- Publications

Responsible Use of Technology: The IBM Case Study

The World Economic Forum Responsible Use of Technology project aims to provide practical resources for organizations to operationalize ethics in their use of technology. This White Paper is the second in a series that highlights processes, tools and organizational constructs that facilitate the responsible design, development and implementation of technology. It presents IBM’s ethics journey, which can encourage organizations to adopt and operationalize technology ethics, and seeks to promote discussion and evaluation of IBM’s methods, tools and experiences. The Forum and its partners in this project hope that more organizations not only operationalize such ethics, but also share their experience with the global community.
World Economic Forum reports may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License , and in accordance with our Terms of Use .
Further reading All related content

3 lessons from IBM on designing responsible, ethical AI
A new case study, co-authored by the World Economic Forum, delves into the lessons learned at IBM in the company's quest to develop ethical AI technology.
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Premium News
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Asking for a Trend
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Ibm, fuelcell energy to use ai in effort to forge longer-life fuel cell systems.
ZURICH, Switzerland, Nov. 28, 2023 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- IBM and FuelCell Energy, Inc. (Nasdaq: FCEL) today announced they will work together to boost the performance of FuelCell Energy’s technology using Foundation Models, a form of generative Artificial Intelligence (AI). The aim of this collaboration is to support both companies’ efforts to lead a global transition to renewable energy sources that emit little to no carbon.
Fuel cells are a source of clean energy that can be used in conjunction with other renewable energy sources or on their own. Through the collaboration, IBM will research ways that FuelCell Energy can extend the life of its fuel cells through an optimal control of operational parameters and their cost effectiveness for customers.
IBM will develop a Foundation Model , a form of generative AI, to create device-level models using FuelCell Energy data. These models will learn from the data and predict the technology's performance. This creates a data-based digital twin of the fuel cell, connecting various data sources and helping to provide a greater understanding of how various operating parameters impact the fuel cell's degradation, enabling potential improvements.
FuelCell Energy’s Chief Technology Officer, Tony Leo, and Alessandro Curioni, VP IBM Research Europe and Africa and Director of IBM Research Europe, Zurich, announced the collaboration at the 2023 Pan-EMEA Media Event at IBM Research Zurich lab in Switzerland.
“We hope that IBM’s AI will help FuelCell Energy replace the traditional, time-intensive and expensive accelerated life testing process when it comes to electrochemical energy production to quickly and efficiently propel forward the world’s transition to clean energy,” said Curioni.
“Our collaboration with IBM is an opportunity for FuelCell Energy to leverage emerging AI technology to improve our product performance for our customers and for IBM to extend its AI technology to the study of electrochemical catalytic processes,” said Leo. “We are excited to tap some of the greatest minds in the application of artificial intelligence, particularly in pursuit of joint commitments to enabling a world empowered by clean energy.”
About FuelCell Energy FuelCell Energy, Inc. (NASDAQ: FCEL): FuelCell Energy is a global leader in sustainable clean energy technologies that address some of the world’s most critical challenges around energy, safety, and global urbanization. It collectively holds more than 450 fuel cell technology patents in the United States and globally. As a leading global manufacturer of proprietary fuel cell technology platforms, FuelCell Energy is uniquely positioned to serve customers worldwide with sustainable products and solutions for businesses, utilities, governments, and municipalities. The Company’s solutions are designed to enable a world empowered by clean energy, enhancing the quality of life for people around the globe.
About IBM IBM is a leading provider of global hybrid cloud and AI, and consulting expertise. We help clients in more than 175 countries capitalize on insights from their data, streamline business processes, reduce costs and gain the competitive edge in their industries. More than 4,000 government and corporate entities in critical infrastructure areas such as financial services, telecommunications and healthcare rely on IBM’s hybrid cloud platform and Red Hat OpenShift to affect their digital transformations quickly, efficiently and securely.
IBM’s breakthrough innovations in AI, quantum computing, industry-specific cloud solutions and consulting deliver open and flexible options to our clients. All of this is backed by IBM’s legendary commitment to trust, transparency, responsibility, inclusivity and service.
Visit www.ibm.com for more information.
Katia Moskvitch [email protected] +41 782089666
FuelCell Energy:
[email protected] 203.205.2491
Kathleen Blomquist [email protected] 203.546.5844
More From Forbes
Ibm shares quantum use cases in dazzling new book.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
The IBM Institute for Business Value (IBV) has published a beautiful book, good to read and also a substantial addition to any executive office: the fourth edition of The Quantum Decade . The 168-page tome written by over 70 professionals in every industry, clearly lays out the appropriate problems, the approaches to solutions, and the amazing technology being invented as we speak. With dozens of uses cases, and in-depth portrayals, this book is a must-read for every CEO and CTO. Here’s a summary of select sections I found particularly interesting, and a few use cases from the book.
IBM has published a playbook to prepare senior management for the coming Quantum age.
Quantum Thinking
The IBV did a CEO study in 2021 that revealed that 89% of over 3,000 chief executives surveyed did not consider quantum computing as a key technology for delivering business results in the next two to three years. While this lack of recognition may be understandable in the short term, given quantum computing's disruptive potential in the coming decade, CEOs need to start mobilizing resources to understand and engage with quantum technology now. IBV research also finds that in 2023, organizations invested 7% of their R&D budget in quantum computing , up 29% from 2021. By 2025, this is expected to further increase by another 25%.
Ignoring quantum computing could pose significant risks, the authors assert, with consequences potentially greater than missing out on the opportunity presented by artificial intelligence a decade ago. Phase 1 of the quantum computing playbook involves acknowledging that the computing landscape is undergoing a fundamental shift. This shift from analytics to discovery of forward-looking models that can run on Quantum opens up possibilities for uncovering solutions that were previously impossible.
The newly installed and operational IBM Quantum System Two at the IBM Thomas Waston Research Center ... [+] in Yorktown Heights, NY.
Phase 2 involves asking important questions: How might quantum computing disrupt and reshape your business model? How could it enhance your existing AI and classical computing workflows? What could be the "killer app" for quantum computing in your industry? How can your organization deepen its quantum computing capabilities, either internally or through partnerships with ecosystems? This is the time to experiment, iterate with scenario planning, and cultivate talent proficient in quantum computing to educate internal stakeholders and leverage deep tech resources.
Best High-Yield Savings Accounts Of 2024
Best 5% interest savings accounts of 2024.
A rendering of the eventual 100,000-qubit system under development at IBM.
IBM says it is important to note that quantum computing doesn't replace classical computing. Instead, quantum forms a progressive partnership with classical computing and AI, where the three work together iteratively, becoming more powerful as a collective than they are individually. In the hardware configuration above, each Quantum chassis is surrounded by classical computers, and the black rows are likely inference processing servers. So one needs to think about how to factor the solution to take advantage of these closely-knit but disparate systems.
CEO Arvind Krishna visiting IBM’s quantum computing data center in Poughkeepsie, New York.
Phase 3, known as Quantum Advantage, marks a significant milestone where quantum computing demonstrates its ability to perform specific tasks more efficiently, cost-effectively, or with better quality than classical computers. Today, IBM’s quantum systems deliver utility-scale performance: the point at which quantum computers can now serve as scientific tools to explore new classes of problems beyond brute-force, classical simulation of quantum mechanics. Quantum utility is an important step toward “advantage,” when the combination of quantum computers with classical systems enables significantly better performance than classical systems alone. As advancements in hardware, software, and algorithms in quantum computing converge, they enable substantial performance improvements over classical computing, unlocking new opportunities for competitive advantage across industries
However, achieving business value from quantum computing requires prioritizing the right use cases—those with the potential to truly transform an organization or an entire industry. Identifying and focusing on these strategic use cases is crucial for realizing the benefits of quantum technology. Here are a few examples that IBM articulates in the book.
Exxon Mobile and the Global Supply Chain
ExxonMobil is exploring the potential of quantum computing to optimize global shipping routes, a crucial component of international trade that relies heavily on maritime transport. With around 90% of the world's trade carried by sea, involving over 50,000 ships and potentially 20,000 containers per ship, optimizing these routes is a complex challenge beyond the capabilities of classical computers. In partnership with IBM, ExxonMobil is leveraging the IBM Quantum Network, which it joined in 2019 as the first energy company, to develop methods for mapping the global routing of merchant ships to quantum computers.
The core advantage of quantum computing in this context lies in its ability to minimize incorrect solutions and enhance correct ones, making it particularly suited for complex optimization problems. Utilizing the Qiskit quantum optimization module, ExxonMobil has tested various quantum algorithms to find the most effective ones for this task. They found that heuristic quantum algorithms and the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE)-based optimization showed promise, particularly when the right ansatz (a physics term for an educated guess) is chosen.
This exploration into quantum computing for maritime shipping optimization not only has the potential to significantly impact the logistics and transportation sectors but also demonstrates broader applications in other industries facing similar optimization challenges, such as goods delivery, ride-sharing services, and urban waste management.
The University of California and Machine Learning
Researchers from IBM Quantum and the University of California, Berkeley have developed a breakthrough algorithm in quantum machine learning, demonstrating a theoretical Quantum Advantage. Traditional quantum machine learning algorithms often required quantum states of data, but this new approach works with classical data, making it more applicable to real-world scenarios.
The team focused on supervised machine learning, where they utilized quantum circuits to map classical data into a higher dimensional space—a task naturally suited for quantum computing due to the high-dimensional nature of multiple qubit states. They then estimated a quantum kernel, a measure of similarity between data points, which was used within a classical support vector machine to effectively separate the data.
In late 2020, the researchers provided solid proof that their quantum feature map circuit outperforms all possible binary classical classifiers when only classical data is available. This advancement opens up new possibilities for quantum computing in various applications, such as forecasting, predicting properties from data, or conducting risk analysis, marking a significant step forward in the field of quantum machine learning.
E.ON and Machine Learning
E.ON, a major energy operator in Europe, is leveraging quantum computing to enhance risk management and achieve its emission reduction goals. With a vast customer base and a significant increase in renewable assets expected by 2030, the company faces the challenge of managing weather-related risks and ensuring affordable energy costs. Collaborating with IBM, E.ON has implemented quantum computing strategies to conduct complex Monte Carlo simulations across various factors like locations, contracts, and weather conditions.
Key quantum computing applications include:
- Using quantum nonlinear transformations for calculating energy contract gross margins via quantum Taylor expansions.
- Performing risk analysis with quantum amplitude estimation to improve dynamic circuit leveraging.
- Integrating quadratic speed-ups in classical Monte Carlo methods to optimize hardware resources.
These strategies have enabled real-time planning, finer risk diversification, and more frequent portfolio risk reassessments, thus aiding in the renegotiation of hedging contracts. E.ON views quantum computing as a pivotal technology for advancing machine learning, risk analysis, accelerated Monte Carlo techniques, and combinatorial optimization for logistics and scheduling, marking a significant shift in managing energy-related challenges.
Wells Fargo and Financial Trading
Wells Fargo is actively exploring the potential of quantum computing for practical applications in the financial sector, partnering with IBM within the IBM Quantum Network. This collaboration grants Wells Fargo access to IBM's quantum computers via the cloud, allowing for pioneering work in quantum computing use cases, including sampling, optimization, and machine learning, aimed at deriving valuable results from quantum technologies.
A notable area of investigation between Wells Fargo and IBM is sequence modeling, particularly for predicting mid-price movements in financial markets. This involves analyzing the Limit Order Book, which records ask-and-bid orders on exchanges, and focuses on the mid-price—the average between the lowest ask and the highest bid prices at any moment.
Wells Fargo has explored using quantum hidden Markov models (QHMMs) for stochastic generation, a quantum approach to sequence modeling. QHMMs aim to generate sequences of likely symbols (e.g., representing price increases or decreases) from a given start state, similar to how large language models generate text. This quantum approach has shown to be more efficient than its classical counterpart, hidden Markov models (HMMs), offering new ways to enhance artificial intelligence technology in finance through the more efficient definition of stochastic process languages.
JSR and Chip Manufacturing
IBM and JSR are exploring how quantum computing could shape the future of computer chip manufacturing. Gordon Moore famously predicted in 1965 that the number of transistors on a computer chip would double approximately every two years, a forecast that has held true for decades, known as "Moore's Law." This progress has been largely enabled by innovations in semiconductor manufacturing, notably the development of a photoresist-based method by IBM in the 1980s. This technique, which uses a light-sensitive material to print transistors on chips, became widespread, with companies like JSR Corporation becoming leading producers.
The continuous miniaturization and performance improvement of chips are challenged by the costs and complexities of designing new photoresist molecules, a task for which modern supercomputers struggle due to the difficulty of simulating quantum-scale phenomena. Quantum computing, which operates on the principles of quantum mechanics, offers a potential solution by efficiently simulating molecular systems, including those comprising photoresist materials.
In a collaborative effort, IBM and JSR Corporation have started to explore the application of quantum computing in this field. A 2022 study demonstrated the use of IBM Quantum hardware to simulate small molecules akin to parts of a photoresist. This research represents a step toward utilizing quantum computing for developing new materials, potentially ensuring that Moore’s Law can continue to apply well into the future by enabling further advancements in semiconductor technology.
Conclusions
As you can see, the new edition of IBM’s Quantum Decade is a fabulous resource that should start more conversations and exploration in board rooms around the world. And thats exactly what IBM intended; by collaborating with early thinkers, we can jump start the Quantum Journey and accelerate the time to real-world solutions.
Disclosures : This article expresses the author's opinions and
should not be taken as advice to purchase from or invest in the companies mentioned. Cambrian AI Research is fortunate to have many, if not most, semiconductor firms as our clients, including Blaize, BrainChip, CadenceDesign, Cerebras, D-Matrix, Eliyan, Esperanto, FuriosaAI, Graphcore, GML, IBM, Intel, Mythic, NVIDIA, Qualcomm Technologies, Si-Five, SiMa.ai, Synopsys, Ventana Microsystems, Tenstorrent and scores of investment clients. We have no investment positions in any of the companies mentioned in this article and do not plan to initiate any in the near future. For more information, please visit our website at https://cambrian-AI.com .

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
SAFe Case Studies
The Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) has gained popularity in recent years as a way for organizations to achieve agile development at scale. However, many companies may still wonder how exactly SAFe can benefit their organization and what results they can expect. In this article, we’ll explore real-world case studies of companies that have successfully implemented SAFe, highlighting the challenges they faced, the benefits they achieved, and the lessons they learned along the way.
SAFe Implementation at Intel
Intel, a multinational technology company, implemented SAFe in 2012 to improve their software development process. Their main challenges included poor communication between teams, lack of transparency in the development process, and difficulty in tracking progress. By adopting SAFe, Intel was able to align their development teams around a common goal, improve communication and collaboration, and increase transparency into the development process. As a result, they achieved a 25% reduction in time-to-market and a 30% improvement in software quality.
SAFe Implementation at Philips
Philips, a global technology company, faced a challenge of aligning their development teams across multiple locations and time zones. They adopted SAFe in 2016, which helped them to standardize their development practices, improve collaboration, and ensure alignment across teams. With SAFe, Philips was able to achieve a 50% reduction in time-to-market and a 30% increase in productivity.
SAFe Implementation at IBM
IBM, a multinational technology company, adopted SAFe in 2014 to improve their development process and increase the speed of delivery. Their main challenges included long release cycles, difficulty in coordinating teams, and lack of transparency in the development process. By implementing SAFe, IBM was able to reduce release cycles from 12 months to 3 months, improve team coordination, and increase transparency into the development process. They achieved a 50% reduction in time-to-market and a 40% increase in productivity.
Lessons Learned from SAFe Case Studies
From these case studies, we can draw several key lessons about implementing SAFe successfully. First, it’s important to have executive buy-in and a clear understanding of the benefits of SAFe. Second, it’s essential to have a dedicated team to lead the implementation and provide guidance to the organization. Third, it’s crucial to start with a pilot project to test and refine the implementation approach. Finally, it’s important to continuously monitor and adjust the implementation as needed.
Tips for Implementing SAFe
Based on these lessons learned, here are some tips for organizations looking to implement SAFe:
- Start with a pilot project to test and refine the implementation approach.
- Have a dedicated team to lead the implementation and provide guidance to the organization.
- Ensure executive buy-in and a clear understanding of the benefits of SAFe.
- Provide training to all employees involved in the implementation process.
- Continuously monitor and adjust the implementation as needed.
- Be prepared to make changes to the organization’s culture and processes to fully realize the benefits of SAFe.
In conclusion, the case studies of Intel, Philips, and IBM demonstrate the benefits of implementing SAFe, including reduced time-to-market, improved software quality, and increased productivity. By following the tips outlined in this article, organizations can successfully implement SAFe and achieve similar results. As more companies adopt agile at scale, SAFe is likely to continue to gain popularity as a framework for achieving success in large-scale agile development.

- Investor News
- Research News

IBM, FuelCell Energy to Use AI in Effort to Forge Longer-Life Fuel Cell Systems
November 28, 2023 | 3 min read
- No Comments

ZURICH– IBM and FuelCell Energy, Inc. (Nasdaq: FCEL) today announced they will work together to boost the performance of FuelCell Energy’s technology using Foundation Models, a form of generative Artificial Intelligence (AI). The aim of this collaboration is to support both companies’ efforts to lead a global transition to renewable energy sources that emit little to no carbon.
Fuel cells are a source of clean energy that can be used in conjunction with other renewable energy sources or on their own. Through the collaboration, IBM will research ways that FuelCell Energy can extend the life of its fuel cells through an optimal control of operational parameters and their cost effectiveness for customers.
IBM will develop a Foundation Model , a form of generative AI, to create device-level models using FuelCell Energy data. These models will learn from the data and predict the technology’s performance. This creates a data-based digital twin of the fuel cell, connecting various data sources and helping to provide a greater understanding of how various operating parameters impact the fuel cell’s degradation, enabling potential improvements.
FuelCell Energy’s Chief Technology Officer, Tony Leo, and Alessandro Curioni, VP IBM Research Europe and Africa and Director of IBM Research Europe, Zurich, announced the collaboration at the 2023 Pan-EMEA Media Event at IBM Research Zurich lab in Switzerland.
“We hope that IBM’s AI will help FuelCell Energy replace the traditional, time-intensive and expensive accelerated life testing process when it comes to electrochemical energy production to quickly and efficiently propel forward the world’s transition to clean energy,” said Curioni.
“Our collaboration with IBM is an opportunity for FuelCell Energy to leverage emerging AI technology to improve our product performance for our customers and for IBM to extend its AI technology to the study of electrochemical catalytic processes,” said Leo. “We are excited to tap some of the greatest minds in the application of artificial intelligence, particularly in pursuit of joint commitments to enabling a world empowered by clean energy.”
About FuelCell Energy
FuelCell Energy, Inc. (NASDAQ: FCEL): FuelCell Energy is a global leader in sustainable clean energy technologies that address some of the world’s most critical challenges around energy, safety, and global urbanization. It collectively holds more than 450 fuel cell technology patents in the United States and globally. As a leading global manufacturer of proprietary fuel cell technology platforms, FuelCell Energy is uniquely positioned to serve customers worldwide with sustainable products and solutions for businesses, utilities, governments, and municipalities. The Company’s solutions are designed to enable a world empowered by clean energy, enhancing the quality of life for people around the globe.
IBM is a leading provider of global hybrid cloud and AI, and consulting expertise. We help clients in more than 175 countries capitalize on insights from their data, streamline business processes, reduce costs and gain the competitive edge in their industries. More than 4,000 government and corporate entities in critical infrastructure areas such as financial services, telecommunications and healthcare rely on IBM’s hybrid cloud platform and Red Hat OpenShift to affect their digital transformations quickly, efficiently and securely.
IBM’s breakthrough innovations in AI, quantum computing, industry-specific cloud solutions and consulting deliver open and flexible options to our clients. All of this is backed by IBM’s legendary commitment to trust, transparency, responsibility, inclusivity and service.
Visit www.ibm.com for more information.
Katia Moskvitch [email protected] +41 782089666
FuelCell Energy:
[email protected] 203.205.2491
Kathleen Blomquist [email protected] 203.546.5844
Read the most up to date Fuel Cell and Hydrogen Industry news at FuelCellsWorks

Previous Post Feasibility Confirmed for Pioneering Norway-Germany Hydrogen Pipeline Project
Next post forvia accelerates hydrogen activity in north america with a second business award, you may also like.

Ballard Launches 9th Generation High-Performance Fuel Cell Engine for Heavy-Duty Vehicles at Act Expo 2024
Zero-Emission Ship Passes Certification With Flying Colors in Japan

Johnson Matthey and Thyssenkrupp Uhde Join Forces to Offer an Integrated Solution for Blue Ammonia Technology
Author FuelCellsWorks
- Community Guidelines
- Partnerships
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
© 1999-2024 FuelCellsWorks.
All Trelleborg sites
- Group Trelleborg is a world leader in engineered polymer solutions that seal, damp and protect critical applications in demanding environments. /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/trelleborg-group.jpg?rev=b3492bd026aa498f90103f0288dfc4e6
- Antivibration Solutions Helping to remove unwanted vibration and noise in Rail, Marine, Off-highway and Industrial applications /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/antivibration.jpg?rev=cac94d89d97a4764937febb8422dbc03
- Applied Technologies Advanced engineered materials for use in applications from outer space to subsea. These consist of polyimide foam, hollow glass microspheres, PU elastomers, syntactic composite materials and much more /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/tat-megamenu-image-v2.jpg?rev=8038497803864960a89119b56f418636
- Boots Advanced dynamic protection for Automotive Driveshaft and Steering Gears /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/testing-boot-cold-1.jpg?rev=e398df5cfb7d4080a18fb803255e50bc
- Damping Solutions Automotive noise damping shims & insulators /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/damping-solutions.jpg?rev=e4886fdb3c364d319c626e35fe923d04
- Engineered Coated Fabrics Trelleborg’s Engineered Coated Fabrics business unit, a world-leading producer of specialty polymer-coated and calendared materials, operates under the Coated Systems business area. /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/engineered-coated-fabrics.jpg?rev=2fdac9be0f434313920fb532c7262a43
- Fluid Handling Solutions Industrial Hose, Expansion Joint, Oil & Marine Hose, Rubber Sheeting and Mining Applications /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/fhs.jpg?rev=6cf337a4c82642b59e004d0a9199ea15
- Medical Solutions Supporting the Healthcare and Medical industry with advanced polymer engineered components /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/healthcare-and-medical.jpg?rev=627ac8af44794afb8aa913220f959254
- Marine & Infrastructure Highly engineered polymer solutions for marine and civil infrastructure /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/marine-and-infrastructure.jpg?rev=b209d371ac264b6f85b7b8167ef0860c
- Sealing Solutions Sealing and bearing solutions for Industrial, Automotive and Aerospace applications /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/sealing-solutions.jpg?rev=158324dc66494c6a8450812cbd4a794b
- Seals & Profiles Seals for applications in buildings and construction, aerospace, automotive, agriculture, renewable energy and water infrastructure. /marine-and-infrastructure/-/media/group/site-switch/seals-and-profiles.jpg?rev=c630d927a2a9455e851bb1a4fd6da61e
- Chinese (Simplified) | 中文(简体)
A range of scalable LNG bunkering options

Shore to Ship Case Study
Lng vessel bunkering.
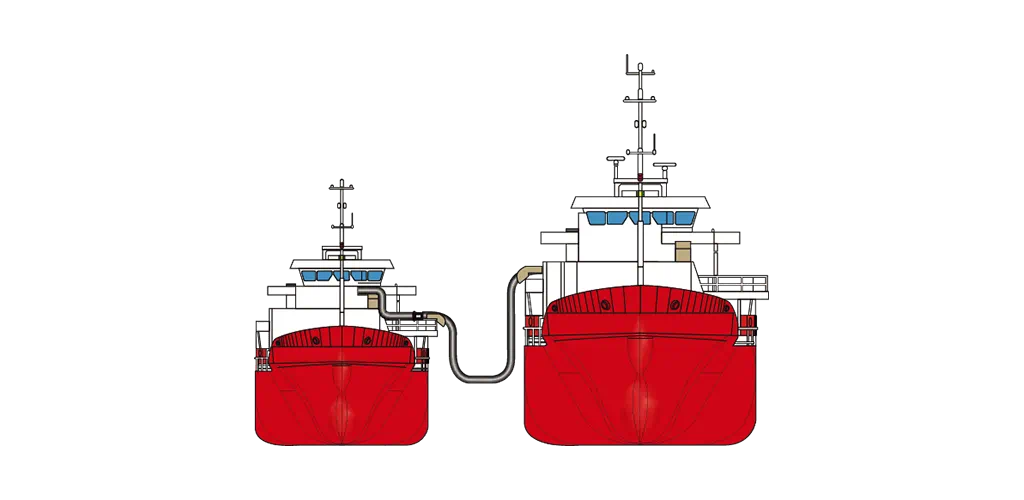
Environmental regulatory pressure is building to cut emissions caused through ship transportation. It is this imposition of stricter sulphur content limits to marine bunker fuel that is driving LNG Bunkering system design as well as the construction of a LNG fueling infrastructure. The declaration of an Emission Control Area (ECA) of 200 nautical miles around the North America coastline in 2012 is a typical development. The currently forecasted stable price of LNG and reliable supply of natural gas as a resource are also key factors as to why LNG is more than a feasible alternative to current fuels.

Safe LNG bunkering
The safe refueling of LNG powered ships and even the safe evacuation of LNG fuel from ships in an emergency is of paramount importance for the protection of LNG bunkering as a commercially viable and acceptable sector. Standards and regulations for LNG bunkering exist and are being developed by organizations such as SIGTTO (Society of International Gas Tankers and Terminal Operators), OCIMF (Oil Companies International Marine Forum), IMO (International Maritime Organization), International Organization for Standardization (ISO), EN (CEN – European Committee for Standardization) and the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association).
Emergency Shut-down Systems (ESD) for LNG Bunkering
Types of lng bunkering, how can we help.

Trelleborg Westbury Ltd
IBM Change Management Case Study
Change is a constant in the business world, and organizations that can effectively manage change are more likely to succeed.
Change management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling change within an organization to minimize negative impacts and maximize benefits.
One company that has successfully implemented change management is IBM.
With a history spanning over a century, IBM has undergone significant changes over the years, including the implementation of change management to ensure a smooth transition.
In this blog post, we will take a closer look at IBM’s change management case study, examining its background, change management strategy, and results.
Brief History and Growth of IBM
IBM, also known as International Business Machines Corporation, is an American multinational technology company that was founded in 1911.
The company was initially formed as the Computing-Tabulating-Recording Company (CTR) through the merger of four separate companies: the Tabulating Machine Company, the Computing Scale Company, the International Time Recording Company, and the Bundy Manufacturing Company.
In 1924, the company was renamed International Business Machines Corporation (IBM). IBM’s early products included tabulating machines, time clocks, and punched card equipment, which were used for data processing and information management.
Over the years, IBM has evolved into a leading provider of enterprise technology solutions, including hardware, software, and services, serving clients in over 170 countries around the world.
IBM experienced significant growth in the mid-20th century, as it became a leading provider of computers and data processing equipment.
In the 1950s, IBM introduced its first electronic computer, the IBM 701, which was followed by a series of other computer models that became increasingly advanced and sophisticated.
IBM also played a key role in the development of the personal computer, releasing its first PC in 1981, which quickly became a standard in the industry.
In the 1990s and early 2000s, IBM shifted its focus to software and services, becoming a leader in areas such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity.
Today, IBM is a major player in the technology industry, with a global workforce of over 350,000 employees and revenue exceeding $70 billion in 2020.
Key drivers of change for IBM
There were three dominant factors that created a need for IBM to implement effective change management processes to successfully navigate the challenges and opportunities it faced.
1. Technological advancement
Technological advancements have been a key driver of change in the technology industry, and IBM was no exception. In the 1980s and 1990s, IBM faced significant disruption as the market shifted from mainframe computers to personal computers, which were smaller, cheaper, and more accessible to individuals and small businesses.
This shift threatened IBM’s dominance in the computer industry, as it had built its reputation on large-scale mainframe computers. To adapt to this changing market, IBM had to shift its focus to services and software, invest in research and development to create new technologies and innovations, and develop new partnerships and alliances to expand its offerings.
Additionally, the emergence of cloud computing and artificial intelligence in the 2000s and 2010s further pushed IBM to adapt and innovate to stay ahead of the competition. These technological advancements required IBM to adopt a more agile and flexible approach to business, with a greater focus on innovation, speed, and collaboration.
2. Globalization
As IBM expanded its operations globally, it faced a range of challenges related to cultural and regulatory differences across different countries and regions. In order to effectively navigate these differences, IBM had to develop a more flexible and adaptable approach to business, one that was able to respond to local market conditions and customer needs while also maintaining a consistent global brand and corporate identity.
This required IBM to invest in building a diverse and multicultural workforce, to establish strong local partnerships and alliances, and to develop a deep understanding of local cultures, languages, and customs.
Additionally, IBM had to comply with local regulations and laws in each country it operated in, which often required significant resources and expertise to navigate. By embracing globalization and developing a more flexible and adaptable approach to business, IBM was able to successfully expand its operations globally and establish a strong global presence.
3. Market competition
IBM faced intense competition from emerging tech companies in the 1990s, particularly in the areas of personal computing and software development.
Companies like Microsoft and Intel were challenging IBM’s dominance in the industry, and IBM had to adapt quickly to remain competitive.
To address this challenge, IBM shifted its focus to services and software, investing heavily in research and development to create new products and innovations that could compete with emerging technologies.
IBM also streamlined its operations to improve efficiency and reduce costs, while exploring new markets and opportunities for growth.
This required IBM to be more agile and responsive to market conditions, and to take calculated risks in pursuing new ventures and partnerships. Ultimately, these efforts enabled IBM to remain a major player in the technology industry and to continue innovating and expanding its offerings.
Change management strategy of IBM
IBM responded to these three drivers of change in several ways, as explained below:
1. Technological advancements
To adapt to rapid technological advancements, IBM invested heavily in research and development to create new products and innovations. It also embraced emerging technologies such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence and developed new partnerships and alliances to expand its offerings.
IBM also shifted its focus to services and software, which helped it to stay competitive as the market shifted away from mainframe computers. Additionally, IBM adopted a more agile and flexible approach to business to enable it to respond quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
2. Globalization
To effectively navigate different cultural and regulatory environments, IBM invested in building a diverse and multicultural workforce, established strong local partnerships and alliances, and developed a deep understanding of local cultures, languages, and customs.
IBM also complied with local regulations and laws in each country it operated in, which required significant resources and expertise to navigate. Additionally, IBM developed a consistent global brand and corporate identity while also maintaining the flexibility to respond to local market conditions and customer needs.
3. Market competition
To remain competitive in the face of intense market competition, IBM explored new markets and product offerings while streamlining its operations to improve efficiency and reduce costs. IBM also invested heavily in research and development to create new products and innovations that could compete with emerging technologies.
IBM adopted a more agile and responsive approach to business, which enabled it to take calculated risks in pursuing new ventures and partnerships. Additionally, IBM developed a culture of innovation and collaboration to foster creativity and agility, which helped it to stay ahead of the competition.
Positive outcomes and results of IBM successful change management implementation
IBM’s successful implementation of change management led to several positive outcomes and results, including:
Increased profitability: IBM’s shift to services and software helped to increase its profitability by creating new revenue streams and reducing costs. By focusing on high-margin businesses such as consulting and software development, IBM was able to improve its financial performance and profitability.
Improved competitiveness: IBM’s investments in research and development, partnerships, and new markets helped it to remain competitive in the face of rapid technological advancements and intense market competition. By adopting an agile and responsive approach to business, IBM was able to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer needs, which helped it to stay ahead of the competition.
Enhanced customer satisfaction: IBM’s focus on innovation, collaboration, and customer service helped to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. By developing new products and services that met customer needs and expectations, and by providing excellent customer service and support, IBM was able to build strong relationships with its customers and earn their trust and loyalty.
Increased employee engagement and retention: IBM’s culture of innovation, collaboration, and diversity helped to increase employee engagement and retention. By fostering a culture of creativity and agility, and by valuing and supporting its employees, IBM was able to attract and retain top talent, which helped it to drive innovation and growth.
Strong brand reputation: IBM’s successful implementation of change management helped to strengthen its brand reputation and identity. By maintaining a consistent global brand while also remaining flexible and responsive to local market conditions and customer needs, IBM was able to build a strong and respected brand reputation that is recognized around the world.
Final Words
IBM’s successful implementation of change management serves as a powerful case study for businesses facing rapid technological advancements, intense market competition, and globalization. By adopting an agile and responsive approach to business, investing in research and development, exploring new markets and partnerships, and fostering a culture of innovation and collaboration, IBM was able to remain competitive and relevant in the technology industry.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

Crisis Communication Team and Its Role and Responsibilities

3 Cs of Change Management – Communication, Collaboration and Commitment

How to Communicate Change to Stakeholders
Making RCU safe for deep sub-millisecond response realtime applications
LinuxTM has long been used for soft realtime applications. More recent work is preparing Linux for more aggressive realtime use, with scheduling latencies in the small number of hundreds of microseconds (that is right, microseconds, not milliseconds). The current Linux 2.6 RCU implementation both helps and hurts. It helps by removing locks, thus reducing latency in general, but hurts by causing large numbers of RCU callbacks to be invoked all at once at the end of the grace period. This batching of callback invocation improves throughput, but unacceptably degrades realtime response for the more discerning realtime applications. This paper describes modifications to RCU that greatly reduce its effect on scheduling latency, without significantly degrading performance for non-realtime Linux servers. Although these modifications appear to prevent RCU from interfering with realtime scheduling, other Linux kernel components are still problematic. We are therefore working on tools to help identify the remaining problematic components and to definitively determine whether RCU is still an issue. In any case, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that anything resembling RCU has been modified to accommodate the needs of realtime applications.
Publication
- Dipankar Sarma
- Paul E. McKenney
- Computer Science
The generalized packet routing problem
Speech transformation solutions, the implications of shared data synchronization techniques on multi-core energy efficiency.
Artificial intelligence is being used in healthcare for everything from answering patient questions to assisting with surgeries and developing new pharmaceuticals.
According to Statista , the artificial intelligence (AI) healthcare market, which is valued at $11 billion in 2021, is projected to be worth $187 billion in 2030. That massive increase means we will likely continue to see considerable changes in how medical providers, hospitals, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, and others in the healthcare industry operate.
Better machine learning (ML) algorithms, more access to data, cheaper hardware, and the availability of 5G have contributed to the increasing application of AI in the healthcare industry, accelerating the pace of change. AI and ML technologies can sift through enormous volumes of health data—from health records and clinical studies to genetic information—and analyze it much faster than humans.
Healthcare organizations are using AI to improve the efficiency of all kinds of processes, from back-office tasks to patient care. The following are some examples of how AI might be used to benefit staff and patients:
- Administrative workflow: Healthcare workers spend a lot of time doing paperwork and other administrative tasks. AI and automation can help perform many of those mundane tasks, freeing up employee time for other activities and giving them more face-to-face time with patients. For example, generative AI can help clinicians with note-taking and content summarization that can help keep medical records as thoroughly as possible. AI might also help with accurate coding and sharing of information between departments and billing.
- Virtual nursing assistants: One study found that 64% of patients are comfortable with the use of AI for around-the-clock access to answers that support nurses provide. AI virtual nurse assistants—which are AI-powered chatbots, apps, or other interfaces—can be used to help answer questions about medications, forward reports to doctors or surgeons and help patients schedule a visit with a physician. These sorts of routine tasks can help take work off the hands of clinical staff, who can then spend more time directly on patient care, where human judgment and interaction matter most.
- Dosage error reduction: AI can be used to help identify errors in how a patient self-administers medication. One example comes from a study in Nature Medicine , which found that up to 70% of patients don’t take insulin as prescribed. An AI-powered tool that sits in the patient’s background (much like a wifi router) might be used to flag errors in how the patient administers an insulin pen or inhaler.
- Less invasive surgeries: AI-enabled robots might be used to work around sensitive organs and tissues to help reduce blood loss, infection risk and post-surgery pain.
- Fraud prevention: Fraud in the healthcare industry is enormous, at $380 billion/year, and raises the cost of consumers’ medical premiums and out-of-pocket expenses. Implementing AI can help recognize unusual or suspicious patterns in insurance claims, such as billing for costly services or procedures that are not performed, unbundling (which is billing for the individual steps of a procedure as though they were separate procedures), and performing unnecessary tests to take advantage of insurance payments.
A recent study found that 83% of patients report poor communication as the worst part of their experience, demonstrating a strong need for clearer communication between patients and providers. AI technologies like natural language processing (NLP), predictive analytics, and speech recognition might help healthcare providers have more effective communication with patients. AI might, for instance, deliver more specific information about a patient’s treatment options, allowing the healthcare provider to have more meaningful conversations with the patient for shared decision-making.
According to Harvard’s School of Public Health , although it’s early days for this use, using AI to make diagnoses may reduce treatment costs by up to 50% and improve health outcomes by 40%.
One use case example is out of the University of Hawaii , where a research team found that deploying deep learning AI technology can improve breast cancer risk prediction. More research is needed, but the lead researcher pointed out that an AI algorithm can be trained on a much larger set of images than a radiologist—as many as a million or more radiology images. Also, that algorithm can be replicated at no cost except for hardware.
An MIT group developed an ML algorithm to determine when a human expert is needed. In some instances, such as identifying cardiomegaly in chest X-rays, they found that a hybrid human-AI model produced the best results.
Another published study found that AI recognized skin cancer better than experienced doctors. US, German and French researchers used deep learning on more than 100,000 images to identify skin cancer. Comparing the results of AI to those of 58 international dermatologists, they found AI did better.
As health and fitness monitors become more popular and more people use apps that track and analyze details about their health. They can share these real-time data sets with their doctors to monitor health issues and provide alerts in case of problems.
AI solutions—such as big data applications, machine learning algorithms and deep learning algorithms—might also be used to help humans analyze large data sets to help clinical and other decision-making. AI might also be used to help detect and track infectious diseases, such as COVID-19, tuberculosis, and malaria.
One benefit the use of AI brings to health systems is making gathering and sharing information easier. AI can help providers keep track of patient data more efficiently.
One example is diabetes. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , 10% of the US population has diabetes. Patients can now use wearable and other monitoring devices that provide feedback about their glucose levels to themselves and their medical team. AI can help providers gather that information, store, and analyze it, and provide data-driven insights from vast numbers of people. Using this information can help healthcare professionals determine how to better treat and manage diseases.
Organizations are also starting to use AI to help improve drug safety. The company SELTA SQUARE, for example, is innovating the pharmacovigilance (PV) process , a legally mandated discipline for detecting and reporting adverse effects from drugs, then assessing, understanding, and preventing those effects. PV demands significant effort and diligence from pharma producers because it’s performed from the clinical trials phase all the way through the drug’s lifetime availability. Selta Square uses a combination of AI and automation to make the PV process faster and more accurate, which helps make medicines safer for people worldwide.
Sometimes, AI might reduce the need to test potential drug compounds physically, which is an enormous cost-savings. High-fidelity molecular simulations can run on computers without incurring the high costs of traditional discovery methods.
AI also has the potential to help humans predict toxicity, bioactivity, and other characteristics of molecules or create previously unknown drug molecules from scratch.
As AI becomes more important in healthcare delivery and more AI medical applications are developed, ethical, and regulatory governance must be established. Issues that raise concern include the possibility of bias, lack of transparency, privacy concerns regarding data used for training AI models, and safety and liability issues.
“AI governance is necessary, especially for clinical applications of the technology,” said Laura Craft, VP Analyst at Gartner . “However, because new AI techniques are largely new territory for most [health delivery organizations], there is a lack of common rules, processes, and guidelines for eager entrepreneurs to follow as they design their pilots.”
The World Health Organization (WHO) spent 18 months deliberating with leading experts in ethics, digital technology, law, and human rights and various Ministries of Health members to produce a report that is called Ethics & Governance of Artificial Intelligence for Health . This report identifies ethical challenges to using AI in healthcare, identifies risks, and outlines six consensus principles to ensure AI works for the public’s benefit:
- Protecting autonomy
- Promoting human safety and well-being
- Ensuring transparency
- Fostering accountability
- Ensuring equity
- Promoting tools that are responsive and sustainable
The WHO report also provides recommendations that ensure governing AI for healthcare both maximizes the technology’s promise and holds healthcare workers accountable and responsive to the communities and people they work with.
AI provides opportunities to help reduce human error, assist medical professionals and staff, and provide patient services 24/7. As AI tools continue to develop, there is potential to use AI even more in reading medical images, X-rays and scans, diagnosing medical problems and creating treatment plans.
AI applications continue to help streamline various tasks, from answering phones to analyzing population health trends (and likely, applications yet to be considered). For instance, future AI tools may automate or augment more of the work of clinicians and staff members. That will free up humans to spend more time on more effective and compassionate face-to-face professional care.
When patients need help, they don’t want to (or can’t) wait on hold. Healthcare facilities’ resources are finite, so help isn’t always available instantaneously or 24/7—and even slight delays can create frustration and feelings of isolation or cause certain conditions to worsen.
IBM® watsonx Assistant™ AI healthcare chatbots can help providers do two things: keep their time focused where it needs to be and empower patients who call in to get quick answers to simple questions.
IBM watsonx Assistant is built on deep learning, machine learning and natural language processing (NLP) models to understand questions, search for the best answers and complete transactions by using conversational AI.
Get email updates about AI advancements, strategies, how-tos, expert perspective and more.
See IBM watsonx Assistant in action and request a demo
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
case studies. JSR Watch the case study. Charting a new future for the global semiconductor industry. Read the story. Boeing ... Technology IBM Quantum Safe IBM Quantum Network Research. Get access. Pricing IBM Quantum Platform. Get started. Qiskit Documentation Learning. Stay connected. Blog LinkedIn YouTube Community Careers.
Read the complete Boeing case study, here. Boeing manufactures the 787 Dreamliner, an aircraft made using advanced materials known as ply composites. Ply composites are lightweight, safe, and strong, enabling these jets to fly further and consume less fuel.
A leading Australian natural gas producer, Woodside (link resides outside of ibm.com) is headquartered in Perth, Australia, and was incorporated in 1954. The company is a pioneer in the liquified natural gas (LNG) industry and is recognized for its capabilities as an integrated upstream energy supplier.
ExxonMobil, one of the world's largest publicly traded energy providers and chemical manufacturers, develops and applies next-generation technologies to help safely and responsibly meet the world's growing needs for energy and high-quality chemical products. About IBM Quantum Network. IBM Quantum Network is a community of Fortune 500 ...
ARMONK, N.Y., Sept. 6, 2019 / PRNewswire / -- In the next three years, as many as 120 million workers in the world's 12 largest economies may need to be retrained or reskilled as a result of AI and intelligent automation, according to a new IBM (NYSE: IBM) Institute for Business Value (IBV) study. In addition, only 41 percent of CEOs surveyed ...
Energy and resources enterprises are modernizing with the help of digital transformation. Hybrid cloud is a key enabler. Industry leaders are taking an innovative approach to customer experience to reduce service delivery costs and drive revenue growth. IBM oil and gas technology solutions help companies redefine how to create and deliver energy.
The World Economic Forum Responsible Use of Technology project aims to provide practical resources for organizations to operationalize ethics in their use of technology. This White Paper is the second in a series that highlights processes, tools and organizational constructs that facilitate the responsible design, development and implementation ...
The study found that surveyed consumers' actions are starting to match their intent. Back in 2021, half of respondents said they were willing to pay a premium for a sustainable brand or products. And this year, almost the same percentage (49%) of respondents say they did pay more—an average of 59% more—for products branded as sustainable or ...
Responsible Use of Technology: - World Economic Forum
Method: In this paper, we use a case study to validate the viability of 7E. Our software under study is the IBM Db2 database system. We upgrade the current cryptographic schemes to post-quantum cryptographic ones (using Kyber and Dilithium schemes) and report our findings and lessons learned.
Your Learning is widely used by IBM employees. According to the organization's internal report, in 2019, 336,000 IBM employees, accounting for 99% of the entire workforce, visited Your Learning, with a record of 9.1M visits. In quarter 1 of 2020 alone, 89% of IBM employees visited Your Learning, with 1.9 million visits and 14.1 million page ...
ZURICH, Switzerland, Nov. 28, 2023 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- IBM and FuelCell Energy, Inc. (Nasdaq: FCEL) today announced they will work together to boost the performance of FuelCell Energy's ...
The 168-page tome written by over 70 professionals in every industry, clearly lays out the appropriate problems, the approaches to solutions, and the amazing technology being invented as we speak ...
By implementing SAFe, IBM was able to reduce release cycles from 12 months to 3 months, improve team coordination, and increase transparency into the development process. They achieved a 50% reduction in time-to-market and a 40% increase in productivity. ... In conclusion, the case studies of Intel, Philips, and IBM demonstrate the benefits of ...
LONDON, Nov. 8, 2023 / PRNewswire / -- Today, IBM (NYSE: IBM) has launched its new report ' Leadership in the Age of AI .'. Based on a survey of 1,600+ senior leaders and C-Suite executives across the UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy and Sweden, the report explores how leadership is transforming as the region's businesses embrace generative AI ...
ZURICH- IBM and FuelCell Energy, Inc. (Nasdaq: FCEL) today announced they will work together to boost the performance of FuelCell Energy's technology using Foundation Models, a form of generative Artificial Intelligence (AI). The aim of this collaboration is to support both companies' efforts to lead a global transition to renewable ...
While leveraging 7E, we conducted a case study to make IBM Db2 database management software quantum-safe. As a result, we validated the 7E roadmap throughout the project. Moreover, we pinpointed operational details needed to execute 7E, recorded lessons learned, delivered takeaway messages, and proposed an enhanced 7E for practitioners so that ...
IBM Cloud Satellite® lets you deploy and run apps consistently across on-premises, edge computing and public cloud environments on a 5G network. And it's all enabled by secure and auditable communications within the IBM Cloud®. A look at the applications and use cases that 5G is enabling to transform the world.
Packaging Manufacturing Mondi Group Lays the foundation for packaging efficiency by using data to steer global operations with IBM and SAP. Read the case study Industrial Products Grupo Zapata . Grupo Zapata uses SAP S/4HANA® on IBM Power® Systems servers and IBM Storage FlashSystem to make data-driven decisions, helping to minimize materials costs and maximize profitability
The solution's IBM Cloud public hosting platform reduces operating costs for the app by 40 percent and scales effortlessly as its user base continues to grow. Read the case study LogDNA. LogDNA saw a clear need to address data sprawl in the modern, cloud-native development stack. Its innovative software-as-a-service (SaaS) platform built on ...
LNG Bunkering is the practice of providing liquefied natural gas fuel to a ship for its own consumption. The key advantage of LNG as a fuel is the vast reduction in pollutant caused by the more traditional method of fueling ships such as heavy fuel oil, marine diesel fuel (MDO) and marine gas oil (MGO). Environmental regulatory pressure is ...
IBM Change Management Case Study. Tahir Abbas March 5, 2023. Change is a constant in the business world, and organizations that can effectively manage change are more likely to succeed. Change management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling change within an organization to minimize negative impacts and maximize benefits.
Making RCU safe for deep sub-millisecond response realtime applications for USENIX ATC 2004 by Dipankar Sarma et al. ... IBM-affiliated at time of publication. Topics. ... Share. Related. Paper. A case study in programming for parallel-processors. Jack L. Rosenfeld. CACM. Talk. Anchoring Trust in a Totally Open Platform. Elaine Palmer, George ...
A recent study found that 83% of patients report poor communication as the worst part of their experience, demonstrating a strong need for clearer communication between patients and providers. AI technologies like natural language processing (NLP), predictive analytics, and speech recognition might help healthcare providers have more effective communication with patients.