
Work Life is Atlassian’s flagship publication dedicated to unleashing the potential of every team through real-life advice, inspiring stories, and thoughtful perspectives from leaders around the world.

Contributing Writer
Work Futurist

Senior Quantitative Researcher, People Insights
Principal Writer


How to build critical thinking skills for better decision-making
It’s simple in theory, but tougher in practice – here are five tips to get you started.
Get stories like this in your inbox
Have you heard the riddle about two coins that equal thirty cents, but one of them is not a nickel? What about the one where a surgeon says they can’t operate on their own son?
Those brain teasers tap into your critical thinking skills. But your ability to think critically isn’t just helpful for solving those random puzzles – it plays a big role in your career.
An impressive 81% of employers say critical thinking carries a lot of weight when they’re evaluating job candidates. It ranks as the top competency companies consider when hiring recent graduates (even ahead of communication ). Plus, once you’re hired, several studies show that critical thinking skills are highly correlated with better job performance.
So what exactly are critical thinking skills? And even more importantly, how do you build and improve them?
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to evaluate facts and information, remain objective, and make a sound decision about how to move forward.
Does that sound like how you approach every decision or problem? Not so fast. Critical thinking seems simple in theory but is much tougher in practice, which helps explain why 65% of employers say their organization has a need for more critical thinking.
In reality, critical thinking doesn’t come naturally to a lot of us. In order to do it well, you need to:
- Remain open-minded and inquisitive, rather than relying on assumptions or jumping to conclusions
- Ask questions and dig deep, rather than accepting information at face value
- Keep your own biases and perceptions in check to stay as objective as possible
- Rely on your emotional intelligence to fill in the blanks and gain a more well-rounded understanding of a situation
So, critical thinking isn’t just being intelligent or analytical. In many ways, it requires you to step outside of yourself, let go of your own preconceived notions, and approach a problem or situation with curiosity and fairness.
It’s a challenge, but it’s well worth it. Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems.
7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper
Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you’ll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it’s better to think of critical thinking less as a distinct skill and more as a collection or category of skills.
To think critically, you’ll need to tap into a bunch of your other soft skills. Here are seven of the most important.
Open-mindedness
It’s important to kick off the critical thinking process with the idea that anything is possible. The more you’re able to set aside your own suspicions, beliefs, and agenda, the better prepared you are to approach the situation with the level of inquisitiveness you need.
That means not closing yourself off to any possibilities and allowing yourself the space to pull on every thread – yes, even the ones that seem totally implausible.
As Christopher Dwyer, Ph.D. writes in a piece for Psychology Today , “Even if an idea appears foolish, sometimes its consideration can lead to an intelligent, critically considered conclusion.” He goes on to compare the critical thinking process to brainstorming . Sometimes the “bad” ideas are what lay the foundation for the good ones.
Open-mindedness is challenging because it requires more effort and mental bandwidth than sticking with your own perceptions. Approaching problems or situations with true impartiality often means:
- Practicing self-regulation : Giving yourself a pause between when you feel something and when you actually react or take action.
- Challenging your own biases: Acknowledging your biases and seeking feedback are two powerful ways to get a broader understanding.
Critical thinking example
In a team meeting, your boss mentioned that your company newsletter signups have been decreasing and she wants to figure out why.
At first, you feel offended and defensive – it feels like she’s blaming you for the dip in subscribers. You recognize and rationalize that emotion before thinking about potential causes. You have a hunch about what’s happening, but you will explore all possibilities and contributions from your team members.
Observation
Observation is, of course, your ability to notice and process the details all around you (even the subtle or seemingly inconsequential ones). Critical thinking demands that you’re flexible and willing to go beyond surface-level information, and solid observation skills help you do that.
Your observations help you pick up on clues from a variety of sources and experiences, all of which help you draw a final conclusion. After all, sometimes it’s the most minuscule realization that leads you to the strongest conclusion.
Over the next week or so, you keep a close eye on your company’s website and newsletter analytics to see if numbers are in fact declining or if your boss’s concerns were just a fluke.
Critical thinking hinges on objectivity. And, to be objective, you need to base your judgments on the facts – which you collect through research. You’ll lean on your research skills to gather as much information as possible that’s relevant to your problem or situation.
Keep in mind that this isn’t just about the quantity of information – quality matters too. You want to find data and details from a variety of trusted sources to drill past the surface and build a deeper understanding of what’s happening.
You dig into your email and website analytics to identify trends in bounce rates, time on page, conversions, and more. You also review recent newsletters and email promotions to understand what customers have received, look through current customer feedback, and connect with your customer support team to learn what they’re hearing in their conversations with customers.
The critical thinking process is sort of like a treasure hunt – you’ll find some nuggets that are fundamental for your final conclusion and some that might be interesting but aren’t pertinent to the problem at hand.
That’s why you need analytical skills. They’re what help you separate the wheat from the chaff, prioritize information, identify trends or themes, and draw conclusions based on the most relevant and influential facts.
It’s easy to confuse analytical thinking with critical thinking itself, and it’s true there is a lot of overlap between the two. But analytical thinking is just a piece of critical thinking. It focuses strictly on the facts and data, while critical thinking incorporates other factors like emotions, opinions, and experiences.
As you analyze your research, you notice that one specific webpage has contributed to a significant decline in newsletter signups. While all of the other sources have stayed fairly steady with regard to conversions, that one has sharply decreased.
You decide to move on from your other hypotheses about newsletter quality and dig deeper into the analytics.
One of the traps of critical thinking is that it’s easy to feel like you’re never done. There’s always more information you could collect and more rabbit holes you could fall down.
But at some point, you need to accept that you’ve done your due diligence and make a decision about how to move forward. That’s where inference comes in. It’s your ability to look at the evidence and facts available to you and draw an informed conclusion based on those.
When you’re so focused on staying objective and pursuing all possibilities, inference can feel like the antithesis of critical thinking. But ultimately, it’s your inference skills that allow you to move out of the thinking process and onto the action steps.
You dig deeper into the analytics for the page that hasn’t been converting and notice that the sharp drop-off happened around the same time you switched email providers.
After looking more into the backend, you realize that the signup form on that page isn’t correctly connected to your newsletter platform. It seems like anybody who has signed up on that page hasn’t been fed to your email list.
Communication

3 ways to improve your communication skills at work
If and when you identify a solution or answer, you can’t keep it close to the vest. You’ll need to use your communication skills to share your findings with the relevant stakeholders – like your boss, team members, or anybody who needs to be involved in the next steps.
Your analysis skills will come in handy here too, as they’ll help you determine what information other people need to know so you can avoid bogging them down with unnecessary details.
In your next team meeting, you pull up the analytics and show your team the sharp drop-off as well as the missing connection between that page and your email platform. You ask the web team to reinstall and double-check that connection and you also ask a member of the marketing team to draft an apology email to the subscribers who were missed.
Problem-solving
Critical thinking and problem-solving are two more terms that are frequently confused. After all, when you think critically, you’re often doing so with the objective of solving a problem.
The best way to understand how problem-solving and critical thinking differ is to think of problem-solving as much more narrow. You’re focused on finding a solution.
In contrast, you can use critical thinking for a variety of use cases beyond solving a problem – like answering questions or identifying opportunities for improvement. Even so, within the critical thinking process, you’ll flex your problem-solving skills when it comes time to take action.
Once the fix is implemented, you monitor the analytics to see if subscribers continue to increase. If not (or if they increase at a slower rate than you anticipated), you’ll roll out some other tests like changing the CTA language or the placement of the subscribe form on the page.
5 ways to improve your critical thinking skills

Beyond the buzzwords: Why interpersonal skills matter at work
Think critically about critical thinking and you’ll quickly realize that it’s not as instinctive as you’d like it to be. Fortunately, your critical thinking skills are learned competencies and not inherent gifts – and that means you can improve them. Here’s how:
- Practice active listening: Active listening helps you process and understand what other people share. That’s crucial as you aim to be open-minded and inquisitive.
- Ask open-ended questions: If your critical thinking process involves collecting feedback and opinions from others, ask open-ended questions (meaning, questions that can’t be answered with “yes” or “no”). Doing so will give you more valuable information and also prevent your own biases from influencing people’s input.
- Scrutinize your sources: Figuring out what to trust and prioritize is crucial for critical thinking. Boosting your media literacy and asking more questions will help you be more discerning about what to factor in. It’s hard to strike a balance between skepticism and open-mindedness, but approaching information with questions (rather than unquestioning trust) will help you draw better conclusions.
- Play a game: Remember those riddles we mentioned at the beginning? As trivial as they might seem, games and exercises like those can help you boost your critical thinking skills. There are plenty of critical thinking exercises you can do individually or as a team .
- Give yourself time: Research shows that rushed decisions are often regrettable ones. That’s likely because critical thinking takes time – you can’t do it under the wire. So, for big decisions or hairy problems, give yourself enough time and breathing room to work through the process. It’s hard enough to think critically without a countdown ticking in your brain.
Critical thinking really is critical
The ability to think critically is important, but it doesn’t come naturally to most of us. It’s just easier to stick with biases, assumptions, and surface-level information.
But that route often leads you to rash judgments, shaky conclusions, and disappointing decisions. So here’s a conclusion we can draw without any more noodling: Even if it is more demanding on your mental resources, critical thinking is well worth the effort.
Advice, stories, and expertise about work life today.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
Critical Thinking
Developing the right mindset and skills.
By the Mind Tools Content Team
We make hundreds of decisions every day and, whether we realize it or not, we're all critical thinkers.
We use critical thinking each time we weigh up our options, prioritize our responsibilities, or think about the likely effects of our actions. It's a crucial skill that helps us to cut out misinformation and make wise decisions. The trouble is, we're not always very good at it!
In this article, we'll explore the key skills that you need to develop your critical thinking skills, and how to adopt a critical thinking mindset, so that you can make well-informed decisions.
What Is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well.
Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly valued asset in the workplace. People who score highly in critical thinking assessments are also rated by their managers as having good problem-solving skills, creativity, strong decision-making skills, and good overall performance. [1]
Key Critical Thinking Skills
Critical thinkers possess a set of key characteristics which help them to question information and their own thinking. Focus on the following areas to develop your critical thinking skills:
Being willing and able to explore alternative approaches and experimental ideas is crucial. Can you think through "what if" scenarios, create plausible options, and test out your theories? If not, you'll tend to write off ideas and options too soon, so you may miss the best answer to your situation.
To nurture your curiosity, stay up to date with facts and trends. You'll overlook important information if you allow yourself to become "blinkered," so always be open to new information.
But don't stop there! Look for opposing views or evidence to challenge your information, and seek clarification when things are unclear. This will help you to reassess your beliefs and make a well-informed decision later. Read our article, Opening Closed Minds , for more ways to stay receptive.
Logical Thinking
You must be skilled at reasoning and extending logic to come up with plausible options or outcomes.
It's also important to emphasize logic over emotion. Emotion can be motivating but it can also lead you to take hasty and unwise action, so control your emotions and be cautious in your judgments. Know when a conclusion is "fact" and when it is not. "Could-be-true" conclusions are based on assumptions and must be tested further. Read our article, Logical Fallacies , for help with this.
Use creative problem solving to balance cold logic. By thinking outside of the box you can identify new possible outcomes by using pieces of information that you already have.
Self-Awareness
Many of the decisions we make in life are subtly informed by our values and beliefs. These influences are called cognitive biases and it can be difficult to identify them in ourselves because they're often subconscious.
Practicing self-awareness will allow you to reflect on the beliefs you have and the choices you make. You'll then be better equipped to challenge your own thinking and make improved, unbiased decisions.
One particularly useful tool for critical thinking is the Ladder of Inference . It allows you to test and validate your thinking process, rather than jumping to poorly supported conclusions.
Developing a Critical Thinking Mindset
Combine the above skills with the right mindset so that you can make better decisions and adopt more effective courses of action. You can develop your critical thinking mindset by following this process:
Gather Information
First, collect data, opinions and facts on the issue that you need to solve. Draw on what you already know, and turn to new sources of information to help inform your understanding. Consider what gaps there are in your knowledge and seek to fill them. And look for information that challenges your assumptions and beliefs.
Be sure to verify the authority and authenticity of your sources. Not everything you read is true! Use this checklist to ensure that your information is valid:
- Are your information sources trustworthy ? (For example, well-respected authors, trusted colleagues or peers, recognized industry publications, websites, blogs, etc.)
- Is the information you have gathered up to date ?
- Has the information received any direct criticism ?
- Does the information have any errors or inaccuracies ?
- Is there any evidence to support or corroborate the information you have gathered?
- Is the information you have gathered subjective or biased in any way? (For example, is it based on opinion, rather than fact? Is any of the information you have gathered designed to promote a particular service or organization?)
If any information appears to be irrelevant or invalid, don't include it in your decision making. But don't omit information just because you disagree with it, or your final decision will be flawed and bias.
Now observe the information you have gathered, and interpret it. What are the key findings and main takeaways? What does the evidence point to? Start to build one or two possible arguments based on what you have found.
You'll need to look for the details within the mass of information, so use your powers of observation to identify any patterns or similarities. You can then analyze and extend these trends to make sensible predictions about the future.
To help you to sift through the multiple ideas and theories, it can be useful to group and order items according to their characteristics. From here, you can compare and contrast the different items. And once you've determined how similar or different things are from one another, Paired Comparison Analysis can help you to analyze them.
The final step involves challenging the information and rationalizing its arguments.
Apply the laws of reason (induction, deduction, analogy) to judge an argument and determine its merits. To do this, it's essential that you can determine the significance and validity of an argument to put it in the correct perspective. Take a look at our article, Rational Thinking , for more information about how to do this.
Once you have considered all of the arguments and options rationally, you can finally make an informed decision.
Afterward, take time to reflect on what you have learned and what you found challenging. Step back from the detail of your decision or problem, and look at the bigger picture. Record what you've learned from your observations and experience.
Critical thinking involves rigorously and skilfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions and beliefs. It's a useful skill in the workplace and in life.
You'll need to be curious and creative to explore alternative possibilities, but rational to apply logic, and self-aware to identify when your beliefs could affect your decisions or actions.
You can demonstrate a high level of critical thinking by validating your information, analyzing its meaning, and finally evaluating the argument.
Critical Thinking Infographic
See Critical Thinking represented in our infographic: An Elementary Guide to Critical Thinking .

You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
How to write a business case.
Getting Approval and Funding for Your Project
How to Reboot Your Career Video
Video Transcript
Add comment
Comments (1)
priyanka ghogare

Try Mind Tools for FREE
Get unlimited access to all our career-boosting content and member benefits with our 7-day free trial.
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Newest Releases

Team Briefings

Onboarding With STEPS
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
New pain points podcast - perfectionism.
Why Am I Such a Perfectionist?
Pain Points Podcast - Building Trust
Developing and Strengthening Trust at Work
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Communicate like a leader.
Dianna Booher
Expert Interviews
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Study Skills
- Critical Thinking
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Top Tips for Study
- Staying Motivated When Studying
- Student Budgeting and Economic Skills
- Getting Organised for Study
- Finding Time to Study
- Sources of Information
- Assessing Internet Information
- Using Apps to Support Study
- What is Theory?
- Styles of Writing
- Effective Reading
- Critical Reading
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Planning an Essay
- How to Write an Essay
- The Do’s and Don’ts of Essay Writing
- How to Write a Report
- Academic Referencing
- Assignment Finishing Touches
- Reflecting on Marked Work
- 6 Skills You Learn in School That You Use in Real Life
- Top 10 Tips on How to Study While Working
- Exam Skills
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to think clearly and rationally, understanding the logical connection between ideas. Critical thinking has been the subject of much debate and thought since the time of early Greek philosophers such as Plato and Socrates and has continued to be a subject of discussion into the modern age, for example the ability to recognise fake news .
Critical thinking might be described as the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking.
In essence, critical thinking requires you to use your ability to reason. It is about being an active learner rather than a passive recipient of information.
Critical thinkers rigorously question ideas and assumptions rather than accepting them at face value. They will always seek to determine whether the ideas, arguments and findings represent the entire picture and are open to finding that they do not.
Critical thinkers will identify, analyse and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct.
Someone with critical thinking skills can:
Understand the links between ideas.
Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas.
Recognise, build and appraise arguments.
Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
Approach problems in a consistent and systematic way.
Reflect on the justification of their own assumptions, beliefs and values.
Critical thinking is thinking about things in certain ways so as to arrive at the best possible solution in the circumstances that the thinker is aware of. In more everyday language, it is a way of thinking about whatever is presently occupying your mind so that you come to the best possible conclusion.
Critical Thinking is:
A way of thinking about particular things at a particular time; it is not the accumulation of facts and knowledge or something that you can learn once and then use in that form forever, such as the nine times table you learn and use in school.
The Skills We Need for Critical Thinking
The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making.
Specifically we need to be able to:
Think about a topic or issue in an objective and critical way.
Identify the different arguments there are in relation to a particular issue.
Evaluate a point of view to determine how strong or valid it is.
Recognise any weaknesses or negative points that there are in the evidence or argument.
Notice what implications there might be behind a statement or argument.
Provide structured reasoning and support for an argument that we wish to make.
The Critical Thinking Process
You should be aware that none of us think critically all the time.
Sometimes we think in almost any way but critically, for example when our self-control is affected by anger, grief or joy or when we are feeling just plain ‘bloody minded’.
On the other hand, the good news is that, since our critical thinking ability varies according to our current mindset, most of the time we can learn to improve our critical thinking ability by developing certain routine activities and applying them to all problems that present themselves.
Once you understand the theory of critical thinking, improving your critical thinking skills takes persistence and practice.
Try this simple exercise to help you to start thinking critically.
Think of something that someone has recently told you. Then ask yourself the following questions:
Who said it?
Someone you know? Someone in a position of authority or power? Does it matter who told you this?
What did they say?
Did they give facts or opinions? Did they provide all the facts? Did they leave anything out?
Where did they say it?
Was it in public or in private? Did other people have a chance to respond an provide an alternative account?
When did they say it?
Was it before, during or after an important event? Is timing important?
Why did they say it?
Did they explain the reasoning behind their opinion? Were they trying to make someone look good or bad?
How did they say it?
Were they happy or sad, angry or indifferent? Did they write it or say it? Could you understand what was said?
What are you Aiming to Achieve?
One of the most important aspects of critical thinking is to decide what you are aiming to achieve and then make a decision based on a range of possibilities.
Once you have clarified that aim for yourself you should use it as the starting point in all future situations requiring thought and, possibly, further decision making. Where needed, make your workmates, family or those around you aware of your intention to pursue this goal. You must then discipline yourself to keep on track until changing circumstances mean you have to revisit the start of the decision making process.
However, there are things that get in the way of simple decision making. We all carry with us a range of likes and dislikes, learnt behaviours and personal preferences developed throughout our lives; they are the hallmarks of being human. A major contribution to ensuring we think critically is to be aware of these personal characteristics, preferences and biases and make allowance for them when considering possible next steps, whether they are at the pre-action consideration stage or as part of a rethink caused by unexpected or unforeseen impediments to continued progress.
The more clearly we are aware of ourselves, our strengths and weaknesses, the more likely our critical thinking will be productive.
The Benefit of Foresight
Perhaps the most important element of thinking critically is foresight.
Almost all decisions we make and implement don’t prove disastrous if we find reasons to abandon them. However, our decision making will be infinitely better and more likely to lead to success if, when we reach a tentative conclusion, we pause and consider the impact on the people and activities around us.
The elements needing consideration are generally numerous and varied. In many cases, consideration of one element from a different perspective will reveal potential dangers in pursuing our decision.
For instance, moving a business activity to a new location may improve potential output considerably but it may also lead to the loss of skilled workers if the distance moved is too great. Which of these is the more important consideration? Is there some way of lessening the conflict?
These are the sort of problems that may arise from incomplete critical thinking, a demonstration perhaps of the critical importance of good critical thinking.
Further Reading from Skills You Need

The Skills You Need Guide for Students

Develop the skills you need to make the most of your time as a student.
Our eBooks are ideal for students at all stages of education, school, college and university. They are full of easy-to-follow practical information that will help you to learn more effectively and get better grades.
In Summary:
Critical thinking is aimed at achieving the best possible outcomes in any situation. In order to achieve this it must involve gathering and evaluating information from as many different sources possible.
Critical thinking requires a clear, often uncomfortable, assessment of your personal strengths, weaknesses and preferences and their possible impact on decisions you may make.
Critical thinking requires the development and use of foresight as far as this is possible. As Doris Day sang, “the future’s not ours to see”.
Implementing the decisions made arising from critical thinking must take into account an assessment of possible outcomes and ways of avoiding potentially negative outcomes, or at least lessening their impact.
- Critical thinking involves reviewing the results of the application of decisions made and implementing change where possible.
It might be thought that we are overextending our demands on critical thinking in expecting that it can help to construct focused meaning rather than examining the information given and the knowledge we have acquired to see if we can, if necessary, construct a meaning that will be acceptable and useful.
After all, almost no information we have available to us, either externally or internally, carries any guarantee of its life or appropriateness. Neat step-by-step instructions may provide some sort of trellis on which our basic understanding of critical thinking can blossom but it doesn’t and cannot provide any assurance of certainty, utility or longevity.
Continue to: Critical Thinking and Fake News Critical Reading
See also: Analytical Skills Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories Introduction to Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP)
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Discover how today’s most successful IT leaders stand out from the rest. .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Read the report .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Collaboration |
- How to build your critical thinking ski ...
How to build your critical thinking skills in 7 steps (with examples)

Critical thinking is, well, critical. By building these skills, you improve your ability to analyze information and come to the best decision possible. In this article, we cover the basics of critical thinking, as well as the seven steps you can use to implement the full critical thinking process.
Critical thinking comes from asking the right questions to come to the best conclusion possible. Strong critical thinkers analyze information from a variety of viewpoints in order to identify the best course of action.
Don’t worry if you don’t think you have strong critical thinking abilities. In this article, we’ll help you build a foundation for critical thinking so you can absorb, analyze, and make informed decisions.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is the ability to collect and analyze information to come to a conclusion. Being able to think critically is important in virtually every industry and applicable across a wide range of positions. That’s because critical thinking isn’t subject-specific—rather, it’s your ability to parse through information, data, statistics, and other details in order to identify a satisfactory solution.
Decision-making tools for agile businesses
In this ebook, learn how to equip employees to make better decisions—so your business can pivot, adapt, and tackle challenges more effectively than your competition.

Top 8 critical thinking skills
Like most soft skills, critical thinking isn’t something you can take a class to learn. Rather, this skill consists of a variety of interpersonal and analytical skills. Developing critical thinking is more about learning to embrace open-mindedness and bringing analytical thinking to your problem framing process.
In no particular order, the eight most important critical thinking skills are:
Analytical thinking: Part of critical thinking is evaluating data from multiple sources in order to come to the best conclusions. Analytical thinking allows people to reject bias and strive to gather and consume information to come to the best conclusion.
Open-mindedness: This critical thinking skill helps you analyze and process information to come to an unbiased conclusion. Part of the critical thinking process is letting your personal biases go and coming to a conclusion based on all of the information.
Problem solving : Because critical thinking emphasizes coming to the best conclusion based on all of the available information, it’s a key part of problem solving. When used correctly, critical thinking helps you solve any problem—from a workplace challenge to difficulties in everyday life.
Self-regulation: Self-regulation refers to the ability to regulate your thoughts and set aside any personal biases to come to the best conclusion. In order to be an effective critical thinker, you need to question the information you have and the decisions you favor—only then can you come to the best conclusion.
Observation: Observation skills help critical thinkers look for things beyond face value. To be a critical thinker you need to embrace multiple points of view, and you can use observation skills to identify potential problems.
Interpretation: Not all data is made equal—and critical thinkers know this. In addition to gathering information, it’s important to evaluate which information is important and relevant to your situation. That way, you can draw the best conclusions from the data you’ve collected.
Evaluation: When you attempt to answer a hard question, there is rarely an obvious answer. Even though critical thinking emphasizes putting your biases aside, you need to be able to confidently make a decision based on the data you have available.
Communication: Once a decision has been made, you also need to share this decision with other stakeholders. Effective workplace communication includes presenting evidence and supporting your conclusion—especially if there are a variety of different possible solutions.
7 steps to critical thinking
Critical thinking is a skill that you can build by following these seven steps. The seven steps to critical thinking help you ensure you’re approaching a problem from the right angle, considering every alternative, and coming to an unbiased conclusion.
First things first: When to use the 7 step critical thinking process
There’s a lot that goes into the full critical thinking process, and not every decision needs to be this thought out. Sometimes, it’s enough to put aside bias and approach a process logically. In other, more complex cases, the best way to identify the ideal outcome is to go through the entire critical thinking process.
The seven-step critical thinking process is useful for complex decisions in areas you are less familiar with. Alternatively, the seven critical thinking steps can help you look at a problem you’re familiar with from a different angle, without any bias.
If you need to make a less complex decision, consider another problem solving strategy instead. Decision matrices are a great way to identify the best option between different choices. Check out our article on 7 steps to creating a decision matrix .
1. Identify the problem
Before you put those critical thinking skills to work, you first need to identify the problem you’re solving. This step includes taking a look at the problem from a few different perspectives and asking questions like:
What’s happening?
Why is this happening?
What assumptions am I making?
At first glance, how do I think we can solve this problem?
A big part of developing your critical thinking skills is learning how to come to unbiased conclusions. In order to do that, you first need to acknowledge the biases that you currently have. Does someone on your team think they know the answer? Are you making assumptions that aren’t necessarily true? Identifying these details helps you later on in the process.
2. Research
At this point, you likely have a general idea of the problem—but in order to come up with the best solution, you need to dig deeper.
During the research process, collect information relating to the problem, including data, statistics, historical project information, team input, and more. Make sure you gather information from a variety of sources, especially if those sources go against your personal ideas about what the problem is or how to solve it.
Gathering varied information is essential for your ability to apply the critical thinking process. If you don’t get enough information, your ability to make a final decision will be skewed. Remember that critical thinking is about helping you identify the objective best conclusion. You aren’t going with your gut—you’re doing research to find the best option
3. Determine data relevance
Just as it’s important to gather a variety of information, it is also important to determine how relevant the different information sources are. After all, just because there is data doesn’t mean it’s relevant.
Once you’ve gathered all of the information, sift through the noise and identify what information is relevant and what information isn’t. Synthesizing all of this information and establishing significance helps you weigh different data sources and come to the best conclusion later on in the critical thinking process.
To determine data relevance, ask yourself:
How reliable is this information?
How significant is this information?
Is this information outdated? Is it specialized in a specific field?
4. Ask questions
One of the most useful parts of the critical thinking process is coming to a decision without bias. In order to do so, you need to take a step back from the process and challenge the assumptions you’re making.
We all have bias—and that isn’t necessarily a bad thing. Unconscious biases (also known as cognitive biases) often serve as mental shortcuts to simplify problem solving and aid decision making. But even when biases aren’t inherently bad, you must be aware of your biases in order to put them aside when necessary.
Before coming to a solution, ask yourself:
Am I making any assumptions about this information?
Are there additional variables I haven’t considered?
Have I evaluated the information from every perspective?
Are there any viewpoints I missed?
5. Identify the best solution
Finally, you’re ready to come to a conclusion. To identify the best solution, draw connections between causes and effects. Use the facts you’ve gathered to evaluate the most objective conclusion.
Keep in mind that there may be more than one solution. Often, the problems you’re facing are complex and intricate. The critical thinking process doesn’t necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision.
6. Present your solution
Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers. It isn’t enough to think for yourself—you also need to share your conclusion with other project stakeholders. If there are multiple solutions, present them all. There may be a case where you implement one solution, then test to see if it works before implementing another solution.
7. Analyze your decision
The seven-step critical thinking process yields a result—and you then need to put that solution into place. After you’ve implemented your decision, evaluate whether or not it was effective. Did it solve the initial problem? What lessons—whether positive or negative—can you learn from this experience to improve your critical thinking for next time?
Depending on how your team shares information, consider documenting lessons learned in a central source of truth. That way, team members that are making similar or related decisions in the future can understand why you made the decision you made and what the outcome was.
Example of critical thinking in the workplace
Imagine you work in user experience design (UX). Your team is focused on pricing and packaging and ensuring customers have a clear understanding of the different services your company offers. Here’s how to apply the critical thinking process in the workplace in seven steps:
Start by identifying the problem
Your current pricing page isn’t performing as well as you want. You’ve heard from customers that your services aren’t clear, and that the page doesn’t answer the questions they have. This page is really important for your company, since it’s where your customers sign up for your service. You and your team have a few theories about why your current page isn’t performing well, but you decide to apply the critical thinking process to ensure you come to the best decision for the page.
Gather information about how the problem started
Part of identifying the problem includes understanding how the problem started. The pricing and packaging page is important—so when your team initially designed the page, they certainly put a lot of thought into it. Before you begin researching how to improve the page, ask yourself:
Why did you design the pricing page the way you did?
Which stakeholders need to be involved in the decision making process?
Where are users getting stuck on the page?
Are any features currently working?
Then, you research
In addition to understanding the history of the pricing and packaging page, it’s important to understand what works well. Part of this research means taking a look at what your competitor’s pricing pages look like.
Ask yourself:
How have our competitors set up their pricing pages?
Are there any pricing page best practices?
How does color, positioning, and animation impact navigation?
Are there any standard page layouts customers expect to see?
Organize and analyze information
You’ve gathered all of the information you need—now you need to organize and analyze it. What trends, if any, are you noticing? Is there any particularly relevant or important information that you have to consider?
Ask open-ended questions to reduce bias
In the case of critical thinking, it’s important to address and set bias aside as much as possible. Ask yourself:
Is there anything I’m missing?
Have I connected with the right stakeholders?
Are there any other viewpoints I should consider?
Determine the best solution for your team
You now have all of the information you need to design the best pricing page. Depending on the complexity of the design, you may want to design a few options to present to a small group of customers or A/B test on the live website.
Present your solution to stakeholders
Critical thinking can help you in every element of your life, but in the workplace, you must also involve key project stakeholders . Stakeholders help you determine next steps, like whether you’ll A/B test the page first. Depending on the complexity of the issue, consider hosting a meeting or sharing a status report to get everyone on the same page.
Analyze the results
No process is complete without evaluating the results. Once the new page has been live for some time, evaluate whether it did better than the previous page. What worked? What didn’t? This also helps you make better critical decisions later on.
Critically successful
Critical thinking takes time to build, but with effort and patience you can apply an unbiased, analytical mind to any situation. Critical thinking makes up one of many soft skills that makes you an effective team member, manager, and worker. If you’re looking to hone your skills further, read our article on the 25 project management skills you need to succeed .
Related resources

Fix these common onboarding challenges to boost productivity

How Asana uses work management for organizational planning

How Asana uses work management to optimize resource planning

Build a cross-functional team in just 4 steps
What Are Critical Thinking Skills? (Example List Included)
Mike Simpson 0 Comments

By Mike Simpson
Ah, critical thinking skills. As a candidate, it’s vital to understand that pretty much all employers are on the hunt for job seekers with critical thinking skills. Why? Because it’s universally helpful on the job.
When employees know how to think critically, they are more effective in their positions. They’ll be more productive and self-sufficient. In the eyes of employers, that matters a ton.
But what are critical thinking skills exactly? And, if you don’t have them, what can you do to improve your ability to think critically?
If you’re asking yourself questions like those, you’re in luck. After all, you’re here, and we’re about to tell you all about the characteristics of critical thinking and how to get better at it. So, if you’re ready to dig in, here’s what you need to know.
What Are Critical Thinking Skills?
If we’re going to talk about critical thinking skills, it’s best to begin by answering a crucial question: what are critical thinking skills?
Well, to figure that out, it’s helpful to know what critical thinking means. According to the Cambridge Dictionary , critical thinking is “the process of thinking carefully about a subject or idea, without allowing feelings or opinions to affect you.” That’s actually a pretty solid place to start.
In many ways, critical thinking is a two-fold process. First, it focuses on information-gathering and fact-analysis. It’s all about understanding a subject thoroughly.
Second, it’s about setting your feelings aside. With critical thinking, it isn’t about what you want the facts to say; it’s about the reality of the situation. It’s a very Vulcans-from-Star-Trek approach to topics. Emotions and personal preference simply aren’t part of the equation in the vast majority of cases. Instead, objectivity reigns.
Alright, so what are critical thinking skills then? Well, critical thinking skills are the soft skills and hard skills that help you assess situations, collect data, analyze information, identify solutions, determine the viability of solutions, and make decisions without letting your emotions run the show. Any capability or trait that makes it easier to do those things can qualify.
In many cases, thinking critically plays a bigger role in your day-to-day than you’d expect. When you approach any task, you usually spend a moment analyzing it. That way, you can find the best path toward success.
When a task is simple, it doesn’t take much time to do a quick critical thinking once over, so you probably don’t even notice you’re doing it. It’s only when an activity is challenging or when something unexpected occurs that your thought process really stands out. As a result, you probably spend far more time thinking critically than you realize.
How Are Critical Thinking Skills Relevant to a Job Search?
Okay, we’ve given you a solid overview of what critical thinking skills are. Now it’s time to talk about the importance of critical thinking during a job search.
When you’re hunting for new opportunities, critical thinking skills are immensely valuable. For example, they can help you figure out if a job opening is genuinely a good fit for your capabilities and career.
When you find a job ad, do you just apply without seeing if it matches your skills and aligns with your goals? Of course not. Instead, you take a look at the requirements, examine the job ad for potential, and decide whether or not that opportunity really fits. That’s critical thinking.
But that’s not the only way these skills make a difference during your job search. They may also help you identify what points to include in your resume and cover letter to stand out to a hiring manager or what to talk about when you’re answering specific job interview questions.
How can it do all of that? Well, when you decide what to list in your resume or cover letter, or add to an interview answer, you have to do some analysis. You consider the hiring manager’s needs. Next, you find a matching accomplishment that highlights what they are after. Then, you figure out present it in an engaging way. That’s all critical thinking, too.
Plus, thinking critically can also make a difference post-interview. You’ll have an easier time assessing your own performance, allowing you to identify areas for improvement. Good stuff, right?
When it comes to why hiring managers prefer candidates with these skills, there are actually several reasons. The biggest is that employees with strong critical thinking skills tend to be more self-sufficient and productive. They are better equipped to assess situations and find their own solutions, and that matters, particularly in faster-paced environments.
Plus, workers that know how to think critically may have an easier time collaborating. They can separate their emotions from the situation, allowing them to focus on what’s best for the team and company.
So, which critical thinking skills are they after? Well, that can depend on the hiring manager. However, most want to see you possess capabilities in four core areas: information-gathering, analysis , problem-solving, and creativity. If you tap into all of those, you usually have what it takes to think critically.
How to Highlight Critical Thinking Skills for Job Search
Okay, at this point, you probably understand the importance of critical thinking skills. Now onto the next part of the equation: how to show off your capabilities during a job search.
Let’s start with the earliest part of the job search: your resume and cover letter. When you’re writing a resume or creating a cover letter , the best thing you can do is focus on achievements.
Highlighting accomplishments where you put your critical thinking skills to work lets you “show” the hiring manager you have what it takes instead of just telling them. After all, anyone can say, “I’m an excellent critical thinker,” even if they aren’t. By having examples, you prove that you have those capabilities. That matters.
How do you pick the right achievements? By using a winning strategy, like the Tailoring Method . The Tailoring Method focuses on relevancy. It helps you choose accomplishments that showcase the skills the hiring manager wants to see, increasing the odds that they’ll view you as an excellent match for their needs.
Now that your resume and cover letter are squared away, it’s time to talk about the interview. Luckily, you can use the Tailoring Method here, too. It’s a great technique for straightforward job interview questions , as well as behavioral interview questions .
When you’re dealing with behavioral interview questions, couple the Tailoring Method with the STAR Method . That way, your answers are engaging and relevant, making them even more impactful.
How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills If You Don’t Have Them
Some people may think that they don’t have any critical thinking skills. In reality, that probably isn’t true.
Nearly everyone develops some critical thinking capabilities over the course of their lives; they just may not realize it. Luckily, that’s a good thing. It means you probably have a solid foundation, even if you don’t know it.
Why does that matter? Well, it means you can focus more on developing what you have. You aren’t actually starting from scratch, which can make it easier.
Ready to take your critical thinking skills to the next level? Great! Here’s how you can.
Understand the Critical Thinking Process
When it comes to how to think critically, there is actually a core process involved. By understanding the steps, you can make sure you approach situations properly.
Usually, the critical thinking process involves:
- Observation
- Information-Gathering
- Brainstorming
Typically, you start by observing the issue at hand. Next, you do some research, helping you gather more information. After that, you focus on brainstorming ideas on how to proceed. Then, you consider each option, identifying the best one. Finally, you decide to proceed, taking actions based on what you’ve learned.
It’s a systematic way to address a range of scenarios. By learning the process, you can put it into use more often, allowing you to increase your skills.
Take Up a Hobby
Many hobbies actually require quite a bit of critical thinking. For example, if you want to have a thriving garden, you need to take several factors into account. Soil condition, water availability, the amount of sunlight, aesthetics… those are just some of the points you need to analyze if you want to succeed.
Arts and crafts can also help you boost critical thinking. When you’re making something, you have to evaluate your options for materials, techniques, and more, ensuring you choose a path that leads to the best final product.
Join a Debate Club
If you’re looking for possibly one of the best critical thinking examples around, debate is probably it. That means, if you want to take your skills up a notch, joining a debate club can be a great option.
You have to support a position – at times one that doesn’t align with your personal beliefs – and try to convince others that your side is correct. You’ll dive into unfamiliar topics, gather data to support the perspective you’re assigned, and choose how to present information in a convincing way.
While you might think that, if you aren’t in high school, that this isn’t an option, that isn’t the case. There are many meetups that focus on debate, giving people of all ages a place to boost their skills.
List of Critical Thinking Skills
There are quite a few characteristics and capabilities that support critical thinking. By knowing which skills fall into that category, you can decide what to showcase during your job search.
So, let’s dig in. Here is a quick list of critical thinking skill examples:
- Self-Reliance
- Decision-Making
- Open-Mindedness
- Deductive Reasoning
- Problem-Solving
- Communication
- Collaboration
- Attention to Detail
- Pattern Recognition
- Interpretation
- Active Listening
- Conceptualization
Now, these aren’t the only skills that can help you think critically. Practically anything that enables you to navigate the process can count.
Additionally, you don’t have to fit all of these skills on your resume to show that you know how to think critically. Instead, you want to highlight a range, demonstrating that you have what it takes to navigate situations effectively and accomplish your goals.
Spend some time reflecting on your work history or educational experiences. Then, identify moments where you used critical thinking to accomplish something noteworthy. Once you have, think about the skills that came into play, and make sure to mention them as you describe what led up to the achievement.
If you’re looking for more skills to put on a resume , we’ve actually taken a deep dive into that topic before. Along with various critical thinking skills, we tap on a ton of other areas, making it easier for you to figure out what you should feature during your job search.

Putting It All Together
In the end, critical thinking skills are essential for nearly every member of the workforce. By elevating yours as much as possible and showcasing them during your job search, you won’t just be a stronger candidate but also a more capable employee. That’s all great stuff. It’ll help you have your ideal career and, ultimately, isn’t that what it’s all about?

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com.
His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others.
Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
About The Author
Mike simpson.

Co-Founder and CEO of TheInterviewGuys.com. Mike is a job interview and career expert and the head writer at TheInterviewGuys.com. His advice and insights have been shared and featured by publications such as Forbes , Entrepreneur , CNBC and more as well as educational institutions such as the University of Michigan , Penn State , Northeastern and others. Learn more about The Interview Guys on our About Us page .
Copyright © 2024 · TheInterviewguys.com · All Rights Reserved
- Our Products
- Case Studies
- Interview Questions
- Jobs Articles
- Members Login

Tips for Online Students , Tips for Students
Why Is Critical Thinking Important? A Survival Guide
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: April 2, 2020

Why is critical thinking important? The decisions that you make affect your quality of life. And if you want to ensure that you live your best, most successful and happy life, you’re going to want to make conscious choices. That can be done with a simple thing known as critical thinking. Here’s how to improve your critical thinking skills and make decisions that you won’t regret.
What Is Critical Thinking?
You’ve surely heard of critical thinking, but you might not be entirely sure what it really means, and that’s because there are many definitions. For the most part, however, we think of critical thinking as the process of analyzing facts in order to form a judgment. Basically, it’s thinking about thinking.
How Has The Definition Evolved Over Time?
The first time critical thinking was documented is believed to be in the teachings of Socrates , recorded by Plato. But throughout history, the definition has changed.
Today it is best understood by philosophers and psychologists and it’s believed to be a highly complex concept. Some insightful modern-day critical thinking definitions include :
- “Reasonable, reflective thinking that is focused on deciding what to believe or do.”
- “Deciding what’s true and what you should do.”
The Importance Of Critical Thinking
Why is critical thinking important? Good question! Here are a few undeniable reasons why it’s crucial to have these skills.
1. Critical Thinking Is Universal
Critical thinking is a domain-general thinking skill. What does this mean? It means that no matter what path or profession you pursue, these skills will always be relevant and will always be beneficial to your success. They are not specific to any field.
2. Crucial For The Economy
Our future depends on technology, information, and innovation. Critical thinking is needed for our fast-growing economies, to solve problems as quickly and as effectively as possible.
3. Improves Language & Presentation Skills
In order to best express ourselves, we need to know how to think clearly and systematically — meaning practice critical thinking! Critical thinking also means knowing how to break down texts, and in turn, improve our ability to comprehend.
4. Promotes Creativity
By practicing critical thinking, we are allowing ourselves not only to solve problems but also to come up with new and creative ideas to do so. Critical thinking allows us to analyze these ideas and adjust them accordingly.
5. Important For Self-Reflection
Without critical thinking, how can we really live a meaningful life? We need this skill to self-reflect and justify our ways of life and opinions. Critical thinking provides us with the tools to evaluate ourselves in the way that we need to.

6. The Basis Of Science & Democracy
In order to have a democracy and to prove scientific facts, we need critical thinking in the world. Theories must be backed up with knowledge. In order for a society to effectively function, its citizens need to establish opinions about what’s right and wrong (by using critical thinking!).
Benefits Of Critical Thinking
We know that critical thinking is good for society as a whole, but what are some benefits of critical thinking on an individual level? Why is critical thinking important for us?
1. Key For Career Success
Critical thinking is crucial for many career paths. Not just for scientists, but lawyers , doctors, reporters, engineers , accountants, and analysts (among many others) all have to use critical thinking in their positions. In fact, according to the World Economic Forum, critical thinking is one of the most desirable skills to have in the workforce, as it helps analyze information, think outside the box, solve problems with innovative solutions, and plan systematically.
2. Better Decision Making
There’s no doubt about it — critical thinkers make the best choices. Critical thinking helps us deal with everyday problems as they come our way, and very often this thought process is even done subconsciously. It helps us think independently and trust our gut feeling.
3. Can Make You Happier!
While this often goes unnoticed, being in touch with yourself and having a deep understanding of why you think the way you think can really make you happier. Critical thinking can help you better understand yourself, and in turn, help you avoid any kind of negative or limiting beliefs, and focus more on your strengths. Being able to share your thoughts can increase your quality of life.
4. Form Well-Informed Opinions
There is no shortage of information coming at us from all angles. And that’s exactly why we need to use our critical thinking skills and decide for ourselves what to believe. Critical thinking allows us to ensure that our opinions are based on the facts, and help us sort through all that extra noise.
5. Better Citizens
One of the most inspiring critical thinking quotes is by former US president Thomas Jefferson: “An educated citizenry is a vital requisite for our survival as a free people.” What Jefferson is stressing to us here is that critical thinkers make better citizens, as they are able to see the entire picture without getting sucked into biases and propaganda.
6. Improves Relationships
While you may be convinced that being a critical thinker is bound to cause you problems in relationships, this really couldn’t be less true! Being a critical thinker can allow you to better understand the perspective of others, and can help you become more open-minded towards different views.
7. Promotes Curiosity
Critical thinkers are constantly curious about all kinds of things in life, and tend to have a wide range of interests. Critical thinking means constantly asking questions and wanting to know more, about why, what, who, where, when, and everything else that can help them make sense of a situation or concept, never taking anything at face value.
8. Allows For Creativity
Critical thinkers are also highly creative thinkers, and see themselves as limitless when it comes to possibilities. They are constantly looking to take things further, which is crucial in the workforce.
9. Enhances Problem Solving Skills
Those with critical thinking skills tend to solve problems as part of their natural instinct. Critical thinkers are patient and committed to solving the problem, similar to Albert Einstein, one of the best critical thinking examples, who said “It’s not that I’m so smart; it’s just that I stay with problems longer.” Critical thinkers’ enhanced problem-solving skills makes them better at their jobs and better at solving the world’s biggest problems. Like Einstein, they have the potential to literally change the world.
10. An Activity For The Mind
Just like our muscles, in order for them to be strong, our mind also needs to be exercised and challenged. It’s safe to say that critical thinking is almost like an activity for the mind — and it needs to be practiced. Critical thinking encourages the development of many crucial skills such as logical thinking, decision making, and open-mindness.
11. Creates Independence
When we think critically, we think on our own as we trust ourselves more. Critical thinking is key to creating independence, and encouraging students to make their own decisions and form their own opinions.
12. Crucial Life Skill
Critical thinking is crucial not just for learning, but for life overall! Education isn’t just a way to prepare ourselves for life, but it’s pretty much life itself. Learning is a lifelong process that we go through each and every day.
How to Think Critically
Now that you know the benefits of thinking critically, how do you actually do it?
How To Improve Your Critical Thinking
- Define Your Question: When it comes to critical thinking, it’s important to always keep your goal in mind. Know what you’re trying to achieve, and then figure out how to best get there.
- Gather Reliable Information: Make sure that you’re using sources you can trust — biases aside. That’s how a real critical thinker operates!
- Ask The Right Questions: We all know the importance of questions, but be sure that you’re asking the right questions that are going to get you to your answer.
- Look Short & Long Term: When coming up with solutions, think about both the short- and long-term consequences. Both of them are significant in the equation.
- Explore All Sides: There is never just one simple answer, and nothing is black or white. Explore all options and think outside of the box before you come to any conclusions.
How Is Critical Thinking Developed At School?
Critical thinking is developed in nearly everything we do. However, much of this important skill is encouraged to be practiced at school, and rightfully so! Critical thinking goes beyond just thinking clearly — it’s also about thinking for yourself.
When a teacher asks a question in class, students are given the chance to answer for themselves and think critically about what they learned and what they believe to be accurate. When students work in groups and are forced to engage in discussion, this is also a great chance to expand their thinking and use their critical thinking skills.
How Does Critical Thinking Apply To Your Career?
Once you’ve finished school and entered the workforce, your critical thinking journey only expands and grows from here!
Impress Your Employer
Employers value employees who are critical thinkers, ask questions, offer creative ideas, and are always ready to offer innovation against the competition. No matter what your position or role in a company may be, critical thinking will always give you the power to stand out and make a difference.
Careers That Require Critical Thinking
Some of many examples of careers that require critical thinking include:
- Human resources specialist
- Marketing associate
- Business analyst
Truth be told however, it’s probably harder to come up with a professional field that doesn’t require any critical thinking!
Photo by Oladimeji Ajegbile from Pexels
What is someone with critical thinking skills capable of doing.
Someone with critical thinking skills is able to think rationally and clearly about what they should or not believe. They are capable of engaging in their own thoughts, and doing some reflection in order to come to a well-informed conclusion.
A critical thinker understands the connections between ideas, and is able to construct arguments based on facts, as well as find mistakes in reasoning.
The Process Of Critical Thinking
The process of critical thinking is highly systematic.
What Are Your Goals?
Critical thinking starts by defining your goals, and knowing what you are ultimately trying to achieve.
Once you know what you are trying to conclude, you can foresee your solution to the problem and play it out in your head from all perspectives.
What Does The Future Of Critical Thinking Hold?
The future of critical thinking is the equivalent of the future of jobs. In 2020, critical thinking was ranked as the 2nd top skill (following complex problem solving) by the World Economic Forum .
We are dealing with constant unprecedented changes, and what success is today, might not be considered success tomorrow — making critical thinking a key skill for the future workforce.
Why Is Critical Thinking So Important?
Why is critical thinking important? Critical thinking is more than just important! It’s one of the most crucial cognitive skills one can develop.
By practicing well-thought-out thinking, both your thoughts and decisions can make a positive change in your life, on both a professional and personal level. You can hugely improve your life by working on your critical thinking skills as often as you can.
Related Articles
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
A Short Guide to Building Your Team’s Critical Thinking Skills
- Matt Plummer

Critical thinking isn’t an innate skill. It can be learned.
Most employers lack an effective way to objectively assess critical thinking skills and most managers don’t know how to provide specific instruction to team members in need of becoming better thinkers. Instead, most managers employ a sink-or-swim approach, ultimately creating work-arounds to keep those who can’t figure out how to “swim” from making important decisions. But it doesn’t have to be this way. To demystify what critical thinking is and how it is developed, the author’s team turned to three research-backed models: The Halpern Critical Thinking Assessment, Pearson’s RED Critical Thinking Model, and Bloom’s Taxonomy. Using these models, they developed the Critical Thinking Roadmap, a framework that breaks critical thinking down into four measurable phases: the ability to execute, synthesize, recommend, and generate.
With critical thinking ranking among the most in-demand skills for job candidates , you would think that educational institutions would prepare candidates well to be exceptional thinkers, and employers would be adept at developing such skills in existing employees. Unfortunately, both are largely untrue.
- Matt Plummer (@mtplummer) is the founder of Zarvana, which offers online programs and coaching services to help working professionals become more productive by developing time-saving habits. Before starting Zarvana, Matt spent six years at Bain & Company spin-out, The Bridgespan Group, a strategy and management consulting firm for nonprofits, foundations, and philanthropists.
Partner Center
- Our Mission
Helping Students Hone Their Critical Thinking Skills
Used consistently, these strategies can help middle and high school teachers guide students to improve much-needed skills.

Critical thinking skills are important in every discipline, at and beyond school. From managing money to choosing which candidates to vote for in elections to making difficult career choices, students need to be prepared to take in, synthesize, and act on new information in a world that is constantly changing.
While critical thinking might seem like an abstract idea that is tough to directly instruct, there are many engaging ways to help students strengthen these skills through active learning.
Make Time for Metacognitive Reflection
Create space for students to both reflect on their ideas and discuss the power of doing so. Show students how they can push back on their own thinking to analyze and question their assumptions. Students might ask themselves, “Why is this the best answer? What information supports my answer? What might someone with a counterargument say?”
Through this reflection, students and teachers (who can model reflecting on their own thinking) gain deeper understandings of their ideas and do a better job articulating their beliefs. In a world that is go-go-go, it is important to help students understand that it is OK to take a breath and think about their ideas before putting them out into the world. And taking time for reflection helps us more thoughtfully consider others’ ideas, too.
Teach Reasoning Skills
Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
One way to teach reasoning is to use problem-solving activities that require students to apply their skills to practical contexts. For example, give students a real problem to solve, and ask them to use reasoning skills to develop a solution. They can then present their solution and defend their reasoning to the class and engage in discussion about whether and how their thinking changed when listening to peers’ perspectives.
A great example I have seen involved students identifying an underutilized part of their school and creating a presentation about one way to redesign it. This project allowed students to feel a sense of connection to the problem and come up with creative solutions that could help others at school. For more examples, you might visit PBS’s Design Squad , a resource that brings to life real-world problem-solving.
Ask Open-Ended Questions
Moving beyond the repetition of facts, critical thinking requires students to take positions and explain their beliefs through research, evidence, and explanations of credibility.
When we pose open-ended questions, we create space for classroom discourse inclusive of diverse, perhaps opposing, ideas—grounds for rich exchanges that support deep thinking and analysis.
For example, “How would you approach the problem?” and “Where might you look to find resources to address this issue?” are two open-ended questions that position students to think less about the “right” answer and more about the variety of solutions that might already exist.
Journaling, whether digitally or physically in a notebook, is another great way to have students answer these open-ended prompts—giving them time to think and organize their thoughts before contributing to a conversation, which can ensure that more voices are heard.
Once students process in their journal, small group or whole class conversations help bring their ideas to life. Discovering similarities between answers helps reveal to students that they are not alone, which can encourage future participation in constructive civil discourse.
Teach Information Literacy
Education has moved far past the idea of “Be careful of what is on Wikipedia, because it might not be true.” With AI innovations making their way into classrooms, teachers know that informed readers must question everything.
Understanding what is and is not a reliable source and knowing how to vet information are important skills for students to build and utilize when making informed decisions. You might start by introducing the idea of bias: Articles, ads, memes, videos, and every other form of media can push an agenda that students may not see on the surface. Discuss credibility, subjectivity, and objectivity, and look at examples and nonexamples of trusted information to prepare students to be well-informed members of a democracy.
One of my favorite lessons is about the Pacific Northwest tree octopus . This project asks students to explore what appears to be a very real website that provides information on this supposedly endangered animal. It is a wonderful, albeit over-the-top, example of how something might look official even when untrue, revealing that we need critical thinking to break down “facts” and determine the validity of the information we consume.
A fun extension is to have students come up with their own website or newsletter about something going on in school that is untrue. Perhaps a change in dress code that requires everyone to wear their clothes inside out or a change to the lunch menu that will require students to eat brussels sprouts every day.
Giving students the ability to create their own falsified information can help them better identify it in other contexts. Understanding that information can be “too good to be true” can help them identify future falsehoods.
Provide Diverse Perspectives
Consider how to keep the classroom from becoming an echo chamber. If students come from the same community, they may have similar perspectives. And those who have differing perspectives may not feel comfortable sharing them in the face of an opposing majority.
To support varying viewpoints, bring diverse voices into the classroom as much as possible, especially when discussing current events. Use primary sources: videos from YouTube, essays and articles written by people who experienced current events firsthand, documentaries that dive deeply into topics that require some nuance, and any other resources that provide a varied look at topics.
I like to use the Smithsonian “OurStory” page , which shares a wide variety of stories from people in the United States. The page on Japanese American internment camps is very powerful because of its first-person perspectives.
Practice Makes Perfect
To make the above strategies and thinking routines a consistent part of your classroom, spread them out—and build upon them—over the course of the school year. You might challenge students with information and/or examples that require them to use their critical thinking skills; work these skills explicitly into lessons, projects, rubrics, and self-assessments; or have students practice identifying misinformation or unsupported arguments.
Critical thinking is not learned in isolation. It needs to be explored in English language arts, social studies, science, physical education, math. Every discipline requires students to take a careful look at something and find the best solution. Often, these skills are taken for granted, viewed as a by-product of a good education, but true critical thinking doesn’t just happen. It requires consistency and commitment.
In a moment when information and misinformation abound, and students must parse reams of information, it is imperative that we support and model critical thinking in the classroom to support the development of well-informed citizens.
- Departments, units, and programs
- College leadership
- Diversity, equity, and inclusion
- Faculty and staff resources
- LAS Strategic Plan

- Apply to LAS
- Liberal arts & sciences majors
- LAS Insider blog
- Admissions FAQs
- Parent resources
- Pre-college summer programs
Quick Links
Request info
- Academic policies and standing
- Advising and support
- College distinctions
- Dates and deadlines
- Intercollegiate transfers
- LAS Lineup student newsletter
- Programs of study
- Scholarships
- Certificates
- Student emergencies
Student resources
- Access and Achievement Program
- Career services
- First-Year Experience
- Honors program
- International programs
- Internship opportunities
- Paul M. Lisnek LAS Hub
- Student research opportunities
- Expertise in LAS
- Research facilities and centers
- Dean's Distinguished Lecture series
- Alumni advice
- Alumni award programs
- Get involved
- LAS Alumni Council
- LAS@Work: Alumni careers
- Study Abroad Alumni Networks
- Update your information
- Nominate an alumnus for an LAS award
- Faculty honors
- The Quadrangle Online
- LAS News email newsletter archive
- LAS social media
- Media contact in the College of LAS
- LAS Landmark Day of Giving
- About giving to LAS
- Building projects
- Corporate engagement
- Faculty support
- Lincoln Scholars Initiative
- Impact of giving
Why is critical thinking important?
What do lawyers, accountants, teachers, and doctors all have in common?

What is critical thinking?
The Oxford English Dictionary defines critical thinking as “The objective, systematic, and rational analysis and evaluation of factual evidence in order to form a judgment on a subject, issue, etc.” Critical thinking involves the use of logic and reasoning to evaluate available facts and/or evidence to come to a conclusion about a certain subject or topic. We use critical thinking every day, from decision-making to problem-solving, in addition to thinking critically in an academic context!
Why is critical thinking important for academic success?
You may be asking “why is critical thinking important for students?” Critical thinking appears in a diverse set of disciplines and impacts students’ learning every day, regardless of major.
Critical thinking skills are often associated with the value of studying the humanities. In majors such as English, students will be presented with a certain text—whether it’s a novel, short story, essay, or even film—and will have to use textual evidence to make an argument and then defend their argument about what they’ve read. However, the importance of critical thinking does not only apply to the humanities. In the social sciences, an economics major , for example, will use what they’ve learned to figure out solutions to issues as varied as land and other natural resource use, to how much people should work, to how to develop human capital through education. Problem-solving and critical thinking go hand in hand. Biology is a popular major within LAS, and graduates of the biology program often pursue careers in the medical sciences. Doctors use critical thinking every day, tapping into the knowledge they acquired from studying the biological sciences to diagnose and treat different diseases and ailments.
Students in the College of LAS take many courses that require critical thinking before they graduate. You may be asked in an Economics class to use statistical data analysis to evaluate the impact on home improvement spending when the Fed increases interest rates (read more about real-world experience with Datathon ). If you’ve ever been asked “How often do you think about the Roman Empire?”, you may find yourself thinking about the Roman Empire more than you thought—maybe in an English course, where you’ll use text from Shakespeare’s Antony and Cleopatra to make an argument about Roman imperial desire. No matter what the context is, critical thinking will be involved in your academic life and can take form in many different ways.
The benefits of critical thinking in everyday life
Building better communication.
One of the most important life skills that students learn as early as elementary school is how to give a presentation. Many classes require students to give presentations, because being well-spoken is a key skill in effective communication. This is where critical thinking benefits come into play: using the skills you’ve learned, you’ll be able to gather the information needed for your presentation, narrow down what information is most relevant, and communicate it in an engaging way.
Typically, the first step in creating a presentation is choosing a topic. For example, your professor might assign a presentation on the Gilded Age and provide a list of figures from the 1870s—1890s to choose from. You’ll use your critical thinking skills to narrow down your choices. You may ask yourself:
- What figure am I most familiar with?
- Who am I most interested in?
- Will I have to do additional research?
After choosing your topic, your professor will usually ask a guiding question to help you form a thesis: an argument that is backed up with evidence. Critical thinking benefits this process by allowing you to focus on the information that is most relevant in support of your argument. By focusing on the strongest evidence, you will communicate your thesis clearly.
Finally, once you’ve finished gathering information, you will begin putting your presentation together. Creating a presentation requires a balance of text and visuals. Graphs and tables are popular visuals in STEM-based projects, but digital images and graphics are effective as well. Critical thinking benefits this process because the right images and visuals create a more dynamic experience for the audience, giving them the opportunity to engage with the material.
Presentation skills go beyond the classroom. Students at the University of Illinois will often participate in summer internships to get professional experience before graduation. Many summer interns are required to present about their experience and what they learned at the end of the internship. Jobs frequently also require employees to create presentations of some kind—whether it’s an advertising pitch to win an account from a potential client, or quarterly reporting, giving a presentation is a life skill that directly relates to critical thinking.
Fostering independence and confidence
An important life skill many people start learning as college students and then finessing once they enter the “adult world” is how to budget. There will be many different expenses to keep track of, including rent, bills, car payments, and groceries, just to name a few! After developing your critical thinking skills, you’ll put them to use to consider your salary and budget your expenses accordingly. Here’s an example:
- You earn a salary of $75,000 a year. Assume all amounts are before taxes.
- 1,800 x 12 = 21,600
- 75,000 – 21,600 = 53,400
- This leaves you with $53,400
- 320 x 12 = 3,840 a year
- 53,400-3,840= 49,560
- 726 x 12 = 8,712
- 49,560 – 8,712= 40,848
- You’re left with $40,848 for miscellaneous expenses. You use your critical thinking skills to decide what to do with your $40,848. You think ahead towards your retirement and decide to put $500 a month into a Roth IRA, leaving $34,848. Since you love coffee, you try to figure out if you can afford a daily coffee run. On average, a cup of coffee will cost you $7. 7 x 365 = $2,555 a year for coffee. 34,848 – 2,555 = 32,293
- You have $32,293 left. You will use your critical thinking skills to figure out how much you would want to put into savings, how much you want to save to treat yourself from time to time, and how much you want to put aside for emergency funds. With the benefits of critical thinking, you will be well-equipped to budget your lifestyle once you enter the working world.
Enhancing decision-making skills
Choosing the right university for you.
One of the biggest decisions you’ll make in your life is what college or university to go to. There are many factors to consider when making this decision, and critical thinking importance will come into play when determining these factors.
Many high school seniors apply to colleges with the hope of being accepted into a certain program, whether it’s biology, psychology, political science, English, or something else entirely. Some students apply with certain schools in mind due to overall rankings. Students also consider the campus a school is set in. While some universities such as the University of Illinois are nestled within college towns, New York University is right in Manhattan, in a big city setting. Some students dream of going to large universities, and other students prefer smaller schools. The diversity of a university’s student body is also a key consideration. For many 17- and 18-year-olds, college is a time to meet peers from diverse racial and socio-economic backgrounds and learn about life experiences different than one’s own.
With all these factors in mind, you’ll use critical thinking to decide which are most important to you—and which school is the right fit for you.
Develop your critical thinking skills at the University of Illinois
At the University of Illinois, not only will you learn how to think critically, but you will put critical thinking into practice. In the College of LAS, you can choose from 70+ majors where you will learn the importance and benefits of critical thinking skills. The College of Liberal Arts & Sciences at U of I offers a wide range of undergraduate and graduate programs in life, physical, and mathematical sciences; humanities; and social and behavioral sciences. No matter which program you choose, you will develop critical thinking skills as you go through your courses in the major of your choice. And in those courses, the first question your professors may ask you is, “What is the goal of critical thinking?” You will be able to respond with confidence that the goal of critical thinking is to help shape people into more informed, more thoughtful members of society.
With such a vast representation of disciplines, an education in the College of LAS will prepare you for a career where you will apply critical thinking skills to real life, both in and outside of the classroom, from your undergraduate experience to your professional career. If you’re interested in becoming a part of a diverse set of students and developing skills for lifelong success, apply to LAS today!
Read more first-hand stories from our amazing students at the LAS Insider blog .
- Privacy Notice
- Accessibility

What You Can Do To Improve Critical-Thinking Skills
In a technology-driven world where we are overwhelmed with information, people often make decisions without thinking things through – and then rue what they have done.
This is because decisions made without data, analysis and facts are decisions made in the dark.
People seem to have forgotten how to check credible sources, access and understand data and look at the facts.
One study of millennial and Gen Z workers in the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany and Japan found that people have so much on their minds, so many distractions overwhelming them, that they struggle to think deeply and reflectively.
But poorly thought-out plans and decisions aren’t good for business or for the career prospects of individuals.
Critical thinking is as important as ever – in business and in life – and here are a few things worth knowing about it:
- It’s possible to train yourself to become a critical thinker, and there are steps you can take that will help. Start with challenging the norm, “We have always done it this way.” Ask these questions: “Why?” “What data supports a different way to look at a problem and come up with a solution?” “How much time have I actually set aside to think?” “How can I look for a solution with the data that I see?”
- When you have mastered critical thinking, you can apply it to your current career, job and company — or to the next one. Critical thinking allows you to replicate success. Once I am working toward a new goal, I look back on the strategy that made me successful and replicate it.
- Stepping back and looking at the big picture is an important part of critical thinking — but so is delving into the details and coming up with a plan, especially as it relates to work. Your plan should rely on four key components. Data : What is it showing me, and where does the success exist? Total addressable market : How much of the market can I capture? Competition : Who are my top competitors, and how do I win against them? And finally, identifying the breaks : Where am I winning and losing, and how can I get better?
- In a hectic world, it’s important to carve out time to think, so people should set aside an hour each day when they can be alone without distractions. Without time to think, you are on a hamster wheel, spinning and spinning but never getting ahead. This time to think should happen daily, shutting out all distractions so you can consider such things as: “What worked, what didn’t, and how do I improve?”
The bottom line is when you start to think in terms of data and solutions and strategies, you can start to see patterns and trends elsewhere in your life — and make changes to win at both your career and life.
Puja Bhola Rios is the author of “ Get It Together: A Winning Formula for Success from the Boss You Need ” and the chief revenue officer for Frame.io, an Adobe company and the world’s premier video review and collaboration platform. Rios previously spent seven years working at Xerox and 13 years at CareerBuilder as senior vice president of Enterprise Sales and Customer Success. She also has been a chronic pain advocate and blogger, and is author of the Huffington Post feature blog, “ Me vs. Fibromyalgia .”

How to teach critical thinking, a vital 21st-century skill
A well-rounded education doesn’t just impart academic knowledge to students — it gives them transferable skills they can apply throughout their lives. Critical thinking is widely hailed as one such essential “ 21st-century skill ,” helping people critically assess information, make informed decisions, and come up with creative approaches to solving problems.
This means that individuals with developed critical thinking skills benefit both themselves and the wider society. Despite the widespread recognition of critical thinking’s importance for future success, there can be some ambiguity about both what it is and how to teach it . 1 Let’s take a look at each of those questions in turn.
What is critical thinking?
Throughout history, humanity has attempted to use reason to understand and interpret the world. From the philosophers of Ancient Greece to the key thinkers of the Enlightenment, people have sought to challenge their preconceived notions and draw logical conclusions from the available evidence — key elements that gave rise to today’s definition of “critical thinking.”
At its core, critical thinking is the use of reason to analyze the available evidence and reach logical conclusions. Educational scholars have defined critical thinking as “reasonable reflective thinking focused on deciding what to believe or do,” 2 and “interpretation or analysis, followed by evaluation or judgment.” 3 Some have pared their definition down to simply “good” or “skillful thinking.”
At the same time, being a good critical thinker relies on certain values like open-mindedness, persistence, and intellectual humility. 4 The ideal critical thinker isn’t just skilled in analysis — they are also curious, open to other points of view, and creative in the path they take towards tackling a given problem.
Alongside teaching students how to analyze information, build arguments, and draw conclusions, educators play a key role in fostering the values conducive to critical thinking and intellectual inquiry. Students who develop both skills and values are well-placed to handle challenges both academically and in their personal lives.
Let’s examine some strategies to develop critical thinking skills and values in the classroom.
How to teach students to think critically — strategies
1. build a classroom climate that encourages open-mindedness.

Fostering a classroom culture that allows students the time and space to think independently, experiment with new ideas, and have their views challenged lays a strong foundation for developing skills and values central to critical thinking.
Whatever your subject area, encourage students to contribute their own ideas and theories when addressing common curricular questions. Promote open-mindedness by underscoring the importance of the initial “brainstorming” phase in problem-solving — this is the necessary first step towards understanding! Strive to create a classroom climate where students are comfortable thinking out loud.
Emphasize to students the importance of understanding different perspectives on issues, and that it’s okay for people to disagree. Establish guidelines for class discussions — especially when covering controversial issues — and stress that changing your mind on an issue is a sign of intellectual strength, not weakness. Model positive behaviors by being flexible in your own opinions when engaging with ideas from students.
2. Teach students to make clear and effective arguments
Training students’ argumentation skills is central to turning them into adept critical thinkers. Expose students to a wide range of arguments, guiding them to distinguish between examples of good and bad reasoning.
When guiding students to form their own arguments, emphasize the value of clarity and precision in language. In oral discussions, encourage students to order their thoughts on paper before contributing.

In the case of argumentative essays , give students plenty of opportunities to revise their work, implementing feedback from you or peers. Assist students in refining their arguments by encouraging them to challenge their own positions.
They can do so by creating robust “steel man” counterarguments to identify potential flaws in their own reasoning. For example, if a student is passionate about animal rights and wants to argue for a ban on animal testing , encourage them to also come up with points in favor of animal testing. If they can rebut those counterarguments, their own position will be much stronger!
Additionally, knowing how to evaluate and provide evidence is essential for developing argumentation skills. Teach students how to properly cite sources , and encourage them to investigate the veracity of claims made by others — particularly when dealing with online media .
3. Encourage metacognition — guide students to think about their own and others’ thinking
Critical thinkers are self-reflective. Guide students time to think about their own learning process by utilizing metacognitive strategies, like learning journals or having reflective periods at the end of activities. Reflecting on how they came to understand a topic can help students cultivate a growth mindset and an openness to explore alternative problem-solving approaches during challenging moments.
You can also create an awareness of common errors in human thinking by teaching about them explicitly. Identify arguments based on logical fallacies and have students come up with examples from their own experience. Help students recognize the role of cognitive bias in our thinking, and design activities to help counter it.
Students who develop self-awareness regarding their own thinking are not just better at problem-solving, but also managing their emotions .
4. Assign open-ended and varied activities to practice different kinds of thinking
Critical thinkers are capable of approaching problems from a variety of angles. Train this vital habit by switching up the kinds of activities you assign to students, and try prioritizing open-ended assignments that allow for varied approaches.
A project-based learning approach can reap huge rewards. Have students identify real-world problems, conduct research, and investigate potential solutions. Following that process will give them varied intellectual challenges, while the real-world applicability of their work can motivate students to consider the potential impact their thinking can have on the world around them.

Classroom discussions and debates are fantastic activities for building critical thinking skills. As open-ended activities, they encourage student autonomy by requiring them to think for themselves.
They also expose students to a diversity of perspectives , inviting them to critically appraise these different positions in a respectful context. Class discussions are applicable across disciplines and come in many flavors — experiment with different forms like fishbowl discussions or online, asynchronous discussions to keep students engaged.
5. Use argument-mapping tools such as Kialo Edu to train students in the use of reasoning
One of the most effective methods of improving students’ critical thinking skills is to train them in argument mapping .
Argument mapping involves breaking an argument down into its constituent parts, and displaying them visually so that students can see how different points are connected. Research has shown that university students who were trained in argument mapping significantly out-performed their peers on critical thinking assessments. 5
While it’s possible — and useful — to map out arguments by hand, there are clear benefits to using digital argument maps like Kialo Edu. Students can contribute simultaneously to a Kialo discussion to collaboratively build out complex discussions as an argument map.
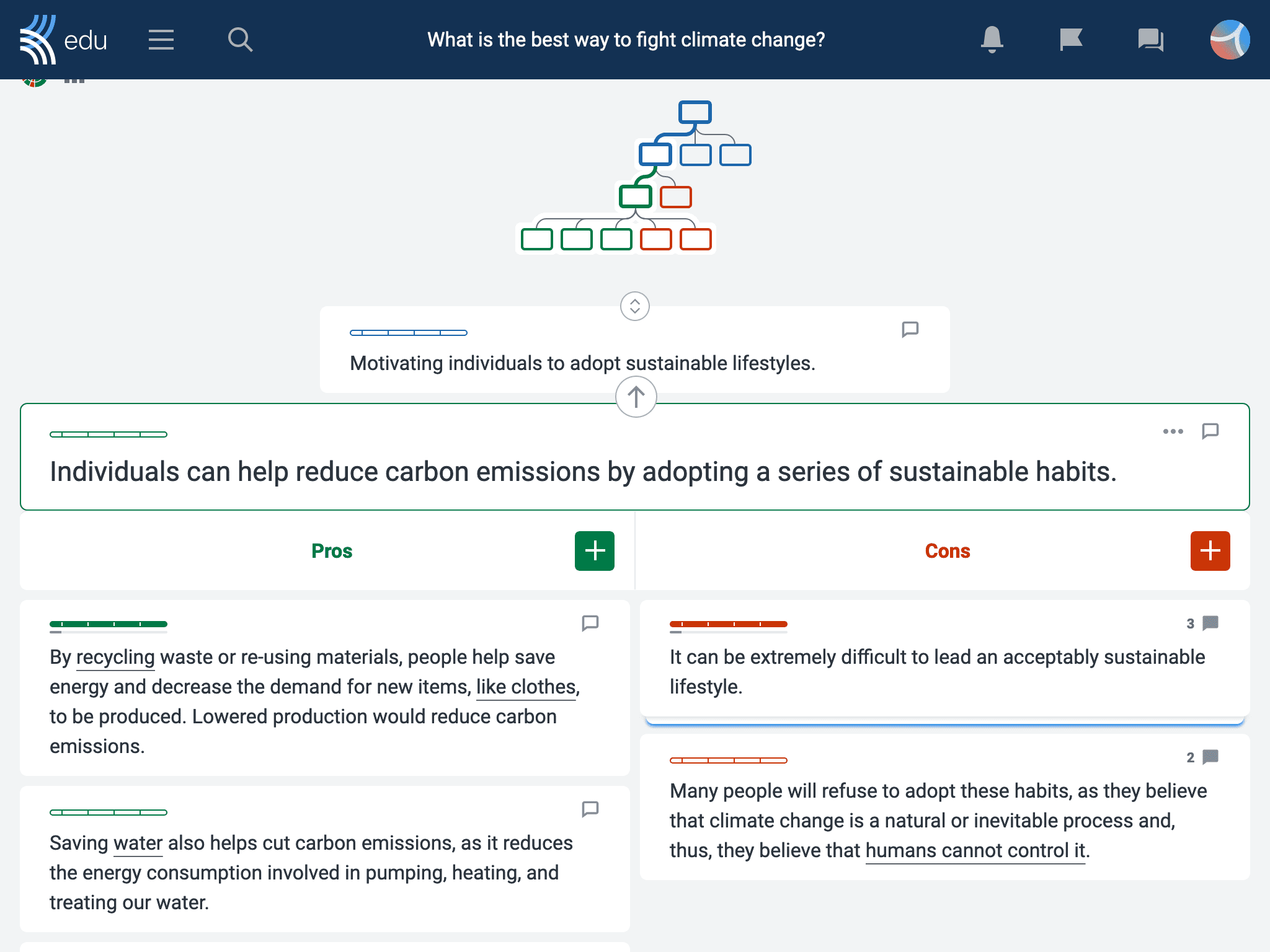
Individual students can plan essays as argument maps before writing. This helps them to stay focused on the line of argument and encourages them to preempt counterarguments. Kialo discussions can even be assigned as an essay alternative when teachers want to focus on argumentation as the key learning goal. Unlike traditional essays, they defy the use of AI chatbots like ChatGPT!
Kialo discussions prompt students to use their reasoning skills to create clear, structured arguments. Moreover, students have a visual, engaging way to respond to the content of the arguments being made, promoting interpretive charity towards differing opinions.
Best of all, Kialo Edu offers a way to track and assess your students’ progress on their critical thinking journey. Educators can assign specific tasks — like citing sources or responding to others’ claims — to evaluate specific skills. Students can also receive grades and feedback on their contributions without leaving the platform, making it easy to deliver constructive, ongoing guidance to help students develop their reasoning skills.
Improving students’ critical thinking abilities is something that motivates our work here at Kialo Edu. If you’ve used our platform and have feedback, thoughts, or suggestions, we’d love to hear from you. Reach out to us on social media or contact us directly at [email protected] .
- Lloyd, M., & Bahr, N. (2010). Thinking Critically about Critical Thinking in Higher Education. International Journal for the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 4 (2), Article 9. https://doi.org/10.20429/ijsotl.2010.040209
- Ennis, R. H. (2015). Critical Thinking: A Streamlined Conception. In: Davies, M., Barnett, R. (eds) The Palgrave Handbook of Critical Thinking in Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, New York.
- Lang-Raad, N. D. (2023). Never Stop Asking: Teaching Students to be Better Critical Thinkers . Jossey-Bass.
- Ellerton, Peter (2019). Teaching for thinking: Explaining pedagogical expertise in the development of the skills, values and virtues of inquiry . Dissertation, The University of Queensland. Available here .
- van Gelder, T. (2015). Using argument mapping to improve critical thinking skills. In The Palgrave Handbook of Critical Thinking in Higher Education (pp. 183–192). doi:10.1057/9781137378057_12.
Want to try Kialo Edu with your class?
Sign up for free and use Kialo Edu to have thoughtful classroom discussions and train students’ argumentation and critical thinking skills.

The State of Critical Thinking 2020
November 2020, introduction.
In 2018, the Reboot Foundation released a first-of-its-kind survey looking at the public’s attitudes toward critical thinking and critical thinking education. The report found that critical thinking skills are highly valued, but not taught or practiced as much as might be hoped for in schools or in public life.
The survey suggested that, despite recognizing the importance of critical thinking, when it came to critical thinking practices—like seeking out multiple sources of information and engaging others with opposing views—many people’s habits were lacking. Significant numbers of respondents reported relying on inadequate sources of information, making decisions without doing enough research, and avoiding those with conflicting viewpoints.
In late 2019, the Foundation conducted a follow up survey in order to see how the landscape may have shifted. Without question, the stakes surrounding better reasoning have increased. The COVID-19 pandemic requires deeper interpretive and analytical skills. For instance, when it comes to news about a possible vaccine, people need to assess how it was developed in order to judge whether it will actually work.
Misinformation, from both foreign and domestic sources, continues to proliferate online and, perhaps most disturbingly, surrounding the COVID-19 health crisis. Meanwhile, political polarization has deepened and become more personal . At the same time, there’s both a growing awareness and divide over issues of racism and inequality. If that wasn’t enough, changes to the journalism industry have weakened local civic life and incentivized clickbait, and sensationalized and siloed content.

Part of the problem is that much of our public discourse takes place online, where cognitive biases can become amplified, and where groupthink and filter bubbles proliferate. Meanwhile, face-to-face conversations—which can dissolve misunderstandings and help us recognize the shared humanity of those we disagree with—go missing.
Critical thinking is, of course, not a cure-all, but a lack of critical thinking skills across the population exacerbates all these problems. More than ever, we need skills and practice in managing our emotions, stepping back from quick-trigger evaluations and decisions, and over-relying on biased or false sources of information.
To keep apprised of the public’s view of critical thinking, the Reboot Foundation conducted its second annual survey in late 2019. Unfortunately, the COVID-19 pandemic forced a delay in the release of the results. Nevertheless, this most recent survey dug deeper than our 2018 poll, and looked especially into how the public understands the state of critical thinking education. For the first time, our team also surveyed teachers on their views on teaching critical thinking.
General Findings
Support for critical thinking skills remains high, but there is also clearly skepticism that individuals are getting the help they need to acquire improved reasoning skills. A very high majority of people surveyed (94 percent) believe that critical thinking is “extremely” or “very important.” But they generally (86 percent) find those skills lacking in the public at large. Indeed, 60 percent of the respondents reported not having studied critical thinking in school. And only about 55 percent reported that their critical thinking skills had improved since high school, with almost a quarter reporting that those skills had deteriorated.
There is also broad support among the public and teachers for critical thinking education, both at the K-12 and collegiate levels. For example, 90 percent think courses covering critical thinking should be required in K-12.
Many respondents (43 percent) also encouragingly identified early childhood as the best age to develop critical thinking skills. This was a big increase from our previous survey (just 20 percent) and is consistent with the general consensus among social scientists and psychologists.
There are worrisome trends—and promising signs—in critical thinking habits and daily practices. In particular, individuals still don’t do enough to engage people with whom they disagree.
Given the deficits in critical thinking acquisition during school, we would hope that respondents’ critical thinking skills continued to improve after they’ve left school. But only about 55 percent reported that their critical thinking skills had improved since high school, with almost a quarter reporting that their skills had actually deteriorated since then.
Questions about respondents’ critical thinking habits brought out some encouraging information. People reported using more than one source of information when making a decision at a high rate (around 77 percent said they did this “always” or “often”) and giving reasons for their opinions (85 percent). These numbers were, in general, higher than in our previous survey (see “Comparing Survey Results” below).
In other areas of critical thinking, responses were more mixed. Almost half of respondents, for example, reported only “sometimes,” “rarely,” or “never” seeking out people with different opinions to engage in discussion. Many also reported only “sometimes,” “rarely,” or “never” planning where (35 percent) or how (36 percent) to get information on a given topic.

These factors are tied closely together. Critical thinking skills have been challenged and devalued at many different levels of society. There is, therefore, no simple fix. Simply cleansing the internet of misinformation, for example, would not suddenly make us better thinkers. Improving critical thinking across society will take a many-pronged effort.
Comparing Survey Results
Several interesting details emerged in the comparison of results from this survey to our 2018 poll. First, a word of caution: there were some demographic differences in the respondents between the two surveys. This survey skewed a bit older: the average age was 47, as opposed to 36.5. In addition, more females responded this time: 57 percent versus 46 percent.
That said, there was a great deal of consistency between the surveys on participants’ general views of critical thinking. Belief in the importance of critical thinking remains high (94 percent versus 96 percent), as does belief that these skills are generally lacking in society at large. Blame, moreover, was spread to many of the same culprits. Slightly more participants blamed technology this time (29 versus 27 percent), while slightly fewer blamed the education system (22 versus 26 percent).
Respondents were also generally agreed on the importance of teaching critical thinking at all levels. Ninety-five percent thought critical thinking courses should be required at the K-12 level (slightly up from 92 percent); and 91 percent thought they should be required in college (slightly up from 90 percent). (These questions were framed slightly differently from year to year, which could have contributed to the small increases.)
One significant change came over the question of when it is appropriate to start developing critical thinking skills. In our first survey, less than 20 percent of respondents said that early childhood was the ideal time to develop critical thinking skills. This time, 43 percent of respondents did so. As discussed below, this is an encouraging development since research indicates that children become capable of learning how to think critically at a young age.
In one potentially discouraging difference between the two surveys, our most recent survey saw more respondents indicate that they did less critical thinking since high school (18 percent versus just 4 percent). But similar numbers of respondents indicated their critical thinking skills had deteriorated since high school (23 percent versus 21 percent).
Finally, encouraging points of comparison emerged in responses to questions about particular critical thinking activities. Our most recent survey saw a slight uptick in the number of respondents reporting engagement in activities like collaborating with others, planning on where to get information, seeking out the opinions of those they disagree with, keeping an open mind, and verifying information. (See Appendix 1: Data Tables.)
These results could reflect genuine differences from 2018, in either actual activity or respondents’ sense of the importance of these activities. But demographic differences in age and gender could also be responsible.
There is reason to believe, however, that demographic differences are not the main factor, since there is no evident correlation between gender and responses in either survey. Meanwhile, in our most recent survey older respondents reported doing these activities less frequently . Since this survey skewed older, it might have been anticipated that respondents would report doing these activities less. But the opposite is the case.
Findings From Teacher Survey
Teachers generally agree with general survey respondents about the importance of critical thinking. Ninety-four percent regard critical thinking as “extremely” or “very important.”
Teachers, like general survey participants, also share concerns that young people aren’t acquiring the critical thinking skills they need. They worry, in particular, about the impact of technology on their students’ critical thinking skills. In response to a question about how their school’s administration can help them teach critical thinking education more effectively, some teachers said updated technology (along with new textbooks and other materials) would help, but others thought laptops, tablets, and smartphones were inhibiting students’ critical thinking development.

This is an important point to clarify if we are to better integrate critical thinking into K-12 education. Research strongly suggests that critical thinking skills are best acquired in combination with basic facts in a particular subject area. The idea that critical thinking is a skill that can be effectively taught in isolation from basic facts is mistaken.
Another common misconception reflected in the teacher survey involves critical thinking and achievement. Although a majority of teachers (52 percent) thought all students benefited from critical thinking instruction, a significant percentage (35) said it primarily benefited high-ability students.
At Reboot, we believe that all students are capable of critical thinking and will benefit from critical thinking instruction. Critical thinking is, after all, just a refinement of everyday thinking, decision-making, and problem-solving. These are skills all students must have. The key is instilling in our young people both the habits and subject-area knowledge needed to facilitate the improvement and refinement of these skills.
Teachers need more support when it comes to critical thinking instruction. In the survey, educators repeatedly mentioned a lack of resources and updated professional development. In response to a question about how administrators could help teachers teach critical thinking more effectively, one teacher asked for “better tools and materials for teaching us how to teach these things.”
Others wanted more training, asking directly for additional support in terms of resources and professional training. One educator put it bluntly: “Provide extra professional development to give resources and training on how to do this in multiple disciplines.”
Media literacy is still not being taught as widely as it should be. Forty-four percent of teachers reported that media literacy courses are not offered at their schools, with just 31 percent reporting required media literacy courses.
This is despite the fact that teachers, in their open responses, recognized the importance of media literacy, with some suggesting it should be a graduation requirement. Many organizations and some governments, notably Finland’s , have recognized the media literacy deficit and taken action to address it, but the U.S. education system has been slow to act.
Thinking skills have been valuable in all places and at all times. But with the recent upheavals in communication, information, and media, particularly around the COVID-19 crisis, such skills are perhaps more important than ever.
Part of the issue is that the production of information has been democratized—no longer vetted by gatekeepers but generated by anyone who has an internet connection and something to say. This has undoubtedly had positive effects, as events and voices come to light that might have previously not emerged. The recording of George Floyd’s killing is one such example. But, at the same time, finding and verifying good information has become much more difficult.
Technological changes have also put financial pressures on so-called “legacy media” like newspapers and television stations, leading to sometimes precipitous drops in quality, less rigorous fact-checking (in the original sense of the term), and the blending of news reports and opinion pieces. The success of internet articles and videos is too often measured by clicks instead of quality. A stable business model for high-quality public interest journalism remains lacking. And, as biased information and propaganda fills gaps left by shrinking newsrooms, polarization worsens. (1)
Traditional and social media both play into our biases and needs for in-group approval. Online platforms have proven ideal venues for misinformation and manipulation. And distractions abound, damaging attention spans and the quality of debate.
Many hold this digital upheaval at least partially responsible for recent political upheavals around the world. Our media consumption habits increasingly reinforce biases and previously held beliefs, and expose us to only the worst and most inflammatory views from the other side. Demagogues and the simple, emotion-driven ideas they advance thrive in this environment of confusion, isolation, and sensationalism.

It’s not only our public discourse that suffers. Some studies have suggested that digital media may be partially responsible for rising rates of depression and other mood disorders among the young. (2)
Coping with this fast-paced, distraction-filled world in a healthy and productive manner requires better thinking and better habits of mind, but the online world itself tends to encourage the opposite. This is not to suggest our collective thinking skills were pristine before the internet came along, only that the internet presents challenges to our thinking that we have not seen before and have not yet proven able to meet.
There are some positive signs, with more attention and resources being devoted to neglected areas of education like civics and media literacy ; organizations trying to address internet-fueled polarization and extremism; and online tools being developed to counter fake news and flawed information.
But we also need to support the development of more general reasoning skills and habits: in other words, “critical thinking.”
Critical thinking has long been a staple of K-12 and college education, theoretically, at least, if not always in practice. But the concept can easily appear vague and merely rhetorical without definite ideas and practices attached to it.
When, for example, is the best age to teach critical thinking? What activities are appropriate? Should basic knowledge be acquired at the same time as critical thinking skills, or separately? Some of these questions remain difficult to answer, but research and practice have gone far in addressing others.
Part of the goal of our survey was to compare general attitudes about critical thinking education—both in the teaching profession and the general public—to what the best and most recent research suggests. If there is to be progress in the development of critical thinking skills across society, it requires not just learning how best to teach critical thinking but diffusing that knowledge widely, especially to parents and educators.
The surveys were distributed through Amazon’s MTurk Prime service.
For the general survey, respondents answered a series of questions about critical thinking, followed by a section that asked respondents to estimate how often they do certain things, such as consult more than one source when searching for information. The questions in the “personal habit” section appeared in a randomized order to reduce question ordering effects. Demographic questions appeared at the end of the survey.
For the teacher survey, respondents were all part of a teacher panel created by MTurk Prime. They also answered a series of questions on critical thinking, especially focused on the role of critical thinking in their classrooms. After that, respondents answered a series of questions about how they teach—these questions were also randomized to reduce question ordering effects. Finally, we asked questions related to the role of media literacy in their classrooms.

To maintain consistency with the prior survey and to explore relationships across time, many of the questions remained the same from 2018. In some cases, following best practices in questionnaire design , we revamped questions to improve clarity and increase the validity and reliability of the responses.
For all surveys, only completed responses coming from IP addresses located in the U.S. were analyzed. 1152 respondents completed the general survey; 499 teachers completed the teacher survey.
The complete set of questions for each survey is available upon request
Detailed Findings and Discussion
As summarized above, the survey produced a number of noteworthy findings. One central theme that emerged was a general pessimism about the state of critical thinking and uncertainty about how to improve it. That is, despite the near-universal acknowledgment of the importance of critical thinking, respondents generally think society at large is doing a bad job of cultivating critical thinking skills. Respondents were, moreover, divided about what needs to be done.
Almost all the people surveyed (94 percent) believe that critical thinking is “extremely” or “very important.” But they generally (86 percent) find those skills lacking in the public at large. These numbers don’t come as a huge surprise—and they echo the 2018 results—but they do suggest broad public support for initiatives that advance critical thinking skills, both inside and outside of schools.
Respondents also reported deficits in their own critical thinking training and practices. They tended not to think critical thinking had been a point of emphasis in their own education, with a substantial majority of over 63 percent reporting that they had not studied critical thinking in school. Around 20 percent said their schools had provided no background in critical thinking at all, and another 20 percent said the background in critical thinking they gained from school was only slight.
There were significant differences among age groups in these self-reports. Around half of respondents in both the 0-19 and 20-39 age groups reported having studied critical thinking in school. Those numbers dwindled among older groups, bottoming out at 11 percent among 80 to 100-year-olds.
This result is likely in part due to the increased popularity of the phrase “critical thinking”: prior generations may have spent a substantial amount of time on reasoning skills without it coming under the same vocabulary. The young are also closer to school-age, of course, so may simply have sharper memories of critical thinking activities. But the differences in responses might also reflect genuine differences in education.
In any case it’s clear that, even recently, many—if not most—students come out of school feeling as if they have not learned how to think critically, despite the fact that there is broad consensus on the importance of these skills. Only around 25 percent of respondents reported receiving an “extremely” or “very” strong background in critical thinking from their schools.
There are a number of potential causes—technology, social norms, misguided educational priorities—but perhaps the most salient is that, as cognitive scientist Tim van Gelder puts it, “critical thinking is hard.” As van Gelder emphasizes, we don’t naturally think reasonably and rationally; instead we tend to rely on narrative, emotion, and intuition—what feels right. (3) Teaching students to think critically requires much more guidance and practice, throughout the curriculum, than is currently being provided.
There is broad support among the public and among teachers for critical thinking education, both at the K-12 and collegiate levels.
Around 90 percent of respondents in the general public said that courses covering critical thinking should be required at the K-12 level, while 94 percent of teachers said critical thinking is important.
And schools usually echo this sentiment as well, citing the phrase “critical thinking” frequently in curricula and other materials. But it remains unclear if, in practice, critical thinking is really the priority it’s made out to be rhetorically.
One problem is a tendency to think critical thinking and reasoning are too complex for younger students to tackle. But research has shown that children start reasoning logically at a very young age. (4) Critical thinking through activities like open-ended dialogue, weighing opposing perspectives, and backing up opinions with reasoning can have a positive effect even at the K-5 level. For example, philosophy for kids courses have shown some positive effects on students’ reading and math skills (gains were even more substantial for disadvantaged students). (5)
Our survey respondents generally agreed that critical thinking skills should be taught from an early age. Forty-three percent favored beginning critical thinking instruction during early childhood (another 27 percent favored beginning at ages 6-12). This was more than a twofold increase over the results from 2018’s survey, in which just 20 percent thought it was best to begin instruction in critical thinking before the age of 6. This increase is encouraging since it’s consistent with recent research that understands critical thinking as part of general cognitive development that starts even before children enter school. (6)
Many teachers likewise support critical thinking instruction beginning at a young age. In the open response, for example, one wrote, “Critical thinking should be explicitly taught in earlier grades than late middle school and high school.”

Another wrote: “By the time students get to high school they should have this skill [critical thinking] well tuned. The pressure to meet standards earlier and earlier makes it harder to teach basic skills like critical thinking.”
Many teachers (55 percent) also thought the emphasis on standardized testing has made it more difficult to incorporate critical thinking instruction in the classroom. For example, one wrote, “Standardized testing has created an environment of quantitative results that don’t always represent qualitative gains.”
Moreover, a plurality of teachers (25 percent) believe that state standardized tests do not assess critical thinking skills well at all, while just 13 percent believe they assess critical thinking skills extremely well. Teachers generally (52 percent) believe that their own tests do a better job of measuring critical thinking skills.
The survey also found some worrisome trends—as well as some promising signs—in how people evaluated their own critical thinking skills and daily practices. In particular, individuals don’t do enough to engage people with whom they disagree.
Given the deficits in critical thinking acquisition during school, it might be hoped that respondents’ critical thinking skills continued to improve after they’ve left school. But only about 55 percent reported that their critical thinking skills had improved since high school, with almost a quarter reporting that their skills had actually deteriorated since then.
This is especially alarming because thinking critically, unlike say learning about calculus or the Russian Revolution, is generally thought to be a lifelong endeavour. We are supposed to become better with age and experience. Research into adult education suggests that it’s never too late to make gains in critical thinking. (7)
Questions about respondents’ critical thinking habits brought out more detailed information. Some of these responses were encouraging. People reported using more than one source of information when making a decision at a high rate (around 77 percent said they did this “always” or “often”), giving reason for their opinions (85 percent), supporting their decisions with information (84 percent), and listening to the ideas of those they disagree with (81 percent). Participants generally reported engaging in more critical thinking activities this time than in our initial survey. (See “Comparing Survey Results” above.)

It’s difficult to totally identify the drivers of these figures. After all, all humans are prone to overestimating the amount and quality of reasoning we do when we come to decisions, solve problems, or research information. But, at the very least, these numbers indicate that people acknowledge that these various critical thinking habits are admirable goals to shoot for.
At the same time and unsurprisingly, these results suggest a reluctance to engage in the more demanding aspects of critical thinking: difficult or unpleasant tasks like seriously considering the possibility that our opponents might be right or thinking carefully about how to approach information-gathering before we engage in it.
Weaknesses in these areas of critical thinking can be especially easily exploited by emotionalized, oversimplified, and sensationalistic news and rhetoric. If people jump in to information-gathering without even a rough plan or method in mind they’re more likely to get swept up by clickbait or worse.
The current media environment requires a mindful and deliberate approach if it is to be navigated successfully. And one’s own opinions will remain under-nuanced, reactive, and prone to groupthink if they’re influenced by the extreme opinions and caricatures that are often found online and on television instead of by engagement with well-reasoned and well-intentioned perspectives.
Poor media consumption habits can have a distorting effect on our political perceptions, especially. Recent research, for example, has identified wildly inaccurate stereotypes among the general public about the composition of political parties. One study found that “people think that 32% of Democrats are LGBT (versus 6% in reality) and 38% of Republicans earn over $250,000 per year (vs. 2% in reality).” (8) The study also suggested, alarmingly, that “those who pay the most attention to political media may […] also [be] the likeliest to possess the most misinformation about party composition.” (9)
The public is worried about the impact of technology on the acquisition of critical thinking skills. They also blamed deficits in critical thinking on changing societal norms and the education system.
Modern technology was the most cited reason for a lack of critical thinking skills among the general public, with “changing societal norms” coming in a close second. Over 200 respondents also cited the educational system (see chart below).
A number of the teachers also mentioned potential drawbacks of technology in the classroom environment. For example, in the open response portion of the survey, which allowed teachers to voice general concerns, one teacher wrote: “Get rid of the laptops and tablets and bring back pencil and paper because the students aren’t learning anything using technology.” Another said: “Personal Electronic devices need to be banned in schools.”
In our own work at the Reboot Foundation, the research team found evidence of negative correlations between technology use at schools and achievement. For example, an analysis of data from the National Assessment of Education Progress (NAEP) showed that fourth graders using tablets “in all or almost all” classes performed significantly worse (the equivalent of a full grade level) than their peers who didn’t use them.
Another recent study the foundation supported also suggested students benefited from using pencil and paper as opposed to technology to do math homework. The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development found similar results a few years ago in their international study of 15-year-olds and computer usage. (10)
There is a great deal the field still doesn’t know about the effects of different kinds of technology on different kinds of learning. But a growing stock of research suggests that schools should be cautious about introducing technology into classrooms and the lives of students in general, especially young students. (11)
It would also be a mistake to slip into simple Luddism though. Technology, obviously, provides benefits as well—making education more accessible, reducing costs, helping teachers to fine-tune instruction to student needs, to name a few. During the coronavirus crisis, moreover, educators have had no choice but to rely and hopefully help improve these tools.
Still, too often in the past schools have turn ed to technology without properly weighing the costs against the benefits, and without determining whether technology is truly needed or effective. A recent RAND Corporation paper, for example, discussed programs “seeking to implement personalized learning” but without “clearly defined evidence-based models to adopt.” (12)
The Reboot survey suggests that members of the public as well as teachers generally share these concerns, both about educational technology specifically and about the general impact of technology on student learning.
While teachers support critical thinking instruction, they are divided about how to teach it, and some educators have beliefs about critical thinking instruction that conflict with established research.
One central question in the research about how to best instill critical thinking skills in students is whether critical thinking should be taught in conjunction with basic facts and knowledge or separated from it.
Teachers were split on this question, with 41 percent thinking students should engage in critical thinking practice while learning basic facts, while 42 percent thought students should learn basic facts first then engage in critical thinking practice. A further 16 percent believe that basic facts and critical thinking should be taught separately. (However, only about 13 percent of teachers surveyed say that content knowledge either doesn’t matter at all or only matters slightly for critical thinking skills.)
The view that knowledge and critical thinking skills can and should be taught separately is mistaken. There is a common view that since information is so widely accessible today, learning basic facts is no longer important. According to this view, it’s only cognitive skills that matter. But the two cannot be so neatly divorced as is often assumed. (13)
Research in cognitive science strongly suggests that critical thinking is not the type of skill that can be divorced from content and applied generically to all kinds of different contexts. As cognitive scientist Daniel T. Willingham argues, “The ability to think critically […] depends on domain knowledge and practice.” (14)
This means students need to practice critical thinking in many different kinds of contexts throughout the curriculum as they acquire the background knowledge needed to reason in a given context. There are of course general skills and habits that can be extrapolated from these various kinds of practice, but it is very unlikely that critical thinking can be taught as a skill divorced from content. “It […] makes no sense,” Willingham writes, “to try to teach critical thinking devoid of factual content.”
This doesn’t necessarily mean standalone critical thinking courses should be rejected. Students can still gain a lot from learning about formal logic, for example, and from learning about metacognition and the best research practices. But these standalone courses or programs should include acquisition of basic factual knowledge as well, and the skills and habits learned in them must be applied and reinforced in other courses and contexts.
Students, moreover, should be reminded that being “critical” is an empty slogan unless they have the requisite factual knowledge to make a cogent argument in a given domain. They need background knowledge to be able to seek out evidence from relevant sources, to develop reliable and nuanced interpretations of information, and to back the arguments they want to make with evidence.

Reboot also asked teachers about which students they thought benefited from critical thinking instruction. A majority (52 percent) thought it benefits all students, but 35 percent said (with the remaining 13 percent thinking it primarily benefits lower-ability students).
The view that critical thinking instruction is only effective for higher achieving students is another common misconception. Everyone is capable of critical thinking, and even, to a certain extent, engages in critical thinking on their own. The key is for students to develop metacognitive habits and subject-area knowledge so that they can apply critical thought in the right contexts and in the right way. Educators should not assume that lower-achieving students will not benefit from critical thinking instruction.
Teachers need more support when it comes to critical thinking instruction, though at least some teacher training and professional development programs do seem to help.
In the survey, educators repeatedly mentioned a lack of resources and updated professional development. In response to a question about how administrators could help teachers teach critical thinking more effectively, one teacher asked for “better tools and materials for teaching us how to teach these things.”
Another said, “Provide opportunities for teachers to collaborate and cross train across subject areas, as well as providing professional development that is not dry or outdated.” Another characteristic comment: “Provide extra professional development to give resources and training on how to do this in multiple disciplines.”
Overall teachers were relatively satisfied that teacher training and professional development programs were helping them teach critical thinking. Forty-six percent said that their teacher training helped them a lot or a great deal, while 50 percent said professional development programs help them a lot or a great deal.
But other teachers reported burdensome administrative tasks and guidelines were getting in the way of teacher autonomy and critical thinking instruction. For example, one teacher wrote, “Earlier in my career I had much more freedom to incorporate instruction of critical thinking into my lessons.”
Media literacy is still not being taught as widely as it should be.
In our survey, teachers rightly recognized that media literacy is closely bound up with critical thinking. One said, “I believe that media literacy goes hand in hand with critical thinking skills and should be a requirement […] especially due to the increase in use of technology among our youth.” Another offered that “media literacy should be a graduation requirement like economics or government.”
But schools, at least judging by teachers’ responses in the survey, have been slow in prioritizing media literacy. More than 44 percent reported that media literacy courses are not offered at their schools, and just around 30 percent reported that media literacy courses are required. That said, the majority of teachers did report teaching typical media literacy skills occasionally in their classes.
For example, over 60 percent said that, in at least one class, they “teach students how to distinguish legitimate from illegitimate sources,” and over two-thirds said they “teach students how to find reliable sources.” (15)
Despite the assumption sometimes made that young people (“digital natives”) must be adept navigators of the internet, recent studies have found that students have trouble evaluating the information they consume online. They have problems recognizing bias and misinformation, distinguishing between advertising and legitimate journalism, and verifying information using credible sources.
Our age is one in which unreliable information proliferates; nefarious interests use the internet to influence public opinion; and social media encourages groupthink, emotional thinking, and pile-on. New skills and training are required to navigate this environment. Our schools must adapt.
This means generating and implementing specific interventions that help students learn to identify markers of misinformation and develop healthy information-gathering habits. The Reboot Foundation’s own research suggests that even quick and immediate interventions can have a positive impact. But it also means instilling students with life-long critical thinking habits and skills which they’ll be able to apply to an ever-changing media landscape.
Despite its importance, which is widely acknowledged by the general public, critical thinking remains a somewhat vague and poorly understood concept. Most people realize that it is of vital importance to individual success and educational attainment, as well as to civic life in a liberal democracy. And most seem to realize that 21st-century challenges and changes make acquiring critical thinking skills of even more urgent importance. But when it comes to instilling them in children and developing them in adults, we are, in many ways, still at square one.
Over the course of the last few decades, K-12 educators have been urged to teach critical thinking, but they have been given conflicting and inconsistent advice on how to do it. There remains a lack of proven resources for them to rely on, a lack of administrative support—and sometimes even a lack of a clear sense of what exactly critical thinking is. Perhaps most importantly, teachers lack the time and freedom within the curriculum to teach these skills.

But there have been a number of insights from cognitive science and other disciplines that suggest a way forward. Perhaps the most important is that critical thinking cannot be understood as a skill on par with learning a musical instrument or a foreign language. It is more complicated than those kinds of skills, involving cognitive development in a number of different areas and integrated with general knowledge learned in other subject areas. Critical thinking courses and interventions that ignore this basic fact may produce some gains, but they will not give students the tools to develop their thinking more broadly and apply critical thought to the world outside of school.
College and continuing education deserve attention too. It should be considered a red flag that only 55 percent of respondents didn’t think they’d made any strides in critical thinking skills since high school. Colleges have long been moving away from a traditional liberal arts curriculum . The critical thinking skills acquired across those disciplines have likely suffered as a result.
In recent years, we’ve seen smart people who should know better time and again exhibit poor judgment online. It is important to remind each other of the importance of stepping back, managing emotions, engaging with others charitably, and seriously considering the possibility that we are wrong. This is especially important when we are searching for information online, an environment that can easily discourage these intellectual virtues. Ramping up media literacy—for both adults and young people—will be a vital part of the solution.
But, ultimately, critical thinking, which touches on so many different aspects of personal and civic life, must be fostered in a multitude of different ways and different domains. A secure, prosperous, and civil future may, quite literally, depend on it.
Appendix 1: Data Tables
When I have a task to do, I collaborate with other people to get ideas.
I plan where to get information on a topic.
[table id=72 /]
I listen to the ideas of others even if I disagree with them.
[table id=73 /]
I keep an open mind to different ideas when making a decision.
[table id=74/]
I make sure the information I use is correct.
[table id=75 /]
I seek out people who tend to have different opinions than me to engage in discussion or debate
[table id=76 /]
To download the PDF of this survey,
(please click here)
(1)* W Gandour, R. (2016) A new information environment: How digital fragmentation is shaping the way we produce and consume news. Knight Center for Journalism in the Americas. https://knightcenter.utexas.edu/books/NewInfoEnvironmentEnglishLink.pdf (2)* Twenge, J. M., Cooper, A. B., Joiner, T. E., Duffy, M. E., & Binau, S. G. (2019). Age, period, and cohort trends in mood disorder indicators and suicide-related outcomes in a nationally representative dataset, 2005–2017. Journal of Abnormal Psychology .
(3)* Gelder, T. V. (2005). Teaching critical thinking: Some lessons from cognitive science. College Teaching , 53 (1), 41-48.
(4)* Gelman, S. A., & Markman, E. M. (1986). Categories and induction in young children. Cognition, 23 , 183-209.
(5)* Gorard, S., Siddiqui, N., & See, B. H. (2015). Philosophy for Children: Evaluation report and executive summary. Education Endowment Foundation. https://educationendowmentfoundation.org.uk/public/files/ Projects/Evaluation_Reports/EEF_Project_Report_PhilosophyForChildren.pdf
(6)* Kuhn, D. (1999). A developmental model of critical thinking. Educational researcher , 28 (2), 16-46.
(7)* Dwyer, C. P., & Walsh, A. (2019). An exploratory quantitative case study of critical thinking development through adult distance learning. Educational Technology Research and Development, 1-19.
(8)* Ahler, D. J., & Sood, G. (2018). The parties in our heads: Misperceptions about party composition and their consequences. The Journal of Politics, 80 (3), 964-981. 964.
(9)* Ibid., 965.
(10)* Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. (2015). Students, computers and learning: Making the connection . https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264239555-en
(11)* Madigan, S., Browne, D., Racine, N., Mori, C., & Tough, S. (2019). Association between screen time and children’s performance on a developmental screening test. JAMA pediatrics, 173(3), 244-250.
(12)* Pane, J. F. (2018). Strategies for implementing personalized learning while evidence and resources are underdeveloped. RAND Corporation. https://www.rand.org/pubs/perspectives/PE314.html
(13)* Wexler, N. (2019). The knowledge gap: The hidden cause of America’s broken education system–and how to fix it. Avery.
(14)* Willingham, D. T. (2007). Critical thinking: Why is it so hard to teach? American Federation of Teachers (Summer 2007) 8-19.
(15)* Wineburg, S., McGrew, S., Breakstone, J., & Ortega, T. (2016). Evaluating information: The cornerstone of civic online reasoning. Stanford Digital Repository, 8, 2018.
please click here.
Privacy Overview

Educator Login
Username or Email
Remember Me
Lost your password?
- Our Curriculum

The West and Environmental Justice
Addressing “Westward Expansion” in the US and environmental justice.
Sustainability Engagement
Students use their voices to call for change. Connecting to personal core values, essay writing, persuasion, speech writing.
Media/Climate Literacy
Students investigate, evaluate strengths and weaknesses of evidence across various media
Industrial Revolution, World History
Focusing on 19th, early 20th Centuries.
Gilded Age and Climate Change
Industrial Revolution in the US, energy and transportation. Progressive Era reforms, and a policy exercise.

The Emerging Crisis in Critical Thinking
Today's college students all too often struggle with real-world problem-solving..
Posted March 21, 2017 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
The mid to late 1990s witnessed the rise of misguided attempts to artificially accelerate brain development in children. Parents began force-feeding infants and toddlers special “educational” DVDs and flashcards in the hopes of taking advantage of unique features of the developing brain to “hardwire genius” by the age of three—or even younger.
Since then, it has become increasingly clear that the brain science of “critical periods” and “neuroplasticity” has been grossly misunderstood and that efforts to artificially harness these important features of brain development by accelerating and distorting real-world learning beyond all reason are not producing the promised results. Recent years have seen only an acceleration of this trend, with parents and teachers adopting rote learning and “baby genius”-style activities.
The first generation of children educated under the “earlier is better,” “wire the brain,” and “baby genius” methodology is now graduating from high school and college, so we can examine the results of these techniques. Unfortunately, rather than creating a generation of “super-geniuses,” there are emerging reports that although modern students are quite adept at memorizing and regurgitating facts presented in class or in reading materials, the ability to reason, think critically, and problem-solve has actually been dramatically reduced in recent years.
A recent article in The Wall Street Journal reported: “On average, students make strides in their ability to reason, but because so many start at such a [critical thinking] deficit, many still graduate without the ability to read a scatterplot, construct a cohesive argument or identify a logical fallacy” [1]
Similarly, in their book, Academically Adrift: Limited Learning on College Campuses , Richard Arum and Josipa Roksa studied 2,400 college students at 24 different universities over a 4-year period [2]. They reported that critical thinking and other skills such as writing were no longer progressing during college as compared to previous generations of students.
In an interview with NPR, Arum sounded the alarm as to why we should be concerned about these findings: “Our country today is part of a global economic system, where we no longer have the luxury to put large numbers of kids through college and university and not demand of them that they are developing these higher-order skills [such as critical thinking] that are necessary not just for them, but for our society as a whole.” [3]
Arum and Roksa describe a number of factors that may be contributing to this decline in critical thinking skills, including pressure on college faculty to make lessons easier in order to get higher course evaluations for their classes.
Why is this happening? What is causing the dearth of thinking ability in young adults, especially after the Herculean efforts parents made during infancy and early childhood to ensure optimal brain development?
One possible explanation is that these college students and recent graduates were at the forefront of the “earlier and earlier education is better” and “rote learning” approaches to teaching preschoolers and even toddlers and babies. Perhaps they—and their developing brains—have been programmed in a way that actually inhibits reasoning, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
In essence, these children—and their developing brains—have been “wired” from an early to memorize and retrieve “facts” on-demand but not to think or reason. Indeed, it is likely that the kind of learning that fosters these skills—namely, intuitive parenting [4]—has been displaced by parenting and teaching styles that overemphasize “teaching to the test,” and treat developing young minds as if they are computer “hard drives” to be inscribed using rote memorization.

Unfortunately, the reported decline in thinking ability is occurring at a time when there are increasing shortages of qualified candidates for jobs in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). Indeed, a young adult whose brain has been “wired” to be innovative, think critically, and problem-solve is at a tremendous competitive advantage in today’s increasingly complex and competitive world.
Because of this, parents should consciously seek to foster independence, problem-solving, critical thinking, and reasoning in their young children. This can be done by implementing an intuitive developmental “dance” between parents and their developing children; which provides everything needed to foster and nurture proper brain development and automatically yields hundreds of thousands of learning opportunities during critical learning periods.
It is vital to bear in mind that the acquisition of problem-solving skills is the direct result of children’s immature, incomplete, and often incorrect attempts to engage with the world that trigger authentic feedback and consequences. Rather than being psychologically damaging events, a child’s unsuccessful attempts are actually opportunities for them to learn persistence and resilience —as well as how to think when things don’t work out quite as they hoped. Indeed, “failure” and overcoming failure are essential events that trigger that neurological development that underpins thinking ability: Opportunities for a child to try—and to fail and then try again—are a crucial part of learning and brain development and should be sought out rather than avoided.
It is time to rethink early childhood priorities—and refocus our efforts as parents and as teachers—to emphasize critical thinking and problem-solving and to abandon misguided attempts to induce pseudo-learning using “baby genius” products and “teaching to the test” educational materials. In the long run, short-term “tricks” that artificially—and temporarily—boost test scores are no match for intuitive parenting and effective teaching; which convey a lifelong competitive advantage by providing a solid foundation for critical thinking and problem-solving.
1. Douglas Belkin, “Test Finds College Graduates Lack Skills for White-Collar Jobs,” Wall Street Journal, January 16, 2015, http://www.wsj.com/articles/test - nds-many-students-ill-prepared-to-enter-work-force-1421432744.
2. Richard Arum and Josipa Roksa, Academically Adrift: Limited Learning on College Campuses (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2011).
3. “A Lack of Rigor Leaves Students ‘Adrift’ in College,” Morning Edition, NPR, February 9, 2011, http://www.npr.org/2011/02/09/133310978/in-college -a-lack-of-rigor-leaves-students-adrift.
4. Stephen M. Camarata (2015). The Intuitive Parent. New York: Current/Penguin/Random House.

Stephen Camarata, Ph.D. is a professor at both the Bill Wilkerson Center and the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, and author of The Intuitive Parent: Why the Best Thing for Your Child Is You .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Top 5 critical thinking skills. Here are five common and impactful critical thinking skills you might consider highlighting on your resume or in an interview: 1. Observation. Observational skills are the starting point for critical thinking. People who are observant can quickly sense and identify a new problem.
Critical thinking skills differ from individual to individual and are utilized in various ways. Examples of common critical thinking skills include: Identification of biases: Identifying biases means knowing there are certain people or things that may have an unfair prejudice or influence on the situation at hand. Pointing out these biases ...
Critical thinking skills will help you connect ideas, make reasonable decisions, and solve complex problems. 7 critical thinking skills to help you dig deeper. Critical thinking is often labeled as a skill itself (you'll see it bulleted as a desired trait in a variety of job descriptions). But it's better to think of critical thinking less ...
6. Ask lots of open-ended questions. Curiosity is a key trait of critical thinkers, so channel your inner child and ask lots of "who," "what," and "why" questions. 7. Find your own reputable ...
The key critical thinking skills are identifying biases, inference, research, identification, curiosity, and judging relevance. Let's explore these six critical thinking skills you should learn and why they're so important to the critical thinking process. 1. Identifying biases.
Critical thinking is the discipline of rigorously and skillfully using information, experience, observation, and reasoning to guide your decisions, actions, and beliefs. You'll need to actively question every step of your thinking process to do it well. Collecting, analyzing and evaluating information is an important skill in life, and a highly ...
The Skills We Need for Critical Thinking. The skills that we need in order to be able to think critically are varied and include observation, analysis, interpretation, reflection, evaluation, inference, explanation, problem solving, and decision making. Specifically we need to be able to: Think about a topic or issue in an objective and ...
The critical thinking process doesn't necessarily lead to a cut-and-dry solution—instead, the process helps you understand the different variables at play so you can make an informed decision. 6. Present your solution. Communication is a key skill for critical thinkers.
Critical thinking (CT) is a metacognitive process, consisting of a number of skills and dispositions, that when used through self-regulatory reflective judgment, increases the chances of producing ...
Consider these ways writing can help enhance critical thinking: 1. Clarity of Thought: Writing requires that you articulate your thoughts clearly and coherently. When you need to put your ideas on ...
Critical thinking skills examples. There are six main skills you can develop to successfully analyze facts and situations and come up with logical conclusions: 1. Analytical thinking. Being able to properly analyze information is the most important aspect of critical thinking. This implies gathering information and interpreting it, but also ...
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
According to the Cambridge Dictionary, critical thinking is "the process of thinking carefully about a subject or idea, without allowing feelings or opinions to affect you.". That's actually a pretty solid place to start. In many ways, critical thinking is a two-fold process. First, it focuses on information-gathering and fact-analysis.
Improves Language & Presentation Skills. In order to best express ourselves, we need to know how to think clearly and systematically — meaning practice critical thinking! Critical thinking also means knowing how to break down texts, and in turn, improve our ability to comprehend. 4. Promotes Creativity.
The key critical thinking skills are analysis, interpretation, inference, explanation, self-regulation, open-mindedness, and problem-solving. To apply the basic principles of critical thinking, follow these steps: identify the problem, gather data, analyze and evaluate, identify assumptions, establish significance, make a decision, and ...
Unsurprisingly, there has been a decline in people's ability to think deeply and reflectively in the past few years. One study, which focused on Millennial and Gen Z workers in the U.S., U.K ...
Consider these basic critical thinking skills to develop to help you become an accomplished critical thinker: Observation: Fundamental to critical thinking, observant people are vigilant and alert to their surroundings and often begin to identify a problem before it fully develops. Reflection: Use curiosity to drive you to ask questions about ...
Critical thinking skills help you process information and make rational decisions. "Critical thinking skills allow us to analyze problems from multiple angles, come up with various solutions, and make informed decisions," says Bayu Prihandito, self-development expert and certified psychology expert. "This not only saves time and resources ...
A Short Guide to Building Your Team's Critical Thinking Skills. by. Matt Plummer. October 11, 2019. twomeows/Getty Images. Summary. Most employers lack an effective way to objectively assess ...
Teach Reasoning Skills. Reasoning skills are another key component of critical thinking, involving the abilities to think logically, evaluate evidence, identify assumptions, and analyze arguments. Students who learn how to use reasoning skills will be better equipped to make informed decisions, form and defend opinions, and solve problems.
Critical thinking skills are often associated with the value of studying the humanities. In majors such as English, students will be presented with a certain text—whether it's a novel, short story, essay, or even film—and will have to use textual evidence to make an argument and then defend their argument about what they've read ...
It's possible to train yourself to become a critical thinker, and there are steps you can take that will help. Start with challenging the norm, "We have always done it this way.". Ask these ...
1. Build a classroom climate that encourages open-mindedness. 2. Teach students to make clear and effective arguments. 3. Encourage metacognition — guide students to think about their own and others' thinking. 4. Assign open-ended and varied activities to practice different kinds of thinking. 5.
4. Study with the help of examples. It is easy to remember information through examples and stories as they reflect the practical implications. They contribute to mindful learning. Real-life examples, anecdotes, analogies, and facts help develop critical thinking skills. 5. Go beyond academic learning.
A very high majority of people surveyed (94 percent) believe that critical thinking is "extremely" or "very important.". But they generally (86 percent) find those skills lacking in the public at large. Indeed, 60 percent of the respondents reported not having studied critical thinking in school.
6. Reflect Critically. Be the first to add your personal experience. 7. Here's what else to consider. Be the first to add your personal experience. Critical thinking is a fundamental skill that ...
Students use their voices to call for change. Connecting to personal core values, essay writing, persuasion, speech writing. READ more.
Arum and Roksa describe a number of factors that may be contributing to this decline in critical thinking skills, including pressure on college faculty to make lessons easier in order to get ...