- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
- 5 minute read
- 114.4K views
Table of Contents
The importance of a well-written research proposal cannot be underestimated. Your research really is only as good as your proposal. A poorly written, or poorly conceived research proposal will doom even an otherwise worthy project. On the other hand, a well-written, high-quality proposal will increase your chances for success.
In this article, we’ll outline the basics of writing an effective scientific research proposal, including the differences between research proposals, grants and cover letters. We’ll also touch on common mistakes made when submitting research proposals, as well as a simple example or template that you can follow.
What is a scientific research proposal?
The main purpose of a scientific research proposal is to convince your audience that your project is worthwhile, and that you have the expertise and wherewithal to complete it. The elements of an effective research proposal mirror those of the research process itself, which we’ll outline below. Essentially, the research proposal should include enough information for the reader to determine if your proposed study is worth pursuing.
It is not an uncommon misunderstanding to think that a research proposal and a cover letter are the same things. However, they are different. The main difference between a research proposal vs cover letter content is distinct. Whereas the research proposal summarizes the proposal for future research, the cover letter connects you to the research, and how you are the right person to complete the proposed research.
There is also sometimes confusion around a research proposal vs grant application. Whereas a research proposal is a statement of intent, related to answering a research question, a grant application is a specific request for funding to complete the research proposed. Of course, there are elements of overlap between the two documents; it’s the purpose of the document that defines one or the other.
Scientific Research Proposal Format
Although there is no one way to write a scientific research proposal, there are specific guidelines. A lot depends on which journal you’re submitting your research proposal to, so you may need to follow their scientific research proposal template.
In general, however, there are fairly universal sections to every scientific research proposal. These include:
- Title: Make sure the title of your proposal is descriptive and concise. Make it catch and informative at the same time, avoiding dry phrases like, “An investigation…” Your title should pique the interest of the reader.
- Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc.
- Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most important. Here you want to introduce the research problem in a creative way, and demonstrate your understanding of the need for the research. You want the reader to think that your proposed research is current, important and relevant.
- Background: Include a brief history of the topic and link it to a contemporary context to show its relevance for today. Identify key researchers and institutions also looking at the problem
- Literature Review: This is the section that may take the longest amount of time to assemble. Here you want to synthesize prior research, and place your proposed research into the larger picture of what’s been studied in the past. You want to show your reader that your work is original, and adds to the current knowledge.
- Research Design and Methodology: This section should be very clearly and logically written and organized. You are letting your reader know that you know what you are going to do, and how. The reader should feel confident that you have the skills and knowledge needed to get the project done.
- Preliminary Implications: Here you’ll be outlining how you anticipate your research will extend current knowledge in your field. You might also want to discuss how your findings will impact future research needs.
- Conclusion: This section reinforces the significance and importance of your proposed research, and summarizes the entire proposal.
- References/Citations: Of course, you need to include a full and accurate list of any and all sources you used to write your research proposal.
Common Mistakes in Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
Remember, the best research proposal can be rejected if it’s not well written or is ill-conceived. The most common mistakes made include:
- Not providing the proper context for your research question or the problem
- Failing to reference landmark/key studies
- Losing focus of the research question or problem
- Not accurately presenting contributions by other researchers and institutions
- Incompletely developing a persuasive argument for the research that is being proposed
- Misplaced attention on minor points and/or not enough detail on major issues
- Sloppy, low-quality writing without effective logic and flow
- Incorrect or lapses in references and citations, and/or references not in proper format
- The proposal is too long – or too short
Scientific Research Proposal Example
There are countless examples that you can find for successful research proposals. In addition, you can also find examples of unsuccessful research proposals. Search for successful research proposals in your field, and even for your target journal, to get a good idea on what specifically your audience may be looking for.
While there’s no one example that will show you everything you need to know, looking at a few will give you a good idea of what you need to include in your own research proposal. Talk, also, to colleagues in your field, especially if you are a student or a new researcher. We can often learn from the mistakes of others. The more prepared and knowledgeable you are prior to writing your research proposal, the more likely you are to succeed.
One of the top reasons scientific research proposals are rejected is due to poor logic and flow. Check out our Language Editing Services to ensure a great proposal , that’s clear and concise, and properly referenced. Check our video for more information, and get started today.

Research Fraud: Falsification and Fabrication in Research Data

Research Team Structure
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 8, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is your plagiarism score.

Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia
Research Proposal Examples for Every Science Field
Looking for research funding can be a daunting task, especially when you are starting out. A great way to improve grant-writing skills is to get inspired by winning research proposal examples.
To assist you in writing a competitive proposal, I have curated a collection of real-life research proposal examples from various scientific disciplines. These examples will allow you to gain inspiration about the way research proposals are structured and written.
Structure of a Research Proposal
A research proposal serves as a road-map for a project, outlining the objectives, methodology, resources, and expected outcomes. The main goal of writing a research proposal is to convince funding agency of the value and feasibility of a research project. But a proposal also helps scientists themselves to clarify their planned approach.
While the exact structure may vary depending on the science field and institutional guidelines, a research proposal typically includes the following sections: Problem, Objectives, Methodology, Resources, Participants, Results&Impact, Dissemination, Timeline, and Budget. I will use this structure for the example research proposals in this article.

Here is a brief description of what each of the nine proposal sections should hold.
A concise and informative title that captures the essence of the research proposal. Sometimes an abstract is required that briefly summarizes the proposed project.

Clearly define the research problem or gap in knowledge that the study aims to address. Present relevant background information and cite existing literature to support the need for further investigation.

State the specific objectives and research questions that the study seeks to answer. These objectives should be clear, measurable, and aligned with the problem statement.

Methodology
Describe the research design, methodology, and techniques that will be employed to collect and analyze data. Justify your chosen approach and discuss its strengths and limitations.

Outline the resources required for the successful execution of the research project, such as equipment, facilities, software, and access to specific datasets or archives.

Participants
Describe the research team’s qualification for implementing the research methodology and their complementary value

Results and Impact
Describe the expected results, outcomes, and potential impact of the research. Discuss how the findings will contribute to the field and address the research gap identified earlier.

Dissemination
Explain how the research results will be disseminated to the academic community and wider audiences. This may include publications, conference presentations, workshops, data sharing or collaborations with industry partners.

Develop a realistic timeline that outlines the major milestones and activities of the research project. Consider potential challenges or delays and incorporate contingency plans.
Provide a detailed budget estimate, including anticipated expenses for research materials, equipment, participant compensation, travel, and other relevant costs. Justify the budget based on the project’s scope and requirements.
Consider that the above-mentioned proposal headings can be called differently depending on the funder’s requirements. However, you can be sure in one proposal’s section or another each of the mentioned sections will be included. Whenever provided, always use the proposal structure as required by the funding agency.
Research Proposal template download
This research proposal template includes the nine headings that we just discussed. For each heading, a key sentence skeleton is provided to help you to kick-start the proposal writing process.

Real-Life Research Proposal Examples
Proposals can vary from field to field so I will provide you with research proposal examples proposals in four main branches of science: social sciences, life sciences, physical sciences, and engineering and technology. For each science field, you will be able to download real-life winning research proposal examples.
To illustrate the principle of writing a scientific proposal while adhering to the nine sections I outlined earlier, for each discipline I will also provide you with a sample hypothetical research proposal. These examples are formulated using the key sentence structure that is included in the download template .
In case the research proposal examples I provide do not hold exactly what you are looking for, use the Open Grants database. It holds approved research proposals from various funding agencies in many countries. When looking for research proposals examples in the database, use the filer to search for specific keywords and organize the results to view proposals that have been funded.
Research Proposals Examples in Social Sciences
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded projects in social sciences.
| (Cultural Anthropology) | |
Here is an outline of a hypothetical Social Sciences research proposal that is structured using the nine proposal sections we discussed earlier. This proposal example is produced using the key sentence skeleton that you will access in the proposal template .
The Influence of Social Media on Political Participation among Young Adults

Social media platforms have become prominent spaces for political discussions and information sharing. However, the impact of social media on political participation among young adults remains a topic of debate.

With the project, we aim to establish the relationship between social media usage and political engagement among young adults. To achieve this aim, we have three specific objectives:
- Examine the association between social media usage patterns and various forms of political participation, such as voting, attending political rallies, and engaging in political discussions.
- Investigate the role of social media in shaping political attitudes, opinions, and behaviors among young adults.
- Provide evidence-based recommendations for utilizing social media platforms to enhance youth political participation.

During the project, a mixed methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews will be used to determine the impact of social media use on youth political engagement. In particular, surveys will collect data on social media usage, political participation, and attitudes. Interviews will provide in-depth insights into participants’ experiences and perceptions.

The project will use survey software, transcription tools, and statistical analysis software to statistically evaluate the gathered results. The project will also use project funding for participant compensation.

Principal investigator, Jane Goodrich will lead a multidisciplinary research team comprising social scientists, political scientists, and communication experts with expertise in political science and social media research.

The project will contribute to a better understanding of the influence of social media on political participation among young adults, including:
- inform about the association between social media usage and political participation among youth.
- determine the relationship between social media content and political preferences among youth.
- provide guidelines for enhancing youth engagement in democratic processes through social media use.

We will disseminate the research results within policymakers and NGOs through academic publications in peer-reviewed journals, presentations at relevant conferences, and policy briefs.

The project will start will be completed within two years and for the first two objectives a periodic report will be submitted in months 12 and 18.
The total eligible project costs are 58,800 USD, where 15% covers participant recruitment and compensation, 5% covers survey software licenses, 55% are dedicated for salaries, and 25% are intended for dissemination activities.
Research Proposal Examples in Life Sciences
Here are real-life research project examples in life sciences.
| | |
| | |
| (postdoctoral fellowship) | |
| (National Institutes of Environmental Health Sciences) |
Here is a hypothetical research proposal example in Life Sciences. Just like the previous example, it consists of the nine discussed proposal sections and it is structured using the key sentence skeleton that you will access in the proposal template .
Investigating the Role of Gut Microbiota in Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome (GUT-MET)
Obesity and metabolic syndrome pose significant health challenges worldwide, leading to numerous chronic diseases and increasing healthcare costs. Despite extensive research, the precise mechanisms underlying these conditions remain incompletely understood. A critical knowledge gap exists regarding the role of gut microbiota in the development and progression of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
With the GUT-MET project, we aim to unravel the complex interactions between gut microbiota and obesity/metabolic syndrome. To achieve this aim, we have the following specific objectives:
- Investigate the composition and diversity of gut microbiota in individuals with obesity and metabolic syndrome.
- Determine the functional role of specific gut microbial species and their metabolites in the pathogenesis of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
During the project, we will employ the following key methodologies:
- Perform comprehensive metagenomic and metabolomic analyses to characterize the gut microbiota and associated metabolic pathways.
- Conduct animal studies to investigate the causal relationship between gut microbiota alterations and the development of obesity and metabolic syndrome.
The project will benefit from state-of-the-art laboratory facilities, including advanced sequencing and analytical equipment, as well as access to a well-established cohort of participants with obesity and metabolic syndrome.

Dr. Emma Johnson, a renowned expert in gut microbiota research and Professor of Molecular Biology at the University of PeerRecognized, will lead the project. Dr. Johnson has published extensively in high-impact journals and has received multiple research grants focused on the gut microbiota and metabolic health.
The project will deliver crucial insights into the role of gut microbiota in obesity and metabolic syndrome. Specifically, it will:
- Identify microbial signatures associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome for potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
- Uncover key microbial metabolites and pathways implicated in disease development, enabling the development of targeted interventions.
We will actively disseminate the project results within the scientific community, healthcare professionals, and relevant stakeholders through publications in peer-reviewed journals, presentations at international conferences, and engagement with patient advocacy groups.
The project will be executed over a period of 36 months. Key milestones include data collection and analysis, animal studies, manuscript preparation, and knowledge transfer activities.
The total eligible project costs are $1,500,000, with the budget allocated for 55% personnel, 25% laboratory supplies, 5% data analysis, and 15% knowledge dissemination activities as specified in the research call guidelines.
Research Proposals Examples in Natural Sciences
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded projects in natural sciences.
| (FNU) | |
| (USGS) (Mendenhall Research Fellowship Program) | |
| (Earth Venture Mission – 3 NNH21ZDA002O) |
Here is a Natural Sciences research proposal example that is structured using the same nine sections. I created this proposal example using the key sentence skeleton that you will access in the proposal template .
Assessing the Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity Dynamics in Fragile Ecosystems (CLIM-BIODIV)
Climate change poses a significant threat to global biodiversity, particularly in fragile ecosystems such as tropical rainforests and coral reefs. Understanding the specific impacts of climate change on biodiversity dynamics within these ecosystems is crucial for effective conservation and management strategies. However, there is a knowledge gap regarding the precise mechanisms through which climate change influences species composition, population dynamics, and ecosystem functioning in these vulnerable habitats.
With the CLIM-BIODIV project, we aim to assess the impact of climate change on biodiversity dynamics in fragile ecosystems. To achieve this aim, we have the following specific objectives:
- Investigate how changes in temperature and precipitation patterns influence species distributions and community composition in tropical rainforests.
- Assess the effects of ocean warming and acidification on coral reef ecosystems, including changes in coral bleaching events, species diversity, and ecosystem resilience.
- Conduct field surveys and employ remote sensing techniques to assess changes in species distributions and community composition in tropical rainforests.
- Utilize experimental approaches and long-term monitoring data to evaluate the response of coral reefs to varying temperature and pH conditions.
The project will benefit from access to field sites in ecologically sensitive regions, advanced remote sensing technology, and collaboration with local conservation organizations to facilitate data collection and knowledge sharing.
Dr. Alexander Chen, an established researcher in climate change and biodiversity conservation, will lead the project. Dr. Chen is a Professor of Ecology at the University of Peer Recognized, with a track record of three Nature publications and successful grant applications exceeding 25 million dollars.
The project will provide valuable insights into the impacts of climate change on biodiversity dynamics in fragile ecosystems. It will:
- Enhance our understanding of how tropical rainforest communities respond to climate change, informing targeted conservation strategies.
- Contribute to the identification of vulnerable coral reef ecosystems and guide management practices for their protection and resilience.
We will disseminate the project results to the scientific community, conservation practitioners, and policymakers through publications in reputable journals, participation in international conferences, and engagement with local communities and relevant stakeholders.
The project will commence on March 1, 2024, and will be implemented over a period of 48 months. Key milestones include data collection and analysis, modeling exercises, stakeholder engagement, and knowledge transfer activities. These are summarized in the Gantt chart.
The total eligible project costs are $2,000,000, with budget allocation for research personnel, fieldwork expenses, laboratory analyses, modeling software, data management, and dissemination activities.
Research Proposal Examples in Engineering and Technology
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded research projects in the field of science and technology.
| (USGS) (Mendenhall Postdoctoral Research Fellowship) | |
| (ROSES E.7 (Support for Open Source Tools, Frameworks, and Libraries)) |
Here is a hypothetical Engineering and Technology research proposal example that is structured using the same nine proposal sections we discussed earlier. I used the key sentence skeleton available in the proposal template to produce this example.
Developing Sustainable Materials for Energy-Efficient Buildings (SUST-BUILD)
The construction industry is a major contributor to global energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. Addressing this issue requires the development of sustainable materials that promote energy efficiency in buildings. However, there is a need for innovative engineering solutions to overcome existing challenges related to the performance, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of such materials.
With the SUST-BUILD project, we aim to develop sustainable materials for energy-efficient buildings. Our specific objectives are as follows:
- Design and optimize novel insulating materials with enhanced thermal properties and reduced environmental impact.
- Develop advanced coatings and surface treatments to improve the energy efficiency and durability of building envelopes.
- Conduct extensive material characterization and simulation studies to guide the design and optimization of insulating materials.
- Utilize advanced coating techniques and perform full-scale testing to evaluate the performance and durability of building envelope treatments.
The project will benefit from access to state-of-the-art laboratory facilities, including material testing equipment, thermal analysis tools, and coating application setups. Collaboration with industry partners will facilitate the translation of research findings into practical applications.
Dr. Maria Rodriguez, an experienced researcher in sustainable materials and building technologies, will lead the project. Dr. Rodriguez holds a position as Associate Professor in the Department of Engineering at Peer Recognized University and has a strong publication record and expertise in the field.
The project will deliver tangible outcomes for energy-efficient buildings. It will:
- Develop sustainable insulating materials with superior thermal performance, contributing to reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in buildings.
- Introduce advanced coatings and surface treatments developed from sustainable materials that enhance the durability and energy efficiency of building envelopes, thereby improving long-term building performance.
We will disseminate project results to relevant stakeholders, including industry professionals, architects, and policymakers. This will be accomplished through publications in scientific journals, presentations at conferences and seminars, and engagement with industry associations.

The project will commence on September 1, 2024, and will be implemented over a period of 36 months. Key milestones include material development and optimization, performance testing, prototype fabrication, and knowledge transfer activities. The milestones are summarized in the Gantt chart.
The total eligible project costs are $1,800,000. The budget will cover personnel salaries (60%), materials and equipment (10%), laboratory testing (5%), prototyping (15%), data analysis (5%), and dissemination activities (5%) as specified in the research call guidelines.
Final Tips for Writing an Winning Research Proposal
Come up with a good research idea.
Ideas are the currency of research world. I have prepared a 3 step approach that will help you to come up with a research idea that is worth turning into a proposal. You can download the Research Idea Generation Toolkit in this article.
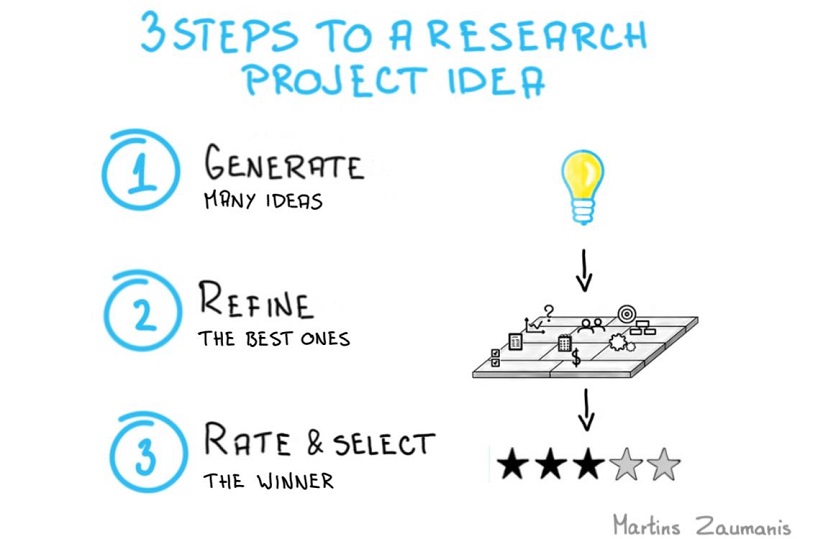
Start with a strong research outline
Before even writing one sentence of the research proposal, I suggest you use the Research Project Canvas . It will help you to first come up with different research ideas and then choose the best one for writing a full research proposal.
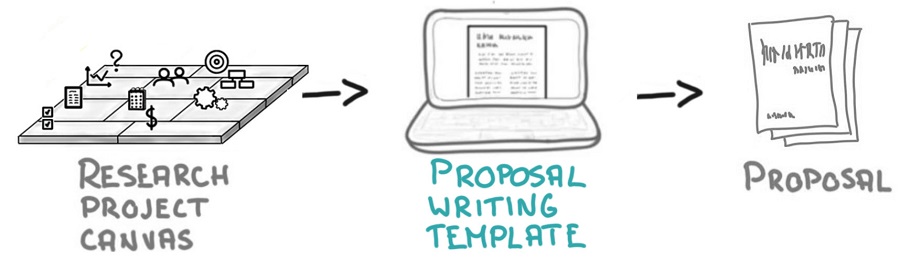
Tailor to the requirements of the project funder
Treat the submission guide like a Monk treats the Bible and follow its strict requirements to the last detail. The funder might set requirements for the topic, your experience, employment conditions, host institution, the research team, funding amount, and so forth.
What you would like to do in the research is irrelevant unless it falls within the boundaries defined by the funder.
Make the reviewer’s job of finding flaws in your proposal difficult by ensuring that you have addressed each requirement clearly. If applicable, you can even use a table with requirements versus your approach. This will make your proposed approach absolutely evident for the reviewers.
Before submitting, assess your proposal using the criteria reviewers have to follow.
Conduct thorough background research
Before writing your research proposal, conduct comprehensive background research to familiarize yourself with existing literature, theories, and methodologies related to your topic. This will help you identify research gaps and formulate research questions that address these gaps. You will also establish competence in the eyes of reviewers by citing relevant literature.
Be concise and clear
Define research questions that are specific, measurable, and aligned with the problem statement.
If you think the reviewers might be from a field outside your own, avoid unnecessary jargon or complex language to help them to understand the proposal better.
Be specific in describing the research methodology. For example, include a brief description of the experimental methods you will rely upon, add a summary of the materials that you are going to use, attach samples of questionnaires that you will use, and include any other proof that demonstrates the thoroughness you have put into developing the research plan. Adding a flowchart is a great way to present the methodology.
Create a realistic timeline and budget
Develop a realistic project timeline that includes key milestones and activities, allowing for potential challenges or delays. Similarly, create a detailed budget estimate that covers all anticipated expenses, ensuring that it aligns with the scope and requirements of your research project. Be transparent and justify your budget allocations.
Demonstrate the significance and potential impact of the research
Clearly articulate the significance of your research and its potential impact on the field. Discuss how your findings can contribute to theory development, practical applications, policy-making, or other relevant areas.
Pay attention to formatting and style guidelines
Follow the formatting and style guidelines provided by your institution or funding agency. Pay attention to details such as font size, margins, referencing style, and section headings. Adhering to these guidelines demonstrates professionalism and attention to detail.
Take a break before editing
After preparing the first draft, set it aside for at least a week. Then thoroughly check it for logic and revise, revise, revise. Use the proposal submission guide to review your proposal against the requirements. Remember to use grammar checking tools to check for errors.
Finally, read the proposal out loud. This will help to ensure good readability.
Seek feedback
Share your proposal with mentors, colleagues, or members of your research community to receive constructive feedback and suggestions for improvement. Take these seriously since they provide a third party view of what is written (instead of what you think you have written).
Reviewing good examples is one of the best ways to learn a new skill. I hope that the research proposal examples in this article will be useful for you to get going with writing your own research proposal.
Have fun with the writing process and I hope your project gets approved!
Learning from research proposal examples alone is not enough
The research proposal examples I provided will help you to improve your grant writing skills. But learning from example proposals alone will take you a rather long time to master writing winning proposals.
To write a winning research proposal, you have to know how to add that elusive X-Factor that convinces the reviewers to move your proposal from the category “good” to the category “support”. This includes creating self-explanatory figures, creating a budget, collaborating with co-authors, and presenting a convincing story.
To write a research proposal that maximizes your chances of receiving research funding, read my book “ Write a Winning Research Proposal “.

This isn’t just a book. It’s a complete research proposal writing toolkit that includes a project ideation canvas, budget spreadsheet, project rating scorecard, virtual collaboration whiteboard, proposal pitch formula, graphics creation cheat sheet, review checklist and other valuable resources that will help you succeed.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:

One comment
Hi Martins, I’ve recently discovered your content and it is great. I will be implementing much of it into my workflow, as well as using it to teach some graduate courses! I noticed that a materials science-focused proposal could be a very helpful addition.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
- MAY 16, 2024
How to Write a Research Proposal in 2024: Structure, Examples & Common Mistakes
by Imed Bouchrika, Phd
Co-Founder and Chief Data Scientist
Whether you are a student whose goal is to complete course requirements or a researcher looking for funding, knowing how to write a research proposal is an important skill. If you have had experience writing a project proposal, you might think that they are the same. However, they are not. The standards for research proposals are much stricter and they have varying guidelines for writing styles and formatting. In fact, those guidelines can change with every discipline or department.
A basic requirement when seeking approval for any type of research project and for applying for study grants or ethics committee approval (Kivunja, 2016) is providing an example of a well-written research proposal, which generally has two purposes. First, it shows and justifies the need to investigate a research problem and, second, it presents a set of workable strategies for conducting the proposed research (Miner & Miner, 2005).
This article aims to describe the common steps taken to prepare a written proposal as attractively as possible to achieve approval and/or funding. It also seeks to discuss key aspects that must be considered to help ensure that you can convert your proposed study into well-conducted actual research work.
How to Write a Research Proposal Table of Contents
- Starting the Proposal Process
- Research Proposal Writing
- Revisions and Proofreading
- Skills Required for a Research Proposal
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Proposal Writing
- Some Good Examples of Research Proposals
I. Starting the Proposal Process
A. preliminary considerations.
Many students and novice researchers, unfortunately, do not completely comprehend what a research proposal structure means, nor do they recognize its value. At any rate, it is safe to say that a research project is only as good as its proposal. A poorly-prepared research proposal format adversely affects the research project although by some means it managed to get approved. Conversely, a well-written proposal not only helps ensure research success but also enhances your potential as a researcher among your evaluators.
Any type of research proposal follows the style, structure, and other writing conventions set by the relevant field of discipline. A research proposal outline’s content typically varies in length, from 3 to 35 pages, with references (and appendices, if necessary). But like any academic activity, start the research proposal template writing process by first carefully reading the instructions. Make sure to clarify anything that needs clarification and only proceed once everything is clear.
A word of caution, though. Maintain considerable control over how you conduct your research—a light, reconnaissance reading will do. People tend to fall into the over-research trap, which wastes valuable time to write. Once your structure of a research proposal has been approved, the researcher gains the right time to conduct deep research.
B. Key Questions to Be Asked
At this stage, it is good to ask these preparatory questions to help you steer your research in the right direction:
- What is the topic I want to study?
- Why is it worthwhile to study it?
- What practical or valuable problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon—and possibly improve—existing research already done about the topic?
- (For students:) How is it important within the subject areas covered in the course/program?
- What are the specific tasks that I must plan to do?
- Can I get those tasks done within the time and resources available?
Generally, a compelling background and significance in research proposal will manifest if it effectively captures your knowledge about the topic and shows your deep interest to conduct the research. Handle it with the purpose of making your readers engaged about the study and what the outcomes will be.
In case you’re still unsure about your topic or in the process of exploring possibilities, it is good to consider how funding agencies across the world are allocating their budgets for research grants. For instance, in the field of market research, the top topics that won the most study grants in 2018 were market measurement (21%), media audience/research (12%), usage and attitude studies (12%), and CRM systems (8%) (ESOMAR, 2019). If you are considering marketing as a major , these are good references. Also, you can search for cutting-edge or controversial debate topics in your field. This way, you will also touch on the current interests of other researchers in your field.
II. Research Proposal Writing
A. introduction.
A research proposal is commonly written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project when enrolling for a research-based postgraduate degree. Graduate and post-graduate students also embark on a university dissertation to obtain a degree or get that Ph.D. Although it is just a course assignment, a student must treat the introduction as the decisive initial pitch for a research inquiry or in-depth investigation of the significance of an issue for study.
After reading the introduction, your readers should be able to clearly understand what you want to do. Likewise, they should be able to appreciate your enthusiasm for the topic and to be engaged in the potential results of the study (Jackowski & Leggett, 2015).
Consider your introduction as a two-four-paragraph narrative that concisely responds to the following questions:
- What is the central problem of the study?
- What is the field of study that is relevant to that core problem?
- What methods should be utilized to analyze that problem?
- Why is this study important?
- What is its significance to the academe and to the world at large?
- Why should someone reading the proposal be concerned about the results of the proposed research?
Take note that most academic institutions and funding agencies do not require an abstract or synopsis before the introduction. However, it is best to check your institution’s guidelines.
B. Background and Significance
This part is for explaining the context of a research proposal and for clearly describing its importance. While some writers integrate this part in the introduction, a number of scholars prefer to write it separately to allow for a smooth flow of a proposal’s narrative.
A good way to approach this section is by assuming that your readers are busy but want to know the gist of your research problem and the entire study (Kivunja, 2016). Remember that this is not an extensive essay that covers everything about your proposed study, but rather a concise text that is enough to elicit interest in your research.
With these in mind and although there is no definitive rule for framing a proposed study’s significance, you should endeavor to address the following key considerations:
- Specify the problem of the study and provide a more detailed elaboration of the research purpose. This is very important when the research problem is multifaceted or complex.
- State the rationale of your research proposal and explain, in an engaging way, why it is worthwhile to conduct.
- Present the core problems or issues that will be addressed. This can be made either in questions or statements.
- Underscore how your research can build upon existing assumptions about the proposed study’s problem.
- Elaborate on the details of your methodology to conduct your study, including the key sources, analytical approach, etc.
- Clearly establish the limits of your proposed study to provide a clear research focus.
- Provide definitions of key terms or concepts, if necessary.
C. Review of Prior Studies and Literature
Your study background and significance are directly related to this section, which primarily offers a more deliberate review and synthesis of existing studies pertinent to your proposed research problem. This part aims to properly situate your proposed study within the bigger scheme of things of what is being investigated, while, at the same time, showing the innovation and originality of your proposed work (Abdulai & Owusu-Ansah, 2014).
Because a literature review often involves heavy information, it is important that this section is smartly structured to allow a reader to comprehend the major contentions that underlie your proposed research vis-a-vis those of other scholars. An effective way to do this is to separate the literature into major themes or conceptual strategies. This is a better approach instead of chronologically or methodically describing sets of studies one by one.
As there are many efficient ways in framing your review of existing related studies, many scholars are following the use of the “five Cs" in writing a literature review (Sudheesh et al., 2016):
- Cite properly in order to maintain the primary focus on the previous studies related to the research problem. If you are not familiar with citation formats, you can check out our guide on how to cite a research paper .
- Compare the methods, outcomes, models, and arguments mentioned in the literature. Identify the various agreements among the authors.
- Contrast the different themes, controversies, methodologies, and arguments underscored in the literature. Explain the main areas where these authors disagree and debate.
- Critique the literature. Identify the engaging arguments used by scholars. Determine the methodologies that appear as most valid, suitable, and reliable.
- Connect the literature to your own particular study area and topic. Discuss whether and how your proposed study draws upon, deviates from, synthesizes, or contributes new knowledge to existing literature.
D. Aims and Research Questions
Once you’ve determined a good angle for your study, it is time to compose your research objectives. Ask yourself: What do you want your readers to know when they read your proposal? Give considerable time to properly frame your objectives and try to write them in a single sentence, if possible.
A research objective will help you stay focused and prevent you from drifting off on tangents (Krathwohl & Smith, 2005). Regardless of the specific topic or problem or method you choose, all study proposals must deal with the various types of research questions , specifically the following:
- What do you plan to achieve? Be straightforward and concise in describing the research problem and what topic you are proposing to study.
- Why do you want to conduct the research? You must also provide compelling evidence that your selected topic is worthy of a thorough examination.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Make sure that your proposed study is doable and provide a clear, coherent set of strategies to complete it.
For some institutions, this section can be included as part of the Introduction, usually placed as the last paragraph of that section. Familiarize yourself with what is a research question if you are having difficulties in this area.
E. Research Design & Methods
This part should be written properly and organized logically since you are not yet conducting the actual research. However, it must build confidence among your readers that it is something worth pursuing.
The underlying purpose here is to convince the reader that your research design and suggested analytical strategies will properly address the problem/s of the study. It also aims to assure the reader that the selected methods offer the means to efficiently interpret the likely study outcomes. Simply put, your research design and methods should be directly connected to the particular objectives of your research (Lyman & Keyes, 2019).
An effective way to frame your study design is by drawing good examples from your literature review. Emulate the good approaches used by other researchers. Be particular about the methodological techniques you intend to use to gather data, the strategies you will utilize to analyze your data, and the external validity measures you will employ.
Make sure to cover the following when describing the methods you will utilize:
- Establish the research process you will engage in, including the method you will use for interpreting the outcomes with regard to the problem of the study.
- Do not simply discuss what you plan to accomplish from using the methods you will select, but also describe how you will use the time while utilizing these techniques.
- Note that the methods section is not merely a collection of activities. Since you have selected the approaches, you should also use it to argue why it is the best approach to examine the study problem. Explain this clearly.
- Finally, foresee and acknowledge any possible obstacles and drawbacks when you undertake your research design and provide a plan of action to solve them.
Remember, there is no such thing as a perfect method for any type of research endeavor. However, if you rigorously follow the best practices employed by those who conducted relevant studies and provide the corresponding rationales why you selected them, then you can readily address any critique that might come your way.
F. Implications and Contribution to Knowledge
This section is where you contend how you think your proposed study will enhance, change, or expand current knowledge in the research topic that will be investigated. By drawing from your research objectives, explain how the expected outcomes will affect future studies, practice, theory, policymaking, procedures, etc. Discussing study implications typically have either methodological, theoretical, or substantive significance (Abdulai & Owusu-Ansah, 2014).
You can use these guide questions when framing the potential ramifications of your proposed research:
- What could the outcomes signify when it comes to disputing the underlying assumptions and theoretical framework that support the research?
- What recommendations for further studies could emerge from the expected study results?
- How will the outcomes affect practitioners in the real-world context of their workplace?
- Will the study results impact forms of interventions, methods, and/or programs?
- How could the outcomes contribute to solving economic, social, or other types of issues?
- Will the outcomes affect policy decisions?
- How will people benefit from your proposed research?
- What specific aspects of life will be changed or enhanced as an outcome of the suggested study?
- How will the research outcomes be implemented and what transformative insights or innovations could emerge when they are implemented?
The purpose of this section is to reflect upon gaps or understudied topics of the existing literature and explain how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be conducted as proposed.
G. Compliance with Ethical Principles
There is nothing fundamentally best or worst when it comes to the scientific writing style. It is just a standardized approach for presenting information that is tailored to facilitate communication. Different scholarly disciplines have diverse publication styles. So this section depends on the protocols set by the target institution or agency.
Nonetheless, it should be noted that fundamental ethical principles guide all scholarly research and writing. If you are observing APA conventions, ethical guidelines are meant to accomplish three objectives, namely, “to protect intellectual property rights, to protect the rights and welfare of research participants, and to ensure the accuracy of scientific knowledge" (APA, 2014, pp. 11).
Every social and behavioral sciences writer (and other scholars who adhere to these principles) advocates these objectives and observes the long-standing standards that their professional groups follow (APA, 2014).
Another major ethical APA principle promotes the need to ensure the accuracy of scientific knowledge. The underlying principle behind the (universal) scientific method comprises observation, which can be verified and repeated by other scholars. Accordingly, scholars are expected to not engage in research writing that involves falsifying or fabricating data. Moreover, researchers should not modify study outcomes just to uphold a hypothesis or to remove problematic data in order to present a more credible report (APA, 2014).
Some universities do not require a detailed budgetary allocation for proposed studies that only involve archival research and simple academic research, although some still do. However, if you are applying for research funding, you will likely be instructed to also include a detailed budget that shows how much every major part of the project will cost.
Be sure to verify what type of costs the funding agency or institution will agree to cover, and only include relevant items in your budget. For every item, include:
- The actual cost present how much money do you need to complete the entire study
- Justification discuss why such budget item is necessary to complete the research
- Source explain how the amount was calculated
Conducting a research project is not the same as buying ingredients when cooking meals. So how do you make a budget when most entries do not have a price tag? To prepare a correct budget, think about:
- Materials Will you need access to any software solutions? Does using a technology tool require installation or training costs?
- Time How much will you need to cover the time spent on your research study? Do you need to take an official leave from your regular work?
- Travel costs Will you need to go to particular places to conduct interviews or gather data? How much must you spend on such trips?
- Assistance Will you hire research assistants for your proposed study? What will they do and how much will you pay them? Will you outsource any other activities (statistical analyses, etc.)?
I. Timetable
The research schedule is another aspect where one should be realistic and to the point. The study turnaround time shows that your proposed study can be finished within the allowed period of completion, e.g., the student’s candidature or the university’s academic calendar.
The timeline must comprise a series of objectives that should be met to complete all the aspects of your academic research requirements (thesis, dissertation, or other degree requisites), from preliminary research to the final editing. Every step must include an expected completion date.
It should likewise contain a statement of the progress that one has made so far. Other relevant research-related activities should also be included, such as paper presentations (if applicable). Finally, it must be noted that the timeline is not a fixed document—a researcher must update it regularly, when necessary.
J. Conclusion
One of the best ways to conclude your research proposal is by presenting a few of your anticipated outcomes. Upon reaching this final stage, you must disclose the conclusions and arguments that you expect to reach. Your reader will know that these are anticipated results based on how much you’ve researched so far and that these expectations will likely change once the complete study has been made.
It is important, nonetheless, that you give your reader a sense of what conclusions may be drawn. This will allow your reader to further assess the significance and validity of your project. It will also indicate to your reader that you have thought ahead and considered the potential outcomes and implications of your research. Writing a r esearch proposal example should allow you to determine if you are communicating all essential information in your conclusion.
K. Appendices
Some funding agencies and academic institutions require proponents of research proposals to include an Appendix section. This contains supplemental material that is not a core element of a proposal’s main narrative but is considered valuable in enhancing the views and arguments raised in the proposal. It may include forms and data like tables, informed consent, clinical/research protocols, data collection instruments, etc.
This supplementary section is also the best part to include one’s latest curriculum vitae if required. You can include all relevant academic and professional experience to present your case as a qualified individual to conduct your proposed research. It will help significantly to present pertinent research works you’ve completed, especially if you have published research reports, articles, etc.
It should be noted that many students and budding researchers who went through the rigors of research actually found the experience so worthwhile that they made it a long-term career. In fact, research as a professional job is one of the better-paying jobs worldwide. According to Glassdoor (2020), the average base pay for professional researchers in the U.S. is $54,411 per year. Among OECD-member countries, Denmark tops the list with an average of 15.65 people employed as professional researchers or scientists for every 1,000 employees in 2018.
III. Revisions and Proofreading
As with any other piece of academic writing, it is essential to redraft, edit, and proofread your research proposal before you submit it (van Ekelenburg, 2010). If you have the opportunity, ask a friend, colleague, or supervisor for feedback and writing suggestions before handing it over to the evaluators.
The peer-review process, whether for professional or student research, was designed not to reject submissions but actually as a quality control system to help researchers improve on their craft (RPS, 2016). Proposal revision can entail careful rewriting, which, in itself, can be a fruitful experience that can be used for the long term.
In academic publishing, proposal rejection is a reality, even for the most seasoned scholarly writers. In fact, the success rate of reapplied proposals is considerably higher compared to the first submissions. For instance, at the European Research Council, new applicants have a success rate of 9-10%. Repeat applications tend to have better success rates, from 14-15% (ERC, 2019).
To really boost your chances of getting a Google Scholar research proposal approval, you might want to consider seeking the help of professional proofreading services to remove grammatical errors, examine your proposal’s structure, and enhance your adherence to the required academic style.

IV. Skills Required for a Research Proposal
It follows that the skills necessary to write research are similar to the set of skills needed to prepare a research proposal (Gilbert, 2006). Here, these necessary skills are grouped into three categories for better understanding:
- Subject knowledge and research skills . A proposal offers anyone the chance to show your familiarity with existing research trends and your mastery of the topic/subject matter.
- Critical thinking skills . A quality example of a research proposal shows one’s above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking.
- Communication skills . The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
It is essential to remember these skills as you work on your research proposal. This is because your readers will be looking for evidence of these important researcher’s skills in how you write. With the success rate for many research grants below 20% (e.g., NIH, Wellcome, NHMRC, etc.), these skills will be key in helping you achieve funding approval.
Research Proposal Success Rates for Selected Funding Organizations
V. common mistakes to avoid in proposal writing.
With rejection rates reaching as high as 97% at prestigious journals, it is only prudent to ensure that you are not making any of these customary mistakes when submitting your research proposal:
Submitting lengthy proposals . When writing research proposals, be to the point. Your submitted document must be focused and concise. Don’t diverge into irrelevant tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
Covering too much research ground . It is common for students to fail in delimiting the contextual boundaries of their studies, be it the topic, time, place, etc. As with any research paper, the proposed research must clearly inform the reader how the study will investigate the problem. Look for some research paper thesis examples so you would know how to clearly communicate the scope of your inquiry.
Not citing major works in a literature review . While it is advised to keep everything in the proposal at a minimum—a few milestone research studies must already be included. Proposals should be grounded in landmark studies that provide the groundwork for appreciating the growth and scope of the issue.
Too much focus on minor issues, yet very few details on major issues . A proposal must focus only a few key study questions to clearly argue why it should be conducted. Mentioning minor issues is acceptable but they should not overpower the major ones, which should control the overall narrative.
Inability to frame a persuasive and coherent argument for the proposed study . This is another common yet crucial mistake of students and grant-seekers. In essence, the research proposal must be able to effectively argue why a study should be approved or funded.
Poor grammar or careless writing . While a research proposal only represents a small part of a complete study, it is expected to be well-written and observes the writing style and guidelines of good academic writing.
VI. Some Good Examples of Research Proposals
If you are looking for a research proposal example for students, here are some made for various disciplines and levels of study that you can emulate or derive valuable ideas from:
Postgraduate Research
- Sample proposal for a Clinical Health Project
- Sample proposal for Social Policy and Criminology
- Sample research proposal for Ph.D. Politics 1
- Sample research proposal for Ph.D. Politics 2
- Sample research proposal for Ph.D. Politics 3
- Sample research proposal for Health Librarianship 1
- Sample research proposal for Health Librarianship 2
- Sample research proposal for Early Learning 1
- Sample research proposal for Early Learning 2
Undergraduate Research
- Sample Research Proposal for Civil Engineering
Although this article had covered as much ground as possible, the truth is that there is no universal style in writing search proposals. In the same manner, there is actually no definitive standard or secret formula behind a winning proposal. This is because every academic or funding institution has its own guidelines and protocols that every candidate or funding application must adhere to.
Nonetheless, integrating the specific instructions and guidelines of your institution with the key considerations and best practices discussed in this article will help ensure the approval of your proposal. Always remember to keep a healthy balance between substance and brevity when writing a research proposal. Share enough ideas just to open the door for your readers’ interest, and then give your “all" once you are given the go-signal to proceed with the proposed study.
Key Insights
- Distinct Nature of Research Proposals: Unlike general project proposals, research proposals have stricter standards and vary significantly in guidelines depending on the discipline and department.
- Purpose of Research Proposals: They justify the need for investigating a research problem and present workable strategies for conducting the proposed research.
- Starting the Proposal: The process includes understanding the structure, adhering to the specific guidelines, and asking key preparatory questions to ensure the research is worthwhile and feasible.
- Writing the Proposal: Essential components include the introduction, background and significance, literature review, research objectives, design and methods, and implications.
- Revisions and Proofreading: It is crucial to thoroughly revise and proofread the proposal, possibly seeking feedback from peers or professional services, to improve quality and adherence to academic standards.
- Skills Required: Successful proposals require subject knowledge, critical thinking, and strong communication skills.
- Common Mistakes: Avoid lengthy proposals, unclear boundaries, neglecting major works in literature reviews, and poor grammar.
What is the main purpose of a research proposal?
A research proposal aims to justify the need for investigating a specific research problem and to present a set of strategies for conducting the proposed research. It helps in obtaining approval or funding by demonstrating the feasibility and significance of the research.
How should I start the process of writing a research proposal?
Begin by understanding the specific guidelines and structure required by your institution or funding agency. Clarify any uncertainties and start by asking key preparatory questions to ensure your research is valuable and feasible. Read the instructions carefully before drafting your proposal.
What should be included in the introduction of a research proposal?
The introduction should concisely explain the central problem of the study, the relevant field, the methods to analyze the problem, the importance of the study, and its significance to academia and society. It should engage readers and make them understand the purpose and potential impact of the research.
How do I approach the literature review section?
Structure the literature review to compare, contrast, critique, and connect previous studies to your proposed research. Use the “five Cs” approach: cite properly, compare methods and outcomes, contrast themes, critique the literature, and connect it to your study to show innovation and relevance.
What are the key components of the research design and methods section?
This section should outline your research process, including data collection methods, analytical strategies, and validity measures. It should build confidence in the feasibility and rigor of your approach, and justify why your chosen methods are the best for addressing the research problem.
Why is it important to discuss the implications and contributions of the research?
Discussing implications shows how your research will enhance or expand current knowledge, affect future studies, practice, theory, policy, and real-world applications. It demonstrates the potential impact and relevance of your research, making it more compelling for approval or funding.
What are common mistakes to avoid when writing a research proposal?
Avoid submitting lengthy or unfocused proposals, covering too much research ground, neglecting major works in the literature review, overemphasizing minor issues, failing to frame a persuasive argument, and submitting proposals with poor grammar or careless writing.
How important is proofreading and revision in the proposal writing process?
Proofreading and revision are crucial to ensure clarity, coherence, and adherence to guidelines. Seeking feedback from peers or professional services can significantly improve the quality of your proposal, increasing the chances of approval or funding.
- Abdulai, R.T., & Owusu-Ansah, A. (2014). Essential ingredients of a good research proposal for undergraduate and postgraduate students in the social sciences. Sage Open , July-September, 115. https://doi.org/10.1177/2158244014548178
- APA (2014). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, 6th Edition . American Psychological Association: Washington, DC. Google Books
- APA (2018). Summary Report of Journal Operations, 2017. American Psychologist, 73 (5), 683-84. https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0000347
- ERC (2019). Rewriting is Rewarding Tips from Repeat Applicants . Brussels: European Research Commission .
- ESOMAR (2019). Global Market Research 2019 . Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ESOMAR .
- Gilbert, N. (Ed.). (2006). From Postgraduate to Social Scientist. A Guide to Key Skills . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage. Google Books
- Glassdoor (2020, August 19). Research Professional Salaries . Mill Valley, CA: Glassdoor .
- Jackowski, M. B., & Leggett, T. (2015). Writing research proposals. Radiologic Technology, 87 (2), 236-238.
- Kivunja, C. (2016). How to write an effective research proposal for higher degree research in higher education: Lessons from practice. International Journal of Higher Education, 5 (2), 163-172. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijhe.v5n2p163
- Krathwohl, D.R., & Smith, N.L. (2005). How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press. Google Books
- Lyman, M., & Keyes, C. (2019). Peer-supported writing in graduate research courses: A mixed methods assessment. International Journal of Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, 31 (1), 11-20. ERIC No. EJ1206978
- Miner, J.T., & Miner, L.E. (2005). Models of Proposal Planning and Writing (pp. 139). Westport, CT: Praeger. Google Books
- NHMRC (2018). Outcomes of funding rounds . Canberra, Australia: National Health and Medical Research Council .
- NIH (2017). Funding Facts . Bethesda, MD: US National Institutes of Health .
- OECD (2019). Researchers. OECD Data . Paris, France: OECD .
- RPS (2016). Peer Review Guidance: Research Proposals . London: Royal Pharmaceutical Society .
- Sudheesh, K., Duggappa, D. R., & Nethra, S. S. (2016). How to write a research proposal? Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, 60 (9), 631-634. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5049.190617
- van Ekelenburg, H. (2010). The art of writing good research proposals. Science Progress, 93 (4), 429-442. https://doi.org/10.3184/003685010X12798150447676
- Wellcome (2019). Grant funding data 2018 to 2019 . London: Wellcome Trust .
Related Articles

How to Write Research Methodology in 2024: Overview, Tips, and Techniques

How to Write a Research Question in 2024: Types, Steps, and Examples

EasyChair : Tutorial of how to request an installation for Conference Management System

Guide2Research Becomes Research.com – New Disciplines, Tools & Layout

Levels of Evidence in Research: Examples, Hierachies & Practice in 2024

How to Write a Research Paper for Publication: Outline, Format & Types in 2024

World Ranking of Top Computer Science Conferences in 2020
Importing references from google scholar to bibtex.

How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper in 2024: Steps and Examples

Needs Analysis in 2024: Definition, Importance & Implementation

Primary Research vs Secondary Research in 2024: Definitions, Differences, and Examples

72 Scholarship Statistics: 2024 Data, Facts & Analysis

2024 Minnesota Nursing License Requirements

2024 Nebraska Nursing License Requirements

2024 Texas Nursing License Requirements

2024 Georgia Nursing License Requirements

2024 Illinois Nursing License Requirements

2024 South Carolina Nursing License Requirements

2024 Louisiana Nursing License Requirements

2024 Alabama Nursing License Requirements

2024 New Mexico Nursing License Requirements
Recently published articles.

What is a Doctorate Degree? 2024 Costs, Admission Requirements & Salary Expectations

Kinesiology Degree Guide: 2024 Costs, Requirements & Job Opportunities

How to Become a Medical Coder – Salary & Requirements in 2024

Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in Utah 2024 – Accredited Schools Online & Campus

Best LPN Programs in Kansas – Accredited Online LPN Programs in 2024

Best Accredited Online Bachelor's Degree Programs for 2024

Best Shortest Online Post-Master's FNP Certificate Programs for 2024

Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in Arizona 2024 – Accredited Schools Online & Campus

MS vs. MA in Counseling: What's the Difference and Which Degree Should You Choose in 2024?

Hospitality and Tourism Degree Guide: 2024 Costs, Requirements & Job Opportunities

Best 12-Month FNP Programs (Online & Campus) for 2024

10 Best Accredited Non-Profit Online Universities for 2024

Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in New Jersey 2024 – Accredited Schools Online & Campus
Best degrees to get in 2024: popular majors that guarantee high salary.

Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in Oklahoma 2024 – Accredited Schools Online & Campus

Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in Illinois 2024 – Accredited Schools Online & Campus

Best Nurse Practitioner Programs in Minnesota 2024 – Accredited Schools Online & Campus

Best Online Human Resources Degree Programs of 2024

Philosophy Degree in 2024: Requirements, Cost, Career & Salary

Best Online Doctorate Degrees in Psychology: Guide to Online Programs for 2024

What to Know About Being a Surgical Technologist in 2024
Newsletter & conference alerts.
Research.com uses the information to contact you about our relevant content. For more information, check out our privacy policy .

Thank you for subscribing!
Confirmation email sent. Please click the link in the email to confirm your subscription.


Science & Quantitative Reasoning Education
Yale undergraduate research, how to write a proposal.
The abstract should summarize your proposal. Include one sentence to introduce the problem you are investigating, why this problem is significant, the hypothesis to be tested, a brief summary of experiments that you wish to conduct and a single concluding sentence. (250 word limit)
Introduction
The introduction discusses the background and significance of the problem you are investigating. Lead the reader from the general to the specific. For example, if you want to write about the role that Brca1 mutations play in breast cancer pathogenesis, talk first about the significance of breast cancer as a disease in the US/world population, then about familial breast cancer as a small subset of breast cancers in general, then about discovery of Brca1 mutations in familial breast cancer, then Brca1’s normal functions in DNA repair, then about how Brca1 mutations result in damaged DNA and onset of familial breast cancer, etc. Definitely include figures with properly labeled text boxes (designated as Figure 1, Figure 2, etc) here to better illustrate your points and help your reader wade through unfamiliar science. (3 pages max)
Formulate a hypothesis that will be tested in your grant proposal. Remember, you are doing hypothesis-driven research so there should be a hypothesis to be tested! The hypothesis should be focused, concise and flow logically from the introduction. For example, your hypothesis could be “I hypothesize that overexpressing wild type Brca1 in Brca1 null tumor cells will prevent metastatic spread in a mouse xenograph model.” Based on your hypothesis, your Specific Aims section should be geared to support it. The hypothesis is stated in one sentence in the proposal.
Specific Aims (listed as Specific Aim 1, Specific Aim 2)
This is where you will want to work with your mentor to craft the experimental portion of your proposal. Propose two original specific aims to test your hypothesis. Don’t propose more than two aims-you will NOT have enough time to do more. In the example presented, Specific Aim 1 might be “To determine the oncogenic potential of Brca1 null cell lines expressing wild type Brca1 cDNA”. Specific aim 2 might be “To determine the metastatic potential of Brca1 null cells that express WT Brca1”. You do not have to go into extensive technical details, just enough for the reader to understand what you propose to do. The best aims yield mechanistic insights-that is, experiments proposed address some mechanisms of biology. A less desirable aim proposes correlative experiments that does not address mechanistically how BRCA1 mutations generate cancer. It is also very important that the two aims are related but NOT interdependent. What this means is that if Aim 1 doesn’t work, Aim 2 is not automatically dead. For example, say you propose in Aim 1 to generate a BRCA1 knockout mouse model, and in Aim 2 you will take tissues from this mouse to do experiments. If knocking out BRCA1 results in early embryonic death, you will never get a mouse that yields tissues for Aim 2. You can include some of your mentor’s data here as “Preliminary data”. Remember to carefully cite all your sources. (4 pages max; 2 pages per Aim)
Potential pitfalls and alternative strategies
This is a very important part of any proposal. This is where you want to discuss the experiments you propose in Aims 1 and 2. Remember, no experiment is perfect. Are there any reasons why experiments you proposed might not work? Why? What will you do to resolve this? What are other possible strategies you might use if your experiments don’t work? If a reviewer spots these deficiencies and you don’t propose methods to correct them, your proposal will not get funded. You will want to work with your mentor to write this section. (1/2 page per Aim)
Cite all references, including unpublished data from your mentor. Last, First, (year), Title, Journal, volume, pages.
*8 page proposal limit (not including References), 1.5 spacing, 12pt Times New Roman font
- View an example of a research proposal submitted for the Yale College First-Year Summer Research Fellowship (PDF).
- View an example of a research proposal submitted for the Yale College Dean’s Research Fellowship and the Rosenfeld Science Scholars Program (PDF) .

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
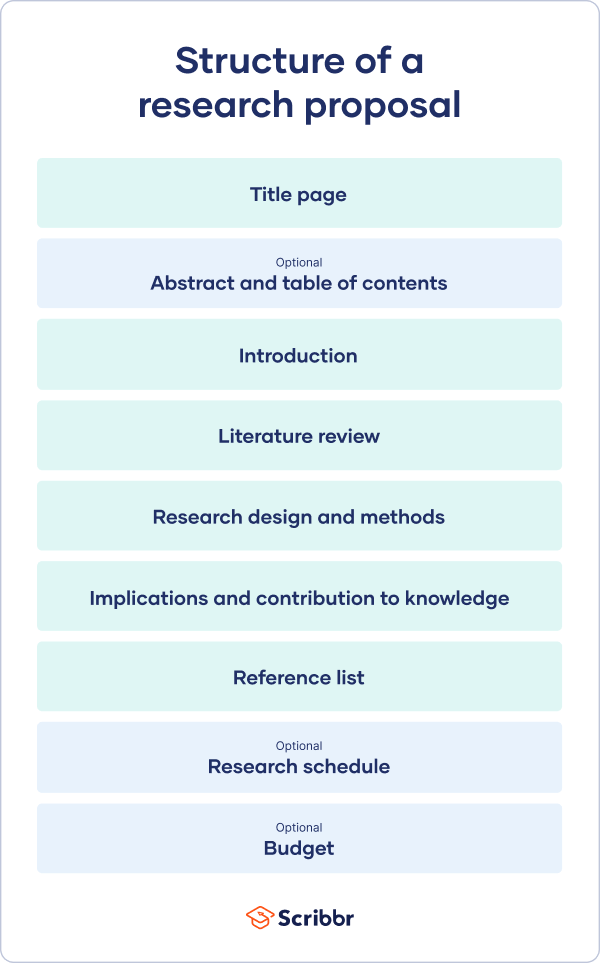
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
- Research Tips and Tools
Advanced Research Methods
- Writing a Research Proposal
- What Is Research?
- Library Research
What Is a Research Proposal?
Reference books.
- Writing the Research Paper
- Presenting the Research Paper
When applying for a research grant or scholarship, or, just before you start a major research project, you may be asked to write a preliminary document that includes basic information about your future research. This is the information that is usually needed in your proposal:
- The topic and goal of the research project.
- The kind of result expected from the research.
- The theory or framework in which the research will be done and presented.
- What kind of methods will be used (statistical, empirical, etc.).
- Short reference on the preliminary scholarship and why your research project is needed; how will it continue/justify/disprove the previous scholarship.
- How much will the research project cost; how will it be budgeted (what for the money will be spent).
- Why is it you who can do this research and not somebody else.
Most agencies that offer scholarships or grants provide information about the required format of the proposal. It may include filling out templates, types of information they need, suggested/maximum length of the proposal, etc.
Research proposal formats vary depending on the size of the planned research, the number of participants, the discipline, the characteristics of the research, etc. The following outline assumes an individual researcher. This is just a SAMPLE; several other ways are equally good and can be successful. If possible, discuss your research proposal with an expert in writing, a professor, your colleague, another student who already wrote successful proposals, etc.
- Author, author's affiliation
- Explain the topic and why you chose it. If possible explain your goal/outcome of the research . How much time you need to complete the research?
- Give a brief summary of previous scholarship and explain why your topic and goals are important.
- Relate your planned research to previous scholarship. What will your research add to our knowledge of the topic.
- Break down the main topic into smaller research questions. List them one by one and explain why these questions need to be investigated. Relate them to previous scholarship.
- Include your hypothesis into the descriptions of the detailed research issues if you have one. Explain why it is important to justify your hypothesis.
- This part depends of the methods conducted in the research process. List the methods; explain how the results will be presented; how they will be assessed.
- Explain what kind of results will justify or disprove your hypothesis.
- Explain how much money you need.
- Explain the details of the budget (how much you want to spend for what).
- Describe why your research is important.
- List the sources you have used for writing the research proposal, including a few main citations of the preliminary scholarship.
- << Previous: Library Research
- Next: Writing the Research Paper >>
- Last Updated: Aug 22, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/research-methods
How to Write a Research Proposal Paper

Table of Contents
What is a research proposal paper, why write a research proposal paper.
- How to Plan a Research Proposal Paper
Components of a Research Proposal Paper
Research proposal examples, help & additional resources, this resource page will help you:.
- Learn what a research proposal paper is.
- Understand the importance of writing a research proposal paper.
- Understand the steps in the planning stages of a research proposal paper.
- Identify the components of a research proposal paper.
A research proposal paper:
- includes sufficient information about a research study that you propose to conduct for your thesis (e.g., in an MT, MA, or Ph.D. program) or that you imagine conducting (e.g., in an MEd program). It should help your readers understand the scope, validity, and significance of your proposed study.
- may be a stand-alone paper or one part of a larger research project, depending on the nature of your assignment.
- typically follows the citation format of your field, which at OISE is APA .
Your instructor will provide you with assignment details that can help you determine how much information to include in your research proposal, so you should carefully check your course outline and assignment instructions.
Writing a research proposal allows you to
- develop skills in designing a comprehensive research study;
learn how to identify a research problem that can contribute to advancing knowledge in your field of interest;
further develop skills in finding foundational and relevant literature related to your topic;
critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem;
see yourself as an active participant in conducting research in your field of study.
Writing a research proposal paper can help clarify questions you may have before designing your research study. It is helpful to get feedback on your research proposal and edit your work to be able to see what you may need to change in your proposal. The more diverse opinions you receive on your proposal, the better prepared you will be to design a comprehensive research study.
How to Plan your Research Proposal
Before starting your research proposal, you should clarify your ideas and make a plan. Ask yourself these questions and take notes:
What do I want to study?
Why is the topic important? Why is it important to me?
How is the topic significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
What problems will it help solve?
How does it build on research already conducted on the topic?
What exactly should I plan to do to conduct a study on the topic?
It may be helpful to write down your answers to these questions and use them to tell a story about your chosen topic to your classmates or instructor. As you tell your story, write down comments or questions from your listeners. This will help you refine your proposal and research questions.
This is an example of how to start planning and thinking about your research proposal assignment. You will find a student’s notes and ideas about their research proposal topic - "Perspectives on Textual Production, Student Collaboration, and Social Networking Sites”. This example is hyperlinked in the following Resource Page:
A research proposal paper typically includes:
- an introduction
- a theoretical framework
- a literature review
- the methodology
- the implications of the proposed study and conclusion
- references
Start your introduction by giving the reader an overview of your study. Include:
- the research context (in what educational settings do you plan to conduct this study?)
- the research problem, purpose (What do you want to achieve by conducting this study?)
- a brief overview of the literature on your topic and the gap your study hopes to fill
- research questions and sub-questions
- a brief mention of your research method (How do you plan to collect and analyze your data?)
- your personal interest in the topic.
Conclude your introduction by giving your reader a roadmap of your proposal.
To learn more about paper introductions, check How to write Introductions .
A theoretical framework refers to the theories that you will use to interpret both your own data and the literature that has come before. Think about theories as lenses that help you look at your data from different perspectives, beyond just your own personal perspective. Think about the theories that you have come across in your courses or readings that could apply to your research topic. When writing the theoretical framework, include
- A description of where the theories come from (original thinkers), their key components, and how they have developed over time.
- How you plan to use the theories in your study / how they apply to your topic.
The literature review section should help you identify topics or issues that will help contextualize what the research has/hasn’t found and discussed on the topic so far and convince your reader that your proposed study is important. This is where you can go into more detail on the gap that your study hopes to fill. Ultimately, a good literature review helps your reader learn more about the topic that you have chosen to study and what still needs to be researched
To learn more about literature reviews check What is a Literature Review .
The methods section should briefly explain how you plan to conduct your study and why you have chosen a particular method. You may also include
- your overall study design (quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods) and the proposed stages
- your proposed research instruments (e.g. surveys, interviews)
- your proposed participant recruitment channels / document selection criteria
- a description of your proposed study participants (age, gender, etc.).
- how you plan to analyze the data.
You should cite relevant literature on research methods to support your choices.
The conclusion section should include a short summary about the implications and significance of your proposed study by explaining how the possible findings may change the ways educators and/or stakeholders address the issues identified in your introduction.
Depending on the assignment instructions, the conclusion can also highlight next steps and a timeline for the research process.
To learn more about paper conclusions, check How to write Conclusions .
List all references you used and format them according to APA style. Make sure that everything in your reference list is cited in the paper, and every citation in your paper is in your reference list.
To learn more about writing citations and references, check Citations & APA .
These are detailed guidelines on how to prepare a quantitative research proposal. Adapted from the course APD2293 “Interpretation of Educational Research”. These guidelines are hyperlinked in the following Resource Page:
Related Resource Pages on ASH
- What is a Literature Review?
- How to Prepare a Literature Review
- How to Understand & Plan Assignments
- Citations and APA Style
- How to Integrate Others' Research into your Writing
- How to Write Introductions
- How to Write Conclusions
Additional Resources
- Writing a research proposal– University of Southern California
- Owl Purdue-Graduate-Specific Genres-Purdue University
- 10 Tips for Writing a research proposal – McGill University
On Campus Services
- Book a writing consultation (OSSC)
- Book a Research Consultation (OISE Library)
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
10 Helpful Steps for Writing a Graduate Research Proposal
The road to obtain a graduate degree is unquestionably long. But we have ten incredibly helpful steps for writing your graduate research proposal. When you finally reach your destination, it will all be worthwhile.
As a graduate student, when you start your journey, you must write, present and defend a graduate research proposal in front of a committee of professors, also known as a graduate advisory committee.
A research proposal is usually short, with only fewer than ten pages, but it has to cover the proposed research in detail. After the committee approves it, you should follow the research plan explained in the research proposal to complete your research project.

Figure 1. The typical timeline in graduate school.
Why is it important to write a research proposal?
There are eight major reasons for graduate students to write a research proposal in graduate school:
- It's required by the graduate school before performing research.
- Students become more familiar with the research project
- They develop research skills and academic writing skills.
- Students develop literature review skills.
- Students learn how to identify the research problem, objective, research questions and hypothesis.
- They learn to explore different methods to collect and analyze data, and to select the most appropriate methods for solving research problems.
- They learn to design research experiments based on logical and chronological steps.
- The process nurtures critical thinking and logical reasoning skills.
What to include in a research proposal
The common elements to include in a good research proposal are:
- Title : The title of a research proposal should be clear and brief.
- Introduction : This part contains the background information of the proposed study leading to the research problem.
- Statement of purpose : This element should include the research objectives.
- Literature review : It should include an overview of findings from the previous studies, the gaps in the previous studies and the findings from a preliminary study.
- Research questions and hypothesis : This includes the research questions and hypothesis.
- Methodology : This element contains a full description of the research procedures, possible problems and alternatives strategies.
- The significance and impact of the study : This part shows how the proposed research will contribute to the field of study.
The 10 steps to writing an incredible research proposal
Below are ten steps for writing a research proposal:
1.Choose a research topic and develop a working title
Having a strong interest in your research topic will certainly help you to keep going when the journey becomes more challenging. The research topic is the subject of your research, which is a part of a broader field of study.
When you pick a research topic, find a topic that is not too narrow nor too broad. You can limit your topic, for example, by focusing on a certain treatment, population group, species, geographical area, period, methodology, or other specific factors.

After selecting a research topic, develop a working title to help you focus on your topic. As you write the proposal, you can keep changing the working title to formulate the perfect title.
2.Perform a literature review
The next step is to conduct a literature review. This step is important because when you write out the background information and knowledge gaps in your topic area, it will help you become more familiar with your research topic.
In addition, performing a literature review will direct you to a research problem . A research problem is a specific area of concern serving as the focus of your proposed research.
When performing a literature review, a graduate student can also discover some ideas for designing their research plan.
To help you conduct a literature review, answer the following questions below:
What have others done so far to solve the research problem?
Some helpful steps to answer this question:
- Understand the experimental designs from previous studies to help you design your own research experiments.
- Learn about appropriate sample sizes, data collection, and statistical analyses from previous studies.
- Investigate and make a list the reagents and equipment you’ll possibly need for your research.
- Learn the research questions, the findings, the impact and the significance of previous studies.
- Find out about any ethical concerns.
What additional studies are still needed to solve the research problem?
- Pay attention to the strength and limitation part of the discussion section of scientific articles. From this part, make notes about the limitations of previous studies to give you an idea about a potential research problem.
- Read the suggestions for future research part of scientific articles. That can serve as a call to action for you to solve those unanswered questions from previous studies.

3.Write an introduction
The introduction of your research proposal builds a framework for the research. This framework is the structure that supports your study and contains the background information. Its function is similar to the role of a foundation in supporting a building—if it is weak, a building will fall apart. Likewise, if your research lacks a strong background as a framework, it’s hard for others to see why it matters.
Writing your introduction can feel a little overwhelming. Where do you begin? How do you know you’re not missing anything?
You might want to read over our article:
How to Write an Effective Introduction Section of a Scientific Article
While the article is more specific to the introduction section of a formal research paper, there are some parts and tips you might find helpful.
4. Write research objectives or aims
In the next step, include research objectives or aims in the research proposal. A research objective is a goal you want to achieve in your research project ( Al-Riyami, 2008 ). Your research objectives must have a strong connection with your research problem.
When developing research objectives, identify all variables associated with the research problem. A variable in the research is a characteristic that you manipulate or observe in your experiment.
There are different types of variables, including an independent variable and dependent variable (Al-Riyami, 2008). An independent variable is a variable you can change in your experiment, whereas a dependent variable is a variable you observe in response to the independent variable. After identifying the variables, connect them to the research objective.
An example of a research objective: to determine the effect of different doses of a novel antibiotic X on the growth rate of some resistant bacterial strains . In this example, the independent variable is the treatment (the different doses of antibiotic X), and the dependent variable is the growth rate of some bacterial strains.

5.State a research question
The next step is to identify a research question. A research question is the key question you want to answer in your proposed study ( Farrugia et al ., 2010 ). A research project can contain several research questions.
Keep in mind that your research question must meet the criteria of a good research question, including specific, feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant (Farrugia et al ., 2010).
In term of feasibility, use current methods and technology to answer the question during your limited time in the graduate school.
An example of a research question : What doses of the antibiotic X are effective to inhibit the growth of some resistant bacterial strains?

6.Formulate a research hypothesis
After developing the research objectives and question, the next step is to formulate a research hypothesis. A research hypothesis is a statement of a possible research outcome.
Some criteria of a good hypothesis ( Prasad et al., 2010 ; Al-Riyami, 2008):
- Logical, precise, and clear
- Testable with research experiments
- Makes a prediction about the relationship between variables
An example of a research hypothesis: The new antibiotic X will significantly prevent the growth of some resistant bacterial strains.

7.Explain research methods
The methodology section containing proposed experimental procedures is required for a research proposal. This section has the detailed plan to solve the research problem. It also reflects the research questions and hypothesis.
After reviewing the credibility and validity of your research methods, your advisory committee will make a decision about the fate of your proposed study. Therefore, when writing the methodology section, keep in mind that others should be able to follow each step in the research design to perform the same experiment.
In this section, you should include these following key points:
- Experimental design : This is the research strategy you choose to solve your problem.
- Samples : It contains the description about the samples for each group of treatment in the proposed study.
- Sample size : This information is important to make sure your sample size is sufficient.
- Materials : It contains the reagents and chemicals needed in the proposed study.
- Equipment : This has the list of equipment needed for the proposed study.
- Protocols of data collection : It contains the procedures needed before collecting your data.
- Ethical issues and consent forms : You may need to include these if your proposed studies will need human participants.
- Data analysis : This part should include the steps to analyze the data.
- Gantt chart : This chart contains tasks in each research project with the timeline for each task.
8.Include potential problems and alternative strategies
When performing your study, you may encounter potential problems. Therefore, include some of the possible problems that may occur during your study and the potential solution for them. By doing so, you can use your backup plan to solve each potential problem when the problems actually occurs.
9.Conduct and include a preliminary study
Perform and include the findings from a preliminary study in your research proposal. A preliminary study is a small-scale pilot study, conducted to test the experimental design ahead of time and increase the likelihood of success. By including the findings from a preliminary study, your advisory committee can visualize and assess the feasibility of your large-scale study.
10.State the potential impact and significance
In the last paragraph of your research proposal, include the potential impact and significance of your proposed study.
The potential impact of your study means the changes that your proposed research would make. These changes can be positive or negative, immediate or long-term, and direct or indirect.
Whereas, the potential significance of your study means the contribution that your proposed research would make. For example, you can explain its contribution to the knowledge in your field of study.
After putting it all together, evaluate the entire proposal to make sure it is strong and well written.
Al-Riyami, A. (2008). How to prepare a Research Proposal. Oman Medical Journal, 23(2), 66–69. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC32824...
Benedetti, A. (n.d.). Research Guides: Advanced Research Methods: Writing a Research Proposal. Guides.library.ucla.edu. Retrieved March 17, 2021, from https://guides.library.ucla.edu/c.php?g=180334&p=1289236.
Crawford, L. (2020). LITERATURE-BASED DEFINITIONS OF CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS. https://us.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-assets/105274_book_item_105274.pdf.
Farrugia, P., Petrisor, B. A., Farrokhyar, F., & Bhandari, M. (2010). Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian Journal of Surgery. Journal Canadien de Chirurgie, 53(4), 278–281. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC29120...
How to choose a research area. (2016, April 8). ASCB. https://www.ascb.org/careers/choose-research-area/
How to Select a Research Topic | University of Michigan-Flint. (2019). Umflint.edu; UM-Flint. https://www.umflint.edu/library/how-select-research-topic.
How To Write a Proposal | Science & Quantitative Reasoning. (n.d.). Science.yalecollege.yale.edu. Retrieved March 17, 2021, from https://science.yalecollege.yale.edu/fellowships/how-write-proposal.
Jacobs, R. L. (2013). Developing a dissertation research problem: A guide for doctoral students in human resource development and adult education. New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development, 25(3), 103–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/nha3.20034.
Kivunja, C. (2018). Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field. International Journal of Higher Education, 7(6), 44. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijhe.v7n6p44.
LibGuides: Writing a Research Proposal: Parts of a Proposal. (2017). Illinois.edu. https://guides.library.illinois.edu/c.php?g=504643&p=3454882.
LibGuides: Research Process: Finding a Research Topic. (2019). Libguides.com. https://ncu.libguides.com/researchprocess/researchtopic.
LibGuides: Research Process: Literature Gap and Future Research. (2012). Libguides.com. https://ncu.libguides.com/researchprocess/literaturegap.
Pajares, F. (n.d.). THE ELEMENTS OF A PROPOSAL. https://www.uky.edu/~eushe2/Pajares/ElementsOfaProposal.pdf.
Prasad, S., Rao, A., & Rehani, E. (2001). DEVELOPING HYPOTHESES & RESEARCH QUESTIONS DEVELOPING HYPOTHESIS AND RESEARCH QUESTIONS. https://www.public.asu.edu/~kroel/www500/hypothesi...
Shardlow, M., Batista-Navarro, R., Thompson, P., Nawaz, R., McNaught, J., & Ananiadou, S. (2018). Identification of research hypotheses and new knowledge from scientific literature. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-018-0639-1
Steps in Developing a Research Proposal. Open.lib.umn.edu; University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing edition, 2015. This edition adapted from a work originally produced in 2010 by a publisher who has requested that it not receive attribution. https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter...
Vining, S. (2019, July 22). Dissertation Proposal | Genetics and Genomics. https://genetics.mcb.uconn.edu/dissertation-propos...
Writing a Research Plan. (2017, December 11). Science | AAAS. https://www.sciencemag.org/careers
Related Articles

The road to obtain a graduate degree is unquestionably long. But we have ten incredibly helpful step...

Guide to Writing the Results and Discussion Sections of a Scientific Article
A quality research paper has both the qualities of in-depth research and good writing (Bordage, 200...

Building a Clear Path and Finishing Graduate School Even When You’re Ready to Give Up
Obtaining a graduate degree can be an arduous, long, and unpredictable journey. Sometimes when this...

How to Master Collaboration Skills in the Graduate School
It’s common for researchers to collaborate in science. By doing so, scientists can share expertise,...
Join our list to receive promos and articles.

- Competent Cells
- Lab Startup
- Z')" data-type="collection" title="Products A->Z" target="_self" href="/collection/products-a-to-z">Products A->Z
- GoldBio Resources
- GoldBio Sales Team
- GoldBio Distributors
- Duchefa Direct
- Sign up for Promos
- Terms & Conditions
- ISO Certification
- Agarose Resins
- Antibiotics & Selection
- Biochemical Reagents
- Bioluminescence
- Buffers & Reagents
- Cell Culture
- Cloning & Induction
- Competent Cells and Transformation
- Detergents & Membrane Agents
- DNA Amplification
- Enzymes, Inhibitors & Substrates
- Growth Factors and Cytokines
- Lab Tools & Accessories
- Plant Research and Reagents
- Protein Research & Analysis
- Protein Expression & Purification
- Reducing Agents
- GoldBio Merch & Collectibles
- {{item.title}} {{item.title}} 0" aria-label="Find options under this page" @click="mobchildshow(true, item.title)" class="more-menu">
- {{subitem.title}}
Writing a research proposal
How to write a research proposal.
For many subjects, writing a research proposal is a key part of your postgraduate research degree application. This is your opportunity to demonstrate your knowledge and how you want to contribute to the subject.
We use the proposal to match your interest with an appropriate supervisor to make sure you have the best support during your degree. We are looking for originality and relevance when assessing the overall quality of your application, including your suitability for this level of study.
We highly recommend that you explore which academic researchers are working in your subject area and contact them first with any questions, this is a good opportunity to firm up your ideas, further explore the topic and talk with others in your field.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal is a concise and coherent document, usually between 1500 – 2000 words, maximum 4 x A4 pages. You should outline your proposed research project, why it is of relevance (rationale), what research questions are you going to ask, what you hope to achieve (aims and objectives) and how you plan to carry out your research (methodology).
Step-by-step
This page is your comprehensive guide to writing a research proposal and will cover seven key elements of a proposal:
Working title
You should include a title for your thesis in the proposal.
Your title may change as you further your research, but at this stage it's important to state succinctly what your research will cover.
Introduction
Briefly identify your idea, what is your ‘research question’?
It could be the theory you want to test, or a more open question. It would be useful to give examples, 3-5 research questions from recently completed PhDs in a relevant field. You should discuss the context around your research topic, such as current debates and issues. The important thing here is that you introduce your research project with clarity and in a way that stimulates your reader’s interest.
Demonstrate the significance of your research project.
To do this, explain why your research is important, what makes it original and how it will contribute to existing knowledge within its field.
Aims and objectives
What are you hoping to achieve with your research?
Try and produce four or five bullet points of objectives for each aim, which demonstrate your understanding of how to meet your research aims. You can use the SMART acronym to support you in creating objectives, which involves making your objectives: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time specific.
Literature Review
Demonstrate your knowledge and awareness of relevant literature
A literature review is a discussion and evaluation of academic literature or a relevant body of knowledge (for practice-based research). You should use this section of your proposal to show that you are familiar with work in your chosen topic area and that your research will contribute something new and/or meaningful to it.
Methodology
Explain how you plan to carry out your research
The methodology section of your research proposal is where you explain how you plan to carry out your research. This should include the research techniques and methods you will use, why these are most appropriate and how you will implement them. You should also include a discussion of the research strategy (general approach) you will adopt, with appropriate justification, including the analytical approach. The section should also contain the range of research findings that will be gathered from the research and how you will analyse or evaluate this. For practice based research, include how will your portfolio of artefacts, code, software, compositions, computer games etc. articulate the originality of your research?
Reference all the materials you used in the preparation your proposal
You may also list references that you didn't directly draw upon, to demonstrate awareness of literature relating to your proposed material.
Support from academic staff in drafting your research proposal
Your research proposal will be read by academics with an interest in your field of research. You are therefore encouraged to contact members of academic staff informally prior to submitting your application to discuss to your research proposal. This can often speed up the applications process, as you can identify the member(s) of staff you have spoken to on your research degree application form.
Use the Huddersfield Research Portal to browse academic staff profiles and search using key words to find staff members who share your research interests.
Changing aspects of your research proposal after gaining a place as a research student
Your research proposal is your starting point, and we understand that as your idea develop s , your proposed research is likely to change. As such, you will not be obliged to adhere to the specifics of your proposal if you are offered a place as a research degree candidate at Huddersfield. However, as the proposal is the foundation of your working relationship with your supervisor(s), you will need to discuss any changes with them first.
Useful tips for writing a research proposal
- Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to be overly complicated.
- Share your proposal: Ask someone you trust (a friend, family member, tutor) to read your proposal and provide some feedback. Do they understand what your research is about? Do they think your aims and objectives are achievable? Does your research engage them?
- Align your proposal topic with University research themes: Whilst it is important to choose a research topic that you are passionate about, your proposal will be assessed (in part) on its fit with our University research themes. You therefore need to choose a topic which aligns with topics of interest to the University or academic school you hoping to work within and make it clear how your project matches up with them.
- Be realistic in your proposal: Your proposal is assessed not only on its quality, originality and fit with our research themes but also the likelihood of completion, so make sure that the scope of your research project is reasonable and realistic .
- Take your time when writing your proposal: There are a lot of elements to a high-quality research proposal, so take the time to ensure that you meet them all. At the University of Huddersfield, there are three opportunities for enrolling onto a research degree programme during the academic year (October, January, and April), meaning less time pressure when working on your proposal and application.
Once you have written your proposal, what next?
Once you have written your research proposal you will need to complete an application form. Look at our how to apply webpage for more information.

How to apply for a research degree
Our step-by-step guide will help you to make the most out of your application for a research degree

Scholarships and funding
Explore our funding options, including scholarships and Doctoral Loans.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.23(2); 2008 Apr

How to prepare a Research Proposal
Health research, medical education and clinical practice form the three pillars of modern day medical practice. As one authority rightly put it: ‘Health research is not a luxury, but an essential need that no nation can afford to ignore’. Health research can and should be pursued by a broad range of people. Even if they do not conduct research themselves, they need to grasp the principles of the scientific method to understand the value and limitations of science and to be able to assess and evaluate results of research before applying them. This review paper aims to highlight the essential concepts to the students and beginning researchers and sensitize and motivate the readers to access the vast literature available on research methodologies.
Most students and beginning researchers do not fully understand what a research proposal means, nor do they understand its importance. 1 A research proposal is a detailed description of a proposed study designed to investigate a given problem. 2
A research proposal is intended to convince others that you have a worthwhile research project and that you have the competence and the work-plan to complete it. Broadly the research proposal must address the following questions regardless of your research area and the methodology you choose: What you plan to accomplish, why do you want to do it and how are you going to do it. 1 The aim of this article is to highlight the essential concepts and not to provide extensive details about this topic.
The elements of a research proposal are highlighted below:
1. Title: It should be concise and descriptive. It must be informative and catchy. An effective title not only prick’s the readers interest, but also predisposes him/her favorably towards the proposal. Often titles are stated in terms of a functional relationship, because such titles clearly indicate the independent and dependent variables. 1 The title may need to be revised after completion of writing of the protocol to reflect more closely the sense of the study. 3
2. Abstract: It is a brief summary of approximately 300 words. It should include the main research question, the rationale for the study, the hypothesis (if any) and the method. Descriptions of the method may include the design, procedures, the sample and any instruments that will be used. 1 It should stand on its own, and not refer the reader to points in the project description. 3
3. Introduction: The introduction provides the readers with the background information. Its purpose is to establish a framework for the research, so that readers can understand how it relates to other research. 4 It should answer the question of why the research needs to be done and what will be its relevance. It puts the proposal in context. 3
The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1
The importance of the statement of the research problem 5 : The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology, work plan and budget etc). It is an integral part of selecting a research topic. It will guide and put into sharper focus the research design being considered for solving the problem. It allows the investigator to describe the problem systematically, to reflect on its importance, its priority in the country and region and to point out why the proposed research on the problem should be undertaken. It also facilitates peer review of the research proposal by the funding agencies.
Then it is necessary to provide the context and set the stage for the research question in such a way as to show its necessity and importance. 1 This step is necessary for the investigators to familiarize themselves with existing knowledge about the research problem and to find out whether or not others have investigated the same or similar problems. This step is accomplished by a thorough and critical review of the literature and by personal communication with experts. 5 It helps further understanding of the problem proposed for research and may lead to refining the statement of the problem, to identify the study variables and conceptualize their relationships, and in formulation and selection of a research hypothesis. 5 It ensures that you are not "re-inventing the wheel" and demonstrates your understanding of the research problem. It gives due credit to those who have laid the groundwork for your proposed research. 1 In a proposal, the literature review is generally brief and to the point. The literature selected should be pertinent and relevant. 6
Against this background, you then present the rationale of the proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing.
4. Objectives: Research objectives are the goals to be achieved by conducting the research. 5 They may be stated as ‘general’ and ‘specific’.
The general objective of the research is what is to be accomplished by the research project, for example, to determine whether or not a new vaccine should be incorporated in a public health program.
The specific objectives relate to the specific research questions the investigator wants to answer through the proposed study and may be presented as primary and secondary objectives, for example, primary: To determine the degree of protection that is attributable to the new vaccine in a study population by comparing the vaccinated and unvaccinated groups. 5 Secondary: To study the cost-effectiveness of this programme.
Young investigators are advised to resist the temptation to put too many objectives or over-ambitious objectives that cannot be adequately achieved by the implementation of the protocol. 3
5. Variables: During the planning stage, it is necessary to identify the key variables of the study and their method of measurement and unit of measurement must be clearly indicated. Four types of variables are important in research 5 :
a. Independent variables: variables that are manipulated or treated in a study in order to see what effect differences in them will have on those variables proposed as being dependent on them. The different synonyms for the term ‘independent variable’ which are used in literature are: cause, input, predisposing factor, risk factor, determinant, antecedent, characteristic and attribute.
b. Dependent variables: variables in which changes are results of the level or amount of the independent variable or variables.
Synonyms: effect, outcome, consequence, result, condition, disease.
c. Confounding or intervening variables: variables that should be studied because they may influence or ‘mix’ the effect of the independent variables. For instance, in a study of the effect of measles (independent variable) on child mortality (dependent variable), the nutritional status of the child may play an intervening (confounding) role.
d. Background variables: variables that are so often of relevance in investigations of groups or populations that they should be considered for possible inclusion in the study. For example sex, age, ethnic origin, education, marital status, social status etc.
The objective of research is usually to determine the effect of changes in one or more independent variables on one or more dependent variables. For example, a study may ask "Will alcohol intake (independent variable) have an effect on development of gastric ulcer (dependent variable)?"
Certain variables may not be easy to identify. The characteristics that define these variables must be clearly identified for the purpose of the study.
6. Questions and/ or hypotheses: If you as a researcher know enough to make prediction concerning what you are studying, then the hypothesis may be formulated. A hypothesis can be defined as a tentative prediction or explanation of the relationship between two or more variables. In other words, the hypothesis translates the problem statement into a precise, unambiguous prediction of expected outcomes. Hypotheses are not meant to be haphazard guesses, but should reflect the depth of knowledge, imagination and experience of the investigator. 5 In the process of formulating the hypotheses, all variables relevant to the study must be identified. For example: "Health education involving active participation by mothers will produce more positive changes in child feeding than health education based on lectures". Here the independent variable is types of health education and the dependent variable is changes in child feeding.
A research question poses a relationship between two or more variables but phrases the relationship as a question; a hypothesis represents a declarative statement of the relations between two or more variables. 7
For exploratory or phenomenological research, you may not have any hypothesis (please do not confuse the hypothesis with the statistical null hypothesis). 1 Questions are relevant to normative or census type research (How many of them are there? Is there a relationship between them?). Deciding whether to use questions or hypotheses depends on factors such as the purpose of the study, the nature of the design and methodology, and the audience of the research (at times even the outlook and preference of the committee members, particularly the Chair). 6
7. Methodology: The method section is very important because it tells your research Committee how you plan to tackle your research problem. The guiding principle for writing the Methods section is that it should contain sufficient information for the reader to determine whether the methodology is sound. Some even argue that a good proposal should contain sufficient details for another qualified researcher to implement the study. 1 Indicate the methodological steps you will take to answer every question or to test every hypothesis illustrated in the Questions/hypotheses section. 6 It is vital that you consult a biostatistician during the planning stage of your study, 8 to resolve the methodological issues before submitting the proposal.
This section should include:
Research design: The selection of the research strategy is the core of research design and is probably the single most important decision the investigator has to make. The choice of the strategy, whether descriptive, analytical, experimental, operational or a combination of these depend on a number of considerations, 5 but this choice must be explained in relation to the study objectives. 3
Research subjects or participants: Depending on the type of your study, the following questions should be answered 3 , 5
- - What are the criteria for inclusion or selection?
- - What are the criteria for exclusion?
- - What is the sampling procedure you will use so as to ensure representativeness and reliability of the sample and to minimize sampling errors? The key reason for being concerned with sampling is the issue of validity-both internal and external of the study results. 9
- - Will there be use of controls in your study? Controls or comparison groups are used in scientific research in order to increase the validity of the conclusions. Control groups are necessary in all analytical epidemiological studies, in experimental studies of drug trials, in research on effects of intervention programmes and disease control measures and in many other investigations. Some descriptive studies (studies of existing data, surveys) may not require control groups.
- - What are the criteria for discontinuation?
Sample size: The proposal should provide information and justification (basis on which the sample size is calculated) about sample size in the methodology section. 3 A larger sample size than needed to test the research hypothesis increases the cost and duration of the study and will be unethical if it exposes human subjects to any potential unnecessary risk without additional benefit. A smaller sample size than needed can also be unethical as it exposes human subjects to risk with no benefit to scientific knowledge. Calculation of sample size has been made easy by computer software programmes, but the principles underlying the estimation should be well understood.
Interventions: If an intervention is introduced, a description must be given of the drugs or devices (proprietary names, manufacturer, chemical composition, dose, frequency of administration) if they are already commercially available. If they are in phases of experimentation or are already commercially available but used for other indications, information must be provided on available pre-clinical investigations in animals and/or results of studies already conducted in humans (in such cases, approval of the drug regulatory agency in the country is needed before the study). 3
Ethical issues 3 : Ethical considerations apply to all types of health research. Before the proposal is submitted to the Ethics Committee for approval, two important documents mentioned below (where appropriate) must be appended to the proposal. In additions, there is another vital issue of Conflict of Interest, wherein the researchers should furnish a statement regarding the same.
The Informed consent form (informed decision-making): A consent form, where appropriate, must be developed and attached to the proposal. It should be written in the prospective subjects’ mother tongue and in simple language which can be easily understood by the subject. The use of medical terminology should be avoided as far as possible. Special care is needed when subjects are illiterate. It should explain why the study is being done and why the subject has been asked to participate. It should describe, in sequence, what will happen in the course of the study, giving enough detail for the subject to gain a clear idea of what to expect. It should clarify whether or not the study procedures offer any benefits to the subject or to others, and explain the nature, likelihood and treatment of anticipated discomfort or adverse effects, including psychological and social risks, if any. Where relevant, a comparison with risks posed by standard drugs or treatment must be included. If the risks are unknown or a comparative risk cannot be given it should be so stated. It should indicate that the subject has the right to withdraw from the study at any time without, in any way, affecting his/her further medical care. It should assure the participant of confidentiality of the findings.
Ethics checklist: The proposal must describe the measures that will be undertaken to ensure that the proposed research is carried out in accordance with the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki on Ethical Principles for Medical research involving Human Subjects. 10 It must answer the following questions:
- • Is the research design adequate to provide answers to the research question? It is unethical to expose subjects to research that will have no value.
- • Is the method of selection of research subjects justified? The use of vulnerable subjects as research participants needs special justification. Vulnerable subjects include those in prison, minors and persons with mental disability. In international research it is important to mention that the population in which the study is conducted will benefit from any potential outcome of the research and the research is not being conducted solely for the benefit of some other population. Justification is needed for any inducement, financial or otherwise, for the participants to be enrolled in the study.
- • Are the interventions justified, in terms of risk/benefit ratio? Risks are not limited to physical harm. Psychological and social risks must also be considered.
- • For observations made, have measures been taken to ensure confidentiality?
Research setting 5 : The research setting includes all the pertinent facets of the study, such as the population to be studied (sampling frame), the place and time of study.
Study instruments 3 , 5 : Instruments are the tools by which the data are collected. For validated questionnaires/interview schedules, reference to published work should be given and the instrument appended to the proposal. For new a questionnaire which is being designed specifically for your study the details about preparing, precoding and pretesting of questionnaire should be furnished and the document appended to the proposal. Descriptions of other methods of observations like medical examination, laboratory tests and screening procedures is necessary- for established procedures, reference of published work cited but for new or modified procedure, an adequate description is necessary with justification for the same.
Collection of data: A short description of the protocol of data collection. For example, in a study on blood pressure measurement: time of participant arrival, rest for 5p. 10 minutes, which apparatus (standard calibrated) to be used, in which room to take measurement, measurement in sitting or lying down position, how many measurements, measurement in which arm first (whether this is going to be randomized), details of cuff and its placement, who will take the measurement. This minimizes the possibility of confusion, delays and errors.
Data analysis: The description should include the design of the analysis form, plans for processing and coding the data and the choice of the statistical method to be applied to each data. What will be the procedures for accounting for missing, unused or spurious data?
Monitoring, supervision and quality control: Detailed statement about the all logistical issues to satisfy the requirements of Good Clinical Practices (GCP), protocol procedures, responsibilities of each member of the research team, training of study investigators, steps taken to assure quality control (laboratory procedures, equipment calibration etc)
Gantt chart: A Gantt chart is an overview of tasks/proposed activities and a time frame for the same. You put weeks, days or months at one side, and the tasks at the other. You draw fat lines to indicate the period the task will be performed to give a timeline for your research study (take help of tutorial on youtube). 11
Significance of the study: Indicate how your research will refine, revise or extend existing knowledge in the area under investigation. How will it benefit the concerned stakeholders? What could be the larger implications of your research study?
Dissemination of the study results: How do you propose to share the findings of your study with professional peers, practitioners, participants and the funding agency?
Budget: A proposal budget with item wise/activity wise breakdown and justification for the same. Indicate how will the study be financed.
References: The proposal should end with relevant references on the subject. For web based search include the date of access for the cited website, for example: add the sentence "accessed on June 10, 2008".
Appendixes: Include the appropriate appendixes in the proposal. For example: Interview protocols, sample of informed consent forms, cover letters sent to appropriate stakeholders, official letters for permission to conduct research. Regarding original scales or questionnaires, if the instrument is copyrighted then permission in writing to reproduce the instrument from the copyright holder or proof of purchase of the instrument must be submitted.

- Planet Earth
- Strange News
How To Write A Science Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal . This tutorial is designed for graduate students who are required to submit a research proposal as a condition of their candidature or who wish to write one for their own purposes.
- What is the purpose of a research proposal?
- Which skills are required for a research proposal?
Zeroing in on the target
IntroductionThis tutorial is designed for graduate students who are required to submit a research proposal as a condition of their candidature or who wish to write one for their own purposes. The purpose of this tutorial is to help you develop an approach for writing a clear and focused research proposal. We will begin by looking at the broad purpose and requirements of proposals. We will then break down the research proposal into its core components and examine them individuallyWhat is the purpose of a research proposal? The purpose of a research proposal can be summarised as follows:To propose a research project that will result in a significant contribution to knowledge. To formulate a detailed plan of the project including methodological approach and theoretical framework. To ensure that the proposed research is achievable within the required time and with the available resources. To demonstrate that you have adequate expertise and experience to undertake the project. Even if the completion of a research proposal is not a requirement of your candidature, it is a good idea to write one.
Video advice: How to Write a Successful Research Proposal
Learn step-by-step how to create a successful research proposal.

Video advice: How to write a research proposal? Learn from scratch.
What is a research proposal, its importance, components. How to write a great research proposal? some important things to remember and tips to increase chances of selection.

Video advice: How To Write A Strong Research Proposal
PROOFREADING / ACADEMIC ESSAY SERVICE (£/$)

What is scientific research proposal?
A research proposal has three main points: 1) Explanation of proposed research (what will be done) 2) Methods and techniques to be employed (how it will be done) 3) Novelty and/or importance of the study (why it should be done)
What are the parts of a science research proposal?
Some main components to a research proposal include title, abstract, , introduction, literature review, method, discussion, and budget .
What is research proposal with example?
A research proposal is a simply a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (i.e. your research topic), why it's worth researching (i.e. your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (i.e. your practical approach).
How do you write a research proposal sample?
When writing your proposal it is important to:
- Highlight its originality or significance.
- Explain how it develops or challenges existing knowledge of your subject.
- Identify the importance of your proposed research.
- Demonstrate why you are the correct person to undertake this research project.
How do you write a proposal example?
How to write a proposal letter
- Introduce yourself and provide background information.
- State your purpose for the proposal.
- Define your goals and objectives.
- Highlight what sets you apart.
- Briefly discuss the budget and how funds will be used.
- Finish with a call to action and request a follow-up.
Related Articles:
- How To Write Research Proposal For Phd In Biotechnology
- How To Write A Robotics Project Proposal
- How To Write Abstract For Science Research Paper
- How To Evaluate The Innovation Of A Research Proposal
- How To Write A Research Paper Biology
- Unsettled Science Behind Proposal to Lift Grey Wolf Protections, Panel States
Science Journalist
Science atlas, our goal is to spark the curiosity that exists in all of us. We invite readers to visit us daily, explore topics of interest, and gain new perspectives along the way.
You may also like

Which Is A Statement Of The Second Law Of Thermodynamics

Can You Plug A Space Heater Into An Extension Cord

What Is The Oldest Living Thing On Earth
Add comment, cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent discoveries

How To Write A Science Report High School

How Simplicity Can Drive Innovation

What Is The Definition Of A Half-Life Geology

What Does Current In Science Mean
- Animals 3041
- Astronomy 8
- Biology 2281
- Chemistry 482
- Culture 1333
- Health 8466
- History 2152
- Physics 913
- Planet Earth 3239
- Science 2158
- Strange News 1230
- Technology 3625
Random fact

Hubble Peers at 10 Billion Years Old Globular Cluster NGC 6752
- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Medical Sciences Guides
Scientific Writing
- Getting Started
- Author Profile
Resources To Support Scientific Writing
- E-books / Print
- Citation Help
- Lit Reviews
- Websites & Tools
Health Professions
The books listed here are available through the library.
General Sciences
A citation style is the syntax in which the citation information is formatted. They vary from discipline to discipline.
Get citation style handouts/help
The following are style manuals which guide writers both in formatting citations and the text for a specific style.
Websites Helpful on How to Write Literature Reviews:
Systematic Reviews : find training/help on conducting systematic reviews
Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review : brief article from PLOS
Writing an Evidence-Based Clinical Literature Review : guidelines from American Family Physician
Literature Reviews: An Overview (video tutorial from NC State University Libraries)
Books (both e-book and print) Helpful on How to Write Literature Reviews:
- AI-Based Literature Review Tools by Daniel Xiao Last Updated Sep 4, 2024 184298 views this year
Need some help with scientific writing? The following links may provide the tips you need, whether you're writing as a student or a scholar:
- AuthorAID Provides networking, mentoring, resources and training for researchers, especially of developing countries, in publishing their work
- AuthorAID's Resource Library PowerPoint presentations, articles, books, videos, links on research writing
Duke University's Graduate School: Scientific Writing Resource : Includes lessons, examples and worksheets on best practices in scientific writing
- F1000 Research: Open for Science Open access publishing platform of articles, posters and data offering transparent peer review and comments
- Instructions to Authors University of Toledo provides links to instructions for authors in more than 6,000 Health/Life Science journals
- Journal/Author Name Estimator (JANE) Paste in your article's title or abstract for suggestions as to which (biomedical) journal to submit for publication
- National Association of Science Writers: articles and resources on best practices in scientific writing
- Last Updated: Aug 29, 2024 4:47 PM
- URL: https://tamu.libguides.com/scientificwriting
DAI is proud to announce a new partnership with Beckman Coulter. If you are looking for a centrifuge, check out what we have. View Centrifuges

- Support & Sales: 800-816-8388
- Find Your Rep
Your Guide to Writing Research Funding Applications

- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Grant funding is critical for all types of research. Without it, many projects wouldn’t even get off the ground, so what’s the key to securing the right funding? The not-so-simple answer: a stellar grant application.
If you’ve ever wondered how to write a successful proposal — or if you’re looking for some new resources and a few refresher tips — we have the right resource for you. In this comprehensive guide, we explore all types of grant funding opportunities, provide a step-by-step proposal breakdown and offer insider tips for ultimate grant application success.
The information in this guide was provided by Mike Hendrickson, Project Manager at BrainXell, Inc; Dr. Shannon M. Lauberth, Associate Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics at Northwestern University; Dr. Darshan Sapkota, Assistant Professor of Biological Sciences at the University of Texas at Dallas; and Dr. Ward Tucker, Director of Research and Development at BioSentinel, Inc.
Find a Grant: What Opportunities Are Available?
This isn’t a comprehensive list, but these are the most popular types of grant funding opportunities.
National Institutes of Health (NIH)
The National Institutes of Health provides more than $32 billion each year for biomedical research funding. The NIH grants and funding opportunities page publishes opportunities daily and issues a table of contents weekly. You can also subscribe to a weekly email for updates.
National Science Foundation (NSF)
The National Science Foundation funds approximately 25% of all federally supported research in higher education. The NSF is divided into a number of specific research areas , including:
- Biological Sciences
- Computer and Information Science and Engineering
- Education and Human Resources
- Engineering
- Environmental Research and Education
- Geosciences
- Integrative Activities
- International Science and Engineering
- Mathematical and Physical Sciences
- Social, Behavioral and Economic Sciences
You can search for NSF funding opportunities here .
Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) and Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR)
SBIR and STTR grants are geared toward small U.S. businesses that are looking for funding opportunities in research or research and development “with the potential for commercialization.” Eligible businesses must be for-profit, located in the United States, and more than 50% owned and controlled by one or more U.S. citizens. The company must also have fewer than 500 employees.
Non-Federal Agencies & Foundations
Many grant opportunities are available through non-federal avenues. This is just a sample of some of the agencies and foundations that provide these types of funding opportunities.
- Alliance for Cancer Gene Therapy
- Alzheimer’s Association
- American Federation for Aging Research
- American Heart Association
- American Cancer Society
- American Chemical Society
- American Diabetes Association
- Foundation for Women’s Wellness
- March of Dimes
Early Stage Investigator Awards
An early stage investigato r is “a new investigator who has completed his or her terminal research degree or medical residency — whichever date is later — within the past 10 years and has not yet competed successfully for a substantial, competing NIH research grant.”
- American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grants
- Pew Scholar Program
- Sidney Kimmel Foundation
- NIH New & Early Stage Investigator Program
Step-By-Step Grant Proposal & Application Breakdown
Once you’ve found your grant opportunity, it’s time to take action. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Build a timeline.
There are a lot of moving parts in the application process, so the first step is to create a timeline. You want to allow yourself enough time to gather information and write the proposal without feeling rushed. Plus, you need to factor in time for editing and internal reviews. Write down the due date of the application and work backwards. Remember, it’s always best to err on the side of having too much time rather than not enough.
2. Create a robust outline.
This is the most important part of the application process, and the more detail, the better. Be specific in your questions, hypothesis, aims and goals. Detail your experiments and expected outcomes.
3. Gather your appropriate tools and resources.
Before you begin writing, make sure you gather everything in one place. If you need to request certain documents, do so now. Create a folder on your computer that houses everything related to your grant application — and make sure to back up your files if you aren’t using Google or another cloud-based provider. It sounds like a simple reminder, but the last thing you want is to lose all your hard work.
4. Read through the application instructions carefully and don’t be afraid to ask questions. Familiarize yourself with the request, rules and requirements.
Read through everything , noting any documents you need to include. Every document that is requested must be included in the application. And if you have any questions about the process or you’re looking for clarification on a particular item, reach out to the program officer. It’s also better to ask questions as early as possible in the process.
5. Include strong preliminary data.
Even if grant requests say it is not necessary to include any data, you are unlikely to be funded if you don’t include any preliminary data. It is a major piece of any application. The stronger the data, the better shot you have of receiving funding.
6. Write, write, write!
Now it’s time to put pen to paper, so to speak. Here are some important tips to keep in mind during this important process:
- Be realistic: If you’re applying for a Phase 1 grant, it’s important to remember that Phase 1 is supposed to be “proof of concept” — in other words, not product development. Some people try to squeeze five years worth of work into one year, but you need to be realistic. Think carefully, and be modest about your objectives. If you end up applying for a Phase 2 grant, the reviewers will look at your goals and objectives for Phase 1. If you didn’t deliver then, there’s a good chance your Phase 2 proposal will be rejected.
- Tell a story. With any type of good writing, you want to build a case — in other words, tell a story. Start with an introduction that hooks the audience. Talk about the wider problem you’re hoping to explore and why you are the right person for the job. Explain your hypothesis and how you plan to tackle it.
- Include two or three specific aims. This is the heart of the grant. Again, be reasonable. Don’t bite off more than you can chew in order to seem overly ambitious. Include two or three challenging yet exciting aims (or goals) that you believe are doable in the set amount of time. Include clear objectives and clear milestones of success.
- Be mindful of your language. Be specific, informative and engaging but also concise. Use active voice and strong verbs like “determine and distinguish.” Quantify information or data.
- Don’t get too technical or use too much jargon. Remember, you know your field inside and out, but your reviewers in some cases may not. Make your application clear and readable. Write for an educated but diverse audience.
- Include preliminary data. It’s important, so it bears repeating!
- Add pictures, illustrations or graphics. No one wants to read a 15-page proposal of extremely dense text. Break up your application with a few visuals.
7. Make sure the budget matches what is allocated.
It sounds obvious, but don’t ask for more than the set budget amount. If you work at a higher education institution, you will likely work with a research office on the budget.
8. Have multiple people review your application.
Once you’ve written your grant proposal (congratulations!), you want to seek out multiple reviewers before you click submit. These reviewers should be inside your company, organization or institution, or experts in your field; you may also benefit from review by non-experts. It’s important to give your reviewers plenty of time, too. Here are some good questions to ask:
- Is the proposal clear and concise?
- Do I need more data?
- Are any parts confusing or in need of additional explanation?
- Am I telling an interesting story?
- Could I add any other visuals?
9. Give yourself enough time to familiarize yourself with the application portal — and then submit!
If you work with a research office, they will upload the application on your behalf. If you don’t, you want to make sure you familiarize yourself with the application portal before your deadline.
Insider Tips for Grant Writing Experience & Creating a Standout Application
We spoke to the experts, and here’s what they had to say:
- Talk to the program officers early and often. There are people who don’t put the time and energy into reviewing the instructions, rules and requirements of a grant application. Make sure you understand everything, and if you don’t, talk to the program officers. Remember — you don’t have to figure out everything by yourself!
- Don’t break the rules. If the application requires certain documents, make sure to include them.
- Don’t be “non-responsive.” This is grant proposal-speak for not answering a question that is asked of you. Reviewers will take note.
- Put yourself in the shoes of a reviewer. What questions will the reviewers have, and how can you answer them ahead of time? Ideally you want to address these questions with preliminary data. If you don’t have the data, it’s important to at least address those questions in your proposal — and how you plan to tackle them.
- Don’t save everything until the last minute. There’s a very good chance you heard this mantra in high school and college — and it still rings true.
- Consider hiring someone who can handle the grant application process. If you have the budget, it may be valuable to hire a person who can handle the administrative and logistical aspects of the application process. Some companies and organizations also hire part-time or full-time grant writers to handle the actual proposal writing.
- Explore all types of funding opportunities. In addition to traditional federal agencies like NIH and NSF that routinely offer grants, you should explore any internal funding opportunities for faculty and researchers. Sign up for as many email lists, newsletters and daily grant alert notifications from federal and non-federal agencies as possible. If you work in an academic setting, ask your department chair about these opportunities.
- Simultaneous submissions are allowed. It’s just illegal to accept funding from two different institutions for the same work.
Ask to help out on a grant application. Grant writing is a skill that is honed with time and experience, and the best way to get better is to practice. Review applications that your colleagues have been working on or ask them if you can help out in any way. Practice makes perfect.
- The Grant Application Writer’s Workbook: It’s one of the best tools and a resource you’ll return to again and again.
- Ask to participate in a review committee. This will give you the opportunity to see grant applications from a different perspective, which will be beneficial in your own funding quests.
- Attend grant writing workshops. This is another important way to gain insight and experience.
- Remember the big picture. As Shannon Lauberth, associate professor at Northwestern University, explains: “Remember that the exercise of writing a grant helps you to carve out clear directions for your lab.”
Grant Application Resources
This is not an exhaustive list, but here are some helpful tools and resources you may want to explore or bookmark:
- Fundamentals of the NIH Grant Process & Need to Know Resources [VIDEO]
- The Grant Application Writer’s Workbook
- NIH Grants Process Overview
- NSF Funding Search
- NIH Guide for Grants and Contracts
- SMARTS — Email alert system about funding opportunities
Specific Questions About Lab Equipment?
D.A.I. Scientific works closely with a variety of federally funded organizations, private businesses and higher education institutions to provide products and services to analytical laboratories in the pharmaceutical, educational, biotechnology and clinical industries. If you’re writing a grant application and need a budgetary quote for equipment, contact us today. Our knowledgeable experts would be happy to help.

Jamie is the regional sales manager of DAI Scientific and leads a team of 13 equipment sales consultants. His background includes 20 years of experience working with customers in academic, clinical, industrial and bio/pharma laboratories.
Jamie works with architects, engineers and lab planners to identify the correct equipment for each user’s specific needs. He also leverages his previous role as a DAI sales representative to help his sales consultants work with customers to ensure informed decisions and customer satisfaction. He stays involved in recent research by continuously attending seminars and educating himself on the products and industries he serves.
Jamie holds a bachelor’s degree in communications from the University of Wisconsin-Whitewater.
Related Posts

North Hennepin Community College
Loyola university’s new center for translational research and education, d.a.i. launches new website.

Quicksearch
- All Results
- Digital Collections
- Archives or Manuscripts
- New Arrivals
Select Data Source
Advanced Search
Limit results by, books+ search results, scientific writing and communication : papers, proposals, and presentations, available from:.

Scientific Writing : Home
- Navigating Scientific Articles
- Writing a Scientific Article
- Library Resources
- AI Tools for Academic Writing and Research

Contact a Librarian
Reserve a Librarian
Library FAQ
You can also contact us by:

What is Scientific Writing?
- Scientific writing is writing designed to communicate scientific ideas clearly and objectively. It is written by scientists for scientists and therefore contains information about complex ideas and often uses technical language specific to a certain field of research.
- Introduction
- Methods and Materials
- This page is designed to connect you to resources and tools that will aid you in reading, writing, and interpreting scientific literature. Watch the video below to get started.
Scientific Writing Basics
- Next: Navigating Scientific Articles >>
- Last Updated: Sep 6, 2024 2:42 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uwp.edu/scientificwriting
University of Wisconsin-Parkside Library | Contact Us 900 Wood Road Kenosha, WI 53141 | (262) 595-3432
How to Write Good Scientific Project Proposals: A Comprehensive Guide
- January 2013

- University of Coimbra
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Kajian Teoritis
- Dan Praktis
- Bagi Mahasiswa

- SPORTS MED ARTHROSC
- Robert E. Leach
- N Roll-Hansen
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS. A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program (GRFP)
View guidelines, important information about nsf’s implementation of the revised 2 cfr.
NSF Financial Assistance awards (grants and cooperative agreements) made on or after October 1, 2024, will be subject to the applicable set of award conditions, dated October 1, 2024, available on the NSF website . These terms and conditions are consistent with the revised guidance specified in the OMB Guidance for Federal Financial Assistance published in the Federal Register on April 22, 2024.
Important information for proposers
All proposals must be submitted in accordance with the requirements specified in this funding opportunity and in the NSF Proposal & Award Policies & Procedures Guide (PAPPG) that is in effect for the relevant due date to which the proposal is being submitted. It is the responsibility of the proposer to ensure that the proposal meets these requirements. Submitting a proposal prior to a specified deadline does not negate this requirement.
Supports fellowships for outstanding graduate students who are pursuing full-time, research-based masters and doctoral degrees in science, technology, engineering or math or STEM education.
The purpose of the NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program (GRFP) is to help ensure the quality, vitality, and diversity of the scientific and engineering workforce of the United States. The program recognizes and supports outstanding graduate students who are pursuing full-time research-based master's and doctoral degrees in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) or in STEM education. The GRFP provides three years of support over a five-year fellowship period for the graduate education of individuals who have demonstrated their potential for significant research achievements in STEM or STEM education. NSF actively encourages submission of applications from the full spectrum of diverse talent that society has to offer which includes underrepresented and underserved communities.
NSF GRFP was established to recruit and support individuals who demonstrate the potential to make significant contributions in STEM. NSF especially encourages applications from undergraduate seniors and Bachelor's degree-holders interested in pursuing research-based graduate study in STEM. First- and second-year graduate students in eligible STEM fields and degree programs are also encouraged to apply.
Program contacts
The Graduate Research Fellowship Operations Center is responsible for processing applications and responding to requests for information. General inquiries regarding the Graduate Research Fellowship Program should be made to:
Graduate Research Fellowship Operations Center, telephone: 866-NSF-GRFP, 866-673-4737 (toll-free from the US and Canada) or 202-331-3542 (international). email: [email protected]
| (866) 673-4737 |
Program events
- August 15, 2024 - Information and Intelligent Systems (IIS) Office Hours
- August 12, 2024 - DEB Virtual Office Hour: Graduate Research Fellowship Program
- July 18, 2024 - IOS Virtual Office Hour: Graduate Research Fellowship Program
- August 15, 2023 - Division of Biological Infrastructure (DBI) Virtual Office…
- August 9, 2023 - MCB Virtual Office Hour: Graduate Research Fellowship Program
Additional program resources
- Non-NSF website with comprehensive information on how to apply, eligibility, phone numbers and email addresses
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for the Graduate Research Fellowship Program
- Administrative Guide for Fellows and Coordinating Officials
- List of Fellows and Honorable Mentions
Awards made through this program
Organization(s).
- Directorate for Biological Sciences (BIO)
- Directorate for Computer and Information Science and Engineering (CISE)
- Directorate for STEM Education (EDU)
- Division of Graduate Education (EDU/DGE)
- Directorate for Engineering (ENG)
- Directorate for Geosciences (GEO)
- Directorate for Mathematical and Physical Sciences (MPS)
- Directorate for Social, Behavioral and Economic Sciences (SBE)
- Directorate for Technology, Innovation and Partnerships (TIP)
- Office of Integrative Activities (OD/OIA)
- Office of International Science and Engineering (OD/OISE)
- Open access
- Published: 04 September 2024
Insights into research activities of senior dental students in the Middle East: A multicenter preliminary study
- Mohammad S. Alrashdan 1 , 2 ,
- Abubaker Qutieshat 3 , 4 ,
- Mohamed El-Kishawi 5 ,
- Abdulghani Alarabi 6 ,
- Lina Khasawneh 7 &
- Sausan Al Kawas 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 967 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Despite the increasing recognition of the importance of research in undergraduate dental education, limited studies have explored the nature of undergraduate research activities in dental schools in the Middle East region. This study aimed to evaluate the research experience of final year dental students from three dental schools in the Middle East.
A descriptive, cross-sectional study was conducted among final-year dental students from three institutions, namely Jordan University of Science and Technology, University of Sharjah (UAE), and Oman Dental College. Participants were asked about the nature and scope of their research projects, the processes involved in the research, and their perceived benefits of engaging in research.
A total of 369 respondents completed the questionnaire. Cross-sectional studies represented the most common research type (50.4%), with public health (29.3%) and dental education (27.9%) being the predominant domains. More than half of research proposals were developed via discussions with instructors (55.0%), and literature reviews primarily utilized PubMed (70.2%) and Google Scholar (68.5%). Regarding statistical analysis, it was usually carried out with instructor’s assistance (45.2%) or using specialized software (45.5%). The students typically concluded their projects with a manuscript (58.4%), finding the discussion section most challenging to write (42.0%). The research activity was considered highly beneficial, especially in terms of teamwork and communication skills, as well as data interpretation skills, with 74.1% of students reporting a positive impact on their research perspectives.
Conclusions
The research experience was generally positive among surveyed dental students. However, there is a need for more diversity in research domains, especially in qualitative studies, greater focus on guiding students in research activities s, especially in manuscript writing and publication. The outcomes of this study could provide valuable insights for dental schools seeking to improve their undergraduate research activities.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The importance of research training for undergraduate dental students cannot be overstressed and many reports have thoroughly discussed the necessity of incorporating research components in the dental curricula [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 ]. A structured research training is crucial to ensure that dental graduates will adhere to evidence-based practices and policies in their future career and are able to critically appraise the overwhelming amount of dental and relevant medical literature so that only rigorous scientific outcomes are adopted. Furthermore, a sound research background is imperative for dental graduates to overcome some of the reported barriers to scientific evidence uptake. This includes the lack of familiarity or uncertain applicability and the lack of agreement with available evidence [ 5 ]. There is even evidence that engagement in research activities can improve the academic achievements of students [ 6 ]. Importantly, many accreditation bodies around the globe require a distinct research component with clear learning outcomes to be present in the curriculum of the dental schools [ 1 ].
Research projects and courses have become fundamental elements of modern biomedical education worldwide. The integration of research training in biomedical academic programs has evolved over the years, reflecting the growing recognition of research as a cornerstone of evidence-based practice [ 7 ]. Notwithstanding the numerous opportunities presented by the inclusion of research training in biomedical programs, it poses significant challenges such as limited resources, varying levels of student preparedness, and the need for faculty development in research mentorship [ 8 , 9 ]. Addressing these challenges is essential to maximize the benefits of research training and to ensure that all students can engage meaningfully in research activities.
While there are different models for incorporating research training into biomedical programs, including dentistry, almost all models share the common goals of equipping students with basic research skills and techniques, critical thinking training and undertaking research projects either as an elective or a summer training course, or more commonly as a compulsory course required for graduation [ 2 , 4 , 10 ].
Dental colleges in the Middle East region are not an exception and most of these colleges are continuously striving to update their curricula to improve the undergraduate research component and cultivate a research-oriented academic teaching environment. Despite these efforts, there remains a significant gap in our understanding of the nature and scope of student-led research in these institutions, the challenges they face, and the perceived benefits of their research experiences. Furthermore, a common approach in most studies in this domain is to confine data collection to a single center from a single country, which in turn limits the value of the outcomes. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to conduct studies with representative samples and preferably multiple institutions in order to address the existing knowledge gaps, to provide valuable insights that can inform future curricular improvements and to support the development of more effective research training programs in dental education across the region. Accordingly, this study was designed and conducted to elucidate some of these knowledge gaps.
The faculty of dentistry at Jordan University of Science and Technology (JUST) is the biggest in Jordan and adopts a five-year bachelor’s program in dental surgery (BDS). The faculty is home to more than 1600 undergraduate and 75 postgraduate students. The college of dental medicine at the University of Sharjah (UoS) is also the biggest in the UAE, with both undergraduate and postgraduate programs, local and international accreditation and follows a (1 + 5) program structure, whereby students need to finish a foundation year and then qualify for the five-year BDS program. Furthermore, the UoS dental college applies an integrated stream-based curriculum. Finally, Oman Dental College (ODC) is the sole dental school in Oman and represents an independent college that does not belong to a university body.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the research experience of final year dental students from three major dental schools in the Middle East, namely JUST from Jordan, UoS from the UAE, and ODC from Oman. Furthermore, the hypothesis of this study was that research activities conducted at dental schools has no perceived benefit for final year dental students.
The rationale for selecting these three dental schools stems from the diversity in the dental curriculum and program structure as well as the fact that final year BDS students are required to conduct a research project as a prerequisite for graduation in the three schools. Furthermore, the authors from these dental schools have a strong scholarly record and have been collaborating in a variety of academic and research activities.
Materials and methods
The current study is a population-based descriptive cross-sectional observational study. The study was conducted using an online self-administered questionnaire and targeted final-year dental students at three dental schools in the Middle East region: JUST from Jordan, UoS from the UAE, and ODC from Oman. The study took place in the period from January to June 2023.
For inclusion in the study, participants should have been final-year dental students at the three participating schools, have finished their research project and agreed to participate. Exclusion criteria included any students not in their final year, those who have not conducted or finished their research projects and those who refused to participate.
The study was approved by the institutional review board of JUST (Reference: 724–2022), the research ethics committee of the UoS (Reference: REC-22-02-22-3) as well as ODC (Reference: ODC-MA-2022-166). The study adhered to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines [ 11 ]. The checklist is available as a supplementary file.
Sample size determination was based on previous studies with a similar design and was further confirmed with a statistical formula. A close look at the relevant literature reveals that such studies were either targeting a single dental or medical school or multiple schools and the sample size generally ranged from 158 to 360 [ 4 , 8 , 9 , 10 , 12 ]. Furthermore, to confirm the sample size, the following 2-step formula for finite population sample size calculation was used [ 13 ]:
Wherein Z is the confidence level at 95% =1.96, P is the population proportion = 0.5, and E is the margin of error = 0.05. Based on this formula, the resultant initial sample size was 384.
Wherein n is the initial sample size = 384, N is the total population size (total number of final year dental students in the 3 schools) = 443. Based on this formula, the adjusted sample size was 206.
An online, self-administered questionnaire comprising 13 questions was designed to assess the research experience of final year dental students in the participating schools. The questionnaire was initially prepared by the first three authors and was then reviewed and approved by the other authors. The questionnaire was developed following an extensive review of relevant literature to identify the most critical aspects of research projects conducted at the dental or medical schools and the most common challenges experienced by students with regards to research project design, research components, attributes, analysis, interpretation, drafting, writing, and presentation of the final outcomes.
The questionnaire was then pretested for both face and content validity. Face validity was assessed by a pilot study that evaluated clarity, validity, and comprehensiveness in a small cohort of 30 students. Content validity was assessed by the authors, who are all experienced academics with remarkable research profiles and experience in supervising undergraduate and postgraduate research projects. The authors critically evaluated each item and made the necessary changes whenever required. Furthermore, Cronbach’s alpha was used to assess the internal consistency/ reliability of the questionnaire and the correlation between the questionnaire items was found to be 0.79. Thereafter, online invitations along with the questionnaire were sent out to a total of 443 students, 280 from JUST, 96 from UoS and 67 from ODC, which represented the total number of final year students at the three schools. A first reminder was sent 2 weeks later, and a second reminder was sent after another 2 weeks.
In addition to basic demographic details, the questionnaire comprised questions related to the type of study conducted, the scope of the research project, whether the research project was proposed by the students or the instructors or both, the literature review part of the project, the statistical analysis performed, the final presentation of the project, the writing up of the resultant manuscript if applicable, the perceived benefits of the research project and finally suggestions to improve the research component for future students.
The outcomes of the study were the students’ research experience in terms of research design, literature review, data collection, analysis, interpretation and presentation, students’ perceived benefits from research, students’ perspective towards research in their future career and students’ suggestions to improve their research experience.
The exposures were the educational and clinical experience of students, research supervision by mentors and faculty members, and participation in extracurricular activities, while the predictors were the academic performance of students, previous research experience and self-motivation.
The collected responses were entered into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet and analyzed using SPSS Statistics software, version 20.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive data were presented as frequencies and percentages. For this study, only descriptive statistics were carried out as the aim was not to compare and contrast the three schools but rather to provide an overview of the research activities at the participating dental schools.
The heatmap generated to represent the answers for question 11 (perceived benefits of the research activity) was created using Python programming language (Python 3.11) and the pandas, seaborn, and matplotlib libraries. The heatmap was customized to highlight the count and percentage of responses in each component, with the highest values shown in red and the lowest values shown in blue.
Potentially eligible participants in this study were all final year dental students at the three dental schools (443 students, 280 from JUST, 96 from UoS and 67 from ODC). All potentially eligible participants were confirmed to be eligible and were invited to participate in the study.
The total number of participants included in the study, i.e. the total number of students who completed the questionnaire and whose responses were analyzed, was 369 (223 from JUST, 80 from UoS and 66 from ODC). The overall response rate was 83.3% (79.6% from JUST, 83.3% from UoS and 98.5% from ODC).
The highest proportion of participants were from JUST ( n = 223, 60.4%), followed by UoS ( n = 80, 21.7%), and then ODC ( n = 66, 17.9%). The majority of the participants were females ( n = 296, 80.4%), while males represented a smaller proportion ( n = 73, 19.6%). It is noteworthy that these proportions reflect the size of the cohorts in each college.
With regards to the type of study, half of final-year dental students in the 3 colleges participated in observational cross-sectional studies (i.e., population-based studies) ( n = 186, 50.4%), while literature review projects were the second most common type ( n = 83, 22.5%), followed by experimental studies ( n = 55, 14.9%). Longitudinal studies randomized controlled trials, and other types of studies (e.g., qualitative studies, case reports) were less common, with ( n = 5, 1.4%), ( n = 10, 2.7%), and ( n = 30, 8.1%) participation rates, respectively. Distribution of study types within each college is shown Fig. 1 .
Distribution in percent of study types within each college. JUST: Jordan University of Science and Technology, UOS: University of Sharjah, ODC: Oman Dental College
The most common scope of research projects among final-year dental students was in public health/health services ( n = 108, 29.3%) followed by dental education/attitudes of students or faculty ( n = 103, 27.9%) (Fig. 2 ). Biomaterials/dental materials ( n = 62, 16.8%) and restorative dentistry ( n = 41, 11.1%) were also popular research areas. Oral diagnostic sciences (oral medicine/oral pathology/oral radiology) ( n = 28, 7.6%), oral surgery ( n = 12, 3.2%) and other research areas ( n = 15, 4.1%) were less common among the participants. Thirty-two students (8.7%) were engaged in more than one research project.
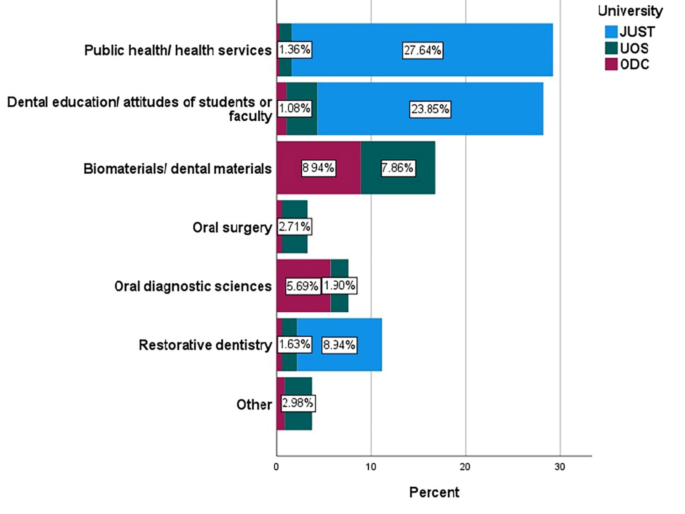
Percentages of the scope of research projects among final-year dental students. JUST: Jordan University of Science and Technology, UOS: University of Sharjah, ODC: Oman Dental College
The majority of research projects were proposed through a discussion and agreement between the students and the instructor (55.0%). Instructors proposed the topic for 36.6% of the research projects, while students proposed the topic for the remaining 8.4% of the projects.
Most dental students (79.1%) performed the literature review for their research projects using internet search engines. Material provided by the instructor was used for the literature review by 15.5% of the students, while 5.4% of the students did not perform a literature review. More than half of the students ( n = 191, 51.7%) used multiple search engines in their literature search. The most popular search engines for literature review among dental students were PubMed (70.2% of cases) and Google Scholar (68.5% of cases). Scopus was used by 12.8% of students, while other search engines were used by 15.6% of students.
The majority of dental students ( n = 276, 74.8%) did not utilize the university library to gain access to the required material for their research. In contrast, 93 students (25.2%) reported using the university library for this purpose.
Dental students performed statistical analysis in their projects primarily by receiving help from the instructor ( n = 167, 45.2%) or using specialized software ( n = 168, 45.5%). A smaller percentage of students ( n = 34, 9.4%) consulted a professional statistician for assistance with statistical analysis. at the end of the research project, 58.4% of students ( n = 215) presented their work in the form of a manuscript or scientific paper. Other methods of presenting the work included PowerPoint presentations ( n = 80, 21.7%) and discussions with the instructor ( n = 74, 19.8%).
For those students who prepared a manuscript at the conclusion of their project, the most difficult part of the writing-up was the discussion section ( n = 155, 42.0%), followed by the methodology section ( n = 120, 32.5%), a finding that was common across the three colleges. Fewer students found the introduction ( n = 13, 3.6%) and conclusion ( n = 10, 2.7%) sections to be challenging. Additionally, 71 students (19.2%) were not sure which part of the manuscript was the most difficult to prepare (Fig. 3 ).
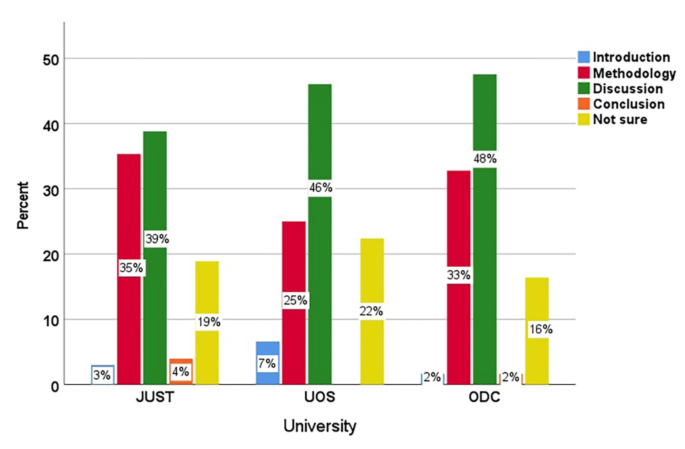
Percentages of the most difficult part reported by dental students during the writing-up of their projects. JUST: Jordan University of Science and Technology, UOS: University of Sharjah, ODC: Oman Dental College
The dental students’ perceived benefits from the research activity were evaluated across seven components, including literature review skills, research design skills, data collection and interpretation, manuscript writing, publication, teamwork and effective communication, and engagement in continuing professional development.
The majority of students found the research activity to be beneficial or highly beneficial in most of the areas, with the highest ratings observed in teamwork and effective communication, where 33.5% rated it as beneficial and 32.7% rated it as highly beneficial. Similarly, in the area of data collection and interpretation, 33.0% rated it as beneficial and 27.5% rated it as highly beneficial. In the areas of literature review skills and research design skills, 28.6% and 34.0% of students rated the research activity as beneficial, while 25.3% and 22.7% rated it as highly beneficial, respectively. Students also perceived the research activity to be helpful for the manuscript writing, with 27.9% rating it as beneficial and 19.2% rating it as highly beneficial.
When it comes to publication, students’ perceptions were more variable, with 22.0% rating it as beneficial and 11.3% rating it as highly beneficial. A notable 29.9% rated it as neutral, and 17.9% reported no benefit. Finally, in terms of engaging in continuing professional development, 26.8% of students rated the research activity as beneficial and 26.2% rated it as highly beneficial (Fig. 4 ).
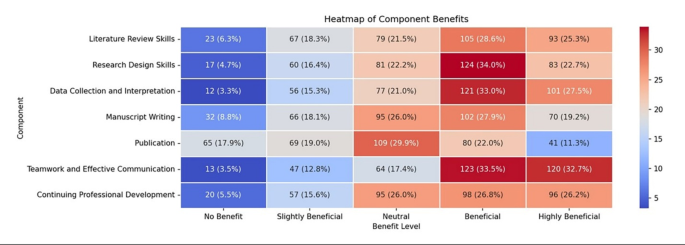
Heatmap of the dental students’ perceived benefits from the research activity
The research course’s impact on students’ perspectives towards being engaged in research activities or pursuing a research career after graduation was predominantly positive, wherein 274 students (74.1%) reported a positive impact on their research perspectives. However, 79 students (21.5%) felt that the course had no impact on their outlook towards research engagement or a research career. A small percentage of students ( n = 16, 4.4%) indicated that the course had a negative impact on their perspective towards research activities or a research career after graduation.
Finally, when students were asked about their suggestions to improve research activities, they indicated the need for more training and orientation ( n = 127, 34.6%) as well as to allow more time for students to finish their research projects ( n = 87, 23.6%). Participation in competitions and more generous funding were believed to be less important factors to improve students` research experience ( n = 78, 21.2% and n = 63, 17.1%, respectively). Other factors such as external collaborations and engagement in research groups were even less important from the students` perspective (Fig. 5 ).
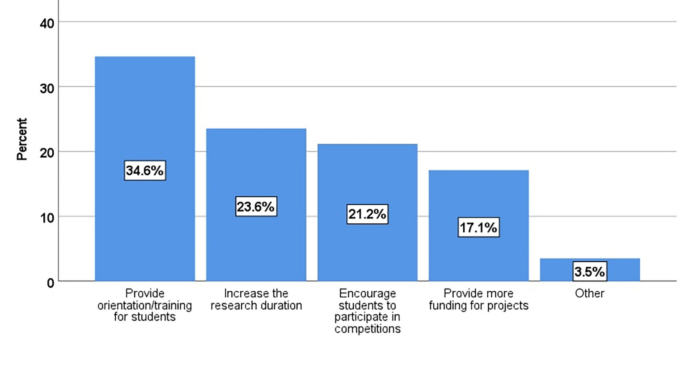
Precentages of dental students’ suggestions to improve research activities at their colleges
To the best of our knowledge, this report is the first to provide a comprehensive overview of the research experience of dental students from three leading dental colleges in the Middle East region, which is home to more than 50 dental schools according to the latest SCImago Institutions Ranking ® ( https://www.scimagoir.com ). The reasonable sample size and different curricular structure across the participating colleges enhanced the value of our findings not only for dental colleges in the Middle East, but also to any dental college seeking to improve and update its undergraduate research activities. However, it is noteworthy that since the study has included only three dental schools, the generalizability of the current findings would be limited, and the outcomes are preliminary in nature.
Cross-sectional (epidemiological) studies and literature reviews represented the most common types of research among our cohort of students, which can be attributed to the feasibility, shorter time and low cost required to conduct such research projects. On the contrary, longitudinal studies and randomized trials, both known to be time consuming and meticulous, were the least common types. These findings concur with previous reports, which demonstrated that epidemiological studies are popular among undergraduate research projects [ 4 , 10 ]. In a retrospective study, Nalliah et al. also demonstrated a remarkable increase in epidemiological research concurrent with a decline in the clinical research in dental students` projects over a period of 4 years [ 4 ]. However, literature reviews, whether systematic or scoping, were not as common in some dental schools as in our cohort. For instance, a report from Sweden showed that literature reviews accounted for less than 10% of total dental students` projects [ 14 ]. Overall, qualitative research was seldom performed among our cohort, which is in agreement with a general trend in dental research that has been linked to the low level of competence and experience of dental educators to train students in qualitative research, as this requires special training in social research [ 15 , 16 ].
In terms of the research topics, public health research, research in dental education and attitudinal research were the most prevalent among our respondents. In agreement with our results, research in health care appears common in dental students` projects [ 12 ]. In general, these research domains may reflect the underlying interests of the faculty supervisors, who, in our case, were actively engaged in the selection of the research topic for more than 90% of the projects. Other areas of research, such as clinical dentistry and basic dental research are also widely reported [ 4 , 10 , 14 , 17 ].
The selection of a research domain is a critical step in undergraduate research projects, and a systematic approach in identifying research gaps and selecting appropriate research topics is indispensable and should always be given an utmost attention by supervisors [ 18 ].
More than half of the projects in the current report were reasonably selected based on a discussion between the students and the supervisor, whereas 36% were selected by the supervisors. Otuyemi et al. reported that about half of undergraduate research topics in a Nigerian dental school were selected by students themselves, however, a significant proportion of these projects (20%) were subsequently modified by supervisors [ 19 ]. The autonomy in selecting the research topic was discussed in a Swedish report, which suggested that such approach can enhance the learning experience of students, their motivation and creativity [ 20 ]. Flexibility in selecting the research topic as well as the faculty supervisor, whenever feasible, should be offered to students in order to improve their research experience and gain better outcomes [ 12 ].
Pubmed and Google Scholar were the most widely used search engines for performing a literature review. This finding is consistent with recent reviews which classify these two search systems as the most commonly used ones in biomedical research despite some critical limitations [ 21 , 22 ]. It is noteworthy that students should be competent in critical appraisal of available literature to perform the literature review efficiently. Interestingly, only 25% of students used their respective university library`s access to the search engines, which means that most students retrieved only open access publications for their literature reviews, a finding that requires attention from faculty mentors to guide students to utilize the available library services to widen their accessibility to available literature.
Statistical analysis has classically been viewed as a perceived obstacle for undergraduate students to undertake research in general [ 23 , 24 ] and recent literature has highlighted the crucial need of biomedical students to develop necessary competencies in biostatistics during their studies [ 25 ]. One obvious advantage of conducting research in our cohort is that 45.5% of students used a specialized software to analyze their data, which means that they did have at least an overview of how data are processed and analyzed to reach their final results and inferences. Unfortunately, the remaining 54.5% of students were, partially or completely, dependent on the supervisor or a professional statistician for data analysis. It is noteworthy that the research projects were appropriately tailored to the undergraduate level, focusing on fundamental statistical analysis methods. Therefore, consulting a professional statistician for more complex analyses was done only if indicated, which explains the small percentage of students who consulted a professional statistician.
Over half of participating students (58.4%) prepared a manuscript at the end of their research projects and for these students, the discussion section was identified as the most challenging to prepare, followed by the methodology section. These findings can be explained by the students’ lack of knowledge and experience related to conducting and writing-up scientific research. The same was reported by Habib et al. who found dental students’ research knowledge to be less than that of medical students [ 26 ]. The skills of critical thinking and scientific writing are believed to be of paramount importance to biomedical students and several strategies have been proposed to enhance these skills especially for both English and non-English speaking students [ 27 , 28 , 29 ].
Dental students in the current study reported positive attitude towards research and found the research activity to be beneficial in several aspects of their education, with the most significant benefits in the areas of teamwork, effective communication, data collection and interpretation, literature review skills, and research design skills. Similar findings were reported by previous studies with most of participating students reporting a positive impact of their research experience [ 4 , 10 , 12 , 30 ]. Furthermore, 74% of students found that their research experience had a positive impact on their perspectives towards engagement in research in the future. This particular finding may be promising in resolving a general lack of interest in research by dental students, as shown in a previous report from one of the participating colleges in this study (JUST), which demonstrated that only 2% of students may consider a research career in the future [ 31 ].
Notably, only 11.3% of our students perceived their research experience as being highly beneficial with regards to publication. Students` attitudes towards publishing their research appear inconsistent in literature and ranges from highly positive rates in developed countries [ 4 ] to relatively low rates in developing countries [ 8 , 32 , 33 ]. This can be attributed to lack of motivation and poor training in scientific writing skills, a finding that has prompted researchers to propose strategies to tackle such a gap as mentioned in the previous section.
Finally, key suggestions by the students to improve the research experience were the provision of more training and orientation, more time to conduct the research, as well as participation in competitions and more funding opportunities. These findings are generally in agreement with previous studies which demonstrated that dental students perceived these factors as potential barriers to improving their research experience [ 8 , 10 , 17 , 30 , 34 ].
A major limitation of the current study is the inclusion of only three dental schools from the Middle East which my limit the generalizability and validity of the findings. Furthermore, the cross-sectional nature of the study would not allow definitive conclusions to be drawn as students’ perspectives were not evaluated before and after the research project. Potential confounders in the study include the socioeconomic status of the students, the teaching environment, previous research experience, and self-motivation. Moreover, potential sources of bias include variations in the available resources and funding to students’ projects and variations in the quality of supervision provided. Another potential source of bias is the non-response bias whereby students with low academic performance or those who were not motivated might not respond to the questionnaire. This potential source of bias was managed by sending multiple reminders to students and aiming for the highest response rate and largest sample size possible.
In conclusion, the current study evaluated the key aspects of dental students’ research experience at three dental colleges in the Middle East. While there were several perceived benefits, some aspects need further reinforcement and revision including the paucity of qualitative and clinical research, the need for more rigorous supervision from mentors with focus on scientific writing skills and research presentation opportunities. Within the limitations of the current study, these outcomes can help in designing future larger scale studies and provide valuable guidance for dental colleges to foster the research component in their curricula. Further studies with larger and more representative samples are required to validate these findings and to explore other relevant elements in undergraduate dental research activities.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Emrick JJ, Gullard A. Integrating research into dental student training: a global necessity. J Dent Res. 2013;92(12):1053–5.
Article Google Scholar
Ramachandra SS. A comprehensive template for inclusion of research in the undergraduate dental curriculum. Health Professions Educ. 2020;6(2):264–70.
Al Sweleh FS. Integrating scientific research into undergraduate curriculum: a new direction in dental education. J Health Spec. 2016;4(1):42–5.
Nalliah RP, Lee MK, Da Silva JD, Allareddy V. Impact of a research requirement in a dental school curriculum. J Dent Educ. 2014;78(10):1364–71.
Lang ES, Wyer PC, Haynes RB. Knowledge translation: closing the evidence-to-practice gap. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49(3):355–63.
Fechheimer M, Webber K, Kleiber PB. How well do undergraduate research programs promote engagement and success of students? CBE Life Sci Educ. 2011;10(2):156–63.
Kingsley K, O’Malley S, Stewart T, Howard KM. Research enrichment: evaluation of structured research in the curriculum for dental medicine students as part of the vertical and horizontal integration of biomedical training and discovery. BMC Med Educ. 2008;8:1–10.
Alsaleem SA, Alkhairi MAY, Alzahrani MAA, Alwadai MI, Alqahtani SSA, Alaseri YFY, et al. Challenges and Barriers toward Medical Research among Medical and Dental students at King Khalid University, Abha, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Front Public Health. 2021;9:706778.
Soe HHK, Than NN, Lwin H, Htay MNNN, Phyu KL, Abas AL. Knowledge, attitudes, and barriers toward research: the perspectives of undergraduate medical and dental students. J Educ Health Promotion. 2018;7(1):23.
Amir LR, Soekanto SA, Julia V, Wahono NA, Maharani DA. Impact of Undergraduate Research as a compulsory course in the Dentistry Study Program Universitas Indonesia. Dent J (Basel). 2022;10(11).
Von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The strengthening the reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007;370(9596):1453–7.
Van der Groen TA, Olsen BR, Park SE. Effects of a Research Requirement for Dental students: a retrospective analysis of students’ perspectives across ten years. J Dent Educ. 2018;82(11):1171–7.
Althubaiti A. Sample size determination: a practical guide for health researchers. J Gen Family Med. 2023;24(2):72–8.
Franzén C. The undergraduate degree project–preparing dental students for professional work and postgraduate studies? Eur J Dent Educ. 2014;18(4):207–13.
Edmunds S, Brown G. Doing qualitative research in dentistry and dental education. Eur J Dent Educ. 2012;16(2):110–7.
Moreno X. Research training in dental undergraduate curriculum in Chile. J Oral Res. 2014;3(2):95–9.
Liu H, Gong Z, Ye C, Gan X, Chen S, Li L, et al. The picture of undergraduate dental basic research education: a scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):569.
Omar A, Elliott E, Sharma S. How to undertake research as a dental undergraduate. BDJ Student. 2021;28(3):17–8.
Otuyemi OD, Olaniyi EA. A 5-year retrospective evaluation of undergraduate dental research projects in a Nigerian University: graduates’ perceptions of their learning experiences. Eur J Dent Educ. 2020;24(2):292–300.
Franzén C, Brown G. Undergraduate degree projects in the Swedish dental schools: a documentary analysis. Eur J Dent Educ. 2013;17(2):122–6.
Thakre SB, Golawar SH, Thakr SS, Gawande AV. Search engines use for effective literature search in biomedical research. 2014.
Gusenbauer M, Haddaway NR. Which academic search systems are suitable for systematic reviews or meta-analyses? Evaluating retrieval qualities of Google Scholar, PubMed, and 26 other resources. Res Synthesis Methods. 2020;11(2):181–217.
Lorton L, Rethman MP. Statistics: curse of the writing class. J Endod. 1990;16(1):13–8.
Leppink J. Helping medical students in their study of statistics: a flexible approach. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2017;12(1):1–7.
Google Scholar
Oster RA, Enders FT. The Importance of Statistical Competencies for Medical Research Learners. J Stat Educ. 2018;26(2):137–42.
Habib SR, AlOtaibi SS, Abdullatif FA, AlAhmad IM. Knowledge and attitude of undergraduate Dental students towards Research. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2018;30(3):443–8.
Florek AG, Dellavalle RP. Case reports in medical education: a platform for training medical students, residents, and fellows in scientific writing and critical thinking. J Med Case Rep. 2016;10:86.
Wortman-Wunder E, Wefes I. Scientific writing workshop improves confidence in critical writing skills among trainees in the Biomedical sciences. J Microbiol Biol Educ. 2020;21(1).
Barroga E, Mitoma H. Critical thinking and scientific writing skills of Non-anglophone Medical students: a model of Training Course. J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(3):e18.
Kyaw Soe HH, Than NN, Lwin H, Nu Htay MNN, Phyu KL, Abas AL. Knowledge, attitudes, and barriers toward research: the perspectives of undergraduate medical and dental students. J Educ Health Promot. 2018;7:23.
Alrashdan MS, Alazzam M, Alkhader M, Phillips C. Career perspectives of senior dental students from different backgrounds at a single Middle Eastern institution. BMC Med Educ. 2018;18(1):283.
Chellaiyan VG, Manoharan A, Jasmine M, Liaquathali F. Medical research: perception and barriers to its practice among medical school students of Chennai. J Educ Health Promot. 2019;8:134.
Jeelani W, Aslam SM, Elahi A. Current trends in undergraduate medical and dental research: a picture from Pakistan. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2014;26(2):162–6.
Yu W, Sun Y, Miao M, Li L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, et al. Eleven-year experience implementing a dental undergraduate research programme in a prestigious dental school in China: lessons learned and future prospects. Eur J Dent Educ. 2021;25(2):246–60.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge final year dental students at the three participating colleges for their time completing the questionnaire.
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Oral and Craniofacial Health Sciences, College of Dental Medicine, University of Sharjah, P.O.Box: 27272, Sharjah, UAE
Mohammad S. Alrashdan & Sausan Al Kawas
Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Surgery, Faculty of Dentistry, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan
Mohammad S. Alrashdan
Department of Adult Restorative Dentistry, Oman Dental College, Muscat, Sultanate of Oman
Abubaker Qutieshat
Department of Restorative Dentistry, Dundee Dental Hospital & School, University of Dundee, Dundee, UK
Preventive and Restorative Dentistry Department, College of Dental Medicine, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, UAE
Mohamed El-Kishawi
Clinical Sciences Department, College of Dentistry, Ajman University, Ajman, UAE
Abdulghani Alarabi
Department of Prosthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Science and Technology, Irbid, Jordan
Lina Khasawneh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
M.A.: Conceptualization, data curation, project administration; supervision, validation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. A.Q: Conceptualization, data curation, project administration; writing - review and editing. M.E: Conceptualization, data curation, project administration; validation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. A.A.: data curation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. L.K.: Conceptualization, data curation, validation, writing - original draft; writing - review and editing. S.A: Conceptualization, writing - review and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Mohammad S. Alrashdan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The current study was approved by the institutional review board of Jordan University of Science and Technology (Reference: 724–2022), the research ethics committee of the University of Sharjah (Reference: REC-22-02-22-3) and Oman Dental College (Reference: ODC-MA-2022-166).
Informed consent
Agreement to the invitation to fill out the questionnaire was considered as an implied consent to participate.
Consent for publication
not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Alrashdan, M.S., Qutieshat, A., El-Kishawi, M. et al. Insights into research activities of senior dental students in the Middle East: A multicenter preliminary study. BMC Med Educ 24 , 967 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05955-5
Download citation
Received : 12 August 2023
Accepted : 24 August 2024
Published : 04 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05955-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Dental research
- Dental education
- Undergraduate
- Literature review
- Publication
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc. Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most ...
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & ...
Here are real-life research proposal examples of funded research projects in the field of science and technology. Funder. Title. US Geological Survey (USGS) (Mendenhall Postdoctoral Research Fellowship) Using Integrated Population Modelling in Decision-support Tools to Connect Science and Decision Makers.
How to Write a Research Proposal in 2024: Structure ...
How To Write a Proposal
How to Write a Research Proposal | Guide With Examples
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers' plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed ...
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Explain what kind of results will justify or disprove your hypothesis. Budget: Explain how much money you need. Explain the details of the budget (how much you want to spend for what). Conclusion: Describe why your research is important. References: List the sources you have used for writing the research proposal, including a few main citations ...
An organized, well-written, concise, complete proposal = an easier to conduct experiment. A good proposal is like a good sales pitch. In the world of graduate studies and scientific research a proposal is the means by which funding is secured. Good writing when paired with a thorough understanding of the subject matter is a valuable skill to ...
Research Proposal (student's preliminary notes) (91.11 KB, PDF) This is an example of how to start planning and thinking about your research proposal assignment. You will find a student's notes and ideas about their research proposal topic - "Perspectives on Textual Production, Student Collaboration, and Social Networking Sites".
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
2.Perform a literature review. The next step is to conduct a literature review. This step is important because when you write out the background information and knowledge gaps in your topic area, it will help you become more familiar with your research topic.
Useful tips for writing a research proposal. Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to ...
Summary: The scientific research proposal is a strong, coherent, integrated, and accurate summary of the suggested study, and it raises the main problems or questions to be solved and answered.
How to write a research proposal? - PMC
It puts the proposal in context. 3. The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1. The importance of the statement of the research problem 5: The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology ...
steps. It begins with selecting a study topic, reviewing. the literature, setting goals, choosing a study design and. appropriate statistical tools, and formulating a research proposal. to obtain ...
How to write a proposal letter. Introduce yourself and provide background information. State your purpose for the proposal. Define your goals and objectives. Highlight what sets you apart. Briefly discuss the budget and how funds will be used. Finish with a call to action and request a follow-up. Science atlas, our goal is to spark the ...
The Handbook of Scientific Proposal Writing offers researchers and research administrators a broad perspective on the process of initiating and conducting funded scientific research projects. Written for students and researchers in all fields and disciplines, this reference offers a holistic approach to conceiving and then converting new ideas ...
If you absolutely have to quote an author ad verbatim, then make sure that you use quotation marks and italics to indicate it. Abstract. An abstract is a brief summary written in the same style as the rest of your application. It will provide the reader with the main points and conclusion of your proposal. 6.
6. Objectives. Identify, select, describe and state a research topic of importance within. the health and medical domain. Review and present literature relevant to the research topic. Select ...
1. Build a timeline. There are a lot of moving parts in the application process, so the first step is to create a timeline. You want to allow yourself enough time to gather information and write the proposal without feeling rushed. Plus, you need to factor in time for editing and internal reviews.
This unique "all-in-one" handbook begins with a discussion of the basic principles of scientific writing style and composition and then applies these principles to writing research papers, review articles, grant proposals, research statements, and résumés, as well as to preparing academic presentations and posters"-- Provided by publisher.
Scientific writing is writing designed to communicate scientific ideas clearly and objectively. It is written by scientists for scientists and therefore contains information about complex ideas and often uses technical language specific to a certain field of research. Most scientific articles contain the following sections: Introduction
Outline. •. PDF | On Jan 21, 2013, Rui Pedro Paiva published How to Write Good Scientific Project Proposals: A Comprehensive Guide | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate.
NSF Graduate Research Fellowship Program (GRFP)
The importance of research training for undergraduate dental students cannot be overstressed and many reports have thoroughly discussed the necessity of incorporating research components in the dental curricula [1,2,3,4].A structured research training is crucial to ensure that dental graduates will adhere to evidence-based practices and policies in their future career and are able to ...