- information
- Jeevana Charithre
- Entertainment


ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ | Fundamental Rights and Duties Essay in Kannada

ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ Fundamental Rights and Duties Essay Mulabhuta Hakkugalu Mattu Kartavyagalu Prabandha in Kannada
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ

ಈ ಲೇಖನಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣವಾದ ಮಾಹಿತಿಯನ್ನು ನಮ್ಮ Post ನಲ್ಲಿ ನೀಡಲಾಗಿದೆ.
ನಾಗರಿಕ ಎಂದರೆ ರಾಜ್ಯ ಮತ್ತು ದೇಶದ ಯಾವುದೇ ಹಳ್ಳಿ ಅಥವಾ ಪಟ್ಟಣದಲ್ಲಿ ನಿವಾಸಿಯಾಗಿ ವಾಸಿಸುವ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿ. ನಾವೆಲ್ಲರೂ ನಮ್ಮ ದೇಶದ ಪ್ರಜೆಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ನಮ್ಮ ಗ್ರಾಮ, ನಗರ, ಸಮಾಜ, ರಾಜ್ಯ ಮತ್ತು ದೇಶದ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ವಿಭಿನ್ನ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಜವಾಬ್ದಾರಿಗಳನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿದ್ದೇವೆ. ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ನಾಗರಿಕನ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಬಹಳ ಮೌಲ್ಯಯುತ ಮತ್ತು ಪರಸ್ಪರ ಸಂಬಂಧ ಹೊಂದಿವೆ.
ವಿಷಯ ವಿವರಣೆ
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಗಳ, ಬೌದ್ಧಿಕ, ನೈತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಆಧ್ಯಾತ್ಮಿಕ ಬೆಳವಣಿಗೆಗೆ ಅಗತ್ಯವಾದ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಗಳ ಅಸ್ತಿತ್ವ ಮತ್ತು ಸರ್ವಾಂಗೀಣ ಅಭಿವೃದ್ಧಿಗೆ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಅಥವಾ ಅವಶ್ಯಕವಾದ ಕಾರಣ, ನವದೀಪ್ ಚೌಧರಿ ಅವರ ಪ್ರಕಾರ ಇದನ್ನು ‘ಮೂಲಭೂತ’ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಇವುಗಳನ್ನು ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಭಾಗ III ವಿಧಿಗಳು 12 ರಿಂದ 35 ರ ವರೆಗಿನ ವಿಧಿಗಳ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿವೆ. ಪ್ರತಿಪಾದಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ೬ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿವೆ.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳಳನ್ನು 1976 ರಲ್ಲಿ 42 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ ಮಾಡುವ ಮೂಲಕ 4 (A) ಹೊಸದಾದ ಭಾಗ ಮಾಡಿಕೊಂಡು 51 (A) ಹೊಸದಾದ ವಿಧಿ ಮಾಡಿಕೊಂಡು ಅದರಲ್ಲಿ 10 ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಸೇರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಮತ್ತು 2002 ರಲ್ಲಿ 86 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ ಮಾಡಿ 11 ಕರ್ತವ್ಯವನ್ನು ಸೇರಿಸಲಾಯಿತು.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು
೧. ಸಮಾನತೆಯ ಹಕ್ಕು (14 – 18).
14,15,16, 17,18 ಪರಿಚ್ಛೇದಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ವಿವರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ವಿಧಿ (14) : ಕಾನೂನಿನ ಮುಂದೆ ಎಲ್ಲರು ಸಮಾನರು. ಕಾನೂನಿಗಿಂತ ಶ್ರೇಷ್ಟರು ಯಾರೂ ಇಲ್ಲ. ಹಾಗಾಗಿ ಕಾನೂನಿಗೆ ಸರ್ವರೂ ತಲೆಬಾಗಲೇಬೇಕು. ಕಾನೂನು ಯಾರಿಗೂ ಅಸಮಾನತೆಯನ್ನು ಬೆಂಬಲಿಸಿಲ್ಲ. ವಿಧಿ (15) : ತಾರತಮ್ಯವನ್ನು ನಿಶೆಧಿಸಿದೆ(ಜಾತಿ, ಲಿಂಗ, ಭಾಷೆ, ಹುಟ್ಟಿದ ಸ್ಥಳದ ಆಧಾರದ ಮೆಲೆ) ವಿಧಿ (16) : ಸಾವ್ರಜನಿಕ ಹುದ್ದೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಸಮಾನ ಅವಕಾಶ ನೀಡ ಬೇಕೆಂದು ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. ವಿಧಿ (17) : ವಿಧಿಅಸ್ಪಶ್ಯತೆ ನಿಷೇಧಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ವಿಧಿ (18) : ಬಿರುದುಗಳ ರದ್ಧತಿ ಎ೦ದು ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತದೆ (ಮಿಲಿಟರಿ ಮತ್ತು ಸರ್ಕಾರಿ ಬಿರುದುಗಳನ್ನು ಬಿಟ್ಟು)
೨. ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು : (ವಿಧಿ 19 ರಿಂದ 22)
ವಿಧಿ19 ರಿಂದ 22 ವರೆಗೆ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ವಿವರಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. 19 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯು ಆರು ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ನೀಡಿದೆ.
- ವಾಕ್ ಮತ್ತು ಅಭಿವ್ಯಕ್ತಿ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ.
- ಅಸ್ತ್ರಗಳಿಲ್ಲದೆ ಶಾಂತಿಯುತವಾಗಿ ಒಂದೆಡೆ ಸೇರುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ.
- ಸಂಘ ಮತ್ತು ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳನ್ನು ರಚಿಸುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ
- ಭಾರತದಾದ್ಯಂತ ಚಲಿಸುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ
- ಭಾರತದ ಯಾವುದೇ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ವಾಸಿಸುವ ಮತ್ತು ಖಾಯಂ ನೆಲೆಸುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ
- ಯಾವುದೇ ವೃತ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ನಡೆಸುವ, ಅಥವಾ ಯಾವುದೇ ವಾಣಿಜ್ಯ ಅಥವಾ ವ್ಯವಹಾರದಲ್ಲಿ ತೊಡಗುವ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 20 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಅಪರಾಧಿಯ ರಕ್ಷಣೆ
- ವಿಧಿ 21 : ಜೀವಿಸುವ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 21 (ಎ) ವಿಧಿ : ಶಿಕ್ಷಣದ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 22 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಬಂದಿಸಿದ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯ ರಕ್ಷಣೆ
೩. ಶೋಷಣೆಯ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ಹಕ್ಕು ( 23 – 24 )
- 23 – 24 ಪರಿಚ್ಛೇದಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ವಿವರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
- 23 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಜೀತ ಪದ್ದತಿ ನಿಷೇಧ.
- 24 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಬಾಲ ಕಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಪದ್ದತಿ ನಿಷೇಧ.
೪.ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು ( 25 – 28 )
25, 26, 27, 28 ನೇ ಪರಿಚ್ಛೇದಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ವಿವರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
- 25 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಯಾವುದೇ ಧರ್ಮವನ್ನು ಸ್ವೀಕರಿಸುವುದು.
- 26 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಧರ್ಮದ ಹೆಸರಿನಲ್ಲಿ ಆಸ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಸಂಪಾದಿಸುವುದು.
- 27 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಒತ್ತಾಯ ಪೂರ್ವಕವಾಗಿ ತೆರಿಗೆ ಪಡೆಯುವಂತಿಲ್ಲ.
- 28 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಭೋದನೆ ಮಾಡುವಂತಿಲ್ಲ.
೫. ಸಾಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಶೈಕ್ಷಣಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ( 29 – 30 )
29, 30 ನೇ ಪರಿಚ್ಛೇದಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ವಿವರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
- 29 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ಅಲ್ಪಸಂಖ್ಯಾತರ ಹಿತರಕ್ಷಣೆ.
- 30 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ : ತಾರತಮ್ಯ ಮಾಡುವಂತಿಲ್ಲ.
೬. ಸಂವಿಧಾನಾತ್ಮಕ ಪರಿಹಾರಗಳ ಹಕ್ಕು ( ವಿಧಿ 32 )
ವಿಧಿ 32 : ಸಂವಿಧಾನಾತ್ಮಕ ಪರಿಹಾರಗಳ ಹಕ್ಕು ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ಮೇಲಿನ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಅನುಷ್ಥಾನಕ್ಕೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನಿಕ ಪರಿಹಾರವನ್ನು ಪಡೆಯುವ ಅವಕಾಶವನ್ನು ಕಲ್ಪಸಿಕೊಡುತ್ತದೆ. ಮತ್ತು ಡಾ/ಬಿ.ಆರ್.ಅಂಬೇಡ್ಕರ 32 ವಿಧಿಯನ್ನು ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಆತ್ಮ ಮತ್ತು ಹೃದಯ ಎಂದು ಕರೆದರು.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ನ್ಯಾಯರಕ್ಷಿತವಲ್ಲ. ಆದರೆ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯ ಉಲ್ಲಂಘನೆಯಾದರೆ ಅವರನ್ನು ಶಿಕ್ಷಿಸಬಹುದು. ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಕೇಳುವಂತೆ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಪಾಲಿಸುವುದು ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ಪೌರನ ಆದ್ಯ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯವಾಗಿದೆ.
- ಸಂವಿಧಾನವನ್ನು ಪಾಲಿಸುವುದು, ಅದರ ಆಶಯಗಳನ್ನು ಗೌರವಿಸುವುದು. ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರಧ್ವಜ ಮತ್ತು ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರಗೀತೆಯನ್ನು ಗೌರವಿಸುವುದು.
- ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ ಹೋರಾಟಕ್ಕೆ ಸ್ಪೂರ್ತಿ ಕೊಟ್ಟ ಆದರ್ಶಗಳನ್ನು ಗೌರವಿಸುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ಪಾಲಿಸುವುದು.
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಾರ್ವಭೌಮತ್ವ, ಅಖಂಡತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಏಕತೆಯನ್ನು ಎತ್ತಿ ಹಿಡಿಯುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ಕಾಪಾಡುವುದು.
- ದೇಶವನ್ನು ರಕ್ಷಿಸುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ದೇಶಸೇವೆಗೆ ಸಿದ್ಧರಿರುವುದು.
- ವಿವಿಧ ಧರ್ಮ, ಭಾಷೆ ಮತ್ತು ಪ್ರಾಂತ್ಯಗಳ ಜನರೊಂದಿಗೆ ಸೌಹಾರ್ದದಿಂದ ಇರುವುದು; ಮಹಿಳೆಯರಿಗೆ ಅಗೌರವ ತೋರುವ ಪದ್ದತಿಗಳನ್ನು ತಿರಸ್ಕರಿಸುವುದು.
- ನಮ್ಮ ವೈವಿಧ್ಯಮಯ ಸಂಸ್ಕೃತಿ ಮತ್ತು ಪರಂಪರೆಯನ್ನು ಗೌರವಿಸುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ಕಾಪಾಡುವುದು.
- ದೇಶದ ಕಾಡು, ವನ್ಯ ಜೀವಿಗಳು, ನದಿಗಳು ಸೇರಿದಂತೆ ಪರಿಸರವನ್ನು ಉಳಿಸಿ ಬೆಳೆಸುವುದು.
- ವೈಜ್ಞಾನಿಕ ಮನೋಧರ್ಮವನ್ನು ಬೆಳೆಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದು. ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆ ಮಾಡುವ ಮತ್ತು ಬದಲಾವಣೆಗೆ ಒಡ್ಡಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವ ಮನಸ್ಥಿತಿ ಬೆಳೆಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದು.
- ಸಾರ್ವಜನಿಕ ಸ್ವತ್ತನ್ನು ಕಾಪಾಡಿಕೊಳ್ಳುವುದು; ಹಿಂಸೆಯನ್ನು ತೊರೆಯುವುದು.
- ಎಲ್ಲಾ ವೈಯಕ್ತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಸಾಮೂಹಿಕ ಚಟುವಟಿಕೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಉನ್ನತಿಯನ್ನು ಸಾಧಿಸಲು ಪ್ರಯತ್ನಿಸಿ ದೇಶದ ಪ್ರಗತಿಗಾಗಿ ಶ್ರಮಿಸುವುದು.
- ಎಲ್ಲಾ ತಂದೆ-ತಾಯಿಯರು/ಪಾಲಕರು/ಪೋಷಕರು 6 ರಿಂದ14 ವರ್ಷ ವಯಸ್ಸಿನ ಮಕ್ಕಳಿಗೆ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣ ಪಡೆಯುವ ಅವಕಾಶ ನೀಡತಕ್ಕದ್ದು.
ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಜೀವನದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಪ್ರಮುಖ ಪಾತ್ರವಹಿಸುತ್ತವೆ. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಸಂಕೀರ್ಣತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಕಷ್ಟದ ಸಮಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಉತ್ತಮ ಮಾನವರಾಗಲು ನಮಗೆ ಸಹಾಯ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಜೊತೆಗೆ ಕೆಲವು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನೂ ಉಲ್ಲೇಖಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ನಾವು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪರಸ್ಪರ ಪ್ರೀತಿಸಬೇಕು ಮತ್ತು ಗೌರವಿಸಬೇಕು ಮತ್ತು ಯಾವುದೇ ವ್ಯತ್ಯಾಸವಿಲ್ಲದೆ ಒಟ್ಟಿಗೆ ಬದುಕಬೇಕು. ನಮ್ಮ ದೇಶವನ್ನು ರಕ್ಷಿಸಲು ನಾವು ಕಾಲಕಾಲಕ್ಕೆ ತ್ಯಾಗ ಮಾಡಬೇಕೆಂದು ನಿರೀಕ್ಷಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಜೊತೆಗೆ ಕೆಲವು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನೂ ಉಲ್ಲೇಖಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಯಾವ ದೇಶದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಿಂದ ಎರವಲಾಗಿ ಪಡೆಯಲಾಗಿದೆ ?
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಯಾವ ದೇಶದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಿಂದ ಎರವಲಾಗಿ ಪಡೆಯಲಾಗಿದೆ.
ಇತರೆ ವಿಷಯಗಳು :
ಮಾನವ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ದಿನಾಚರಣೆ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಪ್ರಬಂಧ
ಭಾರತದ ಚುನಾವಣಾ ವ್ಯವಸ್ಥೆ ಪ್ರಬಂಧ
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
EDITOR PICKS
Irumudi kattu sabarimalaikku lyrics in kannada | ಇರುಮುಡಿ ಕಟ್ಟು ಶಬರಿಮಲೈಕ್ಕಿ ಸಾಂಗ್ ಲಿರಿಕ್ಸ್, atma rama ananda ramana lyrics in kannada | ಆತ್ಮಾರಾಮ ಆನಂದ ರಮಣ ಸಾಂಗ್ ಲಿರಿಕ್ಸ್ ಕನ್ನಡ, ಮಹಾತ್ಮ ಗಾಂಧೀಜಿ ಪ್ರಬಂಧ ಕನ್ನಡ | mahatma gandhi essay in kannada, popular posts, popular category.
- information 267
- Prabandha 227
- Kannada Lyrics 122
- Lyrics in Kannada 57
- Jeevana Charithre 41
- Festival 36
- Kannada News 32
© KannadaNew.com
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Dmca Policy
- SSLC Result 2024 Karnataka

- NOTIFICATION
- CENTRAL GOV’T JOBS
- STATE GOV’T JOBS
- ADMIT CARDS
- PRIVATE JOBS
- CURRENT AFFAIRS
- GENERAL KNOWLEDGE
- Current Affairs Mock Test
- GK Mock Test
- Kannada Mock Test
- History Mock Test
- Indian Constitution Mock Test
- Science Mock Test
- Geography Mock Test
- Computer Knowledge Mock Test
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION
- MENTAL ABILITY
- ENGLISH GRAMMER
- COMPUTER KNOWLDEGE
- QUESTION PAPERS
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು | Fundamental Rights in Kannada

ಮೂಲಭೂತ-ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು, Mulabhuta Hakkugalu in Kannada, fundamental rights in kannada, fundamental rights kannada, pdf, notes, essay, IC Notes
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆ ಉತ್ತರ Mulabhuta Hakkugalu in Kannada
ಮಾನವ ಅಸ್ತಿತ್ವಕ್ಕೆ ಮೂಲಭೂತವಾದ ಮತ್ತು ಮಾನವ ವಿಸ್ತರಣೆಗೆ ನಿರ್ಣಾಯಕವಾದ ಕೆಲವು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿವೆ. ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಅನುಪಸ್ಥಿತಿಯಲ್ಲಿ, ಮನುಷ್ಯನ ಅಸ್ತಿತ್ವವು ನಿಷ್ಪ್ರಯೋಜಕವಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಆದ್ದರಿಂದ, ರಾಜಕೀಯ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಯ ಪಾತ್ರ ಮತ್ತು ಜವಾಬ್ದಾರಿಯು ಮುಖ್ಯವಾಗಿ ಜನರಿಗೆ, ವಿಶೇಷವಾಗಿ ಅಲ್ಪಸಂಖ್ಯಾತರಿಗೆ ಸಮಾನತೆ, ಘನತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳೊಂದಿಗೆ ಘನತೆಯಿಂದ ಬದುಕಲು ಅಧಿಕಾರ ನೀಡುವುದನ್ನು ಒತ್ತಿಹೇಳುತ್ತದೆ.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಕುರಿತು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಸಮಾನತೆಯ ಹಕ್ಕು, ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು, ಶೋಷಣೆ ವಿರುದ್ಧದ ಹಕ್ಕು, ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು, ಸಾಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಶೈಕ್ಷಣಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕು, ಸಾಂವಿಧಾನಿಕ ಪರಿಹಾರದ ಹಕ್ಕು ಎಂದು 6 ವರ್ಗಗಳಾಗಿ ವರ್ಗೀಕರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.

ಸಮಾನತೆಯ ಹಕ್ಕು
ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ಕಾನೂನಿನ ಮುಂದೆ ಸಮಾನತೆಯನ್ನು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿರುತ್ತದೆ, ಇದು ಜಾತಿ, ಧರ್ಮ, ಬಣ್ಣ ಅಥವಾ ಲಿಂಗದ ಆಧಾರದ ಮೇಲೆ ತಾರತಮ್ಯವನ್ನು ನಿಷೇಧಿಸುವುದು, ಕಾನೂನಿನ ಸಮಾನ ರಕ್ಷಣೆ, ಸಾರ್ವಜನಿಕ ಉದ್ಯೋಗದಲ್ಲಿ ಸಮಾನ ಅವಕಾಶ ಮತ್ತು ಅಸ್ಪೃಶ್ಯತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಶೀರ್ಷಿಕೆಗಳ ನಿರ್ಮೂಲನೆಯನ್ನು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿರುತ್ತದೆ. ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ನಾಗರಿಕನಿಗೆ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಸಾರ್ವಜನಿಕ ಸ್ಥಳಗಳಿಗೆ ಸಮಾನ ಪ್ರವೇಶವಿದೆ ಎಂದು ಅದು ಹೇಳುತ್ತದೆ.
ಸಮಾನ ಅವಕಾಶಗಳನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸಲು ಪರಿಶಿಷ್ಟ ಜಾತಿ, ಪರಿಶಿಷ್ಟ ಪಂಗಡಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಇತರ ಹಿಂದುಳಿದ ವರ್ಗಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಯುದ್ಧ ವಿಧವೆಯರು ಮತ್ತು ದೈಹಿಕ ವಿಕಲಚೇತನರಿಗೆ ಹೊರತುಪಡಿಸಿ ಸರ್ಕಾರಿ ಸೇವೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಯಾವುದೇ ಮೀಸಲಾತಿ ಇರುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಭಾರತದಲ್ಲಿ ದಶಕಗಳಿಂದ ಆಚರಣೆಯಲ್ಲಿದ್ದ ಅಸ್ಪೃಶ್ಯತೆ ನಿವಾರಣೆಗಾಗಿ ಈ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ನೀಡಲಾಯಿತು.
ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು
ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ವಾಕ್ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ , ಅಭಿವ್ಯಕ್ತಿ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ ಮತ್ತು ಒಕ್ಕೂಟಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಸಂಘಗಳನ್ನು ರಚಿಸುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯವನ್ನು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿದೆ. ಇದು ಭಾರತದಲ್ಲಿ ಎಲ್ಲಿ ಬೇಕಾದರೂ ಪ್ರಯಾಣಿಸುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ, ಭಾರತದ ಯಾವುದೇ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ವಾಸಿಸುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ ಮತ್ತು ತಮ್ಮ ಆಸಕ್ತಿಯ ಯಾವುದೇ ವೃತ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಆಯ್ಕೆ ಮಾಡುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯವನ್ನು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿದೆ.
ಭಾರತದ ಯಾವುದೇ ಪ್ರಜೆಯು ದೇಶದ ಯಾವುದೇ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ಆಸ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಖರೀದಿಸಲು, ಮಾರಾಟ ಮಾಡಲು ಮತ್ತು ಹೊಂದಲು ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿರುತ್ತಾನೆ ಎಂದು ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ಹೇಳುತ್ತದೆ. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಪ್ರಕಾರ, ಜನರು ಯಾವುದೇ ವ್ಯಾಪಾರ ಅಥವಾ ವ್ಯವಹಾರದಲ್ಲಿ ಪಾಲ್ಗೊಳ್ಳುವ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯವನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿರುತ್ತಾರೆ. ಒಬ್ಬ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಒಂದೇ ಅಪರಾಧಕ್ಕೆ ಎರಡು ಬಾರಿ ಶಿಕ್ಷೆಗೆ ಗುರಿಪಡಿಸಲಾಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ ಮತ್ತು ತನ್ನ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ಸಾಕ್ಷಿಯಾಗಿ ನಿಲ್ಲುವಂತೆ ಒತ್ತಾಯಿಸಲಾಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ ಎಂದು ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ವ್ಯಾಖ್ಯಾನಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಶೋಷಣೆ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ಹಕ್ಕು
ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ಯಾವುದೇ ರೀತಿಯ ಬಲವಂತದ ಕಾರ್ಮಿಕರ ನಿಷೇಧವನ್ನು ಒಳಗೊಂಡಿದೆ. 14 ವರ್ಷಕ್ಕಿಂತ ಕಡಿಮೆ ವಯಸ್ಸಿನ ಮಕ್ಕಳಿಗೆ ಜೀವಕ್ಕೆ ಅಪಾಯವಿರುವ ಗಣಿಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಅಥವಾ ಕಾರ್ಖಾನೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಕೆಲಸ ಮಾಡಲು ಅನುಮತಿಸಲಾಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಪ್ರಕಾರ, ಯಾವುದೇ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಗೆ ಇನ್ನೊಬ್ಬ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಯಾವುದೇ ರೀತಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಶೋಷಿಸುವ ಹಕ್ಕಿಲ್ಲ.
ಆದ್ದರಿಂದ ಮಾನವ ಕಳ್ಳಸಾಗಣೆ ಮತ್ತು ಭಿಕ್ಷಾಟನೆಯನ್ನು ಕಾನೂನು ಅಪರಾಧಗಳಾಗಿ ಮಾಡಲಾಗಿದೆ ಮತ್ತು ಅದರಲ್ಲಿ ಭಾಗಿಯಾಗಿರುವವರಿಗೆ ದಂಡ ವಿಧಿಸಲಾಗುತ್ತದೆ. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಪ್ರಕಾರ ಮಹಿಳೆಯರು ಮತ್ತು ಮಕ್ಕಳ ನಡುವೆ ಅಪ್ರಾಮಾಣಿಕ ಉದ್ದೇಶಗಳಿಗಾಗಿ ಗುಲಾಮಗಿರಿ ಮತ್ತು ಸಂಚಾರವನ್ನು ಅಪರಾಧವೆಂದು ಘೋಷಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಕಾರ್ಮಿಕರ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ಕನಿಷ್ಠ ವೇತನ ಪಾವತಿಯನ್ನು ವ್ಯಾಖ್ಯಾನಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ ಮತ್ತು ಈ ವಿಷಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಯಾವುದೇ ರಾಜಿಗೆ ಅವಕಾಶವಿಲ್ಲ.
ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು
ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಭಾರತದ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ನಾಗರಿಕರಿಗೆ ಆತ್ಮಸಾಕ್ಷಿಯ ಸಂಪೂರ್ಣ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯ ಇರುತ್ತದೆ ಎಂದು ಹೇಳುತ್ತದೆ. ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಜನರು ತಮ್ಮ ಆಯ್ಕೆಯ ಧರ್ಮವನ್ನು ಮುಕ್ತವಾಗಿ ಅಳವಡಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಲು, ಆಚರಿಸಲು ಮತ್ತು ಹರಡಲು ಸಮಾನ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿರುತ್ತಾರೆ.
ಯಾವುದೇ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯ ಯಾವುದೇ ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ವ್ಯವಹಾರಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ರಾಜ್ಯವು ಯಾವುದೇ ರೀತಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಅಡ್ಡಿಪಡಿಸುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಇದರಲ್ಲಿ, ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಧರ್ಮಗಳು ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ದತ್ತಿ ಉದ್ದೇಶಗಳಿಗಾಗಿ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳನ್ನು ಸ್ಥಾಪಿಸುವ ಮತ್ತು ಎತ್ತಿಹಿಡಿಯುವ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿವೆ. ಅಲ್ಲದೆ, ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿಗೆ ಸಂಬಂಧಿಸಿದಂತೆ ಅವರು ತಮ್ಮ ಸ್ವಂತ ವ್ಯವಹಾರಗಳನ್ನು ನಿರ್ವಹಿಸಲು ಸ್ವತಂತ್ರರಾಗಿರುತ್ತಾರೆ.
ಸಾಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಶೈಕ್ಷಣಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕು
ಶಿಕ್ಷಣವು ಪ್ರತಿ ಮಗುವಿನ ಪ್ರಾಥಮಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕು ಆಗಿರುವುದರಿಂದ ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ಅತ್ಯಂತ ಪ್ರಮುಖ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಒಂದಾಗಿದೆ . ಈ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಪ್ರಕಾರ, ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬರೂ ತಮ್ಮ ಆಯ್ಕೆಯ ಸಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಯನ್ನು ಅನುಸರಿಸಲು ಸ್ವತಂತ್ರರು. ಅಲ್ಲದೆ, ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬರೂ ತಮ್ಮ ಆಯ್ಕೆಯ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣವನ್ನು ಪಡೆಯಲು ಮುಕ್ತರಾಗಿದ್ದಾರೆ.
ಯಾವುದೇ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಗೆ ಅವರ ಸಂಸ್ಕೃತಿ, ಜಾತಿ ಅಥವಾ ಧರ್ಮದ ಆಧಾರದ ಮೇಲೆ ಯಾವುದೇ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಪ್ರವೇಶವನ್ನು ನಿರಾಕರಿಸಲಾಗುವುದಿಲ್ಲ. ಇದರ ಪ್ರಕಾರ, ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಅಲ್ಪಸಂಖ್ಯಾತರು ತಮ್ಮದೇ ಆದ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳನ್ನು ಸ್ಥಾಪಿಸುವ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿದ್ದಾರೆ.
ಸಂವಿಧಾನಾತ್ಮಕ ಪರಿಹಾರದ ಹಕ್ಕು
ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಪ್ರಜೆಗಳಿಗೂ ನೀಡಿರುವ ವಿಶೇಷ ಹಕ್ಕು. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಪ್ರಕಾರ, ಯಾವುದೇ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ನಿರಾಕರಿಸಿದ ಸಂದರ್ಭದಲ್ಲಿ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯಕ್ಕೆ ಹೋಗಲು ನಾಗರಿಕನಿಗೆ ಅಧಿಕಾರವಿದೆ. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಉಲ್ಲಂಘನೆಯ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯವು ಯಾರಿಗಾದರೂ ಕಾವಲುಗಾರನಾಗಿ ನಿಂತಿದೆ.
ಸರ್ಕಾರವು ಯಾವುದೇ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಗೆ ಬಲವಂತವಾಗಿ ಅಥವಾ ಉದ್ದೇಶಪೂರ್ವಕವಾಗಿ ಅನ್ಯಾಯ ಮಾಡಿದರೆ ಅಥವಾ ಯಾವುದೇ ಕಾರಣವಿಲ್ಲದೆ ಅಥವಾ ಕಾನೂನುಬಾಹಿರ ಕೃತ್ಯದಿಂದ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಜೈಲಿನಲ್ಲಿರಿಸಿದರೆ, ಈ ಹಕ್ಕು ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯು ಸರ್ಕಾರದ ಕ್ರಮಗಳ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ನ್ಯಾಯಕ್ಕಾಗಿ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯಕ್ಕೆ ಹೋಗಲು ಅನುಮತಿಸುತ್ತದೆ.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆ ಉತ್ತರ
- 2002 ರಲ್ಲಿ 86 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ ಮಾಡಿ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣ ಪಡೆಯುವುದು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನಾಗಿ ಮಾಡುವ ಮೂಲಕ ಮತ್ತೊಂದು ಮೂಲ ಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಸಂವಿಧಾನಕ್ಕೆ ಸೇರ್ಪಡೆ ಮಾಡಲಾಯಿತು .
- 6 ರಿಂದ 14 ವರ್ಷದ ಒಳಗಿನ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಮಕ್ಕಳು ಉಚಿತ ಮತ್ತು ಕಡ್ಡಾಯ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣ ಪಡೆಯುವುದು 21 ಎ ವಿಧಿ ಅಡಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕಾಗಿದೆ .
- 1946 ರ ಕ್ಯಾಬಿನೇಟ್ ಆಯೋಗವು ಕೂಡ ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಅಳವಡಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಬೇಕೆಂದು ಹಾಗೂ ಅದಕ್ಕಾಗಿ ಒಂದು ಸಮಿತಿಯನ್ನು ನೇಮಿಸಬೇಕೆಂದು ಶಿಫಾರಸ್ಸು ಮಾಡಿತು .
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ರಚನಾ ಸಭೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಸಲಹಾ ಸಮಿತಿಯನ್ನು ಸರ್ದಾರ್ ವಲ್ಲಭಬಾಯಿ ಪಟೇಲ್ರವರ ಅಧ್ಯಕ್ಷತೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ನೇಮಿಸಲಾಗಿತ್ತು .
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂರನೇ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ , 12 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯಿಂದ 35 ನೇ ವಿಧಿವರೆಗೆ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ವಿವರಣೆಯನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸಿದೆ .
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಅಮೇರಿಕಾದ ಬಿಲ್ಸ್ ಆಫ್ ರೈಟ್ಸ್ ಎಂಬ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿಂದ ಎರವಲು ಪಡೆಯಲಾಗಿದೆ .
- ಭಾರತದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು “ ಭಾರತದ ಮ್ಯಾಗ್ನಕಾರ್ಟ್ ” ಎಂದು ಕರೆಯುತ್ತಾರೆ .
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು 1949 ನವಂಬರ್ 26 ರಂದು ಅಳವಡಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಲಾಯಿತು .
- ಅಲ್ಪಸಂಖ್ಯಾತರ ಹಿತ ರಕ್ಷಣೆಯನ್ನು 29 ಮತ್ತು 30 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಗಳು ರಕ್ಷಿಸುತ್ತವೆ .
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ 2002 ರಲ್ಲಿ 86 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿಯ ಅನ್ವಯ 6 ರಿಂದ 14 ವರ್ಷದೊಳಗಿನ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಮಕ್ಕಳು ಉಚಿತ & ಕಡ್ಡಾಯ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣ ಪಡೆಯಲು ಅವಕಾಶ ಕಲ್ಪಿಸಲಾಯಿತು ಇದು ಶೈಕ್ಷಣಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನಾಗಿ ಮಾಡಲಾಗಿದೆ . ಎಂದು ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 21 ಎ ವಿಧಿ ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತದೆ .
- ಭಾರತದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ರೂಪಿತವಾಗಲು ಭಾರತ ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರೀಯ ಕಾಂಗ್ರೆಸ್ನ ಅನೇಕ ಬಾರಿಯ ಒತ್ತಾಯದ ಫಲವಾಗಿದೆ .
- ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಉಪಸಮಿತಿಗೆ ಆಚಾರ ಕೃಪಲಾನಿಯವರನ್ನು ಅಧ್ಯಕ್ಷರಾಗಿ ನೇಮಕ ಮಾಡಲಾಯಿತು
- . ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಉಪಸಮಿತಿಯು ಫೆ .27 , 1947 ರಂದು ಮೊದಲ ಬಾರಿಗೆ ಸಭೆ ಸೇರಿತು .
- 1948 ಡಿ .10 ರಂದು ವಿಶ್ವ ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಯ ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಸಭೆಯಲ್ಲಿ ಹೊರಡಿಸಿದ ಮಾನವ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಸಾರ್ವತ್ರಿಕ ಘೋಷಣೆಯಿಂದ ಭಾರತದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಅಳವಡಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಲು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಪ್ರೇರಣೆ ಉಂಟಾಯಿತು .
- ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ನ್ಯಾಯ ಸಂರಕ್ಷಿತವಾಗಿವೆ ಹಾಗೂ ಸಾರ್ವತ್ರಿಕವಾಗಿ ಅನ್ವಯವಾಗುತ್ತವೆ .
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ 7 ( 6 + 1 ) ವಿಧದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ನೀಡಲಾಗಿದೆ .
- ಮೂಲ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ 7 ವಿಧದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿದ್ದವು .
- 1978 ರಲ್ಲಿ ಮಾಡಲಾದ 44 ನೇ ಸಂವಿಧಾನಾತ್ಮಕ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಆಸ್ತಿ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ತೆಗೆದು ಹಾಕಿ ಆರು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಉಳಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಲಾಯಿತು .
- ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಜಾತಿ , ಜನಾಂಗ , ಲಿಂಗ , ಜನ್ಮಸ್ಥಳದ ತಾರತಮ್ಯವಿಲ್ಲದೆ ಎಲ್ಲರಿಗೂ ಅನ್ವಯವಾಗುತ್ತವೆ .
- ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಉಲ್ಲಂಘನೆಯಾದಾಗ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಪ್ರಶ್ನಿಸಬಹುದು .
- ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಪರಿಣಾಮಕಾರಿಯಾದ ಅಂಶಗಳಾಗಿವೆ .
- ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಪ್ರಜಾಪ್ರಭುತ್ವದ ಮೌಲ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಎತ್ತಿ ಹಿಡಿಯುವಲ್ಲಿ ಸಹಕಾರಿಯಾಗಿವೆ .
- 1 ) ಸಮಾನತೆಯ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 2 ) ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 3 ) ಶೋಷಣೆ ವಿರುದ್ಧದ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 4 ) ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 5 ) ಸಾಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಕ ಹಾಗೂ ಶೈಕ್ಷಣಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 6 ) ಸಂವಿಧಾನ ಪರಿಹಾರಾತ್ಮಕ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 7 ) ಶಿಕ್ಷಣದ ಹಕ್ಕು
- 1 ) ಹೇಬಿಯಸ್ ಕಾರ್ಪಸ್ ( ಬಂಧ ಪ್ರತ್ಯೇಕ್ಷಿಕರಣ ) – 24 ಗಂಟೆಯೊಳಗಡೆ ಬಂಧಿಸಿದ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯದ ಮುಂದೆ ಹಾಜರು ಪಡಿಸುವುದು .
- 2 ) ಮ್ಯಾಂಡಮಸ್ ( ಪರಮಾದೇಶ ) – ಕರ್ತವ್ಯವನ್ನು ಮಾಡಲು ಆದೇಶಿಸುವುದು .
- 3 ) ಸರ್ಷಿಯೊರರಿ – ಕೆಳನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯದ ಮೊಕದ್ದಮೆಗಳನ್ನು ಮೇಲಿನ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯಕ್ಕೆ ವರ್ಗಾಯಿಸುವುದು .
- 4 ) ಕೊ – ವಾರೆಂಟ್ – ಅಕ್ರಮವಾಗಿ ಸಾರ್ವಜನಿಕ ಹುದ್ದೆಯನ್ನು ಪಡೆದಿದ್ದರೆ ಅಂತವರ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ಹಾಕುವ ರಿಟ್ .
- 5 ) ಪ್ರೊಹಿಬಿಷನ್ – ಕೆಳಗಿನ ನ್ಯಾಯಾಲಯವು ತನ್ನ ಅಧಿಕಾರ ವ್ಯಾಪ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ಮೀರಿ ನೀಡಿದ ತೀರ್ಪನ್ನು ತಡೆಯಲು ಹೊರಡಿಸುವ ರಿಟ್
- ಸಮಾನತೆಯ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ಮತ್ತು 18 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಗಳು ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತವೆ .
- ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 19 , 20 , 21,22 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ ಗಳು ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತವೆ .
- ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 17 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯು ಅಸ್ಪೃಶ್ಯತಾ ನಿಷೇಧದ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತದೆ .
- ಶೋಷಣೆ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 23 , 24 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತದೆ .
- 24 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯು 14 ವರ್ಷದ ಒಳಗಿನ ಮಕ್ಕಳು ಗಣಿ ಮತ್ತು ಅಪಾಯಕಾರಿ ಕೆಲಸಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ತೊಡಗುವುದನ್ನು ನಿಷೇಧಿಸುತ್ತದೆ ಈ ವಿಧಿಯು ಬಾಲಕಾರ್ಮಿಕ ನಿಷೇಧದ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತದೆ .
- ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತವೆ .
- ಸಾಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಕ ಹಾಗೂ ಶೈಕ್ಷಣಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 29 , 30 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತದೆ .
- ಆಸ್ತಿ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸಿದ್ದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 31 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯನ್ನು ತೆಗೆದು ಹಾಕಿ , ಆಸ್ತಿ ಕಾನೂನಿನ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಅಡಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಸೇರ್ಪಡೆ ಮಾಡಲಾಗಿದೆ .
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 32 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯನ್ನು ಡಾ.ಬಿ.ಆರ್.ಅಂಬೇಡ್ಕರ್ರವರು ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ‘ ಆತ್ಮ ಮತ್ತು ಹೃದಯ ‘ ಎಂದು ವರ್ಣಿಸಿದ್ದಾರೆ .
- ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 32 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯು ಸಂವಿಧಾನ ಪರಿಹಾರ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸುತ್ತದೆ .
- ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿಗೆ ಧಕ್ಕೆ ಉಂಟಾದಾಗ ರಿಟ್ಗಳ ಮೂಲಕ ಸುಪ್ರೀಂ ಕೋರ್ಟ್ ಮತ್ತು ಹೈಕೋರ್ಟ್ಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಪ್ರಶ್ನಿಸಬಹುದು .
- ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿಗೆ ಧಕ್ಕೆ ಉಂಟಾದಾಗ ಹೈಕೋರ್ಟ್ನಲ್ಲಿ 226 ನೇ ವಿಧಿ ಅನ್ವಯ ರಿಟ್ ಮೂಲಕ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಸಂರಕ್ಷಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಬಹುದು .
- ಸಂವಿಧಾನ ಪರಿಹಾರ ಹಕ್ಕಿನಲ್ಲಿ ಒದಗಿಸಿರುವ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮೂಲತಃ ಬ್ರಿಟನ್ನಿನಿಂದ ಎರವಲು ಪಡೆಯಲಾಗಿದೆ .
ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 32 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಯು?
ಸಂವಿಧಾನ ಪರಿಹಾರ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸುತ್ತದೆ .
ಸಮಾನತೆಯ ಹಕ್ಕಿನ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ವಿಧಿಗಳು
14 , 15 , 16 , 17 ಮತ್ತು 18 ನೇ ವಿಧಿಗಳು ತಿಳಿಸುತ್ತವೆ .
ಇತರೆ ವಿಷಯಗಳು
- ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಪ್ರಮುಖ ಲಕ್ಷಣಗಳು ಪ್ರಶ್ನೋತ್ತರಗಳು
- Karnataka GK Questions in Kannada -05
- ಜನರಲ್ ಪ್ರಶ್ನೆಗಳು 2022-06
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Disclaimer

- Current Affairs
- _Current Affairs 2023
- _Current Affairs 2022
- _Current Affairs 2021
- Model Question Papers
- _Kannada PDF Notes
- _Indian Constitution
- _Mental Ability
ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಹುಡುಕಲು ಇಲ್ಲಿ ಸರ್ಚ್ ಮಾಡಿ
[pdf] indian constitution full pdf notes in kannada for all competitive exams download now.

[PDF] Indian Constitution Full PDF Notes in Kannada For All Competitive Exams Download Now
![[PDF] Indian Constitution Full PDF Notes in Kannada For All Competitive Exams Download Now, indian constitution pdf in kannada, p.s. gangadhar indian constitution pdf in kannada download, important articles of indian constitution in kannada, Salient features of Indian Constitution in Kannada pdf [PDF] Indian Constitution Full PDF Notes in Kannada For All Competitive Exams Download Now](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/a/AVvXsEiP6M3W1rfm0s1TFYrHBzYrEBb-yjTfF2roXMlSjn3FU8T2XdU0JfYWdcyWoH60LUeHqM6ANEo6Ppr1wgovHgcPw8NZ7IiBqFnEQJiqA-AsvubBy2JyD1Xsa9ksWy54mkn1rjauaRmYsRSOEy9X3IC29gYAx5UJVBdHZNVl8GaNUnQ3xBuCQlwbZXTthg=w581-h640-rw)
Download Indian Constitution Full PDF Notes in Kannada Download Now :
Download indian constitution full pdf notes in kannada :, why we need indian constitution full pdf notes in kannada pdf :, how to download indian constitution full pdf notes in kannada:, download indian constitution full pdf notes in kannada for free now:, pdf file details.
File Category: Indian Constitution Full PDF Notes in Kannada
Download link: Given Below
File Language: Kannada
Which Department: Education
Which State: Central and State
Published Date: 20-02-2022
File Format Type: PDF
File Size: 2.6 MB
Total Pages: 160 Pages
Download Link: Click Below Blue Color Link To Download Indian Constitution Full PDF Notes in Kannada PDF
Scanned Copy: Yes
Editable text: No
Copy text: No
Print enables: Yes
Quality: High
File Size Reduced: No
Password Protected: No
Password Encrypted: No
Image Available: Yes
Cost: Free of Cost
Strictly For Educational And Knowledge Purpose Only
Download Officers Adda 2021 Magazines PDF Now
💥 also download: officers adda november 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda october 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda september 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda august 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda july 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda june 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda may 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda april 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda march 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda february 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf 💥 also download: officers adda january 2021 kannada monthly current affairs magazine pdf , download akshara dasoha 2021 magazines pdf now, also, download these files, you may like these posts, post a comment.
If you have any doubts please let me know
Buy Products
Important pdf notes, popular posts.

Top-25 Educational Psychology Question Answers Quiz in Kannada For All State TET, CTET, GPSTR and HSTR Part-08
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] Psychology Short Key Points Notes in Kannada For TET, CTET, GPSTR, and HSTR Exam Download Now](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhpE9V81SLi-psDAEfcPpivIBuPxgQxxlqnNbWUWEdbhpzOukBxbJjzIi-cMESabx2ueHu9NmCyGKDOzMupd-TUfWzHuHcRow7ZR6cn4VGYKhqSX_AnyUI3D4ZMAeVKojg5Dp9Gd1CBVbjpTlhanvavnQCOuCsM24InKQOwD9UWUTAQSGO9lg3rl0HeaA/w680/%5BPDF%5D%20Edutube%20Kannada%20Special%20Educational%20Psychology%20Short%20Notes%20in%20Kannada%20For%20TET,%20CTET,%20GPSTR,%20and%20HSTR%20Exam%20Download%20Now.webp)
[PDF] Psychology Short Key Points Notes in Kannada For TET, CTET, GPSTR, and HSTR Exam Download Now

ಸಮಾಜ ವಿಜ್ಞಾನ ಬೋಧನಾಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್ ಮಾಡಿಕೊಳ್ಳಿ Social Science Pedagogy PDF in Kannada Download Now
.webp)
KARTET-2014 Paper-02 Child Development and Pedagogy Quiz in Kannada

Top-25 Educational Psychology Question Answers Quiz in Kannada For All State TET, CTET, GPSTR and HSTR Part-11

Download Karnataka TET Exam Model Question Papers PDF

12 March 2022 Kannada Daily Current Affairs Question Answers Quiz For All Competitive Exams

13 March 2022 Daily Top-10 General Knowledge Question Answers in Kannada for All Competitive Exams
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] Educational Psychology Notes in Kannada PDF Download Now](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhc33y9yH3VYRqVZOeh_OcwwvH2Y2Hnq2xY0vrj-VT85ukHfRiMiT1y0KX3Raa5KtoEY8A9MkyvrVUX4Q9_NoK8vAMiPic0Rmsson-zY2eBzlozlr6TK22SLRCzQCV6kxG7QN7hrSJVap3aqGRzxisWemYFdiJFoYwhHR0gTbTw1OXOWIXy3z7iG-FnAw/w680/%5BPDF%5D%20Educational%20Psychology%20Notes%20in%20Kannada%20PDF%20Download%20Now.webp)
[PDF] Educational Psychology Notes in Kannada PDF Download Now
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] Karnataka TET (KARTET) Paper-01 Kannada Medium Official Model Question Paper PDF Download Now](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhC84cifqrQRsKuT5To1SPJfZpnxKN8vLo8TfKxe0TSI0Gq_XJA_kqnjY67yea43Dop8miSFFAFgBVVvvV53_vADeMjGT88ovrYZnPwtC-DRapvtzW1yY-8kAqzxFNz3B2eIEVIaGUMYbw3D8RRwWZHNx8KrkmRJ2gaNNUwf6Tv16dH7XYYLh5sysDPZw/w680/%5BPDF%5D%20Karnataka%20TET%20(KARTET)%20Paper-01%20Kannada%20Medium%20Official%20Model%20Question%20Paper%20PDF%20Download%20Now.webp)
[PDF] Karnataka TET (KARTET) Paper-01 Kannada Medium Official Model Question Paper PDF Download Now
ಮಹತ್ವದ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಗಳು.
- 10th Standard Notes 13
- 2nd PUC Notes 6
- 6th Standard Notes 12
- 7th Standard Notes 3
- 8th Standard Notes 12
- 9th Standard Notes 5
- Computer PDF Notes 7
- CTET PDF Notes 50
- Economics PDF Notes 6
- English Pedagogy PDF Notes 1
- FDA Study Materials 13
- General Science PDF Notes 25
- Geography PDF Notes 7
- GPSTR PDF Notes 172
- GPSTR Science PDF Notes 15
- HSTR Study Materials 58
- Indian History 64
- K-SET Materials 9
- Karnataka School Notes 47
- KPSC PDF Notes 110
- KSOU Previous Question Papers 7
- Mathematics Pedagogy PDF Notes 1
- Methodology PDF Notes 8
- PDF Notes 510
- PDO Study Materials 26
- PSI PDF Notes 72
- PUC Books 48
- PUC Passing Packages 38
- PUC Question Banks 5
- Science PDF Notes 17
- Science Pedagogy 8
- Social Science PDF Notes 15
- Sulalita Notes 5
- Teachers PDF Materials 18
- Test Series PDF 1
- TET Notes 125
- UGC NET PDF NOTES 24
- UPSC PDF Notes 21
Top Post Ad
Below post ad, search this blog, join our telegram channel, total pageviews, useful contents, subscribe us in youtube, buy products online, buy products from amazon, popular notes.
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] 2nd PUC History Full Notes PDF Download Now ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಇತಿಹಾಸ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhUVuK0RtGS5p3OoQUzB6ys0jgFqyosyTmk3JUSvlMZh3nKLkikoN0QrYJienUKhtjMB9Wlhp3vbQgWw9xh6FDv_eb33n29K0dLYAVI3sLU41F1xC2MGrgfCzBbkIHY1iiVP7ft6hYUXFMr/w680/20210510_141111.webp)
[PDF] 2nd PUC History Full Notes PDF Download Now ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಇತಿಹಾಸ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] 2nd PUC Economics Notes PDF Download Now ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಅರ್ಥಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgJ3Y-PPWZUb-1Nyj-nMfGz_sEUGAtnGnPeDt4guy3GRx041Ibx1FrYsDyzoLCcsToApCtcWQVD04FA48sR_dju7XT81Z5mtUZBlG7vP4pGS_fud87js7OiHI_T_Tqb41LXBEg7-iMmA-sl/w680/20210510_133154.webp)
[PDF] 2nd PUC Economics Notes PDF Download Now ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಅರ್ಥಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] Sulalita 2nd PUC Kannada Notes PDF Download Now ಸುಲಲಿತ ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಕನ್ನಡ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiUXYpcZ_K5Oy-jqbvurW1G6DC2x6T_E5u9g2X4Ub2WUJqyGipREdrQ2nyrddR5hCVuxBdG5TrutgAZ60BI_g3ZAHv2v5GO1FO1OARTKx2FjrJJwu4W5KuC8FC85SrVrxiEabpF8ceuCWp4/w680/kannada+notes.webp)
[PDF] Sulalita 2nd PUC Kannada Notes PDF Download Now ಸುಲಲಿತ ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಕನ್ನಡ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] Sulalita 2nd PUC Economics Notes PDF Download Now ಸುಲಲಿತ ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಅರ್ಥಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh3mMe9QSouNcP-Pc7MCjTft7oGWFyZh5OXO3z3M0CcEDaIMsxdVYlkwAs9duwu_bhFgXU1LCZzZdtqSqVrRI0CzlrhnLFLiGKO1uEv2OfOEv7wTGAp1SM5-g8ZJ0nU2YOFSdD0r-B4jD59/w680/economics+notes.webp)
[PDF] Sulalita 2nd PUC Economics Notes PDF Download Now ಸುಲಲಿತ ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ಅರ್ಥಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] Karnataka Computer Literacy Test (CLT) PDF Study materials Free Download Now](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi57tdFC0y7-t1SovAbGvSUUmuCRKOIJJWVlF5o8IaIvcdsFmLE3-3LvKlob8S6e2o8uf9VXINBuGTDZPp1ycAO_1lnWEnbugjQEYWq34rA2XzuEXtxDDjz5P5bFiPAOdRjKxeVRzGuJCVF/w680/Computer+Literacy+PDF+Notes+%2528www.edutubekannada.com%2529.webp)
[PDF] Karnataka Computer Literacy Test (CLT) PDF Study materials Free Download Now
![fundamental rights and duties of indian constitution essay in kannada [PDF] 2nd PUC Political Science Notes PDF Download Now ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ರಾಜ್ಯಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgUPYEoS_5jVEQQqv-h51u83rNy3HJqjoO-3KDMsqIhTd_gma2x6VZ5e44VUZ1_n1P9MASC2Ym3wHC69VuhS81nE9p4pqdOt-gzveJAsqnXZWCI39fqF4NlDroa5rDWol-LFhVZr4Lfrdte/w680/pltcl+nts.webp)
[PDF] 2nd PUC Political Science Notes PDF Download Now ಪಿಯುಸಿ ದ್ವಿತೀಯ ವರ್ಷದ ರಾಜ್ಯಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಪಿಡಿಎಫ್ ನೋಟ್ಸ್ ಡೌನ್ಲೋಡ್
- 2nd PUC History PDF Book 4
- 2nd PUC Passing Packages 24
- 5th Std English Notes 16
- 9th Notes 5
- 9th Social Science Notes 6
- Akshara Academy Magazines 2021 2
- Akshara Dasoha Magazines 2021 12
- Basavanna Vachanagalu 1
- Best Kannada Book List 1
- Blogger Quiz Generator 1
- CBSE SSLC PDF Notes 2
- Chiguru Model QP 6
- Child Development and Pedagogy Question Answers 15
- Computer Literacy Test Study Materials 6
- Constitution 12
- Current Affairs 276
- Current Affairs 2019 1
- Current affairs 2020 66
- Current affairs 2021 83
- Current Affairs 2023 13
- Current Affairs Magazines 51
- Current Affairs MCQs 196
- Current affairs Quiz 199
- Current Events 2020 63
- Daily Current Affairs 2021 79
- Daily Current Affairs 2022 147
- Daily Current Affairs in Kannada 202
- Daily Top-10 General Knowledge Question Answers 567
- Daily Top-10 Science Question Answers 4
- Dr. K M Suresh Competitive Exam Books 1
- Educational psychology Quiz 69
- English Grammar 17
- English Grammar Quiz 12
- Exam Tips 4
- FDA MCQs 62
- FDA Quiz 297
- Free Coaching Question Papers 1
- General Kannada Quiz 377
- General Knowledge 40
- General Knowledge Question Answers 490
- Geography 22
- Geography QA 7
- Geography Quiz 314
- GK Quiz 388
- GPSTR English Notes 11
- GPSTR Model Question Papers 16
- GPSTR Previous Question Papers 81
- GPSTR Quiz 460
- GPSTR Recruitment 75
- Graduate Primary School Teachers Recruitment Old Question Papers PDF 10
- Great Personalities 4
- History Notes 23
- HSTR Model Question Papers 1
- HSTR Previous Question Papers 5
- HTML Quiz Generator 1
- Husenappa Nayak Free PDF Notes 2
- IAS Parliament Magazine 2021 1
- Indian Constitution 23
- Indian Polity 4
- Jnana Gangothri E-Magazine 2020 11
- Jnana sadhana 1
- Jnana Sadhana Magazines 2021 1
- Job News 59
- K-SET Previous Question Papers 4
- Kannada Grammar 33
- kannada Literature 6
- Kannada Moral Stories 1
- Kannada Vachanagalu 1
- Karnataka History 39
- Karnataka PUC Books 19
- Karnataka School Lesson Plans 16
- Karnataka SSLC Social Science Notes 9
- Karnataka Tet 2020 14
- KARTET Notes 2021 84
- KAS PDF Notes 71
- Key Answers 17
- KPSC MCQs 63
- KPSC Previous Question Papers 12
- KPSC Quiz 307
- KPTCL PDF Notes 4
- KSOU MA External Previous Question Papers 7
- KTBS Text Books PDF 1
- Latest Jobs 75
- Magazines 52
- Magazines 2021 48
- Magzines 2020 2
- Major Awards 3
- MCQs For All Exams 62
- Mental Ability 9
- Mini Papers 56
- Mini Vijayavani Vidyarthimitra 2021 155
- Model Lesson Plans 17
- Model Question Papers 214
- Officers Adda Current Affairs Magazines 17
- Old Question Papers 79
- PDF Books 379
- PDO Solved Question Papers 1
- Police Constable 11
- Police Constable MCQs 63
- Police Constable Study Materials 39
- Police Exam Useful Question Answers 7
- Police Notes 7
- Political Science 5
- Previous Question Papers 1
- PSI Essays 3
- PSI Previous Question Papers 2
- PSI Quiz 307
- Psychology Kannada Books 9
- PUC 1st Year Books 24
- PUC 1st Year Kannada Chapterwise Notes 5
- PUC 1st Year Notes 13
- PUC 1st Year Question Papers 1
- PUC 2nd Year Books 25
- PUC Mathematics Notes 2
- PUC Notes 22
- Question Answers 3
- Question Papers 13
- RRB Question Papers 7
- Science Chapterwise Question Answers 3
- Science Quiz 247
- SDA MCQs PDO MCQs 62
- SDA Quiz 295
- SDA Study Materials 16
- Social Science Notes 39
- Spardha Anavaran Magazine 2021 1
- Spardha Teja Model Question Papers 53
- Spardha Vijetha Magazines 2021 10
- Spardha Vijetha PDF Notes 1
- Spoorthi PG Model Question Papers 50
- SSLC English Notes 11
- SSLC Kannada Notes 16
- SSLC Kannada Workbook 1
- SSLC Mathematics Notes 2
- SSLC Notes 59
- SSLC Passing Packages 40
- SSLC Science Notes 42
- SSLC Science PDF Notes 17
- SSLC Social Science Chapterwise Notes 1
- SSLC Social Science English Medium Notes 7
- SSLC Social Science Notes 65
- SSLC Social Science Passing Packages 2023 6
- SSLC Social Science PDF Notes 17
- Sulalita English Medium Notes 1
- Swami Vivekananda Quotes 1
- Teachers Recruitment 2021 12
- TET 2020 Special 16
- TET CTET Quiz 432
- TET MCQs 62
- TET Model Question Papers 5
- TET Previous Question Papers 5
- Top-10 Educational Psychology Question Answers 1
- Top-10 Geography Question Answers 2
- Top-10 History Question Answers 2
- Top-10 Science Question Answers 1
- Top-100 General Knowledge Question Answers 36
- Top-30 Kannada Question Answers 1
- UPSC Previous Question Papers 1
- Vidyakashi Magazine 38
- Vijaya Karnataka Mini Papers 5
- Vijayavani Vidyarthimitra 105
- Yojana magazine 2021 6
- ಕನ್ನಡ ಕಥೆಗಳು 1
- ಕನ್ನಡ ನೀತಿ ಕಥೆಗಳು 2
- ಕನ್ನಡ ವಚನಗಳು 1
- ಜೀವನ ಚರಿತ್ರೆಗಳು 5
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನ 2
- ಭೂಗೋಳಶಾಸ್ತ್ರ 2
Most Useful Notes

Contact form
Switch to the dark mode that's kinder on your eyes at night time.
Switch to the light mode that's kinder on your eyes at day time.
ಭಾರತ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ | Fundamental Rights and Duties of Indian Constitution Essay in Kannada
ಭಾರತ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ, Fundamental Rights and Duties of Indian Constitution Essay in Kannada bharata samvidhana moolabhootha hakkugalu mattu kartvyagalu prabandha in kannada
Fundamental Rights and Duties of Indian Constitution Essay in Kannada
ಈ ಕೆಳಗಿನ ಪ್ರಬಂಧದಲ್ಲಿ ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ವಿವರವಾಗಿ ತಿಳಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.

ಭಾರತ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ
ನಾಗರಿಕ ಎಂದರೆ ರಾಜ್ಯ ಮತ್ತು ದೇಶದ ಯಾವುದೇ ಹಳ್ಳಿ ಅಥವಾ ಪಟ್ಟಣದಲ್ಲಿ ನಿವಾಸಿಯಾಗಿ ವಾಸಿಸುವ ವ್ಯಕ್ತಿ. ನಾವೆಲ್ಲರೂ ನಮ್ಮ ದೇಶದ ಪ್ರಜೆಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ನಮ್ಮ ಗ್ರಾಮ, ನಗರ, ಸಮಾಜ, ರಾಜ್ಯ ಮತ್ತು ದೇಶದ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ವಿಭಿನ್ನ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಜವಾಬ್ದಾರಿಗಳನ್ನು ಹೊಂದಿದ್ದೇವೆ. ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ನಾಗರಿಕನ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಬಹಳ ಮೌಲ್ಯಯುತ ಮತ್ತು ಪರಸ್ಪರ ಸಂಬಂಧ ಹೊಂದಿವೆ.
ವಿಷಯ ವಿವರಣೆ :
ಪ್ರಸ್ತುತ ಯುಗ ಪ್ರಜಾಪ್ರಭುತ್ವದ ಯುಗ. ಪ್ರಪಂಚದ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ನಾಗರಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಪ್ರಗತಿಪರ ದೇಶಗಳು ಜನರಿಗೆ ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಹೆಚ್ಚು ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ನೀಡುವ ಪರವಾಗಿವೆ. ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಂದು ರಾಜ್ಯ ಅಥವಾ ದೇಶವು ತನ್ನ ನಾಗರಿಕರಿಗೆ ವೈಯಕ್ತಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು, ಧಾರ್ಮಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು, ಸಾಮಾಜಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು, ನೈತಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು, ಆರ್ಥಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ರಾಜಕೀಯ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಂತಹ ಕೆಲವು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ನಾಗರಿಕ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸುತ್ತದೆ. ದೇಶದ ಪ್ರಜೆಗಳಾಗಿ ನಾವು ನೈತಿಕವಾಗಿ ಮತ್ತು ಕಾನೂನಾತ್ಮಕವಾಗಿ ಯಾವಾಗಲೂ ಒಟ್ಟಿಗೆ ನಮ್ಮ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಪೂರೈಸಬೇಕಾಗಿದೆ.
ನಾವು ಪರಸ್ಪರ ಪ್ರೀತಿಸಬೇಕು ಮತ್ತು ಗೌರವಿಸಬೇಕು ಮತ್ತು ಯಾವುದೇ ವ್ಯತ್ಯಾಸವಿಲ್ಲದೆ ಒಟ್ಟಿಗೆ ಬದುಕಬೇಕು. ನಮ್ಮ ದೇಶವನ್ನು ರಕ್ಷಿಸಲು ನಾವು ಕಾಲಕಾಲಕ್ಕೆ ತ್ಯಾಗ ಮಾಡಬೇಕೆಂದು ನಿರೀಕ್ಷಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಜೊತೆಗೆ ಕೆಲವು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನೂ ಉಲ್ಲೇಖಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ವರ್ಗೀಕರಣ:
ಭಾರತೀಯ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂರನೇ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ಆರ್ಟಿಕಲ್ 12 ರಿಂದ 35 ರವರೆಗೆ ವಿವರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಆರ್ಟಿಕಲ್ 12, 13, 33, 34 ಮತ್ತು 35A ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯವಾಗಿ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿಗೆ ಸಂಬಂಧಿಸಿದೆ. 44 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿಯನ್ನು ಅಂಗೀಕರಿಸುವ ಮೊದಲು, ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ನೀಡಲಾದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಏಳು ವರ್ಗಗಳಾಗಿ ವಿಂಗಡಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ, ಆದರೆ ಈ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿಯ ಪ್ರಕಾರ, ಆಸ್ತಿಯ ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನು ಸಾಮಾನ್ಯ ಕಾನೂನು ಹಕ್ಕನ್ನಾಗಿ ಮಾಡಲಾಯಿತು. ಭಾರತೀಯ ನಾಗರಿಕರಿಗೆ ಆರು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳಿವೆ.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು
1. ಸಮಾನತೆಯ ಹಕ್ಕು: ಲೇಖನಗಳು 14 ರಿಂದ 18. 2. ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು: ಆರ್ಟಿಕಲ್ 19 ರಿಂದ 22. 3. ಶೋಷಣೆ ವಿರುದ್ಧ ಹಕ್ಕು: 23 ರಿಂದ 24 ರವರೆಗೆ. 4. ಧರ್ಮದ ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯದ ಹಕ್ಕು: ಲೇಖನಗಳು 25 ರಿಂದ 28. 5. ಸಾಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಶಿಕ್ಷಣ ಸಂಬಂಧಿತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು: ಲೇಖನಗಳು 29 ರಿಂದ 30. 6. ಸಾಂವಿಧಾನಿಕ ಪರಿಹಾರಗಳ ಹಕ್ಕು: ಲೇಖನ 32
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು :
ಸರ್ದಾರ್ ಸ್ವರಣ್ ಸಿಂಗ್ ಸಮಿತಿಯ ಶಿಫಾರಸಿನ ಮೇರೆಗೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 42 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ (1976 AD) ಮೂಲಕ ಸಂವಿಧಾನಕ್ಕೆ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಸೇರಿಸಲಾಯಿತು. ಇದನ್ನು ರಷ್ಯಾದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಿಂದ ತೆಗೆದುಕೊಳ್ಳಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಇದನ್ನು ಭಾಗ 4 (ಎ) ನಲ್ಲಿ ಆರ್ಟಿಕಲ್ 51 (ಎ) ಅಡಿಯಲ್ಲಿ ಇರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳ ಸಂಖ್ಯೆ 11 ಅವುಗಳೆಂದರೆ
- ಸಂವಿಧಾನವನ್ನು ಪಾಲಿಸುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ಅದರ ಆದರ್ಶಗಳು, ಸಂಸ್ಥೆಗಳು, ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರಧ್ವಜ ಮತ್ತು ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರಗೀತೆಯನ್ನು ಗೌರವಿಸುವುದು ಪ್ರತಿಯೊಬ್ಬ ನಾಗರಿಕನ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯವಾಗಿದೆ.
- ಸ್ವಾತಂತ್ರ್ಯಕ್ಕಾಗಿ ನಮ್ಮ ರಾಷ್ಟ್ರೀಯ ಹೋರಾಟಕ್ಕೆ ಸ್ಫೂರ್ತಿ ನೀಡಿದ ಉದಾತ್ತ ಆದರ್ಶಗಳನ್ನು ಪಾಲಿಸುವುದು ಮತ್ತು ಅನುಸರಿಸುವುದು.
- ಭಾರತದ ಸಾರ್ವಭೌಮತ್ವ, ಏಕತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಸಮಗ್ರತೆಯನ್ನು ಅಖಂಡವಾಗಿ ರಕ್ಷಿಸಿ ಮತ್ತು ಇರಿಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಿ.
- ದೇಶವನ್ನು ರಕ್ಷಿಸಿ.
- ಭಾರತದ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಜನರಲ್ಲಿ ಸಾಮರಸ್ಯ ಮತ್ತು ಸಮಾನ ಭ್ರಾತೃತ್ವದ ಮನೋಭಾವವನ್ನು ನಿರ್ಮಿಸಿ.
- ನಮ್ಮ ಸಾಮಾಜಿಕ ಸಂಸ್ಕೃತಿಯ ವೈಭವೋಪೇತ ಸಂಪ್ರದಾಯದ ಮಹತ್ವವನ್ನು ಅರಿತು ಅದನ್ನು ನಿರ್ಮಿಸಿ.
- ನೈಸರ್ಗಿಕ ಪರಿಸರವನ್ನು ರಕ್ಷಿಸಿ ಮತ್ತು ಹೆಚ್ಚಿಸಿ.
- ವೈಜ್ಞಾನಿಕ ಮನೋಭಾವ ಮತ್ತು ಕಲಿಕೆಯ ಪ್ರಜ್ಞೆಯನ್ನು ಬೆಳೆಸಿಕೊಳ್ಳಿ.
- ಸಾರ್ವಜನಿಕ ಆಸ್ತಿಯನ್ನು ರಕ್ಷಿಸಿ.
- ವೈಯಕ್ತಿಕ ಮತ್ತು ಸಾಮೂಹಿಕ ಚಟುವಟಿಕೆಗಳ ಎಲ್ಲಾ ಕ್ಷೇತ್ರಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಉತ್ಕೃಷ್ಟತೆಯತ್ತ ಸಾಗಲು ನಿರಂತರ ಪ್ರಯತ್ನಗಳನ್ನು ಮಾಡಿ.
- ಪೋಷಕರು ಅಥವಾ ಪೋಷಕರಿಂದ 6 ರಿಂದ 14 ವರ್ಷ ವಯಸ್ಸಿನ ಮಕ್ಕಳಿಗೆ ಪ್ರಾಥಮಿಕ ಶಿಕ್ಷಣವನ್ನು ಒದಗಿಸುವುದು (86 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ)
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ನಮ್ಮ ಪ್ರಸ್ತುತ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಭಾಗ IV ರಲ್ಲಿ 42 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ ಕಾಯಿದೆ 1976 ಮೂಲಕ ಸೇರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ. ಪ್ರಸ್ತುತ ನಮ್ಮ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ 51ಎ ವಿಧಿಯ ಅಡಿಯಲ್ಲಿ 11 ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳಿವೆ, ಅವು ಕಾನೂನಿನಿಂದ ಶಾಸನಬದ್ಧ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳಾಗಿವೆ.
ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಜೀವನದಲ್ಲಿ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಪ್ರಮುಖ ಪಾತ್ರವಹಿಸುತ್ತವೆ. ಈ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಸಂಕೀರ್ಣತೆ ಮತ್ತು ಕಷ್ಟದ ಸಮಯದಲ್ಲಿ ಉತ್ತಮ ಮಾನವರಾಗಲು ನಮಗೆ ಸಹಾಯ ಮಾಡಬಹುದು. ಭಾರತದ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳ ಜೊತೆಗೆ ಕೆಲವು ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನೂ ಉಲ್ಲೇಖಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
1. ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಯಾವ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ತಿಳಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ?
ಭಾರತೀಯ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದಲ್ಲಿ ನಾಗರಿಕರ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳನ್ನು ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂರನೇ ಭಾಗದಲ್ಲಿ ಆರ್ಟಿಕಲ್ 12 ರಿಂದ 35 ರವರೆಗೆ ವಿವರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ.
2. ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಎಷ್ಟಿವೆ ?
6 ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಇವೆ.
3. ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳ ನ್ನು ಸಂವಿಧಾನಕ್ಕೆ ಎಷ್ಟನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ ಮೂಲಕ ಸೇರಿಸಲಾಗಿದೆ?
ಸರ್ದಾರ್ ಸ್ವರಣ್ ಸಿಂಗ್ ಸಮಿತಿಯ ಶಿಫಾರಸಿನ ಮೇರೆಗೆ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ 42 ನೇ ತಿದ್ದುಪಡಿ (1976 AD) ಮೂಲಕ ಸಂವಿಧಾನಕ್ಕೆ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳನ್ನು ಸೇರಿಸಲಾಯಿತು.
4. ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಎಷ್ಟಿವೆ ?
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು 11 ಇವೆ.
ಇತರೆ ವಿಷಯಗಳು :
ಕುವೆಂಪು ಅವರ ಬಗ್ಗೆ ಪ್ರಬಂಧ
ನಿರುದ್ಯೋಗ ಪ್ರಬಂಧ
What do you think?
Written by Salahe24
Leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings

ನಿರುದ್ಯೋಗ ಪ್ರಬಂಧ | Unemployment Essay in Kannada

ಪುಸ್ತಕಗಳ ಮಹತ್ವ ಪ್ರಬಂಧ | Importance of Books Essay in Kannada
© 2024 by bring the pixel. Remember to change this
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Forgot password?
Enter your account data and we will send you a link to reset your password.
Your password reset link appears to be invalid or expired.
Privacy policy.
To use social login you have to agree with the storage and handling of your data by this website. %privacy_policy%
Add to Collection
Public collection title
Private collection title
No Collections
Here you'll find all collections you've created before.

Constitution Of India, Indian Penal Code - IPC

Indian Constitution in Kannada language
The Indian Constitution in Kannada language. Latest, new with amendments Indian Constitution in Kannada . PDF download Indian Constitution in Kannada .
PDF Download Indian Constitution in Kannada language

Constitution of India in Kannada
Constitution of india, the constitution of india parts 1 to 22, articles 1 to 395, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Fundamental Rights And Duties In Indian Constitution: Explained In Detail
Contributor

Introduction:
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of the land, which lays down the basic framework and principles for the governance of the country. It was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India on 26th November 1949 and came into effect on 26th January 1950. The Indian Constitution is unique in the sense that it not only guarantees a set of fundamental rights to its citizens but also imposes certain duties and responsibilities upon them. This blog aims to explain the fundamental rights and duties enshrined in the Indian Constitution .
The concept of fundamental rights and duties in the Indian Constitution has evolved significantly since its inception. These elements form the bedrock of Indian democracy, ensuring a balance between individual freedoms and societal responsibilities. Understanding the historical evolution of these rights and duties is crucial to appreciate their current interpretation and application in India's diverse and dynamic society.
Fundamental Rights:
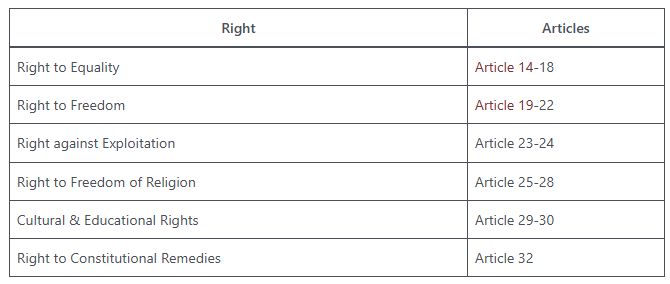
Fundamental rights are the basic rights guaranteed to the citizens of India by the Constitution. These rights are essential for the development of an individual's personality and dignity. The Constitution of India guarantees six fundamental rights to its citizens, which are as follows:
1. Right to Equality:
The right to equality is one of the most important fundamental rights enshrined in the Indian Constitution. It ensures that all individuals are equal before the law and prohibits discrimination based on caste, race, religion, sex or place of birth. This right is guaranteed under Articles 14 -18 of the Constitution.
The Right to Equality, enshrined in In-Depth Analysis of Article 14 of the Indian Constitution " href="/redirection.asp?article_id=1468188&company_id=32736&redirectaddress=https://www.centurylawfirm.in/blog/article-14-of-theindian-constitution/" data-internallinksmanager029f6b8e52c="56" target="_blank">Articles 14 to 18, is foundational to the Indian Constitution, symbolizing the nation's commitment to a just and equitable society. This right challenges historical inequalities and mandates equal treatment under the law, irrespective of a person's background. Landmark cases like 'Kesavananda Bharati vs State of Kerala' have reinforced the importance of equality as a part of the basic structure of the Constitution.
2. Right to Freedom:
The right to freedom guarantees certain freedoms to the citizens of India, such as freedom of speech and expression, freedom of assembly, freedom of association, freedom of movement and freedom of residence. This right is guaranteed under Articles 19 -22 of the Constitution.
The Right to Freedom, covered under Articles 19 to 22, encompasses a broad spectrum of freedoms ranging from speech and expression to movement and residence anywhere in India. It also includes the right to practice any profession and the protection in respect of conviction for offenses. This right is fundamental in ensuring that citizens enjoy liberty in various aspects of their life, balanced with reasonable restrictions for the state's integrity and public order. The Supreme Court 's interpretation in cases like 'Maneka Gandhi vs Union of India' has been pivotal in expanding the understanding and scope of these freedoms.
3. Right against Exploitation:
The right against exploitation prohibits trafficking, forced labour and other forms of exploitation. It is guaranteed under Articles 23-24 of the Constitution.
Articles 23 and 24 of the Indian Constitution prohibit all forms of human trafficking and child labor, ensuring that no citizen is subject to exploitation and forced labor. This right is crucial in combating societal issues like child labor and human trafficking. Through various judicial decisions, the courts have expanded the interpretation of this right to include various forms of exploitation, thus safeguarding the dignity and well-being of vulnerable sections of society.
4. Right to Freedom of Religion:
The right to freedom of religion ensures that every citizen of India has the right to profess, practice and propagate their religion. This right is guaranteed under Articles 25-28 of the Constitution.
Enshrined in Articles 25 to 28, the Right to Freedom of Religion guarantees every citizen the freedom to practice, profess, and propagate their religion. This set of rights establishes India as a secular state, where the state does not endorse any particular religion and ensures freedom of worship. The apex court has continually upheld these freedoms while ensuring they do not infringe on public order and morality.
5. Cultural and Educational Rights:
The Constitution of India guarantees certain cultural and educational rights to the citizens of India. It includes the right to preserve and promote one's culture, the right to education and the right to linguistic and minority rights. These rights are guaranteed under Articles 29-30 of the Constitution.
Articles 29 and 30 protect the rights of minorities to preserve their language, script, and culture, and the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions. These rights are fundamental in upholding India's cultural diversity and ensuring that minority groups can preserve and cultivate their unique heritage and educational practices.
6. Right to Constitutional Remedies:
The right to constitutional remedies is the most important fundamental right enshrined in the Indian Constitution. It provides a mechanism for the citizens to enforce their fundamental rights. This right is guaranteed under Article 32 of the Constitution.
Article 32 is known as the 'heart and soul' of the Indian Constitution, as articulated by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar. It empowers citizens to approach the Supreme Court directly in case of any violation of their fundamental rights. This right is critical in ensuring the protection and enforcement of the fundamental rights, making them not merely declaratory but also enforceable in courts of law.
Fundamental Duties:
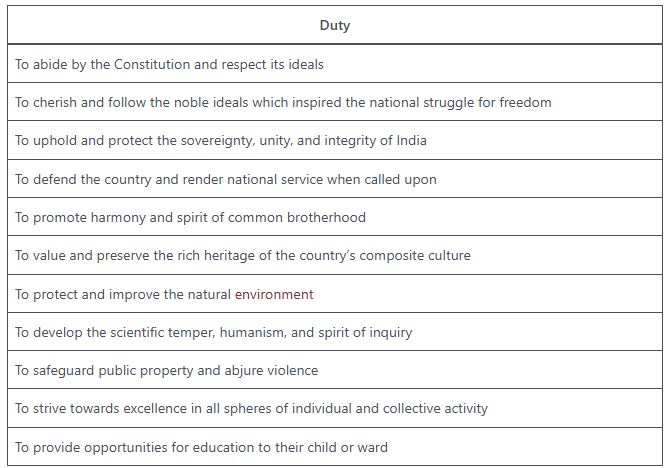
The Indian Constitution imposes certain duties and responsibilities upon its citizens, which are essential for the well-being and progress of the society as a whole. The Fundamental Duties were added to the Constitution by the 42nd Amendment Act, 1976. The Constitution of India provides for 11 fundamental duties which are as follows:
- To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag and the National Anthem.
- To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom.
- To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India.
- To defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so.
- To promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood amongst all the people of India transcending religious, linguistic and regional or sectional diversities.
- To value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture.
- To protect and improve the natural environment including forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife, and to have compassion for living creatures.
- To develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform.
- To safeguard public property and to abjure violence.
- To strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity so that the nation constantly rises to higher levels of endeavour and achievement.
- To provide opportunities for education to their child or ward, between the age of 6 and 14 years.
The fundamental duties, added by the 42nd Amendment in 1976, serve as a reminder of the citizen's role in nation-building and maintaining social harmony. These duties, encompassing respect for national symbols, the environment , and the promotion of scientific temper, are as vital as rights for fostering a responsible and aware citizenry.
Explanation of Fundamental Duties:
- To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag and the National Anthem:
This duty requires every citizen of India to respect and uphold the ideals and institutions of the Constitution, such as democracy, secularism, and socialism. Citizens should also respect the national symbols, such as the National Flag and National Anthem.
- To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom:
This duty requires every citizen of India to respect and follow the ideals of the Indian freedom struggle, such as non-violence, equality, and justice. This duty emphasizes the importance of respecting the sacrifices of our freedom fighters.
- To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India:
This duty requires every citizen of India to defend the sovereignty, unity, and integrity of the country against all threats. It emphasizes the importance of national security and patriotism.
- To defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so:
This duty requires every citizen of India to be ready to defend the country against any external or internal threat. It also emphasizes the importance of national service, such as volunteering for social causes.
- To promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood amongst all the people of India transcending religious, linguistic and regional or sectional diversities:
This duty requires every citizen of India to promote communal harmony and brotherhood among all the people of the country, regardless of their religion, language, or region. It emphasizes the importance of national integration and social cohesion.
- To value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture:
This duty requires every citizen of India to respect and preserve the rich cultural heritage of the country, which is a composite of various cultures, religions, and traditions. It emphasizes the importance of cultural diversity and national unity.
- To protect and improve the natural environment including forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife, and to have compassion for living creatures:
This duty requires every citizen of India to protect and improve the natural environment, including forests, lakes, rivers, and wildlife. It emphasizes the importance of environmental conservation and sustainability.
- To develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform:
This duty requires every citizen of India to develop a scientific temper and a spirit of inquiry and reform. It emphasizes the importance of scientific and rational thinking in the progress of the country.
- To safeguard public property and to abjure violence:
This duty requires every citizen of India to protect public property and abjure violence. It emphasizes the importance of non-violence and respect for public property.
- To strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity so that the nation constantly rises to higher levels of endeavour and achievement:
This duty requires every citizen of India to strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity. It emphasizes the importance of hard work, dedication, and excellence in the progress of the country.
- To provide opportunities for education to their child or ward, between the age of 6 and 14 years:
This duty requires every parent or guardian to provide opportunities for education to their child or ward, between the age of 6 and 14 years. It emphasizes the importance of education in the development of the individual and the progress of the country.
The Fundamental Duties were added to the Indian Constitution through the 42nd Amendment Act of 1976. The main objective of adding Fundamental Duties was to ensure that the citizens of India are conscious of their duties towards the nation and society. Some of the additional information on Fundamental Duties are:
- The Fundamental Duties are not enforceable by law. However, they are fundamental in the governance of the country.
- The Fundamental Duties are based on the principle of "dharma" or duty, which is deeply rooted in Indian culture and tradition.
- The Fundamental Duties are meant to be complementary to the Fundamental Rights. They remind citizens that while they have certain rights, they also have certain obligations towards the society and the country.
- The Fundamental Duties are not exhaustive. They are broad guidelines and principles, which can be interpreted in the light of changing times and circumstances.
- The Fundamental Duties are not limited to citizens alone. They also apply to the government, which is expected to uphold and promote these duties.
Conclusion:
The Indian Constitution provides for both fundamental rights and duties, which are essential for the well-being and progress of the society. While fundamental rights ensure the dignity and development of the individual, fundamental duties emphasize the responsibilities and obligations of the citizens towards the society and the country. It is the duty of every citizen of India to respect and uphold these fundamental rights and duties, which are the foundation of our democracy and the progress of our country. The Fundamental Rights and Duties are the cornerstone of the Indian Constitution. They ensure that every citizen of India is guaranteed certain rights and is aware of their duties towards the society and the country. While the Fundamental Rights protect the dignity and development of the individual, the Fundamental Duties promote social cohesion, patriotism, and national integration. It is the duty of every citizen of India to respect and uphold these Fundamental Rights and Duties, which are the bedrock of our democracy and the progress of our country.
The interplay of fundamental rights and duties is pivotal for the progress and harmony of Indian society. These constitutional provisions not only protect individual liberties but also foster a sense of collective responsibility, crucial for the nation's holistic development.
These rights are protected by Constitutional remedies such as Writs . At Century Law Firm , our team of experienced lawyers has a deep understanding of the complexities involved in writ petitions .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Fundamental Rights and Duties in the Indian Constitution:
- What is the difference between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy?
Fundamental Rights are the individual rights guaranteed by the Constitution, while Directive Principles of State Policy are the guidelines and principles for the governance of the country. While Fundamental Rights are justiciable, Directive Principles of State Policy are not enforceable by the courts.
- Can the Fundamental Rights be suspended during an emergency ?
Yes, during a national emergency declared under Article 352 of the Constitution, the Fundamental Rights can be suspended except for Articles 20 and 21.
- What is the significance of the Right to Constitutional Remedies?
The Right to Constitutional Remedies is considered to be the most important Fundamental Right, as it guarantees the right to approach the Supreme Court of India for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights. It ensures that the individual is not deprived of his or her rights by the state or any other authority.
- What are the Fundamental Duties of an Indian citizen?
The Fundamental Duties of an Indian citizen include respecting the Constitution, national flag, and national anthem, promoting harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood, protecting the natural environment, and striving towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity.
- Are Fundamental Duties enforceable by law?
No, Fundamental Duties are not enforceable by law. However, they serve as a reminder to citizens that they have certain obligations towards the society and the country.
- Can Fundamental Rights be amended?
Yes, Fundamental Rights can be amended, but only to the extent that they do not affect the basic structure of the Constitution.
- What happens if a law is in violation of Fundamental Rights?
If a law is in violation of Fundamental Rights, it can be struck down by the courts as unconstitutional.
- Can Fundamental Rights be restricted by the state?
Yes, Fundamental Rights can be restricted by the state, but only if there is a reasonable basis for such restriction. For example, the right to free speech and expression can be restricted if it poses a threat to national security or public order.
- Are Fundamental Rights absolute?
No, Fundamental Rights are not absolute. They are subject to reasonable restrictions, as mentioned in the Constitution.
- What is the difference between legal rights and Fundamental Rights?
Legal rights are rights that are recognized by law and can be enforced by the courts. Fundamental Rights, on the other hand, are the basic rights guaranteed to citizens by the Constitution. While legal rights can be limited or modified by the law, Fundamental Rights are protected by the Constitution and cannot be taken away or limited by the law.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

Government, Public Sector
Mondaq uses cookies on this website. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies as set out in our Privacy Policy.
- Skip to main content
- High Contrast
- Normal Contrast
- Highlight Links
- Font Size Increase
- Font Size Decrease
- Normal Font
- Text Spacing
- Line Height
- Screen Reader
- विधि और न्याय मंत्रालय, भारत सरकार
- Ministry of Law and Justice, Government of India

Constitution of India in Kannada
Essay on Constitution of India
500+ words indian constitution essay for students and children in english.
A Constitution is a set of rules and regulations guiding the administration of a country. The Constitution is the backbone of every democratic and secular fabric of the nation. The Constitution of India is the longest Constitution in the world, which describes the framework for political principles, procedures and powers of the government. The Constitution of India was written on 26 November 1949 and came into force on 26 January 1950. In this essay on the Constitution of India, students will get to know the salient features of India’s Constitution and how it was formed.
Constitution of India Essay
On 26th January 1950, the Constitution of India came into effect. That’s why 26th January is celebrated as Republic Day in India.
How Was the Constitution of India Formed?
The representatives of the Indian people framed the Indian Constitution after a long period of debates and discussions. It is the most detailed Constitution in the world. No other Constitution has gone into such minute details as the Indian Constitution.
The Constitution of India was framed by a Constituent Assembly which was established in 1946. Dr Rajendra Prasad was elected President of the Constituent Assembly. A Drafting Committee was appointed to draft the Constitution and Dr B.R. Ambedkar was appointed as the Chairman. The making of the Constitution took a total of 166 days, which was spread over a period of 2 years, 11 months and 18 days. Some of the salient features of the British, Irish, Swiss, French, Canadian and American Constitutions were incorporated while designing the Indian Constitution.
Also Read: Evolution and Framing of the Constitution
Features of The Constitution of India
The Constitution of India begins with a Preamble which contains the basic ideals and principles of the Constitution. It lays down the objectives of the Constitution.
The Longest Constitution in the world
The Indian Constitution is the lengthiest Constitution in the world. It had 395 articles in 22 parts and 8 schedules at the time of commencement. Now it has 448 articles in 25 parts and 12 schedules. There are 104 amendments (took place on 25th January 2020 to extend the reservation of seats for SCs and STs in the Lok Sabha and state assemblies) that have been made in the Indian Constitution so far.
How Rigid and Flexible is the Indian Constitution?
One of the unique features of our Constitution is that it is not as rigid as the American Constitution or as flexible as the British Constitution. It means it is partly rigid and partly flexible. Owing to this, it can easily change and grow with the change of times.
The Preamble
The Preamble has been added later to the Constitution of India. The original Constitution does not have a preamble. The preamble states that India is a sovereign, socialist, secular and democratic republic. The objectives stated by the Preamble are to secure justice, liberty, and equality for all citizens and promote fraternity to maintain the unity and integrity of the nation.
Federal System with Unitary Features
The powers of the government are divided between the central government and the state governments. The Constitution divides the powers of three state organs, i.e., executive, judiciary and legislature. Hence, the Indian Constitution supports a federal system. It includes many unitary features such as a strong central power, emergency provisions, appointment of Governors by the President, etc.
Fundamental rights and fundamental duties
The Indian Constitution provides an elaborate list of Fundamental Rights to the citizens of India. The Constitution also provides a list of 11 duties of the citizens, known as the Fundamental Duties. Some of these duties include respect for the national flag and national anthem, integrity and unity of the country and safeguarding of public property.
Also Read: Difference between Fundamental Rights and Fundamental Duties
India is a republic which means that a dictator or monarch does not rule the country. The government is of the people, by the people and for the people. Citizens nominate and elect its head after every five years.
Related Read: Constitution of India – 13 Major Features
The Constitution serves as guidelines for every citizen. It helped India to attain the status of a Republic in the world. Once Atal Bihari Vajpayee said that “governments would come and go, political parties would be formed and dissolved, but the country should survive, and democracy should remain there forever”.
We hope that this essay on the “Constitution of India” must have helped students. For the latest updates on ICSE/CBSE/State Board/Competitive Exams, stay tuned to BYJU’S. Also, download the BYJU’S App for watching interesting study videos.
Also Read: Independence Day Essay | Republic Day Essay | Essay on Women Empowerment
Frequently Asked Questions on Constitution of India Essay
Who is the father of our indian constitution.
Dr. B. R. Ambedkar is the father of our Indian Constitution. He framed and drafted our Constitution.
Who signed the Indian Constitution?
Dr. Rajendra Prasad was the first person from the Constitution Assembly to have signed the Indian Constitution.
What is mentioned in the Preamble of our Indian Constitution?
The preamble clearly communicates the purpose and emphasis the importance of the objectives of the Indian Constitution.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

Fundamental Rights and Duties in Indian Constitution: Explained in Detail

Introduction:
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of the land, which lays down the basic framework and principles for the governance of the country. It was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India on 26th November 1949 and came into effect on 26th January 1950. The Indian Constitution is unique in the sense that it not only guarantees a set of fundamental rights to its citizens but also imposes certain duties and responsibilities upon them. This blog aims to explain the fundamental rights and duties enshrined in the Indian Constitution .
The concept of fundamental rights and duties in the Indian Constitution has evolved significantly since its inception. These elements form the bedrock of Indian democracy, ensuring a balance between individual freedoms and societal responsibilities. Understanding the historical evolution of these rights and duties is crucial to appreciate their current interpretation and application in India’s diverse and dynamic society.
Fundamental Rights:
Fundamental rights are the basic rights guaranteed to the citizens of India by the Constitution. These rights are essential for the development of an individual’s personality and dignity. The Constitution of India guarantees six fundamental rights to its citizens, which are as follows:
1. Right to Equality:
The right to equality is one of the most important fundamental rights enshrined in the Indian Constitution. It ensures that all individuals are equal before the law and prohibits discrimination based on caste, race, religion, sex or place of birth. This right is guaranteed under Articles 14 -18 of the Constitution.
The Right to Equality, enshrined in Articles 14 to 18, is foundational to the Indian Constitution, symbolizing the nation’s commitment to a just and equitable society. This right challenges historical inequalities and mandates equal treatment under the law, irrespective of a person’s background. Landmark cases like ‘Kesavananda Bharati vs State of Kerala’ have reinforced the importance of equality as a part of the basic structure of the Constitution.
2. Right to Freedom:
The right to freedom guarantees certain freedoms to the citizens of India, such as freedom of speech and expression, freedom of assembly, freedom of association, freedom of movement and freedom of residence. This right is guaranteed under Articles 19 -22 of the Constitution.
The Right to Freedom, covered under Articles 19 to 22, encompasses a broad spectrum of freedoms ranging from speech and expression to movement and residence anywhere in India. It also includes the right to practice any profession and the protection in respect of conviction for offenses. This right is fundamental in ensuring that citizens enjoy liberty in various aspects of their life, balanced with reasonable restrictions for the state’s integrity and public order. The Supreme Court ’s interpretation in cases like ‘Maneka Gandhi vs Union of India’ has been pivotal in expanding the understanding and scope of these freedoms.
3. Right against Exploitation:
The right against exploitation prohibits trafficking, forced labour and other forms of exploitation. It is guaranteed under Articles 23-24 of the Constitution.
Articles 23 and 24 of the Indian Constitution prohibit all forms of human trafficking and child labor, ensuring that no citizen is subject to exploitation and forced labor. This right is crucial in combating societal issues like child labor and human trafficking. Through various judicial decisions, the courts have expanded the interpretation of this right to include various forms of exploitation, thus safeguarding the dignity and well-being of vulnerable sections of society.
4. Right to Freedom of Religion:
The right to freedom of religion ensures that every citizen of India has the right to profess, practice and propagate their religion. This right is guaranteed under Articles 25-28 of the Constitution.
Enshrined in Articles 25 to 28, the Right to Freedom of Religion guarantees every citizen the freedom to practice, profess, and propagate their religion. This set of rights establishes India as a secular state, where the state does not endorse any particular religion and ensures freedom of worship. The apex court has continually upheld these freedoms while ensuring they do not infringe on public order and morality.
5. Cultural and Educational Rights:
The Constitution of India guarantees certain cultural and educational rights to the citizens of India. It includes the right to preserve and promote one’s culture, the right to education and the right to linguistic and minority rights. These rights are guaranteed under Articles 29-30 of the Constitution.
Articles 29 and 30 protect the rights of minorities to preserve their language, script, and culture, and the right of minorities to establish and administer educational institutions. These rights are fundamental in upholding India’s cultural diversity and ensuring that minority groups can preserve and cultivate their unique heritage and educational practices.
6. Right to Constitutional Remedies:
The right to constitutional remedies is the most important fundamental right enshrined in the Indian Constitution. It provides a mechanism for the citizens to enforce their fundamental rights. This right is guaranteed under Article 32 of the Constitution.
Article 32 is known as the ‘heart and soul’ of the Indian Constitution, as articulated by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar. It empowers citizens to approach the Supreme Court directly in case of any violation of their fundamental rights. This right is critical in ensuring the protection and enforcement of the fundamental rights, making them not merely declaratory but also enforceable in courts of law.
Fundamental Duties:
The Indian Constitution imposes certain duties and responsibilities upon its citizens, which are essential for the well-being and progress of the society as a whole. The Fundamental Duties were added to the Constitution by the 42nd Amendment Act, 1976. The Constitution of India provides for 11 fundamental duties which are as follows:
- To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag and the National Anthem.
- To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom.
- To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India.
- To defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so.
- To promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood amongst all the people of India transcending religious, linguistic and regional or sectional diversities.
- To value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture.
- To protect and improve the natural environment including forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife, and to have compassion for living creatures.
- To develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform.
- To safeguard public property and to abjure violence.
- To strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity so that the nation constantly rises to higher levels of endeavour and achievement.
- To provide opportunities for education to their child or ward, between the age of 6 and 14 years.
The fundamental duties, added by the 42nd Amendment in 1976, serve as a reminder of the citizen’s role in nation-building and maintaining social harmony. These duties, encompassing respect for national symbols, the environment , and the promotion of scientific temper, are as vital as rights for fostering a responsible and aware citizenry.
Explanation of Fundamental Duties:
- To abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag and the National Anthem:
This duty requires every citizen of India to respect and uphold the ideals and institutions of the Constitution, such as democracy, secularism, and socialism. Citizens should also respect the national symbols, such as the National Flag and National Anthem.
- To cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom:
This duty requires every citizen of India to respect and follow the ideals of the Indian freedom struggle, such as non-violence, equality, and justice. This duty emphasizes the importance of respecting the sacrifices of our freedom fighters.
- To uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India:
This duty requires every citizen of India to defend the sovereignty, unity, and integrity of the country against all threats. It emphasizes the importance of national security and patriotism.
- To defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so:
This duty requires every citizen of India to be ready to defend the country against any external or internal threat. It also emphasizes the importance of national service, such as volunteering for social causes.
- To promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood amongst all the people of India transcending religious, linguistic and regional or sectional diversities:
This duty requires every citizen of India to promote communal harmony and brotherhood among all the people of the country, regardless of their religion, language, or region. It emphasizes the importance of national integration and social cohesion.
- To value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture:
This duty requires every citizen of India to respect and preserve the rich cultural heritage of the country, which is a composite of various cultures, religions, and traditions. It emphasizes the importance of cultural diversity and national unity.
- To protect and improve the natural environment including forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife, and to have compassion for living creatures:
This duty requires every citizen of India to protect and improve the natural environment, including forests, lakes, rivers, and wildlife. It emphasizes the importance of environmental conservation and sustainability.
- To develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform:
This duty requires every citizen of India to develop a scientific temper and a spirit of inquiry and reform. It emphasizes the importance of scientific and rational thinking in the progress of the country.
- To safeguard public property and to abjure violence:
This duty requires every citizen of India to protect public property and abjure violence. It emphasizes the importance of non-violence and respect for public property.
- To strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity so that the nation constantly rises to higher levels of endeavour and achievement:
This duty requires every citizen of India to strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity. It emphasizes the importance of hard work, dedication, and excellence in the progress of the country.
- To provide opportunities for education to their child or ward, between the age of 6 and 14 years:
This duty requires every parent or guardian to provide opportunities for education to their child or ward, between the age of 6 and 14 years. It emphasizes the importance of education in the development of the individual and the progress of the country.
The Fundamental Duties were added to the Indian Constitution through the 42nd Amendment Act of 1976. The main objective of adding Fundamental Duties was to ensure that the citizens of India are conscious of their duties towards the nation and society. Some of the additional information on Fundamental Duties are:
- The Fundamental Duties are not enforceable by law. However, they are fundamental in the governance of the country.
- The Fundamental Duties are based on the principle of “dharma” or duty, which is deeply rooted in Indian culture and tradition.
- The Fundamental Duties are meant to be complementary to the Fundamental Rights. They remind citizens that while they have certain rights, they also have certain obligations towards the society and the country.
- The Fundamental Duties are not exhaustive. They are broad guidelines and principles, which can be interpreted in the light of changing times and circumstances.
- The Fundamental Duties are not limited to citizens alone. They also apply to the government, which is expected to uphold and promote these duties.
Conclusion:
The Indian Constitution provides for both fundamental rights and duties, which are essential for the well-being and progress of the society. While fundamental rights ensure the dignity and development of the individual, fundamental duties emphasize the responsibilities and obligations of the citizens towards the society and the country. It is the duty of every citizen of India to respect and uphold these fundamental rights and duties, which are the foundation of our democracy and the progress of our country. The Fundamental Rights and Duties are the cornerstone of the Indian Constitution. They ensure that every citizen of India is guaranteed certain rights and is aware of their duties towards the society and the country. While the Fundamental Rights protect the dignity and development of the individual, the Fundamental Duties promote social cohesion, patriotism, and national integration. It is the duty of every citizen of India to respect and uphold these Fundamental Rights and Duties, which are the bedrock of our democracy and the progress of our country.
The interplay of fundamental rights and duties is pivotal for the progress and harmony of Indian society. These constitutional provisions not only protect individual liberties but also foster a sense of collective responsibility, crucial for the nation’s holistic development.
These rights are protected by Constitutional remedies such as Writs . At Century Law Firm , our team of experienced lawyers has a deep understanding of the complexities involved in writ petitions .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Fundamental Rights and Duties in the Indian Constitution:
- What is the difference between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy?
Fundamental Rights are the individual rights guaranteed by the Constitution, while Directive Principles of State Policy are the guidelines and principles for the governance of the country. While Fundamental Rights are justiciable, Directive Principles of State Policy are not enforceable by the courts.
- Can the Fundamental Rights be suspended during an emergency ?
Yes, during a national emergency declared under Article 352 of the Constitution, the Fundamental Rights can be suspended except for Articles 20 and 21.
- What is the significance of the Right to Constitutional Remedies?
The Right to Constitutional Remedies is considered to be the most important Fundamental Right, as it guarantees the right to approach the Supreme Court of India for the enforcement of Fundamental Rights. It ensures that the individual is not deprived of his or her rights by the state or any other authority.
- What are the Fundamental Duties of an Indian citizen?
The Fundamental Duties of an Indian citizen include respecting the Constitution, national flag, and national anthem, promoting harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood, protecting the natural environment, and striving towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity.
- Are Fundamental Duties enforceable by law?
No, Fundamental Duties are not enforceable by law. However, they serve as a reminder to citizens that they have certain obligations towards the society and the country.
- Can Fundamental Rights be amended?
Yes, Fundamental Rights can be amended, but only to the extent that they do not affect the basic structure of the Constitution.
- What happens if a law is in violation of Fundamental Rights?
If a law is in violation of Fundamental Rights, it can be struck down by the courts as unconstitutional.
- Can Fundamental Rights be restricted by the state?
Yes, Fundamental Rights can be restricted by the state, but only if there is a reasonable basis for such restriction. For example, the right to free speech and expression can be restricted if it poses a threat to national security or public order.
- Are Fundamental Rights absolute?
No, Fundamental Rights are not absolute. They are subject to reasonable restrictions, as mentioned in the Constitution.
- What is the difference between legal rights and Fundamental Rights?
Legal rights are rights that are recognized by law and can be enforced by the courts. Fundamental Rights, on the other hand, are the basic rights guaranteed to citizens by the Constitution. While legal rights can be limited or modified by the law, Fundamental Rights are protected by the Constitution and cannot be taken away or limited by the law.
Writ Petition – Types, Important Judgements, How and When to File | Lawyer for Writ Petition
In-Depth Analysis of Article 14 of the Indian Constitution
Understanding Article 13 of the Indian Constitution
Popular Posts
- Section 302 IPC: Detailed Analysis, Punishment for Murder, and Legal Implications
- Section 411 of the Indian Penal Code : Dishonestly receiving stolen property – All You Need to Know | IPC
- Section 86 Indian Penal Code (IPC) – All you need to know
Related Posts

Habeas Corpus – Legal Maxim of the Day
Automobile accident lawyers – what they do, how much they charge, and more.
DSpace JSPUI
Egyankosh preserves and enables easy and open access to all types of digital content including text, images, moving images, mpegs and data sets.
- IGNOU Self Learning Material (SLM)
- 02. School of Social Sciences (SOSS)
- Bachelor's Degree Programmes
- Bachelor of Arts (BAG)
- Political Science
- BPSC-132 Indian Government and Politics
- Block-2 Indian Constitution
Items in eGyanKosh are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated.

Essay on Fundamental Rights for Students and Children
500+ words essay on fundamental rights.
There are some basic rights that are very well-known as fundamental to human existence and crucial for human expansion. In the absence of fundamental rights, a man’s existence would be worthless. So, the political institution’s role and responsibility mainly emphasized on empowering the people, especially the minorities to live in dignity with rights of equality, dignity and religious freedom. Fundamental Rights have been classified into 6 categories that are Right to Equality, Right to Freedom, Right against Exploitation, Right to Freedom of Religion, Right to Cultural and Educational, Right to Constitutional Remedy.

Right to Equality
This right includes the equality before the Law which implies a prohibition of discrimination on the basis of caste, creed, color or sex, equal protection of the law, equal opportunity in public employment and abolition of untouchability and titles. It also states that every citizen shall have equal access to all public places.
To provide equal opportunities there will be no reservation in government services except in the case of scheduled caste, scheduled tribes, and other backward classes and for war widows and physically handicapped person. This right was made to abolish untouchability which was practiced in India for decades.
Right to Freedom
This right includes the right to freedom of speech, freedom of expression, and freedom to form unions and associations. It also includes freedom to travel anywhere in India, freedom to live in any part of India, and the freedom to choose any profession of their interest.
This right also states that any citizen of India has the full right to purchase, sell and hold property in any part of the country. According to these rights, people will have the liberty to indulge in any trade or business. This right also defines that a person cannot be convicted twice for the same offense and it also cannot be compelled to stand as a witness against oneself.
Right against Exploitation
This right includes the prohibition of any form of forced labor. Children who are below the age of 14 years are not allowed to work in mines or factories where the risk of life is involved. According to these rights, no person has the right to exploit the other person in any way.
Therefore human trafficking & begging have been made legal offenses and those found involved are to be penalized. According to this rights slavery and traffic among women and children for dishonest purposes has been declared an offense. Payment of minimum wage against the labor is defined and no compromise is allowed in this regard.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Right to Freedom of Religion
These right states that there will be full freedom of conscience for all citizens of India. All people shall have equal right to freely adopt, practice and spread the religion of their choice. The state shall not hinder in any religious affairs of any individual in any manner. In this, all religions have a right to establish and uphold institutions for religious and charitable purposes. Also, they will be free to manage their own affairs with respect to these rights.
Cultural and Educational Right
This right is one of the most important rights as education is the primary right of each child. According to this right, all are free to follow the culture of their choice. Also, all are free to get the education of their choice.
No individual will be denied admission in any of the educational institutes on the basis of their culture, caste or religion. According to this, all the minorities have the right to establish their own educational institutes.
Right to Constitutional Remedy
This right is a very special right given to all the citizens. According to this right, a citizen has the power to go to the court in case of denial of any of the fundamental rights. The court stands as a guard for anybody against the breach of these rights.
If the government forcefully or intentionally does injustice to any individual or if a person is imprisoned without any reason or by the unlawful act then this right allows the person to go to the court for getting justice against the actions of the government.
Fundamental rights play a very significant role in the life of any citizen. These rights can defend during the time of complexity & difficulty and help us grow into a good human being and that’s why all the rights are the needs of people.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Fundamental Rights Essay

Essay on Fundamental Rights
The history of Fundamental Rights (which were lawfully enforceable) probably starts from the Magna Carta, which was a list of Rights extracted from King John by the people of England in 1214 AD. The most significant advancement in the history of Fundamental Rights occurred when through the first 10 amendments, the USA incorporated certain Fundamental Rights into its constitution in the form of the "Bill of Rights." In this Essay on Fundamental Rights, we shall talk about the various Rights provided to Indian citizens and what they stand for.
Long Fundamental Rights Essay in English
Fundamental Rights were borrowed from the constitution of the United States of America.
The constituent assembly of India adopted the constitution of India on 26th November 1949, which came into effect on 26th January 1950. It contains 395 Articles, 22 Parts, and 12 Schedules. Part III (Articles 12 to 35) of the Constitution of India consists of Rights which are essential for the overall development of individuals, are also termed as Fundamental Rights. Fundamental Rights are universal, that is, they apply to all the citizens of India irrespective of their race, birthplace, Religion, caste, gender or gender identity. Earlier there were seven Fundamental Rights, but later on the ‘Right to Property’ was abolished. Currently, we have six Fundamental Rights.
Right to Equality
The Right to EQuality is guaranteed by the constitution of India through articles 14 to 18 (of which article 14 is the most important). Right to EQuality refers to everyone being equal in the eyes of the law. It prohibits discrimination on the grounds of race, caste, creed etc by providing equal opportunity for employment. The article also abolishes untouchability and titles.
Right to Freedom
Articles 19 to 22 guarantee the Right to Freedom in the constitution of India. It guarantees all Indian citizens with Freedom of speech and expression; Freedom to assemble peacefully; Freedom for forming cooperative societies or unions or companies; Freedom to move freely in India; Freedom to reside or settle anywhere in India and the Freedom to practice any profession or carry on any occupation, trade or business of their choice. Although the government has the right to impose certain restrictions on these Freedoms in the interest of the sovereignty and integrity of India.
Right to Information has been given the status of a Fundamental right in 2005, under article 19(1) of the Indian Constitution.
Right Against Exploitation
Articles 23 and 24 guarantees the right against Exploitation and focuses mainly on two provisions. The first being the abolition of human trafficking and Begar (Forced Labour) and secondly, the abolition of employment of children under the age of 14 in jobs with a risky environment like factories, mines etc.
Right to Freedom of Religion
Articles 25 to 28 provide religious Freedom to all Indian citizens. The main objective of this right is to sustain secularism in our country. It assures that all Religions are equal in the eyes of the state and none of them is given preference over the other. It allows the citizens to preach, practise, and propagate the Religion of their choice. It also provides religious communities to set up charitable institutions.
Cultural and Educational Rights
Articles 29 and 30 provide every Indian citizen with Rights to education and cultures. It assures that every citizen gets equal opportunities in terms of education while giving minority communities the right to admission in colleges and universities without any discrimination. It also gives minority communities the right to establish Educational institutions to preserve and develop their culture.
Right to Constitutional Remedies
Articles 32 to 35 empowers all Indian citizens to move to the court of law whenever they are denied their Fundamental Rights. Article 32 is also termed as the citizens right to protect and defend the constitution as it allows the citizens to enforce the constitution through the judiciary.
The main objective of Right to Constitutional Remedies is to enforce Fundamental Rights.
Short Fundamental Rights Essay in English
Fundamental Rights are considered the Rights that are integral to the advancement of the human race. All other Rights are derived as direct consequences or application of their principles from such Rights. Among philosophers, it is an accepted belief that these Rights are nothing but "natural human Rights" that distinguish between humans and animals. So, these have played a rather important role in bringing humans all the way from the Stone Age to the present. It was regarded that such Rights were beyond the complexities of politics. The constitution's protection meant that these Rights could not be put to the vote and were not dependent on politicians or the majority's whims.
Why do we Need Fundamental Rights?
Such Rights are a safeguard for citizens against the government as it is necessary to have the rule of law and not a government or a person. These Rights do not dare to be transgressed by authority as they are explicitly given to the people by the Constitution. The courts are fully required to uphold these Rights and the government is answerable to the courts. After living in subjugation for so long, people have forgotten what liberty means. These Rights offer people the hope and belief that their growth will not be halted. They're free from the rulers' whims. These Rights are, in that sense, the first fruits of the long struggle for Freedom and bring a sense of satisfaction and accomplishment.
Even in Gulf countries or Communist countries, citizens are free. How is our liberty, then, different from theirs? A clear measure of how free we are in the list of Fundamental Rights. For example, every Indian citizen is free to practice a Religion of his choice, but that is not the case in Gulf countries. Our right to speech and expression enables us to criticize the government freely.
In conclusion, we can say that the Indian constitution was framed after a thorough analysis of all the constitutions in the world, and successfully incorporates all the good things existing in them.
Though the above content provided information about Fundamental Rights, it also gave you an outline of how an Essay should be written.
The Essay on Fundamental Rights contained some information about the topic and talked about long and short Essays.
Students might find it difficult to understand how they shall proceed whenever asked to write on any topic.
Since writing is a free form of expression and requires limited skills, there are no rules to it. But, in these times, when everything is advancing, you're expected to be able to deliver the best content.
To equip them with the relevant points, there are some tips listed below.
Go through them and master the skill of writing, thereafter!
Read and Understand the Prompt Before you can start writing, it is important for you to understand the prompt that you're offered. Without comprehending what you've asked to do, your content would never be impactful. The best way to understand it is to dissect it into parts. You might also consider making a small flowchart that clearly defines the flow of ideas in your head. Students shall understand that it is better to spend the first few minutes planning and organising things than to present an unorganised and unclear content. This in no way means that you have to adopt a formulaic approach to it but just try to deliver the best that they can.
Plan the Flow The next important thing for you to do is pen down the flow of points, as specific as the alphabet. Each point should have a ‘what next’ factor attached to it and that is how you can expect yourself to deliver higher Quality content. The importance of working in a planned and organised way is not unknown to any of us and that is what can help us move ahead with the ideas in our heads. Preparing a web with all the details is a great way to do it.
Make a Rough Draft Brainstorming and organising all that you have inside your head related to a particular topic is a good way before you deliver. Students are advised to prepare a small, concise, rough draft of their topics. Drafts are often regarded as crappy stuff but the truth is that it makes you analyse and rethink whatever you've thought till then. And there's where the new flow of ideas comes from. Make sure that your content is answering and giving the information of the prompt.
Follow a Simple Format Students often think that complicating the format or using too many fancy words in a piece of content impresses the reader and that fetches you more marks. However, it doesn't work this way. For good content, words must be easy to understand and they should always have a relatability factor attached so that it becomes easier for the audience to connect and understand whatever you are trying to convey.
Proofread your Content Last but not least, the most important step to do before finalising the content is to proofread it. When we try to pen down things, we often make mistakes. However, reading it once again allows you to study it again and check for mistakes. In case that you've missed anything important, you can further review and add that piece of information too. It may take a little more time of yours but the results would be worth it.

FAQs on Fundamental Rights Essay
1. What do we Conclude from this Essay on Fundamental Rights?
We can conclude that the Fundamental Rights embodied in the Indian Constitution act as a guarantee that as long as they live in Indian democracy, all Indian citizens can and will lead their lives in peace. Such civil liberties prevail over any other law of the land. Fundamental rights protect the citizen’s freedom, rights and liberties from any state invasion, and prevent the establishment of authoritarian and dictatorial rule in the country. They are very essential for the all-round progress of the people and the nation.
2. Which is the most important Fundamental Right?
The most important fundamental right is considered to be the Right to Constitutional Remedies because it ensures the protection of our fundamental rights. In the event of a violation of their fundamental rights, it helps citizens move to court. It also finds that the government does not violate or disrespect citizens' fundamental rights.
3. Can I use and cite resources while writing an Essay?
Of course, you can. In fact, resources make the content more interesting and engaging. Another advantage of using them is that it promotes research. However, you shall make sure the content should be rephrased and not plagiarized. For better clarity and understanding, you can go through some of the sample Essays available online. But, remember, the more you write, the more you learn. Hence, you need to practice writing on as many topics as possible and that way, you can upraise your skills.
4. How should an Essay be written? What should be its format?
The best way to write it is using a simpler format. It shall start with an introduction, have the body in between and should necessarily end with a conclusion. Make sure that whatever ideas you are putting forth to your readers should make absolute sense. Students can consider checking the prompts given on the website of Vedantu and practice writing about them to get better at it.
5. Can the body of the Essay be divided into small paragraphs?
Absolutely! In fact, it is the best way to present any piece of content. It makes your work look more organised and neat. Apart from this, if we consider the viewpoint of humans, they would prefer reading short paragraphs rather than big stories and that’s how you shall proceed. To understand it better, review the sample Essays available on the Vedantu website and their App.
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Essay on Fundamental Duties for Students & Children in English
January 25, 2021 by Sandeep
Essay on Fundamental Duties: The constitution of India has listed down every citizen’s fundamental duties. They are a gentle reminder to every person to perform his duties towards the nation for its well-being. Part 4 –A of the Indian constitution provides insights about fundamental duties. It imposes certain democratic conduct, responsibility and obligations for citizens. Countries like USA, Canada and Australia do not have fundamental duties listed in their constitution.
Essay on Fundamental Duties 500 Words in English
We have provided Fundamental Duties Essay in English, suitable for class 6, 7, 8, 9 & 10.
“O, citizens of Bharat! As our ancient saints and seers, leaders and preceptors have performed their duties righteously, similarly, you shall not falter to execute your duties.” ~ Rig Veda
Our constitution has given us many constitutional or fundamental rights, but we need to remember that it contains some constitutional or fundamental duties too! Rights and Duties are inseparable. The existence of one without other is meaningless. You can’t ask of a right, without a corresponding duty or vice versa. They are the two sides of the same coin. Even, Mahatma Gandhi once said: “The very performance of a duty secures us our right. Rights cannot be divorced from duties.” Surprisingly, the Fundamental Duties weren’t part of the original Indian Constitution, when it was written at the time of Indian Independence. They were later added in the constitution in 1976 through a constitutional amendment.
By observing the duties, it can be concluded that these duties were taken from the Indian traditions, mythologies, religions and practices. These duties were, essentially, the reflection of the Indian way of life. The concept of fundamental duties was taken from the erstwhile U.S.S.R constitution, as the socialist countries considered the rights and duties to be of equal importance. Till then, Japan was the only democratic nation to have duties for its citizens. Still, not having ‘duties’ in the constitution, doesn’t mean that the citizens of that country behave irresponsibly.
- to abide by the Constitution and respect its ideals and institutions, the National Flag and the National Anthem;
- to cherish and follow the noble ideals which inspired our national struggle for freedom;
- to uphold and protect the sovereignty, unity and integrity of India;
- to defend the country and render national service when called upon to do so;
- to promote harmony and the spirit of common brotherhood amongst all the people of India transcending religious, linguistic and regional or sectional diversities; to renounce practices derogatory to the dignity of women;
- to value and preserve the rich heritage of our composite culture;
- to protect and improve the natural environment including forests, lakes, rivers and wildlife, and to have compassion for living creatures;
- to develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform;
- to safeguard public property and to abjure violence;
- to strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity so that the nation constantly rises to higher levels of endeavour and achievement;
- for a parent or guardian, to provide opportunities for education to his child or, as the case may be, ward between the age of six and fourteen years.
The Fundamental duties are a constant reminder that along with rights, there is also some moral obligation of the citizens towards the nation. Various nations worldwide have embodied the principle of ‘responsible citizens’, and moved towards developed countries’ path. In the current times, the fundamental duties are of utmost importance. For example, the duty under Article 51-A(g) asks for protecting the environment, which is extremely needed today in the climate change crisis. The importance of these fundamental duties is immense.
Even the Bhagavad Gita and Ramayana also ask people to perform their duties. Lord Krishna in Gita says, “One should do one’s duties without expectation of any fruits.” Democracy can’t be there unless the citizens become responsible for their country’s progress. For democracy to survive, a high sense of duty is a must. Also, rights and duties have to exist together. Rights without duties can lead to anarchy. Since time immemorial, Indian culture has always stressed upon an individual’s “Kartavya” – the performance of one’s duties towards society, family and his/her country.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ಮುಖ್ಯ ಪುಟ; ಸಮುದಾಯ ಪುಟ; ಪ್ರಚಲಿತ; ಇತ್ತೀಚೆಗಿನ ಬದಲಾವಣೆಗಳು; ಯಾವುದೋ ಒಂದು ಪುಟ
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ Fundamental Rights and Duties Essay Mulabhuta Hakkugalu Mattu Kartavyagalu Prabandha in Kannada Saturday, May 18, 2024. Education. Prabandha. information. Jeevana Charithre ... Fundamental Rights and Duties Essay in Kannada.
fundamental duties in kannada , ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು, kannada fundamental duties kannada, 11 ಮೂಲಭೂತ ...
ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು, Mulabhuta Hakkugalu in Kannada, fundamental rights in kannada, fundamental rights kannada, pdf, notes, essay, IC Notes
File Language: Kannada. Which Department: Education. Which State: Central and State. Published Date: 20-02-2022. File Format Type: PDF. File Size: 2.6 MB. Total Pages: 160 Pages. Download Link: Click Below Blue Color Link To Download Indian Constitution Full PDF Notes in Kannada PDF. Scanned Copy: Yes.
ಭಾರತ ಸಂವಿಧಾನದ ಮೂಲಭೂತ ಹಕ್ಕುಗಳು ಮತ್ತು ಕರ್ತವ್ಯಗಳು ಪ್ರಬಂಧ, Fundamental Rights and Duties of Indian Constitution Essay in Kannada bharata samvidhana moolabhootha hakkugalu mattu kartvyagalu prabandha in kannada
indian constitution (polity) fundamental rights in kannada useful for sda/fda/pdo/kas/ias exams
Constitution of India in Kannada. Title. View / Download. The Constitution (One Hundred and Fifth Amendment) Act, 2021. Accessible Version : View (836 KB) The Constitution (One Hundred and Fourth Amendment) Act, 2019. Accessible Version : View (2 MB) The Constitution of India in Kannada.
The Indian Constitution Fundamental rights in kannada ppt. Apr 8, 2019 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 2 likes • 2,700 views. A. adityagupta4598. A list of Fundamental Rights Discussed in detail in Kannada Language which is required by the people to get introduced with their Rights. Law.
14:15mins. 2. Fundamental Rights in Indian Constitution (in Kannada) 13:18mins. 3. Features of Indian Constitution (in Kannada) 13:45mins. 4. Right to Constitutional Remedy through Writs (in Kannada)
The Preamble of Constitution of India and Fundamental Rights and Duties. Preamble Of Constitution Of India; Fundamental Rights and Duties; ... a "search here" option is been provided. here, the option to type in Kannada is made available. while searching, usage of Unicode font is compulsory. option to search in English is also provided. ...
The Fundamental Duties are defined as the moral obligations of all citizens to help promote a spirit of patriotism and to uphold the unity of India. These duties set out in Part IV-A of the Constitution, concern individuals and the nation. Like the Directive Principles, they are not enforceable by courts unless otherwise made enforceable by ...
Constitution of India in Kannada. CONSTITUTION-OF-INDIA-Kannada. S. No. Title. Updated Date. 1. The Constitution (One Hundred and Fifth Amendment) Act, 2021. 21/12/2021. 2.
5 lessons • 1h 8m. 1. Fundamental Rights (in Kannada ) 13:43mins. 2. Questionary on Fundamental Rights (in Kannada ) 12:20mins. 3. Features of Indian Constitution (in Kannada )
These rights are essential for the development of an individual's personality and dignity. The Constitution of India guarantees six fundamental rights to its citizens, which are as follows: 1. Right to Equality: The right to equality is one of the most important fundamental rights enshrined in the Indian Constitution.
The Fundamental Duties in the Life of an Indian. These are defined as the moral obligations of all citizens to help promote a spirit of patriotism and to uphold the unity of India and concern the individuals and the nation. Included in Part IVA of the Constitution, like the Directive Principles, they are not enforceable by the law.
Title. Date. View / Download. The Constitution (One Hundred and Fifth Amendment) Act, 2021. Accessible Version : View (836 KB) The Constitution (One Hundred and Fourth Amendment) Act, 2019. Accessible Version : View (2 MB) The Constitution of India in Kannada. Accessible Version : View (4 MB)
Hence, the Indian Constitution supports a federal system. It includes many unitary features such as a strong central power, emergency provisions, appointment of Governors by the President, etc. Fundamental rights and fundamental duties. The Indian Constitution provides an elaborate list of Fundamental Rights to the citizens of India.
contents of some of the Fundamental Rights, particularly those Fundamental Rights which have been judicially deduced. Definition of 'the State' 3.5 Fundamental rights guaranteed by the Constitution are, in the absence of specific constitutional provisions, mainly enforceable against „the State‟. The definition of 'the State' in
The Constitution of India guarantees six fundamental rights to its citizens, which are as follows: 1. Right to Equality: The right to equality is one of the most important fundamental rights enshrined in the Indian Constitution. It ensures that all individuals are equal before the law and prohibits discrimination based on caste, race, religion ...
DSpace JSPUI eGyanKosh preserves and enables easy and open access to all types of digital content including text, images, moving images, mpegs and data sets
500+ Words Essay on Fundamental Rights. There are some basic rights that are very well-known as fundamental to human existence and crucial for human expansion. In the absence of fundamental rights, a man's existence would be worthless. So, the political institution's role and responsibility mainly emphasized on empowering the people ...
The most significant advancement in the history of Fundamental Rights occurred when through the first 10 amendments, the USA incorporated certain Fundamental Rights into its constitution in the form of the "Bill of Rights." In this Essay on Fundamental Rights, we shall talk about the various Rights provided to Indian citizens and what they ...
Essay on Fundamental Duties for Students & Children in English. January 25, 2021 by Sandeep. Essay on Fundamental Duties: The constitution of India has listed down every citizen's fundamental duties. They are a gentle reminder to every person to perform his duties towards the nation for its well-being. Part 4 -A of the Indian constitution ...