- Search Search Please fill out this field.

What Is a Feasibility Study?
Understanding a feasibility study, how to conduct a feasibility study.
- Feasibility Study FAQs
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
Feasibility Study
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Group1805-3b9f749674f0434184ef75020339bd35.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
A feasibility study is a detailed analysis that considers all of the critical aspects of a proposed project in order to determine the likelihood of it succeeding.
Success in business may be defined primarily by return on investment , meaning that the project will generate enough profit to justify the investment. However, many other important factors may be identified on the plus or minus side, such as community reaction and environmental impact.
Although feasibility studies can help project managers determine the risk and return of pursuing a plan of action, several steps should be considered before moving forward.
Key Takeaways
- A company may conduct a feasibility study when it's considering launching a new business, adding a new product line, or acquiring a rival.
- A feasibility study assesses the potential for success of the proposed plan or project by defining its expected costs and projected benefits in detail.
- It's a good idea to have a contingency plan on hand in case the original project is found to be infeasible.
Investopedia / Lara Antal
A feasibility study is an assessment of the practicality of a proposed plan or project. A feasibility study analyzes the viability of a project to determine whether the project or venture is likely to succeed. The study is also designed to identify potential issues and problems that could arise while pursuing the project.
As part of the feasibility study, project managers must determine whether they have enough of the right people, financial resources, and technology. The study must also determine the return on investment, whether this is measured as a financial gain or a benefit to society, as in the case of a nonprofit project.
The feasibility study might include a cash flow analysis, measuring the level of cash generated from revenue versus the project's operating costs . A risk assessment must also be completed to determine whether the return is enough to offset the risk of undergoing the venture.
When doing a feasibility study, it’s always good to have a contingency plan that is ready to test as a viable alternative if the first plan fails.
Benefits of a Feasibility Study
There are several benefits to feasibility studies, including helping project managers discern the pros and cons of undertaking a project before investing a significant amount of time and capital into it.
Feasibility studies can also provide a company's management team with crucial information that could prevent them from entering into a risky business venture.
Such studies help companies determine how they will grow. They will know more about how they will operate, what the potential obstacles are, who the competition is, and what the market is.
Feasibility studies also help convince investors and bankers that investing in a particular project or business is a wise choice.
The exact format of a feasibility study will depend on the type of organization that requires it. However, the same factors will be involved even if their weighting varies.
Preliminary Analysis
Although each project can have unique goals and needs, there are some best practices for conducting any feasibility study:
- Conduct a preliminary analysis, which involves getting feedback about the new concept from the appropriate stakeholders
- Analyze and ask questions about the data obtained in the early phase of the study to make sure that it's solid
- Conduct a market survey or market research to identify the market demand and opportunity for pursuing the project or business
- Write an organizational, operational, or business plan, including identifying the amount of labor needed, at what cost, and for how long
- Prepare a projected income statement, which includes revenue, operating costs, and profit
- Prepare an opening day balance sheet
- Identify obstacles and any potential vulnerabilities, as well as how to deal with them
- Make an initial "go" or "no-go" decision about moving ahead with the plan
Suggested Components
Once the initial due diligence has been completed, the real work begins. Components that are typically found in a feasibility study include the following:
- Executive summary : Formulate a narrative describing details of the project, product, service, plan, or business.
- Technological considerations : Ask what will it take. Do you have it? If not, can you get it? What will it cost?
- Existing marketplace : Examine the local and broader markets for the product, service, plan, or business.
- Marketing strategy : Describe it in detail.
- Required staffing : What are the human capital needs for this project? Draw up an organizational chart.
- Schedule and timeline : Include significant interim markers for the project's completion date.
- Project financials .
- Findings and recommendations : Break down into subsets of technology, marketing, organization, and financials.
Examples of a Feasibility Study
Below are two examples of a feasibility study. The first involves expansion plans for a university. The second is a real-world example conducted by the Washington State Department of Transportation with private contributions from Microsoft Inc.
A University Science Building
Officials at a university were concerned that the science building—built in the 1970s—was outdated. Considering the technological and scientific advances of the last 20 years, they wanted to explore the cost and benefits of upgrading and expanding the building. A feasibility study was conducted.
In the preliminary analysis, school officials explored several options, weighing the benefits and costs of expanding and updating the science building. Some school officials had concerns about the project, including the cost and possible community opposition. The new science building would be much larger, and the community board had earlier rejected similar proposals. The feasibility study would need to address these concerns and any potential legal or zoning issues.
The feasibility study also explored the technological needs of the new science facility, the benefits to the students, and the long-term viability of the college. A modernized science facility would expand the school's scientific research capabilities, improve its curriculum, and attract new students.
Financial projections showed the cost and scope of the project and how the school planned to raise the needed funds, which included issuing a bond to investors and tapping into the school's endowment . The projections also showed how the expanded facility would allow more students to be enrolled in the science programs, increasing revenue from tuition and fees.
The feasibility study demonstrated that the project was viable, paving the way to enacting the modernization and expansion plans of the science building.
Without conducting a feasibility study, the school administrators would never have known whether its expansion plans were viable.
A High-Speed Rail Project
The Washington State Department of Transportation decided to conduct a feasibility study on a proposal to construct a high-speed rail that would connect Vancouver, British Columbia, Seattle, Washington, and Portland, Oregon. The goal was to create an environmentally responsible transportation system to enhance the competitiveness and future prosperity of the Pacific Northwest.
The preliminary analysis outlined a governance framework for future decision-making. The study involved researching the most effective governance framework by interviewing experts and stakeholders, reviewing governance structures, and learning from existing high-speed rail projects in North America. As a result, governing and coordinating entities were developed to oversee and follow the project if it was approved by the state legislature.
A strategic engagement plan involved an equitable approach with the public, elected officials, federal agencies, business leaders, advocacy groups, and indigenous communities. The engagement plan was designed to be flexible, considering the size and scope of the project and how many cities and towns would be involved. A team of the executive committee members was formed and met to discuss strategies, lessons learned from previous projects and met with experts to create an outreach framework.
The financial component of the feasibility study outlined the strategy for securing the project's funding, which explored obtaining funds from federal, state, and private investments. The project's cost was estimated to be between $24 billion to $42 billion. The revenue generated from the high-speed rail system was estimated to be between $160 million and $250 million.
The report bifurcated the money sources between funding and financing. Funding referred to grants, appropriations from the local or state government, and revenue. Financing referred to bonds issued by the government, loans from financial institutions, and equity investments, which are essentially loans against future revenue that needs to be paid back with interest.
The sources for the capital needed were to vary as the project moved forward. In the early stages, most of the funding would come from the government, and as the project developed, funding would come from private contributions and financing measures. Private contributors included Microsoft Inc., which donated more than $570,000 to the project.
The benefits outlined in the feasibility report show that the region would experience enhanced interconnectivity, allowing for better management of the population and increasing regional economic growth by $355 billion. The new transportation system would provide people with access to better jobs and more affordable housing. The high-speed rail system would also relieve congested areas from automobile traffic.
The timeline for the study began in 2016 when an agreement was reached with British Columbia to work together on a new technology corridor that included high-speed rail transportation. The feasibility report was submitted to the Washington State land Legislature in December 2020.
What Is the Main Objective of a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is designed to help decision-makers determine whether or not a proposed project or investment is likely to be successful. It identifies both the known costs and the expected benefits.
In business, "successful" means that the financial return exceeds the cost. In a nonprofit, success may be measured in other ways. A project's benefit to the community it serves may be worth the cost.
What Are the Steps in a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study starts with a preliminary analysis. Stakeholders are interviewed, market research is conducted, and a business plan is prepared. All of this information is analyzed to make an initial "go" or "no-go" decision.
If it's a go, the real study can begin. This includes listing the technological considerations, studying the marketplace, describing the marketing strategy, and outlining the necessary human capital, project schedule, and financing requirements.
Who Conducts a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study may be conducted by a team of the organization's senior managers. If they lack the expertise or time to do the work internally it may be outsourced to a consultant.
What Are the 4 Types of Feasibility?
The study considers the feasibility of four aspects of a project:
Technical: A list of the hardware and software needed, and the skilled labor required to make them work.
Financial: An estimate of the cost of the overall project and its expected return.
Market: An analysis of the market for the product or service, the industry, competition, consumer demand, sales forecasts, and growth projections
Organizational: An outline of the business structure and the management team that will be needed.
Feasibility studies help project managers determine the viability of a project or business venture by identifying the factors that can lead to its success. The study also shows the potential return on investment and any risks to the success of the venture.
A feasibility study contains a detailed analysis of what's needed to complete the proposed project. The report may include a description of the new product or venture, a market analysis, the technology and labor needed, as well as the sources of financing and capital. The report will also include financial projections, the likelihood of success, and ultimately, a go-or-no-go decision.
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Ultra-High-Speed Rail Study ."
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Cascadia Ultra High Speed Ground Transportation Framework for the Future ."
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Ultra-High-Speed Rail Study: Outcomes ."
Washington State Department of Transportation. " Ultra-High-Speed Ground Transportation Business Case Analysis ." Page ii.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/request-for-proposal.asp-V1-47ccaf79d2ed4a0eaec15c24a901c5f2.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is a Feasibility Study and its Importance?
This blog talks about how a study that assesses the potential success of a proposed project. Let’s dive in to learn how to conduct this study and comprehend what determines the viability of a project. It will help you understand how the Feasibility Study evaluates the necessity of a project in terms of legal aspects. Read more!

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Project and Infrastructure Financing Training
- Waterfall Project Management Certification Course
- Jira Training
- CGPM (Certified Global Project Manager) Course
- Project Management Office Fundamentals Certification Course

A Feasibility Study is a crucial assessment that is during Project Management conducted to determine the viability and potential success of a project. By thoroughly examining such factors, stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding the project’s feasibility. Apart from the technical and financial considerations, this study ensures a project’s compliance with relevant laws, regulations and industry standards. To give you a better overview, this blog will talk about the multiple aspects associated with this. So, let’s dive in to comprehend the significance of a Feasibility Study. After reading this blog, stakeholders can make well-informed decisions that enhance the chances of a project’s success.
Table of Contents
1) Feasibility Study - An overview
2) Importance of a Feasibility Study
3) Types of Feasibility Studies
4) What is included in a Feasibility Study report?
5) Examples of a Feasibility Study
6) Seven steps to do a Feasibility Study
7) Conclusion
Feasibility Study - An overview
A Feasibility Study is an initial investigation into the potential benefits and viability of a project or endeavour. An impartial appraisal that looks at a project's technical, financial, legal, and environmental elements is what this study provides.

Importance of a Feasibility Study
A Feasibility Study may reveal novel concepts that fundamentally alter the Scope of a Project . Feasibility Studies are of the greatest importance in the decision-making process when it comes to projects, businesses, and investments. They are mostly structured assessments that are focused on various aspects of a proposed project`s Feasibility. The following are some of its advantages:
a) Increases the focus of project teams
b) Finds fresh opportunities
c) Gives important information to help make a "go/no-go" choice.
d) Reduces the number of available business options
e) Finds a good cause to start the project
f) Increases the success rate through the assessment of several factors
g) Assists in making project decisions
h) Identifies grounds for not moving forward
Types of Feasibility Studies
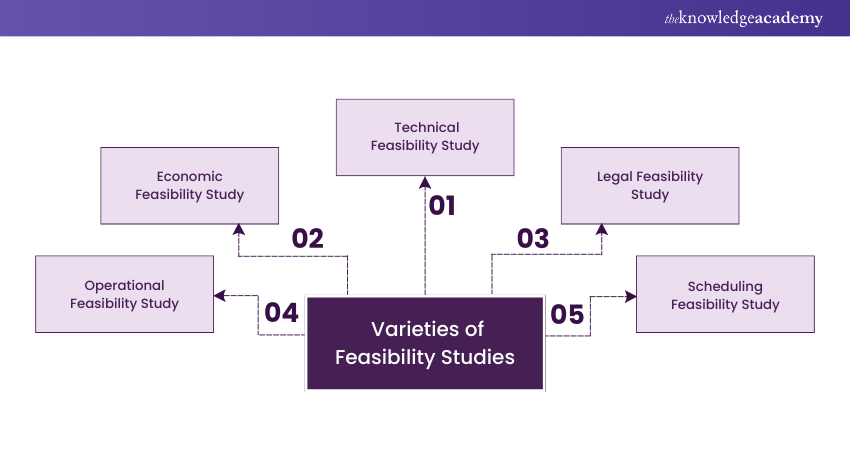
Technical Feasibility Study
A technical Feasibility Study aims to verify whether the organisation is eligible to use its technical in-house resources and expertise to perform successfully. This assessment involves scrutinising various aspects, including the following:
a) Production capacity: Does the company have the resource base to produce that number of products and services for the customers?
b) Facility needs: Will today’s facilities fulfil the standards required, or will new facilities be constructed?
c) Raw materials and supply chain: Are there enough purchases, and have the organisation maintained a supply chain?
d) Regulatory compliance: Does the Project Execution follow the relevant guidelines and professionals bear the relevant certifications to meet the requirements and the industry standards?
Economic Feasibility Study
It is a financial Feasibility Study that primarily examines the project's financial viability. The economic Feasibility Study typically involves several steps:
a) Determining capital requirements: Calculate funding collection, overhead, and other capital.
b) Cost breakdown: Determining and listing all the project costs including the purchase of materials, hardware, labour, and overheard costs are too.
c) Funding sources: Trying out a variety of possible solutions like banks, stakes, or grants.
d) Revenue projection: By using prediction tools such as a cost-benefit analysis or business forecasting to get the level of income, return on investment and profit margin.
e) Financial analysis: Projecting the performance of the Project based on means that are related to a financial analysis and are characterised by the utilisation of such things as cash flow statements, balance sheets and financial projections.
Learn the tools and methods to manage projects by signing up for our Running Small Projects Training now!
Legal Feasibility Study
Legal Feasibility is a type of analysis that seeks to confirm that a pProject follows all the relevant laws and regulations. Key considerations include:
a) Regulatory compliance: Briefing the whole project team about all required laws and regulations that the project has to comply with.
b) Business structure: Assessing the legal systems (e.g., LLCs vs. corporations) that would best protect liability, governance, and minimising taxation, if any.
Operational Feasibility Study
An operational Feasibility Study looks at how effectively a product will meet its needs. It also talks about how easy it will be to use and maintain once it is in place. In addition, this study enumerates the necessity of evaluating a product's utility and the response and suggestions of application development team.
Scheduling Feasibility Study
Proposed project schedules and deadlines are the main subject of a scheduling a Feasibility Study. This evaluation concerns how long team members will need to complete the project. It also highly impacts the business because if the programme isn't finished on time, the planned result might not be realised.
Acquire the necessary skills to effectively deliver projects by signing up for our Project Management Office Fundamentals Training now!
What is included in a Feasibility Study report?
You should make a Feasibility Study report before starting a project. This way you can analyse if your business idea is really viable and will bring you success. When you conduct this study, you would have to consider lots of factors such as if the people are going to buy your product or service, how much competition is out there, if the company can afford it and so on.
The Feasibility Study must include things like how much technology and resources you need and how much you can hope to earn from your investment. The results of this study are put together in a report, which usually includes the following sections:
a) Executive summary
b) Approach to marketing
c) Organisation/staffing
Examples of a Feasibility Study
Feasibility Study has helped decide if big ideas can work. Here are two examples:
University Science Building Upgrade
This example is about a university that wanted to upgrade its old science building from the 1970s. They thought it was outdated and needed a change. To implement this, they evaluated different options and determined how much they would approximately cost. Some people were worried about the project being too expensive or its potential to causeissues in the community. The study also analysed what technology the new building would require, and how effectively it would help students, and also, if it would attract more students.
Along with this, they looked at the financial aspect too, as to how they would sponsor for it and if they would make more money from having additional students. The study showed that the project could work, so they went ahead with the upgrade.
High-speed Rail Project
This example is timed when the Washington State Department of Transportation wanted to see if they could build a fast train connecting Vancouver, Seattle, and Portland. To initiate this, they first focused on how to make decisions about the project in the future.
They discussed it with several people and groups to ensure everyone was okay with the plan. Later, they looked at how to pay for it and thought it would cost between $24 billion and $42 billion. They would get money from the government and maybe from loans and investors.
The study showed that the train could bring lots of good things like better jobs and less traffic. They started looking into this in 2016 and finished the study in 2020. They then shared the report with the government.
Seven steps to do a Feasibility Study
As Feasibility Study is a crucial step in determining a potential of a project, it involves a substantial period of time and resources. Let’s take you through some of the steps involved in the following points:
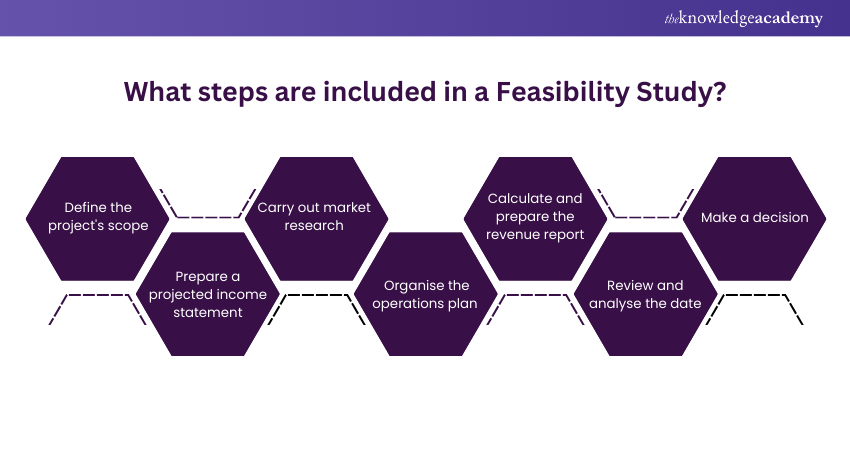
1) Do a preliminary analysis and define the scope of the study
Before going through a Feasibility Study, it is wise that you do just one small check. The time and resources involved in Feasibility Studies may be burdensome; hence, it is imperative to determine if it is worth it as early as possible.
Through this form, one can establish whether the study holds awarding potential and who else should be involved on a higher level. You further this stage by answering questions like what you might win, what pitfalls you will face, and what you need for the success of the project.
2) Prepare a projected income statement
First, while doing a Feasibility Study, you should obtain the income statement projection. In this, the statement calculates earnings and expenditures in subsequent one-year amounts. It is made up of the sum of what you will surely get and the cost you will need to cover.
Smaller businesses tend to need marketing strategies to grow into bigger companies. These facts are extremely important because they help business owners make smart decisions regarding the stage of the business.
3) Carry out market research
Market research is of paramount importance or, naturally, it will be of no use when developing the Feasibility Study. Primarily, it operates to ascertain the viability of the project. This point tells you time, which gives you knowledge of the current market state: Who your customers are, who your competitors are, how big the market is, and how many of it you could have. One way of doing this market research is by asking people questions, referring to experts, and checking very broad social media and other public info to find out what's going on.
4) Organisation and operations plan
Once you've figured out how the market behaves and the scope of your organisation, you can draft the setup of your plan. The detailed work plan for the project will provide the answer to how it will work in a practical form. It tests three aspects of your project, like whether it can be run, whether it is cost-effective, whether it complies with the law, and whether the technology fits.
This is to help you comprehend everything you can do and what you may require to get this project going, for example, the equipment, the materials to start the project, additional costs, and if you need to hire or train people. If you need to, you may make that change if the information you have brought is enough.
5) Calculate and prepare the initial balance of expected revenue and expenses
In this step, you must be expert in handling things from the financial part. You’ll make estimates on how much you may initially spend starting up your project, and then how much your project could make and spend based on that estimate. Among the many issues involved are such as the amount of money you are receiving from your customers, money you owe to others and assets that you own.
Fixed costs, such as variable costs that will change based on the number of goods you produce, and equipment costs also need to be factored in money you may borrow or pay for land and service other companies. Keeping this in mind, you should also consider your business’ off seasons and how much risk you are willing to take. These calculations save a lot of time and effort and can be used to answer the most difficult questions of Feasibility.
6) Review and analyse all data
After going through all the steps, it's crucial to do a thorough review and analysis. This helps ensure that everything is in order and there's nothing that needs adjusting. Take a moment to carefully look back at your work, including the income statement, and compare it with your expenses and debts. Ask yourself: Does everything still seem realistic?
This is also the perfect opportunity to consider any risks that might come up and create contingency plans to handle them. By doing this, you'll be better prepared for any unexpected challenges that may arise.
7) Make a go/No-go decision
Now, it's time to decide if the project can work. This might seem simple, but all the work you've done so far leads up to this moment of decision-making. Before making the final call, there are a few more things to think about. First, consider if the project is worth the time, effort, and money you'll be putting into it. Is the commitment worth it?
Secondly, think about whether the project fits with what your organisation wants to achieve in the long run. Does it align with the organisation’s strategic goals and plans? These factors are essential to consider before making your decision.
Attain the skills to become a stellar Project Manager by signing up for our Project Management Courses now!
Conclusion
You are now more familiar with how a well-executed Feasibility Study is a cornerstone of informed decision-making in Project Management and business ventures. It acts as a critical guide, helping organisations assess the practicality and viability of their initiatives, ultimately minimising risks and increasing the likelihood of success.
Frequently Asked Questions
Employers value skills like analysis, problem-solving, attention to detail, and communication in Feasibility Study specialists. They need to be good at crunching numbers, finding solutions, and explaining complex ideas clearly.
Many industries need expertise in Feasibility Studies, like Construction, Healthcare, Tech, and more. It helps decide if projects are doable.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Project Management Courses , including Introduction to Project Management Certification Course and Project Management Masterclass. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Project Resource Management .
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Project Management Skills, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills in Project Management, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 17th May 2024
Fri 21st Jun 2024
Fri 19th Jul 2024
Fri 16th Aug 2024
Fri 13th Sep 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 8th Nov 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Feb 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 13th Jun 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
What Is a Feasibility Study and How to Conduct It? (+ Examples)
Appinio Research · 26.09.2023 · 28min read

Are you ready to turn your project or business idea into a concrete reality but unsure about its feasibility? Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or a first-time project manager, understanding the intricate process of conducting a feasibility study is vital for making informed decisions and maximizing your chances of success.
This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the complexities of market, technical, financial, and operational feasibility studies. By the end, you'll have a clear roadmap to confidently assess, plan, and execute your project.
What is a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is a systematic and comprehensive analysis of a proposed project or business idea to assess its viability and potential for success. It involves evaluating various aspects such as market demand, technical feasibility, financial viability, and operational capabilities. The primary goal of a feasibility study is to provide you with valuable insights and data to make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project.
Why is a Feasibility Study Important?
Conducting a feasibility study is a critical step in the planning process for any project or business. It helps you:
- Minimize Risks: By identifying potential challenges and obstacles early on, you can develop strategies to mitigate risks.
- Optimize Resource Allocation: A feasibility study helps you allocate your resources more efficiently, including time and money.
- Enhance Decision-Making: Armed with data and insights, you can make well-informed decisions about pursuing the project or exploring alternative options.
- Attract Stakeholders: Potential investors, lenders, and partners often require a feasibility study to assess the project's credibility and potential return on investment.
Now that you understand the importance of feasibility studies, let's explore the various types and dive deeper into each aspect.
Types of Feasibility Studies
Feasibility studies come in various forms, each designed to assess different aspects of a project's viability. Let's delve into the four primary types of feasibility studies in more detail:
1. Market Feasibility Study
Market feasibility studies are conducted to determine whether there is a demand for a product or service in a specific market or industry. This type of study focuses on understanding customer needs, market trends, and the competitive landscape. Here are the key elements of a market feasibility study:
- Market Research and Analysis: Comprehensive research is conducted to gather market size, growth potential , and customer behavior data. This includes both primary research (surveys, interviews) and secondary research (existing reports, data).
- Target Audience Identification: Identifying the ideal customer base by segmenting the market based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior. Understanding your target audience is crucial for tailoring your product or service.
- Competitive Analysis : Assessing the competition within the market, including identifying direct and indirect competitors, their strengths, weaknesses, and market share.
- Demand and Supply Assessment: Analyzing the balance between the demand for the product or service and its supply. This helps determine whether there is room for a new entrant in the market.
2. Technical Feasibility Study
Technical feasibility studies evaluate whether the project can be developed and implemented from a technical standpoint. This assessment focuses on the project's design, technical requirements, and resource availability. Here's what it entails:
- Project Design and Technical Requirements: Defining the technical specifications of the project, including hardware, software, and any specialized equipment. This phase outlines the technical aspects required for project execution.
- Technology Assessment: Evaluating the chosen technology's suitability for the project and assessing its scalability and compatibility with existing systems.
- Resource Evaluation: Assessing the availability of essential resources such as personnel, materials, and suppliers to ensure the project's technical requirements can be met.
- Risk Analysis: Identifying potential technical risks, challenges, and obstacles that may arise during project development. Developing risk mitigation strategies is a critical part of technical feasibility.
3. Financial Feasibility Study
Financial feasibility studies aim to determine whether the project is financially viable and sustainable in the long run. This type of study involves estimating costs, projecting revenue, and conducting financial analyses. Key components include:
- Cost Estimation: Calculating both initial and ongoing costs associated with the project, including capital expenditures, operational expenses, and contingency funds.
- Revenue Projections: Forecasting the income the project is expected to generate, considering sales, pricing strategies, market demand, and potential revenue streams.
- Investment Analysis: Evaluating the return on investment (ROI), payback period, and potential risks associated with financing the project.
- Financial Viability Assessment: Analyzing the project's profitability, cash flow, and financial stability to ensure it can meet its financial obligations and sustain operations.
4. Operational Feasibility Study
Operational feasibility studies assess whether the project can be effectively implemented within the organization's existing operational framework. This study considers processes, resource planning, scalability, and operational risks. Key elements include:
- Process and Workflow Assessment: Analyzing how the project integrates with current processes and workflows, identifying potential bottlenecks, and optimizing operations.
- Resource Planning: Determining the human, physical, and technological resources required for successful project execution and identifying resource gaps.
- Scalability Evaluation: Assessing the project's ability to adapt and expand to meet changing demands and growth opportunities, including capacity planning and growth strategies.
- Operational Risks Analysis: Identifying potential operational challenges and developing strategies to mitigate them, ensuring smooth project implementation.
Each type of feasibility study serves a specific purpose in evaluating different facets of your project, collectively providing a comprehensive assessment of its viability and potential for success.
How to Prepare for a Feasibility Study?
Before you dive into the nitty-gritty details of conducting a feasibility study, it's essential to prepare thoroughly. Proper preparation will set the stage for a successful and insightful study. In this section, we'll explore the main steps involved in preparing for a feasibility study.
1. Identify the Project or Idea
Identifying and defining your project or business idea is the foundational step in the feasibility study process. This initial phase is critical because it helps you clarify your objectives and set the direction for the study.
- Problem Identification: Start by pinpointing the problem or need your project addresses. What pain point does it solve for your target audience?
- Project Definition: Clearly define your project or business idea. What are its core components, features, or offerings?
- Goals and Objectives: Establish specific goals and objectives for your project. What do you aim to achieve in the short and long term?
- Alignment with Vision: Ensure your project aligns with your overall vision and mission. How does it fit into your larger strategic plan?
Remember, the more precisely you can articulate your project or idea at this stage, the easier it will be to conduct a focused and effective feasibility study.
2. Assemble a Feasibility Study Team
Once you've defined your project, the next step is to assemble a competent and diverse feasibility study team. Your team's expertise will play a crucial role in conducting a thorough assessment of your project's viability.
- Identify Key Roles: Determine the essential roles required for your feasibility study. These typically include experts in areas such as market research, finance, technology, and operations.
- Select Team Members: Choose team members with the relevant skills and experience to fulfill these roles effectively. Look for individuals who have successfully conducted feasibility studies in the past.
- Collaboration and Communication: Foster a collaborative environment within your team. Effective communication is essential to ensure everyone is aligned on objectives and timelines.
- Project Manager: Designate a project manager responsible for coordinating the study, tracking progress, and meeting deadlines.
- External Consultants: In some cases, you may need to engage external consultants or specialists with niche expertise to provide valuable insights.
Having the right people on your team will help you collect accurate data, analyze findings comprehensively, and make well-informed decisions based on the study's outcomes.
3. Set Clear Objectives and Scope
Before you begin the feasibility study, it's crucial to establish clear and well-defined objectives. These objectives will guide your research and analysis efforts throughout the study.
Steps to Set Clear Objectives and Scope:
- Objective Clarity: Define the specific goals you aim to achieve through the feasibility study. What questions do you want to answer, and what decisions will the study inform?
- Scope Definition: Determine the boundaries of your study. What aspects of the project will be included, and what will be excluded? Clarify any limitations.
- Resource Allocation: Assess the resources needed for the study, including time, budget, and personnel. Ensure that you allocate resources appropriately based on the scope and objectives.
- Timeline: Establish a realistic timeline for the feasibility study. Identify key milestones and deadlines for completing different phases of the study.
Clear objectives and a well-defined scope will help you stay focused and avoid scope creep during the study. They also provide a basis for measuring the study's success against its intended outcomes.
4. Gather Initial Information
Before you delve into extensive research and data collection, start by gathering any existing information and documents related to your project or industry. This initial step will help you understand the current landscape and identify gaps in your knowledge.
- Document Review: Review any existing project documentation, market research reports, business plans, or relevant industry studies.
- Competitor Analysis: Gather information about your competitors, including their products, pricing, market share, and strategies.
- Regulatory and Compliance Documents: If applicable, collect information on industry regulations, permits, licenses, and compliance requirements.
- Market Trends: Stay informed about current market trends, consumer preferences, and emerging technologies that may impact your project.
- Stakeholder Interviews: Consider conducting initial interviews with key stakeholders, including potential customers, suppliers, and industry experts, to gather insights and feedback.
By starting with a strong foundation of existing knowledge, you'll be better prepared to identify gaps that require further investigation during the feasibility study. This proactive approach ensures that your study is comprehensive and well-informed from the outset.
How to Conduct a Market Feasibility Study?
The market feasibility study is a crucial component of your overall feasibility analysis. It focuses on assessing the potential demand for your product or service, understanding your target audience, analyzing your competition, and evaluating supply and demand dynamics within your chosen market.
Market Research and Analysis
Market research is the foundation of your market feasibility study. It involves gathering and analyzing data to gain insights into market trends, customer preferences, and the overall business landscape.
- Data Collection: Utilize various methods such as surveys, interviews, questionnaires, and secondary research to collect data about the market. This data may include market size, growth rates, and historical trends.
- Market Segmentation: Divide the market into segments based on factors such as demographics, psychographics , geography, and behavior. This segmentation helps you identify specific target markets .
- Customer Needs Analysis: Understand the needs, preferences, and pain points of potential customers . Determine how your product or service can address these needs effectively.
- Market Trends: Stay updated on current market trends, emerging technologies, and industry innovations that could impact your project.
- SWOT Analysis: Conduct a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) analysis to identify internal and external factors that may affect your market entry strategy.
In today's dynamic market landscape, gathering precise data for your market feasibility study is paramount. Appinio offers a versatile platform that enables you to swiftly collect valuable market insights from a diverse audience.
With Appinio, you can employ surveys, questionnaires, and in-depth analyses to refine your understanding of market trends, customer preferences, and competition.
Enhance your market research and gain a competitive edge by booking a demo with us today!
Book a Demo
Target Audience Identification
Knowing your target audience is essential for tailoring your product or service to meet their specific needs and preferences.
- Demographic Analysis: Define the age, gender, income level, education, and other demographic characteristics of your ideal customers.
- Psychographic Profiling: Understand the psychographics of your target audience, including their lifestyle, values, interests, and buying behavior.
- Market Segmentation: Refine your target audience by segmenting it further based on shared characteristics and behaviors.
- Needs and Pain Points: Identify your target audience's unique needs, challenges, and pain points that your product or service can address.
- Competitor's Customers: Analyze the customer base of your competitors to identify potential opportunities for capturing market share.
Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis helps you understand the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, positioning your project strategically within the market.
- Competitor Identification: Identify direct and indirect competitors within your industry or market niche.
- Competitive Advantage: Determine the unique selling points (USPs) that set your project apart from competitors. What value can you offer that others cannot?
- SWOT Analysis for Competitors: Conduct a SWOT analysis for each competitor to assess their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Market Share Assessment: Analyze each competitor's market share and market penetration strategies.
- Pricing Strategies: Investigate the pricing strategies employed by competitors and consider how your pricing strategy will compare.
Leveraging the power of data collection and analysis is essential in gaining a competitive edge. With Appinio , you can efficiently gather critical insights about your competitors, their strengths, and weaknesses. Seamlessly integrate these findings into your market feasibility study, empowering your project with a strategic advantage.
Demand and Supply Assessment
Understanding supply and demand dynamics is crucial for gauging market sustainability and potential challenges.
- Market Demand Analysis: Estimate the current and future demand for your product or service. Consider factors like seasonality and trends.
- Supply Evaluation: Assess the availability of resources, suppliers, and distribution channels required to meet the expected demand.
- Market Saturation: Determine whether the market is saturated with similar offerings and how this might affect your project.
- Demand Forecasting: Use historical data and market trends to make informed projections about future demand.
- Scalability: Consider the scalability of your project to meet increased demand or potential fluctuations.
A comprehensive market feasibility study will give you valuable insights into your potential customer base, market dynamics, and competitive landscape. This information will be pivotal in shaping your project's direction and strategy.
How to Conduct a Technical Feasibility Study?
The technical feasibility study assesses the practicality of implementing your project from a technical standpoint. It involves evaluating the project's design, technical requirements, technological feasibility, resource availability, and risk analysis. Let's delve into each aspect in more detail.
1. Project Design and Technical Requirements
The project design and technical requirements are the foundation of your technical feasibility study. This phase involves defining the technical specifications and infrastructure needed to execute your project successfully.
- Technical Specifications: Clearly define the technical specifications of your project, including hardware, software, and any specialized equipment.
- Infrastructure Planning: Determine the physical infrastructure requirements, such as facilities, utilities, and transportation logistics.
- Development Workflow: Outline the workflow and processes required to design, develop, and implement the project.
- Prototyping: Consider creating prototypes or proof-of-concept models to test and validate the technical aspects of your project.
2. Technology Assessment
A critical aspect of the technical feasibility study is assessing the technology required for your project and ensuring it aligns with your goals.
- Technology Suitability: Evaluate the suitability of the chosen technology for your project. Is it the right fit, or are there better alternatives?
- Scalability and Compatibility: Assess whether the chosen technology can scale as your project grows and whether it is compatible with existing systems or software.
- Security Measures: Consider cybersecurity and data protection measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Technical Expertise: Ensure your team or external partners possess the technical expertise to implement and maintain the technology.
3. Resource Evaluation
Resource evaluation involves assessing the availability of the essential resources required to execute your project successfully. These resources include personnel, materials, and suppliers.
- Human Resources: Evaluate whether you have access to skilled personnel or if additional hiring or training is necessary.
- Material Resources: Identify the materials and supplies needed for your project and assess their availability and costs.
- Supplier Relationships: Establish relationships with reliable suppliers and consistently assess their ability to meet your resource requirements.
4. Risk Analysis
Risk analysis is a critical component of the technical feasibility study, as it helps you anticipate and mitigate potential technical challenges and setbacks.
- Identify Risks: Identify potential technical risks, such as hardware or software failures, technical skill gaps, or unforeseen technical obstacles.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Develop strategies to mitigate identified risks, including contingency plans and resource allocation for risk management.
- Cost Estimation for Risk Mitigation: Assess the potential costs associated with managing technical risks and incorporate them into your project budget.
By conducting a thorough technical feasibility study, you can ensure that your project is technically viable and well-prepared to overcome technical challenges. This assessment will also guide decision-making regarding technology choices, resource allocation, and risk management strategies.
How to Conduct a Financial Feasibility Study?
The financial feasibility study is a critical aspect of your overall feasibility analysis. It focuses on assessing the financial viability of your project by estimating costs, projecting revenue, conducting investment analysis, and evaluating the overall financial health of your project. Let's delve into each aspect in more detail.
1. Cost Estimation
Cost estimation is the process of calculating the expenses associated with planning, developing, and implementing your project. This involves identifying both initial and ongoing costs.
- Initial Costs: Calculate the upfront expenses required to initiate the project, including capital expenditures, equipment purchases, and any development costs.
- Operational Costs: Estimate the ongoing operating expenses, such as salaries, utilities, rent, marketing, and maintenance.
- Contingency Funds: Allocate funds for unexpected expenses or contingencies to account for unforeseen challenges.
- Depreciation: Consider the depreciation of assets over time, as it impacts your financial statements.
2. Revenue Projections
Revenue projections involve forecasting the income your project is expected to generate over a specific period. Accurate revenue projections are crucial for assessing the project's financial viability.
- Sales Forecasts: Estimate your product or service sales based on market demand, pricing strategies, and potential growth.
- Pricing Strategy: Determine your pricing strategy, considering factors like competition, market conditions, and customer willingness to pay.
- Market Penetration: Analyze how quickly you can capture market share and increase sales over time.
- Seasonal Variations: Account for any seasonal fluctuations in revenue that may impact your cash flow.
3. Investment Analysis
Investment analysis involves evaluating the potential return on investment (ROI) and assessing the attractiveness of your project to potential investors or stakeholders.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the expected ROI by comparing the project's net gains against the initial investment.
- Payback Period: Determine how long it will take for the project to generate sufficient revenue to cover its initial costs.
- Risk Assessment: Consider the level of risk associated with the project and whether it aligns with investors' risk tolerance.
- Sensitivity Analysis: Perform sensitivity analysis to understand how changes in key variables, such as sales or costs, affect the investment's profitability.
4. Financial Viability Assessment
A financial viability assessment evaluates the project's ability to sustain itself financially in the long term. It considers factors such as profitability, cash flow, and financial stability.
- Profitability Analysis: Assess whether the project is expected to generate profits over its lifespan.
- Cash Flow Management: Analyze the project's cash flow to ensure it can cover operating expenses, debt payments, and other financial obligations.
- Break-Even Analysis: Determine the point at which the project's revenue covers all costs, resulting in neither profit nor loss.
- Financial Ratios: Calculate key financial ratios, such as debt-to-equity ratio and return on equity, to evaluate the project's financial health.
By conducting a comprehensive financial feasibility study, you can gain a clear understanding of the project's financial prospects and make informed decisions regarding its viability and potential for success.
How to Conduct an Operational Feasibility Study?
The operational feasibility study assesses whether your project can be implemented effectively within your organization's operational framework. It involves evaluating processes, resource planning, scalability, and analyzing potential operational risks.
1. Process and Workflow Assessment
The process and workflow assessment examines how the project integrates with existing processes and workflows within your organization.
- Process Mapping: Map out current processes and workflows to identify areas of integration and potential bottlenecks.
- Workflow Efficiency: Assess the efficiency and effectiveness of existing workflows and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Change Management: Consider the project's impact on employees and plan for change management strategies to ensure a smooth transition.
2. Resource Planning
Resource planning involves determining the human, physical, and technological resources needed to execute the project successfully.
- Human Resources: Assess the availability of skilled personnel and consider whether additional hiring or training is necessary.
- Physical Resources: Identify the physical infrastructure, equipment, and materials required for the project.
- Technology and Tools: Ensure that the necessary technology and tools are available and up to date to support project implementation.
3. Scalability Evaluation
Scalability evaluation assesses whether the project can adapt and expand to meet changing demands and growth opportunities.
- Scalability Factors: Identify factors impacting scalability, such as market growth, customer demand, and technological advancements.
- Capacity Planning: Plan for the scalability of resources, including personnel, infrastructure, and technology.
- Growth Strategies: Develop strategies for scaling the project, such as geographic expansion, product diversification, or increasing production capacity.
4. Operational Risk Analysis
Operational risk analysis involves identifying potential operational challenges and developing mitigation strategies.
- Risk Identification: Identify operational risks that could disrupt project implementation or ongoing operations.
- Risk Mitigation: Develop risk mitigation plans and contingency strategies to address potential challenges.
- Testing and Simulation: Consider conducting simulations or testing to evaluate how the project performs under various operational scenarios.
- Monitoring and Adaptation: Implement monitoring and feedback mechanisms to detect and address operational issues as they arise.
Conducting a thorough operational feasibility study ensures that your project aligns with your organization's capabilities, processes, and resources. This assessment will help you plan for a successful implementation and minimize operational disruptions.
How to Write a Feasibility Study?
The feasibility study report is the culmination of your feasibility analysis. It provides a structured and comprehensive document outlining your study's findings, conclusions, and recommendations. Let's explore the key components of the feasibility study report.
1. Structure and Components
The structure of your feasibility study report should be well-organized and easy to navigate. It typically includes the following components:
- Executive Summary: A concise summary of the study's key findings, conclusions, and recommendations.
- Introduction: An overview of the project, the objectives of the study, and a brief outline of what the report covers.
- Methodology: A description of the research methods , data sources, and analytical techniques used in the study.
- Market Feasibility Study: Detailed information on market research, target audience, competitive analysis, and demand-supply assessment.
- Technical Feasibility Study: Insights into project design, technical requirements, technology assessment, resource evaluation, and risk analysis.
- Financial Feasibility Study: Comprehensive information on cost estimation, revenue projections, investment analysis, and financial viability assessment.
- Operational Feasibility Study: Details on process and workflow assessment, resource planning, scalability evaluation, and operational risks analysis.
- Conclusion: A summary of key findings and conclusions drawn from the study.
Recommendations: Clear and actionable recommendations based on the study's findings.
2. Write the Feasibility Study Report
When writing the feasibility study report, it's essential to maintain clarity, conciseness, and objectivity. Use clear language and provide sufficient detail to support your conclusions and recommendations.
- Be Objective: Present findings and conclusions impartially, based on data and analysis.
- Use Visuals: Incorporate charts, graphs, and tables to illustrate key points and make the report more accessible.
- Cite Sources: Properly cite all data sources and references used in the study.
- Include Appendices: Attach any supplementary information, data, or documents in appendices for reference.
3. Present Findings and Recommendations
When presenting your findings and recommendations, consider your target audience. Tailor your presentation to the needs and interests of stakeholders, whether they are investors, executives, or decision-makers.
- Highlight Key Takeaways: Summarize the most critical findings and recommendations upfront.
- Use Visual Aids: Create a visually engaging presentation with slides, charts, and infographics.
- Address Questions: Be prepared to answer questions and provide additional context during the presentation.
- Provide Supporting Data: Back up your findings and recommendations with data from the feasibility study.
4. Review and Validation
Before finalizing the feasibility study report, conducting a thorough review and validation process is crucial. This ensures the accuracy and credibility of the report.
- Peer Review: Have colleagues or subject matter experts review the report for accuracy and completeness.
- Data Validation: Double-check data sources and calculations to ensure they are accurate.
- Cross-Functional Review: Involve team members from different disciplines to provide diverse perspectives.
- Stakeholder Input: Seek input from key stakeholders to validate findings and recommendations.
By following a structured approach to creating your feasibility study report, you can effectively communicate the results of your analysis, support informed decision-making, and increase the likelihood of project success.
Feasibility Study Examples
Let's dive into some real-world examples to truly grasp the concept and application of feasibility studies. These examples will illustrate how various types of projects and businesses undergo the feasibility assessment process to ensure their viability and success.
Example 1: Local Restaurant
Imagine you're passionate about opening a new restaurant in a bustling urban area. Before investing significant capital, you'd want to conduct a thorough feasibility study. Here's how it might unfold:
- Market Feasibility: You research the local dining scene, identify target demographics, and assess the demand for your cuisine. Market surveys reveal potential competitors, dining preferences, and pricing expectations.
- Technical Feasibility: You design the restaurant layout, plan the kitchen setup, and assess the technical requirements for equipment and facilities. You consider factors like kitchen efficiency, safety regulations, and adherence to health codes.
- Financial Feasibility: You estimate the initial costs for leasing or purchasing a space, kitchen equipment, staff hiring, and marketing. Revenue projections are based on expected foot traffic, menu pricing, and seasonal variations.
- Operational Feasibility: You create kitchen and service operations workflow diagrams, considering staff roles and responsibilities. Resource planning includes hiring chefs, waitstaff, and kitchen personnel. Scalability is evaluated for potential expansion or franchising.
- Risk Analysis: Potential operational risks are identified, such as food safety concerns, labor shortages, or location-specific challenges. Risk mitigation strategies involve staff training, quality control measures, and contingency plans for unexpected events.
Example 2: Software Development Project
Now, let's explore the feasibility study process for a software development project, such as building a mobile app:
- Market Feasibility: You analyze the mobile app market, identify your target audience, and assess the demand for a solution in a specific niche. You gather user feedback and conduct competitor analysis to understand the competitive landscape.
- Technical Feasibility: You define the technical requirements for the app, considering platforms (iOS, Android), development tools, and potential integrations with third-party services. You evaluate the feasibility of implementing specific features.
- Financial Feasibility: You estimate the development costs, including hiring developers, designers, and ongoing maintenance expenses. Revenue projections are based on app pricing, potential in-app purchases, and advertising revenue.
- Operational Feasibility: You map out the development workflow, detailing the phases from concept to deployment. Resource planning includes hiring developers with the necessary skills, setting up development environments, and establishing a testing framework.
- Risk Analysis: Potential risks like scope creep, technical challenges, or market saturation are assessed. Mitigation strategies involve setting clear project milestones, conducting thorough testing, and having contingency plans for technical glitches.
These examples demonstrate the versatility of feasibility studies across diverse projects. Whatever type of venture or endeavor you want to embark on, a well-structured feasibility study guides you toward informed decisions and increased project success.
In conclusion, conducting a feasibility study is a crucial step in your project's journey. It helps you assess the viability and potential risks, providing a solid foundation for informed decision-making. Remember, a well-executed feasibility study not only enables you to identify challenges but also uncovers opportunities that can lead to your project's success.
By thoroughly examining market trends, technical requirements, financial aspects, and operational considerations, you are better prepared to embark on your project confidently. With this guide, you've gained the knowledge and tools needed to navigate the intricate terrain of feasibility studies.
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study in Minutes?
Speed and precision are paramount for feasibility studies, and Appinio delivers just that. As a real-time market research platform, Appinio empowers you to seamlessly conduct your market research in a matter of minutes, putting actionable insights at your fingertips.
Here's why Appinio stands out as the go-to tool for feasibility studies:
- Rapid Insights: Appinio's intuitive platform ensures that anyone, regardless of their research background, can effortlessly navigate and conduct research, saving valuable time and resources.
- Lightning-Fast Responses: With an average field time of under 23 minutes for 1,000 respondents, Appinio ensures that you get the answers you need when you need them, making it ideal for time-sensitive feasibility studies.
- Global Reach: Appinio's extensive reach spans over 90 countries, allowing you to define the perfect target group from a pool of 1,200+ characteristics and gather insights from diverse markets.
Get free access to the platform!
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

07.05.2024 | 28min read
Interval Scale: Definition, Characteristics, Examples

03.05.2024 | 29min read
What is Qualitative Observation? Definition, Types, Examples

02.05.2024 | 32min read
What is a Perceptual Map and How to Make One? (+ Template)
- Contact sales
Start free trial
What Is a Feasibility Study? How to Conduct One for Your Project

Table of Contents
What is a feasibility study, what’s the importance of a feasibility study, what is included in a feasibility study report, types of feasibility study.
- 7 Steps To Do a Feasibility Study
Feasibility Study Examples
Why is a feasibility study so important in project management? For one, the feasibility study or feasibility analysis is the foundation upon which your project plan resides. That’s because the feasibility analysis determines the viability of your project. Now that you know the importance, read on to learn what you need to know about feasibility studies.
A feasibility study is simply an assessment of the practicality of a proposed project plan or method. This is done by analyzing technical, economic, legal, operational and time feasibility factors. Just as the name implies, you’re asking, “Is this feasible?” For example, do you have or can you create the technology that accomplishes what you propose? Do you have the people, tools and resources necessary? And, will the project get you the ROI you expect?

Get your free
Feasibility study template
Use this free Feasibility Study Template for Word to manage your projects better.
A project feasibility study should be done during the project management life cycle after the business case has been completed. So, that’s the “what” and the “when” but how about the “why?” Why is it important to conduct a feasibility study?
An effective feasibility study points a project in the right direction by helping decision-makers have a holistic view of the potential benefits, disadvantages, barriers and constraints that could affect its outcome. The main purpose of a feasibility study is to determine whether the project can be not only viable but also beneficial from a technical, financial, legal and market standpoint.
The findings of your project feasibility study are compiled in a feasibility report that usually includes the following elements.
- Executive summary
- Description of product/service
- Technology considerations
- Product/service marketplace
- Marketing strategy
- Organization/staffing
- Financial projections
- Findings and recommendations
Free Feasibility Study Template
Use this free feasibility study template for Word to begin your own feasibility study. It has all the fundamental sections for you to get started, and it’s flexible enough to adapt to your specific needs. Download yours today.
There are many things to consider when determining project feasibility, and there are different types of feasibility studies you might conduct to assess your project from different perspectives.
Pre-Feasibility Study
A pre-feasibility study, as its name suggests, it’s a process that’s undertaken before the feasibility study. It involves decision-makers and subject matter experts who will prioritize different project ideas or approaches to quickly determine whether the project has fundamental technical, financial, operational or any other evident flaws. If the project proposal is sound, a proper feasibility study will follow.
Technical Feasibility Study
A technical feasibility study consists in determining if your organization has the technical resources and expertise to meet the project requirements . A technical study focuses on assessing whether your organization has the necessary capabilities that are needed to execute a project, such as the production capacity, facility needs, raw materials, supply chain and other inputs. In addition to these production inputs, you should also consider other factors such as regulatory compliance requirements or standards for your products or services.
Economic Feasibility Study
Also called financial feasibility study, this type of study allows you to determine whether a project is financially feasible. Economic feasibility studies require the following steps:
- Before you can start your project, you’ll need to determine the seed capital, working capital and any other capital requirements, such as contingency capital. To do this, you’ll need to estimate what types of resources will be needed for the execution of your project, such as raw materials, equipment and labor.
- Once you’ve determined what project resources are needed, you should use a cost breakdown structure to identify all your project costs.
- Identify potential sources of funding such as loans or investments from angel investors or venture capitalists.
- Estimate the expected revenue, profit margin and return on investment of your project by conducting a cost-benefit analysis , or by using business forecasting techniques such as linear programming to estimate different future outcomes under different levels of production, demand and sales.
- Estimate your project’s break-even point.
- Conduct a financial benchmark analysis with industrial averages and specific competitors in your industry.
- Use pro forma cash flow statements, financial statements, balance sheets and other financial projection documents.
Legal Feasibility Study
Your project must meet legal requirements including laws and regulations that apply to all activities and deliverables in your project scope . In addition, think about the most favorable legal structure for your organization and its investors. Each business legal structure has advantages and disadvantages when it comes to liability for business owners, such as limited liability companies (LLCs) or corporations, which reduce the liability for each business partner.
Market Feasibility Study
A market feasibility study determines whether your project has the potential to succeed in the market. To do so, you’ll need to analyze the following factors:
- Industry overview: Assess your industry, such as year-over-year growth, identify key direct and indirect competitors, availability of supplies and any other trends that might affect the future of the industry and your project.
- SWOT analysis: A SWOT analysis allows organizations to determine how competitive an organization can be by examining its strengths, weaknesses and the opportunities and threats of the market. Strengths are the operational capabilities or competitive advantages that allow an organization to outperform its competitors such as lower costs, faster production or intellectual property. Weaknesses are areas where your business might be outperformed by competitors. Opportunities are external, such as an underserved market, an increased demand for your products or favorable economic conditions. Threats are also external factors that might affect your ability to do well in the market such as new competitors, substitute products and new technologies.
- Market research: The main purpose of market research is to determine whether it’s possible for your organization to enter the market or if there are barriers to entry or constraints that might affect your ability to compete. Consider variables such as pricing, your unique value proposition, customer demand, new technologies, market trends and any other factors that affect how your business will serve your customers. Use market research techniques to identify your target market, create buyer personas, assess the competitiveness of your niche and gauge customer demand, among other things.
7 Steps to Do a Feasibility Study
If you’re ready to do your own feasibility study, follow these 7 steps. You can use this free feasibility study template to help you get started.
1. Conduct a Preliminary Analysis
Begin by outlining your project plan . You should focus on an unserved need, a market where the demand is greater than the supply and whether the product or service has a distinct advantage. Then, determine if the feasibility factors are too high to clear (i.e. too expensive, unable to effectively market, etc.).
2. Prepare a Projected Income Statement
This step requires working backward. Start with what you expect the income from the project to be and then what project funding is needed to achieve that goal. This is the foundation of an income statement. Factor in what services are required and how much they’ll cost and any adjustments to revenues, such as reimbursements, etc.
Related: Free Project Management Templates
3. Conduct a Market Survey or Perform Market Research
This step is key to the success of your feasibility study, so make your market analysis as thorough as possible. It’s so important that if your organization doesn’t have the resources to do a proper one, then it is advantageous to hire an outside firm to do so.
Market research will give you the clearest picture of the revenues and return on investment you can realistically expect from the project. Some things to consider are the geographic influence on the market, demographics, analyzing competitors, the value of the market and what your share will be and if the market is open to expansion (that is, in response to your offer).
4. Plan Business Organization and Operations
Once the groundwork of the previous steps has been laid, it’s time to set up the organization and operations of the planned project to meet its technical, operational, economic and legal feasibility factors. This isn’t a superficial, broad-stroke endeavor. It should be thorough and include start-up costs, fixed investments and operating costs.
These costs address things such as equipment, merchandising methods, real estate, personnel, supply availability, overhead, etc.
5. Prepare an Opening Day Balance Sheet
This includes an estimate of the assets and liabilities, one that should be as accurate as possible. To do this, create a list that includes items, sources, costs and available financing. Liabilities to consider are such things as leasing or purchasing land, buildings and equipment, financing for assets and accounts receivables.
6. Review and Analyze All Data
All of these steps are important, but the review and analysis are especially important to ensure that everything is as it should be and that nothing requires changing or tweaking. Take a moment to look over your work one last time.
Reexamine your previous steps, such as the income statement, and compare them with your expenses and liabilities. Is it still realistic? This is also the time to think about risk and come up with any contingency plans .
7. Make a Go/No-Go Decision
You’re now at the point to make a decision about whether or not the project is feasible. That sounds simple, but all the previous steps lead to this decision-making moment. A couple of other things to consider before making that binary choice are whether the commitment is worth the time, effort and money and whether it aligns with the organization’s strategic goals and long-term aspirations.
Here are some simple feasibility study examples so you have a better idea of what a feasibility study is used for in different industries.
Construction Feasibility Study
For this construction feasibility study example, let’s imagine a large construction company that’s interested in starting a new project in the near future to generate profits.
- Pre-Feasibility Study: The first step is to conduct a preliminary feasibility study. It can be as simple as a meeting where decision-makers will prioritize projects and discuss different project ideas to determine which poses a bigger financial benefit for the organization.
- Technical Feasibility Study: Now it’s time to estimate what resources are needed to execute the construction project, such as raw materials, equipment and labor. If there’s work that can’t be executed by the company with its current resources, a subcontractor will be hired to fill the gap.
- Economic Feasibility Study: Once the construction project management team has established what materials, equipment and labor are needed, they can estimate costs. Cost estimators use information from past projects, construction drawings and documents such as a bill of quantities to come up with an accurate cost estimate. Then, based on this estimate, a profit margin and financial forecasts will be analyzed to determine if there’s economic feasibility.
- Legal Feasibility Study: Now the company needs to identify all potential regulations, building codes and laws that might affect the project. They’ll need to ask for approval from the local government so that they can begin the construction project .
- Market Feasibility Study: Market feasibility will be determined depending on the nature of the project. For this feasibility example, let’s assume a residential construction project will be built. To gauge market potential, they’ll need to analyze variables such as the average income of the households in the city, crime rate, population density and any trends in state migration.
Manufacturing Feasibility Study
Another industry that uses feasibility studies is manufacturing. It’s a test run of the steps in the manufacturing production cycle to ensure the process is designed properly. Let’s take a look at what a manufacturing feasibility study example would look like.
- Feasibility Study: The first step is to look at various ideas and decide which is the best one to pursue. You don’t want to get started and have to stop. That’s a waste of time, money and effort. Look at what you intend to manufacture, does it fill an unserved need, is the market able to support competition and can you manufacture a quality product on time and within your budget?
- Financial Feasibility Study: Find out if your estimated income from the sale of this product is going to cover your costs, both direct and indirect costs. Work backward from the income you expect to make and the expenses you’ll spend for labor, materials and production to determine if the manufacturing of this product is financially feasible.
- Market Feasibility Study: You’ve already determined that there’s a need that’s not being served, but now it’s time to dig deeper to get realistic projections of revenue. You’ll want to define your target demographic, analyze the competitive landscape, determine the total market volume and what your market share will be and estimate what market expansion opportunities there are.
- Technical Feasibility Study: This is where you’ll explore the production , such as what resources you’ll need to produce your product. These findings will inform your financial feasibility study as well as labor, material, equipment, etc., costs have to be within your budget. You’ll also figure out the processes you’ll use to produce and deliver your product to the market, including warehousing and retail distribution.
There could be other feasibility studies you’ll have to make depending on the product and the market, but these are the essential ones that all manufacturers have to look at before they can make an educated decision as to whether to go forward or abandon the idea.
Best Practices for a Feasibility Study
- Use project management software like ProjectManager to organize your data and work efficiently and effectively
- Use templates or any data and technology that gives you leverage
- Involve the appropriate stakeholders to get their feedback
- Use market research to further your data collection
- Do your homework and ask questions to make sure your data is solid
If your project is feasible, then the real work begins. ProjectManager helps you plan more efficiently. Our online Gantt chart organizes tasks, sets deadlines, adds priority and links dependent tasks to avoid delays. But unlike other Gantt software, we calculate the critical path for you and set a baseline to measure project variance once you move into the execution phase.
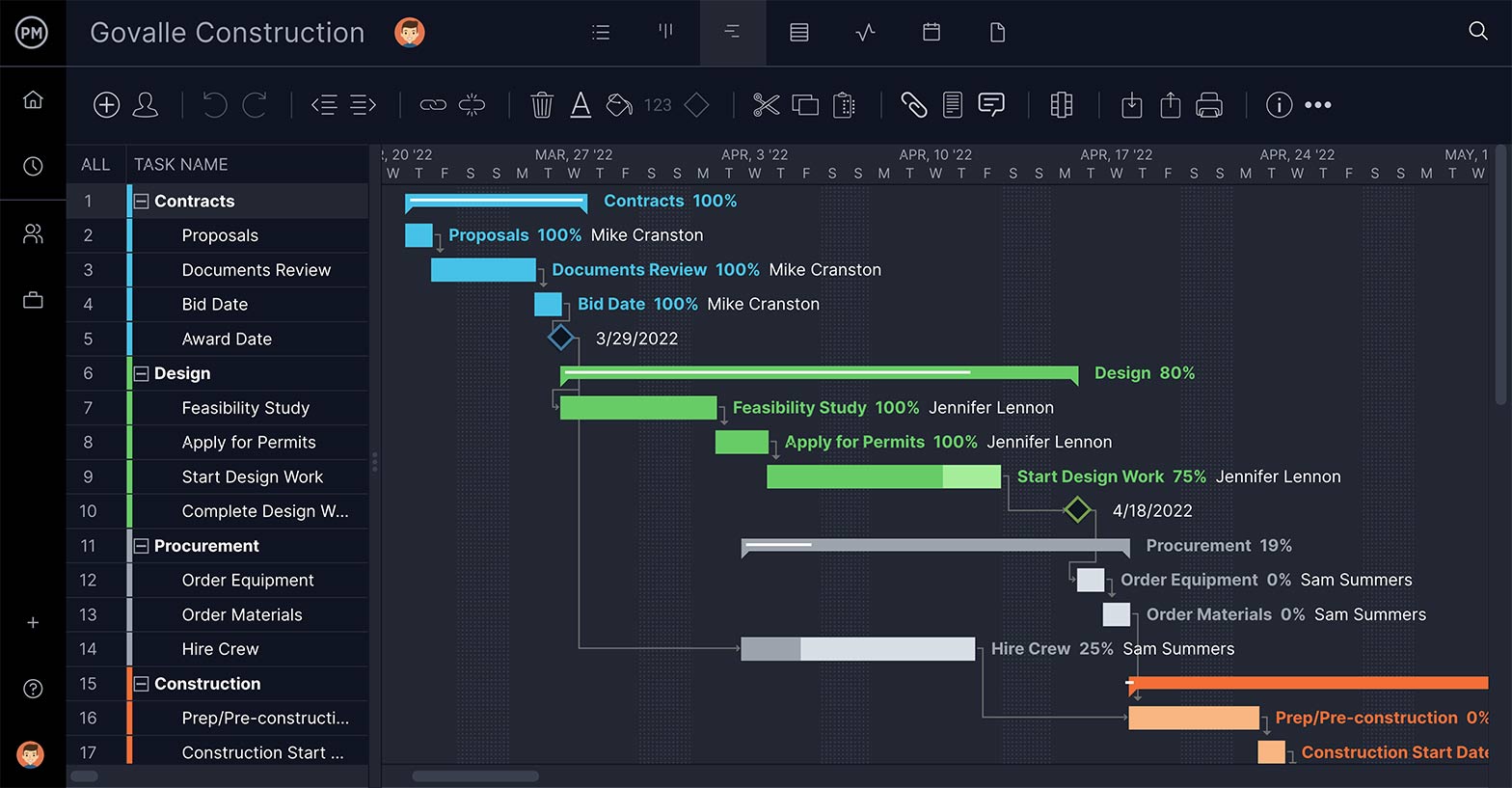
Watch a Video on Feasibility Studies
There are many steps and aspects to a project feasibility study. If you want yours to be accurate and forecast correctly whether your project is doable, then you need to have a clear understanding of all its moving parts.
Jennifer Bridges, PMP, is an expert on all aspects of project management and leads this free training video to help you get a firm handle on the subject.
Here’s a screenshot for your reference!

Pro tip: When completing a feasibility study, it’s always good to have a contingency plan that you test to make sure it’s a viable alternative.
ProjectManager Improves Your Feasibility Study
A feasibility study is a project, so get yourself a project management software that can help you execute it. ProjectManager is an award-winning software that can help you manage your feasibility study through every phase.
Once you have a plan for your feasibility study, upload that task list to our software and all your work is populated in our online Gantt chart. Now you can assign tasks to team members, add costs, create timelines, collect all the market research and attach notes at the task level. This gives people a plan to work off of, and a collaborative platform to collect ideas and comments.
If you decide to implement the project, you already have it started in our software, which can now help you monitor and report on its progress. Try it for yourself with this free 30-day trial.
Transcription
Today we’re talking about How to Conduct A Feasibility Study, but first of all, I want to start with clarifying what a feasibility study is.
Feasibility Analysis Definition
Basically, it’s an assessment of the practicality of a proposed plan or method. Basically, we’ll want to want to know, is this feasible. Some of the questions that may generate this or we can hear people asking are, “Do we have or can we create the technology to do this? Do we have the people resource who can produce this and will we get our ROI, our Return On Investment?”
When to Do a Feasibility Study
So when do we do the feasibility study? So it’s done during a project lifecycle and it’s done after the business case because the business case outlines what we’re proposing. Is it a product or service that we’re proposing?
So why do we do this? The reason we do this is that we need to determine the factors that will make the business opportunity a success.
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study
Well, let’s talk about a few steps that we do in order to conduct the feasibility study.
Well, first of all, we conduct a preliminary analysis of what all’s involved in the business case and what we’re analyzing and what we’re trying to determine is feasible.
Then we prepare a projected income statement. We need to know what are the income streams, how are we gonna make money on this. Where’s the revenue coming from? We also need to conduct a market survey.
We need to know, is this a demand? Is there a market for this? Are customers willing to use this product or use this service?
The fourth one is to plan the business organization and operations. What is the structure, what kind of resources do we need? What kind of staffing requirements do we have?
We also want to prepare an opening day balance sheet. What are the…how again, what are the expenses, what’s the revenue and to ensure that being able to determine if we’re gonna make our ROI.
So we want to review and analyze all of the data that we have and with that, we’re going to determine, we’re going to make a go, no-go decision. Meaning, are we going to do this project or this business opportunity or not.
Well, here are some of the best practices to use during your feasibility study.
One is to use templates, tools and surveys that exist today. The great news is, data is becoming more and more prevalent. There are all kinds of technologies. There are groups that they do nothing but research. Things that we can leverage today.
We want to involve the appropriate stakeholders to ensure that input is being considered from the different people involved.
We also want to use again the market research to ensure we’re bringing in good, reliable data.
Do your homework, meaning act like is if this is your project, if it’s your money. So do your homework and do it well and make sure you give credible data.
What Is a Feasibility Report?
So ultimately in the end what we’re doing is, we’re producing and we’re providing a feasibility report. So in that report, think of this is like a template.
So what you’re gonna do is give it an executive summary of the business opportunity that you’re evaluating and the description of the product or the service.
You want to look at different technology considerations. Is it technology that you’re going to use? Are you going to build the technology?
What kind of product and service marketplace and being able again, to identify the specific market you’re going to be targeting? Also, what is the marketing strategy you’re going to use to target the marketplace?
And also what’s the organizational structure? What are the staffing requirements? What people do you need to deliver the product or service and even support it?
So also we want to know the schedule to be able to have the milestones to ensure that as we’re building things, that as we’re spending money that we’re beginning to bring in income to pay and knowing when we’re going to start recuperating some of the funding. Again, which also ties into the financial projections.
Ultimately in this report, you’re going to provide the findings and the recommendations.
Again, we’ll probably talk about technology. Are you going to build it? Are you going to buy it? What are the marketing strategies for the specific marketplace organization? You may have some recommendations for whether you’re going to insource the staff, maybe you are going to outsource some staff and what that looks like and also financial recommendation.
If you’ve been looking for an all-in-one tool that can help with your feasibility study, consider ProjectManager. We offer five project views and countless features that make it seamless to plan projects, organize tasks and stay connected with your team. See what our software can do for you by taking this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
- Software Categories
Get results fast. Talk to an expert now.
855-718-1369
What is a feasibility study: step-by-step guide.
Key takeaways
- A feasibility study is an essential analytical tool that evaluates the viability of a proposed project on multiple fronts, such as financials, technical requirements, and market demand.
- Conducted during the project initiation phase, this type of study serves as an early checkpoint to identify potential roadblocks and assess risks.
- Feasibility studies act as the first line of defense against project failure, saving time, money, and resources.
In this article...
What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study is an analytical tool used to evaluate the practicality of a proposed project or business idea. It assesses various factors such as financial viability, technical requirements, legal constraints, and market demand. The study aims to answer the question “Are the goals of this project realistically attainable?” by examining data, studies, and other relevant information.
A feasibility study is a crucial step to take before diving into any project and is generally performed during the project initiation phase of project management . It helps identify potential roadblocks, assess risks, and estimate resource allocation; skipping this step can lead to project failure, wasted resources, and financial losses.
Feasibility studies represent one of the many intricacies of project planning . Understanding the other requirements of this crucial step can give you a well-rounded view of how to set your project up for success.
Steps to conduct a feasibility study
Successfully executing a project hinges on thorough planning and risk assessment. Following this step-by-step guide for conducting a feasibility study will help you meticulously evaluate the viability of your project from the outset.
Step 1: Conduct preliminary analysis
This is where you take a good, hard look at your project to determine whether it’s worth pursuing. At this stage, you should also decide if a more detailed feasibility study is necessary.
A few key criteria usually come into play during this initial assessment. First, consider a general sense of the market demand for your project, the resources you have at your disposal, and some ballpark figures for initial costs. If it’s difficult to get clear estimates, it may be worthwhile to invest additional time and resources in a more comprehensive feasibility study. If no significant roadblocks pop up in this preliminary analysis, then you have the green light to proceed.
Some project management software includes useful features that can help you efficiently collect and organize all this data. These features can be very helpful in decision-making, especially when you’re looking at multiple variables.
Step 2: Create a projected income statement
This vital component of the feasibility study involves forecasting the income, expenses, and profitability associated with the proposed project. The projected income statement is akin to peering into a financial crystal ball to see how the numbers might align.
There are several approaches you can take to assess a project’s financial impact. Historical data and industry benchmarks, for example, can serve as reliable guides. These projections are important for assessing financial feasibility and making informed decisions.
The significance of these forecasts cannot be overstated — they help stakeholders understand the project’s potential ROI and ultimately make the go/no-go decision for the project.
Step 3: Survey the market
The market survey stage involves rolling up your sleeves to gather valuable data and insights about your target market(s) and audience(s). Think of it as your project’s reconnaissance mission: You’re scouting the terrain to understand what you’re getting into.
To start, you’ll want to learn your customers’ preferences to see if your project will fulfill a need or solve a problem they currently face. For example, a software company’s research might reveal customer demand for a new feature that aligns with the project’s goals.
Also consider if your project is timely and whether it will make a significant impact now or in the near future, depending on emerging market trends. It may be useful to conduct competitor research as well; knowing what and who you’re up against can help stakeholders decide whether you should move forward with the project and, if so, how you will approach it.
Surveys and interviews are ideal for firsthand quantitative and qualitative data. However, don’t underestimate the power of existing market reports. This preexisting data can offer a broad market landscape view, helping you make data-driven decisions. You can also leverage other research and data collection methods, such as focus groups and publicly available databases like Statista and the U.S. Census Bureau .
Step 4: Review and analyze the data
With all of the necessary information in hand, use tools like a SWOT analysis to evaluate the project’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. A risk assessment is another go-to method that can help you identify potential pitfalls that could derail your project.
At this point in the feasibility study, weigh key metrics and indicators like projected ROI, milestone dates, market penetration rates, and possible vulnerabilities. These gauges, when reviewed in tandem, paint a broader picture of your project’s viability and value.
Step 5: Determine the next steps
Use your research-backed analysis to decide whether the project you’ve proposed is the best way to address the problems it intends to address. If the metrics are favorable and the risks are manageable, you should feel confident advancing to the planning phase. Too many red flags, however, may mean you need to go back to the drawing board.
Here’s a little tech tip to make this decision easier: Many project management software dashboards can compile your key metrics and findings neatly in one visual package. It’s like having a project feasibility snapshot right at your fingertips, which makes it much easier for stakeholders to understand important data and make informed decisions.
Types of feasibility studies
There are different types of feasibility studies that each focus on a unique aspect of projects and project planning . By understanding the nuances of each, you’ll become better equipped to make well-informed decisions, mitigate risks, and ultimately steer your project toward success.
Technical feasibility
Technical feasibility digs into the nuts and bolts of the project. You’re looking at what kind of technology you’ll need, whether it’s available, and if it can be integrated into your current systems. It’s like checking if you have all the ingredients you need before cooking a specific recipe.
Economic feasibility
This study is all about the money — how much the project will cost and what kinds of economic or profitability benefits it will bring forth. With an economic feasibility study, you’re most often doing a cost-benefit analysis to see if the financials add up in your favor. It’s like weighing the pros and cons but in dollar signs.
Legal feasibility
This is your legal checkpoint. You’re looking at any laws or regulations that might create risks or restrict your project. This feasibility study could also involve checking compliance with industry-specific or regional regulations.
Operational feasibility
An operational feasibility study will help you see how the project fits into your current operations and operational goals and resources. After completing this type of study, you should know if your project will require new workflows and if your team can handle project tasks alongside their current workloads.
This study also evaluates whether the organization has the expertise to accomplish all project goals.
Scheduling feasibility
This feasibility study is all about time. You’re considering how long the project will take and whether you can afford any delays. Gantt charts , a feature commonly found in project management software, can be convenient in this type of study.
These visual timelines allow you to map out the entire project schedule, set milestones, and identify potential bottlenecks. You can also easily see if your project’s timeline is realistic or if you need to make adjustments to avoid delays.
Feasibility study examples
Feasibility studies add value to the project lifecycle across diverse industries. With each of these examples, the feasibility study is a critical preliminary step to identify potential roadblocks and assess the likelihood of project success.
Construction
A construction project feasibility study might focus on land evaluation, zoning laws, and material costs to determine if a new housing development is viable. In this example, the study helps avoid legal snags and ensure profitable land use.
A healthcare feasibility study may assess the demand for a new medical facility in a specific location by looking at factors like local population health statistics and existing healthcare infrastructure. This type of research helps determine whether a new facility would serve the community appropriately and utilize resources effectively.
Information technology
An IT feasibility study might analyze the technical requirements, cost, and market demand for a new software application to understand whether the development effort would offer a reasonable return on investment. This information helps project teams avoid sinking time and money into software that no one wants or needs.
Free feasibility study template
Download our feasibility study template for free:
Why are feasibility studies crucial in project management?
In project management, feasibility studies help you gauge whether your project is a go or a no-go, saving you time, money, and a lot of headaches in the long run. But it’s not just about giving your project a thumbs-up or down.
Feasibility studies are also invaluable for decision-making and risk assessment. They provide the data and insights you need to make informed choices. Whether it’s deciding on the project scope, budget, or timeline, these studies offer a comprehensive view of what you’re up against.
Plus, feasibility studies help you identify potential roadblocks and risks, allowing you to prepare effective contingency plans. Operating with a feasibility study as your project’s foundation is like giving your team both a roadmap and a weather forecast to help you better navigate your project journey.
About the author
Looking for software? Try our Project Management Product Selection Tool
Get FREE Expert Advice

How should our experts reach you?
Learn everything you need to know about What Is a Feasibility Study: Step-by-Step Guide. Our experts will reach out to you shortly.
By clicking the button above, I confirm that I have read and agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} AI that works. Coming June 5, Asana redefines work management—again. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Get early access .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Product overview
- All features
- App integrations
CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana Intelligence
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Marketing strategic planning
- Request tracking
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- What's new Learn about the latest and greatest from Asana
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project planning |
- How to use a feasibility study in proje ...
How to use a feasibility study in project management

It can be exciting to run a large, complex project that has a huge potential impact on your organization. On the one hand, you’re driving real change. On the other, failure is intimidating.
What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study—sometimes called a feasibility analysis or feasibility report—is a way to evaluate whether or not a project plan could be successful. A feasibility study evaluates the practicality of your project plan in order to judge whether or not you’re able to move forward with the project.
It does so by answering two questions:
Does our team have the required tools or resources to complete this project?
Will there be a high enough return on investment to make the project worth pursuing?
Feasibility studies are important for projects that represent significant investments for your business. Projects that also have a large potential impact on your presence in the market may also require a feasibility study.
As the project manager , you may not be directly responsible for driving the feasibility study, but it’s important to know what these studies are. By understanding the different elements that go into a feasibility study, you can better support the team driving the feasibility study and ensure the best outcome for your project.
When should you conduct a feasibility study
A feasibility study should be conducted after the project has been pitched but before any work has actually started. The study is part of the project planning process. In fact, it’s often done in conjunction with a SWOT analysis or project risk assessment , depending on the specific project.
Feasibility studies help:
Confirm market opportunities before committing to a project
Narrow your business alternatives
Create documentation about the benefits and detriments of your proposed initiative
Provide more information before making a go/no go decision
You likely don’t need a feasibility study if:
You already know the project is feasible
You’ve run a similar project in the past
Your competitors are succeeding with a similar initiative in market
The project is small, straightforward, and has minimal long-term business impact
Your team ran a similar feasibility study within the past three years
One thing to keep in mind is that a feasibility study is not a project pitch. During a project pitch, you’re evaluating whether or not the project is a good idea for your company, and whether the goals of the project are in line with your overall strategic plan. Typically, once you’ve established that the project is a good idea, you’d then run a feasibility study to confirm the project is possible with the tools and resources you have at your disposal.
Feasibility study vs. project charter
A project charter is a relatively informal document to pitch your project to stakeholders. Think of the charter like an elevator pitch of your project objectives, scope, and responsibilities. Typically, your project sponsor or executive stakeholders reviews the charter before ratifying the project.
A feasibility study should be implemented after the project charter has been ratified. This isn’t a document to pitch whether or not the project is in line with your team’s goals—rather, it’s a way to ensure the project is something you and your team can accomplish.
Feasibility study vs. business case
A business case is a more formalized version of the project charter. While you’d typically create a project charter for small or straightforward initiatives, you should create a business case if you are pitching a large, complex initiative that will make a major impact on the business. This longer, more formal document will also include financial information, and typically involves more senior stakeholders.
After your business case is approved by relevant stakeholders, you’d then run a feasibility study to make sure the work is doable. If you find it isn’t, you might return to your executive stakeholders and request more resources, tools, or time in order to ensure your business case is feasible.
Feasibility study vs. business plan
A business plan is a formal document of your organization’s goals. You typically write a business plan when founding your company, or when your business is going through a significant shift. Your business plan informs a lot of other business decisions, including your three to five year strategic plan .
As you implement your business and strategic plan, you’ll invest in individual projects. A feasibility study is a way to evaluate the practicality of any given individual project or initiative.
4 elements of a feasibility analysis
There are four main elements that go into a feasibility study: technical feasibility, financial feasibility, market feasibility (or market fit), and operational feasibility. You may also see these referred to as the four types of feasibility studies, though most feasibility studies actually include a review of all four elements.
Technical feasibility
A technical feasibility study reviews the technical resources available for your project. This study determines if you have the right equipment, enough equipment, and the right technical knowledge to complete your project objectives . For example, if your project plan proposes creating 50,000 products per month, but you can only produce 30,000 products per month in your factories, this project isn’t technically feasible.
Financial feasibility
Financial feasibility describes whether or not your project is fiscally viable. A financial feasibility report includes a cost/benefit analysis of the project. It also forecasts an expected return on investment (ROI), as well as outlines any financial risks. The goal at the end of the financial feasibility study is to understand the economic benefits the project will drive.
Market feasibility
The market feasibility study is an evaluation of how your team expects the project’s deliverables to perform in the market. This part of the report includes a market analysis, market competition breakdown, and sales projections.
Operational feasibility
An operational feasibility study evaluates whether or not your organization is able to complete this project. This includes staffing requirements, organizational structure, and any applicable legal requirements. At the end of the operational feasibility study, your team will have a sense of whether or not you have the resources, skills, and competencies to complete this work.
Feasibility study checklist
Most feasibility studies are structured in a similar way. These documents serve as an assessment of the practicality of a proposed business idea. Creating a clear feasibility study helps project stakeholders during the decision making process.
A feasibility study contains:
An executive summary describing the project’s overall viability
A description of the product or service being developed during this project
Any technical considerations , including technology, equipment, or staffing
The market survey , including a study of the current market and the marketing strategy
The operational feasibility study , evaluating whether or not your team’s current organizational structure can support this initiative
The project timeline
Financial projections based on your financial feasibility report
6 steps to conduct a feasibility study
You likely won’t be conducting the feasibility study yourself, but you will probably be called on to provide insight and information. To conduct a feasibility study, hire a trained consultant or, if you have an in-house project management office (PMO) , ask if they take on this type of work. In general, here are the steps they’ll take to complete this work:
1. Run a preliminary analysis
Creating a feasibility study is a time-intensive process. Before diving into the feasibility study, it’s important to evaluate the project for any obvious and insurmountable roadblocks. For example, if the project requires significantly more budget than your organization has available, you likely won’t be able to complete it. Similarly, if the project deliverables need to be live and in market by a certain date, but they won’t be available for several months after the fact, the project likely isn’t feasible either. These types of large-scale obstacles make a feasibility study unnecessary, because it’s clear the project is not viable.
2. Evaluate financial feasibility
Think of the financial feasibility study as the projected income statement for the project. This part of the feasibility study clarifies the expected project income and outlines what your organization needs to invest—in terms of time and money—in order to hit the project objectives.
During the financial feasibility study, take into account whether or not the project will impact your business's cash flow. Depending on the complexity of the initiative, your internal PMO or external consultant may want to work with your financial team to run a cost-benefit analysis of the project.
3. Run a market assessment
The market assessment, or market feasibility study, is a chance to identify the demand in the market. This study offers a sense of expected revenue for the project, and any potential market risks you could run into.
The market assessment, more than any other part of the feasibility study, is a chance to evaluate whether or not there’s an opportunity in the market. During this study, it’s critical to evaluate your competitor’s positions and analyze demographics to get a sense of how the project will do.
4. Consider technical and operational feasibility
Even if the financials are looking good and the market is ready, this initiative may not be something your organization can support. To evaluate operational feasibility, consider any staffing or equipment requirements this project needs. What organizational resources—including time, money, and skills—are necessary in order for this project to succeed?
Depending on the project, it may also be necessary to consider the legal impact of the initiative. For example, if the project involves developing a new patent for your product, you will need to involve your legal team and incorporate that requirement into the project plan.
5. Review project points of vulnerability
At this stage, your internal PMO team or external consultant have looked at all four elements of your feasibility study—financials, market analysis, technical feasibility, and operational feasibility. Before running their recommendations by you and your stakeholders, they will review and analyze the data for any inconsistencies. This includes ensuring the income statement is in line with your market analysis. Similarly, now that they’ve run a technical feasibility study, are any liabilities too big of a red flag? (If so, create a contingency plan !)
Depending on the complexity of your project, there won’t always be a clear answer. A feasibility analysis doesn’t provide a black and white decision for a complex problem. Rather, it helps you come to the table with the right questions—and answers—so you can make the best decision for your project and for your team.
6. Propose a decision
The final step of the feasibility study is an executive summary touching on the main points and proposing a solution.
Depending on the complexity and scope of the project, your internal PMO or external consultant may share the feasibility study with stakeholders or present it to the group in order to field any questions live. Either way, with the study in hand, your team now has the information you need to make an informed decision.
Achieve project success with Asana
Done with your feasibility study? You’re ready to run a project! Set your project up for success by tracking your progress in a work management tool , like Asana. From the small stuff to the big picture, Asana organizes work so teams know what to do, why it matters, and how to get it done.
Related resources
How to track utilization rate and drive team profitability

How to accomplish big things with long-term goals
Smooth product launches are simpler than you think

What is stakeholder analysis and why is it important?
- Professional Scrum Product Owner (PSPO)
- SAFe for Government
- Professional Scrum Master (PSM)
- Certified ScrumMaster
- PMI-ACP Exam Prep
- Leading SAFe® 6.0 Certification
- SAFe Scrum Master
- Certified Scrum Product Owner (CSPO)
- SAFe for Teams
- Agile Scrum Foundation
- AgilePM Foundation and Practitioner Certification
- Agile Scrum Master (ASM)
- Kanban Training
- Scrum Fundamentals
PMP Certification
Project Management Fundamentals
CAPM Exam Prep
- Change Management Foundation and Practitioner Certification
- PRINCE2 Foundation & Practitioner Certification (7th Edition)
- PRINCE2 Agile Foundation & Practitioner Certification
- Business Analysis Foundation and Practitioner Certification
- Microsoft Project Training
- JIRA Certification Training
- Lean Project Management
- ITIL 4 Foundation
- VeriSM™ Foundation
- SIAM Foundation
- SIAM Professional
- 7 QC Tools Training
- Minitab Essentials
- Lean Six Sigma Yellow Belt
- Six Sigma Awareness
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
- Design for Six Sigma
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt
- Lean Fundamentals
- Value Stream Mapping
- Quality by Design
- Quality Function Deployment
- BPM and Six Sigma
- RCA through Six Sigma
- DevOps Foundation
- DevOps Master
- DevOps Professional
- Continuous Delivery Architecture
- COBIT 5 Certification
- Corporate Group Training
- 1-to-1 Training
- Join as a Trainer

- Best Project Management Blogs

What is Feasibility Study in Project Management?

Feasibility studies play a crucial role in the early stages of project development, offering invaluable insights into a project’s viability and potential challenges. In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of feasibility study, types, components, Its Importance in project management, the process of conducting a feasibility study with real-world example, and the the differece between feasibility studies and business plans.
Whether you’re new to project management or seeking to deepen your understanding, this guide provides a solid foundation on this critical aspect of project planning.
Table of Contents
- What is feasibility study?
Why Feasibility Study is Important During a Project?
What are the different types of feasibility study, what is included in a feasibility study report, how to conduct a feasibility study, an example of feasibility study, feasibility study vs. business plan, what is feasibility study.
A feasibility study is a crucial assessment tool in project management . It offers a systematic evaluation of a proposed project’s viability. This comprehensive analysis encompasses various dimensions, including technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling considerations.
By analyzing these factors, the feasibility study aims to unearth potential obstacles, assess risks, and identify opportunities associated with the project.
Through this process, stakeholders gain valuable insights to make informed decisions regarding the project’s feasibility and advisability.
Ultimately, the feasibility study culminates in a detailed report outlining its findings, recommendations, and justifications. This report serves as a roadmap for stakeholders, clearly understanding the project’s prospects and potential challenges.
Armed with this information, decision-makers can determine whether to proceed with the project, make adjustments to mitigate risks or abandon it altogether.
Thus, the feasibility study is key in guiding strategic decision-making, ensuring that resources are allocated wisely and projects are set up for success from the outset.
A feasibility study is important during a project for several reasons. Firstly, it serves as a critical decision-making tool, allowing stakeholders to assess the viability and potential risks associated with the project before significant resources are invested.
By conducting the study early in the project lifecycle , organizations can avoid pursuing ventures unlikely to succeed, saving time, money, and effort.
Secondly, a feasibility study helps identify potential obstacles and challenges during the project execution phase. By thoroughly analyzing technical, economic, operational, and legal aspects, the study enables stakeholders to anticipate and mitigate risks, thus enhancing the project’s chances of success.
Moreover, a it provides a structured framework for evaluating different project alternatives and determining the most suitable action. By comparing various scenarios and assessing their feasibility, stakeholders can make well-informed decisions that align with organizational goals and priorities.
Additionally, the findings of a study help in securing buy-in and support from key stakeholders, including investors, sponsors, and senior management.
A comprehensive feasibility study report communicates the motive behind the project, the potential benefits, and the associated risks, thereby instilling confidence and trust in the project’s viability.
Master Feasibility Study and Project Management skills by enrolling in our top project management courses now!
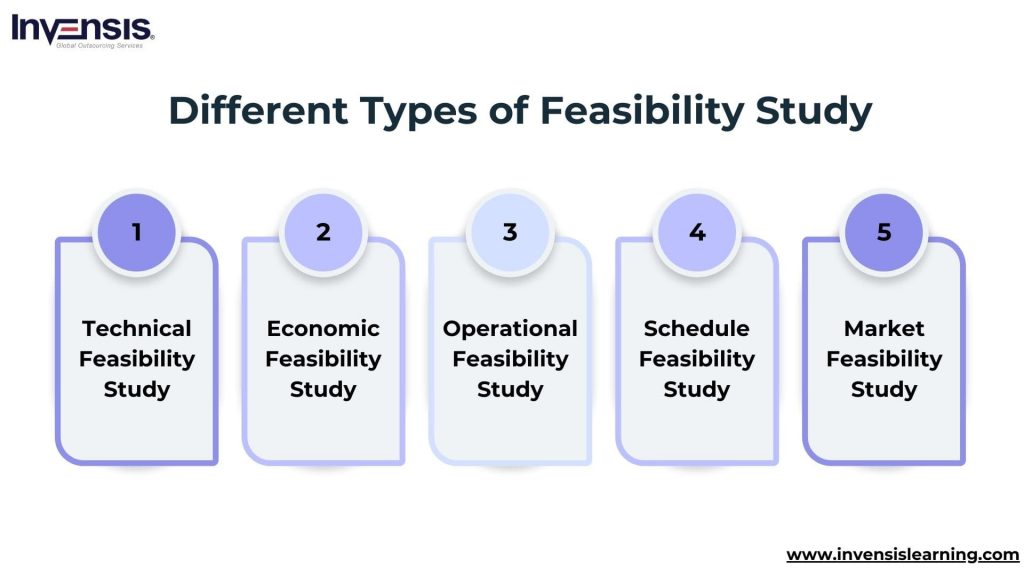
In bringing a project to completion, it’s crucial to gauge its feasibility from multiple angles. This comprehensive assessment examines various aspects, from technical capabilities to market demand.
This section demonstrates the types of feasibility studies essential for project evaluation. From examining technological readiness to analyzing economic viability, operational compatibility, schedule adherence, and market potential, each study plays a crucial role in determining the project’s feasibility.
Join us as we explore the significance of these studies in ensuring successful project outcomes.
Technical Feasibility Study
This study evaluates whether the proposed project can be implemented from a technical perspective. It evaluates factors such as available technology, expertise, infrastructure, and compatibility with existing systems. The goal is to determine if the necessary technical resources and capabilities are available to execute the project successfully.
Economic Feasibility Study
It helps evaluate a project’s financial viability. They analyze costs, benefits, and financial projections to determine whether the project is economically feasible and can generate a satisfactory return on investment (ROI). This study helps stakeholders understand the potential financial risks and rewards associated with the project.
Operational Feasibility Study
Operational feasibility studies consider whether the project aligns with the organization’s operational capabilities and objectives.
They examine factors such as staffing requirements, workflow processes, organizational culture, and potential impacts on day-to-day operations. The goal is to ensure the project can be implemented smoothly and effectively within the existing operational framework.
Schedule Feasibility Study
Schedule feasibility studies evaluate whether the project can be completed within the specified time frame. They analyze project timelines , resource availability, dependencies, and potential risks to determine if the proposed schedule is realistic and achievable. This study helps stakeholders identify and mitigate potential schedule delays or bottlenecks.
Market Feasibility Study
Market feasibility studies focus on assessing the demand for the product or service in the target market. They analyze market trends, customer needs, competitive landscape, and potential market share to determine if there is sufficient demand to support the project. This study helps stakeholders understand the market dynamics and potential opportunities or challenges for the project.
Conducting a feasibility study is essential when initiating a project in project management. This study aims to assess the viability and potential success of the project idea. Several crucial factors are evaluated, including market demand, competition, financial stability, and resource requirements.
A feasibility study in project management encompasses analyzing the technological needs, resource allocation and projected return on investment (ROI).
The findings of the feasibility study are consolidated into a report, typically comprising the following sections:
- Executive Summary
- Project Specifications
- Technological Considerations
- Market Analysis
- Marketing Strategy
- Organizational Structure and Staffing
- Project Schedule
- Financial Forecasts
- Recommendations based on Research
This structured approach ensures that project managers have a comprehensive understanding of the project’s feasibility, enabling informed decision-making and successful project execution.
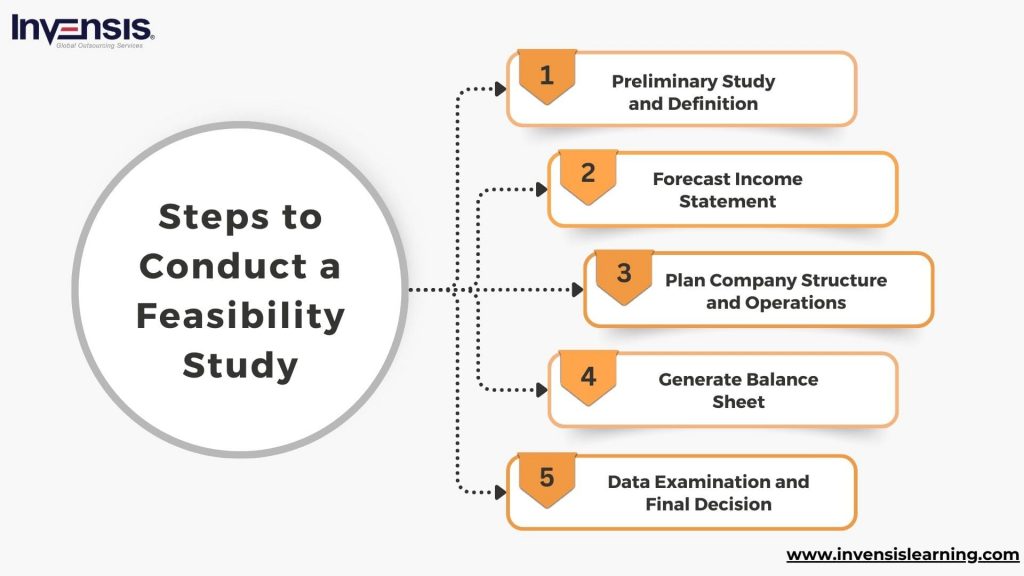
Conducting a feasibility study is crucial for assessing the viability of a project or business opportunity. By analyzing financial projections, market demand, and operational requirements, organizations can make informed decisions about whether to proceed.
This section explores the essential steps in conducting a feasibility study, assisting in effective decision-making and project success.
- Preliminary Study and Definition : Begin by conducting a preliminary study of the business case to define the scope of the feasibility study. Identify the key components to examine and establish realistic objectives. This step sets the foundation for the entire study.
- Forecast Income Statement : Generate a forecasted income statement to understand the project’s potential revenue sources and profitability. Analyze how the project will generate income and assess the feasibility of achieving financial goals. Additionally, conduct a market study to evaluate demand and market potential for the product or service.
- Plan Company Structure and Operations : Develop a plan for the company’s structure and operations. Determine the organizational structure needed for the project and assess resource requirements. Identify any specific personnel needs and outline operational processes to ensure efficient functioning.
- Generate Balance Sheet : Prepare a balance sheet to outline the projected income and expenses associated with the project. Evaluate the financial health of the project and assess the ability to achieve return on investment (ROI). This step provides insights into the project’s financial sustainability.
- Data Examination and Final Decision : Review and analyze all collected data before deciding whether to proceed with the project. Consider factors such as market demand, financial feasibility, operational capabilities, and risk assessment. Based on the findings, determine whether the project aligns with organizational goals and if it presents a viable business opportunity.
Conducting a feasibility study is imperative in manufacturing before embarking on projects like electric vehicle (EV) production. Manufacturers can ensure informed decisions and successful ventures by assessing market demand, financial viability, and technical feasibility.
This comprehensive approach guarantees alignment with market dynamics and technological requirements, fostering competitiveness and sustainable growth in the manufacturing sector.
- Manufacturing Aspect: Let’s consider the production of electric vehicles (EVs) as an example within the manufacturing sector. Before starting the manufacturing process, a comprehensive feasibility study is essential to assess various aspects of the endeavor.
- Financial Aspect: Assessing the financial viability of manufacturing EVs involves analyzing the estimated costs of production, including labor, materials, components, and overhead expenses. Additionally, projected revenue from EV sales must be compared against production costs to determine if the venture is financially possible and can generate a sustainable return on investment.
- Market Aspect: Conducting a market feasibility study involves identifying target demographics for EVs and analyzing consumer preferences and purchasing behaviors. Market research helps estimate potential market demand, determine pricing strategies, and identify market trends and growth opportunities.
- Technical Aspect: Evaluating the technical feasibility of manufacturing EVs entails analyzing production processes, resource requirements, and technological capabilities. This includes assessing manufacturing facilities, equipment needs, supply chain logistics, and compliance with regulatory standards. Technical feasibility studies ensure that the manufacturing process is optimized for efficiency, quality, and scalability.
A feasibility study is conducted early in project development to assess its viability. At the same time, a business plan serves as a detailed roadmap for executing the project post-feasibility study, outlining strategic objectives and operational plans.
it evaluate practicality, market demand, and risks, informing stakeholders’ decisions, whereas business plans provide comprehensive details for guiding the growth and development of the business over time.
Understanding the key role of feasibility studies in project management is essential for aspiring project managers. From grasping the fundamentals of feasibility studies to exploring their significance in project success, this guide provides comprehensive insights into this critical aspect of project planning.
Professionals can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and maximize project success by mastering the art of conducting feasibility studies. Ready to elevate your project management skills? Enroll in Project Management Courses at Invensis Learning today and embark on a journey towards becoming a proficient project management professional.
PRINCE2 Foundation and Practitioner Certification Training
EXIN Business Analysis Foundation and Practitioner Training
Change Management Foundation and Practiitioner Certification Training
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

What is Quality Assurance (QA) in Project Management?

What is Sensitivity Analysis in Project Management?

Mind Mapping in Project Management: How to Use It?
Leave a reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 14,521 Likes
- 444 Followers
- 96,400 Subscribers
- 2,170 Followers
Related Articles

The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Project Management

Risk Analysis Definition – Understanding the Fundamentals of Risk Analysis

Change Manager Roles & Responsibilities

What is Agile Velocity? Everything That You Must Know

Best Project Management Tools for Project Managers – 2024
Popular posts.

The Project Management Life Cycle Explained

Roles and Responsibilities of a Quality Control Inspector

7 Cs of Effective Communication with Example

Top 5 Factors for Project Success

Quality Analyst Job Role and Responsibilities- Explained!
Suggested posts.
- 7 Cs of Effective Communication with Examples
- Project Management Lifecycle
- Project Success Factors
- Quality Control Inspector Job Description
- Risk Management Examples
- QA Manager Job Description
- Quality Management Team Roles and Responsibilities
- Risk Management Tools & Techniques
- Quality Analyst Job Description
- What is Business Value
- Who are Project Stakeholders
- Importance of Project Management
- What is Project Management
- Project Management Skills
- Project Manager Job Description
- Agile Project Manager Interview Questions
- Risk and Compliance Manager Job Description
- Risk Management Process
- Project Scope Management
- Healthcare Project Manager Job Description
- Six Sigma Project Examples
- Risk Analysis Methods
- ITIL Service Lifecycle
- Risk Manager Job Description
POPULAR CATEGORIES
- Best Project Management Blogs 264
- Top Agile Blog Posts 158
- Top Blogs on Quality Management 126
- Latest IT Service Management Blogs 108
- Trending Articles on DevOps 65
- Popular Blogs on IT Security and Governance 55
- Top Blogs on Professional Development 33
- Top Infographics Collection 8
Download E-book Blog
Thank You for submitting your enquiry. One of our training consultants will get in touch with you shortly.
50+ Training and Certification Programs - Upskill Today Learn more about our training programs.

Filter by Keywords
Project Management
Mastering project viability: 7-step guide to a flawless feasibility study.
December 30, 2023
Coming up with a groundbreaking project idea that could skyrocket your company’s success is thrilling! But before diving headfirst into making it a reality, it’s crucial to pause and assess its feasibility . Can this project really succeed? Do you have the necessary tools and resources? Will the results be worth the investment?
Enter feasibility study—the key to answering these critical questions and shaping the destiny of your project.
In this article, we’re delving deep into the world of feasibility studies. We’ll equip you with everything you need to know about conducting a feasibility study and determining whether your project has what it takes to flourish. 🌷
What is a Feasibility Study?
What are the benefits of a feasibility study, types of feasibility studies, step 1: do the preliminary analysis, step 2: make a project scope outline, step 3: prepare a projected income statement, step 4: perform market research, step 5: create an opening-day balance sheet, step 6: review and analyze all data, step 7: reach a go or no-go decision.
A feasibility study examines if a proposed project is doable and evaluates its chances of success. While doing this study, you should pinpoint project goals , delve into market research , and outline the necessary resources and budget for successful project execution.
After the study, the decision-making executives or investors determine whether the project should get the green light based on the feasibility analysis. ✅
The importance of a feasibility study lies in the following:
- Establishing whether a company, team, or organization can fulfill its promises within a reasonable timeframe
- Stopping a company from taking on risky projects
- Providing details on the company’s operations, potential challenges, competitors, and funding sources, along with their allocation
A feasibility study evaluates if your project or product is viable and has the potential to succeed. The main benefits of having a feasibility study report include:
- Risk assessment: It helps identify potential risks and challenges that may arise during project implementation so you can mitigate them in due time
- Cost evaluation: It aids in determining if the project is financially viable and if the potential ROI justifies the expenses
- Resource allocation: It assists in determining the necessary resources —human, financial, and technological—required for the project, helping in effective resource allocation and management
- Market analysis: Feasibility studies help you understand the demand, competition, and potential customer base through market research, shaping the product to fit market needs
- Decision-making: The insights gained from a feasibility study help stakeholders make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the project, modify it, or abandon it altogether
- Legal and regulatory compliance: It helps ensure that the project complies with laws and regulations, minimizing potential legal issues in the future
Conducting various feasibility studies allows you to evaluate your project from diverse angles and perspectives. Feasibility studies can be broadly categorized into several types based on the focus of the assessment:
- Technical feasibility: Evaluates if the proposed project can be implemented from a technical standpoint. It assesses the availability of technology, expertise, and infrastructure required
- Economic feasibility: Analyzes the cost-effectiveness of the project. It estimates potential costs, returns on investment , and the overall financial viability
- Legal feasibility: Examines legal aspects like compliance with laws, regulations, permits, and any potential legal hurdles
- Operational feasibility: Evaluates if the project can meet the organization’s needs and to what extent
- Scheduling feasibility: Digs into the project’s timeframe , assessing if it can be completed within a reasonable and acceptable time
- Market feasibility: Focuses on understanding the market demand, competition, and potential customers suitable for the project’s products or services
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study in 7 Easy Steps
For a successful feasibility study, following the correct steps and ensuring every aspect is thoroughly analyzed is vital. We’re here to guide you through seven simple steps to assess feasibility , ensuring your project is fully prepared for its long-anticipated launch. Let’s take a look!
Running a full feasibility study can eat up time and technical resources. Instead of diving straight into the assessment, try dipping your toes in first by doing a preliminary analysis. Think of it like a test before the big test. 🤓
Here are four simple steps for this initial check :
- Start by laying out what you want from this project and why it matters to your team or business
- Look for similar projects out there and see if they’ve been successful
- Figure out what sets your idea apart—maybe it’s your team, the location, or the technology you use
- Determine the risks by listing out the things that could go wrong
Once you’ve done this check, you’ll better understand whether it’s worth digging deeper into the project’s feasibility.
To gather and easily share all this information, you can rely on ClickUp —a one-stop shop for all your business and project needs!
ClickUp Docs feature is excellent for collecting information in a single document so everything is accessible to all your team members. You can write, edit, leave comments, and collaborate in Docs in real-time.
Need to assign tasks or tag teammates? You can do it in Docs with ease! Plus, you can jazz up your documents with tables and subsections to ensure all data is presented in a structured manner. 🎺
You can also effortlessly create dedicated subpages for each preliminary analysis stage, ensuring streamlined organization of all data. On top of this, you can create easily shareable links and manage permissions efficiently for your team members and stakeholders.
If starting a feasibility report from scratch seems daunting, leverage the ClickUp Project Outline Template ! It breaks things down into steps so you don’t miss a beat. 🥁
It has separate pages for:
- Project timeline
- Budget and investments
- Constraints and assumptions
Like all ClickUp Docs, the template is fully customizable , so feel free to rename pages or create new ones to match your feasibility analysis needs.
To determine your project’s impact, you have to nail down what the project is all about. That means getting a clear idea of its goals, tasks, costs, and deadlines . Plus, you’ll have to identify everyone involved, from stakeholders to clients and customers.
When it’s brainstorming time , nothing beats a good old whiteboard. It’s your canvas for creativity, color-coded organization, and ensuring everyone’s on the same page. But if you’re operating with remote or hybrid teams , the ClickUp Project Scope Whiteboard Template is the perfect solution! ✨
This template has all the benefits of a physical whiteboard but goes the extra mile with additional features, making it a more versatile tool. It includes seven components—information, justification, scope, business objectives, deliverables, exclusions, and assumptions.
You have the freedom to customize it by:
- Adding or removing sticky notes
- Including text, links, files, photos, and drawings
- Sharing it for seamless collaboration 🤝
This ClickUp Whiteboard is a great starting point for organizing your project and brainstorming its key elements. Plus, you can personalize it by adding, erasing, or renaming elements as needed.
Crafting a projected income statement is like looking into your business’s crystal ball for the upcoming year. It tells you all about the estimated revenue and expenses, serving as a vital tool for informed business decisions. Factors shaping this statement include:
- Services provided
- Service fees
- Service volume
- Revenue adjustments
Create a personalized income statement effortlessly with the ClickUp General Ledger Template ! Think of this handy tool as your financial assistant. It easily manages your income statement and your company’s entire financial records, staying on as a powerful sidekick even after your project passes the feasibility analysis! 💪
This template comes with Custom Fields tailor-made to capture every nitty-gritty transaction detail, including transaction dates, receipts, and entry numbers.
After recording transactions, leverage the document’s four main views to generate diverse financial statements:
- Profit & Loss Board view : Provides a financial scoreboard and helps you visualize revenues, expenses, and profits from recorded transactions. It lets you easily track and reclassify items by dragging them across the board
- Balance Sheets Board view : Maps out your assets, liabilities, and equity in one neat ClickUp Dashboard , making sure your financial ship stays on course
- General Ledger and Transaction List views : Allows day-to-day transaction tracking grouped by account title or other parameters
With the template’s comprehensive financial overview, every detail will be accounted for. This gives you the confidence to make accurate financial decisions and successfully navigate the feasibility analysis for your project.
Market research is crucial for understanding what your potential customers want and need , helping you understand whether there’s a market for your product or service. It also lets you size up your competition and determine the best way to position your business for success. 🎉
There are different ways to do market research; one popular method is sending a market survey. ClickUp AI makes creating market research surveys a breeze! Take advantage of its quick, generative power to craft surveys tailored to your brand and audience in the blink of an eye.
All you need to do is ask the right questions and target the desired audience. Then, leave it to the AI assistant to generate significant trends , preferences, and opinions that will shape your business decisions .
Speaking of AI, you can also conduct speedy market research with the ClickUp ChatGPT Prompts For Market Research And Analysis Template ! This handy tool offers hundreds of AI prompts to generate content useful for analyzing market trends and preferences.

Let’s say you need information on the latest industry trends for your marketing strategy. Try the prompt: Can you provide a report on market trends and predictions for [insert name] industry to inform our business strategy? And you’ll get the results you were looking for in a jiff! ⚡
To make sure you cover all the steps in your research and nothing slips through the cracks, leverage the ClickUp Market Research Template as your personal task list .
This Task template guides you through the intricacies of research, encompassing your methodology, data collection methods, and the invaluable findings acquired from existing or prospective customers using Custom Fields.
Within this template, every task is accompanied by a subtask list, enabling you to closely monitor each research step. These tasks include critical actions like defining research scopes and assembling a proficient research team. 🕵🏼♂️
Assignees can easily oversee the progress of each subtask by employing Custom Statuses like Open, Under Review, or Closed, streamlining the monitoring process.
One of the smartest ways to collect all your assets, liabilities, and equity is by starting with an opening-day balance sheet. It’s like a snapshot of where your company stands regarding finances and assets when you’re launching a new project or business venture.
First, input all the assets you’ll need to run your operations smoothly. This includes cash for day-to-day expenses, inventory, equipment, property—all the essentials. Next, list liabilities like loans and leases and how much you’ll need to invest. It may take time, but having these details puts you on the right financial track.
Want to skip the hassle of crafting your balance sheet? The ClickUp Balance Sheet Sample Template has your back! It comes loaded with ready-made tables and fields you can tweak with your financial specifics, and voila—your balance sheet is good to go! 👌
This Doc template comes with dedicated tables for:
- Financial assets
- Non-financial assets
- Liabilities
Feel free to add more rows and columns to fit your business needs and share the document with the whole team for an easy financial rundown.
Now, take a breather and reflect on your plan again. Checking and analyzing things ensures everything’s on track and there’s no need for further customization.
Cross-check the data against its original sources and flag any inconsistencies . The whole point of a feasibility study is to help you make better decisions, so the data you collect needs to back up those choices.
You should review the feasibility study by considering both the upsides and downsides of the project. When it comes to the finances, leave no stone unturned—document all the assumptions.
During this stage, it’s crucial to pinpoint potential risks and have mitigation strategies to tackle them. This can make or break your project feasibility—if the risks involved are worth the reward, your project may get the green light. Otherwise, you may want to reconsider your business idea.
Visualize your project’s risk landscape using the ClickUp Risk Analysis Whiteboard Template ! Pinpoint the probability and severity of each risk from your feasibility study by placing sticky notes on the color-coded Whiteboard map.
When the probability and severity of a potential risk rank as High or Serious, it might signal a need to rethink your approach or brainstorm solutions with your team. Conversely, if most risks fall into the Medium/Low category , your project stands a better chance of getting the thumbs-up. 👍
Congrats, you’ve reached the exciting moment of deciding whether the project will get the green light!
Before taking the plunge, it’s up to relevant clients or stakeholders to decide whether the project is worth their time, effort, and money and if it syncs up with the organization’s big-picture goals. 🖼️
To wrap up and pitch your feasibility study, grab the ClickUp Feasibility Study Executive Summary Template . Leverage its pre-designed layout to provide:
- Project Overview
- Focused Issue
- Proposed Solution
Then, dive into the Project Highlights —impress the stakeholders by summarizing crucial findings like market analysis and project strengths and rely on charts and graphs for that visual punch. 👊
Use the provided tables to note resources, timelines, and other success strategies. Finally, don’t forget the financial forecast —charts and graphs also come in handy here, as they will paint a more vivid picture of the project’s value for money.

Presenting all this information in a slick, structured way will help stakeholders wrap their heads around your idea, making their decision-making journey much smoother.
Conduct a Feasibility Study Effortlessly with ClickUp
Running a comprehensive feasibility study doesn’t happen in a flash. But navigating it becomes much more relaxed when you stick to the seven key steps we’ve laid out and use the appropriate project management tools.
For a seamless journey through your analysis objectives, sign up for a free ClickUp account today ! This powerful tool not only aids in every step of the feasibility study but also serves as an all-in-one project management wizard !
Once your project gets the green light, you’ll love using ClickUp’s treasure trove of project management tools , a library of 1,000+ templates , and numerous collaboration tools to stay on top of your project like a pro! 😎
Questions? Comments? Visit our Help Center for support.
Receive the latest WriteClick Newsletter updates.
Thanks for subscribing to our blog!
Please enter a valid email
- Free training & 24-hour support
- Serious about security & privacy
- 99.99% uptime the last 12 months
Table of Contents
What is a feasibility study, understanding a feasibility study, types of feasibility study, importance of feasibility study, benefits of a feasibility study, what is included in a feasibility study report, tools for conducting a feasibility study, examples of a feasibility study, what is the purpose of a feasibility study, how do you write a feasibility study, 7 steps to do a feasibility study, how to conduct a feasibility study, feasibility study vs. business plan, reasons to do or not to do a feasibility study, enroll today with these pgp on project management to enhance your skills, feasibility study and its importance in project management.

Reviewed and fact-checked by Sayantoni Das
The growth and recognition of project management training have changed significantly over the past few years, and these changes are expected to continue and expand. And with the rise of project management comes the need for a feasibility study.
It can be thrilling to start a complex, large-scale project with a significant impact on your company. You are creating real change. Failure can be scary. This article will help you get started if you have never done a feasibility study on project management.
Getting certified as a project management professional is simple with Simplilearn's PMP Certification . Take advantage of this opportunity by enrolling now.
A feasibility study is a comprehensive evaluation of a proposed project that evaluates all factors critical to its success in order to assess its likelihood of success. Business success can be defined primarily in terms of ROI, which is the amount of profits that will be generated by the project.
A feasibility study evaluates a project's or system's practicality. As part of a feasibility study, the objective and rational analysis of a potential business or venture is conducted to determine its strengths and weaknesses, potential opportunities and threats, resources required to carry out, and ultimate success prospects. Two criteria should be considered when judging feasibility: the required cost and expected value.
As the name implies, a feasibility analysis is used to determine the viability of an idea, such as ensuring a project is legally and technically feasible as well as economically justifiable. It tells us whether a project is worth the investment—in some cases, a project may not be doable. There can be many reasons for this, including requiring too many resources, which not only prevents those resources from performing other tasks but also may cost more than an organization would earn back by taking on a project that isn’t profitable.
A well-designed study should offer a historical background of the business or project, such as a description of the product or service, accounting statements, details of operations and management, marketing research and policies, financial data, legal requirements, and tax obligations. Generally, such studies precede technical development and project implementation.
Become a Project Management Professional
- 6% Growth In Jobs Of Project Management Profiles By 2024
- 22 Million Jobs Estimated For Project Management Professionals By 2027
PMP® Certification Training
- Access to Digital Materials from PMI
- 12 Full-Length Simulation Test Papers (180 Questions Each)
Post Graduate Program in Project Management
- Receive Post Graduate Program Certificate and Alumni Association Membership from UMass Amherst
- 8X higher live interaction in live online classes by industry experts
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Katrina Tanchoco
Shell - manila ,.
The interactive sessions make a huge difference as I'm able to ask for further clarifications. The training sessions are more engaging than the self-paced modules, it's easier now that i first decided to take up the online classroom training, and then followed it up with the self-paced learning (online and readings).
PHC Business Manager , Midlands and Lancashire Commissioning Support Unit
I wanted to transition into the Project Management field and wanted the right opportunity to do so. Thus, I took that leap forward and enrolled in this course. My learning experience was fantastic. It suited my learning style.
Project management is the process of planning, organizing, and managing resources to bring about the successful completion of specific project goals and objectives. A feasibility study is a preliminary exploration of a proposed project or undertaking to determine its merits and viability. A feasibility study aims to provide an independent assessment that examines all aspects of a proposed project, including technical, economic, financial, legal, and environmental considerations. This information then helps decision-makers determine whether or not to proceed with the project.
The feasibility study results can also be used to create a realistic project plan and budget. Without a feasibility study, it cannot be easy to know whether or not a proposed project is worth pursuing.
A feasibility analysis evaluates the project’s potential for success; therefore, perceived objectivity is an essential factor in the credibility of the study for potential investors and lending institutions. There are five types of feasibility study—separate areas that a feasibility study examines, described below.
1. Technical Feasibility
This assessment focuses on the technical resources available to the organization. It helps organizations determine whether the technical resources meet capacity and whether the technical team is capable of converting the ideas into working systems. Technical feasibility also involves the evaluation of the hardware, software, and other technical requirements of the proposed system. As an exaggerated example, an organization wouldn’t want to try to put Star Trek’s transporters in their building—currently, this project is not technically feasible.
2. Economic Feasibility
This assessment typically involves a cost/ benefits analysis of the project, helping organizations determine the viability, cost, and benefits associated with a project before financial resources are allocated. It also serves as an independent project assessment and enhances project credibility—helping decision-makers determine the positive economic benefits to the organization that the proposed project will provide.
3. Legal Feasibility
This assessment investigates whether any aspect of the proposed project conflicts with legal requirements like zoning laws, data protection acts or social media laws. Let’s say an organization wants to construct a new office building in a specific location. A feasibility study might reveal the organization’s ideal location isn’t zoned for that type of business. That organization has just saved considerable time and effort by learning that their project was not feasible right from the beginning.
4. Operational Feasibility
This assessment involves undertaking a study to analyze and determine whether—and how well—the organization’s needs can be met by completing the project. Operational feasibility studies also examine how a project plan satisfies the requirements identified in the requirements analysis phase of system development.
5. Scheduling Feasibility
This assessment is the most important for project success ; after all, a project will fail if not completed on time. In scheduling feasibility, an organization estimates how much time the project will take to complete.
When these areas have all been examined, the feasibility analysis helps identify any constraints the proposed project may face, including:
- Internal Project Constraints: Technical, Technology, Budget, Resource, etc.
- Internal Corporate Constraints: Financial, Marketing, Export, etc.
- External Constraints: Logistics, Environment, Laws, and Regulations, etc.
The importance of a feasibility study is based on organizational desire to “get it right” before committing resources, time, or budget. A feasibility study might uncover new ideas that could completely change a project’s scope. It’s best to make these determinations in advance, rather than to jump in and to learn that the project won’t work. Conducting a feasibility study is always beneficial to the project as it gives you and other stakeholders a clear picture of the proposed project.
Below are some key benefits of conducting a feasibility study:
- Improves project teams’ focus
- Identifies new opportunities
- Provides valuable information for a “go/no-go” decision
- Narrows the business alternatives
- Identifies a valid reason to undertake the project
- Enhances the success rate by evaluating multiple parameters
- Aids decision-making on the project
- Identifies reasons not to proceed
Apart from the approaches to feasibility study listed above, some projects also require other constraints to be analyzed -

Preparing a project's feasibility study is an important step that may assist project managers in making informed decisions about whether or not to spend time and money on the endeavor. Feasibility studies may also help a company's management avoid taking on a tricky business endeavor by providing them with critical information.
An additional advantage of doing a feasibility study is that it aids in the creation of new ventures by providing information on factors such as how a company will work, what difficulties it could face, who its competitors are, and how much and where it will get its funding from. These marketing methods are the goal of feasibility studies, which try to persuade financiers and banks whether putting money into a certain company venture makes sense.
When starting a business, one of the most important steps is to conduct a feasibility study. This study will help to determine if your business idea is viable and has the potential to be successful. Several factors need to be considered when conducting a feasibility study, including the marketability of your product or service, the competition, the financial stability of your company, and more. A feasibility study should cover the amount of technology, resources required, and ROI.
The results of your feasibility studies study are summarized in a feasibility report, which typically comprises the following sections.
- Executive summary
- Specifications of the item or service
- Considerations for the future of technology
- The marketplace for goods and services
- Approach to marketing
- Organization/staffing
- The financial forecasts
- Recommendations based on research
Suggested Best Practices
While every project has its own goals and needs, the following are best practices for conducting a feasibility study.
- Do a preliminary analysis. This includes getting feedback from relevant stakeholders on the new project. Also, look for other business scenarios.
- To ensure that the data is solid, determine and ask queries about it in the initial phase.
- Take a market survey to identify market demand and opportunities for the new concept or business.
- Create an organizational, operational, or business plan. This includes identifying how much labor is required, what costs, and how long.
- Make a projected income statement that involves revenue, operating expenses, and profit.
- Create an opening day balance sheet.
- You will need to identify and address any vulnerabilities or obstacles.
- Take an initial decision to go ahead with the plan.
Suggested Components
Here are the some suggested components for conducting a feasibility study:
- Executive Summary: Write a narrative describing the project, product, or service.
- Technological considerations: Ask yourself what it will take. Are you able to afford it? How much will it cost?
- Current marketplace: Find out the market for your product, service, or plan in the local and global markets.
- Marketing strategy: Define in the detailed description.
- Required staff: What human resources are needed for this project?
- Timeline and schedule: Use important interim markers to indicate when the project will be completed.
- Project financials. Project financials are the different ways managers can account for money spent and earned on projects. One of the most important aspects of financial management is creating and tracking accurate project financials.
A local university was concerned about the state of the science building, which was built in the 1970s. School officials sought to determine the costs and benefits of expanding and upgrading the building, given the scientific and technological advances over the past 20 years. A feasibility study was therefore conducted.
School officials looked at several options and weighed the costs and benefits of updating and expanding the science building. There were concerns expressed by school officials about the project's cost and public reaction. The proposed new science building will be larger than the current one. The community board rejected similar proposals in the past. The feasibility study will address these concerns and any possible legal or zoning issues.
The feasibility study examined the technology requirements of the proposed concept(new science building), the potential benefits for students, and its long-term viability. Modernizing the science facility will increase the scientific research potential and ameliorate its modules. It also would allure new students.
Financial projections provided information about the scope & cost of this project and also provided information on raising funds. This covers issuing an investor's bonds and tapping into its endowment. Projections also help determine how the new science program attracts more fresh students to enroll in offered programs, increasing tuition and fees revenue.
The feasibility study proved that the proposed concept was feasible, which allowed for the expansion and modernization of the science building. The feasibility study would not have allowed school administrators to know if the expansion plans were feasible without it.
A feasibility study is an important first step in starting a new business. It is a detailed examination of whether or not a proposed business venture is likely to be successful. A feasibility study aims to provide information that will help business owners make informed decisions about their new venture.
The feasibility study will answer important questions about the proposed business, including:
- What is the target market for this business?
- Who are the competitors?
- What are the costs associated with starting and running this business?
- What are the potential risks and rewards associated with this venture?
- How much revenue can this business generate?
- What are the estimated profits and losses for this business?
- What is the potential for growth in this industry?
This feasibility study will outline why your business idea is worth pursuing and will also help you identify any potential risks or problems that could occur. When writing a feasibility study, there are a few key things to keep in mind:
- Outline your target market and how you plan to reach them.
- Discuss your product or service in detail and explain why it is unique and needed.
- Outline your financial projections and explain how you plan to make a profit.
1. Conduct a Preliminary Analysis
A preliminary investigation is necessary to determine whether a full feasibility study is warranted. During this stage, key information will be gathered to assess the project's potential and make a preliminary decision about its feasibility. This should include a review of relevant documents, interviews with key personnel, and surveys of potential customers or users.
2. Prepare a Projected Income Statement
To do a feasibility study, you must create a projected income statement. Your projected income statement will show how much money your business is expected to make in the coming year. It will include both your estimated revenue and your estimated expenses. This document will be essential in helping you make informed decisions about your business.
3. Conduct a Market Survey, or Perform Market Research
Conducting market research is an important step in any feasibility study. By understanding the needs and wants of your potential customers, you can determine if there is a market for your product or service. You can also get an idea of what your competition is doing and how to best position your business to meet the needs of your target market.
There are a variety of ways to conduct market research. One popular method is to conduct a survey. You can survey potential customers directly or use data from secondary sources such as surveys conducted by other organizations. You can also use focus groups or interviews to get feedback from potential customers.
Once you have gathered your data, you can use it to create a profile of your ideal customer. This will help you understand your target market and how to reach them.
4. Plan Business Organization and Operations
When starting a business, one of the first things you need is to plan your organization and operations. This involves creating a structure for your company and figuring out the logistics of how you will run it. There are many factors to consider when planning your organization and operations, such as:
- Company Structure: What type of company will you be (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, etc.)? What will the hierarchy look like?
- Location: Where will your business be located? Will you have a physical storefront or operate online only?
- Marketing: How will you promote your business?
5. Prepare an Opening Day Balance Sheet
The opening day balance sheet is a snapshot of the company's financial position at the beginning of the business venture. The purpose of the opening day balance sheet is to give an idea of the amount of money that the company has to work with and track its expenses and income as they occur. This information is vital to making sound business decisions. The opening day balance sheet will include the following:
- Cash on hand
- Accounts receivable
- Prepaid expenses
- Fixed assets
- Accounts payable
- Notes payable
- Long-term liabilities
6. Review and Analyze All Data
The feasibility study should include reviewing and analyzing all data relevant to the proposed project. The data collected should be verified against source documentation, and any discrepancies should be noted. The purpose of the feasibility study is to provide a basis for making a decision, and the data should be sufficient to support that decision.
The analysis should consider both the positive and negative aspects of the proposed project. The financial analysis should be thorough, and all assumptions should be documented. The risk assessment should identify any potential risks and mitigation strategies. The team assigned to the project should review the feasibility study and recommend the organization's leadership.
Organizational leadership should decide whether to proceed with the project based on the feasibility study's findings. If the project is approved, the organization should develop a project plan that includes a detailed budget and timeline
7. Make a Go/No-Go Decision
It is important to know when to cut your losses when starting a business. The go/no-go decision in a feasibility study comes in. The go/no-go decision is a key part of a feasibility study, and it can help you determine whether or not your business idea is worth pursuing.
Making the go/no-go decision is all about risk assessment. You need to weigh the risks and rewards of starting your business and decide whether the potential rewards are worth the risks. If the risks are too high, you may want to reconsider your business idea.
Now, let's discuss a few of the steps we take in order to do the feasibility study.
- To begin, we do a preliminary study of the business case to define what is included and what we are examining and attempting to find is realistic.
- Following that, we generate a forecasted income statement. We need to understand the revenue sources; how are we going to profit from this? Where does the income originate? Additionally, we must do a market study.
- We need to find out whether this is a demand for our product. How much demand does this have? Is there a market for this product or service?
- Plan your company's structure and operations, which is the fourth step. Specifically, what type of organization do we need, and what resources do we have? Do we have any specific personnel needs?
- We also plan to generate a balance sheet on the first day. What are the income and expenses, and how can we be confident we'll be able to decide whether we're going to make our ROI?
- As a result, we plan to go through and examine all of our data before making a final decision on whether or not to go forward. In other words, are we going to pursue this project or business opportunity?
When starting a business, you must create two very important documents: a feasibility study and a business plan. While they may seem similar, they are two different things with different purposes.
A feasibility study is a preliminary document that assesses the feasibility of a proposed business. It looks at the market potential, the competition, the costs and benefits of starting the business, and the risks and rewards involved.
On the other hand, a business plan is a more detailed document that outlines how a business will be run and what its goals are. It includes information about its mission statement, its products and services, its target market, its finances, and its management team.
There are many factors to consider when deciding whether or not to conduct a feasibility study. The most important question is whether the study will help you make a better decision.
Some reasons to do a feasibility study include:
- You are considering a major change or investment
- You want to assess the viability of a new business or product
- You need to understand the risks and potential rewards associated with a project
On the other hand, some reasons not to do a feasibility study include:
- You are pressed for time and don't think the study will provide enough value to justify the time commitment.
- You are confident that your idea is feasible, and a study will only confirm what you already believe.
- The change or investment is not significant enough to warrant the study.
- Digital Project Manager: This program will help you move from technical to managerial positions. This certification is recognized internationally and can open up exciting career opportunities in IT management.
- Post Graduate Program in Project Management: This project management certification course aligns with PMI-PMP(r) and IASSC -Lean Six Sigma. You can attend live online interactive classes and masterclasses.
Program Name PMP® Certification Training Course PMP Plus Post Graduate Program In Project Management glyph Icons All Geos All Geos All Geos University PMI Simplilearn University of Massachusetts Amherst Course Duration 90 Days of Flexible Access to Online Classes 36 Months 6 Months Coding experience reqd No No No Skills you wll learn 8+ PM skills including Work Breakdown Structure, Gantt Charts, Resource Allocation, Leadership and more. 6 courses including Project Management, Agile Scrum Master, Implementing a PMO, and More 9+ skills including Project Management, Quality Management, Agile Management, Design Thinking and More. Additional Benefits -Experiential learning through case studies -Global Teaching Assistance -35PDUs -Learn by working on real-world problems -24x7 Learning support from mentors -Earn 60+ PDU’s -3 year course access Cost $$ $$$$ $$$$ Explore Program Explore Program Explore Program
This article introduces the concept of a feasibility study and provides a few tips on conducting one. A feasibility study is an important tool for evaluating a project before starting it. By understanding the feasibility of a project, you can make better decisions about whether to move forward.
We hope this helped you understand the concept of feasibility study better. To learn more about similar project management concepts , explore our library of Project Management articles or check out our Post Graduate Program in Project Management that covers new trends, emerging practices, tailoring considerations, and core competencies required of a Project Management professional .
Q1. What Is the Main Objective of a Feasibility Study?
Feasibility study helps decision makers to determine the success or failure of a proposed project or investment. It evaluates the predicted cost and benefits of the proposed project.
Q2. What Are the Steps in a Feasibility Study?
The first step in a feasibility study is to conduct the primary analysis and create the projected income statement. Followed by doing a market survey and accordingly planning business operations. The last step is to create a balance sheet to review and analyze data. Based on your analysis, you can decide whether to go or not go ahead with the proposed statement.
Q3. Who Conducts a Feasibility Study?
Feasibility study is done by the senior management of the organization. Sometimes, they take help from mid-senior employees to complete the analysis in short span of time.
Q4. What Are the 5 Types of Feasibility?
The 5 types of feasibility study are Scheduling Feasibility, Operational Feasibility, Legal Feasibility, Economic Feasibility, and Technical Feasibility.
Q5. Why is a Feasibility Study Important?
A feasibility study helps in identifying the financial, market and logistical challenges of a proposed project. It is done by evaluating the estimated funds for the project and return of investment.
Q6. When is the Feasibility Study Done?
The feasibility study is done before the business plan is created.
Q7. What is the Primary Purpose of Conducting a Feasibility Analysis?
The objective of feasibility study is to assess the financial viability of developed plan and whether it will be successful or not.
Our Project Management Courses Duration And Fees
Project Management Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Project Management
Learn from industry experts with free masterclasses.
Career Masterclass: How to Successfully Ace the PMP Exam on Your First Attempt in 2024
How to Successfully Ace the PMP Exam on Your First Attempt in 2024
Career Fast-track
Panel Discussion: The Startup Career Strategy - The Highs and Lows
Recommended Reads
Skilling 4.0: A Study on Digital Readiness
6 Best Places to Study Abroad
A Complete Guide on the Types of Statistical Studies
Free eBook: Salesforce App Builder Study Guide
Case Studies and Success Stories
Best Country to Study Abroad
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
From Idea to Innovation: What Is a Feasibility Study In Research
Learn the process behind feasibility study in research, how it helps research projects, and the factors that make up a successful project.
Have you ever thought of doing something but wondered whether it’s doable or not? Obviously, there will be several constraints when we wish to do something unique. To understand all these constraints and to check whether the idea that we have in our mind is beneficial or not, we do this preparatory work called a feasibility study.
A feasibility study is like a reality check for your idea, helping you determine if it’s really worth pursuing. In this article, we will discuss what is a feasibility study in research , various aspects of the feasibility study, how it is engaged, how it has to be checked, and how it helps us create a perfect model for our idea.
What is a Feasibility Study in Research?
A feasibility study is an in-depth assessment conducted to determine the practicality and viability of a proposed project or idea. It involves evaluating various factors such as technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling aspects to ascertain whether the project can be successfully implemented.
The purpose of a feasibility study is to provide objective and unbiased information to decision-makers, enabling them to make informed choices regarding the project’s future. It helps identify potential risks, challenges, and opportunities associated with the undertaking, allowing stakeholders to gauge its potential outcomes.
By conducting a feasibility study, decision-makers can determine if the project aligns with organizational goals, identify potential hurdles, and develop contingency plans. This systematic assessment ensures that resources are allocated efficiently and that projects with a high chance of success are pursued.
What is the Purpose of the Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study serves as a vital tool for assessing the practicality and viability of a proposed project or initiative before committing significant resources to its implementation. It is a comprehensive evaluation that considers various factors such as technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling aspects, providing stakeholders with crucial insights to make informed decisions.
First and foremost, a feasibility study helps identify the project’s objectives and determine whether they align with the organization’s overall goals. It allows stakeholders to assess the project’s potential benefits and weigh them against the associated risks. By conducting a feasibility study, decision-makers can gain a clearer understanding of the project’s potential impact on the organization’s resources, capabilities, and market position.
Examination of technical feasibility
One key aspect of a feasibility study is the examination of technical feasibility. This involves evaluating whether the proposed project can be implemented using available technology, infrastructure, and expertise. It helps identify potential technical constraints or challenges that may arise during project execution and allows for appropriate contingency planning.
Furthermore, a feasibility study evaluates the economic viability of a project. It involves conducting a detailed cost-benefit analysis to determine the financial implications associated with the project. This analysis helps stakeholders understand the potential return on investment, project profitability, and the timeline for cost recovery.
Related Article: What is Geospatial Analysis? The Plan Before the Actual Plan
Types of Feasibility Studies
There are several types of feasibility studies, each with its own specific focus and objectives. Some of the most common types of feasibility studies include:
- Technical feasibility study: This type of study assesses whether the proposed project can be implemented using available technology, infrastructure, and expertise. It identifies potential technical constraints or challenges that may arise during project execution and allows for appropriate contingency planning.
- Economic feasibility study: This type of study involves conducting a detailed cost-benefit analysis to determine the financial implications associated with the project. It helps stakeholders understand the potential return on investment, project profitability, and the timeline for cost recovery.
- Legal feasibility study: This type of study examines the legal and regulatory requirements associated with the project. By identifying any legal hurdles or compliance issues early on, organizations can ensure that the project aligns with legal frameworks and minimizes the risk of legal complications down the line.
- Operational feasibility study: This type of study assesses whether the project can be smoothly integrated into existing systems and processes. It examines factors such as staffing requirements, training needs, and potential impacts on day-to-day operations.
- Scheduling feasibility study: This type of study helps establish a realistic timeline for project completion. It considers the availability of resources, dependencies, and potential bottlenecks, allowing stakeholders to develop a well-structured project plan and set achievable milestones.
- Market feasibility study: This type of study evaluates the potential demand for the proposed project in the marketplace. It examines factors such as customer preferences, competition, and market trends to determine whether the project is likely to be successful.
- Environmental feasibility study: This type of study assesses the potential environmental impacts of the proposed project. It examines factors such as air and water quality, habitat destruction, and waste management to ensure that the project is sustainable and environmentally responsible.
Overall, the type of feasibility study conducted will depend on the specific objectives of the proposed project and the information needed to make informed decisions about its implementation.
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study?
A feasibility study is an important step in evaluating the viability of a proposed project or business venture. The study is typically conducted before any significant investment is made to determine whether the project is feasible, both financially and operationally. Here are the general steps to conduct a feasibility study:
Step 1 – Define the scope of the study
Clearly define the objectives of the feasibility study and the specific questions that need to be answered. Identify the stakeholders who will be involved in the study and their roles and responsibilities.
Step 2 – Conduct market research
Research the market and competition to determine the potential demand for the product or service, as well as the size and characteristics of the target market. Analyze the existing competition and identify any gaps in the market that the proposed project could fill.
Step 3 – Evaluate the operational feasibility
Assess the operational feasibility of the proposed project, including the availability of resources, skills, and expertise needed to execute the project.
Step 4 – Identify potential risks
Identify potential risks and challenges that could impact the success of the proposed project. Develop contingency plans to mitigate these risks.
Step 5 – Make recommendations
Based on the results of the feasibility study, make recommendations about whether or not to move forward with the proposed project and, if so, what steps should be taken to ensure its success.
It’s important to note that the specific steps and level of detail required for a feasibility study may vary depending on the nature and complexity of the project. A feasibility study is a critical step in the decision-making process and should be conducted thoroughly and objectively to ensure that all aspects of the proposed project have been evaluated.
How to Write a Feasibility Study?
Writing a feasibility study involves conducting a systematic analysis to determine the viability and potential success of a proposed project or initiative. Here are the steps to help you write a feasibility study:
- Executive Summary: Provide a brief overview of the project, its objectives, and the purpose of the feasibility study.
- Introduction : Describe the background and context of the project, including its goals, scope, and any relevant background information.
- Project Description: Provide a detailed description of the project, outlining its objectives, deliverables, and expected outcomes. Include information on the target audience or beneficiaries.
- Market Analysis: Assess the market conditions and demand for the proposed project. Identify the target market, competitors, and potential customers. Analyze market trends, growth prospects, and any potential challenges or risks.
- Technical Feasibility: Evaluate the technical aspects of the project, such as the required infrastructure, technology, resources, and expertise. Determine if the necessary resources and capabilities are available or can be acquired within the project’s constraints.
- Financial Feasibility: Conduct a thorough financial analysis of the project. Estimate the initial investment costs, operational expenses, and projected revenues. Evaluate the project’s profitability, return on investment (ROI), payback period, and other financial indicators. Consider potential funding sources and financing options.
- Organizational Feasibility: Assess the project’s compatibility with the existing organizational structure and capabilities. Evaluate the availability of skilled personnel, management support, and any potential impact on the organization’s operations. Consider any legal, regulatory, or compliance requirements.
- Risk Analysis: Identify and evaluate potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Analyze both internal and external factors that may impact the project’s success. Develop risk mitigation strategies and contingency plans.
- Implementation Plan: Outline a detailed plan for implementing the project. Define the necessary steps, timelines, and responsibilities. Consider resource allocation, project management methodologies, and any potential challenges during the implementation phase.
- Summarize your findings: Write a clear and concise summary of your findings and conclusions. This should include an assessment of the project’s overall feasibility, a description of any risks or challenges, and a recommendation on whether or not to proceed with the project.
Examples of Feasibility Studies
It typically examines various aspects such as technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling factors. Here are some examples of feasibility studies conducted for different purposes:
- New Business Venture: A study to determine the feasibility of opening a new restaurant, including analysis of market demand, location suitability, competition, and financial projections.
- Real Estate Development: An evaluation of the feasibility of constructing a shopping mall, considering factors such as land availability, market demand, construction costs, potential tenants, and expected return on investment.
- Renewable Energy Project: Assessing the feasibility of establishing a solar power plant, including examination of solar resources, land requirements, grid connectivity, financial analysis, and environmental impact.
- Information Technology System: A study to determine the feasibility of implementing a new software system within an organization, analyzing factors like system requirements, compatibility, cost-benefit analysis, and potential impact on existing operations.
These are some examples of feasibility studies and it is very important to note that though the process looks the same for every domain of work, the concept will be different for each one of them so it is important to analyze the domain before getting to work on it.
The World’s Largest Scientifically-Accurate Illustrations Gallery
If you are looking for scientific illustrations, you are in the right place. Mind the Graph is the world’s largest scientifically-accurate illustrations gallery that helps enhance the quality of your research papers and posters. Sign Up Now.

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
How to conduct a feasibility study: Template and examples

Opportunities are everywhere. Some opportunities are small and don’t require many resources. Others are massive and need further analysis and evaluation.

One of your key responsibilities as a product manager is to evaluate the potential success of those opportunities before investing significant money, time, and resources. A feasibility study, also known as a feasibility assessment or feasibility analysis, is a critical tool that can help product managers determine whether a product idea or opportunity is viable, feasible, and profitable.
So, what is a feasibility analysis? Why should product managers use it? And how do you conduct one?
What is a feasibility study?
A feasibility study is a systematic analysis and evaluation of a product opportunity’s potential to succeed. It aims to determine whether a proposed opportunity is financially and technically viable, operationally feasible, and commercially profitable.
A feasibility study typically includes an assessment of a wide range of factors, including the technical requirements of the product, resources needed to develop and launch the product, the potential market gap and demand, the competitive landscape, and economic and financial viability.
Based on the analysis’s findings, the product manager and their product team can decide whether to proceed with the product opportunity, modify its scope, or pursue another opportunity and solve a different problem.
Conducting a feasibility study helps PMs ensure that resources are invested in opportunities that have a high likelihood of success and align with the overall objectives and goals of the product strategy .
What are feasibility analyses used for?
Feasibility studies are particularly useful when introducing entirely new products or verticals. Product managers can use the results of a feasibility study to:
- Assess the technical feasibility of a product opportunity — Evaluate whether the proposed product idea or opportunity can be developed with the available technology, tools, resources, and expertise
- Determine a project’s financial viability — By analyzing the costs of development, manufacturing, and distribution, a feasibility study helps you determine whether your product is financially viable and can generate a positive return on investment (ROI)
- Evaluate customer demand and the competitive landscape — Assessing the potential market size, target audience, and competitive landscape for the product opportunity can inform decisions about the overall product positioning, marketing strategies, and pricing
- Identify potential risks and challenges — Identify potential obstacles or challenges that could impact the success of the identified opportunity, such as regulatory hurdles, operational and legal issues, and technical limitations
- Refine the product concept — The insights gained from a feasibility study can help you refine the product’s concept, make necessary modifications to the scope, and ultimately create a better product that is more likely to succeed in the market and meet users’ expectations
How to conduct a feasibility study
The activities involved in conducting a feasibility study differ from one organization to another. Also, the threshold, expectations, and deliverables change from role to role.
For a general set of guidelines to help you get started, here are some basic steps to conduct and report a feasibility study for major product opportunities or features.
1. Clearly define the opportunity
Imagine your user base is facing a significant problem that your product doesn’t solve. This is an opportunity. Define the opportunity clearly, support it with data, talk to your stakeholders to understand the opportunity space, and use it to define the objective.
2. Define the objective and scope
Each opportunity should be coupled with a business objective and should align with your product strategy.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Determine and clearly communicate the business goals and objectives of the opportunity. Align those objectives with company leaders to make sure everyone is on the same page. Lastly, define the scope of what you plan to build.
3. Conduct market and user research
Now that you have everyone on the same page and the objective and scope of the opportunity clearly defined, gather data and insights on the target market.
Include elements like the total addressable market (TAM) , growth potential, competitors’ insights, and deep insight into users’ problems and preferences collected through techniques like interviews, surveys, observation studies, contextual inquiries, and focus groups.
4. Analyze technical feasibility
Suppose your market and user research have validated the problem you are trying to solve. The next step should be to, alongside your engineers, assess the technical resources and expertise needed to launch the product to the market.
Dig deeper into the proposed solution and try to comprehend the technical limitations and estimated time required for the product to be in your users’ hands.
5. Assess financial viability
If your company hasa product pricing team, work closely with them to determine the willingness to pay (WTP) and devise a monetization strategy for the new feature.
Conduct a comprehensive financial analysis, including the total cost of development, revenue streams, and the expected return on investment (ROI) based on the agreed-upon monetization strategy.
6. Evaluate potential risks
Now that you have almost a complete picture, identify the risks associated with building and launching the opportunity. Risks may include things like regulatory hurdles, technical limitations, and any operational risks.
7. Decide, prepare, and share
Based on the steps above, you should end up with a report that can help you decide whether to pursue the opportunity or not. Either way, prepare your findings, including any recommended modifications to the product scope, and present your final findings and recommendations to your stakeholders.
Make sure to prepare an executive summary for your C-suite; they will be the most critical stakeholders and the decision-makers at the end of the meeting.
Feasibility study example
Imagine you’re a product manager at a digital software company that specializes in building project management tools.
Your team has identified a potential opportunity to expand the product offering by developing a new AI-based feature that can automatically prioritize tasks for users based on their deadlines, workload, and importance.
To assess the viability of this opportunity, you can conduct a feasibility study. Here’s how you might approach it according to the process described above:
- Clearly define the opportunity — In this case, the opportunity is the development of an AI-based task prioritization feature within the existing project management software
- Define the objective and scope — The business objective is to increase user productivity and satisfaction by providing an intelligent task prioritization system. The scope includes the integration of the AI-based feature within the existing software, as well as any necessary training for users to understand and use the feature effectively
- Conduct market and user research — Investigate the demand for AI-driven task prioritization among your target audience. Collect data on competitors who may already be offering similar features and determine the unique selling points of your proposed solution. Conduct user research through interviews, surveys, and focus groups to understand users’ pain points regarding task prioritization and gauge their interest in the proposed feature
- Analyze technical feasibility — Collaborate with your engineering team to assess the technical requirements and challenges of developing the AI-based feature. Determine whether your team has the necessary expertise to implement the feature and estimate the time and resources required for its development
- Assess financial viability — Work with your pricing team to estimate the costs associated with developing, launching, and maintaining the AI-based feature. Analyze the potential revenue streams and calculate the expected ROI based on various pricing models and user adoption rates
- Evaluate potential risks — Identify any risks associated with the development and implementation of the AI-based feature, such as data privacy concerns, potential biases in the AI algorithm, or the impact on the existing product’s performance
- Decide, prepare, and share — Based on your analysis, determine whether the AI-based task prioritization feature is a viable opportunity for your company. Prepare a comprehensive report detailing your findings and recommendations, including any necessary modifications to the product scope or implementation plan. Present your findings to your stakeholders and be prepared to discuss and defend your recommendations
Feasibility study template
The following feasibility study template is designed to help you evaluate the feasibility of a product opportunity and provide a comprehensive report to inform decision-making and guide the development process.
Remember that each study will be unique to your product and market, so you may need to adjust the template to fit your specific needs.
- Briefly describe the product opportunity or feature you’re evaluating
- Explain the problem it aims to solve or the value it will bring to users
- Define the business goals and objectives for the opportunity
- Outline the scope of the product or feature, including any key components or functionality
- Summarize the findings from your market research, including data on the target market, competitors, and unique selling points
- Highlight insights from user research, such as user pain points, preferences, and potential adoption rates
- Detail the technical requirements and challenges for developing the product or feature
- Estimate the resources and expertise needed for implementation, including any necessary software, hardware, or skills
- Provide an overview of the costs associated with the development, launch, and maintenance of the product or feature
- Outline potential revenue streams and calculate the expected ROI based on various pricing models and user adoption rates
- Identify any potential risks or challenges associated with the development, implementation, or market adoption of the product or feature
- Discuss how these risks could impact the success of the opportunity and any potential mitigation strategies
- Based on your analysis, recommend whether to proceed with the opportunity, modify the scope, or explore other alternatives
- Provide a rationale for your recommendation, supported by data and insights from your research
- Summarize the key findings and recommendations from your feasibility study in a concise, easily digestible format for your stakeholders
Overcoming stakeholder management challenges
The ultimate challenge that faces most product managers when conducting a feasibility study is managing stakeholders .
Stakeholders may interfere with your analysis, jumping to conclude that your proposed product or feature won’t work and deeming it a waste of resources. They may even try to prioritize your backlog for you.
Here are some tips to help you deal with even the most difficult stakeholders during a feasibility study:
- Use hard data to make your point — Never defend your opinion based on your assumptions. Always show them data and evidence based on your user research and market analysis
- Learn to say no — You are the voice of customers, and you know their issues and how to monetize them. Don’t be afraid to say no and defend your team’s work as a product manager
- Build stakeholder buy-in early on — Engage stakeholders from the beginning of the feasibility study process by involving them in discussions and seeking their input. This helps create a sense of ownership and ensures that their concerns and insights are considered throughout the study
- Provide regular updates and maintain transparency — Keep stakeholders informed about the progress of the feasibility study by providing regular updates and sharing key findings. This transparency can help build trust, foster collaboration, and prevent misunderstandings or misaligned expectations
- Leverage stakeholder expertise — Recognize and utilize the unique expertise and knowledge that stakeholders bring to the table. By involving them in specific aspects of the feasibility study where their skills and experience can add value, you can strengthen the study’s outcomes and foster a more collaborative working relationship
Final thoughts
A feasibility study is a critical tool to use right after you identify a significant opportunity. It helps you evaluate the potential success of the opportunity, analyze and identify potential challenges, gaps, and risks in the opportunity, and provides a data-driven approach in the market insights to make an informed decision.
By conducting a feasibility study, product teams can determine whether a product idea is profitable, viable, feasible, and thus worth investing resources into. It is a crucial step in the product development process and when considering investments in significant initiatives such as launching a completely new product or vertical.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #product strategy

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Drive growth with these 7 customer feedback tools
A customer feedback tool is a software solution or platform designed to collect, analyze, and manage feedback from customers.

Leader Spotlight: Motivating teams to hit customer-centric outcomes, with Kristina Bailey
Kristina Bailey discusses the careful balance of knowing the business outcomes you want to achieve while balancing customer outcomes.

Exploring augmented products: Beyond the core offering
Augmented products leverage technology and additional services to provide enhanced functionality, convenience, and value to users.

A guide to acceptance test-driven development (ATDD)
ATDD is an agile methodology involving collaboration to define acceptance criteria before starting any development.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- Member Benefits
- Communities
- Grants and Scholarships
- Student Nurse Resources
- Member Directory
- Course Login
- Professional Development
- Institutions Hub
- ONS Course Catalog
- ONS Book Catalog
- ONS Oncology Nurse Orientation Program™
- Account Settings
- Help Center
- Print Membership Card
- Print NCPD Certificate
- Verify Cardholder or Certificate Status

- Trouble finding what you need?
- Check our search tips.

- Oncology Nursing Forum
- Number 5 / September 2018
Feasibility Studies: What They Are, How They Are Done, and What We Can Learn From Them
Anne M. Kolenic
Nursing clinical research is a growing field, and as more nurses become engaged in conducting clinical research, feasibility studies may be their first encounter. Understanding what they are, how to conduct them, and the importance of properly reporting their outcomes is vital to the continued advancement of nursing science.
Become a Member
Purchase this article.
has been added to your cart
Related Articles
Cancer prevention and early detection: a changing field with an unchanging goal, palliative care: building a foundation for clinical oncology nursing practice, vaught's single story and health care's culture of safety, related books.

Core Curriculum for Oncology Nursing (Seventh Edition)

Advanced Oncology Nursing Certification Review and Resource Manual (Third Edition)

Access Device Guidelines: Recommendations for Nursing Practice and Education (Fourth Edition)
- Open access
- Published: 07 September 2015
Maximising the impact of qualitative research in feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials: guidance for researchers
- Alicia O’Cathain 1 ,
- Pat Hoddinott 2 ,
- Simon Lewin 3 , 4 ,
- Kate J. Thomas 1 ,
- Bridget Young 5 ,
- Joy Adamson 6 ,
- Yvonne JFM. Jansen 7 ,
- Nicola Mills 8 ,
- Graham Moore 9 &
- Jenny L. Donovan 8
Pilot and Feasibility Studies volume 1 , Article number: 32 ( 2015 ) Cite this article
48k Accesses
193 Citations
80 Altmetric
Metrics details
Feasibility studies are increasingly undertaken in preparation for randomised controlled trials in order to explore uncertainties and enable trialists to optimise the intervention or the conduct of the trial. Qualitative research can be used to examine and address key uncertainties prior to a full trial. We present guidance that researchers, research funders and reviewers may wish to consider when assessing or undertaking qualitative research within feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials. The guidance consists of 16 items within five domains: research questions, data collection, analysis, teamwork and reporting. Appropriate and well conducted qualitative research can make an important contribution to feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials. This guidance may help researchers to consider the full range of contributions that qualitative research can make in relation to their particular trial. The guidance may also help researchers and others to reflect on the utility of such qualitative research in practice, so that trial teams can decide when and how best to use these approaches in future studies.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The United Kingdom Medical Research Council (UK MRC) guidance on the development and evaluation of complex interventions recommends an early phase of assessing feasibility prior to a full evaluation [ 1 ]. In this feasibility and pilot phase, researchers can identify and address problems which might undermine the acceptability and delivery of the intervention or the conduct of the evaluation. When the outcome evaluation is a randomised controlled trial, this feasibility phase increases the chances of researchers evaluating the optimum intervention using the most appropriate and efficient recruitment practices and trial design. Alternatively, at the feasibility phase, researchers may identify fundamental problems with the intervention or trial conduct and return to the development phase rather than proceed to a full trial. The feasibility phase thus has the potential to ensure that money is not wasted on an expensive trial which produces a null result due to problems with recruitment, retention or delivery of the intervention [ 2 ].
Feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials can draw on a range of methods. Some feasibility studies use quantitative methods only. For example, researchers concerned about whether they could recruit to a trial, and whether the intervention was acceptable to health professionals and patients, undertook a pilot trial with outcomes related to recruitment and surveys to measure the acceptability of the intervention [ 3 ]. Increasingly, qualitative or mixed methods are being used within feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials. A review of 296 journal articles reporting the use of qualitative research with trials published between 2008 and 2010 identified that 28 % of articles reported qualitative research undertaken prior to the full trial [ 4 ]. Qualitative research was not only undertaken with trials of complex interventions but was also used with trials of drugs and devices where researchers recognised the complexity of the patient group receiving the intervention or the complexity of the environment in which the trial was to be undertaken [ 5 ]. Yet, there is little guidance available on how to use qualitative methods within feasibility studies for trials. Here, we offer guidance in order to help researchers maximise the opportunities of this endeavour.
Getting the language right: feasibility studies, pilot studies and pilot trials
Before offering guidance on using qualitative methods at the feasibility phase of a trial, we first need to be clear about the meaning of the term ‘feasibility study’ because the language used to describe the preparatory phase for a trial is inconsistent [ 6 ]. These types of studies can be called feasibility or pilot studies, with researchers making no clear distinction between the two when reporting their studies in journal articles [ 7 ]. The MRC guidance for developing and evaluating complex interventions describes this as the ‘feasibility and piloting’ stage. The UK funding body, the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), offers definitions of feasibility and pilot studies, distinguishing between the two [ 8 ]. A feasibility study is undertaken to address the question ‘can the planned evaluation be done?’. In contrast, pilot studies are miniature versions of the main study. In the case of a randomised controlled trial, the pilot study is a pilot trial. A feasibility study for a randomised controlled trial does not necessarily involve a pilot randomised controlled trial [ 1 ] but may do so, and indeed, some researchers have described their studies as a ‘feasibility study and pilot trial’ in the titles of their journal articles [ 9 ]. Other terms may be used to describe a feasibility study for a trial, for example a ‘formative’ study as part of ‘evidence-based planning’ [ 10 ] or an exploratory pilot study [ 11 ] or a process evaluation with a pilot trial [ 12 ]. In this guidance, we use the term ‘feasibility study’ to describe any study that addresses the question of whether the planned evaluation trial can be done regardless of the labels other researchers might use.
The need for guidance on using qualitative methods in feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials
With the use of qualitative research in feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials becoming increasingly common, guidance on how to do this would be useful to both researchers and those commissioning and reviewing this research. Guidance is available or emerging in areas related to feasibility studies for trials. Guidance exists for undertaking quantitative pilot studies [ 13 , 14 ], and a Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement for reporting feasibility studies (rather than undertaking them) is under development [ 6 ]. UK MRC guidance has recently been developed for process evaluations undertaken alongside randomised controlled trials [ 15 ]. This new guidance recommends that, in most cases, it is useful to use both qualitative and quantitative methods concurrently with a pilot or full trial. It also states that as feasibility studies will usually aim to refine understanding of how the intervention works, and facilitate ongoing adaptation of intervention and evaluation design in preparation for a full trial, qualitative data will likely be of particular value at this stage. However, that guidance does not address in any depth issues specific to the use of qualitative research during the feasibility phase of a trial. There is also guidance for writing proposals for using qualitative research with trials [ 16 ] and reporting qualitative research undertaken with trials [ 5 ]. However, the feasibility phase of a trial is unique in that it may involve the ongoing adaptation of plans for conducting the trial and of the intervention in preparation for the full trial. Therefore, our guidance complements recent and upcoming guidance by focusing on the role of qualitative research specifically rather than the overall feasibility study and by addressing the iterative nature of research that may occur in feasibility studies for trials.
The focus of the guidance
This guidance focuses on how to use qualitative research within a feasibility study undertaken prior to a fully randomised controlled trial where the aim is to improve the intervention or trial conduct for the full trial. Appropriate and well-conducted qualitative research can make an important contribution to feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials. The guidance presented here may help researchers to consider the full range of possible contributions that qualitative research can make in relation to their particular trial and reflect on the utility of this research in practice, so that others can decide when and how best to use qualitative research in their studies. Prior to presenting the guidance, we clarify six issues about the scope of the guidance:
A feasibility study may or may not include a pilot randomised controlled trial.
The feasibility phase follows the development phase of an intervention, in which qualitative methods may also be used [ 1 ]. Although there may be overlap between the development of the intervention and the feasibility phase of the trial, this guidance assumes that an intervention has been developed, but that it might need further modification, including assessment of its practicability in the health care setting.
Qualitative methods can be used alone or in conjunction with quantitative methods, such as modelling and surveys, in the feasibility phase [ 1 ].
The definition of qualitative research is the explicit use of both qualitative data collection and analysis methods. This is distinguished from trialists’ reflective reports on the problems that they encountered in running a feasibility study and from the use of methods that may draw on qualitative approaches but do not meet our definition. For example, some researchers report using ‘observation’ and ‘field notes’ but show no evidence of qualitative data collection or analysis in their article and do not label these as qualitative research [ 8 ]. Reflective practice by trialists and intervention deliverers is important for learning about trial conduct but is not the focus of the guidance presented here.
The guidance focuses on maximising the opportunities of qualitative research by presenting options, rather than delineating required actions. This is based on the understanding that the strengths of qualitative research are its flexibility and responsiveness to emerging issues from the field.
The guidance may be used by researchers when writing proposals and undertaking or reporting qualitative research within feasibility studies. If the feasibility study includes a pilot randomised controlled trial, reporting should follow the CONSORT statement that is currently under development [ 6 ].
Processes used to develop the guidance
This guidance is based on the experience of the authors of this paper. The authors came together in a workshop to write this guidance after meeting to discuss a study of how to maximise the value of qualitative research with randomised controlled trials which had been undertaken by two of the authors of this guidance (AOC, KJT) [ 4 , 5 ]. That study involved undertaking a systematic mapping review of journal articles reporting qualitative research undertaken with randomised controlled trials and interviews with qualitative researchers and trialists; some of these articles are referenced to illustrate points made. Towards the end of this study, the UK MRC Hubs for Trials Methodology Research funded a conference to disseminate the findings from this study and a related 1-day workshop to develop guidance for using qualitative research with trials. The nine workshop members, all of whom are authors of this guidance, were identified for their experience in using qualitative research with trials. One member had also published a review of the use of qualitative research alongside trials of complex interventions [ 17 ].
The workshop focused on feasibility studies because these were identified as an underdeveloped aspect of trial methodology. The workshop members put forward items for the guidance, based on their experience and expert knowledge. Discussion took place about the importance of items and the different viewpoints within each item. Draft guidance was produced by AOC after the workshop. Subsequent development of the guidance was undertaken by email correspondence and meetings between sub-groups of the workshop membership. A draft of the guidance was then presented at a meeting of an MRC Methodology Hub for researchers with experience in undertaking qualitative research in feasibility studies for trials. Attendees viewed the guidance as helpful, and further insights emerged from this process, particularly around the analysis domain of the guidance.
The guidance
The guidance is detailed below and summarised in Table 1 . The structure follows the stages of a research project from identifying research questions to reporting findings and consists of 16 items within five domains: research questions, data collection, analysis, teamwork and reporting. Although the table presents a neat and linear process, in practice, this research is likely to be messy and iterative, with researchers moving backwards and forwards between steps as insights emerge and the priority of different research questions changes. Figure 1 shows how the guidance meshes with this more dynamic process. We illustrate some of the items in the guidance using case studies of published qualitative research undertaken within feasibility studies for trials. Some items tend not to be visible in publications, particularly those on teamworking, and therefore are not illustrated in these case studies.
Key steps for qualitative research in a feasibility study for a trial
Research questions
When designing the feasibility study, consider the full range of questions that could be addressed. Then, consider those best addressed by qualitative research.
Some researchers have produced lists of questions that could be addressed in feasibility studies for trials, focusing on the conduct of the trial and on the intervention [ 8 ]. A review of feasibility and pilot trials identified the range of questions actually addressed in a subset of feasibility studies that included a randomised controlled trial, [ 18 ] although it was not clear which questions were actually addressed by qualitative research. Other researchers have identified frameworks or typologies of questions for feasibility studies. For example, a description of feasibility studies for cancer prevention in the USA identified a typology of the questions addressed and some of the methodologies used [ 19 ]. Qualitative research was identified as useful for issues concerning acceptability, implementation, practicality and expansion (in terms of understanding use of a known intervention in a different sub-group). There is also a framework for the work undertaken by qualitative research with trials [ 4 ]. Using the latter framework, we drew on the literature cited here and our own experience of feasibility studies to identify the range of issues qualitative research can address in a feasibility study for a trial (Table 2 ). Although not noted explicitly in Table 2 , the context in which the intervention is delivered is relevant to a large number of the questions identified in Table 2 and should be considered during a feasibility study as well as in the full trial [ 15 ]. The important role of context within complex intervention trials was highlighted in a recent study which found that contextual threats to trial conduct were often subtle, idiosyncratic and complex [ 20 ], and therefore best explored using qualitative research.
Prioritise the questions for the qualitative research by identifying key uncertainties.
Many questions can be addressed in a feasibility study, but resource limitations require that these are prioritised. The whole team will need to identify the key uncertainties that the feasibility study should address. Thereafter, a search of the evidence base for systematic reviews (including mixed reviews based on both qualitative and quantitative researches) relevant to these uncertainties may yield useful insights. Where no systematic reviews exist, and there is no resource to undertake them, studies of similar interventions or similar types of trials may be helpful. Questions on which there is currently little or no existing evidence can then be prioritised for new primary qualitative research.
Consider often overlooked questions.
Researchers commonly use qualitative research to address the acceptability and feasibility of the intervention [ 10 , 21 – 24 ] or its perceived benefits [ 11 , 22 ]. During our workshop, we identified four important questions that can be overlooked and are worth considering:
How do the intervention components and delivery processes work in the real world?
Guidance for process evaluations recommends developing a logic model or explanatory model of the intervention [ 15 ]. This logic model includes the intervention components and pathways to delivering desired outcomes. However, even if trialists, intervention deliverers, patients and the public, and qualitative researchers have been involved in developing this logic model, some aspects of the intervention in practice may be hidden or not understood, and these hidden aspects may be the key to delivering outcomes. For example, intervention deliverers may adapt the intervention in unanticipated ways in order to deliver it in their local context. Qualitative research, including non-participant observation and interviews with intervention deliverers and recipients, may be helpful in identifying how and why they have done this. This may facilitate replication of the intervention in the subsequent trial or rollout and also raise questions about the most appropriate trial design required. In addition, it may offer insights into which aspects of the intervention should be fixed or flexible in the full trial [ 25 ] and how the intervention needs to be tailored to different contexts. The wider context in which the trial operates may also affect the implementation of the intervention, the control or the trial, for example staff shortages, media scares or the economic climate. Intervention vignettes can be a helpful tool in qualitative interviews to talk potential participants through each step of an intervention in a concrete way [ 26 ].
How does the choice of comparator affect the trial?
The focus of qualitative research undertaken with trials tends to be on the intervention, but qualitative research can also help to understand the control. Interventions can be compared with active controls or usual care, and there may be issues to explore regarding the comparability of an active control and the intervention or the extent to which the trial may change usual care [ 27 ]. Such research may help the trial team to consider whether there is sufficient difference between the groups being compared in any trial. For instance, the planned intervention may not be that different from usual care in some settings and may need to be enhanced prior to use in the full trial. Differences between the intervention and usual care will have implications for the relative effectiveness of the intervention and the transferability of the trial findings to other contexts.
Understanding usual care is also important because it represents a key feature of the context in which the new intervention will be implemented. Where a new intervention represents a fundamental change from usual practice, one would perhaps expect to encounter greater challenges in implementation and would need to pay more attention to the resources and structures required to achieve change compared to where the intervention represents a more incremental change.
To what degree does equipoise exist?
Key stakeholders may not be in equipoise around the intervention [ 28 ]. These stakeholders include the trial designers, recruiters, patient and public representatives and participants, as well as health care staff who are not directly involved in the trial but will use the evidence produced by it. A lack of equipoise amongst stakeholders may lead to poor recruitment practices, low recruitment rates or a lack of utility of the evidence in the real world [ 29 ]. Consideration of the question of equipoise at the feasibility phase can offer opportunities to address this, for example through education, increasing awareness and enabling open discussion of the issues, or highlight the option of not progressing to an expensive full trial [ 30 , 31 ]. This has been highlighted as a particular problem for behavioural intervention trials, with recommendations to explore this issue at the pilot stage of a trial [ 32 ].
Design and data collection
Consider the range of qualitative methods that might be used to address the key feasibility questions, including dynamic or iterative approaches which allow learning from early qualitative research findings to be implemented before further qualitative research is undertaken as part of the feasibility study.
When undertaking qualitative research in feasibility studies for trials, it is common for researchers to undertake a cross-sectional interview study with intervention deliverers and recipients and not to specify explicitly an approach or design [ 12 , 21 , 22 , 24 ]. Although sometimes it may be important to mirror closely the expected approach of the planned full trial in terms of recruitment practices, it may be helpful for the research team to take a flexible approach to the qualitative research. The team may make changes during the feasibility study itself, based on findings from the qualitative research, and then assess the impact of these changes [ 33 ]. This is sometimes called a ‘dynamic approach’. Such changes could include taking action to modify the pilot trial conduct, as well as working with intervention stakeholders to feedback and resolve difficulties in implementing the intervention. Further qualitative research can then be undertaken to inform further improvements throughout the feasibility study. This can help to optimise trial conduct or an intervention rather than simply identify problems with it. Case study 1 describes an example of this dynamic approach to data collection [ 33 ].
Other approaches suitable for feasibility studies include iterative ‘rapid ethnographic assessment’ which has been used to adapt and tailor interventions to the different contexts in which the trial was planned [ 34 ]. This approach applies a range of methods including participant observation, focus groups, interviews and social mapping [ 34 ]. Other researchers have used ‘mixed methods formative research’ at the feasibility stage [ 10 ] and action research where potential participants and practitioners are actively involved in the research to assess the feasibility of an intervention and to ensure a good intervention-context fit [ 35 , 36 ]. For instance, a participatory approach informed by the principles of action research was used to design, implement and evaluate the FEeding Support Team (FEST) intervention [ 35 , 36 ].
A dynamic or iterative approach to qualitative research in a feasibility study, where concurrent changes are made to the intervention or trial conduct, would not be suitable for a full trial where care is taken to protect the experiment. In a fully randomised controlled trial, researchers may be concerned that an excessive volume or intensity of qualitative research may contaminate the experiment by acting as an intervention [ 37 ]. Or, they may be concerned about early reporting of findings of the qualitative research detrimentally affecting staff delivering the intervention or the trial [ 38 ]. Any risks will depend on the size and type of the trial and the qualitative research and may be far outweighed by the benefits in practice of undertaking the qualitative research throughout the full trial. These concerns are less relevant during the feasibility phase.
Select from a range of appropriate qualitative methods to address the feasibility questions and provide a rationale for the choices made; non-participant observation may be an important consideration.
Researchers need to select from a range of qualitative methods including telephone and face-to-face interviews, focus groups, non-participant observation, paper/audio/video diaries, case notes kept by health professionals and discussions in online chat rooms and social media. Decisions on data collection and analysis methods should depend on the research questions posed and the context in which data will be collected. To date, feasibility studies for trials have often tended to rely solely upon interviews or focus group discussions with participants and intervention deliverers and have not drawn on the wider range of methods available [ 21 – 24 ]. Researchers tend also to use focus groups and may do this because they think they are cheap and quick when in practice, they are challenging to both organise and analyse. Some researchers are explicit about why focus groups are the best approach for their study. For example, in a randomised trial on the use of diaphragms to prevent sexually transmitted infection, the research team conducted 12 focus groups with women before and after they received the intervention to consider its acceptability and feasibility. This data collection approach was justified on the basis that the researchers felt focus groups would generate more open discussion [ 10 ]. However, focus groups may be problematic in a feasibility study because they tend towards consensus and can mask dissenting views, with the possibility of premature conceptual closure. It may also be the case that participants who are prepared to talk openly within a group setting may differ from the target population for a trial as, in general, focus groups tend to attract more educated and confident individuals [ 39 ].
Non-participant observation, including the use of audio or video recordings of intervention delivery or recruitment sessions, can help to identify implementation constraints at the feasibility phase. Observation has also proved to be very useful when exploring recruitment practices for a full trial [ 33 , 40 ]. ‘Think aloud’ protocols may also be helpful—for example, in one feasibility study of a technology to deliver behaviour change, the approach was used to allow users to talk about the strengths and weaknesses of the technology as they attempted to use it [ 41 ].
Pay attention to diversity when sampling participants, groups, sites and stage of intervention.
All of the different approaches to sampling in qualitative research—such as purposive, key informant and snowballing—are relevant to feasibility studies. A particular challenge for sampling within the feasibility phase is the need to address the wide range of uncertainties about the full trial or the intervention within the resource limitations of the study.
It can be difficult to decide when enough has been learnt about the trial intervention or the conduct of the trial (or when data saturation has occurred) to recommend moving on to the full trial. Researchers will need to make pragmatic decisions on which emerging analysis themes warrant more data collection and where sufficient data are available. In practice, sample sizes for qualitative research in feasibility studies are usually small (typically between 5 and 20 individuals [ 10 , 12 , 22 – 24 ]). This may be reasonable, given that simulations suggest that 10 users will identify a minimum of 80 % of the problems with the technology during usability testing, and 20 users will identify 95 % of the problems [ 42 ]. However, sample size will be dependent on the study; for example, there may be therapist effects to consider and a need to sample a range of patients using different therapists or a range of contexts.
Diversity of sampling is probably more important at the feasibility phase than the number of interviews or focus groups conducted, and some researchers have rightly highlighted as a limitation the lack of diversity in the sampling process for their qualitative feasibility study [ 20 ]. Paying attention to the diversity of sampling needed may be important for identifying the wide range of problems likely to be faced by the group/s to which the intervention is directed. Including a diverse range of health professionals and patients (for an individual-level trial) and sites (for a cluster trial) can be beneficial. In individual-level multicentre trials, including more than one centre at the feasibility stage can reduce the chance of refining an intervention or trial that will only work within that single centre. As in other forms of qualitative research, sampling may be very broad at the start of the feasibility study, when there are lots of questions and uncertainty, with later sampling focusing on disconfirming cases to test emerging findings.
Appreciate the difference between qualitative research and public and patient involvement.
In the UK and many other settings, it is considered good practice to have public and patient involvement in health research [ 43 ]. This is highly relevant to a feasibility study where patients and the public can contribute to prioritising which key uncertainties to address and are therefore involved at an early stage of the design of the full trial. Indeed, there is guidance available on patient and public involvement in trials, showing how service users can be involved at the feasibility/pilot stage of a trial by being members of the management group, steering committee and research team and by contributing to the design, analysis and reporting of the feasibility study [ 44 ]. A potential concern is that some researchers conflate qualitative research and public and patient involvement; this may be more common during a feasibility study if the public or patient involvement group is asked to provide feedback on the intervention. Although patient and public representatives on research teams can provide helpful feedback on the intervention, this does not constitute qualitative research and may not result in sufficiently robust data to inform the appropriate development of the intervention. That is, qualitative research is likely to be necessary in conjunction with any patient and public involvement. Case study 2 describes an example of a qualitative study undertaken with patient involvement [ 45 ].
Consider the timing of analysis, which might be in stages in a dynamic approach.
For many types of qualitative research, it is suggested that data are analysed as they are collected so that the sampling for the next round of data collection benefits from the analysis of these earlier data. If a dynamic approach is applied in a feasibility study, it is important to have available sufficient resources to analyse the data collected early in the study in order to feed findings back to the wider team and allow changes to be made to the intervention and trial conduct prior to the next set of data collection. This can be quite different from using qualitative research in the full trial, where all data might be collected prior to any formal analysis and sharing of findings with the wider team.
Many different approaches to analysis can be used, including framework, thematic and grounded theory-informed analysis.
Many different approaches can be used to analyse qualitative data in the context of a feasibility study, and the approach should be chosen based on the research question and the skills of the research team. Some researchers simply describe the steps they take within their analysis rather than citing a named approach [ 12 ]. Other researchers use combinations of known approaches such as framework analysis and grounded theory [ 36 ].
Data can cover a breadth of issues, but the analysis may focus on a few key issues.
An important challenge for analysis may be the specificity of the questions that need to be addressed by a qualitative feasibility study, in order to inform trial development. Analysis will need to focus on the questions prioritised at the beginning, or those emerging throughout the feasibility study, from the large amounts of qualitative data generated. The analysis process needs to consider ‘fatal flaws’ that may require tailoring or refining of the intervention or trial conduct, as well as the mechanisms of action for the intervention.
Teamworking
Have a qualitative researcher as part of feasibility study design team.
Planning the feasibility study needs qualitative expertise to determine what can be done, how long it might take, how it is best done and the resources needed. It is therefore important that an expert in qualitative methods be included in both the planning and delivery teams for the feasibility study.
Consider relationships between the qualitative researchers and the wider feasibility study team.
How the qualitative researchers interact with the wider feasibility study team is an important concern. If study participants view the qualitative researchers as closely aligned with the team delivering the intervention or conducting the pilot trial, then participants may feel less able to offer honest criticisms of the intervention or trial conduct. On the other hand, where qualitative researchers work too independently from the wider team, they may not develop a deep understanding of the needs of the trial and the implications of their findings for the trial.
Qualitative researchers may identify issues that are uncomfortable for the rest of the research team. For example, they may consider that an intervention does not simply need refining but has a fundamental flaw or weakness in the context in which it is being tested. This may be particularly difficult if the intervention developer is part of the team. Indeed, some members of the team may not be in equipoise about the intervention (see earlier); they may have strong prior beliefs about its feasibility, acceptability and effectiveness and be unable to acknowledge any weaknesses. However, without openness to change, the qualitative research is unlikely to reach its potential for impact on the full trial. On the other hand, the wider team may need to challenge the findings of the qualitative research to ensure that any proposed changes are necessary. Qualitative researchers may also identify problems with the trial conduct that the rest of the team do not see as important because, for example, the recruitment statistics are adequate or it is an effort to change plans. There may also be tensions between what the trial design team need and what the qualitative researcher sees as important. For instance, the trial team may want to understand the feasibility of the intervention whilst the qualitative researcher is more interested in understanding mechanisms of action of the intervention. The team will need to discuss these differences as they plan and undertake the research. The only solution to these tensions is open communication between team members throughout the feasibility study.
Consider who will make changes to the intervention or trial conduct.
Qualitative researchers can identify strengths and weaknesses of the intervention or the conduct of the trial. However, they are usually not responsible for redesigning the intervention or trial either during the feasibility study (if a dynamic approach is taken) or at the end of the feasibility study when the full trial is being considered and planned. It is helpful to be explicit about who is responsible for making changes based on the qualitative findings and how and when they will do this.
Publish feasibility studies where possible because they help other researchers to consider the feasibility of similar interventions or trials.
Other researchers can learn from feasibility studies, and where this is likely to be the case, we recommend publishing them in peer-reviewed journal articles. Other researchers might be willing to take forward to full trial an intervention that the original researchers were unable or unwilling to take beyond the feasibility study. Or, other researchers might learn how to develop better interventions or trials within the same field or understand which qualitative methods are most fruitful in different contexts. Publishing what went wrong within a feasibility study can be as helpful as publishing what went right. Explicit description of how decisions were made about which research questions and uncertainties were prioritised may help others to understand how to make these types of decisions in their future feasibility studies.
Researchers may choose to publish the qualitative findings in the same article as the findings from the pilot trial or quantitative study or may publish them separately if there are detailed and different stories to tell. For example, Hoddinott and colleagues published separate articles related to the outcome evaluation and the process evaluation of a feasibility study of a breastfeeding intervention for women in disadvantaged areas [ 35 , 36 ]. Feasibility studies may generate multiple papers, each of which will need to tell one part of a coherent whole story. Regardless of how many articles are published from a single feasibility study, identifying each one as a feasibility study in the article title will help other researchers to locate them.
Describe the qualitative analysis and findings in detail.
When publishing qualitative research used with trials, researchers sometimes offer very limited description of the qualitative methods, analysis and findings or rely on limited data collection [ 5 , 17 ]. This ‘qual-lite’ approach limits the credibility of the qualitative research because other researchers and research users cannot assess the quality of the methods and interpretation. This may be due to the word limits of journal articles, especially if a range of quantitative and qualitative methods are reported in the same journal article. Electronic journals allowing longer articles, and the use of supplementary tables, can facilitate the inclusion of both more detail on the methods used and a larger number of illustrative data extracts [ 12 ]. Researchers may wish to draw on guidelines for the reporting of qualitative research [ 46 ].
Be explicit about the learning for a future trial or a similar body of interventions or generic learning for trials.
Qualitative research in a feasibility study for a trial can identify useful learning for the full trial and for researchers undertaking similar trials or evaluating similar interventions. This makes it important to be explicit about that learning in any report or article. Reporting the impact of the qualitative research on the trial, and potential learning for future trials, in the abstract of any journal article can make it easier for other researchers to learn from the qualitative research findings [ 12 ]. Examples of the impact that qualitative research in feasibility studies can have on the full trial include changes in the information given to participants in the full trial [ 10 ], recruitment procedures [ 21 , 28 ], intervention content or delivery [ 12 , 22 , 24 ], trial design [ 23 ] or outcome measures to be used [ 47 ]. For example, in the ProtecT trial, initial expectations were that only a two-arm trial comparing radical treatments would be possible, but following the qualitative research, an active monitoring arm that was acceptable was developed and included in the main trial [ 21 ]. Learning from the qualitative research may be unexpected. For example, the aim of the qualitative research in one feasibility study was to explore the acceptability of the intervention, but in practice, it identified issues about the perceived benefits of the intervention which affected the future trial design [ 23 ]. See case study 3 for an example of qualitative research undertaken with a pilot trial where the learning for the full trial is explicitly reported in the published paper [ 47 ]
Once a feasibility study is complete, researchers must make the difficult decision of whether to progress to the full trial or publish why a full trial cannot be undertaken. There is guidance on how to make this decision, which encourages the systematic identification and appraisal of problems and potential solutions and improves the transparency of decision-making processes [ 48 ]. Too often, progression criteria are framed almost entirely in quantitative terms and it is unclear the extent to which qualitative data may or not play a direct role in informing the decision on whether to proceed to a full trial. For example, if researchers fall just short of a quantitative criterion, but have a sufficient qualitative understanding of why this happened and how to improve it, then it might be possible to proceed. Related to this, qualitative research may identify potential harms at the feasibility stage; the intervention could be modified to avoid these in the full trial, or a decision could be made not to proceed to a full trial even if progression criteria were met.
Conclusions
Exploring uncertainties before a full trial is underway can enable trialists to address problems or optimise the intervention or conduct of the trial. We present guidance that researchers, research funders and reviewers may wish to consider when assessing or undertaking qualitative research in feasibility studies. This guidance consists of 16 items framed around five research domains: research questions, data collection, analysis, teamwork and reporting. A strength of the guidance is that it is based on a combination of experiences from both published feasibility studies and researchers from eight universities in three countries. A limitation is that the guidance was not developed using consensus methods. The guidance is not meant as a straitjacket but as a way of helping researchers to reflect on their practice. A useful future exercise would be to develop worked examples of how research teams have used the guidance to plan and undertake their qualitative research within feasibility studies for trials. This would help to highlight the strengths and limitations of the guidance in different contexts. Using qualitative research with trials is still a developing area, and so, we present this guidance as a starting point for others to build on, as understanding of the importance of this vital stage of preparation for randomised controlled trials grows. Researchers may also wish to reflect on the utility of different qualitative methods and approaches within their studies to help other researchers make decisions about their future feasibility studies.
Abbreviations
Medical Research Council
National Institute for Health Research
United Kingdom
Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, Michie S, Nazareth I, Petticrew M. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2008;337:a1655. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a1655 .
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ioannidis JPA, Greenland S, Hlatky MA, Khoury MJ, Macleod MR, Moher D, et al. Research Waste series: increasing value and reducing waste in research design, conduct, and analysis. Lancet. 2014;383:166–75.
Soliman EZ, Mendis S, Dissanayake WP, Somasundaram NP, Gunaratne PS, Jayasingne IK, et al. A Polypill for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a feasibility study of the World Health Organization. Trials. 2011;12:3.
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Hewison J. What can qualitative research do for randomised controlled trials? A systematic mapping review. BMJ Open. 2013;3:e002889.
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Goode J, Hewison J. Maximising the value of combining qualitative research and randomised controlled trials in health research: the QUAlitative Research in Trials (QUART) study—a mixed methods study. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(38).
Eldridge S, Bond C, Campbell M, Lancaster G, Thabane L, Hopwell S. Definition and reporting of pilot and feasibility studies. Trials. 2013;14 Suppl 1:O18. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-S1-O18 .
PubMed Central Google Scholar
Arain M, Campbell MJ, Cooper CL, Lancaster GA. What is a pilot or feasibility study? A review of current practice and editorial policy. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2010;10:67.
National Institute for Health Research http://www.nets.nihr.ac.uk/glossary/feasibility-studies . Accessed 14 January 2015.
Wesson J, Clemson L, Brodaty H, Lord S, Taylor M, Gitlin L, et al. A feasibility study and pilot randomised trial of a tailored prevention program to reduce falls in older people with mild dementia. BMC Geriatr. 2013;13:89.
Behets FM, Van Damme K, Turner AN, Rabenja NL, Ravelomanana NL, Raharinivo MS, et al. Evidence-based planning of a randomized controlled trial on diaphragm use for prevention of sexually transmitted infections. Sex Transm Dis. 2008;35:238–42.
Hauser M, Lautenschlager M, Gudlowski Y, Ozgürdal S, Witthaus H, Bechdolf A, et al. Psychoeducation with patients at-risk for schizophrenia—an exploratory pilot study. Patient Educ Counsel. 2009;76(1):138–42.
Poston L, Briley AL, Barr S, Bell R, Croker H, Coxon K, et al. Developing a complex intervention for diet and activity behaviour change in obese pregnant women (the UPBEAT trial); assessment of behavioural change and process evaluation in a pilot randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2013;13:148.
Lancaster GA, Dodd S, Williamson PR. Design and analysis of pilot studies: recommendations for good practice. J Eval Clin Pract. 2004;10(2):307–12.
PubMed Google Scholar
Thabane L, Ma J, Chu R, Cheng J, Ismaila A, Rios LP, et al. A tutorial on pilot studies: the what, why and how. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2010;10:1.
Moore G, Audrey S, Barker M, Bond L, Bonell C, Hardeman W, et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2015;350:h1258.
Drabble SJ, O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Rudolph A, Hewison J. Describing qualitative research undertaken with randomised controlled trials in grant proposals: a documentary analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:24.
Lewin S, Glenton C, Oxman AD. Use of qualitative methods alongside randomised controlled trials of complex healthcare interventions: methodological study. BMJ. 2009;339:b3496.
Shanyinde M, Pickering RM, Weatherall M. Questions asked and answered in pilot and feasibility randomised controlled trials. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2011;11:117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-11-117 .
Bowen DJ, Kreuter M, Spring B, Cofta-Woerpel L, Linnan L, Weiner D, et al. How we design feasibility studies. Am J Prev Med. 2009;36(5):452–7.
Wells M, Williams B, Treweek S, Coyle J, Taylor J. Intervention description is not enough: evidence from an in-depth multiple case study on the untold role and impact of context in randomised controlled trials of seven complex interventions. Trials. 2012;13:95.
Dow B, Moore K, Scott P, Ratnayeke A, Wise K, Sims J, et al. Rural carers online: a feasibility study. Aust J Rural Health. 2008;16:221–5.
Jackson C, Cheater FM, Peacock R, Leask J, Trevena L. Evaluating a web-based MMR decision aid to support informed decision-making by UK parents: a before-and-after feasibility study. Health Educ J. 2010;69(1):74–83.
Google Scholar
Ni Mhurchu C, Roberts V, Maddison R, Dorey E, Jiang Y, Jull A, et al. Effect of electronic time monitors on children’s television watching: pilot trial of a home-based intervention. Prev Med. 2009;49(5):413–7.
Mittal D, Owen RR, Lacro JP DP, Landes RD, Edlund M, Valenstein M, et al. Antipsychotic adherence intervention for veterans over 40 with schizophrenia: results of a pilot study. Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses. 2009;24 Suppl 1:S1171.
Hawe P, Shiell A, Riley T. Complex interventions: how ‘out of control’ can a randomised controlled trial be? BMJ. 2004;328(7455):1561–3.
Hoddinott P, Morgan H, Thomson G, Crossland N, Craig L, Britten J, et al. Intervention vignettes as a qualitative tool to refine complex intervention design. Trials. 2013;14 Suppl 1:O55. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-14-S1-O55 .
McCambridge J, Witton J, Elbourne DR. Systematic review of the Hawthorne effect: new concepts are needed to study research participation effects. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(3):267–77.
Mills N, Donovan JL, Smith M, Jacoby A, Neal DE, Hamdy FC. Perceptions of equipoise are crucial to trial participation: a qualitative study of men in the ProtecT study. Control Clin Trials. 2003;24(3):272–82.
de Vasconcellos K, Sneyd JR. Nitrous oxide: are we still in equipoise? A qualitative review of current controversies. Br J Anaesth. 2013;111(6):877–85.
Eborall HC, Dallosso HM, Daly H, Martin-Stacey L, Heller SR. The face of equipoise—delivering a structured education programme within a randomized controlled trial: qualitative study. Trials. 2014;15:15.
Donovan JL, Paramasivan S, de Salis I, Toerien M. Clear obstacles and hidden challenges: understanding recruiter perspectives in six pragmatic randomised controlled trials. Trials. 2014;15:5.
McCambridge J, Kypri K, Elbourne D. In randomization we trust? There are overlooked problems in experimenting with people in behavioral intervention trials. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(3):247–53.
Donovan J, Mills N, Smith M, Brindle L, Jacoby A, Peters T, et al. Quality improvement report: improving design and conduct of randomised trials by embedding them in qualitative research: ProtecT (prostate testing for cancer and treatment) study. Commentary: presenting unbiased information to patients can be difficult. BMJ. 2002;325(7367):766–70.
NIMH Collaborative HIV/STD Prevention Trial Group. Design and integration of ethnography within an international behavior change HIV/sexually transmitted disease prevention trial. AIDS. 2007;21 suppl 2:S37–48.
Hoddinott P, Craig L, Maclennan G, Boyers D, Vale L. The FEeding Support Team (FEST) randomised, controlled feasibility trial of proactive and reactive telephone support for breastfeeding women living in disadvantaged areas. BMJ Open. 2012;2, e000652. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2011-000652 .
Hoddinott P, Craig L, MacLennan G, Boyers D, Vale L. Process evaluation for the FEeding Support Team (FEST) randomised controlled feasibility trial of proactive and reactive telephone support for breastfeeding women living in disadvantaged areas. BMJ Open. 2012;2, e001039. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001039 .
O’Cathain A, Goode J, Drabble SJ, Thomas KJ, Rudolph A, Hewison J. Getting added value from using qualitative research with randomized controlled trials: a qualitative interview study. Trials. 2014;15:215.
Cooper C, O’Cathain A, Hind D, Adamson J, Lawton J, Baird W. Conducting qualitative research within Clinical Trials Units: avoiding potential pitfalls. Contemp Clin Trials. 2014;38(2):338–43.
Hoddinott P, Allen K, Avenell A, Britten J. Group interventions to improve health outcomes: a framework for their design and delivery. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:800.
de Salis I, Tomlin Z, Toerien M, Donovan J. Using qualitative research methods to improve recruitment to randomized controlled trials: the Quartet study. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2008;13 suppl 3:92–6.
Harris LT, Tufano J, Le T, Rees C, Lewis GA, Evert AB, et al. Designing mobile support for glycemic control in patients with diabetes. J Biomed Inform. 2010;43(5 Suppl):S37–40.
Faulkner L. Beyond the five-user assumption: benefits of increased sample sizes in usability testing. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput. 2003;35(3):379–83.
Barber R, Boote JD, Cooper CL. Involving consumers successfully in NHS research: a national survey. Health Expect. 2007;10(4):380–91.
Evans BA, Bedson E, Bell P, Hutchings H, Lowes L, Rea D, et al. Involving service users in trials: developing a standard operating procedure. Trials. 2013;14:219.
Hind D, O’Cathain A, Cooper CL, Parry GD, Isaac CL, Rose A, et al. The acceptability of computerised cognitive behaviour therapy for the treatment of depression in people with chronic physical disease: a qualitative study of people with multiple sclerosis. Psychol Health. 2009;25(6):699–712.
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57.
Farquhar M, Ewing G, Higginson IJ, Booth S. The experience of using the SEIQoL-DW with patients with advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): issues of process and outcome. Qual Life Res. 2010;19(5):619–29.
Bugge C, Williams B, Hagen S, Logan J, Glazener C, Pringle S, et al. A process for Decision-making after Pilot and feasibility Trials (ADePT): development following a feasibility study of a complex intervention for pelvic organ prolapse. Trials. 2013;14:353.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The workshop was funded by the MRC North West and ConDuCT Hubs for Trial Methodology. This work was undertaken with the support of the MRC ConDuCT-II Hub (Collaboration and innovation for Difficult and Complex randomised controlled Trials In Invasive procedures—MR/K025643/1). We would like to thank attendees at the ConDuCT-II Hub workshop on feasibility studies held at the University of Bristol in October 2014 who discussed and commented on a presentation of an earlier version of this guidance. JLD is a NIHR Senior Investigator. SL is supported by funding from the South African Medical Research Council.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Medical Care Research Unit, School of Health and Related Research, University of Sheffield, Regent Street, Sheffield, S1 4DA, UK
Alicia O’Cathain & Kate J. Thomas
Primary Care, Nursing Midwifery and Allied Health Professionals Research Unit, University of Stirling, Stirling, FK9 4LA, Scotland, UK
Pat Hoddinott
Global Health Unit, Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services, Oslo, Norway
Simon Lewin
Health Systems Research Unit, South African Medical Research Council, Cape Town, South Africa
Institute of Psychology, Health and Society, University of Liverpool, Waterhouse Building, Block B, Brownlow Street, Liverpool, L69 3GL, UK
Bridget Young
Department of Health Sciences, University of York, Seebohm Rowntree Building, Heslington, York, YO10 5DD, UK
Joy Adamson
Behavioural and Societal Sciences, Work, Health & Care, Schoemakerstraat 97 (Gebouw A), Delft, 2628 VK, Netherlands
Yvonne JFM. Jansen
School of Social and Community Medicine, University of Bristol, Canynge Hall, 39 Whatley Road, Bristol, BS8 2PS, UK
Nicola Mills & Jenny L. Donovan
Centre for the Development and Evaluation of Complex Interventions for Public Health Improvement, Cardiff University, Cardiff, CF10 3XQ, UK
Graham Moore
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Alicia O’Cathain .
Additional information
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
AOC, JLD, KJT, BY and SL developed the idea and obtained the funding for the workshop. AOC, PH, KJT, BY, JA, YJFMJ, SL, GM and JLD attended the workshop where the core content of the guidance was developed. AOC wrote the first draft of the manuscript. AOC, PH and NM presented the guidance to the researchers engaged in this type of work to further develop the guidance. All authors commented on the drafts of the manuscript and read and approved the final manuscript.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
O’Cathain, A., Hoddinott, P., Lewin, S. et al. Maximising the impact of qualitative research in feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials: guidance for researchers. Pilot Feasibility Stud 1 , 32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40814-015-0026-y
Download citation
Received : 20 February 2015
Accepted : 13 August 2015
Published : 07 September 2015
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40814-015-0026-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Randomised controlled trial
- Feasibility studies
- Pilot studies
- Qualitative methods
Pilot and Feasibility Studies
ISSN: 2055-5784
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Software Engineering Tutorial
- Software Development Life Cycle
- Waterfall Model
- Software Requirements
- Software Measurement and Metrics
- Software Design Process
- System configuration management
- Software Maintenance
- Software Development Tutorial
- Software Testing Tutorial
- Product Management Tutorial
- Project Management Tutorial
- Agile Methodology
- Selenium Basics
Project Management Basics
- Characteristics of Project - Project Management
- What is a Project in Project Management?
- What is Project Management System?
- Role and Responsibilities of a software Project Manager - Software Engineering
- Best Project Management Certifications of 2024
Phases of the Project Management Lifecycle
- What is Stakeholder? Defination, Types and Examples
Types of Feasibility Study in Software Project Development
- Difference between Project Report and Feasibility Report
- Phases of Project Management Process
- Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT)
Project Planning & Execution
- Project Management Process Activities
- Work Breakdown Structure - Software Engineering
- Resource Allocation
- Change Management in Software Engineering
Risk Management in Project
- Principles of Risk Management and Paradigm
- Essential Activities of Risk Management
- What are the Five Steps in Risk Management Process in project management?
- Short note on Risk Assessment and Risk Mitigation
- Methods for Identifying Risks
- Risk Mitigation, Monitoring, and Management (RMMM) plan
- Procedural and Quantitative Approach to Quality Management
Team Collaboration Tips
- What are Remote Project Management Strategies for Collaboration?
- Project Organizations and their Responsibilities
Project Management Methodologies
- What are Agile Family of Flexible Project Management Methodologies?
- Agile Change Management
Agile Methodology Basics
- Agile Development Models - Software Engineering
- Agile Methodology Advantages and Disadvantages
- Agile Software Process and it's Principles
- What are the benefits of Agile?
- Difference between Agile and Scrum Testing
- Agile vs. Waterfall Project Management
Project Management Frameworks
- Scrum (software development)
- What are Epics & User stories in Agile?
Feasibility Study in Software Engineering is a study to evaluate feasibility of proposed project or system. Feasibility study is one of stage among important four stages of Software Project Management Process . As name suggests feasibility study is the feasibility analysis or it is a measure of the software product in terms of how much beneficial product development will be for the organization in a practical point of view. Feasibility study is carried out based on many purposes to analyze whether software product will be right in terms of development, implementation, contribution of project to the organization etc.
Types of Feasibility Study
The feasibility study mainly concentrates on below five mentioned areas. Among these Economic Feasibility Study is most important part of the feasibility analysis and Legal Feasibility Study is less considered feasibility analysis.
- Technical Feasibility : In Technical Feasibility current resources both hardware software along with required technology are analyzed/assessed to develop project. This technical feasibility study gives report whether there exists correct required resources and technologies which will be used for project development. Along with this, feasibility study also analyzes technical skills and capabilities of technical team, existing technology can be used or not, maintenance and up-gradation is easy or not for chosen technology etc.
- Operational Feasibility: In Operational Feasibility degree of providing service to requirements is analyzed along with how much easy product will be to operate and maintenance after deployment. Along with this other operational scopes are determining usability of product, Determining suggested solution by software development team is acceptable or not etc.
- Economic Feasibility: In Economic Feasibility study cost and benefit of the project is analyzed. Means under this feasibility study a detail analysis is carried out what will be cost of the project for development which includes all required cost for final development like hardware and software resource required, design and development cost and operational cost and so on. After that it is analyzed whether project will be beneficial in terms of finance for organization or not.
- Legal Feasibility: In Legal Feasibility study project is analyzed in legality point of view. This includes analyzing barriers of legal implementation of project, data protection acts or social media laws, project certificate, license, copyright etc. Overall it can be said that Legal Feasibility Study is study to know if proposed project conform legal and ethical requirements.
- Schedule Feasibility: In Schedule Feasibility Study mainly timelines/deadlines is analyzed for proposed project which includes how much time teams will take to complete final project which has a great impact on the organization as purpose of project may fail if it can’t be completed on time.
- Cultural and Political Feasibility: This section assesses how the software project will affect the political environment and organizational culture. This analysis takes into account the organization’s culture and how the suggested changes could be received there, as well as any potential political obstacles or internal opposition to the project. It is essential that cultural and political factors be taken into account in order to execute projects successfully.
- Market Feasibility: This refers to evaluating the market’s willingness and ability to accept the suggested software system. Analyzing the target market, understanding consumer wants and assessing possible rivals are all part of this study. It assists in identifying whether the project is in line with market expectations and whether there is a feasible market for the good or service being offered.
- Resource Feasibility: This method evaluates if the resources needed to complete the software project successfully are adequate and readily available. Financial, technological and human resources are all taken into account in this study. It guarantees that sufficient hardware, software, trained labor and funding are available to complete the project successfully.
Aim of Feasibility Study
- The overall objective of the organization are covered and contributed by the system or not.
- The implementation of the system be done using current technology or not.
- Can the system be integrated with the other system which are already exist
Feasibility Study Process
The below steps are carried out during entire feasibility analysis.
- Information assessment: It assesses the original project concept and establishes the main aims and objectives.
- Information collection: It collects the necessary information and data required to evaluate the project’s many components.
- Report writing: It produces an in-depth feasibility report that details the analysis and results.
- General information: It gives a summary of the main points discussed in the report on the feasibility study.
Need of Feasibility Study
Feasibility study is so important stage of Software Project Management Process as after completion of feasibility study it gives a conclusion of whether to go ahead with proposed project as it is practically feasible or to stop proposed project here as it is not right/feasible to develop or to think/analyze about proposed project again.
Along with this Feasibility study helps in identifying risk factors involved in developing and deploying system and planning for risk analysis also narrows the business alternatives and enhance success rate analyzing different parameters associated with proposed project development.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Software Engineering
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
+1 (321) 730-5301

News and Events
Featured news, state and federal space stakeholders release florida spaceport system maritime intermodal transportation study feasibility phase report.

EXPLORATION PARK, Fla.—May 2, 2024— Space Florida, the state’s aerospace finance and development authority, announces the completion of the feasibility phase of the Florida Spaceport System Maritime Intermodal Transportation Study . This study marks preliminary steps in enhancing maritime support for the rapidly growing commercial space transportation sector with the overall objective to assess options to enhance and optimize maritime transportation and infrastructure to support Florida’s spaceport system’s growing needs.
This first-in-the-nation study was conducted over one year and included extensive engineering and stakeholder analyses. The study was initiated in response to requests from federal stakeholders. Download the report and an FAQ document .
As the space industry’s launch activities surge, the demand for specialized maritime infrastructure has become increasingly apparent. The study aims to address this critical need by assessing the feasibility of various maritime support options for spaceport operations in Florida.
Key Findings of the Feasibility Phase
- Asset Inventory and Demand Forecast: Current facilities at Port Canaveral and surrounding areas are insufficient to meet the projected demand for maritime operations related to space launches, necessitating over 9,000 linear feet of dedicated wharf space.
- Strategic Expansion Plans: Through an in-depth alternatives analysis, the study recommends short- and mid-term expansions in the West and Middle Turning Basins, with a visionary long-term expansion northward to meet future industry demands.
- Innovative Concept Designs: Proposed designs include the utilization of existing infrastructure for immediate needs and significant expansions for long-term capacity, ensuring the spaceport system’s ability to support the industry’s growth trajectory.
- Sustainable Business Model: The financial analysis presented in the study outlines a viable business case for the recommended expansions, suggesting a blend of federal grants and revised usage fees to fund the development without imposing undue financial burdens on launch service providers.
“In response to market demands from the commercial space and maritime sectors and our U.S. military partners, Space Florida spearheaded this study to create a unified path that accounts for the aspirations and missions of both space and port operations,” said Rob Long, president and CEO, Space Florida . “By identifying opportunities for development, we’re not only supporting the immediate needs of the space industry but also making certain Florida leads in the new era of global aerospace commerce. With this feasibility phase we can better understand how to leverage our quintamodal state, that enhances our maritime capabilities while supporting the tremendous growth of commercial space.”
“Port Canaveral has a long history of engagement with our nation’s space program. We have supported the maritime operations of commercial space since its onset in our region nearly ten years ago, and the dynamic growth we’re seeing today is evidence of its success,” said Capt. John Murray, Canaveral Port Authority CEO . “We appreciate Space Florida taking on this study and support the comprehensive effort to address the industry’s growing maritime needs. We look forward to continued collaboration with federal and state partners to realize solutions to ensure the industry’s continued success.”
NASA’s Kennedy Space Center is participating in this collaborative effort, looking at potential wharf solutions to support Kennedy’s premier spaceport operations and potentially enabling the continued growth of the space industry.
What’s on the Horizon
- Obtain stakeholder concurrence from landowners and establish Memorandum of Understanding with action items to guide project implementation.
- Identify strategic federal funding opportunities to begin near-term and long-term improvements. Estimated total cost (near-term and long-term improvements): $2.1 billion.
- Work with federal partners to acquire necessary property for construction and identify potential governing and operations entity or entitles.
- Begin implementation study phase.
- Conduct a statewide study to determine how other seaports can support the industry.
Media Contact Alayna Curry, APR Director of Public Relations [email protected]
About Space Florida Space Florida is where leading aerospace companies get everything they need to see their new ideas take off. As the state’s aerospace finance and development authority, Space Florida brings a mix of unrivaled experience, unmatched financial tools, and unbeatable location to the table by providing critical business financing opportunities for the aerospace industry, managing infrastructure investment in the state’s spaceport system, and facilitating research and development, workforce, education, and investment programs.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognizing you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
Cookies Policy
Last updated: December 16, 2020
This Cookies Policy explains what Cookies are and how We use them. You should read this policy so You can understand what type of cookies We use, or the information We collect using Cookies and how that information is used.
Cookies do not typically contain any information that personally identifies a user, but personal information that we store about You may be linked to the information stored in and obtained from Cookies. For further information on how We use, store and keep your personal data secure, see our Privacy Policy.
We do not store sensitive personal information, such as mailing addresses, account passwords, etc. in the Cookies We use.
Interpretation and Definitions
Interpretation.
The words of which the initial letter is capitalized have meanings defined under the following conditions. The following definitions shall have the same meaning regardless of whether they appear in singular or in plural.
Definitions
For the purposes of this Cookies Policy:
- Company (referred to as either "the Company", "We", "Us" or "Our" in this Cookies Policy) refers to Space Florida, 505 Odyssey Way, Suite 300 Exploration Park, FL 32953.
- Cookies means small files that are placed on Your computer, mobile device or any other device by a website, containing details of your browsing history on that website among its many uses.
- Website refers to Space Florida, accessible from https://www.spaceflorida.gov
- You means the individual accessing or using the Website, or a company, or any legal entity on behalf of which such individual is accessing or using the Website, as applicable.
The use of the Cookies
Type of cookies we use.
Cookies can be "Persistent" or "Session" Cookies. Persistent Cookies remain on your personal computer or mobile device when You go offline, while Session Cookies are deleted as soon as You close your web browser.
We use both session and persistent Cookies for the purposes set out below:
Type: Session Cookies
Administered by: Us
Type: Persistent Cookies
Your Choices Regarding Cookies
If You prefer to avoid the use of Cookies on the Website, first You must disable the use of Cookies in your browser and then delete the Cookies saved in your browser associated with this website. You may use this option for preventing the use of Cookies at any time.
If You do not accept Our Cookies, You may experience some inconvenience in your use of the Website and some features may not function properly.
If You'd like to delete Cookies or instruct your web browser to delete or refuse Cookies, please visit the help pages of your web browser.
- For the Chrome web browser, please visit this page from Google: https://support.google.com/accounts/answer/32050
- For the Internet Explorer web browser, please visit this page from Microsoft: http://support.microsoft.com/kb/278835
- For the Firefox web browser, please visit this page from Mozilla: https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/delete-cookies-remove-info-websites-stored
- For the Safari web browser, please visit this page from Apple: https://support.apple.com/guide/safari/manage-cookies-and-website-data-sfri11471/mac
For any other web browser, please visit your web browser's official web pages.
If you have any questions about this Cookies Policy, You can contact us:
- By email: [email protected]
A Heterogeneous Graph Construction Method for Mineral Prospectivity Mapping
- Original Paper
- Published: 02 May 2024
Cite this article

- Luyi Shi 1 ,
- Ying Xu 2 &
- Renguang Zuo 2
70 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Graph-based models have been utilized for mineral prospectivity mapping (MPM), and they have demonstrated excellent performance owing to their adaptable graph structure, which is conducive to comprehensively considering the spatial anisotropy of mineralization compared with pixel- or image-based models. However, widely used graph-based models cannot fully consider the relationship between geological entities and mineralization. A heterogeneous graph is a type of graph structure containing rich heterogeneous information, allowing the consideration of various relationships and the assignment of suitable attributes to various types of nodes. Nodes in heterogeneous graphs can fully integrate heterogeneous information based on specific relations (i.e., edges). This study introduced a novel method for constructing heterogeneous graphs for MPM. The nodes in the graph consist of different types of geological entities, and the edges (relations) represent the links between the geological entities. The constructed heterogeneous graph cannot only effectively express the spatial anisotropy of mineralization but also consider the shape of geological entities and the relationships among geological entities, which is beneficial for modeling complex ore-forming geological processes. This heterogeneous graph was then trained using graph neural networks to obtain a mineral prospectivity map for southwestern Fujian Province, China. In addition, the proposed graph construction method demonstrated higher feasibility and accuracy in MPM compared to conventional graph construction method and convolutional neural networks.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Graph Deep Learning Model for Mapping Mineral Prospectivity
An Interpretable Graph Attention Network for Mineral Prospectivity Mapping
Recognizing Multivariate Geochemical Anomalies Related to Mineralization by Using Deep Unsupervised Graph Learning
Ge, C., Han, F., Zhou, T., & Chen, D. (1981). Geological characteristics of the Makeng iron deposit of marine volcano-sedimentary origin. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 3 , 47–69. (in Chinese with English Abstract).
CAS Google Scholar
Gori, M., Monfardini, G., & Scarselli, F. (2005). A new model for learning in graph domains. IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2 , 729–734.
Google Scholar
Han, F., & Ge, C. (1983). Geological and geochemical features of submarine volcanic hydrothermal-sedimentary mineralization of Makeng iron deposit, Fujian Province. Collection from the Institute of Mineral Deposit Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 7 , 1–118. (in Chinese with English Abstract).
Hu, Z., Dong, Y., Wang, K., & Sun, Y. (2020). Heterogeneous Graph Transformer. Proceedings of The Web Conference, 2020 , 2704–2710.
Ji, H., Wang, X., Shi, C., Wang, B., & Yu, P. (2021). Heterogeneous Graph Propagation Network. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 1–1.
Li, P., Yu, X., Li, H., Qiu, J., & Zhou, X. (2013). Jurassic-Cretaceous tectonic evolution of Southeast China: Geochronological and geochemical constraints of Yanshanian granitoids. International Geology Review, 55 (10), 1202–1219.
Article Google Scholar
Li, S., Chen, J., & Xiang, J. (2020). Applications of deep convolutional neural networks in prospecting prediction based on two-dimensional geological big data. Neural Computing and Applications, 32 (7), 2037–2053.
Li, T., Zuo, R., Xiong, Y., & Peng, Y. (2021). Random-Drop Data Augmentation of Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Mineral Prospectivity Mapping. Natural Resources Research, 30 (1), 27–38.
Rodriguez-Galiano, V. F., Chica-Olmo, M., & Chica-Rivas, M. (2014). Predictive modelling of gold potential with the integration of multisource information based on random forest: A case study on the Rodalquilar area, Southern Spain. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 28 (7), 1336–1354.
Scarselli, F., Gori, M., Tsoi, A. C., Hagenbuchner, M., & Monfardini, G. (2009). Computational capabilities of graph neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 20 , 81–102.
Shu, L., Faure, M., Wang, B., Zhou, X., & Song, B. (2008). Late Palaeozoic-Early Mesozoic geological features of South China: Response to the Indosinian collision events in Southeast Asia. Comptes Rendus Geoscience, 340 (2–3), 151–165.
Singer, D. A. (2021). How Deep Learning Networks could be Designed to Locate Mineral Deposits. Journal of Earth Science, 32 (2), 288–292.
Singer, D. A., & Kouda, R. (1996). Application of a feedforward neural network in the search for Kuroko deposits in the Hokuroku district. Japan. Mathematical Geology, 28 (8), 1017–1023.
Sun, W., Ding, X., Hu, Y.-H., & Li, X.-H. (2007). The golden transformation of the Cretaceous plate subduction in the west Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 262 (3–4), 533–542.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Sun, Y., & Han, J. (2012). Mining heterogeneous information networks: A structural analysis approach. SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 14 (2), 20–28.
Veličković, P., Cucurull, G., Casanova, A., Romero, A., Liò, P., & Bengio, Y. (2018). Graph attention networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1710.10903.
Wang, X., Ji, H., Shi, C., Wang, B., Cui, P., Yu, P., & Ye, Y. (2021). Heterogeneous Graph Attention Network ( arXiv:1903.07293 ).
Wang, Z., & Zuo, R. (2022). Mineral prospectivity mapping using a joint singularity-based weighting method and long short-term memory network. Computers & Geosciences, 158 , 104974.
Wang, Z., Zuo, R., & Zhang, Z. (2015). Spatial analysis of Fe deposits in Fujian Province, China: Implications for mineral exploration. Journal of Earth Science, 26 (6), 813–820.
Xiong, Y., & Zuo, R. (2016). Recognition of geochemical anomalies using a deep autoencoder network. Computers & Geosciences, 86 , 75–82.
Xiong, Y., & Zuo, R. (2018). GIS-based rare events logistic regression for mineral prospectivity mapping. Computers & Geosciences, 111 , 18–25.
Xiong, Y., Zuo, R., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2018). Mapping mineral prospectivity through big data analytics and a deep learning algorithm. Ore Geology Reviews, 102 , 811–817.
Xu, Y., & Zuo, R. (2024). An Interpretable Graph Attention Network for Mineral Prospectivity Mapping. Mathematical Geosciences, 56 , 169–190.
Xu, Y., Zuo, R., & Zhang, G. (2023). The graph attention network and its post-hoc explanation for recognizing mineralization-related geochemical anomalies. Applied Geochemistry, 155 , 105722.
Yang, F., Wang, Z., Zuo, R., Sun, S., & Zhou, B. (2023). Quantification of Uncertainty Associated with Evidence Layers in Mineral Prospectivity Mapping Using Direct Sampling and Convolutional Neural Network. Natural Resources Research, 32 (1), 79–98.
Yang, N., Zhang, Z., Yang, J., & Hong, Z. (2022a). Applications of data augmentation in mineral prospectivity prediction based on convolutional neural networks. Computers & Geosciences, 161 , 105075.
Yang, N., Zhang, Z., Yang, J., & Hong, Z. (2022b). Mineral Prospectivity Prediction by Integration of Convolutional Autoencoder Network and Random Forest. Natural Resources Research, 31 (3), 1103–1119.
Yang, N., Zhang, Z., Yang, J., Hong, Z., & Shi, J. (2021). A convolutional neural network of GoogLeNet applied in mineral prospectivity prediction based on multi-source geoinformation. Natural Resources Research, 30 (6), 3905–3923.
Yin, B., Zuo, R., & Xiong, Y. (2022). Mineral Prospectivity Mapping via Gated Recurrent Unit Model. Natural Resources Research, 31 (4), 2065–2079.
Zhang, Y., Xiong, Y., Kong, X., Li, S., Mi, J., & Zhu, Y. (2018). Deep Collective Classification in Heterogeneous Information Networks. Proceedings of the 2018 World Wide Web Conference on World Wide Web - WWW ’18, 399–408.
Zhang, C., Song, D., Huang, C., Swami, A., & Chawla, N. V. (2019). Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining, 793–803.
Zhang, Z., & Zuo, R. (2014). Sr–Nd–Pb isotope systematics of magnetite: Implications for the genesis of Makeng Fe deposit, southern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 57 , 53–60.
Zhang, Z., Zuo, R., & Cheng, Q. (2015a). Geological Features and Formation Processes of the Makeng Fe Deposit. China. Resource Geology, 65 (3), 266–284.
Zhang, Z., Zuo, R., & Cheng, Q. (2015b). The mineralization age of the Makeng Fe deposit, South China: Implications from U-Pb and Sm–Nd geochronology. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 104 (3), 663–682.
Zhang, Z., Zuo, R., & Xiong, Y. (2016). A comparative study of fuzzy weights of evidence and random forests for mapping mineral prospectivity for skarn-type Fe deposits in the southwestern Fujian metallogenic belt. China. Science China Earth Sciences, 59 (3), 556–572.
Zhou, X., Sun, T., Shen, W., Shu, L., & Niu, Y. (2006). Petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids and volcanic rocks in South China: A response to tectonic evolution. Episodes, 29 (1), 26–33.
Zuo, R. (2014). Identification of geochemical anomalies associated with mineralization in the Fanshan district, Fujian, China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 139 , 170–176.
Zuo, R. (2016). A nonlinear controlling function of geological features on magmatic–hydrothermal mineralization. Scientific Reports, 6 (1), 27127.
Zuo, R., & Carranza, E. J. M. (2011). Support vector machine: A tool for mapping mineral prospectivity. Computers & Geosciences, 37 (12), 1967–1975.
Zuo, R., Carranza, E. J. M., & Wang, J. (2016). Spatial analysis and visualization of exploration geochemical data. Earth-Science Reviews, 158 , 9–18.
Zuo, R., & Wang, J. (2016). Fractal/multifractal modeling of geochemical data: A review. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 164 , 33–41.
Zuo, R., & Wang, Z. (2020). Effects of random negative training samples on mineral prospectivity mapping. Natural Resources Research, 29 , 3443–3455.
Zuo, R., & Xu, Y. (2023). Graph Deep Learning Model for Mapping Mineral Prospectivity. Mathematical Geosciences, 55 (1), 1–21.
Zuo, R., Zhang, Z., Zhang, D., Carranza, E. J. M., & Wang, H. (2015). Evaluation of uncertainty in mineral prospectivity mapping due to missing evidence: A case study with skarn-type Fe deposits in Southwestern Fujian Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 71 , 502–515.
Download references
Acknowledgments
This study was jointed supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42321001, 42172326) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (China) (2023AFA001).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Computer Science, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 430074, China
State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 430074, China
Ying Xu & Renguang Zuo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Renguang Zuo .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Shi, L., Xu, Y. & Zuo, R. A Heterogeneous Graph Construction Method for Mineral Prospectivity Mapping. Nat Resour Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-024-10344-2
Download citation
Received : 08 January 2024
Accepted : 06 April 2024
Published : 02 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-024-10344-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Mineral prospectivity mapping
- Heterogeneous graph
- Graph neural network
- Geological entity
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Feasibility Study: A feasibility study is an analysis of how successfully a project can be completed, accounting for factors that affect it such as economic, technological, legal and scheduling ...
A Feasibility Study is an initial investigation into the potential benefits and viability of a project or endeavour. An impartial appraisal that looks at a project's technical, financial, legal, and environmental elements is what this study provides. Decision-makers can use this information to assess if the project should move forward or not.
A feasibility study, as the name suggests, is designed to reveal whether a project/plan is feasible. It is an assessment of the practicality of a proposed project/plan. A feasibility study is part of the initial design stage of any project/plan. It is conducted in order to objectively uncover the strengths and weaknesses of a proposed project ...
This type of study focuses on understanding customer needs, market trends, and the competitive landscape. Here are the key elements of a market feasibility study: Market Research and Analysis: Comprehensive research is conducted to gather market size, growth potential, and customer behavior data.
3. Conduct a Market Survey or Perform Market Research. This step is key to the success of your feasibility study, so make your market analysis as thorough as possible. It's so important that if your organization doesn't have the resources to do a proper one, then it is advantageous to hire an outside firm to do so.
A feasibility study is an assessment tool that helps determine if a proposed product, service or business will be successful. The study considers many factors, including technical, economic and legal, to evaluate the proposal. There are several types of feasibility studies to consider based on the project. The study provides useful information ...
A project feasibility study is a comprehensive report that examines in detail the five frames of analysis of a given project. It also takes into consideration its four Ps, its risks and POVs, and its constraints (calendar, costs, and norms of quality). The goal is to determine whether the project should go ahead, be redesigned, or else ...
A feasibility study is an essential analytical tool that evaluates the viability of a proposed project on multiple fronts, such as financials, technical requirements, and market demand. Conducted during the project initiation phase, this type of study serves as an early checkpoint to identify potential roadblocks and assess risks.
A feasibility study consists of research conducted before the approval of a project. It is essential to the project life cycle development as it helps determine the likelihood of success before you've spent your resources on a potential lost cause. The study helps determine a project's viability by looking at cost, resource requirements ...
A feasibility study should be conducted after the project has been pitched but before any work has actually started. The study is part of the project planning process. In fact, it's often done in conjunction with a SWOT analysis or project risk assessment, depending on the specific project. Feasibility studies help:
A feasibility study is a crucial assessment tool in project management. It offers a systematic evaluation of a proposed project's viability. This comprehensive analysis encompasses various dimensions, including technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling considerations.
Step 1: Do the preliminary analysis. Running a full feasibility study can eat up time and technical resources. Instead of diving straight into the assessment, try dipping your toes in first by doing a preliminary analysis. Think of it like a test before the big test. 🤓.
Types of Feasibility Study. A feasibility analysis evaluates the project's potential for success; therefore, perceived objectivity is an essential factor in the credibility of the study for potential investors and lending institutions. There are five types of feasibility study—separate areas that a feasibility study examines, described ...
A feasibility study is an in-depth assessment conducted to determine the practicality and viability of a proposed project or idea. It involves evaluating various factors such as technical, economic, legal, operational, and scheduling aspects to ascertain whether the project can be successfully implemented.
Design Options for Feasibility Studies. The choice of an optimal research design depends upon the selected area of focus. This premise holds equally for feasibility studies and for other kinds of research. As the knowledge base and needs for an intervention progress, different questions come to the fore.
For a general set of guidelines to help you get started, here are some basic steps to conduct and report a feasibility study for major product opportunities or features. 1. Clearly define the opportunity. Imagine your user base is facing a significant problem that your product doesn't solve. This is an opportunity.
The feasibility study helps to narrow the scope of the project to identify the best business scenario(s). The business plan deals with only one alternative or scenario. The feasibility study helps to narrow the scope of the project to identify and define two or three scenarios or alternatives.
A feasibility study may be the appropriate first step to help identify whether a larger research study is warranted. A feasibility study is often a critical step to be taken prior to conducting a larger study. The primary aim of a feasibility study is to assess the feasibility of conducting future conclusive randomized, controlled trials (RCTs ...
In implementation research, feasibility and pilot studies perform the same functions as those for intervention trials, ... Thus, the purpose of a Hybrid Type 1 feasibility study is generally to inform the development or refinement of the implementation strategy rather than to test potential effects or mechanisms [22, 47].
A feasibility study provides a blueprint to determine feasibility of a business endeavor or a planned project. A feasibility study is a systematic plan and analysis of the sustainability of a ...
Pilot studies. A Pilot Study is a version of the main study that is run in miniature to test whether the components of the main study can all work together. It is focused on the processes of the main study, for example to ensure recruitment, randomisation, treatment, and follow-up assessments all run smoothly.
Case study 1: Donovan and colleagues undertook qualitative research within a feasibility study for a trial of prostate testing for cancer and treatment. Research question: The authors are explicit in the introduction of the paper that the most important uncertainty for the full trial was whether participants would agree to randomisation.
The below steps are carried out during entire feasibility analysis. Information assessment: It assesses the original project concept and establishes the main aims and objectives. Information collection: It collects the necessary information and data required to evaluate the project's many components. Report writing: It produces an in-depth ...
EXPLORATION PARK, Fla.—May 2, 2024—Space Florida, the state's aerospace finance and development authority, announces the completion of the feasibility phase of the Florida Spaceport System Maritime Intermodal Transportation Study. This study marks preliminary steps in enhancing maritime support for the rapidly growing commercial space transportation sector with the overall objective to ...
Question: The feasibility of a research study should be considered in light of ... The feasibility of a research study should be considered in light of . . . Here's the best way to solve it.
Edge Construction. In graph neural networks, the construction of edges in a graph structure plays a crucial role in the model performance. In the conventional graph-based MPM, edges are constructed between nodes and their adjacent nodes (Fig. 2), involving the aggregation of information on ore-controlling factors from the prediction node set.This method enables the transmission of information ...