- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews

How to Write an Article Review
Last Updated: September 8, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,092,653 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Things You Should Know
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information. [1] X Research source
Preparing to Write Your Review

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.
Writing the Article Review

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [10] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.
Sample Article Reviews

Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/grammarpunct/proofreading/
- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?
Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Oct 25, 2023
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- Its topic.
- Its type.
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Reading Groups: Everything You Need to Know
Product review of the ultenic p30 grooming kit, reading anxiety in children: everything you need to know, iep meetings and parent-teacher conferences: everything you need to know, college disability services and accommodations: everything you need to know, spam vs. phishing: how are these unwanted messages different, how to charge your iphone properly, encouraging your teenager to read: everything you need to know, 8 ways to service an air conditioner, 3 ways to stop a baby from vomiting, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.
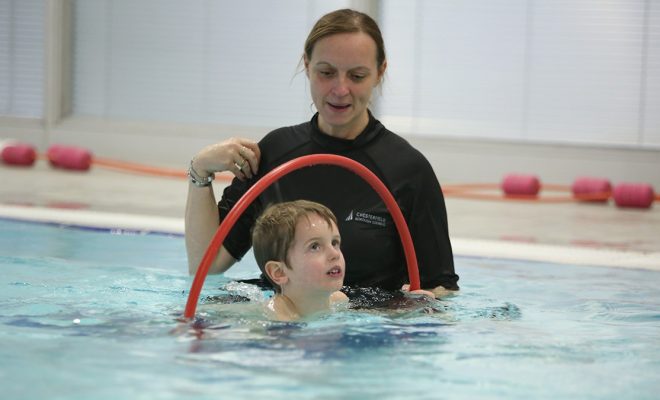

How to Teach Autistic Children to Swim

How to Become SHRM Certified: 12 Steps
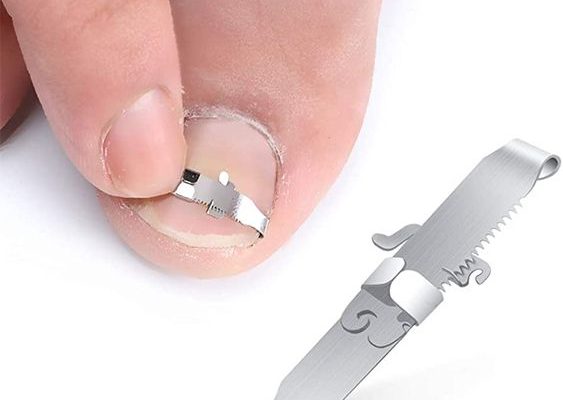
3 Ways to Get Rid of Ingrown Toenails

4 Ways to Fold Long Sleeve Shirts

How to Acidify Soil: 14 Steps

How to Play the Strumstick: 8 Steps
How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format, related articles.
.webp)
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
Writing an article REVIEW
- Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author.
Your review might be guided by the following questions:
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
How to Write an Article Review (from Essaypro.com)
How to Review a Journal Article (from University of Illinois Springfield)
Writing Critical Reviews (from Queen's University Library)
- << Previous: Writing an article SUMMARY
- Next: Writing an article CRITIQUE >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries
How to Write an Article Review: Practical Tips and Examples
Table of contents
- 1 What Is an Article Review?
- 2 Different Types of Article Review
- 3.1 Critical review
- 3.2 Literature review
- 3.3 Mapping review/systematic map
- 3.4 Meta-analysis
- 3.5 Overview
- 3.6 Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
- 3.7 Rapid review
- 3.8 Scoping review
- 3.9 Systematic review
- 3.10 Umbrella review
- 4 Formatting
- 5 How To Write An Article Review
- 6 Article Review Outline
- 7 10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
- 8 An Article Review Example
What Is an Article Review?
Before you get started, learn what an article review is. It can be defined as a work that combines elements of summary and critical analysis. If you are writing an article review, you should take a close look at another author’s work. Many experts regularly practice evaluating the work of others. The purpose of this is to improve writing skills.
This kind of work belongs to professional pieces of writing because the process of crafting this paper requires reviewing, summarizing, and understanding the topic. Only experts are able to compose really good reviews containing a logical evaluation of a paper as well as a critique.
Your task is not to provide new information. You should process what you have in a certain publication.
Different Types of Article Review
In academic writing, the landscape of article reviews is diverse and nuanced, encompassing a variety of formats that cater to different research purposes and methodologies. Among these, three main types of article reviews stand out due to their distinct approaches and applications:
- Narrative. The basic focus here is the author’s personal experience. Judgments are presented through the prism of experiences and subsequent realizations. Besides, the use of emotional recollections is acceptable.
- Evidence. There is a significant difference from the narrative review. An in-depth study of the subject is assumed, and conclusions are built on arguments. The author may consider theories or concrete facts to support that.
- Systematic. The structure of the piece explains the approach to writing. The answer to what’s a systematic review lies on the surface. The writer should pay special attention to the chronology and logic of the narrative.
Understanding 10 Common Types
Don`t rush looking at meta-analysis vs. systematic review. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with other formats and topics of texts. This will allow you to understand the types of essays better and select them based on your request. For this purpose, we`ll discuss the typology of reviews below.
Critical review
The critical review definition says that the author must be objective and have arguments for each thought. Sometimes, amateur authors believe that they should “criticize” something. However, it is important to understand the difference since objectivity and the absence of emotional judgments are prioritized. The structure of this type of review article is as follows:
- Introduction;
- Conclusion.
“Stuffing” of the text is based on such elements as methodology, argumentation, evidence, and theory base. The subject of study is stated at the beginning of the material. Then follows the transition to the main part (facts). The final word summarizes all the information voiced earlier.
It is a mistake to believe that critical reviews are devoid of evaluation. The author’s art lies in maneuvering between facts. Smooth transition from one argument to another and lays out the conclusions in the reader. That is why such texts are used in science. The critical reviews meaning is especially tangible in medical topics.
Literature review
Literature is the basis for this type of work ─ books, essays, and articles become a source of information. Thus, the author should rethink the voiced information. After that, it is possible to proceed to conclusions. The methodology aims to find interconnections, repetitions, and even “gaps” in the literature. One important item is the referencing of sources. Footnotes are possible in the work itself or the list of resources used.
These types of research reviews often explore myths since there are often inconsistencies in mythology. Sometimes, there is contrary information. In this case, the author has to gather all existing theories. The essence does not always lie in the confirmation of facts. There are other different types of reviews for this purpose. In literary reviews, the object of study may be characters or traditions. This is where the author’s space for discovery opens up. Inconsistencies in the data can tell important details about particular periods or cultures. At the same time, patterns reveal well-established facts. Make sure to outline your work before you write. This will help you with essay writing .
Mapping review/systematic map
A mapping review, also known as a systematic map, is a unique approach to surveying and organizing existing literature, providing a panoramic view of the research landscape. This paper systematically categorizes and maps out the available literature on a particular topic, emphasizing breadth over depth. Its primary goal is to present a comprehensive visual representation of the research distribution, offering insights into the overall scope of a subject.
One of the strengths of systematic reviews is that they deeply focus on a research question with detailed analysis and synthesis, while mapping review prioritizes breadth. It identifies and categorizes a broad range of studies without necessarily providing in-depth critique or content synthesis. This approach allows for a broader understanding of the field, making it especially useful in the early stages of research. Mapping reviews excel in identifying gaps in the existing body of literature.
By systematically mapping the distribution of research, researchers can pinpoint areas where studies are scarce or nonexistent, helping to guide future research directions. This makes mapping reviews a valuable tool for researchers seeking to contribute meaningfully to a field by addressing unexplored or underexplored areas.
Meta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a powerful statistical technique. It systematically combines the results of multiple studies to derive comprehensive and nuanced insights. This method goes beyond the limitations of individual studies, offering a more robust understanding of a particular phenomenon by synthesizing data from diverse sources.
Meta-analysis employs a rigorous methodology. It involves the systematic collection and statistical integration of data from multiple studies. This methodological rigor ensures a standardized and unbiased approach to data synthesis. It is applied across various disciplines, from medicine and psychology to social sciences, providing a quantitative assessment of the overall effect of an intervention or the strength of an association.
In evidence-based fields, where informed decision-making relies on a thorough understanding of existing research, meta-analysis plays a pivotal role. It offers a quantitative overview of the collective evidence, helping researchers, policymakers, and practitioners make more informed decisions. By synthesizing results from diverse studies, meta-analysis contributes to the establishment of robust evidence-based practices, enhancing the reliability and credibility of findings in various fields. To present your research findings in the most readable way possible, learn how to write a summary of article .
If the key purpose of systematic review is to maximize the disclosure of facts, the opposite is true here. Imagine a video shot by a quadcopter from an altitude. The viewer sees a vast area of terrain without focusing on individual details. Overviews follow the same principle. The author gives a general picture of the events or objects described.
These types of reviews often seem simple. However, the role of the researcher becomes a very demanding one. The point is not just to list facts. Here, the search for information comes to the fore. After all, it is such reports that, in the future, will provide the basis for researching issues more narrowly. In essence, you yourself create a new source of information ─ students who worry that somebody may critique the author’s article love this type of material. However, there are no questions for the author; they just set the stage for discussions in different fields.
An example of this type of report would be a collection of research results from scientists. For example, statistics on the treatment of patients with certain diseases. In such a case, reference is made to scientific articles and doctrines. Based on this information, readers can speak about the effectiveness of certain treatment methods.
Qualitative Systematic Review/Qualitative Evidence Synthesis
One of the next types of review articles represents a meticulous effort to synthesize and analyze qualitative studies within a specific research domain.
The focus is synthesizing qualitative studies, employing a systematic and rigorous approach to extract meaningful insights. Its significance lies in its ability to provide a nuanced understanding of complex phenomena, offering a qualitative lens to complement quantitative analyses. Researchers can uncover patterns, themes, and contextual nuances that may elude traditional quantitative approaches by systematically reviewing and synthesizing qualitative data.
Often, you may meet discussion: is a systematic review quantitative or qualitative? The application of qualitative systematic reviews extends across diverse research domains, from healthcare and social sciences to education and psychology. For example, this approach can offer a comprehensive understanding of patient experiences and preferences in healthcare. In social sciences, it can illuminate cultural or societal dynamics. Its versatility makes it a valuable tool for researchers exploring, interpreting, and integrating qualitative findings to enrich their understanding of complex phenomena within their respective fields.
Rapid review
If you don’t know how to write an article review , try starting with this format. It is the complete opposite of everything we talked about above. The key advantage and feature is speed. Quick overviews are used when time is limited. The focus can go to individual details (key). Often, the focus is still on the principal points.
Often, these types of review papers are critically needed in politics. This method helps to communicate important information to the reader quickly. An example can be a comparison of the election programs of two politicians. The author can show the key differences. Or it can make an overview based on the theses of the opponents’ proposals on different topics.
Seeming simplicity becomes power. Such texts allow the reader to make a quick decision. The author’s task is to understand potential interests and needs. Then, highlight and present the most important data as concisely as possible. In addition to politics, such reports are often used in communications, advertising, and marketing. Experienced writers mention the one-minute principle. This means you can count on 60 seconds of the reader’s attention. If you managed to hook them ─ bravo, you have done the job!
Scoping review
If you read the official scoping review definition, you may find similarities with the systematic type of review. However, recall is a sequential and logical study in the second case. It’s like you stack things on a shelf by color, size, and texture.
This type of review can be more difficult to understand. The basic concept is to explore what is called the field of subjects. This means, on the one hand, exploring a particular topic through the existing data about it. The author tries to find gaps or patterns by drawing on sources of information.
Another good comparison between systematic and this type of review is imagining as if drawing a picture. In the first case, you will think through every nuance and detail, why it is there, and how it “moves the story.” In the second case, it is as if you are painting a picture with “broad strokes.” In doing so, you can explain your motives for choosing the primary color. For example: “I chose the emerald color because all the cultural publications say it’s a trend”. The same goes for texts.
Systematic review
Sometimes, you may encounter a battle: narrative review vs. systematic review. The point is not to compare but to understand the different types of papers. Once you understand their purpose, you can present your data better and choose a more readable format. The systematic approach can be called the most scientific. Such a review relies on the following steps:
- Literature search;
- Evaluating the information;
- Data processing;
- Careful analysis of the material.
It is the fourth point that is key. The writer should carefully process the information before using it. However, 80% of your work’s result depends on this stage’s seriousness.
A rigorous approach to data selection produces an array of factual data. That is why this method is so often used in science, education, and social fields. Where accuracy is important. At the same time, the popularity of this approach is growing in other directions.
Systematic reviews allow for using different data and methodologies,, but with one important caveat ─ if the author manages to keep the narrative structured and explain the reason for certain methods. It is not about rigor. The task of this type of review is to preserve the facts, which dictates consistency and rationality.
Umbrella review
An umbrella review is a distinctive approach that involves the review of existing reviews, providing a comprehensive synthesis of evidence on a specific topic. The methodology of an umbrella review entails systematically examining and summarizing findings from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
This method ensures a rigorous and consolidated analysis of the existing evidence. The application of an umbrella review is broad, spanning various fields such as medicine, public health, and social sciences. It is particularly useful when a substantial body of systematic reviews exists, allowing researchers to draw overarching conclusions from the collective findings.
It allows the summarization of existing reviews and provides a new perspective on individual subtopics of the main object of study. In the context of the umbrella method, the comparison “bird’s eye view” is often cited. A bird in flight can see the whole panorama and shift its gaze to specific objects simultaneously. What becomes relevant at a particular moment? The author will face the same task.
On the one hand, you must delve into the offshoots of the researched topic. On the other hand, focus on the topic or object of study as a whole. Such a concept allows you to open up new perspectives and thoughts.

Different types of formatting styles are used for article review writing. It mainly depends on the guidelines that are provided by the instructor, sometimes, professors even provide an article review template that needs to be followed.
Here are some common types of formatting styles that you should be aware of when you start writing an article review:
- APA (American Psychological Association) – An APA format article review is commonly used for social sciences. It has guidelines for formatting the title, abstract, body paragraphs, and references. For example, the title of an article in APA format is in sentence case, whereas the publication title is in title case.
- MLA (Modern Language Association): This is a formatting style often used in humanities, such as language studies and literature. There are specific guidelines for the formatting of the title page, header, footer, and citation style.
- Chicago Manual of Style: This is one of the most commonly used formatting styles. It is often used for subjects in humanities and social sciences, but also commonly found in a newspaper title. This includes guidelines for formatting the title page, end notes, footnotes, publication title, article citation, and bibliography.
- Harvard Style: Harvard style is commonly used for social sciences and provides specific guidelines for formatting different sections of the pages, including publication title, summary page, website publisher, and more.
To ensure that your article review paper is properly formatted and meets the requirements, it is crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for the formatting style you are using. This helps you write a good article review.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
How To Write An Article Review
There are several steps that must be followed when you are starting to review articles. You need to follow these to make sure that your thoughts are organized properly. In this way, you can present your ideas in a more concise and clear manner. Here are some tips on how to start an article review and how to cater to each writing stage.
- Read the Article Closely: Even before you start to write an article review, it’s important to make sure that you have read the specific article thoroughly. Write down the central points and all the supporting ideas. It’s important also to note any questions or comments that you have about the content.
- Identify the Thesis: Make sure that you understand the author’s main points, and identify the main thesis of the article. This will help you focus on your review and ensure that you are addressing all of the key points.
- Formulate an Introduction: The piece should start with an introduction that has all the necessary background information, possibly in the first paragraph or in the first few paragraphs. This can include a brief summary of the important points or an explanation of the importance.
- Summarize the Article : Summarize the main points when you review the article, and make sure that you include all supporting elements of the author’s thesis.
- Start with Personal Critique : Now is the time to include a personal opinion on the research article or the journal article review. Start with evaluating all the strengths and weaknesses of the reviewed article. Discuss all of the flaws that you found in the author’s evidence and reasoning. Also, point out whether the conclusion provided by the author was well presented or not.
- Add Personal Perspective: Offer your perspective on the original article, do you agree or disagree with the ideas that the article supports or not. Your critical review, in your own words, is an essential part of a good review. Make sure you address all unanswered questions in your review.
- Conclude the Article Review : In this section of the writing process, you need to be very careful and wrap up the whole discussion in a coherent manner. This is should summarize all the main points and offer an overall assessment.
Make sure to stay impartial and provide proof to back up your assessment. By adhering to these guidelines, you can create a reflective and well-structured article review.
Article Review Outline
Here is a basic, detailed outline for an article review you should be aware of as a pre-writing process if you are wondering how to write an article review.
Introduction
- Introduce the article that you are reviewing (author name, publication date, title, etc.) Now provide an overview of the article’s main topic
Summary section
- Summarize the key points in the article as well as any arguments Identify the findings and conclusion
Critical Review
- Assess and evaluate the positive aspects and the drawbacks
- Discuss if the authors arguments were verified by the evidence of the article
- Identify if the text provides substantial information for any future paper or further research
- Assess any gaps in the arguments
- Restate the thesis statement
- Provide a summary for all sections
- Write any recommendations and thoughts that you have on the article
- Never forget to add and cite any references that you used in your article
10 Tips for Writing an Article Review
Have you ever written such an assignment? If not, study the helpful tips for composing a paper. If you follow the recommendations provided here, the process of writing a summary of the article won’t be so time-consuming, and you will be able to write an article in the most effective manner.
The guidelines below will help to make the process of preparing a paper much more productive. Let’s get started!
- Check what kind of information your work should contain. After answering the key question “What is an article review?” you should learn how to structure it the right way. To succeed, you need to know what your work should be based on. An analysis with insightful observations is a must for your piece of writing.
- Identify the central idea: In your first reading, focus on the overall impression. Gather ideas about what the writer wants to tell, and consider whether he or she managed to achieve it.
- Look up unfamiliar terms. Don’t know what certain words and expressions mean? Highlight them, and don’t forget to check what they mean with a reliable source of information.
- Highlight the most important ideas. If you are reading it a second time, use a highlighter to highlight the points that are most important to understanding the passage.
- Write an outline. A well-written outline will make your life a lot easier. All your thoughts will be grouped. Detailed planning helps not to miss anything important. Think about the questions you should answer when writing.
- Brainstorm headline ideas. When choosing a project, remember: it should reflect the main idea. Make it bold and concise.
- Check an article review format example. You should check that you know how to cite an article properly. Note that citation rules are different in APA and MLA formats. Ask your teacher which one to prioritize.
- Write a good introduction. Use only one short paragraph to state the central idea of the work. Emphasize the author’s key concepts and arguments. Add the thesis at the end of the Introduction.
- Write in a formal style. Use the third person, remembering that this assignment should be written in a formal academic writing style.
- Wrap up, offer your critique, and close. Give your opinion on whether the author achieved his goals. Mention the shortcomings of the job, if any, and highlight its strengths.
If you have checked the tips and you still doubt whether you have all the necessary skills and time to prepare this kind of educational work, follow one more tip that guarantees 100% success- ask for professional assistance by asking the custom writing service PapersOwl to craft your paper instead of you. Just submit an order online and get the paper completed by experts.

An Article Review Example
If you have a task to prepare an analysis of a certain piece of literature, have a look at the article review sample. There is an article review example for you to have a clear picture of what it must look like.
Journal Article on Ayn Rand’s Works Review Example
“The purpose of the article is to consider the features of the poetics of Ayn Rand’s novels “Atlas Shrugged,” “We the living,” and “The Fountainhead.” In the analysis of the novels, the structural-semantic and the method of comparative analysis were used.
With the help of these methods, genre features of the novels were revealed, and a single conflict and a cyclic hero were identified.
In-depth reading allows us to more fully reveal the worldview of the author reflected in the novels. It becomes easier to understand the essence of the author’s ideas about the connection between being and consciousness, embodied in cyclic ideas and images of plot twists and heroes. The author did a good job highlighting the strong points of the works and mentioning the reasons for the obvious success of Ayn Rand.“
You can also search for other relevant article review examples before you start.
In conclusion, article reviews play an important role in evaluating and analyzing different scholarly articles. Writing a review requires critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of the article’s content, style, and structure. It is crucial to identify the type of article review and follow the specific guidelines for formatting style provided by the instructor or professor.
The process of writing an article review requires several steps, such as reading the article attentively, identifying the thesis, and formulating an introduction. By following the tips and examples provided in this article, students can write a worthy review that demonstrates their ability to evaluate and critique another writer’s work.
Learning how to write an article review is a critical skill for students and professionals alike. Before diving into the nitty-gritty of reviewing an article, it’s important to understand what an article review is and the elements it should include. An article review is an assessment of a piece of writing that summarizes and evaluates a work. To complete a quality article review, the author should consider the text’s purpose and content, its organization, the author’s style, and how the article fits into a larger conversation. But if you don’t have the time to do all of this work, you can always purchase a literature review from Papers Owl .
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
How to Write an Article Review That Stands Out

An article review is a critical assessment of another writer’s research paper or scholarly article. Such an activity aims to expand one’s knowledge by evaluating the original author’s research.
Of course, writing an article review could be tricky. But a few expert tips and tricks can get you on the right track. That’s what this interesting blog post is all about. So, ensure you read it till the end to make the most out of it.
Table of Contents
A Step-by-step Guide on How to Write an Article Review
Master the art of writing an article review with this step-by-step guide from professional paper help providers.
Step 1: Select the Right Article
The first step is to pick a suitable article for a review. Choose a scholarly source that’s connected to your area of study. You can look for pieces printed in trustworthy journals or by respected authors.
For Example:
For reviewing an article on climate change, consider selecting one from scientific journals like Nature or Science.
Step 2: Read and Understand the Article
It’s super important to read and understand the article before writing your review. Read the article a few times and jot down the notes as you go. Focus on the main arguments, major points, evidence, and how it’s structured.
Let’s say you’re looking at an article on how social media affects mental health. Ensure to take note of the following:
- The number of people involved
- How the data is analyzed
- The Results
Step 3: Structure and Introduction
To start a solid review, start with an introduction that gives readers the background info they need. Must include the article’s title, the author, and where it was published. Also, write a summary of the main point or argument in the article.
“In the article ‘The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health by John Smith, published in the Journal of Psychology:
The author examines the correlation between excessive social media usage and adolescent mental health disorders.”
Step 4: Summarize the Article
In this part, you’ll need to quickly go over the main points and arguments from the article. Make it short but must cover the most important elements and the evidence that backs them up. Leave your opinions and analysis out of it for now.
For instance, you could write:
“The author discusses various studies highlighting the negative effects of excessive social media usage on mental health.
Smith’s research reveals a significant correlation between
Increased social media consumption and higher rates of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem among teenagers.
The article also explores the underlying mechanisms, such as social comparison and cyberbullying. All are contributing to the adverse mental health outcomes.”
Step 5: Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Now that you’ve given a rundown of the article, it’s time to take a closer look. Think about what the author did well and what could have been done better.
Check out the proof they used and if it seems solid. Give a thorough assessment, and use examples from the text to support your thoughts.
For Example
“While the article presents compelling evidence linking social media usage to mental health issues , it is important to acknowledge some limitations in Smith’s study.
The sample size of the research was relatively small. It comprises only 100 participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Additionally, the study primarily focused on one specific age group, namely adolescents. This way, there’s room for further research on other demographic groups.”
Step 6: Express Your Perspective
Here’s your chance to give your two cents and show off your smarts. Put your spin on the article by pointing out the pros, cons, and other potential improvements. Remember to back up your thoughts with facts and sound arguments.
Continuing with the Previous Example
Despite the limitations, Smith’s research offers valuable insights into the complex relationship between social media and mental health.
Future studies could expand the sample size and include a more diverse range of age groups. It is better to understand the broader impact of social media on mental well-being.
Furthermore, exploring strategies for developing digital literacy programs could be potential avenues for future research.
Step 7: Conclusion and Final Thoughts
At the end of your article review, wrap it up with a brief and powerful conclusion. Give a summary of your main points and overall thoughts about the article.
Point out its importance to the field and the impact of the study. Finish off with a thought-provoking conclusion. Give the reader a sense of finality and emphasize the need for additional research or discussion.
For instance
“In conclusion, John Smith’s article provides valuable insights into the detrimental effects of excessive social media usage on adolescent mental health.
While the research has limitations, it serves as a starting point for further investigation in this rapidly evolving field.
By addressing the research gaps and implementing targeted interventions:
We can strive to promote a healthier relationship between social media and mental well-being in our digitally connected society.”
Step 8: Editing and Proofreading
Before submission, set aside some time for editing and proofreading.
Ensure everything makes sense and everything is correct. Check out how it reads and if your points come across clearly. Get feedback from other people to get a different point of view and make it even better.
Types of Article Reviews
In college, you might be asked to write different types of review articles, including:
Narrative Review
This type of review needs you to look into the author’s background and experiences. You have to go through the specialist’s theories and practices and compare them. For the success of a narrative review, ensure that your arguments are qualitative and make sense.
Evidence Review
For a solid evidence paper, you got to put in the work and study the topic. You’ll need to research the facts, analyze the author’s ideas, their effects, and more.
Systematic Review
This task involves reviewing a bunch of research papers and summarizing the existing knowledge about a certain subject. A systematic paper type uses an organized approach and expects you to answer questions linked to the research.
Tips for Writing a Great Article Review
Here are some expert tips you could use to write an exceptional article review:
1. Figure out the main points you want to cover and why they matter.
- It will help you zero in on the key points.
2. Look for and assess pertinent sources, both from the past and present.
- It will give you a better understanding of the article you’re looking at.
3. Come Up with a Catchy Title, Summarize Your Topic in an Abstract, and Select Keywords
- It will help people read your review and get a good idea of what it’s about.
4. Write the main point of a review along with introducing the topic.
- It should help readers get a better grasp of the topic.
Outline for Writing a Good Article Review
Here’s an outline to write an excellent article review.
Introduction
– Begin with a summary of the article
– Put in background knowledge of the topic
– State why you are writing the review
– Give an overview of the article’s main points
– Figure out why the author choose to write something
– Look at the article and consider what it does well and what it could have done better.
– Highlight the shortcomings in the article
– Restate why you are writing the review
– Sum up the main points in a few sentences
– Suggest what could be achieved in the future research
Review Article Example
Title: “The Power of Vulnerability: A Review of Brené Brown’s Daring Greatly”
Introduction:
In her revolutionary book “Daring Greatly,”
Brené Brown, a renowned researcher and storyteller. Delves into vulnerability and how it can positively impact our lives, both professionally and personally.
Brown’s work has gained lots of praise. Since it resonates with people looking to build real connections in a world that often feels isolated.
This article looks to recap the main ideas and concepts from “Daring Greatly.” Also explains why it is such a captivating and insightful read.
Summary of Key Ideas:
“Daring Greatly” is all about how the vulnerability isn’t a sign of being weak. but it’s actually what it takes to be brave, strong and live a full life.
Brene Brown examines how society and culture can make it hard to be vulnerable. And, how fear of being judged or shamed stops us from being our authentic selves.
The book puts a lot of emphasis on shame and how it affects us.
Brown explains that shame thrives when it’s kept hidden away and can only be cured by being open, understanding, and compassionate.
By admitting our weaknesses, we can create meaningful connections and a sense of community.
Brown looks into the connection between being open to vulnerability and unleashing creative leadership and innovation.
She uses her own experiences and research to support her viewpoint. The book also gives useful advice on how to include vulnerability in different parts of life. Such as relationships, parenting, and the workplace.
Strengths of the Book:
Brown’s book is remarkable for her ability to mix her own experiences with comprehensive research. Combining her stories and evidence makes the material engaging and easy to understand.
Plus, her writing style is so friendly that readers feel they’re being acknowledged and accepted.
There’s advice on how to be kind to yourself. Set your limits, and accept that things won’t always be perfect. It’s like a toolkit to help you build strength and make positive changes.
Final Verdict
This book is really helpful for everyone, no matter who you are. It can help you figure out how to grow in life, have better relationships, and become a better leader. Plus, since it applies to all kinds of people, everyone can get something out of it.
If you want to write a great article review, it’s important to pick the right article, understand and analyze it critically. Finally, express your thoughts on it clearly. Ensure to stay impartial, back up your points with evidence, and write clearly and coherently.
Still if you are having troubles writing an article review, don’t hesitate to count on the expertise of our writers .
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
Article Review
Article Review Writing: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide with Examples

People also read
Learn How to Write an Editorial on Any Topic
Best Tips on How to Avoid Plagiarism
How to Write a Movie Review - Guide & Examples
A Complete Guide on How to Write a Summary for Students
Write Opinion Essay Like a Pro: A Detailed Guide
Evaluation Essay - Definition, Examples, and Writing Tips
How to Write a Thematic Statement - Tips & Examples
How to Write a Bio - Quick Tips, Structure & Examples
How to Write a Synopsis – A Simple Format & Guide
How to Write a Comparative Essay – A Complete Guide
Visual Analysis Essay - A Writing Guide with Format & Sample
List of Common Social Issues Around the World
Writing Character Analysis - Outline, Steps, and Examples
11 Common Types of Plagiarism Explained Through Examples
A Detailed Guide on How to Write a Poem Step by Step
Detailed Guide on Appendix Writing: With Tips and Examples
Struggling to write a review that people actually want to read? Feeling lost in the details and wondering how to make your analysis stand out?
You're not alone!
Many writers find it tough to navigate the world of article reviews, not sure where to start or how to make their reviews really grab attention.
No worries!
In this blog, we're going to guide you through the process of writing an article review that stands out. We'll also share tips, and examples to make this process easier for you.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is an Article Review?
- 2. Types of Article Reviews
- 3. Article Review Format
- 4. How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
- 5. Article Review Outline
- 6. Article Review Examples
- 7. Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
What is an Article Review?
An article review is a critical evaluation and analysis of a piece of writing, typically an academic or journalistic article.
It goes beyond summarizing the content; it involves an in-depth examination of the author's ideas, arguments, and methodologies.
The goal is to provide a well-rounded understanding of the article's strengths, weaknesses, and overall contribution to the field.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Article Reviews
Article reviews come in various forms, each serving a distinct purpose in the realm of academic or professional discourse. Understanding these types is crucial for tailoring your approach.
Here are some common types of article reviews:
Journal Article Review
A journal article review involves a thorough evaluation of scholarly articles published in academic journals.
It requires summarizing the article's key points, methodology, and findings, emphasizing its contributions to the academic field.
Take a look at the following example to help you understand better.
Example of Journal Article Review
Research Article Review
A research article review focuses on scrutinizing articles with a primary emphasis on research.
This type of review involves evaluating the research design, methodology, results, and their broader implications.
Discussions on the interpretation of results, limitations, and the article's overall contributions are key.
Here is a sample for you to get an idea.
Example of Research Article Review
Science Article Review
A science article review specifically addresses articles within scientific disciplines. It includes summarizing scientific concepts, hypotheses, and experimental methods.
The type of review assesses the reliability of the experimental design, and evaluates the author's interpretation of findings.
Take a look at the following example.
Example of Science Article Review
Critical Review
A critical review involves a balanced critique of a given article. It encompasses providing a comprehensive summary, highlighting key points, and engaging in a critical analysis of strengths and weaknesses.
To get a clearer idea of a critical review, take a look at this example.
Critical Review Example
Article Review Format
When crafting an article review in either APA or MLA format, it's crucial to adhere to the specific guidelines for citing sources.
Below are the bibliographical entries for different types of sources in both APA and MLA styles:

How to Write an Article Review? 10 Easy Steps
Writing an effective article review involves a systematic approach. Follow this step-by-step process to ensure a comprehensive and well-structured analysis.
Step 1: Understand the Assignment
Before diving into the review, carefully read and understand the assignment guidelines.
Pay attention to specific requirements, such as word count, formatting style (APA, MLA), and the aspects your instructor wants you to focus on.
Step 2: Read the Article Thoroughly
Begin by thoroughly reading the article. Take notes on key points, arguments, and evidence presented by the author.
Understand the author's main thesis and the context in which the article was written.
Step 3: Create a Summary
Summarize the main points of the article. Highlight the author's key arguments and findings.
While writing the summary ensure that you capture the essential elements of the article to provide context for your analysis.
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis
In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position.
This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Step 5: Evaluate the Author's Evidence and Methodology
Examine the evidence provided by the author to support their thesis. Assess the reliability and validity of the methodology used.
Consider the sources, data collection methods, and any potential biases.
Step 6: Analyze the Author's Writing Style
Evaluate the author's writing style and how effectively they communicate their ideas.
Consider the clarity of the language, the organization of the content, and the overall persuasiveness of the article.
Step 7: Consider the Article's Contribution
Reflect on the article's contribution to its field of study. Analyze how it fits into the existing literature, its significance, and any potential implications for future research or applications.
Step 8: Write the Introduction
Craft an introduction that includes the article's title, author, publication date, and a brief overview.
State the purpose of your review and your thesis—the main point you'll be analyzing in your review.
Step 9: Develop the Body of the Review
Organize your review by addressing specific aspects such as the author's thesis, methodology, writing style, and the article's contribution.
Use clear paragraphs to structure your analysis logically.
Step 10: Conclude with a Summary and Evaluation
Summarize your main points and restate your overall assessment of the article.
Offer insights into its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with any recommendations for improvement or suggestions for further research.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Article Review Outline
Creating a well-organized outline is an essential part of writing a coherent and insightful article review.
This outline given below will guide you through the key sections of your review, ensuring that your analysis is comprehensive and logically structured.
Refer to the following template to understand outlining the article review in detail.
Article Review Format Template
Article Review Examples
Examining article review examples can provide valuable insights into the structure, tone, and depth of analysis expected.
Below are sample article reviews, each illustrating a different approach and focus.
Example of Article Review
Sample of article review assignment pdf
Tips for Writing an Effective Article Review
Crafting an effective article review involves a combination of critical analysis, clarity, and structure.
Here are some valuable tips to guide you through the process:
- Start with a Clear Introduction
Kick off your article review by introducing the article's main points and mentioning the publication date, which you can find on the re-title page. Outline the topics you'll cover in your review.
- Concise Summary with Unanswered Questions
Provide a short summary of the article, emphasizing its main ideas. Highlight any lingering questions, known as "unanswered questions," that the article may have triggered. Use a basic article review template to help structure your thoughts.
- Illustrate with Examples
Use examples from the article to illustrate your points. If there are tables or figures in the article, discuss them to make your review more concrete and easily understandable.
- Organize Clearly with a Summary Section
Keep your review straightforward and well-organized. Begin with the start of the article, express your thoughts on what you liked or didn't like, and conclude with a summary section. This follows a basic plan for clarity.
- Constructive Criticism
When providing criticism, be constructive. If there are elements you don't understand, frame them as "unanswered questions." This approach shows engagement and curiosity.
- Smoothly Connect Your Ideas
Ensure your thoughts flow naturally throughout your review. Use simple words and sentences. If you have questions about the article, let them guide your review organically.
- Revise and Check for Clarity
Before finishing, go through your review. Correct any mistakes and ensure it sounds clear. Check if you followed your plan, used simple words, and incorporated the keywords effectively. This makes your review better and more accessible for others.
In conclusion , writing an effective article review involves a thoughtful balance of summarizing key points, and addressing unanswered questions.
By following a simple and structured approach, you can create a review that not only analyzes the content but also adds value to the reader's understanding.
Remember to organize your thoughts logically, use clear language, and provide examples from the article to support your points.
Ready to elevate your article reviewing skills? Explore the valuable resources and expert assistance at MyPerfectWords.com.
Our team of experienced writers is here to help you with article reviews and other school tasks.
So why wait? Get our essay writing service today!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Dr. Barbara is a highly experienced writer and author who holds a Ph.D. degree in public health from an Ivy League school. She has worked in the medical field for many years, conducting extensive research on various health topics. Her writing has been featured in several top-tier publications.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
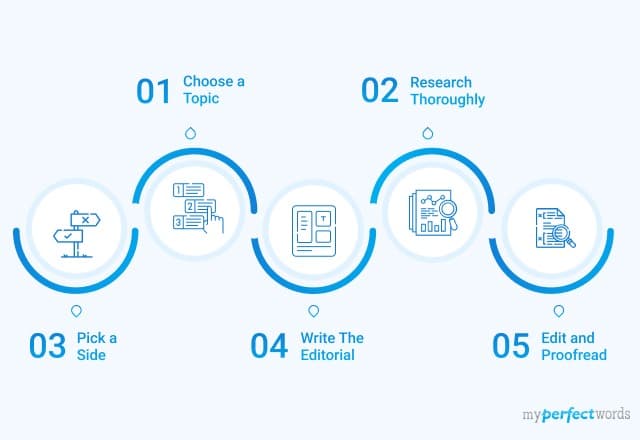

How to Write an Article Review: Tips, Outline, Format

Have you been assigned an article review paper, but you are unsure where to start, or what is a review article at all? There is no need to worry, as EssayService has put together a top guide for you! Find out all about an article review to master your assignment.
What is an Article Review?
In simple terms, an article review essay is like a summary and evaluation of another professional or expert's work. It may also be referred to as a literature review that includes an outline of the most recent research on the subject, or a critical review that focuses on a specific article with smaller scope. Article review can be used for many reasons; for example, a teacher or lecturer may wish to introduce their students to a new subject by reviewing a professional's piece. You can also learn about the most important works of specialists in your industry by looking at relevant article review examples.
Also, a newspaper article review example could be a journalist writing a critique about another competitor's published work.
In comparison, a book review article example could be critiqued by a fellow author or even a student in the chosen field.
Depending on the critique criteria and the work being reviewed, there could also be certain points asked for addition which should be checked and noted by the lecturer or supervisor. Otherwise, follow the article review guidelines from our write my essay service to complete the assignment in no time.
Key points when writing an article review:
Use the article review template from our paper writing service to get through the assignment as fast as possible so you will not waste any time.

How to Start an Article Review?
- Firstly read the work being reviewed as much as possible and look up key phrases and words that are not understood.
- Discuss the work with other professionals or colleagues to collect more opinions and get a more balanced impression.
- Highlight important sections or sentences and refer this to your knowledge in the topic, do you agree or disagree and what does this contribute to the field?
- Then re-write the key arguments and findings into your own words this will help gain better understanding into the paper. This can be just written as an outline also and will help decide which points are wanted to discuss later.
If you feel you do not have enough time to create a critique worthy of your time, then come to EssayService and order a custom Article review online.
You can order essay independent of type, for example:
- nursing essay;
- law essay writing;
- history essays.
The best way to write an effective essay would be to draw up a plan or outline of what needs to be covered and use it for guidance throughout the critique.

Article Review Formatting
There is no one-fits-all article format you can follow in your review. In fact, the formatting is dictated by the citation style specified by your professor in the task requirements. Thus, be sure to clarify the preferred style before you jump straight to writing to handle the given assignment right.
APA Format Article Review
Writing an APA style article review, you will most likely use articles from journals, websites, and newspapers. For each source, you will have to create properly formatted bibliographical entries.
Here is how to write an article review APA:
- Journal: Author’s last name, First and middle initial. (Year of Publication). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Website: Last name, initials. (Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Newspaper: Last name, initials. (Date of Publication). Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
MLA Format Article Review
Tips for citing sources in an article review MLA format:
- Journal: Last name, First name Middle initial. “Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year of Publication): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Accessed.
- Website: Last, First M. “Title.” Website Title. Publisher, Date Published. Web. Date Accessed.
- Newspaper: Last, First M. “Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date of Publication: Page(s). Print.
Article Review Outline
Planning out an outline for your paper will help writing and to put it together so therefore saving you time in the long run.
Some questions to help with the outline of a critique:
- What does the article set out to do or prove?
- Are the main ideas clear and defined?
- How substantial is the evidence?
- Where does the article fit in its specific field?
- Does it provide new knowledge on the topic?
- What are the central theories and assumptions?
- Is the writer conclusive at getting their point across?
Here is a typical article review format to follow:

Use our article review template to get through the assignment as fast as possible so you will not waste any time.
Article Review Title
Firstly start with creating a title for your critique, this should be something to do with the focus of the work that is being reviewed. An approach could be to make it descriptive or also in a more creative way think of something that intrigues the reader. After the title, this is a good place to correctly cite the paper being critiqued and include the important details for example, the author, title of publication, any page references. The style in which the citation is written will depend on which is best for this type of work being reviewed.
Article Review Introduction
The introduction should be a brief glimpse into what the author was writing about and any other details the audience will find interesting. Maybe some background details on the piece that is not already known or something that contributes to the review itself. It is a good idea to start by introducing the work at the start of the paragraph and then include a ' hook '. Include the writer's thesis if there is one and put it at the end but include your own thesis towards the critique near the beginning of this section.
Article Review Body
When constructing the summary section, write down the important points and findings in the piece in your own words. Include how the claims are supported and backed up with evidence but use direct quotes as sparing as possible. Do not put in any information known to professionals in the field or topic, but detail any conclusions the work came to. Make sure the paper is not just copied word for word and is actually summarized by yourself; this will also help the review stage.
To make an accurate critique, break down the work and express opinions on whether it achieves its goals and how useful it is in explaining the topics for an article review. Decide if the paper contributes to its field and is important and credible to the given field. Back up all the claims with evidence from the summary or another source. If using another text, remember to cite it correctly in the bibliography section. Look at how strong the points are and do they contribute to the argument. Try to identify any biases the writer might have and use this to make a fair critique. This part is only for opinions of the piece's significance, not including whether you liked it. Furthermore, the different types of audiences that would benefit from the paper can be mentioned in this section.
Article Review Conclusion
In the conclusion section of the critique, there should only be one or two paragraphs in which a summary of key points and opinions in the piece are included. Also, summarize the paper's significance to its field and how accurate the work is. Depending on the type of critique or work evaluated, it is also possible to include comments on future research or the topic to be discussed further.
If other sources have been used, construct a bibliography section and correctly cite all works utilized in the critique.
The APA format is very common in an article review and stands for American Psychology Association. This will include a 'references list' at the end of the critique and in-text citations, mentioning the author's last name, page number, and publication date.
There are also MLA and Chicago formats for citations with slight differences in a name, like using a 'works cited' page for MLA. More can be found in this guide on the subtle differences between the types of citation methods under the heading 'Creating a bibliography.'
Article Review Example
Article review writing tips.
If you are interested in best scholarships for high school seniors , the following tips will be handy while writing your essay or article:
- Allow enough time to complete the research and writing of the critique. The number one problem with creating a critique is running out of time to make it the best it can be. This can be avoided by effective planning and keeping on time with the deadlines you set out.
- Collect twice more research than you think is needed to write a review. This will help when coming to the writing stage as not all the information collected will be used in the final draft.
- Write in a style that is compatible with the work being critiqued. This will be better for whoever requested the critique and also will make paper easier to construct.
- A summary and evaluation must be written. Do not leave out either part as one complements the other and is vital to create a critique worth reading.
- Be clear and explain well every statement made about the piece . Everything that is unknown to professionals in the field should be explained and all comments should be easy to follow for the reader.
- Do not just describe the work, analyze and interpret it. The critique should be in depth and give the audience some detailed interpretations of the work in a professional way.
- Give an assessment of the quality in the writing and of what standard it is. Evaluate every aspect in the paper so that the audience can see where it fits into the rest of the related works. Give opinions based on fact and do not leave any comments without reason as this will not count for anything.
How to Write an Article Review?
Writing a review article is not that hard if you know what steps to take. Below is a step-by-step guide on how to write a review example quickly and easily.
- Before You Start
Before you start writing your review essay, there are a few pre-writing steps to take. The pre-writing process should consist of the following steps:
- Pick the subject of your review (if it wasn’t specified by your professor);
- Read the article fully multiple times;
- Summarize the main ideas, points, and claims made in the article;
- Define the positive (strong) aspects;
- Identify the gaps or inconsistencies;
- Find the questions that remained unanswered.
All these steps are needed to help you define the direction for your review article and find the main ideas you’d like to cover in it.
After you review articles and define the key ideas, gaps, and other details, map out your future paper by creating a detailed outline.
Here are the core elements that must be included:
- Pre-title page;
- Corresponding author details (optional);
- Running head (only for the APA style);
- Summary page (optional);
- Title page;
- Introduction;
- References/Works Cited;
- Suggested Reading page (optional);
- Tables and Figure Legends (if required by the professor).
This step is vital to organize your thoughts and ensure a proper structure of your work. Thus, be sure not to skip this step.
When you have an outline, students can move on to the writing stage by formulating compelling titles for their article reviews. Titles should be declarative, interrogative, or descriptive to reflect the core focus of the paper.
- Article Citation
After the title should follow a proper citation of the piece you are going to review. Write a citation according to the required style, and feel free to check out a well-written article review example to see how it should look like.
- Article Identification
Start the first paragraph of your review with concise and clear article identification that specifies its title, author, name of the resource (e.g., journal, web, etc.), and the year of publication.
Following the identification, write a short introductory paragraph. It should be to the point and state a clear thesis for your review.
- Summary and Critique
In the main body of your article review, you should first make a detailed but not too extensive summary of the article you reviewed, its main ideas, statements, and findings. In this part, you should also reflect on the conclusion made by the author of the original article.
After a general summary should follow an objective critique. In this part of your paper, you have to state and analyze the main strengths and weaknesses of the article. Also, you need to point out any gaps or unanswered questions that are still there. And clarify your stance on the author’s assertions.
Lastly, you need to craft a compelling conclusion that recaps the key points of your review and gives the final, logical evaluation of the piece that was reviewed.
After this, proofread your work and submit it.
No Time Left For Your Due Assignment
Now we hope you understand how to write a review of an article. However, we know that writing a great article review requires a lot of time to properly research the work. To save your precious time, visit EssayService, where our team of top essay writers will help you. The team can even provide you with the best article review topics! You can learn more at the college essay writing service page where we have free guides with all the essay writing tips and tricks!
Frequently asked questions
She was flawless! first time using a website like this, I've ordered article review and i totally adored it! grammar punctuation, content - everything was on point
This writer is my go to, because whenever I need someone who I can trust my task to - I hire Joy. She wrote almost every paper for me for the last 2 years
Term paper done up to a highest standard, no revisions, perfect communication. 10s across the board!!!!!!!
I send him instructions and that's it. my paper was done 10 hours later, no stupid questions, he nailed it.
Sometimes I wonder if Michael is secretly a professor because he literally knows everything. HE DID SO WELL THAT MY PROF SHOWED MY PAPER AS AN EXAMPLE. unbelievable, many thanks
You Might Also Like

New Posts to Your Inbox!
Stay in touch
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER FEATURE
- 04 December 2020
- Correction 09 December 2020
How to write a superb literature review
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Literature reviews are important resources for scientists. They provide historical context for a field while offering opinions on its future trajectory. Creating them can provide inspiration for one’s own research, as well as some practice in writing. But few scientists are trained in how to write a review — or in what constitutes an excellent one. Even picking the appropriate software to use can be an involved decision (see ‘Tools and techniques’). So Nature asked editors and working scientists with well-cited reviews for their tips.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-03422-x
Interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Updates & Corrections
Correction 09 December 2020 : An earlier version of the tables in this article included some incorrect details about the programs Zotero, Endnote and Manubot. These have now been corrected.
Hsing, I.-M., Xu, Y. & Zhao, W. Electroanalysis 19 , 755–768 (2007).
Article Google Scholar
Ledesma, H. A. et al. Nature Nanotechnol. 14 , 645–657 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Brahlek, M., Koirala, N., Bansal, N. & Oh, S. Solid State Commun. 215–216 , 54–62 (2015).
Choi, Y. & Lee, S. Y. Nature Rev. Chem . https://doi.org/10.1038/s41570-020-00221-w (2020).
Download references
Related Articles

- Research management

Londoners see what a scientist looks like up close in 50 photographs
Career News 18 APR 24
Deadly diseases and inflatable suits: how I found my niche in virology research
Spotlight 17 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships

Researchers want a ‘nutrition label’ for academic-paper facts
Nature Index 17 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Structure peer review to make it more robust
World View 16 APR 24
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
- Other Guides
- Article Review: How's and Why's Explained
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
Article Review: How's and Why's Explained

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
An article review is a critical evaluation of a published journal article. It typically provides an overview of the main points, the author’s arguments, and general quality. Article reviews are usually conducted as part of an academic course or as professional development for educators.
Preparing material before writing an article review requires a thorough study of facts. Assessing what should be stated in your paper plays a crucial role in your research process. The main difficulty is that you should consider the specified information with extra care and formulate your thoughts clearly when writing. It is impossible to write a review article without studying the work. You can't conduct a fair review without having a certain knowledge base. Provided information must be reasonable and contain valid arguments. If these basic characteristics are absent, it indicates that such an evaluation is unfair.
What Is a Review Article?
Writing this type of professional paper requires preparation. A review article or a literature review is an article critique of another author's work that was published previously. Its purpose is to survey existing research and provide readers with your critical assessment of this specific topic. You will be able to create a high-quality article review using these principles:
- main topic in-depth analysis;
- generalization and classification;
- comparison of information from several sources.
When specifying a definition of a review article, a thorough analysis of relevant information and an appropriate database use are a must. The main task is to identify the topic correctly and share the results of your research. The subject of paperwork and the conclusions' validity of its author are your main targets.
Review Article Structure
Preparation for writing a review contains several stages. They include research and making your own opinion. Without an outline of your review article , nothing will work. So it is worth considering an outline and focusing on this issue as well. In addition, your finished work should include:
- criticism and comparison (introduction);
- detailed topic analysis;
- new information.
Finished work should contain a personal conclusion. If you don't include it, an article will be incomplete. You can learn more about how to write such paperwork correctly by exploring the other information below.
How to Write a Good Introduction for a Review Article
Preliminary preparation for writing a piece in a new format will let you:
- determine the author’s focus;
- mark arguments;
- pay attention to structuring.
Studying headlines and arguments plays a critical role in your finished work. Eventually, it makes it more helpful to readers. You should also focus on the introduction of how to start an essay . The introduction makes it possible to get acquainted with a perspective of its topic. For greater efficiency, it is worth pointing out the main thesis. It is important to display issues raised in an article when writing an introduction. When you start your paper, make sure your introduction is catchy enough. It should be interesting and bring some value to your readers. The first few sentences will be your hook for grabbing attention. Tell your audience why you have chosen that particular topic. Also, mention why the subject you surveyed is important.
The Body of Review Article
When studying materials, you should identify different ways of argumentation . Then you will have to highlight them in your work. Please note that the body of article review is an essential component that needs careful work on its details. Remember that your body paragraphs will vary depending on your topic. The bulk of the work includes:
- describing the author's arguments;
- providing a personal assessment.
Study the text of the first paragraphs. Then try to retell them in your own words. Retelling will help you understand your topic better and transfer your attention from the background to the foreground. Ultimately, you will have to summarize what you’ve read. Tell your opinion about its choice of arguments and evidence base.
How to Write Conclusion to Review Article
Writing a conclusion is always hard. You will need to outline the topic raised by the author and share your impressions. Use the citation from the author's work. Identify the most compelling arguments. Then address them in the conclusion of your review article. Also you can try to use our Conclusion Generator to find interesting ideas. You can’t finish reviewing without providing new information. This will mean that your research was unproductive. Discover new sides of a raised topic. Then search for the presence of arguments from similar literature. It will let you compile a summary of materials you have read and offer food for thought.
Review Article Format
Article review format is necessary for a correct presentation of data about used articles and scientific papers. While writing research, you will need to use citations of both the author and other reliable sources. Depending on your choice, you should write a description. It is worth stopping at APA in some cases. This type of data presentation is more common. There are different rules for writing descriptions of citations in MLA format. Special attention is paid to allocating primary information. Initials, titles, indications of sources, and other information are drawn in accordance with the rules. Looking for a book review format ? We have one more blog dedicated to this theme.
APA Format Article Review
Knowing how to cite a quote is mandatory because they can be used as arguments. Studying materials and presenting data about sources in a certain style requires careful focus on the order of placement of bibliographic data. Choosing APA format for article review is a popular decision for authors who prefer citing information from Internet sources, magazines, and newspapers.
MLA Format Article Review
To write this type of paper, people use quotes from literature covering the given topic. Formatting choice depends on your personal preference. However, if you have decided what style to use, you still should follow some basic rules. Article review in MLA format assumes an indication of publication date, bibliographic data, and titles. Don’t make mistakes when citing authors. Take your time to study the requirements.
How to Write an Article Review
In order to write such a paper, you should decide on your goal. As an author, you should use your analytical skills, critical thinking, and logical arguments. If you still don’t understand how to write an article review, you should follow the tips below:
- come up with some catchy title;
- use the author's quotes of your publication;
- don’t forget to include the title that you are analyzing;
- reflect your main ideas in the introduction;
- write a resume.
The final part is displaying your material's strengths and weaknesses. Identifying your opinion about the work is also a goal. Use informed criticism to achieve the desired result.
Last Thoughts on Writing a Review Article
A review article is a type of professional essay writing . So you need to study its subject carefully. Use multiple sources and highlight the main arguments. Then form your own opinion on the given topic. In conclusion of your article review, you should bring new arguments for or against the author's opinion. Use the authors' work with an excellent reputation and quote them in your article sections. Finally, don't forget to summarize and point out your work's strengths and weaknesses. Healthy criticism will let you draw up proper conclusions and challenge the author's opinion.
If you need help with your article review, feel free to contact our essay writing service. Our proficient academic writers will execute a perfect paper while being in touch for immediate revisions all the time.

Rachel R. Hill is a real educational devotee. She prides in writing exceptional general guides while listening to every need of students.
You may also like

FAQ About Article Review
1. what is a systematic article review.
Reviews of publications that highlight important research are thoroughly analyzed by peers and other representatives in its field. Writing a systematic review article will let you provide strong and weak arguments. Besides, it will help you give your reasons and draw correct conclusions. This will require exploring other relevant articles and databases. Research work allows you to identify erroneous conclusions. It also allows you to produce quality material for interested readers.
2. How long should an article review be?
Preparing and writing a review article requires a serious approach to the work being studied. It is rather difficult to determine how much such an article should take. Many things depend on your chosen topic: the volume of source material (number of words), research quality carried out. Ultimately, you will need to show the author's arguments as well as bring yours in order to support or refute a central thought.
3. How to title an article review?
When writing a review, selecting the right title is also an important task. It is permissible to use interrogative, summarizing, and other sentences to fully reflect the main idea. Heading becomes the focus for drawing attention, so it should be appropriate for your work. The finished review article should reflect the selected topic. It also should present a composed heading for a better understanding of readers.
4. Why articles are peer-reviewed?
In their works, researchers raise important questions that cannot be ignored. Reviewing materials allows you to determine your conclusion’s validity and to achieve better results. Conducting new independent research guarantees discovering new sides of an issue. In addition, more readers manage to study the journal article review.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
How to Write an Article Review: Guide with Examples - Studybay

The Knowledge Nest - Community and Society
Welcome to The Knowledge Nest, your go-to resource for all things related to education, learning, and academic success in the community and society. In this insightful guide, we will delve into the art of writing a stellar article review.
1. Introduction to Article Reviews
Article reviews are essential in academic and professional settings as they allow individuals to evaluate and analyze research papers, scholarly articles, and other sources of information. By writing an article review, you not only enhance your critical thinking skills but also contribute to the knowledge base in your field of study.
When writing an article review, it is crucial to provide a comprehensive analysis and offer valuable insights. Here at The Knowledge Nest, we believe in empowering students and researchers to produce high-quality reviews that stand out from the rest.
2. Structure of an Article Review
To craft an exceptional article review, it is essential to follow a well-structured format. Here is a breakdown of the typical sections to include:
- Introduction: Begin your review by presenting the title, author, and publication details of the article you are reviewing. Provide a brief overview of the author's background and the relevance of the article to your field of study.
- Summary: Summarize the main points, arguments, and key findings of the article. Be concise yet comprehensive in your summary.
- Analysis: Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of the article. Evaluate the author's methodology, sources, and supporting evidence. Reflect on the article's relevance and contribution to the field.
- Implications: Discuss the implications of the article's findings and how they relate to existing literature or research in your domain. Highlight any unanswered questions and potential areas for future exploration.
- Conclusion: Sum up your overall assessment of the article. Reiterate its significance and suggest further avenues for research, if applicable.
3. Examples of Well-Written Article Reviews
Here at The Knowledge Nest, we understand that learning by example is an effective way to grasp complex concepts. Below, we have provided a couple of examples to illustrate what a well-written article review should look like:
Example 1: Title of the Article Review
In this example, we present a review of an article titled "Exploring the Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity." The review delves into the author's research methodology, provides a detailed analysis of the findings, and offers insights into the implications of the study.
Example 2: Another Title of the Article Review
Here, we showcase a review of an article titled "The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Transforming Healthcare." The review highlights the strengths and limitations of the research, discusses the potential implications on the healthcare industry, and suggests avenues for further research in this burgeoning field.
4. Tips for Writing an Outstanding Article Review
To help you excel in writing article reviews, we have compiled a list of valuable tips:
- Thoroughly read and understand the article: Before you begin writing, carefully read through the article multiple times to ensure a comprehensive understanding of its content and arguments.
- Take meticulous notes: Make annotations and jot down key points and relevant quotes while reading the article. This will make it easier for you to structure your review effectively.
- Use a formal and academic tone: Since article reviews are scholarly pieces, maintain a professional tone throughout your writing. Avoid using slang or colloquial language.
- Support your claims with evidence: When offering critique or analysis, back up your statements with evidence from the article or other reputable sources. This demonstrates your credibility as a reviewer.
- Proofread and edit: Before submitting your review, thoroughly proofread it to eliminate any grammatical or spelling errors. Pay attention to the overall flow and coherence of your writing.
Writing an article review is an invaluable skill that can enhance your academic and professional growth. By following our comprehensive guide, you will be equipped with the knowledge and tools needed to produce outstanding article reviews that stand out in the competitive landscape.
Remember, continuous practice and refinement of your writing skills will ultimately lead to mastery. The Knowledge Nest is here to support you on your journey towards excellence. Start writing remarkable article reviews today!
Check out our blog at http://theknowledgenest.org/blog/article-review-example for more educational resources and insightful articles.

The Effects of Homeschooling: Essay Example and Writing Tips

Good Topics to Write About ✏️ Essay Themes
Come Up With an Amazing Case Study Template - Studybay
How Do You Write An Argumentative Essay For Middle School

Creative Research Proposal Topics

How to Write a Good Term Paper (Format, Structure, Outline)

Buy College Papers Online - High-Quality and Affordable

Pay For Case Study - Studybay

Derivative of Sec x: A Quick Math Tutorial

Pre-Calculus Homework Help - The Knowledge Nest
- Good Writing
- Revising & Rewriting
- Nonfiction Writing
- Academic Writing
- Travel Writing
- Literary Agents
- Getting Published
- Fiction Writing
- Self-Publishing
- Marketing & Selling Books
- Building a Blog
- Making Money Blogging
- Boosting Blog Traffic
- Online Writing
- eZine Writing
- Making Money Online
- Non-Fiction Writing
- Magazine Writing
- Pitching Query Letters
- Working With Editors
- Professional Writers
- Newspaper Writing
- Making Money Writing
- Running a Writing Business
- Privacy Policy
How to End Your Article: 5 Ways to Write a Powerful Conclusion
- by Laurie Pawlik
- December 30, 2022
- 13 Comments
A good article ends with a conclusion that surprises the reader, yet makes sense. Writing an ending that summarizes your ideas is difficult, but not impossible.
Endings are important. So important, in fact, that some writers say a strong ending is more important than a strong beginning. I disagree. If you don’t hook your reader from the start, she’ll never get to the end.
Nevertheless, ending your article on a high note gives it power to stick with the reader forever. Or a really long time. In this article, you won’t find a “one size fits all” tip on how to end your article because it doesn’t exist. You will, however, find the five most effective ways to write a conclusion.
“It is always important to know when something has reached its end,” writes Paulo Coelho in The Zahir: A Novel of Obsession . “Closing circles, shutting doors, finishing chapters, it doesn’t matter what we call it; what matters is to leave in the past those moments in life that are over.”
Sometimes the ending practically writes itself. Other times you have to wrestle that ending to the ground. Either way, you must be alert. Writing a great conclusion is easier when you have a variety of tools and techniques to choose from. Who goes into battle empty-handed? These five tips for ending your article will help you find the right way to say “The End” without coming out and saying…The End.
Whether you’re writing an article for a national magazine or blogging a little blurb, keep the ending at the back of your mind. What impression do you want to leave the readers with? How do you want them to feel, what do you want them to do? As you research, write and revise your article, stay alert to possible endings. Play with different ideas.
5 Powerful Ways to End Your Article
Some writers say the conclusion of an article could work just as well as the introduction – with a slight modification. I think it depends on your article, writing style, and audience.
Your conclusion rounds out the article, ties up the loose ends. It’s not an afterthought. To be powerful, a strong ending has to develop naturally from the article, essay, or chapter. The conclusion has to both surprise readers and make them feel like they should’ve known it was coming all along.
1. End with a quotation that looks back or looks forward
You don’t necessarily want to add anything too new to the end of your article, but you can include a surprising twist. Readers want the same, but different. So do editors and publishers. So, give your reader more of what you’ve been doing in the article — ending with a little poke in the ribs.
“…don’t make the surprise so foreign that it seems out of place and doesn’t tie into the article. If the quote or surprising statement seems out of place, then you only leave the reader confused, and you have lost the value of what you have built throughout the article,” writes Roger Palms in Effective Magazine Writing: Let Your Words Reach the World .
2. Invite the reader to go in a different direction
The most powerful ending neatly wraps up the article and gives the reader something new to think about. This is difficult for most writers – even seasoned freelancers. Imagine your ending as a fork in the road. Where do you want readers to go? Write two or three different endings, then take a break. Have a nap, visit another world. Now how does the ending feel? Maybe it needs more work, or maybe one of your conclusions does the job.
The bad news is there is no one perfect way to write a powerful ending to your article. This is also the good news! If there was one perfect way to end it, then all writers would use that conclusion. And it would lose its power. You need to find the right ending for your article.
3. Finish with a dollop of something different
“If you say in the first chapter that there is a rifle hanging on a wall, in the second or third chapter it absolutely must go off,” says Paula LaRocque, author of The Book on Writing: The Ultimate Guide to Writing Well . “If it’s not going to be fired, it shouldn’t be hanging there.”
This type of conclusion might involve weaving in (not tacking on) a whole new anecdote, or including a new bit of information that adds to the story you introduced in the lead or body of the article. Many professional freelance writers like to end with a relevant story, a little vignette, something that gives the reader a feeling that the essence of the article or essay was captured.
How do I end my articles? I circle back to the beginning somehow – it depends on the topic, interviewees, audience, article length, and deadline. I often include more information about something I introduced earlier in the article.
“What is this ‘more’ you speak of?”, you ask? It depends on the article you’re writing. That’s the pain and power of writing: so much simply depends on so many things. If you know how to end your article or essay but your writing is flimsy and weak, read How to Write Powerful Words That Grab Attention .
4. If you must summarize, do it with style
Some endings need to clearly restate and summarize the article’s main argument. Other articles don’t need a summary because there wasn’t a stated theme. Does your article need a summary? Ask it. Ask yourself as the writer. Maybe even ask a beta reader. If you’re arguing for or describing something complicated or new to readers, perhaps a summary is the most powerful way to end the article.
A summary isn’t the most creative way to end your article, but you can spice it up with different literary techniques. Use sensory details to fire up your writing, or bring an inanimate object alive with personification. Learn different types of edgy and quirky writing . Sometimes it’s not what you write…it’s how you write it.
Here’s how NOT to end an article:
- “In summary, I would like to say….”
- “The End.”
- “In conclusion, may I reiterate….”
- “I know I said this in my intro and in paragraphs three through thirty, but it cannot be overstated that…”
I take a week to write magazine articles. This allows my brain and the article to tell me how to write a powerful ending. It’s never perfect, but it is as good as I can write it.
5. Circle back to the beginning
The final, most powerful tip on how to end an article: write a conclusion that refers back to your introduction or opening statements. This, says some professional freelance writers, gives readers a feeling of arrival.
You could pick up a word, a phrase, or part of an anecdote from your introduction, and round it out more. Don’t just repeat it; expand on it, color it in, give it some texture and depth. Ideally, leave readers with a hook at the end of your article – something that lodges in their minds so deeply that they can’t forget it right away.
Good writing isn’t just about learning how to end an article with a strong conclusion or conclude an essay with a summary of all your main points. Rather, good writing is about weaving all the aspects of the whole piece together.
Are you writing for a magazine?
In 11 Most Popular Articles to Write for Magazines (Freelance Writing is Easier Than You Think!) I share tips for getting published in magazines.
Getting published in print and online magazines is a lot easier when you know what types of articles editors and publishers need.
I welcome your thoughts on writing good endings – and learning how to listen to your article for the ending it wants to tell. Remember that writing a good ending involves editing and revising; it’s not something you can just tack onto the end.
Need encouragement? Stay in touch! Get my free weekly email

Your First Name Email
* This blog contains affiliate links . If you click a link and buy the product, I'll earn a small commission, but you won't be charged a penny more. Thank you!
Comments Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of new posts by email.
13 thoughts on “How to End Your Article: 5 Ways to Write a Powerful Conclusion”
Great article! Your explanation of how to write a conclusion was very clear and informative. I particularly appreciated the tips on summarizing the main points and tying them together to leave a lasting impact on the reader. Thank you for sharing this valuable information with the writing community
Appreciate the encouragement!
Just to say: Paula LaRocque is quoting (or ripping off?!) master playwright Anton Chekhov there (about the gun that must go off). It’s a pretty famous quote from him: he just says “acts” instead of chapters, since he was a playwright. Just sayin’! Thanks for the tips on endings!
ON YOUR 1ST ORDER
How to Conclude a Literature Review
By Laura Brown on 6th March 2019
The conclusion of the dissertation literature review focuses on a few critical points,
- Highlight the essential parts of the existing body of literature in a concise way.
- Next, you should analyse the current state of the reviewed literature .
- Explain the research gap for your chosen topic/existing knowledge.
- Now, outline the areas for future study by mentioning main agreements and disagreements in the literature.
- Finally, link the research to existing knowledge .
Now, any of you who have been into research would agree that literature review is a very exhausting process and may stress you during your academic career. It is tougher because it requires you to be organised. We have seen many students asking does a literature review need a conclusion.
Well, the answer is simple, a good literature review will always have a proper ending. But there is nothing to worry about how to write a conclusion for a literature review. Here is a complete guide for you in “four” simple yet convenient steps. These steps can really be valuable in providing an excellent presentation to your literature review help . Furthermore, you can ask us for literature review conclusion examples anytime using our live chat or email option.
Now, without further ado, let’s move towards the steps.
How To Write A Literature Review Conclusion

Get Expert Assistance For Literature Review
Here are four major steps which can help you with how to conclude a literature review with ease.
1. Enlist Key Points
The conclusion can also be said as judgement because it gives a clear view of your work, whether you achieved your targeted objectives or not. Typically, it is not too difficult to conclude a review, but it can be challenging as well if not carried out properly.
It is crucial to find key features which should be engaging and useful as well for a reader. So at first, draft or enlist key factors before moving forward towards initialising your summary.
2. Summarise The Key Features Briefly
This is a most sensitive and important step of a dissertation literature review conclusion, where you should stick to the following things to get the job done efficiently.
- Once you are done drafting the important points , here you should mention them briefly.
- You can also take the liberty to agree or disagree with whatever literature you have gone through.
- Make sure you don’t drag your arguments while counter-arguing. Keeping your points specific is key.
- Describe, in one to two lines, how you addressed the previously identified gap .
- It is also important to point out the lapses you have noticed in previous authors’ work. Those lapses could be a misquotation of figures, a wrong pattern of research and so on.
- Alongside this, discuss existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research.
3. Educational Implications Of The Reviewed Literature
After mentioning the key factors, it is suggested to put implications to the already reviewed research. Like, as identifying problems in the already done research and giving recommendations on how these problems can be resolved.
Need Help in Writing Your Literature Review?
4. Indicating Room For Future Research
After completing the whole analysis of the particular research, you will be capable of identifying the work which can be done in future. You can also leave some gaps for future researchers so others can extend your work. This will be the final step, and this is how to end a literature review.
Tips That Can Enlighten Your Conclusion

We hope that things are very clear to you on how to write a conclusion for a literature review. If you want it to be even better and more meaningful, then you should keep the below points in mind.
- It should not be burdened with an unnecessary chain of details.
- It should be as precise and easy to understand as possible.
- You should mention important key points and findings .
- Make sure to put all points in a flow so the reader can understand your research in one go.
- Do not add anything from your own.
“Simply put, touch the prominent factors and leave them unexplained here”.
Get Help to Conclude Your Literature Review
If you are able to keep your focus around these steps and mentioned points, believe us, you will never ask anyone how to conclude literature review.
Looking At Literature Review Conclusion Example
Below are three examples which will help you understand how to conclude a literature review.
1. Firstly, you should summarise the important aspects and evaluate the current state of the existing literature.
Overall, the findings from this literature review highlight the need for further research to address the gaps in knowledge on the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression in college students.
2. Now, along with mentioning the gaps, come up with your approach to future study.
Therefore, to address this gap in the literature, we incorporated larger and more diverse samples, used standardised measures of mindfulness and mental health outcomes, and included longer follow-up periods to assess the long-term effects of mindfulness-based interventions on anxiety and depression.
3. Now summarise on how your findings will contribute to the particular field by linking it to the existing knowledge.
The findings from the study will provide important insights for researchers, clinicians, and educators interested in developing and implementing effective interventions to promote mental health and well-being among college students, and highlight the need for further research to establish the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in this population.
We hope that these examples will bring in more clarification and you can have a better idea about the literature review conclusion.
What basically is a literature review?
What are the 3 primary parts of a literature review, what are the goals of writing a literature review.
There are four primary objectives of writing a literature review:
1. Determining the background from the previous scholarly literature related to the topic.
2. Identifying the gaps between literature to boost further research.
3. Analysing if the theory is applicable and associating a suitable methodology.
Why is a literature review conclusion necessary?
- https://azhin.org/cummings/basiclitreview/conclusions
- https://www.citewrite.qut.edu.au/write/writing-well/litreview.html
- https://psychology.ucsd.edu/undergraduate-program/undergraduate-resources/academic-writing-resources/writing-research-papers/writing-lit-review.html
- https://students.unimelb.edu.au/academic-skills/resources/report-writing/reviewing-the-literature

Laura Brown, a senior content writer who writes actionable blogs at Crowd Writer.
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
The last giants: New evidence for giant Late Triassic (Rhaetian) ichthyosaurs from the UK
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliations Palaeobiology Research Group, School of Earth Sciences, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom, Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, The University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation The Etches Collection – Museum of Jurassic Marine Life, Dorset, United Kingdom
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Paleontology division, Institute of Geosciences, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany
Roles Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Braunton, Devon, United Kingdom
Affiliation Dinosaurs Will Always Be Awesome, DWABA Museum, Orlando, Florida, United States of America
- Dean R. Lomax,
- Paul de la Salle,
- Marcello Perillo,
- Justin Reynolds,
- Ruby Reynolds,
- James F. Waldron

- Published: April 17, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289
- Reader Comments
Giant ichthyosaurs with body length estimates exceeding 20 m were present in the latest Triassic of the UK. Here we report on the discovery of a second surangular from the lower jaw of a giant ichthyosaur from Somerset, UK. The new find is comparable in size and morphology to a specimen from Lilstock, Somerset, described in 2018, but it is more complete and better preserved. Both finds are from the uppermost Triassic Westbury Mudstone Formation (Rhaetian), but the new specimen comes from Blue Anchor, approximately 10 km west along the coast from Lilstock. The more complete surangular would have been >2 m long, from an individual with a body length estimated at ~25 m. The identification of two specimens with the same unique morphology and from the same geologic age and geographic location warrants the erection of a new genus and species, Ichthyotitan severnensis gen. et sp. nov. Thin sections of the new specimen revealed the same histological features already observed in similar giant ichthyosaurian specimens. Our data also supports the previous suggestion of an atypical osteogenesis in the lower jaws of giant ichthyosaurs. The geological age and giant size of the specimens suggest shastasaurid affinities, but the material is too incomplete for a definitive referral. Ichthyotitan severnensis gen. et sp. nov., is the first-named giant ichthyosaur from the Rhaetian and probably represents the largest marine reptile formally described.
Citation: Lomax DR, de la Salle P, Perillo M, Reynolds J, Reynolds R, Waldron JF (2024) The last giants: New evidence for giant Late Triassic (Rhaetian) ichthyosaurs from the UK. PLoS ONE 19(4): e0300289. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289
Editor: Dawid Surmik, University of Silesia, POLAND
Received: November 19, 2023; Accepted: February 24, 2024; Published: April 17, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Lomax et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the manuscript.
Funding: - Initials of the authors who received each award: DRL - Grant numbers awarded to each author: N/A - The full name of each funder: The Royal Commission for the Exhibition of 1851 - URL of each funder website: https://royalcommission1851.org/ Did the sponsors or funders play any role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript?:No, this is part of a Research Fellowship given to DRL.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Abbreviations: BRSMG, Bristol Museum and Art Gallery, Bristol, UK; LACM DI, The Dinosaur Institute, Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, Los Angeles, California, USA; MJML, The Etches Collection Museum of Jurassic Marine Life, Kimmeridge, Dorset, UK; TMP, The Royal Tyrrell Museum of Palaeontology, Alberta, Canada
Introduction
Ichthyosaurs were the first marine tetrapods to attain giant size. The recent discovery of Cymbospondylus youngorum from the early Middle Triassic (Anisian, ~245 Ma) of Nevada, USA, estimated to be around 15–17 m in length, shows that ichthyosaurs reached giant body size as little as 3–5 million years after their first appearance [ 1 , 2 ]. It was during the Late Triassic, however, when the largest known ichthyosaurs emerged, belonging to the family Shastasauridae. These include the Carnian (~230 Ma) Shonisaurus popularis (16 m) [ 3 , 4 ] and middle Norian (~215 Ma) Shonisaurus sikanniensis (21 m) [ 5 ]. The remains of giant ichthyosaurs from the Swiss Late Triassic have also been described recently, including what is believed to be the largest ichthyosaur tooth yet discovered [ 6 ].
In 2018, Lomax et al. [ 7 ] reported on a large, isolated jaw fragment (an incomplete left surangular) from a giant ichthyosaur collected by PdlS in 2016 from the latest Triassic (Rhaetian) in the UK, which provided a reassessment of the purported Aust ‘dinosaurian’ bones that were reinterpreted to belong to the jaws of giant Rhaetian ichthyosaurs. As discussed in Lomax et al., body size estimates (ranging from 22–30+ metres) based on these isolated bones suggest that they probably represent the largest ichthyosaurs known to date, larger even than S . sikanniensis .
This work reports the discovery of another large surangular from a giant Triassic (Rhaetian) ichthyosaur in the UK. The new specimen is a right surangular that is morphologically identical but more complete than the left surangular described by Lomax et al. [ 7 ]. A combination of unique morphological characters observed in both examples suggest that they represent a new taxon. Both specimens were discovered in Somerset, UK, and were collected from strata dating to the latest Rhaetian, approximately 202 Ma [ 7 , 8 ]. The stratigraphic horizon present immediately above the level of both finds represents a period of cataclysm with extensive seismite and tsunamite rocks [ 9 , 10 ], indicative of the Late Triassic global mass extinction event. This extinction greatly reduced both ecomorphological disparity and species diversity and is considered the most poorly understood of the ‘Big Five’ mass extinctions [ 11 – 14 ]. It is probable that this lineage of giant ichthyosaurs vanished during the end-Triassic mass extinction event, and that ichthyosaurs never reached this size again before their extinction in the early Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian), around 94 Ma [ 15 ].
Materials and methods
The newly found specimen that is the focus of this study, BRSMG Cg3178 (herein referred to as the BAS specimen, i.e. the Blue Anchor Surangular), is a large portion of an ichthyosaur surangular from the Westbury Mudstone Formation (latest Rhaetian), or Westbury Formation, collected at Blue Anchor, Somerset, UK (Figs 1 – 3 ; DOI: 10.6084/m9.figshare.25290661 ). A 3D photogrammetry model of the specimen can be found here, DOI: https://sketchfab.com/3d-models/ichthyotitan-severnensis-surangular-2d8556bc9cbd4cf1bd93b33044770a4f . BRSMG Cg2488, known as the Lilstock surangular, is also from the Westbury Mudstone Formation (latest Rhaetian), but was found at Lilstock, Somerset, UK (Figs 1 and 3 ; see supplementary data from [ 7 ] DOI: 10.6084/m9.figshare.5975440 ). As described by Lomax et al. [ 7 ], specimens BRSMG Cb3869, BRSMG Cb3870, and BRSMG Cb4063 are isolated, fragmentary bones from the jaws of giant ichthyosaurs collected from the ‘Rhaetic Bone Bed’ at the base of the Westbury Mudstone Formation (Rhaetian) of Aust Cliff, Gloucestershire, UK; specifically, BRSMG Cb3869 is probably a portion of a very large surangular. Comparisons are made with specimens of Shonisaurus popularis (those discussed in [ 3 ] and also figured in [ 7 ]), the holotype of Shonisaurus sikanniensis (TMP 1994.378.02, [ 5 ]), and the holotype of Cymbospondylus youngorum (LACM DI 157871, [ 1 ]). For further comparative purposes, we also examined MJML K2577, a comparable section of surangular belonging to an example of Ophthalmosaurus icenicus from the Oxford Clay Formation (163 Ma) of the upper Thames Valley, England. No permits were required for the described study, which complied with all relevant regulations. Whilst this manuscript was under review, the authors were made aware of a recent discovery of another large, albeit much smaller fragment of jaw from a giant ichthyosaur collected from Lilstock. The specimen is presently in a private collection, but it adds yet another example to the growing collection of giant Triassic ichthyosaurs in the UK. The specimen is not discussed further.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
Modified from Lomax et al. 2018 [ 7 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289.g001
A. All associated pieces with an approximate outline of the complete surangular, in medial view. The surangular is separated into two main parts, Part #A to the right and Part #B to the left (see text). B. A close-up of the coronoid process in lateral view, showing moderate eminence. C. Bulbous coronoid process in dorsal view with lateral displacement. D. Subcircular cross section at the level of the coronoid process (posterior view, medial to the left). E-F. Comparison of the massively developed M.A.M.E. ridge observed in BAS (E) and the Lilstock surangular (F); arrows indicate top of the ridge. G. Oblique view of the medial surface highlighting part of the overhanging shelf that encloses the Meckelian canal. H. Ventromedial view of the mid-posterior portion of the surangular showing a distinct, continuous, and straight thin groove that might be a suture and could indicate two distinct bones (perhaps including a damaged angular).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289.g002
A-B. Lateral view of both surangulars showing same unique shape; note the upturned, almost 90-degree angle bend and the spatulate-shaped posterior end. C-D. Medial view of both surangulars displaying same morphology posteriorly; anteriorly the Lilstock specimen (D) has been heavily eroded and distorted along its length (see Discussion in Lomax et al. 2018 for more details). Note the position of an elongated foramen on the lateral surface (A-B), identified as part of the fossa surangularis that passes through the bone into the Meckelian canal. See also the damaged (?)angular that is articulated with the surangular and defined by a continuous groove (?suture) as seen in Fig 2H .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289.g003
To inspect the bone histology of the new specimen (BRSMG Cg3178) and compare it with the unique bone histology described for the Aust bones [ 16 ] and for the Lilstock surangular ([ 7 ]; but see [ 17 , 18 ]), we applied the core drill technique following Sander [ 19 ] and Stein and Sander [ 20 ] to produce histological samples to analyse. The core was extracted from the most anterior fragment of the posterior section of the surangular, in the immediate posterior portion of the clearly visible furrow (nutrient foramen), to match the sample area in BRSMG Cg2488 R-101 and BRSMG Cb3869 (see Fig 5). Two thin sections were produced from the core using wet silicon carbide powder of grit sizes 600 and 800 for grinding and polishing processes. Once covered, the thin sections were studied under a Leica DMLP light microscope with transmitted, cross-polarized light and circular polarized light. Circular polarized light [ 21 ] was obtained using a pair of commercially available 3D polarized lenses to replace the crossed polarizers. Photo-micrographs were obtained using a Mounted Dino-Eye camera (software DinoCapture 2.0 ver 1.5.45 © 2016 AnMo Electronics Corporation). Photo-micrographs were merged using Image Composite Editor (ver. 2.0.3 ©2015 Microsoft).
Histological terminology follows [ 22 , 23 ] for general osteohistology. Networks of coarse collagenic fibres integrated in the periosteal bone matrix with no clear connection to external structures are defined as periosteal intrinsic fibres (PIF). PIF appear as a widespread structural character of the entire primary bone matrix scaffold not connected to external structures. A combination of PIF set in amorphous background matrix is defined as intrinsic fibre matrix (IFM). A woven-parallel complex with longitudinal osteons integrating IFM as a woven matrix, is defined as periosteal intrinsic fibre tissue (PIFT). The concepts of PIF, IFM, PIFT, and the concept of ‘template’ remodelling follow [ 18 ].
Nomenclatural acts
The electronic edition of this article conforms to the requirements of the amended International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, and hence the new names contained herein are available under that Code from the electronic edition of this article. This published work and the nomenclatural acts it contains have been registered in ZooBank, the online registration system for the ICZN. The ZooBank LSIDs (Life Science Identifiers) can be resolved and the associated information viewed through any standard web browser by appending the LSID to the prefix http://zoobank.org/ [zoobank.org]. The LSID for this publication is: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:D099EF35-0035-4520-A20E-806A1B8B4109. The electronic edition of this work was published in a journal with an ISSN, and has been archived and is available from the following digital repositories: PubMed Central, LOCKSS.
Discovery and provenance
The BAS specimen (BRSMG Cg3178) was found in multiple pieces, including several parts of the better-preserved posterior portion found in situ (by JR, RR and PdlS). The first piece, representing a large, slightly worn bone section was collected on May 28, 2020, by JR and RR who were fossil collecting at the Blue Anchor location ( Fig 1 ). An anonymous member of the public had left the bone on a large boulder at the top of the beach, presumably thinking that it might be something of interest. JR and RR searched the vicinity of the area and RR found a better preserved, larger section clearly showing the distinct Meckelian canal of an ichthyosaurian surangular. Together, both identified the material as bone and compared the finds with the surangular described by Lomax et al. [ 7 ]. As a result, they informed DRL and PdlS of the discovery. Several trips to the site led to the recovery of additional remains of BRSMG Cg3178, which were found by JR, RR, PdlS, DRL and others (see Acknowledgments).
The most recently collected piece of BRSMG Cg3178 was recovered by PdlS on October 16, 2022. Despite searching the foreshore and in situ location, no more material has come to light, although there remains the strong possibility that more of this individual is out there. As a result, the precise location of the BAS site is not being divulged at this stage due to the potential for more material to be found.
Additional remains collected on the foreshore include eroded pieces of bone, along with isolated rib fragments, vertebrae, and a phalanx all found loose on the beach in the vicinity of the area where BRSMG Cg3178 was found. It is not possible to confidently associate any of the material with the surangular. Two large rib sections were also found embedded in a mass mortality bivalve mollusc bed which is stratigraphically just above where the rest of the surangular pieces were found, which demonstrates these rib sections do not come from the same individual but another potentially large-bodied ichthyosaur. Additionally, a large coprolite containing fish scales was found in the vicinity. Unless stated otherwise, these additional elements are not discussed further.
Similar to the left surangular described by Lomax et al. [ 7 ], the BAS specimen comes from the highest part of the Westbury Mudstone Formation (Upper Triassic, Rhaetian) and was found in twelve distinct pieces ( Fig 2A ). Like the Lilstock surangular, the specimen shows signs of abrasion and encrusting organisms, including multiple bivalves ( Atreta intrusstriata and Plagiostoma giganteum , DRL pers. comm. Crispin Little 2023) and probable scavenging/scratch-like marks (see also [ 7 ] Fig 4 ; Fig 4 ). Considering the stratigraphical position of this specimen, as in the Lilstock surangular, it narrowly predates the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event found in the above Cotham Formation ([ 7 , 24 , 25 ]). Together, these specimens represent the latest Triassic occurrence of giant ichthyosaurs in the UK.
A-B. Associated bivalves, including Atreta intrusstriata (A) and Plagiostoma giganteum (B); it is worth noting that a small group of the latter are preserved adjacent to the coronoid process, see Fig 2C . C-D. Examples of the probable scavenging marks that are also observed in the Lilstock surangular, see Lomax et al. 2018, Fig 4 .
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289.g004
Systematic palaeontology
Ichthyopterygia Owen, 1840
Ichthyosauria de Blainville, 1835
?Merriamosauria Motani, 1999
?Shastasauridae Merriam, 1902
Ichthyotitan severnensis gen. et sp. nov.
LSID for the genus: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:57B85E76-0A91-4EBF-9634-5B5A5FB10B60
LSID for the species: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:53F19051-D7E5-4ADB-8129-48D66B79C7A2
Giant fish lizard of the Severn. Ichthys derived from Greek meaning fish, taken from ichthyosaur meaning “fish lizard”, and - titan (Greek for giant), after the large size. Severn after the River Severn Estuary, Somerset, UK, where the remains were discovered and Latin - ensis pertaining to the location.
BRSMG Cg3178, a large right surangular comprising the posterior end and parts of the middle and anterior sections.
Referred material.
BRSMG Cg2488, a large left surangular comprising the posterior end and a portion of the shaft.
Type locality and horizon.
The type specimen was collected from the Upper Triassic Westbury Mudstone Formation (latest Rhaetian) at Blue Anchor, Somerset, UK. The referred specimen was collected from the Upper Triassic Westbury Mudstone Formation (latest Rhaetian) 0.8 m below the junction with the Cotham Formation, at Lilstock, Somerset, UK.
Giant, probable shastasaurid ichthyosaur distinguished by the presence of the following unique characters of the surangular: upturned, almost 90 degree angle bend at posterior end; subcircular cross section morphology of the shaft at the position of the coronoid, oblong in Shonisaurus ; minor eminence of coronoid process in lateral view, compared with prominent projection in Shonisaurus ; bulbous coronoid process displaced laterally and only occupying half of the width of the dorsal surface; massively developed dorsoventral M.A.M.E. ridge; spatulate shaped posterior end; and possibly dorsoventral height of posterior end in adults being more than 20% larger than in either Shonisaurus popularis or Shonisaurus sikanniensis .
Further to the last character in the diagnosis, this feature can be used to distinguish the new taxon from other giant ichthyosaurs, as mentioned, but this could be problematic for assigning immature or juvenile individuals of I . severnensis that would be smaller than adult specimens of Shonisaurus spp. Therefore, we feel that this character can be used to compare large, presumably adult specimens but might not be useful (unless scaling is taken into consideration) in assigning smaller individuals that may be discovered in the future. Another notable feature that might be of interest is a continuous, straight thin groove in the ventral surface of the BAS specimen. For further details, see the description below. Probable shastasaurid affinities are based on the large size of the ichthyosaur combined with the Upper Triassic age, a time when the largest-known ichthyosaurs (the Shastasauridae) existed.
Description and analysis
The holotype of Ichthyotitan severnensis (BRSMG Cg3178, BAS specimen) is a large, robust but incomplete right surangular, uncrushed and preserved in three dimensions (Figs 2 , 3A and 3C ). The only referred material comprises the Lilstock specimen (BRSMG Cg2488), which represents a near identical albeit less complete left surangular, preserved in three dimensions with a length of 96 cm ( Fig 3B and 3D ). The BAS specimen was chosen as the holotype because it is more complete and is generally better preserved. The Lilstock surangular was described in detail by Lomax et al. [ 7 ] and is, where appropriate, compared here with the new specimen. Relatively few surangulars are known from the largest Triassic ichthyosaurs and uncrushed three-dimensional preservation of isolated ones is rare. This is partly the reason why such bones have previously been misidentified [ 7 ].
The holotype is separated into at least 12 distinct sections that are associated and split into two main portions, termed Part #A and Part #B to aid with description ( Fig 2A ). The best-preserved part of the surangular is the middle to posterior portion (Part #A), made up of five key segments, which is approximately 99 cm in length. A more anterior section (Part #B) of the surangular was found scattered in five pieces on the foreshore and shows a moderate amount of wear from erosion. This section measures 46 cm long. The connecting material between these two sections of the surangular, along with the anterior-most portion, have not been found. Two additional pieces of the anterior portion were collected but the position of only one of them could be approximately located on the surangular (see Fig 2A ). We can be confident of the association between the anterior and posterior portions due to them being found in the immediate vicinity of each other, along with their size and their shared morphology. The combined preserved length of Part #A and Part #B measures 145 cm. Based on the extrapolation of measurements of the tapering thickness of the anterior portion, which indicates a potential minimum gap between the two main sections of 38 cm ( Fig 2A ), combined with the additional piece from the anterior region suggests a significant portion of the anterior is missing. We estimate the total length of the surangular to be >2 m ( Fig 2A ).
As in the Lilstock specimen, the posterior end of the BAS surangular is thick and dorsoventrally tall with an almost 90-degree curve (Figs 2A and 3 ). Lomax et al. [ 7 ] considered that the curvature might be the result of taphonomic distortion in the Lilstock specimen, but the preservation in BAS is much better and confirms that the curvature is natural. Nevertheless, when compared side-by-side in medial view, the Lilstock surangular is clearly distorted at the posterior-most end where the straightened edge of the dorsal surface is rotated posteriorly, a feature that is correctly oriented and in a natural position in the BAS specimen (compare Fig 3C and 3D ). As discussed in [ 7 ], a similar but less marked curvature occurs in the surangular of Shonisaurus sikanniensis and a slight curve is present in S . popularis . Lomax et al. [ 7 ] further noted that there might be some differences in the degree of curvature among taxa, stating that it is impossible to determine the significance with such a small sample size. However, we now have both the Lilstock and BAS specimens with the same degree of dorsoventral curvature. Overall, the rear section of the BAS surangular is remarkably similar in size and morphology to the Lilstock specimen. The maximum dorsoventral height is at the posterior end of the surangular and is 26 cm, as preserved.
A small, bulbous coronoid process with minor eminence is present and is laterally directed and laterally displaced, making it difficult to observe in lateral view (Figs 2B, 2C , 3A and 3C ); this morphology differs greatly from Shonisarus popularis which has a prominent triangular coronoid process (compare Fig 2A with [ 7 ], Fig 7A). It only occupies half of the width of the dorsal surface in the coronoid region and the medial side shows a slight concavity in this region ( Fig 2C ). Its surface is pitted with numerous forward-directed foramina and muscle scars. Note that due to distortion present in the Lilstock specimen, the identification observed herein on the BAS specimen shows that the coronoid process was misidentified in Lomax et al. [ 7 ] leading to the incorrect placement of the M.A.M.E. (M. adductor mandibulae externus) process in the Lilstock surangular ( Fig 3 ). Slightly anterior to the coronoid process, this part of the bone is subcircular in cross section, unlike in the surangular of Shonisarus popularis , which is distinctly oblong in cross section (see Fig 19 in [ 3 ]). As a result of the robustness at the point of the coronoid process, this section of the surangular is wider than it is anteriorly ( Fig 2D ).
There is a minor reduction in the dorsoventral height immediately posterior to the coronoid process. However, the height then greatly increases dorsally at the point of the almost 90-degree curve, marked by the presence of a massive, prominent and extensive M.A.M.E. ridge on the medial side for muscle attachment ( Fig 3 ). The ridge shows clear muscle attachment scars, as in the Lilstock specimen. A thin process curves dorsally from a point posterior to the M.A.M.E. at an angle of 90 degrees to the main shaft of the bone. This process carries prominent vertical ridges and furrows on its medial side (Figs 2E, 2F , 3C and 3D ), as reported in the Cuers ichthyosaur [ 26 ]. The purpose of this feature is unknown.
The Meckelian canal is prominently visible along the medial side of both parts (Part #A and #B; Figs 2A , 3C ) and would have provided a conduit for the passage of nerves and blood vessels (and cartilage during bone growth). It is partially filled with a light grey matrix and preserves bivalves in some places (Figs 2H and 4B ). The distalmost part of the posterior end of the ramus narrows laterally and expands dorsoventrally forming a large, spatula-shaped concavity for the reception of the articular bone (not present). Towards the anterior-mid section of Part #A, there is evidence of a broken, overhanging shelf enclosing the Meckelian canal dorsally along most of its length, from the anterior to the region of the coronoid process. In one area this is complete (Figs 2G, 2H and 3C ) and is likely for the reception of the dentary. In the posterior region, the Meckelian canal opens up posteriorly into a large fossa pierced by a number of foramina, the largest of which connects through the bone to the fossa surangularis on the lateral side ( Fig 3 ). The fossa surangularis opens into a number of forward-directed, elongated foramina on the lateral side of the rear section of the bone and into a continuous fossa along the lateral side of the anterior section (Figs 2A and 3A ); this fossa is visible in the bone cross sections. It is also observed in the Lilstock specimen and another large section of probable surangular (BRSMG Cb3869), where those bones also bear multiple, fine longitudinal indentations, preserved across the lateral and dorsal surfaces.
As described above, the posterior part of the surangular (Part #A) is the better preserved of the two main portions, showing little erosion or distortion. However, the anterior part of the surangular (Part #B) is more complex in cross-sectional outline than the posterior, showing complex concave facets on both the medial and lateral surfaces. Presumably, these are for the reception of the dentary on the lateral side, and the splenial on the medial side. The large lateral groove on this anterior portion probably represents the fossa surangularis in this region. This feature is also seen in the Cuers ichthyosaur ([ 26 ] Fig 2 ), a large incomplete surangular [see 7 ].
A damaged portion of bone is present ventral to the Meckelian canal, best viewed along the lower medial side (see e.g. Fig 2H ). Through direct comparison with the holotype of the Early Triassic Cymbospondylus youngorum (DRL and JFW pers. obs.), for which a well-preserved and articulated skull exists, the position of the bone suggests that it is probably part of the angular. It is present along the entire length of the surangular and can be seen on both the anterior and posterior sections, although best preserved on the posterior part (Part #A). There is a distinct, continuous, and straight thin groove (a probable suture) visible between the two bones at the surface. However, a close examination of the internal bone structure, visible in cross section, shows that it is continuous across the bone junction, with no discontinuity in cell structure and no intervening matrix. This may indicate that the bones were possibly fused together in life with no fossa separating them. If so, this would be unusual and possibly unique among ichthyosaurs, perhaps related to the large size and presumed mature nature of the individual. On a section of bone just anterior to the coronoid process, a vestigial suture between the surangular and (?)angular can be seen to disappear completely, further confirming the apparent fusion. A similar morphology is present in at least one of the Aust bones (BRSMG Cb3869), as also alluded to by Huene [ 27 ]. The Lilstock surangular is poorly preserved in ventral view, but direct observations suggest that there might also be a faint groove.
Results of core sampling
The section taken from BRSMG Cg3178, the BAS specimen ( Fig 5A and 5B middle), shows good preservation, although multiple osteons showing irregular breakage rims without clear Howship’s lacunae, and a long diagonal fracture in its lower half (Figs 5B and 6A ) indicate diagenetic or taphonomic-related damage. The bone histology is characterized by a highly vascularized woven-parallel complex [ 22 , 23 ] (Figs 5B , 6A and 6B ). Vascular canals are strictly longitudinally oriented (Figs 5B and 6A ). The primary bone matrix is characterized by a complex of networks of intrinsic longitudinal mineralized collagen fibres (periosteal intrinsic fibres, or PIF [ 18 ]) ( Fig 6D, 6E and 6G ). Under cross-polarized light, PIF appear bright against an isotropic amorphous dark background matrix ( Fig 6D ). PIF appear as circular or spirally coiled structures under circularly polarized view ( Fig 6D, 6E and 6G ). The network of PIF set in an amorphous dark matrix ( Fig 6D ) defines an intrinsic fibre matrix, IFM, [ 18 ] (and see Materials and methods ). IFM is identifiable both in the trabeculae interstitial bone ( Fig 6G ) and, as primary matrix of the rest of the cortex ( Fig 6D and 6E ). The section can be subdivided into an innermost half of spongious trabecular bone (trabecular region), and a compact cortex that can be further subdivided for description purposes, into a deep cortex and an outer cortex ( Fig 5B ).
A. Comparable sections for core drill(s) sampling position indicated by a white circle of (from left to right) BRSMG-Cb-3869 (an Aust bone, most probably a surangular), BRSMG Cg3178 (BAS surangular), BRSMG-Cg-2488 R-101 (Lilstock surangular). White arrows point to elongated surangular foramen. B. Binary drawings produced from stitched photos of the thin sections (respectively BRSMG-Cb-3869, BRSMG Cg3178 and BRSMG-Cg-2488 R-101) showing longitudinal vascularization and larger nutrient canals. Blue bars (upper) indicate extension of outer cortex, orange (middle) for deep cortex and pink (lower) for spongious trabecular bone.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289.g005
A. Composite image of thin section under circular polarized light. B. Close-up of the external margin of the outer cortex, showing the presence of multiple growth marks (GMs), open vascular canals and cortical vascular canals with all degrees of maturity (simple canals, primary osteons and secondary osteons), supporting an ongoing active and continuous growth. Note the evident darker border of the lumen of a diagonal canal running from the top left toward the margin of the large nutrient canal (NC) showing further longitudinal vascularization. C. Concentric secondary osteon in the outer cortex under lambda filter. D. Close-up of the upper margin of the nutrient canal under crossed polarized (left) and circular polarized light (right). The growth marks appear as alternated tightly packed rows of brighter and darker periosteal intrinsic fibres (PIF). The same tight packing of the GMs occurs also deeper in the cortex. E. Lateral margin of the nutrient canal under circular polarized view. PIF are evident as bright yellow and blue coiled structures. The presence of simple canals alongside osteons, indicates primary deposition of bone along the margin of the large nutrient canal. F. Concentric secondary osteon in the trabecular bone under transmitted light. It is evident the high amount of osteocyte lacunae and the presence of plump irregular shaped ones in the lamellar bone. G. Trabecular bone under circular polarized view. The presence of primary matrix and concentric secondary osteons indicate that the trabeculae are secondary, produced from compact bone made cancellous. White arrows (D, E, G) point at PIF; white arrowheads point at resorption lines in concentric osteons (C, F, G); white dotted lines indicate borders of primary osteons (C, F, G); yellow arrow heads (B, D) point at rows of GMs. Abbreviations. LB, Lamellar bone; NC, Nutrient canal; OC, Open periosteal canal; PO, Primary osteon; RC, Resorption cavity; SC, Simple canal; SO, Secondary osteon.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289.g006
The trabecular region presents secondary trabeculae constituted by compact bone made cancellous (sensu [ 22 ]) (Figs 5B , 6A and 6G ). The trabeculae are composed by islands of IFM bordered by large resorption cavities (RC) and hemiosteons ( Fig 6A and 6G ). RC and hemiosteons are lined by relatively few layers of lamellar bone ( Fig 6G ). It is possible to observe a preferential orientation of the trabecular bone in the horizontal plane (Figs 5B and 6A ).
Passing from the trabecular region to the deep cortex, the size of the RC gradually diminishes (Figs 5B and 6A ), giving space to a highly vascularized, well-arranged compact bone showing large numbers of secondary osteons that generally appear in an in-row arrangement ( Fig 6A ). The in-row arrangement appears parallel or slightly subparallel to the subperiosteal outer surface. The primary tissue constituting the compact cortex is periosteal intrinsic fibre tissue (PIFT) observed by Perillo and Sander [ 18 ].
A close inspection following the methods described in [ 16 , 18 ] shows that secondary osteons present successive resorption lines inside the osteon lamellar infill ( Fig 6C and 6F ). This phenomenon results from a consistent spatial correspondence between basal metabolic unit development and previously existing vascular canals. Secondary osteons develop preferentially inside preexisting osteons, either primary or secondary (in the latter case these are named concentric osteons). This phenomenon defines a ‘template’ remodelling [ 18 ]. It is nonetheless possible to see many resorption cavities in the deep cortex, although some of this may be related to preparation damages due to their shape. The number of resorption cavities present in the deep cortex increases the overall porosity of the bone structure (Figs 5B and 6A ) and suggests an advanced resorption front [ 28 ].
In the deep cortex, going toward the subperiosteal surface, the number of primary osteons, immature secondary osteons and concentric secondary osteons increases, while the amount of resorption cavities and non-concentric osteons decreases. Compared to the cancellous bone, the compact cortex shows also an increased amount of PIF clearly visible ( Fig 6B and 6E ). In the upper deep cortex and outer cortex, it is possible to identify numerous (~15) closely positioned wavey GMs formed by the alternation of brighter and darker layers of PIF ( Fig 6B and 6D ). The width and colour of the GMs is variable with darker and brighter ones alternating with no clear pattern. These GMs embrace the primary osteon and vascular canals and originate from periosteal apposition but do not show changes in tissue type, being always composed of IFM. Given the absence of a change of tissue type, these GMs are not identifiable as LAGs (see Discussion ). By close inspection, a scarce number of similar GMs, are identifiable in the rest of the deep cortex, always embracing the parallel rows of osteons but showing less continuity due to the higher number of RC.
A large longitudinal resorption cavity (diameter around 0.75 mm, area around 2 mm 2 ) occupies the upper central area of the section in the deep cortex (Figs 5B and 6A ), and is identifiable as a nutrient canal. The rim of the canals shows primary IFM ( Fig 6E ), primary osteons and simple canals, as well as Howship’s lacunae, indicating that this area was actively subjected to osteogenic and osteoclastic processes through the developmental stages of the animal. The large nutrient canal is connected to the outer surface by a large diagonal canal ( Fig 6A and 6B ). The section of the canal lumen measuring 0.3 mm in diameter (but tapering to 0.15 mm in its middle, assuming an hourglass shape). The diagonal canal is detectable by the darker colour of its lumen wall compared to the surrounding bone ( Fig 6A and 6B ). The borders of the diagonal canal show a clear continuity with the surrounding periosteal rims of the outer cortex as suggested by the organization of osteons and GMs ( Fig 6B ). The lumen wall of the diagonal canal shows longitudinal simple canals and secondary osteons orderly arranged parallel to its diagonal orientation ( Fig 6B ). Both under cross polarized view and circularly polarized view the canal lumen wall shows the presence of PIF ( Fig 6B and 6D ), indicating it is made of IFM.
In correspondence with the border of the large nutrient canal, the GMs show a clear descending down turning ( Fig 6B ). This skewed arrangement indicates that the periosteal apposition process was influenced by the presence of the major nerve and/or blood vessel occupying the nutrient canal.
The outer cortex shows simple canals, primary osteons and incipient concentric secondary osteons ( Fig 6B and 6D ). It is not possible to identify an External Fundamental System. The subperiosteal surface is characterized by various open periosteal canals (Figs 5B , 6A and 6B ). The latter show rims with no signs of breakage, therefore are identifiable as genuine biological open canals. The occurrence of open periosteal canals and simple canals indicates active growth at the time of death, as for some of the Aust bones described by [ 16 ]; see also [ 7 ]. The borders of the nutrient canal show primary bone tissue with simple vascular canals and primary osteons, resembling the condition observed on the outer cortex ( Fig 5B, 5D and 5E ). Numerous osteocyte lacunae are evident in the entirety of the section: dynamic flattened osteocytes are commonly found in lamellar bone ( Fig 5C, 5E and 5G ), while plump or irregular shaped ones are found both in the PIFT matrix and in its lamellar bone ( Fig 5F and 5C ).
A note on size estimations
When describing the Lilstock surangular, Lomax et al. [ 7 ] used large shastasaurid ichthyosaurs to provide a rough total length estimate of the ichthyosaur and for one of the Aust bones (BRSMG Cb3869), but emphasised the need for caution with such estimates when dealing with isolated remains. To determine these size estimates, using a simple scaling factor, they compared (1) the maximum dorsoventral height at the posterior end of the Lilstock surangular with the same point in the surangular of the large Shonisaurus sikanniensis and (2) the height of the Lilstock surangular at the coronoid process compared with the same in a smaller shastasaurid, Besanosaurus leptorhynchus [ 29 ]. Based on these comparisons, Lomax et al. [ 7 ] found that the Lilstock ichthyosaur had an estimated total length of between 26 and 22 m respectively and further stated that it is reasonable to suggest that the Lilstock ichthyosaur was on the order of 20–25 m long.
However, being better preserved than the Lilstock specimen, the BAS surangular has revealed that the identification of the position of the coronoid process and M.A.M.E. process on the Lilstock surangular are incorrect (see Fig 3 ) and therefore the size estimate compared with B . leptorhynchus is inaccurate. The position used by [ 7 ] for the measurement of the coronoid process (2) in the Lilstock surangular is actually the position of the M.A.M.E. Therefore, we use the position of the dorsoventral height of the M.A.M.E. in BAS, which measures 19 cm, and is the same height as that previously identified as the coronoid (now M.A.M.E.) in Lilstock, compared with the same point in B . leptorhynchus that measures approximately 3.5–4 cm at the M.A.M.E. (based on the illustration by Bindellini et al., [ 30 ], Fig 4 ; see also [ 7 ]). Note, however, that [ 30 ] follow a different terminology and refer to the M.A.M.E. in B . leptorhynchus as the coronoid process, but we regard their coronoid process as the M.A.M.E.; nevertheless, the measurement and scaling remains the same regardless of the identification. Based on this revised comparison, it suggests that the Lilstock/BAS ichthyosaurs are almost five times larger than Besanosaurus (which has a total body length of 5.4 m) with the largest total length estimate of 25 m, thus still in the 20–25 m range given by Lomax et al. [ 7 ].
To test the simple scaling further, we also compared the BAS specimen with a posterior section of surangular from an example of the common Upper Jurassic ophthalmosaurid ichthyosaur, Ophthalmosaurus icenicus (MJML K2577; Fig 7 ). This specimen was chosen due to the same portion of surangular being three-dimensionally preserved and the fact that the M.A.M.E. and coronoid processes can easily be identified and compared between both specimens (see Fig 7 ). As a result, we could provide a new scaling comparison. This time, by comparing the distance between the M.A.M.E. and coronoid processes in the Ophthalmosaurus specimen (measuring 4 cm) and the same in BAS (measuring 20 cm), this suggests an individual with an estimated body length five times greater, at 25 m long, the same estimate as presented above.
A. BRSMG Cg3178 and MJML K2577 illustrating the distance between the M.A.M.E. and coronoid process. B. BRSMG Cg2488 and MJML K2577 are positioned obliquely in lateral view (with MJML K2577 rotated and held closer to the camera), illustrating the general shape of the ichthyosaurian surangular.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0300289.g007
It is also worth reiterating the point made by Lomax et al. [ 7 ] that if the Aust specimen BRSMG Cb3869 is part of a surangular, which appears correct (see Fig 5A ), then by using the same simple scaling this individual would be estimated at a very speculative 30+ m. Based on the analysis of the BRSMG Cb3869 bone microstructure [ 16 , 18 ], this section is from an animal that was still growing at the time of death [ 16 , 18 ] and might be due to prolonged growth strategies as previously suggested (see Discussion in [ 7 ]).
Confidently assigning isolated, fragmentary, or poorly preserved remains to a specific taxon is challenging and can be problematic when key features are lacking, or insufficient material is preserved. When describing the Lilstock surangular, Lomax et al. [ 7 ] considered that the specimen might have possible shastasaurid affinities based on its geologic age and giant size. They further showed that it had an unusual morphology that appeared unique but refrained from assigning a specific name to the specimen due to its incompleteness, taphonomic distortion and the fact that it was represented by an isolated bone. Moreover, surangulars from the largest Triassic ichthyosaurs are poorly known and any three-dimensional specimens are rare, therefore making direct comparisons difficult. However, those specimens that could be compared were found to differ from the Lilstock specimen [ 7 ].
The discovery of yet another surangular (BRSMG Cg3178) possessing the same morphology as the Lilstock specimen, but which is much better preserved and more complete, provides additional support for the identification of something unique. Moreover, it illustrates that the Lilstock specimen was not simply a single bone with an unusual morphology. Although we appreciate that this new taxon is based on two large incomplete surangulars, we feel that having two identical bones showing the same unique morphology, and which were collected from the same geological formation separated by ~10 km, is enough to warrant the erection of a new taxon. Furthermore, these specimens are approximately 202 million years old, from the late Rhaetian, and appear roughly 13 million years after the stratigraphically latest giant Triassic ichthyosaurs with a name, Shonisaurus sikanniensis from British Columbia, Canada [ 5 ], and Himalayasaurus tibetensis from Tibet, China [ 31 ]. Thus, given the differences in surangular morphology compared with Shonisaurus (e.g. compare the surangular morphology with S . popularis figured in [ 7 ], Fig 7a ) along with the stratigraphic and geographic separation, it is highly unlikely that Ichthyotitan severnensis is an example of Shonisaurus or Himalayasaurus , which would also suggest an extremely long stratigraphic record and a much wider palaeogeographical distribution than what is known for both genera. Having two examples of the same bone with the same unique features from the same stratigraphic time zone supports the erection of a new taxon.
Considering the Rhaetian age and similar morphology of the bones, an argument could perhaps be made for the Aust bones (at least BRSMG Cb3869) and the Cuers ichthyosaur, a large surangular from the Rhaetian of France [ 26 ]; identified as a surangular by [ 7 ], to represent additional examples of I . severnensis . However, given that the Aust bones are stratigraphically slightly older (see [ 7 ], Fig 3 ), are much less complete and therefore do not show all the diagnostic features found in both the Lilstock and BAS specimens, we do not assign them to this species in this study. Similarly, although the Cuers ichthyosaur is more complete and shows some similarities with both specimens (see [ 26 ], Fig 2 ), the posterior end is somewhat poorly preserved and does not show the defining features necessary for positive identification. Nonetheless, these findings demonstrate that giant Rhaetian ichthyosaurs were present in the Tethys during this time. Similarly, it is worth noting that a fragmentary ichthyosaur comprising 17 ribs and two vertebral centra was recently discovered in the Gabbs Valley Range of Nevada, USA. Although this specimen has yet to be formally described, it demonstrates that giant ichthyosaurs were also present in Panthalassa during the Rhaetian [ 32 ].
Based on the core sampling results, the thin sections confirm that the BAS specimen shares peculiar histological characters with sections produced by other giant ichthyosaur specimens 16–18]. The same unique histology of the bones is supported by the presence of: 1) PIFT, 2) GMs determined by different arrangement e/o density of layers of PIF, 3) strictly longitudinal vascularization, 4) concentric osteons determining a cortical ‘template remodelling’. Thus, the results of this study are in agreement with the conclusions reached previously [ 16 – 18 ]. Furthermore, even in its absence, we predict that longitudinal sections of this specimen would most likely show the same structural collagen fibres arranged in a herringbone pattern, as observed in other giant ichthyosaurs [ 17 , 18 ]. The presence of a nutrient foramen in the BAS specimen, as with similar structures observed in both BRSMG Cg2488 R-101 and BRSMG Cb3869, further supports the anatomical homology hypothesized for these specimens [ 7 , 17 , 18 ]. Finally, it is noticeable that the horizontally oriented trabeculae, and the ratio of trabecular bone to compact cortex are also reminiscent of what was observed in BRSMG-Cb-3870 [ 16 – 18 ]. Although the consequences of matching histology paired with similar morphology of these specimens are intriguing, the lack of a more refined taxonomic resolution of the fragmentary material prevents support to any stable conclusion regarding the phylogenetic attribution to Ichthyotitan .
In the context of understanding the growth patterns and the developmental stage of BRSMG Cg3178, it is relevant to discuss the nature of the GMs we observed. The closely spaced GMs are, at first glance, reminiscent of LAGs forming the external fundamental system (EFS), which would advocate for an adult state of the animal and for the reaching of a stoppage in growth (i.e. [ 33 ]). Due to the same similarity, the identification of LAGs and the occurrence of an EFS was proposed by Redelstorff et al. [ 16 ] for another similar specimen (BRSMG-Cb-3870). It is noticeable, however, that the same study highlighted the thick width of BRSMG-Cb-3870 EFS as unusual and offered an alternative hypothesis to their conclusions. The GMs described here are characterized by a combination of higher brightness, lower brightness, and colour change of the same primary bone (IFM) and show no clear tissue type change (no lamellar bone or parallel fibered bone). This sharply contrasts with what defines LAGs [ 22 ], as already supported by [ 18 ], which described the same GMs from the specimens studied therein. The GMs described here are structures derived by modulations of orientation and density of longitudinal coarse fibres (PIF) deposited by active periosteal apposition [ 18 ] but with no clear connection to slowdown in growth. The identification of GMs as simple marks derived by changes in density and orientation of coarse longitudinal fibres is not unheard of, although it was observed in metaplastic tissue [ 34 , Fig 2e and 2f ]. To conclude, we do not observe an EFS given the absence in the outermost cortex of few layers of tightly packed LAGs. The absence of an EFS supports that the animal had yet to reach an asymptotic growth stage. The occurrence of the GMs already in the upper deep cortex, with no appreciable trend toward a diminishing space within them in the outer cortex, can be used as a further argument to exclude an ongoing progressive reduction in growth rate.
Further support for ongoing growth is offered by outer cortex vascularization. In both BRSMG-Cb-3870 [ 16 , 18 ] and our specimen, as well as in BRSMG Cg2488 R-101 [ 18 ] and BRSMG Cb3869 [ 16 , 18 ], the occurrence of multiple open periosteal canals and high vascularization in the outer cortex indicate that growth by periosteal apposition was not ceased at the moment of death. The few histological analysis carried on ichthyosaur rostra found them to be more compact than postcranial material [ 35 ]. We can therefore support that the high vascularization is a genuine indicator of active growth rather than being related to an increased osteoporotic specialization of the lower jaw. The sign of primary bone apposition and osteoclast activity around the large nutrient canal would indicate an ongoing reshaping of the nutrient canal overtime, through the development of the animal.
The absence of more complete and articulated remains prevents us to frame this specimen in a developmental series. Nonetheless, the histological features of the specimen here described (presence of primary bone, high superficial cortical vascularization, absence of EFS and a non-completely remodelled cortex) indicate a still growing subadult or an early adult. Lomax et al. [ 7 ] mentioned that processes like heterochronic sustained growth rates may have enabled the Late Triassic ichthyosaurs to reach giant sizes (~25+ m). However, more comparative histological data (e.g. juvenile specimens of Ichthyotitan and more histological samples of Triassic ichthyosaurs) is needed to identify such developmental strategies in Ichthyotitan .
Conclusions
A large ichthyosaur surangular was collected in 2016 from the UK Upper Triassic and was formally described by Lomax et al. [ 7 ] who also reinterpreted the Aust ‘dinosaurian’ bone shafts as belonging to the jaws of giant Triassic ichthyosaurs, something which had also been noted by Huene [ 27 ]. Recent support for these assertions was presented by Perillo et al. [ 17 ] who further assessed these claims by analysing the bone histology of the Lilstock specimen and the Aust bones. As such, they tested the “ Huene-Lomax hypothesis ” histologically and found that the histology of these bones supports an ichthyosaurian affinity (see also the “ Giant Ichthyosaur hypothesis ” in [ 18 ]).
The discovery of another giant ichthyosaur surangular from the Somerset coast of the UK provides additional support for the conclusions presented by [ 7 ] and the findings of [ 17 , 18 ]. The new specimen matches the Lilstock surangular in overall shape, bears the same unique morphology and comes from the same stratigraphic age (Westbury Mudstone Formation, Upper Triassic, latest Rhaetian). The specimen is, however, more complete and better preserved than the Lilstock surangular and includes a large portion of the anterior section, showing distinct facets for the dentary and a section of what is possibly the angular, which appears fused to the surangular. We herein formally assign these two specimens to a new genus and species, Ichthyotitan severnensis , which is the first-named giant ichthyosaur from the Rhaetian. This taxon has an estimated body length of around 25 m, or at least somewhere in the 20–26 m range and represents the largest estimate for a prehistoric marine reptile. The histological analysis agrees with similar specimens and advocates for a still growing sub-adult or early adult animal that had yet to reach an asymptotic growth stage. It is, however, worth reiterating that this is based on fragmentary remains and thus more complete specimens are required to confirm the giant size. Furthermore, if the estimates for the Aust bones are correct, as per Lomax et al. [ 7 ], then those individuals probably represent the largest ichthyosaurs known.
As summarized by Lomax et al. [ 7 ], these giant fragmentary jaw bones may easily be missed or could be mistaken for the remains of dinosaurs because of their size. The authors hoped that the description and identification of the Lilstock specimen would lead to more discoveries, which ultimately led to the identification of the BAS specimen described herein. It is our hope that more complete remains of this enigmatic giant ichthyosaur will be discovered in time. If any additional material is found, we kindly encourage the finders to contact the authors.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Prof Judy Massare for discussions around the newly collected specimen. Dr Ramues Gallois is thanked for his comments and field observations on the stratigraphy, and Dr Crispin Little is thanked for his identification of the bivalves. Dr Sarah Strachan is kindly acknowledged for reviewing the histology text and providing information that improved those sections in the paper. We also acknowledge the help of Beatrice Reynolds, Rosabel Reynolds, Tammy Humphreys, Carol Skiggs and Natalie Lomax for help in collecting additional pieces of the BAS specimen. The photogrammetry model(s) in the supplementary data were created by Steven Dey (ThinkSee3D) who is kindly acknowledged for his help and expertise. Barbara Billett is thanked for sharing details of the newly collected jaw fragment from Lilstock, which she found, and which is briefly mentioned in the materials section. Thanks also to Deborah Hutchinson (BRSMG), Brandon Strilisky, Tom Courtenay, and Dr Don Henderson (TMP), and Erika Durazo, Dr Nathan Smith, and Beau Campbell (LACM DI) for access to and assistance with specimens in collections at their institutions. DRL thanks Dr Bill Korth for discussions regarding the etymology of the name. Thanks are also due to Olaf Dülfer, Pia Schultz and Lucrezia Ferrari for assistance during preparation of the thin sections at Bonn University. DRL wishes to acknowledge The Royal Commission for the Exhibition of 1851 for generous support in the form of a Research Fellowship. Finally, thanks to the editor, Dr Dawid Surmik, for his support and encouragement and thanks to two anonymous reviewers for your helpful comments and suggestions that helped to improve this manuscript.
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 17. Perillo M., Sander P. M., Konietzko-Meier D. Giant shadows in Late Triassic seas: histological analysis on putative and genuine giant ichthyosaurs bones. In: Belvedere M, Mecozzi B, Amore O, Sardella R (eds.). Abstract book of the XIX Annual Conference of the European Association of Vertebrate Palaeontologists, Benevento/Pietraroja, Italy. PalaeoVertebrata, Special Volume 1. 2022; 224.
- 20. Stein, K. and Sander, P.M. Histological core drilling: a less destructive method for studying bone histology. In: M.A. Brown, J.F. Kane, and W.G. Parker (eds.), Methods In Fossil Preparation. Proceedings of the First Annual Fossil Preparation and Collections Symposium, Petrified Forest National Park, Holbrook, Arizona. 2009; 69–80.
- 22. de Buffrénil V., Quihlac A. Bone Tissue Types: A Brief Account of Currently Used Categories. 183–188. In de Buffrénil V., de Ricqlès A.J., Zylberberg L., & Padian K. (Eds.). Vertebrate Skeletal Histology and Paleohistology (1st ed.). Boca Raton, CRC Press; 2021a; 838 pp.
- 23. Buffrénil V. de, Quihlac A. Bone Remodeling. 229–241. In de Buffrénil V., de Ricqlès A.J., Zylberberg L., & Padian K. (Eds.). (2021). Vertebrate Skeletal Histology and Paleohistology (1st ed.). Boca Raton, CRC Press; 2021b; 838 pp.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
- Share full article

St. Vincent Dives Headfirst Into the Darkness
Seven albums and 17 years into an acclaimed solo career, the musician Annie Clark said she craved “a pummeling” on her new LP: “I want something to feel dangerous.”
Supported by

By Lindsay Zoladz
Reporting from New York and Los Angeles
- April 18, 2024
On a recent Tuesday night in a dressing room of the Brooklyn Paramount Theater, Annie Clark, the 41-year-old musician who records as St. Vincent, thumbed through a shelf of secondhand records and sipped a glass of pink champagne. Clark, invited to D.J. the venue’s grand reopening party, was the room’s first inhabitant since a major renovation restored the former movie palace; a pristine, new-car smell lingered.
Holding court among a few members of her team and her 23-year-old sister, Clark was an attentive host in this antiseptic space, ready with a witty remark (the carefully curated LPs were probably “someone’s deceased grandma’s record collection”) or a topped-off beverage. She wore a cream-colored silk blouse, black kitten-heeled shoes and a gauzy black bow tied artfully around her neck.
Even in a moment of relative repose, Clark possessed a feline hyper-awareness of her surroundings. Dave Grohl, who plays drums on two tracks off St. Vincent’s blistering new album “All Born Screaming,” later told me in a phone interview, “When you’re talking to her and you’re looking in those eyes, you can only wonder what reels are whirring in her brain, every second.” He added, amused, “I’ve never seen her with her eyelids half closed.”
Clark is a gifted and nimble guitarist with a dexterously spiky playing style that contrasts with the moony smoothness of her voice. She is also known for the absolute commitment of her live performances. “What she does is so transformative,” said the musician Cate Le Bon, Clark’s close friend of over a decade, in a video interview. “When I see her play, it freaks me out sometimes. I can be even helping her get ready for a show, and it’s like I know nothing of the woman who’s onstage.”

Seven albums and 17 years into an acclaimed solo career, Clark has eked out a singular space in music, occasionally intersecting with the mainstream but for the most part staying uncompromisingly countercultural. She has collaborated with both David Byrne and Dua Lipa ; the riot grrrl pioneers Sleater-Kinney and the post-post-riot-grrrl pop star Olivia Rodrigo . She was one of four female musicians asked to front Nirvana for a night in 2014 when the band was inducted into the Rock & Roll Hall of Fame. “She’s obviously outrageously talented,” Grohl said. “For her to play a Nirvana song was, maybe, a lot less complicated than her own music.”
I first met up with Clark in March, when we drank iced coffee beneath the shady pergola outside her manager’s Hollywood office. She carried a black Loewe handbag and wore a white T-shirt bearing the name of the Swedish punk band Viagra Boys. Clark has, in the past, embodied various characters and donned costumes — a gray-haired cult leader on the cover of her 2014 self-titled album; a louche ’70s glamour girl on her 2021 release “Daddy’s Home” — but these days she’s more or less dressing as herself.
“I’ve certainly played with persona, because I’m queer,” Clark said from behind large sunglasses. “That’s how I play and make sense of my life. All of that just seems absolutely natural to me, to play with persona and identity and to put it in the work.”
But adopting an over-the-top persona, she said, is not something she finds particularly compelling right now. “I’m more interested in that which is raw and essential,” she said. “You’re alive or you’re dead. And if you’re alive, you’d better live it, because it’s short.”
In some sense, Clark is coming off the greatest commercial success of her career, and one that is decidedly more sunshiny than the work she’s known for: During a session with the ubiquitous producer Jack Antonoff, who collaborated on her two previous albums, Clark helped write “Cruel Summer,” the sugar-rush pop song that Taylor Swift released on her 2019 album “Lover.”
“It was something Jack and I worked on and made its way to Taylor and made it back, as those things go,” Clark said. Though it was not initially released as a single, Swift’s formidable fan base has, in the past year, willed it into becoming the unofficial anthem of her Eras Tour and a No. 1 hit four years after its initial release. Clark attended a show in Los Angeles last year and found it surreal to witness 90,000 people singing along. “I’ve never seen anything like it, much less been a part of anything like it,” she said.
And yet, she has no interest in replicating that formula in her own music. In fact, “All Born Screaming,” due April 26, contains some of the heaviest, darkest and weirdest St. Vincent music to date. “That’s what I want from music right now, personally,” Clark said, safe in the shade of the California sun. “I would like a pummeling. I want something to feel dangerous.”
CLARK HAS A reputation for being guarded with journalists, in part because she does not like talking about her personal life. Unsurprisingly, she did not want to specify why themes of grief and loss permeate her new album, because she does not think it would make much difference to the listener. In one of our later conversations, she said that she believed a performer’s duty is simply “to shock and console” ad infinitum. Explaining oneself is superfluous to that job description.
“Generally everyone is misunderstood, and you realize it’s not your job to make people understand you,” Le Bon said. “It’s your job to work and align yourself with your own integrity. I think that’s even harder to harness when you’re an artist as big as Annie. But she does.”
“She’s almost certainly wildly misunderstood by people,” she added, “but there’s a perverse joy in that.”
Le Bon, who is from Wales, met Clark when she was opening for a St. Vincent tour in 2011. She said that at first she found it difficult to get to know Clark: “She was very mysterious, doing yoga a lot of the time,” Le Bon said. Eventually, however, Le Bon found a way into a “really rewarding” friendship. “She’s so honest without agenda, and that’s a rare thing in the world we both exist in,” Le Bon said. “She asks the tough questions, she gives you the real answers.”
Clark was born in Tulsa, Okla., and raised mostly in the Dallas suburbs. She picked up the guitar at 12 and showed a precocious talent; in her early teens, she sat in with her music teacher’s band and chose a song with a high level of difficulty, Jimi Hendrix’s “The Wind Cries Mary.” Her aunt and uncle play as the jazz duo Tuck and Patti, and they brought her on tour one summer as a roadie to show her the realities of touring life. She loved it. “Some of my fondest memories of touring are from those really early days,” she said.
Le Bon said she sees a stark demarcation between the somewhat severe and imperious musical figure “St. Vincent,” and, as she put it, “Annie Clark from Dallas.” Annie Clark from Dallas slowly emerged, in our conversations, as a funny, genial and lightly self-deprecating person who enjoys modern comedy (she quoted “30 Rock” from memory and referenced both “Veep” and “Waiting for Guffman”), is close with her many siblings, and on at least one occasion has drunk too much pink champagne at a party celebrating the reopening of an old Brooklyn theater to make it to Pilates the next morning.
But I witnessed something switch over in her when we met one afternoon at Electric Lady Studios in the West Village, where Clark worked on parts of her last several albums. “This is the room where I recorded the vocals for ‘Violent Times,’ ‘Broken Man’ and ‘Sweetest Fruit,’” she said, referring to songs on the new album. She jumped up from a couch to demonstrate how she’d sung into a particular microphone. Then she got distracted by the studio’s wall of consoles and patch bays.
“Where is this 67 patched at the moment?” she asked herself with sudden ease, like an expat shifting into her native tongue. “Oh yeah, through the 1073. But where’s the 1176?”
“All Born Screaming” began with a sonic puzzle: “How do I render the sound inside my head?” After “hours and hours and hours basically making postindustrial dance music in my studio by myself,” Clark said she realized that the sound in her head was something she would not be able to explain to anyone else. So, although she has been a very involved co-producer on each of her other albums, she decided “All Born Screaming” was something she would have to produce herself.
She approached the task with characteristic zeal. She asked her friend and collaborator Cian Riordan to give her engineering lessons, and he found her an impressively apt pupil. “She would show up, there would be coffee, she’d have a notepad ready,” Riordan said in a phone interview. “She’s extremely focused. There was so much intention with everything.”
She mastered compression, mic shootouts, signal flow. To his dismay, Riordan eventually found Clark starting down a path that he had seen trip up many musicians in the digital age: analog synthesizers.
“Any time someone brings modular synths into the studio, that’s usually my cue to be like, ‘I’m going to go somewhere else, because this is going to be a giant waste of time,’” Riordan said. “But with her, it was really incredible to watch. She would buy all these esoteric things that I didn’t even know about, and I’d come back and they were all synced up and she’d be making music on them. It was fun to see her take it so far.”
Clark said those synths allowed her to build a new sonic world. “You’re actually harnessing electricity,” she explained. Her enthusiasm was palpable; her speech kicked up its tempo. “It’s going through unique circuitry, and you are at the helm, so you’re like a god of lightning.”
CLARK HAS LONG been someone who gets a thrill out of testing her limits and rising to challenges, but around the time of her brightly barbed 2017 album “Masseduction” she was beginning to hit a wall. “It would be like, ‘Sure you can go from Memphis to Beijing to Champaign, Ill., in a weekend,” she said. “Sure you can. See if you can pull this off.” But suddenly, after years of “going, going, going,” she noted, “my body just kind of shut down. My stomach — everything about my stomach hurt.” She stopped drinking and went into what she calls “nun mode,” throwing herself headfirst into studio work.
It wasn’t until the pandemic, though, that she was truly forced to slow down and stay put. She got very good at D.I.Y. projects and installed a lot of light fixtures. She also finished building her home studio and worked on a record that had been gestating for a while. During the pandemic, “Some artists went very interior and quiet, understandably,” she said. “Then, you know,” she laughed. “Some people put on wigs.”
She was referring to “Daddy’s Home,” the heavily stylized ’70s-inspired album she made in response to her father’s release from prison, after he served eight years for conspiracy, fraud and money laundering. “Daddy’s Home” won a Grammy for best alternative album and featured some imaginative experiments, but it was a polarizing release that generated some criticism online.
Clark is aware of this and thinks the album was in part a casualty of bad timing. “The story sort of became, not that I made a record about a difficult familial time, but that, like, ‘OK, good, we have someone to blame for the prison-industrial complex,’” she said. “It’s like, oh wait — that’s not quite what I was going for. But those were the times. Everyone’s lives upturned and everyone was increasingly online and there was a lot of fervor in general.”
For “All Born Screaming,” Clark went back to basics and drew inspiration from “that sort of rock that is the first music that felt like it was mine, and not music from another generation.” She was talking about Nine Inch Nails, Tori Amos and, yes, even that band she helped induct into the Rock & Roll Hall of Fame. While working on the bracing head banger “Flea,” she realized she needed some enormously forceful percussion. The only person she could imagine playing on it was Grohl. So she wrote to him saying as much, and a few days later he was in her home studio, laying down drum tracks for that and the back half of “Broken Man.”
“He’s a great drummer because he’s a great songwriter, right?” Clark said. “He adds so much power and electricity and vibrance, but he’s always supporting the song. He takes a song from a nine to, like, a hundred.”
“All Born Screaming” is sequenced like a journey from darkness into light; its brooding first track is titled, appropriately, “Hell Is Near.” The title-track finale ends up somewhere more comfortably earthbound, but while she was making the song, it was torturing Clark, who just “couldn’t crack the feel of it.” She called Le Bon and played her what she had. Le Bon told her, “Give me a beer, a bass and two hours.”
It worked. The song is bouncy and delightfully off-kilter, strange in St. Vincent’s inimitable, specific way. Clark said the song sprung from the realization that, as she put it, “Joy and suffering are equal, necessary parts of the whole thing. And the only reason to live is for love and the people we love and that’s kind of it.”
“It’s not easy," she added. “But it’s simple.”
Find the Right Soundtrack for You
Trying to expand your musical horizons take a listen to something new..
St. Vincent dives headfirst into the darkness.
Taylor Swift sells a rainbow of vinyl albums. Fans keep buying them.
Sabrina Carpenter drops a perky bop, and 10 more new songs. Hear the Playlist .
How the trumpeter Jeremy Pelt chronicles Black jazz history.
Lost tapes from major musicians are out there. These guys find them .
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Identify the article. Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4.
Both a reaction paper and an article review will start with a content summary. ️. For scholarly material, you will present a structured review after the summary. ️. For popular magazine content, you will write a response that sums up your emotions, thoughts, and reactions that the material aroused.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification. 3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review's introduction, briefly ...
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow: Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
Writing an article REVIEW. A journal article review is written for a reader who is knowledgeable in the discipline and is interested not just in the coverage and content of the article being reviewed, but also in your critical assessment of the ideas and argument that are being presented by the author. ... Conclusion: A brief overall assessment ...
The structure of this type of review article is as follows: Introduction; Summary; Analysis; Conclusion. "Stuffing" of the text is based on such elements as methodology, argumentation, evidence, and theory base. The subject of study is stated at the beginning of the material.
Step 2: Read and Understand the Article. It's super important to read and understand the article before writing your review. Read the article a few times and jot down the notes as you go. Focus on the main arguments, major points, evidence, and how it's structured. For Example:
Step 4: Identify the Author's Thesis. In this step, pinpoint the author's main thesis or central argument. Understand the purpose of the article and how the author supports their position. This will serve as a foundation for your critique.
Article Identification. Start the first paragraph of your review with concise and clear article identification that specifies its title, author, name of the resource (e.g., journal, web, etc.), and the year of publication. Intro. Following the identification, write a short introductory paragraph.
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
A well-written review article must summarize key research findings, reference must-read articles, describe current areas of agreement as well as controversies and debates, point out gaps in current knowledge, depict unanswered questions, and suggest directions for future research ( 1 ). During the last decades, there has been a great expansion ...
For an article review, your task is to identify, summarize, and evaluate the ideas and information the author has presented. You are being asked to make judgments, positive or negative, about the content of the article. The criteria you follow to do this will vary based upon your particular academic discipline and the parameters of your ...
A review article is a type of professional essay writing. So you need to study its subject carefully. Use multiple sources and highlight the main arguments. Then form your own opinion on the given topic. In conclusion of your article review, you should bring new arguments for or against the author's opinion.
1. Restate your research question and objectives. 2. Synthesize your main findings. 3. Evaluate the quality and relevance of the sources. 4. Suggest implications and recommendations for future ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a ...
Step 1: Restate the problem. The first task of your conclusion is to remind the reader of your research problem. You will have discussed this problem in depth throughout the body, but now the point is to zoom back out from the details to the bigger picture. While you are restating a problem you've already introduced, you should avoid phrasing ...
Provide General Information About the Article. The next stage is to provide your readers with general information about the source you're going to review. For example, a couple of sentences about the author, one's expertise. Readers should understand the context to be able to support or decline your point of view.
The review highlights the strengths and limitations of the research, discusses the potential implications on the healthcare industry, and suggests avenues for further research in this burgeoning field. 4. Tips for Writing an Outstanding Article Review. To help you excel in writing article reviews, we have compiled a list of valuable tips:
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
As you research, write and revise your article, stay alert to possible endings. Play with different ideas. 5 Powerful Ways to End Your Article. Some writers say the conclusion of an article could work just as well as the introduction - with a slight modification. I think it depends on your article, writing style, and audience.
In conclusion, when writing a review, it is best to clearly focus on fixed ideas, to use a procedural and critical approach to the literature and to express your findings in an attractive way. Keywords: How to write, review, writing. The importance of review articles in health sciences is increasing day by day. Clinicians frequently benefit ...
By Laura Brown on 6th March 2019. The conclusion of the dissertation literature review focuses on a few critical points, Highlight the essential parts of the existing body of literature in a concise way. Next, you should analyse the current state of the reviewed literature. Explain the research gap for your chosen topic/existing knowledge.
See how to write a good conclusion for a project, essay or paper to get the grade. Strong conclusion examples pave the way for the perfect paper ending. See how to write a good conclusion for a project, essay or paper to get the grade. ... This is the end of a book review by Nanette Scarpellini for the Journal of Air Transportation World Wide ...
Giant ichthyosaurs with body length estimates exceeding 20 m were present in the latest Triassic of the UK. Here we report on the discovery of a second surangular from the lower jaw of a giant ichthyosaur from Somerset, UK. The new find is comparable in size and morphology to a specimen from Lilstock, Somerset, described in 2018, but it is more complete and better preserved.
Ed Skrein's antagonist performance stands out amid a sea of uninspired filler in Rebel Moon - Part Two: The Scargiver. Zack Snyder's unsatisfying conclusion to his bombastic space opera is ...
April 19, 2024 at 6:56 AM PDT. Listen. 1:38. President Joe Biden 's trade chief said that she expects a conclusion on a review of tariffs on more than $300 billion in Chinese goods "soon ...
(Aaron Dessner of the National, who lends a more muted and organic sensibility to Swift's sound, produced and helped write five tracks on the first album, and the majority of "The Anthology.")
Overnight, TikTok unveiled "The Ultimate Taylor Swift In-App Experience," offering fans digital goodies like a "Tortured Poets-inspired animation" on their feed. Before the album's ...
April 18, 2024. On a recent Tuesday night in a dressing room of the Brooklyn Paramount Theater, Annie Clark, the 41-year-old musician who records as St. Vincent, thumbed through a shelf of ...