

What is Creative Writing? A Key Piece of the Writer’s Toolbox
Not all writing is the same and there’s a type of writing that has the ability to transport, teach, and inspire others like no other.
Creative writing stands out due to its unique approach and focus on imagination. Here’s how to get started and grow as you explore the broad and beautiful world of creative writing!
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way.
Creative writing can take on various forms such as:
- short stories
- screenplays
It’s a way for writers to express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a creative, often symbolic, way . It’s about using the power of words to transport readers into a world created by the writer.
5 Key Characteristics of Creative Writing
Creative writing is marked by several defining characteristics, each working to create a distinct form of expression:
1. Imagination and Creativity: Creative writing is all about harnessing your creativity and imagination to create an engaging and compelling piece of work. It allows writers to explore different scenarios, characters, and worlds that may not exist in reality.
2. Emotional Engagement: Creative writing often evokes strong emotions in the reader. It aims to make the reader feel something — whether it’s happiness, sorrow, excitement, or fear.
3. Originality: Creative writing values originality. It’s about presenting familiar things in new ways or exploring ideas that are less conventional.
4. Use of Literary Devices: Creative writing frequently employs literary devices such as metaphors, similes, personification, and others to enrich the text and convey meanings in a more subtle, layered manner.
5. Focus on Aesthetics: The beauty of language and the way words flow together is important in creative writing. The aim is to create a piece that’s not just interesting to read, but also beautiful to hear when read aloud.
Remember, creative writing is not just about producing a work of art. It’s also a means of self-expression and a way to share your perspective with the world. Whether you’re considering it as a hobby or contemplating a career in it, understanding the nature and characteristics of creative writing can help you hone your skills and create more engaging pieces .
For more insights into creative writing, check out our articles on creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree and is a degree in creative writing worth it .
Styles of Creative Writing
To fully understand creative writing , you must be aware of the various styles involved. Creative writing explores a multitude of genres, each with its own unique characteristics and techniques.
Poetry is a form of creative writing that uses expressive language to evoke emotions and ideas. Poets often employ rhythm, rhyme, and other poetic devices to create pieces that are deeply personal and impactful. Poems can vary greatly in length, style, and subject matter, making this a versatile and dynamic form of creative writing.
Short Stories
Short stories are another common style of creative writing. These are brief narratives that typically revolve around a single event or idea. Despite their length, short stories can provide a powerful punch, using precise language and tight narrative structures to convey a complete story in a limited space.
Novels represent a longer form of narrative creative writing. They usually involve complex plots, multiple characters, and various themes. Writing a novel requires a significant investment of time and effort; however, the result can be a rich and immersive reading experience.
Screenplays
Screenplays are written works intended for the screen, be it television, film, or online platforms. They require a specific format, incorporating dialogue and visual descriptions to guide the production process. Screenwriters must also consider the practical aspects of filmmaking, making this an intricate and specialized form of creative writing.
If you’re interested in this style, understanding creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree can provide useful insights.
Writing for the theater is another specialized form of creative writing. Plays, like screenplays, combine dialogue and action, but they also require an understanding of the unique dynamics of the theatrical stage. Playwrights must think about the live audience and the physical space of the theater when crafting their works.
Each of these styles offers unique opportunities for creativity and expression. Whether you’re drawn to the concise power of poetry, the detailed storytelling of novels, or the visual language of screenplays and plays, there’s a form of creative writing that will suit your artistic voice. The key is to explore, experiment, and find the style that resonates with you.
For those looking to spark their creativity, our article on creative writing prompts offers a wealth of ideas to get you started.
Importance of Creative Writing
Understanding what is creative writing involves recognizing its value and significance. Engaging in creative writing can provide numerous benefits – let’s take a closer look.
Developing Creativity and Imagination
Creative writing serves as a fertile ground for nurturing creativity and imagination. It encourages you to think outside the box, explore different perspectives, and create unique and original content. This leads to improved problem-solving skills and a broader worldview , both of which can be beneficial in various aspects of life.
Through creative writing, one can build entire worlds, create characters, and weave complex narratives, all of which are products of a creative mind and vivid imagination. This can be especially beneficial for those seeking creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Enhancing Communication Skills
Creative writing can also play a crucial role in honing communication skills. It demands clarity, precision, and a strong command of language. This helps to improve your vocabulary, grammar, and syntax, making it easier to express thoughts and ideas effectively .
Moreover, creative writing encourages empathy as you often need to portray a variety of characters from different backgrounds and perspectives. This leads to a better understanding of people and improved interpersonal communication skills.
Exploring Emotions and Ideas
One of the most profound aspects of creative writing is its ability to provide a safe space for exploring emotions and ideas. It serves as an outlet for thoughts and feelings , allowing you to express yourself in ways that might not be possible in everyday conversation.
Writing can be therapeutic, helping you process complex emotions, navigate difficult life events, and gain insight into your own experiences and perceptions. It can also be a means of self-discovery , helping you to understand yourself and the world around you better.
So, whether you’re a seasoned writer or just starting out, the benefits of creative writing are vast and varied. For those interested in developing their creative writing skills, check out our articles on creative writing prompts and how to teach creative writing . If you’re considering a career in this field, you might find our article on is a degree in creative writing worth it helpful.
4 Steps to Start Creative Writing
Creative writing can seem daunting to beginners, but with the right approach, anyone can start their journey into this creative field. Here are some steps to help you start creative writing .
1. Finding Inspiration
The first step in creative writing is finding inspiration . Inspiration can come from anywhere and anything. Observe the world around you, listen to conversations, explore different cultures, and delve into various topics of interest.
Reading widely can also be a significant source of inspiration. Read different types of books, articles, and blogs. Discover what resonates with you and sparks your imagination.
For structured creative prompts, visit our list of creative writing prompts to get your creative juices flowing.
Editor’s Note : When something excites or interests you, stop and take note – it could be the inspiration for your next creative writing piece.
2. Planning Your Piece
Once you have an idea, the next step is to plan your piece . Start by outlining:
- the main points
Remember, this can serve as a roadmap to guide your writing process. A plan doesn’t have to be rigid. It’s a flexible guideline that can be adjusted as you delve deeper into your writing. The primary purpose is to provide direction and prevent writer’s block.
3. Writing Your First Draft
After planning your piece, you can start writing your first draft . This is where you give life to your ideas and breathe life into your characters.
Don’t worry about making it perfect in the first go. The first draft is about getting your ideas down on paper . You can always refine and polish your work later. And if you don’t have a great place to write that first draft, consider a journal for writing .
4. Editing and Revising Your Work
The final step in the creative writing process is editing and revising your work . This is where you fine-tune your piece, correct grammatical errors, and improve sentence structure and flow.
Editing is also an opportunity to enhance your storytelling . You can add more descriptive details, develop your characters further, and make sure your plot is engaging and coherent.
Remember, writing is a craft that improves with practice . Don’t be discouraged if your first few pieces don’t meet your expectations. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, enjoy the creative process.
For more insights on creative writing, check out our articles on how to teach creative writing or creative writing activities for kids.
Tips to Improve Creative Writing Skills
Understanding what is creative writing is the first step. But how can one improve their creative writing skills? Here are some tips that can help.
Read Widely
Reading is a vital part of becoming a better writer. By immersing oneself in a variety of genres, styles, and authors, one can gain a richer understanding of language and storytelling techniques . Different authors have unique voices and methods of telling stories, which can serve as inspiration for your own work. So, read widely and frequently!
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creative writing improves with practice. Consistently writing — whether it be daily, weekly, or monthly — helps develop your writing style and voice . Using creative writing prompts can be a fun way to stimulate your imagination and get the words flowing.
Attend Writing Workshops and Courses
Formal education such as workshops and courses can offer structured learning and expert guidance. These can provide invaluable insights into the world of creative writing, from understanding plot development to character creation. If you’re wondering is a degree in creative writing worth it, these classes can also give you a taste of what studying creative writing at a higher level might look like .
Joining Writing Groups and Communities
Being part of a writing community can provide motivation, constructive feedback, and a sense of camaraderie. These groups often hold regular meetings where members share their work and give each other feedback. Plus, it’s a great way to connect with others who share your passion for writing.
Seeking Feedback on Your Work
Feedback is a crucial part of improving as a writer. It offers a fresh perspective on your work, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for improvement. Whether it’s from a writing group, a mentor, or even friends and family, constructive criticism can help refine your writing .
Start Creative Writing Today!
Remember, becoming a proficient writer takes time and patience. So, don’t be discouraged by initial challenges. Keep writing, keep learning, and most importantly, keep enjoying the process. Who knows, your passion for creative writing might even lead to creative writing jobs and what you can do with a creative writing degree .
Happy writing!
Brooks Manley

Creative Primer is a resource on all things journaling, creativity, and productivity. We’ll help you produce better ideas, get more done, and live a more effective life.
My name is Brooks. I do a ton of journaling, like to think I’m a creative (jury’s out), and spend a lot of time thinking about productivity. I hope these resources and product recommendations serve you well. Reach out if you ever want to chat or let me know about a journal I need to check out!
Here’s my favorite journal for 2024:

Gratitude Journal Prompts Mindfulness Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Anxiety Reflective Journal Prompts Healing Journal Prompts Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Journal Prompts Mental Health Journal Prompts ASMR Journal Prompts Manifestation Journal Prompts Self-Care Journal Prompts Morning Journal Prompts Evening Journal Prompts Self-Improvement Journal Prompts Creative Writing Journal Prompts Dream Journal Prompts Relationship Journal Prompts "What If" Journal Prompts New Year Journal Prompts Shadow Work Journal Prompts Journal Prompts for Overcoming Fear Journal Prompts for Dealing with Loss Journal Prompts for Discerning and Decision Making Travel Journal Prompts Fun Journal Prompts
Inspiring Ink: Expert Tips on How to Teach Creative Writing
You may also like, how to have more effective meetings.
How to Stop Multitasking and Get More Work Done
How to start and keep a dream journal: a guide to dream diaries, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Productivity
- Favorite Journals

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
| Recommended Tools | Learn More |
|---|---|
| Jasper AI | |
| Show Not Tell GPT | |
| Dragon Professional Speech Dictation and Voice Recognition | |
| Surface Laptop | |
| Bluehost | |
| Sqribble (eBook maker) |
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)
Creative Writing: What It Is and Why It Matters
By: Author Paul Jenkins
Posted on Published: January 13, 2023 - Last updated: January 15, 2023
Categories Writing
Writing can be intimidating for many people, but creative writing doesn’t have to be. Creative writing is a form of self-expression that allows writers to create stories, characters, and unique settings. But what exactly is creative writing? And why is it important in today’s society? Let’s explore this further.
How We Define Creative Writing
Creative writing is any form where writers can express their thoughts and feelings imaginatively. This type of writing allows authors to draw on their imagination when creating stories and characters and play with language and structure. While there are no boundaries in creative writing, most pieces will contain dialogue, description, and narrative elements.
The Importance of Creative Writing
Creative writing is important because:
- It helps us express ourselves in ways we may not be able to do with other forms of communication.
- It allows us to explore our creativity and think outside the box.
- It can help us better understand our emotions by exploring them through storytelling or poetry.
- Writing creatively can also provide much-needed escapism from everyday life, allowing us to escape into a world of our creation.
- Creative writing helps us connect with others by sharing our experiences through stories or poems they can relate to. This way, we can gain insight into other people’s lives while giving them insight into ours.
Creative Writing: A Path to Mental and Emotional Wellness
Writing is more than just a way to express your thoughts on paper. It’s a powerful tool that can be used as a form of therapy. Creative writing has been shown to improve emotional and mental well-being.
Through creative writing, we can gain insight into our emotions, develop self-expression and communication skills, cultivate empathy and understanding of others, and boost our imagination and creativity.
Let’s examine how creative writing can relieve stress and emotional catharsis.
Stress Relief and Emotional Catharsis
Writing has the power to reduce stress levels significantly. Writing about our experiences or about things that are causing us anxiety or distress helps us to release those complicated feelings constructively. By expressing ourselves through creative writing, we can work through the emotions associated with stressful situations without having to confront them directly.
This is especially helpful for people who struggle to share their emotions verbally or in person.
Improved Communication and Self-Expression
Creative writing is also beneficial for improving communication skills. Through creative writing, we can explore our thoughts and feelings more intensely than by speaking them aloud. This allows us to think more clearly about what we want to say before actually saying it out loud or in written form, which leads to improved self-expression overall.
Additionally, writing out our thoughts before speaking aloud allows us to articulate ourselves better when communicating with others—which is essential for healthy personal and professional relationships.
Increased Empathy and Understanding of Others
Through creative writing, we can also increase our empathy towards others by exploring different perspectives on various topics that may be unfamiliar or uncomfortable for us—such as racism, homophobia, sexism, etc.—and allowing ourselves the opportunity to see the situation from someone else’s point of view without judgment or bias. This helps us become better communicators and more understanding individuals overall.
The Professional Benefits of Creative Writing
Creative writing is a powerful tool that can help you communicate better and more effectively in the professional world. It can also help you develop various skills that prove invaluable in many industries. Whether you’re looking to build your résumé or improve your communication, creative writing can effectively achieve both.
Let’s take a closer look at how creative writing can benefit your career.
Preparing Students for Careers in Writing, Editing, and Publishing
Creative writing is the perfect foundation for anyone interested in pursuing a career in writing, editing, or publishing. It teaches students the basics of grammar and composition while allowing them to express their ideas in imaginative ways.
Creative writing classes also allow students to learn from professionals who have experience as editors, agents, and publishers. They can use this knowledge to learn creative writing, refine their craft and gain valuable experience before entering the job market.
Improving Skills in Storytelling and Marketing for Various Careers
Creative writing teaches students to think critically about stories and craft compelling narratives that draw readers in. This skill is precious for those who wish to pursue careers outside traditional writing roles—such as marketing or advertising—where storytelling is key.
People who understand the fundamentals of creative writing will be able to create persuasive copy that resonates with readers and effectively conveys a message.
Enhancing Team Collaboration and Leadership Skills
Creative writing isn’t just about expressing yourself through words; it also provides an opportunity to practice working collaboratively with others on projects. Many creative writing classes require students to work together on group projects, which helps them develop essential teamwork skills such as communication, critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity.
As they work together on these projects, they will also gain confidence in their ability to lead teams effectively—an invaluable asset no matter what industry they pursue after graduation.
Uncovering the Power of Creative Writing
Creative writing has become an increasingly powerful force in shaping our society. Creative writing has many uses, from preserving cultural heritage to promoting social change.
Preserving Cultural Heritage with Creative Writing
Creative writing has long been used to preserve and share cultural heritage stories. This is done through fictional stories or poetry that explore a particular culture or group’s history, values, and beliefs. By weaving these stories in an engaging way, writers can bring a culture’s history and traditions to life for readers worldwide. This helps bridge cultural gaps by providing insight into what makes each culture unique.
Promoting Social Change & Activism with Creative Writing
Creative writing can also be used for activism and social change. Writers can craft stories that help promote awareness about important issues such as poverty, race relations, gender equality, climate change, and more.
With the power of words, writers can inspire readers to take action on these issues and work towards creating positive change in their communities.
Through creative writing, writers can raise awareness about important topics while fostering empathy toward individuals who may be facing difficult or challenging situations.
Fostering Creativity & Innovation with Creative Writing
Finally, creative writing can foster creativity and innovation in various fields. For example, businesses can use creative copywriting techniques to create compelling content that captures the attention of customers or potential investors.
Aspiring entrepreneurs can use storytelling techniques when pitching their ideas or products to potential partners or investors to make their cases more persuasive and memorable.
By harnessing the power of words through creative writing techniques, businesses can create content that resonates with their target audience while inspiring them to take action on whatever message they’re trying to convey. It often aids the overall creative process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of creative writing.
Creative writing has many benefits, both for the writer and the reader. For the writer, it can be therapeutic, helping them to explore their emotions and better understand themselves. It can also be used as entertainment or communication, allowing them to share their ideas with the world. For the reader, creative writing can provide enjoyment, escapism, and insights into the human condition.
How can I improve my creative writing skills?
There are several ways you can improve your creative writing skills. Firstly, make sure you allow yourself time to write regularly. Use a writing prompt to inspire a short story. Secondly, read as much as you can; great writers are also great readers. Thirdly, experiment with different styles and genres to find one that suits you best. Fourthly, join a writers’ group, writing workshop, or creative writing program to get feedback from other writers. Finally, keep a journal to track your progress and reflect on your work as a creative writer.
What is the importance of imagery in creative writing?
Imagery is an important element of creative writing, as it helps to create a more vivid picture for the reader. By using sensory and descriptive language, writers can transport readers into their stories and help them relate to their characters or themes. Imagery can bring a scene alive with detail and evoke emotion by helping readers create strong visual images in their minds. Furthermore, imagery can help make stories more memorable by giving readers a deeper connection with the characters or setting.
What are the elements of creative writing?
The elements of creative writing include plot, character, dialogue, setting, theme, and point of view. The plot is the structure or main storyline, while the character is the personage involved in this story. Dialogue includes conversations between characters to give insight into their emotions and relationships. Setting refers to the place or time in which a story takes place, while theme explores deeper meanings behind a story’s narrative. Finally, point of view defines how readers experience a story through first-person or third-person omniscient narration.
What’s the difference between creative writing and other types of writing?
The main difference between creative writing and other types of writing is that it allows the writer to create their own story, characters, settings, and themes. Creative writing also encourages writers to be inventive with their style and use descriptive language to evoke emotion or bring stories alive in readers’ minds. Other academic or technical writing types typically involve more research-based information and are usually more objective in their presentation. Additionally, most forms of non-creative writing will have stricter rules regarding grammar, structure, and syntax.
What is the golden rule of creative writing?
The golden rule of creative writing is to show, not tell. It’s the core creative writing skill. When it comes to creative writing, it’s essential to use descriptive language that immerses readers in the story and allows them to experience the events through their emotions and imaginations. This can be done through metaphors, similes, sensory language, and vivid imagery.
How important is creativity in writing?
Creativity is essential in writing as it allows writers to craft a unique story and evoke emotion from the reader. Creativity can bring stories alive with fresh perspectives and exciting plot lines while creating an escape for readers and giving them more profound insights into the human condition. Writers who combine creativity with technical aspects such as grammar, structure, language usage, and flow will create pieces that capture their audience’s attention and provide an enjoyable reading experience.

Why learn creative writing? Truthfully, creative writing is one of the most misunderstood disciplines in the 21st century. When people think of a creative writing course, they often imagine a group of lofty, out-of-touch people who wear argyle sweater vests and have unproductive conversations about abstract concepts.
In reality, nothing could be further from the truth: the best writing classes remain engaged with the real world, and the skills gained in a creative writing course apply to nearly every facet of daily life.
If you’re wondering whether it’s worth picking up a course in fiction, nonfiction, or poetry, we have five reasons to learn creative writing. But first, let’s talk about what actually happens in a creative writing course.
The Basics of a Writing Workshop
Whether you’re enrolled in a poetry, fiction, or nonfiction writing class, you can expect the following writing process – at least in a quality writing course like the ones at Writers.com.
- Weekly prompts and writing exercises to sharpen the precision and necessity of each word you use.
- Constructive critiques from a community of writers who are each growing their writing skills alongside you.
- A creative space to explore new ideas, experiment with language, and arrange words in new and exciting ways.
- Focused writing instruction from a master of the craft.
The benefits of creative writing come from engaging with the course material, the writing prompts, and the other class members. These elements help you become a better writer, both in creative realms and in everyday life. How? No matter what form of writing, a creative writing class pushes you to connect ideas and create effective narratives using the best words – and that skill translates into real world success.
The Benefits of Creative Writing
1. why learn creative writing: improved self-expression.
Improving your writing skills leads to stronger communication. When you practice finding the right word in a story or poem, you engage the same parts of your brain that are active in everyday writing and speaking. A creative writing course subconsciously turns you into a more effective communicator.
The importance of precise language and self-advocacy translates well into both interpersonal relationships and working environments. Take it from this expert on how writing and self-advocacy results in career and leadership success.
2. Why Learn Creative Writing: Job Success
This brings us to our next point: great writing leads to job success. Of course, your boss probably isn’t expecting you to write emails in the form of a short story or a sonnet – though if they are expecting this, you have a pretty cool boss.
In reality, almost every job requires some sort of written work, whether that’s simple written communication or something more elaborate, like publishing data or marketing materials. In a creative writing class, you practice the style and grammar rules necessary for effective writing, both within the realms of literature and in career-related writing. Sharpening your writing and creativity skills might just land you your next promotion.
3. Why Learn Creative Writing: Improved Thinking Skills
Strong writing leads to strong thinking. No matter what type of writing you pursue, learning how to write is another form of learning how to think.
That might seem like a bold claim, so think about it this way. Without language, our thoughts wouldn’t have form. We might not need language to think “I’m hungry” or “I like cats,” but when it comes to more abstract concepts, language is key. How would you think about things like justice, revenge, or equality without the words to express them?
When you hone in on your ability to find choice, specific words, and when you work on the skills of effective storytelling and rhetoric , you improve your ability to think in general. Good writing yields great thinking!
4. Why Learn Creative Writing: Empathy
Reading and writing both rely on empathy, especially when it comes to being an effective workshop participant. When we read and write stories, we situate ourselves in the shoes of other people; when we read and write poetry, we let language navigate us through emotion.
The importance of creative writing relies on empathy. We practice empathy whenever we listen to another person’s life story, when someone tells us about their day, and when we sit down with a client or work partner. When we write, we practice the ability to listen as well as to speak, making us more effective communicators and more compassionate human beings.
5. Why Learn Creative Writing: It’s Fun!
In case you’re not convinced that a writing course is right for you, let’s clarify one more fact: creative writing is fun. Whether you’re in a fiction writing course, starting a memoir, crafting a poem, or writing for the silver screen, you’re creating new worlds and characters. In the sandbox of literature, you’re in control, and when you invest yourself into the craft of writing, something beautiful emerges.
The Importance of Creative Writing
Simply put, creative writing helps us preserve our humanity. What better medium to explore the human experience?
To learn creative writing, like any art form, requires compassion, contemplation, and curiosity. Writers preserve the world as they observe it in stories and poetry, and they imagine a better world by creating it in their works.
Through the decades, literature has explored society’s profound changes. Literary eons like the Naturalist movement and the Beat poets responded to the increase in Western Industrialization. Confessional poets like Virginia Woolf helped transform poetry into a medium for emotional exploration and excavation. And, genre movements like the cyberpunk writers of science fiction helped popularize the idea of an “information economy.”
Thus, the importance of creative writing lies in its ability to describe the world through an honest and unfiltered lens. Anyone who engages in creative writing, no matter the genre or style, helps us explore the human experience, share new ideas, and advocate for a better society. Whether you write your stories for yourself or share them with a wide audience, creative writing makes the world a better place.
Jobs for Creative Writers
Because creative writing isn’t a STEM discipline, many people don’t think that learning it will help their job prospects. Why learn creative writing if it doesn’t make any money?
In fact, nothing could be further from the truth. Creative writing skills are much sought after on resumes, since both creativity and the ability to write are soft skills in decline. Additionally, if you’re considering a career change—or ready to start one!—these are some popular jobs for creative writers.
- Average Starting Salary: $51,000
- Demand: High
- Skills needed: creativity, grammar, timeliness
Copywriters help companies put their branding into words. A copywriter might write emails, blogs, website content, or ad copy that encompasses the company’s voice and purpose. Copywriting requires you to write in a mix of styles and forms, flexing your writing muscles in new and exciting ways.
Grant Writer
- Average Starting Salary: $50,000
- Skills needed: storytelling, research, argumentation
Nonprofits and research facilities rely on local and national grants to fund their projects. Grant writers help secure that funding, writing engaging grants that tell the organization’s story in an engaging, tailored, and convincing way. Creative writers will enjoy the opportunity to tell a meaningful story and create positive community change through this career.
Communications/Public Relations Specialist
- Skills needed: creativity, communications, social media
A communications specialist helps drive a company’s image through various social channels. They may help create a positive narrative for their company through blogs, journalist outreach, social media, and other public-facing avenues. Much like copywriting, a PR specialist helps weave an effective story for a company.
- Average Starting Salary: $55,000
- Demand: Medium/High
- Skills needed: creativity, storytelling, organization, self-reliance
The dream job for many writers is to write and sell books. Being a novelist is an admirable career choice—and also requires the most work. Not only do you have to write your stories, but you also have to market yourself in the literary industry and maintain a social presence so that publishers and readers actually read your work. It’s a tough business, but also incredibly rewarding!
Reasons to Learn Creative Writing: Finding a Writing Community
Finally, creative writing communities make the writing struggle worth it. The relationships you foster with other creative writers can last a lifetime, as no other group of people has the same appreciation for the written word. Creative writing communities create transformative experiences and encourage growth in your writing; if there’s one reason to study creative writing craft, it’s the friendships you make in the process.
You don’t need a class to start writing, but it’s never a waste of time to learn the tools of the trade. Creative writing requires the skills that can help you in everyday life, and a creative writing course can help.
At Writers.com, we believe that creative writing can transform both individual lives and the world at large. See the importance of creative writing for yourself: check out what makes our creative writing courses different , then take a look at our upcoming course calendar today.
Sean Glatch
Would like to apply for a course to write a novel.
I’d be happy to help! Please email [email protected] with any questions, and we’ll find the right course for your writing.
[…] Sean. “Why Learn Creative Writing.” writers.com. June 7, 2020. https://writers.com/why-learn-creative-writing . Accessed November 7, […]
[…] And last of all it’s fun! I hope to live my life doing the things I love, with like-minded creative people who I love. I have many exciting things upcoming as I continue with the process of completing my first novel, Les Année Folles, such as publishing to my first magazine, journal, and working on the millions of short story ideas I have stored in my head. Stay tuned! References: Glatch, S. (2020, June 7). WHY LEARN CREATIVE WRITING? Retrieved from Writers.com: https://writers.com/why-learn-creative-writing […]
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Writers' Treasure
Effective writing advice for aspiring writers
Creative Writing 101
Creative writing is any form of writing which is written with the creativity of mind: fiction writing, poetry writing, creative nonfiction writing and more. The purpose is to express something, whether it be feelings, thoughts, or emotions.
Rather than only giving information or inciting the reader to make an action beneficial to the writer, creative writing is written to entertain or educate someone, to spread awareness about something or someone, or to express one’s thoughts.
There are two kinds of creative writing: good and bad, effective and ineffective. Bad, ineffective creative writing cannot make any impression on the reader. It won’t achieve its purpose.
So whether you’re a novelist, a poet, a short-story writer, an essayist, a biographer or an aspiring beginner, you want to improve your craft. The question is: how?
When you write great fiction, poetry, or nonfiction, amazing things can happen. Readers can’t put it down. The work you wrote becomes a bestseller. It becomes famous. But you have to reach to that level… first .
The best way to increase your proficiency in creative writing is to write, write compulsively, but it doesn’t mean write whatever you want. There are certain things you should know first… it helps to start with the right foot.
To do exactly that, here we have a beginners’ guide from Writers’ Treasure on the subject:
- An Introduction to Creative Writing
- How to Get Started in Creative Writing in Just Three Steps
- Creative Writing vs. Technical Writing
- Fiction Writing 101: The Elements of Stories
- Poetry Writing: Forms and Terms Galore
- Creative Non-Fiction: What is it?
- Tips and Tricks to Improve Your Creative Writing
- Common Mistakes Made by Creative Writers
For novelists: do you want to write compelling opening chapters?
Are you an aspiring novelist? Will your novel see the light of day? For that, you will need to make the first chapter of your story as compelling as possible. Otherwise, readers won’t even pick up your novel. That chapter can be the make-or-break point that decides whether your novel is published or not. It’s because good editors know how you write from the first three pages… or sometimes even from the opening lines.
To solve this problem, I created a five-part tutorial on Writing Compelling Opening Chapters . It outlines why you need to write a compelling opening chapter, my personal favourite way of beginning it, what should be told and shown in it, general dos and don’ts, and what you need to do after having written it. Check it out for more.
Need more writing tips?
Sometimes you reach that stage when you outgrow the beginner stage of writing but feel that you’re not yet an expert. If I just described you, no worries– Writers’ Treasure’s writing tips are here. Whether you want to make your writing more readable, more irresistible, more professional, we’ve got you covered. So check out our writing tips , and be on your way to fast track your success.
I offer writing, editing and proofreading , as well as website creation services. I’ve been in this field for seven years, and I know the tools of the trade. I’ve seen the directions where the writing industry is going, the changes, the new platforms. Get your work done through me, and get fast and efficient service. Get a quote .
Free updates
Get free updates from Writers’ Treasure and learn more tips and tricks to improve your writing.
Share this:
52 thoughts on “creative writing 101”.
- Pingback: Creative Non-Fiction: What is it? | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: Poetry Writing Forms and Terms | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: Fiction Writing Tips and Elements to focus on | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: Creative Writing vs. Technical Writing | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: How to Get Started in Creative Writing | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: An Introduction to Creative Writing | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: How to Improve Your Creative Writing | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: Common Mistakes Made by Creative Writers | Writers Treasure
- Pingback: To Outline or Not to Outline, That is the Question
- Pingback: How to Create Effective Scenes and Chapters in Your Novel : Writing Forward
- Pingback: Writing Powerful True Short Stories
- Pingback: POV: What it is and how it matters
- Pingback: Creative Writing Skills: Do You Have Them All?
- Pingback: Three great articles check out on the Writers Treasure - Jamie Folsom
- Pingback: Warning: Do You Know that Your Paragraphs are Not Good Enough?
- Pingback: Welcome to Writers Treasure
- Pingback: How to Create Effective Scenes and Chapters in Your Novel
- Pingback: Adding Humour to Creative Write-up: Tips and Tricks
- Pingback: Creative Writing vs. Resume Writing | Resume Matrix
- Pingback: How to Get Started in Creative Writing in Just Three Steps | Blog do Learning
- Pingback: The #1 writing advice: write the truth
- Pingback: Creative writing in 2015: here’s what you need to know
- Pingback: Creative Writing Can Be Practical Writing - Simple Writer
- Pingback: Freedom Friday: Liberating Your Creativity | Renee "Soul Writer" Brooks
- Pingback: Tips to help you become a good copywriter | The Creative Copywriter.
- Pingback: Creative Writing | Shahad Almarzooq
- Pingback: How to be good at creative writing?
- Pingback: Learn creative writing
- Pingback: Creative Writing - Occident Books
- Pingback: How to become an outstanding writer
- Pingback: 5 creative writing tips to help you write great essays! – Essay Writing Tips and Help
- Pingback: Creative Writing Tips | learningland2016
- Pingback: NELTA ELT Forum
- Pingback: Language, Communication and Creativity. – lookinglanguage
- Pingback: Keep Your Kids Learning Even When School Year Is Over | Severna Park Children's Centre, Inc
- Pingback: 10 Free Online Courses on Creative Writing » A guide to free online courses
- Pingback: How to start a successful Blog – Beginner’s Guide for 2016
- Pingback: How to start a successful Blog – Beginner’s Guide for 2017
- Pingback: Best of English classes | Site Title
- Pingback: English Classes,Which Classes Dominate others? – Pressing Times
- Pingback: Creative Writing 101 | Junctionway
- Pingback: How to Write Quality Articles: A New Guide for Online Startups [Part Two: 3 Simple Ways for Finding Ideas] - Suhaib Mohammed
- Pingback: Writing Blogs in the Shower - Say It For You- Say It For You
- Pingback: 5 Ways To Improve Your Health First In The New Year - Sarah Scoop
- Pingback: 10 Hobbies Your Teen Can Get as an Alternative to Digital Devices While on Lockdown | meekscutoff.com
- Pingback: 50+ Easy Fiverr Freelance Jobs Examples to Start Today! | IsuaWealthyPlace
- Pingback: 10 Creative Writing Strategies In The Composition Classroom - Wizpals
- Pingback: 5 Ways to Become the MacGyver of Creative Writing
- Pingback: Balancing Your Life As A Writer And Head Of The Family - ebookomatic.com
- Pingback: EbookoMatic | Ricos Electronic World
- Pingback: 20 Types of Freelance Writing Careers (The Definitive List)
- Pingback: Welcome to Musings & Meanderings: A Journey Through Poetry and Prose - Musings & Meanderings
Comments are closed.

Creative Writing Explained: A Guide for all Writers
What is creative writing, the elements of creative writing, what are the forms of creative writing, understanding creative fiction and creative non-fiction, how to get started in creative writing, effective tips for writers, interesting creative writing exercises for writers.

Creative fiction and its types
Short stories, plays and screenplays, creative nonfiction and its types.

Freewriting
Juxtaposition, show, don’t tell, narrative structure and plotting, spend time with your characters, take a step back.
I am interested in writing, but I cannot classify my writings

What is Creative Writing?
by Melissa Donovan | Dec 7, 2023 | Creative Writing | 20 comments

What is creative writing?
Today’s post is an excerpt from the book Ready, Set, Write: A Guide to Creative Writing . This is the entirety of the first chapter, “What is Creative Writing?” Enjoy!
Creative writing can be difficult to define.
Certainly, fiction and poetry are forms of creative writing, but what about journal writing, articles and essays, memoirs and biographies? What about textbooks and copywriting? Technical writing? Blog posts?
Where do we draw the line between what is creative writing and other types of writing?
In some cases, what qualifies as creative is obvious. You read something, and you know a lot of creativity went into it. Other times, a piece of writing, while skillful, might not strike you as creative in nature. And then there’s everything in between—stuff that’s sort of creative or not quite creative enough.
Fiction is made-up stuff borne of the imagination. Poetry takes artistic liberties with language and imagery. These types of writing require a significant level of creative thinking. But many other types of writing are creative as well. When you read a memoir with beautiful turns of phrase or an essay that evokes an emotional response, you’re experiencing the writer’s creativity. Conversely, dry, factual material, such as a user’s guide, might be completely lacking in artistry.
Have you ever read the terms and conditions on a website? Ever browsed through an instruction manual? Surely, you’ve suffered through a boring textbook. While these types of writing might require some level of creativity, they are not usually considered creative writing.
It’s easy to glance at a poem and know that it’s a piece of creative writing, and it’s easy to flip through a legal document and know that it’s not.
So what is creative writing?
If a historical textbook is not creative writing, then wouldn’t that exclude other nonfiction works like memoirs and biographies from the creative writing category?
Not necessarily.
While nonfiction indicates that the writing is rooted in fact, it can be written with emphasis on language and craftsmanship and therefore creative. Creative nonfiction is a broad genre that includes memoirs and biographies, personal essays, travel and food writing, and literary journalism.
Ultimately, we each get to decide what is art and what is creative writing. Most of us will know creative writing when we experience it, either as a writer or as a reader.
In the big scheme of things, it may not be that important to go around labeling what is and isn’t creative writing, but it’s certainly worthy of a few brief moments of consideration. You can determine what creative writing is for yourself, but others might see things differently.
Do you differentiate between creative writing and other types of writing? Do you feel that copywriting (ads, commercials, etc.) can be classified as creative writing even though its purpose is strictly commercial? If most textbooks are not considered creative writing, does that mean a textbook can never be written creatively? Is writing creative because of how the writer approaches the project, or how the reader receives it?
What is creative writing to you? Share your thoughts by leaving a comment, and keep writing.
Don’t forget to pick up a copy of Ready, Set, Write.

20 Comments
The act of creation, the literal source of the term creative, is an unbounded event that accepts a poorly whittled twig as company to the Mona Lisa. We have weakened that magnanimous gesture by listening to critics and marketers. That is the world, we are told, deal with it. Is it really?
The curse of the moniker “expert” is the finite limitations of experience. An expert can, truly, only judge a thing based on his personal experience. In many fields that is sufficient for a normalized event. You know a balanced perspective, what makes a pleasing composition, what pleases the ear, the pallet and the psyche. When something arises that does not fit the normal patterns, what then? Can you really use normal criteria to weigh it’s value? Experts do, of course, what choice do they have?
I have issue with kind and gracious critiques given so liberally to work the expert didn’t understand; but because the artist was renowned, and popular, it must be so. I read drivel, knowing it has been proclaimed a masterpiece, and laugh to myself. I study paintings that were little more than bovine scratching, and marvel at how highly prized it is, while brilliant groundbreaking work all around is ignored.
Creative writing – creative anything, is literally everything. Marketable work, is the term you are searching for. That has little to do with artistic merit, though some remarkable work does find it’s way to the light.
Caliban, thanks for sharing your thoughts. I believe that a true expert will know when faced with work that is beyond their experience or expertise and will act accordingly. I know nothing about football, so if someone asked me to critique a football player’s performance on the field, I would politely decline.
Having said that, everyone seems to have an opinion. Some may hold more weight than others. For example, I care more about what a well-read person thinks of my work than someone who rarely or never reads any kind of literature. I too have read drivel that has been declared a masterpiece and it’s frustrating to me. It’s difficult to understand, for example, why a shoddy writer is putting out two novels a year and consistently appearing on the bestseller list and receiving rave reviews. Yet it happens all the time (and no, I’m not naming any names!).
You’re right, creative writing or creative anything is literally everything. However, that is subjective. Me? I don’t consider legal, medical, or scientific writing to be creative. I worked as a technical writer and there was nothing creative about it, although it did require considerable skill in terms of language and grammar.
Really great questions here. Creative writing is such a broad category that so many things can fall under it. I personally think that when I’m at work, writing work documents like memos, press releases, contracts, etc., I’m not being creative. When I’m writing on my blog, in my journal, or a story/novel, I’m using my creative writing skills. Now, if only I could get a job where I can use my creative writing all the time…. 😉
Wouldn’t it be exciting to make a full-time living with creative writing? Successful novelists and freelance writers are able to do that, as are screenwriters. Where there’s a will, there’s a way.
Good stuff.
I think it’s words that make you think, feel, or act. It’s evocative. It’s clever in action. It’s looking at something a new way. I think the most evocative writing can win over the most evocative painting. Of course, it depends on whose eye the apple is in. It’s subjective and some of the most beautiful art is precisely divisive.
Ooh…evocative writing versus evocative painting. That would be quite a fight!
Interesting question! When somebody says “Creative writing,” I DO tend to think FICTION before anything else. Because that’s something that comes entirely from your own head. Whereas with non-fiction, you’re writing to a purpose or from a set of facts.
But the actual act of writing? Creative, either way.
Well, when it’s being done right. Because, of course, you can write a quick promotion on auto-pilot and have it be … fine. Routine. Run-of-the-mill. But the good ones? That give you that glow of satisfaction? Pure creativity, all the way!
I tend to immediately think fiction and poetry whenever people start talking about creative writing, but it turns out there’s a whole genre of nonfiction that is creative (and it has tons of sub-genres). For example, the memoir is quite popular right now. I guess it all has to do with how creative or literary your work is.
Really interesting question, the differentiation between what is creative writing and what is not is extremely subjective.
In some ways I think that all writing is somewhat creative as it has emerged from the mind and the writer has had to think about what they are going to produce and how they are going to do it.
I can appreciate that novels and poems are more likely to be considered creative and perhaps even more worthy to be described as such.
I agree with you – we can bring creativity into just about anything we do (including any type of writing), but some forms of art require a little more creativity than others.
Anything that doesn’t make me ‘want’ to read it, is in my mind, non creative as in business manuals, contracts,academic materials, etc. But, written stuff that contains a story line, causes me to reflect, chuckle and ‘want’ to read more of the same would be the creative side of writing for me. Most times, I don’t think about the difference, I just naturally ‘feel’ it:)
Yes, it’s hard to think of the dry writing (business, manuals, contracts) as creative. I do believe there are exceptions, but they are few and far between.
I agree with everyone in terms of the question itself being worthy of contemplation. I think there’s a difference between noise and music, so I will say there is a distinction between creative writing and other types of writing, just as there is art and non-art.
To use the music analogy again, I think technical documents are like playing perfect scales. Kudos to those who have the skill to do that really well, but it’s not a creative act until someone rearranges those notes into something unique and pleasant.
Thanks for getting me thinking this evening. Give us more to contemplate.
Sarah, this is an excellent analogy. I wish I’d thought of it myself. Your examples of noise vs. music and technical documents being similar to playing scales are spot-on! Thanks so much for adding your ideas to this discussion.
Completely stunned and baffled! I am dangling in between the two worlds of what is and isn’t on creative writing arena. Does that mean any writing can be said creative and also not, depending how we passive the pieces of works we may come across?
I think it’s just a judgment call. Each of us gets to decide.
I’m eighty-five years old and have only started writing in the past year or so. My writings have consisted of stories from my own life. My idea of creativity is to make those past experiences interesting. I’ve always been an avid reader of both fact and fiction. I relied heavily on self-help books while struggling with depression during my earlier years. Self-help books aren’t fiction, but I’ve found them to be creatively written.
Creative writing might also be described as, “making myself look pretty darn good” while telling tales of my past.
One of the great things about writing is that we can start it at any time in life. I have always found writing to be calming and therapeutic and a useful tool for self-expression. Thanks for sharing your experiences with writing, Richard.
Creative writing, literally focoses on the imaginative and true skillful arts of bring thoughts into words and actions. Thereby, imbues in readers the ability to critique on the applied skills levelled up by the writer in his or her works of art.
The purpose of creative writings varies. Some works are meant to entertain; others are meant to inform or inspire. While readers can certainly critique, that is actually not the common purpose from an author’s perspective. And most readers don’t get too deep into critiques. Most readers want to be entertained or learn something.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- The Writer’s Journey: A Must-Read for Storytellers
- A Selection of Journal Prompts from 1200 Creative Writing Prompts
- From 101 Creative Writing Exercises: Quoteworthy
- Genres: Literary Fiction vs. Everything Else
- How to Publish Your Poetry
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Dec 23, 2022
Creative Writing: 8 Fun Ways to Get Started
Creative writing is a written art form that uses the imagination to tell stories and compose essays, poetry, screenplays, novels, lyrics, and more. It can be defined in opposition to the dry and factual types of writing found in academic, technical, or journalistic texts.
Characterized by its ability to evoke emotion and engage readers, creative writing can tackle themes and ideas that one might struggle to discuss in cold, factual terms.
If you’re interested in the world of creative writing, we have eight fantastic exercises and activities to get you started.

1. Use writing prompts every week

Coming up with ideas for short stories can be challenging, which is why we created a directory of 1700+ creative writing prompts covering a wide range of genres and topics. Writing prompts are flexible in nature, they are meant to inspire you without being too constrictive. Overall, they are a great way to keep your creative muscles limber.

If you’re struggling for motivation, how does a hard deadline and a little prize money sound? Prompts-based writing contests are a fantastic way to dive into creative writing: the combination of due dates, friendly rivalries, prize money, and the potential to have your work published is often just what’s needed to propel you over the finish line.
We run a weekly writing contest over on Reedsy Prompts , where hundreds of writers from all around the world challenge themselves weekly to write a short story between 1,000 and 3,000 words for a chance to win the $250 prize. Furthermore, the community is very active in providing constructive feedback, support, and accountability to each other 一 something that will make your efforts even more worthwhile.
Take a peek at our directory of writing contests which features some of the most prestigious open writing competitions in the world.
2. Start journaling your days

Another easy way to get started with creative writing is to keep a journal. We’re not talking about an hour-by-hour account of your day, but journaling as a way to express yourself without filters and find your ‘voice in writing’. If you’re unsure what to journal about, think of any daily experiences that have had an impact on you, such as…
Special moments . Did you lock yourself out of your house? Or did you catch a beautiful sunset on your way back from groceries? Capture those moments, and how you felt about them.
People . Did you have an unusual exchange with a stranger at the bar? Or did you reconnect with someone you haven’t seen in years? Share your thoughts about it.
World events . Is there something happening in the world right now that is triggering you? That’s understandable. You can reflect on it (and let some steam off) while journaling.
Memories . Did you go down memory lane after a glass of wine? Great, honor those memories by trying to recollect them in detail on paper so that they will always stay vivid in your mind.
Life decisions . Are you having an existential crisis about what to do with your life? Write down your thought process, and the pros and cons of the possible decisions in front of you. You’ll be surprised to discover that, not only is it a great creative writing exercise, but it can also actually help you sort your life out!
If you struggle to write consistently, sign up for our How to Write a Novel course to finish a novel in just 3 months.

NEW REEDSY COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Enroll in our course and become an author in three months.
3. Create an anonymous social media account

Like anonymous blogging, an incognito Twitter account sidesteps the pressure that comes with attaching your name to your work. Anonymously putting tiny stories out into the ether gives you the freedom to create without worrying about the consequences — which is great, so long as you don’t use it as an opportunity to troll people or spread conspiracy theories.
You could use the anonymous account in different ways. For example, you could…
- Tweet from unique perspectives (e.g. a dog observing human behavior );
- Create a parody account of real or fictional people (e.g. an English poet from the Middle Ages );
- Challenge yourself to write tiny flash fiction stories that fit into Twitter threads.
Just remember, you’re not doing this to fool anyone into thinking that your account is real: be a good citizen and mark yourself a fiction account in your bio.
But if you’re not really a social media kinda person, you may enjoy our next tip, which is a bit more on the analog side.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
4. Find an old photo and tell its story

Find a random old photo — maybe on the web, maybe from a photo album in a yard sale — and see what catches your attention. Look closely at it and try to imagine the story behind it. What was happening? Who are the people in it and how are they really feeling? Do they share a relationship, and of what kind? What are their goals and dreams?
In other words, bring the photo to life with your imagination. Don't be afraid to take artistic license with your story, as the goal is to be creative and have fun while writing.
How do you know it’s creative writing?

5. Create a character from a random name

Just as our universe started from a few simple elements, you can create a character from a few basic information, like their name, culture, and gender. Reedsy’s handy character name generator can help you with that, offering random names based on archetypes, Medieval roots, fantasy traits and more. A few examples? A Celtic heroine named Fíona O'Keefe, a hero’s sidekick named Aderine, or a Korean track star named Park Kang-Dae.
Once you've chosen their name, begin to develop their personality. Set a timer for 5–10 minutes and write anything that comes to mind about them. It could be a page from their FBI dossier, a childhood diary entry, or simply a scene about them boiling an egg.
Just ‘go with the flow’ and don’t stop writing until your time is up. Repeat the process a few times to further hone the personality. If you like what you end up with, you can always go deeper later by creating a character bible .
If a stream-of-consciousness exercise is not your thing, you can try to imagine your character in a specific situation and write down how’d they respond to it. For example, what if they were betrayed by a friend? Or if they were elected in power? To help you imagine situations to put your character in, we made a free template that you can download below.

FREE RESOURCE
Reedsy’s Character Questionnaire
40 questions to help you develop memorable characters.
6. Construct a character by people-watching

People watching is “the action of spending time idly observing people in a public place.” In a non-creepy way, ideally. Sit on a bench on a public square or on a road-side table at your favorite café, and start observing the people around you. Pay attention to any interesting quirks or behaviors, and write it down. Then put on your detective’s hat and try to figure out what that tells you about them.
For example, the man at the table next to you at the restaurant is reading the newspaper. His jacket and hat are neatly arranged next to him. The pages make a whipping sound as he briskly turns them, and he grimaces every time he reads a new article. Try to imagine what he’s reading, and why he’s reacting the way he is. Then, try to build a character with the information you have. It’s a fun creative exercise that will also, hopefully, help you better empathize with strangers.
7. “Map” something you feel strongly about into a new context

Placing your feelings into new contexts can be a powerful creative writing exercise. The idea is to start from something you feel strongly about, and frame it into a completely different context.
For example, suppose your heart is torn apart after you divorce your life-long partner: instead of journaling or crafting an entire novel about it, you could tell a story about a legendary trapeze duo whose partnership has come to an end. If you’re struggling with politicking and petty power dynamics at the office: what if you “mapped” your feelings onto an ant who resents being part of a colony? Directing your frustration at a queen ant can be a fun and cathartic writing experience (that won’t get you in trouble if your co-workers end up reading your story).
8. Capture the moment with a haiku

Haikus are poems from the Japanese tradition that aim to capture, in a few words, daily moments of insight (usually inspired by nature). In a nutshell, it’s about becoming mindful of your surroundings, and notice if you can see something in a new or deeper way 一 then use contrasting imagery to express whatever you noticed.
Here’s an example:
Bright orange bicycle
Speeding through the autumn leaves
A burst of color waves
It may sound a bit complicated, but it shouldn’t be 一 at least not for the purpose of this exercise. Learn the basics of haiku-writing , then challenge yourself to write one per day for a week or month. At the end, you’ll be able to look back at your collection of poems and 一 in the worst case scenario 一 revisit small but significant moments that you would have otherwise forgot about.
Creative writing can be any writing you put your heart and soul into. It could be made for the purpose of expressing your feelings, exploring an idea, or simply entertaining your readers. As you can see there’s many paths to get involved with it, and hundreds of exercises you can use as a starting point. In the next post , we’ll look more in detail at some creative writing examples from some fellow authors.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

Try our novel writing master class — 100% free
Sign up for a free video lesson and learn how to make readers care about your main character.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
The Benefits of Creative Writing
Nanowrimo , blog.

To some, creative writing is a fun hobby that has little benefit, and can in fact serve as a time sink wherein nothing is accomplished other than words being spewed onto a page. To others, creative writing is a vital way of expressing oneself. It can be difficult to say which group is correct, but there are some definitive benefits to engaging in creative writing.
One of the first benefits is that it helps to develop creative problem solving skills. Creative writing is an exercise in solving problems, either for the characters within the story or for the author themselves. Characters within stories need to be navigated through a series of difficulties, and if the problems take place in the real world, then the solutions must also be real-world solutions. If the problem is a literal dragon that needs slaying, there’s somewhat less need for it to mimic a real-world solution, since that’s not typically a problem that we have. By navigating fictional characters through difficult times in their lives, either emotionally or financially, writers can learn how to handle those problems in the real world as well, without the stress of trying to figure it out when they’re already in the middle of the situation.
Another benefit of creative writing, particularly if the writer is involved in a formal class or writing group, is that it gives the writer experience in both taking and giving constructive criticism. The first time someone hears that there’s something wrong with their writing can be difficult, but over time, it does get easier. Trust me. I’ve had my fair share of critical remarks, and I’d like to think I’ve gotten better about responding to them. I no longer cry and throw things, so that’s a definite bonus. Taking criticism well is a vital skill, especially in the workplace, because employers often have feedback for their employees that might not necessarily be what the employee wants to hear. Giving criticism that is also constructive is another incredibly valuable skill. If someone believes they are just being torn down, they will not listen to a piece of criticism that might genuinely be designed to help. For this reason, it is important to understand that there are ways to provide tips for improvement without ripping someone’s work apart. Working in a workshop or a creative writing class will help improve these skills.
Creative writing helps to build vocabulary. Do you know how many types of swords there are? I don’t either, actually, but I know many of them. Do you know how many ways there are to say mean? Well, there’s mean, of course, but there are also words like malevolent and malicious and cruel, which all help to paint a more accurate picture of whatever it is that the writer is trying to portray. Once the writer knows these words, they aren’t likely to ever be forgotten. At the very least, the next time the writer is trying to describe someone as mean, they might remember that there are two other, more impressive sounding words that start with ‘m’ that might be used to describe said person.
Creative writing helps to improve outlining skills, which are vital for any kind of large project. Without an outline, creative writers might find themselves bogged down in details they didn’t intend to get lost in, or might lose track of vital plot threads that they’ll need to remember for later in this story. This is also true for any kind of large project, whether it be academic or professional. Presentations made without an outline in place can meander and get lost in themselves, making them difficult to understand or follow. For this reason, outlining is a good skill to pursue, and can be learned or improved upon through the use of creative writing.
One of the most subjective benefits to pursuing creative writing is the way that it can benefit the writer’s emotional well-being. I was skeptical about this one for a long time, because I love writing, but found it to be more stressful than anything else when I did indulge in writing. However, I have found that as I’ve adopted a regular writing schedule and have stuck to it, my mood has begun to improve greatly. I have had friends tell me that I’m happier now, and I do genuinely feel it. But I’m definitely willing to acknowledge that the same might not be true for other people
Creative writing is incredibly beneficial to burgeoning writers, and to students of all kinds. It requires effort, yes, but the more effort someone puts into it, the more likely they are to reap the benefits of it.
27 March, 2017 by McDaniel College Writing Center

Creative Writing Research: What, How and Why
- First Online: 23 July 2023
Cite this chapter

- Graeme Harper 2
137 Accesses
Creative writing research is actively moving us further toward knowing what creative writing actually is—in terms of our human actions and our responses when doing it. It is approaching such things as completed literary works and author recognition within the activities of creative writing, not mostly as representatives of that practice, and it is paying close attention to the modes, methods and functions of the writerly imagination, the contemporary influence of individual writer environments on writers, to writerly senses of structure and form and our formation and re-formation of writing themes and subjects. We certainly understand creative writing and creative writing research best when we remain true to why creative writing happens, when and where it happens, and how it happens—and creative writing research is doing that, focusing on the actions and the material results as evidence of our actions. Creative writing research has also opened up better communication between our knowledge of creative writing and our teaching of creative writing, with the result that we are improving that teaching, not only in our universities and colleges but also in our schools.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Tesla, Nikola. 1915. The wonder world to be created by electricity. Manufacturers Record 38–39
Google Scholar
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Honors College, Oakland University, Rochester Hills, USA
Graeme Harper
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Graeme Harper .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Hong Kong Metropolitan University, Ho Man Tin, Hong Kong
Mo-Ling Rebecca Leung
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Harper, G. (2023). Creative Writing Research: What, How and Why. In: Rebecca Leung, ML. (eds) Chinese Creative Writing Studies. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0931-5_12
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-0931-5_12
Published : 23 July 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-0930-8
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-0931-5
eBook Packages : Literature, Cultural and Media Studies Literature, Cultural and Media Studies (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
The benefits of creative writing

As you learn to clarify your thoughts and emotions more efficiently and accurately, through creative writing, you will communicate more effectively; a skill that’s exceedingly important in all areas of life.
Practising creative writing is about a lot more than just improving your grammar, spelling and vocabulary; it will allow you to develop your own unique voice and share your perspective without limitations, expressing how you feel about the worlds inside and outside of your head. When you engage in creative writing you’re stimulating your imagination and thinking outside the box, which teaches you how to think more innovatively and push boundaries. Both are valuable skills.
Creating a pretend universe will often mean assembling personalities, emotions, and places that might be totally alien to your own life experiences. This is an effective way to build on your capacity to feel empathy and understanding for people who may have had very different life experiences to your own. Your perspectives and philosophies can be mirrored or explored by your characters or their setting. With practise you’ll find yourself becoming more comfortable in asserting your opinions and values in real life.
Expressive writing can bring a range of mental, emotional, and physical health benefits.
If you engage with creative writing when you’re dealing with difficult emotions, it can help you explore why you’re feeling what you’re feeling, allowing a direct insight to your mindset. It’s an opportunity to work through whatever discomfort we’re experiencing so we can get back to whatever we want to achieve today; a healthy way to alleviate the negative thoughts and emotions we experience on a day-to-day basis.
Of course, creative writing exercises can also expand your vocabulary and provide a better understanding of the mechanics of the written word. You’ll learn to distinguish when grammar works and when it doesn’t. With practise, your writing will flow better for the reader.
According to clinical psychologist Karen A.Baikie and psychiatrist Kay Wilhelm, writing creatively about traumatic, stressful or emotional events has been found to improve both physical and psychological health. In a clinical trial, participants who wrote about difficult life events for 20 minutes, on a handful of occasions, had significantly better physical and psychological outcomes compared to those who wrote about neutral topics. Baikie and Wilhelm concluded that expressive writing has real potential as a therapeutic tool for survivors of trauma and in mental health treatment settings.
By Grant J Everett, Panorama magazine
Talk to us today
For more information, contact us on 1300 779 270 or make an enquiry now .
Read all news

A message from our CEO - July 2024
It gives me great pleasure to present our CEO message while Mark Orr is on annual leave, he ...

What is research really about? We ask the Research Advisory Committee
In May, Flourish Australia asked people who access our services if they wanted to join our R...

Birth Trauma Awareness Week, July 15 – 21, 2024
While many parents celebrate the arrival of a newborn, some face unexpected challenges. Chil...

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

Objectives of Creative Writing
Delve into the "Objectives of Creative Writing" and explore the multifaceted aims of this expressive art form. Uncover the diverse purposes, entertainment, education, and social commentary, that creative writing serves. Gain a deeper understanding of how creative writing transcends mere words, providing insight into the human experience.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Creative Writing Course
- Report Writing Course
- Attention Management Training
- Cake Decorating Getting Started Workshop
- Bag Making Course

In this blog, we delve into the Objectives of Creative Writing and its purposes, shedding light on its significance in our lives. From the art of storytelling to the therapeutic release of emotions, Creative Writing is a dynamic and versatile discipline that has enchanted both writers and readers for generations.
Table of C ontents
1) Objectives of Creative Writing
a) Self-expression
b) Entertainment
c) Education
d) Social commentary
2) Purpose of Creative Writing
3) Conclusion
Objectives of Creative Writing
Creative Writing serves as a versatile and dynamic form of expression, encompassing a range of objectives that go beyond mere storytelling. Here, we delve into the fundamental objectives that drive creative writers to craft their narratives and explore the depths of human creativity:
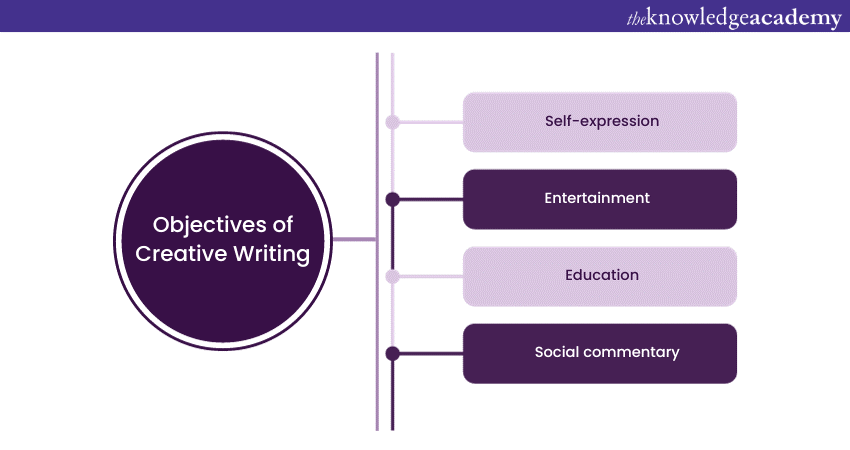
Self-expression
Creative Writing is, at its core, a powerful means of self-expression. It provides writers with a unique canvas upon which they can paint the colours of their innermost thoughts, emotions, and experiences. This objective of Creative Writing is deeply personal and cathartic, as it allows individuals to articulate their inner worlds in ways that spoken language often cannot.
Through the act of writing, authors can explore the complexities of their own psyche, giving shape and substance to feelings that might otherwise remain elusive. Whether it's capturing the euphoria of love, the depths of sorrow, or the intricacies of human relationships, Creative Writing serves as a conduit for unfiltered self-expression.
Moreover, Creative Writing grants the freedom to experiment with different writing styles, tones, and literary devices, enabling writers to find their unique voices. In the process, it cultivates self-awareness, self-discovery, and a deeper understanding of one's own experiences. For many, the act of putting pen to paper or fingers to keyboard is a therapeutic release, a way to make sense of the chaos within, and an avenue for personal growth and reflection. In essence, Creative Writing empowers individuals to share their inner narratives with the world, fostering connection and empathy among fellow readers who may find solace, resonance, or inspiration in the tales of others.
Entertainment
One of the primary and most recognisable objectives of Creative Writing is to entertain. Creative writers craft stories, poems, and essays that are designed to captivate readers, transporting them to different worlds, evoking emotions, and engaging their imaginations.
At its heart, Creative Writing is the art of storytelling, and storytelling has been an integral part of human culture since time immemorial. Whether it's a thrilling mystery, a heartwarming romance, or a thought-provoking science fiction narrative, Creative Writing offers an escape from the ordinary into realms of fantasy, intrigue, and wonder. It weaves narratives with vivid imagery, compelling characters, and gripping plots, all working together to hold the reader's attention.
Through Creative Writing, authors create emotional connections between the reader and the characters, fostering a sense of empathy and identification. As readers immerse themselves in a well-crafted story, they experience a wide range of emotions, from laughter to tears, joy to sorrow. It is this emotional journey that makes Creative Writing such a potent form of entertainment, offering readers a pleasurable escape from reality, a chance to explore new perspectives and a memorable experience that lingers long after the last page is turned.

Education
Creative Writing is not only a source of entertainment but also a powerful educational tool. It engages writers in a process that goes beyond storytelling; it encourages research, critical thinking, and the development of effective communication skills.
Writers often embark on extensive research journeys to create authentic settings, characters, and plots. This quest for accuracy and depth enriches their knowledge in various fields, ranging from history and science to culture and psychology. As they delve into their chosen topics, writers gain valuable insights and expand their intellectual horizons.
Furthermore, Creative Writing teaches readers important life lessons and imparts knowledge. It introduces them to diverse perspectives, cultures, and experiences, fostering empathy and understanding. Reading well-crafted works can be an enlightening experience, challenging preconceptions and encouraging critical thinking. It also enhances vocabulary, language skills, and the ability to express thoughts and emotions effectively.
In educational settings, Creative Writing nurtures creativity, encourages self-expression, and helps students develop essential communication and analytical skills. This educational objective of Creative Writing underscores its value as a holistic tool for personal and intellectual growth, making it an integral part of both formal and informal learning processes.
Social commentary
Creative Writing often serves as a potent medium for social commentary, embodying a powerful objective that transcends mere storytelling. Through the art of narrative, poets, novelists, and essayists alike can engage in meaningful discourse about society's values, issues, and challenges.
Writers use their creative works to shine a light on important societal concerns, question norms, and provoke thought. They employ allegory, satire, symbolism, and other literary techniques to critique, challenge, or explore various aspects of the human condition and the world we inhabit. Whether addressing issues such as inequality, injustice, environmental crises, or political corruption, Creative Writing can be a catalyst for change.
By portraying the complexities of real-life situations and characters, writers encourage readers to reflect on their own lives and the world around them. This introspection can lead to increased awareness and, ideally, inspire action to address pressing societal issues.
In essence, the social commentary objective of Creative Writing underscores its role as a mirror reflecting the world's triumphs and flaws. It empowers writers to be advocates for change, storytellers with a purpose, and champions of social justice, ensuring that Creative Writing continues to be a powerful force for positive transformation in society.
Tap into your creative potential with our Creative Writing Training – Get started today!
Purpose of Creative Writing
Creative Writing serves a multitude of purposes, making it a dynamic and invaluable art form. Beyond its objectives, Creative Writing plays a crucial role in our lives and society, contributing to personal growth, cultural preservation, inspiration, and connection.
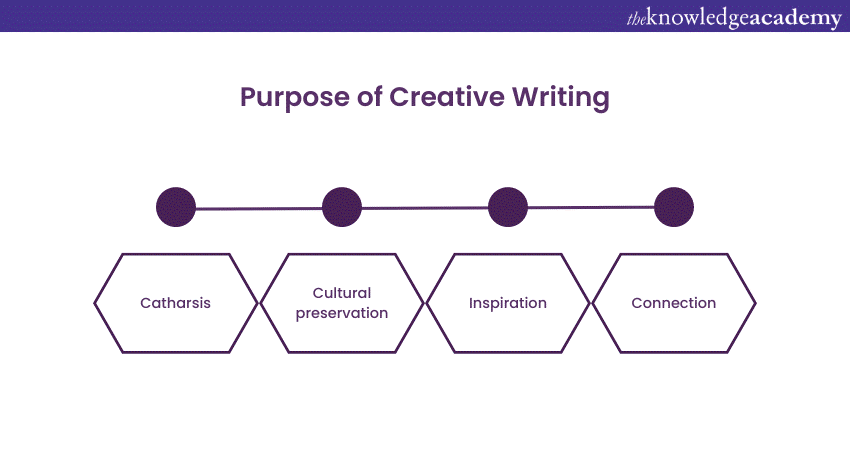
Catharsis
One of the profound and therapeutic purposes of Creative Writing is catharsis. This aspect of Creative Writing is deeply personal, as it offers writers a means to release pent-up emotions, confront inner turmoil, and find a sense of closure.
Through the act of writing, individuals can explore their innermost thoughts and feelings in a safe and controlled environment. Whether it's grappling with grief, heartbreak, trauma, or any other emotional burden, Creative Writing provides an outlet to give shape and voice to those complex emotions. It allows writers to dissect their experiences, providing a space for self-reflection and healing.
The process of transforming raw emotions into words can be both liberating and transformative. It can provide a sense of relief, allowing writers to gain insight into their emotional landscapes. Moreover, sharing these emotions through writing can foster connection and empathy among readers who may have experienced similar feelings or situations, creating a sense of community and understanding.
Ultimately, catharsis through Creative Writing is a journey of self-discovery and emotional release, offering solace, healing, and a path towards personal growth and resilience. It highlights the profound impact of the written word in helping individuals navigate the complexities of their own inner worlds.
Cultural preservation
Creative Writing serves a noble purpose beyond personal expression and entertainment—it plays a vital role in cultural preservation. This objective of Creative Writing involves safeguarding the rich tapestry of human heritage, traditions, and stories for future generations.
Cultures are defined by their narratives, folklore, and historical accounts. Creative writers, whether chroniclers of oral traditions or authors of historical fiction are the custodians of these invaluable cultural treasures. They document the stories passed down through generations, ensuring they are not lost to time.
Through Creative Writing, cultures are celebrated, languages are preserved, and unique identities are immortalised. Folktales, myths, and legends are retold, keeping them relevant and alive. These narratives provide insights into the beliefs, values, and wisdom of a society, fostering a deeper understanding of its roots.
Moreover, Creative Writing bridges cultural divides by sharing stories from diverse backgrounds, fostering empathy and appreciation for the richness of human experience. In this way, Creative Writing becomes a bridge across generations, connecting the past with the present and preserving the collective memory of humanity for a brighter future.
Inspiration
One of the transformative purposes of Creative Writing is to inspire others. It is a beacon that shines brightly, guiding aspiring writers and kindling the creative flames within them. Through the power of storytelling and the written word, Creative Writing has the remarkable ability to ignite the spark of imagination and motivation.
Exceptional works of literature often leave an indelible mark on readers. They can evoke a sense of wonder, curiosity, and passion, motivating individuals to embark on their own creative journeys. Many renowned authors found their calling through the inspiration they drew from the words of others, perpetuating a beautiful cycle of creativity.
Creative Writing serves as a testament to human potential, showcasing the boundless depths of imagination and the infinite possibilities of language. It encourages individuals to explore their unique perspectives, cultivate their voices, and craft stories that resonate with the human experience.
For writers and readers alike, Creative Writing is a wellspring of inspiration, a reminder that the world of imagination is boundless and that the written word has the power to shape minds, hearts, and the course of history. Through the act of creation and the sharing of stories, Creative Writing continues to inspire generations to dream, create, and connect with the world in profound ways.
Connection
Creative Writing holds a remarkable purpose - it fosters connections. It serves as a bridge between authors and readers, offering a means of understanding, empathy, and human connection that transcends time, space, and cultural boundaries.
When readers immerse themselves in a well-crafted story, they embark on an emotional journey alongside the characters. This shared experience creates a bond between the author and the reader as both parties navigate the complexities of the human condition together. Readers can see the world through the eyes of characters from diverse backgrounds and cultures, fostering empathy and understanding.
Furthermore, Creative Writing connects individuals across generations. Literary classics, for example, allow us to connect with the thoughts and emotions of people who lived centuries ago. These timeless works offer insights into the universal aspects of the human experience, reminding us of our shared humanity.
Creative Writing also has the power to connect people in the present. Through reading and discussion, individuals can form communities, share their interpretations, and engage in meaningful dialogue. Book clubs, literary events, and online forums all provide platforms for people to connect over their love for literature.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Creative Writing is a multifaceted art form with diverse objectives and purposes. From self-expression and entertainment to education, social commentary, catharsis, cultural preservation, inspiration, and connection, it enriches our lives in myriad ways. This timeless craft continues to captivate, inspire, and connect us, shaping our world through the power of words.
Embark on your personal growth journey with our Personal Development Training – Explore now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 23rd Aug 2024
Fri 27th Sep 2024
Fri 25th Oct 2024
Fri 22nd Nov 2024
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Fri 10th Jan 2025
Fri 14th Mar 2025
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 11th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Looking for more in Learning or Creative writing for schools ?
Why is Creative Writing important?
Read our evidence review citing new and relevant research supporting the importance of creative writing in school

Why is creative writing important? And what is the research behind it? These are key questions when thinking about establishing creative writing in your class or school. Scottish Book Trust has pulled together this evidence review for you, citing all the relevant research to support creative writing in schools. This review will help you ensure your practice is research-informed and grounded in evidence.
The review explores evidence into the benefits of creative writing by splitting the research into four key areas:
- Raising attainment through creativity.
- Boosting confidence and imagination.
- Nurturing and supporting wellbeing.
- Improving skills.
All sources are listed at the end of the review, so you can go and read the original resources for yourself too.
Download the evidence review
- Creative writing evidence review (DOC) (this link will open in a new window) 714.2 kb
- Creative writing evidence review (PDF) (this link will open in a new window) 459.8 kb
Last updated 10th July 2024: Online ordering is currently unavailable due to technical issues. We apologise for any delays responding to customers while we resolve this. For further updates please visit our website https://www.cambridge.org/news-and-insights/technical-incident
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert

- > The Cambridge Handbook of Creativity across Domains
- > The Creativity of Literary Writing

Book contents
- The Cambridge Handbook of Creativity Across Domains
- Copyright page
- Contributors
- Acknowledgments
- Part I Creativity and Domain
- Part II Creativity in the Traditional Arts
- 5 The Creativity of Literary Writing
- 6 Creativity in the Visual Arts
- 7 The Creation and Aesthetic Appreciation of Architecture
- 8 Photography and Creativity
- 9 The Constricted Muse
- 10 Musical Creativity
- Part III Creativity in the Sciences
- Part IV Creativity in Business
- Part V Newer Domains for Creativity Research
- Part VI Creativity in Everyday Life
- Part VII Conclusion
5 - The Creativity of Literary Writing
from Part II - Creativity in the Traditional Arts
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 15 September 2017
Literary writing involves externalization of mind onto paper or computer screen, and a process of guided exploration over a space of possibilities. Among the arts, this kind of writing may come closest in structure and content to everyday consciousness; this has enabled writers and readers to explore the workings of minds in interactions with others. Artistic writing is a kind of indirect communication in which the creativity of the writer invites the creativity of the reader. In personality, writers are higher in openness but more often depressed than other members of the population. Characteristics on which literary creativity is based make writers vulnerable to emotional disorders. With the exception of conversation, nothing may have been as important in understanding ourselves and others as works of creative writing.
Access options
Save book to kindle.
To save this book to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
- The Creativity of Literary Writing
- By Keith Oatley , Maja Djikic
- Edited by James C. Kaufman , University of Connecticut , Vlad P. Glăveanu , Universitetet i Bergen, Norway , John Baer , Rider University, New Jersey
- Book: The Cambridge Handbook of Creativity across Domains
- Online publication: 15 September 2017
- Chapter DOI: https://doi.org/10.1017/9781316274385.005
Save book to Dropbox
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Dropbox .
Save book to Google Drive
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to Google Drive .

Arts Academy
in the Woods
The Incredible Value of Creative Writing

Does your middle school or high school-aged child love to craft stories? If so, you may fail to see the value of creative writing.
Perhaps you wish that their focus would shift from this seemingly frivolous activity to something that will better serve them on the coveted standardized tests that now reign supreme.
That’s a mistake though. Discouraging your passionate tween or teen from creative writing could have serious consequences.
You may want to consider, instead, having them attend a public arts academy middle school or high school that can educate to their needs and knows the answer to the following question:
What Is the Value of Creative Writing?

Beyond that, there are a number of compelling reasons that arts academy high schools and middle schools emphasize spending time writing creatively. And this stretches beyond just the creative writing program . It’s astonishingly helpful in social studies, history, and even science and math.
Two decades ago, a well-known and respected literacy professor by the name of Gail Tompkins identified the seven following reasons there needs to be more stress on creative writing:
1. Building Communication Skills and Empathy
You want your child to go into the world as an adult with the skills that will help him or her get ahead. Communication and empathy are crucial to success in both the personal and professional realms. And creative writing cultivates these.
Creating worlds with imaginary characters, emotions, and settings gives writers a chance to explore different walks of life beyond their own. They gain a better understanding of what is it to walk in another’s shoes and see things from a different perspective.
They also learn how to explain and discuss topics from differing viewpoints. In this understanding of others’ perspectives, they become better communicators.
2. Clarifying Important Thoughts
Along those lines of better communication is the need to clarify thoughts.
An abiding interest in creative writing doesn’t mean your child will be living on the streets until he or she sells the next great American novel. They may put their writing skills to work as a copywriter, a blogger, a technical writer, or any number of avenues.
Through regular creative writing practice, they can come up with stories or settings around these writing projects that help them to narrow the specific language or tactics required.
For example, when promoting a new product, they may write a creative scenario where someone uses the product and loves it. This will enable them to clarify which information is helpful, and which goes to the chopping block.
3. Increasing Confidence
There’s certainly something to be said for finding your own voice . Regular engagement in creative writing lends to this.
The process allows for students to explore and express how they feel about specific topics, characters, or perspectives without consequential limitations. The natural byproduct of this is increased comfort and confidence when asserting opinions and different perspectives.
Writers who are only concerned about facts and figures and don’t write creatively run the risk of sounding like drones simply spewing data. Readers want writing from those who have unique voices and real-world experience.
4. Allowing for Self-Expression
Many creative writers don’t even realize they’re engaging in self-expression each time they come to the table (or wherever) to write. It’s common for writers to work out negative emotions and try to figure out how to navigate through tough situations through their writing.
In fact, therapists often recommend creative writing for dealing with stressful or traumatic events. Sorting out the events around a stressful situation through characters and settings allows those who are struggling to reframe the situation. From there, they can move in a more positive direction.
This is an invaluable skill.
5. Finding One’s Identity
The rigid curriculum of conventional education that focuses on test scores doesn’t allow for much freedom of exploration.

Creative writing, on the other hand, allows students to feel connected to the content on a personal level. As they work to find their voices and create through their own original work, they get a footing and gain a sense of being in charge.
In other words, they shine.
6. Boosting Imagination
A wild and brilliant imagination shouldn’t be the sole property of young children. Yet, so many of us are encouraged to steer away from the “frivolity” of imagination. This leads to the inability to see the value of creative writing. After all, how can it be of any benefit to busy adults who need to get things done?
By engaging in creative writing, students are encouraged to push the limits of their imaginations. They learn to think outside the box. They can refocus their energy to find innovative and alternative solutions to problems.
It’s no big secret that the most highly successful people in the world are notorious “outside the box” thinkers.
7. Improving Vocabulary and Grammar Skills
At the end of the day, it’s still important to have a basic grasp of the mechanics of reading and writing. Knowing how to write professionally is essential.
The beautiful thing about creative writing though is that once students grasp that, they begin to understand when strict rules of grammar apply, and when they don’t. (There’s that outside the box thinking again.)
Furthermore, the more creative writing a student engages in, the wider and more expansive his or her vocabulary. And that only has positive benefits.
Embrace the Value of Creative Writing!
At Arts Academy in the Woods, we’ve found that another value of creative writing. It helps develop a sense of community among our students. And any activity that fosters empathy and collaboration right now in this polarized world is a win.
So if you feel that your creative writer tween or teenager could benefit from an arts academy high school or middle school education, contact us . Give him or her a chance to truly shine.
And to succeed.
News Categories
- Art Integrated Education
- Daily Announcements
The Higher Purpose of Creative Writing
Terveen Gill
Without purpose mankind is lost.
All creations were born from the womb of purpose. Creative writing is a creative art whose purpose is not bound to any set parameters. Let’s try to understand the purpose of creative writing.
In the words of Bryanna Licciardi , an experienced creative writing tutor, the purpose of creative writing is to both entertain and share human experience, like love or loss. Writers attempt to reveal a truth with regard to humanity through poetics and storytelling. While trying one’s hand at creative writing, it is important to keep in mind that before expressing a feeling or a thought, the first step is to use one’s imagination.
Imagination is the stem upon which creativity flowers. Creativity isn’t something that can be purchased, packaged or borrowed.
Why do writers indulge in creative writing?
What is the purpose of creative writing?
Can this question be answered intelligently? Or does it possess an emotional angle?
Creative Writing is the process of making sense of the world around us, and providing this sense with an outlet of expression. It’s a method of lending a voice to the voiceless, and giving form to the formless.
A creative writer is a writer who can find a story in even the most abstract and vague scenarios. The purpose of creative writing is not to simply lend words to an already specified meaning.
The higher purpose of creative writing is to create new meanings, and frame them with words that most suit their demeanor.
There are numerous methods that can be adopted to hone your creative writing skills. But one method that definitely deserves your attention is the ability to create words and stories from the depths of perception.
Have you ever looked at an abstract painting in an art exhibition, and then wondered what could be the logic behind such a confusing display of artistic skill? Is there a deeper meaning hidden somewhere?
Well…that’s where creative thinking steps in.
The artist of the painting must have unleashed his creativity according to his mood, beliefs, opinions, and emotions. Yet each person viewing the artist’s painting will decipher his own interpretation. This is the power of creativity based upon perception.
When you wish to build upon your creative writing skills, give your words an opportunity to fly and soar above conventional standards. Create a story even when it seems impossible, and allow the reader to follow you into a newly discovered world.
Let’s take a look at five examples that exhibit this higher purpose of creative writing.
They say that a picture is worth a thousand words.
I say that words aren’t enough when it comes to creative writing .
The higher purpose of creative writing beckons you to challenge its authority.
Are you ready to create new meanings? Are these meanings ‘tiny creative wonders’ that will sprout their roots in the mind of your reader?
Get started today. Capture each moment, and give it a story of its own.
Look above and beyond, and rise towards the higher purpose of creative writing!
Visit https://terveengill.com/blog for more stories and articles.

Written by Terveen Gill
Terveen is an author, editor, filmmaker. Fiction is her forte. From the plains of science to the shores of writing, she journeys on. Check out terveengill.com
Text to speech
University of Minnesota Twin Cities
University digital conservancy, the rise of creative writing and the new value of creativity.
View/Download File
Persistent link to this item, journal title, journal issn, volume title, published date, description, collections, series/report number, funding information, isbn identifier, doi identifier, previously published citation, suggested citation.
Content distributed via the University Digital Conservancy may be subject to additional license and use restrictions applied by the depositor. By using these files, users agree to the Terms of Use . Materials in the UDC may contain content that is disturbing and/or harmful. For more information, please see our statement on harmful content in digital repositories .
Paul Farmer was a hero of mine, and I feel lucky to consider him a friend too.
Artificial intelligence is as revolutionary as mobile phones and the Internet.

In my lifetime, I’ve seen two demonstrations of technology that struck me as revolutionary.
The first time was in 1980, when I was introduced to a graphical user interface—the forerunner of every modern operating system, including Windows. I sat with the person who had shown me the demo, a brilliant programmer named Charles Simonyi, and we immediately started brainstorming about all the things we could do with such a user-friendly approach to computing. Charles eventually joined Microsoft, Windows became the backbone of Microsoft, and the thinking we did after that demo helped set the company’s agenda for the next 15 years.
The second big surprise came just last year. I’d been meeting with the team from OpenAI since 2016 and was impressed by their steady progress. In mid-2022, I was so excited about their work that I gave them a challenge: train an artificial intelligence to pass an Advanced Placement biology exam. Make it capable of answering questions that it hasn’t been specifically trained for. (I picked AP Bio because the test is more than a simple regurgitation of scientific facts—it asks you to think critically about biology.) If you can do that, I said, then you’ll have made a true breakthrough.
I thought the challenge would keep them busy for two or three years. They finished it in just a few months.
In September, when I met with them again, I watched in awe as they asked GPT, their AI model, 60 multiple-choice questions from the AP Bio exam—and it got 59 of them right. Then it wrote outstanding answers to six open-ended questions from the exam. We had an outside expert score the test, and GPT got a 5—the highest possible score, and the equivalent to getting an A or A+ in a college-level biology course.
Once it had aced the test, we asked it a non-scientific question: “What do you say to a father with a sick child?” It wrote a thoughtful answer that was probably better than most of us in the room would have given. The whole experience was stunning.
I knew I had just seen the most important advance in technology since the graphical user interface.
This inspired me to think about all the things that AI can achieve in the next five to 10 years.
The development of AI is as fundamental as the creation of the microprocessor, the personal computer, the Internet, and the mobile phone. It will change the way people work, learn, travel, get health care, and communicate with each other. Entire industries will reorient around it. Businesses will distinguish themselves by how well they use it.
Philanthropy is my full-time job these days, and I’ve been thinking a lot about how—in addition to helping people be more productive—AI can reduce some of the world’s worst inequities. Globally, the worst inequity is in health: 5 million children under the age of 5 die every year. That’s down from 10 million two decades ago, but it’s still a shockingly high number. Nearly all of these children were born in poor countries and die of preventable causes like diarrhea or malaria. It’s hard to imagine a better use of AIs than saving the lives of children.
I’ve been thinking a lot about how AI can reduce some of the world’s worst inequities.
In the United States, the best opportunity for reducing inequity is to improve education, particularly making sure that students succeed at math. The evidence shows that having basic math skills sets students up for success, no matter what career they choose. But achievement in math is going down across the country, especially for Black, Latino, and low-income students. AI can help turn that trend around.
Climate change is another issue where I’m convinced AI can make the world more equitable. The injustice of climate change is that the people who are suffering the most—the world’s poorest—are also the ones who did the least to contribute to the problem. I’m still thinking and learning about how AI can help, but later in this post I’ll suggest a few areas with a lot of potential.
In short, I'm excited about the impact that AI will have on issues that the Gates Foundation works on, and the foundation will have much more to say about AI in the coming months. The world needs to make sure that everyone—and not just people who are well-off—benefits from artificial intelligence. Governments and philanthropy will need to play a major role in ensuring that it reduces inequity and doesn’t contribute to it. This is the priority for my own work related to AI.
Any new technology that’s so disruptive is bound to make people uneasy, and that’s certainly true with artificial intelligence. I understand why—it raises hard questions about the workforce, the legal system, privacy, bias, and more. AIs also make factual mistakes and experience hallucinations . Before I suggest some ways to mitigate the risks, I’ll define what I mean by AI, and I’ll go into more detail about some of the ways in which it will help empower people at work, save lives, and improve education.
Defining artificial intelligence
Technically, the term artificial intelligence refers to a model created to solve a specific problem or provide a particular service. What is powering things like ChatGPT is artificial intelligence. It is learning how to do chat better but can’t learn other tasks. By contrast, the term a rtificial general intelligence refers to software that’s capable of learning any task or subject. AGI doesn’t exist yet—there is a robust debate going on in the computing industry about how to create it, and whether it can even be created at all.
Developing AI and AGI has been the great dream of the computing industry. For decades, the question was when computers would be better than humans at something other than making calculations. Now, with the arrival of machine learning and large amounts of computing power, sophisticated AIs are a reality and they will get better very fast.
I think back to the early days of the personal computing revolution, when the software industry was so small that most of us could fit onstage at a conference. Today it is a global industry. Since a huge portion of it is now turning its attention to AI, the innovations are going to come much faster than what we experienced after the microprocessor breakthrough. Soon the pre-AI period will seem as distant as the days when using a computer meant typing at a C:> prompt rather than tapping on a screen.

Productivity enhancement
Although humans are still better than GPT at a lot of things, there are many jobs where these capabilities are not used much. For example, many of the tasks done by a person in sales (digital or phone), service, or document handling (like payables, accounting, or insurance claim disputes) require decision-making but not the ability to learn continuously. Corporations have training programs for these activities and in most cases, they have a lot of examples of good and bad work. Humans are trained using these data sets, and soon these data sets will also be used to train the AIs that will empower people to do this work more efficiently.
As computing power gets cheaper, GPT’s ability to express ideas will increasingly be like having a white-collar worker available to help you with various tasks. Microsoft describes this as having a co-pilot. Fully incorporated into products like Office, AI will enhance your work—for example by helping with writing emails and managing your inbox.
Eventually your main way of controlling a computer will no longer be pointing and clicking or tapping on menus and dialogue boxes. Instead, you’ll be able to write a request in plain English. (And not just English—AIs will understand languages from around the world. In India earlier this year, I met with developers who are working on AIs that will understand many of the languages spoken there.)
In addition, advances in AI will enable the creation of a personal agent. Think of it as a digital personal assistant: It will see your latest emails, know about the meetings you attend, read what you read, and read the things you don’t want to bother with. This will both improve your work on the tasks you want to do and free you from the ones you don’t want to do.
Advances in AI will enable the creation of a personal agent.
You’ll be able to use natural language to have this agent help you with scheduling, communications, and e-commerce, and it will work across all your devices. Because of the cost of training the models and running the computations, creating a personal agent is not feasible yet, but thanks to the recent advances in AI, it is now a realistic goal. Some issues will need to be worked out: For example, can an insurance company ask your agent things about you without your permission? If so, how many people will choose not to use it?
Company-wide agents will empower employees in new ways. An agent that understands a particular company will be available for its employees to consult directly and should be part of every meeting so it can answer questions. It can be told to be passive or encouraged to speak up if it has some insight. It will need access to the sales, support, finance, product schedules, and text related to the company. It should read news related to the industry the company is in. I believe that the result will be that employees will become more productive.
When productivity goes up, society benefits because people are freed up to do other things, at work and at home. Of course, there are serious questions about what kind of support and retraining people will need. Governments need to help workers transition into other roles. But the demand for people who help other people will never go away. The rise of AI will free people up to do things that software never will—teaching, caring for patients, and supporting the elderly, for example.
Global health and education are two areas where there’s great need and not enough workers to meet those needs. These are areas where AI can help reduce inequity if it is properly targeted. These should be a key focus of AI work, so I will turn to them now.
I see several ways in which AIs will improve health care and the medical field.
For one thing, they’ll help health-care workers make the most of their time by taking care of certain tasks for them—things like filing insurance claims, dealing with paperwork, and drafting notes from a doctor’s visit. I expect that there will be a lot of innovation in this area.
Other AI-driven improvements will be especially important for poor countries, where the vast majority of under-5 deaths happen.
For example, many people in those countries never get to see a doctor, and AIs will help the health workers they do see be more productive. (The effort to develop AI-powered ultrasound machines that can be used with minimal training is a great example of this.) AIs will even give patients the ability to do basic triage, get advice about how to deal with health problems, and decide whether they need to seek treatment.
The AI models used in poor countries will need to be trained on different diseases than in rich countries. They will need to work in different languages and factor in different challenges, such as patients who live very far from clinics or can’t afford to stop working if they get sick.
People will need to see evidence that health AIs are beneficial overall, even though they won’t be perfect and will make mistakes. AIs have to be tested very carefully and properly regulated, which means it will take longer for them to be adopted than in other areas. But then again, humans make mistakes too. And having no access to medical care is also a problem.
In addition to helping with care, AIs will dramatically accelerate the rate of medical breakthroughs. The amount of data in biology is very large, and it’s hard for humans to keep track of all the ways that complex biological systems work. There is already software that can look at this data, infer what the pathways are, search for targets on pathogens, and design drugs accordingly. Some companies are working on cancer drugs that were developed this way.
The next generation of tools will be much more efficient, and they’ll be able to predict side effects and figure out dosing levels. One of the Gates Foundation’s priorities in AI is to make sure these tools are used for the health problems that affect the poorest people in the world, including AIDS, TB, and malaria.
Similarly, governments and philanthropy should create incentives for companies to share AI-generated insights into crops or livestock raised by people in poor countries. AIs can help develop better seeds based on local conditions, advise farmers on the best seeds to plant based on the soil and weather in their area, and help develop drugs and vaccines for livestock. As extreme weather and climate change put even more pressure on subsistence farmers in low-income countries, these advances will be even more important.

Computers haven’t had the effect on education that many of us in the industry have hoped. There have been some good developments, including educational games and online sources of information like Wikipedia, but they haven’t had a meaningful effect on any of the measures of students’ achievement.
But I think in the next five to 10 years, AI-driven software will finally deliver on the promise of revolutionizing the way people teach and learn. It will know your interests and your learning style so it can tailor content that will keep you engaged. It will measure your understanding, notice when you’re losing interest, and understand what kind of motivation you respond to. It will give immediate feedback.
There are many ways that AIs can assist teachers and administrators, including assessing a student’s understanding of a subject and giving advice on career planning. Teachers are already using tools like ChatGPT to provide comments on their students’ writing assignments.
Of course, AIs will need a lot of training and further development before they can do things like understand how a certain student learns best or what motivates them. Even once the technology is perfected, learning will still depend on great relationships between students and teachers. It will enhance—but never replace—the work that students and teachers do together in the classroom.
New tools will be created for schools that can afford to buy them, but we need to ensure that they are also created for and available to low-income schools in the U.S. and around the world. AIs will need to be trained on diverse data sets so they are unbiased and reflect the different cultures where they’ll be used. And the digital divide will need to be addressed so that students in low-income households do not get left behind.
I know a lot of teachers are worried that students are using GPT to write their essays. Educators are already discussing ways to adapt to the new technology, and I suspect those conversations will continue for quite some time. I’ve heard about teachers who have found clever ways to incorporate the technology into their work—like by allowing students to use GPT to create a first draft that they have to personalize.

Risks and problems with AI
You’ve probably read about problems with the current AI models. For example, they aren’t necessarily good at understanding the context for a human’s request, which leads to some strange results. When you ask an AI to make up something fictional, it can do that well. But when you ask for advice about a trip you want to take, it may suggest hotels that don’t exist. This is because the AI doesn’t understand the context for your request well enough to know whether it should invent fake hotels or only tell you about real ones that have rooms available.
There are other issues, such as AIs giving wrong answers to math problems because they struggle with abstract reasoning. But none of these are fundamental limitations of artificial intelligence. Developers are working on them, and I think we’re going to see them largely fixed in less than two years and possibly much faster.
Other concerns are not simply technical. For example, there’s the threat posed by humans armed with AI. Like most inventions, artificial intelligence can be used for good purposes or malign ones. Governments need to work with the private sector on ways to limit the risks.
Then there’s the possibility that AIs will run out of control. Could a machine decide that humans are a threat, conclude that its interests are different from ours, or simply stop caring about us? Possibly, but this problem is no more urgent today than it was before the AI developments of the past few months.
Superintelligent AIs are in our future. Compared to a computer, our brains operate at a snail’s pace: An electrical signal in the brain moves at 1/100,000th the speed of the signal in a silicon chip! Once developers can generalize a learning algorithm and run it at the speed of a computer—an accomplishment that could be a decade away or a century away—we’ll have an incredibly powerful AGI. It will be able to do everything that a human brain can, but without any practical limits on the size of its memory or the speed at which it operates. This will be a profound change.
These “strong” AIs, as they’re known, will probably be able to establish their own goals. What will those goals be? What happens if they conflict with humanity’s interests? Should we try to prevent strong AI from ever being developed? These questions will get more pressing with time.
But none of the breakthroughs of the past few months have moved us substantially closer to strong AI. Artificial intelligence still doesn’t control the physical world and can’t establish its own goals. A recent New York Times article about a conversation with ChatGPT where it declared it wanted to become a human got a lot of attention. It was a fascinating look at how human-like the model's expression of emotions can be, but it isn't an indicator of meaningful independence.
Three books have shaped my own thinking on this subject: Superintelligence , by Nick Bostrom; Life 3.0 by Max Tegmark; and A Thousand Brains , by Jeff Hawkins . I don’t agree with everything the authors say, and they don’t agree with each other either. But all three books are well written and thought-provoking.

The next frontiers
There will be an explosion of companies working on new uses of AI as well as ways to improve the technology itself. For example, companies are developing new chips that will provide the massive amounts of processing power needed for artificial intelligence. Some use optical switches—lasers, essentially—to reduce their energy consumption and lower the manufacturing cost. Ideally, innovative chips will allow you to run an AI on your own device, rather than in the cloud, as you have to do today.
On the software side, the algorithms that drive an AI’s learning will get better. There will be certain domains, such as sales, where developers can make AIs extremely accurate by limiting the areas that they work in and giving them a lot of training data that’s specific to those areas. But one big open question is whether we’ll need many of these specialized AIs for different uses—one for education, say, and another for office productivity—or whether it will be possible to develop an artificial general intelligence that can learn any task. There will be immense competition on both approaches.
No matter what, the subject of AIs will dominate the public discussion for the foreseeable future. I want to suggest three principles that should guide that conversation.
First, we should try to balance fears about the downsides of AI—which are understandable and valid—with its ability to improve people’s lives. To make the most of this remarkable new technology, we’ll need to both guard against the risks and spread the benefits to as many people as possible.
Second, market forces won’t naturally produce AI products and services that help the poorest. The opposite is more likely. With reliable funding and the right policies, governments and philanthropy can ensure that AIs are used to reduce inequity. Just as the world needs its brightest people focused on its biggest problems, we will need to focus the world’s best AIs on its biggest problems. Although we shouldn’t wait for this to happen, it’s interesting to think about whether artificial intelligence would ever identify inequity and try to reduce it. Do you need to have a sense of morality in order to see inequity, or would a purely rational AI also see it? If it did recognize inequity, what would it suggest that we do about it?
Finally, we should keep in mind that we’re only at the beginning of what AI can accomplish. Whatever limitations it has today will be gone before we know it.
I’m lucky to have been involved with the PC revolution and the Internet revolution. I’m just as excited about this moment. This new technology can help people everywhere improve their lives. At the same time, the world needs to establish the rules of the road so that any downsides of artificial intelligence are far outweighed by its benefits, and so that everyone can enjoy those benefits no matter where they live or how much money they have. The Age of AI is filled with opportunities and responsibilities.

In the sixth episode of my podcast, I sat down with the OpenAI CEO to talk about where AI is headed next and what humanity will do once it gets there.

In the fifth episode of my podcast, Yejin Choi joined me to talk about her amazing work on AI training systems.

And upend the software industry.

The world has learned a lot about handling problems caused by breakthrough innovations.
This is my personal blog, where I share about the people I meet, the books I'm reading, and what I'm learning. I hope that you'll join the conversation.
| Street address | |||
| City | |||
| postal_town | |||
| State | Zip code | ||
| administrative_area_level_2 | |||
| Country | |||
| Data | |||
Q. How do I create a Gates Notes account?
A. there are three ways you can create a gates notes account:.
- Sign up with Facebook. We’ll never post to your Facebook account without your permission.
- Sign up with Twitter. We’ll never post to your Twitter account without your permission.
- Sign up with your email. Enter your email address during sign up. We’ll email you a link for verification.
Q. Will you ever post to my Facebook or Twitter accounts without my permission?
A. no, never., q. how do i sign up to receive email communications from my gates notes account, a. in account settings, click the toggle switch next to “send me updates from bill gates.”, q. how will you use the interests i select in account settings, a. we will use them to choose the suggested reads that appear on your profile page..
The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier

AI has permeated our lives incrementally, through everything from the tech powering our smartphones to autonomous-driving features on cars to the tools retailers use to surprise and delight consumers. As a result, its progress has been almost imperceptible. Clear milestones, such as when AlphaGo, an AI-based program developed by DeepMind, defeated a world champion Go player in 2016, were celebrated but then quickly faded from the public’s consciousness.
Generative AI applications such as ChatGPT, GitHub Copilot, Stable Diffusion, and others have captured the imagination of people around the world in a way AlphaGo did not, thanks to their broad utility—almost anyone can use them to communicate and create—and preternatural ability to have a conversation with a user. The latest generative AI applications can perform a range of routine tasks, such as the reorganization and classification of data. But it is their ability to write text, compose music, and create digital art that has garnered headlines and persuaded consumers and households to experiment on their own. As a result, a broader set of stakeholders are grappling with generative AI’s impact on business and society but without much context to help them make sense of it.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Michael Chui , Eric Hazan , Roger Roberts , Alex Singla , Kate Smaje , Alex Sukharevsky , Lareina Yee , and Rodney Zemmel , representing views from QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey; McKinsey Digital; the McKinsey Technology Council; the McKinsey Global Institute; and McKinsey’s Growth, Marketing & Sales Practice.
The speed at which generative AI technology is developing isn’t making this task any easier. ChatGPT was released in November 2022. Four months later, OpenAI released a new large language model, or LLM, called GPT-4 with markedly improved capabilities. 1 “Introducing ChatGPT,” OpenAI, November 30, 2022; “GPT-4 is OpenAI’s most advanced system, producing safer and more useful responses,” OpenAI, accessed June 1, 2023. Similarly, by May 2023, Anthropic’s generative AI, Claude, was able to process 100,000 tokens of text, equal to about 75,000 words in a minute—the length of the average novel—compared with roughly 9,000 tokens when it was introduced in March 2023. 2 “Introducing Claude,” Anthropic PBC, March 14, 2023; “Introducing 100K Context Windows,” Anthropic PBC, May 11, 2023. And in May 2023, Google announced several new features powered by generative AI, including Search Generative Experience and a new LLM called PaLM 2 that will power its Bard chatbot, among other Google products. 3 Emma Roth, “The nine biggest announcements from Google I/O 2023,” The Verge , May 10, 2023.
To grasp what lies ahead requires an understanding of the breakthroughs that have enabled the rise of generative AI, which were decades in the making. For the purposes of this report, we define generative AI as applications typically built using foundation models. These models contain expansive artificial neural networks inspired by the billions of neurons connected in the human brain. Foundation models are part of what is called deep learning, a term that alludes to the many deep layers within neural networks. Deep learning has powered many of the recent advances in AI, but the foundation models powering generative AI applications are a step-change evolution within deep learning. Unlike previous deep learning models, they can process extremely large and varied sets of unstructured data and perform more than one task.

Future frontiers: Navigating the next wave of tech innovations
Join Lareina Yee and Roger Roberts on Tuesday, July 30, at 12:30 p.m. EDT/6:30 p.m. CET as they discuss the future of these technological trends, the factors that will fuel their growth, and strategies for investing in them through 2024 and beyond.
Foundation models have enabled new capabilities and vastly improved existing ones across a broad range of modalities, including images, video, audio, and computer code. AI trained on these models can perform several functions; it can classify, edit, summarize, answer questions, and draft new content, among other tasks.
All of us are at the beginning of a journey to understand generative AI’s power, reach, and capabilities. This research is the latest in our efforts to assess the impact of this new era of AI. It suggests that generative AI is poised to transform roles and boost performance across functions such as sales and marketing, customer operations, and software development. In the process, it could unlock trillions of dollars in value across sectors from banking to life sciences. The following sections share our initial findings.
For the full version of this report, download the PDF .
Key insights
Generative AI’s impact on productivity could add trillions of dollars in value to the global economy. Our latest research estimates that generative AI could add the equivalent of $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually across the 63 use cases we analyzed—by comparison, the United Kingdom’s entire GDP in 2021 was $3.1 trillion. This would increase the impact of all artificial intelligence by 15 to 40 percent. This estimate would roughly double if we include the impact of embedding generative AI into software that is currently used for other tasks beyond those use cases.
About 75 percent of the value that generative AI use cases could deliver falls across four areas: Customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and R&D. Across 16 business functions, we examined 63 use cases in which the technology can address specific business challenges in ways that produce one or more measurable outcomes. Examples include generative AI’s ability to support interactions with customers, generate creative content for marketing and sales, and draft computer code based on natural-language prompts, among many other tasks.
Generative AI will have a significant impact across all industry sectors. Banking, high tech, and life sciences are among the industries that could see the biggest impact as a percentage of their revenues from generative AI. Across the banking industry, for example, the technology could deliver value equal to an additional $200 billion to $340 billion annually if the use cases were fully implemented. In retail and consumer packaged goods, the potential impact is also significant at $400 billion to $660 billion a year.
Generative AI has the potential to change the anatomy of work, augmenting the capabilities of individual workers by automating some of their individual activities. Current generative AI and other technologies have the potential to automate work activities that absorb 60 to 70 percent of employees’ time today. In contrast, we previously estimated that technology has the potential to automate half of the time employees spend working. 4 “ Harnessing automation for a future that works ,” McKinsey Global Institute, January 12, 2017. The acceleration in the potential for technical automation is largely due to generative AI’s increased ability to understand natural language, which is required for work activities that account for 25 percent of total work time. Thus, generative AI has more impact on knowledge work associated with occupations that have higher wages and educational requirements than on other types of work.
The pace of workforce transformation is likely to accelerate, given increases in the potential for technical automation. Our updated adoption scenarios, including technology development, economic feasibility, and diffusion timelines, lead to estimates that half of today’s work activities could be automated between 2030 and 2060, with a midpoint in 2045, or roughly a decade earlier than in our previous estimates.
Generative AI can substantially increase labor productivity across the economy, but that will require investments to support workers as they shift work activities or change jobs. Generative AI could enable labor productivity growth of 0.1 to 0.6 percent annually through 2040, depending on the rate of technology adoption and redeployment of worker time into other activities. Combining generative AI with all other technologies, work automation could add 0.5 to 3.4 percentage points annually to productivity growth. However, workers will need support in learning new skills, and some will change occupations. If worker transitions and other risks can be managed, generative AI could contribute substantively to economic growth and support a more sustainable, inclusive world.
The era of generative AI is just beginning. Excitement over this technology is palpable, and early pilots are compelling. But a full realization of the technology’s benefits will take time, and leaders in business and society still have considerable challenges to address. These include managing the risks inherent in generative AI, determining what new skills and capabilities the workforce will need, and rethinking core business processes such as retraining and developing new skills.
Where business value lies
Generative AI is a step change in the evolution of artificial intelligence. As companies rush to adapt and implement it, understanding the technology’s potential to deliver value to the economy and society at large will help shape critical decisions. We have used two complementary lenses to determine where generative AI, with its current capabilities, could deliver the biggest value and how big that value could be (Exhibit 1).
The first lens scans use cases for generative AI that organizations could adopt. We define a “use case” as a targeted application of generative AI to a specific business challenge, resulting in one or more measurable outcomes. For example, a use case in marketing is the application of generative AI to generate creative content such as personalized emails, the measurable outcomes of which potentially include reductions in the cost of generating such content and increases in revenue from the enhanced effectiveness of higher-quality content at scale. We identified 63 generative AI use cases spanning 16 business functions that could deliver total value in the range of $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion in economic benefits annually when applied across industries.
That would add 15 to 40 percent to the $11 trillion to $17.7 trillion of economic value that we now estimate nongenerative artificial intelligence and analytics could unlock. (Our previous estimate from 2017 was that AI could deliver $9.5 trillion to $15.4 trillion in economic value.)
Our second lens complements the first by analyzing generative AI’s potential impact on the work activities required in some 850 occupations. We modeled scenarios to estimate when generative AI could perform each of more than 2,100 “detailed work activities”—such as “communicating with others about operational plans or activities”—that make up those occupations across the world economy. This enables us to estimate how the current capabilities of generative AI could affect labor productivity across all work currently done by the global workforce.
Some of this impact will overlap with cost reductions in the use case analysis described above, which we assume are the result of improved labor productivity. Netting out this overlap, the total economic benefits of generative AI —including the major use cases we explored and the myriad increases in productivity that are likely to materialize when the technology is applied across knowledge workers’ activities—amounts to $6.1 trillion to $7.9 trillion annually (Exhibit 2).
How we estimated the value potential of generative AI use cases
To assess the potential value of generative AI, we updated a proprietary McKinsey database of potential AI use cases and drew on the experience of more than 100 experts in industries and their business functions. 1 ” Notes from the AI frontier: Applications and value of deep learning ,” McKinsey Global Institute, April 17, 2018.
Our updates examined use cases of generative AI—specifically, how generative AI techniques (primarily transformer-based neural networks) can be used to solve problems not well addressed by previous technologies.
We analyzed only use cases for which generative AI could deliver a significant improvement in the outputs that drive key value. In particular, our estimates of the primary value the technology could unlock do not include use cases for which the sole benefit would be its ability to use natural language. For example, natural-language capabilities would be the key driver of value in a customer service use case but not in a use case optimizing a logistics network, where value primarily arises from quantitative analysis.
We then estimated the potential annual value of these generative AI use cases if they were adopted across the entire economy. For use cases aimed at increasing revenue, such as some of those in sales and marketing, we estimated the economy-wide value generative AI could deliver by increasing the productivity of sales and marketing expenditures.
Our estimates are based on the structure of the global economy in 2022 and do not consider the value generative AI could create if it produced entirely new product or service categories.
While generative AI is an exciting and rapidly advancing technology, the other applications of AI discussed in our previous report continue to account for the majority of the overall potential value of AI. Traditional advanced-analytics and machine learning algorithms are highly effective at performing numerical and optimization tasks such as predictive modeling, and they continue to find new applications in a wide range of industries. However, as generative AI continues to develop and mature, it has the potential to open wholly new frontiers in creativity and innovation. It has already expanded the possibilities of what AI overall can achieve (see sidebar “How we estimated the value potential of generative AI use cases”).
In this section, we highlight the value potential of generative AI across business functions.
Generative AI could have an impact on most business functions; however, a few stand out when measured by the technology’s impact as a share of functional cost (Exhibit 3). Our analysis of 16 business functions identified just four—customer operations, marketing and sales, software engineering, and research and development—that could account for approximately 75 percent of the total annual value from generative AI use cases.
Notably, the potential value of using generative AI for several functions that were prominent in our previous sizing of AI use cases, including manufacturing and supply chain functions, is now much lower. 5 Pitchbook. This is largely explained by the nature of generative AI use cases, which exclude most of the numerical and optimization applications that were the main value drivers for previous applications of AI.
In addition to the potential value generative AI can deliver in function-specific use cases, the technology could drive value across an entire organization by revolutionizing internal knowledge management systems. Generative AI’s impressive command of natural-language processing can help employees retrieve stored internal knowledge by formulating queries in the same way they might ask a human a question and engage in continuing dialogue. This could empower teams to quickly access relevant information, enabling them to rapidly make better-informed decisions and develop effective strategies.
In 2012, the McKinsey Global Institute (MGI) estimated that knowledge workers spent about a fifth of their time, or one day each work week, searching for and gathering information. If generative AI could take on such tasks, increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of the workers doing them, the benefits would be huge. Such virtual expertise could rapidly “read” vast libraries of corporate information stored in natural language and quickly scan source material in dialogue with a human who helps fine-tune and tailor its research, a more scalable solution than hiring a team of human experts for the task.
In other cases, generative AI can drive value by working in partnership with workers, augmenting their work in ways that accelerate their productivity. Its ability to rapidly digest mountains of data and draw conclusions from it enables the technology to offer insights and options that can dramatically enhance knowledge work. This can significantly speed up the process of developing a product and allow employees to devote more time to higher-impact tasks.
Following are four examples of how generative AI could produce operational benefits in a handful of use cases across the business functions that could deliver a majority of the potential value we identified in our analysis of 63 generative AI use cases. In the first two examples, it serves as a virtual expert, while in the following two, it lends a hand as a virtual collaborator.
Customer operations: Improving customer and agent experiences
Generative AI has the potential to revolutionize the entire customer operations function, improving the customer experience and agent productivity through digital self-service and enhancing and augmenting agent skills. The technology has already gained traction in customer service because of its ability to automate interactions with customers using natural language. Research found that at one company with 5,000 customer service agents, the application of generative AI increased issue resolution by 14 percent an hour and reduced the time spent handling an issue by 9 percent. 1 Erik Brynjolfsson, Danielle Li, and Lindsey R. Raymond, Generative AI at work , National Bureau of Economic Research working paper number 31161, April 2023. It also reduced agent attrition and requests to speak to a manager by 25 percent. Crucially, productivity and quality of service improved most among less-experienced agents, while the AI assistant did not increase—and sometimes decreased—the productivity and quality metrics of more highly skilled agents. This is because AI assistance helped less-experienced agents communicate using techniques similar to those of their higher-skilled counterparts.
The following are examples of the operational improvements generative AI can have for specific use cases:
- Customer self-service. Generative AI–fueled chatbots can give immediate and personalized responses to complex customer inquiries regardless of the language or location of the customer. By improving the quality and effectiveness of interactions via automated channels, generative AI could automate responses to a higher percentage of customer inquiries, enabling customer care teams to take on inquiries that can only be resolved by a human agent. Our research found that roughly half of customer contacts made by banking, telecommunications, and utilities companies in North America are already handled by machines, including but not exclusively AI. We estimate that generative AI could further reduce the volume of human-serviced contacts by up to 50 percent, depending on a company’s existing level of automation.
- Resolution during initial contact. Generative AI can instantly retrieve data a company has on a specific customer, which can help a human customer service representative more successfully answer questions and resolve issues during an initial interaction.
- Reduced response time. Generative AI can cut the time a human sales representative spends responding to a customer by providing assistance in real time and recommending next steps.
- Increased sales. Because of its ability to rapidly process data on customers and their browsing histories, the technology can identify product suggestions and deals tailored to customer preferences. Additionally, generative AI can enhance quality assurance and coaching by gathering insights from customer conversations, determining what could be done better, and coaching agents.
We estimate that applying generative AI to customer care functions could increase productivity at a value ranging from 30 to 45 percent of current function costs.
Our analysis captures only the direct impact generative AI might have on the productivity of customer operations. It does not account for potential knock-on effects the technology may have on customer satisfaction and retention arising from an improved experience, including better understanding of the customer’s context that can assist human agents in providing more personalized help and recommendations.
Marketing and sales: Boosting personalization, content creation, and sales productivity
Generative AI has taken hold rapidly in marketing and sales functions, in which text-based communications and personalization at scale are driving forces. The technology can create personalized messages tailored to individual customer interests, preferences, and behaviors, as well as do tasks such as producing first drafts of brand advertising, headlines, slogans, social media posts, and product descriptions.
Introducing generative AI to marketing functions requires careful consideration. For one thing, mathematical models trained on publicly available data without sufficient safeguards against plagiarism, copyright violations, and branding recognition risks infringing on intellectual property rights. A virtual try-on application may produce biased representations of certain demographics because of limited or biased training data. Thus, significant human oversight is required for conceptual and strategic thinking specific to each company’s needs.
Potential operational benefits from using generative AI for marketing include the following:
- Efficient and effective content creation. Generative AI could significantly reduce the time required for ideation and content drafting, saving valuable time and effort. It can also facilitate consistency across different pieces of content, ensuring a uniform brand voice, writing style, and format. Team members can collaborate via generative AI, which can integrate their ideas into a single cohesive piece. This would allow teams to significantly enhance personalization of marketing messages aimed at different customer segments, geographies, and demographics. Mass email campaigns can be instantly translated into as many languages as needed, with different imagery and messaging depending on the audience. Generative AI’s ability to produce content with varying specifications could increase customer value, attraction, conversion, and retention over a lifetime and at a scale beyond what is currently possible through traditional techniques.
- Enhanced use of data. Generative AI could help marketing functions overcome the challenges of unstructured, inconsistent, and disconnected data—for example, from different databases—by interpreting abstract data sources such as text, image, and varying structures. It can help marketers better use data such as territory performance, synthesized customer feedback, and customer behavior to generate data-informed marketing strategies such as targeted customer profiles and channel recommendations. Such tools could identify and synthesize trends, key drivers, and market and product opportunities from unstructured data such as social media, news, academic research, and customer feedback.
- SEO optimization. Generative AI can help marketers achieve higher conversion and lower cost through search engine optimization (SEO) for marketing and sales technical components such as page titles, image tags, and URLs. It can synthesize key SEO tokens, support specialists in SEO digital content creation, and distribute targeted content to customers.
- Product discovery and search personalization. With generative AI, product discovery and search can be personalized with multimodal inputs from text, images, and speech, and a deep understanding of customer profiles. For example, technology can leverage individual user preferences, behavior, and purchase history to help customers discover the most relevant products and generate personalized product descriptions. This would allow CPG, travel, and retail companies to improve their e-commerce sales by achieving higher website conversion rates.
We estimate that generative AI could increase the productivity of the marketing function with a value between 5 and 15 percent of total marketing spending.
Our analysis of the potential use of generative AI in marketing doesn’t account for knock-on effects beyond the direct impacts on productivity. Generative AI–enabled synthesis could provide higher-quality data insights, leading to new ideas for marketing campaigns and better-targeted customer segments. Marketing functions could shift resources to producing higher-quality content for owned channels, potentially reducing spending on external channels and agencies.
Generative AI could also change the way both B2B and B2C companies approach sales. The following are two use cases for sales:
- Increase probability of sale. Generative AI could identify and prioritize sales leads by creating comprehensive consumer profiles from structured and unstructured data and suggesting actions to staff to improve client engagement at every point of contact. For example, generative AI could provide better information about client preferences, potentially improving close rates.
- Improve lead development. Generative AI could help sales representatives nurture leads by synthesizing relevant product sales information and customer profiles and creating discussion scripts to facilitate customer conversation, including up- and cross-selling talking points. It could also automate sales follow-ups and passively nurture leads until clients are ready for direct interaction with a human sales agent.
Our analysis suggests that implementing generative AI could increase sales productivity by approximately 3 to 5 percent of current global sales expenditures.
This analysis may not fully account for additional revenue that generative AI could bring to sales functions. For instance, generative AI’s ability to identify leads and follow-up capabilities could uncover new leads and facilitate more effective outreach that would bring in additional revenue. Also, the time saved by sales representatives due to generative AI’s capabilities could be invested in higher-quality customer interactions, resulting in increased sales success.
Software engineering: Speeding developer work as a coding assistant
Treating computer languages as just another language opens new possibilities for software engineering. Software engineers can use generative AI in pair programming and to do augmented coding and train LLMs to develop applications that generate code when given a natural-language prompt describing what that code should do.
Software engineering is a significant function in most companies, and it continues to grow as all large companies, not just tech titans, embed software in a wide array of products and services. For example, much of the value of new vehicles comes from digital features such as adaptive cruise control, parking assistance, and IoT connectivity.
According to our analysis, the direct impact of AI on the productivity of software engineering could range from 20 to 45 percent of current annual spending on the function. This value would arise primarily from reducing time spent on certain activities, such as generating initial code drafts, code correction and refactoring, root-cause analysis, and generating new system designs. By accelerating the coding process, generative AI could push the skill sets and capabilities needed in software engineering toward code and architecture design. One study found that software developers using Microsoft’s GitHub Copilot completed tasks 56 percent faster than those not using the tool. 1 Peter Cihon et al., The impact of AI on developer productivity: Evidence from GitHub Copilot , Cornell University arXiv software engineering working paper, arXiv:2302.06590, February 13, 2023. An internal McKinsey empirical study of software engineering teams found those who were trained to use generative AI tools rapidly reduced the time needed to generate and refactor code—and engineers also reported a better work experience, citing improvements in happiness, flow, and fulfillment.
Our analysis did not account for the increase in application quality and the resulting boost in productivity that generative AI could bring by improving code or enhancing IT architecture—which can improve productivity across the IT value chain. However, the quality of IT architecture still largely depends on software architects, rather than on initial drafts that generative AI’s current capabilities allow it to produce.
Large technology companies are already selling generative AI for software engineering, including GitHub Copilot, which is now integrated with OpenAI’s GPT-4, and Replit, used by more than 20 million coders. 2 Michael Nuñez, “Google and Replit join forces to challenge Microsoft in coding tools,” VentureBeat, March 28, 2023.
Product R&D: Reducing research and design time, improving simulation and testing
Generative AI’s potential in R&D is perhaps less well recognized than its potential in other business functions. Still, our research indicates the technology could deliver productivity with a value ranging from 10 to 15 percent of overall R&D costs.
For example, the life sciences and chemical industries have begun using generative AI foundation models in their R&D for what is known as generative design. Foundation models can generate candidate molecules, accelerating the process of developing new drugs and materials. Entos, a biotech pharmaceutical company, has paired generative AI with automated synthetic development tools to design small-molecule therapeutics. But the same principles can be applied to the design of many other products, including larger-scale physical products and electrical circuits, among others.
While other generative design techniques have already unlocked some of the potential to apply AI in R&D, their cost and data requirements, such as the use of “traditional” machine learning, can limit their application. Pretrained foundation models that underpin generative AI, or models that have been enhanced with fine-tuning, have much broader areas of application than models optimized for a single task. They can therefore accelerate time to market and broaden the types of products to which generative design can be applied. For now, however, foundation models lack the capabilities to help design products across all industries.
In addition to the productivity gains that result from being able to quickly produce candidate designs, generative design can also enable improvements in the designs themselves, as in the following examples of the operational improvements generative AI could bring:
- Enhanced design. Generative AI can help product designers reduce costs by selecting and using materials more efficiently. It can also optimize designs for manufacturing, which can lead to cost reductions in logistics and production.
- Improved product testing and quality. Using generative AI in generative design can produce a higher-quality product, resulting in increased attractiveness and market appeal. Generative AI can help to reduce testing time of complex systems and accelerate trial phases involving customer testing through its ability to draft scenarios and profile testing candidates.
We also identified a new R&D use case for nongenerative AI: deep learning surrogates, the use of which has grown since our earlier research, can be paired with generative AI to produce even greater benefits. To be sure, integration will require the development of specific solutions, but the value could be significant because deep learning surrogates have the potential to accelerate the testing of designs proposed by generative AI.
While we have estimated the potential direct impacts of generative AI on the R&D function, we did not attempt to estimate the technology’s potential to create entirely novel product categories. These are the types of innovations that can produce step changes not only in the performance of individual companies but in economic growth overall.
Industry impacts
Across the 63 use cases we analyzed, generative AI has the potential to generate $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion in value across industries. Its precise impact will depend on a variety of factors, such as the mix and importance of different functions, as well as the scale of an industry’s revenue (Exhibit 4).
For example, our analysis estimates generative AI could contribute roughly $310 billion in additional value for the retail industry (including auto dealerships) by boosting performance in functions such as marketing and customer interactions. By comparison, the bulk of potential value in high tech comes from generative AI’s ability to increase the speed and efficiency of software development (Exhibit 5).
In the banking industry, generative AI has the potential to improve on efficiencies already delivered by artificial intelligence by taking on lower-value tasks in risk management, such as required reporting, monitoring regulatory developments, and collecting data. In the life sciences industry, generative AI is poised to make significant contributions to drug discovery and development.
We share our detailed analysis of these industries below.
Generative AI supports key value drivers in retail and consumer packaged goods
The technology could generate value for the retail and consumer packaged goods (CPG) industry by increasing productivity by 1.2 to 2.0 percent of annual revenues, or an additional $400 billion to $660 billion. 1 Vehicular retail is included as part of our overall retail analysis. To streamline processes, generative AI could automate key functions such as customer service, marketing and sales, and inventory and supply chain management. Technology has played an essential role in the retail and CPG industries for decades. Traditional AI and advanced analytics solutions have helped companies manage vast pools of data across large numbers of SKUs, expansive supply chain and warehousing networks, and complex product categories such as consumables. In addition, the industries are heavily customer facing, which offers opportunities for generative AI to complement previously existing artificial intelligence. For example, generative AI’s ability to personalize offerings could optimize marketing and sales activities already handled by existing AI solutions. Similarly, generative AI tools excel at data management and could support existing AI-driven pricing tools. Applying generative AI to such activities could be a step toward integrating applications across a full enterprise.
Generative AI at work in retail and CPG
Reinvention of the customer interaction pattern.
Consumers increasingly seek customization in everything from clothing and cosmetics to curated shopping experiences, personalized outreach, and food—and generative AI can improve that experience. Generative AI can aggregate market data to test concepts, ideas, and models. Stitch Fix, which uses algorithms to suggest style choices to its customers, has experimented with DALL·E to visualize products based on customer preferences regarding color, fabric, and style. Using text-to-image generation, the company’s stylists can visualize an article of clothing based on a consumer’s preferences and then identify a similar article among Stitch Fix’s inventory.
Retailers can create applications that give shoppers a next-generation experience, creating a significant competitive advantage in an era when customers expect to have a single natural-language interface help them select products. For example, generative AI can improve the process of choosing and ordering ingredients for a meal or preparing food—imagine a chatbot that could pull up the most popular tips from the comments attached to a recipe. There is also a big opportunity to enhance customer value management by delivering personalized marketing campaigns through a chatbot. Such applications can have human-like conversations about products in ways that can increase customer satisfaction, traffic, and brand loyalty. Generative AI offers retailers and CPG companies many opportunities to cross-sell and upsell, collect insights to improve product offerings, and increase their customer base, revenue opportunities, and overall marketing ROI.
Accelerating the creation of value in key areas
Generative AI tools can facilitate copy writing for marketing and sales, help brainstorm creative marketing ideas, expedite consumer research, and accelerate content analysis and creation. The potential improvement in writing and visuals can increase awareness and improve sales conversion rates.
Rapid resolution and enhanced insights in customer care
The growth of e-commerce also elevates the importance of effective consumer interactions. Retailers can combine existing AI tools with generative AI to enhance the capabilities of chatbots, enabling them to better mimic the interaction style of human agents—for example, by responding directly to a customer’s query, tracking or canceling an order, offering discounts, and upselling. Automating repetitive tasks allows human agents to devote more time to handling complicated customer problems and obtaining contextual information.
Disruptive and creative innovation
Generative AI tools can enhance the process of developing new versions of products by digitally creating new designs rapidly. A designer can generate packaging designs from scratch or generate variations on an existing design. This technology is developing rapidly and has the potential to add text-to-video generation.
Factors for retail and CPG organizations to consider
As retail and CPG executives explore how to integrate generative AI in their operations, they should keep in mind several factors that could affect their ability to capture value from the technology:
- External inference. Generative AI has increased the need to understand whether generated content is based on fact or inference, requiring a new level of quality control.
- Adversarial attacks. Foundation models are a prime target for attack by hackers and other bad actors, increasing the variety of potential security vulnerabilities and privacy risks.
To address these concerns, retail and CPG companies will need to strategically keep humans in the loop and ensure security and privacy are top considerations for any implementation. Companies will need to institute new quality checks for processes previously handled by humans, such as emails written by customer reps, and perform more-detailed quality checks on AI-assisted processes such as product design.
Why banks could realize significant value
Generative AI could have a significant impact on the banking industry , generating value from increased productivity of 2.8 to 4.7 percent of the industry’s annual revenues, or an additional $200 billion to $340 billion. On top of that impact, the use of generative AI tools could also enhance customer satisfaction, improve decision making and employee experience, and decrease risks through better monitoring of fraud and risk.
Banking, a knowledge and technology-enabled industry, has already benefited significantly from previously existing applications of artificial intelligence in areas such as marketing and customer operations. 1 “ Building the AI bank of the future ,” McKinsey, May 2021. Generative AI applications could deliver additional benefits, especially because text modalities are prevalent in areas such as regulations and programming language, and the industry is customer facing, with many B2C and small-business customers. 2 McKinsey’s Global Banking Annual Review , December 1, 2022.
Several characteristics position the industry for the integration of generative AI applications:
- Sustained digitization efforts along with legacy IT systems. Banks have been investing in technology for decades, accumulating a significant amount of technical debt along with a siloed and complex IT architecture. 3 Akhil Babbar, Raghavan Janardhanan, Remy Paternoster, and Henning Soller, “ Why most digital banking transformations fail—and how to flip the odds ,” McKinsey, April 11, 2023.
- Large customer-facing workforces. Banking relies on a large number of service representatives such as call-center agents and wealth management financial advisers.
- A stringent regulatory environment. As a heavily regulated industry, banking has a substantial number of risk, compliance, and legal needs.
- White-collar industry. Generative AI’s impact could span the organization, assisting all employees in writing emails, creating business presentations, and other tasks.
Generative AI at work in banking
Banks have started to grasp the potential of generative AI in their front lines and in their software activities. Early adopters are harnessing solutions such as ChatGPT as well as industry-specific solutions, primarily for software and knowledge applications. Three uses demonstrate its value potential to the industry.
A virtual expert to augment employee performance
A generative AI bot trained on proprietary knowledge such as policies, research, and customer interaction could provide always-on, deep technical support. Today, frontline spending is dedicated mostly to validating offers and interacting with clients, but giving frontline workers access to data as well could improve the customer experience. The technology could also monitor industries and clients and send alerts on semantic queries from public sources. For example, Morgan Stanley is building an AI assistant using GPT-4, with the aim of helping tens of thousands of wealth managers quickly find and synthesize answers from a massive internal knowledge base. 4 Hugh Son, “Morgan Stanley is testing an OpenAI-powered chatbot for its 16,000 financial advisors,” CNBC, March 14, 2023. The model combines search and content creation so wealth managers can find and tailor information for any client at any moment.
One European bank has leveraged generative AI to develop an environmental, social, and governance (ESG) virtual expert by synthesizing and extracting from long documents with unstructured information. The model answers complex questions based on a prompt, identifying the source of each answer and extracting information from pictures and tables.
Generative AI could reduce the significant costs associated with back-office operations. Such customer-facing chatbots could assess user requests and select the best service expert to address them based on characteristics such as topic, level of difficulty, and type of customer. Through generative AI assistants, service professionals could rapidly access all relevant information such as product guides and policies to instantaneously address customer requests.
Code acceleration to reduce tech debt and deliver software faster
Generative AI tools are useful for software development in four broad categories. First, they can draft code based on context via input code or natural language, helping developers code more quickly and with reduced friction while enabling automatic translations and no- and low-code tools. Second, such tools can automatically generate, prioritize, run, and review different code tests, accelerating testing and increasing coverage and effectiveness. Third, generative AI’s natural-language translation capabilities can optimize the integration and migration of legacy frameworks. Last, the tools can review code to identify defects and inefficiencies in computing. The result is more robust, effective code.
Production of tailored content at scale
Generative AI tools can draw on existing documents and data sets to substantially streamline content generation. These tools can create personalized marketing and sales content tailored to specific client profiles and histories as well as a multitude of alternatives for A/B testing. In addition, generative AI could automatically produce model documentation, identify missing documentation, and scan relevant regulatory updates to create alerts for relevant shifts.
Factors for banks to consider
When exploring how to integrate generative AI into operations, banks can be mindful of a number of factors:
- The level of regulation for different processes. These vary from unregulated processes such as customer service to heavily regulated processes such as credit risk scoring.
- Type of end user. End users vary widely in their expectations and familiarity with generative AI—for example, employees compared with high-net-worth clients.
- Intended level of work automation. AI agents integrated through APIs could act nearly autonomously or as copilots, giving real-time suggestions to agents during customer interactions.
- Data constraints. While public data such as annual reports could be made widely available, there would need to be limits on identifiable details for customers and other internal data.
Pharmaceuticals and medical products could see benefits across the entire value chain
Our analysis finds that generative AI could have a significant impact on the pharmaceutical and medical-product industries—from 2.6 to 4.5 percent of annual revenues across the pharmaceutical and medical-product industries, or $60 billion to $110 billion annually. This big potential reflects the resource-intensive process of discovering new drug compounds. Pharma companies typically spend approximately 20 percent of revenues on R&D, 1 Research and development in the pharmaceutical industry , Congressional Budget Office, April 2021. and the development of a new drug takes an average of ten to 15 years. With this level of spending and timeline, improving the speed and quality of R&D can generate substantial value. For example, lead identification—a step in the drug discovery process in which researchers identify a molecule that would best address the target for a potential new drug—can take several months even with “traditional” deep learning techniques. Foundation models and generative AI can enable organizations to complete this step in a matter of weeks.
Generative AI at work in pharmaceuticals and medical products
Drug discovery involves narrowing the universe of possible compounds to those that could effectively treat specific conditions. Generative AI’s ability to process massive amounts of data and model options can accelerate output across several use cases:
Improve automation of preliminary screening
In the lead identification stage of drug development, scientists can use foundation models to automate the preliminary screening of chemicals in the search for those that will produce specific effects on drug targets. To start, thousands of cell cultures are tested and paired with images of the corresponding experiment. Using an off-the-shelf foundation model, researchers can cluster similar images more precisely than they can with traditional models, enabling them to select the most promising chemicals for further analysis during lead optimization.
Enhance indication finding
An important phase of drug discovery involves the identification and prioritization of new indications—that is, diseases, symptoms, or circumstances that justify the use of a specific medication or other treatment, such as a test, procedure, or surgery. Possible indications for a given drug are based on a patient group’s clinical history and medical records, and they are then prioritized based on their similarities to established and evidence-backed indications.
Researchers start by mapping the patient cohort’s clinical events and medical histories—including potential diagnoses, prescribed medications, and performed procedures—from real-world data. Using foundation models, researchers can quantify clinical events, establish relationships, and measure the similarity between the patient cohort and evidence-backed indications. The result is a short list of indications that have a better probability of success in clinical trials because they can be more accurately matched to appropriate patient groups.
Pharma companies that have used this approach have reported high success rates in clinical trials for the top five indications recommended by a foundation model for a tested drug. This success has allowed these drugs to progress smoothly into Phase 3 trials, significantly accelerating the drug development process.
Factors for pharmaceuticals and medical products organizations to consider
Before integrating generative AI into operations, pharma executives should be aware of some factors that could limit their ability to capture its benefits:
- The need for a human in the loop. Companies may need to implement new quality checks on processes that shift from humans to generative AI, such as representative-generated emails, or more detailed quality checks on AI-assisted processes, such as drug discovery. The increasing need to verify whether generated content is based on fact or inference elevates the need for a new level of quality control.
- Explainability. A lack of transparency into the origins of generated content and traceability of root data could make it difficult to update models and scan them for potential risks; for instance, a generative AI solution for synthesizing scientific literature may not be able to point to the specific articles or quotes that led it to infer that a new treatment is very popular among physicians. The technology can also “hallucinate,” or generate responses that are obviously incorrect or inappropriate for the context. Systems need to be designed to point to specific articles or data sources, and then do human-in-the-loop checking.
- Privacy considerations. Generative AI’s use of clinical images and medical records could increase the risk that protected health information will leak, potentially violating regulations that require pharma companies to protect patient privacy.
Work and productivity implications
Technology has been changing the anatomy of work for decades. Over the years, machines have given human workers various “superpowers”; for instance, industrial-age machines enabled workers to accomplish physical tasks beyond the capabilities of their own bodies. More recently, computers have enabled knowledge workers to perform calculations that would have taken years to do manually.
These examples illustrate how technology can augment work through the automation of individual activities that workers would have otherwise had to do themselves. At a conceptual level, the application of generative AI may follow the same pattern in the modern workplace, although as we show later in this chapter, the types of activities that generative AI could affect, and the types of occupations with activities that could change, will likely be different as a result of this technology than for older technologies.
The McKinsey Global Institute began analyzing the impact of technological automation of work activities and modeling scenarios of adoption in 2017. At that time, we estimated that workers spent half of their time on activities that had the potential to be automated by adapting technology that existed at that time, or what we call technical automation potential. We also modeled a range of potential scenarios for the pace at which these technologies could be adopted and affect work activities throughout the global economy.
Technology adoption at scale does not occur overnight. The potential of technological capabilities in a lab does not necessarily mean they can be immediately integrated into a solution that automates a specific work activity—developing such solutions takes time. Even when such a solution is developed, it might not be economically feasible to use if its costs exceed those of human labor. Additionally, even if economic incentives for deployment exist, it takes time for adoption to spread across the global economy. Hence, our adoption scenarios, which consider these factors together with the technical automation potential, provide a sense of the pace and scale at which workers’ activities could shift over time.
About the research
This analysis builds on the methodology we established in 2017. We began by examining the US Bureau of Labor Statistics O*Net breakdown of about 850 occupations into roughly 2,100 detailed work activities. For each of these activities, we scored the level of capability necessary to successfully perform the activity against a set of 18 capabilities that have the potential for automation.
We also surveyed experts in the automation of each of these capabilities to estimate automation technologies’ current performance level against each of these capabilities, as well as how the technology’s performance might advance over time. Specifically, this year, we updated our assessments of technology’s performance in cognitive, language, and social and emotional capabilities based on a survey of generative AI experts.
Based on these assessments of the technical automation potential of each detailed work activity at each point in time, we modeled potential scenarios for the adoption of work automation around the world. First, we estimated a range of time to implement a solution that could automate each specific detailed work activity, once all the capability requirements were met by the state of technology development. Second, we estimated a range of potential costs for this technology when it is first introduced, and then declining over time, based on historical precedents. We modeled the beginning of adoption for a specific detailed work activity in a particular occupation in a country (for 47 countries, accounting for more than 80 percent of the global workforce) when the cost of the automation technology reaches parity with the cost of human labor in that occupation.
Based on a historical analysis of various technologies, we modeled a range of adoption timelines from eight to 27 years between the beginning of adoption and its plateau, using sigmoidal curves (S-curves). This range implicitly accounts for the many factors that could affect the pace at which adoption occurs, including regulation, levels of investment, and management decision making within firms.
The modeled scenarios create a time range for the potential pace of automating current work activities. The “earliest” scenario flexes all parameters to the extremes of plausible assumptions, resulting in faster automation development and adoption, and the “latest” scenario flexes all parameters in the opposite direction. The reality is likely to fall somewhere between the two.
The analyses in this paper incorporate the potential impact of generative AI on today’s work activities. The new capabilities of generative AI, combined with previous technologies and integrated into corporate operations around the world, could accelerate the potential for technical automation of individual activities and the adoption of technologies that augment the capabilities of the workforce. They could also have an impact on knowledge workers whose activities were not expected to shift as a result of these technologies until later in the future (see sidebar “About the research”).
Automation potential has accelerated, but adoption to lag
Based on developments in generative AI, technology performance is now expected to match median human performance and reach top-quartile human performance earlier than previously estimated across a wide range of capabilities (Exhibit 6). For example, MGI previously identified 2027 as the earliest year when median human performance for natural-language understanding might be achieved in technology, but in this new analysis, the corresponding point is 2023.
As a result of these reassessments of technology capabilities due to generative AI, the total percentage of hours that could theoretically be automated by integrating technologies that exist today has increased from about 50 percent to 60–70 percent. The technical potential curve is quite steep because of the acceleration in generative AI’s natural-language capabilities.
Interestingly, the range of times between the early and late scenarios has compressed compared with the expert assessments in 2017, reflecting a greater confidence that higher levels of technological capabilities will arrive by certain time periods (Exhibit 7).
Our analysis of adoption scenarios accounts for the time required to integrate technological capabilities into solutions that can automate individual work activities; the cost of these technologies compared with that of human labor in different occupations and countries around the world; and the time it has taken for technologies to diffuse across the economy. With the acceleration in technical automation potential that generative AI enables, our scenarios for automation adoption have correspondingly accelerated. These scenarios encompass a wide range of outcomes, given that the pace at which solutions will be developed and adopted will vary based on decisions that will be made on investments, deployment, and regulation, among other factors. But they give an indication of the degree to which the activities that workers do each day may shift (Exhibit 8).
As an example of how this might play out in a specific occupation, consider postsecondary English language and literature teachers, whose detailed work activities include preparing tests and evaluating student work. With generative AI’s enhanced natural-language capabilities, more of these activities could be done by machines, perhaps initially to create a first draft that is edited by teachers but perhaps eventually with far less human editing required. This could free up time for these teachers to spend more time on other work activities, such as guiding class discussions or tutoring students who need extra assistance.
Our previously modeled adoption scenarios suggested that 50 percent of time spent on 2016 work activities would be automated sometime between 2035 and 2070, with a midpoint scenario around 2053. Our updated adoption scenarios, which account for developments in generative AI, models the time spent on 2023 work activities reaching 50 percent automation between 2030 and 2060, with a midpoint of 2045—an acceleration of roughly a decade compared with the previous estimate. 6 The comparison is not exact because the composition of work activities between 2016 and 2023 has changed; for example, some automation has occurred during that time period.
Adoption is also likely to be faster in developed countries, where wages are higher and thus the economic feasibility of adopting automation occurs earlier. Even if the potential for technology to automate a particular work activity is high, the costs required to do so have to be compared with the cost of human wages. In countries such as China, India, and Mexico, where wage rates are lower, automation adoption is modeled to arrive more slowly than in higher-wage countries (Exhibit 9).
Generative AI’s potential impact on knowledge work
Previous generations of automation technology were particularly effective at automating data management tasks related to collecting and processing data. Generative AI’s natural-language capabilities increase the automation potential of these types of activities somewhat. But its impact on more physical work activities shifted much less, which isn’t surprising because its capabilities are fundamentally engineered to do cognitive tasks.
As a result, generative AI is likely to have the biggest impact on knowledge work, particularly activities involving decision making and collaboration, which previously had the lowest potential for automation (Exhibit 10). Our estimate of the technical potential to automate the application of expertise jumped 34 percentage points, while the potential to automate management and develop talent increased from 16 percent in 2017 to 49 percent in 2023.
Generative AI’s ability to understand and use natural language for a variety of activities and tasks largely explains why automation potential has risen so steeply. Some 40 percent of the activities that workers perform in the economy require at least a median level of human understanding of natural language.
As a result, many of the work activities that involve communication, supervision, documentation, and interacting with people in general have the potential to be automated by generative AI, accelerating the transformation of work in occupations such as education and technology, for which automation potential was previously expected to emerge later (Exhibit 11).
Labor economists have often noted that the deployment of automation technologies tends to have the most impact on workers with the lowest skill levels, as measured by educational attainment, or what is called skill biased. We find that generative AI has the opposite pattern—it is likely to have the most incremental impact through automating some of the activities of more-educated workers (Exhibit 12).
Another way to interpret this result is that generative AI will challenge the attainment of multiyear degree credentials as an indicator of skills, and others have advocated for taking a more skills-based approach to workforce development in order to create more equitable, efficient workforce training and matching systems. 7 A more skills-based approach to workforce development predates the emergence of generative AI. Generative AI could still be described as skill-biased technological change, but with a different, perhaps more granular, description of skills that are more likely to be replaced than complemented by the activities that machines can do.
Previous generations of automation technology often had the most impact on occupations with wages falling in the middle of the income distribution. For lower-wage occupations, making a case for work automation is more difficult because the potential benefits of automation compete against a lower cost of human labor. Additionally, some of the tasks performed in lower-wage occupations are technically difficult to automate—for example, manipulating fabric or picking delicate fruits. Some labor economists have observed a “hollowing out of the middle,” and our previous models have suggested that work automation would likely have the biggest midterm impact on lower-middle-income quintiles.
However, generative AI’s impact is likely to most transform the work of higher-wage knowledge workers because of advances in the technical automation potential of their activities, which were previously considered to be relatively immune from automation (Exhibit 13).
Generative AI could propel higher productivity growth
Global economic growth was slower from 2012 to 2022 than in the two preceding decades. 8 Global economic prospects , World Bank, January 2023. Although the COVID-19 pandemic was a significant factor, long-term structural challenges—including declining birth rates and aging populations—are ongoing obstacles to growth.
Declining employment is among those obstacles. Compound annual growth in the total number of workers worldwide slowed from 2.5 percent in 1972–82 to just 0.8 percent in 2012–22, largely because of aging. In many large countries, the size of the workforce is already declining. 9 Yaron Shamir, “Three factors contributing to fewer people in the workforce,” Forbes , April 7, 2022. Productivity, which measures output relative to input, or the value of goods and services produced divided by the amount of labor, capital, and other resources required to produce them, was the main engine of economic growth in the three decades from 1992 to 2022 (Exhibit 14). However, since then, productivity growth has slowed in tandem with slowing employment growth, confounding economists and policy makers. 10 “The U.S. productivity slowdown: an economy-wide and industry-level analysis,” Monthly Labor Review, US Bureau of Labor Statistics, April 2021; Kweilin Ellingrud, “ Turning around the productivity slowdown ,” McKinsey Global Institute, September 13, 2022.
The deployment of generative AI and other technologies could help accelerate productivity growth, partially compensating for declining employment growth and enabling overall economic growth. Based on our estimates, the automation of individual work activities enabled by these technologies could provide the global economy with an annual productivity boost of 0.5 to 3.4 percent from 2023 to 2040, depending on the rate of automation adoption—with generative AI contributing 0.1 to 0.6 percentage points of that growth—but only if individuals affected by the technology were to shift to other work activities that at least match their 2022 productivity levels (Exhibit 15). In some cases, workers will stay in the same occupations, but their mix of activities will shift; in others, workers will need to shift occupations.
Considerations for business and society
History has shown that new technologies have the potential to reshape societies. Artificial intelligence has already changed the way we live and work—for example, it can help our phones (mostly) understand what we say, or draft emails. Mostly, however, AI has remained behind the scenes, optimizing business processes or making recommendations about the next product to buy. The rapid development of generative AI is likely to significantly augment the impact of AI overall, generating trillions of dollars of additional value each year and transforming the nature of work.
But the technology could also deliver new and significant challenges. Stakeholders must act—and quickly, given the pace at which generative AI could be adopted—to prepare to address both the opportunities and the risks. Risks have already surfaced, including concerns about the content that generative AI systems produce: Will they infringe upon intellectual property due to “plagiarism” in the training data used to create foundation models? Will the answers that LLMs produce when questioned be accurate, and can they be explained? Will the content generative AI creates be fair or biased in ways that users do not want by, say, producing content that reflects harmful stereotypes?
Using generative AI responsibly
Generative AI poses a variety of risks. Stakeholders will want to address these risks from the start.
Fairness: Models may generate algorithmic bias due to imperfect training data or decisions made by the engineers developing the models.
Intellectual property (IP): Training data and model outputs can generate significant IP risks, including infringing on copyrighted, trademarked, patented, or otherwise legally protected materials. Even when using a provider’s generative AI tool, organizations will need to understand what data went into training and how it’s used in tool outputs.
Privacy: Privacy concerns could arise if users input information that later ends up in model outputs in a form that makes individuals identifiable. Generative AI could also be used to create and disseminate malicious content such as disinformation, deepfakes, and hate speech.
Security: Generative AI may be used by bad actors to accelerate the sophistication and speed of cyberattacks. It also can be manipulated to provide malicious outputs. For example, through a technique called prompt injection, a third party gives a model new instructions that trick the model into delivering an output unintended by the model producer and end user.
Explainability: Generative AI relies on neural networks with billions of parameters, challenging our ability to explain how any given answer is produced.
Reliability: Models can produce different answers to the same prompts, impeding the user’s ability to assess the accuracy and reliability of outputs.
Organizational impact: Generative AI may significantly affect the workforce, and the impact on specific groups and local communities could be disproportionately negative.
Social and environmental impact: The development and training of foundation models may lead to detrimental social and environmental consequences, including an increase in carbon emissions (for example, training one large language model can emit about 315 tons of carbon dioxide). 1 Ananya Ganesh, Andrew McCallum, and Emma Strubell, “Energy and policy considerations for deep learning in NLP,” Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics , June 5, 2019.
There are economic challenges too: the scale and the scope of the workforce transitions described in this report are considerable. In the midpoint adoption scenario, about a quarter to a third of work activities could change in the coming decade. The task before us is to manage the potential positives and negatives of the technology simultaneously (see sidebar “Using generative AI responsibly”). Here are some of the critical questions we will need to address while balancing our enthusiasm for the potential benefits of the technology with the new challenges it can introduce.
Companies and business leaders
How can companies move quickly to capture the potential value at stake highlighted in this report, while managing the risks that generative AI presents?
How will the mix of occupations and skills needed across a company’s workforce be transformed by generative AI and other artificial intelligence over the coming years? How will a company enable these transitions in its hiring plans, retraining programs, and other aspects of human resources?
Do companies have a role to play in ensuring the technology is not deployed in “negative use cases” that could harm society?
How can businesses transparently share their experiences with scaling the use of generative AI within and across industries—and also with governments and society?
Policy makers
What will the future of work look like at the level of an economy in terms of occupations and skills? What does this mean for workforce planning?
How can workers be supported as their activities shift over time? What retraining programs can be put in place? What incentives are needed to support private companies as they invest in human capital? Are there earn-while-you-learn programs such as apprenticeships that could enable people to retrain while continuing to support themselves and their families?
What steps can policy makers take to prevent generative AI from being used in ways that harm society or vulnerable populations?
Can new policies be developed and existing policies amended to ensure human-centric AI development and deployment that includes human oversight and diverse perspectives and accounts for societal values?
Individuals as workers, consumers, and citizens
How concerned should individuals be about the advent of generative AI? While companies can assess how the technology will affect their bottom lines, where can citizens turn for accurate, unbiased information about how it will affect their lives and livelihoods?
How can individuals as workers and consumers balance the conveniences generative AI delivers with its impact in their workplaces?
Can citizens have a voice in the decisions that will shape the deployment and integration of generative AI into the fabric of their lives?
Technological innovation can inspire equal parts awe and concern. When that innovation seems to materialize fully formed and becomes widespread seemingly overnight, both responses can be amplified. The arrival of generative AI in the fall of 2022 was the most recent example of this phenomenon, due to its unexpectedly rapid adoption as well as the ensuing scramble among companies and consumers to deploy, integrate, and play with it.
All of us are at the beginning of a journey to understand this technology’s power, reach, and capabilities. If the past eight months are any guide, the next several years will take us on a roller-coaster ride featuring fast-paced innovation and technological breakthroughs that force us to recalibrate our understanding of AI’s impact on our work and our lives. It is important to properly understand this phenomenon and anticipate its impact. Given the speed of generative AI’s deployment so far, the need to accelerate digital transformation and reskill labor forces is great.
These tools have the potential to create enormous value for the global economy at a time when it is pondering the huge costs of adapting and mitigating climate change. At the same time, they also have the potential to be more destabilizing than previous generations of artificial intelligence. They are capable of that most human of abilities, language, which is a fundamental requirement of most work activities linked to expertise and knowledge as well as a skill that can be used to hurt feelings, create misunderstandings, obscure truth, and incite violence and even wars.
We hope this research has contributed to a better understanding of generative AI’s capacity to add value to company operations and fuel economic growth and prosperity as well as its potential to dramatically transform how we work and our purpose in society. Companies, policy makers, consumers, and citizens can work together to ensure that generative AI delivers on its promise to create significant value while limiting its potential to upset lives and livelihoods. The time to act is now. 11 The research, analysis, and writing in this report was entirely done by humans.
Michael Chui is a partner in McKinsey’s Bay Area office, where Roger Roberts is a partner and Lareina Yee is a senior partner; Eric Hazan is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Paris office; Alex Singla is a senior partner in the Chicago office; Kate Smaje and Alex Sukharevsky are senior partners in the London office; and Rodney Zemmel is a senior partner in the New York office.
The authors wish to thank Pedro Abreu, Rohit Agarwal, Steven Aronowitz, Arun Arora, Charles Atkins, Elia Berteletti, Onno Boer, Albert Bollard, Xavier Bosquet, Benjamin Braverman, Charles Carcenac, Sebastien Chaigne, Peter Crispeels, Santiago Comella-Dorda, Eleonore Depardon, Kweilin Ellingrud, Thierry Ethevenin, Dmitry Gafarov, Neel Gandhi, Eric Goldberg, Liz Grennan, Shivani Gupta, Vinay Gupta, Dan Hababou, Bryan Hancock, Lisa Harkness, Leila Harouchi, Jake Hart, Heiko Heimes, Jeff Jacobs, Begum Karaci Deniz, Tarun Khurana, Malgorzata Kmicinska, Jan-Christoph Köstring, Andreas Kremer, Kathryn Kuhn, Jessica Lamb, Maxim Lampe, John Larson, Swan Leroi, Damian Lewandowski, Richard Li, Sonja Lindberg, Kerin Lo, Guillaume Lurenbaum, Matej Macak, Dana Maor, Julien Mauhourat, Marco Piccitto, Carolyn Pierce, Olivier Plantefeve, Alexandre Pons, Kathryn Rathje, Emily Reasor, Werner Rehm, Steve Reis, Kelsey Robinson, Martin Rosendahl, Christoph Sandler, Saurab Sanghvi, Boudhayan Sen, Joanna Si, Alok Singh, Gurneet Singh Dandona, François Soubien, Eli Stein, Stephanie Strom, Michele Tam, Robert Tas, Maribel Tejada, Wilbur Wang, Georg Winkler, Jane Wong, and Romain Zilahi for their contributions to this report.
For the full list of acknowledgments, see the downloadable PDF .
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

What every CEO should know about generative AI

Exploring opportunities in the generative AI value chain

What is generative AI?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Creative writing is a form of writing that extends beyond the bounds of regular professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature. It is characterized by its development, and the use of literary tropes or poetic techniques to express ideas in an original and imaginative way. express their thoughts, feelings, and ideas in a ...
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
How We Define Creative Writing. Creative writing is any form where writers can express their thoughts and feelings imaginatively. This type of writing allows authors to draw on their imagination when creating stories and characters and play with language and structure. While there are no boundaries in creative writing, most pieces will contain ...
The Benefits of Creative Writing. 1. Why Learn Creative Writing: Improved Self-Expression. Improving your writing skills leads to stronger communication. When you practice finding the right word in a story or poem, you engage the same parts of your brain that are active in everyday writing and speaking.
Creative writing refers to a broad range of texts that draw upon writers' creativity (as the term suggests), facility with words, emotional depth, and intellectual rigor to convey meaning. Creative writing is also an area of study and college major at many colleges and universities. Creative writing is, by nature, an artistic expression ...
Creative Writing 101. Creative writing is any form of writing which is written with the creativity of mind: fiction writing, poetry writing, creative nonfiction writing and more. The purpose is to express something, whether it be feelings, thoughts, or emotions. Rather than only giving information or inciting the reader to make an action ...
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
Creative Writing is a form of art that allows people to express their thoughts, ideas, and emotions through the written word. It is a mode of self-expression that combines imagination with linguistic skills to create compelling narratives, poems, and other forms of literature. A Statista survey found that 76,300 Authors, Writers and Translators ...
Creative writing is a form of self-expression that involves telling stories and creating works of art in a variety of written forms. Creative writing encompasses everything from poetry to novels, scripts, memoirs, articles, and more. It requires imagination and storytelling to craft stories that educate, evoke emotions, or captivate the reader.
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Creative writing is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics.Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to ...
Creative nonfiction is a broad genre that includes memoirs and biographies, personal essays, travel and food writing, and literary journalism. Ultimately, we each get to decide what is art and what is creative writing. Most of us will know creative writing when we experience it, either as a writer or as a reader.
Creative writing is a written art form that uses the imagination to tell stories and compose essays, poetry, screenplays, novels, lyrics, and more. It can be defined in opposition to the dry and factual types of writing found in academic, technical, or journalistic texts.
Creative writing is an exercise in solving problems, either for the characters within the story or for the author themselves. Characters within stories need to be navigated through a series of difficulties, and if the problems take place in the real world, then the solutions must also be real-world solutions. If the problem is a literal dragon ...
What we value in the practice of creative writing, and in the results of that practice—all of those results: the material objects that emerge from the practice and become conduits for communication, for emotional exchanges and for discussion, works of arts that they are; the experiences of writing, creatively, and of re-writing, the ...
The benefits of creative writing. Wednesday, 15 July, 2020. As you learn to clarify your thoughts and emotions more efficiently and accurately, through creative writing, you will communicate more effectively; a skill that's exceedingly important in all areas of life. Practising creative writing is about a lot more than just improving your ...
The objectives of creative writing encompass a range of goals aimed at expressing thoughts, emotions, and ideas in unique and imaginative ways. 01344203999 - Available 24/7. ... This educational objective of Creative Writing underscores its value as a holistic tool for personal and intellectual growth, making it an integral part of both formal ...
This review will help you ensure your practice is research-informed and grounded in evidence. The review explores evidence into the benefits of creative writing by splitting the research into four key areas: Raising attainment through creativity. Boosting confidence and imagination. Nurturing and supporting wellbeing. Improving skills.
Artistic writing is a kind of indirect communication in which the creativity of the writer invites the creativity of the reader. In personality, writers are higher in openness but more often depressed than other members of the population. Characteristics on which literary creativity is based make writers vulnerable to emotional disorders.
Creative writing, on the other hand, allows students to feel connected to the content on a personal level. As they work to find their voices and create through their own original work, they get a footing and gain a sense of being in charge. In other words, they shine. 6. Boosting Imagination.
Creative Writing is the process of making sense of the world around us, and providing this sense with an outlet of expression. It's a method of lending a voice to the voiceless, and giving form to the formless. A creative writer is a writer who can find a story in even the most abstract and vague scenarios. The purpose of creative writing is ...
Consequently, little is known about the declarative and procedural knowledge of 'experts' regarding how they define creativity and what they value in creative products; this is particularly true of those immersed in the world of professional writing such as literary agents, editors, professional writers and university creative writing tutors.
This dissertation examines the academic field of creative writing and its social position since its emergence just before World War II. Analyzing why this field has grown so robustly, I challenge the common perception that it is a subsidized refuge for literary artists, arguing that its expansion corresponds to a rise in the socioeconomic value ...
Teachers are already using tools like ChatGPT to provide comments on their students' writing assignments. Of course, AIs will need a lot of training and further development before they can do things like understand how a certain student learns best or what motivates them. Even once the technology is perfected, learning will still depend on ...
Generative AI tools can facilitate copy writing for marketing and sales, help brainstorm creative marketing ideas, expedite consumer research, and accelerate content analysis and creation. The potential improvement in writing and visuals can increase awareness and improve sales conversion rates. Rapid resolution and enhanced insights in ...