What is Philosophy: Meaning and Importance | Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment

What Is Philosophy: Introduction
Philosophy definition: socrates, importance of philosophy in life, the value of philosophy, what is philosophy: conclusion, works cited.
Philosophy is the search for knowledge through applying logic and reason. Socrates claimed that such knowledge was obtainable through interaction with the environment. Socrates, particularly, demonstrated that philosophy dealt with exploring subjects, although such exploration seldom created knowledge about the subject.
Plato’s Socratic dialogues convey that philosophy is self-examining, examining other features of existence and acknowledgement of knowledge limits. In the Euthyphro, Plato reveals the nature of philosophy through the dialogues of Socrates as he goes to face the trial against corrupting young men.
Socrates asks Euthryphro whether he understands divine things so much that he can accuse his father of doing wicked things (Plato 3). He goes ahead and dares Euthyphro to define pious to him, in order that he would apply it in his defense. Euthyphro replies to him that pious is seeking for justice.
Socrates seems unsatisfied with this answer and requests him to describe the specific traits of pious actions. Socrates concern is to find out the specific qualities that lead to an action being pious. In response, Euthyphro argues that pious actions are those that make the gods happy (Plato 5).
However, Socrates disputes this definition, noting that the Greek gods were always in conflict. He claims that disputes among the gods resulted from the debates about what was moral or immoral and actions that could please some gods and annoy other gods were both morally right and wrong, as per the definition. This makes Euthyphro to surrender in his efforts of explaining the character of piety to Socrates. He does not offer a concise definition and Plato accomplishes his task of showing that the aspects of piety are unknown.
Socrates also demonstrates the significance of this lack of definite knowledge in the Apology, as he describes qualities of wisdom. While defending himself against not having faith in the gods, Socrates puts forward that he has faith in spirituality, and it is thus ridiculous to claim that he does not believe in gods themselves when he believes in their things (Plato 29). Indeed, Socrates spent his entire life trying to come into terms with the words of the oracle at Delphi, that he was the wisest man.
Since he did not consider himself wise, Socrates lived in pursuit of finding a person who was wiser than he was. Socrates followed artisans, politicians, and others who considered themselves as wise, but after evaluating them, he discovered that they were not wise, although they were knowledgeable.
Socrates described them as skilled men and professionals, but they could not prove their knowledge. This directed Socrates to his philosophical thought that the wisest person is the one who claims to know nothing. By saying so, Socrates meant that we could not claim to know something, unless we can proof our knowledge of what we claim to know.
This makes me to think that all matters have a room for doubt, and it is through justification that human beings get to understand the truth. A good illustration of uncertainty is clear in the Apology, as Socrates explains why he does not feel sorry for his life. He says that fear of death should not influence our choices because we even do not know what death is and we should not fear that which we do not know.
Lastly, Socrates demonstrates the value of philosophy through his answers to those who think that he should stop the practice of examining others and leave Athens.
“…..but can you hold your tongue and then you may go into a foreign city and no one will interfere with you?….and if I say again that daily to discourse virtue, and of those other things about which you hear me examining myself and others, is the greatest good of man and that the unexamined life is not worth living.” (Plato 39)
Socrates points out that our societies is lacking something so important, because we only concentrate on immediate satisfaction and fail to think about issues deeply. He explains that many people tend to ignore philosophical issues and consider them a waste of time because they tend to focus on providing solutions to questions that cannot have answers. Yet, is it not a contradiction that he poses questions when he thinks that they cannot have answers?
To understand whether an unexamined life is worth living, we must first understand whether life itself is worth living. During happy moments, we all feel that life is worthy living but when demands of this life overpower us, we feel as if life is unworthy. It is in our lowest moments that we also try to test whether our lives are valuable.
At these times, we tend to explore our lives so that we can get the most from it. Therefore, philosophy is valuable, especially for those who choose to think philosophically with an open mind. All we need to do is to select our values and learn the habit of thought and reflection.
In conclusion, I will say that philosophy means different things to different people, but it deals with logic, reflection and questions in search for wisdom.
Plato. Five Dialogues: Euthyphro, Apology, Crito, Meno, Phaedo . G.M.A. Grube, trans. Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing Company, 1981. Print.
- Divine Command Theory Definition
- Piety and holiness—dialogue of Socrates and Euthyphro
- Socrates: The Unexamined Life Is Not Worth Living
- Ethical and Moral Views of Immanuel Kant and John Stuart Mill
- The Dialog “Crito” by Socrates
- Concept of the Cartesian Dualism in Philosophy
- Arstippus and Epicurus
- Hegel’s Philosophical Theories
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, December 19). What is Philosophy: Meaning and Importance | Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-philosophy/
"What is Philosophy: Meaning and Importance | Essay." IvyPanda , 19 Dec. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-philosophy/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'What is Philosophy: Meaning and Importance | Essay'. 19 December.
IvyPanda . 2018. "What is Philosophy: Meaning and Importance | Essay." December 19, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-philosophy/.
1. IvyPanda . "What is Philosophy: Meaning and Importance | Essay." December 19, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-philosophy/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "What is Philosophy: Meaning and Importance | Essay." December 19, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-is-philosophy/.
Chapter 1: What is Philosophy and Who Cares?
Why is philosophy important.
What is the value of philosophy? Philosophy is a branch of human inquiry and as such it aims at knowledge and understanding. We might expect that the value of philosophy lies in the value of the ends that it seeks, the knowledge and understanding it reveals. But philosophy is rather notorious for failing to establish definitive knowledge on the matters it investigates. I’m not so sure this reputation is well deserved. We do learn much from doing philosophy. Philosophy often clearly reveals why some initially attractive answers to big philosophical questions are deeply problematic, for instance. But granted, philosophy often frustrates our craving for straightforward convictions. In our first reading, Bertrand Russell argues that there is great value in doing philosophy precisely because it frustrates our desire for quick easy answers. In denying us easy answers to big questions and undermining complacent convictions, philosophy liberates us from narrow minded conventional thinking and opens our minds to new possibilities. Philosophy often provides an antidote to prejudice not by settling big questions, but by revealing just how hard it is to settle those questions. It can lead us to question our comfortably complacent conventional opinions.
With this in mind, please read Chapter 5 from Bertrand Russell’s Problems of Philosophy , “The Value of Philosophy,” and then read the following analysis and response to it.
We humans are very prone to suffer from a psychological predicament we might call “the security blanket paradox.” We know the world is full of hazards, and like passengers after a shipwreck, we tend to latch on to something for a sense of safety. We might cling to a possession, another person, our cherished beliefs, or any combination of these. The American pragmatist philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce speaks of doubt and uncertainty as uncomfortable anxiety-producing states. This would help explain why we tend to cling, even desperately, to beliefs we find comforting. This clinging strategy, however, leads us into a predicament that becomes clear once we notice that having a security blanket just gives us one more thing to worry about. In addition to worrying about our own safety, we now are anxious about our security blanket getting lost or damaged. The asset becomes a liability. The clinging strategy for dealing with uncertainty and fear becomes counterproductive.
While not calling it by this name, Russell describes the intellectual consequences of the security blanket paradox vividly:
The man who has no tincture of philosophy goes through life imprisoned in the prejudices derived from common sense, from the habitual beliefs of his age or his nation, and from convictions which have grown up in his mind without the cooperation or consent of his deliberate reason. . . The life of the instinctive man is shut up within the circle of his private interests. . . In such a life there is something feverish and confined, in comparison with which the philosophic life is calm and free. The private world of instinctive interests is a small one, set in the midst of a great and powerful world which must, sooner or later, lay our private world in ruins.The primary value of philosophy according to Russell is that it loosens the grip of uncritically held opinion and opens the mind to a liberating range of new possibilities to explore.The value of philosophy is, in fact, to be sought largely in its very uncertainty. . . Philosophy, though unable to tell us with certainty what is the true answer to the doubts which it raises, is able to suggest many possibilities which enlarge our thoughts and free them from the tyranny of custom. Thus, while diminishing our feeling of certainty as to what things are, it greatly increases our knowledge as to what they may be; it removes the somewhat arrogant dogmatism of those who have never traveled into the region of liberating doubt, and it keeps alive our sense of wonder by showing familiar things in an unfamiliar aspect.
Here we are faced with a stark choice between the feeling of safety we might derive from clinging to opinions we are accustomed to and the liberation that comes with loosening our grip on these in order to explore new ideas. The paradox of the security blanket should make it clear what choice we should consider rational. Russell, of course, compellingly affirms choosing the liberty of free and open inquiry. Must we remain forever uncertain about philosophical matters? Russell does hold that some philosophical questions appear to be unanswerable (at least by us). But he doesn’t say this about every philosophical issue. In fact, he gives credit to philosophical successes for the birth of various branches of the sciences. Many of the philosophical questions we care most deeply about, however – like whether our lives are significant, whether there is objective value that transcends our subjective interests – sometimes seem to be unsolvable and so remain perennial philosophical concerns. But we shouldn’t be too certain about this either. Russell is hardly the final authority on what in philosophy is or isn’t resolvable. Keep in mind that Russell was writing 100 years ago and a lot has happened in philosophy in the mean time (not in small part thanks to Russell’s own definitive contributions). Problems that looked unsolvable to the best experts a hundred years ago often look quite solvable by current experts. The sciences are no different in this regard. The structure of DNA would not have been considered knowable fairly recently. That there was such a structure to discover could not even have been conceivable prior to Mendel and Darwin (and here we are only talking 150 years ago).
Further, it is often possible to make real progress in understanding issues even when they can’t be definitively settled. We can often rule out many potential answers to philosophical questions even when we can’t narrow things down to a single correct answer. And we can learn a great deal about the implications of and challenges for the possible answers that remain.
Even where philosophy can’t settle an issue, it’s not quite correct to conclude that there is no right answer. When we can’t settle an issue this usually just tells us something about our own limitations. There may still be a specific right answer; we just can’t tell conclusively what it is. It’s easy to appreciate this point with a non-philosophical issue. Perhaps we can’t know whether or not there is intelligent life on other planets. But surely there is or there isn’t intelligent life on other planets. Similarly, we may never establish that humans do or don’t have free will, but it still seems that there must be some fact of the matter. It would be intellectually arrogant of us to think that a question has no right answer just because we aren’t able to figure out what that answer is.
- What is the Value of Philosophy. Authored by : W. Russ Payne. Provided by : Bellevue College. Located at : https://commons.bellevuecollege.edu/wrussellpayne/an-introduction-to-philosophy/ . Project : https://commons.bellevuecollege.edu/wrussellpayne/an-introduction-to-philosophy/. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial

Privacy Policy
Philosophy: What and Why?
Find a job in philosophy, what is philosophy.
Philosophy is the systematic and critical study of fundamental questions that arise both in everyday life and through the practice of other disciplines. Some of these questions concern the nature of reality : Is there an external world? What is the relationship between the physical and the mental? Does God exist? Others concern our nature as rational, purposive, and social beings: Do we act freely? Where do our moral obligations come from? How do we construct just political states? Others concern the nature and extent of our knowledge: What is it to know something rather than merely believe it? Does all of our knowledge come from sensory experience? Are there limits to our knowledge? And still others concern the foundations and implications of other disciplines: What is a scientific explanation? What sort of knowledge of the world does science provide? Do scientific theories, such as evolutionary theory, or quantum mechanics, compel us to modify our basic philosophical understanding of, and approach to, reality? What makes an object a work of art? Are aesthetic value judgments objective? And so on.
The aim in Philosophy is not to master a body of facts, so much as think clearly and sharply through any set of facts. Towards that end, philosophy students are trained to read critically, analyze and assess arguments, discern hidden assumptions, construct logically tight arguments, and express themselves clearly and precisely in both speech and writing.
Here are descriptions of some of the main areas of philosophy:
Epistemology studies questions about knowledge and rational belief. Traditional questions include the following: How can we know that the ordinary physical objects around us are real (as opposed to dreamed, or hallucinated, as in the Matrix)? What are the factors that determine whether a belief is rational or irrational? What is the difference between knowing something and just believing it? (Part of the answer is that you can have false beliefs, but you can only know things that are true. But that’s not the whole answer—after all, you might believe something true on the basis of a lucky guess, and that wouldn’t be knowledge!) Some other questions that have recently been the subject of lively debate in epistemology include: Can two people with exactly the same evidence be completely rational in holding opposite beliefs? Does whether I know something depend on how much practical risk I would face if I believed falsely? Can I rationally maintain confident beliefs about matters on which I know that others, who are seemingly every bit as intelligent, well-informed, unbiased and diligent as I am, have come to opposite conclusions?
Metaphysics is the study of what the world is like—or (some would say) what reality consists in. Metaphysical questions can take several forms. They can be questions about what exists (questions of ontology); they can be questions what is fundamental (as opposed to derivative); and they can be questions about what is an objective feature of the world (as opposed to a mere consequence the way in which creatures like us happen to interact with that world). Questions that are central to the study of metaphysics include questions about the nature of objects, persons, time, space, causation, laws of nature, and modality. The rigorous study of these questions has often led metaphysicians to make surprising claims. Plato thought that alongside the observable, concrete world there was a realm of eternal, unchanging abstract entities like Goodness, Beauty, and Justice. Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz claimed that the world was composed of tiny indivisible souls, called monads. Even today contemporary metaphysicians have been known to doubt the existence of ordinary objects, to deny the possibility of free will, and to argue that our world is just one of a plurality of worlds.
Logic is the study of the validity of patterns of inference. Logic is not a branch of psychology: It does not concern how people actually reason or which kinds of reasoning they find intuitively compelling. Rather, logic concerns the question of when a claim is conclusively supported by other claims. For instance, the inference from the claims “it is raining” and “if it is raining then the streets are wet” to the claim “the streets are wet” is logically valid – the premises conclusively support the conclusion. The validity of this specific inference, and of other inferences of the same form, is tied to the nature of the concept “if … then”. More generally, the notion of logical validity is closely connected to the nature of concepts such as “and”, “or”, “not”, “if … then”, “all”, and “some”. In studying the notion of logical validity, logicians have developed symbolic languages. These enable us to state claims clearly and precisely, and to investigate the exact structure of an argument. These languages have turned out to be useful within philosophy and other disciplines, including mathematics and computer science. Some of the questions about logic studied by members of the philosophy department include: Given that logic is not an empirical science, how can we have knowledge of basic logical truths? What is the connection between logic and rationality? Can mathematics be reduced to logic? Should we revise logic to accommodate vague or imprecise language? Should we revise logic to answer the liar paradox and other paradoxes concerning truth?
Political philosophy is the philosophical study of concepts and values associated with political matters. For one example, is there any moral obligation to do what the law says just because the law says so, and if so on what grounds? Many have said we consent to obey. Did you consent to obey the laws? Can one consent without realizing it? Are there other grounds for an obligation to obey the law? Another central question is what would count as a just distribution of all the wealth and opportunity that is made possible by living in a political community? Is inequality in wealth or income unjust? Much existing economic inequality is a result of different talents, different childhood opportunities, different gender, or just different geographical location. What might justify inequalities that are owed simply to bad luck? Some say that inequality can provide incentives to produce or innovate more, which might benefit everyone. Others say that many goods belong to individuals before the law enters in, and that people may exchange them as they please even if this results in some having more than others. So (a third question), what does it mean for something to be yours, and what makes it yours?
The Philosophy of Language is devoted to the study of questions concerned with meaning and communication. Such questions range from ones that interact closely with linguistic theory to questions that are more akin to those raised in the study of literature. Very large questions include: What is linguistic meaning? How is the meaning of linguistic performances similar to and different from the meanings of, say, gestures or signals? What is the relationship between language and thought? Is thought more fundamental than language? Or is there some sense in which only creatures that can speak can think? To what extent does the social environment affect the meaning and use of language? Other questions focus on the communicative aspect of language, such as: What is it to understand what someone else has said? What is it to assert something? How is assertion related to knowledge and belief? And how is it that we can gain knowledge from others through language? Yet other questions focus on specific features of the languages we speak, for example: What is it a name to be a name of a particular thing? What's the relationship between the meanings of words and the meanings of sentences? Is there an important difference between literal and figurative uses of language? What is metaphor? And how does it work?
Ethics is the study of what we ought to do and what sorts of people we ought to be. Ethicists theorize about what makes acts right and wrong and what makes outcomes good and bad, and also about which motivations and traits of character we should admire and cultivate. Some other questions that ethicists try to answer are closely related to the central ones. They include: What does it mean to act freely? Under what conditions are we responsible for our good and bad acts? Are moral claims true and false, like ordinary descriptive claims about our world, and if they are what makes them so?
The History of Philosophy plays a special role in the study of philosophy. Like every other intellectual discipline, philosophy has of course a history. However, in the case of philosophy an understanding of its history - from its ancient and medieval beginnings through the early modern period (the 17th and 18th centuries) and into more recent times - forms a vital part of the very enterprise of philosophy, whether in metaphysics and epistemology or in ethics, aesthetics, and political philosophy. To study the great philosophical works of the past is to learn about the origins and presuppositions of many of the problems that occupy philosophy today. It is also to discover and to come to appreciate different ways of dealing with these problems, different conceptions of what the fundamental problems of philosophy are, and indeed different ways of doing philosophy altogether. And it is also the study of works—from Plato and Aristotle, through Kant and Mill and more recent writers—that have shaped much of Western culture far beyond academic philosophy. Many of the most creative philosophers working today have also written on various topics in the history of philosophy and have found their inspiration in great figures of the past.
Why Study Philosophy?
This question may be understood in two ways: Why would one engage in the particular intellectual activities that constitute philosophical inquiry? And how might the study of philosophy affect my future career prospects?
Philosophy as intellectual activity may have a number of motivations:
- Intellectual curiosity: philosophy is essentially a reflective-critical inquiry motivated by a sense of intellectual “wonder.” What is the world like? Why is it this way, rather than another? Who am I? Why am I here?
- Interest in cultural and intellectual history: as a discipline, philosophy pays a great deal of attention to its history, and to the broader cultural and intellectual context in which this history unfolds.
- Sharpening thinking skills: the study of philosophy is especially well suited to the development of a variety of intellectual skills involved in the analysis of concepts, the critique of ideas, the conduct of sound reasoning and argumentation; it is important to emphasize that philosophical inquiry also fosters intellectual creativity (developing new concepts, or new approaches to problems, identifying new problems, and so on).
- Sharpening writing skills: the writing of philosophy is especially rigorous
Philosophy might affect future career prospects in a number of ways:
- Some philosophy concentrators go on to graduate school to earn a Ph.D. in philosophy. Most of those become professors of philosophy, which means that their professional lives are devoted to research and teaching in philosophy.
- A philosophy concentration is not limiting: in fact, the skills it develops and sharpens are transferable to a wide variety of professional activities. Obvious examples include the application of reasoning and argumentation skills to the practice of law; less obvious examples include the application of analytical and critical skills to journalism, investment banking, writing, publishing, and so on; even less obvious examples include putting one’s philosophical education to work in business entrepreneurship, political and social activism, and even creative arts.

1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
Philosophy, One Thousand Words at a Time
What is Philosophy?
Author: Thomas Metcalf Category: Metaphilosophy Word count: 1000
Listen here , video below
If you’ve ever wondered whether God exists, whether life has purpose, whether beauty is in the eye of the beholder, what makes actions right or wrong, or whether a law is fair or just, then you’ve thought about philosophy. And these are just a few philosophical topics.
But what is philosophy? The question is itself a philosophical question. This essay surveys some answers.

1. Defining Philosophy
The most general definition of philosophy is that it is the pursuit of wisdom, truth, and knowledge. [1] Indeed, the word itself means ‘love of wisdom’ in Greek.
Whenever people think about deep, fundamental questions concerning the nature of the universe and ourselves, the limits of human knowledge, their values and the meaning of life, they are thinking about philosophy. Philosophical thinking is found in all parts of the world, present, and past. [2]
In the academic world, philosophy distinguishes a certain area of study from all other areas, such as the sciences and other humanities. Philosophers typically consider questions that are, in some sense, broader and/or more fundamental than other inquirers’ questions: [3] e.g., physicists ask what caused some event; philosophers ask whether causation even exists ; historians study figures who fought for justice; philosophers ask what justice is or whether their causes were in fact just; economists study the allocation of capital; philosophers debate the ethical merits of capital ism .
When a topic becomes amenable to rigorous, empirical study, it tends to be “outsourced” to its own field, and not described in the present day as “philosophy” anymore: e.g., the natural sciences were once called “natural philosophy,” but we don’t now just think about whether matter is composed of atoms or infinitely divisible: we use scientific experiments. [4] And most of the different doctoral degrees are called “Doctor of Philosophy” even when they’re in sociology or chemistry.
Philosophical questions can’t be straightforwardly investigated through purely empirical means: [5] e.g., try to imagine a lab experiment testing whether societies should privilege equality over freedom—not whether people believe we should, but whether we actually should . What does moral importance look like in a microscope?
The main method of academic philosophy is to construct and evaluate arguments (i.e., reasons intended to justify some conclusion). Such conclusions might be that some theory is true or false or might be about the correct analysis or definition of some concept. These arguments generally have at least some conceptual, intellectual, or a priori , i.e., non-empirical, content. And philosophers often incorporate relevant scientific knowledge as premises in arguments. [6]
2. Branches of Philosophy
Philosophy deals with fundamental questions. But which questions, specifically, is philosophy about? Here’s a standard categorization: [7]
Logic : Logicians study good and bad arguments and reasoning, and they study formal, symbolic languages intended to express propositions, sentences, or arguments. [8]
Metaphysics : Metaphysicians study what sorts of entities exist, what the world and its constituents are made of, and how objects or events might cause or explain each other. [9]
Epistemology : Epistemologists study knowledge, evidence, and justified belief. An epistemologist might study whether we can trust our senses and whether science is trustworthy. [10]
Values : In value theory, philosophers study morality, politics, and art, among other topics. For example: What makes wrong actions wrong? How do we identify good people and good lives? What makes a society just or unjust? [11]
There are many sub-branches within these fields. Many other fields— the sciences, art, literature, and religion—have a “philosophy of” attached to them: e.g., philosophers of science might help interpret quantum mechanics; philosophers of religion often consider arguments about the existence of God. [12]
There are also unique and important philosophical discussions about certain populations or communities, such as feminist philosophy and Africana philosophy. [13] People from all cultures contribute to philosophy, more than are typically discussed in Western philosophy courses. [14] Western academic philosophy has often neglected voices from non-Western cultures, and women’s voices. [15]
Philosophers sometimes import tools, knowledge, and language from other fields, such as using the formal tools of statistics in epistemology and the insights from special relativity in the philosophy of time. [16] When your project is understanding all of existence [17] in the broadest and most fundamental way, you need all the help you can get.
3. The Point(s) of Philosophy
Academic philosophy doesn’t present a body of consensus knowledge the way chemistry and physics do. [18] Do philosophical questions have correct answers? Does philosophical progress exist? Does philosophy get closer to the truth over time? [19] These are all matters of philosophical debate. [20] And philosophical debates are rarely resolved with certainty.
So what’s the point? Here are some answers: [21]
- To discover truth, wherever and whatever it is. [22]
- To learn how to better live our lives. [23]
- To understand our own views, including their strengths and weaknesses.
- To examine our own lives and be more conscious of our choices and their implications.
- To learn how to better think and reason. Recall: The main method of philosophy is to present and examine arguments. [24]
And arguably, all of us are already naturally interested in at least some philosophical questions. Many people find that philosophy is a lot of fun. And it’s difficult to dispute that it is very important to find the answers to philosophical questions, if the answers exist. It’s important to know, for instance, that slavery is wrong and whether scientific consensus is generally trustworthy. So as long as it’s at least possible to find the answers to these questions, we should try.
Also, there are strong correlations between studying philosophy and high achievement in other academic areas, such as GRE scores and professional-school admission. [25]
4. Conclusion
We’ve contrasted philosophy with other fields. We’ve looked at the branches of philosophy. And we’ve looked at the purposes or benefits of philosophy. But what is philosophy, really? Given everything we’ve said so far, we can provide at least a partial definition of ‘philosophy’ as follows:
A largely (but not exclusively) non-empirical inquiry that attempts to identify and answer fundamental questions about the world, including about what’s valuable and disvaluable.
Is this a good definition? That’s a philosophical question too.
Acknowledgments
This entry has benefited enormously from the comments and suggestions of Shane Gronholz, Chelsea Haramia, Dan Lowe, and Nathan Nobis.
[1] Berkeley 2003 [1710]: 5; Blackburn 1999: 1.
[2] Some of the oldest formal philosophy writing we have is attributed to a group of ancient Greek philosophers called the ‘Pre-Socratics,’ because they wrote before Socrates and Plato did (cf. Curd 2019). The earliest Upanishads may go back even further (Olivelle 1998: 4 ff.).
[3] This is similar to Encyclopaedia Britannica’s (n.d.) definition: “the rational, abstract, and methodical consideration of reality as a whole or of fundamental dimensions of human existence and experience.”
[4] See e.g., Berryman 2020 on ancient atomism.
[5] Metcalf 2018.
[6] Most philosophers believe that the sciences provide knowledge relevant to traditional philosophical issues. That is, most philosophers endorse the meta-philosophy of ‘naturalism,’ according to which philosophy should be informed by the natural sciences. The usual justification for naturalism is based on the track-record of the natural sciences, including their tending toward consensus. See Bourget and Chalmers 2014: 476; Metcalf 2018; and Papineau 2019. For examples of the relevance of science to traditional philosophical issues, see Ingram and Tallent (2019: § 8); Wilce 2019; and Knobe and Nichols 2019. In these examples, special relativity may be relevant to philosophy of time; quantum mechanics may be relevant to philosophy of logic; and social science may be relevant to ethics.
[7] This is a version of common anthologies’ categorizations. See e.g., Blackburn 1999: vii and Rosen et al. 2015.
[8] Logicians can also study logics about obligation (McNamara 2019), about necessity and possibility (Garson 2019), and whether useful logics can contain sentences that are both true and false simultaneously (Priest et al. 2019).
[9] Van Inwagen and Sullivan 2019.
[10] Steup 2019; Metcalf 2020.
[11] Value theorists also study specific topics, such as our obligations to animals (Gruen 2019) and whether governments can be legitimate (Peter 2019). See also Haramia 2018 (the entry on applied ethics in 1000-Word Philosophy ) for an overview of applied ethics.
[12] Indeed, one area where people see many connections is with religion. So what’s the difference between philosophy and religion? This is not an easy question to answer, but most religious practice proceeds from a shared starting-point consensus body of putative knowledge, and these beliefs are almost all about God or gods, the afterlife, and how to live a pious life. In contrast, in philosophy, everything is constantly open to question, and the topics are much broader than gods and the afterlife.
[13] See e.g., McAfee 2019 and Outlaw 2019.
[14] Van Norden 2017.
[15] See e.g., Van Norden (op. cit.) and Buxton and Whiting 2020.
[16] Indeed, one popular metaphilosophical view is methodological naturalism about philosophy, according to which philosophy should use the methods of the natural sciences. Some naturalists go so far as to say that traditional philosophical methods should be replaced by scientific methods. See Metcalf 2018 and Papineau 2019 for more discussion. As for tools and knowledge from other fields, statistical and probabilistic analysis is common in many areas of philosophy (see, e.g., Weisberg 2019) and special relativity may tell us something important about the philosophy of time (Ingram and Tallant 2019).
[17] And maybe even the objects that don’t exist; see Reicher 2019.
[18] Bourget and Chalmers 2014. Arguably, there is consensus about many philosophical questions, but we don’t consider those questions in academic philosophy, at least not anymore. For example, almost everyone knows that slavery is wrong and that women should be allowed to vote if anyone is. See also Gutting 2009 for a general survey of some apparent philosophical discoveries.
[19] Cf. Chalmers 2015.
[20] See, e.g., Miller 2019.
[21] See Bierce 2008; de Montaigne 1987: 204; Russell 2010: 20 for some other statements about the nature or purpose of philosophy.
[22] Bierce 2008.
[23] De Montaigne 1987: 204.
[24] See e.g., Groarke 2019.
[25] Daily Nous n.d. However, we do not yet know what proportion of this is a ‘selection effect’—people who are already smart major in philosophy—and how much of this is a ‘treatment effect,’ i.e., majoring in philosophy actually makes you smarter.
Berkeley, George. 2003 [1710]. A Treatise Concerning the Principles of Human Knowledge . Mineola, NY: Dover Philosophical Classics.
Berryman, Sylvia. 2019. “Ancient Atomism.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Winter 2019 Edition.
Bierce, Ambrose. 2008. “The Devil’s Dictionary.” In Project Gutenberg (ed.), Project Gutenberg.
Blackburn, Simon. 1999. Think: A Compelling Introduction to Philosophy . Oxford, UK and New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Bourget, David and David J. Chalmers. 2014. “What Do Philosophers Believe?” Philosophical Studies 170(3): 465-500.
Buxton, Rebecca and Lisa Whiting. 2020. The Philosopher Queens: The Lives and Legacies of Philosophy’s Unsung Women. London, UK: Unbound Publishers.
Chalmers, David J. 2015. “Why Isn’t There More Progress in Philosophy?” Philosophy 90(1): 3-31.
Curd, Patricia. 2019. “Presocratic Philosophy.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Daily Nous. n.d. “Value of Philosophy.”
De Montaigne, Michel. 1987. Complete Essays . Tr. M. A. Screech. London, UK: Penguin Books.
The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica. N.d. “Philosophy.” In The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica (eds.), Encyclopaedia Britannica , Online Edition.
Garson, James. 2019. “Modal Logic.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Groarke, Leo. 2019. “Informal Logic.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Winter 2019 Edition.
Gruen, Lori. 2019. “The Moral Status of Animals.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Gutting, Gary. 2009. What Philosophers Know: Case Studies in Recent Analytic Philosophy . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press.
Ingram, David and Jonathan Tallant. 2019. “Presentism.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Knobe, Joshua and Shaun Nichols. 2019. “Experimental Philosophy.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Winter 2019 Edition.
Markosian, Ned. 2019. “Time.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
McAfee, Noëlle. 2019. “Feminist Philosophy.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Winter 2019 Edition.
McNamara, Paul. 2019. “Deontic Logic.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Miller, Alexander. 2019. “Realism.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Olivelle, Patrick (tr. and ed.). 1998. The Early Upaniṣads: Annotated Text and Translation . New York, NY and Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Outlaw, Lucius T. Jr. 2019. “Africana Philosophy.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Papineau, David. 2019. “Naturalism.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Peter, Fabienne. 2019. “Political Legitimacy.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Priest, Graham et al. 2019. “Paraconsistent Logic.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Reicher, Maria. 2019. “Nonexistent Objects.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Rosen, Gideon et al. 2015. The Norton Introduction to Philosophy , Second Edition. New York, NY and London, UK: W. W. Norton & Company Ltd.
Russell, Bertrand. 2010. The Philosophy of Logical Atomism . Oxford, UK: Routledge Classics.
Sartwell, Crispin. 2019. “Beauty.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Steup, Matthias. 2019. “Epistemology.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Van Inwagen, Peter and Meghan Sullivan. 2019. “Metaphysics.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Van Norden, Bryan W. 2017. Taking Back Philosophy: A Multicultural Manifesto . New York, NY: Columbia University Press.
Weisberg, Jonathan. 2019. “Formal Epistemology.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Wilce, Alexander. 2019. “Quantum Logic and Probability Theory.” In E. N. Zalta (ed.), The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy , Winter 2019 Edition.
Related Essays
Arguments: Why Do You Believe What You Believe? by Thomas Metcalf
Critical Thinking: What is it to be a Critical Thinker? by Carolina Flores
Philosophy as a Way of Life by Christine Darr
Applied Ethics by Chelsea Haramia
Epistemology, or Theory of Knowledge by Thomas Metcalf
Philosophy and its Contrast with Science by Thomas Metcalf
Philosophical Inquiry in Childhood by Jana Mohr Lone
All Essays at 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
PDF Download
Download this essay in PDF.
Audio and Video
Listen here
Translation
About the author.
Tom Metcalf is an associate professor at Spring Hill College in Mobile, AL. He received his PhD in philosophy from the University of Colorado, Boulder. He specializes in ethics, metaethics, epistemology, and the philosophy of religion. Tom has two cats whose names are Hesperus and Phosphorus. shc.academia.edu/ThomasMetcalf
Follow 1000-Word Philosophy on Facebook , Twitter and subscribe to receive email notifications of new essays at 1000WordPhilosophy.com
Share this:, 9 thoughts on “ what is philosophy ”.
- Pingback: Felsefe Nedir – Thomas Metcalf – Veritas Analitik Felsefe Dergisi
- Pingback: Artificial Intelligence: The Possibility of Artificial Minds – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: 철학이란 무엇인가? – Thomas Metcalf - Doing Philosophy
- Pingback: Philosophy of Color – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Philosophy as a Way of Life – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Arguments: Why Do You Believe What You Believe? – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Modal Logic: Axioms and Systems for Alethic Modal Logic – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Philosophy and Its Contrast with Science – 1000-Word Philosophy: An Introductory Anthology
- Pingback: Online Philosophy Resources Weekly Update - Daily Nous
Comments are closed.
Quick links
- Make a Gift
- Directories
Why Study Philosophy?
What is philosophy, and why should i study it.
“Philosophy” comes from Greek words meaning “love of wisdom.” Philosophy uses the tools of logic and reason to analyze the ways in which humans experience the world. It teaches critical thinking, close reading, clear writing, and logical analysis; it uses these to understand the language we use to describe the world, and our place within it. Different areas of philosophy are distinguished by the questions they ask. Do our senses accurately describe reality? What makes wrong actions wrong? How should we live? These are philosophical questions, and philosophy teaches the ways in which we might begin to answer them.
Students who learn philosophy get a great many benefits from doing so. The tools taught by philosophy are of great use in further education, and in employment. Despite the seemingly abstract nature of the questions philosophers ask, the tools philosophy teaches tend to be highly sought-after by employers. Philosophy students learn how to write clearly, and to read closely, with a critical eye; they are taught to spot bad reasoning, and how to avoid it in their writing and in their work. It is therefore not surprising that philosophy students have historically scored more highly on tests like the LSAT and GRE, on average, than almost any other discipline. Many of our students combine studying philosophy with studying other disciplines.
The most important reason to study philosophy is that it is of enormous and enduring interest. All of us have to answer, for ourselves, the questions asked by philosophers. In this department, students can learn how to ask the questions well, and how we might begin to develop responses. Philosophy is important, but it is also enormously enjoyable, and our faculty contains many award-winning teachers who make the process of learning about philosophy fun. Our faculty are committed to a participatory style of teaching, in which students are provided with the tools and the opportunity to develop and express their own philosophical views.
Critical Thinking “It was in philosophy where I learned rigorous critical thinking, a skill that is invaluable when creating art.” - Donald Daedalus, BA ‘05, Visual Artist “Philosophy taught me to think critically and was the perfect major for law school, giving me an excellent start to law school and my career.” - Rod Nelson, BA ‘75, Lawyer
Tools for Assessing Ethical Issues “The courses I took for my minor in philosophy ... have provided a valuable framework for my career work in the field of global health and have given me a strong foundation for developing a structured, logical argument in various contexts.” - Aubrey Batchelor, Minor ‘09, Global Health Worker “Bioethics is an everyday part of medicine, and my philosophy degree has helped me to work through real-world patient issues and dilemmas.” - Teresa Lee, BA ‘08 Medical Student “The ability to apply an ethical framework to questions that have developed in my career, in taking care of patients ... has been a gift and something that I highly value.” - Natalie Nunes, BA ‘91, Family Physician Analytic Reasoning “... philosophy provided me with the analytical tools necessary to understand a variety of unconventional problems characteristic of the security environment of the last decade.” - Chris Grubb, BA ‘98, US Marine “Philosophy provides intellectual resources, critical and creative thinking capacity that are indispensable for success in contemporary international security environment “ - Richard Paz, BA ‘87, US Military Officer
Understanding Others’ Perspectives “... philosophy grounds us in an intellectual tradition larger than our own personal opinions. ... *making+ it is easier to be respectful of and accommodating to individual differences in clients (and colleagues)...” - Diane Fructher Strother, BA ‘00, Clinical Psychologist “... comprehensive exposure to numerous alternative world/ethical views has helped me with my daily interaction with all different types of people of ethnic, cultural, and political orientation backgrounds.” - David Prestin, BA ‘07, Engineer
Evaluating Information “Analyzing information and using it to form logical conclusions is a huge part of philosophy and was thus vital to my success in this position.” - Kevin Duchmann, BA ‘07, Inventory Control Analyst
Writing Skills “My philosophy degree has been incredibly important in developing my analytical and writing skills.” - Teresa Lee, BA ‘08, Medical Student
- YouTube
- Newsletter
- More ways to connect
1.1 What Is Philosophy?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify sages (early philosophers) across historical traditions.
- Explain the connection between ancient philosophy and the origin of the sciences.
- Describe philosophy as a discipline that makes coherent sense of a whole.
- Summarize the broad and diverse origins of philosophy.
It is difficult to define philosophy. In fact, to do so is itself a philosophical activity, since philosophers are attempting to gain the broadest and most fundamental conception of the world as it exists. The world includes nature, consciousness, morality, beauty, and social organizations. So the content available for philosophy is both broad and deep. Because of its very nature, philosophy considers a range of subjects, and philosophers cannot automatically rule anything out. Whereas other disciplines allow for basic assumptions, philosophers cannot be bound by such assumptions. This open-endedness makes philosophy a somewhat awkward and confusing subject for students. There are no easy answers to the questions of what philosophy studies or how one does philosophy. Nevertheless, in this chapter, we can make some progress on these questions by (1) looking at past examples of philosophers, (2) considering one compelling definition of philosophy, and (3) looking at the way academic philosophers today actually practice philosophy.
Historical Origins of Philosophy
One way to begin to understand philosophy is to look at its history. The historical origins of philosophical thinking and exploration vary around the globe. The word philosophy derives from ancient Greek, in which the philosopher is a lover or pursuer ( philia ) of wisdom ( sophia ). But the earliest Greek philosophers were not known as philosophers; they were simply known as sages . The sage tradition provides an early glimpse of philosophical thought in action. Sages are sometimes associated with mathematical and scientific discoveries and at other times with their political impact. What unites these figures is that they demonstrate a willingness to be skeptical of traditions, a curiosity about the natural world and our place in it, and a commitment to applying reason to understand nature, human nature, and society better. The overview of the sage tradition that follows will give you a taste of philosophy’s broad ambitions as well as its focus on complex relations between different areas of human knowledge. There are some examples of women who made contributions to philosophy and the sage tradition in Greece, India, and China, but these were patriarchal societies that did not provide many opportunities for women to participate in philosophical and political discussions.
The Sages of India, China, Africa, and Greece
In classical Indian philosophy and religion, sages play a central role in both religious mythology and in the practice of passing down teaching and instruction through generations. The Seven Sages, or Saptarishi (seven rishis in the Sanskrit language), play an important role in sanatana dharma , the eternal duties that have come to be identified with Hinduism but that predate the establishment of the religion. The Seven Sages are partially considered wise men and are said to be the authors of the ancient Indian texts known as the Vedas . But they are partly mythic figures as well, who are said to have descended from the gods and whose reincarnation marks the passing of each age of Manu (age of man or epoch of humanity). The rishis tended to live monastic lives, and together they are thought of as the spiritual and practical forerunners of Indian gurus or teachers, even up to today. They derive their wisdom, in part, from spiritual forces, but also from tapas , or the meditative, ascetic, and spiritual practices they perform to gain control over their bodies and minds. The stories of the rishis are part of the teachings that constitute spiritual and philosophical practice in contemporary Hinduism.
Figure 1.2 depicts a scene from the Matsya Purana, where Manu, the first man whose succession marks the prehistorical ages of Earth, sits with the Seven Sages in a boat to protect them from a mythic flood that is said to have submerged the world. The king of serpents guides the boat, which is said to have also contained seeds, plants, and animals saved by Manu from the flood.
Despite the fact that classical Indian culture is patriarchal, women figures play an important role in the earliest writings of the Vedic tradition (the classical Indian religious and philosophical tradition). These women figures are partly connected to the Indian conception of the fundamental forces of nature—energy, ability, strength, effort, and power—as feminine. This aspect of God was thought to be present at the creation of the world. The Rig Veda, the oldest Vedic writings, contains hymns that tell the story of Ghosha, a daughter of Rishi Kakshivan, who had a debilitating skin condition (probably leprosy) but devoted herself to spiritual practices to learn how to heal herself and eventually marry. Another woman, Maitreyi, is said to have married the Rishi Yajnavalkya (himself a god who was cast into mortality by a rival) for the purpose of continuing her spiritual training. She was a devoted ascetic and is said to have composed 10 of the hymns in the Rig Veda. Additionally, there is a famous dialogue between Maitreyi and Yajnavalkya in the Upanishads (another early, foundational collection of texts in the Vedic tradition) about attachment to material possessions, which cannot give a person happiness, and the achievement of ultimate bliss through knowledge of the Absolute (God).
Another woman sage named Gargi also participates in a celebrated dialogue with Yajnavalkya on natural philosophy and the fundamental elements and forces of the universe. Gargi is characterized as one of the most knowledgeable sages on the topic, though she ultimately concedes that Yajnavalkya has greater knowledge. In these brief episodes, these ancient Indian texts record instances of key women who attained a level of enlightenment and learning similar to their male counterparts. Unfortunately, this early equality between the sexes did not last. Over time Indian culture became more patriarchal, confining women to a dependent and subservient role. Perhaps the most dramatic and cruel example of the effects of Indian patriarchy was the ritual practice of sati , in which a widow would sometimes immolate herself, partly in recognition of the “fact” that following the death of her husband, her current life on Earth served no further purpose (Rout 2016). Neither a widow’s in-laws nor society recognized her value.
In similar fashion to the Indian tradition, the sage ( sheng ) tradition is important for Chinese philosophy . Confucius , one of the greatest Chinese writers, often refers to ancient sages, emphasizing their importance for their discovery of technical skills essential to human civilization, for their role as rulers and wise leaders, and for their wisdom. This emphasis is in alignment with the Confucian appeal to a well-ordered state under the guidance of a “ philosopher-king .” This point of view can be seen in early sage figures identified by one of the greatest classical authors in the Chinese tradition, as the “Nest Builder” and “Fire Maker” or, in another case, the “Flood Controller.” These names identify wise individuals with early technological discoveries. The Book of Changes , a classical Chinese text, identifies the Five (mythic) Emperors as sages, including Yao and Shun, who are said to have built canoes and oars, attached carts to oxen, built double gates for defense, and fashioned bows and arrows (Cheng 1983). Emperor Shun is also said to have ruled during the time of a great flood, when all of China was submerged. Yü is credited with having saved civilization by building canals and dams.
These figures are praised not only for their political wisdom and long rule, but also for their filial piety and devotion to work. For instance, Mencius, a Confucian philosopher, relates a story of Shun’s care for his blind father and wicked stepmother, while Yü is praised for his selfless devotion to work. In these ways, the Chinese philosophical traditions, such as Confucianism and Mohism, associate key values of their philosophical enterprises with the great sages of their history. Whether the sages were, in fact, actual people or, as many scholars have concluded, mythical forebearers, they possessed the essential human virtue of listening and responding to divine voices. This attribute can be inferred from the Chinese script for sheng , which bears the symbol of an ear as a prominent feature. So the sage is one who listens to insight from the heavens and then is capable of sharing that wisdom or acting upon it to the benefit of his society (Cheng 1983). This idea is similar to one found in the Indian tradition, where the most important texts, the Vedas, are known as shruti , or works that were heard through divine revelation and only later written down.
Although Confucianism is a venerable world philosophy, it is also highly patriarchal and resulted in the widespread subordination of women. The position of women in China began to change only after the Communist Revolution (1945–1952). While some accounts of Confucianism characterize men and women as emblematic of two opposing forces in the natural world, the Yin and Yang, this view of the sexes developed over time and was not consistently applied. Chinese women did see a measure of independence and freedom with the influence of Buddhism and Daoism, each of which had a more liberal view of the role of women (Adler 2006).
A detailed and important study of the sage tradition in Africa is provided by Henry Odera Oruka (1990), who makes the case that prominent folk sages in African tribal history developed complex philosophical ideas. Oruka interviewed tribal Africans identified by their communities as sages, and he recorded their sayings and ideas, confining himself to those sayings that demonstrated “a rational method of inquiry into the real nature of things” (Oruka 1990, 150). He recognized a tension in what made these sages philosophically interesting: they articulated the received wisdom of their tradition and culture while at the same time maintaining a critical distance from that culture, seeking a rational justification for the beliefs held by the culture.
Connections
The chapter on the early history of philosophy covers this topic in greater detail.
Among the ancient Greeks, it is common to identify seven sages. The best-known account is provided by Diogenes Laërtius, whose text Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers is a canonical resource on early Greek philosophy. The first and most important sage is Thales of Miletus . Thales traveled to Egypt to study with the Egyptian priests, where he became one of the first Greeks to learn astronomy. He is known for bringing back to Greece knowledge of the calendar, dividing the year into 365 days, tracking the progress of the sun from solstice to solstice, and—somewhat dramatically—predicting a solar eclipse in 585 BCE. The eclipse occurred on the day of a battle between the Medes and Lydians. It is possible that Thales used knowledge of Babylonian astronomical records to guess the year and location of the eclipse. This mathematical and astronomical feat is one of Thales’s several claims to sagacity. In addition, he is said to have calculated the height of the pyramids using the basic geometry of similar triangles and measuring shadows at a certain time of day. He is also reported to have predicted a particularly good year for olives: he bought up all the olive presses and then made a fortune selling those presses to farmers wanting to turn their olives into oil. Together, these scientific and technical achievements suggest that at least part of Thales’s wisdom can be attributed to a very practical, scientific, and mathematical knowledge of the natural world. If that were all Thales was known for, he might be called the first scientist or engineer. But he also made more basic claims about the nature and composition of the universe; for instance, he claimed that all matter was fundamentally made of up water. He also argued that everything that moved on its own possessed a soul and that the soul itself was immortal. These claims demonstrate a concern about the fundamental nature of reality.
Another of the seven sages was Solon , a famed political leader. He introduced the “Law of Release” to Athens, which cancelled all personal debts and freed indentured servants, or “debt-slaves” who had been consigned to service based on a personal debt they were unable to repay. In addition, he established a constitutional government in Athens with a representative body, a procedure for taxation, and a series of economic reforms. He was widely admired as a political leader but voluntarily stepped down so that he would not become a tyrant. He was finally forced to flee Athens when he was unable to persuade the members of the Assembly (the ruling body) to resist the rising tyranny of one of his relatives, Pisistratus. When he arrived in exile, he was reportedly asked whom he considered to be happy, to which he replied, “One ought to count no man happy until he is dead.” Aristotle interpreted this statement to mean that happiness was not a momentary experience, but a quality reflective of someone’s entire life.
Beginnings of Natural Philosophy
The sage tradition is a largely prehistoric tradition that provides a narrative about how intellect, wisdom, piety, and virtue led to the innovations central to flourishing of ancient civilizations. Particularly in Greece, the sage tradition blends into a period of natural philosophy, where ancient scientists or philosophers try to explain nature using rational methods. Several of the early Greek schools of philosophy were centered on their respective views of nature. Followers of Thales, known as the Milesians , were particularly interested in the underlying causes of natural change. Why does water turn to ice? What happens when winter passes into spring? Why does it seem like the stars and planets orbit Earth in predictable patterns? From Aristotle we know that Thales thought there was a difference between material elements that participate in change and elements that contain their own source of motion. This early use of the term element did not have the same meaning as the scientific meaning of the word today in a field like chemistry. But Thales thought material elements bear some fundamental connection to water in that they have the capacity to move and alter their state. By contrast, other elements had their own internal source of motion, of which he cites the magnet and amber (which exhibits forces of static electricity when rubbed against other materials). He said that these elements have “soul.” This notion of soul, as a principle of internal motion, was influential across ancient and medieval natural philosophy. In fact, the English language words animal and animation are derived from the Latin word for soul ( anima ).
Similarly, early thinkers like Xenophanes began to formulate explanations for natural phenomena. For instance, he explained rainbows, the sun, the moon, and St. Elmo’s fire (luminous, electrical discharges) as apparitions of the clouds. This form of explanation, describing some apparent phenomenon as the result of an underlying mechanism, is paradigmatic of scientific explanation even today. Parmenides, the founder of the Eleatic school of philosophy, used logic to conclude that whatever fundamentally exists must be unchanging because if it ever did change, then at least some aspect of it would cease to exist. But that would imply that what exists could not exist—which seems to defy logic. Parmenides is not saying that there is no change, but that the changes we observe are a kind of illusion. Indeed, this point of view was highly influential, not only for Plato and Aristotle, but also for the early atomists, like Democritus , who held that all perceived qualities are merely human conventions. Underlying all these appearances, Democritus reasoned, are only atomic, unchanging bits of matter flowing through a void. While this ancient Greek view of atoms is quite different from the modern model of atoms, the very idea that every observable phenomenon has a basis in underlying pieces of matter in various configurations clearly connects modern science to the earliest Greek philosophers.
Along these lines, the Pythagoreans provide a very interesting example of a community of philosophers engaged in understanding the natural world and how best to live in it. You may be familiar with Pythagoras from his Pythagorean theorem, a key principle in geometry establishing a relationship between the sides of a right-angled triangle. Specifically, the square formed by the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the two squares formed by the remaining two sides. In the figure below, the area of the square formed by c is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares formed by a and b. The figure represents how Pythagoras would have conceptualized the theorem.
The Pythagoreans were excellent mathematicians, but they were more interested in how mathematics explained the natural world. In particular, Pythagoras recognized relationships between line segments and shapes, such as the Pythagorean theorem describes, but also between numbers and sounds, by virtue of harmonics and the intervals between notes. Similar regularities can be found in astronomy. As a result, Pythagoras reasoned that all of nature is generated according to mathematical regularities. This view led the Pythagoreans to believe that there was a unified, rational structure to the universe, that the planets and stars exhibit harmonic properties and may even produce music, that musical tones and harmonies could have healing powers, that the soul is immortal and continuously reincarnated, and that animals possess souls that ought to be respected and valued. As a result, the Pythagorean community was defined by serious scholarship as well as strict rules about diet, clothing, and behavior.
Additionally, in the early Pythagorean communities, it was possible for women to participate and contribute to philosophical thought and discovery. Pythagoras himself was said to have been inspired to study philosophy by the Delphic priestess Themistoclea. His wife Theano is credited with contributing to important discoveries in the realms of numbers and optics. She is said to have written a treatise, On Piety , which further applies Pythagorean philosophy to various aspects of practical life (Waithe 1987). Myia, the daughter of this illustrious couple, was also an active and productive part of the community. At least one of her letters has survived in which she discusses the application of Pythagorean philosophy to motherhood. The Pythagorean school is an example of how early philosophical and scientific thinking combines with religious, cultural, and ethical beliefs and practices to embrace many different aspects of life.
How It All Hangs Together
Closer to the present day, in 1962, Wilfrid Sellars , a highly influential 20th-century American philosopher, wrote a chapter called “Philosophy and the Scientific Image of Man” in Frontiers of Science and Philosophy . He opens the essay with a dramatic and concise description of philosophy: “The aim of philosophy, abstractly formulated, is to understand how things in the broadest possible sense of the term hang together in the broadest possible sense of the term.” If we spend some time trying to understand what Sellars means by this definition, we will be in a better position to understand the academic discipline of philosophy. First, Sellars emphasizes that philosophy’s goal is to understand a very wide range of topics—in fact, the widest possible range. That is to say, philosophers are committed to understanding everything insofar as it can be understood. This is important because it means that, on principle, philosophers cannot rule out any topic of study. However, for a philosopher not every topic of study deserves equal attention. Some things, like conspiracy theories or paranoid delusions, are not worth studying because they are not real. It may be worth understanding why some people are prone to paranoid delusions or conspiratorial thinking, but the content of these ideas is not worth investigating. Other things may be factually true, such as the daily change in number of the grains of sand on a particular stretch of beach, but they are not worth studying because knowing that information will not teach us about how things hang together. So a philosopher chooses to study things that are informative and interesting—things that provide a better understanding of the world and our place in it.
To make judgments about which areas are interesting or worthy of study, philosophers need to cultivate a special skill. Sellars describes this philosophical skill as a kind of know-how (a practical, engaged type of knowledge, similar to riding a bike or learning to swim). Philosophical know-how, Sellars says, has to do with knowing your way around the world of concepts and being able to understand and think about how concepts connect, link up, support, and rely upon one another—in short, how things hang together. Knowing one’s way around the world of concepts also involves knowing where to look to find interesting discoveries and which places to avoid, much like a good fisherman knows where to cast his line. Sellars acknowledges that other academics and scientists know their way around the concepts in their field of study much like philosophers do. The difference is that these other inquirers confine themselves to a specific field of study or a particular subject matter, while philosophers want to understand the whole. Sellars thinks that this philosophical skill is most clearly demonstrated when we try to understand the connection between the natural world as we experience it directly (the “manifest image”) and the natural world as science explains it (the “scientific image”). He suggests that we gain an understanding of the nature of philosophy by trying to reconcile these two pictures of the world that most people understand independently.
Read Like a Philosopher
“philosophy and the scientific image of man”.
This essay, “ Philosophy and the Scientific Image of Man ” by Wilfrid Sellars, has been republished several times and can be found online. Read through the essay with particular focus on the first section. Consider the following study questions:
- What is the difference between knowing how and knowing that? Are these concepts always distinct? What does it mean for philosophical knowledge to be a kind of know-how?
- What do you think Sellars means when he says that philosophers “have turned other special subject-matters to non-philosophers over the past 2500 years”?
- Sellars describes philosophy as “bringing a picture into focus,” but he is also careful to recognize challenges with this metaphor as it relates to the body of human knowledge. What are those challenges? Why is it difficult to imagine all of human knowledge as a picture or image?
- What is the scientific image of man in the world? What is the manifest image of man in the world? How are they different? And why are these two images the primary images that need to be brought into focus so that philosophy may have an eye on the whole?
Unlike other subjects that have clearly defined subject matter boundaries and relatively clear methods of exploration and analysis, philosophy intentionally lacks clear boundaries or methods. For instance, your biology textbook will tell you that biology is the “science of life.” The boundaries of biology are fairly clear: it is an experimental science that studies living things and the associated material necessary for life. Similarly, biology has relatively well-defined methods. Biologists, like other experimental scientists, broadly follow something called the “scientific method.” This is a bit of a misnomer, unfortunately, because there is no single method that all the experimental sciences follow. Nevertheless, biologists have a range of methods and practices, including observation, experimentation, and theory comparison and analysis, that are fairly well established and well known among practitioners. Philosophy doesn’t have such easy prescriptions—and for good reason. Philosophers are interested in gaining the broadest possible understanding of things, whether that be nature, what is possible, morals, aesthetics, political organizations, or any other field or concept.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-philosophy/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Nathan Smith
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Philosophy
- Publication date: Jun 15, 2022
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-philosophy/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-philosophy/pages/1-1-what-is-philosophy
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Philosophy Break Your home for learning about philosophy
Introductory philosophy courses distilling the subject's greatest wisdom.
Reading Lists
Curated reading lists on philosophy's best and most important works.
Latest Breaks
Bite-size philosophy articles designed to stimulate your brain.

Why Is Philosophy Important Today, and How Can It Improve Your Life?
From clarity to tolerance: here’s your quick guide to why philosophy is important today, as well as how it can improve your life.
7 MIN BREAK
P hilosophy essentially involves thinking hard about life’s big questions , including — as we discuss in our article on what philosophy is, how it works, as well as its four core branches — why we are here, how we can know anything about the world, and what our lives are for.
Here at Philosophy Break, we believe the practice of philosophy is the antidote to a world saturated by information, and the more that people engage with philosophy, the more fulfilling their lives will be.
The addictive nature of the digital world, for instance, afflicts many of us. The relentless torrent of information saturates our attention spans. But life is finite, and the things we give attention to define our lives. It’s crucial to break free from the turbulent current and come up for air.
As Roman Stoic philosopher Seneca put it almost 2,000 years ago in his brilliant treatise, On the Shortness of Life :
It is not that we have a short time to live, but that we waste a lot of it. Life is long enough, and a sufficiently generous amount has been given to us for the highest achievements if it were all well invested. But when it is wasted in heedless luxury and spent on no good activity, we are forced at last by death’s final constraint to realize that it has passed away before we knew it was passing. So it is: we are not given a short life but we make it short, and we are not ill-supplied but wasteful of it… Life is long if you know how to use it.
Streaming services hook us into one more episode, those of us with smartphones check them without thinking; but the compulsion to watch, to shop, to hit refresh on our newsfeeds — all of it can be reined in by contemplating the world around us, and our place within it.
How can we best spend our lives on earth? What makes you happy? What gives you purpose?

A lot of the anxieties and uncertainties we feel in our lives, from wondering if our occupations give us the meaning we need, to not being able to come to terms with death, are at root philosophical problems. And philosophers have confronted and had hugely insightful things to say about these problems for thousands of years.
Critically engaging with the enduring wisdom of philosophy is a fantastic way to both inform ourselves about the problems inherent within the human condition, and also face up to those problems and calm our existential fears and anxieties.
By engaging with the ideas of great thinkers throughout history, we’re empowered to think for ourselves — be it on matters of meaning and existence, how to make a better world, or simply working out what’s worth pursuing in life.
For as Socrates , the famous ancient Greek martyr of philosophy , declared:
The unexamined life is not worth living.
Philosophical contemplation is the starting gun that jolts us out of going through life as if we’re only going through the motions, living only according to the expectations of others, or living by norms we’ve never really thought about, let alone endorsed.
Philosophy opens our eyes to the multitudinous ways we can spend our lives, engendering tolerance for those whose practices differ from our own, and reawakening a childlike wonder and appreciation for the sheer mystery and opportunity lying at the heart of existence.
Why is philosophy important today?
P hilosophy is sometimes considered outdated — a perception not helped by the subject’s apparent obsession with reaching back over thousands of years to consider the works of ancient figures like Socrates , Plato , Aristotle , and Confucius .
But the point of philosophy in modern times remains the point philosophy has always had: to answer the fundamental questions that lie at the heart of the human condition.
Philosophy plays a crucial role in this regard not just in personal study and exploration, but formally in academia and modern research projects. And, even as time mercilessly advances, it turns out ancient figures whose works have survived over millennia still have some of the most interesting things to say about our human predicament, making their wisdom worth republishing and studying generation after generation.
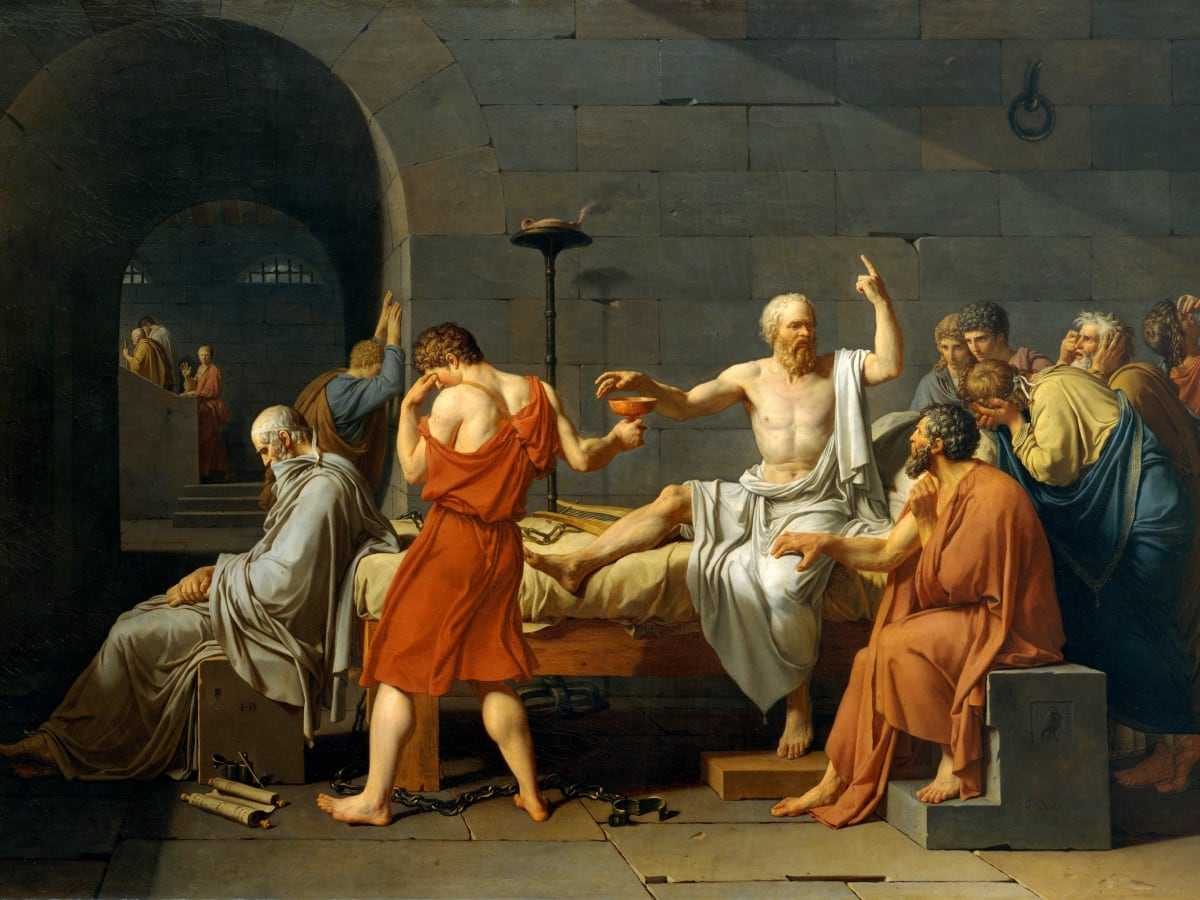

Now, it might be thought that some of the questions philosophy touches on, such as the basic nature of the universe , or the emergence of consciousness , have been superseded by more specialist scientific subjects.
For example, physicists are at the forefront of investigating the fundamental nature of reality. Likewise, neuroscientists are leading the way in unlocking the secrets of the brain.
But philosophy is not here to compete with these brilliant, fascinating research projects, but to supplement, clarify, and even unify them.
For instance, when physicists share their latest mathematical models that predict the behavior of matter, philosophers ask, “okay, so what does this behavior tell us about the intrinsic nature of matter itself? What is matter? Is it physical, is it a manifestation of consciousness? — and why does any of this stuff exist in the first place?”
Equally, when neuroscientists make progress in mapping the brain, philosophers are on hand to digest the consequences the latest research has for our conceptions of consciousness and free will .
And, just as pertinently, while computer scientists continue to advance the sophistication of AI, philosophers discuss the implications an ever-growing machine intelligence has for society , and dissect the urgent ethical and moral concerns accompanying them.
With its focus on argument and clarity, philosophy is particularly good at rooting out the assumptions and contradictions that lie at the core of commonsensical thinking, sharpening our insight into truth, and lending security to the foundations of knowledge in all areas of research — especially the sciences, operating as they do at the frontiers of what we know.
The Sleep of Reason Produces Monsters
T he practice of philosophical reflection is not just important for progressing research, however: it is crucial for successfully navigating a world in which competing responsibilities, information, and forces pull us in various directions.
This is exactly what the Spanish painter and printmaker Francisco Goya understood when he produced his famous etching, The Sleep of Reason Produces Monsters , depicted below.

In his analysis of Goya’s etching, contemporary philosopher Simon Blackburn notes in his book Think that “there are always people telling us what we want, how they will provide it, and what we should believe”, forcefully continuing:
Convictions are infectious, and people can make others convinced of almost anything. We are typically ready to believe that our ways, our beliefs, our religions, our politics are better than theirs, or that our God-given rights trump theirs or that our interests require defensive or pre-emptive strikes against them. In the end, it is ideas for which people kill each other. It is because of ideas about what the others are like, or who we are, or what our interests or rights require, that we go to war, or oppress others with a good conscience, or even sometimes acquiesce in our own oppression by others.
With so much at stake, sleeps of reason must be countered to stop the dangerous spread of misinformation. Blackburn recommends philosophical awakening as the antidote:
Reflection enables us to step back, to see our perspective on a situation as perhaps distorted or blind, at the very least to see if there is argument for preferring our ways, or whether it is just subjective.
By deploying critical thinking and the rigor of philosophy, we are less likely to be duped or led by those who — intentionally or unintentionally — malform our thinking.
Blackburn’s advocacy for critical philosophical reflection can be paired with the full motto of Goya’s etching:
Imagination abandoned by reason produces impossible monsters: united with her, she is the mother of the arts and the source of her wonders.
Philosophy’s transformative power
B eyond the clarification of knowledge, the greatest philosophy — like the greatest science — has enormous explanatory power that can transform how we see the world.
Just as Albert Einstein’s theory of relativity skewers our everyday notion of time, so Friedrich Nietzsche’s dissection of morality challenges our everyday notions of ‘good’ and ‘evil’, John Locke’s analysis of color challenges our very idea of whether perception is reality, and Lucretius’s timeless reflection on death helps us cope with our mortality.

The world is uncertain, and the value of philosophy lies precisely in facing up to this uncertainty — and in finding footholds for knowledge and progress in spite of it. As the 20th-century philosophical giant Bertrand Russell summarizes in his wonderful exposition on why philosophy matters :
Philosophy is to be studied, not for the sake of any definite answers to its questions since no definite answers can, as a rule, be known to be true, but rather for the sake of the questions themselves; because these questions enlarge our conception of what is possible, enrich our intellectual imagination and diminish the dogmatic assurance which closes the mind against speculation; but above all because, through the greatness of the universe which philosophy contemplates, the mind also is rendered great, and becomes capable of that union with the universe which constitutes its highest good.
Discover philosophy’s greatest wisdom
I f you’re interested in learning more about philosophy, our celebrated introductory philosophy course, Life’s Big Questions , distills philosophy’s best answers to some of life’s most troubling questions, taking you on a whirlwind five-day journey of reflection, understanding, and discovery. Here are the questions covered:
Why does anything exist? Is the world around us ‘real’? What makes us conscious? Do we have free will? How should we approach life?
Enroll today, and each day over five days, you’ll receive beautifully-packaged materials that distill philosophy’s best answers to these questions from the last few millennia. Interested in learning more? Explore the course now .
By choosing to learn more about philosophy, a wonderful journey of self-discovery awaits you... have fun exploring!
Life’s Big Questions: Your Concise Guide to Philosophy’s Most Important Wisdom
Why does anything exist? Do we have free will? How should we approach life? Discover the great philosophers’ best answers to life’s big questions.
★★★★★ (50+ reviews for our courses)
Latest Course Reviews:
★★★★★ Very good
VERIFIED BUYER
★★★★★ Great intro
★★★★★ Great
See All Course Reviews
PHILOSOPHY 101
- What is Philosophy?
- Why is Philosophy Important?
- Philosophy’s Best Books
- About Philosophy Break
- Support the Project
- Instagram / Threads / Facebook
- TikTok / Twitter
Philosophy Break is an online social enterprise dedicated to making the wisdom of philosophy instantly accessible (and useful!) for people striving to live happy, meaningful, and fulfilling lives. Learn more about us here . To offset a fraction of what it costs to maintain Philosophy Break, we participate in the Amazon Associates Program. This means if you purchase something on Amazon from a link on here, we may earn a small percentage of the sale, at no extra cost to you. This helps support Philosophy Break, and is very much appreciated.
Access our generic Amazon Affiliate link here
Privacy Policy | Cookie Policy
© Philosophy Break Ltd, 2024


Unit 1: What Is Philosophy?
The Value of Philosophy
Bertrand Russell

We need to consider what is the value of philosophy and why it ought to be studied. It is the more necessary to consider this question, in view of the fact that many people, under the influence of science or of practical affairs, are inclined to doubt whether philosophy is anything better than innocent but useless trifling, hairsplitting distinctions, and controversies on matters concerning which knowledge is impossible.
This view of philosophy appears to result, partly from a wrong conception of the ends of life, partly from a wrong conception of the kind of goods which philosophy strives to achieve. Physical science, through the medium of inventions, is useful to innumerable people who are wholly ignorant of it; thus the study of physical science is to be recommended, not only, or primarily, because of the effect on the student, but rather because of the effect on mankind in general. This utility does not belong to philosophy. If the study of philosophy has any value at all for others than students of philosophy, it must be only indirectly, through its effects upon the lives of those who study it. It is in these effects, therefore, if anywhere, that the value of philosophy must be primarily sought.
But further, if we are not to fail in our endeavor to determine the value of philosophy, we must first free our minds from the prejudices of what are wrongly called “practical” people. The “practical” person, as this word is often used, is one who recognizes only material needs, who realizes that people must have food for the body, but is oblivious of the necessity of providing food for the mind. If all people were well off, if poverty and disease had been reduced to their lowest possible point, there would still remain much to be done to produce a valuable society; and even in the existing world the goods of the mind are at least as important as the goods of the body. It is exclusively among the goods of the mind that the value of philosophy is to be found; and only those who are not indifferent to these goods can be persuaded that the study of philosophy is not a waste of time.
Philosophy, like all other studies, aims primarily at knowledge. The knowledge it aims it is the kind of knowledge which gives unity and system to the body of the sciences, and the kind which results from a critical examination of the grounds of our convictions, prejudices, and beliefs. But it cannot be maintained that philosophy has had any very great measure of success in its attempts to provide definite answers to its questions. If you ask a mathematician, a mineralogist, a historian, or any other person of learning, what definite body of truths has been ascertained by his science, his answer will last as long as you are willing to listen. But if you put the same question to a philosopher, he will, if he is candid, have to confess that his study has not achieved positive results such as have been achieved by other sciences. It is true that this is partly accounted for by the fact that, as soon as definite knowledge concerning any subject becomes possible, this subject ceases to be called philosophy, and becomes a separate science. The whole study of the heavens, which now belongs to astronomy, was once included in philosophy; Newton’s great work was called “the mathematical principles of natural philosophy.” Similarly, the study of the human mind, which was, until very lately, a part of philosophy, has now been separated from philosophy and has become the science of psychology. Thus, to a great extent, the uncertainty of philosophy is more apparent than real: those questions which are already capable of definite answers are placed in the sciences, while those only to which, at present, no definite answer can be given, remain to form the residue which is called philosophy.
This is, however, only a part of the truth concerning the uncertainty of philosophy. There are many questions—and among them those that are of the profoundest interest to our spiritual life—which, so far as we can see, must remain insoluble to the human intellect unless its powers become of quite a different order from what they are now. Has the universe any unity of plan or purpose, or is it a fortuitous concourse of atoms? Is consciousness a permanent part of the universe, giving hope of indefinite growth in wisdom, or is it a transitory accident on a small planet on which life must ultimately become impossible? Are good and evil of importance to the universe or only to humanity? Such questions are asked by philosophy, and variously answered by various philosophers. But it would seem that, whether answers be otherwise discoverable or not, the answers suggested by philosophy are none of them demonstrably true. Yet, however slight may be the hope of discovering an answer, it is part of the business of philosophy to continue the consideration of such questions, to make us aware of their importance, to examine all the approaches to them, and to keep alive that speculative interest in the universe which is apt to be killed by confining ourselves to definitely ascertainable knowledge…
The value of philosophy is, in fact, to be sought largely in its very uncertainty. The person who has no tincture of philosophy goes through life imprisoned in the prejudices derived from common sense, from the habitual beliefs of his age or his nation, and from convictions which have grown up in his mind without the cooperation or consent of his deliberate reason. To such a person the world tends to become definite, finite, obvious; common objects rouse no questions, and unfamiliar possibilities are contemptuously rejected. As soon as we begin to philosophize, on the contrary, we find, as we saw in our opening chapters, that even the most everyday things lead to problems to which only very incomplete answers can be given. Philosophy, though unable to tell us with certainty what is the true answer to the doubts which it raises, is able to suggest many possibilities which enlarge our thoughts and free them from the tyranny of custom. Thus, while diminishing our feeling of certainty as to what things are, it greatly increases our knowledge as to what they may be; it removes the somewhat arrogant dogmatism of those who have never traveled into the region of liberating doubt, and it keeps alive our sense of wonder by showing familiar things in an unfamiliar aspect.
Apart from its utility in showing unsuspected possibilities, philosophy has a value—perhaps its chief value—through the greatness of the objects which it contemplates, and the freedom from narrow and personal aims resulting from this contemplation. The life of the instinctive person is shut up within the circle of his private interests: family and friends may be included, but the outer world is not regarded except as it may help or hinder what comes within the circle of instinctive wishes. In such a life there is something feverish and confined, in comparison with which the philosophic life is calm and free. The private world of instinctive interests is a small one, set in the midst of a great and powerful world which must, sooner or later, lay our private world in ruins. Unless we can so enlarge our interests as to include the whole outer world, we remain like a garrison in a beleaguered fortress, knowing that the enemy prevents escape and that ultimate surrender is inevitable. In such a life there is no peace, but a constant strife between the insistence of desire and the powerlessness of will. In one way or another, if our life is to be great and free, we must escape this prison and this strife.
One way of escape is by philosophic contemplation. Philosophic contemplation does not, in its widest survey, divide the universe into two hostile camps—friends and foes, helpful and hostile, good and bad—it views the whole impartially. Philosophic contemplation, when it is unalloyed, does not aim at proving that the rest of the universe is akin to humanity. All acquisition of knowledge is an enlargement of the Self, but this enlargement is best attained when it is not directly sought. It is obtained when the desire for knowledge is alone operative, by a study which does not wish in advance that its objects should have this or that character, but adapts the Self to the characters which it finds in its objects. This enlargement of Self is not obtained when, taking the Self as it is, we try to show that the world is so similar to this Self that knowledge of it is possible without any admission of what seems alien. The desire to prove this is a form of self-assertion, and like all self-assertion, it is an obstacle to the growth of Self which it desires, and of which the Self knows that it is capable. Self-assertion, in philosophic speculation as elsewhere, views the world as a means to its own ends; thus it makes the world of less account than Self, and the Self sets bounds to the greatness of its goods. In contemplation, on the contrary, we start from the not-Self, and through its greatness the boundaries of Self are enlarged; through the infinity of the universe the mind which contemplates it achieves some share in infinity.
For this reason greatness of soul is not fostered by those philosophies which assimilate the universe to Humanity. Knowledge is a form of union of Self and not-Self; like all union, it is impaired by dominion, and therefore by any attempt to force the universe into conformity with what we find in ourselves. There is a widespread philosophical tendency towards the view which tells us that humanity is the measure of all things, that truth is person-made, that space and time and the world of universals are properties of the mind, and that, if there be anything not created by the mind, it is unknowable and of no account for us. This view, if our previous discussions were correct, is untrue; but in addition to being untrue, it has the effect of robbing philosophic contemplation of all that gives it value, since it fetters contemplation to Self. What it calls knowledge is not a union with the not-Self, but a set of prejudices, habits, and desires, making an impenetrable veil between us and the world beyond. The person who finds pleasure in such a theory of knowledge is like the person who never leaves the domestic circle for fear his word might not be law.
The true philosophic contemplation, on the contrary, finds its satisfaction in every enlargement of the not-Self, in everything that magnifies the objects contemplated, and thereby the subject contemplating. Everything, in contemplation, that is personal or private, everything that depends upon habit, self-interest, or desire, distorts the object, and hence impairs the union which the intellect seeks. By thus making a barrier between subject and object, such personal and private things become a prison to the intellect. The free intellect will see as God might see, without a here and now, without hopes and fears, without the trammels of customary beliefs and traditional prejudices, calmly, dispassionately, in the sole and exclusive desire of knowledge—knowledge as impersonal, as purely contemplative, as it is possible for humanity to attain. Hence also the free intellect will value more the abstract and universal knowledge into which the accidents of private history do not enter, than the knowledge brought by the senses, and dependent, as such knowledge must be, upon an exclusive and personal point of view and a body whose sense-organs distort as much as they reveal.
The mind which has become accustomed to the freedom and impartiality of philosophic contemplation will preserve something of the same freedom and impartiality in the world of action and emotion. It will view its purposes and desires as parts of the whole, with the absence of insistence that results from seeing them as infinitesimal fragments in a world of which all the rest is unaffected by any one person’s deeds. The impartiality which, in contemplation, is the unalloyed desire for truth, is the very same quality of mind which, in action, is justice, and in emotion is that universal love which can be given to all, and not only to those who are judged useful or admirable. Thus, contemplation enlarges not only the objects of our thoughts, but also the objects of our actions and our affections: it makes us citizens of the universe, not only of one walled city at war with all the rest. In this citizenship of the universe consists humanity’s true freedom, and his liberation from the thralldom of narrow hopes and fears.
Thus, to sum up our discussion of the value of philosophy: Philosophy is to be studied, not for the sake of any definite answers to its questions, since no definite answers can, as a rule, be known to be true, but rather for the sake of the questions themselves; because these questions enlarge our conception of what is possible, enrich our intellectual imagination, and diminish the dogmatic assurance which closes the mind against speculation; but above all because, through the greatness of the universe which philosophy contemplates, the mind also is rendered great, and becomes capable of that union with the universe which constitutes its highest good.
Citation and Use
The text was taken from the following work.
Bertrand Russell, The Problems of Philosophy (Urbana, IL: Project Gutenberg, 2004), http://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/5827 .
The use of this work is governed by the Public Domain.
Media Attributions
- Bertrand_Russell_1957 is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
This work ( The Value of Philosophy by Bertrand Russell) is free of known copyright restrictions.
Share This Book
- Faculty of Arts
- School of Historical and Philosophical Studies
- Current students
- Undergraduate
Philosophy essay writing guide
Introduction.
This guide is intended to give new students of philosophy some preliminary advice about writing philosophy essays at university. For many of you, writing a philosophy essay will be something of a new experience, and no doubt many of you will be a little unsure of what to expect, or of what is expected of you. Most of you will have written essays in school for English, History, etc. A philosophy essay is something a little different again. However, it is not an unfathomable, mysterious affair, nor one where anything goes.
Just what a philosophy essay is will depend a lot, as you'd expect, on just what philosophy is. Defining philosophy is always a more or less controversial business, but one way to think of what is done in university philosophy departments is to think of the difference between having a philosophy and doing philosophy. Virtually everyone "has a philosophy" in the sense that we have many basic beliefs about the world and ourselves and use certain key concepts to articulate those beliefs. Many of us initially come to thus "have a philosophy" (or elements of several philosophies) often only unconsciously, or by following "what's obvious" or "what everybody knows", or by adopting a view because it sounds exciting or is intellectually fashionable.
"Doing philosophy", on the other hand, is a self-conscious unearthing and rigorous examination of these basic beliefs and key concepts. In doing so, we try to clarify the meanings of those beliefs and concepts and to evaluate critically their rational grounds or justification. Thus, rather than having their heads in the clouds, philosophers are really more under the surface of our thinking, examining the structures that support - or fail to support - those who trust that they have their feet on the ground. Such examination may even help to develop new and firmer ground.
Doing philosophy, then, begins with asking questions about the fundamental ideas and concepts that inform our ways of looking at the world and ourselves, and proceeds by developing responses to those questions which seek to gain insight into those ideas and concepts - and part of that development consists in asking further questions, giving further responses, and so on. Human beings across the world have been engaged in this sort of dialogue of question and response for many centuries - even millennia - and a number of great traditions of reflection and inquiry have evolved that have fundamentally influenced the development of religion, art, science and politics in many cultures. The influence of philosophical thinking on Western civilization, in particular, can be traced back more than 2,500 years to the Ancient Greeks.
In philosophy, a good essay is one that, among other things, displays a good sense of this dialectic of question and response by asking insightful, probing questions, and providing reasoned, well-argued responses. This means that you should not rest content with merely an unintegrated collection of assertions, but should instead work at establishing logical relations between your thoughts. You are assessed not on the basis of what you believe, but on how well you argue for the position you adopt in your essay, and on how interesting and insightful your discussion of the issues is. That is to say, you are assessed on how well you do philosophy, not on what philosophy you end up having. Nonetheless, you ought to make sure that your essay's discussion is relevant to the topic. (See Section 5.2 below on relevance.)
It is hoped that you enjoy the activity of essay writing. If you have chosen to study Arts, it is likely that you will have a particular interest in - even a passion for - ideas and the variety of forms and genres in which ideas are expressed and explored. The argumentative or discursive formal academic essay is one such form, and one which can be a pleasure to read and to write. Thus, the assessment that is set in philosophy courses is primarily an invitation to you to pursue what is already (or, hopefully, soon to be) your own interest in writing to explore ideas. However, your immediate goal in writing an academic philosophy essay ought not to be to write a personal testament, confession or polemic. Rather, you should primarily aim at articulating, clearly and relatively dispassionately, your philosophical thinking on the topic at hand. Nevertheless, the kind and degree of personal development one can gain from taking up the challenge to think and to write carefully, clearly and thoroughly is certainly something to be greatly valued.
This guide is intended to help you get started in the business of writing philosophy essays. As you practise your philosophical writing skills, you will develop your own technique, and learn what is appropriate in each particular case. So you may well come to "work around" many of these guidelines. Nonetheless, it is important that you pass through that which you seek to pass beyond.* In addition to your own writing, your reading of other philosophers will help you to develop your sense of what constitutes good philosophical writing. As you read, note the various styles and techniques that philosophical authors employ in their treatment of philosophical issues. Practice and studying good examples, then, are the most valuable ways to develop your essay writing skills.
This guide is, moreover, only one of many publications that introduce philosophy students to essay writing. Some others you may like to consult include:
- A. P. Martinich, Philosophical Writing, 2nd ed. (Oxford: Blackwell, 1997)
- J. Feinberg and R. Shafer-Landau, Doing Philosophy: A Guide to the Writing of Philosophy Papers, 2nd ed. (Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, 2001)
- Z. Seech, Writing Philosophy Papers, 4th ed. (Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, 2003)
- R. Solomon, "Writing Philosophy", Appendix to his The Big Questions: A Short Introduction to Philosophy, 6th ed. (Belmont, Calif.: Wadsworth, 2001)
- S. Gorovitz et al., Philosophical Analysis: An Introduction to its Language and Techniques, 3rd ed. (New York: Random House, 1979)
Also, the websites of many philosophy departments in universities around Australia and the world contain downloadable essay writing guides or links to them.
*This phrase is adapted from Jacques Bouveresse, "Why I am so very unFrench", in Alan Montefiore, ed., Philosophy in France Today (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1983), p. 12.
What do I do in a Philosophy essay?
Philosophy essay topics are not designed to provide an intellectual obstacle course that trips you up so as to delight a malicious marker. They are designed to invite you to "grapple with" with some particular philosophical problem or issue. That is to say, they are designed to offer you an opportunity to demonstrate your understanding of a particular philosophical problem or issue, and to exhibit your own philosophical skills of analysis, argumentation, etc. These twin goals are usually best achieved by ensuring that your essay performs two basic functions (your understanding and your skills apply to both):
an exposition of the problem or issue in question (often as it is posed in some particular text); and a critical discussion of the problem or text
These two functions can, but need not always, correspond to physically or structurally distinct sections of your essay. See Section 5.1.
The expository ("setting forth") aspect of your essay is where you should make clear what the issue is and why it is an issue. Where you are dealing with an issue as it is presented in some particular text, your aim should be to make clear what it is that the author in question meant in their text, what they see as the issue and why they see it as an issue. This does not involve merely quoting or paraphrasing a text. Of course, occasional quotation and paraphrase may be appropriate - sometimes necessary - but these ought not to constitute the sole or major content of your exposition. Where you do quote or paraphrase, make sure you attribute your sources in footnotes or endnotes. (See Section 7.)
Exposition is, then, primarily a matter of developing in your own words what you think the issue is or what you think the text means. In all expository work you should always try to give a fair and accurate account of a text or problem, even when the exposition becomes more interpretive rather than simply descriptive. You ought to be patient and sympathetic in your exposition, even if you intend later to criticise heavily the philosopher in question. Indeed, the better the exposition in this regard, usually the more effective the critique.
An important part of exposition is your analysis of the text or issue. Here you should try to "break down" the text, issue or problem into its constitutive elements by distinguishing its different parts. (E.g. "There are two basic kinds of freedom in question when we speak of freedom of the will. First, … . Second, …", or "There are three elements in Plato's conception of the soul, namely... He establishes these three elements by means of the following two arguments... ") This also involves showing the relationships between those elements, relationships which make them "parts of the whole".
As well as laying out these elements within a text or issue, you can also (when appropriate or relevant) show how a text or issue "connects up with" other texts, issues, or philosophical and/or historical developments, which can help to shed further light on the matter by giving it a broader context. (eg "Freedom of the will is importantly connected to the justification of punishment", or "Plato's tripartite theory of the soul bears interesting resemblances to Freud's analysis of the psyche", or "Kant's transcendental idealism can be seen as reconciling the preceding rationalist and empiricist accounts of knowledge".)
An exposition of a text need not always simply follow the author's own view of what it means. You should, of course, demonstrate that you understand how the author themself understands their work, but an exposition can sometimes go beyond this, giving another reading of the text. (eg "Heidegger might deny it, but his Being and Time can be read as developing a pragmatist account of human understanding.") A given text or issue may well be susceptible to a number of plausible or reasonable interpretations. An exposition should aim to be sensitive to such variety. When appropriate, you should defend your interpretations against rivals and objections. Your interpretation ought, though, to be aimed at elucidating the meaning or meanings of the text or issue and not serve merely as a "coat-hanger" for presenting your own favoured views on the matter in question, which should be left to your ...
Critical discussion
This is where your thought gets more of the centre stage. Here you should attempt to develop a response to the issues which your exposition has made clear, and/or, in the case of a discussion of some particular text, attempt to give a critical appraisal of the author's treatment of the issue. In developing a response to a philosophical problem, argumentation is, again, of central importance. Avoid making unsupported assertions; back up your claims with reasons, and connect up your ideas so that they progress logically toward your conclusions. Consider some of the various objections to and questions about your views that others might or have put forward, and try to respond to them in defence of your own line of thinking. Your goal here should be to discuss what you have expounded so as to come to some conclusion or judgement about it. ("Critical" is derived from the Ancient Greek for "to decide, to judge".) Critical discussion is thus not necessarily "destructive" or "negative"; it can be quite constructive and positive.
In the case of a critical appraisal of a particular author's text, you can negatively criticise the author's arguments by pointing out questionable assumptions, invalid reasoning, etc. If, on the other hand, you think that the text is good, then your critical discussion can be positive. This can be done by revealing its "hidden virtues" (that is, by showing that there is more to the author's arguments and views than what lies on the surface) and/or by defending an author against possible and/or actual criticisms. (eg "Norman Malcolm argues that Descartes is mistaken in assuming that dreams and waking episodes have the same content.* However, Malcolm fails to appreciate the subtlety of Descartes' argument in the First Meditation, which allows Descartes to claim . . .") Just to expound an author's arguments and then say "I disagree" or "That seems right" is not really enough - you need to "have something to say" about it. Of course, by all means go on, after finding fault with some philosopher, to answer in your own way the questions tackled or raised by the author. (eg "Simone de Beauvoir's analysis of women's oppression in The Second Sex suffers from serious weaknesses, as I have shown in Section 2 above. A better way to approach the issue, I shall now argue, is to . . .".)
Where you are not primarily concerned with evaluating or responding to a particular text, your critical discussion can be more focused on your own constructive response to the issue. (eg "Having used Dworkin's account to clarify the meanings of the concepts of 'the sanctity of life' and 'voluntariness', I shall now argue that voluntary euthanasia is morally permissible because its voluntariness respects what is of value in the notion of the sanctity of life" - where you now leave Dworkin behind as a source and move on to give your own account.)
* See Norman Malcolm, "Dreaming and Skepticism", in Willis Doney, ed., Descartes: A Collection of Critical Essays (London: Macmillan, 1967), p. 56.
Guide to researching and writing Philosophy essays
5th edition by Steven Tudor , for the Philosophy program, University of Melbourne, 2003.
This fifth edition of How to Write a Philosophy Essay: A Guide for Students (previous editions titled A Guide to Researching and Writing Philosophy Essays ) was prepared in consultation with members of the Philosophy program, the University of Melbourne. For advice and assistance on this and earlier editions, thanks are due to Graham Priest, Barry Taylor, Christopher Cordner, Doug Adeney, Josie Winther, Linda Burns, Marion Tapper, Kimon Lycos, Brendan Long, Jeremy Moss, Tony Coady, Will Barrett, Brian Scarlett, and Megan Laverty. Some use was also made of materials prepared by the Philosophy Departments of La Trobe University, the University of Queensland, and The Australian National University.
Disclaimer: University, Faculty and program rules
Please note: this booklet does not provide authoritative statements of the official policies or rules of the University of Melbourne, the Faculty of Arts, or the Philosophy program with regard to student essays and examinations or any other matters. Students should, therefore, not rely on this booklet for such information, for which they should consult the various appropriate notice boards, handbooks, websites, and/or members of staff.
Essay topics
What do philosophy essay topics look like? There are, very roughly, two basic kinds of philosophy essay topics: "text-focused" topics and "problem-focused" topics. Text-focused topics ask you to consider some particular philosopher's writing on some issue. (eg "Discuss critically David Hume's account of causation in Part III of Book I of his A Treatise of Human Nature " or "Was Wittgenstein right to say that 'the meaning of a word is its use in the language', in his Philosophical Investigations, Sec. 43?"). Problem-focused topics are more directly about a particular philosophical problem or issue, without reference to any particular philosopher's text. (eg "Is voluntary euthanasia morally permissible?" or "What is scientific method?")
There is another sort of topic, one which presents a statement and asks you to discuss it, where that statement is a "made up" or, at least, unattributed quote. (eg. "'Without belief in God, people cannot be moral'. Discuss.") I shall regard these as variations of the problem-focused type of topic. Where you are asked to discuss some such statement "with reference to" some specified text or philosopher, then that topic becomes more text-focused. (eg "'Without belief in God, people cannot be moral'. Discuss with reference to J.L. Mackie's Ethics: Inventing Right and Wrong. ") Occasionally, a topic presents an unattributed statement, but the statement is, in fact, a quote from a particular philosopher you've been studying, or, at least, a good paraphrase of their thinking. (An example of the latter: "'All the ideas in our minds originate from either sense perception or our reflection upon sensory information.' Discuss.", in a course devoted to John Locke, whose views are summed up in the quoted statement, though those words are not actually his.) Should you take such topics as problem- or text-focused? Rather unhelpfully, I'll say only that it depends on the case. You might ask your lecturer or tutor about it. Whichever way you do take it, be clear in your essay which way you are taking it.
The difference between text-focused and problem-focused essay topics is, however, not very radical. This is because, on the one hand, any particular philosopher's text is about some philosophical problem or question, while, on the other hand, most philosophical problems (certainly virtually all those you will be given as essay topics at university) will have been written about by previous philosophers.
The basic way to approach text-focused topics, then, is to treat the nominated text as an attempt by one philosopher to deal with a particular philosophical problem or issue. The essay topic will, generally speaking, be inviting you to do philosophy with that philosopher, to engage with them in thinking about the issue, whether that engagement proves to be as an ally or an adversary. The chosen text will usually be one which has been (or deserves to be) influential or significant in the history of philosophy, but the task is not to pay homage to past masters. But, even if homage is your thing, the best way to do that here is to engage with the master philosophically.
With regard to problem-focused topics, you will often find your exploration of the problem aided by taking some text or texts which have dealt with it as reference points or prompts. This is not always strictly necessary, but many of you starting out in philosophy will find it helpful to do so - it can help you give focus to your response to the question. (Thus, you might, in an essay on the topic "Is voluntary euthanasia morally permissible?" take it upon yourself to use, for example, Ronald Dworkin's Life's Dominion and Peter Singer's Practical Ethics as reference points. Or, in an essay on the topic "What is scientific method?", you might set up your answer via a comparison of the two different accounts in Karl Popper's The Logic of Scientific Discovery and Paul Feyerabend's Against Method.*) How will you know which texts to adopt as reference points or prompts, if none is mentioned in the essay topic itself? One way is to consider what texts have already been mentioned with regard to the topic in your course reading guide and in lectures and tutorials. Another way is to do some of your own research. On this see Section 4 below.
* In this guide, in giving examples of how to go about answering an essay question, I am not necessarily giving any concrete or reliable advice for any particular topic. The examples are primarily to do with the form or style or strategy you might find helpful.
Researching your essay
To do research for your philosophy essay you need to do only two things: read and think. Actually, for problem-focused essays, thinking is the only truly necessary bit, but it's highly likely that you will find your thinking much assisted if you do some reading as well. Philosophical research at university is a little different to research in most other disciplines (especially the natural sciences), in that it is not really about "collecting data" to support or refute explanatory theories. Rather, the thinking that's involved in philosophical research (as part of one's preparation for philosophical writing) is more a matter of reflecting critically upon the problems in front of one. Researching the writings of other philosophers should, therefore, be primarily directed towards helping you with that reflection rather than aiming at gathering together and reporting on "the relevant findings" on a particular topic. In many other disciplines, a "literature review" is an important research skill, and sometimes philosophy academics do such reviews - but it is rare that philosophy students are asked to do one.
What, then, to read? It should be clear from your lectures and tutorials what some starting points for your reading might be. (All courses provide reading guides; many also have booklets of reading material.) Your tutor and lecturer are also available for consultation on what readings you might begin with for any particular topic in that subject. Independent research can also uncover useful sources, and evidence of this in your essay can be a pleasing sign of intellectual independence. Make sure, though, that what you come up with is relevant to the topic. (See Section 5.2 below on relevance.) Whichever way you proceed, your reading should be purposive and selective.
In the case of essay questions that refer to a particular text, you should familiarise yourself thoroughly with this text. Usually, such a text will be a primary text, i.e. one in which a philosopher writes directly about a philosophical issue. Texts on or about a primary text are called secondary texts. (Many philosophical works will combine these two tasks, and discuss other philosophical texts while also dealing directly with a philosophical issue.) Some secondary texts can be helpful to students. However, don't think you will only ever understand a primary text if you have a nice friendly secondary text to take you by the hand through the primary text. More often than not, you need to have a good grasp of the primary text in order to make sense of the secondary text.
How much to read? The amount of reading you do should be that which maximises the quality of your thinking - that is, you should not swamp yourself with vast slabs of text that you can't digest, but nor should you starve your mind of ideas to chew over. There is, of course, no simple rule for determining this optimal amount. Be wary, though, of falling into the vice of looking for excuses not to read some philosopher or text, as in "Oh, that's boring old religious stuff" or "She's one of those obscure literary feminist types", or "In X Department they laugh at you if you mention those authors in tutes". If someone wants a reason not to think, they'll soon come up with one.
Philosophical writings
Most philosophical writings come in either of two forms: books or articles. Articles appear either in books that are edited anthologies or in academic journals, such as Philosophical Quarterly or Australasian Journal of Philosophy. Some academic journals are also on the internet. Most articles in the journals are written by professional philosophers for professional philosophers; similarly with many books. But by no means let this put you off. Everyone begins philosophy at the deep end - it's really the only kind there is!
There are, however, many books written for student audiences. Some of these are general introductions to philosophy as a whole; others are introductions to particular areas or issues (eg biomedical ethics or philosophy of science). Among the general introductions are various philosophical dictionaries, encyclopedias and "companions". These reference works collect short articles on a wide range of topics and can be very useful starting points for newcomers to a topic. Among the most useful of the general reference works are:
- Edward Craig, ed., The Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy (10 vols.) (London: Routledge, 1998)
- Paul Edwards, ed., The Encyclopedia of Philosophy (8 vols.) (New York: Macmillan, 1967)
- Robert Audi, ed., The Cambridge Dictionary of Philosophy, 2nd ed. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999)
- Ted Honderich, ed., The Oxford Companion to Philosophy (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1995)
- Simon Blackburn, The Oxford Dictionary of Philosophy (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1996)
- Thomas Mautner, ed., The Penguin Dictionary of Philosophy (London: Penguin, 1998)
- J.O. Urmson and Jonathan Ree, eds., The Concise Encyclopedia of Western Philosophy and Philosophers (London: Routledge, 1993)
- Edward N. Zalta, ed., The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (an internet-based reference work: plato.stanford.edu/ )
Note taking
Note taking, like your reading, should not be random, but ought to be guided by the topic in question and by your particular lines of response to the issues involved. Note taking for philosophy is very much an individual art, which you develop as you progress. By and large it is not of much use to copy out reams of text as part of your researches. Nor is it generally helpful to read a great number of pages without making any note of what they contain for future reference. But between these two extremes it is up to you to find the mean that best helps you in getting your thoughts together.
Libraries and electronic resources
The University's Baillieu Library (including the Institute of Education Resource Centre), which is open to all members of the University, contains more than 2,500 years' worth of philosophical writings. The best way to become acquainted with them is by using them, including using the catalogues (including the Baillieu's on-line catalogues and subject resources web-pages), following up a work's references (and references in the references), intelligent browsing of the shelves, etc.
In the main Baillieu Library, the philosophical books are located (mostly) between 100–199 in the Dewey decimal system, and philosophical journals are located in the basement. The Reference section on the ground floor also has some relevant works. The Education Resource Centre also has a good philosophy collection.
In addition to hard-copy philosophical writings, there is also a variety of electronic resources in philosophy, mostly internet-based. The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy was already mentioned above. Links to other useful internet sites (such as the Australasian Association of Philosophy website) can be found through the Baillieu Library's web-page and the Philosophy Department's web-page.
A strong word of warning, however, for the would-be philosophical web-surfer: because anyone can put material on a website, all kinds of stuff, of varying levels of quality, is out there - and new-comers to philosophy are usually not well placed to sort their way through it. Unless you have a very good understanding of what you're looking for - and what you're not looking for - most of you will be much better off simply carefully reading and thinking about a central text for your course, eg Descartes' First Meditation, rather than wandering about the internet clicking on all the hits for "Descartes". Exercise your mind, not your index finger.
Writing your essay
Planning and structuring your essay.
It is very important that you plan your essay, so that you have an idea of what you are going to write before you start to write it. Of course, you will most likely alter things in later drafts, but you should still start off by having a plan. Planning your essay includes laying out a structure. It is very important that your essay has a clearly discernible structure, ie that it is composed of parts and that these parts are logically connected. This helps both you and your reader to be clear about how your discussion develops, stage by stage, as you work through the issues at hand.
Poor essay structure is one of the most common weaknesses in student philosophy essays. Taking the time to work on the structure of your essay is time well spent, especially since skill in structuring your thoughts for presentation to others should be among the more enduring things you learn at university. A common trap that students fall into is to start their essay by writing the first sentence, then writing another one that seems to follow that one, then another one that sort of fits after that one, then another that might or might not have some connection with the previous one, and so on until the requisite 1,500 words are used up. The result is usually a weak, rambling essay.
There are, of course, no hard and fast rules about how to structure a philosophy essay. Again, it is a skill you develop through practice, and much will depend on the particular topic at hand. Nonetheless, it might be helpful to begin by developing an essay structure around the basic distinction between your exposition and your critical discussion (as discussed above). In this it will be important that you make clear who is putting forward which point, that is, make it clear whether you are presenting your own thoughts or are expounding someone else's. (Again, confusion in this regard is a common problem in student essays.) It can often help your structuring if you provide headings for different sections (possibly numbered or lettered). Again, this helps both your reader to follow your discussion and you to develop your thoughts. At each stage, show clearly the logical relations between and the reasons for your points, so that your reader can see clearly why you say what you say and can see clearly the development in your discussion.
Another key to structuring your essay can be found in the old adage "Tell 'em what you're gonna tell 'em. Tell 'em. Then tell 'em what you've told 'em", which provides you with a ready-made structure: Introduction, Main Body, and Conclusion.
In your Introduction, first introduce the issues the essay is concerned with. In doing so, try to state briefly just what the problem is and (if there is space) why it is a problem. This also applies, of course, to issues covered in text-focused essay topics. Next, tell the reader what it is that you are going to do about those problems in the Main Body. This is usually done by giving a brief sketch or overview of the main points you will present, a "pre-capitulation", so to speak, of your essay's structure. This is one way of showing your reader that you have a grasp (indeed, it helps you get a grasp) of your essay as a structured and integrated whole, and gives them some idea of what to expect by giving them an idea of how you have decided to answer the question. Of course, for reasons of space, your Introduction might not be very long, but something along these lines is likely to be useful.
In your Main Body, do what you've said you'll do. Here is where you should present your exposition(s) and your critical discussion(s). Thus, it is here that the main philosophical substance of your essay is to be found. Of course, what that substance is and how you will present it will depend on the particular topic before you. But, whatever the topic, make clear at each stage just what it is you are doing. You can be quite explicit about this. (eg "I shall now present Descartes' ontological argument for the existence of God, as it is presented in his Fifth Meditation. There will be three stages to this presentation.") Don't think that such explicitness must be a sign of an unsophisticated thinker.
A distinct Conclusion is perhaps not always necessary, if your Main Body has clearly "played out" your argument. So you don't always have to present a grand summation or definitive judgement at the end. Still, often for your own sake, try to state to yourself what it is your essay has achieved and see if it would be appropriate to say so explicitly. Don't feel that you must come up with earth-shattering conclusions. Of course, utter banality or triviality are not good goals, either. Also, your essay doesn't always have to conclude with a "solution" to a problem. Sometimes, simply clarifying an issue or problem is a worthy achievement and can merit first-class honours. A good conclusion to a philosophy essay, then, will usually combine a realistic assessment of the ambit and cogency of its claims with a plausible proposal that those claims have some philosophical substance.
What you write in your essay should always be relevant to the question posed. This is another common problem in student essays, so continually ask yourself "Am I addressing the question here?" First-class answers to a question can vary greatly, but you must make sure that your essay responds to the question asked, even if you go on to argue that the question as posed is itself problematic. (eg "To ask ‘What is scientific method?' presupposes that science follows one basic method. However, I shall argue that there are, in fact, several different scientific methods and that these are neither unified nor consistent.") Be wary, however, of twisting a topic too far out of shape in order to fit your favoured theme. (You would be ill-advised, for example, to proceed thus: "What is scientific method? This is a question asked by many great minds. But what is a mind? In this essay, I shall discuss the views of Thomas Aquinas on the nature of mind.")
This requirement of relevance is not intended as an authoritarian constraint on your intellectual freedom. It is part of the skill of paying sustained and focused attention to something put before you - which is one of the most important skills you can develop at university. If you do have other philosophical interests that you want to pursue (such as Aquinas on mind), then please do pursue them, in addition to writing your essay on the set topic. At no stage does the requirement of relevance prevent you from pursuing your other interests.
Citing Philosophical "Authorities"
There might be occasions when you want to quote other philosophers and writers apart from when you are quoting them because they are the subject of your essay. There are two basic reasons why you might want to do this. First, you might quote someone because their words constitute a good or exemplary expression or articulation of an idea you are dealing with, whether as its proponent, critic, or simply its chronicler. (eg "As Nietzsche succinctly put the point, 'There are no moral phenomena at all, only a moral interpretation of phenomena'.*") You may or may not want to endorse the idea whose good expression you have quoted, but simply want to use the philosopher as a spokesperson for or example of that view. But be clear about what you think the quote means and be careful about what you are doing with the quote. It won't do all the work for you.
The second reason you might want to quote a philosopher is because you think their words constitute an "authoritative statement" of a view. Here you want to use the fact that, eg Bertrand Russell maintained that there are two kinds of knowledge of things (namely, knowledge by acquaintance and knowledge by description) in support of your claim that there are two such kinds of knowledge of things. However, be very careful in doing this, for the nature of philosophical authority is not so simple here. That is to say, what really matters is not that Bertrand Russell the man held that view; what matters are his reasons for holding that view. So, when quoting philosophers for this second reason, be careful that you appreciate in what exactly the authority lies - which means that you should show that you appreciate why Russell maintained that thesis. Of course, you can't provide long arguments for every claim you make or want to make use of; every essay will have its enabling but unargued assumptions. But at least be clear about these. (eg "For the purposes of this essay, I shall adopt Russell's thesis* that ...").
* Friedrich Nietzsche, Beyond Good and Evil, trans. R.J. Hollingdale (Harmondsworth: Penguin, 1973 [first German ed.1886]), Sec. 108.
* See Bertrand Russell, The Problems of Philosophy (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1967 [first pub. 1912]), Ch. 5.
Philosophy is by its nature a relatively abstract and generalising business. (Note that abstractness and generality are not the same thing. Nor do vagueness and obscurity automatically attend them.) Sometimes a longish series of general ideas and abstract reasonings can become difficult for the reader (and often the writer) to follow. It can often help, therefore, to use some concrete or specific examples in your discussion. (Note that there can be different levels of concreteness and specificity in examples.)
Examples can be taken from history, current events, literature, and so on, or can be entirely your own invention. Exactly what examples you employ and just how and why you use them will, of course, depend on the case. Some uses might be: illustration of a position, problem or idea to help make it clearer; evidence for, perhaps even proof of, a proposition; a counter-example; a case-study to be returned to at various points during the essay; or a problem for a theory or viewpoint to be applied to. Again, be clear about what the example is and how and why you use it. Be careful not to get distracted by, or bogged down in, your examples. Brevity is usually best.
English expression
There's another old saying: "If you can't say what you mean, then you can't mean what you say" - and this very much applies to philosophical writing. Thus, in writing philosophically, you must write clearly and precisely. This means that good philosophical writing requires a good grasp of the language in which it is written, including its grammar and vocabulary. (See Section 9.3 for advice for people from non-English speaking backgrounds.) A high standard of writing skills is to be expected of Arts graduates. Indeed, this sort of skill will last longer than your memory of, for example, the three parts of the Platonic soul (though it is also hoped that some of the content of what you study will also stick). So use your time at university (in all your subjects) to develop these skills further.
Having a mastery of a good range of terms, being sensitive to the subtleties of their meaning, and being able to construct grammatically correct and properly punctuated sentences are essential to the clear articulation and development of your thoughts. Think of grammar, not as some old-fashioned set of rules of linguistic etiquette, but rather as the "internal logic" of a sentence, that is, as the relationships between the words within a sentence which enable them to combine to make sense.
Virtually all sentences in philosophical writing are declarative (ie. make statements), as opposed to interrogative, imperative or exclamatory types of sentences. There is some place, though, for interrogative sentences, ie. questions. (Note that, in contrast, this guide, which is not in the essay genre, contains many imperative sentences, ie. commands.) As you craft each (declarative) sentence in your essay, remember the basics of sentence construction. Make clear what the sentence is about (its subject) and what you are saying about it (the predicate). Make clear what the principal verb is in the predicate, since it is what usually does the main work in saying something about the subject. Where a sentence consists of more than one clause (as many do in philosophical writing), make clear what work each clause is doing. Attend closely, then, to each and every sentence you write so that its sense is clear and is the sense you intend it to have. Think carefully about what it is you want each particular sentence to do (in relation to both those sentences immediately surrounding it and the essay as a whole) and structure your sentence so that it does what you want it to do. To help you with your own sentence construction skills, when reading others' philosophical works (or indeed any writing) attend closely to the construction of each sentence so as to be alive to all the subtleties of the text.
Good punctuation is an essential part of sentence construction. Its role is to help to display the grammar of a sentence so that its meaning is clear. As an example of how punctuation can fundamentally change the grammar and, hence, meaning of a sentence, compare (i) "Philosophers, who argue for the identity of mind and brain, often fail to appreciate the radical consequences of that thesis." and (ii) "Philosophers who argue for the identity of mind and brain often fail to appreciate the radical consequences of that thesis." In the first sentence it is asserted (falsely, as it happens) that all philosophers argue for the identity of mind and brain; in the second, only some philosophers are said to argue for the identity of mind and brain. Only the punctuation differs in the two strings of identical words, and yet the meanings of the sentences are very different. Confusions over this sort of thing are common weaknesses in student essays, and leave readers asking themselves "What exactly is this student trying to say?"
It will be assumed that you can spell - which is not a matter of pressing the "spell-check" key on a word-processor. A good dictionary and a good thesaurus should always be within reach as you write your essay.
Also, try to shorten and simplify sentences where you can do so without sacrificing the subtlety and inherent complexity of the discussion. Where a sentence is becoming too long or complex, it is likely that too many ideas are being bundled up together too closely. Stop and separate your ideas out. If an idea is a good or important one, it will usually deserve its own sentence.
Your "intra-sentential logic" should work very closely with the "inter-sentential logic" of your essay, ie. with the logical relations between your sentences. (This "inter-sentential logic" is what "logic" is usually taken to refer to.) For example, to enable sentences P and Q to work together to yield sentence R as a conclusion, you need to make clear that there are elements within P and Q which connect up to yield R. Consider the following example: "Infanticide is the intentional killing of a human being. However, murder is regarded by all cultures as morally abhorrent. Therefore, people who commit infanticide should be punished." This doesn't work as an argument, because the writer has not constructed sentences which provide the connecting concepts in the various subjects and predicates, even though each sentence is grammatically correct (and possibly even true).
If you are concerned to write not only clearly and precisely, but also with some degree of grace and style (and I hope you are), it's still best to get the clarity and precision right first, in a plain, straightforward way, and then to polish things up afterwards to get the style and grace you want. But don't sacrifice clarity and precision for the sake of style and grace - be prepared to sacrifice that beautiful turn of phrase if its presence is going to send your discussion down an awkward path of reasoning. Aim to hit the nail on the head rather than make a loud bang. What you are likely to find, however, is that a philosophy essay which really is clear and precise will have a large measure of grace and style in its very clarity and precision.
Remember that obscurity is not a sign of profundity. (Some profound thought may well be difficult to follow, but that doesn't mean that one can achieve profundity merely through producing obscure, difficult-to-read writing.) Your marker is interested in what's actually in your essay, not what's possibly inside your head (or indeed what's possibly in some book you happen to have referred to in your essay). So avoid hinting at or alluding suggestively to ideas, especially where they are meant to do some important work in your essay. Instead, lay them out explicitly and directly. Of course, you won't have space to spell out every single idea, so work out which ideas do the most important work and make sure that you at least get those ideas clearly articulated. In expounding a text or problem that ultimately just is vague, muddled, or obscure, try to convey such vagueness, muddle or obscurity clearly, rather than simply reproducing it in your own writing. That is, be clear that and how a text or problem has such features, and then perhaps do your best to make matters clearer.
Despite these stern pronouncements, don't be afraid of sometimes saying things which happen to sound a little odd, if you have tried various formulations and think you have now expressed your ideas just as they should be expressed. Philosophy is often an exploratory business, and new ways of seeing and saying things can sometimes be a part of that exploration.
The need for clarity and precision in philosophical writing sometimes means that you need to stipulate your own meaning for a term. When you want to use a particular word in a particular way for the purposes of your essay - as a "technical term" - be clear about it. (eg "In this essay, I shall intend ‘egoism' to mean ...") Also, be consistent in your technical meanings, or else note when you are not. Be wary, though, of inventing too many neologisms or being too idiosyncratic in your stipulations.
With regard to what "authorial pronoun" to adopt in a philosophy essay, it's standard to write plainly in the first person singular ("I", "me", "my", etc.) rather than use the royal "we" (as in "we shall argue that ..."), or the convoluted quasi-legal indirect form ("It is submitted that ..."), or the scientific objectivity of a physics experimental report. Nonetheless, stick closer to "I argue", "I suggest", "my definition", etc., than to "I wish", "I hate", "my feeling", etc. A philosophy essay is still something more intellectual and formal than a personal reminiscence, polemic, or proclamation. In terms of audience, it's probably best to think of your reader as someone who is intelligent, open to discussion and knows a little about the topic you're writing on, but perhaps is not quite clear or decided about the issues, or needs convincing of the view you want to put forward, or is curious about what you think about the issues.
Try also to use non-discriminatory language, ie. language which does not express or imply inequality of worth between people on the basis of sex, gender, race, ethnicity, sexuality, and so on. As you write, you will be considering carefully your choice of words to express your thoughts. You will almost always find that it is possible to avoid discriminatory language by rephrasing your sentences.
Other things to avoid:
- waffle and padding
- vagueness and ambiguity
- abbreviations (this guide I'm writing isn't an eg. of what's req'd. in a phil. essay)
- colloquialisms (which can really get up your reader's nose)
- writing whose syntax merely reflects the patterns of informal speech
- unnecessary abstractness or indirectness
- unexplained jargon
- flattery and invective
- overly-rhetorical questions (do you really need me to tell you what they are?) and other flourishes
There are many guides to good writing available. Anyone who writes (whether in the humanities or the sciences, whether beginners or experienced professionals) will do well to have some on hand. Most good bookshops and libraries will have some. Among the most consulted works are (check for the latest editions):
- J. M. Williams and G. C. Colomb, Style: Toward Clarity and Grace (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1995)
- W. Strunk and E. B. White, The Elements of Style, 4th ed. (New York: Longman, 2000)
- E. Gowers, The Complete Plain Words, 3rd ed. (Harmondsworth: Penguin, 1987)
- R. W. Burchfield, ed., The New Fowler's Modern English Usage (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1996)
- Pam Peters, The Cambridge Australian English Style Guide (Melbourne: Cambridge University Press, 1995)
- Australian Government Publishing Service, Style Manual for Authors, Editors and Printers, 5th ed. (Canberra: AGPS, 1995)
Vocabulary of logical argument
Closely related to the above points about English expression is the importance of having a good grasp of what can rather generally be called "the vocabulary of logical argument". These sorts of terms are crucial in articulating clearly and cogently a logical line of argument. Such argumentation will, of course, be of central importance in whatever discipline you are studying, indeed in any sphere of life that requires effective thinking and communication. I have in mind terms such as these (grouped a little loosely):
all, any, every, most, some, none, a, an, the that, this, it, he, she, they if . . . , then. . . ; if and only if . . . , then . . . ; unless either . . . or . . .; neither . . . nor . . . not, is, are therefore, thus, hence, so, because, since, follows, entails, implies, infer, consequence, conditional upon moreover, furthermore which, that, whose and, but, however, despite, notwithstanding, nevertheless, even, though, still possibly, necessarily, can, must, may, might, ought, should true, false, probable, certain sound, unsound, valid, invalid, fallacious, supported, proved, contradicted, rebutted, refuted, negated logical, illogical, reasonable, unreasonable, rational, irrational assumption, premise, belief, claim, proposition argument, reason, reasoning, evidence, proof
Most of these are quite simple terms, but they are crucial in argumentative or discursive writing of all kinds. (Many are themselves the subject of study in logic, a branch of philosophy). The sloppy use of these sorts of terms is another common weakness in students' philosophy essays. Pay close and careful attention to how you employ them. Moreover, pay close and careful attention to how the authors you read use them. For further discussion of some of these terms and others, see:
- Basic Philosophical Vocabulary, prepared by the staff of the Philosophy Department and available from the programs Office
- Wesley C. Salmon, Logic, 2nd ed. (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1973)
- Antony Flew, Thinking About Thinking (London: Fontana, 1985)
- Graham Priest, Logic: A Very Short Introduction (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000)
- Joel Rudinow and Vincent E. Barry, Invitation to Critical Thinking, 4th ed. (Fort Worth, Texas: Harcourt Brace, 1999)
Revising your essay
It is virtually essential that you write a first draft of your essay and then work on that draft to work towards your finished essay. Indeed, several drafts may well be necessary in order to produce your best possible work. It is a rare philosopher indeed who can get things perfectly right on the first attempt, so be prepared to revise and re-develop what you write. Don't be too precious about what you have written, if it appears that it should be sacrificed in the revision process. There is usually a very marked difference between essays which are basically first draft rush-jobs done the night before they are due and those which have been revised and polished. Give yourself time to revise by starting writing early on. For most philosophy students, the greater part of the work in essay writing is in the writing, not in the preliminary researches and planning stages. So be wary of thinking "I've done all the research. I only need to write up my notes, which I can do the night before the essay's due". This is likely to lead to a weak, perhaps non-existent, essay (and very likely a sleepless night).
Stick to the word limit given for your essay. Why are word limits imposed? First, to give the markers a fair basis for comparing student essays. Second, to give you the opportunity to practise the discipline of working creatively under constraints. Skill in this discipline will stand you in very good stead in any sphere where circumstances impose limitations. Again, word limits are not constraints on your intellectual freedom. Outside your essay you are free to write without limit. But even there you'll probably find that your creativity is improved by working under a self-imposed discipline.
As a general rule, most student essays that fall well short of the word limit are weak or lazy attempts at the task, and most essays that go well over the limit are not much stronger or the result of much harder work - the extra length is often due to unstructured waffle or padding which the writer hasn't thought enough about so as to edit judiciously. If you structure your essay clearly, you'll find it easier to revise and edit, whether in order to contract or expand it. ("Hmm, let's see: section 2 is much longer than section 4, but is not as important, so I'll cut it down. And I should expand section 3, because that's a crucial step. And I can shift that third paragraph in the Introduction to the Conclusion.")
Plagiarism and originality
Plagiarism is essentially a form of academic dishonesty or cheating. At university level, such dishonesty is not tolerated and is dealt with severely, usually by awarding zero marks for a plagiarised essay or, in some cases, dismissing a student from the university.
When you submit your essay, you are implicitly stating that the essay is your own original and independent work, that you have not submitted the same work for assessment in another subject, and that where you have made use of other people's work, this is properly acknowledged. If you know that this is not in fact the case, you are being dishonest. (In a number of university departments, students are in fact required to sign declarations of academic honesty.)
Plagiarism is the knowing but unacknowledged use of work by someone else (including work by another student, and indeed oneself - see below) and which is being presented as one's own work. It can take a number of forms, including:
- copying : exactly reproducing another's words
- paraphrasing : expressing the meaning of another's words in different words
- summarising : reproducing the main points of another's argument
- cobbling : copying, paraphrasing or summarising the work of a number of different people and piecing them together to produce one body of text
- submitting one's own work when it has already been submitted for assessment in another subject
- collusion : presenting an essay as your own independent work when in fact it has been produced, in whole or part, in collusion with one or more other people
None of the practices of copying, paraphrasing, summarizing or cobbling is wrong in itself, but when one or more is done without proper acknowledgment it constitutes plagiarism. Therefore, all sources must be adequately and accurately acknowledged in footnotes or endnotes. (See Section 7.) Plagiarism from the internet in particular can be a temptation for a certain kind of student. However, be warned: there is a number of very good internet and software tools for identifying plagiarism.
With regard to collusion, it's undoubtedly often very helpful to discuss one's work with others, be it other students, family members, friends or teachers. Indeed, philosophy thrives on dialogue. However, don't kid yourself that you would simply be extending that process if you were to ask your interlocutor to join with you in the writing of your essay, whether by asking them to tell you what you should write or to write down some of their thoughts for you to reproduce in your essay. At the end of the day, you must be the one to decide what goes into your essay.
Originality
Students sometimes worry about whether they will be able to develop "original ideas", especially in light of the fact that nearly every philosophical idea one comes up with seems to have been thought of before by someone else. There is no denying that truly original work in philosophy is well rewarded, but your first aim should be to develop ideas that you think are good and not merely different. If, after arguing for what you believe is right, and arguing in way that you think is good, you then discover that someone else has had the same idea, don't throw your work away - you should feel vindicated to some extent that your thinking has been congruent with that of another (possibly great) philosopher. (If you have not yet handed your essay in when you make this discovery, make an appropriately placed note to that effect.) Don't be fooled, however, into thinking that plagiarism can be easily passed off as congruent thinking. Of course, if that other philosopher's ideas have helped you to develop your ideas, then this is not a matter of congruent ideas but rather of derivative ideas, and this must be adequately acknowledged. If, after developing your ideas, you discover that they are original, then that is an added bonus. But remember that it is more important to be a good philosopher than an original one.
Quotations, footnotes, endnotes and bibliography
Quotations in your essay should be kept to a minimum. The markers know the central texts pretty well already and so don't need to have pages thereof repeated in front of them. Of course, some quotation will usually be important and useful - sometimes essential - in both exposition and critical discussion.
When you quote the words of someone else directly, you must make the quotation clearly distinct from your own text, using quotation marks . (eg "Descartes said that 'it is prudent never to trust completely those who have deceived us even once.'* He makes this claim …" - where the words quoted from Descartes are in 'single quotation marks'. Note that it is relatively arbitrary whether one uses 'single' or "double" quotation marks for "first order" quotations, but whichever style you adopt, use it consistently in the one essay.) Alternatively, where the quoted passage is greater than three lines, put the quoted words in a separate indented paragraph , so that your essay would look like this:
In his First Meditation , Descartes argues as follows:
Whatever I have up till now accepted as most true I have acquired either from the senses or through the senses. But from time to time I have found that the senses deceive, and it is prudent never to trust completely those who have deceived us even once.* In this essay I shall argue that prudence does not in fact require us to distrust our senses and that Descartes's sceptical method is therefore seriously flawed.
In both cases, the quotations must be given proper referencingin a footnote or endnote.
When you are not quoting another person directly, but are still making use of their work - as in indirect quotations (eg "Descartes says that it is wise not to trust something that has deceived us before"*), paraphrases, summaries, and cobblings - you must still acknowledge your debts, using footnotes or endnotes.
* Rene Descartes, Meditations on First Philosophy , trans. John Cottingham (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1986 [first French ed., 1641]), p. 12.
Footnotes and endnotes
Footnotes appear at the foot of the same page on which the cited material appears, clearly separated from the main body of the text, each one clearly numbered. Endnotes appear at the end of the essay, again clearly separated from the main body of text, numbered and headed "Endnotes" or "Notes". Either method is acceptable, but you should choose one and stick with it throughout the one essay.
Below are some examples of how to put the relevant referencing information in footnotes and endnotes. This is not intended as an exercise in pedantry, but as a guide to how to provide the information needed for adequate referencing. The reason we provide this information is to enable our readers to find the sources we use in order to verify them and to allow them to pursue the material further if it interests them. In your own researches you will come to value good referencing in the texts you read as a helpful source of further references on a topic. Again, it is this sort of research skill that an Arts graduate will be expected to have mastered.
There are various conventions for writing up footnotes and endnotes. The Philosophy Department does not require that any particular convention be followed, only that you be consistent in your use of the convention that you do choose. For other conventions see the style guides mentioned above, or simply go to some texts published by reputable publishers and see what formats they employ.
Imagine, then, that the following are endnotes at the end of your essay. I will explain them below.
- James Rachels, The Elements of Moral Philosophy , 2nd ed. (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993), p. 25.
- Philippa Foot, "Moral Relativism", in Michael Krausz and Jack W. Meiland, eds., Relativism: Cognitive and Moral (Notre Dame, Indiana: University of Notre Dame Press, 1982), p. 155.
- Ibid., p. 160.
- Immanuel Kant, Groundwork of the Metaphysic of Morals, trans. H. J. Paton (New York: Harper and Row, 1964 [first German ed., 1785]), p. 63.
- Thomas Hobbes, Leviathan, (London: Dent, 1973 [first pub. 1651]),p. 65.
- Rachels, The Elements, p. 51.
- Peter Winch, "The Universalizability of Moral Judgements", The Monist 49 (1965), p. 212.
- Antony Duff, "Legal Punishment", The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Spring 2001 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.), plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2001/entries/legal-punishment/ at 15 June 2003, sec. 6.
Notes explained
- This is your first reference to a book called The Elements of Moral Philosophy. The title is given in full and in italics. If you are unable to use italics, then you should underline the title. The book's author is James Rachels. It's the 2nd edition of that book, which was published in New York, by the publishers McGraw-Hill, in 1993. The page you have referred to in your main text is page 25
- This is your first reference to Philippa Foot's article, "Moral Relativism", the title of which is put in "quotation marks". This article appeared in a book (title in italics) which is an anthology of different articles, and which was edited by Krausz and Meiland (names in full). The rest is in the same style as note (1)
- "Ibid." is short for "ibidem", which means "in the same place" in Latin. Use it on its own when you want to refer to exactly the same work and page number as in the immediately preceding note. So here the reference is again to Foot's article at page 155
- Ditto, except this time you refer to a different page in Foot's article, namely page 160
- This is reference to a book by Kant. Same book details as per note (1), except that, because this is a translation, you include the translator's name, and the date of the first edition in the original language
- This is a book reference again, so it's the same as note (1), except that, because it's an old book, you include the date of the original edition. (How old does a book have to be before it merits this treatment? There is no settled view. Note, though, that this convention is not usually followed for ancient authors)
- Here you are referring to Rachels' book again, but, because you are not in the very next note after a reference to it, you can't use "ibid.". Simply give the author's surname and a short title of the book, plus page reference. There is also a common alternative to this, whereby you give the surname, and write "op. cit." (which is short for "opere citato", which is Latin for "in the work already cited") and page reference (eg "Rachels, op. cit., p. 51.") Your reader then has to scan back over the notes to see what that "op." was exactly. The first option (author plus short title) is usually easier on the reader
- This is a reference to an article by Peter Winch in a journal called The Monist. The article's title is in "quotes", the journal title is in italics. The volume of the journal is 49, the year of publication is 1965, the page referred to is p. 212
- This is a reference to an article in the internet-based Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. The article is titled "Legal Punishment" and was written by Antony Duff. The Encyclopedia was edited by Edward N. Zalta. Note that I have basically followed the mode of citation that the Encyclopedia itself recommends. (This is one sign of the site being a reputable one. Where a site makes such a recommendation, it's best to follow it.) I have, however, also added the date on which the article was retrieved from the site, and put the author's given name first, to be consistent with the other footnotes. I have also added the reference to section 6, in an effort to be more precise as to where in the article the material I used came from. Since web pages aren't numbered in the manner of hard copy works, it will help if you are able to refer to some other feature, such as paragraphs or sections, so as to pin-point your reference. In the absence of a site recommending a mode of citation to its own material, the basic information needed for adequate citation of internet-based material is (where identifiable) the author, the document title, the year the document was created, the website name, the uniform resource locator (URL) in <arrow-brackets>, date of retrieval, and a pin-point reference*
* I am here following the mode of citation of internet materials recommended in Melbourne University Law Review Association Inc, Australian Guide to Legal Citation , 2nd ed. (Melbourne: Melbourne University Law Review Association Inc, 2002), pp. 70-73. I have, though, added the desirability of a pin-point reference.
Bibliography
At the end of your essay (after your endnotes, if used) you should list in a bibliography all of the works referred to in your notes, as well as any other works you consulted in researching and writing your essay. The list should be in alphabetical order, going by authors' surnames. The format should be the same as for your notes, except that you drop the page references and should put surnames first. So the bibliography of our mock-essay above would look like this:
- Duff, Antony, "Legal Punishment", The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Spring 2001 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.), plato.stanford.edu/archives/spr2001/entries/legal-punishment/ at 15 June 2003
- Foot, Philippa, "Moral Relativism", in Michael Krausz and Jack Meiland, eds., Relativism: Cognitive and Moral (Notre Dame, Indiana: University of Notre Dame Press, 1982)
- Hobbes, Thomas, Leviathan (London: Dent, 1973 [first pub.1651])
- Kant, Immanuel, Groundwork of the Metaphysic of Morals , trans. H.J. Paton (New York: Harper and Row, 1964 [first German ed. 1785])
- Rachels, James, The Elements of Moral Philosophy , 2nd ed., (New York: McGraw-Hill, 1993)
- Winch, Peter, "The Universalizability of Moral Judgements", The Monist 49 (1965)
Presentation of essays and seeking advice
Generally, you should present an essay that is legible (hand-writing is OK, but typed or word-processed essays are preferable), in English, on one side of pieces of paper that are somewhere in the vicinity of A4 size and are fixed together . You should attach a completed Cover Sheet provided by the Philosophy program. Plastic document covers, spiral binding and other forms of presentational paraphernalia are not necessary (nor are they usually even desirable, as they mostly just get in the marker's way).
Late essays
Late essays are penalised . (For details of penalties consult the Philosophy program's notice board.)
Essays not handed in
Essays not handed in at all get zero marks. An essay that is handed in but gets a mark below 50 (and so is technically a "failed" essay) still gets some marks. (At least, it will so long as it's not so extremely late that the deducted marks wipe out all the marks it would have received if handed in on time.) All marks received for your essay (whether pass or fail) go toward your final score in the subject. Therefore, even if you think your essay is bound to fail (but please let your marker be the judge of that), or the due date has already passed, or both, it is still in your interests to hand your essay in .
Tutors and lecturers
Philosophy staff are not there just to be listened to by you; they are also there to listen to you. So don't hesitate to contact your tutor or lecturer to discuss questions or problems you have concerning your work.
If you have a legitimate excuse, you may be granted an extension on the due date for your essay by the lecturer in charge. Similarly, special consideration may also be granted when illness or other circumstances adversely affect your work. Applications for special consideration are made online via the Special Consideration web page.
Student counselling
Some personal or non-philosophical academic difficulties you might have you might want to discuss with someone other than your tutor or lecturer. Student Counselling and Psychological Services are there for you to discuss all sorts of problems you might encounter. Please consult your student diary for details on the counselling service.
English language assistance
As noted above, good philosophical writing requires a good grasp of the language in which it is written. If you are from a non-English speaking background and are having difficulties with your English expression in an academic context, you might like to make use of the services provided by Student Services Academic Skills . Many native English speakers, too, can benefit from short "refresher" courses and workshops run by the Centre. Please consult your student diary for details about this service.
A bit on Philosophy exams
Essays of the sort discussed so far in this guide are not the only form of assessment in the Philosophy program - examinations are also set. What is to be said about them?
First, not much that is different from what's been said above about philosophy essays. This is because what you write in a philosophy exam is none other than a philosophy essay . Have a look at past philosophy exam papers, in the Gibson and Baillieu libraries, to get a feel for them. The only basic difference between essays and exams is the matter of what constraints you're working under. Essays have word limits; exams have time limits . Again, stick to them. (Actually, you'll be made to stick to them by the exam invigilators.)
It's best, then, to think about how long to spend writing on an exam essay topic, rather than about how many words to write on it. Simple arithmetic will tell you how much time to spend on each exam question. (eg if you have a 2-hour exam and have to answer 3 questions, each worth one-third of the exam mark, then spend 40 minutes on each question.) Avoid the trap of "borrowing time" from a later question in order to perfect your answer to an earlier question, and then working faster on the later questions to catch up on lost time - this is likely to get you in a tangle. There are no word limits in philosophy exam essays, but don't think that the more you scrawl across the page, the more marks you'll get. Nonetheless, use the time you've got so as to maximise your display of your philosophical understanding and skills in answering the question.
Planning and structuring remain very important in exam essays. With regard to the niceties of footnotes, endnotes and bibliographies, etc., these are not necessary, so don't waste time on these. However, if you quote or refer to a specific passage from a text, do indicate clearly that it is a quotation or reference. (The principle of being clear as to who is saying what remains central.) If you have the reference handy, just put it briefly in the text of your exam essay. (eg "As Descartes says in Meditation I (p. 12), . . ." or "'[I]t is prudent never to trust completely those who have deceived us even once' (Descartes, Meditation I, p. 12)".) Generally speaking, you will show your familiarity with any relevant texts by how you handle them in your discussion. This is also true for your non-exam essays.
Your preparation for the exam should have been done well before entering the exam hall. Note that various subjects have restrictions on what texts and other items can be brought into the exam hall. (Consult the Philosophy program's notice board for details.) Many subjects will have "closed book" exams. Even if an exam is "open book", if you are properly prepared, you should not need to spend much time at all consulting texts or notes during the exam itself.
You won't have time for redrafting and revising your exam essay (which makes planning and structuring your answers before you start writing all the more important). If you do want to delete something, just cross it out clearly. Don't waste time with liquid paper or erasers. Write legibly . Don't wr. "point form" sav. time. Diff. kn. mean. use incomp. sent.
Finally, read the instructions at the beginning of the exam paper. They are important. (eg it's not a good strategy to answer two questions from Part A, when the Instructions tell you to answer two questions, one from Part A and one from Part B.) Note the (somewhat quaint) University practice of starting Reading Time some time before the stated time for the exam. Philosophy exams usually have 15 minutes of reading time. (Check for each of your exams.) So, if your exam timetable says the exam is at 2.15 pm, with reading time of 15 minutes, then the reading time starts at 2.00 pm and the writing time starts at 2.15pm - so get to the exam hall well before 2.00 pm. Reading time is very important. Use it to decide which questions you'll answer and to start planning your answers.
Checklist of questions
- Do I understand the essay question ? Do I know when the essay is due ?
- Do I know which texts to consult? Do I know where to find them?
- Have I made useful notes from my reading of the relevant texts?
- Have I made a plan of how I'll approach the question in my essay?
- Have I given myself enough time to draft and redraft my essay?
- Have I written a clearly structured essay? Is it clear what each stageis doing? Do I do what I say I'll do in my Introduction?
- Have I clearly distinguished exposition and critical discussion ? Have I given a fair and accurate account of the author(s) in question?
- Is my response to the topic relevant ? Do I answer the question? Have I kept my essay within the general bounds of the topic?
- Have I displayed a good grasp of the vocabulary of logical argument ? Are my arguments logically valid and sound? Are my claims supported by reasons ? Am I consistent within my essay?
- Is my English expression clear and precise ? Are my grammar, punctuation and spelling correct? Have I said what I meant to say? Is my writing legible?
- Have I fully acknowledged all my sources in footnotes or endnotes? Are my quotations accurate? Have I included a bibliography ?
- Do I need to revise any part of my essay again?
- Have I made a copy or photocopy of my essay for myself?
- Have I kept the receipt for my handed-in essay?
Why Is Philosophy Important?
Philosophy is a subject that most people tend to ignore or avoid. However, experts say that philosophy is an essential part of understanding and appreciating the world around us.
So, this leads us to the question, why is philosophy important ? Will it help us with our day-to-day life?
According to experts, here are the top reasons why:
Table of Contents

It illuminates and helps us ponder and create at the boundaries of what we know
It allows us to push the boundaries of what we know, it helps us explore topics with reason and humanity, it put all else into perspective: career, life, moral reasoning, etc, it is crucial in teaching us to debate with civility, it is a fundamental part of being a human, philosophy courses build skills, textbooks are excellent but not always required, promotes critical thinking and reasoning skills, increases ethical awareness and self-reflection, furthers a passion for learning, it can open people to the world of ideas at an early age, you’ll gain valuable insight into human nature, you’ll learn how to understand yourself better, you’ll learn how to be a better person, it will teach you about the things that we can all do and understand, frequently asked questions.
Scott Foulkrod, J.D.

Associate Professor of Philosophy and Legal Studies, Harrisburg University of Science and Technology
Philosophy is important because it illuminates and helps us ponder and create at the boundaries of what we know and what we would like to know or create in science, religion, politics, and many other fields of inquiry and life.
To begin with, it is human nature, what we know and inquires into areas that we explore and can only imagine at the moment.
It starts from a base of accepted knowledge and then expands with a thought, “what if?” Einstein imagined what it would be like to travel on a beam of light.
Many have wondered whether and what God is. Psychology and many other fields that we endeavor to understand as science are ever-changing explorations and explanations of thought.
Philosophy is where reasonable people disagree on a topic, where we live in so many issues such as religion, politics, law, and even scientific inquiry.
It allows us to push the boundaries of what we know into what we would like to learn next or challenge what we think we know.
Some of my former students have told me that our philosophy class was the most important one they took in college because it put all else into perspective with career, life, and moral reasoning about not only can we, but should we, or how should we go about this?
For millennia we have endeavored to solve questions about our existence, the beginning and nature of the universe, the presence and intent of God, who should govern us, and how laws we should live by.
We should use reasoning to decide our actions’ morality, and as important as these questions are, we have not reached any specific agreement.
Philosophy helps us explore these topics with reason and humanity in our attempt to come to solutions we can for a time live with, even while we continue to debate and study them as society changes and boundaries of our technology dissolve.
It is human nature to imagine and explore, and philosophy lives at these boundaries in specific fields such as science and technology .
Former students have told me that our philosophy course was their most important because it put all else into perspective : career, life, moral reasoning, asking not only can we, but should we, and how we should go about doing it.
The value of philosophy today is as crucial as ever in teaching us to debate with civility .
When we leave mere personal passion and use reason, evidence, and empathy, we bring people with us and to us, not to win, but to offer others with our informed hope as we try to create something better for ourselves, our planet, and other species with whom we share it.
Karen Southall Watts

Instructor of Humanities and Success Skills, Bellingham Technical College | Author, “ The Solo Workday “
Socrates famously said, “The unexamined life is not worth living.” Those of us drowning in dirty laundry, unpaid bills, or endless task lists are now collectively rolling our eyes.
Yet, the search for meaning in life is not limited to academics in ivory towers. When given a bit of time and space , we all long to know why we’re here and how we fit in.
Not everyone will get the luxury of taking philosophy classes, but philosophy—the study of the nature of existence—is a fundamental part of being human.
Ask employers what they want in new hires and what job candidates lack.
You will hear some combinations of the following:
- soft skills
- communication skills
- interpersonal skills
- problem-solving skills
- critical thinking skills
Related: Why is Critical Thinking Important?
Philosophy courses, and other humanities-based classes that fall under this broad heading, build these essential skills. Students in these classes learn how to examine the human experience and discuss issues that are sensitive and often complex.
Philosophy and related courses teach us how to think, and having carefully thought about something, how to share those thoughts with others.
People love to gather and talk about life, from early morning coffee groups to book clubs to Death Cafe’s to the comment section on YouTube. Connecting with others and pondering the meaning of our lives is normal, natural, and not limited to formal classroom settings.
Philosophy, and the shared language of philosophical discussion, give us the means to find society in a world that is often overwhelming, chaotic, and cruel.
Philosophical discussion is the arena where we learn to argue with respect, debate with civility, and analyze with care .
Dr. Anneke Schmidt

Educational Researcher | Founder, Skill & Care
There are many reasons why teaching Philosophy in schools can benefit students’ development. Here is a brief list of the main advantages:
The discipline of philosophy provides students with the thought processes necessary to analyze issues, solve problems, and make decisions.
Philosophy can improve students’ reasoning, argumentation, listening, and speaking skills by engaging them in inquiry and debates. Students who study philosophical works develop more vital reasoning skills through class discussion.
Another benefit of teaching philosophy in schools is that it encourages ethical thinking. The study of philosophy helps students develop a sense of right and wrong, enabling them to apply their knowledge of ethics to their everyday lives.
Philosophy is more than just an academic subject. It requires students to reflect on the important moral issues in their lives, examines why these are considered “moral” problems, and understand the consequences of acting upon one’s convictions.
It can also cultivate respect for different cultures and ideas through exposure to different philosophical theories about life and death, happiness, beauty, etc., and challenge one’s preconceived notions about self and society.
One common criticism of teaching philosophy in schools is that the discipline only helps students be eloquent in their verbal expression but fails to teach them any factual knowledge or common sense .
This, however, is a narrow view of what philosophy entails. Philosophy has been known as the “love of wisdom.” It requires systematic and rigorous thinking to understand the complexities of human existence.
The discipline can thus stimulate a passion for lifelong learning and lead students into subjects like history, mathematics, science, or literature.
Getting children involved in philosophy at an early age will help them develop a sense of wonder and instill a love for reading.
It will enable them to ask questions about the things around them that they do not understand, thus encouraging their learning abilities.
Brian Gawor

Vice President of Research, RNL
We’re moving, as a society, away from “stuff.” We’re in an idea and experience economy, and people care more about their purpose and meaning today than the next shiny thing they can buy.
Philosophy opened me to the world of ideas at an early age and has made me more able to connect with people and make a change in every organization I’ve served.
I remember buying a “philosophy for dummies” comic book series my first year in college. And great professors helped me dive into the world of ideas. It changed my life.
I learned about marketing and technology on the job. But because I was introduced to the world of ideas and purpose early , I’ve been better and more resilient as a professional .
In a time of stress, turmoil, and demands from the world, It’s easy to get caught up in the “when” and “how.” Philosophy allows us to focus on the “why,” and that’s crucial to happiness, success, and fulfillment.
Lynda Fairly

Co-founder, Numlooker
Philosophy has been around since the very beginning of time, so it’s no surprise that it continues to be a topic of interest.
While many are laughing at the thought of a career in philosophy if they can’t see any practical applications for its study, this field is worth exploring because it can teach you about yourself, love, and even help you understand other people better.
Here are just some of the reasons why it’s an excellent subject to take up and consider as a career option.
Philosophy will teach you the psychology behind why we think, act, and react to the things in life that we do.
It will teach you about human nature, which is essential for understanding others and predicting the actions and reactions of your fellow humans.
Many people mistakenly believe that only other people know how they feel or think, but we experience life much like everyone else when it comes down to it.
If you consider yourself a “soulful person” or a “hard-headed thinker,” philosophy will show you specific ways of learning more about yourself through literature.
Many people know that philosophy can help you become a better person, but it’s the most important aspect of this subject.
Philosophy will teach you about the things that we can all do and understand but don’t because we may not have experienced them first-hand or been taught about them on a deep or meaningful level.
Why is philosophy still important today?
Philosophy helps us to understand the fundamental questions that shape our existence.
Who are we? What is the nature of reality? What is the meaning of life?
These are not just abstract musings for armchair philosophers, but questions that touch the very core of our being. By grappling with these questions, we can gain a deeper understanding of ourselves and our place in the world.
But philosophy isn’t just about asking big questions — it’s also about developing critical thinking skills. Philosophy teaches us to analyze arguments, identify fallacies, and evaluate evidence. In a world where we are bombarded with information from all sides, these skills are more important than ever. They enable us to separate fact from fiction, to think logically and rationally, and to make informed decisions.
Furthermore, philosophy can help us to navigate ethical dilemmas and moral quandaries. It provides us with frameworks for thinking about what is right and wrong, just and unjust, good and bad. Whether we are considering the ethics of artificial intelligence or the morality of gene editing, philosophy offers us tools to engage with these complex issues in a thoughtful and nuanced way.
Finally, philosophy can inspire us to live better lives. From the ancient Greeks to modern thinkers like Jean-Paul Sartre, philosophers have explored what it means to live a fulfilling life. By studying their ideas, we can gain insights into how to cultivate happiness, meaning, and purpose in our own lives.
Why is philosophy important in education?
Philosophy is important in education because it provides a framework for understanding the world and our place in it. At its core, philosophy is about asking big questions and seeking answers through rational inquiry.
By incorporating philosophical inquiry into education, we can help students develop critical thinking skills, cultivate a love of learning, and become well-rounded individuals.
One of the key benefits of studying philosophy is that it teaches us to ask questions and seek answers. This is a skill that is essential in all areas of life, from personal relationships to professional endeavors. By encouraging students to ask questions and think critically, we can help them become independent thinkers who are capable of solving problems and making informed decisions.
Another important aspect of philosophy in education is that it provides a foundation for ethical thinking. Ethics is the branch of philosophy that explores questions of right and wrong, and it is essential for students to develop a strong ethical framework in order to navigate the complex moral challenges of the world. By studying ethics, students can learn to think deeply about their values and beliefs, and develop a sense of responsibility to others.
Finally, philosophy is important in education because it teaches us to appreciate the beauty and complexity of the world around us. Philosophy encourages us to explore questions about the nature of reality, the meaning of life, and the relationship between humanity and the universe.
By engaging with these questions, students can gain a deeper understanding of themselves and the world, and develop a sense of wonder and awe about the mysteries of existence.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
As you found this post useful...
Share it on social media!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
The Editors
About The Philosophy Foundation
- National Thinking Classroom Awards
Testimonials
- Talks & Papers
World Philosophy Day
- Online courses
- Other educational settings
- Resources for children
- Resources for teachers
- Young Plato Documentary
- Holiday Clubs
- Other settings
- Think and Drink
- Philosophical enquiry (P4C)
- Thinking Classroom Programme
- Universities
- Games for Thinking
- Films / Podcasts
- Thought Adventures
- Anything within reason
- Hodja Stories
- What's on
What is Philosophy?

The aim of philosophy, abstractly formulated, is to understand how things in the broadest possible sense of the term hang together in the broadest possible sense of the term.
Wilfrid Sellars
A definition of philosophy is notoriously difficult. However, it is important, for anyone writing or training about doing philosophy, first of all to spell out what they mean by it so that the reader has some idea about what kind of philosophy they will encounter and, when training people to facilitate philosophy, to provide criteria.
The Philosophy Foundation’s account attempts to capture something of its spirit, structure, content, method, aims and hopes, but our account is inextricably personal to us and culturally specific. So, consistent with the philosophical spirit we’ve tried to illustrate here, one might wonder whether philosophy is – at least in addition to what we have said it is – something other than what we have said it is; to accept our account uncritically would not be very philosophical, after all.
The short answer
Philosophy is a way of thinking about certain subjects such as ethics, thought, existence, time, meaning and value. That 'way of thinking' involves 4 Rs: r esponsiveness, r eflection, r eason and r e-evaluation. The aim is to deepen understanding. The hope is that by doing philosophy we learn to think better, to act more wisely, and thereby help to improve the quality of all our lives.
The longer one
You can read our longer definition on the document below.
In Philosophy it’s not that there are no answers it’s just that the answers are very difficult to find.
Adam, aged 11
The film version
Peter Worley speaking at the Battle of Ideas 2015 ' Can Children Do Philosophy? '
Types of questions we explore
- Who should be in charge? How should we decide?
- What is fairness?
- What is responsibility?
- What is beauty? Who decides?
- Are some things absolutely wrong or right, or is it all relative?
- Is zero a number?
- What is freedom?
- Would you like to live forever if you could?
- Are people of equal value?
Philosophy’s not asking questions, it’s understanding questions
Child, aged 10

Talks & Papers

- Philosophy for Children
- Philosophy for Adults
Member Login

- Terms of use
- Privacy policy
© 2024 The Philosophy Foundation | RO 21-27 Lamb’s Conduit Street, London WC1N 3GS | Company number: 7416912 | Registered charity number 1140338
Website by on-IDLE
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site you are agreeing to our use of cookies.

Your complimentary articles
You’ve read one of your four complimentary articles for this month.
You can read four articles free per month. To have complete access to the thousands of philosophy articles on this site, please
Question of the Month
What is the meaning of life, the following answers to this central philosophical question each win a random book. sorry if your answer doesn’t appear: we received enough to fill twelve pages….
Why are we here? Do we serve a greater purpose beyond the pleasure or satisfaction we get from our daily activities – however mundane or heroic they may be? Is the meaning of life internal to life, to be found inherently in life’s many activities, or is it external, to be found in a realm somehow outside of life, but to which life leads? In the internal view it’s the satisfaction and happiness we gain from our actions that justify life. This does not necessarily imply a selfish code of conduct. The external interpretation commonly makes the claim that there is a realm to which life leads after death. Our life on earth is evaluated by a supernatural being some call God, who will assign to us some reward or punishment after death. The meaning of our life, its purpose and justification, is to fulfill the expectations of God, and then to receive our final reward. But within the internal view of meaning, we can argue that meaning is best found in activities that benefit others, the community, or the Earth as a whole. It’s just that the reward for these activities has to be found here, in the satisfactions that they afford within this life, instead of in some external spirit realm.
An interesting way to contrast the internal and external views is to imagine walking through a beautiful landscape. Your purpose in walking may be just to get somewhere else – you may think there’s a better place off in the distance. In this case the meaning of your journey through the landscape is external to the experience of the landscape itself. On the other hand, you may be intensely interested in what the landscape holds. It may be a forest, or it may contain farms, villages. You may stop along the way, study, learn, converse, with little thought about why you are doing these things other than the pleasure they give you. You may stop to help someone who is sick: in fact, you may stay many years, and found a hospital. What then is the meaning of your journey? Is it satisfying or worthwhile only if you have satisfied an external purpose – only if it gets you somewhere else? Why, indeed, cannot the satisfactions and pleasures of the landscape, and of your deeds, be enough?
Greg Studen, Novelty, Ohio
A problem with this question is that it is not clear what sort of answer is being looked for. One common rephrasing is “What is it that makes life worth living?”. There are any number of subjective answers to this question. Think of all the reasons why you are glad you are alive (assuming you are), and there is the meaning of your life. Some have attempted to answer this question in a more objective way: that is to have an idea of what constitutes the good life . It seems reasonable to say that some ways of living are not conducive to human flourishing. However, I am not convinced that there is one right way to live. To suggest that there is demonstrates not so much arrogance as a lack of imagination.
Another way of rephrasing the question is “What is the purpose of life?” Again we all have our own subjective purposes but some would like to think there is a higher purpose provided for us, perhaps by a creator. It is a matter of debate whether this would make life a thing of greater value or turn us into the equivalent of rats in a laboratory experiment. Gloster’s statement in King Lear comes to mind: “As flies to wanton boys we are to the gods – they kill us for their sport.” But why does there have to be a purpose to life separate from those purposes generated within it? The idea that life needs no external justification has been described movingly by Richard Taylor. Our efforts may ultimately come to nothing but “the day was sufficient to itself, and so was the life.” ( Good and Evil , 1970) In the “why are we here?” sense of the question there is no answer. It would be wrong, however, to conclude that life is meaningless. Life is meaningful to humans, therefore it has meaning.
Rebecca Linton, Leicester
When the question is in the singular we search for that which ties all values together in one unity, traditionally called ‘the good’. Current consideration of the good demands a recognition of the survival crises which confront mankind. The threats of nuclear war, environmental poisoning and other possible disasters make it necessary for us to get it right. For if Hannah Arendt was correct concerning the ‘banality of evil’ which affected so many Nazi converts and contaminated the German population by extension, we may agree with her that both Western rational philosophy and Christian teaching let the side down badly in the 20th century.
If we then turn away from Plato’s philosophy, balanced in justice, courage, moderation and wisdom; from Jewish justice and Christian self-denial; if we recognize Kant’s failure to convince populations to keep his three universal principles, then shall we look to the moral relativism of the Western secular minds which admired Nietzsche? Stalin’s purges of his own constituents in the USSR tainted this relativist approach to the search for the good. Besides, if nothing is absolute, but things have value only relative to other things, how do we get a consensus on the best or the worst? What makes your social mores superior to mine – and why should I not seek to destroy your way? We must also reject any hermit, monastic, sect or other loner criteria for the good life. Isolation will not lead to any long-term harmony or peace in the Global Village.
If with Nietzsche we ponder on the need for power in one’s life, but turn in the opposite direction from his ‘superman’ ideal, we will come to some form of the Golden Rule [‘Do unto others as you would have them do unto you’]. However, we must know this as an experiential reality. There is life-changing power in putting oneself in the place of the other person and feeling for and with them. We call this feeling empathy .
Persons who concentrate on empathy should develop emotional intelligence. When intellectual intelligence does not stand in the way of this kind of personal growth, but contributes to it, we can call this balance maturity . Surely the goal or meaning of human life is therefore none other than finding oneself becoming a mature adult free to make one’s own decisions, yet wanting everyone in the world to have this same advantage. This is good!
Ernie Johns, Owen Sound, Ontario
‘Meaning’ is a word referring to what we have in mind as ‘signification’, and it relates to intention and purpose. ‘Life’ is applied to the state of being alive; conscious existence. Mind, consciousness, words and what they signify, are thus the focus for the answer to the question. What seems inescapable is that there is no meaning associated with life other than that acquired by our consciousness, inherited via genes, developed and given content through memes (units of culture). The meanings we believe life to have are then culturally and individually diverse. They may be imposed through hegemony; religious or secular, benign or malign; or identified through deliberate choice, where this is available. The range is vast and diverse; from straightforward to highly complex. Meaning for one person may entail supporting a football team; for another, climbing higher and higher mountains; for another, being a parent; for another, being moved by music, poetry, literature, dance or painting; for another the pursuit of truth through philosophy; for another through religious devotions, etc. But characteristic of all these examples is a consciousness that is positively and constructively absorbed, engaged, involved, fascinated, enhanced and fulfilled. I would exclude negative and destructive desires; for example of a brutal dictator who may find torturing others absorbing and engaging and thus meaningful. Such cases would be too perverse and morally repugnant to regard as anything other than pathological.
The meaning of life for individuals may diminish or fade as a consequence of decline or difficult or tragic circumstances. Here it might, sadly, be difficult to see any meaning of life at all. The meaning is also likely to change from one phase of life to another, due to personal development, new interests, contexts, commitments and maturity.
Colin Brookes, Woodhouse Eaves, Leicestershire
It is clearly internet shopping, franchised fast food and surgically-enhanced boobs. No, this is not true. I think the only answer is to strip back every layer of the physical world, every learnt piece of knowledge, almost everything that seems important in our modern lives. All that’s left is simply existence. Life is existence: it seems ‘good’ to be part of life. But really that’s your lot! We should just be thankful that our lifespan is longer than, say, a spider, or your household mog.
Our over-evolved human minds want more, but unfortunately there is nothing more. And if there is some deity or malignant devil, then you can be sure they’ve hidden any meaning pretty well and we won’t see it in our mortal lives. So, enjoy yourself; be nice to people, if you like; but there’s no more meaning than someone with surgically-enhanced boobs, shopping on the net while eating a Big Mac.
Simon Maltman, By email
To ask ‘What is the meaning of life?’ is a poor choice of words and leads to obfuscation rather than clarity. Why so?
To phrase the question in this fashion implies that meaning is something that inheres in an object or experience – that it is a quality which is as discernible as the height of a door or the solidity of matter. That is not what meaning is like. It is not a feature of a particular thing, but rather the relationship between a perceiver and a thing, a subject and an object, and so requires both. There is no one meaning of, say, a poem, because meaning is generated by it being read and thought about by a subject. As subjects differ so does the meaning: different people evaluate ideas and concepts in different ways, as can be seen from ethical dilemmas. But it would be wrong to say that all these meanings are completely different, as there are similarities between individuals, not least because we belong to the same species and are constructed and programmed in basically the same way. We all have feelings of fear, attachment, insecurity and passion, etc.
So to speak of ‘the meaning of life’, is an error. It would be more correct to refer to the ‘meanings of life’, but as there are currently around six billion humans on Earth, and new psychological and cultural variations coming into being all the time, to list and describe all of these meanings would be a nigh on impossible task.
To ‘find meaning in life’ is a better way of approaching the issue, ie, whilst there is no single meaning of life, every person can live their life in a way which brings them as much fulfilment and contentment as possible. To use utilitarian language, the best that one can hope for is a life which contains as great an excess of pleasure over pain as possible, or alternatively, a life in which as least time as possible is devoted to activities which do not stimulate, or which do nothing to promote the goals one has set for oneself.
Steve Else, Swadlincote, Derbyshire
The meaning of life is not being dead.
Tim Bale, London
The question is tricky because of its hidden premise that life has meaning per se . A perfectly rational if discomforting position is given by Nietzsche, that someone in the midst of living is not in a position to discern whether it has meaning or not, and since we cannot step outside of the process of living to assess it, this is therefore not a question that bears attention.
However, if we choose to ignore the difficulties of evaluating a condition while inside it, perhaps one has to ask the prior question, what is the meaning of meaning ? Is ‘meaning’ given by the greater cosmos? Or do we in our freedom construct the category ‘meaning’ and then fill in the contours and colours? Is meaning always identical with purpose? I might decide to dedicate my life to answering this particular question, granting myself an autonomously devised purpose. But is this identical with the meaning of my life? Or can I live a meaningless life with purpose? Or shall meaning be defined by purpose? Some metaphysics offer exactly this corollary – that in pursuing one’s proper good, and thus one’s meaning, one is pursuing one’s telos or purpose. The point of these two very brief summaries of approaches to the question is to show the hazards in this construction of the question.
Karen Zoppa, The University of Winnipeg
One thing one can hardly fail to notice about life is that it is self-perpetuating. Palaeontology tells us that life has been perpetuating itself for billions of years. What is the secret of this stunning success? Through natural selection, life forms adapt to their environment, and in the process they acquire, one might say they become , knowledge about that environment, the world in which they live and of which they are part. As Konrad Lorenz put it, “Life itself is a process of acquiring knowledge.” According to this interpretation of evolution, the very essence of life (its meaning?) is the pursuit of knowledge : knowledge about the real world that is constantly tested against that world. What works and is in that sense ‘true’, is perpetuated. Life is tried and proven knowledge that has withstood the test of geological time. From this perspective, adopting the pursuit of knowledge as a possible meaning of one’s life seems, literally, a natural choice. The history of science and philosophy is full of examples of people who have done just that, and in doing so they have helped human beings to earn the self-given title of Homo sapiens – man of knowledge.
Axel Winter, Wynnum, Queensland
Life is a stage and we are the actors, said William Shakespeare, possibly recognizing that life quite automatically tells a story just as any play tells a story. But we are more than just actors; we are the playwright too, creating new script with our imaginations as we act in the ongoing play. Life is therefore storytelling. So the meaning of life is like the meaning of ‘the play’ in principle: not a single play with its plot and underlying values and information, but the meaning behind the reason for there being plays with playwright, stage, actors, props, audience, and theatre. The purpose of the play is self-expression , the playwright’s effort to tell a story. Life, a grand play written with mankind’s grand imagination, has this same purpose.
But besides being the playwright, you are the audience too, the recipient of the playwrights’ messages. As playwright, actor, and audience you are an heir to both growth and self-expression. Your potential for acquiring knowledge and applying it creatively is unlimited. These two concepts may be housed under one roof: Liberty. Liberty is the freedom to think and to create. “Give me liberty or give me death,” said Patrick Henry, for without liberty life has no meaningful purpose. But with liberty life is a joy. Therefore liberty is the meaning of life.
Ronald Bacci, Napa, CA
The meaning of life is understood according to the beliefs that people adhere to. However, all human belief systems are accurate or inaccurate to varying degrees in their description of the world. Moreover, belief systems change over time: from generation to generation; from culture to culture; and era to era. Beliefs that are held today, even by large segments of the population, did not exist yesterday and may not exist tomorrow. Belief systems, be they religious or secular, are therefore arbitrary. If the meaning of life is wanted, a meaning that will transcend the test of time or the particulars of individual beliefs, then an effort to arrive at a truly objective determination must be made. So in order to eliminate the arbitrary, belief systems must be set aside. Otherwise, the meaning of life could not be determined.
Objectively however, life has no meaning because meaning or significance cannot be obtained without reference to some (arbitrary) belief system. Absent a subjective belief system to lend significance to life, one is left with the ‘stuff’ of life, which, however offers no testimony as to its meaning. Without beliefs to draw meaning from, life has no meaning, but is merely a thing ; a set of facts that, in and of themselves, are silent as to what they mean. Life consists of a series of occurrences in an infinite now, divorced of meaning except for what may be ascribed by constructed belief systems. Without such beliefs, for many the meaning of life is nothing .
Surely, however, life means something . And indeed it does when an individual willfully directs his/her consciousness at an aspect of life, deriving from it an individual interpretation, and then giving this interpretation creative expression. Thus the meaning in the act of giving creative expression to what may be ephemeral insights. Stated another way, the meaning of life is an individual’s acts of creation . What, exactly is created, be it artistic or scientific, may speak to the masses, or to nobody, and may differ from individual to individual. The meaning of life, however, is not the thing created, but the creative act itself ; namely, that of willfully imposing an interpretation onto the stuff of life, and projecting a creative expression from it.
Raul Casso, Laredo, Texas
Rather than prattle on and then discover that I am merely deciding what ‘meaning’ means, I will start out with the assumption that by ‘meaning’ we mean ‘purpose.’ And because I fear that ‘purpose’ implies a Creator, I will say ‘best purpose.’ So what is the best purpose for which I can live my life? The best purpose for which I can live my life is, refusing all the easy ways to destroy. This is not as simple as it sounds. Refusing to destroy life – to murder – wouldn’t just depend on our lack of homicidal impulses, but also on our willingness to devote our time to finding out which companies have murdered union uprisers; to finding out whether animals are killed out of need or greed or ease; to finding the best way to refuse to fund military murder, if we find our military to be murdering rather than merely protecting. Refusing to destroy resources, to destroy loves, to destroy rights, turns out to be a full-time job. Oh sure, we can get cocky and say “Well, oughtn’t we destroy injustice? Or bigotry? Or hatred?” But we would be only fooling ourselves. They’re all already negatives: to destroy injustice, bigotry, and hatred is to refuse the destruction of justice, understanding, and love. So, it turns out, we finally say “Yes” to life, when we come out with a resounding, throat-wrecking “NO!”
Carrie Snider, By email
I propose that the knowledge we have now accumulated about life discloses quite emphatically that we are entirely a function of certain basic laws as they operate in the probably unique conditions prevailing here on Earth.
The behaviour of the most elementary forms of matter we know, subatomic particles, seems to be guided by four fundamental forces, of which electromagnetism is probably the most significant here, in that through the attraction and repulsion of charged particles it allows an almost infinite variation of bonding: it allows atoms to form molecules, up the chain to the molecules of enormous length and complexity we call as nucleic acids, and proteins. All these are involved in a constant interaction with surrounding chemicals through constant exchanges of energy. From these behaviour patterns we can deduce certain prime drives or purposes of basic matter, namely:
1. Combination (bonding).
2. Survival of the combination, and of any resulting organism.
3. Extension of the organism, usually by means of replication.
4. Acquisition of energy.
Since these basic drives motivate everything that we’re made of, all the energy, molecules and chemistry that form our bodies, our brains and nervous systems, then whatever we think, say and do is a function of the operation of those basic laws Therefore everything we think, say and do will be directed towards our survival, our replication and our demand for energy to fuel these basic drives. All our emotions and our rational thinking, our loves and hates, our art, science and engineering are refinements of these basic drives. The underlying drive for bonding inspires our need for interaction with other organisms, particularly other human beings, as we seek ever wider and stronger links conducive to our better survival. Protection and extension of our organic integrity necessitates our dependence on and interaction with everything on Earth.
Our consciousness is also necessarily a function of these basic drives, and when the chemistry of our cells can no longer operate due to disease, ageing or trauma, we lose consciousness and die. Since I believe we are nothing more than physics and chemistry, death terminates our life once and for all. There is no God, there is no eternal life. But optimistically, there is the joy of realising that we have the power of nature within us, and that by co-operating with our fellow man, by nurturing the resources of the world, by fighting disease, starvation, poverty and environmental degradation, we can all conspire to improve life and celebrate not only its survival on this planet, but also its proliferation. So the purpose of life is just that: to involve all living things in the common purpose of promoting and enjoying what we are – a wondrous expression of the laws of Nature, the power of the Universe.
Peter F. Searle, Topsham, Devon
“What is the meaning of life?” is hard to get a solid grip on. One possible translation of it is “What does it all mean?” One might spend a lifetime trying to answer such a heady question. Answering it requires providing an account of the ultimate nature of the world, our minds, value and how all these natures interrelate. I’d prefer to offer a rather simplistic answer to a possible interpretation of our question. When someone asks “What is the meaning of life?,” they may mean “What makes life meaningful?” This is a question I believe one can get a grip on without developing a systematic philosophy.
The answer I propose is actually an old one. What makes a human life have meaning or significance is not the mere living of a life, but reflecting on the living of a life.
Even the most reflective among us get caught up in pursuing ends and goals. We want to become fitter; we want to read more books; we want to make more money. These goal-oriented pursuits are not meaningful or significant in themselves. What makes a life filled with them either significant or insignificant is reflecting on why one pursues those goals. This is second-order reflection; reflection on why one lives the way one does. But it puts one in a position to say that one’s life has meaning or does not.
One discovers this meaning or significance by evaluating one’s life and meditating on it; by taking a step back from the everyday and thinking about one’s life in a different way. If one doesn’t do this, then one’s life has no meaning or significance. And that isn’t because one has the wrong sorts of goals or ends, but rather has failed to take up the right sort of reflective perspective on one’s life. This comes close to Socrates’ famous saying that the unexamined life is not worth living. I would venture to say that the unexamined life has no meaning.
Casey Woodling, Gainesville, FL
For the sake of argument, let’s restrict the scope of the discussion to the human species, and narrow down the choices to
1) There is no meaning of life, we simply exist;
2) To search for the meaning of life; and
3) To share an intimate connection with humankind: the notion of love.
Humans are animals with an instinct for survival. At a basic level, this survival requires food, drink, rest and procreation. In this way, the meaning of life could be to continue the process of evolution. This is manifested in the modern world as the daily grind.
Humans also have the opportunity and responsibility of consciousness. With our intellect comes curiosity, combined with the means to understand complex problems. Most humans have, at some point, contemplated the meaning of life. Some make it a life’s work to explore this topic. For them and those like them, the question may be the answer.
Humans are a social species. We typically seek out the opposite sex to procreate. Besides the biological urge or desire, there is an interest in understanding others. We might simply gain pleasure in connecting with someone in an intimate way. Whatever the specific motivation, there is something that we crave, and that is to love and be loved.
The meaning of life may never be definitively known. The meaning of life may be different for each individual and/or each species. The truth of the meaning of life is likely in the eye of the beholder. There were three choices given at the beginning of this essay, and for me, the answer is all of the above.
Jason Hucsek, San Antonio, TX
Next Question of the Month
The next question is: What Is The Nature Of Reality? Answers should be less than 400 words. Subject lines or envelopes should be marked ‘Question Of The Month’. You will be edited.
This site uses cookies to recognize users and allow us to analyse site usage. By continuing to browse the site with cookies enabled in your browser, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our privacy policy . X
- Writing Home
- Writing Advice Home
Writing a Philosophy Essay
- Printable PDF Version
- Fair-Use Policy
Is there a God? Are there objective, universal moral norms or rules? What is meant by ‘reality’? Do we have free will? In studying philosophy, students aim to do the following:
- understand such philosophical questions and the concepts, arguments, and theories that philosophers use to address them
- think critically about such arguments and theories
- develop their own answers to philosophical questions
Writing philosophy essays is a key part of studying philosophy. Make sure first to understand the assignment, looking out for the questions asked and paying attention to prompts such as “outline” or “evaluate” or “compare”. Most philosophy assignments will ask you to demonstrate your understanding of the subject through exposition of arguments and theories, and many will also test your ability to assess these arguments and theories by writing a critical evaluation of them. Write your paper so that the reader understands how your exposition and evaluation answer the questions and address all parts of the assignment.
Read the Texts Carefully, Asking Questions
Before you write a paper, though, you need to understand the course texts and recommended readings. Philosophical works need to be read slowly and with focused attention. As you read, ask yourself the following:
- What philosophical question(s) is the author addressing?
- What exactly is meant by key ideas or concepts in the text (e.g., Plato’s “Forms”, Aristotle’s “substance” and “accident”, Kant’s “categorical imperative,” Sartre’s “being-for-itself”)? Each discipline has its own technical language, which students must learn.
- What arguments does the author make (e.g., Aquinas’s five arguments for the existence of God)?
- What theories does the author propose (e.g., a dualist mind-body theory or—one of its competitors—a physicalist theory of mind)?
Organize Your Ideas into a Logical Structure
Take notes as you read. Then put your ideas for the essay into a logical order. Because philosophy papers proceed by logical argument, creating a point-form outline that captures the structure of your argument is generally a good strategy. An outline will allow you to spot problems in your argument more easily.
Augment Your Thesis with a Road Map that Reveals the Structure of Your Argument
Most assignments will require you to present a clear thesis statement that sums up the position for which you are arguing. In the introduction you should also provide a ‘road map’—a few sentences that announce in sequence what you intend to accomplish in each of the key stages of your paper. Road maps often rely on first person (“First, I will analyze . . . “), but if your professor prefers that you don’t use the first person, you can instead describe what your essay will accomplish (“First, the essay will analyze . . . “).
Show Your Understanding through Clear and Accurate Exposition
Try to make your expository writing as clear and accurate as possible, and try to show the logical connections between the different parts of a philosophical system. Avoid vague or overly brief exposition, serious omissions, or misunderstandings.
In some first year courses, an early assignment may ask you to write a short paper expounding but not evaluating a concept or theory. For example: “Explain what Plato means by Forms.” Subsequent assignments in the course usually involve evaluation as well as exposition (e.g., “Outline and evaluate Plato’s theory of Forms”). In some courses, assignments may call for detailed interpretation of a text rather than an assessment of it. “Was Hume an idealist?”, “Was Wittgenstein a behaviourist?” and “Was Marx a nihilist about morality?” are examples. Such questions are posed when there is disagreement among scholars about how to interpret a philosopher. In such essays, you will need to examine texts very closely, find passages which support a yes or no answer, choose where you stand in the debate, and defend your answer.
Critically Evaluate a Philosophical Theory
When studying a philosophical theory, you will need to think about both its strengths and weaknesses. For example, is a particular theory of art (such as the view that art is the expression of emotion) comprehensive: does it apply to all the arts and all types of art, or only to some? Is it logically consistent or does it contain contradictions? Are there counterexamples to it?
As you think about your topic, read the course materials, and take notes, you should work out and assemble the following:
- the strengths of a philosopher’s theory
- the arguments the philosopher gives in support of the theory and those the philosopher did not provide but which might still support it
- possible criticisms of those arguments
- how the philosopher has replied or could reply to these criticisms
Finally, ask yourself how you would evaluate those replies: do they work or not? Be selective, especially in a shorter paper. In a 1,000-word essay, for instance, discuss one or two arguments in favour and one or two against. In a 2,000- or 2,500-word paper, you can include more arguments and possible replies. Finally, plan carefully: leave enough space for your assessment.
A different type of critical evaluation assignment may ask for a comparative appraisal of two or more theories. For example, “Which account of human decision-making is stronger: X’s free will theory or Y’s determinist theory?” In such essays, your thesis could be that one account is better than the other or, perhaps, that neither account is clearly superior. You might argue that each has different strengths and weaknesses.
Develop Your Own Answers to Philosophical Questions
In the type of critical assessments above, you are already, to some extent, articulating your own philosophical positions. As you read texts in a course on, say, philosophy of mind or philosophy of art, you should be asking, based on what you have read so far, which theory is the best? Don’t be content to just understand theories and know their strengths and weaknesses. Push yourself to think out your own account of mind or art.
Some upper-year essay assignments may throw a fundamental philosophical question at you: “What is art?”, “Do we have free will?”, “What is morality?”, or “What is reality?”. Here, you will present your own answer, giving reasons, answering objections, and critically evaluating alternative approaches. Your answer/thesis might be an existing theory or a synthesis of two or more theories, or (more rarely) a completely new theory. Now you are not only expounding theories or critically evaluating them; you are also developing your own philosophy!
- Facts and Figures
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- Non-traditional Admissions
- Pay Deposit
- Undergraduate Majors
- Graduate Programs
- Honors College
- Study Abroad
- Professional & Continuing
- Online Programs
- Career Planning
- Living on Campus
- Clubs & Organizations
- Spirit & Traditions
- About Harrisonburg
- Pay Your Deposit
- Office of Financial Aid
- Freshman Scholarships
- James Madison University -->
- Philosophy & Religion
- Majors & Minors
- Philosophy Program
- Philosophy on the Web
- Careers for Philosophy Majors
- Why Study Religion?
- Religion Program
- Careers for Religion Majors
- Faculty & Staff
- Awards & Grants
- Graduate requirements checklist: Philosophy concentration (BA)
- Graduate requirements checklist: Interdisciplinary philosophy concentration (BA)
- Phi Sigma Tau
- Links to helpful philosophy websites
- Advice on graduate study in philosophy
- Undergraduate philosophy journals
- Dr. William W. Thomas Memorial Scholarship in Religion
- Hobbie Scholarship
- Theta Alpha Kappa Honor Society
- Advice on graduate study in religion
- Logic and Reasoning Institute
- In Memoriam

Philosophy makes a central contribution to the educational enterprise through its demands upon intellectual activity. Education in philosophy involves becoming aware of major figures and developments in the history of philosophy, learning up-to-date techniques and accepted answers to philosophical questions, and learning critical, interpretive, and evaluative skills that, in the overall scheme of things, may be considered to be of greatest value.
Graduates of the philosophy program at James Madison University are expected to have come to terms with difficult texts dealing with advanced philosophical arguments. These readings are often quite diverse in method and content. Further, a variety of written work is part of the philosophy student's assignments, and it is expected that these assignments be carefully composed and thoughtfully addressed. Finally, informed discussion is essential to philosophy and philosophical education. This verbal interaction is expected to occur as a routine part of course offerings.
Much of what is learned in philosophy can be applied in virtually any endeavor. This is both because philosophy touches so many subjects and, especially, because many of its methods can be used in any field.
The study of philosophy helps us to enhance our ability to solve problems, our communication skills, our persuasive powers, and our writing skills. Below is a description of how philosophy helps us develop these various important skills.
General Problem Solving Skills:
The study of philosophy enhances a person's problem-solving capacities. It helps us to analyze concepts, definitions, arguments, and problems. It contributes to our capacity to organize ideas and issues, to deal with questions of value, and to extract what is essential from large quantities of information. It helps us, on the one hand, to distinguish fine and subtle differences between views and, on the other hand, to discover common ground between opposing positions. It also helps us to synthesize a variety of views or perspectives into one unified whole.
Communication Skills:
Philosophy contributes uniquely to the development of expressive and communicative powers. It provides some of the basic tools of self-expression - for instance, skills in presenting ideas through well-constructed, systematic arguments - that other fields either do not use or use less extensively. Philosophy helps us express what is distinctive in our views, it enhances our ability to explain difficult material, and it helps us to eliminate ambiguities and vagueness from our writing and speech.
Persuasive Powers:
Philosophy provides training in the construction of clear formulations, good arguments, and appropriate examples. It, thereby, helps us to develop our ability to be convincing. We learn to build and defend our own views, to appreciate competing positions, and to indicate forcefully why we consider our own views preferable to alternatives. These capacities can be developed not only through reading and writing in philosophy, but also through the philosophical dialogue, both within and outside the classroom, that is so much a part of a thorough philosophical education.
Writing Skills:
Writing is taught intensively in many philosophy courses, and many regularly assigned philosophical texts are also excellent as literary essays. Philosophy teaches interpretive writing through its examination of challenging texts, comparative writing through emphasis on fairness to alternative positions, argumentative writing through developing students' ability to establish their own views, and descriptive writing through detailed portrayal of concrete examples. Concrete examples serve as the anchors to which generalizations must be tied. Structure and technique, then, are emphasized in philosophical writing. Originality is also encouraged, and students are generally urged to use their imagination to develop their own ideas.
The general uses of philosophy just described are obviously of great academic value. It should be clear that the study of philosophy has intrinsic rewards as an unlimited quest for understanding of important, challenging problems. But philosophy has further uses in deepening an education, both in college and in the many activities, professional and personal, that follow graduation. Two of these further uses are described below.
Understanding Other Disciplines:
Philosophy is indispensable for our ability to understand other disciplines. Many important questions about a discipline, such as the nature of its concepts and its relation to other disciplines, are philosophical in nature. Philosophy of science, for example, is needed to supplement the understanding of the natural and social sciences that derives from scientific work itself. Philosophy of literature and philosophy of history are of similar value in understanding the humanities, and philosophy of art (aesthetics) is important in understanding both the visual and the performing arts. Philosophy is, moreover, essential in assessing the various standards of evidence used by other disciplines. Since all fields of knowledge employ reasoning and must set standards of evidence, logic and epistemology have a general bearing on all these fields.
Development of Sound Methods of Research and Analysis:
Still another value of philosophy in education is its contribution to our capacity to frame hypotheses, to do research, and to put problems in manageable form. Philosophical thinking strongly emphasizes clear formulation of ideas and problems, selection of relevant data, and objective methods for assessing ideas and proposals. It also emphasizes development of a sense of the new directions suggested by new hypotheses and questions one encounters while doing research. Philosophers regularly build on both the successes and failures of their predecessors. A person with philosophical training can readily learn to do the same in any field.
Among the things that people educated in philosophy can do are the following. They can do research on a variety of subjects. They can get information and organize it. They can write clearly and effectively. They can communicate well, usually both orally and in writing. They can generate ideas on many different sorts of problems. They can formulate and solve problems. They can elicit hidden assumptions and articulate overlooked alternatives. They can persuade people to take unfamiliar views or novel options seriously. They can summarize complicated materials without undue simplification. They can integrate diverse data and construct useful analogies. They can distinguish subtle differences without overlooking similarities. They can also adapt to change, a capacity of growing importance in the light of rapid advances in so many fields. And well educated philosophers can usually teach what they know to others. This ability is especially valuable at a time when training and retraining are so often required by rapid technological changes.
These abilities are quite general, but they bear directly on the range of careers for which philosophers are prepared. Philosophers have the skills necessary for an enormous range of both academic and non-academic jobs. The kind of basic education which philosophical training provides is eminently useful in some major aspects of virtually any occupation.
Below are lists of philosophy courses that are particularly appropriate for people studying, aspiring to, or working in disciplines outside of philosophy, as these philosophy courses help to deepen one's understanding of other fields of study, to answer some of the fundamental questions that arise in other disciplines, and to clarify the relationship between one discipline and another field of study.
Note : this text is adapted from three sources: (1) Philosophy: A Brief Guide for Undergraduates (a publication of the American Philosophical Association), (2) Careers for Philosophers (prepared by the American Philosophical Association Committee on Career Opportunities, and (3) The Philosophy Major (a statement prepared under the auspices of the Board of Officers of the American Philosophical Association). These texts are available online at apaonline.org .
Back to Top
- Expenditures
- Accessibility
- Social Media

- Table of Contents
- Random Entry
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Advanced Tools
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Entry Contents
Bibliography
Academic tools.
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
There are roughly two philosophical literatures on “happiness,” each corresponding to a different sense of the term. One uses ‘happiness’ as a value term, roughly synonymous with well-being or flourishing. The other body of work uses the word as a purely descriptive psychological term, akin to ‘depression’ or ‘tranquility’. An important project in the philosophy of happiness is simply getting clear on what various writers are talking about: what are the important meanings of the term and how do they connect? While the “well-being” sense of happiness receives significant attention in the contemporary literature on well-being, the psychological notion is undergoing a revival as a major focus of philosophical inquiry, following on recent developments in the science of happiness. This entry focuses on the psychological sense of happiness (for the well-being notion, see the entry on well-being ). The main accounts of happiness in this sense are hedonism, the life satisfaction theory, and the emotional state theory. Leaving verbal questions behind, we find that happiness in the psychological sense has always been an important concern of philosophers. Yet the significance of happiness for a good life has been hotly disputed in recent decades. Further questions of contemporary interest concern the relation between the philosophy and science of happiness, as well as the role of happiness in social and political decision-making.
1.1 Two senses of ‘happiness’
1.2 clarifying our inquiry, 2.1 the chief candidates, 2.2 methodology: settling on a theory, 2.3 life satisfaction versus affect-based accounts, 2.4 hedonism versus emotional state, 2.5 hybrid accounts, 3.1 can happiness be measured, 3.2 empirical findings: overview, 3.3 the sources of happiness, 4.1 doubts about the value of happiness, 4.2 restoring happiness to the theory of well-being, 4.3 is happiness overrated, 5.1 normative issues, 5.2 mistakes in the pursuit of happiness, 5.3 the politics of happiness, other internet resources, related entries, 1. the meanings of ‘happiness’.
What is happiness? This question has no straightforward answer, because the meaning of the question itself is unclear. What exactly is being asked? Perhaps you want to know what the word ‘happiness’ means. In that case your inquiry is linguistic. Chances are you had something more interesting in mind: perhaps you want to know about the thing , happiness, itself. Is it pleasure, a life of prosperity, something else? Yet we can’t answer that question until we have some notion of what we mean by the word.
Philosophers who write about “happiness” typically take their subject matter to be either of two things, each corresponding to a different sense of the term:
- A state of mind
- A life that goes well for the person leading it
In the first case our concern is simply a psychological matter. Just as inquiry about pleasure or depression fundamentally concerns questions of psychology, inquiry about happiness in this sense—call it the (long-term) “psychological sense”—is fundamentally the study of certain mental states. What is this state of mind we call happiness? Typical answers to this question include life satisfaction, pleasure, or a positive emotional condition.
Having answered that question, a further question arises: how valuable is this mental state? Since ‘happiness’ in this sense is just a psychological term, you could intelligibly say that happiness isn’t valuable at all. Perhaps you are a high-achieving intellectual who thinks that only ignoramuses can be happy. On this sort of view, happy people are to be pitied, not envied. The present article will center on happiness in the psychological sense.
In the second case, our subject matter is a kind of value , namely what philosophers nowadays tend to call prudential value —or, more commonly, well-being , welfare , utility or flourishing . (For further discussion, see the entry on well-being . Whether these terms are really equivalent remains a matter of dispute, but this article will usually treat them as interchangeable.) “Happiness” in this sense concerns what benefits a person, is good for her, makes her better off, serves her interests, or is desirable for her for her sake. To be high in well-being is to be faring well, doing well, fortunate, or in an enviable condition. Ill-being, or doing badly, may call for sympathy or pity, whereas we envy or rejoice in the good fortune of others, and feel gratitude for our own. Being good for someone differs from simply being good, period: perhaps it is always good, period, for you to be honest; yet it may not always be good for you , as when it entails self-sacrifice. Not coincidentally, the word ‘happiness’ derives from the term for good fortune, or “good hap,” and indeed the terms used to translate it in other languages often have similar roots. In this sense of the term—call it the “well-being sense”—happiness refers to a life of well-being or flourishing: a life that goes well for you.
Importantly, to ascribe happiness in the well-being sense is to make a value judgment : namely, that the person has whatever it is that benefits a person. [ 1 ] If you and I and have different values, then we may well differ about which lives we consider happy. I might think Genghis Khan had a happy life, because I think what matters for well-being is getting what you want; while you deny this because you think a life of evildoing, however “successful,” is sad and impoverished.
Theories of well-being—and hence of “happiness” in the well-being sense—come in three basic flavors, according to the best-known taxonomy (Parfit 1984): hedonism, desire theories, and objective list theories. Whereas hedonists identify well-being roughly with experiences of pleasure, desire theorists equate it with the satisfaction of one’s desires— actually getting what you want, versus merely having certain experiences. Both hedonism and desire theories are in some sense subjectivist, since they ground well-being in the individual’s subjective states. Objective list theorists, by contrast, think some things benefit us independently of our attitudes or feelings: there are objective prudential goods. Aristotelians are the best-known example: they take well-being ( eudaimonia ) to consist in a life of virtuous activity—or more broadly, the fulfillment of our human capacities. A passive but contented couch potato may be getting what he wants, and he may enjoy it. But he would not, on Aristotelian and other objective list theories, count as doing well, or leading a happy life.
Now we can sharpen the initial question somewhat: when you ask what happiness is, are you asking what sort of life benefits a person? If so, then your question concerns matters of value, namely what is good for people—the sort of thing that ethical theorists are trained to address. Alternatively, perhaps you simply want to know about the nature of a certain state of mind—happiness in the psychological sense. In this case, some sort of psychological inquiry will be needed, either philosophical or scientific. (Laypersons often have neither sort of question in mind, but are really asking about the sources of happiness. Thus it might be claimed, say, that “happiness is being with good friends.” This is not a view about the nature or definition of happiness, but rather a theory about the sorts of things that tend to make us happy. It leaves unanswered, or takes for granted, the question of just what happiness is , such that friends are a good source of it.)
In short, philosophical “theories of happiness” can be about either of at least two different things: well-being, or a state of mind. [ 2 ] Accordingly, there are essentially two bodies of philosophical literature about “happiness” and two sets of debates about its nature, though writers often fail to distinguish them. Such failures have generated much confusion, sometimes yielding bogus disagreements that prove to be merely verbal. [ 3 ] For instance, some psychologists identify “happiness” with attitudes of life satisfaction while remaining neutral on questions of value, or whether Bentham, Mill, Aristotle, or any other thinker about the good life was correct. Such researchers employ the term in the psychological sense. Yet it is sometimes objected against such claims that life satisfaction cannot suffice for “happiness” because other things, like achievement or knowledge, matter for human well-being. The objectors are confused: their opponents have made no claims about well-being at all, and the two “sides,” as it were, are simply using ‘happiness’ to talk about different things. One might just as sensibly object to an economist’s tract on “banks” that it has nothing to say about rivers and streams.
Which use of ‘happiness’ corresponds to the true meaning of the term in contemporary English? Arguably, both. The well-being usage clearly dominates in the historical literature through at least the early modern era, for instance in translations of the ancient Greeks’ ‘ eudaimonia ’ or the Latin ‘ beatitudo ’, though this translation has long been a source of controversy. Jefferson’s famous reference to “the pursuit of happiness” probably employed the well-being sense. Even later writers such as Mill may have used the term in its well-being sense, though it is often difficult to tell since well-being itself is often taken to consist in mental states like pleasure. In ordinary usage, the abstract noun ‘happiness’ often invites a well-being reading. And the locution ‘happy life ’ may not naturally take a psychological interpretation, for the simple reason that lives aren’t normally regarded as psychological entities.
Contrast this with the very different meaning that seems to attach to talk of “ being happy.” Here it is much less clear that we are talking about a property of a person’s life; it seems rather to be a property of the person herself. To be happy, it seems, is just to be in a certain sort of psychological state or condition. Similarly when we say that so-and-so “is happy” (as opposed to saying that he is leading a happy life). This psychological usage, arguably, predominates in the current vernacular. Researchers engaged in the self-described “science of happiness” usually do not take themselves to be making value judgments when they proclaim individuals in their studies to be happy. Nor, when asserting that a life satisfaction study shows Utahans to be happier than New Yorkers, are they committing themselves to the tendentious claim that Utahans are better off . (If they are, then the psychology journals that are publishing this research may need to revise their peer-review protocols to include ethicists among their referees.) And the many recent popular books on happiness, as well as innumerable media accounts of research on happiness, nearly all appear to take it for granted that they are talking about nothing more than a psychological condition.
Henceforth ‘happiness’ will be used in the long-term psychological sense, unless otherwise specified. Note, however, that a number of important books and other works on “happiness” in recent decades have employed the well-being sense of the term. Books of this sort appear to include Almeder 2000, Annas 1993, 2011, Bloomfield 2014, Cahn and Vitrano 2015, Kenny and Kenny 2006, McMahon 2005, McPherson 2020, Noddings 2003, Russell 2013, White 2006, and Vitrano 2014, though again it is not always clear how a given author uses the term. For discussion of the well-being notion, see the entry on well-being . [ 4 ]
2. Theories of happiness
Philosophers have most commonly distinguished two accounts of happiness: hedonism , and the life satisfaction theory. Hedonists identify happiness with the individual’s balance of pleasant over unpleasant experience, in the same way that welfare hedonists do. [ 5 ] The difference is that the hedonist about happiness need not accept the stronger doctrine of welfare hedonism; this emerges clearly in arguments against the classical Utilitarian focus on happiness as the aim of social choice. Such arguments tend to grant the identification of happiness with pleasure, but challenge the idea that this should be our primary or sole concern, and often as well the idea that happiness is all that matters for well-being.
Life satisfaction theories identify happiness with having a favorable attitude toward one’s life as a whole. This basic schema can be filled out in a variety of ways, but typically involves some sort of global judgment: an endorsement or affirmation of one’s life as a whole. This judgment may be more or less explicit, and may involve or accompany some form of affect. It may also involve or accompany some aggregate of judgments about particular items or domains within one’s life. [ 6 ]
A third theory, the emotional state view, departs from hedonism in a different way: instead of identifying happiness with pleasant experience, it identifies happiness with an agent’s emotional condition as a whole, of what is often called “emotional well-being.” [ 7 ] This includes nonexperiential aspects of emotions and moods (or perhaps just moods), and excludes pleasures that don’t directly involve the individual’s emotional state. It might also include a person’s propensity for experiencing various moods, which can vary over time, though several authors have argued against this suggestion (e.g., Hill 2007, Klausen 2015, Rossi 2018). Happiness on such a view is more nearly the opposite of depression or anxiety—a broad psychological condition—whereas hedonistic happiness is simply opposed to unpleasantness. For example, a deeply distressed individual might distract herself enough with constant activity to maintain a mostly pleasant existence—broken only by tearful breakdowns during the odd quiet moment—thus perhaps counting as happy on a hedonistic but not emotional state view. The states involved in happiness, on an emotional state view, can range widely, far more so that the ordinary notion of mood or emotion. On one proposal, happiness involves three broad categories of affective state, including “endorsement” states like joy versus sadness, “engagement” states like flow or a sense of vitality, and “attunement” states like tranquility, emotional expansiveness versus compression, and confidence. Given the departures from commonsensical notions of being in a “good mood,” happiness is characterized in this proposal as “psychic affirmation,” or “psychic flourishing” in pronounced forms.
A fourth family of views, hybrid theories , attempts an irenic solution to our diverse intuitions about happiness: identify happiness with both life satisfaction and pleasure or emotional state, perhaps along with other states such as domain satisfactions. The most obvious candidate here is subjective well-being , which is typically defined as a compound of life satisfaction, domain satisfactions, and positive and negative affect. (Researchers often seem to identify happiness with subjective well-being, sometimes with life satisfaction, and perhaps most commonly with emotional or hedonic state.) The chief appeal of hybrid theories is their inclusiveness: all the components of subjective well-being seem important, and there is probably no component of subjective well-being that does not at times get included in “happiness” in ordinary usage.
How do we determine which theory is correct? Traditional philosophical methods of conceptual or linguistic analysis can give us some guidance, indicating that some accounts offer a better fit with the ordinary concept of happiness. Thus it has been argued that hedonism is false to the concept of happiness as we know it; the intuitions taken to support hedonism point instead to an emotional state view (Haybron 2001). And some have argued that life satisfaction is compatible with profoundly negative emotional states like depression—a suffering artist might not value emotional matters much, and wholeheartedly affirm her life (Carson 1981, Davis 1981b, Haybron 2005, Feldman 2010). Yet it might seem counterintuitive to deem such a person happy. At the same time, people do sometimes use ‘happiness’ to denote states of life satisfaction: life satisfaction theories do seem faithful to some ordinary uses of ‘happiness’. The trouble is that HAPPINESS appears to be a “mongrel concept,” as Ned Block (1995) called the concept of consciousness: the ordinary notion is something of a mess. We use the term to denote different things in different contexts, and often have no clear notion of what we are referring to. This suggests that accounts of happiness must be somewhat revisionary, and that we must assess theories on grounds other than simple fidelity to the lay concept of happiness—“descriptive adequacy,” in Sumner’s (1996) terms. One candidate is practical utility: which conception of happiness best answers to our interests in the notion? We talk about happiness because we care about it. The question is why we care about it, and which psychological states within the extension of the ordinary term make the most sense of this concern. Even if there is no simple answer to the question what happiness is, it may well turn out that our interests in happiness cluster so strongly around a particular psychological kind that happiness can best, or most profitably, be understood in terms of that type of state (Haybron 2003). Alternatively, we may choose to distinguish different varieties of happiness. It will be less important how we use the word, however, than that we be clear about the nature and significance of the phenomena that interest us.
The debate over theories of happiness falls along a couple of lines. The most interesting questions concern the choice between life satisfaction and affect-based views like hedonism and the emotional state theory. [ 8 ] Proponents of life satisfaction see two major advantages to their account. First, life satisfaction is holistic , ranging over the whole of one’s life, or the totality of one’s life over a certain period of time. It reflects not just the aggregate of moments in one’s life, but also the global quality of one’s life taken as a whole (but see Raibley 2010). And we seem to care not just about the total quantity of good in our lives, but about its distribution—a happy ending, say, counts for more than a happy middle (Slote 1982, Velleman 1991). Second, life satisfaction seems more closely linked to our priorities than affect is, as the suffering artist case illustrates. While a focus on affect makes sense insofar as we care about such matters, most people care about other things as well, and how their lives are going relative to their priorities may not be fully mirrored in their affective states. Life satisfaction theories thus seem to fit more closely with liberal ideals of individual sovereignty, on which how well my life is going for me is for me to decide. My satisfaction with my life seems to embody that judgment. Of course a theory of happiness need not capture everything that matters for well-being; the point is that a life satisfaction view might explain why we should care so much about happiness, and so enjoy substantive as well as intuitive support. [ 9 ]
But several objections have been raised against life satisfaction views. The most common complaint has already been noted, namely that a person could apparently be satisfied with her life even while leading a highly unpleasant or emotionally distressed existence, and it can seem counterintuitive to regard such a person as happy (see section 2.2). Some life satisfaction theorists deny that such cases are possible (Benditt 1978), but it could also be argued that such possibilities are part and parcel of life satisfaction’s appeal: some people may not get much pleasure out of life because they don’t care particularly about affective matters, and a life satisfaction theory allows that they can, in their own fashion, be happy.
Two other objections are more substantive, raising questions about whether life satisfaction has the right sort of importance. One concern is whether people often enough have well-grounded attitudes of life satisfaction or dissatisfaction. Evaluating one’s life as a whole can be a complicated business, and there is some question whether people typically have well-defined attitudes toward their lives that accurately reflect how well their lives measure up relative to their priorities. Some research, for instance, suggests that life satisfaction reports tend to reflect judgments made on the spot, drawing on whatever information comes readily to mind, with substantial influences by transient contextual factors like the weather, finding a dime, etc. (Schwarz and Strack 1999). Debate persists over whether this work undermines the significance of life satisfaction judgments, but it does raise a question whether life satisfaction attitudes tend to be well-enough grounded to have the kind of importance that people normally ascribe to happiness.
The third objection is somewhat intricate, so it will require some explaining. The claim is that a wide range of life satisfaction attitudes might be consistent with individuals’ perceptions of how well their lives are going relative to what they care about, raising doubts about the importance of life satisfaction (Haybron 2016). You might reasonably be satisfied when getting very little of what you want, or dissatisfied when getting most of what you want. One reason for this is that people tend to have many incommensurable values, leaving it open how to add them up. Looking at the various ups and downs of your life, it may be arbitrary whether to rate your life a four out of ten, or a seven. A second reason is that life satisfaction attitudes are not merely assessments of subjective success or personal welfare: they involve assessments of whether one’s life is good enough —satisfactory. Yet people’s values may radically underdetermine where they should set the bar for a “good enough” life, again rendering the judgment somewhat arbitrary. Given your values, you might reasonably be satisfied with a two, or require a nine to be satisfied. While it may seem important how well people see their lives going relative to what they care about, it is not obviously so important whether people see their lives going well enough that they are willing to judge them satisfactory.
If life satisfaction attitudes are substantially arbitrary relative to subjective success, then people might reasonably base those attitudes on other factors, such as ethical ideals (e.g., valuing gratitude or noncomplacency) or pragmatic concerns (e.g., comforting oneself). Shifts in perspective might also reasonably alter life satisfaction attitudes. After the funeral, you might be highly satisfied with your life, whereas the high school reunion leaves you dissatisfied; yet neither judgment need be mistaken, or less authoritative.
As a result, life satisfaction attitudes may be poor indicators of well-being, even from the individual’s own point of view. That people in a given country register high levels of life satisfaction may reflect nothing more than that they set the bar extremely low; they might be satisfied with anything short of pure agony. Another country’s citizens might be dissatisfied with their lives, but only because they set the bar much higher. Relative to what they care about, people in the dissatisfied nation could be better off than those in the satisfied nation. To take another example, a cancer patient might be more satisfied with his life than he was before the diagnosis, for he now looks at his life from a different perspective and emphasizes different virtues like fortitude and gratitude as opposed to (say) humility and non-complacency. Yet he need not think himself better off at all: he might believe himself worse off than he was when he was less satisfied. Neither judgment need seem to him or us to be mistaken: it’s just that he now looks at his life differently. Indeed, he might think he’s doing badly, even as he is satisfied with his life: he endorses it, warts and all, and is grateful just have his not-so-good life rather than some of the much worse alternatives.
For present purposes, the worry is that life satisfaction may not have the kind of significance happiness is normally thought to have. This may pose a difficulty for the identification of life satisfaction with happiness: for people frequently seem to use happiness as a proxy for well-being, a reasonably concrete and value-free stand-in that facilitates quick-and-dirty assessments of welfare. Given the discovery that someone is happy, we might infer that he is doing well; if we learn that someone is unhappy, we may conclude that she is doing poorly. Such inferences are defeasible: if we later find that the happy Ned’s wife and friends secretly hate him, we need not decide that he isn’t happy after all; we simply withdraw the conclusion that he is doing well. So long as happiness tracks well-being well enough in most cases, this sort of practice is perfectly respectable. But if we identify happiness with life satisfaction, then we may have a problem: maybe Sally is satisfied only because she values being grateful for the good things in life. This sort of case may not be merely a theoretical possibility: perhaps the very high rates of self-reported life satisfaction in the United States and many other places substantially reflects a broad acceptance of norms of gratitude and a general tendency to emphasize the positives, or perhaps a sense that not to endorse your life amounts to a lack of self-regard. It is not implausible that most people, even those enduring great hardship, can readily find grounds for satisfaction with their lives. Life may have to be pretty hard for a person to be incapable of affirming it.
Despite these concerns there is significant intuitive appeal in the idea that to be happy is to be satisfied with one’s life. Perhaps a different way of conceiving life satisfaction, for instance dispensing with the global judgment and aggregating particular satisfactions and dissatisfactions, would lessen the force of these objections. Alternatively, it is possible that idealized or qualified forms of life satisfaction would mitigate these concerns for some purposes, such as a theory of well-being. [ 10 ]
A second set of issues concerns the differences between the two affect-based views, hedonism and emotional state. The appeal of hedonism is fairly obvious: the pleasantness of our experience is plainly a matter of great significance; many have claimed it to be the only thing that matters. What, by contrast, motivates the emotional state account, which bears obvious similarities to hedonism yet excludes many pleasures from happiness? The question of motivation appears to be the chief worry facing the emotional state theory: what’s to be gained by focusing on emotional state rather than pleasure?
One argument for taking such a view is intuitive: some find it implausible to think that psychologically superficial pleasures invariably make a difference in how happy one is—the typical pleasure of eating a cracker, say, or even the intense pleasure of an orgasm that nonetheless fails to move one, as can happen with meaningless sexual activity. The intuitive distinction seems akin to distinctions made by some ancient philosophers; consider, for instance, the following passage from Epictetus’s Discourses :
‘I have a headache.’ Well, do not say ‘Alas!’ ‘I have an earache.’ Do not say ‘Alas!’ And I am not saying that it is not permissible to groan, only do not groan in the centre of your being . ( Discourses , 1.18.19, emphasis added).
The Stoics did not expect us never to feel unpleasant sensations, which would plainly be impossible; rather, the idea was not to let such things get to us , to impact our emotional conditions.
Why should anyone care to press such a distinction in characterizing happiness? For most people, the hedonic difference between happiness on an emotional state versus a hedonistic view is probably minimal. But while little will be lost, what will be gained? One possibility is that the more “central” affects involving our emotional conditions may bear a special relation to the person or the self , whereas more “peripheral” affects, like the pleasantness of eating a cracker, might pertain to the subpersonal aspects of our psychologies. Since well-being is commonly linked to ideas of self-fulfillment, this sort of distinction might signal a difference in the importance of these states. Another reason to focus on emotional condition rather than experience alone may be the greater psychological depth of the former: its impact on our mental lives, physiology, and behavior is arguably deeper and more pervasive. This enhances the explanatory and predictive significance of happiness, and more importantly its desirability: happiness on this view is not merely pleasant, but a major source of pleasure and other good outcomes (Fredrickson 2004, Lyubomirsky, King et al . 2005). Compare health on this score: while many think it matters chiefly or entirely because of its connection with pleasure, there are few skeptics about the importance of health. As well, emotional state views may capture the idea that happiness concerns the individual’s psychological orientation or disposition : to be happy, on an emotional state theory, is not just to be subjected to a certain sequence of experiences, but for one’s very being to manifest a favorable orientation toward the conditions of one’s life—a kind of psychic affirmation of one’s life. This reflects a point of similarity with life satisfaction views of happiness: contra hedonism, both views take happiness to be substantially dispositional, involving some sort of favorable orientation toward one’s life. But life satisfaction views tend to emphasize reflective or rational endorsement, whereas emotional state views emphasize the verdicts of our emotional natures.
While hedonism and emotional state theories are major contenders in the contemporary literature, all affect-based theories confront the worries, noted earlier, that motivate life satisfaction views—notably, their looser connection with people’s priorities, as well as their limited ability to reflect the quality of people’s lives taken as a whole.
Given the limitations of narrower theories of happiness, a hybrid account such as a subjective well-being theory may seem an attractive solution. This strategy has not been fully explored in the philosophical literature, though Sumner’s “life satisfaction” theory may best be classified as a hybrid (1996; see also Martin 2012). In any event, a hybrid approach draws objections of its own. If we arrive at a hybrid theory by this route, it could seem like either the marriage of two unpromising accounts, or of a promising account with an unpromising one. Such a union may not yield wholesome results. Second, people have different intuitions about what counts as happiness, so that no theory can accommodate all of them. Any theory that tries to thus risks pleasing no one. A third concern is that the various components of any hybrid are liable to matter for quite different reasons, so that happiness, thus understood, might fail to answer to any coherent set of concerns. Ascriptions of happiness could be relatively uninformative if they cast their net too widely.
3. The science of happiness
With the explosive rise of empirical research on happiness, a central question is how far, and how, happiness might be measured. [ 11 ] There seems to be no in-principle barrier to the idea of measuring, at least roughly, how happy people are. Investigators may never enjoy the precision of the “hedonimeter” once envisaged by Edgeworth to show just how happy a person is (Edgeworth 1881). Indeed, such a device might be impossible even in principle, since happiness might involve multiple dimensions that either cannot be precisely quantified or summed together. If so, it could still be feasible to develop approximate measures of happiness, or at least its various dimensions. Similarly, depression may not admit of precise quantification in a single number, yet many useful if imprecise measures of depression exist. In the case of happiness, it is plausible that even current measures provide information about how anxious, cheerful, satisfied, etc. people are, and thus tell us something about their happiness. Even the simplest self-report measures used in the literature have been found to correlate well with many intuitively relevant variables, such as friends’ reports, smiling, physiological measures, health, longevity, and so forth (Pavot 2008).
Importantly, most scientific research needs only to discern patterns across large numbers of individuals—to take an easy case, determining whether widows tend to be less happy than newlyweds—and this is compatible with substantial unreliability in assessing individual happiness. Similarly, an inaccurate thermometer might be a poor guide to the temperature, but readings from many such thermometers could correlate fairly well with actual temperatures—telling us, for instance, that Minnesota is colder than Florida.
This point reveals an important caveat: measures of happiness could correlate well with how happy people are, thus telling us which groups of people tend to be happier, while being completely wrong about absolute levels of happiness. Self-reports of happiness, for instance, might correctly indicate that unemployed people are considerably less happy than those with jobs. But every one of those reports could be wrong, say if everyone is unhappy yet claims to be happy, or vice-versa, so long as the unemployed report lower happiness than the employed. Similarly, bad thermometers may show that Minnesota is colder than Florida without giving the correct temperature.
Two morals emerge from these reflections. First, self-report measures of happiness could be reliable guides to relative happiness, though telling us little about how happy, in absolute terms, people are. We may know who is happier, that is, but not whether people are in fact happy. Second, even comparisons of relative happiness will be inaccurate if the groups being compared systematically bias their reports in different ways. This worry is particularly acute for cross-cultural comparisons of happiness, where differing norms about happiness may undermine the comparability of self-reports. The French might report lower happiness than Americans, for instance, not because their lives are less satisfying or pleasant, but because they tend to put a less positive spin on things. For this reason it may be useful to employ instruments, including narrower questions or physiological measures, that are less prone to cultural biasing. [ 12 ]
The discussion thus far has assumed that people can be wrong about how happy they are. Is this plausible? Some have argued that (sincerely) self-reported happiness cannot, even in principle, be mistaken. If you think you’re happy, goes a common sentiment, then you are happy. This claim is not plausible on a hedonistic or emotional state view of happiness, since those theories take judgments of happiness to encompass not just how one is feeling at the moment but also past states, and memories of those can obviously be spurious. Further, it has been argued that even judgments of how one feels at the present moment may often be mistaken, particularly regarding moods like anxiety. [ 13 ]
The idea that sincere self-reports of happiness are incorrigible can only be correct, it seems, given a quite specific conception of happiness—a kind of life satisfaction theory of happiness on which people count as satisfied with their lives so long as they are disposed to judge explicitly that they are satisfied with their lives on the whole. Also assumed here is that self-reports of happiness are in fact wholly grounded in life satisfaction judgments like these—that is, that people take questions about “happiness” to be questions about life satisfaction. Given these assumptions, we can plausibly conclude that self-reports of happiness are incorrigible. One question is whether happiness, thus conceived, is very important. As well, it is unlikely that respondents invariably interpret happiness questions as being about life satisfaction. At any rate, even life satisfaction theorists might balk at this variant of the account, since life satisfaction is sometimes taken to involve, not just explicit global judgments of life satisfaction, but also our responses to the particular things or domains we care about. Some will hesitate to deem satisfied people who hate many of the important things in their lives, however satisfied they claim to be with their lives as a whole.
In a similar vein, the common practice of measuring happiness simply by asking people to report explicitly on how “happy” they are is sometimes defended on the grounds that it lets people decide for themselves what happiness is. The reasoning again seems to presuppose, controversially, that self-reports of happiness employ a life satisfaction view of happiness, the idea being that whether you are satisfied (“happy”) will depend on what you care about. Alternatively, the point might be literally to leave it up to the respondent to decide whether ‘happy’ means hedonic state, emotional state, life satisfaction, or something else. Thus one respondent’s “I’m happy” might mean “my experience is generally pleasant,” while another’s might mean “I am satisfied with my life as a whole.” It is not clear, however, that asking ambiguous questions of this sort is a useful enterprise, since different respondents will in effect be answering different questions.
To measure happiness through self-reports, then, it may be wiser to employ terms other than ‘happiness’ and its cognates—terms whose meaning is relatively well-known and fixed. In other words, researchers should decide in advance what they want to measure—be it life satisfaction, hedonic state, emotional state, or something else—and then ask questions that refer unambiguously to those states. [ 14 ] This stratagem may be all the more necessary in cross-cultural work, where finding suitable translations of ‘happy’ can be daunting—particularly when the English meaning of the term remains a matter of contention (Wierzbicka 2004).
This entry focuses on subjective well-being studies, since that work is standardly deemed “happiness” research. But psychological research on well-being can take other forms, notably in the “eudaimonic”—commonly opposed to “hedonic”—literature, which assesses a broader range of indicators taken to represent objective human needs, such as meaning, personal growth, relatedness, autonomy, competence, etc. [ 15 ] (The assimilation of subjective well-being to the “hedonic” realm may be misleading, since life satisfaction seems primarily to be a non -hedonic value, as noted earlier.) Other well-being instruments may not clearly fall under either the “happiness” or eudaimonic rubrics, for instance extending subjective well-being measures by adding questions about the extent to which activities are seen as meaningful or worthwhile (White and Dolan 2009). An important question going forward is how far well-being research needs to incorporate indicators beyond subjective well-being.
The scientific literature on happiness has grown to proportions far too large for this article to do more than briefly touch on a few highlights. [ 16 ] Here is a sampling of oft-cited claims:
- Most people are happy
- People adapt to most changes, tending to return over time to their happiness “set point”
- People are prone to make serious mistakes in assessing and pursuing happiness
- Material prosperity has a surprisingly modest impact on happiness
The first claim, that most people are happy, appears to be a consensus position among subjective well-being researchers (for a seminal argument, see Diener and Diener 1996). The contention reflects three lines of evidence: most people, in most places, report being happy; most people report being satisfied with their lives; and most people experience more positive affect than negative. On any of the major theories of happiness, then, the evidence seems to show that most people are, indeed, happy. Yet this conclusion might be resisted, on a couple of grounds. First, life satisfaction theorists might question whether self-reports of life satisfaction suffice to establish that people are in fact satisfied with their lives. Perhaps self-reports can be mistaken, say if the individual believes herself satisfied yet shows many signs of dissatisfaction in her behavior, for instance complaining about or striving to change important things in her life. Second, defenders of affect-based theories—hedonistic and emotional state views—might reject the notion that a bare majority of positive affect suffices for happiness. While the traditional view among hedonists has indeed been that happiness requires no more than a >1:1 ratio of positive to negative affect, this contention has received little defense and has been disputed in the recent literature. Some investigators have claimed that “flourishing” requires greater than a 3:1 ratio of positive to negative affect, as this ratio might represent a threshold for broadly favorable psychological functioning (e.g., Larsen and Prizmic 2008). While the evidence for any specific ratio is highly controversial, if anything like this proportion were adopted as the threshold for happiness, on a hedonistic or emotional state theory, then some of the evidence taken to show that people are happy could in fact show the opposite. In any event, the empirical claim relies heavily on nontrivial philosophical views about the nature of happiness, illustrating one way in which philosophical work on happiness can inform scientific research.
The second claim, regarding adaptation and set points, reflects well-known findings that many major life events, like being disabled in an accident or winning the lottery, appear strongly to impact happiness only for a relatively brief period, after which individuals may return to a level of happiness not very different from before. [ 17 ] As well, twin studies have found that subjective well-being is substantially heritable, with .50 being a commonly accepted figure. Consequently many researchers have posited that each individual has a characteristic “set point” level of happiness, toward which he tends to gravitate over time. Such claims have caused some consternation over whether the pursuit and promotion of happiness are largely futile enterprises (Lykken and Tellegen 1996; Millgram 2000). However, the dominant view now seems to be that the early claims about extreme adaptation and set points were exaggerated: while adaptation is a very real phenomenon, many factors—including disability—can have substantial, and lasting, effects on how happy people are. [ 18 ] This point was already apparent from the literature on correlates and causes of happiness, discussed below: if things like relationships and engaging work are important for happiness, then happiness is probably not simply a matter of personality or temperament. As well, the large cross-national differences in measured happiness are unlikely to be entirely an artifact of personality variables. Note that even highly heritable traits can be strongly susceptible to improvement. Better living conditions have raised the stature of men in the Netherlands by eight inches—going from short (five foot four) to tall (over six feet)—in the last 150 years (Fogel 2005). Yet height is considered much more heritable than happiness, with typical heritability estimates ranging from .60 to over .90 (e.g., Silventoinen, Sammalisto et al . 2003). [ 19 ]
The question of mistakes will be taken up in section 5.2. But the last claim—that material prosperity has relatively modest impacts on happiness—has lately become the subject of heated debate. For some time the standard view among subjective well-being researchers was that, beyond a low threshold where basic needs are met, economic gains have only a small impact on happiness levels. According to the well-known “Easterlin Paradox,” for instance, wealthier people do tend to be happier within nations, but richer nations are little happier than less prosperous counterparts, and—most strikingly—economic growth has virtually no impact (Easterlin 1974). In the U.S., for example, measured happiness has not increased significantly since at least 1947, despite massive increases in wealth and income. In short, once you’re out of poverty, absolute levels of wealth and income make little difference in how happy people are.
Against these claims, some authors have argued that absolute income has a large impact on happiness across the income spectrum (e.g., Stevenson and Wolfers 2008). The question continues to be much debated, but in 2010 a pair of large-scale studies using Gallup data sets, including improved measures of life satisfaction and affect, suggested that both sides may be partly right (Kahneman and Deaton 2010; Diener, Ng et al . 2010). Surveying large numbers of Americans in one case, and what is claimed to be the first globally representative sample of humanity in the other, these studies found that income does indeed correlate substantially (.44 in the global sample), at all levels, with life satisfaction—strictly speaking, a “life evaluation” measure that asks respondents to rate their lives without saying whether they are satisfied. Yet the correlation of household income with the affect measures is far weaker: globally, .17 for positive affect, –.09 for negative affect; and in the United States, essentially zero above $75,000 (though quite strong at low income levels). For more recent discussions of empirical work, see Jebb et al. 2018 along with relevant chapters in Diener et al. 2018 and the annual World Happiness Reports from 2012 onward (Helliwell et al. 2012). Research on the complex money-happiness relationship resists simple characterization, but a crude summary is that the connection tends to be positive and substantial, strong at lower income levels while modest to weak or even negative at higher incomes, and stronger and less prone to satiation for life evaluation than emotional well-being metrics. But again, these are very rough generalizations that gloss over a variety of important factors and admit of many exceptions across both individuals and societies.
In short, the relationship between money and happiness may depend on which theory of happiness we accept: on a life satisfaction view, the relationship may be strong; whereas affect-based views may yield a much weaker connection, again above some modest threshold. Here, again, philosophical views about the nature and significance of happiness may play an important role in understanding empirical results and their practical upshot. Economic growth, for instance, has long been a top priority for governments, and findings about its impact on human well-being may have substantial implications for policy.
It is important to note that studies of this nature focus on generic trends, not specific cases, and there is no dispute that significant exceptions exist—notably, populations that enjoy high levels of happiness amid low levels of material prosperity. Among others, a number of Latin American countries, Maasai herders, Inughuit hunter-gatherers, and Amish communities have registered highly positive results in subjective well-being studies, sometimes higher than those in many affluent nations, and numerous informal accounts accord with the data. [ 20 ] Such “positive outliers” suggest that some societies can support high levels of happiness with extremely modest material holdings. The importance of money for happiness may depend strongly on what kind of society one inhabits. An interesting question, particularly in light of common environmental concerns, is how far the lessons of such societies can, or should, be transferred to other social forms, where material attainment and happiness are presently more tightly coupled. Perhaps some degree of decoupling of happiness and money would be desirable.
So the role of money in happiness appears, at this juncture, to be a mixed bag, depending heavily on how we conceive of happiness and what range of societies we are considering. What (else), then, does matter most for happiness? There is no definitive list of the main sources of happiness in the literature, partly because it is not clear how to divide them up. But the following items seem generally to be accepted as among the chief correlates of happiness: supportive relationships, engagement in interesting and challenging activities, material and physical security, a sense of meaning or purpose, a positive outlook, and autonomy or control. [ 21 ] Significant correlates may also include—among many others—religion, good governance, trust, helping others, values (e.g., having non-materialistic values), achieving goals, not being unemployed, and connection with the natural environment. [ 22 ]
An illustrative study of the correlates of happiness from a global perspective is the Gallup World Poll study noted earlier (Diener, Ng et al . 2010; see also Jebb et al. 2020). In that study, the life satisfaction measure was more strongly related to material prosperity, as noted above: household income, along with possession of luxury conveniences and satisfaction with standard of living. The affect measures, by contrast, correlated most strongly with what the authors call “psychosocial prosperity”: whether people reported being treated with respect in the last day, having family and friends to count on, learning something new, doing what they do best, and choosing how their time was spent.
What these results show depends partly on the reliability of the measures. One possible source of error is that this study might exaggerate the relationship between life satisfaction and material attainments through the use of a “ladder” scale for life evaluation, ladders being associated with material aspirations. Errors might also arise through salience biases whereby material concerns might be more easily recalled than other important values, such as whether one has succeeded in having children; or through differences in positivity biases across income levels (perhaps wealthier people tend to be more “positive-responding” than poorer individuals). Another question is whether the affect measures adequately track the various dimensions of people’s emotional lives. However, the results are roughly consonant with other research, so they are unlikely to be entirely an artifact of the instruments used in this study. [ 23 ] A further point of uncertainty is the causal story behind the correlations—whether the correlates, like psychosocial prosperity, cause happiness; whether happiness causes them; whether other factors cause both; or, as is likely, some combination of the three.
Such concerns duly noted, the research plausibly suggests that, on average, material progress has some tendency to help people to better get what they want in life, as found in the life satisfaction measures, while relationships and engaging activities are more important for people’s emotional lives. What this means for happiness depends on which view of happiness is correct.
4. The importance of happiness
Were you to survey public attitudes about the value of happiness, at least in liberal Western democracies, you would likely find considerable support for the proposition that happiness is all that really matters for human well-being. Many philosophers over the ages have likewise endorsed such a view, typically assuming a hedonistic account of happiness. (A few, like Almeder 2000, have identified well-being with happiness understood as life satisfaction.)
Most philosophers, however, have rejected hedonistic and other mental state accounts of well-being, and with them the idea that happiness could suffice for well-being. [ 24 ] (See the entry on well-being .) Objections to mental state theories of well-being tend to cluster around two sets of concerns. First, it is widely believed that the non-mental conditions of our lives matter for well-being: whether our families really love us, whether our putative achievements are genuine, whether the things we care about actually obtain. The most influential objection of this sort is Robert Nozick’s experience machine case, wherein we are asked to imagine a virtual reality device that can perfectly simulate any reality for its user, who will think the experience is genuine (Nozick 1974). Would you plug in to such a machine for life? Most people would not, and the case is widely taken to vitiate mental state theories of well-being. Beyond having positive mental states, it seems to matter both that our lives go well and that our state of mind is appropriately related to how things are. [ 25 ]
A second set of objections concerns various ways in which a happy person might nonetheless seem intuitively to be leading an impoverished or stunted life. The most influential of these worries involves adaptation , where individuals facing oppressive circumstances scale back their expectations and find contentment in “small mercies,” as Sen put it. [ 26 ] Even a slave might come to internalize the values of his oppressors and be happy, and this strikes most as an unenviable life indeed. Related worries involve people with diminished capacities (blindness, Down Syndrome), or choosing to lead narrow and cramped or simpleminded lives (e.g., counting blades of grass). Worries about impoverished lives are a prime motivator of Aristotelian theories of well-being, which emphasize the full and proper exercise of our human capacities.
In the face of these and other objections most commentators have concluded that neither happiness nor any other mental state can suffice for well-being. Philosophical interest in happiness has consequently flagged, since its theoretical importance becomes unclear if it does not play a starring role in our account of the good.
Even as happiness might fail to suffice for well-being, well-being itself may be only one component of a good life , and not the most important one at that. Here ‘good life’ means a life that is good all things considered, taking account of all the values that matter in life, whether they benefit the individual or not. Kant, for example, considered both morality and well-being to be important but distinct elements of a good life. Yet morality should be our first priority, never to be sacrificed for personal happiness.
In fact there is a broad consensus, or near-consensus, among ethical theorists on a doctrine we might call the priority of virtue : broadly and crudely speaking, the demands of virtue or morality trump other values in life. [ 27 ] We ought above all to act and live well, or at least not badly or wrongly. This view need not take the strong form of insisting that we must always act as virtuously as possible, or that moral reasons always take precedence. But it does mean, at least, that when being happy requires acting badly, one’s happiness must be sacrificed. If it would be wrong to leave your family, in which you are unhappy, then you must remain unhappy, or find more acceptable ways to seek happiness.
The mainstream views in all three of the major approaches to ethical theory—consequentialism, deontology, and virtue ethics—agree on some form of the priority of virtue. Where these views chiefly differ is not on the importance of being good, but on whether being good necessarily benefits us. Virtue ethicists tend to answer in the affirmative, the other two schools in the negative. Building virtue into well-being, as Aristotelians do, may seem to yield a more demanding ethics, and in some ways it does. Yet many deontologists and consequentialists—notably Kant—advocate sterner, more starkly moralistic visions of the good life than Aristotle would ever have dreamt of (e.g., Singer 1972).
Happiness, in short, is believed by most philosophers to be insufficient for well-being, and still less important for the good life. These points may seem to vitiate any substantial role for happiness in ethical thought. However, well-being itself is still regarded as a central concept in ethical thought, denoting one of the chief elements of a good life even if not the sole element. And there are reasons for thinking happiness important, both practically and theoretically, despite the worries noted above.
Even if happiness does not suffice for well-being—a point that not all philosophers would accept—it might still rate a privileged spot in theories of well-being. This could happen in either of two ways.
First, happiness could be a major component of a theory of well-being. Objective list theories of well-being sometimes include happiness or related mental states such as enjoyment among the fundamental constituents of well-being. A more ambitious proposal, originated by L.W. Sumner, identifies well-being with authentic happiness —happiness that is authentic in the sense of being both informed and autonomous (Sumner 1996). The root idea is that well-being involves being happy, where one’s happiness is a response of one’s own (autonomous), to a life that genuinely is one’s own (informed). The authenticity constraint is meant to address both experience machine-type worries and “happy slave” objections relating to adaptation, where happiness may be non-autonomous, depending on manipulation or the uncritical acceptance of oppressive values. Since these have been the most influential objections to mental state accounts of well-being, Sumner’s approach promises to considerably strengthen the position of happiness-centered approaches to well-being, and several philosophers have developed variants or close relations of the authentic happiness theory (Brülde 2007, Haybron 2008a, Tiberius and Plakias 2010, Višak 2015). The approach remains fairly new, however, so its long-term prospects remain unclear. [ 28 ]
A second strategy forsakes the project of giving a unitary theory of well-being, recognizing instead a family of two or more kinds of prudential value. Happiness could be central to, or even exhaustive of, one of those values. Shelly Kagan, for instance, has suggested that welfare hedonism could be correct as a theory of how well a person is doing, but not of how well a person’s life is going, which should perhaps be regarded as a distinct value (Kagan 1992, 1994). In short, we might distinguish narrow and wide well-being concepts. An experience machine user might be doing well in the narrow sense, but not the wide—she is doing well, though her life is quite sad. Happiness might, then, suffice for well-being, but only in the narrow sense. Others have made similar points, but uptake has been limited, perhaps because distinguishing multiple concepts of prudential value makes the already difficult job of giving a theory of well-being much harder, as Kagan pointedly observes. [ 29 ] An interesting possibility is that the locution ‘happy life’, and the corresponding well-being sense of happiness, actually refers to a specific variety of well-being—perhaps well-being in the wide sense just suggested, or well-being taken as an ideal state, an ultimate goal of deliberation. This might explain the continued use of ‘happiness’ for the well-being notion in the philosophical literature, rather than the more standard ‘wellbeing.’
The preceding section discussed ways that happiness might figure prominently even in non-mental state theories of well-being. The question there concerned the role of happiness in theories of well-being. This is a different question from how important happiness is for well-being itself. Even a theory of well-being that includes no mention at all of happiness can allow that happiness is nonetheless a major component or contributor to well-being, because of its relation to the things that ultimately constitute well-being. If you hold a desire theory of well-being, for instance, you will very likely allow that, for most people, happiness is a central aspect of well-being, since most people very much desire to be happy. Indeed, some desire theorists have argued that the account actually yields a form of hedonism, on the grounds that people ultimately desire nothing else but happiness or pleasure (Sidgwick 1907 [1966], Brandt 1979, 1989).
Happiness may be thought important even on theories normally believed to take a dismissive view of it. Aristotelians identify well-being with virtuous activity, yet Aristotle plainly takes this to be a highly pleasant condition, indeed the most pleasant kind of life there is (see, e.g., NE , Bk. I 8; Bk. VII 13). You cannot flourish, on Aristotelian terms, without being happy, and unhappiness is clearly incompatible with well-being. Even the Stoics, who notoriously regard all but a virtuous inner state as at best indifferent, would still assign happiness a kind of importance: at the very least, to be unhappy would be unvirtuous; and virtue itself arguably entails a kind of happiness, namely a pleasant state of tranquility. As well, happiness would likely be a preferred indifferent in most cases, to be chosen over unhappiness. To be sure, both Aristotelian and Stoic accounts are clear that happiness alone does not suffice for well-being, that its significance is not what common opinion takes it to be, and that some kinds of happiness can be worthless or even bad. But neither denies that happiness is somehow quite important for human well-being.
In fact it is questionable whether any major school of philosophical thought denies outright the importance of happiness, at least on one of the plausible accounts of the matter. Doubts about its significance probably owe to several factors. Some skeptics, for example, focus on relatively weak conceptions of happiness, such as the idea that it is little more than the simple emotion of feeling happy—an idea that few hedonists or emotional state theorists would accept. Or, alternatively, assuming that a concern for happiness has only to do with positive states. Yet ‘happiness’ also serves as a blanket term for a domain of concern that involves both positive and negative states, namely the kinds of mental states involved in being happy or unhappy. Just as “health” care tends to focus mainly on ill health, so might happiness researchers choose to focus much of their effort on the study and alleviation of unhappiness—depression, suffering, anxiety, and other conditions whose importance is uncontroversial. The study of happiness need be no more concerned with smiles than with frowns.
5. The pursuit and promotion of happiness
The last set of questions we will examine centers on the pursuit of happiness, both individual and collective. Most of the popular literature on happiness discusses how to make oneself happier, with little attention given to whether this is an appropriate goal, or how various means of pursuing happiness measure up from an ethical standpoint. More broadly, how if at all should one pursue happiness as part of a good life?
We saw earlier that most philosophers regard happiness as secondary to morality in a good life. The individual pursuit of happiness may be subject to nonmoral norms as well, prudence being the most obvious among them. Prudential norms need not be as plain as “don’t shoot yourself in the foot.” On Sumner’s authentic happiness view of well-being, for instance, we stand to gain little by pursuing happiness in inauthentic ways, for instance through self-deception or powerful drugs like Huxley’s soma , which guarantees happiness come what may (Huxley 1932 [2005]). The view raises interesting questions about the benefits of less extreme pharmaceuticals, such as the therapeutic use of antidepressants; such medications can make life more pleasant, but many people worry whether they pose a threat to authenticity, perhaps undercutting their benefits. It is possible that such drugs involve prudential tradeoffs, promoting well-being in some ways while undermining it in others; whether the tradeoffs are worth it will depend on how, in a given case, the balance is struck. Another possibility is that such drugs sometimes promote authenticity, if for instance a depressive disorder prevents a person from being “himself.”
Looking to more broadly ethical, but not yet moral, norms, it may be possible to act badly without acting either immorally or imprudently. While Aristotle himself regarded acting badly as inherently imprudent, his catalogue of virtues is instructive, as many of them (wit, friendliness, etc.) are not what we normally regard as moral virtues. Some morally permissible methods of pursuing happiness may nonetheless be inappropriate because they conflict with such “ethical” virtues. They might, for instance, be undignified or imbecilic.
Outwardly virtuous conduct undertaken in the name of personal happiness might, if wrongly motivated, be incompatible with genuine virtue. One might, for instance, engage in philanthropy solely to make oneself happier, and indeed work hard at fine-tuning one’s assistance to maximize the hedonic payoff. This sort of conduct would not obviously instantiate the virtue of compassion or kindness, and indeed might be reasonably deemed contemptible. Similarly, it might be admirable, morally or otherwise, to be grateful for the good things in one’s life. Yet the virtue of gratitude might be undermined by certain kinds of gratitude intervention, whereby one tries to become happier by focusing on the things one is grateful for. If expressions of gratitude become phony or purely instrumental, the sole reason for giving thanks being to become happy—and not that one actually has something to be thankful for—then the “gratitude” might cease to be admirable, and may indeed be unvirtuous. [ 30 ]
A different question is what means of pursuing happiness are most effective . This is fundamentally an empirical question, but there are some in-principle issues that philosophical reflection might inform. One oft-heard claim, commonly called the “paradox of hedonism,” is that the pursuit of happiness is self-defeating; to be happy, don’t pursue happiness. It is not clear how to interpret this dictum, however, so that it is both interesting and true. It is plainly imprudent to make happiness one’s focus at every moment, but doubtful that this has often been denied. Yet never considering happiness also seems an improbable strategy for becoming happier. If you are choosing among several equally worthwhile occupations, and have good evidence that some of them will make you miserable, while one of them is likely to be highly fulfilling, it would not seem imprudent to take that information into account. Yet to do so just is to pursue happiness. The so-called paradox of hedonism is perhaps best seen as a vague caution against focusing too much on making oneself happy, not a blanket dismissal of the prospects for expressly seeking happiness—and for this modest point there is good empirical evidence (Schooler, Ariely et al . 2003, Lyubomirsky 2007).
That happiness is sometimes worth seeking does not mean we will always do a good job of it (Haybron 2008b). In recent decades a massive body of empirical evidence has gathered on various ways in which people seem systematically prone to make mistakes in the pursuit of their interests, including happiness. Such tendencies have been suggested in several domains relating to the pursuit of happiness, including (with recent surveys cited):
- Assessing how happy we are, or were in the past (Haybron 2007)
- Predicting (“forecasting”) what will make us happy (Gilbert 2006)
- Choosing rationally (Kahneman and Tversky 2000, Gilovitch, Griffin et al . 2002, Hsee and Hastie 2006)
A related body of literature explores the costs and benefits of (ostensibly) making it easier to pursue happiness by increasing people’s options; it turns out that having more choices might often make people less happy, for instance by increasing the burdens of deliberation or the likelihood of regret (Schwartz 2004). Less discussed in this context, but highly relevant, is the large body of research indicating that human psychology and behavior are remarkably prone to unconscious social and other situational influences, most infamously reported in the Milgram obedience experiments (Doris 2002, 2015, Haybron 2014). Human functioning, and the pursuit of happiness, may be more profoundly social than many commentators have assumed. [ 31 ]
Taken together, this research bears heavily on two central questions in the philosophical literature: first, the broad character of human nature (e.g., in what sense are we rational animals? How should we conceive of human autonomy?); second, the philosophical ideals of the good society and good government.
Just a decade ago the idea of happiness policy was something of a novelty. While it remains on the fringes in some locales, notably the United States, in much of the world there has been a surge of interest in making happiness an explicit target of policy consideration. Attention has largely shifted, however, to a broader focus on well-being to reflect not just happiness but also other welfare concerns of citizens, and dozens of governments now incorporate well-being metrics in their national statistics. [ 32 ]
Let’s consider the rationale for policies aimed at promoting well-being. In political thought, the modern liberal tradition has tended to assume an optimistic view of human nature and the individual’s capacities for prudent choice. Partly for this reason, the preservation and expansion of individual freedoms, including people’s options, is widely taken to be a central goal, if not the goal, of legitimate governments. People should be freed to seek the good life as they see it, and beyond that the state should, by and large, stay out of the well-being-promotion business.
This vision of the good society rests on empirical assumptions that have been the subject of considerable debate. If it turns out that people systematically and predictably err in the pursuit of their interests, then it may be possible for governments to devise policies that correct for such mistakes. [ 33 ] Of course, government intervention can introduce other sorts of mistakes, and there is some debate about whether such measures are likely to do more harm than good (e.g., Glaeser 2006).
But even if governments cannot effectively counteract human imprudence, it may still be that people fare better in social forms that influence or even constrain choices in ways that make serious mistakes less likely. (Food culture and its impact on health may be an instructive example here.) The idea that people tend to fare best when their lives are substantially constrained or guided by their social and physical context has recently been dubbed contextualism ; the contrary view, that people do best when their lives are, as much as possible, determined by the individuals themselves, is individualism (Haybron 2008b). Recent contextualists include communitarians and many perfectionists, though contextualism is not a political doctrine and is compatible with liberalism and even libertarian political morality. Contextualism about the promotion of well-being is related to recent work in moral psychology that emphasizes the social character of human agency, such as situationism and social intuitionism. [ 34 ]
Quite apart from matters of efficacy, there are moral questions about the state promotion of happiness, which has been a major subject of debate, both because of the literature on mistakes and research suggesting that the traditional focus of state efforts to promote well-being, economic growth, has a surprisingly modest impact on happiness. One concern is paternalism : does happiness-based policy infringe too much on personal liberty? Some fear a politics that may too closely approximate Huxley’s Brave New World, where the state ensures a drug-induced happiness for all (Huxley 1932 [2005]). Extant policy suggestions, however, have been more modest. Efforts to steer choice, for instance in favor of retirement savings, may be paternalistic, but advocates argue that such policies can be sufficiently light-handed that no one should object to them, in some cases even going so far as to deem it “libertarian paternalism” (Thaler and Sunstein 2008). [ 35 ] The idea is that gentle “nudges,” like setting default options on hiring forms to setting aside money for retirement, interfere only trivially with choice, imposing little or no cost for those who wish to choose differently, and would very likely be welcomed by most of those targeted.
Also relatively light-handed, and perhaps not paternalistic at all, are state efforts to promote happiness directly through social policy, for instance by prioritizing unemployment over economic growth on the grounds that the former has a larger impact on happiness. Other policies might include trying to reduce commute times, or making walkable neighborhoods and green space a priority in urban planning, again on happiness grounds. Some may deem such measures paternalistic insofar as they trade freedom (in the form of economic prosperity) for a substantive good, happiness, that people value unevenly, though it has also been argued that refusing to take citizens’ values like happiness into consideration in policy deliberation on their behalf can amount to paternalism (Haybron and Alexandrova 2013).
A related sort of objection to happiness-based policy argues that happiness, or even well-being, is simply the wrong object of policy, which ought instead to focus on the promotion of resources or capabilities (Rawls 1971, Nussbaum 2000, Quong 2011, Sen 2009). Several reasons have been cited for this sort of view, one being that policies aimed at promoting happiness or well-being violate commonly accepted requirements of “liberal neutrality,” according to which policy must be neutral among conceptions of the good. According to this constraint, governments must not promote any view of the good life, and happiness-based policy might be argued to flout it. Worries about paternalism also surface here, the idea being that states should only focus on affording people the option to be happy or whatever, leaving the actual achievement of well-being up to the autonomous individual. As we just saw, however, it is not clear how far happiness policy initiatives actually infringe on personal liberty or autonomy. A further worry is that, happiness isn’t really, or primarily, what matters for human well-being (Nussbaum 2008).
But a major motivation for thinking happiness the wrong object of policy is that neither happiness nor well-being are the appropriate focus of a theory of justice . What justice requires of society, on this view, is not that it make us happy; we do not have a right to be happy. Rather, justice demands only that each has sufficient opportunity (in the form of resources or capabilities, say) to achieve a good life, or that each gets a fair share of the benefits of social cooperation. However plausible such points may be, it is not clear how far they apply to many proposals for happiness-based policy, save the strongest claims that happiness should be the sole aim of policy: many policy decisions are not primarily concerned with questions of social justice, nor with constitutional fundamentals, the focus of some theories of justice. Happiness could be a poor candidate for the “currency” of justice, yet still remain a major policy concern. Indeed, the chief target of happiness policy advocates has been, not theories of justice, but governments’ overwhelming emphasis on promoting GDP and other indices of economic growth. This is not, in the main, a debate about justice, and as of yet the philosophical literature has not extensively engaged with it.
However, the push for happiness-based policy is a recent development. In coming years, such questions will likely receive considerably more attention in the philosophical literature.
- Adler, Matthew D., 2019, Measuring Social Welfare: An Introduction , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Adler, M. D., and M. Fleurbaey (eds.), 2015, The Oxford Handbook of Well-Being and Public Policy , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Ahuvia, A., et al., 2015, “Happiness: An Interactionist Perspective,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 5(1): 1–18.
- Alexandrova, A., 2005, “Subjective Well-Being and Kahneman’s ‘Objective Happiness’,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 6: 301–324.
- –––, 2008, “First-Person Reports and the Measurement of Happiness,” Philosophical Psychology , 21(5): 571–583.
- –––, 2017, A Philosophy for the Science of Well-Being , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Alexandrova, A. and D. M. Haybron, 2012, “High Fidelity Economics,” in The Elgar Companion to Recent Economic Methodology , W. Hands and J. Davis (eds.). Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar.
- –––, 2016, “Is Construct Validation Valid?,” Philosophy of Science , 83(5): 1098–1109.
- Almeder, R., 2000, Human Happiness and Morality , Buffalo, NY: Prometheus Press.
- Andreou, C., 2010, “A Shallow Route to Environmentally Friendly Happiness: Why Evidence That We Are Shallow Materialists Need Not Be Bad News for the Environment(Alist),” Ethics, Place & Environment , 13(1): 1–10.
- Ang, J. M. S., 2019, “Can Existentialists Be Happy? Authentic Life, Authentic Happiness,” Science, Religion and Culture , 6(1): 122–129.
- Angier, T., 2015, “Happiness: Overcoming the Skill Model,” International Philosophical Quarterly , 55(1): 5–23.
- Angner, E., 2009, “The Politics of Happiness,” Philosophy and Happiness , L. Bortolotti (ed.), New York: Palgrave, 1–26.
- –––, 2010, “Are subjective measures of well-being ‘direct’?” Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 89(1): 115–130.
- –––, 2011, “The Evolution of Eupathics: The Historical Roots of Subjective Measures of Well-Being,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 1(1): 4–41.
- –––, 2013a, “Is it possible to measure happiness?,” European Journal for Philosophy of Science , 3(2): 221–240.
- –––, 2013b, “Is Empirical Research Relevant to Philosophical Conclusions?,” Res Philosophica , 90(3): 365–85.
- –––, 2016, A Course in Behavioral Economics , second edition, London: Palgrave.
- Annas, J., 1993, The Morality of Happiness , New York: Oxford.
- –––, 2011, Intelligent Virtue , New York: Oxford.
- Argyle, M., 1999, “Causes and Correlates of Happiness,” Well-Being: The Foundations of Hedonic Psychology , D. Kahneman, E. Diener and N. Schwarz (eds.). New York: Russell Sage Foundation: 3–25.
- –––, 2002, The Psychology of Happiness , New York: Routledge.
- Austin, A., 2015, “On Well-Being and Public Policy: Are We Capable of Questioning the Hegemony of Happiness?,” Social Indicators Research , 127(1): 1–16.
- Badhwar, N., 2008, “Is Realism Really Bad for You? A Realistic Response,” The Journal of Philosophy , 105(2): 85–107.
- –––, 2014, Well-Being: Happiness in a Worthwhile Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2015, “Happiness,” in The Routledge Handbook of Philosophy of Well-Being , ed. G. Fletcher, New York: Routledge, 323–35.
- Bagaric, M., and J. McConvill, 2005, “Goodbye Justice, Hello Happiness: Welcoming Positive Psychology to the Law,” Deakin Law Review , 10(1): 1–26.
- Barrow, R., 1980, Happiness and Schooling , New York: St. Martin’s Press.
- –––, 1991, Utilitarianism: A Contemporary Statement , Brookfield, VT: Edward Elgar.
- Beck, B., and B. Stroop, 2015, “A Biomedical Shortcut to (Fraudulent) Happiness? An Analysis of the Notions of Well-Being and Authenticity Underlying Objections to Mood Enhancement,” Well-Being in Contemporary Society , J. H. Søraker, et al. (eds.), Berlin: Springer, 115–34.
- Becker, L. C., 2012, Habilitation, Health, and Agency , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Belliotti, R. A., 2004, Happiness Is Overrated , New York: Rowman & Littlefield.
- –––, 2013, “The Seductions of Happiness,” The Oxford Handbook of Happiness , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Benditt, T. M., 1974, “Happiness,” Philosophical Studies , 25: 1–20.
- –––, 1978, “Happiness and Satisfaction – A Rejoinder to Carson,” The Personalist , 59: 108–9.
- Besser, L. L., 2014, Eudaimonic Ethics , New York: Routledge.
- Besser-Jones, L., 2013, “The Pursuit and Nature of Happiness,” Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 103–21.
- Billon, A., 2016, “Irrationality and Happiness: A (Neo-) Shopenhauerian Argument for Rational Pessimism,” Journal of Ethics and Social Philosophy , 11(1): 1–27.
- Bishop, M., 2012, “The Network Theory of Well-Being: An Introduction,” The Baltic International Yearbook of Cognition, Logic and Communication , 7: 1–29.
- –––, 2015, The Good Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Biswas-Diener, R., 2018, “The Subjective Well-Being of Small Societies,” Handbook of Well-Being , E. Diener, S. Oishi, and L. Tay (eds.), Salt Lake City: DEF Publishers.
- Biswas-Diener, R., J. Vittersø and E. Diener, 2005, “Most People are Pretty Happy, but There is Cultural Variation: The Inughuit, The Amish, and The Maasai,” The Journal of Happiness Studies , 6(3): 205–226.
- Blackson, T., 2009, “On Feldman’s Theory of Happiness,” Utilitas , 21(3): 393–400.
- Block, N., 1995, “On a Confusion About A Function of Consciousness,” Behavioral and Brain Sciences , 18: 227–247.
- Bloomfield, P., 2014, The Virtues of Happiness , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Bognar, G., 2010, “Authentic Happiness,” Utilitas , 22(3): 272–284.
- Bok, D., 2010a, The Politics of Happiness: What Government Can Learn from the New Research on Well-Being , Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Bok, S., 2010b, Exploring Happiness: From Aristotle to Brain Science , New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Bortolotti, L. (ed.), 2009, Philosophy and Happiness , New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Bosch, M. van den, and W. Bird, 2018, Oxford Textbook of Nature and Public Health: The Role of Nature in Improving the Health of a Population , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Bramble, B., 2016, “The Experience Machine,” Philosophy Compass , 11(3): 136–45.
- Brandt, R. B., 1959, Ethical Theory , Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
- –––, 1979, A Theory of the Good and the Right , New York: Oxford.
- –––, 1989, “Fairness to Happiness,” Social Theory & Practice , 15: 33–58.
- –––, 1992, Morality, Utilitarianism, and Rights , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Brülde, B., 2007, “Happiness theories of the good life,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 8(1): 15–49.
- –––, 2015, “Well-Being, Happiness and Sustainability,” Well-Being in Contemporary Society , Happiness Studies Book Series, J. H. Søraker, et al. (eds.), Berlin: Springer, 157–76.
- Brannmark, J., 2003, “Leading lives: On happiness and narrative meaning,” Philosophical Papers , 32(3): 321–343.
- Bruni, L., F. Comim, and M. Pugno (eds.), 2008, Capabilities and Happiness , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Buss, S., 2004, “The Irrationality of Unhappiness and the Paradox of Despair,” Journal of Philosophy , CI(4): 171–200.
- Cahn, S. M. and C. Vitrano (eds.), 2008, Happiness: Classical and Contemporary Readings in Philosophy , New York: Oxford.
- –––, 2015, Happiness and Goodness: Philosophical Reflections on Living Well , New York: Columbia University Press.
- Campbell, R., 1973, “The Pursuit Of Happiness,” Personalist , 54: 325–337.
- Capaldi, C. A. et al., 2015, “Flourishing in Nature: A Review of the Benefits of Connecting with Nature and Its Application as a Wellbeing Intervention,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 5(4): 1–16.
- Capuccino, C., 2013, “Happiness and Aristotle’s Definition of Eudaimonia,” Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 1–26.
- Carson, T. L., 1978a, “Happiness and Contentment: A Reply to Benditt,” The Personalist , 59: 101–7.
- –––, 1978b, “Happiness and the Good Life,” Southwestern Journal of Philosophy , 9: 73–88.
- –––, 1979, “Happiness and the Good Life: a Rejoinder to Mele,” Southwestern Journal of Philosophy , 10: 189–192.
- –––, 1981, “Happiness, Contentment, and the Good Life,” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 62: 378–92.
- Cashen, M, 2012, “Happiness, Eudaimonia, and The Principle of Descriptive Adequacy,” Metaphilosophy , 43(5): 619–35.
- Cavallaro, M., and G. Heffernan, 2019, “From Happiness to Blessedness: Husserl on Eudaimonia, Virtue, and the Best Life,” HORIZON. Studies in Phenomenology , 8(2): 353–388.
- Chappell, T., 2013, “Eudaimonia, Happiness, and the Redemption of Unhappiness,” Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 27–52.
- Charry, E. T., 2010, God and the Art of Happiness , Grand Rapids: Eerdmans Publishing Company.
- Chekola, M., 2007, “Happiness, Rationality, Autonomy and the Good Life,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 8(1): 51–78.
- Christakis, N., J. Fowler, Simon, i. Schuster, P. D. Audio and L. Findaway World, 2009, Connected: The surprising power of our social networks and how they shape our lives , New York: Little, Brown and Co.
- Clark, A., et al., 2018, The Origins of Happiness: The Science of Well-Being over the Life Course , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Cohen Kaminitz, S., forthcoming, “Looking Good or Feeling Well? Understanding the Combinations of Well-Being Indicators Using Insights from the Philosophy of Well-Being,” Social Indicators Research , online first 12 February 2020. doi:10.1007/s11205-020-02289-9
- David, S., Boniwell, I., and A. Ayers (eds.), 2013, The Oxford Handbook of Happiness , New York: Oxford.
- Davis, W., 1981a, “Pleasure and Happiness,” Philosophical Studies , 39: 305–318.
- –––, 1981b, “A Theory of Happiness,” American Philosophical Quarterly , 18: 111–20.
- de Boer, J., 2014, “Scaling Happiness,” Philosophical Psychology , 27(5): 703–18.
- De Brigard, F., 2010, “If You like It, Does It Matter If It’s Real?,” Philosophical Psychology , 23(1): 43–57.
- de Lazari-Radek, K., and Singer, P., 2014, The Point of View of the Universe: Sidgwick and Contemporary Ethics , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Den Uyl, D. and T. R. Machan, 1983, “Recent Work on the Concept of Happiness,” American Philosophical Quarterly , 20: 115–34.
- Diener, E., 2008, “Myths in the Science of Happiness, and Directions for Future Research,” The Science of Subjective Well-Being , M. Eid and R. J. Larsen (eds.), New York: Guilford Press: 493–514.
- Diener, E. and R. Biswas-Diener, 2008, Happiness: unlocking the mysteries of psychological wealth , Malden, MA: Blackwell.
- Diener, E. and C. Diener, 1996, “Most People Are Happy,” Psychological Science , 7(3): 181–185.
- Diener, E., R. E. Lucas, U. Schimmack and J. F. Helliwell, 2009, Well-Being for Public Policy , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Diener, E., R. E. Lucas and C. N. Scollon, 2006, “Beyond the Hedonic Treadmill: Revising the Adaptation Theory of Well-Being,” American Psychologist , 61(4): 305–314.
- Diener, E., W. Ng, J. Harter and R. Arora, 2010, “Wealth and happiness across the world: Material prosperity predicts life evaluation, whereas psychosocial prosperity predicts positive feeling,” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 99(1): 52–61.
- Diener, E. and M. Seligman, 2004, “Beyond Money: Toward an economy of well-being,” Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 5(1): 1–31.
- Diener, E. and E. M. Suh (eds.), 2000, Culture and Subjective Well-Being , Cambridge, Mass., MIT Press.
- Diener, E., E. M. Suh, R. E. Lucas and H. L. Smith, 1999, “Subjective Well-Being: Three Decades of Progress,” Psychological Bulletin , 125(2): 276–302.
- Dolan, P., and L. Kudrna, 2016, “Sentimental Hedonism: Pleasure, Purpose, and Public Policy,” Handbook of Eudaimonic Well-Being , J. Vittersø (ed.), Berlin: Springer, 437–52.
- Dolan, P. and M. P. White, 2007, “How can measures of subjective well-being be used to inform public policy?” Perspectives on Psychological Science , 2(1): 71–85.
- Doris, J. M., 2002, Lack of Character , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 2009, “Skepticism about persons,” Philosophical Issues , 19(1): 57–91.
- –––, 2015, Talking to Our Selves , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Easterlin, R. A., 1974, “Does Economic Growth Improve the Human Lot?” Nations and Households in Economic Growth: Essays in Honor of Moses Abramovitz , P. A. David and M. W. Reder (eds.), New York: Academic Press.
- –––, 2003, “Explaining Happiness,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America , 100(19): 11176–11183.
- –––, 2005, “Building a Better Theory of Well-Being,” Economics and Happiness , L. Bruni and P. L. Porta (eds.), New York: Oxford, 29–65.
- Ebenstein, A. O., 1991, The Greatest Happiness Principle: An Examination of Utilitarianism , New York: Garland.
- Edgeworth, F. Y., 1881, Mathematical Psychics: an Essay on the Application of Mathematics to the Moral Sciences , London: Kegan Paul.
- Eid, M. and R. J. Larsen (eds.), 2008, The Science of Subjective Well-Being , New York: Guilford.
- Elster, J., 1983, Sour Grapes , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Epictetus, The Discourses as Reported by Arrian, The Manual, and Fragments , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1925.
- Euler, S. S., 2019, “Psychological Universals in the Study of Happiness: From Social Psychology to Epicurean Philosophy,” Science, Religion and Culture , 6(1): 130–37.
- Everett, D. L., 2009, Don’t sleep, there are snakes: Life and language in the Amazonian jungle , New York: Random House.
- Feldman, F., 2004, Pleasure and the Good Life , New York: Oxford.
- –––, 2010, What Is This Thing Called Happiness? , New York: Oxford.
- –––, 2019, “An Improved Whole Life Satisfaction Theory of Happiness?,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 9(2):1–7.
- Flanagan, O., 2007, The Really Hard Problem: Meaning in a Material World , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Flanagan, O., M. Letourneau, and W. Zhao, 2019, “Particulars of Well-Being,” Science, Religion and Culture , 6(1): 1–5.
- Fletcher, G., 2013, “A Fresh Start for the Objective-List Theory of Well-Being,” Utilitas , 25(2): 206–20.
- Fleurbaey, M., and D. Blanchet, 2013, Beyond GDP: Measuring Welfare and Assessing Sustainability , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Fogel, R. W., 2005, “Changes in the disparities in chronic diseases during the course of the 20th century,” Perspectives in biology and medicine , 48(1 Supplement): S150-S165.
- Fraser, C., 2013, “Happiness in Classical Confucianism: Xúnzǐ,” E. Minar (ed.), Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 53–79.
- Frederick, S. and G. Loewenstein, 1999, “Hedonic Adaptation,” Well-Being: The Foundations of Hedonic Psychology , D. Kahneman, E. Diener and N. Schwarz (eds.), New York: Russell Sage Foundation Press: 302–29.
- Fredrickson, B. L., 2004, “The Broaden-and-Build Theory of Positive Emotions,” Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences , 359(1449): 1367–1377
- Fredrickson, B. L. and D. Kahneman, 1993, “Duration neglect in retrospective evaluations of affective episodes,” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 65(1): 45–55.
- Fredrickson, B. L. and M. F. Losada, 2005, “Positive Affect and the Complex Dynamics of Human Flourishing,” American Psychologist , 60(7): 678–686.
- Frey, B. S., 2008, Happiness: A Revolution in Economics , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Frumkin, H., 2001, “Beyond toxicity: Human health and the natural environment,” American Journal of Preventive Medicine , 20(3): 234–240.
- Gilbert, D., 2006, Stumbling on Happiness , New York: Knopf.
- Gilovitch, T., D. Griffin and D. Kahneman (eds.), 2002, Heuristics and Biases: The Psychology of Intuitive Judgment , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Glaeser, E. L., 2006, “Paternalism and Psychology,” University of Chicago Law Review , 73(1): 133–156.
- Goldman, A. H., 2016, “Happiness is an Emotion,” The Journal of Ethics , 21(1): 1–16.
- –––, 2019, Life’s Values: Pleasure, Happiness, Well-Being, and Meaning , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Goldstein, I., 1973, “Happiness: The Role of Non-Hedonic Criteria in Its Evaluation,” International Philosophical Quarterly , 13: 523–34.
- –––, 1981, “Cognitive Pleasure and Distress,” Philosophical Studies , 39: 15–23.
- –––, 1989, “Pleasure and Pain: Unconditional, Intrinsic Values,” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 50(2): 255–276.
- Goldstein, I., 2002, “Are emotions feelings? A further look at hedonic theories of emotions,” Consciousness and Emotion , 3(1): 21–33.
- Graham, C., 2009, Happiness around the world: The paradox of happy peasants and miserable millionaires , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Graham, M., 2017, “A Fate Worse Than Death? The Well-Being of Patients Diagnosed as Vegetative With Covert Awareness,” Ethical Theory and Moral Practice , 20(5): 1–16.
- Griffin, J., 1979, “Is Unhappiness Morally More Important Than Happiness?” Philosophical Quarterly , 29: 47–55.
- –––, 1986, Well-Being: Its Meaning, Measurement, and Moral Importance , Oxford: Clarendon Press.
- –––, 2000, “Replies,” Well-Being and Morality , R. Crisp and B. Hooker (eds.), New York: Oxford: 281–313.
- –––, 2007, “What Do Happiness Studies Study?” Journal of Happiness Studies , 8(1): 139–148.
- Griswold, C., 1996, “Happiness, Tranquillity, and Philosophy,” Critical Review , 10(1): 1–32.
- Haidt, J., 2001, “The emotional dog and its rational tail: A social intuitionist approach to moral judgment,” Psychological Review , 108(4): 814–834.
- Hare, R. M., 1963, Freedom and Reason , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Hausman, D. M., 2010, “Hedonism and Welfare Economics,” Economics and Philosophy , 26(3): 321–44.
- –––, 2011, Preferences, Value, Choice, and Welfare , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Hausman, D. M. and B. Welch, 2009, “Debate: To Nudge or Not to Nudge,” Journal of Political Philosophy , 18(1): 123–136.
- Hawkins, J., 2008, “Well-Being, Autonomy, and the Horizon Problem,” Utilitas , 20(2): 1–27.
- –––, 2014a, “Well-Being, Time, and Dementia,” Ethics , 124(3): 507–542.
- –––, 2014b, “Well-Being: What Matters Beyond the Mental?,” in Oxford Studies in Normative Ethics (Volume 4), M. Timmons (ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2016, “The Experience Machine and the Experience Requirement,” The Routledge Handbook of the Philosophy of Well-Being , G. Fletcher (ed.), New York: Routledge.
- –––, 2019, “Well-Being, The Self, and Radical Change,” Oxford Studies in Normative Ethics, Vol 9 , M. Timmons (ed.), New York: Oxford University Press, 251.
- Haybron, D. M., 2001, “Happiness and Pleasure,” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 62(3): 501–528.
- –––, 2003, “What Do We Want from a Theory of Happiness?” Metaphilosophy , 34(3): 305–329.
- –––, 2005, “On Being Happy or Unhappy,” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 71(2): 287–317.
- –––, 2007, “Do We Know How Happy We Are?” Nous , 41(3): 394–428.
- –––, 2008a, “Happiness, the Self, and Human Flourishing,” Utilitas , 20(1): 21–49.
- –––, 2008b, The Pursuit of Unhappiness: The Elusive Psychology of Well-Being , New York, Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2011, “Central Park: Nature, Context, and Human Wellbeing,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 1(2): 235–254.
- –––, 2013a, Happiness: A Very Short Introduction , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2013b, “The Proper Pursuit of Happiness,” Res Philosophica , 90(3): 387–411.
- –––, 2014, “Adventures in Assisted Living: Well-Being and Situationist Psychology,” The Philosophy and Psychology of Character and Happiness , N. E. Snow and F. V. Trivigno (eds.), New York: Routledge, 1–25.
- –––, 2016, “Mental State Approaches to Well-Being,” The Oxford Handbook of Well-Being and Public Policy , M. D. Adler & M. Fleurbaey (eds.), New York: Oxford, 347–378.
- Haybron, D. M., and A. Alexandrova, 2013, “Paternalism in Economics,” Paternalism: Theory and Practice , C. Coons and M. Weber (eds.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 157–77.
- Haybron, D. M., and V. Tiberius, 2015, “Well-Being Policy: What Standard of Well-Being?,” Journal of the American Philosophical Association , 1(4): 712–33.
- Headey, B., 2007, The Set-Point Theory of Well-Being Needs Replacing: On the Brink of a Scientific Revolution? , DIW Berlin: German Institute for Economic Research.
- –––, 2008, “The Set-Point Theory of Well-Being: Negative Results and Consequent Revisions,” Social Indicators Research , 85(3): 389–403.
- Hersch, G., 2015, “Can an Evidential Account Justify Relying on Preferences for Well-Being Policy?,” Journal of Economic Methodology , 22(3): 1–13.
- –––, 2017, “Ignoring Easterlin: Why Easterlin’s Correlation Findings Need Not Matter to Public Policy,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 19(8): 2225–2241.
- –––, 2020, “No Theory-Free Lunches in Well-Being Policy,” The Philosophical Quarterly , 70(278): 43–64.
- Hill, S., 2007, “Haybron on Mood Propensity and Happiness,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 10(2): 215–28.
- Hindriks, F., & Douven, I., 2018, “Nozick’s experience machine: An empirical study,” Philosophical Psychology , 31(2): 1–21.
- Ho, S. M., W. Duan, and S. C. Tang, 2014, “The Psychology of Virtue and Happiness in Western and Asian Thought,” The Philosophy and Psychology of Character and Happiness , N. E. Snow and F. V. Trivigno (eds.), New York: Routledge, 223–46.
- Houlden, V., et al., 2018, “The Relationship between Greenspace and the Mental Wellbeing of Adults: A Systematic Review,” PLOS ONE , 13(9): 1–35.
- Hsee, C. K. and R. Hastie, 2006, “Decision and experience: Why don’t we choose what makes us happy?” Trends in Cognitive Sciences , 10(1): 31–37.
- Hurka, T., 2010, The Best Things in Life: A Guide to What Really Matters , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Huxley, A., 1932 [2005], Brave New World and Brave New World Revisited , New York: Harper Perennial Modern Classics.
- Inglehart, R., R. Foa, C. Peterson and C. Welzel, 2008, “Development, freedom, and rising happiness: A global perspective, 1981–2007” Perspectives on Psychological Science , 3(4): 264–285.
- Inglehart, R. and H.-D. Klingemann, 2000, “Genes, Culture, Democracy, and Happiness,” Culture and Subjective Well-Being , E. Diener and E. M. Suh (eds.), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press: 165–183.
- Intelisano, S., Krasko, J., & Luhmann, M., 2019, “Integrating Philosophical and Psychological Accounts of Happiness and Well-Being,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 8: 1–40.
- Jebb, A. T., L. Tay, E. Diener, and S. Oishi, 2018, “Happiness, Income Satiation and Turning Points around the World,” Nature Human Behaviour , 2(1): 33–38.
- Joshanloo, M., 2013, “A Comparison of Western and Islamic Conceptions of Happiness,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 14(6): 1857–74.
- –––, 2014, “Eastern Conceptualizations of Happiness: Fundamental Differences with Western Views,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 15(2): 475–93.
- Joshanloo, M., and D. Weijers, 2019, “A Two-Dimensional Conceptual Framework for Understanding Mental Well-Being,” PLoS ONE , 14(3): e0214045.
- Kagan, S., 1992, “The Limits of Well-Being,” Social Philosophy and Policy , 9(2): 169–89.
- –––, 1994, “Me and My Life,” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 94: 309–324.
- Kahane, Guy, 2011, “Reasons to Feel, Reasons to Take Pills,” Enhancing Human Capacities , J. Savulescu, R. Ter Meulen, and G. Kahane (eds.), Oxford: John Wiley & Sons, 166–78.
- Kahneman, D., 1999, “Objective Happiness,” Well-Being: The Foundations of Hedonic Psychology , D. Kahneman, E. Diener and N. Schwarz (eds.), New York: Russell Sage Foundation: 3–25.
- Kahneman, D. and A. Deaton, 2010, “High income improves evaluation of life but not emotional well-being,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 107(38): 16489–16493.
- Kahneman, D., E. Diener and N. Schwarz (eds.), 1999, Well-Being: The Foundations of Hedonic Psychology , New York: Russell Sage Foundation Press.
- Kahneman, D., B. L. Fredrickson, C. A. Schreiber and D. A. Redelmeier, 1993, “When More Pain Is Preferred to Less: Adding a Better End,” Psychological Science , 4(6): 401–405.
- Kahneman, D. and A. Tversky (eds.), 2000, Choices, Values, and Frames , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Kauppinen, A., 2013, “Meaning and Happiness,” Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 161–185.
- Kazez, J., 2007, The Weight of Things: Philosophy and the Good Life , Malden, MA: Wiley-Blackwell.
- Kekes, J., 1982, “Happiness,” Mind , 91: 358–76.
- –––, 1988, The Examined Life , Lewisburg: Bucknell University Press.
- –––, 1992, “Happiness,” Encyclopedia of Ethics , L. C. Becker and C. B. Becker (eds.), New York: Garland: 430–435.
- Kellert, S. R. and E. O. Wilson (eds.), 1995, The Biophilia Hypothesis , Washington, D.C.: Island Press.
- Kelman, M., 2005, “Hedonic Psychology and the Ambiguities of ‘Welfare’,” Philosophy & Public Affairs , 33(4): 391–412.
- Kenny, A. and C. Kenny, 2006, Life, Liberty and the Pursuit of Utility , Charlottesville, VA: Imprint Academic.
- Keyes, C. L., 2002, “The mental health continuum: From languishing to flourishing in life,” Journal of Health and Social Behavior , 43(2): 207–222.
- Kim, R., 2020, Confucianism and the Philosophy of Well-Being , New York: Routledge.
- Klausen, S. H., 2015, “Happiness, Dispositions and the Self,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 17(3): 777–780.
- –––, 2019, “Understanding Older Adults’ Wellbeing from a Philosophical Perspective,” Journal of Happiness Studies , online first.
- Kraut, R., 1979, “Two Conceptions of Happiness,” The Philosophical Review , 138: 167–97.
- –––, 2018, The Quality of Life: Aristotle Revised , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Kristjánsson, K., 2010, “Positive psychology, happiness, and virtue: The troublesome conceptual issues,” Review of general psychology , 14(4): 296.
- –––, 2012, “Positive Psychology and Positive Education: Old Wine in New Bottles?” Educational Psychologist , 47(2): 86–105.
- –––, 2018, “The flourishing–happiness concordance thesis: Some troubling counterexamples,” The Journal of Positive Psychology , 13(6): 541–552.
- Krueger, A., D. Kahneman, C. Fischler, D. Schkade, N. Schwarz and A. Stone, 2009, “Time Use and Subjective Well-Being in France and the U.S,” Social Indicators Research ,(93): 7–18.
- Larsen, R. J. and Z. Prizmic, 2008, “Regulation of Emotional Well-Being: Overcoming the Hedonic Treadmill,” The Science of Subjective Well-Being , M. Eid and R. J. Larsen (eds.), New York: Guilford Press: 258–289.
- Lauinger, W., 2015, “A Framework for Understanding Parental Well-Being,” Philosophia , 43(3): 847–868.
- Layard, R., 2005, Happiness: Lessons from a new science , New York: Penguin.
- LeBar, M., and D. Russell, 2013, “Well-Being and Eudaimonia: A Reply to Haybron,” Aristotelian Ethics in Contemporary Perspective , 21: 52.
- Lin, E., 2015, “How to Use the Experience Machine,” Utilitas , 28(3): 314–32.
- Loewenstein, G. and E. Haisley, 2008, “The Economist as Therapist: Methodological Ramifications of ‘Light’ Paternalism,” The Foundations of Positive and Normative Economics , A. Caplin and A. Schotter (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 210–248.
- Lucas, R. E., 2008, “Personality and Subjective Well-Being,” The Science of Subjective Well-Being , M. Eid and R. J. Larsen (eds.), New York: Guilford Press: 171–194.
- Lucas, R. E., A. E. Clark, Y. Georgellis and E. Diener, 2004a, “Re-Examining Adaptation and the Setpoint Model of Happiness: Reactions to Changes in Marital Status,” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 84: 527–539.
- –––, 2004b, “Unemployment alters the set point for life satisfaction,” Psychological Science , 15(1): 8–13.
- Luhmann, M., and S. Intelisano, 2018, “Hedonic Adaptation and the Set Point for Subjective Well-Being,” Handbook of Well-Being , E. Diener, S. Oishi, and L. Tay (eds.), Salt Lake City: DEF Publishers.
- Lumber, R., M. Richardson, and D. Sheffield, 2017, “Beyond Knowing Nature: Contact, Emotion, Compassion, Meaning, and Beauty Are Pathways to Nature Connection,” PLOS ONE , 12(5): e0177186.
- Luo, S., 2018, “Happiness and the Good Life: A Classical Confucian Perspective,” Dao , 71(2): 1–18.
- Lykken, D. and A. Tellegen, 1996, “Happiness is a stochastic phenomenon,” Psychological Science , 7(3): 186–9.
- Lyubomirsky, S., 2007, The How of Happiness , New York: Penguin.
- Lyubomirsky, S., L. King and E. Diener, 2005, “The Benefits of Frequent Positive Affect: Does Happiness Lead to Success?” Psychological Bulletin , 131(6): 803–855.
- Lyubomirsky, S., K. M. Sheldon and D. Schkade, 2005, “Pursuing Happiness: The Architecture of Sustainable Change,” Review of General Psychology , 9(2): 111–131.
- MacLeod, A. K., 2015, “Well-Being: Objectivism, Subjectivism or Sobjectivism?,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 16 1073–1089.
- Martin, M. W., 2012, Happiness and the Good Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- May, T., 2015, A Significant Life Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Mayerfeld, J., 1996, “The Moral Asymmetry of Happiness and Suffering,” Southern Journal of Philosophy , 34: 317–338.
- –––, 1999, Suffering and Moral Responsibility , New York: Oxford.
- McFall, L., 1989, Happiness , New York: Peter Lang.
- McMahon, D. M., 2005, Happiness: A History , New York: Atlantic Monthly Press.
- McPherson, D., 2020, Virtue and Meaning: A Neo-Aristotelian Perspective , Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Metz, T., 2014, “Gross National Happiness: A Philosophical Appraisal,” Ethics and Social Welfare , 8(3): 218–32.
- Meynell, H., 1969, “Human Flourishing,” Religious Studies , 5: 147–154.
- Millgram, E., 2000, “What’s the Use of Utility,” Philosophy and Public Affairs , 29(2): 113–136.
- Mitchell, P., 2018, “Adaptive Preferences, Adapted Preferences,” Mind , 127(508): 1003–25.
- Moller, D., 2011, “Wealth, Disability, and Happiness,” Philosophy & Public Affairs , 39(2): 177–206.
- Montague, R., 1967, “Happiness,” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , 67: 87–102.
- Morris, S., 2011, “In defense of the hedonistic account of happiness,” Philosophical Psychology , 24(2): 261 – 281.
- –––, 2015, Science and the End of Ethics , New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
- Mulligan, K., 2016, “Happiness, Luck and Satisfaction.,” ARGUMENTA , 1(2): 133–45.
- Mulnix, J. W., & Mulnix, M. J., 2015a, Happy Lives, Good Lives: A Philosophical Examination , Peterborough, ON: Broadview Press.
- ––– (eds.), 2015b, Theories of Happiness: An Anthology , Peterborough, ON: Broadview Press.
- Murphy, M. C., 2001, Natural Law and Practical Rationality , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Myers, D. G. and E. Diener, 1995, “Who Is Happy?” Psychological Science , 6(1): 10–19.
- Nettle, D., 2005, Happiness: The Science Behind Your Smile , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Noddings, N., 2003, Happiness and Education , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Nozick, R., 1974, Anarchy, State, and Utopia , New York: Basic Books.
- –––, 1989, The Examined Life , New York: Simon and Schuster.
- Nussbaum, M. C., 2000, Women and Human Development: The Capabilities Approach , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 2008, “Who Is the Happy Warrior? Philosophy Poses Questions to Psychology,” The Journal of Legal Studies , 37(s2): S81-S113.
- Oishi, S., Choi, H., Buttrick, N., et al., 2019, “The psychologically rich life questionnaire,” Journal of Research in Personality , 81: 257–270.
- Parducci, A., 1995, Happiness, Pleasure, and Judgement: The Contextual Theory and Its Applications , Mahwah, NJ: L. Erlbaum Associates.
- Parfit, D., 1984, Reasons and Persons , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Paul, L. A., 2016, Transformative Experience , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Pavot, W., 2008, “The Assessment of Subjective Well-Being: Successes and Shortfalls,” The Science of Subjective Well-Being , M. Eid and R. J. Larsen (eds.), New York: Guilford Press, 124–140.
- Phillips, J., L. Misenheimer and J. Knobe, 2011, “The Ordinary Concept of Happiness (and Others Like It),” Emotion Review , 71: 929–937.
- Phillips, J., S. Nyholm, and S. Liao, 2014, “The Good in Happiness,” Oxford Studies in Experimental Philosophy (Volume 1), T. Lombrozo, S. Nichols, and J. Knobe (eds.), 253–93.
- Phillips, J., De Freitas, J., Mott, C., Gruber, J., & Knobe, J., 2017, “True happiness: The role of morality in the folk concept of happiness,” Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 146(2): 165–181.
- Posner, E. and C. R. Sunstein (eds.), 2010, Law and Happiness , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Purcell, S., 2013, “Natural Goodness and the Normativity Challenge: Happiness Across Cultures,” Proceedings of the American Catholic Philosophical Association , 87: 183–94.
- Quong, J., 2011, Liberalism Without Perfection , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Raibley, J., 2010, “Well-being and the priority of values,” Social Theory and Practice , 36(4): 593–620.
- –––, 2011, “Happiness is not Well-Being,” Journal of Happiness Studies , 13(6): 1105–1121.
- –––, 2012, “Health and Well-Being,” Philosophical Studies , 165(2): 469–89.
- –––, 2013, “Values, Agency, and Welfare,” Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 187–214.
- Rawls, J., 1971, A Theory of Justice , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Raz, J., 1986, The Morality of Freedom , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2004, “The Role of Well-Being,” Philosophical Perspectives , 18(1): 269–294.
- Rescher, N., 1972, Welfare: The Social Issues In Philosophical Perspective , Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press.
- –––, 1980, Unpopular Essays on Technological Progress , Pittsburgh: University of Pittsburgh Press.
- Ricard, M., 2006, Happiness: A Guide to Developing Life’s Most Important Skill , New York: Little, Brown and Co.
- Roberts, R. C., 2019, “Joys: A Brief Moral and Christian Geography,” Faith and Philosophy , 36(2): 195–222.
- Rodogno, R., 2014, “Happiness and Well-Being: Shifting the Focus of the Current Debate,” South African Journal of Philosophy , 33(4): 433–46.
- –––, 2015, “Prudential Value or Well-Being,” Handbook of Value , T. Brosch and D. Sander (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 287–312.
- Rodogno, R., Krause-Jensen, K., & Ashcroft, R. E., 2016, “‘Autism and the good life’: a new approach to the study of well-being,” Journal of Medical Ethics , 42(6): 401–408.
- Ross, L. and R. E. Nisbett, 1991, The Person and the Situation: Perspectives of Social Psychology , Philadelphia: Temple University Press.
- Rossi, M., 2018, “Happiness, Pleasures, and Emotions,” Philosophical Psychology , 31(6): 898–919.
- Rossi, M., & Tappolet, C., 2016, “Virtue, Happiness, and Well-Being,” The Monist , 99(2): 112–127.
- Russell, D., 2013, Happiness for Humans , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Ryan, R. M. and E. L. Deci, 2001, “On happiness and human potentials: A review of research on hedonic and eudaimonic well-being,” Annual Review of Psychology , 52: 141–166.
- Ryff, C. D., 1989, “Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being,” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 57(6): 1069–1081.
- Samson, C., 2019, “Indigenous and Western Views of Happiness: An Essay on the Politics of Contentment,” Regimes of Happiness: Comparative and Historical Studies , B. Turner, J. T. Jen, and Y. Contreras-Vejar (eds.), London: Anthem Press, 219–34.
- Savulescu, J., R. Ter Meulen, and G. Kahane, 2011, Enhancing Human Capacities , Oxford: John Wiley & Sons.
- Scanlon, T., 1999, What We Owe to Each Other , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Schooler, J. W., D. Ariely and G. Loewenstein, 2003, “The Pursuit and Assessment of Happiness Can Be Self-Defeating,” The Psychology of Economic Decision , I. Brocas and J. Carillo (eds.), New York: Oxford University.
- Schultz, B., 2017, The Happiness Philosophers , Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Schwartz, B., 2004, The Paradox of Choice , New York: HarperCollins.
- Schwarz, N. and F. Strack, 1999, “Reports of Subjective Well-Being: Judgmental Processes and Their Methodological Implications,” Well-Being: The Foundations of Hedonic Psychology , D. Kahneman, E. Diener and N. Schwarz (eds.), New York: Russell Sage Foundation Press: 61–84.
- Schwitzgebel, E., 2008, “The Unreliability of Naive Introspection,” Philosophical Review , 117(2): 245–273.
- –––, 2011, Perplexities of Consciousness , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Schwitzgebel, E. and R. T. Hurlburt, 2007, Describing Inner Experience? Proponent Meets Skeptic , Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Scruton, R., 1975, Reason and Happiness. Nature and Conduct , R. S. Peters (ed.), New York: Macmillan: 139–61.
- Seligman, M., 2002, Authentic Happiness , New York: Free Press.
- –––, 2011, Flourish: A Visionary New Understanding of Happiness and Well-being , New York: Simon & Schuster.
- Sen, A., 1987a, Commodities and Capabilities , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 1987b, On Ethics and Economics , Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- –––, 2009, The Idea of Justice , Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Sidgwick, H., 1907 [1966], The Methods of Ethics , New York: Dover Publications.
- Silventoinen, K., S. Sammalisto, M. Perola, D. I. Boomsma, B. K. Cornes, C. Davis, L. Dunkel, M. De Lange, J. R. Harris and J. V. B. Hjelmborg, 2003, “Heritability of adult body height: a comparative study of twin cohorts in eight countries,” Twin Research , 6(5): 399–408.
- Singer, P., 1972, “Famine, Affluence, and Morality,” Philosophy and Public Affairs , 1(3): 229–243.
- Singh, R., and A. Alexandrova, forthcoming, “Happiness Economics as Technocracy,” Behavioural Public Policy , first online 12 Dec 2019: doi:10.17863/CAM.46854
- Sizer, L., 2010, “Good and good for you: An affect theory of happiness,” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research , 80(1): 133–163.
- Skidelsky, E., 2014, “What Can We Learn From Happiness Surveys?,” Journal of Practical Ethics , 2(2): 20–32.
- –––, 2017, “Happiness, Pleasure, and Belief,” Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 95(3): 435–446.
- Slote, M., 1982, “Goods and Lives,” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 63: 311–26.
- –––, 1983, Goods and Virtues , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Smart, J. J. C., 1973, “An Outline of a System of Utilitarian Ethics,” Utilitarianism: For and Against , J. J. C. Smart and B. Williams, New York: Cambridge University Press: 3–74.
- Snow, N. E., and Trivigno, F. V., 2014, The Philosophy and Psychology of Character and Happiness , New York: Routledge.
- Sosis, C., 2012, “Happiness: The Potential Power of Environment,” The Baltic International Yearbook of Cognition, Logic and Communication , 7: 1–10.
- –––, 2014, “Hedonic possibilities and heritability statistics,” Philosophical Psychology , 27(5): 681–702.
- Spahn, A., 2015, “Can Technology Make Us Happy?,” Well-Being in Contemporary Society , J. H. Søraker, et al. (eds.), Cham: Springer, 93–113.
- Sprigge, T. L. S., 1987, The Rational Foundations of Ethics , New York: Routledge and Kegan Paul.
- –––, 1991, “The Greatest Happiness Principle,” Utilitas , 3(1): 37–51.
- Stenberg, J., 2019, “The All-Happy God,” Faith and Philosophy , 36(4): 423–41.
- Stevenson, C. M., 2018, “Experience Machines, Conflicting Intuitions and the Bipartite Characterization of Well-Being,” Utilitas , 30(4): 383–98.
- Stevenson, B. and J. Wolfers, 2008, “Economic Growth and Subjective Well-Being: Reassessing the Easterlin Paradox,” Brookings Papers on Economic Activity , Spring 2008: 1–87.
- Stiglitz, J. E., J.-P. Fitoussi, and M. Durand, 2019, Measuring What Counts: The Global Movement for Well-Being , New York: New Press.
- Stiglitz, J. E., Amartya. Sen, and J.-Paul. Fitoussi, 2009, Report by the Commission on the Measurement of Economic Performance and Social Progress , Paris: Commission on the Measurement of Economic Performance and Social Progress.
- Sugden, R., 2008, “Capability, Happiness, and Opportunity,” Capabilities and Happiness , L. Bruni, F. Comim, and M. Pugno (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 299–322.
- Suikkanen, J., 2011, “An Improved Whole Life Satisfaction Theory of Happiness,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 1(1): 1–18.
- –––, 2019. “The Advice Models of Happiness: A Response to Feldman,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 9(2), available online , doi:10.5502/ijw.v9i2.837
- Sumner, L. W., 1996, Welfare, Happiness, and Ethics , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2000, “Something In Between,” Well-Being and Morality , R. Crisp and B. Hooker (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press, 1–19.
- Tatarkiewicz, W., 1976, Analysis of Happiness , The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
- Telfer, E., 1980, Happiness , New York: St. Martin’s Press.
- Thaler, R. H. and C. R. Sunstein, 2008, Nudge : improving decisions about health, wealth, and happiness , New Haven: Yale University Press.
- Thomas, D. A. L., 1968, “Happiness,” Philosophical Quarterly , 18: 97–113.
- Tiberius, V., 2006, “Well-Being: Psychological Research for Philosophers,” Philosophy Compass , 1: 493–505.
- –––, 2008, The Reflective Life , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 2014, Moral Psychology: A Contemporary Introduction , New York: Routledge
- –––, 2018, Well-Being As Value Fulfillment , New York: Oxford University Press, USA.
- Tiberius, V. and A. Plakias, 2010, “Well-Being,” The Moral Psychology Handbook , J. Doris, G. Harman, S. Nichols, et al . (eds.), New York: Oxford University Press.
- Trout, J. D., 2005, “Paternalism and Cognitive Bias,” Law and Philosophy , 24: 393–434.
- –––, 2009, The Empathy Gap: Building bridges to the good life and the good society , New York: Viking Press.
- Trout, J. D., and S. A. Buttar, 2000, “Resurrecting ‘Death Taxes’: Inheritance, Redistribution, and the Science of Happiness,” Journal of Law & Politics , 16(4): 765–847.
- van der Deijl, Willem, 2016, “What Happiness Science Can Learn from John Stuart Mill,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 6(1): 164–79.
- –––, 2017a, “Are Measures of Well-Being Philosophically Adequate?,” Philosophy of the Social Sciences , 47(3): 209–34.
- –––, 2017b, The Measurement of Wellbeing in Economics: Philosophical Explorations , Ph.D. Dissertation, Erasmus University Rotterdam.
- –––, 2017c, “Which Problem of Adaptation?,” Utilitas , 29(4): 474–92.
- van der Rijt, J.-W., 2013, “Public Policy and the Conditional Value of Happiness,” Economics and Philosophy , 29(3): 381–408.
- –––, 2015, “The Political Turn Towards Happiness,” Well-Being in Contemporary Society , J. H. Søraker, et al. (eds.), Cham: Springer, 215–31.
- Veenhoven, R., 1984, Conditions of Happiness , Dordrecht: D. Reidel.
- –––, 1997, “Advances in Understanding Happiness,” Revue Québécoise de Psychologie , 18: 29–79.
- –––, 2005, “Is Life Getting Better? How Long and Happily Do People Live in Modern Society?” European Psychologist , 10(4): 330–343.
- Velleman, J. D., 1991, “Well-Being and Time,” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly , 72(1): 48–77.
- Verhoef, A., 2018, “Paul Ricoeur: Philosophy, Theology and Happiness,” Stellenbosch Theological Journal , 4(2): 151–66.
- Vitrano, C., 2010, “The subjectivity of happiness,” Journal of Value Inquiry , 44(1): 47–54.
- –––, 2014, The Nature and Value of Happiness , Boulder: Westview Press.
- Višak, T., 2015, “Sacrifices of Self Are Prudential Harms: A Reply to Carbonell,” The Journal of Ethics , 19(2): 219–29.
- Vittersø, J., ed., 2016, Handbook of Eudaimonic Well-Being , Berlin: Springer.
- Von Wright, G. H., 1963, The Varieties of Goodness , London: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- Walker, M., 2011, “Happy-People-Pills for All,” International Journal of Wellbeing , 1(1): 1–22.
- Waterman, A. S., 1993, “Two Conceptions of Happiness: Contrasts of Personal Expressiveness (Eudaimonia) and Hedonic Enjoyment,” Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 64(4): 678–691.
- –––, ed., 2013, The Best within Us: Positive Psychology Perspectives on Eudaimonia , Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Weijers, D., 2013, “Intuitive Biases in Judgments about Thought Experiments: The Experience Machine Revisited,” Philosophical Writings , 41(1): 17–31.
- –––, 2014, “Nozick’s experience machine is dead, long live the experience machine!,” Philosophical Psychology , 27(4): 513–535.
- White, M. D., 2013, “Can We—and Should We—Measure Well-Being?,” Review of Social Economy , 71(4): 526–33.
- White, M. P. and P. Dolan, 2009, “Accounting for the Richness of Daily Activities,” Psychological Science , 20(8): 1000–1008.
- White, N. P., 2006, A Brief History of Happiness , Oxford: Blackwell.
- Wierzbicka, A., 2004, “‘Happiness’ in cross-linguistic & cross-cultural perspective,” Daedalus , 133(2): 34–43.
- Williams, B., 1981, Moral Luck. Moral Luck , New York, Cambridge University Press: 20–39.
- Wilson, J., 1968, “Happiness,” Analysis , 29: 13–21.
- Wodak, D., 2019, “What If Well-Being Measurements Are Non-Linear?,” Australasian Journal of Philosophy , 97(1): 29–45.
- Wong, D. B., 2013, “On Learning What Happiness Is,” Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 81–101.
- Wren-Lewis, S, 2013, “Well-Being as a Primary Good: Towards Legitimate Well-Being Policy,” Philosophy & Public Policy Quarterly , 31(2): 2–9.
- –––, 2014, “How successfully can we measure well-being through measuring happiness?,” South African Journal of Philosophy , 33: 417–432.
- –––, 2019, The Happiness Problem: Expecting Better in an Uncertain World , Chicago, IL: Policy Press.
- Zamuner, E., 2013, “Happiness, Consciousness, and the Ontology of Mind,” Philosophical Topics , 41(1): 237–54.
- Zhang, E. Y., 2019, “Forgetfulness and Flow: ‘Happiness’ in Zhuangzi’s Daoism,” Science, Religion and Culture , 6(1): 77–84.
How to cite this entry . Preview the PDF version of this entry at the Friends of the SEP Society . Look up topics and thinkers related to this entry at the Internet Philosophy Ontology Project (InPhO). Enhanced bibliography for this entry at PhilPapers , with links to its database.
- World Database of Happiness , Erasmus University of Rotterdam.
- Positive Psychology Center , University of Pennsylvania.
- The Happiness and Well-Being Project , with Suggested Readings and links to Funded Research , Saint Louis University.
Aquinas, Thomas | Aristotle | Bentham, Jeremy | character, moral: empirical approaches | communitarianism | consequentialism | economics: philosophy of | emotion | ethics: ancient | ethics: virtue | hedonism | Kant, Immanuel | liberalism | Mill, John Stuart | moral psychology: empirical approaches | pain | paternalism | Plato | pleasure | well-being
Acknowledgments
For helpful comments, many thanks are due to Anna Alexandrova, Robert Biswas-Diener, Thomas Carson, Irwin Goldstein, Richard Lucas, Jason Raibley, Eric Schwitzgebel, Stephen Schueller, Adam Shriver, Edward Zalta, and an anonymous referee for the SEP. Portions of Section 2 are adapted from Haybron 2008, “Philosophy and the Science of Subjective Well-Being,” in Eid and Larsen, The Science of Subjective Well-Being , and used with kind permission of Guilford Press.
Copyright © 2020 by Dan Haybron < dan . haybron @ slu . edu >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054
Home — Essay Samples — Philosophy — Ethics — Credo Beliefs: The Pillars of Personal Philosophy
Credo Beliefs: The Pillars of Personal Philosophy
- Categories: Ethics Spirituality
About this sample

Words: 839 |
Published: Jun 6, 2024
Words: 839 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read
Table of contents
The genesis of beliefs, the significance of a credo, the evolution of a credo, the role of a credo in contemporary society.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr Jacklynne
Verified writer
- Expert in: Philosophy Religion

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
2 pages / 1020 words
6 pages / 2770 words
5 pages / 2147 words
1 pages / 552 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Ethics
Utilitarianism is a prominent ethical theory that has influenced moral philosophy for centuries. In this essay, we will explore the definition and history of utilitarianism, examining its association with renowned philosophers [...]
Being a responsible person means taking the necessary steps to ensure that one is doing the right thing in the right way. It involves being accountable for one's actions and making wise considerations when faced with difficult [...]
In Harper Lee's novel "To Kill a Mockingbird," one of the most memorable characters is Atticus Finch, a lawyer who defends Tom Robinson, a black man falsely accused of raping a white woman. Atticus's decision to take on this [...]
Ethics and values are foundational principles that guide human behavior and shape the moral fabric of society. They define what is right and wrong, influence decision-making, and determine the standards by which individuals and [...]
Revenge is a complex and controversial topic that has been debated for centuries. Some argue that revenge is a natural human instinct, while others believe it is never justified. In this essay, we will explore the various [...]
Overview of the author's moral and ethical stance based on Levinas' theory Connection to biblical passage "Thou shalt not kill" Discussion of how scripture and Catholic teachings inform the author's conscience [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is the Importance of a Concept Paper and How to Write It

A concept paper is a brief document that outlines the main idea, objectives, and potential outcomes of a proposed research project. It is typically used as a pre-proposal to gather support and feedback for more extensive research projects and can also serve as a tool to secure funding. The primary purpose of a concept paper is to provide a clear and compelling argument for why the proposed research project is worth pursuing. It should include the research title, a brief statement of the problem, the significance of the research, the type of data to be collected, the planned research methods and the potential outcomes of the study.
Table of Contents
- Core elements of a concept paper
Keep it concise and to the point
Use clear and easy-to-understand language, provide a clear and compelling argument, tailor your concept paper to the specific funder, proofread and edit your concept paper, be specific when providing details.
An impactful concept paper is written in a way that can be easily understood by a wide range of readers, including those who may not have a background in the specific field of research. This is particularly important when seeking funding, as the concept paper will be used to convince potential funders of the importance and relevance of the research.
Core elements of a concept paper
Several key elements must be addressed and included in a concept paper to make it compelling enough to secure the funding needed for research.
- Create a clear and concise title, as this is one of the most essential elements of a concept paper. The title should be specific and descriptive and must be able to capture the reader’s interest. It should accurately reflect the main idea of the research project in a simple, easy-to-understand way. Avoid using complex language or making the title too lengthy.
- When writing the concept paper, explain the background for the research and provide a clear context for the proposed research project. Experts suggest including a brief overview of the current scenario and any relevant research that may have been conducted in the past. The paper should also explain the relevance of the research and why it is essential to pursue.
- Present a comprehensive literature review to highlight the gaps in knowledge that you plan to address in your research. It is essential to summarize relevant literature on the topic and highlight key studies and findings in the concept paper. This will help identify possible gaps in current research and explain how the proposed project aims to address these.
- Outline the problem statement accurately. The concept paper should include a problem statement that explains why the research topic needs to be investigated. It is crucial to clearly and concisely state the problem or research question that the proposed project aims to address.
- Share the methodology being followed in the research . Researchers must explain the research methods, sampling techniques, data collection processes, and data analysis plans in the concept paper. Remember also to explain why the specified methodology is appropriate for the study.
- Provide a realistic timeline for the research project in the concept note, one that states when specific milestones and deadlines are expected to be met. Explain the various stages of the research and how the results will be disseminated and reported to the funders.
Proven tips on writing an impactful concept paper
Early career academics and researchers often find writing a compelling concept paper to be a challenging task. To help make the process easier, we offer several simple tips that can help you write an effective concept paper to secure funding for your research. Here are some of the more important points to keep in mind:
A concept paper should provide a clear, brief and to-the-point overview of the proposed research project. Experts suggest keeping the concept paper short and using no more than five single-spaced pages. It is best to ensure that essential formatting elements like sub-heads and page numbers are used for easy reading.
Use language that is appropriate for the audience you are trying to address. Ideally, a concept paper should be written in a way that is easily understood, even by those who may not have a background in the specific field of research.
A concept paper should provide a clear and persuasive argument for why the proposed research project is worth pursuing and why it is essential to investigate. Using data and numbers to explain the project’s reasoning makes it more effective and interesting for readers.
When seeking funding for your research, it is important to tailor your concept paper to the particular funder. This includes addressing the specific funding priorities and requirements of the funder and explaining how your proposed research aligns with those priorities.
Before submitting it, be sure to proofread and edit it carefully to ensure that it is free of errors and clearly written.
This is important as sponsors will want to know how much funds are required. They will also seek details like how you plan to measure the progress of your research.
Given just how important it can be, it always helps to spend some time thinking about the best way to structure and present the concept paper. This will go a long way in helping you get the funding you require.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a high-quality conference paper.
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- What are Journal Guidelines on Using Generative AI Tools
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
How to Write the First Draft of a Research Paper with Paperpal?
Introducing paperpal predictive text suggestions: transform ideas into words faster than ever , you may also like, how paperpal can boost comprehension and foster interdisciplinary..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, how to ace grant writing for research funding..., powerful academic phrases to improve your essay writing , how paperpal’s research feature helps you develop and..., how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., how to write a successful book chapter for..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with....
- Newsletters
- Account Activating this button will toggle the display of additional content Account Sign out
Navel Gazing
John dickerson’s notebooks: the meaning behind all this navel gazing.
The season finale of Navel Gazing explores John Dickerson’s search for meaning in a box of notebooks
Listen & Subscribe
Choose your preferred player:
- Apple Podcasts
- Amazon Music
Please enable javascript to get your Slate Plus feeds.
Get Your Slate Plus Podcast
If you can't access your feeds, please contact customer support.
Thanks! Check your phone for a link to finish setting up your feed.
Please enter a 10-digit phone number.
Listen on your phone: RECOMMENDED
Enter your phone number and we'll text you a link to set up the podcast in your app:
We'll only text you about setting up this podcast, no spam.
Listen on your computer:
Apple Podcasts will only work on MacOS operating systems since Catalina . We do not support Android apps on desktop at this time.
Listen on your device: RECOMMENDED
These links will only work if you're on the device you listen to podcasts on.
Set up manually:
How does this work?
We're sorry, but something went wrong while fetching your podcast feeds. Please contact us at [email protected] for help.
Episode Notes
In this week’s essay, John discusses instinct versus obligation, his daughter’s wit, how he has changed since episode one, and more.
Notebook Entries:
Notebook 58, page 10. September 16, 2021
“You don’t measure your life the way you measure your writing.” - Nan
Notebook 75, page 46-47. September 2021
When your dog dies and son goes to college and you are confronted with your life’s work it all boils down to one alarm: the clock is ticking. If a scream is better than a thesis, I was hearing some kind of scream, but what was the thesis?
References:
Everything Is Copy – HBODocs
The Power of Regret – Daniel Pink
The Mezzanine – Nicholson Baker
“ The Creative Process ” – James Baldwin
Slouching Towards Bethlehem – Joan Didion
“ Three Paths Toward the Meaning of Life ” - Arthur Brooks for The Atlantic
Podcast production by Cheyna Roth.
Email us at [email protected]
About the Show
Political Gabfest host John Dickerson has been a journalist for more than three decades, reporting about presidential campaigns, political scandals, and the evolving state of our democracy. Along the way, he’s also been recording his observations in notebooks he has carried in his back pocket. He has captured his thoughts about life, parenthood, death, friendship, writing, God, to-do lists, and more. On the Navel Gazing podcast, John Dickerson invites you to join him in figuring out what these 30 years of notebooks mean: sorting out what makes a life—or a day in a life—noteworthy.
John Dickerson is host of CBS News Prime Time With John Dickerson , co-host of the Slate Political Gabfest, host of the Whistlestop podcast, and author of The Hardest Job in the World .
- Personal Essay

Why the Puerto Rican Day Parade Matters This Summer More Than Ever
:upscale()/2024/05/30/792/n/49351773/tmp_MOYTin_3cfc2aa471d8c228_Main_PS24_05_Identity_DominicanSpaghetti_1456x1000.jpg)
New York City's annual Puerto Rican Day Parade is almost upon us, and it's incredible that almost seven decades have passed since the parade's inception. But it's also hard for me to imagine a time without it — the Puerto Rican community's contributions to New York are that intrinsic. In every neighborhood, in every barrio, on every block in this city of 18 million people, if you look hard enough, you'll see our influence — from the corner bodegas to the salsa blaring from passing cars to the flags hanging from power lines or draped from windows. We're a prideful people, and the parade celebrates that pride.
But I have to be honest: I can count on one hand the amount of times I've actually attended the parade, which falls on Puerto Rican weekend. That doesn't mean the parade has become less important to me. On the contrary, I think the Puerto Rican Day Parade might just be more meaningful than ever — for me and most Boricuas.
The Puerto Rican parade has always been political in nature. In fact, it originated with a different parade altogether, the Hispanic Day Parade. However, in 1958, buoyed by the waves of Puerto Rican immigration to New York City and the burgeoning desire among the community to have the unique aspects of their culture represented and celebrated, the Puerto Rican Day Parade was born. The impact of this cannot be understated. After the collapse of the island's agricultural infrastructure in the aftermath of World War II, many Boricuas were forced to leave the island in search of employment and a better life. Instead, they found themselves crammed into NYC tenement apartments in crime-addled neighborhoods where poverty abounded. The parade not only gave the community an opportunity to focus on the positive and inspiring aspects of Puerto Rican culture, but it also forced city officials to acknowledge the rapidly growing social and political power of Puerto Ricans.
My grandparents were a part of that influx. My mother still remembers how the elders would get the kids up at the crack of dawn on that second Sunday in June to make the trip over to Fifth Avenue. They would line up along the curb with pots of food and snacks and wait hours for the parade to begin. It was that important to Puerto Rican communities living in NYC.
But for me, the parade has never been the main event, at least not the Fifth Avenue one. Instead, I have always viewed it as a fixed center that takes place every second weekend of June, from which all kinds of events and celebrations of Puerto Rican culture radiate. There's my personal favorite, the festival on 116th, the Saturday before the parade, where the streets are closed to traffic and pedestrians can take in the sounds, smells, and tastes that are unique to the island, complete with local Boricuas putting on impromptu stoop-side jam sessions. Then, of course, there's the club scene, where NYC-based artists and island-bred performers get a chance to rock stages across the five boroughs.
As a kid, the promise of all these options had me looking forward to Puerto Rican weekend all year round. I remember going to the Fifth Avenue parade with cousins, decked out in flags and bandanas — one cousin even used markers to turn a plain white tank into a celebration of our pride. As I got older, the parade on Knickerbocker Avenue in Bushwick became my preferred destination. You could usually catch me standing on the corner of Bleecker Street in a pair of limited-edition Air Force 1s that featured the Puerto Rican flag, an alcapurria from La Isla Cuchifrito in hand. Meanwhile, back in the apartment, my parents would have the main parade playing on the TV while they ate breakfast, sipped coffee, and beamed with pride. From the streets below, flags mounted on car antennas would wave proudly in the breeze, and car horns would blare in acknowledgment as cries of "Boricua" rose high above the traffic. This was the real main event, the energy reverberating on every city corner. If you didn't go to the parade — and even if you didn't watch it on TV — the parade would find you. You would know that you were a part of something so much bigger — that even if you didn't speak Spanish, even if you didn't dance salsa, you were still a part of a people that had crossed oceans to find a better life and, through the merit of their culture, enriched the lives and the city around them.
But as time passed, the number of Puerto Rican flags in my neighborhood began to dwindle. The noise that once accompanied our raucous celebrations of Puerto Rican pride became fainter, the parties fewer and further between. The cement stoops that had once been host to our barbecues became condos, silent towers of glass and steel that no longer told our story. The city even tried to remove the "Avenue of Puerto Rico" sign that has proudly hung on Graham Avenue in Brooklyn for decades. This is the aftermath of gentrification, which is all too often marketed under the banner of urban renewal to divert attention away from the true displacement and cultural erosion that are its byproducts. It's also not a new phenomenon. The San Juan Hill neighborhood of Manhattan once gave rise to a hotbed of Black and Puerto Rican talent, including Thelonious Monk and Arturo Alfonso Schomburg. Today, the neighborhood is no more. Instead, we call it Lincoln Center.
So, as rents rise and more Puerto Ricans pack up and move away, the Puerto Rican Day Parade and the many accompanying celebrations serve as an important reminder — not only of how far we've come and what we've achieved, but that we're still here. Sure, maybe there aren't as many of us. But our voices are still powerful when raised in unison. And they don't get any louder than during that second weekend in June when we get to remind the world of everything our little island has done, pa' que tú lo sepa.
Miguel Machado is a journalist with expertise in the intersection of Latine identity and culture. He does everything from exclusive interviews with Latin music artists to opinion pieces on issues that are relevant to the community, personal essays tied to his Latinidad, and thought pieces and features relating to Puerto Rico and Puerto Rican culture.
Rainbow flag meaning: A brief history lesson on how the Pride flag came to be

Since its creation in 1978, the pride flag has become a universal symbol for the LGBTQ+ community. It represents visibility and hope and reflects the diversity within the LGBTQ+ community.
While the flag is easily recognized, its history may not be as well-known to everyone. Did you know the current rainbow flag is an updated design of the original?
Here is a history lesson on how the pride rainbow flag came to be and the meaning behind its colors.
What do the colors of the Pride flag mean?
Each of the pride flag's six rainbow colors has a unique meaning:
- Orange: Healing
- Yellow: Sunlight
- Green: Nature
- Blue: Serenity
- Purple: Spirit
When is Pride Month 2024? How the celebration of LGBTQ+ identities came to be.
The history of the Gilbert Baker pride flag
In the 1970s, Harvey Milk – the first openly gay elected official in California – tasked activist Gilbert Baker to design a symbol of hope for the gay community.
"Harvey Milk was a friend of mine, an important gay leader in San Francisco in the ’70s, and he carried a really important message about how important it was to be visible," Baker said in an interview with the Museum of Modern Art in 2015 . "A flag really fit that mission, because that’s a way of proclaiming your visibility, or saying, 'This is who I am!'"
The original Pride flag had eight stripes , each symbolizing:
- Hot pink: Sex
- Turquoise: Magic
- Indigo: Serenity
Prior to the rainbow flag, the pink triangle was used as a symbol for the LGBTQ+ community, according to Baker. In Nazi Germany, people were forced to wear pink triangles. While the symbol was reclaimed, the community wanted a new symbol.
"We needed something beautiful, something from us," Baker said in the MoMA interview . "The rainbow is so perfect because it really fits our diversity in terms of race, gender, ages, all of those things."
The original pride flag was flown for the first time at the San Francisco Gay Freedom Day Parade celebration on June 25, 1978 , the History Channel reports.
Pride 2024: Latest news and events honoring LGBTQ rights.
How did the Pride flag come to be?
The original flag was made by hand, but as they started to be mass-produced, the hot pink stripe was removed due to manufacturing difficulties, the New York Times reports .
Parade organizers also wanted the rainbow to have an even number of stripes so to split and line the street along parade routes. Baker then removed the turquoise stripe, replacing it for blue , the History Channel reports.
More Pride Flags explained
Progress Pride Flag | Lesbian Pride Flag | Transgender Pride Flag | Bisexual Pride Flag | Pansexual Pride Flag | Asexual Pride Flag | Intersex Pride Flag | Gender Identity Flags
Just Curious for more? We've got you covered
USA TODAY is exploring the questions you and others ask every day. From " What are the colors of the Intersex Pride flag? " to " When was gay marriage legalized in the U.S.? " to " What does deadnaming mean? " − we're striving to find answers to the most common questions you ask every day. Head to our Just Curious section to see what else we can answer.
The state of AI in early 2024: Gen AI adoption spikes and starts to generate value
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI) , 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago. Respondents’ expectations for gen AI’s impact remain as high as they were last year , with three-quarters predicting that gen AI will lead to significant or disruptive change in their industries in the years ahead.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Alex Singla , Alexander Sukharevsky , Lareina Yee , and Michael Chui , with Bryce Hall , representing views from QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and McKinsey Digital.
Organizations are already seeing material benefits from gen AI use, reporting both cost decreases and revenue jumps in the business units deploying the technology. The survey also provides insights into the kinds of risks presented by gen AI—most notably, inaccuracy—as well as the emerging practices of top performers to mitigate those challenges and capture value.
AI adoption surges
Interest in generative AI has also brightened the spotlight on a broader set of AI capabilities. For the past six years, AI adoption by respondents’ organizations has hovered at about 50 percent. This year, the survey finds that adoption has jumped to 72 percent (Exhibit 1). And the interest is truly global in scope. Our 2023 survey found that AI adoption did not reach 66 percent in any region; however, this year more than two-thirds of respondents in nearly every region say their organizations are using AI. 1 Organizations based in Central and South America are the exception, with 58 percent of respondents working for organizations based in Central and South America reporting AI adoption. Looking by industry, the biggest increase in adoption can be found in professional services. 2 Includes respondents working for organizations focused on human resources, legal services, management consulting, market research, R&D, tax preparation, and training.
Also, responses suggest that companies are now using AI in more parts of the business. Half of respondents say their organizations have adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from less than a third of respondents in 2023 (Exhibit 2).
Gen AI adoption is most common in the functions where it can create the most value
Most respondents now report that their organizations—and they as individuals—are using gen AI. Sixty-five percent of respondents say their organizations are regularly using gen AI in at least one business function, up from one-third last year. The average organization using gen AI is doing so in two functions, most often in marketing and sales and in product and service development—two functions in which previous research determined that gen AI adoption could generate the most value 3 “ The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier ,” McKinsey, June 14, 2023. —as well as in IT (Exhibit 3). The biggest increase from 2023 is found in marketing and sales, where reported adoption has more than doubled. Yet across functions, only two use cases, both within marketing and sales, are reported by 15 percent or more of respondents.
Gen AI also is weaving its way into respondents’ personal lives. Compared with 2023, respondents are much more likely to be using gen AI at work and even more likely to be using gen AI both at work and in their personal lives (Exhibit 4). The survey finds upticks in gen AI use across all regions, with the largest increases in Asia–Pacific and Greater China. Respondents at the highest seniority levels, meanwhile, show larger jumps in the use of gen Al tools for work and outside of work compared with their midlevel-management peers. Looking at specific industries, respondents working in energy and materials and in professional services report the largest increase in gen AI use.
Investments in gen AI and analytical AI are beginning to create value
The latest survey also shows how different industries are budgeting for gen AI. Responses suggest that, in many industries, organizations are about equally as likely to be investing more than 5 percent of their digital budgets in gen AI as they are in nongenerative, analytical-AI solutions (Exhibit 5). Yet in most industries, larger shares of respondents report that their organizations spend more than 20 percent on analytical AI than on gen AI. Looking ahead, most respondents—67 percent—expect their organizations to invest more in AI over the next three years.
Where are those investments paying off? For the first time, our latest survey explored the value created by gen AI use by business function. The function in which the largest share of respondents report seeing cost decreases is human resources. Respondents most commonly report meaningful revenue increases (of more than 5 percent) in supply chain and inventory management (Exhibit 6). For analytical AI, respondents most often report seeing cost benefits in service operations—in line with what we found last year —as well as meaningful revenue increases from AI use in marketing and sales.
Inaccuracy: The most recognized and experienced risk of gen AI use
As businesses begin to see the benefits of gen AI, they’re also recognizing the diverse risks associated with the technology. These can range from data management risks such as data privacy, bias, or intellectual property (IP) infringement to model management risks, which tend to focus on inaccurate output or lack of explainability. A third big risk category is security and incorrect use.
Respondents to the latest survey are more likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider inaccuracy and IP infringement to be relevant to their use of gen AI, and about half continue to view cybersecurity as a risk (Exhibit 7).
Conversely, respondents are less likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider workforce and labor displacement to be relevant risks and are not increasing efforts to mitigate them.
In fact, inaccuracy— which can affect use cases across the gen AI value chain , ranging from customer journeys and summarization to coding and creative content—is the only risk that respondents are significantly more likely than last year to say their organizations are actively working to mitigate.
Some organizations have already experienced negative consequences from the use of gen AI, with 44 percent of respondents saying their organizations have experienced at least one consequence (Exhibit 8). Respondents most often report inaccuracy as a risk that has affected their organizations, followed by cybersecurity and explainability.
Our previous research has found that there are several elements of governance that can help in scaling gen AI use responsibly, yet few respondents report having these risk-related practices in place. 4 “ Implementing generative AI with speed and safety ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 13, 2024. For example, just 18 percent say their organizations have an enterprise-wide council or board with the authority to make decisions involving responsible AI governance, and only one-third say gen AI risk awareness and risk mitigation controls are required skill sets for technical talent.
Bringing gen AI capabilities to bear
The latest survey also sought to understand how, and how quickly, organizations are deploying these new gen AI tools. We have found three archetypes for implementing gen AI solutions : takers use off-the-shelf, publicly available solutions; shapers customize those tools with proprietary data and systems; and makers develop their own foundation models from scratch. 5 “ Technology’s generational moment with generative AI: A CIO and CTO guide ,” McKinsey, July 11, 2023. Across most industries, the survey results suggest that organizations are finding off-the-shelf offerings applicable to their business needs—though many are pursuing opportunities to customize models or even develop their own (Exhibit 9). About half of reported gen AI uses within respondents’ business functions are utilizing off-the-shelf, publicly available models or tools, with little or no customization. Respondents in energy and materials, technology, and media and telecommunications are more likely to report significant customization or tuning of publicly available models or developing their own proprietary models to address specific business needs.
Respondents most often report that their organizations required one to four months from the start of a project to put gen AI into production, though the time it takes varies by business function (Exhibit 10). It also depends upon the approach for acquiring those capabilities. Not surprisingly, reported uses of highly customized or proprietary models are 1.5 times more likely than off-the-shelf, publicly available models to take five months or more to implement.
Gen AI high performers are excelling despite facing challenges
Gen AI is a new technology, and organizations are still early in the journey of pursuing its opportunities and scaling it across functions. So it’s little surprise that only a small subset of respondents (46 out of 876) report that a meaningful share of their organizations’ EBIT can be attributed to their deployment of gen AI. Still, these gen AI leaders are worth examining closely. These, after all, are the early movers, who already attribute more than 10 percent of their organizations’ EBIT to their use of gen AI. Forty-two percent of these high performers say more than 20 percent of their EBIT is attributable to their use of nongenerative, analytical AI, and they span industries and regions—though most are at organizations with less than $1 billion in annual revenue. The AI-related practices at these organizations can offer guidance to those looking to create value from gen AI adoption at their own organizations.
To start, gen AI high performers are using gen AI in more business functions—an average of three functions, while others average two. They, like other organizations, are most likely to use gen AI in marketing and sales and product or service development, but they’re much more likely than others to use gen AI solutions in risk, legal, and compliance; in strategy and corporate finance; and in supply chain and inventory management. They’re more than three times as likely as others to be using gen AI in activities ranging from processing of accounting documents and risk assessment to R&D testing and pricing and promotions. While, overall, about half of reported gen AI applications within business functions are utilizing publicly available models or tools, gen AI high performers are less likely to use those off-the-shelf options than to either implement significantly customized versions of those tools or to develop their own proprietary foundation models.
What else are these high performers doing differently? For one thing, they are paying more attention to gen-AI-related risks. Perhaps because they are further along on their journeys, they are more likely than others to say their organizations have experienced every negative consequence from gen AI we asked about, from cybersecurity and personal privacy to explainability and IP infringement. Given that, they are more likely than others to report that their organizations consider those risks, as well as regulatory compliance, environmental impacts, and political stability, to be relevant to their gen AI use, and they say they take steps to mitigate more risks than others do.
Gen AI high performers are also much more likely to say their organizations follow a set of risk-related best practices (Exhibit 11). For example, they are nearly twice as likely as others to involve the legal function and embed risk reviews early on in the development of gen AI solutions—that is, to “ shift left .” They’re also much more likely than others to employ a wide range of other best practices, from strategy-related practices to those related to scaling.
In addition to experiencing the risks of gen AI adoption, high performers have encountered other challenges that can serve as warnings to others (Exhibit 12). Seventy percent say they have experienced difficulties with data, including defining processes for data governance, developing the ability to quickly integrate data into AI models, and an insufficient amount of training data, highlighting the essential role that data play in capturing value. High performers are also more likely than others to report experiencing challenges with their operating models, such as implementing agile ways of working and effective sprint performance management.
About the research
The online survey was in the field from February 22 to March 5, 2024, and garnered responses from 1,363 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, 981 said their organizations had adopted AI in at least one business function, and 878 said their organizations were regularly using gen AI in at least one function. To adjust for differences in response rates, the data are weighted by the contribution of each respondent’s nation to global GDP.
Alex Singla and Alexander Sukharevsky are global coleaders of QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and senior partners in McKinsey’s Chicago and London offices, respectively; Lareina Yee is a senior partner in the Bay Area office, where Michael Chui , a McKinsey Global Institute partner, is a partner; and Bryce Hall is an associate partner in the Washington, DC, office.
They wish to thank Kaitlin Noe, Larry Kanter, Mallika Jhamb, and Shinjini Srivastava for their contributions to this work.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, a senior editor in McKinsey’s Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Moving past gen AI’s honeymoon phase: Seven hard truths for CIOs to get from pilot to scale

A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024

Implementing generative AI with speed and safety

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Philosophy Definition: Socrates. Plato's Socratic dialogues convey that philosophy is self-examining, examining other features of existence and acknowledgement of knowledge limits. In the Euthyphro, Plato reveals the nature of philosophy through the dialogues of Socrates as he goes to face the trial against corrupting young men.
Philosophy is a branch of human inquiry and as such it aims at knowledge and understanding. We might expect that the value of philosophy lies in the value of the ends that it seeks, the knowledge and understanding it reveals. But philosophy is rather notorious for failing to establish definitive knowledge on the matters it investigates.
The aim in Philosophy is not to master a body of facts, so much as think clearly and sharply through any set of facts. Towards that end, philosophy students are trained to read critically, analyze and assess arguments, discern hidden assumptions, construct logically tight arguments, and express themselves clearly and precisely in both speech ...
The meaning of life might be the true story of life's origins and significance.[7] In this sense, life cannot be meaningless, but its meaning might be pleasing or disappointing to us. When people like Tolstoy regard life as meaningless, they seem to be thinking that the truth about life is bad news.[8] 2.
arguments or theories in philosophy papers, you must always practice philosophy. This means that you should explain the argument in your own words and according to your own understanding of the steps involved in it. You will need to be very clear on the precise logical structure of an author's argument (N.B. this may not be
The question is itself a philosophical question. This essay surveys some answers. 'Philosophy' in a dictionary. 1. Defining Philosophy. The most general definition of philosophy is that it is the pursuit of wisdom, truth, and knowledge.[1] Indeed, the word itself means 'love of wisdom' in Greek.
What is Philosophy, and Why Should I Study It? "Philosophy" comes from Greek words meaning "love of wisdom." Philosophy uses the tools of logic and reason to analyze the ways in which humans experience the world. It teaches critical thinking, close reading, clear writing, and logical analysis; it uses these to understand the language we use to describe the world, and our place within it.
essay-writing in philosophy. It is now presented to you as a handbook for students on the basics of philosophical writing. As supervisors ourselves, the four of us began the project out of a desire ... the essay, to make its meaning obvious and clear. assigned is asking you. Of course, there are numerous ways of tackling the same question; in ...
Philosophy (φιλοσοφία, 'love of wisdom', in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, value, mind, and language.It is a rational and critical inquiry that reflects on its own methods and assumptions. Historically, many of the individual sciences, such as physics and psychology, formed part of philosophy.
Among the ancient Greeks, it is common to identify seven sages. The best-known account is provided by Diogenes Laërtius, whose text Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers is a canonical resource on early Greek philosophy. The first and most important sage is Thales of Miletus.Thales traveled to Egypt to study with the Egyptian priests, where he became one of the first Greeks to learn ...
Here at Philosophy Break, we believe the practice of philosophy is the antidote to a world saturated by information, and the more that people engage with philosophy, the more fulfilling their lives will be. The addictive nature of the digital world, for instance, afflicts many of us. The relentless torrent of information saturates our attention ...
It is exclusively among the goods of the mind that the value of philosophy is to be found; and only those who are not indifferent to these goods can be persuaded that the study of philosophy is not a waste of time. Philosophy, like all other studies, aims primarily at knowledge. The knowledge it aims it is the kind of knowledge which gives ...
The Purpose of Philosophy. What is the subject matter . of philosophy? There is no universally accepted answer to this question. Opinions differ, from those who regard it as contemplation of all time and all existence - the queen of the sciences, the keystone of the entire arch of human knowledge - to those who wish to dismiss it as
Guide to researching and writing Philosophy essays. 5th edition by Steven Tudor, for the Philosophy program, University of Melbourne, 2003. This fifth edition of How to Write a Philosophy Essay: A Guide for Students (previous editions titled A Guide to Researching and Writing Philosophy Essays) was prepared in consultation with members of the ...
The Meaning of Life. Many major historical figures in philosophy have provided an answer to the question of what, if anything, makes life meaningful, although they typically have not put it in these terms (with such talk having arisen only in the past 250 years or so, on which see Landau 1997).
Philosophy is important because it illuminates and helps us ponder and create at the boundaries of what we know and what we would like to know or create in science, religion, politics, and many other fields of inquiry and life. To begin with, it is human nature, what we know and inquires into areas that we explore and can only imagine at the ...
The short answer. Philosophy is a way of thinking about certain subjects such as ethics, thought, existence, time, meaning and value. That 'way of thinking' involves 4 Rs: r esponsiveness, r eflection, r eason and r e-evaluation. The aim is to deepen understanding. The hope is that by doing philosophy we learn to think better, to act more ...
Ernie Johns, Owen Sound, Ontario. 'Meaning' is a word referring to what we have in mind as 'signification', and it relates to intention and purpose. 'Life' is applied to the state of being alive; conscious existence. Mind, consciousness, words and what they signify, are thus the focus for the answer to the question.
develop their own answers to philosophical questions. Writing philosophy essays is a key part of studying philosophy. Make sure first to understand the assignment, looking out for the questions asked and paying attention to prompts such as "outline" or "evaluate" or "compare". Most philosophy assignments will ask you to demonstrate ...
Philosophy of education is the branch of applied or practical philosophy concerned with the nature and aims of education and the philosophical problems arising from educational theory and practice. Because that practice is ubiquitous in and across human societies, its social and individual manifestations so varied, and its influence so profound ...
Philosophy makes a central contribution to the educational enterprise through its demands upon intellectual activity. Education in philosophy involves becoming aware of major figures and developments in the history of philosophy, learning up-to-date techniques and accepted answers to philosophical questions, and learning critical, interpretive, and evaluative skills that, in the overall scheme ...
There are roughly two philosophical literatures on "happiness," each corresponding to a different sense of the term. One uses 'happiness' as a value term, roughly synonymous with well-being or flourishing. The other body of work uses the word as a purely descriptive psychological term, akin to 'depression' or 'tranquility'.
This essay delves into the nature of credo beliefs, examining their origins, significance, and the role they play in shaping our lives. Say no to plagiarism. Get a tailor-made essay on ... Utilitarianism is a prominent ethical theory that has influenced moral philosophy for centuries. In this essay, we will explore the definition and history of ...
Cheyene McClain May 18, 2024 PHL 210 2-2 Essay Thinking About Philosophy Prior to this course, I didn't know much about philosophy and all that it entails. Personally, I didn't even know the actual meaning behind philosophy. Through our course readings, I have learned that philosophy is where individuals have the experience to be able to not only seek but they try to understand the conclusions ...
A concept paper is a brief document that outlines the main idea, objectives, and potential outcomes of a proposed research project. It is typically used as a pre-proposal to gather support and feedback for more extensive research projects and can also serve as a tool to secure funding. The primary purpose of a concept paper is to provide a ...
Slouching Towards Bethlehem - Joan Didion. " Three Paths Toward the Meaning of Life " - Arthur Brooks for The Atlantic. Podcast production by Cheyna Roth. Email us at navelgazingpodcast ...
Writer Miguel Machado pens a personal essay for PS on why the Puerto Rican Day Parade still carries so much meaning for Boricuas today.
Here is a history lesson on how the pride rainbow flag came to be and the meaning behind its colors. What do the colors of the Pride flag mean? Each of the pride flag's six rainbow colors has a ...
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI), 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our ...