business partners (including expectations and how to end such a partnership if things don’t work out).
It can help you value a business if you want to sell it.
Here, we will help you get started creating your business plan whether you’re a freelancer or an entrepreneur. You’ll get to know what goes into a business plan for a start-up business. It’s enough to get you started.
Now, this article can’t teach you everything you need to know about business planning. Excellent books that run to hundreds of pages which define everything in detail for a complex business plan await you on a shelf or in a warehouse. Using these, when your business grows bigger and more successful, you’ll have to find more in-depth knowledge and advice. When you’re 6 to 24 months down the road and need to develop your business plan further, that’ll probably be the right time to pick up one of those heavy books and start a more in-depth planning exercise.

Author/Copyright holder: Philip Wilson. Copyright terms and licence: CC BY-ND 2.0
Planning a business means planning to succeed in business.
What Should Be In Your First Business Plan?
Your first business plan will be for your own use, so it doesn’t need to be a thing of beauty which has been professionally polished. It shouldn’t be more than a couple of pages. You can save that long, polished business plan for the day that you want to use the plan to secure investment in your business or to help you guide your employees in the right direction. It should take a maximum of one day to create your first business plan.
Your First Business Plan Should Include
1. a brief company description.
The name of your company, the date it was formed, the names of any shareholders, your company registration number, your address, etc. In the future, you’ll add a bit more detail to this section and add important milestones in the development of your business. To start, keep it short and simple.
2. A description of the services you offer
This should also include a description of how they stand out (your unique selling points – USPs) from your competition. For example, it might be that your logo design is proven to increase brand recognition by 40% or that your sales copy delivers increased sales by 25%.
3. A simple market analysis
Who are your customers? Who are your competitors? What’s the size of the market you will serve? How will the market grow in the next few years? You should make a simple SWOT analysis where you define the opportunities and the threats in your market as well as your business’s strengths and weaknesses: nothing too complex—just enough detail to be sure that you understand the market you are working in.

Market analysis is often done using a simple SWOT analysis – where you assess the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your business and competitors.
4. An implementation strategy
How will you sell your services? How will you put those plans into action? What milestones will you use to show progress in your plan?
5. A personal summary
In essence, this a canned version of your CV—what’s your background? Your key accomplishments? Your overall relevant experience?
6. A financial plan
What are your projected sales? What will your cash flow look like? How much profit do you expect to make? For this exercise, be pessimistic and realistic; do not assume you will be working for forty hours a week, every week, at your maximum rate from the outset. It’s unlikely that you will achieve that—ever. It’s much better to underestimate your financial performance and overachieve than vice versa. Never forget that you’re going to spend a lot of time on unpaid work, from accounting to marketing to administration. And, perhaps, you would like some time for vacation as well?
7. A short summary or executive summary
The summary is often called the “executive summary”, of the whole plan. This will help when you come to selling your services; it’s the basis of your elevator pitch – which is what you’d say to your ideal clients if you were trapped in an elevator with them for five minutes.
Your executive summary should include:
what your core service is
who your main customers are
why they should choose you and your services over your competitors
how you will sell your services

It can’t be clearer than, this can it? You would think that it doesn’t matter if your executive summary sucks if it’s only meant for yourself. But really, the executive summary can be your biggest help and guide in understanding and summarizing what your main services are, what makes your services more attractive than your competitors’, who you sell your services to and how you sell them.
It takes time to develop your elevator pitch and executive summary as it should only sum up the very essence of your business plan. That’s why you should start by defining the rest of your business plan and then, at the very end of your process of making your business plan, you’ll be able to define the essence and the executive summary of your business plan.
You should always place your executive summary in the very beginning of your business plan.
Best practice: Ideally, you’ll be able to explain your executive summary as an elevator pitch in only a few sentences. You should continue working on your executive summary until you are able to explain your perfect pitch in one minute. You should also practice an elaborated version of your pitch which should take approximately five minutes. You’ll find it harder to explain yourself in one minute than in five.
You can start practicing by inserting your answers into this short sentence: “My core service is (xxx) which is essential to (xx customers), because I can help them (in xx ways) compared to my competitors.”
When you think you’ve nailed the two versions of your elevator pitch, you should try saying it out loud, and when you can say it in approximately one- and five-minute versions, you should pitch your executive summaries to your friends, family, and, of course, your peers—and get their feedback before you reach out to your future clients.
You’ll find that you will improve your pitch every time you practice it. Most likely, you will find that for each pitch you make, you can make it shorter and more precise. Your friends’ and peers’ questions and feedback will help you crystallize what your soon-to-be business is all about.
It may feel a bit odd the first few times you try your pitch, but you’ll soon understand that this is the best way to get to the core of what you will be doing as a freelancer or entrepreneur. This way, it will be much easier to move from planning to executing the plan in the near future.
Length of your first business plan
Keep your plan as short as possible. Aim for two pages. A short, simple plan is easy to review and refer to. If you write something resembling a book, it will serve no purpose except to take up a lot of time that could be spent doing something useful when you write it. You’ll never want to read it or see it again if it’s that long. Keep it short, sweet and to the point.
The Take Away
A business plan serves a purpose for a start-up whether you’re a freelancer or an entrepreneur. It helps you define what you do so that you can explain this clearly and succinctly to customers. It helps you see if your plans are going astray so that you can take corrective action. It helps you think about your position in your market and how to be competitive.
Writing a business plan for your own use should be a simple, straightforward exercise. You don’t need to worry about presentation, spelling or grammar – no one else will see it. You just need to capture the relevant information.
Later on, when your business is better established, you’ll want to update the plan, and if you then intend to show it to other people, you might want to read up on how to develop a more complex plan.
You might also, at that point, consider using a software tool for writing your business plan. However, to start with—keep it simple. Don’t get bogged down with the process; if you spend more than a day on this, you’re spending too much time and overthinking things. You can always go back and correct your business plan’s course when you’ve started working.
References & Where to Learn More
Hero Image: Author/Copyright holder: Pixabay. Copyright terms and licence: CC0
You can also find some great example business plans here: 500+ Free business plan examples
How to Create a UX Portfolio

Get Weekly Design Insights
Topics in this article, what you should read next, how to change your career from graphic design to ux design.
- 1.4k shares
How to Change Your Career from Marketing to UX Design
- 1.1k shares
- 3 years ago
How to Change Your Career from Web Design to UX Design
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding UX Roles and Which One You Should Go For
How to write the conclusion of your case study

- 5 years ago
7 Tips to Improve Your UX Design Practice
How to create the perfect structure for a UX case study

5 Inspiring Freelance Designers’ Websites and Portfolios

- 4 years ago
7 Powerful Steps for Creating the Perfect Freelance CV
Tips for Writing a CV for a UX Job Application
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Which Comes First: Vision Or Mission?
Posted by Rick DeMarco on 10 September 2015
Tags: Vision , Mission , Planning , Strategy

Employee engagement is one of the most significant challenges facing organizations today. In order for companies to deliver exceptional customer experiences, they must create a culture in which employees understand, believe in and are committed to achieving the vision and delivering on the strategy / brand promise. But before you can begin to address a strategy or programs to create that culture of engagement, there must be alignment of the vision, culture, and business strategy within the organization.
As we talk to clients about their strategic planning process, we hear repeatedly that there is some confusion over the difference between vision and mission, strategy and tactics, and the role of culture in helping to facilitate action plans. We believe that the process starts with a clear vision. It’s hard to engage people unless they know where you’re going. Vision is inherently future-oriented. Think about the vision painted by Martin Luther King, “I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin, but by the content of their character”. Another example is the vision from the U.S. space program in the 1960’s, “landing a man on the moon”. In both of these cases, their vision drove the development of a mission, strategy, and tactics. It represented a very clear view of a desired future. Once that vision is defined and articulated, you can begin to build the other dimensions of the planning process that will become the foundation for engaging and inspiring all team members.
After much spirited debate and discussion, we decided to put stake in the ground and created a simple diagram that defines each element of the strategic planning process and their relationship to each other. This is how we see the relationship and the flow from vision to tactics:

Only three MPs in the past 25 years have gone the other way - from main opposition to government - all leaving the Conservatives to join Labour.
Defecting to smaller parties happens more often, such as moves from both Conservative and Labour to Change UK during the Brexit years, or Douglas Carswell and Mark Reckless heading over to UKIP ahead of the referendum.
Our flagship Sunday morning show, hosted by Trevor Phillips , is live on Sky News from 8.30am until 10am, and we have a packed line-up for you this morning.
In January 2023, Rishi Sunak made five promises.
Since then, he and his ministers have rarely missed an opportunity to list them. In case you haven't heard, he promised to:
• Halve inflation • Grow the economy • Reduce debt • Cut NHS waiting lists and times • Stop the boats
See below how he is doing on these goals:
By Adam Boulton , Sky News commentator
The Labour Party is in shock over the leadership's decision to welcome the defection of the right-wing former Conservative MP Natalie Elphicke.
The day before she literally "crossed the floor" before Prime Minister's Questions to sit on the opposition benches, Elphicke distributed a leaflet in her Dover constituency attacking Sir Keir Starmer.
On Wednesday, as MPs looked on aghast on both sides, he reached back from the front bench to shake her hand, and later posed for smiling photographs with her.
Elphicke is the second Tory MP in a fortnight to switch to Labour. Both she and Dr Dan Poulter have said that they will stand down at the general election and will not fight for re-election in their old constituencies or, at the time of writing, in another seat.
Labour insists that neither of them has been promised elevation to the House of Lords in an upcoming honours list.
You can read more from Adam below:
More than 100 MPs have said they will not be standing at the next general election.
Those who have announced their intention to leave parliament range from the longest-serving female MP, Labour's Harriet Harman, to one of those only elected at the last election in 2019, Conservative MP Dehenna Davison.
This election is seeing the constituency boundaries changed, leading to some MPs deciding to step aside as their seat is gutted or entirely excised.
The vast majority of those leaving are Conservatives, with more than 60 Tory MPs stepping aside.
The average age of Labour MPs standing down is 67 - a full 11 years higher than the Conservatives at 56 and the SNP at 55.
Here is a full list of all the MPs standing down at the next election:
By Jenness Mitchell , Scotland reporter
The Scottish parliament is celebrating its 25th anniversary.
The inaugural meeting took place on 12 May 1999, less than a week after Scots went to the polls to vote in the first Holyrood election.
First Minister John Swinney was one of the 129 MSPs elected into the new parliament all those years ago.
Holyrood has had seven first ministers since 1999: Donald Dewar (1999-2000), Henry McLeish (2000-2001), Jack McConnell (2001-2007), Alex Salmond (2007-2014), Nicola Sturgeon (2014-2023), Humza Yousaf (2023-2024) and John Swinney (2024-present).
Alison Johnstone MSP, presiding officer of the Scottish parliament, told Sky News that reaching 25 is a "significant milestone" for Holyrood.
You can read more from Sky News below:
Accusations MP Natalie Elphicke lobbied the justice secretary in 2020 to interfere in her then-husband's sex offences trial are "nonsense", her spokesperson has said.
It is claimed the Dover MP, who recently defected from Conservative to Labour, approached Sir Robert Buckland when he was lord chancellor and justice secretary before the hearing of Charlie Elphicke's case.
The Sunday Times reported that she allegedly told Sir Robert that it was unfair the case was the first to be heard at Southwark Crown Court after the COVID lockdown and that it was being overseen by Lady Justice Whipple.
One person present viewed her comments as a bid to have the case moved to a lower-profile court to spare her partner public scrutiny, while another saw it as an attempt to replace the senior judge, according to the newspaper.
Good morning!
Welcome back to the Politics Hub on Sunday, 12 May.
Sunday Morning With Trevor Phillips will be live from 8.30am, with a host of political guests - and an in-the-know panel - to talk you through this week in Westminster.
Until then, here's what you need to know:
Accusations MP Natalie Elphicke lobbied the justice secretary in 2020 to interfere in her then-husband's sex offences trial are "nonsense", her spokesperson has said;
It is claimed the Dover MP, who recently defected from Conservative to Labour, approached Sir Robert Buckland when he was lord chancellor and justice secretary before the hearing of Charlie Elphicke's case;
Sunday is also the 25th anniversary of the Scottish parliament , which held its inaugural meeting on 12 May 1999, less than a week after Scots went to the polls to vote in the first Holyrood election;
And today, applications open for access to the second government expansion of free childcare provision , due to come into effect from September 2024.
And here's who will join Trevor Phillips this morning:
- Foreign Secretary David Cameron at 8.30am;
- Labour's Jonathan Ashworth at 8.55am;
Follow along for all the latest news and analysis throughout today.
Across the UK, anger is brewing amongst some farmers.
Protests have already been held in London, Dover and Cardiff, with more planned - mirroring similar tensions seen across Europe in the last six months.
They say they’re annoyed about cheap foreign imports and changes to subsidies forcing them to give up land in favour of environmental schemes.
But what does this mean for the food on our table - and does British produce risk becoming a luxury product for the wealthy only?
On the Sky News Daily , Niall Paterson is joined by West of England and Wales correspondent Dan Whitehead to find out why farmers are so concerned, and speaks to Liz Webster, the founder of Save British Farming, about why she believes eating British isn't just good for our farmers - it's good for the nation's health, too.
In response to our report, Farming Minister Mark Spencer, said: "We firmly back our farmers. British farming is at the heart of British trade, and we put agriculture at the forefront of any deals we negotiate, prioritising new export opportunities, protecting UK food standards and removing market access barriers.
"We've maintained the £2.4bn annual farming budget and recently set out the biggest ever package of grants which supports farmers to produce food profitably and sustainably."
The Welsh government said: "A successful future for Welsh farming should combine the best of our traditional farming alongside cutting-edge innovation and diversification.
"It will produce the very best of Welsh food to the highest standards, while safeguarding our precious environment and addressing the urgent call of the climate and nature emergencies."
👉 Listen above then tap here to follow the Sky News Daily wherever you get your podcasts 👈
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The objective is a qualitative statement about what a business aims to achieve over a specified timeframe. The chosen timeframe of a strategic plan is typically 3-5 years and for an annual operating plan 1 year. The goals are the quantifiable targets or intended results to be accomplished. These typically are financial figures or other ...
Existing companies use the strategic plan to grow their business, while entrepreneurs use business plans to start a company. There is also a different timeframe for each plan. Generally, a strategic plan is conducted over several years while a business plan, with all the right components, can operate in less than a year.
A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state. A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
Strategic plans constitute the basis of operations and responsibilities within the business. These plans lay the paths out for each member of the organization to follow and define the functional outline and the key outcomes for every project and process within the business. A strategic plan goes on to define the operations and their outcomes ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
The executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it's a summary of the complete business plan. Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan.
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
While it comes first in your business plan, you should write it last, once you've put together all your information in the following sections. Try to keep the executive summary concise—no more than one or two pages. - Your mission statement. - A description of your product/service. - Where your business is based.
The steps below will guide you through the process of creating a business plan and what key components you need to include. 1. Create an executive summary. Start with a brief overview of your entire plan. The executive summary should cover your business plan's main points and key takeaways.
Learn about the best business plan software. 1. Write an executive summary. This is your elevator pitch. It should include a mission statement, a brief description of the products or services your ...
First, let's look at the difference between a business and a strategic plan. For review: A business plan covers the "who" and "what" of the business. The strategic plan gives us long-term goals and explains "how" the business will get there, providing a long-term view. In broader terms, the business plan tells us who by showing us:
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
A business strategy is foundational to a company's success. It helps leaders set organizational goals and gives companies a competitive edge. It determines various business factors, including: Price: How to price goods and services based on customer satisfaction and cost of raw materials.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
We've discovered that roughly two-thirds of respondents (67.03%) stated they set goals first while just over a quarter (27.47%) said that strategy comes first in their business. The remaining 5.49% were undecided. What muddies the waters somewhat is the fact that companies tend to focus on strategy more.
Step 1: Assess your current business strategy and business environment. Before you can define where you're going, you first need to define where you are. Understanding the external environment, including market trends and competitive landscape, is crucial in the initial assessment phase of strategic planning.
Putting your strategic plan into practice (our final step) is the key to making it all work during the strategy implementation plan, and getting these details 80% right in a timely fashion is much more important than getting them 100% right in a year. 3. Putting your strategic plan into practice.
A strategic plan is focused on advancing all aspects of a business toward a common goal (s), exploiting opportunities, building market share and engaging with stakeholders. A business plan is focused more on the nuts and bolts, looking at the operational, financial aspects as well as improving performance.
Creating a goal is a way to measure what you want to achieve as an organization. Strategy is about choices, trade-offs, and defining what kind of unique value you are going to deliver to specific customers in our competitive landscape. Strategy is creating a powerful position within the marketplace. In business, it's about getting focused ...
1. A brief company description. The name of your company, the date it was formed, the names of any shareholders, your company registration number, your address, etc. In the future, you'll add a bit more detail to this section and add important milestones in the development of your business. To start, keep it short and simple.
Which Comes First: Vision Or Mission? Employee engagement is one of the most significant challenges facing organizations today. In order for companies to deliver exceptional customer experiences, they must create a culture in which employees understand, believe in and are committed to achieving the vision and delivering on the strategy / brand ...
Strategy or Structure are part of the same growth strategy. Here are the steps for Evolution of Growth. Step 1 It all starts with a Mission/Vision/Purpose, Core Values, and a passion to add value ...
Asked if he has a plan to deter people, Sir Keir says his primary goal is to stop the people-smuggling gangs. He says that saying a deterrence like Rwanda works is not borne out by the evidence ...