The Research Whisperer
Just like the thesis whisperer – but with more money, when is a paper published.

When a paper is published could seem obvious but this is not a trivial question.
For some time now, a research article can display several different dates that can prove confusing when trying to work out when a scholarly publication is actually released. In the hardcopy print era, before the Web shook up the academic publishing system, the publication date was always associated with the issued date, the moment at which an article was included in an issue and publicly distributed. This was true because serial publications had to publish articles in groups each time for economic reasons. As the print journals released their articles in periodical issues (biannual, quarterly, monthly, etc.), it was easy to determine when an article was published. The issue indicated the moment. Now, that information is missing on the websites of some academic journals, and we have to estimate the date according to the volume and issue number (e.g. Begell house, ATS Journals).
With the advent of online publishing and the adaptation of print journals to the digital environment, many of the traditional conventions are not necessary. Among them, the grouping of articles in regular issues is technically unnecessary because each paper can be released individually. Although most journals still use the format of volumes and issues, many of the newer electronic journals are giving up this practice (e.g. F1000 Research, eLife, PLOS ONE [which still uses volumes and issues as a convention for citation but not as a way to organize the publication]). This is causing uncertainty with regard to the publication date because it is common to establish, on one hand, the online publication date and, on the other hand, the date when an article is finally assigned to an issue. This is causing confusion about when an article is published and which date is the actual one.
A possible solution might be to ask Crossref (a place where most of the academic publishers deposit their metadata) when a bibliographic record is initially created. However, if we have a glance at the Crossref API , we can find up to eight dates associated with a publication: Indexed date, posted date, updated date, accepted date, deposited date, created date, published-online date, and issued date. This gets worse when each publisher interprets the meaning of each field differently. For instance, Febs Press (Wiley group) assigns the same date to published-online and issued date, whereas Spinger considers created date and published-online date the same thing, but different to issue date. This multiplicity of dates and meanings does not do anything but increase the confusion about the publication date.

Why is it so important to know exactly when a publication is published?
First, classic bibliometrics was focused almost exclusively on citation impact. This metric has an important delay because it takes a long time from when a paper is published till when it might start to be cited; papers are rarely cited within a year. In this sense, accuracy is not so important because we measure citations by years, not months or days (e.g. Journal Impact Factor). However, the appearance of other metrics (e.g. social media mentions, document views, bookmarking saves) that occur in short time spans, is demanding greater precision. The analysis of these new impact indicators has demonstrated that they happen in the first months, days, or hours in the lifespan of a publication. This immediacy requires the specification of the moment in which an article is made publicly available to understand how and when the social, academic and usage impact is generated. Therefore, current bibliometric studies demand a more precise definition of when a paper is published.
A second reason is related to the research evaluation. The delay between the moment in which a paper is accessible on the publisher’s platform and the moment when it is finally issued can be very long. It is common to see that a paper is accessible in one year but is not printed till the next. This detail could have consequences for the evaluation of research careers when time windows are set up. Important contributions that would improve the assessment of researchers could be excluded because they are published online but not formally assigned to an issue. Many evaluation agencies only consider the final issue date of a publication, in spite of the fact that many papers are accepted and accessible on the Web before that.
At a macro level, when statistics about the aggregate production of organizations and countries are created, the consolidation of those figures would require several years because online papers counted in one year would have to be moved to the next year when they are finally issued. It is crucial to know the precise publication date in order to correctly value the performance of researchers in a time period as well as to obtain a reliable picture about the research effort of organizations and countries.
The third reason is related to the previous point and concerns the difficulties when scientific information systems such as citation indexes or academic search engines come up against different publication dates. Two records of the same publication with different publication dates may be wrongly considered distinct, increasing the risk of duplication. In addition, multiple dates require a great effort of updating because bibliographic databases have to be alert to when the definitive publication date occurs. All these continuous verifications consume much time and many economic resources in the maintenance of scholarly information systems.
What can we do?
As a first step, a clear definition about the meaning of ‘publication date’ should be established. Publishers, through Crossref, must indicate the precise moment in which the paper is definitively released. In my opinion, that date should be the moment when the paper is made publicly accessible on the Web or another medium. That is the time when articles come to life, when they start to be read, mentioned, saved, and cited. Therefore, the online or web date should be considered the principal date for bibliometric studies, research evaluation and information systems. In 2021, Clarivate stated that only the web publishing date (Early Access) would be used for computing the Journal Impact Factor .
The next step would be to define international standards that allow us to respond easily, quickly, and accurately whenever a paper’s publication date is sought.
————————————-

José has authored the books Academic search engines: A Quantitative Outlook and Social Network Sites for Scientists: A Quantitative Survey.
Twitter: @JLOrtegaPriego
ORCID: 0000-0001-9857-1511
Share this:
[…] “We can find up to eight dates associated with a publication” and “this gets worse when each p… — When is a paper “published”? (via Retraction Watch) […]
“The delay between the moment in which a paper is accessible on the publisher’s platform and the moment when it is finally issued can be very long. It is common to see that a paper is accessible in one year but is not printed till the next.”
Journals die. When a journal disappears, there will be papers that are publicly available but never ‘published’ since the journal died before those papers could get an issue number and a ‘published’ date. That’s totally unfair on the authors.
[…] When is a paper published? […]
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
How to Find the Date an Article Was Published
Whether you are citing an article in your research paper or just wanted to check the freshness of Google search results. There are times when you want to find out when an article was first published on the website. In general, 3 ways to do so
- Check for the published date either right below the headline of an article or at the end
- Copy paste the URL on Internet Archive
- Reverse Google search the title and look for last update dates.
While these tricks work most of the time, it’s hard to tell the difference between the published date and last updated date. Most search engines such as Google pick up the last updated date as published dates. And Internet archive isn’t also reliable all of the time.
Fortunately, there is a simple way to find out when the article was first published on the website. All you have to do is look at the source code for the published date or even better if the article has any images, find out when those images were uploaded. Follow the simple steps.
- Right click on the website and click on ‘View Source code’
- In the source code page, press Cmd + F for Mac or CTRL + F for Windows to bring up the ‘Find’ box
- Search for keywords like publish year – ‘2019’, ‘2018’, ‘2017’ etc alternatively, you can also search for ‘published_time’
- Analyze the highlighted part of the source code
Analyze the data
Many websites don’t have ‘Last Updated’ or ‘Published Date’ in the source code, especially if it’s a page or research article. So, it’s better to look at other metrics such as media upload date. Given the site is made in Wordpress (most of them are) and the webpage has images, it’s better to look at upload year/month of image.
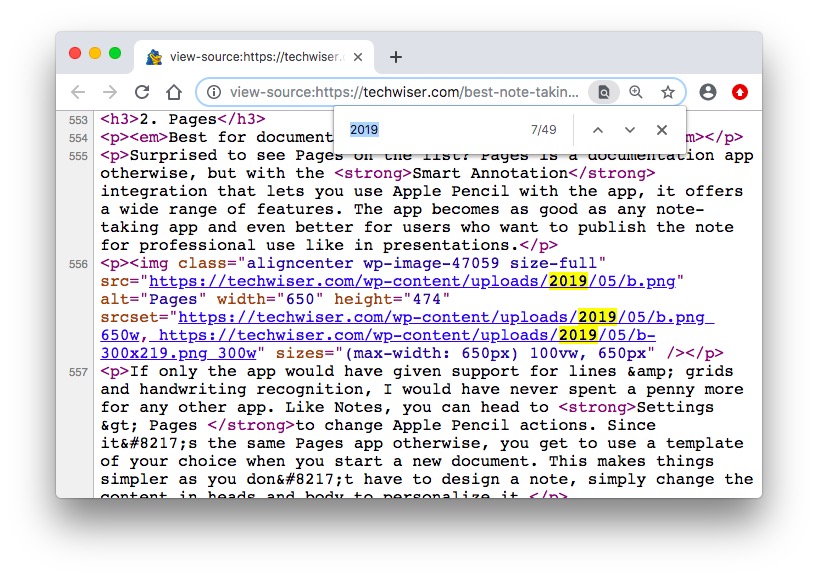
For example, if the code looks something like this /wp-content/uploads/2019/05, it means, the image was uploaded on May 2019. If more images are uploaded on the same date, there are good chances the article was first published on that day. Off course, it goes without saying, you should not consider the upload date for logo, favicon, etc as they were most probably uploaded when the site was designed.
Mrinal Saha
Mrinal is a tech geek who spends half of his day reading and writing about tech. While the nights are spent on shooting or editing YouTube videos. Feel free to geek out with him on-
You may also like
How to add song tracks to your instagram..., what do various icons and symbols mean in..., how to setup telegram channel subscription and use..., how to send multiple photos in email, 7 ways to read telegram messages without marking..., how to transfer images from google photos to..., what do various icons and symbols mean on..., 2 ways to send a snap to multiple..., what is the difference between incognito and guest..., 3 things to do if your chrome extension..., leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
| Level of Information | Text Example |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | |
| Level 2 | |
| Level 3 | |
| Level 4 | |
| Level 5 |
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
| Level of Information | Text Example |
|---|---|
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 | |
| Level 1 |
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal
- Open access
- Published: 30 April 2020
- Volume 36 , pages 909–913, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Clara Busse ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0178-1000 1 &
- Ella August ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5151-1036 1 , 2
281k Accesses
15 Citations
707 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common pitfalls for each section and recommend strategies to avoid them. Further, we give advice about target journal selection and authorship. In the online resource 1 , we provide an example of a high-quality scientific paper, with annotations identifying the elements we describe in this article.
Similar content being viewed by others

How to Choose the Right Journal

The Point Is…to Publish?

Writing and publishing a scientific paper
Explore related subjects.
- Artificial Intelligence
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Writing a scientific paper is an important component of the research process, yet researchers often receive little formal training in scientific writing. This is especially true in low-resource settings. In this article, we explain why choosing a target journal is important, give advice about authorship, provide a basic structure for writing each section of a scientific paper, and describe common pitfalls and recommendations for each section. In the online resource 1 , we also include an annotated journal article that identifies the key elements and writing approaches that we detail here. Before you begin your research, make sure you have ethical clearance from all relevant ethical review boards.
Select a Target Journal Early in the Writing Process
We recommend that you select a “target journal” early in the writing process; a “target journal” is the journal to which you plan to submit your paper. Each journal has a set of core readers and you should tailor your writing to this readership. For example, if you plan to submit a manuscript about vaping during pregnancy to a pregnancy-focused journal, you will need to explain what vaping is because readers of this journal may not have a background in this topic. However, if you were to submit that same article to a tobacco journal, you would not need to provide as much background information about vaping.
Information about a journal’s core readership can be found on its website, usually in a section called “About this journal” or something similar. For example, the Journal of Cancer Education presents such information on the “Aims and Scope” page of its website, which can be found here: https://www.springer.com/journal/13187/aims-and-scope .
Peer reviewer guidelines from your target journal are an additional resource that can help you tailor your writing to the journal and provide additional advice about crafting an effective article [ 1 ]. These are not always available, but it is worth a quick web search to find out.
Identify Author Roles Early in the Process
Early in the writing process, identify authors, determine the order of authors, and discuss the responsibilities of each author. Standard author responsibilities have been identified by The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) [ 2 ]. To set clear expectations about each team member’s responsibilities and prevent errors in communication, we also suggest outlining more detailed roles, such as who will draft each section of the manuscript, write the abstract, submit the paper electronically, serve as corresponding author, and write the cover letter. It is best to formalize this agreement in writing after discussing it, circulating the document to the author team for approval. We suggest creating a title page on which all authors are listed in the agreed-upon order. It may be necessary to adjust authorship roles and order during the development of the paper. If a new author order is agreed upon, be sure to update the title page in the manuscript draft.
In the case where multiple papers will result from a single study, authors should discuss who will author each paper. Additionally, authors should agree on a deadline for each paper and the lead author should take responsibility for producing an initial draft by this deadline.
Structure of the Introduction Section
The introduction section should be approximately three to five paragraphs in length. Look at examples from your target journal to decide the appropriate length. This section should include the elements shown in Fig. 1 . Begin with a general context, narrowing to the specific focus of the paper. Include five main elements: why your research is important, what is already known about the topic, the “gap” or what is not yet known about the topic, why it is important to learn the new information that your research adds, and the specific research aim(s) that your paper addresses. Your research aim should address the gap you identified. Be sure to add enough background information to enable readers to understand your study. Table 1 provides common introduction section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.

The main elements of the introduction section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Methods Section
The purpose of the methods section is twofold: to explain how the study was done in enough detail to enable its replication and to provide enough contextual detail to enable readers to understand and interpret the results. In general, the essential elements of a methods section are the following: a description of the setting and participants, the study design and timing, the recruitment and sampling, the data collection process, the dataset, the dependent and independent variables, the covariates, the analytic approach for each research objective, and the ethical approval. The hallmark of an exemplary methods section is the justification of why each method was used. Table 2 provides common methods section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Results Section
The focus of the results section should be associations, or lack thereof, rather than statistical tests. Two considerations should guide your writing here. First, the results should present answers to each part of the research aim. Second, return to the methods section to ensure that the analysis and variables for each result have been explained.
Begin the results section by describing the number of participants in the final sample and details such as the number who were approached to participate, the proportion who were eligible and who enrolled, and the number of participants who dropped out. The next part of the results should describe the participant characteristics. After that, you may organize your results by the aim or by putting the most exciting results first. Do not forget to report your non-significant associations. These are still findings.
Tables and figures capture the reader’s attention and efficiently communicate your main findings [ 3 ]. Each table and figure should have a clear message and should complement, rather than repeat, the text. Tables and figures should communicate all salient details necessary for a reader to understand the findings without consulting the text. Include information on comparisons and tests, as well as information about the sample and timing of the study in the title, legend, or in a footnote. Note that figures are often more visually interesting than tables, so if it is feasible to make a figure, make a figure. To avoid confusing the reader, either avoid abbreviations in tables and figures, or define them in a footnote. Note that there should not be citations in the results section and you should not interpret results here. Table 3 provides common results section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Discussion Section
Opposite the introduction section, the discussion should take the form of a right-side-up triangle beginning with interpretation of your results and moving to general implications (Fig. 2 ). This section typically begins with a restatement of the main findings, which can usually be accomplished with a few carefully-crafted sentences.
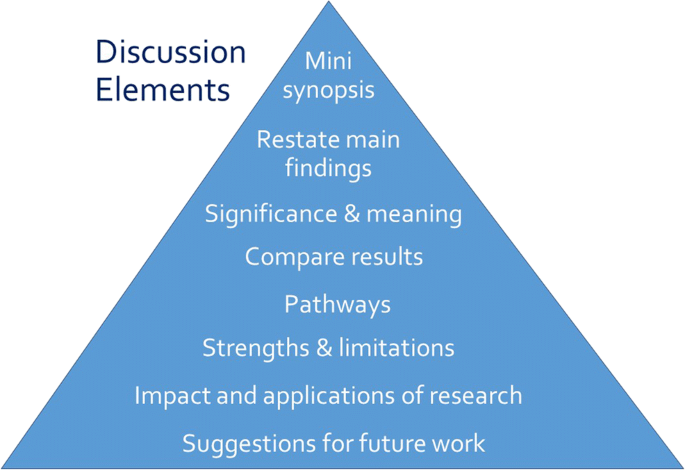
Major elements of the discussion section of an original research article. Often, the elements overlap
Next, interpret the meaning or explain the significance of your results, lifting the reader’s gaze from the study’s specific findings to more general applications. Then, compare these study findings with other research. Are these findings in agreement or disagreement with those from other studies? Does this study impart additional nuance to well-accepted theories? Situate your findings within the broader context of scientific literature, then explain the pathways or mechanisms that might give rise to, or explain, the results.
Journals vary in their approach to strengths and limitations sections: some are embedded paragraphs within the discussion section, while some mandate separate section headings. Keep in mind that every study has strengths and limitations. Candidly reporting yours helps readers to correctly interpret your research findings.
The next element of the discussion is a summary of the potential impacts and applications of the research. Should these results be used to optimally design an intervention? Does the work have implications for clinical protocols or public policy? These considerations will help the reader to further grasp the possible impacts of the presented work.
Finally, the discussion should conclude with specific suggestions for future work. Here, you have an opportunity to illuminate specific gaps in the literature that compel further study. Avoid the phrase “future research is necessary” because the recommendation is too general to be helpful to readers. Instead, provide substantive and specific recommendations for future studies. Table 4 provides common discussion section pitfalls and recommendations for addressing them.
Follow the Journal’s Author Guidelines
After you select a target journal, identify the journal’s author guidelines to guide the formatting of your manuscript and references. Author guidelines will often (but not always) include instructions for titles, cover letters, and other components of a manuscript submission. Read the guidelines carefully. If you do not follow the guidelines, your article will be sent back to you.
Finally, do not submit your paper to more than one journal at a time. Even if this is not explicitly stated in the author guidelines of your target journal, it is considered inappropriate and unprofessional.
Your title should invite readers to continue reading beyond the first page [ 4 , 5 ]. It should be informative and interesting. Consider describing the independent and dependent variables, the population and setting, the study design, the timing, and even the main result in your title. Because the focus of the paper can change as you write and revise, we recommend you wait until you have finished writing your paper before composing the title.
Be sure that the title is useful for potential readers searching for your topic. The keywords you select should complement those in your title to maximize the likelihood that a researcher will find your paper through a database search. Avoid using abbreviations in your title unless they are very well known, such as SNP, because it is more likely that someone will use a complete word rather than an abbreviation as a search term to help readers find your paper.
After you have written a complete draft, use the checklist (Fig. 3 ) below to guide your revisions and editing. Additional resources are available on writing the abstract and citing references [ 5 ]. When you feel that your work is ready, ask a trusted colleague or two to read the work and provide informal feedback. The box below provides a checklist that summarizes the key points offered in this article.

Checklist for manuscript quality
Data Availability
Michalek AM (2014) Down the rabbit hole…advice to reviewers. J Cancer Educ 29:4–5
Article Google Scholar
International Committee of Medical Journal Editors. Defining the role of authors and contributors: who is an author? http://www.icmje.org/recommendations/browse/roles-and-responsibilities/defining-the-role-of-authosrs-and-contributors.html . Accessed 15 January, 2020
Vetto JT (2014) Short and sweet: a short course on concise medical writing. J Cancer Educ 29(1):194–195
Brett M, Kording K (2017) Ten simple rules for structuring papers. PLoS ComputBiol. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005619
Lang TA (2017) Writing a better research article. J Public Health Emerg. https://doi.org/10.21037/jphe.2017.11.06
Download references
Acknowledgments
Ella August is grateful to the Sustainable Sciences Institute for mentoring her in training researchers on writing and publishing their research.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Maternal and Child Health, University of North Carolina Gillings School of Global Public Health, 135 Dauer Dr, 27599, Chapel Hill, NC, USA
Clara Busse & Ella August
Department of Epidemiology, University of Michigan School of Public Health, 1415 Washington Heights, Ann Arbor, MI, 48109-2029, USA
Ella August
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ella August .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
(PDF 362 kb)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Busse, C., August, E. How to Write and Publish a Research Paper for a Peer-Reviewed Journal. J Canc Educ 36 , 909–913 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Download citation
Published : 30 April 2020
Issue Date : October 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Manuscripts
- Scientific writing
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
How to publish your paper
On this page, journal specific instructions, nature journal pledge to authors, how to publish your research in a nature journal, editorial process, about advance online publication, journals' aop timetable, frequently asked questions.
For more information on how to publish papers in a specific Nature Portfolio title, please visit the author instructions page for the journal that is of interest to you.
Top of page ⤴
Editors of the Nature journals strive to provide authors with an outstandingly efficient, fair and thoughtful submission, peer-review and publishing experience. Authors can expect all manuscripts that are published to be scrutinized for peer-review with the utmost professional rigor and care by expert referees who are selected by the editors for their ability to provide incisive and useful analysis. Editors weigh many factors when choosing content for Nature journals, but they strive to minimize the time taken to make decisions about publication while maintaining the highest possible quality of that decision.
After review, editors work to increase a paper's readability, and thereby its audience, through advice and editing, so that all research is presented in a form that is both readable to those in the field and understandable to scientists outside the immediate discipline. Research is published online without delay through our Advance Online Publication system. Nature journals provide more than 3,000 registered journalists with weekly press releases that mention all research papers to be published. About 800,000 registered users receive e-mailed tables of contents, and many papers are highlighted for the nonspecialist reader on the journal's homepage, contents pages and in News and Views.
Throughout this process, the editors of Nature journals uphold editorial, ethical and scientific standards according to the policies outlined on the author and referee site as well as on our journal websites. We periodically review those policies to ensure that they continue to reflect the needs of the scientific community, and welcome comments and suggestions from scientists, either via the feedback links on the author and referees' website or via our author blog, Nautilus , or peer-review blog, Peer to Peer .
The Nature journals comprise the weekly, multidisciplinary Nature, which publishes research of the highest influence within a discipline that will be of interest to scientists in other fields, and fifteen monthly titles, publishing papers of the highest quality and of exceptional impact: Nature Biotechnology, Nature Cell Biology, Nature Chemical Biology, Nature Chemistry, Nature Climate Change, Nature Communications, Nature Genetics, Nature Geoscience, Nature Immunology, Nature Materials, Nature Medicine, Nature Methods, Nature Nanotechnology, Nature Neuroscience, Nature Photonics, Nature Physics, Nature Protocolsand Nature Structural and Molecular Biology. These journals are international, being published and printed in the United States, the United Kingdom and Japan. See here for more information about the relationship between these journals.
Nature and the Nature monthly journals have Impact Factors that are among the highest in the world. The high prestige of these journals brings many rewards to their authors, but also means that competition for publication is severe, so many submissions have to be declined without peer-review.
The Nature journals differ from most other journals in that they do not have editorial boards, but are instead run by professional editors who consult widely among the scientific community in making decisions about publication of papers. This article is to provide you with an overview of the general editorial processes of these unique journals. Although the journals are broadly similar and share editorial policies , all authors should consult the author information pages of the specific Nature journal before submitting, to obtain detailed information on criteria for publication and manuscript preparation for that journal, as some differences exist.
The following sections summarise the journals' editorial processes and describe how manuscripts are handled by editors between submission and publication. At all stages of the process, you can access the online submission system and find the status of your manuscript.
Presubmission enquiries
Many Nature journals allow researchers to obtain informal feedback from editors before submitting the whole manuscript. This service is intended to save you time — if the editors feel it would not be suitable, you can submit the manuscript to another journal without delay. If you wish to use the presubmission enquiry service, please use the online system of the journal of your choice to send a paragraph explaining the importance of your manuscript, as well as the abstract or summary paragraph with its associated citation list so the editors may judge the manuscript in relation to other related work. The editors will quickly either invite you to submit the whole manuscript (which does not mean any commitment to publication), or will say that it is not suitable for the journal. If you receive a negative response, please do not reply. If you are convinced of the importance of your manuscript despite editors' reservations, you may submit the whole manuscript using the journal's online submission system. The editors can then make a more complete assessment of your work. Note that not all Nature journals offer a presubmission enquiry service.
Initial submission
When you are ready to submit the manuscript, please use the online submission system for the journal concerned. When the journal receives your manuscript, it will be assigned a number and an editor, who reads the manuscript, seeks informal advice from scientific advisors and editorial colleagues, and compares your submission to other recently published papers in the field. If the manuscript seems novel and arresting, and the work described has both immediate and far-reaching implications, the editor will send it out for peer review, usually to two or three independent specialists. However, because the journals can publish only a few of the manuscripts in the field or subfield concerned, many manuscripts have to be declined without peer review even though they may describe solid scientific results.
Transfers between Nature journals
In some cases, an editor is unable to offer publication, but might suggest that the manuscript is more suitable for one of the other Nature journals. If you wish to resubmit your manuscript to the suggested journal, you can simply follow the link provided by the editor to transfer your manuscript and the reviewers' comments to the new journal. This process is entirely in your control: you can choose not to use this service and instead to submit your manuscript to any other Nature or nature research journal, with or without including the reviewers' comments if you wish, using the journal's usual online submission service. For more information, please see the manuscript transfers page .
Peer review
The corresponding author is notified by email when an editor decides to send a manuscript for review. The editors choose referees for their independence, ability to evaluate the technical aspects of the paper fully and fairly, whether they are currently or recently assessing related submissions, and whether they can review the manuscript within the short time requested.
You may suggest referees for your manuscript (including address details), so long as they are independent scientists. These suggestions are often helpful, although they are not always followed. Editors will honour your requests to exclude a limited number of named scientists as reviewers.
Decisions and revisions
If the editor invites you to revise your manuscript, you should include with your resubmitted version a new cover letter that includes a point-by-point response to the reviewers' and editors' comments, including an explanation of how you have altered your manuscript in response to these, and an estimation of the length of the revised version with figures/tables. The decision letter will specify a deadline, and revisions that are returned within this period will retain their original submission date.
Additional supplementary information is published with the online version of your article if the editors and referees have judged that it is essential for the conclusions of the article (for example, a large table of data or the derivation of a model) but of more specialist interest than the rest of the article. Editors encourage authors whose articles describe methods to provide a summary of the method for the print version and to include full details and protocols online. Authors are also encouraged to post the full protocol on Nature Protocols' Protocol Exchange , which as well as a protocols database provides an online forum for readers in the field to add comments, suggestions and refinements to the published protocols.
After acceptance
Your accepted manuscript is prepared for publication by copy editors (also called subeditors), who refine it so that the text and figures are readable and clear to those outside the immediate field; choose keywords to maximize visibility in online searches as well as suitable for indexing services; and ensure that the manuscripts conform to house style. The copy editors are happy to give advice to authors whose native language is not English, and will edit those papers with special care.
After publication
All articles are published in the print edition and, in PDF and HTML format, in the online edition of the journal, in full. Many linking and navigational services are provided with the online (HTML) version of all articles published by the Nature journals.
All articles and contact details of corresponding authors are included in our press release service, which means that your work is drawn to the attention of all the main media organizations in the world, who may choose to feature the work in newspaper and other media reports. Some articles are summarized and highlighted within Nature and Nature Portfolio publications and subject-specific websites.
Journals published by Nature Portfolio do not ask authors for copyright, but instead ask you to sign an exclusive publishing license . This allows you to archive the accepted version of your manuscript six months after publication on your own, your institution's, and your funder's websites.
Disagreements with decisions
If a journal's editors are unable to offer publication of a manuscript and have not invited resubmission, you are strongly advised to submit your manuscript for publication elsewhere. However, if you believe that the editors or reviewers have seriously misunderstood your manuscript, you may write to the editors, explaining the scientific reasons why you believe the decision was incorrect. Please bear in mind that editors prioritise newly submitted manuscripts and manuscripts where resubmission has been invited, so it can take several weeks before letters of disagreement can be answered. During this time, you must not submit your manuscript elsewhere. In the interests of publishing your results without unnecessary delay, we therefore advise you to submit your manuscript to another journal if it has been declined, rather than to spend time on corresponding further with the editors of the declining journal.
Nature journals offer Advance Online Publication (AOP).
We believe that AOP is the best and quickest way to publish high-quality, peer-reviewed research for the benefit of readers and authors. Papers published AOP are the definitive version: they do not change before appearing in print and can be referenced formally as soon as they appear on the journal's AOP website. In addition, Nature publishes some papers each week via an Accelerated Article Preview (AAP) workflow. For these papers, we upload the accepted manuscript to our website as an AAP PDF, without subediting of text, figures or tables, but with some preliminary formatting. AAP papers are clearly indicated by a watermark on each page of the online PDF.
Each journal's website includes an AOP table of contents, in which papers are listed in order of publication date (beginning with the most recent). Each paper carries a digital object identifier (DOI), which serves as a unique electronic identification tag for that paper. As soon as the issue containing the paper is printed, papers will be removed from the AOP table of contents, assigned a page number and transferred to that issue's table of contents on the website. The DOI remains attached to the paper to provide a persistent identifier.
Nature publishes many, but not all, papers AOP, on Mondays and Wednesdays.
For the monthly Nature journals publishing primary research, new articles are uploaded to the AOP section of their web sites once each week. Occasionally, an article may be uploaded on other days.
The monthly Nature Reviews journals also upload new articles to the AOP section of their web sites once each week.
Q. Which articles are published AOP?
A. Original research is published AOP — that is, Articles and Letters, and for the Nature journals that publish them, Brief Communications. Associated News and Views articles may be published with the AOP Article or Letter or when the papers are published in the print/online edition of the journal. Nature occasionally publishes other article types AOP, for example News and Commentaries.
Q. Is the AOP version of the article definitive?
A. Yes. Only the final version of the paper is published AOP, exactly as it will be published in the printed edition. The paper is thus complete in every respect except that instead of having a volume/issue/page number, it has a DOI (digital object identifier). This means that the paper can be referenced as soon as it appears on the AOP site by using the DOI. Nature also publishes some papers each week via an Accelerated Article Preview workflow, where the accepted version of the paper is uploaded as a PDF to our website without subediting of text, figures and tables, but with some preliminary formatting. These papers are clearly identified by a watermark on each page of the PDF.
Q. What is a Digital Object Identifier?
A. The DOI is an international, public, "persistent identifier of intellectual property entities" in the form of a combination of numbers and letters. For Nature Portfolio journals, the DOI is assigned to an item of editorial content, providing a unique and persistent identifier for that item. The DOI system is administered by the International DOI Foundation, a not-for-profit organization. CrossRef, another not-for-profit organization, uses the DOI as a reference linking standard, enables cross-publisher linking, and maintains the lookup system for DOIs. Nature Portfolio is a member of CrossRef.
Q. What do the numbers in the DOI signify?
A. The DOI has two components, a prefix (before the slash) and a suffix (after the slash). The prefix is a DOI resolver server identifer (10) and a unique identifier assigned to the publisher—for example, the identifier for Nature Portfolio is 1038 and the entire DOI prefix for an article published by Nature Portfolio is 10.1038. The suffix is an arbitrary number provided by the publisher. It can be composed of numbers and/or letters and does not necessarily have any systematic significance. Each DOI is registered in a central resolution database that associates it with one or more corresponding web locations (URLs). For example, the DOI 10.1038/ng571 connects to http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng571.
Q. Can I use the DOI in a reference citation?
A. Yes, instead of giving the volume and page number, you can give the paper's DOI at the end of the citation. For example, Nature papers should be cited in the form;
Author(s) Nature advance online publication, day month year (DOI 10.1038/natureXXX).
After print publication, you should give the DOI as well as the print citation, to enable readers to find the paper in print as well as online. For example;
Author(s) Nature volume, page (year); advance online publication, day month year (DOI 10.1038/natureXXX).
Q. How can I use a DOI to find a paper?
A. There are two ways:
- DOIs from other articles can be embedded into the linking coding of an article's reference section. In Nature journals these appear as "|Article|" in the reference sections. When |Article| is clicked, it opens another browser window leading to the entrance page (often the abstract) for another article. Depending on the source of the article, this page can be on the Nature Portfolio's site or a site of another publisher. This service is enabled by CrossRef.
- A DOI can be inserted directly into the browser. For example, for the DOI 10.1038/ng571, typing http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ng571 brings up the entrance page of the article.
Q. What is the official publication date?
A. Many journals, and most abstracting and indexing services (including Medline and Thomson-Reuters) cite the print date as the publication date. Publishers usually state both the 'online publication date' and the 'print publication date'. Nature Portfolio publishes both dates for our own papers, in the hope that scientific communities, as well as abstracting and indexing services, will recognize these dates.
We endeavour to include both the online publication date and the usual print citation in reference lists of Nature Portfolio papers, where a paper has been published online before being published in print. Given the use of the DOI in locating an online publication in the future, we encourage authors to use DOIs in reference citations.
For legal purposes (for example, establishing intellectual property rights), we assume that online publication constitutes public disclosure. But this is for the courts to decide; Nature Portfolio's role as a publisher is to provide clear documentation of the publication history, online and in print.
Q. Must I be a subscriber to read AOP articles?
A. Yes. AOP papers are the same as those in the print/online issues: while abstracts are freely available on any Nature Portfolio journal's web site, access to the full-text article requires a paid subscription or a site license.
Q. Does Medline use DOIs?
A. Medline currently captures DOIs with online publication dates in its records, and is developing an enhanced level of support for the DOI system.
Q. Does Thomson-Reuters use DOIs?
A. Thomson Reuters captures DOIs in its records at the same time as the volume/issue/page number. Therefore, it is not using the DOI to capture information before print publication, but rather as an additional piece of metadata.
Q. How does AOP affect the Impact Factor?
A. Impact factors are calculated by Thomson-Reuters. At present, Thomson-Reuters bases its calculations on the date of print publication alone, so until or unless it changes its policy, AOP has no effect on impact factors.
Q. What are the page numbers in PDFs of AOP papers?
A. For convenience, the PDF version of every AOP article is given a temporary pagination, beginning with page 1. This is unrelated to the final pagination in the printed article.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window
Publish with Elsevier
Learn about the publication process and how to submit your manuscript. This tutorial will help you find the right journal and maximize the chance to be published.

Your step-by-step guide to publishing with Elsevier
Every year, we accept and publish more than 470,000 journal articles so you are in safe hands. Publishing in an Elsevier journal starts with finding the right journal for your paper. We have tools, resources and services to help you at each stage of the publication journey to enable you to research, write, publish, promote and track your article. Let us help you make the most out of your next publication!
1. Find a journal
Find out the journals that could be best suited for publishing your research. For a comprehensive list of Elsevier journals check our Journal Catalog . You can also match your manuscript using the JournalFinder tool, then learn more about each journal. You can find information about how to log in to each journal’s editorial system here .
JournalFinder
Search the world's leading source of academic journals for a list of recommended journals that best match your research paper. You can search by using your abstract, or by using keywords and other details .
Read the journal's aims and scope to make sure it is a match
Check whether you can submit — some journals are invitation only
Use journal metrics to understand the impact of a journal
If available, check the journal at Journal Insights opens in new tab/window for additional info about impact, speed and reach
2. Prepare your paper for submission
Download our get published quick guide opens in new tab/window , which outlines the essential steps in preparing a paper. (This is also available in Chinese opens in new tab/window ). It is very important that you stick to the specific "guide for authors" of the journal to which you are submitting. This can be found on the journal's home page.
You can find information about the publishing process in the understanding the publishing process opens in new tab/window guide. It covers topics such as authors' rights, ethics and plagiarism, and journal and article metrics.
If you have research data to share, make sure you read the guide for authors to find out which options the journal offers to share research data with your article.
Read about publishing in a special issue
Use an external editing service, such as Elsevier’s Author Services opens in new tab/window if you need assistance with language
Free e-learning modules on preparing your manuscript can be found on Researcher Academy opens in new tab/window
Mendeley opens in new tab/window makes your life easier by helping you organize your papers, citations and references, accessing them in the cloud on any device, wherever you are
3. Submit and revise
You can submit to most Elsevier journals using our online systems. The system you use will depend on the journal to which you submit. You can access the relevant submission system via the "submit your paper" link on the Elsevier.com journal homepage of your chosen journal.
Alternatively, if you have been invited to submit to a journal, follow the instructions provided to you. Once submitted, your paper will be considered by the editor and if it passes initial screening, it will be sent for peer review by experts in your field. If deemed unsuitable for publication in your chosen journal, the editor may suggest you transfer your submission to a more suitable journal, via an article transfer service.
Check the open access options on the journal's homepage
Consider the options for sharing your research data
Be accurate and clear when checking your proofs
Inform yourself about copyright and licensing
4. Track your paper
Track your submitted paper.
You can track the status of your submitted paper online. The system you use to track your submission will be the same system to which you submitted. Use the reference number you received after submission to track your submission. Unsure about what the submission status means? Check out this video opens in new tab/window .
In case of any problems, contact the Support Center opens in new tab/window .
Track your accepted paper
Once your paper is accepted for publication, you will receive a reference number and a direct link that lets you follow its publication status via Elsevier’s "Track Your Accepted Article" service.
Even without a notification you can track the status of your article by entering your article reference number and corresponding author surname in Track your accepted article opens in new tab/window .
5. Share and promote
Now that your article is published, you can promote it to achieve a bigger impact for your research. Sharing research, accomplishments and ambitions with a wider audience makes you more visible in your field. This helps you get cited more, enabling you to cultivate a stronger reputation, promote your research and move forward in your career.
After publication, celebrate and get noticed opens in new tab/window !
Unable to find the answer to your question? Visit our support center for more information on all Elsevier solutions.

Unlocking Research
Open research at cambridge, it’s hard getting a date (of publication).
As part of Open Access Week 2017 , the Office of Scholarly Communication is publishing a series of blog posts on open access and open research. In this post Maria Angelaki describes how challenging it can be to interpret publication dates featured on some publishers’ websites.
More than three weeks a year. That’s how much time we spend doing nothing but determining the publication date of the articles we process in the Open Access team.
To be clear about what we are talking about here: All we need to know for HEFCE compliance is when the final Version of Record was made available on the publisher’s website. Also, if there is a printed version of the journal, for our own metadata, we need to know the Issue publication date too.
Surely, it can’t be that hard.
Defining publication date
The Policy for open access in Research Excellence framework 2021 requires the deposit of author’s outputs within three months of acceptance. However, the first two years of this policy has allowed deposits as late as three months from the date of publication.
It sounds simple doesn’t it? But what does “date of publication” mean? According to HEFCE the Date of Publication of a journal article is “ the earliest date that the final version-of-record is made available on the publisher’s website. This generally means that the ‘early online’ date, rather than the print publication date, should be taken as the date of publication. ”
When we create a record in Apollo , the University of Cambridge’s institutional repository, we input the acceptance date, the online publication date and the publication date.
We define the “online publication date” as the earliest online date the article has appeared on the publisher’s website and “publication date” as the date the article appeared in a print issue. These two dates are important since we rely on them to set the correct embargoes and assess compliance with open access requirements.
The problems can be identified as:
- There are publishers that do not feature clearly the “online date” and the “paper issue date”. We will see examples further on.
- To make things more complicated, some publishers do not always specify which version of the article was published on the “online date”. It can variously mean the author’s accepted manuscript (AAM), corrected proof, or the Version of Record (VoR), and there are sometimes questions in the latter as to whether these include full citation details.
- Lastly, there are cases where the article is first published in a print issue and then published online. Often print publications are only identified as “Spring issue’ or the like.
How can we comply with HEFCE’s deposit timeframes if we do not have a full publication date cited in the publisher’s website? Ideally, it would only take a minute or so for anybody depositing articles in an institutional repository to find the “correct” publication date. But these confusing cases mean the minute inevitably becomes several minutes, and when you are uploading 5000 odd papers a year this turns into 17 whole days.
Setting rules for consistency
In the face of all of this ambiguity, we have had to devise a system of ‘rules’ to ensure we are consistent. For example:
- If a publication year is given, but no month or day, we assume that it was 1 st January.
- If a publication year and month are given but no day, we assume that it was 1 st of the month.
- If we have an online date of say, 10 th May 2017 and a print issue month of May 2017, we will use the most specific date (10 th May 2017) rather than assuming 1 st May 2017 (though it is earlier).
- Unless the publisher specifies that the online version is the accepted manuscript, we regard it as the final VOR with or without citation details.
- If we cannot find a date from any other source, we try to check when the pdf featured on the website was created.
This last example does start to give a clue to why we have to spend so much time on the date problem.
By way of illustration, we have listed below some examples by publisher of how this affects us. This is a deliberate attempt to name and shame, but if a publisher is missing from this list, it is not because they are clear and straightforward on this topic. We just ran out of space. To be fair though, we have also listed one publisher as an example to show how simple it is to have a clear and transparent article publication history.
Taylor & Francis – ‘published online’
Publication date of an article online.
There are several ways you can read an article. If the article is open access or if you subscribe, then you can download a pdf of the article from the publisher website. Otherwise, you see the online version on the website. The two versions of a particular article are below, the pdf and the online HTML version.

Both the pdf and the online version of the article list the article history as: Received 14 March 2016 Accepted as 23 December 2016 Published online 12 January 2017
and also cite the Volume, year of publication and issue.
But does the ‘Published online’ date refer to when the Version of Record was made available online or the first time the Accepted Manuscript was made available online? We can’t distinguish this to provide the date for HEFCE.
Publication date of the printed journal
While we know the volume, year of publication and issue number, we don’t know what the exact publication date of the printed journal is for our metadata records. If we drill a bit more and we visit past volumes of the journal, we can see that the previous complete year (2016) features 12 issues. So we can make an educated guess that the issue number refers to the publication month (in our example it is issue 5, so it is May 2017).
However, we are wrong. The 12 issues refer to the online publication issues and not the print issues. According to Taylor & Francis’ agents customer service page they “have a number of journals where the print publication schedule differs to the online”. They have a list of those journals available and in our case we can see that this particular journal has 12 online issues but 4 paper issues in a year. So when did this actual article appear in print? Who knows.
Implications
Remember the 17 days a year? This is the type of activity that fills the time. Do we really need to do this time consuming exercise? Some might suggest that we contact the publisher and ask, but it is time-consuming and not always successful.
Elsevier’s Articles in Press
Elsevier’s description of Articles in Press states they are “articles that have been accepted for publication in Elsevier journals but have not yet been assigned to specific issues”. They could be any of an Accepted Manuscript, a Corrected Proof or an Uncorrected Proof. Elsevier have a page that answers questions about ‘grey areas’ and in a section discussing whether it is permissible for Elsevier to remove an article for some reason, they state they do not remove articles that have been published but “…papers made available in our “Articles in Press” (AiP) service do not have the same status as a formally published article…)”
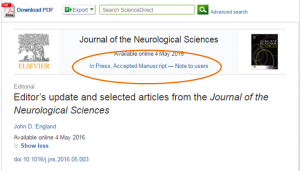
So we have a disconnect. The earliest online date is not the final published version as per HEFCE’s requirement. There is no way of determining the date when the final published date does actually appear online, so we need to wait until the article is allocated an issue and volume for us to determine the date. This could be some considerable time AFTER the work has been finalised. So open access is delayed, we risk non compliance and waste huge amounts of time.
Well done, Wiley
Wiley features all possible stages of the article’s various publication stages making it easy to distinguish the VoR online publication date, exactly what HEFCE (and we) require.
Article published in an issue
This is an example of when an article is published online and the print issue is published too.
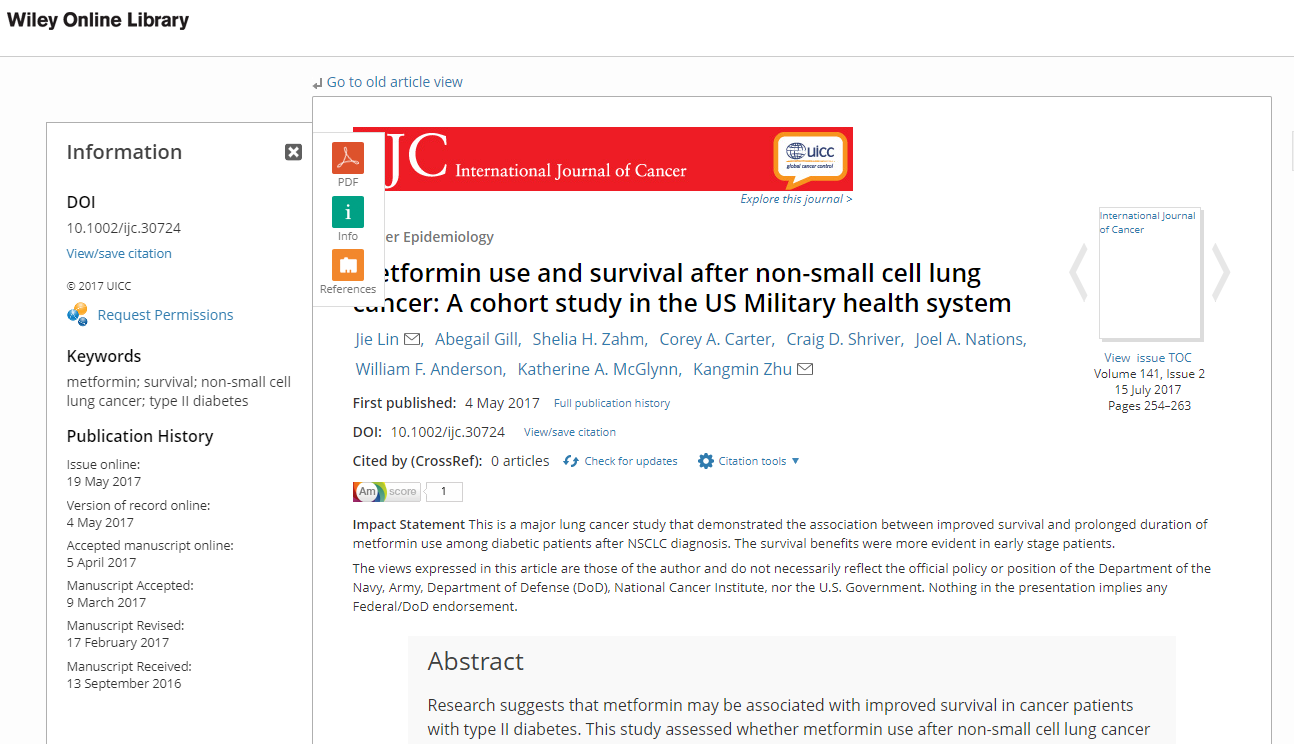
Article published online (awaiting for a print issue date)
Wiley states the publication history clearly even when an article is published online but not yet included in a publication issue.
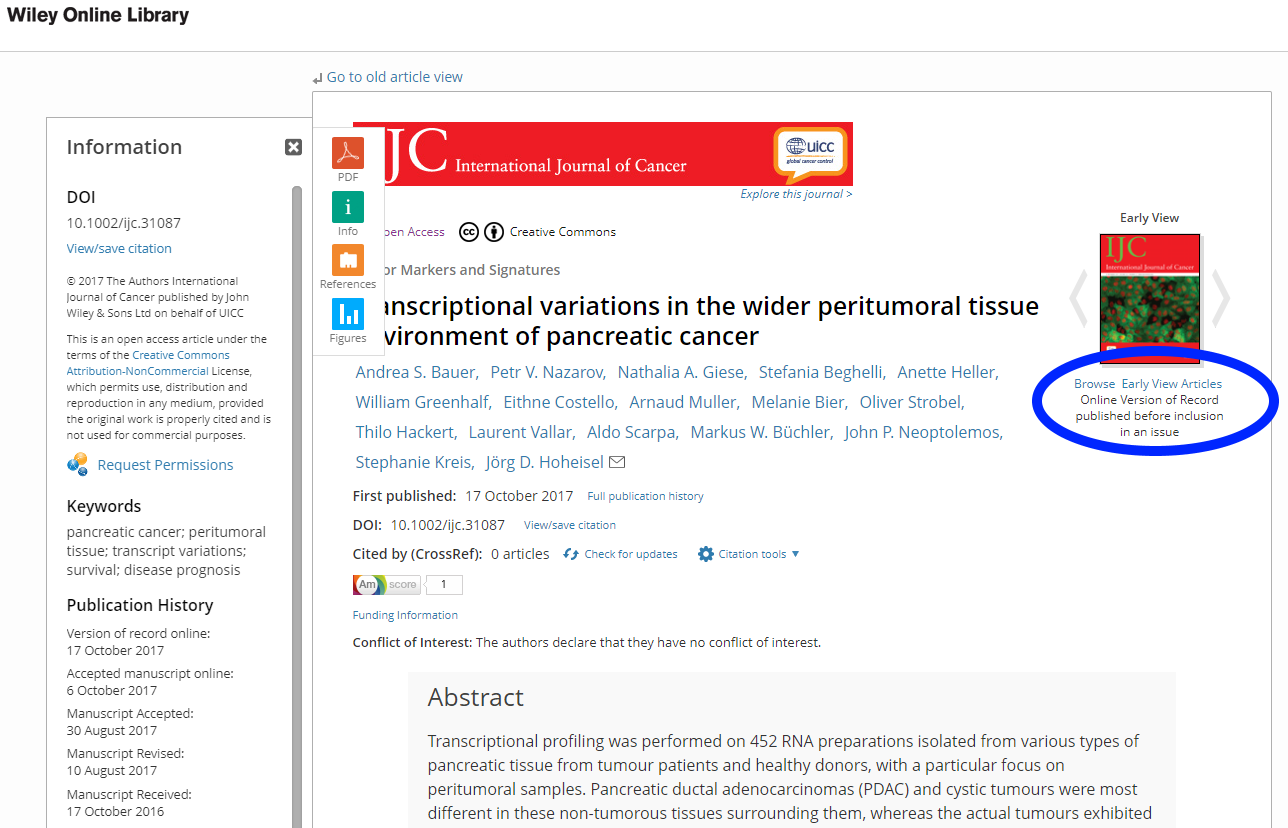
If you have a closer look at the screenshot, Wiley regards as “First published” the VoR online publication date (shown also on the left under Publication History) and not the Accepted Manuscript online date.
In this case, the publisher clearly states which version they refer to when the term “First Published” is used and also gives the reader the full history of the article’s “life stages” as well as inform us that the article is yet not included in an issue (circle on the right).
Conclusions
If you have made it this far through the blog post, you are probably working in this area and have some experience of this issue. If you are new to the topic, hopefully the above examples have illustrated how frustrating it is sometimes to find the correct information in order to comply with not only HEFCE’s timeframe requirements, but other open access compliance issues, especially when you set embargoes.
A simple task can become an expensive exercise because we are wasting valuable working hours. We are in the business of supporting the research community to openly share research outputs, not in the business of deciphering information in publishers’ websites.
We need clear information in order to effectively deposit an article to our institutional repository and meet whatever requirements need to be met. It is not unreasonable to expect consistency and standards in the display of publication history and dates of articles.
5 thoughts on “ It’s hard getting a date (of publication) ”
- Pingback: Scare campaigns, we have seen a few | Unlocking Research
Do you have any advice for trying to find out dates of publication for Emerald articles? Every time I go onto their website I think, “am I missing something? The publication date must be somewhere!”
- Pingback: Manuscript detectives – submitted, accepted or published? | Unlocking Research
- Pingback: ‘No free labor’ – we agree. | Unlocking Research
Should an author change the year of an article listed on CV (or future citations) if the in print comes out the next year from the online version? For ex: online version of published article was 2017. Now just came out in press (2018). What’s the correct way to list this publication?

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
Published on November 19, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on January 20, 2023.
The formatting of a research paper is different depending on which style guide you’re following. In addition to citations , APA, MLA, and Chicago provide format guidelines for things like font choices, page layout, format of headings and the format of the reference page.
Scribbr offers free Microsoft Word templates for the most common formats. Simply download and get started on your paper.
APA | MLA | Chicago author-date | Chicago notes & bibliography
- Generate an automatic table of contents
- Generate a list of tables and figures
- Ensure consistent paragraph formatting
- Insert page numbering
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Formatting an apa paper, formatting an mla paper, formatting a chicago paper, frequently asked questions about research paper formatting.
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial.
- Set 1 inch page margins.
- Apply double line spacing.
- If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page.
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Watch the video below for a quick guide to setting up the format in Google Docs.
The image below shows how to format an APA Style title page for a student paper.
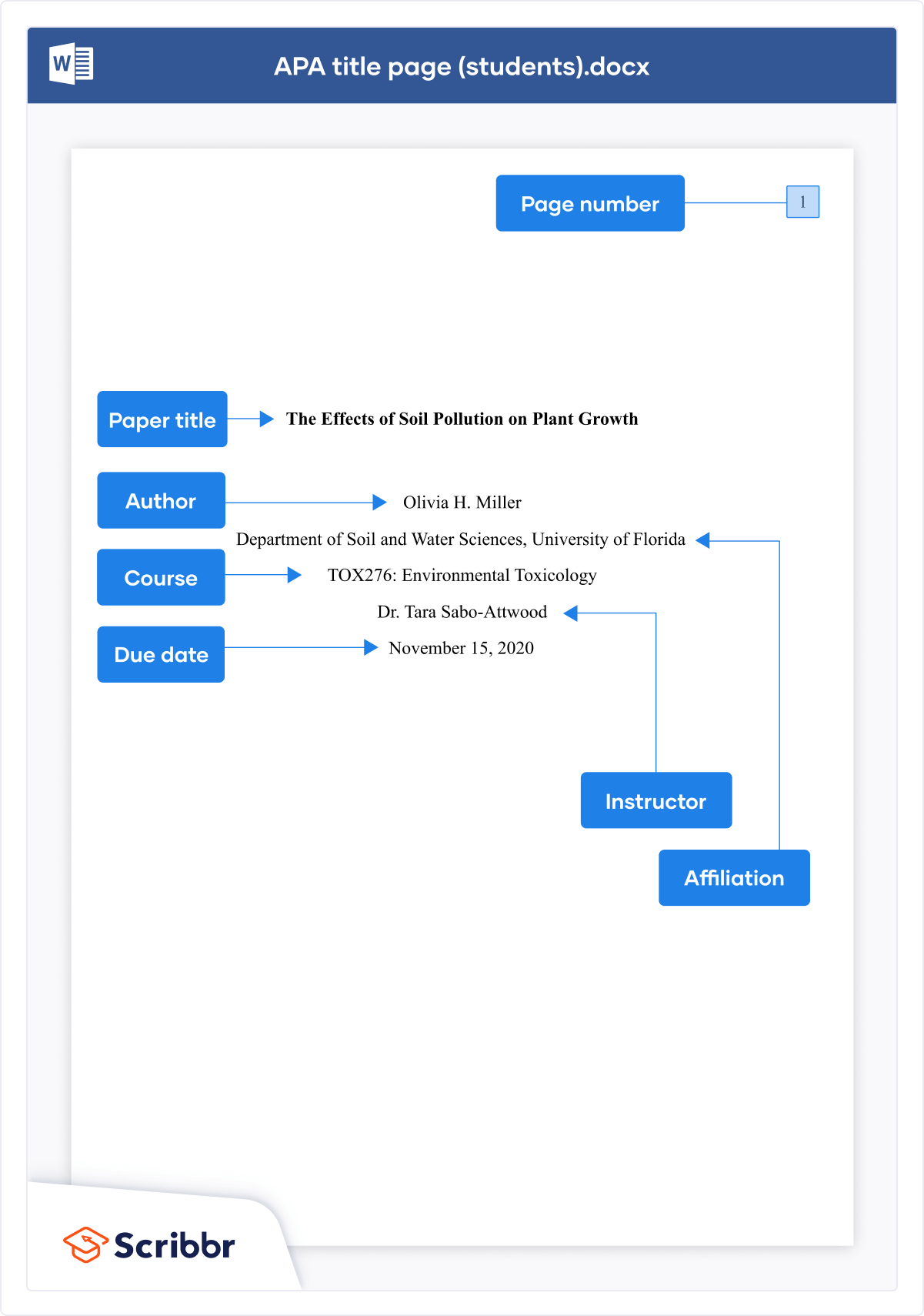
Running head
If you are submitting a paper for publication, APA requires you to include a running head on each page. The image below shows you how this should be formatted.
For student papers, no running head is required unless you have been instructed to include one.
APA provides guidelines for formatting up to five levels of heading within your paper. Level 1 headings are the most general, level 5 the most specific.
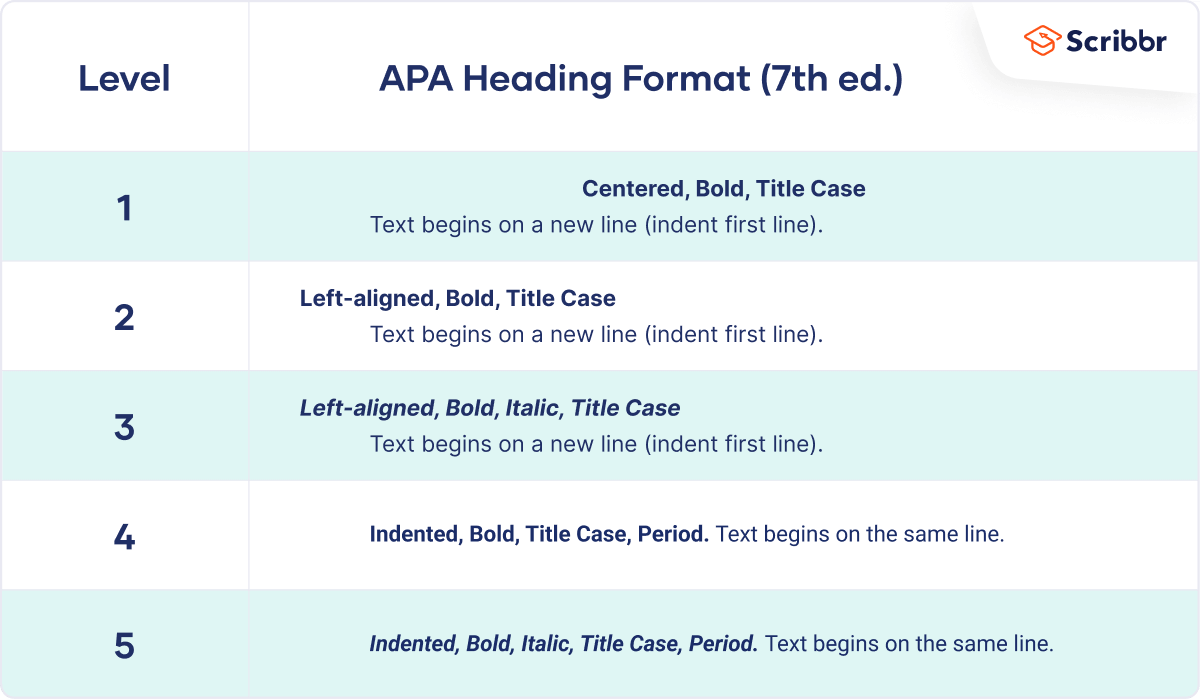
Reference page
APA Style citation requires (author-date) APA in-text citations throughout the text and an APA Style reference page at the end. The image below shows how the reference page should be formatted.
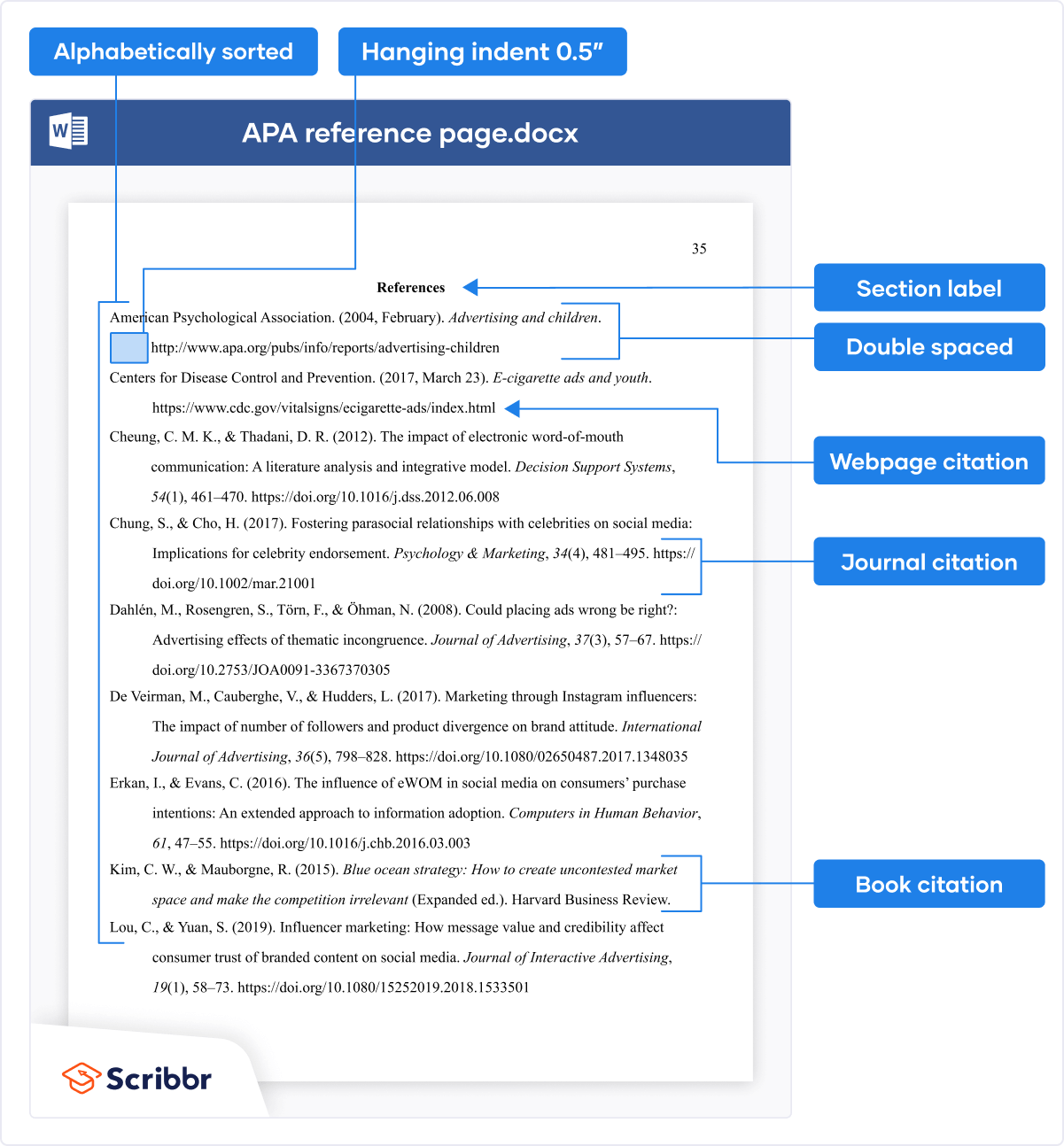
Note that the format of reference entries is different depending on the source type. You can easily create your citations and reference list using the free APA Citation Generator.
Generate APA citations for free
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The main guidelines for writing an MLA style paper are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use title case capitalization for headings .
Check out the video below to see how to set up the format in Google Docs.
On the first page of an MLA paper, a heading appears above your title, featuring some key information:
- Your full name
- Your instructor’s or supervisor’s name
- The course name or number
- The due date of the assignment
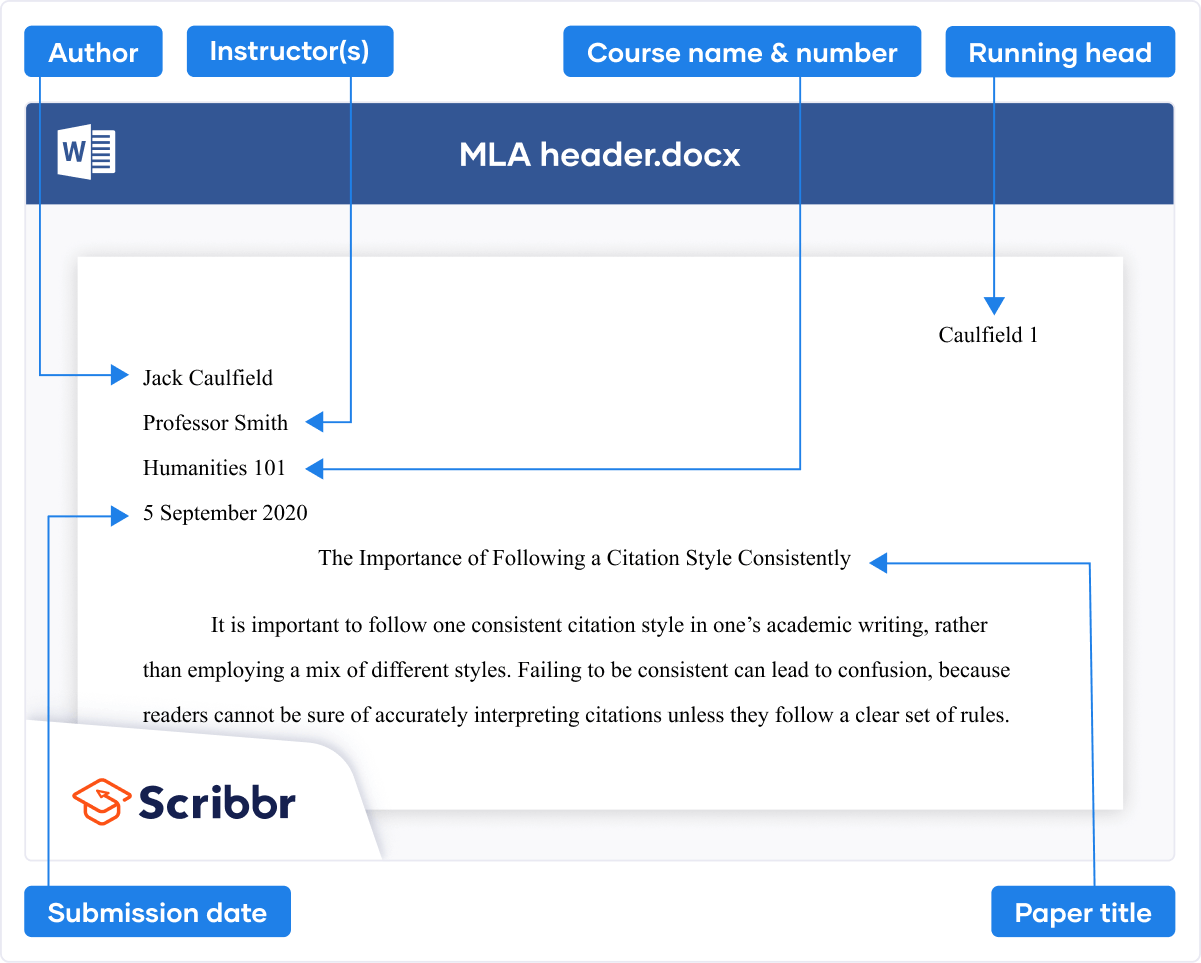
Page header
A header appears at the top of each page in your paper, including your surname and the page number.
Works Cited page
MLA in-text citations appear wherever you refer to a source in your text. The MLA Works Cited page appears at the end of your text, listing all the sources used. It is formatted as shown below.
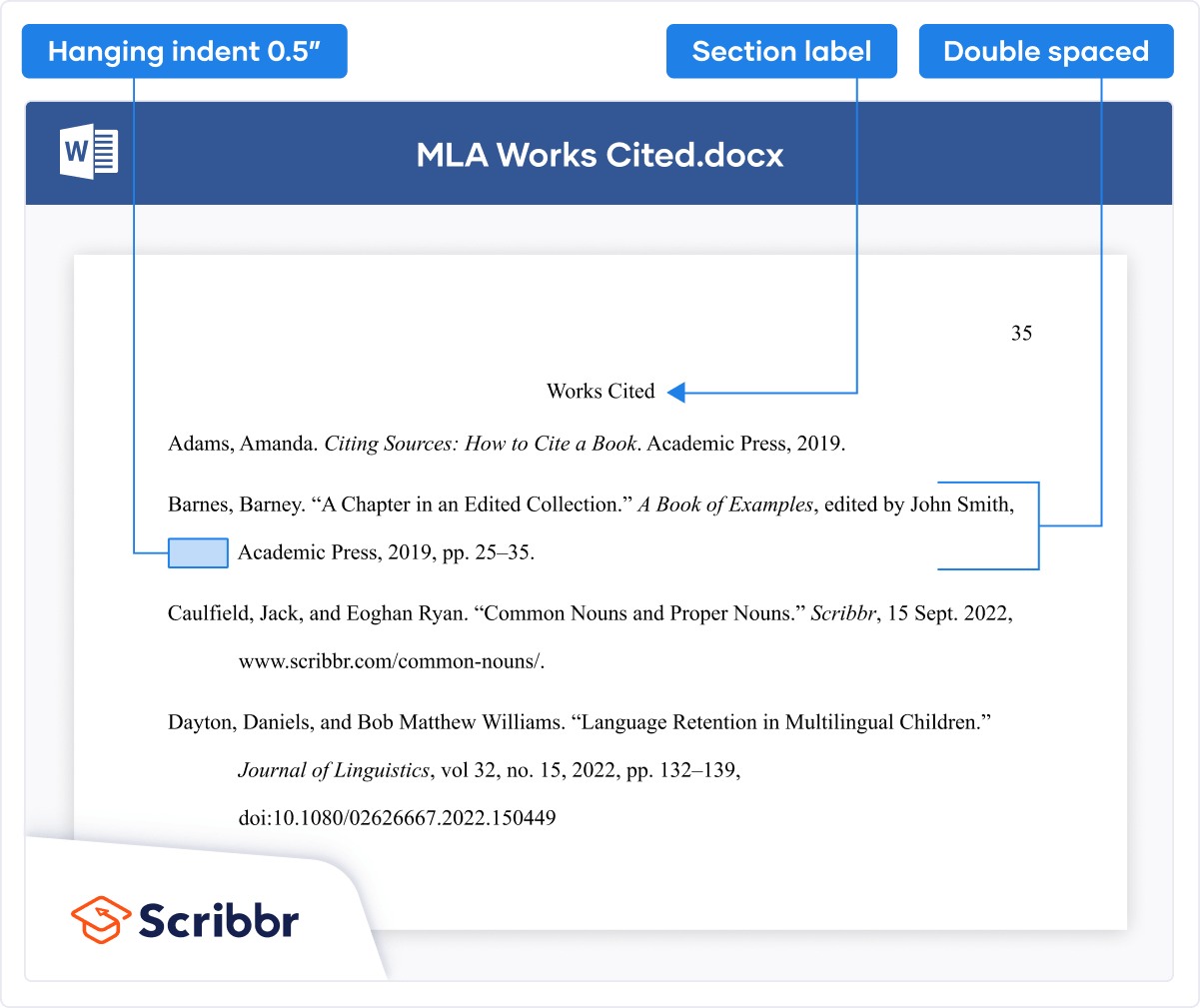
You can easily create your MLA citations and save your Works Cited list with the free MLA Citation Generator.
Generate MLA citations for free
The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman.
- Use 1 inch margins or larger.
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
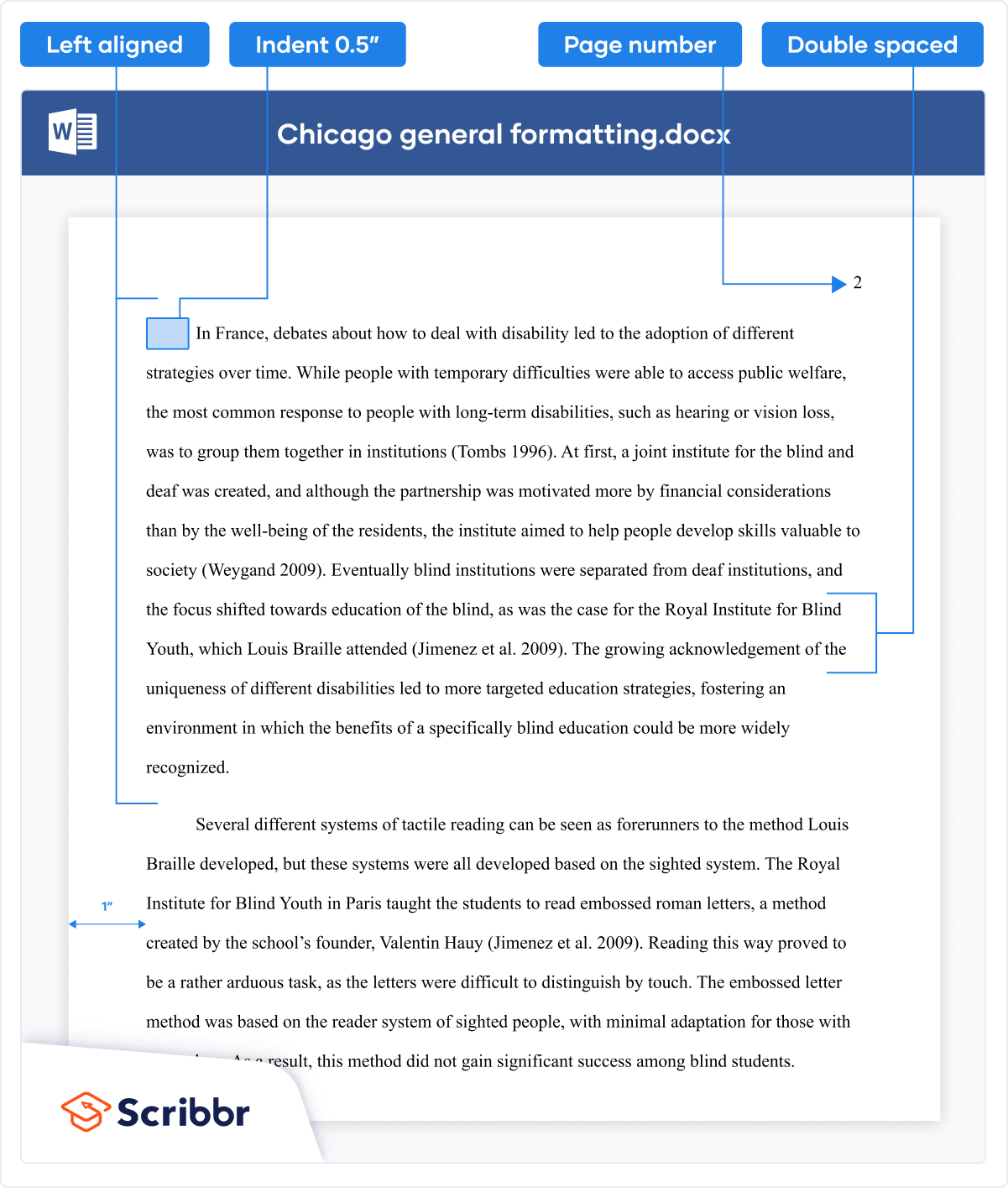
Chicago doesn’t require a title page , but if you want to include one, Turabian (based on Chicago) presents some guidelines. Lay out the title page as shown below.
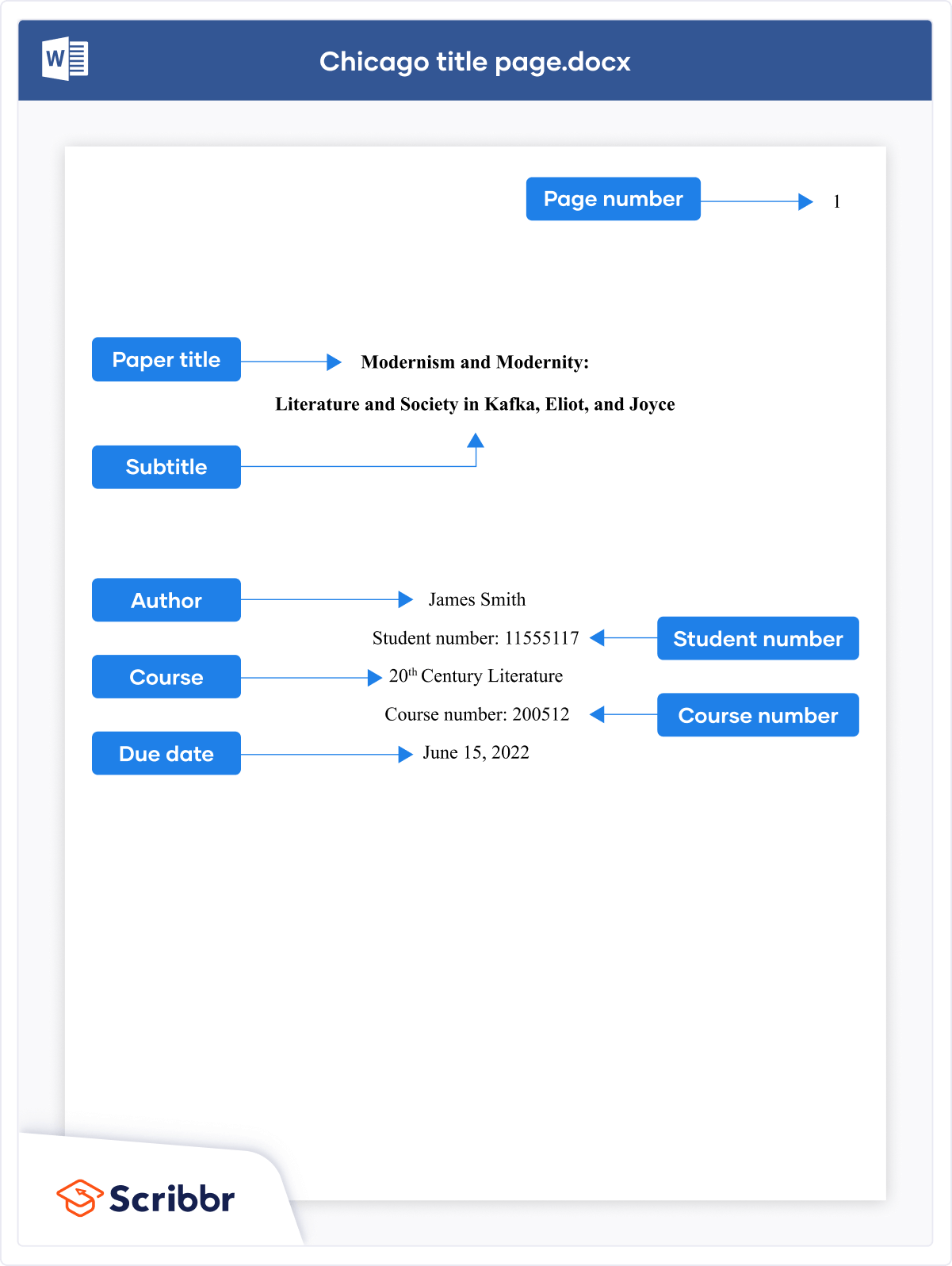
Bibliography or reference list
Chicago offers two citation styles : author-date citations plus a reference list, or footnote citations plus a bibliography. Choose one style or the other and use it consistently.
The reference list or bibliography appears at the end of the paper. Both styles present this page similarly in terms of formatting, as shown below.
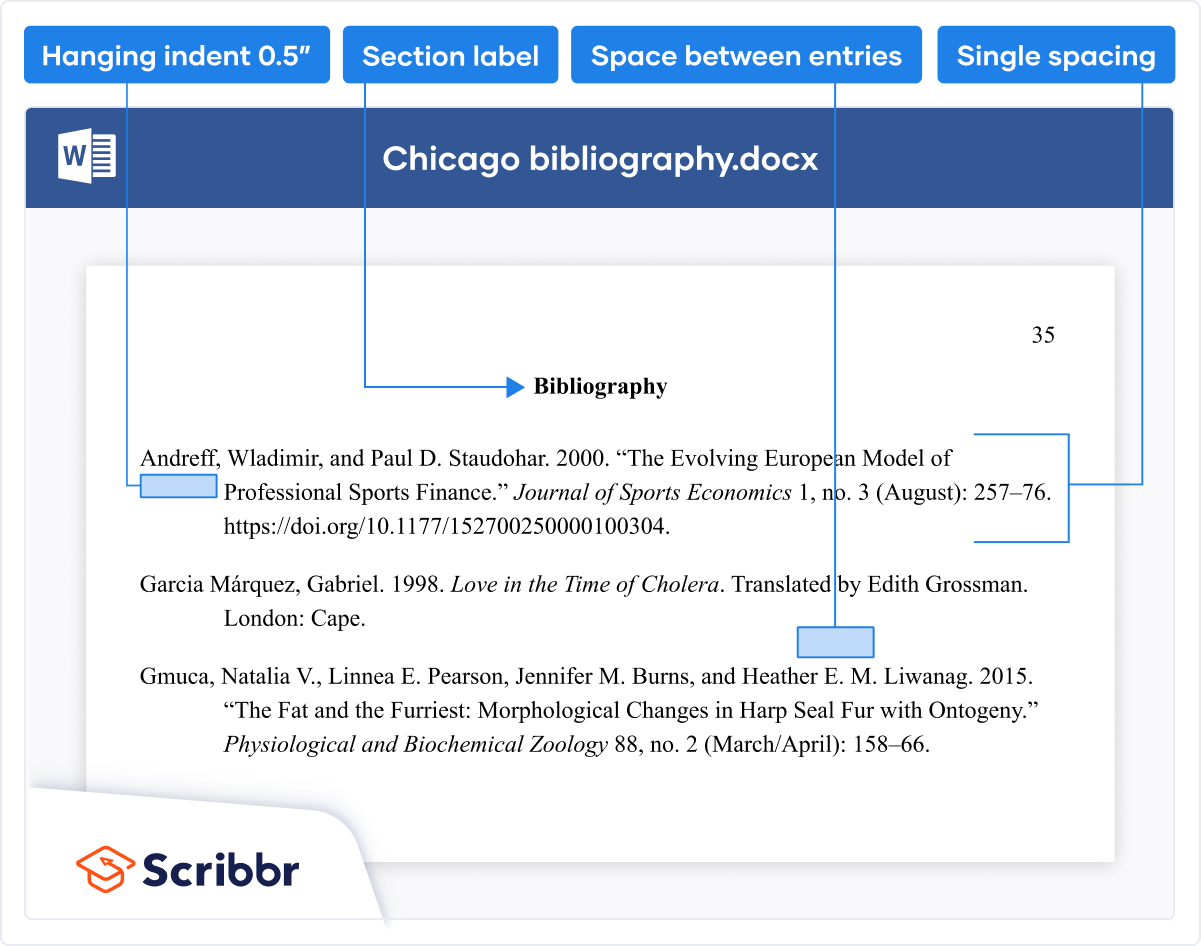
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Apply double line spacing
- Include a title page
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, January 20). Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-format/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa format for academic papers and essays, mla format for academic papers and essays, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, what is your plagiarism score.

APA Citation Style
- APA 7th Edition Overview
- ...Articles?
- ...Websites?
- ...Other Sources?
- ...ChatGPT?
Date Definition
APA defines the 'date' element as the publication date (American Psychological Association, 2019, p. 289).
There are 5 forms to format the date:
- Year, month, and day
- Year and month
- Year and season
- Date ranges
The reference category of the work you are trying to cite will determine how the date is formatted. The most common way to cite the date of a work is with solely the year. However, digital resources are typically the exception.
General rules:
- Enclose the date within parentheses for both in-text citations and for the reference list.
- For the date in the reference list, enclose the date with parentheses and follow with a period.
- For dates with month values spell out the name of the month
- For books use the copyright date
- For journals use the journal's year of volume
- For works with no date, use "(n.d.)" with no spaces between the 'n' or 'd.' Use for in-text citations and in the reference list
- (2021, September 9)
- (2021, Spring)
See pp. 289-291 in APA Seventh Edition
Online Media
The Online Media category as defined by APA includes webpages, websites, and social media. Here are a few rules about the date format:
- Do not use the copyright date in the webpage footer, unless it is known that it pertains to the cited content
- Use more precise dates for sources published/updated more frequently (e.g. blog posts)
For updated or reviewed works
- Do not use the 'last reviewed' date
- Use the "last updated" date, if it pertains to the content you are citing
Morey, M. C. (2019). Physical activity and exercise in older adults. UpToDate. Retrieved July, 22, 2019, from https://www.uptodate.com/contents/physical-activity-and-exercise-in-older-adults
*Example taken from p. 319 of APA Seventh Edition
**For best practices for constantly updated sources, especially social media posts, cite the archived version of the webpage
See pp. 290, 329 in APA Seventh Edition
Unpublished or Informally published
- Do not record information about publication status. Use the production date for the date for informally published works
- Smith, J. (in press). Title of work. Journal name 1 (2), pp 1-14. http//doi.thisisawebsite.org.
- Smith (in press) is researching...
- The research shows that 15% of people chose option A (Smith, in press).
See p. 290 in APA Seventh Edition
APA 7th Edition Manual
American Psychological Association . (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/000165-000
- << Previous: Author
- Next: Title >>
- Last Updated: Feb 19, 2024 12:03 PM
- URL: https://libguides.library.tmc.edu/APA
Research Foundations: Locate Citation Information
- Information Literacy
- The Information Timeline
- Popular, Scholarly, & Trade Publications
- Primary, Secondary, & Tertiary Materials
- Information Formats
- Evaluate Information
- Chapter 1 Self Quiz
- The Pre-Research Process
- Decide on a Topic
- Find Background Information
- Refine Your Topic
- Develop a Thesis Statement
- Choose Keywords
- Create Search Statements
- Chapter 2 Self Quiz
- Search the Library Catalog
- Call Numbers
- Request Books
- Book Research Streamlined
- Viewing eBooks
- Access Media
- Chapter 3 Self Quiz
- About Library Databases
- Find Articles in Databases
- Modify Your Search
- Reading Scholarly Articles
- Chapter 4 Self Quiz
- Citation Styles
- Locate Citation Information
- Copyright & Fair Use
- Creative Commons
- Find & Attribute Images
- Chapter 5 Self Quiz
Locating Citation Information
No matter which citation style you use, the first step to crediting your sources is locating the citation information. Regardless of the information format, all citations will include a minimum of title of the work, author or authors, and date of publication. Below are examples from books, ebooks, articles from databases, and academic journal articles that illustrate where to find the identifying citation information.
Book / eBook Title Page

title page of a book
Title - Full title and subtitles
Edition - books that have been revised or expanded more than once will often have an edition number
Author(s) or Editor(s) - may include one or more authors or editors of the book
Publisher - the company that published the book
Publishing City - if there are multiple cities, cite the first city listed
- Book Title Page Example A larger, printable version of the title page example.
Book / eBook Copyright Page

copyright page of a book
Copyright / Publication Year - if there are multiple dates, choose the most recent
- Book Copyright Page Example A larger, printable version of the copyright page example.
Academic Journal Article

example academic journal article
Academic journal articles' citations differ from book sources, and thus require you to identify a few unique pieces of information.
Author(s) - may include one or more authors of the article
Page Number - cite the entire page range in which the article appears
Publication - name of the journal the article was published in
Volume / Issue Number - identifies the exact edition of the journal where the article appears
Publication Date - date formats vary; use the format the journal provides or the citation style requires
Most citation information will appear on the first page of the article; however, the location of that information will vary from journal to journal. You can find the placement of the journal name, page number, publication date, and volume and issue number located on the top or bottom of the article’s page. The publication date may be a single year (2013), a distinct month (October 2010), specific publication cycle (Fall 2007), or an exact date (June 28, 2005). The page range of the article is another cirtical piece of citation information. Some article in printed or PDF format, will have the page numbers visible. Other articles in a digital, or HTML, format may not have obvious page ranges.
- Academic Journal Article Example A larger, printable version of the journal article example.
Database Articles
There is no uniform approach to locating citation information based solely on the article itself. Many journals follow a relatively consistent format. Magazine and newspaper articles may only offer an article's title with the text and identify an author or source. Again, you are not likely to encounter standardization in the presentation of the article.
Some citation styles or professors require that you include the name of the database if retrieved through a library database. This can be tricky to discern if you are not familiar with the databases. Fortunately, most databases provide essential citation information for each article directly on the results pages or the article description page. Knowing this saves a lot of time and effort when reviewing articles.

example of citation information for a database article
Additionally, many databases will create an article's citation for you, in the citation style you choose. These computer-generated citations require careful review, as they may not be fully correct. Most databases will create citations that have the right information, in the right order. The biggest drawback to using databases created citations is in the formatting. Many will not include the correct spacing, punctuation, and capitalization for the citation style. Some articles, particularly those only available in HTML format, display just the first page number rather than the entire range. You may not be able to verify an exact page range without access to a PDF format in these instances. Always remeber to check these citations again an official style guide before including in a research project.

example of a database generated citation
- << Previous: Citation Styles
- Next: Plagiarism >>
- Last Updated: May 2, 2024 9:24 AM
- URL: https://libguides.seminolestate.edu/researchfoundations
- Insights blog
How to publish your research
A step-by-step guide to getting published.
Publishing your research is an important step in your academic career. While there isn’t a one-size-fits-all approach, this guide is designed to take you through the typical steps in publishing a research paper.
Discover how to get your paper published, from choosing the right journal and understanding what a peer reviewed article is, to responding to reviewers and navigating the production process.
Step 1: Choosing a journal

Choosing which journal to publish your research paper in is one of the most significant decisions you have to make as a researcher. Where you decide to submit your work can make a big difference to the reach and impact your research has.
It’s important to take your time to consider your options carefully and analyze each aspect of journal submission – from shortlisting titles to your preferred method of publication, for example open access .
Don’t forget to think about publishing options beyond the traditional journals format – for example, open research platform F1000Research , which offers rapid, open publication for a wide range of outputs.
Why choose your target journal before you start writing?
The first step in publishing a research paper should always be selecting the journal you want to publish in. Choosing your target journal before you start writing means you can tailor your work to build on research that’s already been published in that journal. This can help editors to see how a paper adds to the ‘conversation’ in their journal.
In addition, many journals only accept specific manuscript formats of article. So, by choosing a journal before you start, you can write your article to their specifications and audience, and ultimately improve your chances of acceptance.
To save time and for peace of mind, you can consider using manuscript formatting experts while you focus on your research.

How to select the journal to publish your research in
Choosing which journal to publish your research in can seem like an overwhelming task. So, for all the details of how to navigate this important step in publishing your research paper, take a look at our choosing a journal guide . This will take you through the selection process, from understanding the aims and scope of the journals you’re interested in to making sure you choose a trustworthy journal.
Don’t forget to explore our Journal Suggester to see which Taylor & Francis journals could be right for your research.
Go to guidance on choosing a journal
Step 2: Writing your paper
Writing an effective, compelling research paper is vital to getting your research published. But if you’re new to putting together academic papers, it can feel daunting to start from scratch.
The good news is that if you’ve chosen the journal you want to publish in, you’ll have lots of examples already published in that journal to base your own paper on. We’ve gathered advice on every aspect of writing your paper, to make sure you get off to a great start.
How to write your paper
How you write your paper will depend on your chosen journal, your subject area, and the type of paper you’re writing. Everything from the style and structure you choose to the audience you should have in mind while writing will differ, so it’s important to think about these things before you get stuck in.
Our writing your paper guidance will take you through everything you need to know to put together your research article and prepare it for submission. This includes getting to know your target journal, understanding your audiences, and how to choose appropriate keywords.
You can also use this guide to take you through your research publication journey .

You should also make sure you’re aware of all the Editorial Policies for the journal you plan to submit to. Don’t forget that you can contact our editing services to help you refine your manuscript.
Discover advice and guidance for writing your paper
Step 3: Making your submission
Once you’ve chosen the right journal and written your manuscript, the next step in publishing your research paper is to make your submission .
Each journal will have specific submission requirements, so make sure you visit Taylor & Francis Online and carefully check through the instructions for authors for your chosen journal.
How to submit your manuscript
To submit your manuscript you’ll need to ensure that you’ve gone through all the steps in our making your submission guide. This includes thoroughly understanding your chosen journal’s instructions for authors, writing an effective cover letter, navigating the journal’s submission system, and making sure your research data is prepared as required.
You can also improve your submission experience with our guide to avoid obstacles and complete a seamless submission.

To make sure you’ve covered everything before you hit ‘submit’ you can also take a look at our ‘ready to submit’ checklist (don’t forget, you should only submit to one journal at a time).
Understand the process of making your submission
Step 4: Navigating the peer review process
Now you’ve submitted your manuscript, you need to get to grips with one of the most important parts of publishing your research paper – the peer review process .
What is peer review?
Peer review is the independent assessment of your research article by independent experts in your field. Reviewers, also sometimes called ‘referees’, are asked to judge the validity, significance, and originality of your work.
This process ensures that a peer-reviewed article has been through a rigorous process to make sure the methodology is sound, the work can be replicated, and it fits with the aims and scope of the journal that is considering it for publication. It acts as an important form of quality control for research papers.

Peer review is also a very useful source of feedback, helping you to improve your paper before it’s published. It is intended to be a collaborative process, where authors engage in a dialogue with their peers and receive constructive feedback and support to advance their work.
Almost all research articles go through peer review, although in some cases the journal may operate post-publication peer review, which means that reviews and reader comments are invited after the paper is published.
If you’ll like to feel more confident before getting your work peer reviewed by the journal, you may want to consider using an in-depth technical review service from experts.
Understanding peer review
Peer review can be a complex process to get your head around. That’s why we’ve put together a comprehensive guide to understanding peer review . This explains everything from the many different types of peer review to the step-by-step peer review process and how to revise your manuscript. It also has helpful advice on what to do if your manuscript is rejected.
Visit our peer review guide for authors
Step 5: The production process
If your paper is accepted for publication, it will then head into production . At this stage of the process, the paper will be prepared for publishing in your chosen journal.
A lot of the work to produce the final version of your paper will be done by the journal production team, but your input will be required at various stages of the process.
What do you need to do during production?
During production, you’ll have a variety of tasks to complete and decisions to make. For example, you’ll need to check and correct proofs of your article and consider whether or not you want to produce a video abstract to accompany it.
Take a look at our guide to the production process to find out what you’ll need to do in this final step to getting your research published.
Your research is published – now what?
You’ve successfully navigated publishing a research paper – congratulations! But the process doesn’t stop there. Now your research is published in a journal for the world to see, you’ll need to know how to access your article and make sure it has an impact .
Here’s a quick tip on how to boost your research impact by investing in making your accomplishments stand out.
Below you’ll find helpful tips and post-publication support. From how to communicate about your research to how to request corrections or translations.
How to access your published article
When you publish with Taylor & Francis, you’ll have access to a new section on Taylor & Francis Online called Authored Works . This will give you and all other named authors perpetual access to your article, regardless of whether or not you have a subscription to the journal you have published in.
You can also order print copies of your article .
How to make sure your research has an impact
Taking the time to make sure your research has an impact can help drive your career progression, build your networks, and secure funding for new research. So, it’s worth investing in.
Creating a real impact with your work can be a challenging and time-consuming task, which can feel difficult to fit into an already demanding academic career.
To help you understand what impact means for you and your work, take a look at our guide to research impact . It covers why impact is important, the different types of impact you can have, how to achieve impact – including tips on communicating with a variety of audiences – and how to measure your success.

Keeping track of your article’s progress
Through your Authored Works access , you’ll be able to get real-time insights about your article, such as views, downloads and citation numbers.
In addition, when you publish an article with us, you’ll be offered the option to sign up for email updates. These emails will be sent to you three, six and twelve months after your article is published to let you know how many views and citations the article has had.
Corrections and translations of published articles
Sometimes after an article has been published it may be necessary to make a change to the Version of Record . Take a look at our dedicated guide to corrections, expressions of concern, retractions and removals to find out more.
You may also be interested in translating your article into another language. If that’s the case, take a look at our information on article translations .
Go to your guide on moving through production
Explore related posts
Insights topic: Get published
Use a trusted editing service to help you get published
5 practical tips for writing an academic article

5 ways to avoid the wrong journal and find the right one
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write and Publish Your Research in a Journal
Last Updated: May 26, 2024 Fact Checked
Choosing a Journal
Writing the research paper, editing & revising your paper, submitting your paper, navigating the peer review process, research paper help.
This article was co-authored by Matthew Snipp, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Cheyenne Main . C. Matthew Snipp is the Burnet C. and Mildred Finley Wohlford Professor of Humanities and Sciences in the Department of Sociology at Stanford University. He is also the Director for the Institute for Research in the Social Science’s Secure Data Center. He has been a Research Fellow at the U.S. Bureau of the Census and a Fellow at the Center for Advanced Study in the Behavioral Sciences. He has published 3 books and over 70 articles and book chapters on demography, economic development, poverty and unemployment. He is also currently serving on the National Institute of Child Health and Development’s Population Science Subcommittee. He holds a Ph.D. in Sociology from the University of Wisconsin—Madison. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 705,929 times.
Publishing a research paper in a peer-reviewed journal allows you to network with other scholars, get your name and work into circulation, and further refine your ideas and research. Before submitting your paper, make sure it reflects all the work you’ve done and have several people read over it and make comments. Keep reading to learn how you can choose a journal, prepare your work for publication, submit it, and revise it after you get a response back.
Things You Should Know
- Create a list of journals you’d like to publish your work in and choose one that best aligns with your topic and your desired audience.
- Prepare your manuscript using the journal’s requirements and ask at least 2 professors or supervisors to review your paper.
- Write a cover letter that “sells” your manuscript, says how your research adds to your field and explains why you chose the specific journal you’re submitting to.

- Ask your professors or supervisors for well-respected journals that they’ve had good experiences publishing with and that they read regularly.
- Many journals also only accept specific formats, so by choosing a journal before you start, you can write your article to their specifications and increase your chances of being accepted.
- If you’ve already written a paper you’d like to publish, consider whether your research directly relates to a hot topic or area of research in the journals you’re looking into.

- Review the journal’s peer review policies and submission process to see if you’re comfortable creating or adjusting your work according to their standards.
- Open-access journals can increase your readership because anyone can access them.

- Scientific research papers: Instead of a “thesis,” you might write a “research objective” instead. This is where you state the purpose of your research.
- “This paper explores how George Washington’s experiences as a young officer may have shaped his views during difficult circumstances as a commanding officer.”
- “This paper contends that George Washington’s experiences as a young officer on the 1750s Pennsylvania frontier directly impacted his relationship with his Continental Army troops during the harsh winter at Valley Forge.”

- Scientific research papers: Include a “materials and methods” section with the step-by-step process you followed and the materials you used. [5] X Research source
- Read other research papers in your field to see how they’re written. Their format, writing style, subject matter, and vocabulary can help guide your own paper. [6] X Research source

- If you’re writing about George Washington’s experiences as a young officer, you might emphasize how this research changes our perspective of the first president of the U.S.
- Link this section to your thesis or research objective.
- If you’re writing a paper about ADHD, you might discuss other applications for your research.

- Scientific research papers: You might include your research and/or analytical methods, your main findings or results, and the significance or implications of your research.
- Try to get as many people as you can to read over your abstract and provide feedback before you submit your paper to a journal.

- They might also provide templates to help you structure your manuscript according to their specific guidelines. [11] X Research source

- Not all journal reviewers will be experts on your specific topic, so a non-expert “outsider’s perspective” can be valuable.

- If you have a paper on the purification of wastewater with fungi, you might use both the words “fungi” and “mushrooms.”
- Use software like iThenticate, Turnitin, or PlagScan to check for similarities between the submitted article and published material available online. [15] X Research source

- Header: Address the editor who will be reviewing your manuscript by their name, include the date of submission, and the journal you are submitting to.
- First paragraph: Include the title of your manuscript, the type of paper it is (like review, research, or case study), and the research question you wanted to answer and why.
- Second paragraph: Explain what was done in your research, your main findings, and why they are significant to your field.
- Third paragraph: Explain why the journal’s readers would be interested in your work and why your results are important to your field.
- Conclusion: State the author(s) and any journal requirements that your work complies with (like ethical standards”).
- “We confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal.”
- “All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission to [insert the name of the target journal].”

- Submit your article to only one journal at a time.
- When submitting online, use your university email account. This connects you with a scholarly institution, which can add credibility to your work.

- Accept: Only minor adjustments are needed, based on the provided feedback by the reviewers. A first submission will rarely be accepted without any changes needed.
- Revise and Resubmit: Changes are needed before publication can be considered, but the journal is still very interested in your work.
- Reject and Resubmit: Extensive revisions are needed. Your work may not be acceptable for this journal, but they might also accept it if significant changes are made.
- Reject: The paper isn’t and won’t be suitable for this publication, but that doesn’t mean it might not work for another journal.

- Try organizing the reviewer comments by how easy it is to address them. That way, you can break your revisions down into more manageable parts.
- If you disagree with a comment made by a reviewer, try to provide an evidence-based explanation when you resubmit your paper.

- If you’re resubmitting your paper to the same journal, include a point-by-point response paper that talks about how you addressed all of the reviewers’ comments in your revision. [22] X Research source
- If you’re not sure which journal to submit to next, you might be able to ask the journal editor which publications they recommend.

Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- If reviewers suspect that your submitted manuscript plagiarizes another work, they may refer to a Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE) flowchart to see how to move forward. [23] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- ↑ https://www.wiley.com/en-us/network/publishing/research-publishing/choosing-a-journal/6-steps-to-choosing-the-right-journal-for-your-research-infographic
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13187-020-01751-z
- ↑ https://libguides.unomaha.edu/c.php?g=100510&p=651627
- ↑ https://www.canberra.edu.au/library/start-your-research/research_help/publishing-research
- ↑ https://writingcenter.fas.harvard.edu/conclusions
- ↑ https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/writing-an-abstract-for-your-research-paper/
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/gp/authors-editors/book-authors-editors/your-publication-journey/manuscript-preparation
- ↑ https://apus.libanswers.com/writing/faq/2391
- ↑ https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/library/keyword/search-strategy
- ↑ https://ifis.libguides.com/journal-publishing-guide/submitting-your-paper
- ↑ https://www.springer.com/kr/authors-editors/authorandreviewertutorials/submitting-to-a-journal-and-peer-review/cover-letters/10285574
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/sep02/publish.aspx
- ↑ Matthew Snipp, PhD. Research Fellow, U.S. Bureau of the Census. Expert Interview. 26 March 2020.
About This Article

To publish a research paper, ask a colleague or professor to review your paper and give you feedback. Once you've revised your work, familiarize yourself with different academic journals so that you can choose the publication that best suits your paper. Make sure to look at the "Author's Guide" so you can format your paper according to the guidelines for that publication. Then, submit your paper and don't get discouraged if it is not accepted right away. You may need to revise your paper and try again. To learn about the different responses you might get from journals, see our reviewer's explanation below. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
RAMDEV GOHIL
Oct 16, 2017
Did this article help you?

David Okandeji
Oct 23, 2019
Revati Joshi
Feb 13, 2017
Shahzad Khan
Jul 1, 2017
Apr 7, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Why are most papers not dated?
Many of the research papers that I have read are not dated in terms of publication date. By dating I mean including at least the publication year. The papers I refer to are mostly free PDFs from the internet on various topics, usually affiliated with some academic institution (mostly universities).
One can then only guess the publication date from the dates of newest references. Does this weird trend have some reasoning? If I wrote a paper or even its draft and made it public I would clearly date it.
It seems I have missed the option of checking the PDF document properties which show a creation date. But this still does not answer the question of not including the date within the body of the document itself.
- publications
- 5 What is your field? In my areas of interest (CFD, finite elements, etc), submission or acceptance dates and publication dates are very common. Also, there's almost always a copyright statement on the article that includes the year. – Bill Barth Commented May 5, 2015 at 12:21
- 5 @Kozuch Is is possible that you are asking why the PDF of the paper doesn't have the date printed on it? On the publishers' websites, you typically find these dates. The PDFs on authors' homepages are typically self-compiled using the standard style used for reviewing, which simply does not feature the dates. Authors are often required to use a self-compiled version. Also, only few people see this is as a problem, as for a citation, only the year is mandatory to be included, and the authors' homepages, which link to the PDFs, have the years on them in most cases. – DCTLib Commented May 5, 2015 at 12:25
- 9 Yeah, if you're not looking at the officially published version on the journal or conference page, then you're not looking at a "published" article but a preprint or a draft. You need to get to the original source which will be the publisher's page. – Bill Barth Commented May 5, 2015 at 12:27
- 3 I am really not sure what you are talking about. Many journal styles have a submission / acceptance / publication date on the PDF. Even for the ones that don't (typically workshops and conferences), finding the year of the conference only is a trivial Google search. And if you can't find anything about the paper either in IEEEXplorer, ACM, DBLP, etc. - well, chances are it's not reliable anyway. – xLeitix Commented May 5, 2015 at 12:35
- 4 Are you talking about the random "free tutorial" someone writes up (which rarely has a publication date), or are you actually reading research/peer-review-quality papers? – apnorton Commented May 5, 2015 at 15:11
3 Answers 3
"The papers I refer to are mostly free PDFs from the internet on various topics" – then it's most likely one or both of:
- It is not a peer-reviewed paper published by a reputable journal. Be careful what you read, there are plenty of quack theories out there
- You are viewing a preprint, and by finding the article on the journal's website you will find the date. Also, the final version of the article will probably be better formatted, and may be better written and have mistakes corrected (this depends upon the stage of publication at which the preprint was circulated).
Many preprints are circulated prior to publication, so you may not find a better version yet. It's still really poor form for an author not to date a preprint. If a preprint is a few years old and has not yet been published, you have to wonder why .
I can not recall ever seeing a journal that does not put the journal name, date, and issue number on at least the first page. It would be very poor practice not to do this, because taken on its own it is impossible (without further research) to tell where the article came from. It's common even to date every page with the journal name, date, and issue number.
I suspect that if you're seeing this trend in most of the "papers" you read, that you really aren't reading research articles written by legitimate researchers. Ask your advisor or lecturer for the names of the most relevant journals in the field, and start from there.
- 4 In my area (pure maths), many preprints aren’t dated, and even for published papers, the preprint is often the easiest version to find. So while most of the papers I read have a date in principle, the specific pdf I read them from is very often undated. – PLL Commented May 5, 2015 at 12:56
- 5 @PLL, but when you cite them, you go find the publication date, right? – Bill Barth Commented May 5, 2015 at 13:10
- 3 @BillBarth: of course, yes — one cites the journal version, not the preprint. – PLL Commented May 5, 2015 at 14:34
- 1 Most PDFs you find are pre-prints, and the standard workflow of many journals and conferences does not include dates in preprints. – jakebeal Commented May 5, 2015 at 19:51
- 7 @Moriarty I highly disagree: when I search online and Google Scholar pops up with a PDF, it's probably a pre-print, not the paywalled final version. That's the one I'm going to read, even when I have journal access, because it's one click rather than a bunch of fiddling with library portals. And those preprints are almost always missing the final date. The date is then easy to find online, it's just not in the PDF. – jakebeal Commented May 6, 2015 at 11:55
Most (CS) papers that you find on the websites of the publishers have the bibliographical information in the PDF, typically on the first page of the paper. This typically includes the year. These papers are however also typically behind paywalls, meaning that you won't get access to these unless you (a) buy a copy of the article, or (b) have access through your institutional subscription.
Many research paper PDFs that you find freely on the internet are self-archived versions of the papers . These are PDFs provided by the authors on their personal or institutional web pages and not prepared by the publisher. While these do not constitute the official versions of the papers, authors normally do not modify the content of the PDF so that the official and unofficial versions of the papers get out of sync. Now it happens to be that most paper style files provided to the authors for writing their papers with for a specific venue do not feature a field for the bibliographical information. Rather, the information is later added by the publisher. Thus, the information is missing on the PDF made by the authors themselves.
It should also be noted that only few people see this as a problem. The bibliographical information is contained on the authors' webpages from which you often download the papers. Also, you mainly need the bibliographical information for citing the paper, and for that, you can pretty much always download the whole bibliographical information entry for a paper from the publisher's website. Just type the paper title into your favorite search machine and click onto the respective result. For computer science, most papers are in DBLP anyway, which also gives you a complete bibliography entry at the expense of a mouse click.
- +1 for bib data from the publisher even if you get the paper direct from the researcher. You can also quickly compare the abstract in case your search engine took you to a similarly-named paper from the same authors (e.g. you forgot to put quotes round the title). – Chris H Commented May 5, 2015 at 14:19
I agree that it is extremely frustrating to not have a date on a technical paper. It is often impossible to tell the currency and hence whether any conclusions represent the latest thinking. The only reason I can think of is that most technical papers are published by technical associations, who then generate revenue by selling access to papers. By not including a date, researchers are unable to identify currency and are thereby forced to purchase more papers than they need, hence generating more revenue for the publishing house or society.
- 1 unable to identify currency and are thereby forced to purchase more papers than they need --- I'm confused. Don't most published papers include a received date, a date that (in my experience) is nearly always provided to those (such as myself) who do not have access to papers behind a paywall? "randomly chosen" example 1 (gives received, accepted, published dates at bottom of the web page) and "randomly chosen" example 2 (also gives received, accepted, published dates) – Dave L Renfro Commented Apr 22, 2021 at 9:34
- @DaveLRenfro You’re right. However, the paper itself, e.g. the PDF, does not indicate the date it was published. It is part of the metadata that you see in a citation. – Asim Jalis Commented Nov 8, 2023 at 23:16
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged publications ..
- Featured on Meta
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Announcing a change to the data-dump process
Hot Network Questions
- A simplified Blackjack C++ OOP console game
- How can you trust a forensic scientist to have maintained the chain of custody?
- Why cant we save the heat rejected in a heat engine?
- "Authorized ESTA After Incorrectly Answering Criminal Offense Question: What Should I Do?"
- Comparing force-carrying particles
- Melee Opportunist--making opportunity attacks have some bite for melee characters
- Using ExplSyntax with tasks to create a custom \item command - Making \item backwards compatible
- Is there a theorem that says we don't limit our notion of conservative extension by only focussing on set models?
- R Squared Causal Inference
- Seth and Cain take turns picking numbers from 1 to 50. Who wins?
- "apt install emacs" linuxmint22 requires a mail system
- Enable all snapping types in QGIS using Python
- Is it possible to create a board position where White must make the move that leads to stalemating Black to avoid Black stalemating White?
- Can the subjunctive mood be combined with ‘Be to+infinitive’?
- Canceling factors in a ratio of factorials
- Distribute realized geometry based on field values
- What does it mean when vanishing points of a box is not on the horizon level?
- In theory, could an object like 'Oumuamua have been captured by a three-body interaction with the sun and planets?
- Is the error in translation of Genesis 19:5 deliberate?
- How to ensure a BSD licensed open source project is not closed in the future?
- Short story involving a dystopian future, suspended animation, and a dumbing of society solution
- How can I draw water level in a cylinder like this?
- Hotspot vs home internet
- What is it called when perception of a thing is replaced by an pre-existing abstraction of that thing?
- Privacy Policy

Home » How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step Guide
How to Publish a Research Paper – Step by Step Guide
Table of Contents

Publishing a research paper is an important step for researchers to disseminate their findings to a wider audience and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their field. Whether you are a graduate student, a postdoctoral fellow, or an established researcher, publishing a paper requires careful planning, rigorous research, and clear writing. In this process, you will need to identify a research question , conduct a thorough literature review , design a methodology, analyze data, and draw conclusions. Additionally, you will need to consider the appropriate journals or conferences to submit your work to and adhere to their guidelines for formatting and submission. In this article, we will discuss some ways to publish your Research Paper.
How to Publish a Research Paper
To Publish a Research Paper follow the guide below:
- Conduct original research : Conduct thorough research on a specific topic or problem. Collect data, analyze it, and draw conclusions based on your findings.
- Write the paper : Write a detailed paper describing your research. It should include an abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Choose a suitable journal or conference : Look for a journal or conference that specializes in your research area. You can check their submission guidelines to ensure your paper meets their requirements.
- Prepare your submission: Follow the guidelines and prepare your submission, including the paper, abstract, cover letter, and any other required documents.
- Submit the paper: Submit your paper online through the journal or conference website. Make sure you meet the submission deadline.
- Peer-review process : Your paper will be reviewed by experts in the field who will provide feedback on the quality of your research, methodology, and conclusions.
- Revisions : Based on the feedback you receive, revise your paper and resubmit it.
- Acceptance : Once your paper is accepted, you will receive a notification from the journal or conference. You may need to make final revisions before the paper is published.
- Publication : Your paper will be published online or in print. You can also promote your work through social media or other channels to increase its visibility.
How to Choose Journal for Research Paper Publication
Here are some steps to follow to help you select an appropriate journal:
- Identify your research topic and audience : Your research topic and intended audience should guide your choice of journal. Identify the key journals in your field of research and read the scope and aim of the journal to determine if your paper is a good fit.
- Analyze the journal’s impact and reputation : Check the impact factor and ranking of the journal, as well as its acceptance rate and citation frequency. A high-impact journal can give your paper more visibility and credibility.
- Consider the journal’s publication policies : Look for the journal’s publication policies such as the word count limit, formatting requirements, open access options, and submission fees. Make sure that you can comply with the requirements and that the journal is in line with your publication goals.
- Look at recent publications : Review recent issues of the journal to evaluate whether your paper would fit in with the journal’s current content and style.
- Seek advice from colleagues and mentors: Ask for recommendations and suggestions from your colleagues and mentors in your field, especially those who have experience publishing in the same or similar journals.
- Be prepared to make changes : Be prepared to revise your paper according to the requirements and guidelines of the chosen journal. It is also important to be open to feedback from the editor and reviewers.
List of Journals for Research Paper Publications
There are thousands of academic journals covering various fields of research. Here are some of the most popular ones, categorized by field:
General/Multidisciplinary
- Nature: https://www.nature.com/
- Science: https://www.sciencemag.org/
- PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/
- Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS): https://www.pnas.org/
- The Lancet: https://www.thelancet.com/
- JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association): https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama
Social Sciences/Humanities
- Journal of Personality and Social Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/psp
- Journal of Consumer Research: https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/journals/jcr
- Journal of Educational Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/edu
- Journal of Applied Psychology: https://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/apl
- Journal of Communication: https://academic.oup.com/joc
- American Journal of Political Science: https://ajps.org/
- Journal of International Business Studies: https://www.jibs.net/
- Journal of Marketing Research: https://www.ama.org/journal-of-marketing-research/
Natural Sciences
- Journal of Biological Chemistry: https://www.jbc.org/
- Cell: https://www.cell.com/
- Science Advances: https://advances.sciencemag.org/
- Chemical Reviews: https://pubs.acs.org/journal/chreay
- Angewandte Chemie: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/15213765
- Physical Review Letters: https://journals.aps.org/prl/
- Journal of Geophysical Research: https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/2156531X
- Journal of High Energy Physics: https://link.springer.com/journal/13130
Engineering/Technology
- IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=5962385
- IEEE Transactions on Power Systems: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=59
- IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=42
- IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/RecentIssue.jsp?punumber=87
- Journal of Engineering Mechanics: https://ascelibrary.org/journal/jenmdt
- Journal of Materials Science: https://www.springer.com/journal/10853
- Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/browse/jcej
- Journal of Mechanical Design: https://asmedigitalcollection.asme.org/mechanicaldesign
Medical/Health Sciences
- New England Journal of Medicine: https://www.nejm.org/
- The BMJ (formerly British Medical Journal): https://www.bmj.com/
- Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA): https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama
- Annals of Internal Medicine: https://www.acpjournals.org/journal/aim
- American Journal of Epidemiology: https://academic.oup.com/aje
- Journal of Clinical Oncology: https://ascopubs.org/journal/jco
- Journal of Infectious Diseases: https://academic.oup.com/jid
List of Conferences for Research Paper Publications
There are many conferences that accept research papers for publication. The specific conferences you should consider will depend on your field of research. Here are some suggestions for conferences in a few different fields:
Computer Science and Information Technology:
- IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM): https://www.ieee-infocom.org/
- ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Data Communication: https://conferences.sigcomm.org/sigcomm/
- IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP): https://www.ieee-security.org/TC/SP/
- ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS): https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/
- ACM Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (CHI): https://chi2022.acm.org/
Engineering:
- IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA): https://www.ieee-icra.org/
- International Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (ICMAE): http://www.icmae.org/
- International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering (ICCEE): http://www.iccee.org/
- International Conference on Materials Science and Engineering (ICMSE): http://www.icmse.org/
- International Conference on Energy and Power Engineering (ICEPE): http://www.icepe.org/
Natural Sciences:
- American Chemical Society National Meeting & Exposition: https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/meetings/national-meeting.html
- American Physical Society March Meeting: https://www.aps.org/meetings/march/
- International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology (ICEST): http://www.icest.org/
- International Conference on Natural Science and Environment (ICNSE): http://www.icnse.org/
- International Conference on Life Science and Biological Engineering (LSBE): http://www.lsbe.org/
Social Sciences:
- Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association (ASA): https://www.asanet.org/annual-meeting-2022
- International Conference on Social Science and Humanities (ICSSH): http://www.icssh.org/
- International Conference on Psychology and Behavioral Sciences (ICPBS): http://www.icpbs.org/
- International Conference on Education and Social Science (ICESS): http://www.icess.org/
- International Conference on Management and Information Science (ICMIS): http://www.icmis.org/
How to Publish a Research Paper in Journal
Publishing a research paper in a journal is a crucial step in disseminating scientific knowledge and contributing to the field. Here are the general steps to follow:
- Choose a research topic : Select a topic of your interest and identify a research question or problem that you want to investigate. Conduct a literature review to identify the gaps in the existing knowledge that your research will address.
- Conduct research : Develop a research plan and methodology to collect data and conduct experiments. Collect and analyze data to draw conclusions that address the research question.
- Write a paper: Organize your findings into a well-structured paper with clear and concise language. Your paper should include an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Use academic language and provide references for your sources.
- Choose a journal: Choose a journal that is relevant to your research topic and audience. Consider factors such as impact factor, acceptance rate, and the reputation of the journal.
- Follow journal guidelines : Review the submission guidelines and formatting requirements of the journal. Follow the guidelines carefully to ensure that your paper meets the journal’s requirements.
- Submit your paper : Submit your paper to the journal through the online submission system or by email. Include a cover letter that briefly explains the significance of your research and why it is suitable for the journal.
- Wait for reviews: Your paper will be reviewed by experts in the field. Be prepared to address their comments and make revisions to your paper.
- Revise and resubmit: Make revisions to your paper based on the reviewers’ comments and resubmit it to the journal. If your paper is accepted, congratulations! If not, consider revising and submitting it to another journal.
- Address reviewer comments : Reviewers may provide comments and suggestions for revisions to your paper. Address these comments carefully and thoughtfully to improve the quality of your paper.
- Submit the final version: Once your revisions are complete, submit the final version of your paper to the journal. Be sure to follow any additional formatting guidelines and requirements provided by the journal.
- Publication : If your paper is accepted, it will be published in the journal. Some journals provide online publication while others may publish a print version. Be sure to cite your published paper in future research and communicate your findings to the scientific community.
How to Publish a Research Paper for Students
Here are some steps you can follow to publish a research paper as an Under Graduate or a High School Student:
- Select a topic: Choose a topic that is relevant and interesting to you, and that you have a good understanding of.
- Conduct research : Gather information and data on your chosen topic through research, experiments, surveys, or other means.
- Write the paper : Start with an outline, then write the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion sections of the paper. Be sure to follow any guidelines provided by your instructor or the journal you plan to submit to.
- Edit and revise: Review your paper for errors in spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Ask a peer or mentor to review your paper and provide feedback for improvement.
- Choose a journal : Look for journals that publish papers in your field of study and that are appropriate for your level of research. Some popular journals for students include PLOS ONE, Nature, and Science.
- Submit the paper: Follow the submission guidelines for the journal you choose, which typically include a cover letter, abstract, and formatting requirements. Be prepared to wait several weeks to months for a response.
- Address feedback : If your paper is accepted with revisions, address the feedback from the reviewers and resubmit your paper. If your paper is rejected, review the feedback and consider revising and resubmitting to a different journal.
How to Publish a Research Paper for Free
Publishing a research paper for free can be challenging, but it is possible. Here are some steps you can take to publish your research paper for free:
- Choose a suitable open-access journal: Look for open-access journals that are relevant to your research area. Open-access journals allow readers to access your paper without charge, so your work will be more widely available.
- Check the journal’s reputation : Before submitting your paper, ensure that the journal is reputable by checking its impact factor, publication history, and editorial board.
- Follow the submission guidelines : Every journal has specific guidelines for submitting papers. Make sure to follow these guidelines carefully to increase the chances of acceptance.
- Submit your paper : Once you have completed your research paper, submit it to the journal following their submission guidelines.
- Wait for the review process: Your paper will undergo a peer-review process, where experts in your field will evaluate your work. Be patient during this process, as it can take several weeks or even months.
- Revise your paper : If your paper is rejected, don’t be discouraged. Revise your paper based on the feedback you receive from the reviewers and submit it to another open-access journal.
- Promote your research: Once your paper is published, promote it on social media and other online platforms. This will increase the visibility of your work and help it reach a wider audience.
Journals and Conferences for Free Research Paper publications
Here are the websites of the open-access journals and conferences mentioned:
Open-Access Journals:
- PLOS ONE – https://journals.plos.org/plosone/
- BMC Research Notes – https://bmcresnotes.biomedcentral.com/
- Frontiers in… – https://www.frontiersin.org/
- Journal of Open Research Software – https://openresearchsoftware.metajnl.com/
- PeerJ – https://peerj.com/
Conferences:
- IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) – https://globecom2022.ieee-globecom.org/
- IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM) – https://infocom2022.ieee-infocom.org/
- IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM) – https://www.ieee-icdm.org/
- ACM SIGCOMM Conference on Data Communication (SIGCOMM) – https://conferences.sigcomm.org/sigcomm/
- ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS) – https://www.sigsac.org/ccs/CCS2022/
Importance of Research Paper Publication
Research paper publication is important for several reasons, both for individual researchers and for the scientific community as a whole. Here are some reasons why:
- Advancing scientific knowledge : Research papers provide a platform for researchers to present their findings and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. These papers often contain novel ideas, experimental data, and analyses that can help to advance scientific understanding.
- Building a research career : Publishing research papers is an essential component of building a successful research career. Researchers are often evaluated based on the number and quality of their publications, and having a strong publication record can increase one’s chances of securing funding, tenure, or a promotion.
- Peer review and quality control: Publication in a peer-reviewed journal means that the research has been scrutinized by other experts in the field. This peer review process helps to ensure the quality and validity of the research findings.
- Recognition and visibility : Publishing a research paper can bring recognition and visibility to the researchers and their work. It can lead to invitations to speak at conferences, collaborations with other researchers, and media coverage.
- Impact on society : Research papers can have a significant impact on society by informing policy decisions, guiding clinical practice, and advancing technological innovation.
Advantages of Research Paper Publication
There are several advantages to publishing a research paper, including:
- Recognition: Publishing a research paper allows researchers to gain recognition for their work, both within their field and in the academic community as a whole. This can lead to new collaborations, invitations to conferences, and other opportunities to share their research with a wider audience.
- Career advancement : A strong publication record can be an important factor in career advancement, particularly in academia. Publishing research papers can help researchers secure funding, grants, and promotions.
- Dissemination of knowledge : Research papers are an important way to share new findings and ideas with the broader scientific community. By publishing their research, scientists can contribute to the collective body of knowledge in their field and help advance scientific understanding.
- Feedback and peer review : Publishing a research paper allows other experts in the field to provide feedback on the research, which can help improve the quality of the work and identify potential flaws or limitations. Peer review also helps ensure that research is accurate and reliable.
- Citation and impact : Published research papers can be cited by other researchers, which can help increase the impact and visibility of the research. High citation rates can also help establish a researcher’s reputation and credibility within their field.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Tables in Research Paper – Types, Creating Guide...

Research Paper Title Page – Example and Making...

Research Objectives – Types, Examples and...

Future Research – Thesis Guide

Theoretical Framework – Types, Examples and...

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The next step would be to define international standards that allow us to respond easily, quickly, and accurately whenever a paper's publication date is sought. ————————————-José Luis Ortega is Tenure Scientist in the Institute for Advanced Social Studies (IESA) of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC). He is a ...
The current norm is to use the publication date ("print date") which, in your case, would be 2022 (more precisely, Sept 2022, the date the issue came out). This is how the journal itself formats the citation (see bottom of this page): Borsos, B., Kovács, A. & Tihanyi, N. Tight upper and lower bounds for the reciprocal sum of Proth primes.
Depending on your browser, the menu option may read "View Page Info" or similar. Variation: The keyboard shortcut to open the source code directly is Control+U on Windows and Command+U on Mac. 2. Press Ctrl + F (Windows) or ⌘ Command + F (Mac). This will open the "Find" function on your browser.
Follow the simple steps. Right click on the website and click on 'View Source code'. In the source code page, press Cmd + F for Mac or CTRL + F for Windows to bring up the 'Find' box. Search for keywords like publish year - '2019', '2018', '2017' etc alternatively, you can also search for 'published_time'. Analyze the ...
The publication process explained. The path to publication can be unsettling when you're unsure what's happening with your paper. Learn about staple journal workflows to see the detailed steps required for ensuring a rigorous and ethical publication. Your team has prepared the paper, written a cover letter and completed the submission form.
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research. ... million publication pages and stay up to date with what ...
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Communicating research findings is an essential step in the research process. Often, peer-reviewed journals are the forum for such communication, yet many researchers are never taught how to write a publishable scientific paper. In this article, we explain the basic structure of a scientific paper and describe the information that should be included in each section. We also identify common ...
The DOI is usually clearly visible when you open a journal article on an academic database. It is often listed near the publication date, and includes "doi.org" or "DOI:". If the database has a "cite this article" button, this should also produce a citation with the DOI included. If you can't find the DOI, you can search on ...
For example, Nature papers should be cited in the form; Author (s) Nature advance online publication, day month year (DOI 10.1038/natureXXX). After print publication, you should give the DOI as ...
4. Track your paper. 5. Share and promote. 1. Find a journal. Find out the journals that could be best suited for publishing your research. For a comprehensive list of Elsevier journals check our Journal Catalog. You can also match your manuscript using the JournalFinder tool, then learn more about each journal.
Beyond this, the title should indicate the research methodology and topic of the paper. The abstract should provide a summary of the objective, methods, results, and significance of the research. Most researchers are likely to find published papers through an electronic search (either via subject databases, or search engines such as Google).
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
As part of Open Access Week 2017, the Office of Scholarly Communication is publishing a series of blog posts on open access and open research. In this post Maria Angelaki describes how challenging it can be to interpret publication dates featured on some publishers' websites. More than three weeks a year. That's how much time … Continue reading It's hard getting a date (of publication) →
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
The Date of Publication for Journals and Standards on IEEE Xplore represents the very first instance of public dissemination of content. IEEE Xplore had previously made distinctions between physical print date, date of current version, online publication date, etc. This has been simplified with one official date of record.
Date Definition. APA defines the 'date' element as the publication date (American Psychological Association, 2019, p. 289). There are 5 forms to format the date: The reference category of the work you are trying to cite will determine how the date is formatted. The most common way to cite the date of a work is with solely the year.
You can find the placement of the journal name, page number, publication date, and volume and issue number located on the top or bottom of the article's page. The publication date may be a single year (2013), a distinct month (October 2010), specific publication cycle (Fall 2007), or an exact date (June 28, 2005).
Step 1: Choosing a journal. Choosing which journal to publish your research paper in is one of the most significant decisions you have to make as a researcher. Where you decide to submit your work can make a big difference to the reach and impact your research has. It's important to take your time to consider your options carefully and ...
8. This journal (like many if not most journals) publishes articles online before formally assigning them to issues. Cite the issue date. Prior to most journals moving completely online, journals would formally accept articles and then take weeks to months before publishing articles.
3. Submit your article according to the journal's submission guidelines. Go to the "author's guide" (or similar) on the journal's website to review its submission requirements. Once you are satisfied that your paper meets all of the guidelines, submit the paper through the appropriate channels.
Many of the research papers that I have read are not dated in terms of publication date. By dating I mean including at least the publication year. The papers I refer to are mostly free PDFs from the internet on various topics, usually affiliated with some academic institution (mostly universities).
To Publish a Research Paper follow the guide below: Conduct original research: Conduct thorough research on a specific topic or problem. Collect data, analyze it, and draw conclusions based on your findings. Write the paper: Write a detailed paper describing your research.