

How to decide between postgraduate research and coursework
It can be a little tricky figuring out which postgraduate degree is for you. That’s why we’ve done the work for you to clarify the differences between a coursework degree and a research degree, and where each could take your career.
The main difference between these two styles is coursework has classes and research has a thesis.
Postgraduate coursework: advanced classes
In a nutshell: an advanced continuation of undergrad-style learning.
Choosing a coursework degree means you’ll attend lectures and tutorials, complete assignments and sit exams – just like your first degree. You’ll be taught discrete units that are part of a set program and at a higher academic level than your undergrad.
Coursework degrees aim to deepen your knowledge and enhance your undergraduate degree with postgraduate training, focusing you towards a specific profession. Alternatively, you can use your undergraduate degree to pivot and pursue a new area of study at postgraduate level.
For instance, you may have completed a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English and Japanese, then realised you’d like be a high school teacher, so you enrol in a Master of Teaching (Secondary) .
Or perhaps you did a Bachelor of Science majoring in Engineering Science and after working for a couple of years, you now want to start your own business. Enrolling in a Graduate Certificate in Entrepreneurship and Innovation could get you there.
Also bear in mind, some coursework courses can involve a research element such as the completion of a minor thesis. This forms part of training your time management and written skills.
If you’re looking to complete a degree part time or solely online, you can find a postgraduate coursework degree to suit you. There are graduate certificates, graduate diplomas and master’s degrees, and we’ve explained the difference between these too.
Postgraduate research: independent thesis
In a nutshell: solo research project to produce an original thesis.
Taking on a postgraduate research degree provides you with the unique opportunity to follow your interest in an area of research and contribute to the field.
You’ll work on your own project, under the guidance of an academic supervisor who you have chosen, with the aim of producing, presenting and submitting a final thesis. This final thesis is the culmination of your original research and investigation – an original contribution to knowledge.
You can often undertake any project of your choosing, as long as you can find a supervisor to connect with. Once you’ve found a potential supervisor, meet with them to discuss your project proposal and see if they agree to supervise you.
If you’re interested in completing a PhD or are thinking about a career in academia, a research degree is a popular decision. This type of study enables you to demonstrate your capacity to conduct research independently and form a distinct contribution to an area.
So what’s ‘honours’, then?
Honours is the opportunity to extend your undergraduate degree by a year – a sort of bridging year between undergrad and postgrad. The benefit is setting yourself apart from other undergraduate grads, as employers value the skills gained from the independent research project you’ll complete.
Honours is reserved for students who demonstrate strong academic performance in their final-year units. You may be invited to consider honours or you can apply directly . Students considering a research master’s or PhD are strongly encouraged to complete an honours year as a research training exercise and a taster of what’s to come in the research life.
Still can’t decide? See what some of our coursework and research graduates have to say .
Explore more article topics
- Research and phd
Don't miss a moment
Stay up-to-date with the latest information about studying at UWA including, our courses and career pathways, event and webinars, key dates, what uni life is really like, tips for studying plus, so much more!
Related stories
Continue seeking wisdom.


What is a Graduate Degree?

For those considering graduate school , it’s important to take the time to understand what an advanced degree program entails. Read on to learn about the different types of graduate programs, the time commitment, cost, and enrollment conditions required, and what students should expect at this level of advanced study.
An undergraduate degree —either a bachelor’s or associate degree—is considered a baseline educational requirement in many professions. As such, the pursuit of this degree has become commonplace among high school graduates. As of 2018, 69 percent of students chose to complete their undergraduate degree immediately after earning their high school diploma.
A graduate degree —including master’s degrees , doctorates , and PhDs —provides an advanced understanding of a specific topic or field, and demonstrates a commitment to lifelong learning that many employers value. Those who choose to enroll in graduate school often do so with a series of focused, career-oriented goals in mind, which sets the stage for a substantially different type of learning environment than one might experience during an undergraduate career.
Interested in earning an advanced degree?
Explore Northeastern’s 200+ programs to find the one that will best help you achieve your goals.
FIND YOUR PROGRAM
Types of Graduate Degrees
Students embarking on graduate school should begin by determining if an academic or professional degree is right for them.
Students who desire a career in a specific field (such as law, pharmaceuticals, medicine, or education) may opt to pursue a professional degree . These programs emphasize hands-on learning and often require students to obtain substantial real-world experience prior to graduation.
Academic (or research) degrees align with a single, specific area of study or field. Students in pursuit of these degrees are required to develop an in-depth understanding of their subject area and complete a thesis or capstone project to demonstrate their knowledge.
Learn More: Professional Degree Vs. Academic Degree: What’s the Difference?
Master’s Degree
Although master’s degrees may be the most common form of graduate study, there are various professional and academic graduate-level degrees that students should consider. Some of the most common include:
- Master of Arts Degree (MA): An MA is a type of academic master’s degree that correlates most directly with humanities-based subject areas such as communications, teaching, languages, and more. Classes in these programs are primarily discussion-based and might require fieldwork, a thesis, or a capstone project prior to graduation. Some common MA programs include Homeland Security , English , and Elementary Education .
- Master of Science Degree (MS) : An MS is another type of academic master’s degree which typically correlates with advanced study in fields that relate to science and mathematics. Courses in these programs often require extensive lab work or research and culminate with thesis or capstone projects, as well. Some common MS programs include Cybersecurity , Corporate & Organizational Communication , Leadership , and Project Management .
- Master of Fine Arts (MFA): An MFA is a professional degree for artists in fields such as graphic design, music, theater, film, and more. Alongside a practical and abstract exploration of their art, graduates of these programs often receive the credentials necessary to teach at the undergraduate level. Some common MFA programs include Information Design & Visualization , Creative Writing, and Acting.
- Master of Professional Studies (MPS) : An MPS is an interdisciplinary degree focused on a single area of professional study. Unlike MA or MS degrees, these programs are typically more hands-on in nature and require an internship, work-study, or co-op experience prior to graduation. Some common MPS programs include Analytics , Informatics , and Digital Media .
Professional Doctorate
A professional doctorate is focused on the advanced practice of knowledge and skills, making it a degree for those who are more professionally oriented. While these programs also help to develop research skills, the main focus is to apply knowledge to industry to solve new and emerging problems.
- Juris Doctor (JD): This degree provides students with the practical skills and expansive knowledge needed to practice law in America. While JD programs share some commonalities with other graduate-level law degrees, such as a Master of Legal Studies or a Master of Laws , there are key differences between the three.
- Doctor of Education (EdD): This is another professional doctorate degree not to be confused with a PhD in Education . This type of program is for educators and professionals who want to direct and implement change within their organizations. These degrees are designed to prepare students to become leaders in their communities.
- Doctor of Medicine (MD): Students hoping to pursue a career in medicine or surgery pursue this professional doctorate degree.
- Doctor of Pharmacy (PharmD) : Individuals pursuing a career in the pharmaceutical industry must obtain a PharmD. These programs include components of research, teaching, and clinical practice.
Learn More: Why Earn a Professional Doctoral Degree?
Doctor of Philosophy (PhD)
A PhD is a postgraduate doctoral degree based on extensive research in a given field. Students can earn a PhD in areas such as technology, humanities, social sciences, and more. Individuals who complete their PhDs often pursue a career in academia, though some may continue on to complete similar research for the remainder of their career. Some common PhD programs include Counseling Psychology , Bioengineering , and Pharmacology . PhDs are not to be confused with professional/clinical doctorates , which are designed to provide students with the practical skills needed to excel in their career.
How Long Does it Take to Earn a Graduate Degree
The timeline for completion of a graduate degree will vary depending on three factors:
- The type of degree you pursue.
- Your desired subject area.
- The specific institution at which you are studying.
On average, however, those enrolled in a master’s program full-time will likely complete their degree within one-and-a-half to three years. Individuals who pursue their master’s degree part-time might take longer than three years to complete it, depending on how many credits they enroll in each semester.
Most PhD and professional doctoral candidates will finish their degrees in five to six years, though the time commitment may vary depending on the subject area. Some more intensive degree programs, like an MD, can take up to eight years to complete.
Learn More: How Long Does It Take to Earn a Master’s Degree?
Graduate Degree Requirements
Requirements for different graduate programs vary greatly depending on the subject, institution, and whether or not it is a culminating degree. The most common requirement, however, is an undergraduate degree, as this acts as a base for advanced learning.
Other application requirements for specific graduate programs might include:
- A statement of purpose
- Your educational transcripts
- A portfolio of your work
- Professional/academic recommendations
- Any additional written assignments
You may also need to take and submit your scores for a subject-specific exam (e.g. LSAT, MCAT, etc.) or for the general Graduate Record Examination (GRE) , which is a requirement for many graduate programs globally.
The Cost of A Graduate Degree
The cost of a graduate degree will also vary greatly depending on what program and what institution you are considering. Yet, many people make incorrect assumptions about the price of graduate school based on their knowledge of undergraduate costs.
“Many of us have in our heads the sticker price of $30,000 to $40,000 per year for undergraduate education,” Sean Gallagher , executive director of the Center for the Future of Higher Education and Talent Strategy at Northeastern told U.S. News & Report in 2017. “So we say, ‘OK, it’s two years for a graduate degree, so it’s going to cost me $70,000 to $80,000 or more.’ And while there are certainly programs at that price point, there are many programs where you can get the entire graduate degree for between $20,000 and $40,000.”
No matter the program, graduate school will be both an educational and financial investment in your career. As such, institutions like Northeastern have adopted a variety of financial aid options for students to help hedge the cost of graduate studies. Students can utilize scholarships, grants, and even tuition reimbursement programs through their employers to help pay for their advanced education.
Learn More: Paying for Grad School: Where and How to Start
5 Characteristics of a Strong Graduate Program
#1) flexible learning options.
In most universities, graduate programs are designed to accommodate the needs of working professionals and are thus offered in a variety of exceedingly flexible formats.
Firstly, students at the graduate level can choose to enroll in either a part-time or full-time capacity. A part-time graduate program offers working professionals the opportunity to take on only as many classes as they can handle per semester, and work toward finishing their degree at their own speed. Full-time students, on the other hand, must be enrolled in a specific number of credit hours per semester as determined by the university, and will work toward completing their program in a linear manner. At Northeastern, for example, full-time students must be enrolled in nine quarter hours of graduate credits per semester.
Universities like Northeastern also offer a variety of graduate programs in online , on-ground, and hybrid formats to best fit the needs of any given students. Taking online or hybrid courses is an effective way for students who are already working in their field to balance their coursework with their other professional commitments, as well.
For those who aren’t ready to commit to an entire graduate program, some universities also offer graduate certificates in many in-demand areas of study. Certificate programs provide either a condensed understanding of basic advanced principles as they relate to an area of study, or a very niche look at a specific aspect of the subject. Though the amount of knowledge attained in a certificate program is vastly less than that of a full graduate degree, some prefer this condensed format of study for its reduced cost and shorter time commitment.
#2) A Focused Curriculum
By the time a student reaches graduate school, they are likely no longer in the exploring phase of their education. Instead, these students have often experienced life as a working professional, determined which area of study best aligns with their passions, and have made the educated decision to become an expert on that topic through the pursuit of a graduate degree.
For this reason, many graduate programs offer students a far more unified educational experience than at the undergraduate level. Often, this will be reflected in a common curriculum that all students within a single program must follow. While they may still be able to pick the specific topics that most interest them off this predetermined list of classes, each course will relate back to their base area of study. This is done in an effort to give students a much more in-depth exploration of that specific topic rather than a surface-level understanding of many, unrelated ones.
Students in graduate school still have the opportunity to customize their education to best fit their needs, however. In fact, programs like those at Northeastern recognize that one of the most impactful offerings they can give their students is the chance to declare a concentration within their degree and tailor their studies in a way that aligns with their professional aspirations.
#3) Opportunities for Hands-On Learning
Northeastern University is known for its emphasis on experiential learning at all phases of a student’s educational journey, offering opportunities for real-world, hands-on learning through internships, work-study, co-ops, and more. There are also a variety of graduate-specific experiential learning opportunities for students, such as Northeastern’s Experiential Network (XN) initiative.
A Closer Look: Northeastern’s XN initiative offers students the opportunity to participate in six-week-long, virtual projects for active organizations within the university’s expansive network. These projects align with students’ academic work, allowing them to apply what they learn in the classroom to these real-world scenarios. Following the format of gig-economy work experiences, students spend 30-40 hours on each project and, in that time, practice making decisions and completing work that will have a genuine impact on these organizations’ success.
In general, graduate degrees tend to be research- or capstone-oriented in nature, meaning that, depending on a student’s area of study, they will be frequently honing their practical abilities alongside their theoretical skills. Graduate programs emphasize this type of learning in an effort to develop well-rounded professionals in each field. These hands-on learning opportunities also offer students unparalleled exposure to different facets of their industry—as well as different types of workplaces—which can then be used to help them make an educated employment decision after graduation.
#4) An Industry-Aligned Network
Students have a unique advantage when it comes to networking in grad school . Between the opportunities to make connections in the classroom, at university-hosted events, and even in the professional world through hands-on learning experiences, these students are in the ideal setting to build their network.
Connecting with Classmates
Your classmates in grad school will likely be equally as driven and passionate about the exact same area of study as you are. You will also have the opportunity to grow together throughout your time in the program, resulting in a slew of common experiences and relationships that will help to keep you connected with and looking out for one another throughout your career. Although they may start out as your classmates, these individuals have the potential to become powerful players in the professional industry post-graduation, as well.
Connecting with Professors
Smaller class sizes and a more collaborative learning environment allow students to develop more personal connections with their professors during grad school than in their undergraduate studies. These relationships can be some of the most important in regards to your career, as professors at top universities like Northeastern are industry leaders and have connections that can be used to make introductions or open doors to potential employment opportunities after graduation.
Connecting with Industry Professionals
Given the emphasis on hands-on learning in grad school, students have the chance to develop their professional networks in their region and with organizations that they may be able to work with post-graduation. Having these types of industry-aligned connections is vital in today’s competitive job market, especially since a connection that has worked with you first-hand in a professional environment can speak to your qualifications in a far more concrete and impactful way than those who are only able to speak to your abilities abstractly.
Students who take the time to develop their professional network while in graduate school — whether online or on-ground —have the potential to see the positive impact of those connections for the remainder of their professional career.
#5) Substantial Impact on Your Career
Many students pursue graduate degrees to advance their careers. Whether that means getting a promotion, increasing their current salary, or even transitioning fields, these students are looking to make a positive change by showing employers the extent of their knowledge, network, and exposure to experiential learning.
While these goals are often achieved during the pursuit of a graduate degree, students’ careers can be impacted by graduate study in more ways than one. The overall career outlook for graduate degree holders, for instance, is incredibly positive compared to those with only a bachelor’s or associate degree.
For example, the current jobless rate for individuals with a master’s degree or higher is 12.5 percent lower than those who only hold a bachelor’s degree. Similarly, in regard to salary, those with a graduate degree earn 28 percent more than those with just an undergraduate degree on average. These individuals will also make over a million dollars more than those with just a high school diploma in their lifetime.
What’s more, graduates of advanced degree programs are some of the most in-demand within organizations today. When it comes to applying for a new role, 61 percent of employers are finding that the skills required for their open positions have evolved to require a higher education among applicants. By 2022, it is also expected that 18 percent of all jobs will require a graduate degree. Earning an advanced degree will help improve your skills and demonstrate your commitment to career development—two of the best ways to stand out in today’s competitive job market .
Explore Your Options at Northeastern
Ready to take the leap? Consider advancing your career with a graduate degree from Northeastern, a top-40 university . Evaluate the personal and professional benefits of a graduate degree, then explore Northeastern’s 200+ master’s , doctorate , and certificate programs to find the one that best aligns with your career goals.
Browse the Grad School Tips & Advice category of the Northeastern Graduate blog for more content like this from Northeastern University Graduate Programs .

Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About shayna joubert, related articles.

Why Earn a Professional Doctoral Degree?

5 Tips to Get the Most out of Grad School

Is Earning a Graduate Certificate Worth It?
Did you know.
Advanced degree holders earn a salary an average 25% higher than bachelor's degree holders. (Economic Policy Institute, 2021)
Northeastern University Graduate Programs
Explore our 200+ industry-aligned graduate degree and certificate programs.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

Top Higher Education Conferences To Attend in 2024

Grad School or Work? How To Balance Both

Is a Master’s in Computer Science Worth the Investment?

Should I Go to Grad School: 4 Questions To Consider
- FindAMasters
- Taught Masters vs Research Masters Degrees
Taught Masters vs Research Masters - Which is Right for Me?
Written by Ben Taylor
Masters degrees can be either postgraduate taught programmes (PGT) or postgraduate research programmes (PGR). Taught Masters are typically 12 months long full-time and are delivered through a series of modules comprised with regular coursework and assessments. Research Masters are also usually 12 months long however the course is predominantly comprised of independent research supported by a supervisor.
There’s a big contrast between these two kinds of Masters, and one type may be more suitable for your goals than the other. This page will explain the key differences between taught Masters and research Masters, and hopefully help you decide which kind of postgraduate programme is right for you.
On this page
Taught vs research masters – what’s the difference.
The difference between postgraduate taught degrees and postgraduate research degrees largely comes down to the level of independence you have during your studies.
Research Masters require students to undertake extensive research training, while postgraduate taught Masters involve a mixture of lectures, seminars and coursework.
- Taught Masters (PGT) degrees are a lot like undergraduate programmes. You’ll complete a series of modules following a set timetable of seminars, lectures and other activities. You’ll be much more responsible for studying independently in your free time, but the academics in charge of your course will lead you through it.
- Research Masters (PGR) degrees are more independent in nature. You won’t have as many timetabled units (in fact, you may not have any). Instead, you’ll focus on one or more extended projects. You’ll still receive support and guidance from an expert supervisor, but the focus of your programme will be on your own research work.
The majority of Masters-level programmes are taught courses. They include popular degrees like the Master of Arts (MA) and Master of Science (MSc) , as well as shorter Postgraduate Certificate (PGCert) and Postgraduate Diploma (PGDip) courses.
You can study these courses to acquire more advanced skills and training for a profession, or as a preparation for postgraduate research at PhD level.
Postgraduate research programmes are also available at Masters level. These include the Master of Research (MRes) and Master of Philosophy (MPhil) . Some Masters qualifications, such as the Master of Letters (MLitt) , can actually be taught or research degrees.
Masters by research vs Masters by coursework
A Masters by coursework is usually professional and vocational in nature, involving a series of set modules, while a Masters by research entails the completion of a significant, independent research project. This terminology is more common in Australia .
Writing a dissertation
Taught Masters do involve a substantial piece of research in its own right: the dissertation . This will be your chance to undertake an extended individual project, pursuing your own specific academic interests in a way that forms a significant part of your postgraduate course.
Should I study a taught or research Masters?
Your choice of PGT degree or PGR degree should depend on your career goals, academic interests and the way in which you prefer to study:
- If you want to acquire more advanced subject knowledge and gain an additional qualification before entering the employment market, a taught postgraduate course such as an MA or MSc may be best for you. We've taken a look at how the MA, MSc and MRes compare over on our blog.
- If you have a specific profession in mind, you could be better served by an accredited taught programme. This will usually be a Postgraduate Certificate or Diploma , but may also take the form of a full taught course, such as the Masters in Social Work or a Legal Practice Course .
- If you are interested in academic research – or a profession in which research skills are valuable – you may wish to think about an MRes . This will allow you to focus on an independent project in order to gain associated research skills, or evaluate whether a longer research degree (such as a PhD ) is likely to appeal to you.
- If you are considering an academic career , you might be able to register for an MPhil after your undergraduate degree and upgrade to a PhD upon making sufficient progress.
Can I do a PhD after taking a taught Masters?
Most PhD programmes ask that applicants have any kind of Masters in an appropriate subject. So, even if you study a taught Masters degree, you’ll be eligible to take a PhD if you satisfy the various entry requirements.
Of course, if you already know that you want to study at PhD level, then it’s worth considering a research Masters if there’s one available in your subject. An MRes would be ideal preparation for PhD study, allowing you to undertake more extensive research and receive specific training in appropriate methods. Another option would be to register for an MPhil and then upgrade to a PhD .
Is there a difference in fees for taught and research Masters?
In some cases, you can expect a research Masters to be cheaper than its taught equivalent. This is normally the case in the Humanities, where an MRes could cost less than an MA. Similarly, the yearly tuition fees for a PhD are often cheaper than a taught Masters.
Things are different in the Sciences, however: an MRes in a scientific subject usually has the same fees as an MSc degree. Both kinds of Masters typically involve extensive laboratory work.
The table below shows a summary of this data, reflecting the tendency for some research programmes to be cheaper than their taught counterparts.
| Type | E.g. | UK | International |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classroom | (Arts / Social Sciences) | £8,740 | £17,109 |
| Laboratory | (Science / Engineering) | £10,306 | £20,167 |
| Research | / | £4,000+ | £10,000+ |
* Based on the 2021-22 Reddin Survey of UK postgraduate fees , published by the Complete University Guide , as well as additional research and calculation by FindAMasters. Figures given are broad averages only and will not necessarily reflect fees for specific courses.
Is funding the same for taught and research Masters?
Essentially, the funding situation for taught and research Masters is the same. Check out our guide to Masters funding for more information on financing your course.
It’s worth noting that the UK government’s postgraduate loans are available for all Masters (including the MPhil). Standalone MPhils are not eligible for the PhD loans , but these loans are available for MPhils that are intended to become a PhD.
Search for a Masters
Ready to find your perfect Masters – taught or research? We've got thousands of courses listed on FindAMasters.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice

Exploring higher education options? Learn exactly what an integrated Masters degree is and how it can help fast-track you in your chosen field with our guide.

Some professional Masters degrees are designed to prepare students to work in specific jobs, such as Social Work, Engineering and Architecture qualifications.

Masters degree apprenticeships are a Level 7 qualification equal to a full-time Masters degree - but how do they work? Read our guide to learn this and more.

This guide covers the extra costs associated with studying GEM and an overview of where to find alternative financial support.

This guide covers how funding for Graduate Entry Medicine tuition fees and cost of living support works across the UK and for International students.

The Juris Doctor is a graduate-entry degree in Law. It is the main way of qualifying as a lawyer in the USA, and is also available in a number of other countries. This guide covers entry requirements, career options and more!
FindAMasters. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about Masters study?
Select your nearest city
- Aberystwyth
- Beaconsfield
- Bishop Burton
- Bournemouth
- Bridlington
- Chatham Maritime
- Cirencester
- East Malling
- Hemel Hempstead
- High Wycombe
- Huddersfield
- Isle of Man
- Jordanstown
- London Central
- London East
- London South
- London West
- Londonderry
- Loughborough
- Middlesbrough
- Milton Keynes
- Musselburgh
- Northampton
- Potters Bar
- Saffron Waldon
- Scarborough
- Southampton
- St Leonards on Sea
- Stoke on Trent
- Wolverhampton
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAMasters, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, application tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAMasters account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest Masters news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite courses, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your Masters courses? Log in here .

Let us help you find a Masters
Never miss a course
Enter our ambassador competition
Get funding news, tips and advice
Hear about upcoming events
Sign up to our newsletter today
We've been helping students find the right postgraduate course for over a decade.
Login to your account
Enter your username below to login to your account.

- Current Students
- Give to UNE

Future Students
Scripting must be enabled to use this site., difference between postgraduate research and coursework, what is the difference between postgraduate coursework and postgraduate research programs.
There are a few key differences between postgraduate coursework and postgraduate research programs.
Postgraduate Coursework
Postgraduate coursework programs deliver content through a set unit program (similar to an undergraduate Bachelor degree), but at a more advanced level. Coursework will allow you to deepen your knowledge within a discipline, or to pursue a new or additional study area at an advanced level.
Postgraduate degrees which can be studied through coursework include Graduate Certificates , Graduate Diplomas and Masters degrees.
Postgraduate Research
Postgraduate research programs (also known as Higher Degree Research ) allow you to develop your knowledge and experience within your field by completing a major research project under the supervision of an academic .
Postgraduate research degrees which you can study include Masters by research or Doctorate ( PhD ) programs.
Additional Information
For a comprehensive list of courses available, please refer to the Prospective Student Catalogue , or for further information view our Postgraduate Study page.
For further information regarding postgraduate coursework programs, please contact the Future Students Team through the Contact Us tab, online Live Chat , phone to 1800 818 865, or via Facebook .
For further information regarding postgraduate research programs, please submit your enquiry to Higher Degree Research through the Contact Us tab, or phone (02) 6773 3715 for assistance.
The feedback you provide will help us improve our answers for other people.
People who viewed this answer also viewed
- How to Enrol (or Re-Enrol)
- Difference between a Major, Specialisation and Area of Study
- What is Postgraduate Study?
- CRICOS Provider Number
- Information about Trimesters

- StumbleUpon

- Right to Information
- Accessibility
- CRICOS Provider Number 00003G
- TEQSA Provider Code: PRV12054 Australian University
- ABN: 75 792 454 315
- UNE is a member of the Regional Universities Network
© University of New England, 2017

The University of New England respects and acknowledges that its people, programs and facilities are built on land, and surrounded by a sense of belonging, both ancient and contemporary, of the world's oldest living culture. In doing so, UNE values and respects Indigenous knowledge systems as a vital part of the knowledge capital of Australia.
© University of New England, 2021

Which Master? Postgraduate Taught vs Research (Differences)

Find Master ’ s degrees in Europe now
💡 Taught Masters vs Research Masters:
There are many types of Master’s degrees, and most of these are Taught Masters . In the United Kingdom, such programmes are also called postgraduate taught or PGT for short. They typically require completing a set number of modules and a thesis (also called dissertation), plus sometimes work experience through a placement. The type of dissertation you will undertake will depend on the type of Master’s degree you are enrolled in, and might for example include your own small research project. Most postgraduate taught degrees have these elements of independent work and research to varying extents.
In contrast, a Research Master ’ s degree will focus on, you guessed it, research. In the UK, such programmes are also called postgraduate research or PGR (although this term may also refer to doctorate programmes). Rather than attending classes every semester and completing module assignments, you will need to focus on an independent research project – under supervision, of course. The course will still include a few taught modules, most often on research methodologies, but it will require you to work independently for most of the time.
Master’s degrees in the UK are usually one year full-time or two years part-time, but in other countries the duration may differ.
Remember: A final dissertation will be compulsory for all Master ’ s degrees. However, a dissertation for an MRes will typically be longer than that for an MA or MSc.
Typically, Research Masters will lead to an MRes degree. At some universities, however, you'll instead be awarded an MPhil (Master of Philosophy) or MLitt (Master of Letters). For more information, have a look at our detailed glossary.
🤔 Is a Research Master’s the same as a PhD?
No, a Research Master’s degree is not the same as a PhD. Although for both degrees you will need to complete a dissertation based on an independent research project, there are notable differences:
- The first difference is the duration : A Master’s degree will typically last one to two years, while a PhD usually takes up about three to five years. The research project you’ll undertake during a doctorate degree will therefore be longer and broader than one you would pursue in a Master’s degree.
- As a PhD student, you’re expected to publish research papers in journals before you are awarded your degree. MRes students might occasionally do that during or after their studies, but it’s rarely obligatory.
- As a PhD student, you’ll most often be expected to take on other duties , such as teaching.
If you wish to pursue doctoral research and a career in academia, a research Master’s degree could be a great option for you as it will allow you to get to grips with and gather valuable experience and training on independent research early on in your studies.
👀 Overview: What’s the difference?
There are a few differences between Taught Masters and Research Masters , and not all of them are obvious.
The table below outlines some of the main elements to consider when choosing which of the two degrees to pursue after your Bachelor’s degree:
| Differences | Taught Master’s degree | Research Master’s degree |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed and structured | Flexible | |
| Often ca. 2/3 taught courses, ca. 1/3 research project or dissertation | Mostly independent research, but could have a couple of taught modules as well | |
| Broader understanding of a particular discipline | Deeper insight into a specific subject or issue | |
| Typically Master of Science (MSc), Master of Arts (MA), Master of Laws (LLM), Master of Business Administration (MBA), etc. | Typically Master of Research (MRes), Master of Philosophy (MPhil), Master of Letters (MLitt) | |
| Students that want more advanced knowledge on a specific discipline before entering the job market or pursuing academic research. | Students that prefer working on an in-depth research project and are interested in staying in academia. |
Study in Europe: Find your Master ’ s degrees
🏛️ Which should you choose?
The choice between a taught Master’s and a research Master’s depends on a few factors.
- First of all, do you enjoy research more than coursework? Then an MRes may be more suitable – but remember that any Master’s degree, especially an MSc, will have a research component.
- Then, it’s crucial to understand how you like to work and study. Do you particularly enjoy working independently? Perhaps then you can consider an MRes. In a taught Master’s, you’ll have a more solid structure, timetables and regular deadlines to keep you on track, but these may not be as readily available during an MRes, so consider which environment you are more likely to thrive in.
- Another important consideration is what you want to do after your Master’s degree. If you want to enter the labour market immediately, and you are not particularly interested in focusing on research training, then perhaps a taught Master’s degree is more suited.
💸 Is there a difference in fees between Taught and Research Masters?
No, normally, you won’t find a huge difference in tuition fees between taught and research Master’s degrees. Only in some instances, Postgraduate Research Masters tend to be cheaper.
📝 Can I do a PhD after taking a Taught Master’s Degree?
Yes, you can pursue a PhD after any type of Master’s course, provided that you have a degree in a relevant subject. All taught postgraduate degrees involve some independent work and research, especially for your dissertation, which will prepare you for further research should you choose to pursue a PhD.
Some taught Masters require more independent research work than others, particularly when it comes to the dissertation after completing the taught modules. Consult the curriculum or ask admissions staff to get a better idea of what to expect.
While a taught Master’s degree won’t prevent you from doing a PhD further down the line, it’s vital that you have a good idea of what requirements you will have to fulfil in order to be admitted to the PhD, and how you can best prepare.
If you already have a clear idea of what field you’d like to conduct your doctoral research in, you could take advantage of the joint Master’s – PhD programmes on offer at some universities.
These four-year programmes – also called “combined” or “integrated” degrees – offer the chance to complete a Master’s degree in the first year and to progress seamlessly to PhD research in the next three.
Looking for Masters in Europe? Have a look at these English-taught degrees 👀

Author: Claudia Civinini
Claudia has many years of experience as a reporter and writer on international education and student mobility. Originally from Italy, she holds a BA in Communication and Media Studies from the University of Genova; a Graduate Diploma in Education, Secondary Education and Teaching from the Australian Catholic University; and a joint MSc in Educational Neuroscience from UCL and Birkbeck, University of London. Claudia has previously worked as Chief Reporter for the English Language Gazette, as Senior Reporter for the PIE News (Professionals in International Education), and as Reporter for Tes.

You might be interested in this:

- Student Services Online
- Class search
- Student email
- Change my password
- MyCDES+ (job board)
- Course outlines
- Learning essentials
- Libraries and Learning Services
- Forms, policies and guidelines
- Campus Card
- Enrol in courses
- Postgraduate students
- Summer school
- AskAuckland
- Student Hubs
- Student IT Hub
- Student Health and Counselling
- Harassment, bullying, sexual assault and other violence
- Complaints and incidents
- Career Development and Employability Services (CDES)
- Ratonga Hauātanga Tauira | Student Disability Services (SDS)
- Rainbow support
- Covid-19 information for our community
- Emergency information
- Report concerns, incidents and hazards
- Health and safety topics
- Staff email
- Staff intranet
- ResearchHub
- PeopleSoft HR
- Forms register
- Careers at the University
- Education Office
- Early childhood centres
- University Calendar
- Opportunities
- Update your details
- Make a donation
- Publications
- Photo galleries
- Video and audio
- Career services
- Virtual Book Club
- Library services
- Alumni benefits
- Office contact details
- Alumni and friends on social media
- No events scheduled for today You have no more events scheduled for today
- Next event:
- Show {0} earlier events Show {0} earlier event
- Event_Time Event_Name Event_Description
- My Library Account
- Change Password
- Edit Profile
- My GPA Grade Point Average About your GPA GPA not available Why can't I see my GPA?
- My Progress
- Points Required Completed points My Progress Progress not available All done!
- Student hubs
- Health and counselling
- All support
- Health, safety and well-being
Breadcrumbs List.
- Ngā akoranga | Study
- International students
- Study options for international students
- Postgraduate study for international students
- You are currently on: Taught or research masters
Taught or research masters
Masters degrees at the University of Auckland are generally offered as either research or taught (coursework) masters. Find out more about the benefits of both for international students.
What is a masters degree?
A masters degree is a degree programme demonstrably in advance of undergraduate level, that provides training in scholarship and research.
This allows you to build on your previous study by increasing your knowledge in a specific subject area, enhancing your career prospects and understanding. It offers transferrable skills, researched alongside leading academic staff, rigorous intellectual analysis and problem solving.
Masters degrees usually consist of full time study of either:
- one year (120 points)
- 18 months (180 points)
- or two years (240 points)
Our masters programmes are generally 180 points (18 months of full-time study) or 240 points (two years of full-time study). If you have already completed a year of postgraduate study, e.g. a postgraduate diploma, you may be admitted directly to a 120 point version (one year of full-time study).
Eligibility for the different options depends on the prior study you have completed. Some programmes will only include some of these options.
A masters degree can be structured as either a research or a taught programme and will have a points value assigned to it.
- Research masters include a thesis or research portfolio of at least 90 points.
- Taught masters are comprised of mainly taught courses, but can include a dissertation or research project of less than 90 points.
What's the difference between a taught or research masters?
Taught masters.
Taught (or coursework) masters degrees will give you advanced specialist training in your chosen field. They are usually completed by coursework only, although some can include a dissertation.
Taught masters programmes are becoming increasingly popular with international students at the University of Auckland. With a focus on applied learning and preparation for work, these programmes can produce well-rounded graduates with a broad range of technical and soft skills.
We offer taught masters degrees across various disciplines.
Research masters
As New Zealand’s premier research-led university, we also offer research masters for international students.
A research masters degree provides you with the opportunity to develop advanced research skills and present findings in a documented scholarly form such as a thesis. Your research should make an independent contribution to learning or offer a critical perspective on existing scholarship or methodology.
The University of Auckland has earned a great reputation for delivering academic and research excellence within a supportive learning environment. We give you the opportunity to learn from and collaborate with outstanding academic staff from New Zealand and around the world.
The University has built a broad academic community of researchers, scholars and students who are ready to support you as you challenge current beliefs, form and test new ideas, and embark on an enriching and fulfilling career. We look forward to welcoming you as a member of our community.
Related links
- Postgraduate study options
- New programmes
- How programmes are structured
- Find a study option
We're sorry but you will need to enable Javascript to access all of the features of this site.
Stanford Online
Computer science ms degree.
Stanford School of Engineering
Get Started
In the Stanford Computer Science Master's degree , you will complete coursework covering the fundamental aspects of computer science and deepen your expertise in at least one specialized area of study.
If you want to pursue the degree on a part-time basis, so as not to interrupt your career, you can enroll in as few as one course per quarter.
For added flexibility, you can take courses online or in-person on Stanford’s campus. Each quarter, numerous computer science and other engineering courses are available online. While most specializations within the computer science degree require attending some in-person classes, you can complete the Artificial Intelligence, Information Management and Analytics, and Systems Specializations entirely through online coursework. (Note that students interested in earning the master's degree part-time or online must reside in the United States.)
If you want more flexibility than the part-time master's degree, you can apply to take individual courses or pursue a graduate certificate without being formally admitted to Stanford master’s degree program. Choose from many options, including Foundations in Computer Science , Artificial Intelligence , Cybersecurity , Visual Computing , Software Systems , and Advanced Software Systems . Upon successful completion of each course, you will receive academic credit and a Stanford University transcript.
If you later choose to apply and are admitted into a master's degree program at Stanford, you may apply up to 18 units towards the master's degree (pending department approval).
Not sure which of these credentials is right for you? Compare our graduate certificate vs. master’s degree .
How Much It Will Cost
How long it will take.
To earn the Master of Science in Computer Science Degree, you must complete 45 units.
- As a part-time student, you can expect to finish the degree in 3 to 5 years.
- As a full-time student, you can expect to finish the degree in 1 to 2 years.
What You Need to Get Started
For admissions information , please visit the department's site or contact [email protected] .
For degree requirements , please review either the department's Guide to the MSCS Program Sheet or Stanford Bulletin . See the department's FAQs page .
For more about the policies, procedures, and logistics, please review our website .
While this degree can be completed online, it depends on your program plan and area of focus. Most courses in the Computer Science department are offered only on campus. Specific online course offerings depend heavily on your program plan, area of focus, and the online course offerings for any given academic quarter. Students who are outside the US cannot pursue the master's degree online.
What Our Learners Are Saying
Meet roslyn.
Roz discusses the connection between design and computer science as well as the goals accomplished by the courses she took through Stanford Online.
Watch Video
You May Also Like

Foundations in Computer Science Graduate Certificate

Artificial Intelligence Graduate Certificate

Advanced Software Systems Graduate Certificate

Introductory Programming Graduate Certificate
- Engineering
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Science & Security
- Business & Management
- Energy & Sustainability
- Data Science
- Medicine & Health
- Explore All
- Technical Support
- Master’s Application FAQs
- Master’s Student FAQs
- Master's Tuition & Fees
- Grades & Policies
- Graduate Application FAQs
- Graduate Student FAQs
- Graduate Tuition & Fees
- Community Standards Review Process
- Academic Calendar
- Exams & Homework FAQs
- HCP History
- Enrollment FAQs
- Tuition, Fees, & Payments
- Custom & Executive Programs
- Free Online Courses
- Free Content Library
- School of Engineering
- Graduate School of Education
- Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability
- School of Humanities & Sciences
- Stanford Human Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI)
- Graduate School of Business
- Stanford Law School
- School of Medicine
- Learning Collaborations
- Stanford Credentials
- What is a digital credential?
- Grades and Units Information
- Our Community
- Get Course Updates

Graduate coursework options
You can apply for more than 340 award programs ranging from Graduate Certificates to Masters and PhD study in a wide range of study areas and disciplines.
Graduate degree options include:
Graduate certificates
A Graduate certificate is six month course where you can choose from more than 25 discipline areas. It's a perfect stepping stone to help you return to tertiary study after some time away.
Find Graduate certificates
Graduate diplomas
The Graduate Diploma is similar to an undergraduate major and ideally suited as an introduction to a new discipline. It's perfect for professional development and as a preparatory program for graduate studies.
Find Graduate diplomas
Masters by coursework
Masters by coursework is normally one to two years of study. It provides advanced specialist or professional training in a particular discipline or interdisciplinary area and can lead to professional accreditation. Some also offer pathways to doctorate specialisations.
Find Masters by coursework
Professional doctorates
Professional doctorates enable you to carry out advanced academic and professional study that directly relates to a professional role. Completion normally requires doing coursework and a thesis.
Find Professional doctorates
Professional and Continuing Education
There are also professional and continuing education programs you can take outside of your degree to give you a leading edge in your field of expertise.
View programs
Need help understanding your options?
Get in touch with our student support team at Stop 1 to discuss what graduate coursework degrees you can apply for.
Taught vs research masters: What's the difference and which should I choose?

Table of Contents
1. taught masters meaning, 2. popular taught master courses, 1. research masters meaning, 2. popular research master courses, 1. curriculum and structure, 2. coursework, 3. duration, 3. specialisation, 4. supervision, 5. employability, taught vs research masters: which should you choose, 1. career aspirations, 2. interest in research, 3. program structure, 4. academic background, 5. time commitment, postgraduate taught vs research, can i do a phd after taking a taught masters, taught vs research masters: fee difference, frequently asked questions.
So you’ve decided you want to do a masters degree and you have a rough idea of which courses you like the sound of and where you might want to study. So all that’s left to do now is apply, right?
Not quite. There’s actually one more decision to make, that you might not even have known about in the first place: would you rather study a taught or research masters?
Both course types involve a high level of academic study and independent work . However, a taught course offers a more familiar structure and a wider variety of subjects. It also offers more assessment modules than a research-based course, which puts more focus on in-depth research and writing. Not sure which option to choose? We’ve got you covered. Without further ado, here are the difference between taught and research masters, so you can choose the course that’s best for you.
Also Read: Canada vs USA for masters
What is a taught master's degree?
As the name suggests, the majority of a taught masters course revolves around a series of modules, each with seminars, lectures and assignments or exams.
Most taught masters degrees will also generally require you to complete a final dissertation or major research project. In other words, a masters taught degree is like a continuation of an undergraduate degree.
Also Read: 6 Masters degrees in Engineering Management that will change your life
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- Master of Science (MSc)
- Master of Arts (MA)
- Master of Engineering (MEng)
- Master of Public Health (MPH)
What is a research masters degree?
A research masters is very different, both in terms of course content and structure. Rather than taking a variety of modules, each with a mixture of exams and coursework, the progression of a research masters is more fluid. You may start the course with an introductory module or set of classes focusing on developing your research and writing skills, but after that, you’ll likely have little to no timetabled hours. Instead, you will be spending your time working independently on one or more extended research projects.
- Master of Research (MRes)
- Master of Philosophy (MPhil)
Taught vs research masters
Taught masters and research masters are two distinct types of masters programs that offer different approaches to education and learning. Here are the main difference between taught and research masters:
Taught masters are structured programs with a predetermined curriculum. Students take a set of modules or courses covering specific subject areas relevant to their field of study. These programs are more structured and organised, with clear learning outcomes. Unlike taught masters, research masters offer more flexibility in terms of the curriculum. Students have more freedom to design their research project within the scope of their field of study.
The focus of taught masters is on coursework, where students attend lectures, seminars, and workshops. They are assessed through exams, assignments, projects, and sometimes a dissertation or thesis. The centrepiece of a research master's program is the research project or thesis. Students are required to conduct independent research under the guidance of a supervisor or mentor.
Taught masters typically last one to two years , depending on the country and the program's requirements. Research masters may take longer to complete than Taught Masters due to the in-depth research and analysis involved.
Students often choose a specialisation within the field, but their coursework is determined by the university or department. Research masters are more research-oriented, with a significant emphasis on original research and exploration of a particular subject area.
While students have access to academic staff for guidance and support, they generally have less individualised supervision than in research-focused programs. Research masters offer more individualised supervision and mentorship as students work closely with their research advisors throughout the process.
Taught masters are generally designed to enhance employability by providing students with practical skills and knowledge relevant to their chosen career path. Research masters are often considered a pathway to a Ph.D. or further research-based careers in academia or industry.
Here's a table summarising the key difference between taught and research masters:
| Aspect | Taught Masters | Research Masters |
|---|---|---|
| Curriculum | Predetermined coursework with set modules | Research-oriented with thesis/research project |
| Coursework | Focus on attending lectures, seminars, and workshops | Emphasis on independent research and analysis |
| Duration | Typically 1 to 2 years | May take longer due to research requirements |
| Specialisation | Specialisation within the field | More freedom to design the research project |
| Supervision | Less individualised supervision | More individualised supervision and mentorship |
| Employability | Enhances employability with practical skills and knowledge | A pathway to further research-based careers |
When it comes to deciding between a taught or research masters, you should first ask yourself what motivates you to study and what you’ve enjoyed most about your undergraduate degree. If your favourite part of your degree was researching and writing a dissertation, and you want to further develop your academic skills and potentially go on to do a PhD then it’s worth looking into research masters courses. But if you have a specific career goal outside of academia, a taught masters will allow you to gain a broader range of skills and experience to enhance your CV.
One final consideration should be what are you best at?
For example, if you struggle with essays but tend to do well in exams and presentations, then a taught masters with a wider variety of assessment modes might be a better fit for you.
At the end of the day, regardless of which option you choose, studying for a master’s degree is an invaluable experience and either course is sure to open a lot of doors for you further down the line.
Thinking about studying your taught or research masters course abroad? Let us help you find your perfect course and university today!
Should I study a taught or research Masters?
Deciding between a taught or research master's program depends on your academic and career goals, as well as your personal preferences and strengths. Here are some factors to consider when making your decision:
Consider your career goals and the type of role you wish to pursue after completing your master's degree. If you aim to work in a profession that values specialised knowledge and practical skills, a taught master's program may be more suitable. On the other hand, if you are interested in a career in research, academia, or a field that requires advanced research capabilities, a research master's program may be a better fit.
Reflect on your interest in research. Are you passionate about conducting independent research and contributing to the knowledge in your field? If research excites you and you enjoy the process of inquiry, a research master's program could be an excellent choice.
Compare the structure and content of both types of programs. Taught master's programs typically involve a mix of lectures, seminars, and coursework, while research master's programs focus on a more significant research project. Assess which learning approach aligns better with your preferred style of study.
Consider your academic background and strengths. Research master's programs often require a strong academic record and a solid foundation in the chosen field of study, as the emphasis is on conducting original research. If your academic strengths lie in coursework and exams, a taught master's program may suit you better.
Evaluate the time commitment required for each type of program. Research master's degrees tend to be longer and more intense, as they involve substantial research and writing. Taught master's programs are usually shorter and may be more suitable if you wish to enter the job market sooner.
Take the time to research different programs, talk to current students and faculty members, and seek advice from academic advisors to make an informed choice that aligns with your aspirations.
Postgraduate education in the United Kingdom offers two main pathways
- Postgraduate research programs
- Postgraduate taught programs
Postgraduate research programs focus on independent and original research, where students delve deep into a specific research question or topic within their chosen field. They work closely with a research supervisor and complete a research thesis or dissertation to contribute new knowledge to their discipline. These programs are suitable for individuals pursuing careers in academia or research.
On the other hand, postgraduate taught programs emphasise structured classroom-based learning. Students follow a set curriculum, attending lectures, seminars, and practical sessions to gain specialised knowledge and practical skills. Assessment in these programs involves coursework, exams, and sometimes a dissertation or research project.
The choice between postgraduate research vs taught depends on individual interests and career aspirations. If you have a passion for conducting independent research and want to contribute to your field, a postgraduate research program might be the right fit. However, if you seek specialised skills and industry-focused expertise, a postgraduate taught program may be more suitable.
Many students wonder if they can pursue a Ph.D. after completing a taught master's degree. The answer is yes, it is indeed possible. Universities and research institutions often welcome students who have successfully completed a taught master's program and wish to continue their academic journey by undertaking a Ph.D. program.
Completing a taught master's degree can serve as a stepping stone toward a research-based Ph.D. program. While some additional effort may be required to strengthen your research profile, many students successfully make the transition and go on to make significant contributions in their chosen fields of study.
In general, Taught Masters programs tend to be more structured and may involve a higher number of taught modules or courses, which can lead to higher tuition fees. These programs often focus on providing practical skills and knowledge that are directly applicable to the job market, and the additional resources required for delivering coursework can contribute to higher fees.
On the other hand, while the fees for Research Masters can still be substantial, they might be slightly lower than Taught Masters in some cases. This is because Research Masters programs often have fewer taught modules, and students spend a significant portion of their time conducting research, which may require fewer resources compared to a more structured coursework-based program.
Which degree is right for me in the UK?
If you prefer a structured and specialised curriculum with classroom-based learning, a taught Masters may be suitable. On the other hand, if you have a strong interest in conducting independent research and contributing to your field, a research Masters could be a better fit.
Taught vs Research, which is better?
The choice between taught vs research Masters depends on your academic and career objectives. A taught Masters offers a structured curriculum with specific subject knowledge, while a research Masters focuses on independent research and academic inquiry.
What is the difference between taught and research masters?
The main difference between taught and research masters lies in their core focus. A taught Masters emphasises classroom-based learning, lectures, and assessments, providing specialised subject knowledge and skills. In contrast, a research Masters centres around conducting independent research, contributing to the existing knowledge in a field, and developing strong research skills.
Are Masters by research better?
A Masters by research offers an opportunity to engage in independent and in-depth research, making it ideal for students pursuing a career in academia or research-oriented professions. However, a taught Masters may suit those seeking specialised skills and industry-focused expertise. The decision should align with your aspirations and preferred learning style.
Why are research Masters cheaper?
Research Masters programs are often cheaper than taught Masters because they require less institutional resources.
Is a Masters by research a full Masters?
Yes, a Masters by research is considered a full Masters degree. It is a postgraduate qualification that requires the completion of a research project, dissertation, or thesis. Know someone considering postgraduate studies? Share the insights in our 'Taught vs Research Masters' article with them.
Refer a friend and help them make the right choice for their academic journey.
Guest Author | Study Abroad Expert
Disclaimer: The views and opinions shared in this site solely belong to the individual authors and do not necessarily represent t ...Read More
Virtual Counselling - Start your study abroad plan, from home!
How to improve your English language skills
Top 10 courses to study whilst stuck at home
10 Top universities in UK for masters in business analytics
5 Reasons you should study engineering in the UK
5 Reasons why Industrial and Robotics Engineering at Gannon University is the perfect major
Future student support
Scripting must be enabled to use this site., search knowledge base, what is a coursework program.
Coursework is defined under the Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF) as a method of teaching and learning that leads to the acquisition of skills and knowledge that does not include a major research component. Bachelor's programs and postgraduate coursework programs are all coursework programs.
Search the Future Students website for programs available at UQ.
Was this answer helpful?
Related answers.
- What is a higher degree by research (HDR)?
- If I apply for a masters by coursework program and my GPA is not high enough, what are my entry options?
- As an international applicant, how do I convert my current GPA into an Australian equivalent?
- When do applications close?
- Do I need to have a supervisor before submitting my higher degree by research (HDR) application?

Cognition & Co
South African Psychology Student Network
Masters by Dissertation vs. Coursework Masters

If you’re studying psychology and looking to register as a psychologist in the future, it is likely that you’ve heard about the above-mentioned qualifications. To clear up any misconceptions about these types of masters programmes, Cognition & Co have put together the following article highlighting the differences between them;
Masters by Dissertation:
A Masters by Dissertation is a purely academic M degree whereby students are required to conduct research that culminates in a dissertation. Different universities call these qualifications by different names (Academic Masters / Masters by Research, etc), however they all follow a similar format.
Most of these programmes can be done part-time through distance learning institutions however students will need to be in contact with their allocated supervisor. A supervisors’ role is to help, support and guide students through their research, ensuring the quality of the dissertation.
While a Masters by Dissertation is heavily research orientated, these degrees are different to a Research Masters degree in South Africa. A Research Masters is a full-time (sometimes part-time) coursework programme offered by some universities ( Wits ) which can lead to an HPCSA registration as a Research Psychologist .
Unlike a Research Masters, a Masters by Dissertation does not lead to registration with the HPCSA. Even once a student has completed a Masters by Dissertation, they are still not allowed to call themselves a Psychologist, nor will they be able to counsel clients, regardless of their dissertation topic or title.
These degrees are highly valued in academic circles and would certainly put any graduate in good stead to work in some form of higher education. Completing a dissertation also opens doors in terms of publishing one’s dissertation and having that accolade added to one’s portfolio.
Coursework Masters:
In order to become an HPCSA registered Psychologist in South Africa, students will need to complete a Masters Degree that includes a coursework aspect, as well as a dissertation. These are typically all full-time programmes (except some Research Masters) where students will spend their time between classes and supervision on a university campus, as well as at practicals in hospitals, clinics, or schools.
Again, universities may call these coursework programmes by different names (sometimes called Professional Masters), but they are typically M degrees in a specialized area of psychology. These specialized areas are defined by the HPCSA and are broken into different registered categories; i.e. Clinical , Counselling , Educational , Industrial , Research , and more recently Neuropsychology .
The duration of a coursework degree is also specific to the different universities. Many universities offer these degrees over a period of two years, however there are a number of universities that allow students to complete both their coursework and dissertation in just one year. Once a student has completed their 1 or 2 years of coursework, they may then register with the HPCSA as an Intern Psychologist and begin their 1 year internship. Following the completion of a 1 year internship, graduates may write their respective board exam with the HPCSA and upon passing will receive the title; Psychologist.
It is also important to note that students following the route ending in registration as a Clinical Psychologist, will also need to complete one year of community service once they have successfully passed their board exams .
To find out more about the route to becoming a Psychologist in South Africa, click the link provided above. Students are also welcome to contact us with questions or queries by clicking here .
3 Replies to “Masters by Dissertation vs. Coursework Masters”
- Pingback: Improve Your Honours Average? Pursue a Master's by Dissertation instead. - Cognition & Co
- Pingback: Things I wish I was told before my Undergraduate Degree in Psychology - Cognition & Co
- Pingback: Navigating Studying Psychology Abroad – Cognition & Co
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

The difference between a postgraduate vs master’s degree

At UNSW, you’re spoilt for choice with over 400 programs on offer.
But when it comes to navigating undergraduate, postgraduate and research programs, the terminology can get a little confusing. If you’re interested in taking your studies further and want to know the difference between a postgraduate degree and a master’s degree, we have good news for you.
They’re the same! Let us explain…
What is a postgraduate degree?
A postgraduate degree is (almost) any type of university program you undertake after completing undergraduate study. ‘Postgraduate’ is a handy umbrella term that helps us classify the “level” of study of a particular program. Postgraduate programs include master’s degrees, as well as graduate certificates and graduate diplomas.
What is a master’s degree?
A master’s degree is a type of postgraduate degree. They’re often longer than graduate certificates and graduate diplomas, taking between 1-2 years to complete. They involve advanced study of your chosen field and allow you to further enhance your skills, develop a specialisation and gain more academic and professional experience in the field.
There are two main types of master's degrees:
Course-based: Focuses on coursework and shorter research papers
Research-based: Requires an extensive thesis project
Master’s degrees can help you advance into leadership roles, increase your earning potential, and prepare for doctoral programs.

Choosing between a master’s and other postgraduate programs
If you’re keen to take on postgraduate study but aren’t sure if a master’s degree is right for you, we’ve broken down the key differences and things to be aware of before making a decision.
Duration: Postgraduate degrees can range from 1-6+ years depending on the program level. Graduate diplomas and graduate certificates can take as little as six months while PhD and other doctoral programs can take up to six years. Master’s degrees are the sweet spot, generally taking 1-2 years to complete.
Cost: Postgraduate degrees vary in cost depending on factors like degree type, university, program prestige and whether you study domestically or internationally. Master's degrees are typically cheaper than doctoral degrees. The average cost of a master’s degree for domestic students is between $6,000 –$11,000 annually. For international students, it’s between $20,000 – $37,000 per year. We encourage all students to check their eligibility for scholarships to support their studies.
Flexibility : Many postgraduate degrees offer flexible part-time options, catering to working professionals. Flexibility can depend on university policies and degree requirements. As with most programs, a master’s degree can be taken part-time but will extend the time to completion.
Can I change my Master's specialisation after a bachelor's degree?
Yes, many master’s programs are open to students from all academic backgrounds. This means you can change focus areas entirely or specialise further within your field. Depending on your undergraduate program, you may be eligible for Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) to reduce your postgraduate study load.
Why should I do a master’s degree?
Studying a master’s degree offers many potential benefits, including:
- Higher salary prospects and job opportunities
- Preparation for PhD programs through research experience
- Specialised knowledge to stand out in your field
- Personal growth and development opportunities
What are some popular master’s degree options at UNSW?
We are known for producing Australia’s most employable graduates*. Our postgraduate programs are recognised all over the world. Here are some of our most popular master’s programs:
Master of Engineering
Master of Laws
Master of Commerce
Master of Information Technology
Master of Architecture
Master of Education
Master of Public Health
Master of Clinical Optometry
Master of Data Science
Master of Mathematics
Master of Actuarial Studies
*AFR Top 100 Future Leaders Awards 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024
Connect with us
Sign up to our newsletter - we'll keep you updated on degree information, scholarships and upcoming events.
Ready to explore your study options?
What is Coursework at University?
In University by Think Student Editor October 5, 2023 Leave a Comment
Compared to the rest of the British education system, university can seem so very different. Lessons are now lectures or seminars, you have complete independence, and you even have the option to live on campus. Plus, there are so many other differences on top of this. This might make you wonder if the components of studying at university are different as well, especially in terms of how the course works. One of the components that’s important to look at in this way is coursework and how it differs at university.
In short, at university coursework is similar to at previous levels of education, where coursework is a form of assessment without exams that helps to make up your grade. At university, this is because successfully completing coursework helps you to pass modules, allowing you to get your qualification. This coursework can come in many different forms and the types you do will depend on your course and your university. However, some of the main types are essays, reports and projects, including research projects such as dissertations.
Continue reading to learn more about what coursework is at university. This article will take you through how coursework works at university and what some of the main types of university coursework are.
Table of Contents
Is there coursework at university?
When thinking about coursework, we tend to be more familiar with the term when it’s associated with school or college. In this case, coursework is a form of internally assessed assignment that will make up a part of your grade.
As a form of assessment, it will often be essential to help you to get your qualification, whether that’s for a GCSE/ National 5 qualification, an A-Level/ Higher or Advanced Higher or a more vocational qualification, such as a BTEC or a T-Level. For more information about what coursework is like at this stage, check out this guide by NI Direct.
As university can feel so different from school or college, you may be wondering whether or not there even is coursework at university and whether it works in the same way.
Simply put, yes, there is coursework at university . In fact, some universities state that most modules will have some form of coursework involved in them.
Students take a range of modules to make up their degree programmes. This means that students are very likely to do at least a bit of coursework in a few of their modules across the course of their studies. You can learn more about this by checking out this page on the University of St Andrews website.
What do you do in coursework at university?
At university there is so much more variation in what you can study and how you study it. From the different classifications of degree, even just within the undergraduate level, from foundation degrees to all the different kinds of bachelor’s degree, such as the BA, BSc or LLB, to all of the other kinds of qualification that you can do at university.
Due to all of this variation, there should be no surprise that in each of these different kinds of courses, students will be taught in different ways. Moreover, there isn’t any actual standardisation across universities, meaning that even on very similar courses, students can be taught with completely different methods.
As a result of this, the coursework that you do at university will completely depend on your course and your university. However, there are some common types of coursework that are done.
Some of these main ones are essays, reports and projects . For more information about what different types of coursework at university might be, you can check out this page by the University of Leeds.
You can learn more about these in their respective sections below.
Is an essay a type of coursework at university?
An essay is an academic piece of writing where students will have to make an argument in response to a certain question. In secondary school and college, you may have come across essays in the form of exam questions, where they would be valued in terms of their marks. For example, you may have had to do a “10-marker”, a “20-marker” and so on.
Alternatively, you may have come across them as part of your own coursework or NEAs, particularly in humanities subjects, where the knowledge and argument you present would be more detailed and in-depth. For university study, essays as a form of coursework, are more similar to the latter as they will need to be well-researched and in-depth .
However, university is at a higher level that school and college . As a result, university essays will need to be as well with students needing to carry out some independent research and reading before they can start the essay rather than relying just on what they have been taught.
You can learn more about essays as a form of coursework at university on this page by the University of Nottingham.
Is a report a type of coursework at university?
Reports and lab reports are a type of coursework that you will probably not have directly come across in previous study, although you may have done something a bit similar. Unlike an essay, a report is purely factual and objective, where the main aim is to present findings and to analyse the data collected, rather than to make an argument.
While they are particularly present in the sciences and social science subjects, reports are a form of coursework that can be used across a large variety of different subjects. Due to this, there are many different types of report and which one you may have to undertake as a part of your coursework will depend on your degree.
For more information about this, look at this page on the University of York’s website.
One of the main types of report is a lab report. This is a type of report done by sciences students after an experiment has been done. You can learn more about them by checking out this guide by the University of Nottingham.
Is a project a type of coursework at university?
For university study, a project as a form of coursework can refer to a few different modes of study. First of all, when talking about a project, we might be referring to a research project.
A research project is an extended essay that students complete by undertaking and then presenting their own research and comparing this to the preexisting ideas. This kind of research project will typically be big and may even be an entire module.
In cases like this, the research project will most likely be in the form of a dissertation or even a thesis if done at doctorate level. You can learn more about this type of project by looking at this page on the University of Sheffield’s website and for more on dissertations, look at the following section.
However, projects can also be in the form of group projects that can vary a bit more across universities. For example, at Imperial College London, students undertake a multidisciplinary group project to try and come up with solutions to the biggest social challenges. You can learn more about this on this page on their website.
Also, the University of Edinburgh Business School runs group consultancy projects at both undergraduate and master’s degree levels. For more information about this, check out this page on their website.
Is a dissertation a type of coursework at university?
At university in the UK, a dissertation is a type of research project that can be taken by students for either a bachelor’s degree or a master’s degree. As an extended essay, students will need to produce an answer to a specific question of somewhere between 5,000 and 50,000 words depending on the university and whether it is a bachelor’s or master’s degree that you’re doing.
There are different kinds of dissertation and depending on which kind students do will depend on how they go about writing it. For an empirical dissertation, students will need to carry out research and collect data first hand to use as part of their dissertation. Whereas for a non-empirical dissertation, students will have to research into data and information that is pre-existing.
You can learn more about what a dissertation is by looking at this Think Student article .
As previously mentioned, one of the main types of coursework at university are projects, including research projects. This means that yes, dissertations are a type of coursework at university as they are types of research project.
Undergraduate vs. Graduate: Educate Yourself On The Difference
- Undergraduate Meaning
- Undergraduate Student And Degree
- Graduate Meaning
- Graduate Degree And Student
- Graduate Origin
- Postgraduate Meaning
⚡ Quick summary
The main difference between undergraduate and graduate is that undergraduate is always used in the context of the first level of college or university education (the level where you can earn a bachelor’s degree ). In terms like graduate student and graduate degree , graduate refers to a level of advanced education beyond the undergraduate level, especially a master’s degree or doctorate . The noun graduate is more general, simply referring to a person who has completed a level of education (someone who has graduated ).
The difference between undergraduate and graduate is a difference of degrees (*throws graduation cap in the air to celebrate the pun*).
The level of education that each word involves varies depending on how the word is being used, and there are situations in which both words can be used in the same situation. For example, you can become a graduate student after graduating with an undergraduate degree.
The word graduate can mean very different things depending on whether it’s used as a noun (as in recent high school graduates ), an adjective (as in graduate student and graduate degree ), or a verb (as in I plan to graduate next May ). The same goes for its shortened form, grad , which can be used as a noun (as in Congrats, grads! ) or an adjective (as in grad program ).
Undergraduate can also be used both as a noun (as in I’m an undergraduate at Stanford University ) or an adjective (as in I’m working toward my undergraduate degree ). It can be shortened to undergrad in both cases.
By the end of this article, you’ll have an advanced degree in all the different ways graduate, grad , undergraduate , and undergrad are used, and what they mean in each case.
What does undergraduate mean?
An undergraduate is “a student in a university or college who has not received a first, especially a bachelor’s, degree.” For example, a college student might say I’m an undergraduate at the University of Texas if they were pursuing a bachelor’s degree there.
Undergraduate is also commonly used as an adjective in this same context, in terms like undergraduate student , undergraduate degree , and undergraduate studies.
Undergraduate is often shortened to undergrad as both a noun and an adjective.
In undergraduate, the prefix under- is used to indicate a lower rank or status. The educational status of an undergraduate student is below that of a graduate student.
What’s the difference between wisdom and knowledge ? Here’s a lesson on the two terms.
What is an undergraduate student ? And what is an undergraduate degree ?
An undergraduate student is a student who is pursuing a degree at the first level of higher education (meaning the level after high school) at a college or university. Undergraduate students are typically those working to earn a bachelor’s degree (or, less commonly, an associate’s degree ). These degrees are often referred to with the general term undergraduate degree.
Outside of the US, an undergraduate degree is sometimes called a first degree. There are also other types of undergraduate degrees outside of the US, such as a foundation degree (which, like an associate’s degree, is typically a two-year degree).
What does graduate mean?
As a noun, the word graduate [ graj -oo-it ] refers to “a person who has received a degree or diploma on completing a course of study.” In other words, a graduate is someone who has completed a particular level of schooling or an educational program—a child who just finished kindergarten and a doctor who just completed medical school are both graduates. It can even be used figuratively , as in She’s a graduate of the school of hard knocks.
As a verb, graduate [ graj -oo-eyt ] means “to receive a degree or diploma on completing a course of study.” The process of graduating—and the ceremony itself—is called graduation .
As an adjective, graduate [ graj -oo-it ] means something more specific. It’s used to indicate that a student, degree, or educational program is an advanced one, beyond the level of a bachelor’s degree. This sense of graduate is most commonly used in terms like graduate degree, graduate school , graduate program, and graduate student.
What is a graduate degree ? And what is a graduate student ?
Graduate degree typically refers to a degree beyond a bachelor’s, most commonly a master’s.
A graduate student is a student who’s pursuing an advanced degree after having earned their undergraduate degree (such as a bachelor’s degree) by graduating from an undergraduate program. Calling someone a graduate student most often means they are pursuing their master’s degree, but it may be another advanced degree, such as a PhD (You’d most commonly call such students PhD students. Or you might say they are working toward their doctorate or their doctoral degree.)
To earn a graduate degree, graduate students go to a division of a university known as graduate school , and such a program is often called a graduate program. In all of these terms, graduate is often shortened to grad : grad school , grad student , grad program . (A student doesn’t become a graduate student until they take graduate-level courses. For example, if a student graduates with a bachelor’s degree and then later pursues a different bachelor’s degree, they are still an undergraduate student .)
Some graduate studies are referred to in more specific ways: medical students go to medical school to earn their medical degree ; law students go to law school to earn their law degree.
Do you know the difference between these highly-esteemed graduate degrees and titles: PhD, MD, and Dr ?
Where does the word graduate come from?
Graduate comes from the Medieval Latin graduārī, meaning “to take a degree.” It ultimately derives from the Latin gradus, meaning “a step.” Each time you graduate, you take a step to the next level of education.
What does postgraduate mean?
The adjective postgraduate is sometimes used in the same way as the adjective sense of the word graduate, especially in the UK, as in postgraduate student or postgraduate studies.
Postgraduate should not be confused with postdoctoral , which refers to studies, research, or professional work above the level of a doctorate.
How to use undergraduate vs. graduate
The best way to sort out the different meanings of undergraduate and graduate is to determine whether each word is being used as a noun, an adjective, or a verb. Here’s an easy breakdown of the differences.
- undergraduate (noun): A college student pursuing a non-advanced degree, most commonly a bachelor’s degree. Can be shortened to undergrad.
- undergraduate (adjective): Used in the context of colleges and university programs ( undergraduate programs ) where students are pursuing a degree (generally referred to as an undergraduate degree ) that is not an advanced degree. Also sometimes shortened to undergrad.
- graduate (noun): A person who has completed a particular level of schooling or educational program. Can be shortened to grad.
- graduate (verb): To complete a level of schooling (and, typically, to receive a degree or diploma). You can graduate from kindergarten, high school, college, graduate school, medical school, etc.
- graduate (adjective): Used in the context of advanced schooling—a level beyond a bachelor’s degree, most commonly a master’s program. Used in terms like graduate student , graduate school , graduate degree , graduate program , graduate courses , etc. Often shortened to grad.
Examples of undergraduate, undergrad, graduate, and grad used in a sentence
Let’s look at some examples of these words in actual, real-life use to get the meanings straight.
- As an undergraduate, she had studied engineering; as a graduate student, she switched to architecture.
- I completed my undergraduate degree after five years and a lot of hard work.
- As a graduate student, you will be expected to complete a thesis.
- You should start thinking about graduate school applications before you graduate.
- Most of the applicants for this position are recent college graduates.
- I’m still an undergrad, but I’m hoping to start grad school next fall.
- I’m a UGA grad, but I almost went to Georgia Tech.
Go Behind The Words!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
No matter who is graduating, here are tips on how to craft a perfect congratulations card for their achievement.
Trending Words

Hobbies & Passions
Current Events
[ rif -raf ]
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

Master’s Study Tracks
Customize your ms or meng degree to fit your career goals..
With your advisor, select technical elective courses from an array of in-demand fields and foundational research areas.

Software Engineering
Our highly dedicated and experienced computer engineering faculty includes leading researchers who literally wrote the book on programming .
In the Software Engineering Track, students will take courses on Programming, Computer Architechture, Systems, Computing, and others from the graduate course catalog. We’ll make you a great programmer!
Computer Hardware Engineering
Duke ECE master’s students learn in the classroom and the lab from faculty working on new, resilient hardware architectures for emerging platforms ranging from major datacenters to personal mobile devices.
Students in the Computer Hardware Engineering track will be instructed by experts in the field with industry and research experience alike. The coursework includes Computer Architecture, Applications of Hardware, Hardware/Software Interface, Digitial System Design, Programming and other courses from the graduate course catalog.

Machine Learning & Big Data
Our focus on data analysis and machine learning provides master’s students with the tools to manage, interpret and gain new insights from data.
Studying in the Machine Learning/Big Data track will help you gain a thorough grounding in the mathematical foundations of Big Data, training in practical programming, and instruction in machine learning, statistics and information theory.
As a student, you’ll join a vibrant community rich in cross-campus initiatives focused on data science and machine learning, such as the Rhodes Information Initiative at Duke (iiD) .
Quantum Software & Hardware
Students will learn from a software and hardware focus that prepares them to program and control quantum information devices and design, fabrication and testing of quantum devices.
Duke ECE is home to international leaders in information physics research, embodied in pathbreaking programs in metamaterials, quantum devices, and optical systems.
Master’s students will learn from a faculty team with deep interdisciplinary research strengths and a track record of entrepreneurship and innovation.

Semiconductor Technology
Duke ECE’s master’s track in semiconductor technology is led by international leaders in the areas of nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, microfluidic systems, integrated optics, sensors, integrated multifunctional devices/systems, energy conversion devices, and quantum sensors.
Semiconductor technology research at Duke is highly interdisciplinary, and includes the fabrication of devices and circuits through the state-of-the-art Shared Materials Instrumentation Facility (SMiF) cleanroom and characterization lab.
This track is designed to prepare master’s students either to engage in PhD research or to obtain engineering jobs in the semiconductor industry.
Duke also offers an interdisciplinary Master of Engineering in Photonics and Optical Sciences featuring coursework in both ECE and the Duke Department of Biomedical Engineering.
Master’s Contacts

Kevyn Light
Senior Program Coordinator

Graduate Program Coordinator

Miroslav Pajic
Director of Master’s Studies, Professor in the Department of ECE

Krista Turner
Master’s Program Coordinator
Ready to Join Us?
Tepper School of Business

Tepper Online Hybrid MBA: Part-Time Program. Full-On Experience.
The tepper online hybrid mba allows you to earn a stem-designated mba in a part-time, online format that’s laser-focused on the future of business — informed by data, powered by humans..
Request Information
Apply Now
- How It Works
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Online Hybrid MBA Class Profile
- Online Hybrid MBA Curriculum
- Events and Class Visits
A Top-Ranked Online MBA
#2 online mba program, u.s. news & world report (2024), fortune (2024), #2 online mba program, u.s. schools, financial times (2024), why choose the tepper online hybrid mba.
In this top-ranked online program, you’ll work in collaborative teams alongside whip-smart peers with diverse backgrounds and skill sets.
Guided by the same dynamic faculty who teach our Full-Time MBA program, you’ll pursue an analytics-focused curriculum as you learn to harness emerging technologies and wield data to fuel better decisions.
Have you completed undergraduate business coursework in the past 10 years? You may be eligible for our Online Hybrid Accelerated MBA format. In our Online Hybrid Accelerated MBA format, you’ll earn the same degree, faster. See if you’re eligible.
Identical Degree. Flexible Format.
In our Online Hybrid MBA format, you can count on the same challenging and rewarding core coursework taught by our professors who lead the Tepper Full-Time MBA program. You will graduate with an identical STEM-designated MBA — ready to lead at the speed of change.

Follow 7 steps to progress toward admission and earn an application fee waiver!
GET STARTED
Have you completed undergraduate business coursework? You may be eligible for our Online Hybrid Accelerated MBA format.
Explore an Accelerated MBA
“With an online program, you want to feel you’re part of something, not out there on your own. During the application process, Tepper was so responsive and accommodating. It felt like people really cared about me personally, and that has continued during my time here.”
- Amarachi Ude, MBA 2024, Industrial Engineer, FedEx Ground

Lasting Connections
Community is a hallmark of the Tepper School experience.
You’ll complement your Online Hybrid MBA with in-person Access Weekends — immersive opportunities to forge close ties with your colleagues, take classes, and participate in professional development activities. Both in Pittsburgh and online, you'll tackle team-based projects, soak up diverse perspectives, and strengthen bonds with faculty and fellow students that will continue throughout your career.
Professional Growth
Working with your own leadership coach , you’ll create a customized leadership development plan to guide you to greater empathy, self-awareness, and effectiveness — preparing you to lead tomorrow’s workforce with insight.
It’s where you’ll realize your leadership potential. You’ll graduate ready to manage people, build networks of influence, inspire others to join in your pursuit of a common goal, and execute that goal with excellence.
Application Deadlines
- Round 1: Oct. 1, 2024
- Round 2: Jan. 6, 2025
- Round 3: March 3, 2025
- Round 4: May 5, 2025
- Round 5 (Online Hybrid Only): June 9, 2025
Deadline details
We are offering GMAT/GRE/EA waivers on a case-by-case basis.
Find Out More
Are You a "Right Fit" Candidate?
The Admit.me Index (AMI) — a free, automated profile review for MBA candidates — gives you a candidate profile score, details of what affected your score, and recommends opportunities to strengthen your candidacy.
Get your report in just 5 minutes and see how your profile compares to the "perfect" candidate and to the schools you are targeting. The score is not expressly indicative of your likelihood of being admitted into the Tepper MBA program and we encourage you to contact our admissions team to discuss your results.
Get Your Report

Flexible Format
Not much room in your life for the challenges of a master’s degree? Our Online Hybrid flexible format is for you.
Live, interactive classes meet just two evenings a week and include offline content that you’ll complete at your own pace. You'll also come to campus multiple times per year, where you'll strengthen the online connections you’ve made.
Part-Time Schedule, Full-Time Benefits
Personalized leadership training. Professional career services . Access to many professional clubs. An international alumni community that’s there for you. Enjoy all the Tepper MBA advantages as you pursue a flexible online MBA. No matter how you pace your studies, you get the full Tepper School experience.
Find answers to the most common questions about the online MBA in our Online Hybrid MBA FAQs .

Scholarships Available
EXPLORE SCHOLARSHIPS
- Building The Intelligent Future: Strategic Plan 2024-2030
- Course List
- Academic Calendar
- Privacy Policy
- Statement of Assurance
- Tepper Information Center
- Tepper Gear Store
Pathways for Paraprofessionals
Fill out the interest form
Pathways for paras

A pathway designed for working paras

Access scholarship money to cut costs
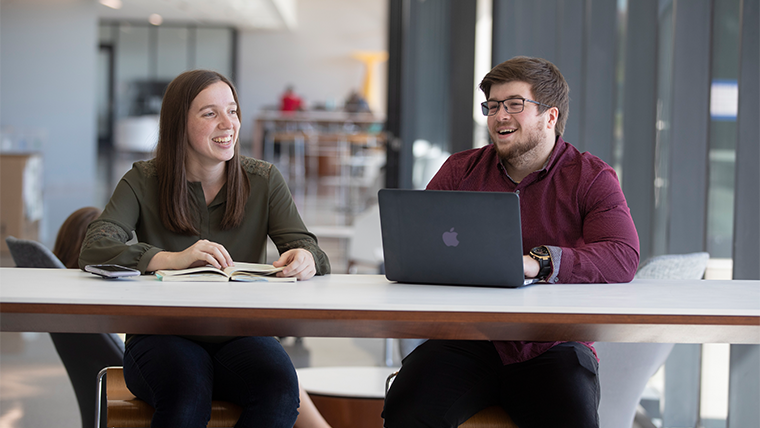

Graduate sooner

Count your career towards your coursework
Pathways for paraprofessionals checklist.
Become a Special Education teacher through the Pathways for Paras registered apprenticeship program at Missouri State University! It is highly important that you complete each of these tasks.
PLA Course Assessment Cost
From para to special educator to principal.
- Read Marks story

- Missouri State continues to be the largest teacher education preparation institute in the state. We support preparing the highest quality of educators while ensuring that we partner with our K-12 schools.
- Missouri State is the only certified apprenticeship for special education.
- The Pathways for Paraprofessionals Program offers a teacher certification in K-12 Mild/Moderate Cross-Categorical Special Education that you work on collaboratively with other paraprofessionals from area public school districts.
- Using grants, scholarships, and other sources of funding, completing the program could be at little or no cost to you.
- Paraprofessionals earn college credit for practicum and student teaching on-the-job while earning a salary as a paraprofessional.
- 100% of the Missouri State University Professional Education coursework is offered after school hours (late afternoon or early evening), online, or summers at a site in a regional location or at Missouri State University.
- Depending on your current number of college credits, there is the potential for paraprofessionals to finish the degree in 2-3 years (if they attend full-time in the fall and spring and take courses in the summer).
- While not required, the MSU Special Education Program offers two Accelerated Masters in Education Program options that allow 12 mixed credit hours to count in both the Bachelor’s of Science in Education (BSED) and the Master’s of Science in Education (MSED) degree program options, thus allowing completion of BSED degree with certification in K-12 Special Education and completion of 12 hours towards a Master’s degree upon graduation.
- The paraprofessional must work for a school district. And meet the admissions requirements of Missouri State University.
- Applicants must hold a position or have opportunities to work and collaborate with a K-12 Mild/Moderate Cross-Categorical Special Education classroom while participating in the program.
- Recommendation of paraprofessional for Pathways to Paras Program
- Review of program requirements & approval of field placement competencies in the paraprofessional’s position
- Approval of Lead Teacher as appropriate “cooperating teacher” for supervision and mentoring of paraprofessional seeking teacher certification.
- Missouri State University offers an alternative certification option for persons with a non teaching bachelor's degree OR a teaching degree in a field other than special education. The MSED: Special Education Alternative Certification Track (MSED: SPE-SEACT) provides candidates with a Masters degree + Missouri Certification in K-12 Mild/Moderate Cross-Categorical Special Education.
- Candidates who work as paraprofessionals in a K-12 Mild/Moderate Cross-Categorical Special Education program can complete their field placement at their job site.
- MSED: SPE-SEACT students are eligible for Missouri Department of Elementary & Secondary Education (DESE) Provisional Certification in K-12 Mild/Moderate Cross-Categorical Special Education, which allows them to serve as the teacher-of-record while completing certification & degree requirements.
- MSED: SPE-SEACT courses are fully available online via INET or Zoom platforms.
Missouri State University-West Plains offers an Associate Arts in Teaching Degree ( https://wp.missouristate.edu/academics/teaching.htm ) we are working on creating a seamless transition from our West Plains courses into our Pathways for Paras program to ensure t we have a full continuum of supports to help you achieve your dream.
Paraprofessional must agree to:
- Engage in full completion of employment responsibilities while completing certification and degree coursework
- Conduct field experience and course competencies on-the-job while working collaboratively with Lead Teacher in their school district
- Complete 2 years of coursework in conjunction with employment in an approved K-12 Special Education Paraprofessional position to replace required Student Teaching semester [MO DESE requires verification of 2 years of supervised paraprofessional employment while concurrently completing coursework toward certification.] Two years of employment and coursework must be completed at the same time during the Pathways for Paras program (prior years of service do not count toward the two-year minimum).
The cost of tuition per credit hour can be found here: https://www.missouristate.edu/costs/undergraduate-costs.htm . For most of our students there are multiple financial aid opportunities through grants and scholarships which can support you moving forward and make this a fiscally responsible decision. Common grant funding includes the FASTrack Grant, the TEACH grant , and the College of Education scholarships . Additionally, if you school district participates in the Learn while you earn portion of the program up to half of your coursework can be taught on site. These courses have no tuition paid and can reduce the total cost by up to 50%.
Interested school districts can contact us to think about creating a district or collaborative multi-district cohort. With this model, almost half of the required coursework (Bachelor’s or Masters) could be offered by professionals within your district with district priorities and experiences to help you be ready for the demands of your job. This coursework would be on a schedule to ensure it meets your needs and tailored to fit the specific needs and courses of the individuals within your cohort. Cost associated with each course would be minimal (i.e. small assessment fee!) and would be included on your diploma and transcript as a Missouri State University course before your degree completion. Once certified you would be able to teach anywhere within Missouri.
Interested school districts can contact us to create a district or collaborative multi-district cohort. With this model, almost half of the required coursework (Bachelor’s or Masters) could be offered by professionals within your district with district priorities and experiences to help you be ready for the demands of your job. This coursework would be on a schedule to ensure it meets your needs and tailored to fit the specific needs and courses of the individuals within your cohort. Cost associated with each course would be minimal (i.e. small assessment fee but no tuition to the university) and would be included on your diploma and transcript as a Missouri State University course before your degree completion. Once certified you would be able to teach anywhere within Missouri.
We are hoping to have you identify when you would like to start this program, and if your district is participating in the Learn While You Earn initiative. Please note that this district component is NOT a requirement. All coursework can be taken through the university. For coursework taken at the university, all courses are online and either in a strictly online format or are facilitated via an online format such as zoom. As for coursework which can be taught by your district, this is up to the district and them meeting your needs but also the needs of the district. It is common for course offerings to occur in the evening, professional development days, back to school days, or other times which you may have already reported to the district. Many of these classes that are taught by your district you will see are practicums or are based around application of knowledge. This is perfect to complete on the job as you will already be doing these skills. As said before though, if you school is not participating it is not a worry. You can still hold your paraeducator position and these practicum courses be your paraeducator/teaching placement, but the content presented will be done through the university.
At this time, this is the only pathway for paraeducators. However, the state allows students to test into other certification areas such as early childhood once you have a degree. All information on the additional assessments can be found here: https://dese.mo.gov/media/pdf/content-assessments-add-additional-area-certification . We will work with your unique situation to see how your experience will fit into certification and make recommend a summer placement in a traditional K-12 setting or other alternative options to ensure that we are meeting the state requirements. After admission this will all be individualized with your advisor.
We have pathways for individuals at the graduate level to gain initial certification and also achieve their masters. The advantage of this program is that individuals in this track can qualify for a provisional teaching license where they can be a teacher of record and be hired as the teacher for a K-12 classroom.
- Can you look at my transcripts and tell me what classes I need? Unfortunately, looking at transcripts before you are submitted can only give a general idea and may not be an accurate assessment of what coursework is needed. We encourage you to apply (at the undergraduate level this is free) and then we can give you an accurate assessment with your official transcripts.
- What will the “Learn while you Earn” courses look like? As for coursework which can be taught by your district, this is up to the district and them meeting your needs but also the needs of the district. It is common for course offerings to occur in the evening, professional development days, back to school days, or other times which you may have already reported to the district. Many of these classes that are taught by your district you will see are practicums or are based around application of knowledge. This is perfect to complete on the job as you will already be doing these skills. As said before though, if you school is not participating it is not a worry. You can still hold your paraeducator position and these practicum courses be your paraeducator/teaching placement, but the content presented will be done through the university.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
4 mins. It can be a little tricky figuring out which postgraduate degree is for you. That's why we've done the work for you to clarify the differences between a coursework degree and a research degree, and where each could take your career. The main difference between these two styles is coursework has classes and research has a thesis.
Masters by Coursework programs typically involve a structured curriculum where students attend classes, complete assignments, and take exams. These programs are designed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of a specific field or discipline. On the other hand, Masters by Research programs focus on independent research and the ...
A Master by Coursework is a professional qualification involving the study of a specified set of core units and a selection of eligible elective units. Undertaking a coursework program will mean that you will attend classes, complete assignments and sit exams where applicable. Some Masters by Coursework also require the completion of a minor thesis as part of the course.
A graduate degree—including master's degrees, doctorates, and PhDs—provides an advanced understanding of a specific topic or field, and demonstrates a commitment to lifelong learning that many employers value. Those who choose to enroll in graduate school often do so with a series of focused, career-oriented goals in mind, which sets the ...
A master's degree is a graduate degree that allows students to build advanced knowledge of a specialized body of theoretical and applied knowledge, forge a deeper understanding of their area of study, and develop a range of skills applicable to their trade. With a master's degree, you can typically have more opportunities to advance your ...
Masters degrees can be either postgraduate taught programmes (PGT) or postgraduate research programmes (PGR). Taught Masters are typically 12 months long full-time and are delivered through a series of modules comprised with regular coursework and assessments. Research Masters are also usually 12 months long however the course is predominantly ...
Online master's degree costs + time to graduation. An in-person master's degree costs between $30,000 and $120,000, depending on whether you attend a public or private institution [ 6 ]. However, many online master's degrees tend to cost less. For example, the University of Colorado Boulder's Master of Science in Computer Science ...
A master's program is the course of study you enroll in when working on your master's degree—the graduate degree you can typically pursue after first earning your bachelor's. Obtaining a master's degree offers professional, personal, and academic benefits, and can be a lucrative step in terms of your education and career goals.
A Master of Science degree conferred from Columbia University, an Ivy League university in New York City. A master's degree [note 1] (from Latin magister) is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities or colleges upon completion of a course of study demonstrating mastery or a high-order overview of a specific field of study or area of professional practice. [1]
There are a few key differences between postgraduate coursework and postgraduate research programs. Postgraduate Coursework. Postgraduate coursework programs deliver content through a set unit program (similar to an undergraduate Bachelor degree), but at a more advanced level. Coursework will allow you to deepen your knowledge within a discipline, or to pursue a new or additional study area at ...
Course-based master's degrees are based on structured course modules taught through lectures, seminars, laboratory work or distance learning, while research-based master's degrees require the student to carry out their own research project(s) in a specialised field of study. Research master's degrees normally take a little longer than ...
No, a Research Master's degree is not the same as a PhD. Although for both degrees you will need to complete a dissertation based on an independent research project, there are notable differences: ... Yes, you can pursue a PhD after any type of Master's course, provided that you have a degree in a relevant subject. All taught postgraduate ...
A masters degree is a degree programme demonstrably in advance of undergraduate level, that provides training in scholarship and research. ... Taught (or coursework) masters degrees will give you advanced specialist training in your chosen field. They are usually completed by coursework only, although some can include a dissertation.
A master's degree in information technology relates to the broader computer science degree, but there are a few major distinctions that separate the two. Master's degrees in information technology typically focus on coursework that includes information systems development and operating systems concepts.
The M.S. degree in Computer Science is intended as a terminal professional degree and does not lead to the Ph.D. degree. Most students planning to obtain the Ph.D. degree should apply directly for admission to the Ph.D. program. Some students, however, may wish to complete the master's program before deciding whether to pursue the Ph.D. To give such students a greater opportunity to become ...
Graduate coursework options. You can apply for more than 340 award programs ranging from Graduate Certificates to Masters and PhD study in a wide range of study areas and disciplines. Graduate degree options include: Graduate certificates. A Graduate certificate is six month course where you can choose from more than 25 discipline areas.
Taught master's programs typically involve a mix of lectures, seminars, and coursework, while research master's programs focus on a more significant research project. Assess which learning approach aligns better with your preferred style of study. 4. Academic Background. Consider your academic background and strengths.
Coursework is defined under the Australian Qualifications Framework (AQF) as a method of teaching and learning that leads to the acquisition of skills and knowledge that does not include a major research component. Bachelor's programs and postgraduate coursework programs are all coursework programs.
While a Masters by Dissertation is heavily research orientated, these degrees are different to a Research Masters degree in South Africa. A Research Masters is a full-time (sometimes part-time) coursework programme offered by some universities which can lead to an HPCSA registration as a Research Psychologist. Unlike a Research Masters, a ...
Duration: Postgraduate degrees can range from 1-6+ years depending on the program level. Graduate diplomas and graduate certificates can take as little as six months while PhD and other doctoral programs can take up to six years. Master's degrees are the sweet spot, generally taking 1-2 years to complete. Cost: Postgraduate degrees vary in ...
At university in the UK, a dissertation is a type of research project that can be taken by students for either a bachelor's degree or a master's degree. As an extended essay, students will need to produce an answer to a specific question of somewhere between 5,000 and 50,000 words depending on the university and whether it is a bachelor's ...
⚡ Quick summary. The main difference between undergraduate and graduate is that undergraduate is always used in the context of the first level of college or university education (the level where you can earn a bachelor's degree).In terms like graduate student and graduate degree, graduate refers to a level of advanced education beyond the undergraduate level, especially a master's degree ...
Degree Options & Requirements. Only graduate-level courses (500 and above) satisfy MS degree requirements. ... 30 units of graduate-level coursework as determined by the curricular track course requirements; Up to 6 units of ungraded research (if desired, to substitute for standard coursework)
This track is designed to prepare master's students either to engage in PhD research or to obtain engineering jobs in the semiconductor industry. Duke also offers an interdisciplinary Master of Engineering in Photonics and Optical Sciences featuring coursework in both ECE and the Duke Department of Biomedical Engineering.
Identical Degree. Flexible Format. In our Online Hybrid MBA format, you can count on the same challenging and rewarding core coursework taught by our professors who lead the Tepper Full-Time MBA program. You will graduate with an identical STEM-designated MBA — ready to lead at the speed of change.
1. Complete the Make Up Orientation Course in Canvas. Students can self-enroll in the Make Up Orientation course through Canvas. All modules should be completed and reviewed in order to complete the Make Up Orientation process. Self-Enroll in the Make Up Orientation Course. 2. Participate in Drop In Advising
Last year the course received 13 applications for every place, and was the top rated undergraduate degree in the field, according to The Complete University Guide 2024.
All coursework can be taken through the university. For coursework taken at the university, all courses are online and either in a strictly online format or are facilitated via an online format such as zoom.
Traditional: This MSW degree program is designed to take two years of full-time study and typically incorporates foundational coursework in social work with more specialized topics, like children, young adults, and families. You will likely be expected to complete up to 70 credits and around 900 to 1200 field education hours.
Complete curriculum and program requirements for the Computer Information Systems, B.S. can be found in the Clemson Course Catalog. Combined Bachelors/Masters. The School of Computing allows students to apply up to nine hours of graduate credit (6000- and 8000-level courses) toward both the bachelor's and master's degrees.