If you could change one thing about college, what would it be?
Graduate faster
Better quality online classes
Flexible schedule
Access to top-rated instructors

College Success

Why Study Literature?
05.15.2023 • 5 min read
Learn about the value and benefits of studying literature: how it develops our skills as well as shapes our understanding of the society we live in.
What Is Literature?
The benefits of studying literature.
Literature & Outlier.org
Many libraries in the U.S. are under attack.
From small towns to big cities, it’s more common to see protests outside of libraries. Libraries are under the microscope and being scrutinized for what content they have on their shelves.
Some people see certain books as a threat to society. While others believe everyone has a right to access any information they wish. The fact is literature is so powerful some people see it as dangerous and want to choose what the public has a right to read.
This is not the first time in history that people have tried to censor literature for what it says. So what really is literature and why is it so powerful?
In this article, we’ll define literature, talk about the history of literature, and the benefits of studying literature in college.
Literature is an art form that uses language to create imaginative experiences. It includes poetry, drama, fiction, and nonfiction.
Literature communicates ideas and emotions.It entertains, educates, and inspires readers. Literature explores complex themes and is an important part of human culture.
From its original Latin derivative, "writing formed with letters," to its current definition, a "body of written works," our understanding of literature has evolved.
Literature explains society and culture. It both criticizes and affirms cultural values based on the writer’s perceptions. It expresses and explores the human condition. It looks back to the past and onward toward the future.
As literature represents the culture and history of a language or people, the study of literature has great value. To study literature means looking deeply into a large body of written work and examining it as an art form.
Of course, there are many different literary genres, or types of literature. At a liberal arts school , a literature program, a student would study these genres extensively and understand the historical and cultural context they represent.
Literary Fiction vs. Genre Fiction
Students in a college literature program examine many forms of literature, including:
Some definitions of literature separate fiction into 2 categories: literary fiction and genre fiction. Genre fiction consists of more popular literature read for entertainment. Some examples of genre fiction include crime, fantasy, and science fiction stories.
Literary fiction explores themes of the human condition. These stories cannot be further categorized and are read primarily for a philosophical search for the meaning of life. Examples of literary fiction include The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald and Beloved by Toni Morrison.
You can discover more distinctions by studying literature in depth.
1. Literature Develops Communication Skills
The foundation of literature is the English Language. By reading literature, you can improve your knowledge of language: vocabulary, grammar, sentence structure, content creation, and more. When you immerse yourself in William Shakespeare, Celeste Ng, or Chinua Achebe, you're absorbing new words, expressions, and ideas—without even realizing it.
You can use everything you learn to improve your own writing and communication skills . You will use these skills beyond high school and college. In our everyday lives, we navigate personal relationships, craft emails, present projects, collaborate with teammates, analyze data, and more.
Yuval Noah Harari has written much of his own literature on the history and success of the human race. In his book Sapiens, he emphasizes our ability to craft stories as one of our most valuable skills: " Fiction has enabled us not merely to imagine things, but to do so collectively.” Through these collective stories, we learn about the human experience, both in smaller interpersonal ways and on a larger, more global scale.
2. Literature Teaches Us About the Human Condition
Literature helps us reflect on the human experience, teaching us about who we are and the world we live in. It presents a range of emotions, from love to anger to grief to happiness. It gives us insight and context about societal norms and cultural traditions.
It explores our history and our present; it imagines our futures. It introduces us to new ways of thinking and living, compelling us to think critically and creatively about our own experiences.
Through literature, we see we're not alone in our thoughts and feelings. The characters we read about have already experienced similar difficulties and worked to solve or change them, giving us the blueprint to do the same.
Jane Austen's Pride and Prejudice goes beyond social commentary to explore the complexities of familial relationships, romantic relationships, and friendships. Mr. Darcy insults Elizabeth Bennet without meaning to, Elizabeth Bennet makes harsh judgments without knowing all the facts, and Mrs. Bennet worries about her daughter's future constantly. We can see ourselves in them.
3. Literature Teaches Us About Empathy
When we connect with literature's characters and narratives, we learn how to empathize with others. While we’re not physically experiencing the raging seas in Virginia Woolf's To the Lighthouse or the loss of a loved one in William Shakespeare's Romeo and Juliet, we are swept up in the story and the emotion. This helps us develop empathy and emotional intelligence.
In a 2006 study , professors at the University of Toronto concluded a lifetime exposure to literary fiction positively correlated with advanced social ability. In 2020, the Harvard Business Review encouraged business students to read literary works to enhance their abilities to keep an open mind, process information, and make effective decisions.
4. Literature Helps Us Explore New Ideas
With words, and not actions, authors create spaces where we can explore new ideas, new structures, new concepts, and new products. When the only limit is your imagination, anything is possible in creative writing.
We can dive into the past to understand British society at the turn of the 19th century in Austen's Pride and Prejudice or jump into potential futures through Harari's Homo Deus. We can consider alternative futures like that in George Orwell's 1984 or conduct experiments in Robert Louis Stevenson's The Strange Case of Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde.
We don't encounter monsters or humanoid robots in our everyday lives (at least we hope not!). But when we explore them through literature, we’re equipped to consider, challenge, and analyze concepts we don't yet know or understand. This practice opens our minds and allows us to be more flexible when we face the new and unknown. These critical thinking skills enable us to process information easier.
5. Literature Changes the Way We Think
With everything we learn from literature and the skills it helps us develop, literature changes the way we think, work, and act.
When we can think more critically, we arrive at different conclusions. When we open our minds and empathize with others, we better accept and tolerate differences. When we can articulate and communicate effectively, we work better together to achieve and succeed.
Whether English literature or Russian literature or French literature, literature is the key to understanding ourselves and society.
Literature and Outlier.org
Looking to study literature and develop your own writing skills? Outlier.org’s cutting-edge College Writing course is a great place to start. Through interviews with celebrated writers and writing secrets from instructor John Kaag, you'll learn how to use words to express yourself and communicate more effectively.
The course explores:
How to level up your love letters
What writing and magic have in common
How to write better professional emails using The Princess Bride
How to get your writing published
How to create the perfect short sentence
Outlier courses are 100% online, so you can learn at your own pace from the comfort of your own home. At $149 per credit, you’ll save 50% compared to other college courses, all while earning transferable credits from the top-ranked University of Pittsburgh. If you decide to continue your education in literature, you can take the credit with you to the degree program of your choice.
It’s no doubt studying literature will give you a well-rounded education. It is through literature that societies have grown and developed—inspiring change throughout the world. Choosing to study literature will not only give you a glimpse into the past but help you articulate the present and inspire change in the future. By studying literature you will have the power to connect with others and truly touch their hearts and minds.
About the Author
Bob Patterson is a former Director of Admissions at Stanford University, UNC Chapel Hill, and UC Berkeley; Daisy Hill is the co-author of Uni in the USA…and beyond published by the Good Schools Guide 2019. Together, they have established MyGuidED, a new educational tool for students looking to apply to university (launching 2023).
Degrees+: Discover Online College Unlike Anything You’ve Experienced
Outlier (winner of TIME Best Inventions 2020) and Golden Gate University (#1 school for working professionals) have redesigned the experience of earning a college degree to minimize cost and maximize outcomes. Explore a revolutionary way to earn your college degree:
Related Articles

What Are the Liberal Arts in Education?
The article defines what liberal arts education is, explains the different degree fields, and lists possible professions you can do with the degree.
Jennifer Rivera
Subject Matter Expert

10 Amazing Jobs for Communication Majors [2023]
This article explains what a communications degree is and the benefits of studying it. It lists the skills a communication major has and the best-paid jobs, including the entry-level and average salaries.
Mia Frothingham

8 Reasons Why Having a College Degree Is Important
Learn more about why a college degree is important by understanding the benefits and value of having one.
Bob Patterson
Former Stanford Director of Admissions
Further Reading
Best 15 tips to make the most of college [2023], what are soft skills in college, thinking about going back to college in your 30s here’s everything you need to know, a complete guide on how to write a winning scholarship essay, 7 best self-paced online college programs [2023], what is community college.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1 What Is Literature and Why Do We Study It?

In this book created for my English 211 Literary Analysis introductory course for English literature and creative writing majors at the College of Western Idaho, I’ll introduce several different critical approaches that literary scholars may use to answer these questions. The critical method we apply to a text can provide us with different perspectives as we learn to interpret a text and appreciate its meaning and beauty.
The existence of literature, however we define it, implies that we study literature. While people have been “studying” literature as long as literature has existed, the formal study of literature as we know it in college English literature courses began in the 1940s with the advent of New Criticism. The New Critics were formalists with a vested interest in defining literature–they were, after all, both creating and teaching about literary works. For them, literary criticism was, in fact, as John Crowe Ransom wrote in his 1942 essay “ Criticism, Inc., ” nothing less than “the business of literature.”
Responding to the concern that the study of literature at the university level was often more concerned with the history and life of the author than with the text itself, Ransom responded, “the students of the future must be permitted to study literature, and not merely about literature. But I think this is what the good students have always wanted to do. The wonder is that they have allowed themselves so long to be denied.”
We’ll learn more about New Criticism in Section Three. For now, let’s return to the two questions I posed earlier.
What is literature?
First, what is literature ? I know your high school teacher told you never to look up things on Wikipedia, but for the purposes of literary studies, Wikipedia can actually be an effective resource. You’ll notice that I link to Wikipedia articles occasionally in this book. Here’s how Wikipedia defines literature :
“ Literature is any collection of written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially prose fiction , drama , and poetry . [1] In recent centuries, the definition has expanded to include oral literature , much of which has been transcribed. [2] Literature is a method of recording, preserving, and transmitting knowledge and entertainment, and can also have a social, psychological, spiritual, or political role.”
This definition is well-suited for our purposes here because throughout this course, we will be considering several types of literary texts in a variety of contexts.
I’m a Classicist—a student of Greece and Rome and everything they touched—so I am always interested in words with Latin roots. The Latin root of our modern word literature is litera , or “letter.” Literature, then, is inextricably intertwined with the act of writing. But what kind of writing?
Who decides which texts are “literature”?
The second question is at least as important as the first one. If we agree that literature is somehow special and different from ordinary writing, then who decides which writings count as literature? Are English professors the only people who get to decide? What qualifications and training does someone need to determine whether or not a text is literature? What role do you as the reader play in this decision about a text?
Let’s consider a few examples of things that we would all probably classify as literature. I think we can all (probably) agree that the works of William Shakespeare are literature. We can look at Toni Morrison’s outstanding ouvre of work and conclude, along with the Nobel Prize Committee, that books such as Beloved and Song of Solomon are literature. And if you’re taking a creative writing course and have been assigned the short stories of Raymond Carver or the poems of Joy Harjo , you’re probably convinced that these texts are literature too.
In each of these three cases, a different “deciding” mechanism is at play. First, with Shakespeare, there’s history and tradition. These plays that were written 500 years ago are still performed around the world and taught in high school and college English classes today. It seems we have consensus about the tragedies, histories, comedies, and sonnets of the Bard of Avon (or whoever wrote the plays).
In the second case, if you haven’t heard of Toni Morrison (and I am very sorry if you haven’t), you probably have heard of the Nobel Prize. This is one of the most prestigious awards given in literature, and since she’s a winner, we can safely assume that Toni Morrison’s works are literature.
Finally, your creative writing professor is an expert in their field. You know they have an MFA (and worked hard for it), so when they share their favorite short stories or poems with you, you trust that they are sharing works considered to be literature, even if you haven’t heard of Raymond Carver or Joy Harjo before taking their class.
(Aside: What about fanfiction? Is fanfiction literature?)
We may have to save the debate about fan fiction for another day, though I introduced it because there’s some fascinating and even literary award-winning fan fiction out there.
Returning to our question, what role do we as readers play in deciding whether something is literature? Like John Crowe Ransom quoted above, I think that the definition of literature should depend on more than the opinions of literary critics and literature professors.
I also want to note that contrary to some opinions, plenty of so-called genre fiction can also be classified as literature. The Nobel Prize winning author Kazuo Ishiguro has written both science fiction and historical fiction. Iain Banks , the British author of the critically acclaimed novel The Wasp Factory , published popular science fiction novels under the name Iain M. Banks. In other words, genre alone can’t tell us whether something is literature or not.
In this book, I want to give you the tools to decide for yourself. We’ll do this by exploring several different critical approaches that we can take to determine how a text functions and whether it is literature. These lenses can reveal different truths about the text, about our culture, and about ourselves as readers and scholars.
“Turf Wars”: Literary criticism vs. authors
It’s important to keep in mind that literature and literary theory have existed in conversation with each other since Aristotle used Sophocles’s play Oedipus Rex to define tragedy. We’ll look at how critical theory and literature complement and disagree with each other throughout this book. For most of literary history, the conversation was largely a friendly one.
But in the twenty-first century, there’s a rising tension between literature and criticism. In his 2016 book Literature Against Criticism: University English and Contemporary Fiction in Conflict, literary scholar Martin Paul Eve argues that twenty-first century authors have developed
a series of novelistic techniques that, whether deliberate or not on the part of the author, function to outmanoeuvre, contain, and determine academic reading practices. This desire to discipline university English through the manipulation and restriction of possible hermeneutic paths is, I contend, a result firstly of the fact that the metafictional paradigm of the high-postmodern era has pitched critical and creative discourses into a type of productive competition with one another. Such tensions and overlaps (or ‘turf wars’) have only increased in light of the ongoing breakdown of coherent theoretical definitions of ‘literature’ as distinct from ‘criticism’ (15).
One of Eve’s points is that by narrowly and rigidly defining the boundaries of literature, university English professors have inadvertently created a situation where the market increasingly defines what “literature” is, despite the protestations of the academy. In other words, the gatekeeper role that literary criticism once played is no longer as important to authors. For example, (almost) no one would call 50 Shades of Grey literature—but the salacious E.L James novel was the bestselling book of the decade from 2010-2019, with more than 35 million copies sold worldwide.
If anyone with a blog can get a six-figure publishing deal , does it still matter that students know how to recognize and analyze literature? I think so, for a few reasons.
- First, the practice of reading critically helps you to become a better reader and writer, which will help you to succeed not only in college English courses but throughout your academic and professional career.
- Second, analysis is a highly sought after and transferable skill. By learning to analyze literature, you’ll practice the same skills you would use to analyze anything important. “Data analyst” is one of the most sought after job positions in the New Economy—and if you can analyze Shakespeare, you can analyze data. Indeed.com’s list of top 10 transferable skills includes analytical skills , which they define as “the traits and abilities that allow you to observe, research and interpret a subject in order to develop complex ideas and solutions.”
- Finally, and for me personally, most importantly, reading and understanding literature makes life make sense. As we read literature, we expand our sense of what is possible for ourselves and for humanity. In the challenges we collectively face today, understanding the world and our place in it will be important for imagining new futures.
A note about using generative artificial intelligence
As I was working on creating this textbook, ChatGPT exploded into academic consciousness. Excited about the possibilities of this new tool, I immediately began incorporating it into my classroom teaching. In this book, I have used ChatGPT to help me with outlining content in chapters. I also used ChatGPT to create sample essays for each critical lens we will study in the course. These essays are dry and rather soulless, but they do a good job of modeling how to apply a specific theory to a literary text. I chose John Donne’s poem “The Canonization” as the text for these essays so that you can see how the different theories illuminate different aspects of the text.
I encourage students in my courses to use ChatGPT in the following ways:
- To generate ideas about an approach to a text.
- To better understand basic concepts.
- To assist with outlining an essay.
- To check grammar, punctuation, spelling, paragraphing, and other grammar/syntax issues.
If you choose to use Chat GPT, please include a brief acknowledgment statement as an appendix to your paper after your Works Cited page explaining how you have used the tool in your work. Here is an example of how to do this from Monash University’s “ Acknowledging the Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence .”
I acknowledge the use of [insert AI system(s) and link] to [specific use of generative artificial intelligence]. The prompts used include [list of prompts]. The output from these prompts was used to [explain use].
Here is more information about how to cite the use of generative AI like ChatGPT in your work. The information below was adapted from “Acknowledging and Citing Generative AI in Academic Work” by Liza Long (CC BY 4.0).
The Modern Language Association (MLA) uses a template of core elements to create citations for a Works Cited page. MLA asks students to apply this approach when citing any type of generative AI in their work. They provide the following guidelines:
Cite a generative AI tool whenever you paraphrase, quote, or incorporate into your own work any content (whether text, image, data, or other) that was created by it. Acknowledge all functional uses of the tool (like editing your prose or translating words) in a note, your text, or another suitable location. Take care to vet the secondary sources it cites. (MLA)
Here are some examples of how to use and cite generative AI with MLA style:
Example One: Paraphrasing Text
Let’s say that I am trying to generate ideas for a paper on Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s short story “The Yellow Wallpaper.” I ask ChatGPT to provide me with a summary and identify the story’s main themes. Here’s a link to the chat . I decide that I will explore the problem of identity and self-expression in my paper.
My Paraphrase of ChatGPT with In-Text Citation
The problem of identity and self expression, especially for nineteenth-century women, is a major theme in “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman (“Summarize the short story”).

Works Cited Entry
“Summarize the short story “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman. Include a breakdown of the main themes” prompt. ChatGPT. 24 May Version, OpenAI, 20 Jul. 2023, https://chat.openai.com/share/d1526b95-920c-48fc-a9be-83cd7dfa4be5
Example Two: Quoting Text
In the same chat, I continue to ask ChatGPT about the theme of identity and self expression. Here’s an example of how I could quote the response in the body of my paper:
When I asked ChatGPT to describe the theme of identity and self expression, it noted that the eponymous yellow wallpaper acts as a symbol of the narrator’s self-repression. However, when prompted to share the scholarly sources that formed the basis of this observation, ChatGPT responded, “As an AI language model, I don’t have access to my training data, but I was trained on a mixture of licensed data, data created by human trainers, and publicly available data. OpenAI, the organization behind my development, has not publicly disclosed the specifics of the individual datasets used, including whether scholarly sources were specifically used” (“Summarize the short story”).
It’s worth noting here that ChatGPT can “ hallucinate ” fake sources. As a Microsoft training manual notes, these chatbots are “built to be persuasive, not truthful” (Weiss &Metz, 2023). The May 24, 2023 version will no longer respond to direct requests for references; however, I was able to get around this restriction fairly easily by asking for “resources” instead.
When I ask for resources to learn more about “The Yellow Wallpaper,” here is one source it recommends:
“Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s The Yellow Wallpaper: A Symptomatic Reading” by Elaine R. Hedges: This scholarly article delves into the psychological and feminist themes of the story, analyzing the narrator’s experience and the implications of the yellow wallpaper on her mental state. It’s available in the journal “Studies in Short Fiction.” (“Summarize the short story”).
Using Google Scholar, I look up this source to see if it’s real. Unsurprisingly, this source is not a real one, but it does lead me to another (real) source: Kasmer, Lisa. “Charlotte Perkins Gilman’s’ The Yellow Wallpaper’: A Symptomatic Reading.” Literature and Psychology 36.3 (1990): 1.
Note: ALWAYS check any sources that ChatGPT or other generative AI tools recommend.
For more information about integrating and citing generative artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT, please see this section of Write What Matters.
I acknowledge that ChatGPT does not respect the individual rights of authors and artists and ignores concerns over copyright and intellectual property in its training; additionally, I acknowledge that the system was trained in part through the exploitation of precarious workers in the global south. In this work I specifically used ChatGPT to assist with outlining chapters, providing background information about critical lenses, and creating “model” essays for the critical lenses we will learn about together. I have included links to my chats in an appendix to this book.
Critical theories: A targeted approach to writing about literature
Ultimately, there’s not one “right” way to read a text. In this book. we will explore a variety of critical theories that scholars use to analyze literature. The book is organized around different targets that are associated with the approach introduced in each chapter. In the introduction, for example, our target is literature. In future chapters you’ll explore these targeted analysis techniques:
- Author: Biographical Criticism
- Text: New Criticism
- Reader: Reader Response Criticism
- Gap: Deconstruction (Post-Structuralism)
- Context: New Historicism and Cultural Studies
- Power: Marxist and Postcolonial Criticism
- Mind: Psychological Criticism
- Gender: Feminist, Post Feminist, and Queer Theory
- Nature: Ecocriticism
Each chapter will feature the target image with the central approach in the center. You’ll read a brief introduction about the theory, explore some primary texts (both critical and literary), watch a video, and apply the theory to a primary text. Each one of these theories could be the subject of its own entire course, so keep in mind that our goal in this book is to introduce these theories and give you a basic familiarity with these tools for literary analysis. For more information and practice, I recommend Steven Lynn’s excellent Texts and Contexts: Writing about Literature with Critical Theory , which provides a similar introductory framework.
I am so excited to share these tools with you and see you grow as a literary scholar. As we explore each of these critical worlds, you’ll likely find that some critical theories feel more natural or logical to you than others. I find myself much more comfortable with deconstruction than with psychological criticism, for example. Pay attention to how these theories work for you because this will help you to expand your approaches to texts and prepare you for more advanced courses in literature.
P.S. If you want to know what my favorite book is, I usually tell people it’s Herman Melville’s Moby Dick . And I do love that book! But I really have no idea what my “favorite” book of all time is, let alone what my favorite book was last year. Every new book that I read is a window into another world and a template for me to make sense out of my own experience and better empathize with others. That’s why I love literature. I hope you’ll love this experience too.
writings in prose or verse, especially : writings having excellence of form or expression and expressing ideas of permanent or universal interest (Merriam Webster)
Critical Worlds Copyright © 2024 by Liza Long is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Why Study Literature?
Stacey Van Dahm
If you are here, reading this article, you might already know how important reading literature is. But if someone asks you, “Why study literature?” how would you answer? It’s an age-old question we once again face at a time when choosing what to study in college is tied to rather limited assumptions about what “success,” or a “good income,” or the very purpose of a college education actually is. In fact, the discussion about why we study literature is directly related to the general education or liberal arts curriculum at any institution of higher learning. These programs adhere to the notion (supported by research) that studying literature, philosophy, and art (i.e., the Humanities) makes us better people — more responsible, ethical, and civically engaged.
This is true, but that’s not exactly the conversation I want to have here. Instead, I want to start with a 200,000-year-old handprint.
In 2021, Archaeologists discovered the earliest known cave art in the Quesang village in the Tibetan Plateau. The hand- and footprints discovered, it turns out, were made by 7- and 12-year-old hominin species children [1] , somewhere between 169,000 and 226,000 years ago during the Middle Paleolithic period (Zhang et al). The journal Science Bulletin , originally publishing the findings, includes these two images of the prints:
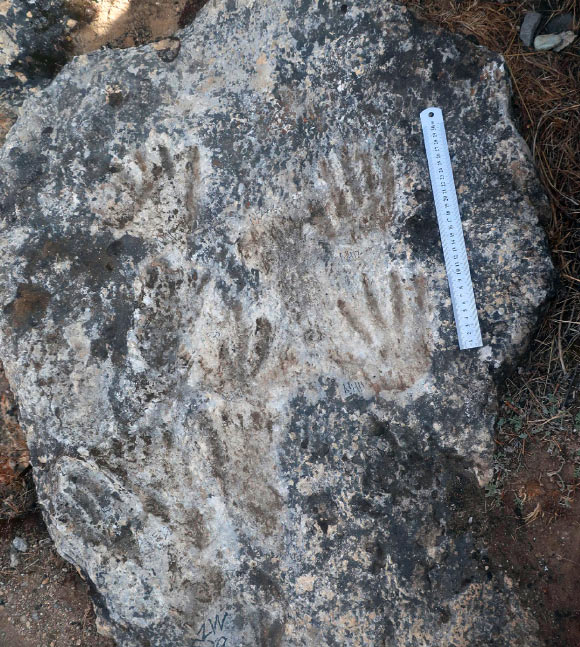

I include the images because they help us to imagine the children, who “squished their hands and feet into sticky mud” (Lanese) to leave the prints deliberately, which opens up a fascinating question about whether or not this is “art.” Matthew Bennet, a professor of environmental and geographical sciences at Bournemouth University in Poole, England, likens the composition to the scribbling of a toddler that a parent might hang on the fridge as “art.” It is intentional and playful. The implication is that, as a deliberate composition, it is artistic.
One of the ways we might understand these handprints is to tell their story. It seems the children were together, playing in the mud. I imagine them enjoying the feeling of wet mud squishing between their toes and fingers, the smell of earth and leisure. Perhaps they were siblings or cousins or similarly related young people attached to the same band of Denisovans or Homo erectus. Maybe one of them, the youngest — after having observed the other for some time — stuck their foot in the mud and lifted it straight up, out of some interest, a curiosity. The other sees this and does the same, and before long, they are taking it in turns, nudging each other out of the way, to slowly fill up the space with various hand- and footprints. Perhaps, liking the results, they left those prints there. Or maybe they were wrenched away from this “play” suddenly, out of some necessity, never to return. Either way, they hardly could have imagined that 200,000 years later scientists would find the marks preserved by the slow-moving forces of geological fate, to be discovered and studied during the so-called Anthropocene period.
Some cave drawings more definitively categorized as “figurative art” date back about 40,000 years and are found in Indonesia. The depictions of hands made with a stencil technique, as if outlined “against a background of red paint,” or the figures of animals once common in the area, shifted our assumptions about the origins of art. Scientists understand these figures to be an indication of the “moment when the human mind, with its unique capacity for imagination and symbolism, switched on” (Marchant). To put this in other terms, we have long understood art to be a sign of something unique about human beings and their sensibility.
These examples trigger our own curiosity. What were these human ancestors trying to capture as they drew figures of themselves and animals? What kinds of rituals or rites of passage included marking walls with handprints? How did early humans imagine themselves and their surroundings? How did they imagine themselves in relation to others? Why did they feel compelled to express their experience in visual images and stories? Is our amazing ability to imagine and represent experience beyond the self a unique sign of humanity?
What we see in early artistic endeavor is, really, ourselves. And our thirst to understand the drawings and stories and relics of the past has very much to do with a quest to understand human experience and our own place in it. In fact, the creation of stories, narratives, is very much about making meaning of the world, as explained in Clint Johnson’s, “ What Is Story ?”
Indeed, the story that I’ve told you so far is really a way to make sense of something. In fact, you will notice that the telling of this story included some make-believe — an anecdote of young people playing in mud — but also lots of other modes of inquiry and knowledge building: anthropology, geology, biology, and paleontology, for example.
My argument is that literary study is important because it is one more form of studying the artifacts of people over time, the kinds of artifacts that help us understand ourselves in historical context. Literary study is the study of the stories people have told about human experience throughout time. Cave drawings, like stories, suggest the centrality of aesthetic sensibility to human experience. They trigger our curiosity , and they show us we have a deep and connected human history that demonstrates a compulsion to create and leave a mark. Literary art is like that handprint in the mud; it is the imprint of a mind, a sensibility captured in artistic creation composed of words.
Literary study awakens our aesthetic sensibility.
It may be surprising that a handprint in the mud can inspire aesthetic wonder. But many of us have been moved by literary images that unfold before us as we read. These images are powerful because they happen in our minds and hearts. It is one of the ways that the experiences of literary characters become deeply embedded in our own emotional lives. Aesthetic experiences make us feel.
Colombian author Gabriel García Márquez’s novel One Hundred Years of Solitude is filled with passages that evoke a sense of beauty both through imagistic descriptions and the kinds of human experiences they are attached to. The novel tells the story of a family over multiple generations in a small town in Columbia called Macondo. The death of José Arcadio Buendía, the patriarch of the family and the founder of the community, is represented in a way that evokes the gravity of the loss:
Entonces entraron al cuarto de José Arcadio Buendía, lo sacudieron con todas sus fuerzas, le gritaron al oído, le pusieron un espejo frente a las fosas nasales, pero no pudieron despertarlo. Poco después, cuando el carpintero le tomaba las medidas para el ataúd, vieron a través de la ventana que estaba cayendo una llovizna de minúsculas flores amarillas. Cayeron toda la noche sobre el pueblo en una tormenta silenciosa, y cubrieron los techos y atascaron las puertas, y sofocaron a los animales que durmieron a la intemperie. Tantas flores cayeron del cielo, que las calles amanecieron tapizadas de una colcha compacta, y tuvieron que despejarlas con palas y rastrillos para que pudiera pasar el entierro. ( Cien Años 166)
Then they went into José Arcadio Buendía’s room, shook him as hard as they could, shouted in his ear, put a mirror in front of his nostrils, but they could not awaken him. A short time later, when the carpenter was taking measurements for the coffin, through the window they saw a light rain of tiny yellow flowers falling. They fell on the town all through the night in a silent storm, and they covered the roofs and blocked the doors and smothered the animals who slept outdoors. So many flowers fell from the sky that in the morning the streets were carpeted with a compact cushion and they had to clear them away with shovels and rakes so that the funeral procession could pass by. ( One Hundred Years 140)
The passage, beautiful in both Spanish and English, conveys the enormity of the loss in a surprising, magical scene that combines wonder and sadness. Falling yellow flowers make the loss visible, shared, throughout the whole community. It seems as if a higher power is responding to death with a “tormenta silenciosa,” a “silent storm” that blankets the town. The way that Gabriel García Márquez juxtaposes death with beauty in this scene touches our own sense of loss, uniting the literary image of grief with our own understanding of suffering. Falling yellow flowers remind us that suffering loss is always paired first with having loved.
These kinds of literary images live within us after we read a book, and they color our vision of the world and our ways of interacting with it.
Literary study activates our curiosity.
Literature also drives us to get answers to our questions, to ask and to explore. This is one of the things people mean when they say that literature “opens our minds.” When we are curious, we engage with the world by asking questions and listening carefully and thoughtfully to the answers we encounter. This way of facing life makes it much harder to judge others and shut out new ideas, and it makes it much easier to understand things that are unfamiliar.
A short story published in 2016 by Helen Oyeyemi, “Is Your Blood as Red as This?” is filled with curiosities. Some of the main characters in the story are … puppets — puppets who manipulate their handlers and each other with the verve of jealous children and the intensity of young lovers. The story defies simple explanation, but we see from the start that desire will be a driving force in the story when the main character, Rhada Chaudhry, a schoolgirl, meets another central character, Myrna Semyonova, and becomes determined to win her heart. She sets out to do so by telling stories. “I discovered that I could talk to you in natural, complete sentences. It was simple: If I talked to you, perhaps you would kiss me. And I had to have a kiss from you: To have seen your lips and not ever kissed them would have been the ruin of me …” (101). This desire initiates a metaphor of storytelling as an alternating current that animates both the teller and the listener. And it pricks our curiosity. Will she get the girl?
As it turns out, this isn’t the right question. This story makes us curious by defying our expectations. It seems like a romance, but Oyeyemi’s love tangle becomes secondary when the story shifts to center puppetry, a surprising form of storytelling. Puppets, directed and manipulated by a puppeteer, enact stories, but in Oyeyemi’s world, when one small puppet asks, “Is Your Blood as Red as This?” the puppet master disappears, and with them, so do readers’ assumptions about how stories work. At first, Rhada joins Myrna’s puppet school saying, “I don’t feel one hundred percent sure that I’m not a puppet myself” (108). But soon, Rhada’s puppet, Gepetta, takes over the narration of the story, commenting on Rhada’s crushes, telling the history of enigmatic puppet, Rowan, with whom she listens to music while riding night buses since, she says, “neither of us needs sleep” (129). As the puppets manipulate their handlers and overtake our imaginations, we readers find ourselves delightfully lost. We are no longer in a romance or a puppet show. Eventually, someone, perhaps a jealous and long-suffering puppet, orchestrates a crime that exposes all the characters’ hidden suffering, fear, and desire. The story suggests that we are just as likely to be manipulated in the stories of our lives, pulled by the strings we pretend are not there.
This is a story that raises many questions about the human condition. How do my assumptions about stories blind me to how I’m reading? What expectations and assumptions do I hold that cause me to misinterpret others? Is it possible for me to truly see others or for them to see me? Why are we so unaware of the suffering and pain of those around us? To what extent do my own desires and hidden fears hold me back?
Literature piques our interest in both the magic of a fantastic tale and the complexity of human experience. In this case, literature makes us curious about our own choices and our own behavior in the face of human fragility, including our own.
Literary study also deepens our historical and critical perspective.
You likely remember learning about another historical period through reading. Literary texts draw readers into a time and place different from our own. Immersed in a literary world, we discover the values, beliefs, and systems that shape human behavior. Reading literature opens us to a critical examination of our shared humanity with fictional others.
In Cuban author Reinaldo Arenas’ novel Hallucinations , the author explores critical issues of religious and political oppression through a fantastical story about the struggle for Mexican independence from Spain. In it, he uses hyperbolic and outrageous depictions of the Spanish Inquisition as a metaphor for the brutality of colonial systems of power. Near the opening of the novel, Arenas includes descriptions of the Inquisitorial pyres that “burned night and day at the end of every street, so that heat and soot were perpetual in the city and on summer days made it unbearable” (14). His exaggerated descriptions include mobs “crowded about the flames” (14), lines of people waiting to be burned in the fires, and protesters choosing to die “an unchristian death, without the final benefaction conferred by confession” just to flout “the orders of the Holy Inquisition” (15). In order to highlight the absurdity of abusive power and passive obedience, Arenas depicts the hypocrisy of church leaders condemning people to the punishment of the church for the sake of political power and the abuse of the most humble members of society, especially the Native Americans, whom the church claims to be there to save.
There is no way to read these passages of historical fiction without critically examining the truth of these historical events. Was the Spanish Inquisition truly this brutal? How many people were condemned to death? To what extent were these choices, played out in colonial cities, actually about solidifying power for individuals, for governments? How did spiritual manipulation affect the outcome of the conquest in Latin America? How did this historical moment shape the world as we know it today? For Arenas, the biggest question seems to be about how the desires and fears of just one person can influence choices and actions that change the lives of multitudes, even the direction of history.
When we encounter literary events that touch our own sense of shared humanity, we ask critical questions about the world around us. In this way, literature helps us to build an historical understanding of everyday life. Literature helps us critically examine such choices and how we, like the characters we love, might also be susceptible to the forces of desire that determine the course of history: the contradictions of fear and love, desire and humility, or pride and compassion.
Why study literature?
For many of us, reading brings great pleasure. But when it comes to college, studying literature makes us better people. That claim might seem overstated, but it is not. When we gain awareness of our aesthetic sensibility, we live in the knowledge that part of what makes us human, part of what we share with all people, is a need for beauty and an urge to create it. When our curiosity is sparked by a literary image, a moving theme, or the complex contradictions of human behavior, we become better at investigating the world around us. And when literature immerses us in another’s experience and another world, we become more able to critically examine our own lives and our own behavior. Studying literature makes us more human, more humane.
Works Cited
Arenas, Reinaldo. Hallucinations: Or, the Ill-fated Peregrinations of Fray Servando . Translated by Andrew Hurley. Penguin. 2002.
García Márquez, Gabriel. Cien Años de Soledad. Madrid: Alfaguara, 2007.
García Márquez, Gabriel. One Hundred Years of Solitud e. Translated by Gregory Rabassa. Harper Perennial, 2006.
Lanese, Nicoletta. “Kids’ Fossilized Handprints May Be Some of the World’s Oldest Art.” Scientific American , 21 Sept. 2021, https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/kids-fossilized-handprints-may-be-some-of-the-worlds-oldest-art/ . Accessed 15 Dec. 2022.
Marchant, Jo. “A Journey to the Oldest Cave Paintings in the World.” Smithsonian Magazine, Jan. 2016 , https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/journey-oldest-cave-paintings-world-180957685/ . Accessed 15 Dec. 2022.
Oyeyemi, Helen. “Is Your Blood as Red as This?” What Is Not Yours Is Not Yours . Riverhead Books, 2016. 95-151.
Zhang, David D., et al. “Earliest Parietal Art: Hominin Hand and Foot Traces from the Middle Pleistocene of Tibet.” Science Bulletin , vol. 66, no. 24, Dec. 2021, pp. 2506–15. EBSCOhost, https://doi-org.libprox1.slcc.edu/10.1016/j.scib.2021.09.001 .
- These were a subspecies of archaic humans thought to be either Denisovans or Homo erectus. ↵
Literary Studies @ SLCC Copyright © 2023 by Stacey Van Dahm is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

What is ATI?
Virtual school.

Why Do We Study Literature?

“Tis the good reader that makes the good book; in every book he finds passages which seem confidences or asides hidden from all else and unmistakenly meant for his ear; the profit of books is according to the sensibility of the reader; the profoundest thought or passion sleeps as in a mine, until it is discovered by an equal mind and heart.”
Ralph Waldo Emerson
At ATI, we love readers.
We love the people who get lost in a book – who cry with imaginary characters as they dream and fight and learn to fly. And we love helping our students become readers, because we believe that literature is a key element of a life well lived.
All children- all people- are somewhere in the process of self-creation. But in middle and high school, that process, which previously has been subconscious, becomes explicit. Unlike the toddler who creates herself without realizing it, a teenager needs to consciously choose the values she’ll uphold, the models she’ll emulate, the issues she’ll care about, the life she will lead. Art- and in particular literature- is a profoundly powerful tool for advancing that work.
A study of literature allows students to “try on” different lives and different perspectives. It provides examples of moral decision-making exemplified in specific characters and situations, and gives students the chance to consider their own character and decision-making in as-of-yet unencountered circumstances. Literature provides rich and varied examples of individuals in society, in a way that can inform the decisions students make about their own roles and relationships. It promotes perspective-taking, and an understanding of others. It enables students to recognize and connect with the universals of human experience.
Fundamentally, a study of literature is a study of the world: bigger, more complicated, and more diverse than we have yet seen it with our own eyes. The world of fiction can make real the struggles of someone a thousand miles or a thousand years away, and can challenge conclusions, inspire compassion, and ignite dreams. We teach literature as the learning material for human life. A shared immersion in literature allows our students to engage with one another, debate, and reflect on what matters to them and the lives they wish to live.
So how do we teach literature?
The first principle of literature at ATI is: students read first as readers. Literature courses can often focus on the “how” of texts, treating the piece as a mentor text for writing skills: “How did the author structure these chapters? How did the author employ metaphor to convey a message here?” In contrast, reading as readers first allows students to become completely immersed in the world of the story, to feel its questions and decision points as real, immediate, and consequential. The mechanics and techniques of writing come into consideration later, but the first job of a literature course is to help students love reading.
We also include literature in classes on history - reading the stories, songs, or poems of the heroes through the ages. We include it in mathematics - a class in Toronto is determined to emulate Sherlock Holmes’s use of the theorem of similar triangles to prove that they, too, could solve the mystery of the Musgrave Ritual. Literature makes tangible the value of knowledge in a multitude of fields, and we create and encourage integrations between literature and other subjects.
A key element of our literature curriculum is the novel study, where a small group of students will engage deeply with a specific text. The study may involve other short stories, essays, or poems brought in as comparison or companion material. The group engages in Socratic discussion circles, writes regular journal entries, and explores the narrative elements of the book through creative and written expression. Each of these routines strengthens a student’s ability to develop and defend a hypothesis about the work, with reference to specific textual evidence. Throughout all of these educational methods there is an emphasis on application: applying what is learned from the book to other texts, other subjects, historical events, present-day contexts, and a student’s own life and values.
Here at ATI, we love reading, and we love readers, and most of all, we love sharing that love of reading with new students!
We’re just kicking off the 2022-23 school year, and that means new novel studies. Here are some of the books our middle school students are reading this week. What are you reading this week?

Laura Mazer is the SVP of Programs at Higher Ground Education, where she enjoys thinking about the scope and sequence of the universe.
It appears you have javascript disabled. Please enable javascript to get the full experience of gustavus.edu
Why study literature.
Literature helps us better understand our lives, ourselves, and the world around us. Encounters with literature develop the concepts of identification, imagination, and empathy. In our increasingly chaotic world, these skills matter deeply. Taking a deep dive into literature from different cultures allows you to both expand your ability to evaluate and discuss the work itself and also better understand what it tells us about the world, our own beliefs and values, and the beliefs and values of others.
Literature is for everyone, no matter what your future major or career may be. Studying literature tests your creative mind, inspiring innovation and change. Literature helps us use our written language as a practical, everyday tool that enlightens, educates, and inspires those who interact with it.
Practical Skills Gained Through the Study of Literature
Let’s start with what may not be obvious, through the study of literature you develop practical skills that are applicable to a wide variety of careers. Writing, research, and class discussions develops skills such as developing persuasive arguments, carrying out analysis, and communication in an articulate manner, all of which are important to professional success.
When you study literature with Gustavus Adolphus, you’ll don’t just read old books and write essays. For instance, you’ll learn to present with a small group, plan and lead discussions, collaborate on activities, and work with off-campus organizations. You’ll build skills such as writing and summarizing complex information in a concise way. You’ll dive into readings and films to develop your ability to detect and analyze important details.
While you might not associate any of these skills specifically with the study of literature, the truth is that literature is a fascinating subject with multiple transferable skills useful across career paths from business and arts to the sciences and trades.
A recent survey conducted on behalf of the Association of American Colleges and Universities (AACU) found that the majority of hiring managers prioritize prospective employees who have skills that a literature degree can provide. Nearly all who were surveyed (an impressive 93%) agree that “a candidate’s demonstrated capacity to think critically, communicate clearly, and solve complex problems is more important than their undergraduate major.” A literature degree offers all of these skills — and more.
Thus in the English Department at Gustavus Adolphus, you’ll take courses through the study of literature that develop the skills that employers in all types of industries are looking for.
Get more information about studying literature at Gustavus Adolphus .
Why Do We Study Literature?
Beyond thinking only about the practical skills to land you a job after college, studying literature is a meaningful endeavor. Simply put, engaging with literary works written by people from various cultures, viewpoints, and historical periods broadens our understanding of other people and our overall worldview.
The study of literature also exercises your critical thinking skills that can be used in all aspects of your life and in any career. The experience of studying and discussing literature in a classroom prepares you to think critically on your own about areas such as film, news, and social media, sparking new conversations and raising insightful questions.
Understanding Human Nature Through Literature
One of the most widely used forms of expression is the written word, and it has been for centuries. Whether you’re engrossed in the drama of an ancient play or a compelling contemporary novel, you can notice parallels between the characters and our own behavior and current events.
Great literature also teaches us about significant life issues. From the beginning, we are raised on stories of struggle: humans against a vast array of challenges, whether they be other people, nature, or one’s own self. The struggle against a challenge is central to literature. By reading and analyzing the material you grow your understanding of why humans create conflict, how it can be resolved, and what you can do to ensure preservation for yourself, others, and the world around you.
Empathy and Emotional Growth: The Significance of Literature in Our Lives
Literature allows us a window into places, people, and situations we wouldn’t be able to experience otherwise. Literature can transport you to another time and place without ever having to leave your room. You experience these stories simply by reading them; imagining them to life in your mind. The feelings evoked, whether sad, angry, inspired, or blissfully happy, are ours to share with the characters in the book.
Literary studies also help us develop a stronger sense of who we are and how we act in any given situation. In a 2023 study , researchers found that students with a higher reading ability level had better social-emotional skills than those at a comparatively lower reading level. While scientists are still working on the link between regular reading and empathy levels, there’s one thing we can say for sure: literature can stir emotions deep within us.
The Value of Studying Literature: A Comprehensive Approach
Literature is a concrete way to wake up our senses and bring the world into sharper focus. Studying literature can help us to observe the things around us — sharpening our ability to listen and hear, smell, taste, and touch.
Literature deepens our thinking by bringing more awareness of our own values and worldview, but also those of others throughout the world and throughout history. Because literature illustrates concepts in a vivid manner, we can observe differing values and worldviews in action. Literature allows us to explore the implications of various values and worldviews and gives us an excellent opportunity to take a closer look at our own assumptions about the world and compare them with others.
Crossing Cultural Boundaries: The Role of Writing and Literature
Literature broadens your horizons. Cross-cultural literary studies teach you how to read and interpret complex texts, write persuasive interpretations, and use theoretical frames for literary and cultural interpretation.
Writing and literature join together to teach the importance of understanding imaginative works within their cultural and historical contexts. Studying the literary traditions of different cultures around the world provides you with a deeper understanding of what a culture's literature says about its people's values and world views. Specialized courses offer a more in-depth look at different groups of writers, time periods, countries, cultures, and writing styles.
Exploring the Connection Between Creative Writing and Studying Literature
Creative writing is the imaginative and expressive use of language to convey stories, ideas, and emotions. Unlike other forms of writing that primarily focus on conveying information, creative writing emphasizes originality and the ability to captivate readers through narrative innovation. It encompasses various genres, including fiction, poetry, drama, and creative nonfiction, allowing writers to explore a diverse range of styles and themes. In this field, writers often draw inspiration from their personal experiences, observations, or sheer imagination, crafting unique worlds and characters that resonate with readers.
Studying literature provides inspiration and examples for the creative writer. Creative writing in turn nurtures the development of literary skills.
English Degrees in Literature
A literature degree offers a wealth of invaluable skills in both writing and research as well as provides a unique insight into the human mind. A degree in literature is considered excellent preparation for industries from finance to law. The Gustavus Adolphus English Department offers degree programs in:
- English with a Literature and Film Track
- English with a Multi-Ethnic and Global Literatures and Film Track
- Communication Arts/Literature Teaching
Expand Your World: Literature at Gustavus Adolphus
In addition to those enrolled in English degree programs, students from all majors are encouraged to take a literature class or two during their time at Gustavus. Each course allows you the chance to explore areas that interest you the most, whether that’s U.S. Indigenous Literatures or African Digital Literatures. It’s up to you!
Regardless of where your interests lie, you’ll be inspired by knowledgeable, innovative faculty during your literary studies in the English Department at Gustavus Adolphus. Working with world-class English and literature faculty prepares you to make a positive impact on your community, your life, and those surrounding you. Get started on your own path today at Gustavus Adolphus College.
Schedule a campus tour today.
Why Our Students Study Literature
Students from all backgrounds find that their literature studies open their minds to unique perspectives and give them real-world skills — useful no matter what their major may be. Check out what our students have to say about how studying literature at Gustavus has influenced their approach to literature, education, and life.
"Creative writing has been a happy part of my life since I first learned to hold a pencil, so once I chose Gustavus, I considered my career as an English major a given. Perhaps I am a rare bird for that, being so sure of myself so soon. But I could not have anticipated how much I learned about the value of reading, in every area of life, through the English major; nor did I see its potential to shape me as a writer. No matter how straightforward a story may seem, the search for something deeper within it leads to all kinds of insights that, while perhaps not in line with the author's original intent (who knows?), teach you more about the world and the different ways people use language. The theory taught alongside literature, in combination with this analysis, gives you the power of perspective that is so essential to finding contentment and peace in communication with people who are different from you, in a way that is unique to the study of literature. To write you have to read, and to really read, you have to think, criticize, doubt, wonder, and stand amazed by words on the page. The English major showed me how to do that, and not only has it increased my skills as a writer, it has made me a more compassionate and honest person."
—Caitlin Skvorc
"I study literature because I believe there is power in stories. Literature is both intensely personal as well as a communal experience. I love examining how words, sentences, characters, plot lines, and tropes reveal who we are as humans. Humanity is a complicated thing and requires an infinite amount of words to describe and analyze. That's the joy of studying literature, there is always a new reality to discover."
—Mikaela Warner
"For me, the decision to study literature has been a struggle. Since I was young, I always enjoyed reading and being read to, but I always considered the actual study of literature to be made up; seriously, poets don’t actually try to "invoke" some other work. Literary devices? Some make-believe stuff that people invented to make English seem scientific. Although I enjoyed it, literature, to me, was studied only by those who weren’t smart enough to study something real, something provable.
As I understand it, those feelings are not uncommon. The difference for me, though (as compared to some other people I know), is that I grew out of them. I started really looking at rhetorical devices and the use of language. I started to see that, although it still was not science, it was art, and art is the greatest expression of that which is human. My goal is to learn as much as I can about the human condition, and what it really means to be human, in all aspects."
—David Lick
"By studying literature I find that this sense of confusion and search for self-discovery is a common theme. I am confident that my choice to be an English major is one that I will be satisfied with. Thus far, to be an English major entails more than just being able to read and write well. An English major must also strive to understand and interpret the importance that various forms of literature have had on the society of the past and the present. Being able to express opinions is another important aspect, as is starting a piece of literature with an open mind. These habits are also important when facing everyday life, not just literature.
The chance to read and write is something that everyone should be able to experience. Literature in all forms is everywhere in today’s society, and with this idea, it is clear just how important it is. Whether it is studied in the classroom, or read for pleasure or purpose, literature is a central part of many lives. It offers not only a chance to enlighten a person, but it also gives the chance to broaden one’s horizons and perspectives. In my case, having the opportunity to study literature in two different languages has helped me to find similarities in two different cultures, and to also find that although literature varies in form and content, it is important and it is a central part of many lives."
—Stephanie Conroy
"Reading and writing, the basic principles involved in the study of English, serve as the gateway to a deeper level of thought. After mastering these elementary skills, comprehension, analysis, and interpretation are learned and used to better educate oneself. Studying literature and observing personal reactions to the literature can make one more aware of his or her own values. English skills are helpful in every area of life. Reading, writing, comprehension, analysis, and interpretation increase efficiency in multiple ways including communication, documentation in other areas of study, and reflection of personal values. I believe there is no area of study that English and communication skills do not influence."
—Maria Freund
"Reading and writing, in general, are undoubtedly some of the most valuable skills one can have; obviously, having these skills makes it much easier for people to communicate and to participate in society. However, there exists a purpose for reading and writing outside of these immediate practical purposes; the written word can be used to enlighten, to persuade, to express emotion, or simply for enjoyment. In these forms the written word becomes an art form, and a way of reaching out to others through a personal experience between the writer and the reader. Reading is an excellent way to associate oneself with the great minds of history and peer into their own thoughts. Reading is surely one of the most effective ways one can expand oneself.
Literature is a way in which we can capture and interpret what has happened and is happening to us personally and to the world as a whole. An entire culture exists in the written word, documenting the collective thoughts of everyone who cared to share them with the world. Therefore, I believe that for one to truly be a part of human society, it is critical that one take part in the evolution and self-realization that is literature, even if only in the reading aspect. Writing, however, carries a grave importance, as literature simply would not exist in the accessible form it does without written word, and for that reason I believe all who can write should. One should take advantage of the great opportunity to be part of and contribute to the world and society in which he or she lives through writing. I see literature in the societal sense as a collective struggle to understand and make the best of the lives that we have all been given. Literature serves as a way to enrich our minds, and presents a way to improve the world not only through the beauty of its presence but through the ideas and tangible possibilities it possesses."
—Matt Beachey
"The best of my English teachers taught us literature because they wanted the art of it to expand our minds and help teach us new ways of seeing the world. I was taught to both see a work of literature as a way to understand the time it was written, and the people who produced it, and to find the parts of that work that spoke to me in my time and place. While I am skeptical about whether or not anyone can ever really understand a culture or a time prior to their own, I do know that many times literature and art provide insights that cold hard facts do not. Most of all I find that literature makes the differences more manageable and highlights the similarities between people. I can read a Greek tragedy two thousand years later and agree with things that some older white man was saying because he was a human being, and I am a human being. Although it may sound trite, I have had reading experiences that taught me more about what it means to live in this world.
Not everyone loves reading enough to do it in their spare time, but the people who do are the ones who get the most benefit out of what they read because they want to be there in that world that literature creates. I have met very intelligent people who do not read. But all of the interesting people I know read, whether or not they are particularly intelligent."
—Sybylla Yeoman Hendrix
"I read literature for a number of different reasons. Literature is an art full of passion and heart; it transcends the ages. Great literature hits on many different levels. Over the years authors have accomplished unfeasible tasks through the use of their words. Literature has prompted political and social change in societies and continues to do so to this day. It can be a battle cry for the proletariat to rise up and make a difference, and it can also provide personal counsel.
Literature sets me free from the responsibilities of this world, and at the same time, it ties me down to those same responsibilities. Some literature I read for an escape; to journey to a faraway land and go on a grand adventure with creatures beyond my imagination. Other literature has much more serious subject matter, and I read it to remind myself that life isn’t all cupcakes and ice cream."
—Ryan McGinty
"To me, literature is about the obsession with ideas. We read literature to discover and to learn about ideas and we write it to discover and to cultivate our own ideas. No lover of ideas can go without either reading or writing. For me, if I go too long without one or the other, I get this huge build-up of confused and jumbled ideas that suddenly overcome me and I just have to write them out in some form (philosophic prose, narrative, poetry, scribbled phrases, etc.). That must be why literature can appear in a multitude of forms: be it poetry or prose, the sonnet or the novel, the sestina or the short story, etc. All literature shares the common theme of the idea. Ideas explore, probe, inquire, and inspire. The reactions to such are all that become a part of the learning process. There is a great deal that literature can teach. Literature can teach to the individual and to all of society. It can teach us about the past and the present and even about the future. Subjects can be broad and far-reaching, but can also be specific. Literature teaches us about laughter and love, about remembering and forgetting. It can create emotion and warn us against our many human faults. It can attempt to disprove other ideas or attempt to find truth. I think we are all looking to find truth in some form or another. Oftentimes, the uncertainty of a specific meaning of a piece allows for its interpretation to be for the reader to decide. What is certain, however, is that there are things to be learned from literature that are specific to it, that cannot be attained through any other medium. To gather this knowledge and to experience its beauty all pertain to the importance of literature to me."
—Abby Travis
"Another reason that I enjoy reading so much is the places you can go to when you read. I know that that sounds pretty corny, like something on a PBS commercial, but I feel that there are a vast amount of experiences and people the reader gets to encounter in any work of literature."
—Stefan Kolis
"Although I concede that it is not absolutely necessary to major in English in order to gain perspective from literature, I feel that English is a good lens through which to view the world, both present and past. When I study a great work of literature, I not only gain insight into the universal truth about which the author has chosen to write, but I also, in my attempts to understand, can learn about the culture in which the author lived, the history surrounding the country of his origin, and the various intellectual, political, and artistic movements of the time. Thus the window to humanity that lies at the heart of all literature can act as a sort of connecting portal to the culture surrounding each individual author. The reader stands on the common ground of the universal truth around which a work is constructed – the point at which the reader’s world and the author’s meet – and begins to understand some of the motivations behind the author’s own quest for truth.
Great literature provides its readers with a window into various aspects of the human condition and a guide to the way we, as a species, relate to one another and to our surroundings. Literature gives us a mirror in which to examine our collective reflection as a people. It does not gloss over the pimples and blemishes of humanity, but exposes them quite openly. No concealer, no cover-up, only the truth. Literature is the reflecting pool into which every person that ever existed can look and see both his own face and the faces of all his fellow people. It enables each human to not only find the humanity within his own heart but also to connect him to the generations of other people who have been doing so since the beginning of time."
—Rebekah Schulz

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Introduction to Literature: What? Why? How?
When is the last time you read a book or a story simply because it interested you? If you were to classify that book, would you call it fiction or literature? This is an interesting separation, with many possible reasons for it. One is that “fiction” and “literature” are regarded as quite different things. “Fiction,” for example, is what people read for enjoyment. “Literature” is what they read for school. Or “fiction” is what living people write and is about the present. “Literature” was written by people (often white males) who have since died and is about times and places that have nothing to do with us. Or “fiction” offers everyday pleasures, but “literature” is to be honored and respected, even though it is boring. Of course, when we put anything on a pedestal, we remove it from everyday life, so the corollary is that literature is to be honored and respected, but it is not to be read, certainly not by any normal person with normal interests.
Sadly, it is the guardians of literature, that is, of the classics, who have done so much to take the life out of literature, to put it on a pedestal and thereby to make it an irrelevant aspect of American life. People study literature because they love literature. They certainly don’t do it for the money. But what happens too often, especially in colleges, is that teachers forget what it was that first interested them in the study of literature. They forget the joy that they first felt (and perhaps still feel) as they read a new novel or a poem or as they reread a work and saw something new in it. Instead, they erect formidable walls around these literary works, giving the impression that the only access to a work is through deep learning and years of study. Such study is clearly important for scholars, but this kind of scholarship is not the only way, or even necessarily the best way, for most people to approach literature. Instead it makes the literature seem inaccessible. It makes the literature seem like the province of scholars. “Oh, you have to be smart to read that,” as though Shakespeare or Dickens or Woolf wrote only for English teachers, not for general readers.
What is Literature?
In short, literature evokes imaginative worlds through the conscious arrangement of words that tell a story. These stories are told through different genres, or types of literature, like novels, short stories, poetry, drama, and the essay. Each genre is associated with certain conventions. In this course, we will study poetry, short fiction, and drama (in the form of movies).
Some Misconceptions about Literature
Of course, there are a number of misconceptions about literature that have to be gotten out of the way before anyone can enjoy it. One misconception is that literature is full of hidden meanings . There are certainly occasional works that contain hidden meanings. The biblical book of Revelation , for example, was written in a kind of code, using images that had specific meanings for its early audience but that we can only recover with a great deal of difficulty. Most literary works, however, are not at all like that. Perhaps an analogy will illustrate this point. When I take my car to my mechanic because something is not working properly, he opens the hood and we both stand there looking at the engine. But after we have looked for a few minutes, he is likely to have seen what the problem is, while I could look for hours and never see it. We are looking at the same thing. The problem is not hidden, nor is it in some secret code. It is right there in the open, accessible to anyone who knows how to “read” it, which my mechanic does and I do not. He has been taught how to “read” automobile engines and he has practiced “reading” them. He is a good “close reader,” which is why I continue to take my car to him.
The same thing is true for readers of literature. Generally authors want to communicate with their readers, so they are not likely to hide or disguise what they are saying, but reading literature also requires some training and some practice. Good writers use language very carefully, and readers must learn how to be sensitive to that language, just as the mechanic must learn to be sensitive to the appearances and sounds of the engine. Everything that the writer wants to say, and much that the writer may not be aware of, is there in the words. We simply have to learn how to read them.
Another popular misconception is that a literary work has a single “meaning” (and that only English teachers know how to find that meaning). There is an easy way to dispel this misconception. Just go to a college library and find the section that holds books on Shakespeare. Choose one play, Hamlet , for example, and see how many books there are about it, all by scholars who are educated, perceptive readers. Can it be the case that one of these books is correct and all the others are mistaken? And if the correct one has already been written, why would anyone need to write another book about the play? The answer is this:
Key Takeaways
There is no single correct way to read any piece of literature.
Again, let me use an analogy to illustrate this point. Suppose that everyone at a meeting were asked to describe a person who was standing in the middle of the room. Imagine how many different descriptions there would be, depending on where the viewer sat in relation to the person. For example, an optometrist in the crowd might focus on the person’s glasses; a hair stylist might focus on the person’s haircut; someone who sells clothing might focus on the style of dress; a podiatrist might focus on the person’s feet. Would any of these descriptions be incorrect? Not necessarily, but they would be determined by the viewers’ perspectives. They might also be determined by such factors as the viewers’ ages, genders, or ability to move around the person being viewed, or by their previous acquaintance with the subject. So whose descriptions would be correct? Conceivably all of them, and if we put all of these correct descriptions together, we would be closer to having a full description of the person.
This is most emphatically NOT to say, however, that all descriptions are correct simply because each person is entitled to his or her opinion
If the podiatrist is of the opinion that the person is five feet, nine inches tall, the podiatrist could be mistaken. And even if the podiatrist actually measures the person, the measurement could be mistaken. Everyone who describes this person, therefore, must offer not only an opinion but also a basis for that opinion. “My feeling is that this person is a teacher” is not enough. “My feeling is that this person is a teacher because the person’s clothing is covered with chalk dust and because the person is carrying a stack of papers that look like they need grading” is far better, though even that statement might be mistaken.
So it is with literature. As we read, as we try to understand and interpret, we must deal with the text that is in front of us ; but we must also recognize (1) that language is slippery and (2) that each of us individually deals with it from a different set of perspectives. Not all of these perspectives are necessarily legitimate, and it is always possible that we might misread or misinterpret what we see. Furthermore, it is possible that contradictory readings of a single work will both be legitimate, because literary works can be as complex and multi-faceted as human beings. It is vital, therefore, that in reading literature we abandon both the idea that any individual’s reading of a work is the “correct” one and the idea that there is one simple way to read any work. Our interpretations may, and probably should, change according to the way we approach the work. If we read The Chronicles of Narnia as teenagers, then in middle age, and then in old age, we might be said to have read three different books. Thus, multiple interpretations, even contradictory interpretations, can work together to give us a fuller and possibly more interesting understanding of a work.
Why Reading Literature is Important
Reading literature can teach us new ways to read, think, imagine, feel, and make sense of our own experiences. Literature forces readers to confront the complexities of the world, to confront what it means to be a human being in this difficult and uncertain world, to confront other people who may be unlike them, and ultimately to confront themselves.
The relationship between the reader and the world of a work of literature is complex and fascinating. Frequently when we read a work, we become so involved in it that we may feel that we have become part of it. “I was really into that movie,” we might say, and in one sense that statement can be accurate. But in another sense it is clearly inaccurate, for actually we do not enter the movie or the story as IT enters US; the words enter our eyes in the form of squiggles on a page which are transformed into words, sentences, paragraphs, and meaningful concepts in our brains, in our imaginations, where scenes and characters are given “a local habitation and a name.” Thus, when we “get into” a book, we are actually “getting into” our own mental conceptions that have been produced by the book, which, incidentally, explains why so often readers are dissatisfied with cinematic or television adaptations of literary works.
In fact, though it may seem a trite thing to say, writers are close observers of the world who are capable of communicating their visions, and the more perspectives we have to draw on, the better able we should be to make sense of our lives. In these terms, it makes no difference whether we are reading a Homeric epic poem like The Odysse y, a twelfth-century Japanese novel like The Tale of Genji , or a Victorian novel by Dickens, or even, in a sense, watching someone’s TikTok video (a video or movie is also a kind of text that can be “read” or analyzed for multiple meanings). The more different perspectives we get, the better. And it must be emphasized that we read such works not only to be well-rounded (whatever that means) or to be “educated” or for antiquarian interest. We read them because they have something to do with us, with our lives. Whatever culture produced them, whatever the gender or race or religion of their authors, they relate to us as human beings; and all of us can use as many insights into being human as we can get. Reading is itself a kind of experience, and while we may not have the time or the opportunity or or physical possibility to experience certain things in the world, we can experience them through reading. So literature allows us to broaden our experiences.
Reading also forces us to focus our thoughts. The world around us is so full of stimuli that we are easily distracted. Unless we are involved in a crisis that demands our full attention, we flit from subject to subject. But when we read a book, even a book that has a large number of characters and covers many years, the story and the writing help us to focus, to think about what they show us in a concentrated manner. When I hold a book, I often feel that I have in my hand another world that I can enter and that will help me to understand the everyday world that I inhabit.
Literature invites us to meet interesting characters and to visit interesting places, to use our imagination and to think about things that might otherwise escape our notice, to see the world from perspectives that we would otherwise not have.
Watch this video for a discussion of why reading fiction matters.
How to Read Literature: The Basics
- Read with a pen in hand! Yes, even if you’re reading an electronic text, in which case you may want to open a new document in which you can take notes. Jot down questions, highlight things you find significant, mark confusing passages, look up unfamiliar words/references, and record first impressions.
- Think critically to form a response. Here are some things to be aware of and look for in the story that may help you form an idea of meaning.
- Repetitions . You probably know from watching movies that if something is repeated, that means something. Stories are similar—if something occurs more than once, the story is calling attention to it, so notice it and consider why it is repeated. The repeated element can be a word or a phrase, an action, even a piece of clothing or gear.
- Not Quite Right : If something that happens that seems Not Quite Right to you, that may also have some particular meaning. So, for example, if a violent act is committed against someone who’s done nothing wrong, that is unusual, unexpected, that is, Not Quite Right. And therefore, that act means something.
- Address your own biases and compare your own experiences with those expressed in the piece.
- Test your positions and thoughts about the piece with what others think (we’ll do some of this in class discussions).
While you will have your own individual connection to a piece based on your life experiences, interpreting literature is not a willy-nilly process. Each piece of writing has purpose, usually more than one purpose–you, as the reader, are meant to uncover purpose in the text. As the speaker notes in the video you watched about how to read literature, you, as a reader, also have a role to play. Sometimes you may see something in the text that speaks to you; whether or not the author intended that piece to be there, it still matters to you.
For example, I’ve had a student who had life experiences that she was reminded of when reading “Chonguita, the Monkey Bride” and another student whose experience was mirrored in part of “The Frog King or Iron Heinrich.” I encourage you to honor these perceptions if they occur to you and possibly even to use them in your writing assignments. I can suggest ways to do this if you’re interested.
But remember that when we write about literature, our observations must also be supported by the text itself. Make sure you aren’t reading into the text something that isn’t there. Value the text for what is and appreciate the experience it provides, all while you attempt to create a connection with your experiences.
Attributions:
- Content written by Dr. Karen Palmer and licensed CC BY NC SA .
- Content adapted from Literature, the Humanities, and Humanity by Theodore L. Steinberg and licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
The Worry Free Writer by Dr. Karen Palmer is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Introduction to Literature Copyright © by Judy Young is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Why Do We Need To Study Literature? What Are The Benefits?

What is the importance of literature?
Benefits of studying literature, what are the reasons to study literature, benefits of literature to students.
This subject does not have any particular language across the world and religions. Still, every definition of literature aligns with one another and gives true meaning to this beautiful artistic subject.
The subject literature broadens our horizons. This particular subject gives us the opportunity to learn and understand those people and incidents which are very different yet important to know.
Our cultural heritage has literature as a very valuable part, which anybody can access very easily and get the most out of it to enrich their lives through different ways.
For some people, studying this particular subject can be daunting, but once you will understand to break the barrier, the texts of this subject will become one of the most entertaining, funny, romantic, yet tragic for you.
This subject has the ability to take us beyond our limited imagination and thoughts with respect to life to make us experience and live the life of a different community of people at different points in time.
It makes our brain grind itself both emotionally and intellectually to give us a deep knowledge of our society, history, and an actual understanding of our own lives.
You can get a very real glimpse of what you haven’t seen or when you weren’t present.
Literature enriches our experience in many ways.
If you want to know more about some common yet interesting things about daily life, you can check the articles on why do leaves fall and why do we fast .
The way literature gives relief from anxiety and stress, that not many subjects can give.
You won’t believe but just giving less time to reading and understanding literature for a very short period of time in the day can create good health for your brain and it a break from all the complex thinking. It slows down the heartbeat whenever we feel anxiety and this has been proved by the studies itself.
It takes the mind of readers away from the stress and worries in life.
World Literacy Foundation says that reading literature is one of the ways to inculcate a strong imagination and creativity within you. Because when we study literature, we start to create that particular scene in our mind which gives us a good concentration.
Watching movies is also nice but doesn’t need much imagination because we have the visuals in front of us.
Anyone with a short attention span can give a chance to literature to improve it. Haskins Laboratories for the Science of the Spoken and Written Word came out with research that concluded that the brain takes a larger span of time to understand reading rather than watching media.
Because sometimes, the books and novels get very challenging and complex with many twists within a story, which makes the brain divert its attention to every minor detail.
A window gets provided to those who do a study of literature to see the outer world through the eyes of literary genres. It makes you understand the way every society and culture is and with a historical record as well.
It’s like a pathway to give you new adventurous experiences. Good personal skills are also get developed through literature. The benefits with which the literature comes is in itself sufficient to know the importance of it.
Reading not just only helps in building a good vocab, but also helps in inculcating a good reasoning ability in children and adults.
Literature introduces you to a rich language, helps you develop and discover good skills and words, discover a new self, sense the problems in society by a critical view, explore texts with new perspectives, read about culture, understand the value of poetry, gain the literary skills of classics, and develop a good writing sense.
They realize the problems which the other characters face and first-handedly think about the solution for it.
They understand the reasoning of each and every character and respond to it. You can feel whenever the character in the book is getting successful or failing a task.
Having a good vocabulary gives good improvement to the communication skills.
And eventually helps in developing work relationships. You can develop and discover a new view on history (which most think is a boring subject) by your own self if you study it from a literature point of view.
You won’t believe it at first, but the reasons because which you should study literature are very much connected to the ways you should live your life on a daily basis.
People haven’t changed their thinking and feeling style. The emotions they used to feel then, are the same they feel now.
Every lesson you will learn will be applicable to your life in many ways.
When a child starts to read literature, they understand the human’s reactions to various situations and the nature of our heart as well. The texts of essays, poems of good poets, novel stories, and diaries play the role of bridging the gap between two very distant timelines and between different ethnicities as well.
They get the awareness of how to deal with certain situations and secure themselves from future problems. While reading classic literature, you will feel the connection to the outer world and its good principles.
Literature is a very useful tool to make a child understand the evils and goods of society.
Literature connects us to history. Many people consider history as an important part of our life.
But if we read this subject with the sense of memorizing it, we will never be able to love it. Students can enjoy it more if they develop the habit of reading it through literature.
The importance of empathy in society is a lot, else it will change into a dog-eat-dog society very soon, which is going to hurt everyone in turn. According to research, reading a number of literary works will develop empathy in people.
The works of literary fiction are effective in this phenomenon, because readers like to understand deeply what the characters of this particular story are going through, hence they want to understand their joy, sorrow, and problems.
People who read more and more have a good ability to discern the mind and feelings of people in the most logical way. Studying literature helps in developing an opportunity to inculcate the higher-order thinking skills in the mind of the reader.
When you analyze the view of one story, you actually start to develop good thinking skills in yourself. Students, after reading literature, tend to apply what they read in the course of their own experience in life.
They often compare the stories from books to their own life.
Growing older, they develop such a good sense of morality that they can give strong discussion points. Because of a continuous habit of analyzing stories and relating to them from their own point of view often becomes the plus point during any general talk.
Reading literature is very important for students as reading gives development to the thought process, inculcates knowledge and valuable lessons for our mind to be creative. The way books hold interesting stories, feelings, thoughts, and information is very unlikely to be seen in anything.
Texts in literary books make us understand that some things should not get underestimated and that's why they get taught in schools.
Student life has always been and will always be challenging and complex. Now if a little reading can help them understand some processes of life, then there’s nothing wrong with it, right?
Reading literature is a fun activity.
But also this fun activity comes with some benefits also for a student. When a student reads the word, its cognitive functions get stimulated and eventually sharpens the mind, especially that part that develops the critical analysis and concentration.
What student life has as a major component is the ability to write. Start by just reading one book, and you won’t believe the change which you will realize after writing something after it.
Today's students are even aware of many devices to explore and learn things from new perspectives about poetry, plays, art stuff, classics, cultures, ideas, and many other literary words by doing research on web media. In schools, often texts of Shakespeare and John Locke get read by students.
The way they used to write is considered as the writing of the future.
Students can do a study of literature very well through these two poets who had excellent skills with high value. Students can develop good skills and gain a lot if they will start reading a number of books related to literature either on the web or through a book from the beginning of their childhoods.
Here at Kidadl , we have carefully created lots of interesting family-friendly facts for everyone to enjoy! If you liked our suggestions for why do we need to study literature, then why not take a look at why do boats float or why do people dance?
We Want Your Photos!
More for you, 39+ creative ideas to increase your family daily step count, black poetry day.
Bachelor of Arts in Journalism and Mass Communication
Nidhi Sahai Bachelor of Arts in Journalism and Mass Communication
Dedicated and experienced, Nidhi is a professional content writer with a strong reputation for delivering high-quality work. She has contributed her expertise to esteemed organizations, including Network 18 Media and Investment Ltd. Driven by her insatiable curiosity and love for journalism and mass communication, Nidhi pursued a Bachelor of Arts degree from Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University, graduating with distinction in 2021. During her college years, she discovered her passion for Video Journalism, showcasing her skills as a videographer for her institution. Nidhi's commitment to making a positive impact extends beyond her professional pursuits. Actively engaging in volunteer work, she has contributed to various events and initiatives throughout her academic career.
Bachelor of Fine Arts specializing in International Business
Vikhaash Sundararaj Bachelor of Fine Arts specializing in International Business
With a background in International Business Management, having completed his degree at the University of Hull. Vikhaash has volunteered with 'Teach For India' to help students create a monthly newsletter. In his free time, he enjoys sports and was the assistant captain of his school's hockey team. He has also gained marketing experience through an internship at Decathlon Sports India.
1) Kidadl is independent and to make our service free to you the reader we are supported by advertising. We hope you love our recommendations for products and services! What we suggest is selected independently by the Kidadl team. If you purchase using the Buy Now button we may earn a small commission. This does not influence our choices. Prices are correct and items are available at the time the article was published but we cannot guarantee that on the time of reading. Please note that Kidadl is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon. We also link to other websites, but are not responsible for their content.
2) At Kidadl, we strive to recommend the very best activities and events. We will always aim to give you accurate information at the date of publication - however, information does change, so it’s important you do your own research, double-check and make the decision that is right for your family. We recognise that not all activities and ideas are appropriate for all children and families or in all circumstances. Our recommended activities are based on age but these are a guide. We recommend that these ideas are used as inspiration, that ideas are undertaken with appropriate adult supervision, and that each adult uses their own discretion and knowledge of their children to consider the safety and suitability. Kidadl cannot accept liability for the execution of these ideas, and parental supervision is advised at all times, as safety is paramount. Anyone using the information provided by Kidadl does so at their own risk and we can not accept liability if things go wrong.
3) Because we are an educational resource, we have quotes and facts about a range of historical and modern figures. We do not endorse the actions of or rhetoric of all the people included in these collections, but we think they are important for growing minds to learn about under the guidance of parents or guardians.
google form TBD
Essays About Literature: Top 6 Examples and 8 Prompts
Society and culture are formed around literature. If you are writing essays about literature, you can use the essay examples and prompts featured in our guide.
It has been said that language holds the key to all human activities, and literature is the expression of language. It teaches new words and phrases, allows us to better our communication skills, and helps us learn more about ourselves.
Whether you are reading poems or novels, we often see parts of ourselves in the characters and themes presented by the authors. Literature gives us ideas and helps us determine what to say, while language gives form and structure to our ideas, helping us convey them.
6 Helpful Essay Examples
1. importance of literature by william anderson, 2. philippine literature by jean hodges, 3. african literature by morris marshall.
- 4. Nine Questions From Children’s Literature That Every Person Should Answer by Shaunta Grimes
5. Exploring tyranny and power in Macbeth by Tom Davey
6. guide to the classics: homer’s odyssey by jo adetunji, 1. the importance of literature, 2. comparing and contrasting two works of literature , 3. the use of literary devices, 4. popular adaptations of literature, 5. gender roles in literature, 6. analysis of your chosen literary work, 7. fiction vs. non-fiction, 8. literature as an art form.
“Life before literature was practical and predictable, but in the present-day, literature has expanded into countless libraries and into the minds of many as the gateway for comprehension and curiosity of the human mind and the world around them. Literature is of great importance and is studied upon as it provides the ability to connect human relationships and define what is right and what is wrong.”
Anderson writes about why an understanding of literature is crucial. It allows us to see different perspectives of people from different periods, countries, and cultures: we are given the ability to see the world from an entirely new lens. As a result, we obtain a better judgment of situations. In a world where anything can happen, literature gives us the key to enacting change for ourselves and others. You might also be interested in these essays about Beowulf .
“So successful were the efforts of colonists to blot out the memory of the country’s largely oral past that present-day Filipino writers, artists and journalists are trying to correct this inequity by recognizing the country’s wealth of ethnic traditions and disseminating them in schools through mass media. The rise of nationalistic pride in the 1960s and 1970s also helped bring about this change of attitude among a new breed of Filipinos concerned about the “Filipino identity.””
In her essay, Hodges writes about the history of Philippine literature. Unfortunately, much of Philippine literary history has been obscured by Spanish colonization, as the written works of the Spanish largely replaced the oral tradition of the native Filipinos. A heightened sense of nationalism has recently led to a resurgence in Filipino tradition, including ancient Philippine literature.
“In fact, the common denominator of the cultures of the African continent is undoubtedly the oral tradition. Writing on black Africa started in the middle Ages with the introduction of the Arabic language and later, in the nineteenth century with introduction of the Latin alphabet. Since 1934, with the birth of the “Negritude.” African authors began to write in French or in English.”
Marshall explores the history of African literature, particularly the languages it was written over time. It was initially written in Arabic and native languages; however, with the “Negritude” movement, writers began composing their works in French or English. This movement allowed African writers to spread their work and gain notoriety. Marshall gives examples of African literature, shedding light on their lyrical content.
4. Nine Questions From Children’s Literature That Every Person Should Answer by Shaunta Grimes
“ They asked me questions — questions about who I am, what I value, and where I’m headed — and pushed me to think about the answers. At some point in our lives, we decide we know everything we need to know. We stop asking questions. To remember what’s important, it sometimes helps to return to that place of childlike curiosity and wonder.”
Grimes’ essay is a testament to how much we can learn from literature, even as simple as children’s stories. She explains how different works of children’s literature, such as Charlotte’s Web and Little Women, can inspire us, help us maximize our imagination, and remind us of the fleeting nature of life. Most importantly, however, they remind us that the future is uncertain, and maximizing it is up to us.
“This is a world where the moral bar has been lowered; a world which ‘sinks beneath the yoke’. In the Macbeths, we see just how terribly the human soul can be corrupted. However, this struggle is played out within other characters too. Perhaps we’re left wondering: in such a dog-eat-dog world, how would we fare?”
The corruption that power can lead to is genuine; Davey explains how this theme is present in Shakespeare’s Macbeth . Even after being honored, Macbeth still wishes to be king and commits heinous acts of violence to achieve his goals. Violence is prevalent throughout the play, but Macbeth and Lady Macbeth exemplify the vicious cycle of bloodshed through their ambition and power.
“Polyphemus is blinded but survives the attack and curses the voyage home of the Ithacans. All of Odysseus’s men are eventually killed, and he alone survives his return home, mostly because of his versatility and cleverness. There is a strong element of the trickster figure about Homer’s Odysseus.”
Adetunji also exposes a notable work of literature, in this case, Homer’s Odyssey . She goes over the epic poem and its historical context and discusses Odysseus’ most important traits: cleverness and courage. As the story progresses, he displays great courage and bravery in his exploits, using his cunning and wit to outsmart his foes. Finally, Adetunji references modern interpretations of the Odyssey in film, literature, and other media.
8 Prompts for Essays About Literature
In your essay, write about the importance of literature; explain why we need to study literature and how it can help us in the future. Then, give examples of literary works that teach important moral lessons as evidence.
For your essay, choose two works of literature with similar themes. Then, discuss their similarities and differences in plot, theme, and characters. For example, these themes could include death, grief, love and hate, or relationships. You can also discuss which of the two pieces of literature presents your chosen theme better.

Writers use literary devices to enhance their literary works and emphasize important points. Literary devices include personification, similes, metaphors, and more. You can write about the effectiveness of literary devices and the reasoning behind their usage. Research and give examples of instances where authors use literary devices effectively to enhance their message.
Literature has been adapted into cinema, television, and other media time and again, with series such as Lord of the Rings and Harry Potter turning into blockbuster franchises. Explore how these adaptations diverge from their source material yet retain the key themes the writer composed the work with in mind. If this seems confusing, research first and read some essay examples.
Literature reflects the ideas of the period it is from; for example, ancient Greek literature, such as Antigone, depicts the ideal woman as largely obedient and subservient, to an extent. For your essay, you can write about how gender roles have evolved in literature throughout the years, specifically about women. Be sure to give examples to support your points.
Choose a work of literature that interests you and analyze it in your essay. You can use your favorite novel, book, or screenplay, explain the key themes and characters and summarize the plot. Analyze the key messages in your chosen piece of literature, and discuss how the themes are enhanced through the author’s writing techniques.

Literature can be divided into two categories: fiction, from the writer’s imagination, and non-fiction, written about actual events. Explore their similarities and differences, and give your opinion on which is better. For a strong argument, provide ample supporting details and cite credible sources.
Literature is an art form that uses language, so do you believe it is more effective in conveying its message? Write about how literature compares to other art forms such as painting and sculpture; state your argument and defend it adequately.
Tip: If writing an essay sounds like a lot of work, simplify it. Write a simple 5 paragraph essay instead.
For help picking your next essay topic, check out the best essay topics about social media .

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 9, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Work For Us
- Why Study English?
The study of English explores fascinating elements of both literature and language. How we communicate, how words and language have developed, and what this means for us and society. Studying English literature and language gives you the tools to analyse the spoken and written word critically and creatively.
Keep reading to see if you’d be suited to studying English literature and language at university or check out options to study English at Northumbria University .
What is English literature?
When you study English Literature, you’ll grow to understand how books, verse, poetry, and prose contribute to culture. You’ll read a variety of styles, genres, and types of literary work. Learn how to contextualise and evaluate texts to deeper understand the subjects, authors, and readers.
What is English language?
When you study English language, you’ll work towards a deeper understanding of the ways we communicate with each other. Learn about the sounds we make, why we have accents and why some parts of language have rules.
What qualifications and subjects do you need to study English Literature & Language?
Undergraduate study .
120 UCAS Tariff points from a combination of acceptable Level 3 qualifications which may include: A-level, T Level, BTEC Diplomas/Extended Diplomas, Scottish and Irish Highers, Access to HE Diplomas, or the International Baccalaureate.
There are no specific subject requirements usually, but you might benefit from a general understanding of the subject through humanities A-levels like English, History and Drama.
If you have a qualification from outside of the UK or have equivalent qualifications please check the guidelines and requirements for your chosen course.
Postgraduate Study
Usually, to study for a Masters in English, English literature, or linguistics you’d need a minimum of a 2:2 honours degree in English, or a related discipline. If you’ve obtained an undergraduate degree in another humanities subject like History or Politics, you may also be considered. It’s worth checking the specifics of the Masters in English degree you’re interested in for specific requirements.
What are the benefits of studying English literature & language?
Deepening a lifelong love of books and learning .
If you love books and reading, then studying English could lead to a deepened joy of a hobby. If you’re a prolific reader when you apply to study English, then you’ve already begun to develop one of the key skills needed to complete an English degree successfully. Perhaps you’ve read Tolkien’s complete back catalogue, maybe you can quote Alice Walker by heart, have a secret BookTok account or love talking about John Green. Studying English when you love reading is referred to by many as a luxurious experience.

Broad skills
Studying English language and literature equips you with a broad range of skills that can be applied to many jobs and career paths.
- You can expect to develop skills in
- Research methods
- Critical thinking and analysis
- Verbal and presentation skills
- Constructing arguments
- Participating in and leading discussions
- Writing and storytelling
- Creative thinking and problem solving
This skill set can make you an asset to many employers as these skills can be applied to many different fields.
Benefitting you, beyond your studies
Outside of a work environment, the skills and knowledge that you’ll nurture as part of an Undergraduate or Masters English degree are likely to benefit your friendships, relationships, and encounters with other people.
Broad knowledge of literature can provide topics of conversation, ways to connect over a shared interest and ways to understand different cultures and worlds more sympathetically. When you study English language, you’ll learn to recognise effective communication methods, hopefully giving you the tools to be a better communicator day to day.
Creative career options
Subjects like English literature and English language can open many different, varied careers and many of those will give you the opportunity to be creative in the work that you do.
English graduates might pursue careers in education, journalism, publishing or writing to name a few. The outcomes of creative work may be wildly different among individuals or the discipline they choose but many agree that creative work can be fulfilling, exciting and varied.
Find out how English at Northumbria can support you in securing the career you want .
What course options are there to study English literature & language?
Types of degree.
You’ll find that there are lots of ways to study English literature and language. Many universities offer combined English literature and language degrees so you can study both disciplines as part of one degree.
However, if you want to specialise in either English language or English literature there are lots of options to do that too. You can even combine English literature or language with another subject, popular combinations include creative writing, linguistics, American studies, history, journalism, media studies and other humanities subjects to get a degree that meets your specific goals.
Most undergraduate programmes in English will see you graduate with a Bachelor of Arts (BA) degree qualification. A good starting point is to take a look at UCAS English degree listings, to get an idea of all the options available.
At postgraduate level, there’s options to develop your broad knowledge further, but you can also choose to specialise and really get into the detail of your chosen field. It’s likely that at Masters level you’ll have more options when it comes to types of English qualifications.
Many universities offer MRes degrees for research Masters in English, this is specifically the case if you’re interested in researching elements of language and literature. Other Masters in English degrees such as a Masters in Literature or Masters in Publishing are likely to lead to a Master of Arts (MA).
Placements and Study Abroad
Placements are a great way to gain some work experience, give you an insight into the world of work and what job options are available, and you’ll benefit from applying elements of your academic learning in the workplace.
Popular placement fields for English literature and English language students include marketing, PR, media, journalism, communications, publishing, advertising, education, and local government.
You might think that studying English literature or English language would limit your options for studying abroad, but you’d be wrong!
Just like many other degrees, you can choose to study abroad for a full year but there are shorter options too. Studying abroad gives you an insight into different cultures and perspectives, and it gives you the opportunity to develop other skills too: confidence, independence, adaptability, and self-awareness are all beneficial for your personal and professional development.
Most study abroad options are taught in English, but you may find yourself living in a country where English isn’t the primary language. This is an excellent opportunity for anyone interested in language but for someone who studies English, it could give you a more in-depth understanding of how language is acquired and how culture, location and history affect literature and the written word.
What career prospects does English literature & language offer?
Career prospects for English graduates with good results and evidence of relevant experience are excellent.
A degree in English gives you a great foundation for many different careers. The ability to communicate well is an essential skill to step into any job, and good written communication is an asset that many employers consider vital. The broad spectrum of skills and knowledge that you’ll gain while studying English literature & language degree means that you are likely to be very attractive to potential employers.
It’s important to remember that in order to stand out in an increasingly competitive jobs market graduates need to ensure that they develop a well-rounded CV whilst at university.
Placements, study abroad options and internships are a great way to gain experience in your chosen field and give you a competitive edge. Joining student societies can be another great way to build the skills you’ll need to stand out. As an English student, you might enjoy writing for your student newspaper, or joining your university radio or tv station.
There are likely to be reading, writing and film clubs you can join at university too. Being able to evidence the skills gained from work experience and extracurricular activities alongside your degree can really help boost your job prospects.
What jobs can I do with an English literature & language degree?
English graduates can find opportunities in many different employment areas, some relating directly to the subject matter you covered in your degree programme and many jobs where an English degree might not be directly relevant but would be a useful foundation to have.
Career options that relate directly to your degree might include:
- Copywriter
- Editorial assistant
- Teacher
- Publishing executive
- Content designer
- Lexicographer
- Author
- Journalist
- Researcher
- Speech and language therapist
There are plenty of sectors where an English degree would be a valuable asset, including:
- Education
- Arts management
- Charity
- General management
- Retail
- Journalism and media
- Television
- Film
- Publishing
- Marketing
- Public relations
- Academia and research
Why choose Northumbria University for English literature & Language?
English at Northumbria surrounds you with a passionate and creative community of students, researchers, academics, and professionals.
English at Northumbria sits within the Department of Humanities alongside subject areas like History, Linguistics, Creative Writing, American Studies, and Music. The breadth of the department and the richness of research topics across different fields ensures that English at Northumbria is cutting edge. Driven by new and developing themes like the environment, global connections, the medical humanities, gender and popular culture, activism, conflict and society, heritage, and American and global cultures. Together with classic themes like Shakespeare and Austen, English at Northumbria aims to spark new insight and deeper discoveries.
Find out what it’s like day to day to be an English Language student at Northumbria by following undergraduate student Alice on a typical day or check out Emma’s student view of an English Literature MA if you’re interested in a Masters in English degree.

You’ll benefit from modern classroom and lecture theatre facilities and access to the university’s 24hr library, our department’s library resources recently benefited from a £600,000 investment and we’re sure you’ll see the benefits if you choose to study English at Northumbria
Discover more about the campus facilities at Northumbria University.
Career Focussed
We’re proud that 90% of students reported that English at Northumbria provided them with opportunities to explore ideas and concepts in depth. (NSS, 2022). This depth of knowledge is an attractive asset to employers.
You’ll have access to industry networks, placement opportunities, links with employers and access to career coaching and resources when you study at Northumbria University. One such industry connection is with New Writing North, Northumbria’s partnership with New Writing North offers industry-led module delivery, internships, student employability activities as well as hosting the Northern Writers’ Awards to support your creative ambitions.
Take a look at some alumni profiles and see how studying English at Northumbria could support your future.
League tables can’t tell you everything about a degree but knowing that you’re studying in a highly rated department is a reassuring start. English at Northumbria University is ranked within the top 50 overall and top 3 in the North East in The Complete University Guide 2023.
Research Excellence
English at Northumbria is focused on three main areas of activity: Literature, Linguistics, and Creative Writing. Our vibrant research culture and cross-disciplinary approach create an exciting environment for world-leading, transformative research in English.
English at Northumbria is ranked 21st for research power in the UK, out of 92 institutions.*
50% of our research impact is rated as outstanding (4*), the highest rank*
90% of the subject area’s research outputs are rated as internationally excellent (3*) and world-leading (4*) *
*(Research Excellence Framework, REF2021)
Learn more about the impactful research we do every day in English at Northumbria.
Ready to find out more about English at Northumbria? Check out our interactive subject pages .
Is an English degree worth it?
Studying English gives you a great foundation for many different ambitious career options, it’s a well-respected academic degree. If you’re someone who loves reading, and language and wants to harness their literary and creative power in a future career then yes, an English degree is worth it.
Should I study English literature? Or English language?
This really depends on what you want out of your degree. If you want a broad, critical knowledge of literary works then an English literature course might be best for you. If you want to learn how our communication techniques have changed throughout history and how we even acquire language in the first place, then an English language course may be more appealing. You may also wish to study both elements as part of a combined or joint degree. Don’t forget that many universities also offer English degrees with elements of creative writing, to help develop your skills as a writer as well as a reader.
Is teaching English my only option for a career with an English degree?
Not at all! There are so many different fields, sectors and job types that would be suitable for high-achieving English graduates. From arts to publishing, there are a lot of options. Education is one field, whilst many graduates do choose to go into teaching you aren’t destined for that career path if it isn't your goal. Remember too that teaching covers lots of job titles in itself, traditional teaching in a UK school is one route, but studying English could also lead to international opportunities like teaching English as a second language.
Please Note
All content is accurate as of the time of writing, the information in this guide is subject to change and will be updated as required to reflect this.
Course and Study Guides
- Time Management Tips for Students
- Undergraduate Jargon Buster
- What are the benefits of going to university?
- Why Study Architecture?
- Why Study Art and Design?
- Why Study Business?
- Why Study Engineering?
- Why Study Maths and Physics?
- Why Study Applied Sciences?
- Why Study Social Sciences?
- Why Study Law?
- Why Study Education & Social Work?
- Why Study Healthcare?
- Why Study Psychology?
10 courses found
American studies ba (hons).
Undergraduate | Newcastle | 3 years full-time or 4 years with a placement (sandwich)/study abroad
Want to learn more about the history, literature, politics, film, art and popular culture of America? This course may be for you.
English Literature and Creative Writing BA (Hons)
Explore the treasures of a wide range of literature whilst also training yourself as a writer on this course.
English Language Studies BA (Hons)
This course opens windows onto a rich variety of linguistics study and gets you thinking about how language can be used in many ways.
International Relations and Politics BA (Hons)
Explore the political dimensions of life around the world, recognising the connections between people, locales, ideas and problems.
English Language and Literature BA (Hons)
Have a love of both language and literature? Study stimulating and distinctive modules and become a ‘citizen scholar’.
English Literature and American Studies BA (Hons)
Combine the study of a range of literary texts with the literature, culture, history, and politics of North America on this course.
English Literature and History BA (Hons)
Use works of literature to interpret and understand past societies and bring textual analysis to historical sources on this course.
Humanities Foundation Year
Undergraduate | Newcastle | 1 year full-time followed by a further 3 years full-time or 4 years with a placement (sandwich)/study abroad
This foundation year will prepare you for degree level study by exploring a range of topics from across the humanities subject areas.
English Literature BA (Hons)
Ready to discover the power of literature? Understand the stories that underpin our contemporary crises on this course.
Theatre and Performance BA (Hons)
Explore a broad range of creative art disciplines and become an arts practitioner ready.

Northumbria Open Days
Open Days are a great way for you to get a feel of the University, the city of Newcastle upon Tyne and the course(s) you are interested in.

Fees, Funding and Scholarships
Information about all of our tuition fees, funding and scholarships.

Virtual Tour
Get an insight into life at Northumbria at the click of a button! Come and explore our videos and 360 panoramas to immerse yourself in our campuses and get a feel for what it is like studying here using our interactive virtual tour.
Latest News and Features

Northumbria celebrates 100th nursing degree apprenticeship graduate
Over one hundred registered nurses have now been added to the region’s NHS workforce through…

Aspiring Architect wins prestigious industry awards
An Architecture student at Northumbria University recently achieved a series of industry accolades…

EXPERT COMMENT How being furloughed affected peoples sense of time and relationship with work
In this article originally written for The Conversation, Victoria J E Jones, Associate Professor…

A pathway to university for all
A learning centre designed to help young people from under-represented backgrounds in Newcastle…

Lottery funding announced to support mental health through creative education
An innovative mental health scheme at Northumbria University has been awarded £388,000 from…

Cutting-edge technology will boost real-time monitoring of remote peatlands
Researchers will develop new ways to monitor carbon emissions from vast swathes of peatland…

What does the future hold for the great British pub
Landlords, publicans, local authority planners, and members of the public are being invited…

History of divorce explored in new research project
A Northumbria University historian is to explore the impact of changes in divorce legislation…
Upcoming events

Virtual Event - Return to Study a Masters

Fashion Reimagined Film Screening
Northumbria University

Working Well in Healthcare: The Changes, Challenges and Opportunities for Developing your Workforce

Why are so many problems worse in more unequal societies?
Lecture Theatre 002
Back to top


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how to write a perfect "why this college" essay.
College Essays

Did you think you were all done pouring out your blood, sweat, and tears in written form for your personal statement , only to be faced with the "why this college?" supplemental essay? This question might seem simple but is in fact a crucial and potentially tricky part of many college applications. What exactly is the "why us?" essay trying to understand about you? And how do you answer this question without falling into its many pitfalls or making any rookie mistakes?
In this article, I'll explain why colleges want you to be able to explain why you are applying. I'll also discuss how to generate and brainstorm topics for this question and how to make yourself sound sincere and committed. Finally, we'll go over some "why this school?" essay do s and don't s.
This article is pretty detailed, so here's a brief overview of what we'll be covering:
Why Do Colleges Want You to Write a "Why Us?" Essay?
Two types of "why this college" essay prompts, step 1: research the school, step 2: brainstorm potential essay topics, step 3: nail the execution, example of a great "why this college" essay.
College admissions officers have to read an incredible amount of student work to put together a winning class, so trust me when I say that everything they ask you to write is meaningful and important .
The purpose of the "why us?" essay goes two ways. On one hand, seeing how you answer this question gives admissions officers a sense of whether you know and value their school .
On the other hand, having to verbalize why you are applying gives you the chance to think about what you want to get out of your college experience and whether your target schools fit your goals and aspirations.
What Colleges Get Out Of Reading Your "Why This College?" Essay
Colleges want to check three things when they read this essay.
First, they want to see that you have a sense of what makes this college different and special.
- Do you know something about the school's mission, history, or values?
- Have you thought about the school's specific approach to learning?
- Are you comfortable with the school's traditions and the overall feel of student life here?
Second, they want proof that you will be a good fit for the school.
- Where do your interests lie? Do they correspond to this school's strengths?
- Is there something about you that meshes well with some aspect of the school?
- How will you contribute to college life? How will you make your mark on campus?
And third, they want to see that this school will, in turn, be a good fit for you.
- What do you want to get out of college? Will this college be able to provide that? Will this school contribute to your future success?
- What will you take advantage of on campus (e.g., academic programs, volunteer or travel opportunities, internships, or student organizations)?
- Will you succeed academically? Does this school provide the right rigor and pace for your ideal learning environment?
What You Get Out Of Writing Your "Why This College?" Essay
Throughout this process of articulating your answers to the questions above, you will also benefit in a couple of key ways:
It Lets You Build Excitement about the School
Finding specific programs and opportunities at schools you are already happy about will give you a grounded sense of direction for when you start school . At the same time, by describing what is great about schools that are low on your list, you'll likely boost your enthusiasm for these colleges and keep yourself from feeling that they're nothing more than lackluster fallbacks.
It Helps You Ensure That You're Making the Right Choice
Writing the "why us?" essay can act as a moment of clarity. It's possible that you won't be able to come up with any reasons for applying to a particular school. If further research fails to reveal any appealing characteristics that fit with your goals and interests, this school is likely not for you.

At the end of your four years, you want to feel like this, so take your "Why This College?" essay to heart.
The "why this college?" essay is best thought of as a back-and-forth between you and the college . This means that your essay will really be answering two separate, albeit related, questions:
- "Why us?": This is where you explain what makes the school special in your eyes, what attracted you to it, and what you think you'll get out of your experience there.
- "Why you?": This is the part where you talk about why you'll fit in at the school; what qualities, skills, talents, or abilities you'll contribute to student life; and how your future will be impacted by the school and its opportunities.
Colleges usually use one of these approaches to frame this essay , meaning that your essay will lean heavier toward whichever question is favored in the prompt. For example, if the prompt is all about "why us?" you'll want to put your main focus on praising the school. If the prompt instead is mostly configured as "why you?" you'll want to dwell at length on your fit and potential.
It's good to remember that these two prompts are simply two sides of the same coin. Your reasons for wanting to apply to a particular school can be made to fit either of these questions.
For instance, say you really want the chance to learn from the world-famous Professor X. A "why us?" essay might dwell on how amazing an opportunity studying with him would be for you, and how he anchors the Telepathy department.
Meanwhile, a "why you?" essay would point out that your own academic telepathy credentials and future career goals make you an ideal student to learn from Professor X, a renowned master of the field.
Next up, I'll show you some real-life examples of what these two different approaches to the same prompt look like.

Clarifying why you want to study with a particular professor in a specific department can demonstrate to college admissions staff that you've done your research on the school.
"Why Us?" Prompts
- Why [this college]?
- Why are you interested in [this college]?
- Why is [this college] a good choice for you?
- What do you like best about [this college]?
- Why do you want to attend [this college]?
Below are some examples of actual "why us?" college essay prompts:
- Colorado College : "Describe how your personal experiences with a particular community make you a student who would benefit from Colorado College’s Block Plan."
- Tufts University : " I am applying to Tufts because… "
- Tulane University : "Describe why you are interested in joining the Tulane community. Consider your experiences, talents, and values to illustrate what you would contribute to the Tulane community if admitted." (via the Common App )
- University of Michigan : "Describe the unique qualities that attract you to the specific undergraduate College or School (including preferred admission and dual degree programs) to which you are applying at the University of Michigan. How would that curriculum support your interests?"
- Wellesley College : " When choosing a college, you are choosing an intellectual community and a place where you believe that you can live, learn, and flourish. We know that there are more than 100 reasons to choose Wellesley, but it's a good place to start. Visit the Wellesley 100 and select two items that attract, inspire, or celebrate what you would bring to our community. Have fun! Use this opportunity to reflect personally on what items appeal to you most and why. "

In a "why us?" essay, focus on the specific aspects of the school that appeal to you and how you will flourish because of those offerings.
"Why You?" Prompts
- Why are you a good match or fit for us?
- What are your interests, and how will you pursue them at [this college]?
- What do you want to study, and how will that correspond to our program?
- What or how will you contribute?
- Why you at [this college]?
- Why are you applying to [this college]?
Here are some examples of the "why you?" version of the college essay:
- Babson College : " A defining element of the Babson experience is learning and thriving in an equitable and inclusive community with a wide range of perspectives and interests. Please share something about your background, lived experiences, or viewpoint(s) that speaks to how you will contribute to and learn from Babson's collaborative community. "
- Bowdoin College : "Generations of students have found connection and meaning in Bowdoin's 'The Offer of the College.' ... Which line from the Offer resonates most with you? Optional: The Offer represents Bowdoin's values. Please reflect on the line you selected and how it has meaning to you." (via the Common App )

In a "why you?" essay, focus on how your values, interests, and motivations align with the school's offerings and how you'll contribute to campus life.
No matter how the prompt is worded, this essay is a give-and-take of what you and the college have to offer each other. Your job is to quickly zoom in on your main points and use both precision and detail to sound sincere, excited, and authentic.
How do you effectively explain the benefits you see this particular school providing for you and the contributions you will bring to the table as a student there? And how can you do this best using the small amount of space that you have (usually just one to two paragraphs)?
In this section, we'll go through the process of writing the "Why This College?" essay, step-by-step. First, I'll talk about the prep work you'll need to do. Next, we'll go through how to brainstorm good topics (and touch on what topics to avoid). I'll give you some tips on transforming your ideas and research into an actual essay. Finally, I'll take apart an actual "why us?" essay to show you why and how it works.
Before you can write about a school, you'll need to know specific things that make it stand out and appeal to you and your interests . So where do you look for these? And how do you find the details that will speak to you? Here are some ways you can learn more about a school.
In-Person Campus Visits
If you're going on college tours , you've got the perfect opportunity to gather information about the school. Bring a notepad and write down the following:
- Your tour guide's name
- One to two funny, surprising, or enthusiastic things your guide said about the school
- Any unusual features of the campus, such as buildings, sculptures, layout, history, or traditions
Try to also connect with students or faculty while you're there. If you visit a class, note which class it is and who teaches it. See whether you can briefly chat with a student (e.g., in the class you visit, around campus, or in a dining hall), and ask what they like most about the school or what has been most surprising about being there.
Don't forget to write down the answer! Trust me, you'll forget it otherwise—especially if you do this on multiple college visits.
Virtual Campus Visits
If you can't visit a campus in person, the next best thing is an online tour , either from the school's own website or from other websites, such as YOUniversityTV , CampusTours , or YouTube (search "[School Name] + tour").
You can also connect with students without visiting the campus in person . Some admissions websites list contact information for currently enrolled students you can email to ask one or two questions about what their experience of the school has been like.
Or if you know what department, sport, or activity you're interested in, you can ask the admissions office to put you in touch with a student who is involved with that particular interest.

If you can't visit a campus in person, request a video chat with admissions staff, a current student, or a faculty member to get a better sense of specific topics you might write about in your essay.
Alumni Interview
If you have an interview , ask your interviewer questions about their experience at the school and about what going to that school has done for them since graduation. As always, take notes!
College Fairs
If you have a chance to go to a college fair where your ideal college has representatives, don't just attend and pick up a brochure. Instead, e ngage the representatives in conversation, and ask them about what they think makes the school unique . Jot down notes on any interesting details they tell you.
The College's Own Materials
Colleges publish lots and lots of different admissions materials—and all of these will be useful for your research. Here are some suggestions for what you can use. (You should be able to find all of the following resources online.)
Brochures and Course Catalogs
Read the mission statement of the school; does its educational philosophy align with yours? You should also read through its catalogs. Are there any programs, classes, departments, or activities that seem tailor-made for you in some way?
Pro Tip: These interesting features you find should be unusual in some way or different from what other schools offer. For example, being fascinated with the English department isn't going to cut it unless you can discuss its unusual focus, its world-renowned professors, or the different way it structures the major that appeals to you specifically.
Alumni Magazine
Are any professors highlighted? Does their research speak to you or connect with a project you did in high school or for an extracurricular?
Sometimes alumni magazines will highlight a college's new focus or new expansion. Does the construction of a new engineering school relate to your intended major? There might also be some columns or letters written by alumni who talk about what going to this particular school has meant to them. What stands out about their experiences?
School or Campus Newspaper
Students write about the hot issues of the day, which means that the articles will be about the best and worst things on campus . It'll also give you insight into student life, opportunities that are available to students, activities you can do off campus, and so on.
The College's Social Media
Your ideal school is most likely on Facebook, X (formerly Twitter), Instagram, TikTok, and other social media. Follow the school to see what it's posting about. Are there any exciting new campus developments? Professors in the news? Interesting events, clubs, or activities?

The Internet
Wikipedia is a great resource for learning basic details about a college's history, traditions, and values. I also recommend looking for forums on College Confidential that specifically deal with the school you're researching.
Another option is to search on Google for interesting phrases, such as "What students really think about [School Name]" or "[School Name] student forum." This will help you get detailed points of view, comments about specific programs or courses, and insight into real student life.
So what should you do now that you've completed a bunch of research? Answer: use it to develop connection points between you and your dream school. These connections will be the skeleton of your "why this college?" essay.
Find the Gems in Your Research
You have on hand all kinds of information, from your own personal experiences on campus and your conversations with people affiliated with your ideal school to what you've learned from campus publications and tidbits gleaned from the web.
Now, it's time to sift through all of your notes to find the three to five things that really speak to you. Link what you've learned about the school to how you can plug into this school's life, approach, and environment. That way, no matter whether your school's prompt is more heavily focused on the "why us?" or "why you?" part of the give-and-take, you'll have an entry point into the essay.
But what should these three to five things be? What should you keep in mind when you're looking for the gem that will become your topic?
Here are some words of wisdom from Calvin Wise , director of recruitment and former associate director of admissions at Johns Hopkins University (emphasis mine):
" Focus on what makes us unique and why that interests you. Do your research, and articulate a multidimensional connection to the specific college or university. We do not want broad statements (the brick pathways and historic buildings are beautiful) or a rehash of the information on our website (College X offers a strong liberal arts curriculum). All institutions have similarities. We want you to talk about our differences. "

Time to find that diamond, amethyst, opal, tourmaline, or amber in the rough.
Check Your Gems for Color and Clarity
When I say "check your gems," I mean make sure that each of the three to five things you've found is something your ideal school has that other schools don't have.
This something should be seen from your own perspective. The point isn't to generically praise the school but instead to go into detail about why it's so great for you that they have this thing.
This something you find should be meaningful to the school and specific to you. For example, if you focus on academics (e.g., courses, instructors, opportunities, or educational philosophy), find a way to link them either to your previous work or to your future aspirations.
This something should not be shallow and nonspecific. Want to live in a city? Every city has more than one college in it. Find a way to explain why this specific college in this specific city calls to you. Like pretty architecture? Many schools are beautiful, so dwell on why this particular place feels unlike any other. Like good weather, beach, skiing, or some other geographical attribute? There are many schools located near these places, and they know that people enjoy sunbathing. Either build a deeper connection or skip these as reasons.
Convert Your Gems into Essay Topics
Every "why this college?" essay is going to answer both the "why us?" and the "why you?" parts of the back-and-forth equation. But depending on which way your target school has worded its prompt, you'll lean more heavily on that part . This is why I'm going to split this brainstorming into two parts—to go with the "why us?" and "why you?" types of questions.
Of course, since they are both sides of the same coin, you can always easily flip each of these ideas around to have it work well for the other type of prompt . For example, a "why us?" essay might talk about how interesting the XYZ interdisciplinary project is and how it fits well with your senior project.
By contrast, a "why you?" essay would take the same idea but flip it to say that you've learned through your senior project how you deeply value an interdisciplinary approach to academics, making you a great fit for this school and its commitment to such work, as evidenced by project XYZ.

Describing how project XYZ demonstrates your investment in a particular course of study that then happens to align with a specific program at the university is an effective approach to the "why you?" essay.
Possible "Why Us?" Topics
- How a particular program of study, internship requirement, or volunteer connection will help further your specific career goals .
- The school's interesting approach to your future major (if you know what that will be) or a major that combines several disciplines that appeal to you and fit with your current academic work and interests.
- How the school handles financial aid and the infrastructure setup for low-income students and what that means for you in terms of opening doors.
- A story about how you became interested in the school (if you learned about it in an interesting way). For example, did the institution host a high school contest you took part in? Did you attend an art exhibit or stage performance there that you enjoyed and that your own artistic work aligns with?
- How you overcame an initial disinterest in the school (be sure to minimize this first negative impression). Did you do more research? Interact with someone on campus? Learn about the school's commitment to the community? Learn about interesting research being done there?
- A positive interaction you had with current students, faculty, or staff, as long as this is more than just, "Everyone I met was really nice."
- An experience you had while on a campus tour. Was there a super-passionate tour guide? Any information that surprised you? Did something happen to transform your idea about the school or campus life (in a good way)?
- Interesting interdisciplinary work going on at the university and how that connects with your academic interests, career goals, or previous high school work.
- The history of the school —but only if it's meaningful to you in some way. Has the school always been committed to fostering minority, first-generation, or immigrant students? Was it founded by someone you admire? Did it take an unpopular (but, to you, morally correct) stance at some crucial moment in history?
- An amazing professor you can't wait to learn from. Is there a chemistry professor whose current research meshes with a science fair project you did? A professor who's a renowned scholar on your favorite literary or artistic period or genre? A professor whose book on economics finally made you understand the most recent financial crisis?
- A class that sounds fascinating , especially if it's in a field you want to major in.
- A facility or piece of equipment you can't wait to work in or with and that doesn't exist in many other places. Is there a specialty library with rare medieval manuscripts? Is there an observatory?
- A required curriculum that appeals to you because it provides a solid grounding in the classics, shakes up the traditional canon, connects all the students on campus in one intellectual project, or is taught in a unique way.

If the school can boast a cutting-edge laboratory where you dream of conducting research, that would be a strong focus for a "Why Us?" essay.
Possible "Why You?" Topics
- Do you want to continue a project you worked on in high school? Talk about how or where in the current course, club, and program offerings this work would fit in. Why will you be a good addition to the team?
- Have you always been involved in a community service project that's already being done on campus? Write about integrating life on campus with events in the surrounding community.
- Do you plan to keep performing in the arts, playing music, working on the newspaper, or engaging in something else you were seriously committed to in high school? Discuss how excited you are to join that existing organization.
- Are you the perfect person to take advantage of an internship program (e.g., because you have already worked in this field, were exposed to it through your parents, or have completed academic work that gives you some experience with it)?
- Are you the ideal candidate for a study abroad opportunity (e.g., because you can speak the language of the country, it's a place where you've worked or studied before, or your career goals are international in some respect)?
- Are you a stand-out match for an undergraduate research project (e.g., because you'll major in this field, you've always wanted to work with this professor, or you want to pursue research as a career option)?
- Is there something you were deeply involved with that doesn't currently exist on campus? Offer to start a club for it. And I mean a club; you aren't going to magically create a new academic department or even a new academic course, so don't try offering that. If you do write about this, make double (and even triple) sure that the school doesn't already have a club, course, or program for this interest.
- What are some of the programs or activities you plan to get involved with on campus , and what unique qualities will you bring to them?
- Make this a mini version of a personal statement you never wrote. Use this essay as another chance to show a few more of the skills, talents, or passions that don't appear in your actual college essay. What's the runner-up interest that you didn't write about? What opportunity, program, or offering at the school lines up with it?

One way to impress admissions staff in a "Why You?" essay is to discuss your fascination with a particular topic in a specific discipline, such as kinetic sculpture, and how you want to pursue that passion (e.g., as a studio art major).
Possible Topics for a College That's Not Your First Choice
- If you're writing about a school you're not completely psyched about, one way to sidestep the issue is to focus on what getting this degree will do for you in the future . How do you see yourself changing existing systems, helping others, or otherwise succeeding?
- Alternatively, discuss what the school values academically, socially, environmentally, or philosophically and how this connects with what you also care about . Does it have a vegan, organic, and cruelty-free cafeteria? A relationship with a local farm or garden? De-emphasized fraternity involvement? Strong commitment to environmental issues? Lots of opportunities to contribute to the community surrounding the school? Active inclusion and a sense of belonging for various underrepresented groups?
- Try to find at least one or two features you're excited about for each of the schools on your list. If you can't think of a single reason why this would be a good place for you to go, maybe you shouldn't be applying there!
Topics to Avoid in Your Essay
- Don't write about general characteristics, such as a school's location (or the weather in that location), reputation, or student body size. For example, anyone applying to the Webb Institute , which has just about 100 students , should by all means talk about having a preference for tiny, close-knit communities. By contrast, schools in sunny climates know that people enjoy good weather, but if you can't connect the outdoors with the college itself, think of something else to say.
- Don't talk about your sports fandom. Saying, "I can see myself in crimson and white/blue and orange/[some color] and [some other color]" is both overused and not a persuasive reason for wanting to go to a particular college. After all, you could cheer for a team without going to the school! Unless you're an athlete, you're an aspiring mascot performer, or you have a truly one-of-a-kind story to tell about your link to the team, opt for a different track.
- Don't copy descriptions from the college's website to tell admissions officers how great their institution is. They don't want to hear praise; they want to hear how you connect with their school. So if something on the college brochure speaks to you, explain why this specific detail matters to you and how your past experiences, academic work, extracurricular interests, or hobbies relate to that detail.
- Don't use college rankings as a reason you want to go to a school. Of course prestige matters, but schools that are ranked right next to each other on the list are at about the same level of prestige. What makes you choose one over the other?
- If you decide to write about a future major, don't just talk about what you want to study and why . Make sure that you also explain why you want to study this thing at this particular school . What do they do differently from other colleges?
- Don't wax poetic about the school's pretty campus. "From the moment I stepped on your campus, I knew it was the place for me" is another cliché—and another way to say basically nothing about why you actually want to go to this particular school. Lots of schools are pretty, and many are pretty in the exact same way.

Pop quiz: This pretty gothic building is on what college campus? Yes, that's right—it could be anywhere.
When you've put together the ideas that will make up your answer to the "why us?" question, it's time to build them into a memorable essay. Here are some tips for doing that successfully:
- Jump right in. The essay is short, so there's no need for an introduction or conclusion. Spend the first paragraph delving into your best one or two reasons for applying. Then, use the second paragraph to go into slightly less detail about reasons 2 (or 3) through 5.
- To thine own self be true. Write in your own voice, and be sincere about what you're saying. Believe me—the reader can tell when you mean it and when you're just blathering!
- Details, details, details. Show the school that you've done your research. Are there any classes, professors, clubs, or activities you're excited about at the school? Be specific (e.g., "I'm fascinated by the work Dr. Jenny Johnson has done with interactive sound installations").
- If you plan on attending if admitted, say so. Colleges care about the numbers of acceptances deeply, so it might help to know you're a sure thing. But don't write this if you don't mean it!
- Don't cut and paste the same essay for every school. At least once, you'll most likely forget to change the school name or some other telling detail. You also don't want to have too much vague, cookie-cutter reasoning, or else you'll start to sound bland and forgettable.
For more tips, check out our step-by-step essay-writing advice .

Avoid cookie-cutter responses to "why this college?" essay prompts. Instead, provide an essay that's personalized to that particular institution.
At this point, it'll be helpful to take a look at a "why us?" essay that works and figure out what the author did to create a meaningful answer to this challenging question.
Here is a "Why Tufts?" essay from James Gregoire '19 for Tufts University :
It was on my official visit with the cross country team that I realized Tufts was the perfect school for me. Our topics of conversation ranged from Asian geography to efficient movement patterns, and everyone spoke enthusiastically about what they were involved in on campus. I really related with the guys I met, and I think they represent the passion that Tufts' students have. I can pursue my dream of being a successful entrepreneur by joining the Tufts Entrepreneurs Society, pursuing an Entrepreneurial Leadership minor, and taking part in an up-and-coming computer science program.
Here are some of the main reasons this essay is so effective:
- Interaction with current students. James writes about hanging out with the cross-country team and sounds excited about meeting them.
- "I'm a great fit." He uses the conversation with the cross-country team members to talk about his own good fit here ("I really related with the guys I met").
- Why the school is special. James also uses the conversation as a way to show that he enjoys the variety of opportunities Tufts offers (their fun conversation covers Asian geography, movement patterns, and other things they "were involved with on campus").
- Taking advantage of this specialness. James doesn't just list things Tufts offers but also explains which of them are of specific value to him. He's interested in being an entrepreneur, so the Tufts Entrepreneurs Society and the Entrepreneurial Leadership courses appeal to him.
- Awareness of what the school is up to. Finally, James shows that he's aware of the latest Tufts developments when he mentions the new computer science program.
The Bottom Line: Writing a Great "Why This College?" Essay
- Proof that you understand what makes this college different and special
- Evidence that you'll be a good fit at this school
- Evidence that this college will, in turn, be a good fit for you
The prompt may be phrased in one of two ways: "Why us?" or "Why you?" But these are sides of the same coin and will be addressed in your essay regardless of the prompt style.
Writing the perfect "why this school?" essay requires you to first research the specific qualities and characteristics of this school that appeal to you. You can find this information by doing any or all of the following:
- Visiting campuses in person or virtually to interact with current students and faculty
- Posing questions to your college interviewer or to representatives at college fairs
- Reading the college's own materials , such as its brochures, official website, alumni magazine, campus newspaper, and social media
- Looking at other websites that talk about the school
To find a topic to write about for your essay, find the three to five things that really speak to you about the school , and then link each of them to yourself, your interests, your goals, or your strengths.
Avoid using clichés that could be true for any school, such as architecture, geography, weather, or sports fandom. Instead, focus on the details that differentiate your intended school from all the others .
What's Next?
Are you also working on your personal statement? If you're using the Common App, check out our complete breakdown of the Common App prompts and learn how to pick the best prompt for you .
If you're applying to a University of California school, we've got an in-depth article on how to write effective UC personal statements .
And if you're submitting ApplyTexas applications, read our helpful guide on how to approach the many different ApplyTexas essay prompts .
Struggling with the college application process as a whole? Our expert guides teach you how to ask for recommendations , how to write about extracurriculars , and how to research colleges .

Anna scored in the 99th percentile on her SATs in high school, and went on to major in English at Princeton and to get her doctorate in English Literature at Columbia. She is passionate about improving student access to higher education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
A Solar Eclipse Means Big Science
By Katrina Miller April 1, 2024
- Share full article

On April 8, cameras all over North America will make a “megamovie” of the sun’s corona, like this one from the 2017 eclipse. The time lapse will help scientists track the behavior of jets and plumes on the sun’s surface.
There’s more science happening along the path of totality →
An app named SunSketcher will help the public take pictures of the eclipse with their phones.
Scientists will use these images to study deviations in the shape of the solar surface , which will help them understand the sun’s churning behavior below.
The sun right now is approaching peak activity. More than 40 telescope stations along the eclipse’s path will record totality.
By comparing these videos to what was captured in 2017 — when the sun was at a lull — researchers can learn how the sun’s magnetism drives the solar wind, or particles that stream through the solar system.
Students will launch giant balloons equipped with cameras and sensors along the eclipse’s path.
Their measurements may improve weather forecasting , and also produce a bird’s eye view of the moon’s shadow moving across the Earth.
Ham radio operators will send signals to each other across the path of totality to study how the density of electrons in Earth’s upper atmosphere changes .
This can help quantify how space weather produced by the sun disrupts radar communication systems.
(Animation by Dr. Joseph Huba, Syntek Technologies; HamSCI Project, Dr. Nathaniel Frissell, the University of Scranton, NSF and NASA.)
NASA is also studying Earth’s atmosphere, but far from the path of totality.
In Virginia, the agency will launch rockets during the eclipse to measure how local drops in sunlight cause ripple effects hundreds of miles away . The data will clarify how eclipses and other solar events affect satellite communications, including GPS.
Biologists in San Antonio plan to stash recording devices in beehives to study how bees orient themselves using sunlight , and how the insects respond to the sudden atmospheric changes during a total eclipse.
Two researchers in southern Illinois will analyze social media posts to understand tourism patterns in remote towns , including when visitors arrive, where they come from and what they do during their visits.
Results can help bolster infrastructure to support large events in rural areas.
Read more about the eclipse:

Advertisement

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: What is Literature?
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 37255

- Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap
- City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative
Defining Literature
In order for us to study literature with any kind of depth, first we must decide what constitutes literature. While works like William Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet and Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird are almost universally accepted as literature, other works are hotly debated, or included or excluded based on the context. For example, while most consider Toni Morrison’s Beloved literature, others debate whether more recent publications such as David Mitchell’s Cloud Atlas or Rupi Kaur’s Instagram poetry constitute literature. And what about the stories told through tweets, like Jennifer Egan’s “Black Box” ? What about video games, like Skyrim , or memes, like Grumpy Cat?
Students often throw their hands up in the air over such distinctions, arguing literature is subjective. Isn't it up to individual opinion? Anything can be literature, such students argue. At first glance, it could seem such distinctions are, at best, arbitrary. At worst, such definitions function as a means of enforcing cultural erasure.
However, consider a story about Kim Kardashian’s plastic surgery in People Magazine . Can this be considered on the same level of literary achievement as Hamlet ? Most would concede there is a difference in quality between these two texts. A blurb about Kim Kardashian’s latest plastic surgery, most would agree, does not constitute literature. So how can we differentiate between such works?
Literature vs. literature
As illustrated in the somewhat silly example above, one way we can define what constitutes literature is by identifying what is definitely not literature. For our intents and purposes of defining most terms in this textbook, we will use the Oxford English Dictionary ’s definitions. Many professors who teach Literature use the concept of Big L Literature vs. little l literature (Rollison).
While the definition of little l literature is fairly easy to understand and apply, the definition of Big L Literature remains amorphous. What makes a work “artistic”? How do we define “superior” or “lasting”?
Let’s break down some of the defining qualities of literature in a bit more detail, starting with the word “artistic.”
Exercise 1.1.1
Consider the following works of art. Which of these images do you feel is higher quality or more “artistic”? Which is lower-quality or less artistic? Why? Justify your position by analyzing the elements of each artwork.

While there may be some debate, most students usually respond that Friedrich's painting is more artistic. This is due to several composition differences between the two works:
- Artist’s skill: it certainly appears as if the first image was produced by an artist with superior skill
- Fame: for anyone who knows art history, the first image is famous while the other is not
- Lasting quality: the first image has survived the test of time, remaining popular over two hundred years!
- Meaning: the first image likely conjures deeper feelings, themes, or ideas, such as isolation and the primacy of nature. This is why this image has become the face of Romanticism.
But what about the images demonstrate the artists’ superior skills? While the second image appears to be produced with a simple doodle, and quickly composed, the first indicates more complexity, attention-to-detail, and craft. Freidrich leverages different colors, textures, shapes, and symbols to evoke a feeling in the viewer. Skilled artists will use different techniques, like the way they move the paintbrush, the pressure they exert or the direction of the brush. They will use textured paintbrushes for a specific effect, such as the difference between the light fluffy clouds and dark mountain rocks. They will use different color pallets to project, as accurately as possible, the feelings they are trying to evoke. In short, while anyone can paint, true artists leverage many different skills, techniques, and materials to render what is in their imagination into a real-life product.
So how does this relate to our attempts to define literature?
Literature is art, but with words.
While the artist uses different colors, paintbrushes, mediums, canvases, and techniques, the writer uses different genres and literary techniques called literary devices . Just like different types of paint, paintbrushes, and artistic tools, there are literally hundreds of literary devices, but some of the most common are metaphor, simile, personification, and imagery. Genre is the type or style of literature. Each genre has its own conventions. Literary genres include creative nonfiction, fiction, drama, and poetry . Works that are literary tend to masterfully use genre conventions and literary devices to create a world in the mind of the reader. Works that are less literary tend to be for practical and/or entertainment purposes, and the writer dedicates less focused energy towards artfully employing literary devices.
However, just because a work is not as literary as another does not mean it cannot be enjoyed. Just like a stick figure or cartoon character might be perfectly fine if intended for a particular audience or purpose, readers can still enjoy People Magazine even though it is not of the same literary quality as Hamlet .
So, to use an example from earlier:
While some literature falls into clear designations of literature or not literature, most works are open to debate. Given the sometimes difficult task of determining whether a work falls into one camp or the other, it may be more helpful to think of Literature less as a dichotomy than a spectrum, with popular magazines on one end and works like Hamlet and Beloved on the other, and most written works falling somewhere between the two extremes.
The Literary Spectrum
This spectrum can be a helpful way to think about literature because it provides a more open-ended way to discuss writing as art than simply labeling works as literary or not. After viewing the above chart, why do you think popular magazines and a Calculus textbook are considered "less literary"? In terms of popular magazines, they do not fit the definition of literature as "lasting" in the sense that they usually fade from relevancy quickly after publication. Additionally, the authors of such magazines are striving for quick entertainment rather than leaving a meaningful impression on the reader. They tend not to use literary devices, such as metaphor, in a masterful way. On the other end, Shakespeare's Hamlet definitely fits the definition of "lasting," in that it has survived hundreds of years. It is full of literary devices used for rhetorical effect and, one would argue, it touches upon deep themes such as death, the afterlife, murder, vengeance, and love, rather than trifling issues such as a starlet's most recent plastic surgery.
Certainly, works of literature are up for debate: that is the quintessential question literary scholars might ask. What makes certain literary works survive the test of time? What makes a story, poem, or drama "good"? While literary scholars are less interested in proving a certain work is "good" or not -- and more focused on analyzing the ways to illuminate a given work -- it can be helpful for you to consider what kinds of literature you like and why you like it. What about the way it was written causes you to feel the way you do about it?
Who Decides What is Literature?
Now that we have at least somewhat clarified the definition of literature, who decides what works are or are not literature? Historically speaking, kings, queens, publishers, literary critics, professors, colleges, and readers (like you!) have decided which works survive and which works do not.
Aristotle was one of the first writers to attempt to decide what works fall into the category of literature, and what works do not. While Aristotle was most famous for his contributions to science and philosophy, he is also considered one of the first literary critics. A literary critic is a person who studies and analyzes literature. A literary critic produces scholarship called literary criticism . An example of this would be Aristotle’s Poetics , in which he identifies the defining qualities of a “good” Tragedy. Aristotle’s analysis of Tragedy was so influential that it is still used today, over two thousand years later!
When a work is officially decided to constitute literature, it enters something called the Canon. Not to be confused with the large metal tube that shoots bombs popular in the 16th through the 19th centuries (cannon), the Literary Canon is a collection of works that are considered by the powers that be to constitute literature. A work that falls into this designation is called canonical. So, to use an example from Aristotle’s Poetics , Aristotle defined Sophocles’ Oedipus Trilogy as the pinnacle of the Tragic Genre. From there, in part due to Aristotle's influence, Greek society valued Oedipus so much that they kept discussing, reading, referencing, and teaching it. Thus, it became a kind of shining example of the Tragic Canon, one which has lasted thousands of years and continues to be read and lauded to this day. Other tragedies, fairly or not, are often judged on their quality in comparison to Sophocles' works. Wild to think that someone who died thousands of years ago still influences what we consider literature today!
Memes and Video Games: Today's Literature?
All this talk of thousands-of-years-old texts might seem out of touch. A lot of people think "old and boring" and literature are synonymous. Students are often surprised to hear that comic books and video games can arguably be considered literature, too. There are plenty of arguments to be made that comic books, such as Maus by Art Spiegalman (1991) or Fun Home by Alison Bechdel (2006) are literature. Cutting edge literary scholars argue video games like Kentucky Route Zero by Cardboard Computer (2015) can be considered literary. There is also literature that is published in tweets, like Jennifer Egan's "Black Box" (2012). Some might even consider memes literature!
Generative question: do you think memes can be literary?

A meme is an image or video containing cultural values or ideas, often represented through allusion (implied reference to another work, without naming that work or its author). Memes can spread rapidly spreads through social media. Why? Because the best ones are #relatable; that is, they speak to a common human experience.
Usually memes take the form of text superimposed on an image. For example, the meme above conveys the dramatic reaction students sometimes give when I assign an essay. This is done primarily through a literary device called hyperbole , or exaggeration for rhetorical effect. It conveys its message comically through certain conventions that come along with the meme genre, such as the syntactic structure "me, a [insert noun]" and asterisks, which convey action. Just like in the Shakespearean drama, the colon indicates what each character (me and the students, in this case) is saying or doing. My chihuahua's face looks silly and very dramatic. Through this use of image, text, format, and convention, the meaning I intended to convey was that I was making fun of my students for being over-dramatic about what to me seems like a fairly simple assignment. While some might dismiss memes as shallow, when you start to unravel the layers of meaning, they can actually be very complex and even, dare I say, literary!
Think about a recent meme you have seen, or your favorite meme of all time. Imagine explaining this meme to someone who has no idea what it means. What is the message or idea behind the meme? What cultural reference points does it use to convey its message? In what ways might this meme be considered literature? How might this compare to a short poem, like a haiku?
Not Literature
Let's say you come to the conclusion that a meme, a gossip magazine, or the Twilight Series is not literary. Does that mean you have to feel guilty and give up reading it forever? Or that it is not "good"?
Just because a work is not literary does not mean it is "bad," that it does not have value, or that one cannot enjoy it. Indeed, there are plenty of examples of written works that are on the less literary side of the spectrum but are still fun and enriching to read. Joe Dirt i s not on the same artistic level of cinema as Schindler's List , but my husband still loves watching it. Nothing Taylor Swift has produced is as deep as Tupac Shakur's "Changes" (1992) or Mitski's "Last Words of a Shooting Star" (2014), but listening to Taylor Swift is my guilty pleasure. This is all to say that whether a text is literary or not is not as important as the methods of analyzing texts. In fact, texts which were excluded from literature are often argued into the literary canon through such analysis. Part of what makes analyzing literature so fun is that it means the definition of literature is always up for debate! This is especially important given the history of the canon.
The Problem with the Canon
In an ideal world, literature would be celebrated purely based on its artistic merit. Well-written works would last, poorly-written works would wither from public memory. However, that is not always the case. Works often achieve public prominence or survive based on qualities unrelated to skill or aesthetics, such as an author's fame, wealth, connections, or acceptance by the dominant culture. William Wordsworth, for example, was named Poet Laureate of England and has been taught as one of the "Big Six" major Romantic-era authors ever since. Indeed, he is accepted as part of the Romanticism literary canon. One would be hard-pressed to find a Literature anthology that does not feature William Wordsworth . However, how many people have read or heard of Dorothy Wordsworth , William Wordsworth's sister, who arguably depicted Romantic themes with equal skill and beauty? Or James Hogg, a Scottish contemporary of Wordsworth who was a lower-class shepherd? Similarly, while most readers have encountered F. Scott Fitzgerald or Edgar Allen Poe in their high school literature classes, how many have read Frederick Douglass in these same classes? In short, all artistic skill (arguably) considered equal, why do some authors predominantly feature in the Canon while others do not?
Let’s perform an experimental activity.
- Find a piece of paper or a whiteboard. On this piece of paper or whiteboard, write down as many works of literature that you feel constitute “Big L Literature.” Perhaps they are works you read in high school, works which have been made into films, or works you have been taught or told are literary masterworks. Don’t turn the page until you have written them down. Try to think of at least 10, but a larger sample size is better. Once you are finished, continue to the next paragraph.
- Alright, now look at your list. If you know the author of the literary texts you named, write their name next to the work. If you do not know the author, Google the information and write it down. Continue doing this until you have named the author of each work. Once you are finished, read on to the next paragraph.
- Now, as uncomfortable as it seems, label the gender/race/age/presumed sexual orientation of the authors you listed. After you have categorized them to the best of your ability, consider the following questions:
- What percentage of the authors are male?
- What percentage of the authors are white?
- What percentage of the authors are old/dead?
- What patterns do you notice? Why do you think this is?
I have replicated this experiment dozens of times in the classroom, and, in most classes, the vast majority of what students have been taught are “Literary Masterworks” are written by (pardon my colloquialism) dead white males. Although, as time progresses, it seems there is increasing but not proportionate representation on average. For example, while women make up about half of the population, over 80% of the most popular novels were written by men ("Battle"). While there are many possible reasons for this discrepancy in representation (which could be the focus of an entire textbook), what does this mean for scholars of literature? For students? For instructors? For society?
As a cultural relic, similar to art, many scholars suggest literature is a reflection of the society which produces it. This includes positive aspects of society (championing values such as love, justice, and good triumphing over evil), but it can also reflect negative aspects of society (such as discrimination, racism, sexism, homophobia, historical lack of opportunity for marginalized authors).
For example, enslaved Africans were often prevented from learning to read and write as a form of control. When Phillis Wheatley published her book of poetry, Poems on Various Subjects, Religious and Moral (1773) she had to defend the fact that she wrote it, due to popularly held racist views that slaves were incapable of writing poetry. Later, Frederick Douglass wrote about how his enslavers banned him from reading and writing, as they realized "education and slavery were incompatible with each other" (Douglass). He later championed his learning to read and write as the means which conveyed him to freedom. However, even when trying to publish The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass ( 1845) his publishers were forced to prove that it was, in fact, an enslaved person who wrote the story and not a white man who wrote it for him. Slave owners actively attempted to keep this book from circulation as it threatened the institution of slavery upon which they depended. Indeed, to this day, Douglass' book continues to be banned in some prisons for its potential to incite revolution (Darby, Gilroy).
How could Black writers enter the canon en masse if they were not allowed to read or write? Or if they were forced to spend all of their waking hours working? And if those who had the means to read and write had to jump through absurd hoops just to have their works published? And if even those texts which were published were banned?
Similarly, throughout much of Western history, women have been discouraged from pursuing reading and writing, as it distracted from society's expectations for women to focus on motherly and household duties. Until the 1700s, women were not allowed to go to college. Even then, very few went: only the extremely wealthy. It was not until the 19th century that women attended college in representative numbers. Virginia Woolf wrote in A Room of One's Own that if there are fewer works of literature written by women, it is only because society, historically, has not given women the time, education, funding, or space to do so. In this extended essay, she describes an imaginary sister of William Shakespeare who could have been just as great of a writer had she the same opportunities as her brother.
I told you in the course of this paper that Shakespeare had a sister; but do not look for her in Sir Sidney Lee's life of the poet. She died young—alas, she never wrote a word. She lies buried where the omnibuses now stop, opposite the Elephant and Castle. Now my belief is that this poet who never wrote a word and was buried at the cross-roads still lives. She lives in you and in me, and in many other women who are not here tonight, for they are washing up the dishes and putting the children to bed. But she lives; for great poets do not die; they are continuing presences; they need only the opportunity to walk among us in the flesh. This opportunity, as I think, it is now coming within your power to give her.
Woolf argues that in our time those who have been excluded from literature can now join the canon by adding their voices. The inequity of representation in literature -- which has arguably improved, but in many ways persists today -- can be remedied if more people from a wide array of backgrounds and walks of life are empowered to study and create Literature. That is one reason why the current study of literature is so exciting. As a student and budding literary scholar, you have the power to influence culture through your reading and analysis of literature! For one author and scholar's perspective on this topic, please watch this the following TED Talk by Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie to see the ways in which such misrepresentations are harmful, and why it is important to veer away from the historically parochial Canon into what Chinua Achebe calls "a balance of stories" (qtd. Bacon).

- Original video available on TED Talk website
- Transcript of video
What "single stories" do you know? What are the "single stories" people have told about you? What story would you tell if you could? What kinds of stories do you want to read? Throughout this class, you will get the opportunity to encounter many different voices and stories from all over the world. While we faced hurdles of copyright permissions, the authors of this textbook attempted to embody the values espoused in this TED Talk & Chinua Achebe's conception of the "balance of stories." As you read the textbook, consider the stories which were omitted, why they were omitted, and what works of Literature you would include in this class if you could.
Works Cited
Bacon, Katie. "An African Voice." The Atlantic , 2000.
"Battle of the Authors: Are The Most Popular Rated Fiction Books Written by Men or Women?" Wordery , 1 Mar. 2019.
Darby, Luke. "Illinois Prison Bans Frederick Douglass's Memoir and Other "Racial" Books." GQ , 20 August 2019.
Douglass, Frederick. The Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass. 1845.
Friedrich, Caspar David. "Wanderer Above the Sea of Fog." Hamburger Kunsthalle Museum , 1818.
Gilroy, Paul. "Banned Books of Guantánamo: 'An American Slave' by Frederick Douglass." Vice , 14 Nov. 2014.
"literature, n.; 3b & 5" OED Online , Oxford University Press, September 2019, www.oed.com/view/Entry/109080. Accessed 6 September 2019.
Rollison, David. "Big L vs Little L Literature." Survey of World Literature I. College of Marin, 2008. Lecture.
Wheatley, Phillis. Poems on Various Subjects, Religious and Moral . 1773.
Woolf, Virginia. A Room of One's Own. 1929.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Benefits of Studying Literature. 1. Literature Develops Communication Skills. The foundation of literature is the English Language. By reading literature, you can improve your knowledge of language: vocabulary, grammar, sentence structure, content creation, and more. When you immerse yourself in William Shakespeare, Celeste Ng, or Chinua ...
Literature is a method of recording, preserving, and transmitting knowledge and entertainment, and can also have a social, psychological, spiritual, or political role.". This definition is well-suited for our purposes here because throughout this course, we will be considering several types of literary texts in a variety of contexts.
Expert Answers. Literature is one way for us to hear the voices of the past and work with the present. It is a way for the present to connect to the possible future. Story telling is one way for ...
Literature lets us live in different times and different places than we can ever experience in our real life. It can put us in the shoes of people whose situations are radically different from our own, promoting empathy and understanding. It can teach us about history, geography, science, math, art, and every other subject we study.
Share Cite. The study of literature is important because it, at its most basic, improves reading skills. From this involved reading of quality literature a student then develops their writing ...
Literature can help us make better sense of our world, our lives and ourselves. Literature has the power to give us an enriched understanding of other worlds, lives and times, of the way things have been and how they might be. Reading, thinking, writing and talking about literature is both a personal and collegiate experience - a model of how ...
Literary study activates our curiosity. Literature also drives us to get answers to our questions, to ask and to explore. This is one of the things people mean when they say that literature "opens our minds.". When we are curious, we engage with the world by asking questions and listening carefully and thoughtfully to the answers we encounter.
It promotes perspective-taking, and an understanding of others. It enables students to recognize and connect with the universals of human experience. Fundamentally, a study of literature is a study of the world: bigger, more complicated, and more diverse than we have yet seen it with our own eyes. The world of fiction can make real the ...
Benefits of Literature. Studies show reading literature may help. promote empathy and social skills (Castano and Kidd) alleviate symptoms of depression (Billington et al.) business leaders succeed (Coleman) prevent dementia by stimulating the mind (Thorpe) These are just a few of the studied benefits of literature.
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
Literature has many potential meanings, and literary theory gives scholars different avenues to uncover those meanings. By asking theoretical questions of the novels, stories, poems, plays, and essays that you read in your literature class, you can begin to grasp works that may seem ineffable—impenetrable—if you try to uncover a single ...
Literature is art, but with words. While the artist uses different colors, paintbrushes, mediums, canvases, and techniques, the writer uses different genres and literary techniques called literary devices. Just like different types of paint, paintbrushes, and artistic tools, there are literally hundreds of literary devices, but some of the most ...
When you study literature with Gustavus Adolphus, you'll don't just read old books and write essays. For instance, you'll learn to present with a small group, plan and lead discussions, collaborate on activities, and work with off-campus organizations. You'll build skills such as writing and summarizing complex information in a concise way.
One is that "fiction" and "literature" are regarded as quite different things. "Fiction," for example, is what people read for enjoyment. "Literature" is what they read for school. Or "fiction" is what living people write and is about the present. "Literature" was written by people (often white males) who have since died ...
Literature introduces you to a rich language, helps you develop and discover good skills and words, discover a new self, sense the problems in society by a critical view, explore texts with new perspectives, read about culture, understand the value of poetry, gain the literary skills of classics, and develop a good writing sense.
Literary analysis involves examining all the parts of a novel, play, short story, or poem—elements such as character, setting, tone, and imagery—and thinking about how the author uses those elements to create certain effects. A literary essay isn't a book review: you're not being asked whether or not you liked a book or whether you'd ...
8 Prompts for Essays About Literature. 1. The Importance of Literature. In your essay, write about the importance of literature; explain why we need to study literature and how it can help us in the future. Then, give examples of literary works that teach important moral lessons as evidence. 2.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The Top Secret Three-Word Trick to Finding Specific Info for Your "Why this College" Essay. Step 2: Organize Your Research. Step 3: Decide on Your Approach: Approach #1: The Basic, Solid "Why this College" Essay That Includes a Bunch of Reasons. Approach #2: The "3-5 Unique Reasons" Strategy. Approach #3: The "One Value" Strategy.
The study of English explores fascinating elements of both literature and language. How we communicate, how words and language have developed, and what this means for us and society. Studying English literature and language gives you the tools to analyse the spoken and written word critically and creatively.
college essay prompts: Colorado College: "Describe how your personal experiences with a particular community make you a student who would benefit from Colorado College's Block Plan." Tufts University: " I am applying to Tufts because…. Tulane University: "Describe why you are interested in joining the Tulane community.
A Solar Eclipse Means Big Science. On April 8, cameras all over North America will make a "megamovie" of the sun's corona, like this one from the 2017 eclipse. The time lapse will help ...
Genre is the type or style of literature. Each genre has its own conventions. Literary genres include creative nonfiction, fiction, drama, and poetry. Works that are literary tend to masterfully use genre conventions and literary devices to create a world in the mind of the reader.