myCBSEguide
- Social Responsibilities of Business...

Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Notes Business Studies
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
CBSE Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes in PDF are available for free download in myCBSEguide mobile app. The best app for CBSE students now provides Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes Business Studies latest chapter wise notes for quick preparation of CBSE exams and school-based annual examinations. Class 11 Business Studies notes on Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes Business Studies are also available for download in CBSE Guide website.
CBSE Guide Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes
CBSE guide notes are the comprehensive notes which covers the latest syllabus of CBSE and NCERT. It includes all the topics given in NCERT class 11 Business Studies textbook. Users can download CBSE guide quick revision notes from myCBSEguide mobile app and my CBSE guide website.
Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes Business Studies
Download CBSE class 11th revision notes for Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes Business Studies in PDF format for free. Download revision notes for Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes Business Studies and score high in exams. These are the Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes Business Studies prepared by team of expert teachers. The revision notes help you revise the whole chapter in minutes. Revising notes in exam days is on of the best tips recommended by teachers during exam days.
Download Revision Notes as PDF
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
CONCEPT OF SOCIAL , RESPONSIBILITY : A business is a part of society. So, a business enterprise should do business and earn money in ways that fulfill the aspirations of the society. Thus social responsibility relates to the voluntary efforts on the part of the businessmen to contribute to the social well being. The businessmen make use of resources of society and earn money from the members of society so they must do something for the society.
Arguments in favour of Social Responsibility :
There is a need for Social Responsibility of business for Existence and Growth:
1. Justification for Existence and Growth : Business is the creation of society therefore it should respond according to the demands of the society. To survive and grow in society for long run the business must provide continuous services to the society.
2. Long term Interest of the firm : A firm can improve its image and builds goodwill in the long run when its highest goal is to serve the society . If it indulges in unfair Trade Practices e.g. adulteration, hoarding, black marketing, it may not be able to exist for long.
3. Avoidance of government regulations : Business can avoid the problem of government regulations by voluntarily assuming social responsibilities.
4. Availability of resources with business : Business has valuable financial and human resources which can be effectively used for solving problems of the society.
5. Better environment for doing business : It is the social responsibility of business enterprise to provide better Quality of life and standard of living to people. So, business will get better community to conduct business.
6. Contribution to social problems : Some of the social problems have been created by business firms themselves such as pollution, creation of unsafe workplaces, discrimination etc, Therefore, it is the moral obligation of business to solve such social problems.
Arguments Against Social Responsibility
Major arguments against social responsibility are:
1. Profit Motive – A business is an economic entity that is guided by profit motive. It should not waste its energies and resources in fulfilling social responsibility.
2. Burden on consumers – Involvement of business in social responsibilities involve a lot of expenditure which will ultimately be borne by the customers.
3. Lack of Social Skills -The business firms and managers have the skills to handle business operation. They are not expert to tackle the social problems like poverty, over population etc. Therefore, social problems must be tackled by social experts.
4. Lack of public support – Generally public does not like business involvement in social problems. Therefore, business cannot fulfill social responsibility because of lack of public confidence & cooperation.
SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY TOWARDS DIFFERENT INTEREST GROUPS
2. Responsibility Towards workers: (i) Providing fair compensation and benefits, (ii) Providing good and safe Working conditions, (iii) To develop a sense of belongingness.
3. Responsibility toward consumers: (i) To supply right quality of goods & services at reasonable prices. (ii) To ensure regular and adequate supply of products. (iii) To inform them about new products and new uses of existing products. (iv) To handle the customers grievance promptly.
4. Responsibility Towards Government – (i) To pay taxes honestly (ii) To observe rules laid down by the government, (iii) to avoid corrupting government employees.
5. Responsibility towards community – (i) To make available opportunities for employment, (ii) To avoid polluting the environment, (iii) To up lift the weaker sections of society
BUSINESS AND ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION:
Meaning of Environment: The environment is defined as the totality of man’s surroundings – both natural and man-made. Natural Resources-all land, water, air and man-made – cultural heritage, socio-economic institutions and the people.
Meaning of Environmental pollution – It means injection of harmful substances into the environment. The greatest problem that industries and businessmen are creating is that of pollution – which is the result of industrial production. So, protection of environment is must.
Causes of Pollution: Many industrial organizations have been responsible for causing air, water, land and noise pollution.
1. Air Pollution – Due to smoke, chemical emitted by factories, vehicle. It has created a hole in the ozone layer leading to global warming.
2. Water pollution – Due to chemicals and waste dumped into the rivers, streams & lakes. It has led to the death of several aquatic animals and posed a serious problem to human life.
3. Land Pollution – Due to dumping of garbage and toxic wastes which affect the fertility of land and makes it unfit for agriculture.
4. Noise Pollution : Caused by the running factories and vehicles. Noise pollution can be responsible for many diseases like loss of hearing, violent behaviour and mental disorder.
NEED EOR POLLUTION CONTROL
1. To ensure healthy life – Many diseases like cancer, heart attack and lung complications all caused by pollutants in the environment. Pollution control is must to keep a check on these diseases.
2. To ensure safety – Due to environmental pollution and smoke, the visibility is reducing due to which chances of accidents have been increasing. To reduce the number of accidents there must be a check on pollution.
3. Economic Losses : Pollutants in the environment bringing heavy economic losses for the country, for example Taj Mahal is losing its beauty due to pollution.
4. Improved Public Image : A firm that adopts pollution control measures enjoys a good reputation as a socially responsible enterprise.
ROLE OF BUSINESS ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION:
1. Eco-friendly and clean or low waste technology should be used by industrial organization. 2. Industrial Wastes should be recycled as far as possible. 3. Plant and machinery should be modernized to minimize pollution. 4. The business houses should comply with the laws and regulations enacted for prevention of pollution. 5. Positive steps should be taken to save environment. These include plantation of trees, cleaning of rivers, ponds etc.
BUSINESS ETHICS: Refers to the moral values or standards or norms which govern the activities of a businessman. Ethics define what is right and what is wrong. By ethic we mean the business practices which are desirable from the point of view of Society. The purpose of business ethics is to guide the managers and employees in performing their job. Example of business ethics are charging fair price from customers, giving fair treatment to workers, earning reasonable profits and paying taxes tithe government honestly.
ELEMENTS OF BUSINESS ETHICS
1. Top management commitment – The CEO and higher level managers must be committed to ethical norms of behavior. This would set an example for all employers and encourage them to follow ethical practice.
2. Publication of code – Code of ethics is a formal written document of the principles, values and standards that guide a firms actions. It may cover areas like honesty, quality, safety, health care etc.
3. Establishment of compliance mechanism : A suitable mechanism should be developed to comply with the ethical standards of the enterprise. The mechanism should be properly communicated to all in the organization.
4. Employee involvement : It is the employees of the lower levels who implement ethical principal so they must be involved in the process of developing ethical code.
5. Measuring results : Although it is difficult to measure the ethical results but it must be verified and audited that have for work is being carried according to ethical standards.
CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes and Key Points
Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes Business Studies. CBSE quick revision note for class-11 Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry, Biology and other subject are very helpful to revise the whole syllabus during exam days. The revision notes covers all important formulas and concepts given in the chapter. Even if you wish to have an overview of a chapter, quick revision notes are here to do if for you. These notes will certainly save your time during stressful exam days.
- Mathematics
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Computer Science
- Informatics Practices
To download Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics class 11 Notes, sample paper for class 11 Chemistry, Physics, Biology, History, Political Science, Economics, Geography, Computer Science, Home Science, Accountancy, Business Studies, and Home Science; do check myCBSEguide app or website. myCBSEguide provides sample papers with solution, test papers for chapter-wise practice, NCERT solutions, NCERT Exemplar solutions, quick revision notes for ready reference, CBSE guess papers and CBSE important question papers. Sample Paper all are made available through the best app for CBSE students and myCBSEguide website.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Sources of Business Finance class 11 Notes Business Studies
- Business Services class 11 Notes Business Studies
- International Business class 11 Notes Business Studies
- Internal Trade class 11 Notes Business Studies
- Small Business class 11 Notes Business Studies
- Emerging Modes of Business class 11 Notes Business Studies
- Private, Public and Global Enterprises class 11 Notes Business Studies
- Forms of Business Organisation class 11 Notes Business Studies
5 thoughts on “Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Notes Business Studies”
I liked my cbse guide because it helps me a lot for preparing notes this site is very helpful thank you so much for being so helpful
It is best website for students thank you mycbseguide.com
It help students to make study easy THANKs mycbseguide.com
It helps students to make study easy. It is so helpful for students
It helps students to make study easy.
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Business Studies Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
October 9, 2019 by phani
Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter wise Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks in your examinations.
NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies Business Studies Sample Papers
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. Multiple Choice Questions Question 1. Social responsibility is (a) Same as legal responsibility (b) Broader than legal responsibility (c) Narrower than legal responsibility (d) None of them Question 2. If business is to operate in a society which is full of diverse and complicated problems, it may have (a) Little chance of success (b) Great chance of success (c) Little chance of failure (d) No relation with success or failure Question 3. Business people have the skills to solve (a) All social problems (b) Some social problems (c) No social problems (d) All economic problems Question 4. That an enterprise must behave as a good citizen is an example of its responsibility towards (a) Owners (b) Workers (c) Consumers (d) Community Question 5. Environmental protection can best be done by the efforts of (a) Business people (b) Government (c) Scientists (d) All the people Question 6. Carbon monoxide emitted by automobile directly contributes to (a) Water pollution (b) Noise pollution (c) Land pollution (d) Air Pollution Question 7. Which of the following can explain the need for pollution control? (a) Cost savings (b) Reduced risk of liability (c) Reduction of health hazards (d) All of them Question 8. Which of the following is capable of doing maximum good to society? (a) Business success (b) Laws and regulations (c) Ethics (d) Professional management Question 9. Ethics is important for (a) Top management (b) Middle-level managers (c) Non-managerial employees (d) All of them Question 10. Which of the following alone can ensure effective ethics programme in a business enterprise? (a) Publication of code (b) Involvement of employees (c) Establishment of compliance mechanisms (d) None of them Answers: 1. (b) 2. (a) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. (d) 6. (d) 7. (c) 8. (c) 9. (d) 10. (c)
II. Short Answer Type Questions Question 1. What do you understand by social responsibility of business? How is it different from legal responsibility? Answer: Social responsibility of business refers to its obligation to take those decisions and perform those actions which are desirable in terms of the objective and values of our society. It refers to the obligation of business towards various social groups like employees, consumers, investors, government etc. In the words of H. R. Bowen, “Social responsibility of business is to pursue those policies, to make those decisions or to follow those lines of action which are desirable in terms of the objectives and values of our society Legal responsibility is the responsibility that a business has by virtue of law. Differences between Social and Legal Responsibility.
- Legal responsibility is compulsory under any of the laws, acts and constitution. Social responsibility is not backed by legal provisions.
- Legal responsibility is compulsion while social responsibility is a choice.
- Many a time, legal responsibility is fulfilled in the name of social responsibility.
- There are no punishments for organizations not following their social responsibility but legal action can be taken against organizations not following their legal responsibility.
Question 2. What is environment? What is environmental pollution? Answer: By environment, we mean our surroundings, which have an impact on our lives. It is the sum total of the surroundings and resources, including both biotic resources (i.e., living creatures such as plants and animals) and abiotic resources (i.e., non-living things, such as air, water and land) that affect our existence and quality of life. However, because of the rapid increase in population and industrialisation, the excessive use of resources has resulted in their degradation and depletion. Also, the discharge of harmful substances into the environment has contributed towards pollution. Environmental pollution can be classified into the following four types.
- Air Pollution : It is caused by the emission of harmful gases into the atmosphere.
- Water Pollution: It is caused by the discharge of industrial and household wastes into the rivers, thereby degrading the quality of water.
- Land Pollution: This is caused by dumping toxic wastes on land, which in turn damages it, making it unfit for agriculture.
- Noise Pollution: It is caused by noise from factories and vehicles, which may cause serious health problems such as loss of hearing or mental disorders.
Question 3. What is business ethics? Mention the basic elements of business ethics. Answer: Business ethics refers to the values and principles that govern the behaviour of individuals in an organisation such that the business activities are desirable from the viewpoint of society. The main purpose of business ethics is to guide managers and other employees to perform their jobs in a manner that is socially acceptable. The following are some of the elements of business ethics.
- Top management commitment : Top-level officers, such as CEO’s and senior managers, must strongly follow the ethical codes and guide the other employees in adopting such behaviour.
- Publication of a code: Enterprises must clearly define the ethical code of conduct, which would include quality standards, laws governing production and health and safety standards for the employees.
- Establishment of compliance mechanism: In addition to standards, an enterprise must also devise a mechanism through which compliance with the code of conduct can be measured.
- Involvement of employees at all levels: The successful implementation of ethical standards requires the involvement of all the employees at all levels.
- Measurement of results: Although it is difficult to measure the end results of implementation of ethical standards, the top management should take steps to measure the degree of compliance with the ethical codes.
Question 4. Briefly explain (a) Air pollution, (b) Water pollution, and (c) Land pollution. Answer: (a) Air Pollution: This kind of pollution is caused by the emission of harmful gases into the atmosphere. Smoke and chemicals emitted by factories and vehicles degrade the air quality and causes air pollution. (b) Water Pollution: Discharge of industrial and household wastes into rivers, streams or lakes causes degradation of the water quality. Over time, the increase in water pollution often results in the deaths of several animals and poses serious threats to human beings. (c) Land Pollution: This is caused due to the dumping of toxic materials and wastes on land, which in turn damages the quality of land, making it unfit and unproductive for agriculture and crop plantation.
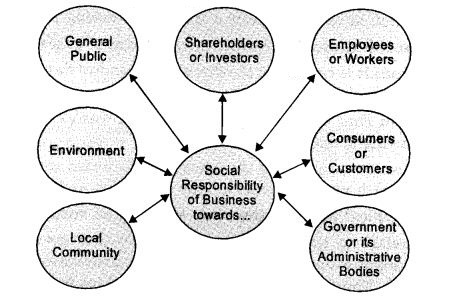
- Shareholders or investors who contribute funds for business.
- Employees and others that make up its personnel.
- Consumers or customers who consume and/or use its outputs (products and/or services).
- Government and local administrative bodies that regulate its commercial activities in their jurisdictions.
- Members of a local community who are either directly or indirectly influenced by its activities in their area.
- Surrounding environment of a location from where it operates.
- The general public that makes up a big part of society.
III. Long Answer Type Questions Question 1. Build up arguments for and against social responsibilities. Answer: Arguments for Social Responsibility:
- Justification for Existence and Growth: Although the main motive of any business is profit but the prosperity and growth of business is not possible without a continuous service to the society. Therefore, it is justified for a business to assume social responsibility.
- Avoidance of Government Regulation: Businessmen can avoid the problem of government regulations by assuming social responsibilities voluntarily which helps to reduce the need for new laws.
- Maintenance of Society: Those people who do not get a return for their hardships get indulged in anti-legal activities. Therefore, it is advisable for business enterprises to assume their social responsibilities.
- Long Term Interest of the Firm: If consumers, workers, shareholders, government officials feel that they are not getting what they deserve, they start to withdraw their hands from business. It may prove more expensive for an enterprise.
- Availability of Resources with Business: A business enterprise has effective human and financial resources to solve many of the social problems.
- Converting Problems into Opportunities: Business can make risky situations useful by using their efficiency.
- Better Environment for Doing Business: Business system should do something to meet needs before it is confronted with a situation when its own survival is endangered.
- Holding Business responsible for Social Problems: Environmental pollution, unsafe workplaces, corruption in public institutions and discriminatory practices in employment are some of the problems which have caused due to business enterprises.
Arguments against Social Responsibility:
- Violation of Profit Maximization: As per this argument, business enterprises claim that our objective is profit maximization. Business can reduce its cost and raise profits and then only it can meet its social responsibility.
- Lack of Social Skills: Business enterprises neither have skill nor experience to solve all types of social problems. Therefore, it should be handled by specialized agencies.
- Burden on Consumers: Many of the social responsibilities cost a lot and its burden falls on consumers only.
- Lack of Broad Public Support: Business cannot operate successfully because of lack of cooperation and confidence on behalf of public to business enterprises.
Question 2. Discuss the forces which are responsible for increasing concern of business enterprises towards social responsibility. Answer: The following are the forces which are responsible for increasing the concern of business enterprises for social responsibility.
- Threat of Public Regulation: The government is meant to safeguard the interests of society. Thus, in case the government feels that a business enterprise is behaving in a manner that is not socially desirable, then it can regulate the operations of that enterprise accordingly.
- Pressure of Labour Movement: The increase in capital mobility over time has increased the pressure on business enterprises to pay attention to the welfare of workers, by providing them with healthy working conditions along with good remuneration.
- Impact of Consumer Consciousness: As consumers today are aware of their rights and responsibilities, they take their decisions more rationally. Thus, business enterprises are made to work more efficiently and produce better products at reasonable rates to satisfy their customers.
- Development of Social Standards: Business enterprises are not merely profit-making entities. For their long-term growth and existence, they require fulfilling the new standards of social welfare.
- Development of Business Education: The spread of education over time has made consumers, investors, employees and owners aware of social problems, thereby making them more sensitive to social issues.
- Relationship Between Social Interest and Business Interest: No business enterprise can work in isolation from society. Thus, there should be a balance between business interests and social interests, such that the business can grow by doing the maximum good to society.
- Development of a Professional Managerial Class: Every business professional pursues the goal of profit maximization. But today’s professional managers make efforts to satisfy the interests of all members of society.
Question 3. ‘Business is essentially, a social institution and not merely a profit making activity.’ Explain. Answer: The primary objective of any business enterprise is profit maximization. This is because profit acts as a measure of success and at the same time is the main source of income for an enterprise. Also, profits are often used to finance the expansion projects of a business enterprise. However, it is argued that business enterprises are not merely profit-making entities. They are considered as social institutions, too, as they are created by society. As every business makes use of society’s resources in terms of human and physical capital, it cannot work in isolation from society. Its operations are affected by social problems such as unemployment and poverty. Thus, a need arises to create a balance between the business interests and social interests of a business enterprise, such that it can grow by doing the maximum good to society. Hence, we can say that a business enterprise is a social institution and not merely a profit-making entity. In this regard, the following are some of the responsibilities that must be fulfilled by an enterprise:
- Paying taxes on time.
- Paying fair wages to employees.
- Supplying quality products at reasonable prices to customers.
- Cooperating with the government in solving social problems, such as unemployment, poverty and illiteracy.
A business has some responsibility towards:
- Government and local administrative bodies that regulate its commercial activities in their jurisdictions.
- The general public that makes up a big part of society.
Question 4. Why do the enterprises need to adopt pollution control measures? Answer: Pollution control is necessary for preserving and improving the quality of environmental resources. As business activities such as production, transportation, distribution, storage and consumption are often assumed to cause the maximum destruction to society’s resources, a need arises for adopting pollution control measures. Following are some of the reasons why business enterprises need to adopt pollution control measures,
- Reduced health hazards: Pollutants in the environment cause diseases such as cancers and respiratory problems. Thus, pollution control measures will not only help in reducing the incidence of diseases but also help people enjoy a good and healthy life.
- Reduced risk of liability: Enterprises are often held responsible for polluting the environment and are asked to compensate. Pollution control helps in reducing the risk of such liabilities.
- Cost savings: Efficient pollution control mechanisms help in reducing the cost of waste disposal and the cost of cleaning up production plants. This in turn helps firms to reduce their costs.
- Improved public image: An increase in the education level has made people more aware about environmental problems. As a result, they have started realising the need to protect the environment. Thus, business enterprises which adopt pollution control measures enjoy a good reputation in the society.
- Other social benefits: Pollution control helps a firm to enjoy various other benefits such as cleaner surroundings, better quality of life for its employees as well as owners and increased availability of good quality resources.
Question 5. What steps can an enterprise take to protect the environment from the dangers of pollution? Answer: Various business activities such as production, transportation and consumption of goods often result in over exploitation of natural resources. Thus, it is the responsibility of every business enterprise to control discharge of pollutants into the environment. The following steps can be taken by the business enterprises to control pollution.
- Control by top managers: The top management of every organisation should be committed to creating, developing and maintaining a work culture conducive to environmental protection and pollution prevention.
- Control by employees : Employees at all the levels of an organisation should be committed to keeping the environment clean and protected.
- Better technology: Enterprises should employ good and superior technologies of production and use scientific techniques for waste disposal. This will ensure environmental protection and pollution control.
- Follow rules: Enterprises must conform to the rules and regulations enacted by the government for the prevention of environmental pollution.
- Increased awareness: By conducting workshops and training programmes, business enterprises must make an effort to spread awareness among its employees of the need to conserve the environment.
- Assessment programmes: An efficient mechanism for the periodic assessment of pollution control programmes may also be adopted, in order to weigh their costs and benefits.
Question 6. Explain the various elements of business ethics. Answer: Business ethics can be defined as the code of conduct that a business must follow, such that it takes up only those activities that are desirable from the viewpoint of society. The purpose of business ethics is to guide managers and other employees in an organisation in performing their jobs in a manner that is socially acceptable. Business ethics should be followed in the day-to-day working of a business enterprise. The following are some of the elements of business ethics.
- Commitment by top management: Top-level officers, such as the CEO’s and other higher level managers, must sincerely follow the ethical code of conduct. They should also guide other employees in their organisation in adopting the code.
- Publication of a code: An enterprise must clearly define the ethical code of conduct to be followed in the organisation. The code should include quality standards for work, laws governing production and employee’s health and safety standards.
- Establishment of compliance mechanism: In addition to setting performance standards, an enterprise must also devise a mechanism through which it can measure the actions of individual employees. This should be done in order to confirm whether the ethical standards are being met.
- Involvement of employees at all levels: The successful implementation of ethical standards depends to a large extent on the involvement of employees at different levels. This is because it is the employees who actually implement the ethical codes.
- Measurement of results: Although it is difficult to measure the end results of implementation of ethical standards, the top management should take steps to monitor compliance. Also, it must take serious action against any unethical behaviour in the organisation.
MORE QUESTIONS SOLVED
I. Very Short Answer Type Questions Question 1. Define corporate social responsibility. Answer: Corporate social responsibility is a comprehensive set of policies, practices and programmes which are integrated into business operations, supply claims, and decision making process throughout the company, wherever the company does business and includes responsibility for current actions as well as past and future actions.
Question 2. What is the relation between ethics and moral values? Answer: Ethics refer to the entire body of moral values which a society attaches to the actions of human beings.
Question 3. What do you mean by the principles derived from social values which guide and govern the conduct of businessmen? Answer: Business ethics are principles derived from social values which guide and govern the conduct of businessmen.
Question 4. Mention two responsibilities of business towards customers. Answer: Supply of right quality of goods and proper precaution against adulteration.
Question 5. Give any two reasons supporting social responsibilities. Answer: (i) It is in long term interest of the business. (ii) It is justified for growth and existence of business.
Question 6. Give any two reasons against social obligation. Answer: (i) It violates the goal of profit maximization (ii) Its burden falls on consumers.
Question 7. Name any two factors which affect the ethical behaviour of a business. Answer: Awareness amongst people, overall environment of the area where business is located.
Question 8. Define pollution. Answer: Pollution is change in the physical, chemical and biological characteristics, air, land and water.
Question 9. Give any one point of difference between ethics and law. Answer: Ethics are self-imposed while laws are imposed by an external governing authority.
Question 10. Do businessmen have skill to tackle social problems? Answer: Yes, businessmen have skills to tackle some but not all social problems.
Question 11. What is environmental pollution? Answer: When the quality of environment degrades due to mixture of unwanted elements in it, it is called environmental pollution.
Question 12. What is the reality of social responsibilities? Answer: In reality, social responsibility takes form of lip service only. There is no genuine effort from a business. Many a time firms play their legal roles in the name of social responsibility.
Question 13. What is code of ethics? Answer: An enterprise must clearly define the ethical code of conduct to be followed in the organisation. The code should include quality standards for work, laws governing production and employee’s health and safety standards.
Question 14. Give any one difference between ethics and law. Answer: Business ethics refer to the socially determined moral principles which should govern business activities. Laws are determined by the legal bodies of a country.
II. Short Answer Type Questions Question 1. What are the core objectives of social responsibility of business? Answer: The core objectives of social responsibility of business are as follows:
- It is a concept that implies a business must operate (function) with a firm mindset to protect and promote the interest and welfare of society.
- Profit (earned through any means) must not be its only highest objective else contributions made for betterment and progress of a society must also be given a prime importance.
- It must fulfill its social responsibilities honestly in regard to the welfare of society in which it operates and whose resources and infrastructures it makes use of to earn huge profits.
- It should never neglect (avoid) its responsibilities towards society in which it flourishes.
Question 2. What are the obligations of a business in the name of social responsibility? Answer: The social responsibility of business comprises of the following obligations:
- A business must give a proper dividend to its shareholders or investors.
- It must provide fair wages and salaries with good working conditions.
- It must provide a regular supply of good quality goods and/or services to its consumers/customers at reasonable prices.
- It must abide by all government rules and regulations, support its business related policies and should pay fair taxes without keeping any delays or dues.
- It must also contribute for the betterment of a local community by doing generous activities like building schools, colleges, hospitals, etc.
- It must take immense care to see that its activities neither directly nor indirectly create havoc on the vitality of its surrounding environment.
- It should maintain a stringent policy to curb or control pollution in regard to contamination of air, water, land, sound and radiation leakages. It must hire experienced professional individuals who are experts in their respective fields.
- It should also offer social-welfare services to the general public.
Question 3. Name any four elements of business ethics. Answer: Business ethics can be defined as the code of conduct that a business must follow, such that it takes up only those activities that are desirable from the viewpoint of society. The purpose of business ethics is to guide managers and other employees in an organisation in performing their jobs in a manner that is socially acceptable. The following are some of the elements of business ethics.
- Top-level officers, such as the CEO’s and other higher level managers, must sincerely follow the ethical code of conduct. They should also guide other employees in their organisation in adopting the code.
- An enterprise must clearly define the ethical code of conduct to be followed in the organisation. The code should include quality standards for work, laws governing production and employee’s health and safety standards.
- In addition to setting performance standards, an enterprise must also devise a mechanism through which it can measure the actions of individual employees. This should be done in order to confirm whether the ethical standards are being met.
- The successful implementation of ethical standards depends to a large extent on the involvement of employees at different levels. This is because it is the employees who actually implement the ethical codes.
- Although it is difficult to measure the end results of implementation of ethical standards, the top management should take steps to monitor compliance. Also, it must take serious action against any unethical behaviour in the organisation.
Question 4. Explain the obligations of business towards owners and investors. Answer: It is the responsibility of a business to pay attention on the maintenance and expansion of returns for all of its shareholders on important management issue, and constantly strives to improve its business performance and financial structure. The company’s dividend policy calls for maintaining stable dividends, and Casio determines the allocation of profit by taking into account all factors such as profit levels, financial position, the dividend pay out ratio, and future business development and forecasts.
Question 5. How can a business enterprise improve its public image by performing social responsibilities? Answer: Public relations is a potent tool for shaping consumer perception and building a company’s image. Corporations that actively promote their social responsibility activities often take steps to publicise these efforts through the media. Getting the word out about corporate donations, employee volunteer programmes, or other CSR initiatives is a powerful branding tool that can build publicity for you in both online and print media.
Question.6. What obligation does a businessman have towards the government? Answer: Social responsibility of business towards government’s regulatory bodies or agencies is quite sensitive from the license point of view. If permission is not granted or revoked abruptly, it can result in huge losses to an organization. Therefore, compliance in this regard is necessary. Furthermore, a business must also function within the demarcation of rules and policies as formulated from time to time by the government of state or nation. It should respect laws and abide by all established regulations while performing within the jurisdiction of state. Some examples of activities a business can do in this regard:
- Paying fair taxes on time,
- Following labor, environmental and other laws, etc.
- Seeking permissions wherever necessary,
- Licensing an organization,
If laws are respected and followed, it creates goodwill of business in the eyes of authorities. Overall, if a government is satisfied it will make favourable commercial policies, which will ultimately open new opportunities and finally benefit the organization sooner or later.
Question 7. Give any four reasons against the social responsibilities of business. Answer: Arguments against social responsibility
- Violation of Profit Maximisation: As per this argument, business enterprises claim that our objective is profit maximisation. Business can reduce its cost and raise profits and then only it can meet its social responsibility.
- Lack of Social Skills: Business enterprises neither have skill nor experience to solve all types of social problems. Therefore, it should be handled by specialised agencies.
- Lack of Broad Public Support : Business cannot operate successfully because of lack of cooperation and confidence from public to business enterprises.
Question 8. What are the responsibilities of business towards employees and customers? Answer: Social responsibility of business towards its employees: It is important because they are the wheels of an organization. Without their support, the commercial institution simply can’t function or operate. If a business takes care of the needs of its human resource (for e.g. office staff, employees, workers, etc.) wisely, it will boost the motivation and working spirit within an organization. A happy employee usually gives his best to the organization in terms of quality labour and timely output than an unsatisfied one. A pleasant working environment helps in improving the efficiency and productivity of working people. A good remuneration policy attracts new talented professionals who can further contribute to its growth and expansion.Thus, if personnel are satisfied, then they will work together very hard and aid in increasing the production, sales and profit. Social responsibility of business towards its consumers or customers: It matters a lot from sales and profit point of view. Its success is directly dependent on their level of satisfaction. Higher their rate of satisfaction, greater is the chances to succeed. If a business rolls out good-quality products and/or delivers better quality services that too at reasonable prices, then it is natural to attract lots of customers. If the quality- price ratio is maintained well and consumers get worth for their money spends, this will surely satisfy them. In the long run, customer loyalty and retention will grow, and this will ultimately lead to profitability.
Question 9. Describe the obligations of business towards owners and shareholders . Answer: Social responsibility of business towards its shareholders or investors is most important of all other obligations. If a business satisfies its investors, they are likely to invest more money in a project. As a result, more funds will flow in and the same can be utilized to modernise, expand and diversify the existing activities on a larger scale. Happy financiers can fulfill the rising demand of funds needed for its growth and expansion.
- They need to give a fair return to shareholders.
- They need to give true and fair information to shareholders.
- They need to give them proper opportunity to participate.
Question 10. Which eight problems have been identified by the United Nations which cause damage to natural environment? Answer: Following eight problems have been identified by the United Nations which cause damage to natural environment: 1. Ozone depletion 2. Global warming 3. Fresh water quality and quantity 4. Deforestation 5. Land degradation 6. Solid and hazardous waste 7. Water pollution 8. Danger to biological diversity.
III. Long Answer Type Questions Question 1. Social responsibility is not an area of business. Do you agree? Justify. Answer: It can be justified by considering case for and case against social responsibility: The case in favour of taking up social responsibilities.
- Existence and growth: Business enterprises exist to make profits by providing goods and services to consumers. Thus, we can say that their long-term growth prospect depends not only on their profits but also on how efficiently they serve the society. Therefore, taking up social responsibilities supports the existence and growth of a business enterprise.
- Avoidance of government intervention: Business enterprises should always work in line with society’s values and ethics. This would help them fulfill their social responsibilities, which in turn would make them less prone to government intervention.
- Better environment for doing business: Businesses make use of society’s resource of human capital. Thus, by providing employment to people, they help solve the social problems of unemployment and poverty, thereby creating a favorable environment for business.
The case against taking up social responsibilities:
- Violation of profit maximization objectives: It is argued that a business enterprise exists to make a profit. Thus, if it engages itself in solving social problems, then it may not have enough resources to meet its primary objective of profit maximization.
- Burden on consumers : It is argued that when a business enterprise is engaged in solving social problems such as environment pollution and unemployment, its expenditures increase. This increased financial burden is ultimately passed on to the consumers in the form of higher prices of products.
- Lack of social skills: Business persons are basically trained to solve business- related problems such as minimizing cost, maximizing profits and increasing sales. However, they are not specialised in solving social problems. Thus, it is argued that social problems must be solved only by specialised agencies, which have the required training and skills.
Question 2. Explain the need for social responsibility. Answer: Need of social responsibility is essentially a moral question because it can be answered differently by different people depending on what is right and what is wrong for a person. Social responsibility is needed to be followed because:
- Showing a true commitment: The most successful corporate social responsibility programmes integrate these two types of CSR together to show a true commitment to a cause. For example, a company that uses sustainable materials in their products, donates financial resources to environmental causes, and allows employees to take paid time off for volunteering at environmental charities would be showing a true commitment to the environment that goes beyond any single CSR initiative.
- Social media visibility: One of the reasons that corporations should have visible CSR campaigns is due to the importance and prevalence of social media. Corporations that want to protect their brand understand that social media is an integral part of public perception. When a corporation exercises social responsibility in the form of fund raising or setting up employee giving programmes, using social media to promote these actions helps to create a positive branding environment and it is a great way to engage with your audience on a deeper level that goes beyond your products or services.
- Public relations benefits: Public relations is a potent tool for shaping consumer perception and building a company’s image. Corporations that actively promote their social responsibility activities often take steps to publicise these efforts through the media. Getting the word out about corporate donations, employee volunteer programmes, or other CSR initiatives is a powerful branding tool that can build publicity for you in both online and print media.
- Government relations: Corporations that put an emphasis oh corporate social responsibility typically have an easier experience when dealing with politicians and government regulators. In contrast, businesses that present a reckless disregard for social responsibility tend to find themselves finding off various inquiries and probes, often brought on*at the insistence of public service organizations. The more positive the public perception is that a corporation takes social responsibility seriously, the less likely it is that activist groups will launch public campaigns and demand government inquiries against it.
- Building a positive workplace environment: Finally, one of the greatest benefits of promoting social responsibility in the workplace is the positive environment you build for your employees. When employees and management feel they are working for a company that has a true conscience, they will likely be more enthusiastic and engaged in their jobs. This can build a sense of community and teamwork which brings everyone together and leads to happier, more productive employees.
Question 3. What is corporate social responsibility? Is it similar to business ethics? Answer: The World Business Council for Sustainable Development in its publication Making Good Business Sense by Lord Holme and Richard Watts, used the following definition. Corporate Social Responsibility is the continuing commitment by business to behave ethically and contribute to economic development while improving the quality of life of the workforce and their families as well as of the local community and society at large. The same report gave some evidence of the different perceptions of what this should mean from a number of different societies across the world. Definition: CSR is about capacity building for sustainable livelihoods. It respects cultural differences and finds the business opportunities in building the skills of employees, the community and the Government from Ghana, through to CSR is about business giving back to society from the Philippines. Traditionally in the United States, CSR has been defined much more in terms of a philanthropic model. Companies make profits, unhindered except by fulfilling their duty to pay taxes. Then they donate a certain share of the profits to charitable causes. It is seen as tainting the act for the company to receive any benefit from the giving. It is not same as business ethics. Business ethics is a personal concept and is wider in many senses than CSR.
Question 4. Why should a business do any thing for society at large? Answer: The term “Corporate Social Responsibility” is still widely used even though related concepts, such as sustainability, corporate citizenship, business ethics, stakeholder management, corporate responsibility, and corporate social performance, are vying to replace it. In different ways, these expressions refer to the ensemble of policies, practices, investments, and concrete results deployed and achieved by a business corporation in the pursuit of its stakeholders’ interests. There is no single CSR business case—no single rationalisation for how CSR improves the bottom line. Over the years, researchers have developed many arguments. In general, these arguments can be grouped based on approach, topics addressed, and underlying assumptions about how value is created and defined. According to this categorization, CSR is a viable business choice as it is a tool to:
- implement cost and risk reductions;
- gain competitive advantage;
- develop corporate reputation and legitimacy; and
- seek win-win outcomes through synergistic value creation.
Question 5. Explain the reality of social responsibility. Answer: In reality, social responsibility receives only lip service. Some business houses fulfill its legal responsibility in the name of social responsibility. There are some factors and reasons which have forced and persuaded business organizations to fulfill their social responsibility which are as follows:
- Threat of public regulation: India is a democracy where Government is expected to be welfare state. If any business organization acts in a socially irresponsible manner, then an action may be taken against them to safeguard people’s interest. In reality, business houses do not assume their social responsibility on their own but due to threat of public action.
- Pressure of labour movement: In the last century, labour movement for extracting gains for the working class throughout the world has become powerful. Labour laws are also followed not out of a sense of social responsibility but because of increasing pressure of labour movement.
- Impact of consumer consciousness: Consumers are also becoming aware of their rights since enactment of Consumer Protection Act, 1986. Under this Act, consumers are entitled to file a case if he is cheated in any ways.
- Development of social standard for business: As per new social standards, a business is considered to be legitimate only if it fulfills its social responsibilities. No business can be done in isolation with the society. The performance of a business is judged on social standards.
- Development of business education: Nowadays businessmen are professionally qualified due to changing pattern of form of business. It is also making it socially more responsible. Education has made people more conscious as employees, customers, investors and owners.
- Relationship between social interest and business interest: Businessmen are able to find that social interest and business interest are correlated. The concept which existed earlier that no business can grow without exploitation of others does not exist any more.
- Development of professional, managerial class: Professional management is also educated of the benefits it can get by fulfilling its social responsibility. Professional managers are more interested in satisfying a multiple group of interest groups in society for running their enterprises successfully than attaining goal of profit maximization only.
Question 6. “A business owes curtain obligations towards different groups.” Identify those groups and explain the obligation of business towards those groups. Or Explain social responsibility of a business towards different interest groups. Answer: Social responsibility of government towards different groups is explained below:
- Shareholders or investors: Social responsibility of business towards its shareholders or investors is most important of all other obligations. If a business satisfies its funders, they are likely to invest more money in a project. As a result, more funds will flow in and the same can be utilised to modernize, expand and diversify the existing activities on a larger scale. Happy financiers can fulfill the rising demand of funds needed for its growth and expansion.
- Personnel: Social responsibility of business towards its personnel is important because they are the wheels of an organization. Without their support, the commercial institution simply can’t function or operate. If a business takes care of the needs of its human resource (for e.g. of office staff, employees, workers, etc.) wisely, it will boost the motivation and working spirit within an organization. A happy employee usually gives his best to the organization in terms of quality labour and timely output than an unsatisfied one. A pleasant working environment helps in improving the efficiency and productivity of working people. A good remuneration policy attracts new talented professionals who can further contribute in its growth and expansion. Thus, if personnel are satisfied, then they will work together very hard and aid in increasing the production, sales and profit.
- Consumers or customers: Social responsibility of business towards its consumers or customers matters a lot from sales and profit point of view. Its success is directly dependent on their level of satisfaction. Higher their rate of satisfaction greater is the chances to succeed. If a business rolls out good-quality products and/or delivers better quality services that too at reasonable prices, then it is natural to attract lots of customers. If the quality-price ratio is maintained well and consumers get worth for their money spends, this will surely satisfy them. In the long run, customer loyalty and retention will grow, and this will ultimately lead to profitability.
- Government: Social responsibility of business towards government’s regulatory bodies or agencies is quite sensitive from the license’s point of view. If permission is not granted or revoked abruptly, it can result in huge losses to an organization. Therefore, compliance in this regard is necessary. Furthermore, a business must also function within the demarcation of rules and policies as formulated from time to time by the government of state or nation. It should respect laws and abide by all established regulations while performing within the jurisdiction of state. Some examples of activities a business can do in this regard: (a) Licensing an organization, (b) Seeking permissions wherever necessary, (c) Paying fair taxes on time, (d) Following labour, environmental and other laws, etc. (e) If laws are respected and followed, it creates goodwill of business in the eyes of authorities. Overall, if a government is satisfied it will make favourable commercial policies, which will ultimately open new opportunities and finally benefit the organization sooner or later. Therefore, satisfaction of government and local administrative bodies is equally important for legal continuation of business.
- Local community: Social responsibility of business towards the local community of its established area is significant. This is essential for smooth functioning of its activities without any agitations or hindrances. A business has a responsibility towards the local community besides which it is established and operates from. Industrial activities carried out in a local area affect the lives of many people who reside in and around it. So, as a compensation for their hardship, an organization must do something or other to alleviate the intensity of suffering. (a) As a service to the local community, a business can build. (b) A trust-run hospital or health centre for local patients. (c) A primary and secondary school for local children. (d) A diploma and degree college for local students. (e) An employment centre for recruiting skilled local people, etc. Such activities to some extent may satisfy the people that make local community and hence their changes of agitations against an establishment are greatly reduced. This will ensure the longevity of a business in the long run.
- Environment: Social responsibility of business with respect to its surrounding environment can’t be sidelined at any cost. It must show a keen interest to safeguard and not harm the vitality of the nature. A business must take enough care to check that its- activities don’t create a negative impact on the environment. For example, dumping of industrial wastes without proper treatment must be strictly avoided. Guidelines as stipulated in the environmental laws must be sincerely followed. Lives of all living beings are impacted either positively or negatively depending on how well their surrounding environment is maintained (naturally or artificially). Humans also are no exception to this. In other words, health of an environment influences the health of our society. Hence, environmental safety must not be an option else a top priority of every business.
- Community: Finally, social responsibility of business in general can also contribute to make the lives of people a little better.
- Some examples of services towards public include: (a) Building and maintaining devotional or spiritual places and gardens for people, (b) Sponsoring the education of poor meritorious students, (c) Organizing events for a social cause, etc. (d) Such philanthropic actions create a goodwill or fame for the business organization in the psyche of general public, which though slowly but ultimately pay off in the due course of time.
IV. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Question 1. “Like an individual, business enterprise should also be a loyal citizen to the state.” Discuss. Answer: It has been rightly said that like an individual, a business enterprise should also be a loyal citizen to the state. Therefore, it has to be kept in mind.
- Social needs of our country while deciding on what goods and services are to be produced. Therefore, a businessman in India must prefer necessities to cosmetics and dog food in a country like India where 26% people are below poverty line.
- Production of liquor, tobacco and other undesirable products should be avoided.
- Production method should be used. If a country is labour abundant, the business should give preference to labour intensive techniques.
Question 2. Describe the reality of social responsibilities of a company. Answer: The biggest problem with CSR is not that it has limitations, nor is it concerning its questionable ability to sufficiently address the problems it intends to ameliorate. Rather, it is the fact that it takes people to a completely wrong direction. For many large corporations, CSR is primarily a strategy to divert attention away from the negative social and environmental impacts of their activities. In the Asian context, CSR mostly involves activities like adopting villages for what they call a ‘holistic development’, in which they provide medical and sanitation facilities, build school and houses, and helping villagers become self-reliant by teaching them vocational and business skills. Such corporate strategies have been effectively hegemonic, providing a strong legitimacy and license for corporations to sustain the exploitation of human and natural resources. More importantly, it leads people to wrongly assume that the business houses, and not the states, are responsible for citizens’ basic rights to better education, clean water, healthcare, etc. It disciplines the uninformed poor motivating them to behave in ways that make state regulation obsolete, while leaving them at the mercy of market forces.
Question 3. Business ethics and social responsibility are not synonyms but are closely related. Substantiate. Answer: Business ethics and social responsibility are the words that are almost used as a common parlance interchangeably. While social responsibility is self explanatory, ethics is a word that puts one in a dilemma. Social responsibility looks clearly defined and demarcated. Companies have a policy of social responsibility known as Corporate Social Responsibility whereby they commit to follow their businesses in such a way so as to benefit the community at large. But ethics is a loose term that is dependent upon a person’s conscience. There are certain differences between the two and the two are not overlapping completely. Business Ethics To understand business ethics, first we need to understand and spell out clearly the word ‘ethics’. Derived from ancient Greek word ethos, ethics has come to mean moral character. Ethical behaviour is what is good or right. Ethical senses always make use of good, bad, right and wrong. Applying this definition to business, we come to a conclusion that though the primary objective of any business or company is to maximize by the decisions taken by the company for the operation of business. Business ethics is the behaviour of any business that it indulges in its dealings with the community or society. For some, making money is all they are interested in, and this is capitalism in its dirtiest form. These people are least concerned with the bad effects of their business practices and the harm they are doing to the society at large. When companies do not engage in good business ethics, they are penalised by the law. But such cases are rare and the profits of companies engaging in unethical behaviour are far more than these punitive fines. Social Responsibility Man is a social animal and cannot live in isolation. He is expected to behave in a manner that is socially and morally acceptable to others. The same applies to businesses. Though the primary objective of any business is to earn maximum profits for the owners and shareholders, it is also expected to conduct its operations in a manner that it fulfills its social obligations also. For example, though it is not binding on any private sector company to provide employment to the disabled or weaker sections of the society, it is considered to be a part of the social responsibility of the company to absorb people from such sections of the society. Similarly though there is not written law to compel a company to engage in acts to do something to reduce pollution or to do something for the betterment of environment, taking up projects to clean up environment are considered to be a part of the social responsibility of the company. Difference between Business Ethics and Social Responsibility Though business ethics and social responsibility seem to be overlapping, there has always been a contradiction between the two.
- Companies, though they are committed to be socially responsible for their behaviour have been found to be engaging in acts that cannot be called ethical.
- What is good for the society is sometimes not good for the business, and what is good for the business is almost always not good for the society.
- If the society is conscious, it responds in such a way that businesses are forced to behave responsibly. The same applies to the administration and the judiciary of any country.
- For example, selling of liquor and tobacco in any society is not against business ethics though it may be against the principles of social responsibility. The same applies to lotteries and gambling. But it is certainly against business ethics as well as against social responsibility to entice minors to engage in smoking and drinking.
V. Value Based Questions Question 1. If you start a business, which objective will be of utmost importance to you and why? Answer: If I start my own business, my social objectives will be of utmost importance to me because:
- It will create employment opportunities in the economy. I will make use of such methods which are desirable from society point of view.
- It will help me to provide good quality product at reasonable prices to my customers.
- It will keep environment pollution free.
- When I will concentrate on these objectives. It will satisfy my consumers and employees. Consumer satisfaction will lead to improvement in my goodwill and market standing. Employee satisfaction will lead to increase in productivity. These two factors will increase profits in the long run automatically.
Question 2. What do you mean by the principle derived from social values which guide and govern the conduct of businessmen? Explain the factors governing these principles and values. Answer: Social Return on Investment (SROI) is a principle based method for measuring extra-financial value (i.e., environmental and social value not currently reflected in conventional financial accounts) relative to resources invested. It can be used by any entity to evaluate impact on stakeholders, identify ways to improve performance, and enhance the performance of investments. A network was formed in 2006 to facilitate the continued evolution of the method. Over 570 practitioners globally are members of the SROI Network. The SROI method as it has been standardized by the SROI Network provides a consistent quantitative approach to understanding and managing the impact of a project, business, organisation, fund or policy. It accounts for stake holders views of impact, and puts financial ‘proxy’ values on all those impacts identified by stakeholders which do not typically have market values. The aim is to include the values of people that are often excluded from markets in the same terms as used in markets, that is money, in order to give people a voice in resource allocation decisions. Some SROI users employ a version of the method that does not require that all impacts be assigned a financial proxy. Instead the “numerator” includes monetized, quantitative but not monetized, qualitative, and narrative types of information about value. Benefits that cannot be Monetized: There will be some benefits that are important to stakeholders but which cannot be monetized. An SROI analysis should not be restricted to one number, but seen as a framework for exploring an organization’s social impact, in which monetization plays an important but not an exclusive role. Focus on Monetization: One of the dangers of SROI is that people may focus on monetization without following the rest of the process, which is crucial to proving and improving. Moreover, an organisation must be clear about its mission and values and understand how its activities change the world – not only what it does but also what difference it makes. This clarity informs stakeholder engagement. Therefore, if an organisation seeks to monetize its impact without having considered its mission and stakeholders, then it risks choosing inappropriate indicators; and as a result the SROI calculations can be of limited use or even misconstrued. Needs considerable Capacity: SROI is time and resource, intensive. It is most easily used when an organisation is already measuring the direct and longer term results of its work with people, groups, or the environment. Some outcomes not easily associated with monetary value: Some outcomes and impacts (for example, increased self-esteem, improved family relationships) cannot be easily associated with a monetary value. In order to incorporate these benefits into the SROI ratio proxies for these values would be required. SROI analysis is a developing area and as SROI evolves it is possible that methods of monetizing more outcomes will become available and that there will be increasing number of people using the same proxies.
Question 3. “The business is responsible for aggravating pollution, so it becomes the moral duty of businessmen to take some positive steps for controlling this problem.” In the light of this statement explain the role of businessmen in checking pollution. Answer: The statement is perfectly correct. In this regard, a businessman can play the following role:
- He may ensure that he makes use of eco friendly methods of production as far as possible.
- He may ensure that in case any pollution occurs, the waste is discharged in proper manner as per the provisions of pollution control boards.
- He may also create awareness amongst employees on how can they minimize this pollution by initiating workshops, seminars etc.
NCERT Solutions Accountancy Business Studies Indian Economic Development Commerce
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics PDF
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics are one of the most important tools in study material that students can get as it will aid them to study properly and reduce any stress that they face during the academic year before.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics

SelfStudys provides chapter-wise Business Studies Revision Notes and short key notes for the CBSE board examination in free downloadable PDF format so students can practice it for their studies and get better in their board examinations. The CBSE Class 11 Revision notes are made for some important subjects such as Maths, English, Hindi, Physics, Chemistry and Biology. These core subjects can be very difficult for students and the revision notes for every chapter will enable them to have a skilful studying pattern with which they can achieve so much better and also enjoy studying the subject.
Last-minute revision is never easy. Our CBSE Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics revision notes summarise key points of a chapter in an easy to remember form. They provide students with an additional edge and help boost confidence before appearing for their examinations. The CBSE Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics have been widely compiled by teachers with close to 15 years of experience and after studying the last ten years of examination papers. Further, they are all made with the latest educational year's subject material so that any deviation in the syllabus is considered as well. CBSE Class 11 Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics revision notes are very important and useful because, for the science and maths subjects, it is essential that all questions are explained in a quick and efficient manner. By studying from certain revision notes and using sample papers, students will no doubt be able to relieve any tension before the examinations as they will be fully prepared in advance for their board exams. Also, the CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics PDF is easy to read and includes all the material, all clearly described and in a short manner. Students can also use the sample papers that Selfstudys provides for Class 11 along with the CBSE Class 11 Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics revision notes provided. Together, students will be prepared to answer every type of question, both objective and subjective and aim for the best in their last year of school.
One of the most essential aspects when studying in Class 11, is to make Business Studies Revision Notes. Students who make Business Studies Revision Notes generally are capable to get good marks as they contain the difficulties and little details that could not be included in the textbook being used. The NCERT is the directorate that conducts the CBSE board, which is a nationwide curriculum followed by lacs of students in the country. SelfStudys provides CBSE Class 11 Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics revision notes that can be used as per the students’ requirements. The Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics revision notes can be simply downloaded in a PDF format directly with the weblink. The CBSE Business Studies Revision Notes are available from class 6 to 10 for all their subjects while Class 11 and 12 students can refer revision notes for the core subjects like Maths, Physics, Chemistry and Biology.
Importantance of CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics for Students
All the revision notes have been made in accordance with the latest CBSE syllabus so that there is no mistake if changes have been created by the CBSE board. The Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics revision notes have been made by teachers who have vast experience and know exactly what is needed. Further, students will be able to see chapter-wise Business Studies Revision Notes with short key notes that could raise their preparations. The CBSE Business Studies Revision Notes are prepared with each chapter explained in a concise manner from the latest edition of the books. The CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics are available in a PDF format so that students can simply refer to it whenever required thorough SelfStudys. The teachers who prepare these Business Studies Revision Notes have done so after rigorously going through the last ten year's question papers and then taking them down. Because of the large amount of content present in most of the books, it can be difficult for students to keep up with all of it. The Business Studies Revision Notes can play a role in helping easier studying methods. SelfStudys is one of India’s leading education platforms for students all over the country.
Why Is CBSE Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics Important?
The studying process is student-specific I.e., some students prefer kinesthetic studying, some are auditory students, and others may find visual studying to be more efficient. But these different processes are just a part of the studying experience, the other important aspect is the revision. Students have to strengthen their studying, hence revisions are a way to begin about this phase.
- Enables the student to strengthen their studying
- Students become more confident during examinations
- Exam stress and anxiety are decreased
- Reduced chances of making easy, but conspicuous mistakes
- Saves valuable time during examinations
- The correctness of answers are higher
CBSE Science Revision Notes for Class 11
Download Revision Notes of All Chapters for the latest Science syllabus. Our Revision Notes cover CBSE Physics, Biology and Chemistry subjects.
CBSE Maths Revision Notes for Class 11
Download circles, trigonometry and more with Maths Revision Notes for CBSE students. Get key points for all Maths chapter before your examinations to get higher marks.
CBSE Hindi Revision Notes for Class 11
Answer questions related to Vyakaran with our Class 11 Vyakaran Revision Notes. Study the chapters easily to prepare for your Hindi exams.
CBSE Social Science Revision Notes for Class 11
Download the key points in History, Civics, Geography and Economics with our Class 11 Social Science Revision Notes. Our Social Science Revision Notes for Class 11 cover History, Civics, Geography and Economics subjects.
CBSE English Revision Notes for Class 11
Download English key questions and answers in our Revision Notes. Get better marks with CBSE English Revision Notes for Class 11. Our key Notes contain Comprehension and Composition Revision Notes.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

- CBSE Class 11th
Social Responsibilities of business and Business ethics Class 11 Notes: CBSE 11th Business Studies Chapter 6, Download PDF
Cbse class 11 social responsibilities of business and business ethics notes: revision notes for class 11 business studies chapter 6 have been presented in this article. also, find attached links to important resources for preparation for the upcoming annual examination 2023-2024..

Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Notes: Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has altered its syllabus for the current academic session 2023-2024. As a process of alteration, it has deleted some topics and chapters from Class 11 Business Studies NCERT. Check the deleted syllabus by clicking on the link present below. Also, check the latest CBSE Syllabus 2024, CBSE Sample Paper 2024, and CBSE Exam Pattern 2024. These resources play an important role in preparation for examinations. Similarly, study materials are also equally vital for preparation. Links to some study materials for Class 11 Business Studies have been attached below.
This article presents revision notes for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6, Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics. Revision notes are a great source of study materials that consists of all important topics, definitions, and diagrams from the chapter. It breaks down the complex unit into simple subdivisions, thus making it easy to understand and remember.
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 1
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 2
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 3
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 4
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 5
Mind Maps for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies 2023-2024(PDF)
MCQs for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies 2023-2024(PDF)
Revision Notes for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 are presented below:
What is Social Responsibility of business?
Social responsibility of a business is its obligation to take those decisions and perform those actions which are desirable in terms of the objectives and values of society. It motivates businesses to adhere to environment-friendly business standards and do something for society.
- Justification for existence and growth
- Long-term interest of the firm
- Avoidance of government regulation
- Maintenance of society
- Availability of resources with business
- Converting problems into opportunities
- Better environment for doing business
- Holding businesses responsible for social problems
- Violation of profit maximisation objective
- Burden on consumers
- Lack of social skills
- Lack of broad public support
- Threat of public regulation
- Pressure of labour movement
- Impact of consumer consciousness
- Development of social standards for business
- Development of business education
- Relationship between social interest and business interest
- Development of professional, managerial class
- Economic responsibility - Business is an economic activity. Its foremost job is to produce goods and services and sell them to the consumers as per their needs, to gain profit.
- Legal responsibility - Every business has to function within the laws of the land. These laws are made for the benefit of the people of the country and thus business enterprises should be legally and socially responsible.
- Ethical responsibility - This deals with the behavior of the firm that is expected by society and not codified by law.
- Discretionary responsibility - It is voluntarily taken by business organizations. For example, providing charitable contributions to educational institutions or helping the affected people during floods or earthquakes.
- Responsibility towards the shareholders or owners - has the responsibility to provide a fair return to the shareholders or owners on their capital investment and to ensure the safety of such investment.
- Responsibility towards the workers - It should try to create the right kind of working conditions so that it can win the cooperation of workers
- Responsibility towards the consumers - Supply of the right quality and quantity of goods and services to consumers at reasonable prices constitutes the responsibility of an enterprise toward its customers.
- Responsibility towards the government and community - An enterprise must respect the laws of the country and pay taxes regularly and honestly must protect the natural environment.
Causes of pollution
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Land pollution
- Noise pollution
- Reduction of health hazards
- Reduced risk of liability
- Cost savings
- Improved public image
- Other social benefits
- A commitment by the top management of the company to create, maintain and develop a work culture for environmental protection and pollution prevention.
- Ensuring that commitment to environmental protection is implemented by all divisions and employees.
- Developing policies regarding the purchase of good quality raw materials, employing superior technology, using scientific techniques of disposal and treatment of wastes, and developing employee skills for the purpose of pollution control.
- Abiding by the laws of government for environmental protection.
- Participating in environmental conservation programs organized by the government.
- Arrange educational workshops and training to share technical information and experience with suppliers, dealers, and customers to get them actively involved in pollution control programs.
What is business ethics?
Ethics is concerned with what is right and what is wrong in human behavior judged on the basis of a standard form of conduct/behavior of individuals, as approved by society in a particular field of activity. Thus, business ethics are the morals and values that businesses have to adapt to thrive in society.
CBSE Class 11 Syllabus 2023-24 (All Subjects)
CBSE Class 11 Deleted Syllabus 2023-24 (All Subjects)
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- India Post GDS Merit List 2024
- RBI Grade B Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Admit Card 2024
- SSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- UP Police Constable Question Paper 2024 PDF
- India GDS Merit List 2024 PDF
- UP Police Exam Analysis 2024 Live Updates
- OPSC OCS Result 2024
- Sri Krishna
- Janmashtami Wishes in Hindi
- Education News
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 11 Study Material
Latest Education News
NDA 2 Question Paper 2024: Download UPSC Paper 1 and 2 PDF Here
Vande Bharat Sleeper Train: आधुनिक इंटीरियर से मिलेगी लग्ज़री की फील, देखें शानदार तस्वीरें
RMLAU Result 2024 OUT at rmlau.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
IGNOU June TEE Result 2024 OUT at ignou.ac.in; Direct Link to Download Term End Exam UG and PG Grade Card
India's First Vande Bharat Sleeper Train: पहली वंदे भारत स्लीपर ट्रेन कब और किसी रूट पर दौड़ेगी? जानें
List of ICC Chairman: जय शाह बने सबसे युवा चेयरमैन, अब तक के ICC अध्यक्ष की पूरी लिस्ट यहां देखें
eShram Card: क्या है ई-श्रम कार्ड? लाभ, पात्रता और ऑनलाइन अप्लाई की सभी डिटेल्स यहां देखें, e-shram Card Download का तरीका
PM Kisan Beneficiary Status: डायरेक्ट Link से देखें PM-Kisan Samman Nidhi बेनिफिशियरी स्टेटस
UPI ID Without Bank Account: बिना बैंक खाता के UPI ID कैसे बनाएं? देखें सभी स्टेप
National Teachers Award 2024: ये हैं देश के सर्वश्रेष्ठ शिक्षक, जिन्हें मिलेगा राष्ट्रीय पुरस्कार
उत्तर प्रदेश के 8 रेलवे स्टेशनों को मिले नए नाम, यहां देखें नई लिस्ट
Paris Paralympics 2024 India Medals list: भारत ने जीते कितने पदक,पढ़ें सबके नाम
NEET PG Scorecard 2024 Out: NBEMS Releases NEET PG Score Card at nbe.edu.in, Check Details
KLEE Result 2024 Date: Kerala 5-year and 3-year LLB Exam Results Anytime Soon at cee.kerala.gov.in, Check Qualifying Marks Here
DU NCWEB 2nd Cut-off 2024 for BA, BCom Out at ncweb.du.ac.in, Download PDFs Here
TS ICET Counselling 2024 Registration Begins Today, Apply at icet.tsche.ac.in
Top 10 Most Expensive Luxury Cars of 2024
Who is Yash Dhull? Indian cricketer's Journey from Surgery to Success!
What is the difference between a leopard and a cheetah? In a nutshell!
US Open 2024: Women's Singles and Doubles Draw and Key Matchups
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Business Studies chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics [Latest edition]

Advertisements
Solutions for chapter 6: social responsibilities of business and business ethics.
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 6 of CBSE NCERT for Class 11 Business Studies.
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Short Answer Questions [Pages 158 - 159]
What do you understand by social responsibility of business? How is it different from legal responsibility?
What is environment? What is environmental pollution?
What is business ethics? Mention the basic elements of business ethics?
Briefly explain Air pollution.
Briefly explain Water pollution
Briefly explain Land pollution.
What are the major areas of social responsibility of business?
State the meaning of Corporate Social Responsibility as per the Companies Act 2013.
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Long Answer Questions [Page 159]
Build up argument for and against social responsibilities.
Discuss the forces which are responsible for increasing concern of business enterprises towards social responsibility.
'Business is essentially a social institution and not merely a profit making activity'. Explain.
Why do the enterprises need to adopt pollution control measures?
What steps can an enterprise take to protect the environment from the dangers of pollution?
Explain the various elements of business ethics?.
Discuss the guidelines enumerated by the Companies Act 2013 for Corporate Social Responsibility.
NCERT solutions for Class 11 Business Studies chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Class 11 Business Studies CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 11 Business Studies CBSE 6 (Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Class 11 Business Studies chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics are Concept of Social Responsibility, Case of Social Responsibility, Meaning of Environment Protection and Business, Role of Environment Protection and Business, Concept of Business Ethics, Elements of Business Ethics, Introduction to Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics, Need for Social Responsibility, Kinds of Social Responsibility, Social Responsibility Towards Different Interest Groups, Causes of Pollution, Need for Pollution Control and Business.
Using NCERT Class 11 Business Studies solutions Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Class 11 Business Studies students prefer NCERT Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 6, Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Business Studies additional questions for Mathematics Class 11 Business Studies CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.

- Maharashtra Board Question Bank with Solutions (Official)
- Balbharati Solutions (Maharashtra)
- Samacheer Kalvi Solutions (Tamil Nadu)
- NCERT Solutions
- RD Sharma Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions
- TS Grewal Solutions
- ICSE Class 10 Solutions
- Selina ICSE Concise Solutions
- Frank ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
- CBSE Study Material
- Maharashtra State Board Study Material
- Tamil Nadu State Board Study Material
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Study Material
- Mumbai University Engineering Study Material
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CBSE Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- Maharashtra State Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Arts
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Commerce
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 12 Science
- CISCE ICSE / ISC Board Previous Year Question Paper With Solution for Class 10
- Entrance Exams
- Video Tutorials
- Question Papers
- Question Bank Solutions
- Question Search (beta)
- More Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Shaalaa App
- Ad-free Subscriptions
Select a course
- Class 1 - 4
- Class 5 - 8
- Class 9 - 10
- Class 11 - 12
- Search by Text or Image
- Textbook Solutions
- Study Material
- Remove All Ads
- Change mode
- Sample Paper
- Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Books
- NCERT Audio Books
- NCERT Exempler
- Model Papers
- Past Year Question Paper
- Writing Skill Format
- RD Sharma Solutions
- HC Verma Solutions
- CG Board Solutions
- UP Board Solutions
- Careers Opportunities
- Courses & Career
- Courses after 12th
Home » 11th Class » NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics (PDF)
NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics (PDF)
NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics is here. You can read and download Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 PDF from this page of aglasem.com. Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics is one of the many lessons in NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies in the new , updated version of 2023-24 . So if you are in 11th standard , and studying Business Studies textbook (named Business Studies ), then you can read Ch 6 here and afterwards use NCERT Solutions to solve questions answers of Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics.
NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
The complete Chapter 6 , which is Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics , from NCERT Books for Class 11 Business Studies is as follows.
NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics PDF Download Link – Click Here To Download The Complete Chapter PDF
NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Full Book PDF Download Link – Click Here To Download The Complete Book PDF
NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics PDF
The direct link to download class 11 Business Studies NCERT Book PDF for chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics is given above. However if you want to read the complete lesson on Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics then that is also possible here at aglasem. So here is the complete class 11 Business Studies Ch 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics.

NCERT Book for Class 11 Business Studies
Besides the chapter on Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics, you can read or download the NCERT Class 11 Business Studies PDF full book from aglasem. Here is the complete book:
- Chapter 1 – Business, Trade and Commerce
- Chapter 2 – Forms of Business Organisation
- Chapter 3 – Private, Public and Global Enterprises
- Chapter 4 – Business Services
- Chapter 5 – Emerging Modes of Business
- Chapter 6 – Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
- Chapter 7 – Formation of A Company
- Chapter 8 – Sources of Business Finance
- Chapter 9 – MSME and Business Entrepreneurship
- Chapter 10 – Internal Trade
- Chapter 11 – International Business
- NCERT Books for Class 11
Similarly all the subject-wise class 11 books at aglasem.com are as follows.
- NCERT Book Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Book Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies
- NCERT Book Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Book Class 11 Economics
- NCERT Book Class 11 English
- NCERT Book Class 11 Geography
- NCERT Book Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Book Class 11 History
- NCERT Book Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Book Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Book Class 11 Political Science
- NCERT Book Class 11 Psychology
- NCERT Book Class 11 Sociology
All class-wise books of National Council of Educational Research and Training are as follows.
- NCERT Books for Class 1
- NCERT Books for Class 2
- NCERT Books for Class 3
- NCERT Books for Class 4
- NCERT Books for Class 5
- NCERT Books for Class 6
- NCERT Books for Class 7
- NCERT Books for Class 8
- NCERT Books for Class 9
- NCERT Books for Class 10
- NCERT Books for Class 12
Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics NCERT Textbook – An Overview
The highlights of this Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics chapter PDF are as follows.
| Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Class | 11 |
| Subject | Business Studies |
| Book | Business Studies |
| Chapter Number | Ch 6 |
| Chapter Name | Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics |
| Book Portion Here | NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Ch 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics |
| Download Format | |
| Version | NCERT Book (New, Updated) 2023-24 |
| Complete Book | |
| All Class 11 Books | |
| All Textbooks | |
| NCERT Books in Hindi | |
| NCERT Solutions | |
| More Study Material |
If you have any queries on NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics, then please ask in comments below. And if you found the Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics PDF helpful, then do share with your friends on telegram, facebook, whatsapp, twitter, and other social media! :)
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel .
NCERT Book Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 9 Financial Statements – II (PDF)
Ncert book class 11 chemistry chapter 7 redox reactions (pdf), related posts.

AP Inter 1st Year Previous Year Question Papers – Download PDF Andhra Pradesh Board PYQP
Ap inter 1st year sanskrit question paper | ap pyqp pdf download, ap inter 1st year surveying theory question paper | ap pyqp pdf download, ap inter 1st year tamil question paper | ap pyqp pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply, cbse board quick links.
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Papers
- CBSE Question Papers
- CBSE Practice Papers
CISCE Board Quick Links
- CISCE Time Table
- CISCE Results
- CISCE Specimen Papers
- CISCE Syllabus
- CISCE Question Papers
Class Wise Study Material
Board exams 2023.
- Solved Sample Papers
- Revision Notes
- State Board

Study Material
- Class Notes
- Courses After Class 12th
- JEE Main 2024
- Fashion & Design
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
© 2019 aglasem.com
Discover more from AglaSem Schools
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading
NCERT Notes for Class 11 business studies Chapter 6 SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF BUSINESS AND BUSINESS ETHICS
Class 11 business studies chapter 6 social responsibilities of business and business ethics.
NCERT Notes for Class 11 business studies Chapter 6 SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF BUSINESS AND BUSINESS ETHICS, (business studies) exam are Students are taught thru NCERT books in some of state board and CBSE Schools. As the chapter involves an end, there is an exercise provided to assist students prepare for evaluation. Students need to clear up those exercises very well because the questions with inside the very last asked from those.
Sometimes, students get stuck with inside the exercises and are not able to clear up all of the questions. To assist students, solve all of the questions and maintain their studies without a doubt, we have provided step by step NCERT Notes for the students for all classes. These answers will similarly help students in scoring better marks with the assist of properly illustrated Notes as a way to similarly assist the students and answering the questions right.
Class 11 business studies Chapter 6 SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF BUSINESS AND BUSINESS ETHICS
Social responsibility, kinds of social responsibility, 1- legal responsibility, 2- ethical responsibility, 3- economic responsibility, 4- discretionary responsibility, importance of social responsibility in business/ why should business is socially responsible, 1- public image, 2- to avoid govt. regulation, 3- employee satisfaction, 4- consumer awareness, 5- moral justification, 6- survival and growth, 7- better environment for doing business.
If a business firm voluntarily helps in solving society’s problems such as poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, etc.it gets better environment to conduct its business.
“Business is not merely profit making enterprise, but essentially a social institution”. Comment.
Social responsibilities of business can be classified into the following four categories.( Here explain 4 kinds of social responsibility, i.e, economic, legal, ethical and discretionary responsibilities ).
Arguments against social responsibility
1- it is against profit maximization objective, 2- burden on consumers, 3- lack of social skills, 4- lack of broad public support, social responsibility of business towards different interest groups, 1- responsibility towards owners, 2- responsibility towards investor.
Investors are those who provide finance by way of investment in debentures, bonds, deposits etc…Banks, financial institutions and investing public are all included in the category.
3- Responsibility towards employees
Responsibilities of business towards its employees are:
4- Responsibility towards Government
5- responsibility towards suppliers, 6- responsibility towards customers, 7- responsibility of business towards the society, business ethics, elements of business ethics, 1- top management commitment, 2- publication of a ‘code’, 3- establishment of compliance mechanism, 4- involving employees at all levels, 5- measuring results, environmental pollution and role of business.
Pollution means injection of harmful substances into the environment causing serious damages to human and other life. Pollution causes undesirable change in the physical, chemical or biological characteristics of our air, land and water that can harmfully affect human and other life. Based on the nature and type of environment affected, pollution may be categorized into four:
1- Air Pollution
Impact of air pollution, 2- noise pollution, 3- water pollution, causes of water pollution, impact of water pollution, 4- land pollution, causes of land pollution, effects of land pollution, need/importance of pollution control, 1- improved public image, 2- reduced risk of liability, 3- reduction of health hazards, 4- preventing economic losses, 5- other social benefits, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

Class 11th Business Studies - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
By QB365 on 09 Sep, 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Subject - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Social responsibilities of business and business ethics case study questions with answer key.
11th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Business Studies
Maruti Suzuki strives to minimize the carbon footprint of its manufacturing facilities, products and supply chain operations. The Company believes that investing in environment friendly technologies makes business sense as it brings good returns in the medium to long term. The environment policy of the Company promotes energy conservation, 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle),green procurement, environment friendly mobility and environment consciousness among its direct stakeholders. Going beyond compliance, the Company works closely with its parent company, Suzuki Motor Corporation, to introduce the latest environment friendly technologiesin India, much ahead of statutory requirements. Maruti Suzuki became the first automobile company in India to register a Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). In due course, the Company will earn tradable carbon credits. The Company sends all its hazardous waste to the cement industry for co-processing. All new vehicles are free of hazardous substances and comply with European End of Life vehicle regulations. The Company is working towards continuously improving the fuel efficiency of its cars. The Company has designed and implemented various initiatives to achieve zero injury and fatality. These included a rigorous work permit system and an online incident reporting system called Work Safe Online, through which incidents including nearmiss cases are captured and reported. The Safety and Welfare Department ensures workplace safety, undertakes awareness and training programmes and executes a safety activity plan that is planned and rolled out each month. In addition to plant level safety committees, departmental safety committees have been formed. The Central Safety Leadership Council(CSLC)comprises top management from all business verticals and reviews safety performance of the Company on a quarterly basis. All contractors and service providers working within the Company premises are required to observe 'Safety, Health and Environment' conditions. Separate training and awareness sessions are organised to sensitize them on occupational safety. Source: https: / / www.marutisuzuki.com/social-performance.aspx Quoting lines from the above passage, mention social responsibilities that Maruti Suzuki is fulfilling.
Maruti Suzuki strives to minimize the carbon footprint of its manufacturing facilities, products and supply chain operations. The Company believes that investing in environment friendly technologies makes business sense as it brings good returns in the medium to long term. The environment policy of the Company promotes energy conservation, 3Rs (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle),green procurement, environment friendly mobility and environment consciousness among its direct stakeholders. Going beyond compliance, the Company works closely with its parent company, Suzuki Motor Corporation, to introduce the latest environment-friendly technologies in India, much ahead of statutory requirements. Maruti Suzuki became the first automobile company in India to register a Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) project with the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). In due course, the Company will earn tradable carbon credits. The Company sends all its hazardous waste to the cement industry for co-processing. All new vehicles are free of hazardous substances and comply with European End of Life vehicle regulations. The Company is working towards continuously improving the fuel efficiency of its cars. The Company has designed and implemented various initiatives to achieve zero injury and fatality. These included a rigorous work permit system and an online incident reporting system called Work Safe Online, through which incidents including nearmiss cases are captured and reported. The Safety and Welfare Department ensures workplace safety, undertakes awareness and training programmes and executes a safety activity plan that is planned and rolled out each month. In addition to plant level safety committees, departmental safety committees have been formed. The Central Safety Leadership Council(CSLC)comprises top management from all business verticals and reviews safety performance of the Company on a quarterly basis. All contractors and service providers working within the Company premises are required to observe 'Safety, Health and Environment' conditions. Separate training and awareness sessions are organised to sensitize them on occupational safety. Source: https: / / wwnw.marutisuzuki.com/social-performace.aspx Do you think it will affect earning capacity of the company adversely? Justify your answer.
Ten years ago only about a dozen Fortune 500 companies issued a CSR or sustainability report. Now the majority does. More than 8,000 businesses around the world have signed the UN Global Compact pledging to show good global citizenship in the areas of human rights, labor standards and environmental protection. The next generation of business leaders is even more likely to prioritize CSR. According to data released this month by Net Impact, the nonprofit that aims to help businesses promote sustainability, 65% of MBAs surveyed say they want to make a social or environmental difference through their jobs. Consumer Protection Act, 1986 and jago grahak jago campaigns have made consumers aware of their rights and businesses cannot afford to ignore their duties towards consumers. Today, amid a lingering recession that has dented corporate profits and intensified pressure from shareholders, companies are devising new CSR models. Rather than staffing a modest CSR department - and slapping it on the org chart as a small offshoot of the public relations (PR) or philanthropy division - many companies are instead trying to embed CSR into their operations because they have realized threat social interest and business interest are closely connected. Workers are no more illiterate. They are aware of their rights and in these situations, companies cannot afford to ignore their duties towards labour. Quoting lines from the above passage clarify reality of social responsibility.
*****************************************
Social responsibilities of business and business ethics case study questions with answer key answer keys.
(a) Concern for environment : That investing in environment friendly technologies makes business sense as it brings good returns in the medium to long term. The environment policy of the Company promotes energy conservation, 3 Rs (Reduce, Reuse and Recycle),green procurement, environment friendly mobility and environment consciousness among its direct stakeholders. (b) Optimum Utilization of national Resources: The Company sends all its hazardous waste to the cement industry for co-processing. All new vehicles are free of hazardous substances and comply with European End of Life vehicle regulations. The Company is working towards continuously improving the fuel efficiency of its cars. (c) Safety of employees: The Company has designed and implemented various initiatives to achieve zero injury and fatality. These included a rigorous work permit system and an online incident reporting system called Work Safe Online, through which incidents including near-miss cases are captured and reported. The Safety and Welfare Department ensures workplace safety, undertakes awareness and training programmes and executes a safety activity plan that is planned and rolled out each month. In addition to plant level safety committees, departmental safety committees have been formed. The Central Safety Leadership Council (CSLC) comprises top management from all business verticals and reviews safety performance of the Company on a quarterly basis. All contractors and service providers working within the Company premises are required to observe 'Safety, Health and Environment' conditions. Separate training and awareness sessions are organised to sensitize them on occupational safety.
No, it will not affect earning capacity of the company adversely. (a) No doubt, it involves cost but it will increase sales as people will prefer to buying fuel efficient cars. (b) Recycling and reuse will reduce cost. (c) Safety of employees will increase employees' morale and motivation. It will increase their productivity and employee turnover will decrease.
(a) Threat of Public Regulation: Ten years ago only about a dozen Fortune 500 companies issued a CSR or sustainability report. Now the majority does. More than 8,000 businesses around the world have signed the UN Global Compact pledging to show good global citizenship in the areas of human rights, labor standards and environmental protection. (b) Development of Professional Managerial class: According to data released this month by Net Impact, the nonprofit that aims to help businesses promote sustainability, 65% of MBAs surveyed say they want to make a social or environmental difference through their jobs. Consumer Protection Act, 1986and jago grahakjago campaigns have made consumers' aware oftheir rights and businesses cannot afford to ignore their duties towards consumers. (c) Relationship between social interest and public interest: Today, amid a lingering recession that has dented corporate profits and intensified pressure from shareholders, companies are devising new CSR models. Rather than staffing a modest CSR department - and slapping it on the org chart as a small offshoot of the public relations (PR) or philanthropy division - many companies are instead trying to embed CSR into their operations because they have realized threat social interest and business interest are closely connected. (d) Pressure of labour movement: Workers are no more illiterate. They are aware of their rights and in these situations, companies cannot afford to ignore their duties towards labour.
Related 11th Standard CBSE Business Studies Materials
11th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 11th physics motion in a straight line chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 11th physics units and measurements chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 11th chemistry structure of atom chapter case study question with answers, cbse 11th chemistry some basic concept of chemistry chapter case study questions with answers, 11th biology biological classification chapter case study question with answers cbse, 11th biology the living world chapter case study question with answers cbse.

Class 11th Applied Mathematics - Coordinate Geometry Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
Class 11th applied mathematics - basics of financial mathematics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - descriptive statistics case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - probability case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - calculus case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - mathematical reasoning case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - algebra case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th applied mathematics - numbers, quantification and numerical applications case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 11th biology - chemical coordination and integration case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

11th Standard CBSE Study Materials

11th Standard CBSE Subjects

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics
- Class 11 Important Question
- Business Studies
- Chapter 6: Social Responsibilities Of Business And Business Ethics

CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter-6 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics are present in this article. Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics is such a chapter which is of great importance thus the students of CBSE Class 11 are advised to study this chapter with full concentration and not to miss out on these important questions and answers presented by us.
Free PDF download of Important Questions with Answers for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics prepared by expert Business Studies teachers from the latest edition of CBSE(NCERT) books. Register for Online tuition on Vedantu.com to score more marks in the CBSE examination.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics - Topics Covered
So, what are the topics that are covered in Chapter 6 of CBSE Class 11 Business Studies? Let us check the following to find out:
Social Responsibility
Need for social responsibilities
The case against social responsibility
Reality of social responsibility
Kinds of social responsibilities
Social responsibility towards different interest groups
Business and environment pollution
Role of business in environmental protection
Business ethics
Elements of business ethics
Study Important Questions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 – Social Responsibilties of Business and Business Ethics
Very short answer questions (1 or 2 marks).
1. Define social responsibility of a business?
Ans: Social responsibility is an ethical paradigm that implies that an entity, whether it is an organization or an individual, has a responsibility to behave in the best interests of the society as a whole. Every individual has a responsibility to fulfill in order to maintain a balance between the economy and the ecosystem.
2. Write two examples of business ethics?
Ans: Two examples of business ethics are law-abiding and trustworthiness.
3. State two effects of noise pollution?
Ans: Two effects of noise pollution are:
Loss of hearing
Malfunctioning of the heart due to sudden, loud noise.
4. What is environmental pollution?
Ans: The whole of man's surroundings, both natural and man-made, is characterized as the environment. These surroundings also include resources that are beneficial to human life. Natural resources, such as land, water, air, fauna and flora, and raw materials, as well as artificial resources, such as cultural heritage, socioeconomic institutions, and people, are examples of resources. Pollution, or the release of dangerous compounds into the environment, is termed as environmental pollution. It can take the form of air, water, noise and land pollution.
5. "Companies have social responsibility towards shareholders or owners' how?
Ans: The organization must offer shareholders regular, accurate, and complete information on its operations as well as it’s future growth plans. A fair and reasonable return should also be provided to the owners of the company.
6. What do you mean by Discretionary responsibility?
Ans: Discretionary responsibility basically means the voluntary responsibility fulfilled by the business.
7. Explain how the labour movement has helped companies to fulfill their social responsibility?
Ans: Labour movement for extracting gains for the working class throughout the world has become very powerful. This has compelled businesses to consider the welfare of their employees rather than adopting a "hire and fire" strategy.
8. 'Social responsibility is a burden on consumers' Describe the statement?
Ans: Social responsibilities like pollution control and environmental protection are very costly and often require huge financial investments. Instead of carrying the burden of social duty, businesspeople simply pass it to their customers by demanding higher costs.
9. 'To avoid government regulation, businessmen follow the concept of social responsibility’. How much do you agree with this statement?
Ans: I agree with this statement.
The government regulations and legal restrictions limit the freedom and autonomy of the business enterprises, the businessmen are thought to be able to escape the problem of government restrictions by voluntarily taking on social duties, hence reducing the need for new legislation.
For example, the Central Pollution Control Board takes care of issues related to environmental pollution, and if a business firm follows appropriate measures to avoid environmental pollution, then the interference of the said board could be reduced.
10. Why is social responsibility emphasized? State one need for social responsibility?
Ans: Every individual has a responsibility to fulfill in order to maintain a balance between the economy and the ecosystems. A company's image and brand can be built through being socially responsible. A corporation can establish a reputation for being not just financially successful, but also socially responsible by creating a positive image by fulfilling its responsibility towards the society.
Short Answer Questions (3 or 4 Marks)
11. Why is business responsible for Environment Protection?
Ans: The whole of man's surroundings - both natural and man-made - is characterized as the environment. These surroundings also include resources that are beneficial to human life. Natural resources, such as land, water, air, fauna and flora, and raw materials, as well as artificial resources, such as cultural heritage, socioeconomic institutions, and people, are examples of resources.
Pollution is the release of dangerous compounds into the environment, which is mostly caused by industrial activity. Pollution changes the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of air, land, and water, as the environment can only absorb a certain quantity of pollutants. Hazardous pollutants include hazardous wastes, poisonous by-products, and compounds that have toxic qualities which the environment cannot absorb. As a result, pollution endangers environmental quality, human health, and natural and man-made resources.
A business takes abundant resources from the environment in terms of raw material, wood, air, water etc in order to run its business. Hence, it is fair enough that the business pays back to the society and the environment by protecting, preserving as well as conserving the environment.
A business is responsible through its commitment from the company's senior management to establish, maintain and grow a work culture that promotes environmental preservation and pollution prevention.
12. Enumerate any three responsibilities of business towards employees.
Ans: The following are three company responsibilities towards employees:
Provide appropriate working conditions in order to gain employee collaboration.
The company must respect the employees' democratic freedom to form unions.
A fair wage and a fair deal from management must also be guaranteed to the employee.
13. Why should a business assume social responsibility?
Ans : The businesses should assume social responsibility because:
Improving Companies Brand:
A company's image and brand can be built through being socially responsible.
A corporation can establish a reputation for being not just financially successful but also socially aware by creating a positive image.
Engaging Customer
A social responsibility policy can impact the buying decision of the customers.
Some buyers are ready to pay a higher price for a product if they know that a percentage of the proceeds will go to a good cause.
Retaining Top Talent
Many employees want to feel like they are a part of something bigger.
Social responsibility and powers employees to leverage the corporate resources at their disposal to do good.
Helping Company Stand Out of Competition
Companies that are involved in the community stand out from the crowd.
Improving the brand's image by cultivating relationships with customers and their communities.
14. Explain the major cause of environmental pollution.
Ans: The major causes of environmental pollution are:
Air Pollution:
It is primarily due to automotive emissions of carbon monoxide, which contribute to air pollution. Similarly, manufacturing plants damage the air with smoke and other toxins.
As a result of the pollution, a hole in the ozone layer has been formed, thus leading to severe global warming.
Water Pollution
Chemical and garbage disposal are the primary causes of water pollution.
Water contamination has killed a number of animals and is a severe threat to human life.
Land Pollution
Land pollution occurs when harmful waste is dumped on it.
This degrades the land's quality, rendering it unsuitable for cultivation or plantation.
Noise Pollution
Noise pollution from industry and cars is not only an irritation, but also a major health threat.
Noise pollution has been linked to a variety of illnesses, including hearing loss, heart failure, and mental illness.
15. Define business ethics and explain its significance?
Ans: Ethics are concerned with what is right and what is wrong in human behavior judged on the basis of a standard form of conduct/behavior of individuals, as approved by the society in a particular field of activity. The relationship between company objectives, procedures, and processes and the society welfare is the subject of business ethics.
The moral principles, and the socially defined behaviour which governs a business and its activities is referred to as business ethics. Ethical business is a good business. Ethical business behavior improves public image, earns people's confidence, and leads to greater success.
Business Ethics is important due to the following points:
It helps to establish a company's image and brand.
It has an impact on clients' purchasing decisions.
Employees believe they are a part of a trustworthy and ethical company.
It helps to have an edge in a competitive market.
16. LMN Ltd. is filing its income tax returns on time. They are also updating their shareholders about their projects and providing for return to them. Towards which interest group are they fulfilling their responsibility? Which values are being followed by the Co.?
Ans: They are fulfilling their responsibilities towards the shareholders, owners, and the government.
An organization must offer regular, accurate, and complete information to its shareholders regarding its operations as well as future growth plans. The job of the commercial enterprise is to offer a fair return to the shareholders or owners. An organization must adhere to the country's rules and pay taxes to the government on a timely and accurate basis.
The following are the values that the company adheres to:
Legal Responsibility: Every business has a legal obligation to follow the laws of the state, as the business who follows the legal aspects of the country is said to be a socially responsible business. By paying the tax returns on time, the business is fulfilling its legal responsibilities.
Ethical Values: The company offers regular updated information to its shareholders, along with consistent returns. Hence, it is following the ethical values of fairness, transparency etc.
17. A B C Ltd. deals in health drinks. It is found that there are components of pesticides in their drinks. Mention which 2 kinds of responsibilities and 2 values are missing from this approach.
Ans: Two Kinds of Responsibility missing from the company’s approach are as follows:
Ethical Responsibility: Socially acceptable behavior that is not prescribed in law. There is an involvement of voluntary action in performing this responsibility
Legal Responsibility: Every business has a legal obligation to follow the laws of the state, as the business who follows the legal aspects of the country is said to be a socially responsible business.
Two Kinds of values missing from the company’s approach are as follows:
Social Value: When a company's primary purpose is "service to society," it and its image stand to profit the most in the long run. If a company performs its social obligation, it benefits itself. The public image of any firm would also be improved when it supports social goals which are missing in the company, as the company failed to provide service to society by providing them with safe and healthy health drinks.
Honesty and Transparency: The company claims its products to be ‘health’ drinks, despite the fact that it has pesticides and chemicals in it, which could jeopardize the health of the consumers. The company sure lacks the essence of honesty and transparency in its values.
18. XYZ Co. is providing facilities for their female staff like day care centres for kids and work from home facilities. By doing this they are following social responsibilities towards which interest group? Also, what values are they presenting?
Ans: They are following social responsibility towards the staff or employee group. The right kind of working conditions to be given so that it can win the cooperation of staff. The company is providing work from home opportunities to female staff, along with day care facilities, hence the company is being empathetic towards its staff, and treating them with dignity and respect.
In the above case, the company us showcasing the the following values:
Social Values : By treating the female staff with dignity and respect, and providing for the day care facilities and work from home opportunity, the company is showcasing the social values of cooperation, understandability, empathy etc.
Also, the values of autonomy and freedom are also showcased towards women. As mothers and professionals at the same time, the woman feels more empowered and autonomous to work and continue their professional careers without worrying about their children.
Long Answer Questions (5 or 6 marks)
19. Explain the forces which are responsible for increasing concern of business enterprises towards social responsibility.
Ans: The forces are as follows:
The Interests of Stakeholders:
To get the support of employees, it has become necessary for organizations to discharge its possibility towards their employees.
Also, the customer does not purchase what is being provided to him, he buys what he wants. As a result of consumer sovereignty, firms have been pushed to take social responsiveness toward them, as satisfying social commitments is good for the enterprises' long-term survival.
Long-Run Survival:
When the firm's primary purpose is to serve society, the firm and its image stand to gain the most benefit in the long term.
If a company performs its social obligation, it benefits itself.
When a company promotes social aims, its public image improves, which further leads to long term survival and success of the business.
Self-Enlightenment:
With increase in the level of education and understanding of businesses that they are the creations of the society, they are motivated to work for the cause of social good.
Rather than legislative interference being the cause of social responsibility, firms have human social responsibility on their own.
Government Regulation:
Businessmen are said to be able to avoid government regulation by voluntarily taking on social duties, which helps to lessen the need for new legislation.
The Central Pollution Control Board, for example, is in charge of environmental pollution issues, and in case the company does not adhere to the norms of this board, the board can take serious consequences against it.
There are abundant resources available with the organizations that hold the power to partly solve the social problems.
Businesses are dependent on society and its resources in indescribable ways, hence it is fair enough that it pays back the society both economically and socially.
Business Responsible for Social Problems:
Businesses have either generated or perpetuated social problems, hence it has a moral obligation to get involved in tackling these challenges rather than relying on other social institutions to do so.
Pressure of Labour Movement:
The labour movement has grown in strength around the world in order to obtain gains for the working class.
This has compelled businesses to consider the welfare of their employees rather than pursuing a "hire and fire" policy.
Impact of Consumer Consciousness:
Development of education and Mass media and increasing competition in the market has made the consumer conscious of his right and power in determining market forces.
Now, the customer is the king and is much aware of his rights, hence the businesses have started following a customer oriented approach, to keep them happy and satisfied.
Development of Social Standard for Business:
Various social standards have been set for business in terms of its responsibilities towards various interest groups, hence it becomes crucial for the firms to adhere to these social standards and contribute to the society in order to ensure its long run survival.
There is no way to run a business without interacting with the rest of the world.
Relationship between social interest and business interest:
Companies have begun to recognize that social and business goals are not mutually exclusive. They are, instead, complementary to one another.
The long-term benefit of business is in providing good service to society.
Development of Professional, Managerial Class:
Professional managers are more concerned in fulfilling a variety of interest groups in society when it comes to running their business than simply making a profit.
20. It is in the interest of business to fulfill its social responsibilities towards different interest groups. Explain?
Ans: The responsibilities that the businesses are supposed to fulfill in the interest of different interest groups are:
Responsibility towards the Shareholders or Owners:
Shareholders must also be given regular, accurate, and complete information about the company's operations and growth plans.
The responsibility of a business enterprise is to provide a profit to its shareholders or owners.
Responsibility towards the Workers:
The right kind of working condition to be given so that it can win the cooperation of the workers.
The company must respect the workers' democratic freedom to form unions.
The worker must also be assured of a fair wage and a fair deal from the management.
Responsibility towards the Consumers:
The obligation of an organization towards its customers is to provide the correct quality and quantity of goods and services to consumers at fair pricing.
Adulteration, poor quality, a lack of required services and civility to consumers, misleading and dishonest advertising, and so on must all be avoided by the business.
Responsibility towards the Government and Community:
An organization must follow the rules of the country and pay taxes on a timely and accurate basis.
It must act like a good citizen and adhere to the society's widely accepted values.
21. MNO Ltd., A renowned computer company follows the vision of "reaching new heights with its people on its side"', It not only provides quality products but also provides various facilities to its employees for 5 years of service. It also provides computer skills to youth in remote areas for free.
(a) What according to you are the business ethics of the company?
Ans: Ethics is concerned with what is right and what is wrong in human behaviour judged on the basis of a standard form of conduct/behavior of individuals, as approved by society in a particular field of activity. The relationship between company objectives, procedures, and processes and the good of society is the subject of business ethics. The socially decided moral norms that should regulate company activity are referred to as business ethics. Ethical business is good business. For example honesty, transparency, social welfare, integrity etc.
(b) Is it fulfilling its social responsibilities towards which interest groups?
Ans: It is fulfilling social responsibility towards its customers, employees and society.
Customers: The company provides quality products to its customers.
Employees: It provides various facilities to their employees for their 5 years service.
Society/ Community: The company is also providing computer skills to youth in remote areas free of cost, which in turn will lead to skilled India, and make the youth capable of finding a suitable job for themselves. Also, due to this, the growth in rural areas would be made possible.
22. There is a group discussion taking place in class XI regarding social responsibility of business' Ravi feels that a business should be socially responsible towards the society it exists in while shama is against it as the basic objective of a business is to earn projects. Whom do you think you will favour? Write points with respect to your opinion.
Ans: I will favour Ravi. Social responsibility is important for the success of the business. The following points highlights the importance of social responsibility:
Protect the Interests of Stakeholders:
The customer does not purchase what is being provided to him, he buys what he wants. Hence, as a result of consumer sovereignty, firms have been pushed to take social responsiveness toward them, as satisfying social commitments is good for the enterprises' long-term survival.
When a company promotes social aims, its public image improves as well, which further leads to the long term survival and success of the business.
Avoids Government Regulation:
Government regulations are unwelcome because they stifle individual liberty.
For example, the Central Pollution Control Board takes care of issues related to environmental pollution, and if a business firm follows appropriate measures to avoid environmental pollution, then the interference of the said board could be reduced.
Given the vast financial and personnel resources at its disposal, it can assist society in better addressing its challenge.
Professionalization and Better Environment:
Businesses are becoming more socially oriented as management becomes more professional.
The ethics of profession by and manager to social values and growing concern for society.
A society with fewer problems provides a better environment for a firm to conduct its business.
Business businesses have either generated or perpetuated social problems.
Business has a moral obligation to get involved in tackling these challenges rather than relying on other social institutions to do so.
Converting Problems into Opportunities:
Business with its history of converting risky situations into two profitable deals, can not only solve social problems but it can also make them effectively useful by accepting the challenge.
Resource Utilisation:
Businesses have abundant financial, managerial, technical resources. Hence, these resources can be put to use into solving various social challenges and issues.
23. State the factors against social responsibility?
Ans: The factors against social responsibility are:
Violation of Profit Maximization Objective:
Business exists mainly for profit maximization. Hence social responsibility is somewhat contradictory to the primary objective of profit maximization.
Profit maximization through higher efficiency and lower costs is the best way for business to fulfil its social obligation.
Burden on Consumers:
Pollution control and environmental protection, like social responsibility, are very expensive and frequently necessitate financial commitment.
Instead than bearing the burden of social responsibility, they simply pass it to the consumer by demanding a greater price.
Lack of Social Skills:
Businesspeople lack the essential knowledge and training to solve social issues.
Other specialized agencies should deal with social issues.
Lack of Broad Public Support:
Business engagement or meddling in social programmes is disliked by the general public.
As a result, businesses are unable to thrive due to a lack of public trust in collaborative efforts to solve societal problems.
24. Describe the role of social responsibility in today's era?
Ans: The role of social responsibility is explained in the following points:
Threat to Public Regulation:
Action is taken to regulate business entities that operate in a socially irresponsible manner in order to protect the interests of the public.
One of the main reasons why businesses are concerned about social responsibility is the fear of government regulation.
Hence social responsibility plays an important role in protecting the interests of the public, and avoiding any threat from them as well as the government.
Development of Business Education:
More and more individuals are becoming aware of the social purpose of business as a result of its rich content on social responsibility.
Relationship between Social Interest and Business Interest:
Professional management education at universities and specialized management schools has resulted in the formation of a distinct class of professionals.
25. What is the need to control pollution and how should businesses contribute to environmental protection?
Ans: The need for Pollution Control is:
To Reduce Health Risks: There is mounting evidence that pollution in the environment causes various diseases such as cancer, heart attacks, and lung difficulties. Hence, there is an urgent need to control pollution.
To Reduce Risk of Liability: It is conceivable for a company to be held accountable for compensating people who have been harmed by the toxicity of gaseous, liquid, or solid pollutants it has released into the environment.
Cost Savings: Faulty manufacturing technology produces more trash, resulting in higher waste disposal and facility cleaning costs. Therefore steps to control pollution will ultimately help the firms to save their costs and expenses.
Improved Public Image: A company that advocates for environmental causes will have a positive reputation and be seen as a socially responsible business.
Other Social Benefits: Controlling pollution has a number of other advantages, including improved visibility, cleaner buildings, a higher quality of life, and the availability of natural resources in their purest form.
Role of Business in Environment Protection:
Organizational Commitment: It shows the commitment an organization has towards the environment of which it is a part. The firm’s commitment can be seen by the company's senior management building, maintaining, and developing a work culture that promotes environmental protection and pollution prevention. Assuring that the company's commitment to environmental preservation is shared by all divisions and workers.
Policies and Programmes: Through the formulation of defined policies and programmes for acquiring high-quality raw materials, using advanced technology, employing scientific waste disposal, treatment procedures, and improving employee skills, the firm can contribute in environment protection and conservation.
Rules and Regulations: Adherence to the government's pollution-prevention rules and regulations is another way a firm can fulfil its role towards environment preservation.
Participation: The firm's participation in government programmes aimed at preventing deforestation, managing dangerous substances, cleaning up dirty waterways, and planting trees also leads to environmental protection and conservation.
Evaluation: The firms conduct periodic evaluation of pollution control programmes in terms of costs and benefits so as to improve environmental protection efforts.
Organizing Workshops: The firm’s efforts into organizing educational workshops and training materials to share technical knowledge and expertise with suppliers, dealers, and customers also contributes towards pollution control programmes.
Benefits of Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics
Students are required to study these important questions and answers of CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics in order to enjoy the following benefits:
The important questions and answers will help the students to study the concepts which are of utmost importance and thus chances of appearing in the question paper in the Business studies exam is maximum.
Students can know the important concepts and portions from the chapter - Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics by knowing the important questions from this chapter.
Along with the important questions, the answers related to each question are also given. This will help the students to find and check the correct answers.
The students can use this study material before the examination day if they want to study only the important topics from the specific chapter.
With the help of these important questions and answers the students will understand what type of questions might appear in the exam. They get familiar with the question types.
The students will also be confident once they study the important questions and answers from this chapter, as questions beyond this will be quite easy or will not appear in the exam at all.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 ‘Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics’ - Extra Questions (Solved) for Practice
Solve the following questions for your further practice:
1. What are the basic elements of business ethics?
Ans. The basic elements of business ethics are as follows:
Commitment from Top Management
Formation of a “code”
Establishing a compliance mechanism.
Involving employees at all levels.
Measuring results
2. What are the 4 types of pollution?
Ans. The four types of pollution are:
Soil Pollution
Air Pollution
Tips to Study Better
Students are advised to check on this tips list which might help you in improving your scores of Business Studies:
Business Studies is a theoretical subject which must be first understood and then prepared by writing questions and answers.
Students are required to solve the exercise questions as well at the end of each chapter.
Students should also follow the NCERT study material in order to get a complete overview of the examination paper.
The chapters of Business Studies can be better understood after the students had prepared the HOTS (High Order Thinking Skills) questions.
Check up with the previous years questions in order to have confidence in the exam hall.
The compilation of important questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - "Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics" is a significant asset for students. These thoughtfully selected questions cover essential topics related to ethical business practices and corporate social responsibility, offering a focused approach to exam preparation. They enable students to assess their understanding, identify key concepts, and reinforce their knowledge in this crucial aspect of the business world. Vedantu’s important questions not only align with the examination pattern but also emphasize the importance of ethical considerations and social responsibility, preparing students not just for academic success but also for responsible and ethical decision-making in their future business endeavors. Overall, they are an indispensable resource for Class 11 Business Studies students.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics
1. What are the responsibilities of a business towards employees?
Training, promotion, proper selection, fair compensation, safety, health, worker education, comfortable working conditions, participatory management, and so on are all examples of a company's responsibility to its employees. When making decisions that influence the employees' interests, they should be trusted. Apart from these the companies also have social responsibilities to adhere to. As part of their social responsibilities, managers must examine if their actions are likely to promote the public good, advance the core principles of our society, and help maintain and strengthen its harmony.
2. What are the major areas of social responsibility of business?
Social responsibilities are often divided into three categories. They are environmental, charitable and moral responsibilities. To be environmentally responsible is to act in a manner as ecologically beneficial as possible. An organization's ethical obligation is to operate in a fair and ethical way. As a result of philanthropic duty, a company's goal is to actively improve the world and society. An organization's commitment to do well in the areas outlined above should be the basis for all of its financial decisions. For a more detailed explanation of this chapter, visit Vedantu.
3. What are business ethics?
The collection of moral standards that govern how firms function, how business decisions are made, and how people are treated is defined as business ethics. When moral standards are used by a corporation to determine how best to treat its workers, shareholders, and customers, this is an example of business ethics. To be ethical in the business world, one must adhere to acceptable corporate principles and procedures while dealing with difficult issues such as corporate governance, bribery, racism, social responsibility, and so on.
4. Is it a must for a business to be socially responsible?
Yes, it indeed is. Being a socially responsible business can help enhance the reputation of any company or brand. Employees with a sense of social responsibility can use the business resources at their disposal to accomplish good. Formal corporate social responsibility initiatives can improve employee morale and increase workplace efficiency. Hence, being socially responsible is very crucial for any business firm or company and it requires a certain moral code to assert its will to abide by them and to be true to their creed.
5. How can I download the PDF of Solutions of Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6?
The solutions are easily available on the Vedantu site.
Visit the page NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6.
The webpage with Vedantu’s Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 will open.
To download this, click on the Download PDF button and you can view the solutions offline.
You can also access different modules and address your other queries or doubts with the experts of Vedantu.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Business Studies Notes And Questions
Please refer to Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Business Studies notes and questions with solutions below. These revision notes and important examination questions have been prepared based on the latest Business Studies books for Class 11 . You can go through the questions and solutions below which will help you to get better marks in your examinations.
Class 11 Business Studies Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Notes and Questions
Social Responsibility
It is very clear that no business can be survived without the support of the society, as it is run by the people, through the people and for the people. Because of the same reason it has certain responsibilities towards the society. Social responsibility refers to the obligations of the businessmen which are desirable in terms of the objectives and values of our society.
Arguments for social responsibility
1. Existence and growth – Prosperity and growth of business is possible only through rendering continuous service to society.
2. Long term interest of the firm – A firm and its image stands to gain more profits in the long run when it accepts service as the highest goal. Supporting social goals enhances public image of any firm.
3. Avoidance of government regulations – Businessman should voluntarily assume social responsibilities, so that they can avoid government regulations. Eg: Environmental pollution.
4. Maintenance of society – If the people feel that they are not getting their due from the business, they will not support such business organisations.
5. Availability of resources with business – Available resources with the business such as managerial talent and financial resource can be utilized to solve the problems of the society when it is needed.
6. Converting problems into opportunities – Business is always looking for converting risky situations to opportunities, this quality can be utilized for solving the problems in the society.
7. Better environment for doing business – A society with fewer problems and complaints provides better environment for the business.
8. Holding business responsible for social problems – Some of the social problems such as pollution, unsafe work environment, discrimination in employment etc. are created by business enterprises themselves, so that it is their moral obligation to solve them.
Arguments against social responsibility
1. Violation of objective – Business is an economic entity and it s main objective is profit maximization. If the business organizations are engaged in social activities their profit will be reduced. It will affect the success of the business. 2. Burden on consumers – It is an argument that the cost of social responsibility will be shifted to the consumers by charging higher prices. 3. Lack of social skill – It is an argument that the business people have no skill to take up social work as they are always engaged in business activities. 4. Lack of public support – Public usually do not like business interference in social programs, so that they cannot operate successfully in such areas.
Reality of Social Responsibility
1. Threat of public regulation – When business enterprises act in a socially irresponsible manner, government will act by regulating them for safeguarding public interest. 2. Pressure of labour movement – Labour movement has become very powerful now-adays,so that the businessmen are forced to protect the interest of the workers. 3. Consumer consciousness – Business enterprises have started customer oriented policies as they are aware about their rights and privileges. 4. Development of social standard for business – Newly developed social standards consider only legitimate economic activities along with serving the society. Then only the business can survive and grow. 5. Development of business education – Because of development of business education, people are aware of the social purpose of business. 6. Relationship between social interest and business interest – Businessmen have realized that social interest and business interest are not contradictory, but they are complementary to each other. 7. Development of professional managerial class – Professional management education has created a class of professional managers who have got a positive attitude towards the social responsibility as compared to the earlier class of owner managers.
Kinds of Social Responsibility 1. Economic responsibility – Since the business is an economic entity, it has to produce goods and services that society wants and sells them at a profit. 2. Legal responsibility – Business enterprises have the responsibility to operate within the laws of the country. 3. Ethical responsibility – It refers to the moral principles to be followed by the businessmen in relation to the society. Eg: Protecting religious sentiments and dignity of people while advertising a product. 4. Discretionary responsibility – This is voluntary obligation of a business enterprise. Eg; giving charity to an educational institution, helping people in natural calamities etc.
Social Responsibility towards different Interest Groups As a socio-economic institution business is always in touch with various groups such as owners, employees, customers, suppliers etc. and it has to discharge certain responsibilities as follows:
1. Owners: a. Safety of investment. b. Adequate return on investment. c. Accurate financial information should be provided.
2. Employees: a. Fair wages b. Job security c. Promotion opportunities d. Welfare measures e. Better working conditions f. Participation in management
3. Consumers: a. Regular supply of commodities. b. Better quality c. Reasonable Price d. Avoidance of unfair trade practices.
4. Suppliers: a. Better relationship b. Prompt payment.
5. Government and Community: a. Lawful business. b. Prompt payment of tax. c. Help the government in socio-economic development (employment opportunities, literacy, poverty etc.) d. Optimum use of natural resources. e. Concentrate in safety and welfare of the people. f. Control pollution as far as possible.
Business & Environmental Protection
The health and well being of people depends on the quality of environment in which they live and work. Rapid industrialization and growing traffic have caused a great damage to the environment. Pollution is the injection of harmful substances into the environment largely because of industrial production. It changes the physical, chemical and biological characteristics of air, water and land.
Causes and Types of Environment Pollution: 1. Air Pollution: It is the contamination of air by the accumulation of harmful or toxic substances which will create serious health problems to living organisms, monuments etc. 2. Water Pollution: Water is said to be polluted when it is changed in the quality as a result of waste disposal and other human activities, so that it become less suitable for drinking. 3. Land Pollution / Soil Pollution: It may be due to the dumping of non-degradable waste material into the land from industrial units, hospitals, hotels, dwelling units etc. This damages the quality of soil making it unfit for cultivation. 4. Noise / Sound Pollution: It may cause damages to the human body and mind, thesmooth functioning of hospitals, educational institutions etc. Industrial units,Automobiles etc. are the major sound pollutants.
Need for pollution control 1. Reduction of health hazards – Major diseases like cancer, heart attacks etc. are caused by pollutants in the environment. Pollution control measures only can prevent such diseases up to a certain extent. 2. Reduce risk of liability – I n case a disaster has been take place the entire liability will be borne by the enterprise. E.g. Union Carbide Tragedy in Bhopal. 3. Cost savings – Effective pollution control strategy helps to reduce cost of operating business. If they use improper technology with greater wastes leading to high waste disposal cost. 4. Public image – A business enterprise which follows good pollution control measures can enjoy a good reputation in the society and will be perceived as a socially responsible enterprise. 5. Other social benefits – It includes clear visibility, clean buildings and monuments,quality life and availability of pure natural products.
Role of business in Environmental Protection 1. Top level management should create a work culture for environmental protection and pollution control. 2. Sharing the ideas and technical information regarding environmental protection among the employees. 3. Use good quality materials. 4. Adopt modern technology. 5. Follow the rules and regulations by the government. 6. Scientific methods of waste management. 7. Support in government programs like clearing up of polluted water sources, plantation of trees, checking deforestation etc. 8. Timely assessment of pollution control programs.
BUSINESS ETHICS
The word “ethics” derived from the Greek word “ethos” which means character or sentiments of community. Ethics specifies what is good or bad, fair or unfair, right or wrong. Business ethics refers to the moral principles followed by a businessman in his dealings with the people and it involves better quality, fair price, justice, courage, thrift etc. Business ethics helps to win the confidence of customers which will ensure the prosperity and progress of the business.
Examples of ethical business practices: 1. Fair and reasonable price 2. Correct weight and measures 3. Disclose actual profit and prompt payment of tax 4. Fair treatment to the employees 5. Sale of genuine products to customers 6. Take reasonable profit 7. No bribes
Common unethical business practices are as follows: 1. Adulteration 2. Poor quality 3. Black marketing and hoarding 4. Misleading advertisements 5. Fake goods 6. Deceptive packaging 7. Pollution of environment 8. Exploitation of workers
Elements of business ethics Practicing business ethics means doing things in conformity with existing norms or standards of society. The main elements are:
1. Top management commitment – The top level managers need to be openly strong in ethical matters, so that they can guide their organization towards ethically upright behavior.
2. Publication of a “Code’ – Code means a written document which contains the moral principles to be followed by the organization. It covers the areas like honesty, adherence to laws, quality, health and safety in workplace, employment practices fairness in selling etc.
3. Establishment of compliance mechanism – A suitable mechanism should be introduced to ensure that actual decisions and practices comply with firm’s ethical standards. Eg: Paying attention to values and ethics in recruiting employees.
4. Involving employees at all levels – Involvement of employees in all the levels in ethical programs is a must, then only they can do accordingly. Eg: Conducting a group discussion among the employees in small groups to discuss the ethical policies to be followed in the firm.
5. Measuring results – The firm can monitor the actual performance with ethical standards and they can take necessary steps for further course of action.

We hope the above Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Business Studies are useful for you. If you have any questions then post them in the comments section below. Our teachers will provide you an answer. Also refer to MCQ Questions for Class 11 Business Studies
Related Posts

Excretory Products and their Elimination Class 11 Biology Notes and Questions

Environmental Chemistry Class 11 Chemistry Notes and Questions

Class 11 Biology Notes And Questions
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 – Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics
Home » CBSE » Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 – Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 – Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
Due to its diversity, Business Studies is one of the most internationally studied courses in the world. Business studies is a broad subject in the social sciences that focuses on various disciplines such as accounting, finance, organisation, human resources management, and marketing. The sixth chapter of the Class 11 curriculum is Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics; this chapter discusses various social responsibilities of business and business ethics. This chapter covers concepts such as the need for Social Responsibility, identifying social responsibility towards different interest groups, concepts of business ethics and so on. Chapter 6 carries a significant amount of weightage in the examination. Students can easily access Chapter 6 Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions and much more once they register themselves on the Extramarks website.
Quick Links
Business studies are more of a theoretical subject which requires constant reading and revision of chapters. . At Extramarks, we understand the value of solving important questions. Extramarks, one of the leading educational platforms, has a repository of resources such as the NCERT Textbook, NCERT Exemplar, other reference books, past year exam papers , and so on. These resources are prepared in accordance with the NCERT textbook and CBSE guidelines. Our Business Studies subject matter experts have collected step-by-step solutions after extensive research to help students understand the topics and help them to study independently without any further assistance. Students can register with Extramarks and access Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6.
Not just the Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 6 Important Questions, Extramarks has a repository of resources to offer for all classes and competitive exams. Students can easily find materials like NCERT Solutions, CBSE revision notes , past year question papers, NCERT books, and more on the Extramarks website.
Get Access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions 2022-23 with Solutions
Sign Up and get complete access to CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Important Questions for other chapters too:
| 1 | Chapter 1 | |
| 2 | Chapter 2 | |
| 3 | Chapter 3 | |
| 4 | Chapter 4 | |
| 5 | Chapter 5 | |
| 6 | Chapter 6 | Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics |
| 7 | Chapter 7 | |
| 8 | Chapter 8 | |
| 9 | Chapter 9 | |
| 10 | Chapter 10 | |
| 11 | Chapter 11 | |
Social Responsibility of Business Class 11 Questions and Answers
An extensive collection of Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Important Questions has been created by subject matter experts Extramarks business studies using references from various primary and secondary sources. These questions and their step-by-step solutions help students better comprehend all the topics covered in Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6.
Given below are a few Important Questions from Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 and their solutions:
Q1. State the meaning of Corporate Social Responsibility as per the Companies Act 2013.
Answer. Corporate social responsibility refers to the obligation businesses have to play in achieving social development goals and maintaining a balance between environmental preservation, social advancement, and economic development.
The Companies Act’s section 135 governs CSR and applies to businesses that has:
- Yearly revenue of Rs. 1000 crore
- A net value of 500 billion rupees
- A 5-crore rupee net profit
Schedule VII covers eliminating gender disparity, eradicating hunger and poverty, and fostering a sustainable environment.
Q2. Briefly describe the idea of corporate social responsibility.
Answer. In today’s culture, business is acknowledged and regarded as a social and economic activity. To meet the requirements of society, the business operates within accepted social standards. Society provides the business with all the factors of production, including personnel, machinery, materials, money, and equipment, since the business’s life depends on society.
Society establishes, maintains, and administers its activities in the public interest. In other words, social responsibility is the company’s duty to many societal groups and profit-making.
Q3. What do you mean by social responsibility in business? How is it different from legal responsibility?
Answer. It refers to a corporate organization’s obligations and responsibilities to society and its constituents. Additionally, it demands that the business engages in several socially valuable actions. As a result of the constant exploitation of social resources by businesses, it is part of their duty to contribute to society’s advancement.
Legal obligations can only be fulfilled according to the law. Still, social responsibilities are more focused on improving society by creating work opportunities for women, the physically challenged, and the impoverished.
Q4. ‘Social responsibility is a burden on consumers’ Describe this claim.
Answer. Environmental protection and pollution prevention are costly social obligations that frequently require significant financial outlays. Businesspeople transfer the expense of doing their socially responsible job onto their customers by requesting higher prices.
Q5. Discuss the guidelines enumerated by the Companies Act 2013 for Corporate Social Responsibility.
Answer. Corporate social responsibility generally refers to a company’s duties and commitments to society. Businesses with:
- 1,000 crores or more in annual income,
- a net worth of at least 500 billion rupees, or
- 5 crore or more in net profit
The Companies Act, 2013, oversees corporate social responsibility in India (under Clause 135).
You may learn more about how the Companies Act of 2013 defines CSR by reading the following suggestions:
- A corporate social responsibility committee, made up of three or more board members, including at least one independent director, is required.
- Companies must invest 2% of their average net earnings over the preceding three fiscal years to follow the Corporate Social Responsibility Policy.
- Only CSR projects that are specified in a company’s corporate social responsibility policy—which is based on the recommendations of the corporate social responsibility committee—should be undertaken by businesses in India.
- A company shall adhere to the rules outlined in Schedule VII of the Act while conducting CSR-related activities.
- People will not consider CSR initiatives if they simply serve the interests of the company’s employees or their families.
Q6. Build up arguments for and against social responsibilities.
Answer. The following are arguments for social responsibilities:
- Self-enlightenment: As businesses gain more knowledge and awareness of their position as society’s creators, they are compelled to strive for the greater good. Public expectations are shaped by the voluntary moral and social responsibility norms that managers choose and uphold. Consequently, businesses take on social responsibility on their own rather than as a result of legislative interference.
- Survival in the long run: In the long term, a corporation and its reputation stand to gain the most when its primary goal is to “serve society.” A business gains when it fulfils its social responsibility. When a company achieves social objectives, it also boosts its reputation with the public.
- Safeguard stakeholders’ interests: Businesses must now go above to satisfy their employees if they want their support. The customer does not purchase the thing that is being presented to them. They buy precisely what they want. Due to increased customer awareness, businesses must embrace social responsiveness toward their clients. Therefore, fulfilling social commitments contributes to a business’s long-term success.
- Limits governmental regulation: Government rules are undesirable because they limit one’s freedom. It is believed that business people may avoid the issue of governmental constraints by voluntarily performing social tasks, which will lessen the need for new laws.
Environmental contamination concerns are handled by organisations like the Central Pollution Control Board.
- Criticising the corporate community for societal issues: Businesses are responsible for creating or sustaining societal issues. Therefore, corporations have a moral duty to actively participate in finding solutions to these problems rather than ignoring them and hoping that other social organisations will take care of them.
- Resources: Large-scale resources available to business enterprises can be used to address societal issues partially. A company may help society handle its issues more effectively given the massive financial and human resources at its disposal. Businesses must operate in society’s best interests both economically and socially since they are a product of society.
- Transforming challenges into opportunity: By taking on the challenge, a business with a track record of effectively negotiating lucrative outcomes in trying circumstances can not only assist in mitigating societal issues but also successfully transform them into assets.
The following are arguments against social responsibilities:
- Consumers’ burden: Environmental protection and pollution control are expensive societal obligations that usually require significant financial outlays. Businesspeople frequently demand more excellent prices from their consumers rather than shouldering the responsibility of doing the right thing.
- Profit maximization: It is the only business goal, and it is violated. Any consideration of social responsibility is therefore incompatible with this objective. The most effective approach for the company to fulfill its social responsibility is to maximize profits through improved efficiency and reduced expenses.
- Widespread popular opposition: The public dislikes business involvement or social program interference. As a result of a lack of public trust and cooperation in resolving social concerns, a business cannot prosper.
- Lack of social skills: Businesspeople lack the necessary abilities and education to address social concerns. Social concerns should be handled by other specialist organisations instead.
Q7. Write a short note on the topic of CSR?
Answer. Every type of commercial firm must behave in a morally righteous way. However, corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a term employed explicitly concerning a firm. It may be summed up as earning financial success while upholding moral principles and considering other people, communities, and the environment. It entails resolving the demands placed on corporations by the law, morality, commerce, and other societal norms, including the requirement that they make choices and perform acts that fairly balance the interests of all stakeholders. Across the board, business operations, supply claims, and decision-making processes are linked with a complete set of CSR policies, practices, and initiatives.
Q8. What are the major areas of social responsibility of business?
Answer. An entity, whether an organisation or an individual, must act in society’s interests according to the ethical paradigm of social responsibility. Everyone has to fulfil this to preserve a balance between the economy and ecosystems.
The following are some of the central business social responsibility initiatives:
- Legal responsibility: Every company is required by law to abide by the nation’s laws. A company is socially responsible if it complies with all applicable rules and regulations.
- Economic responsibility: The economic duty of a company enterprise, or the responsibility to provide goods and services that society wants and sell for a profit, is its primary social responsibility.
- Discretionary responsibility: Discretionary responsibility implies that the firm must safeguard the capital invested by abstaining from speculative behaviour such as gifts to charities, etc. and should engage only in profitable commercial ventures.
- Ethical responsibility: Referred to as socially acceptable conduct that is not protected by law. Some volunteer help is needed for this project.
Q9. What is the environment? What is environmental pollution?
Answer. The biotic and abiotic resources within and around us make up the environment. It affects the way we live. However, due to industrialisation and rapid population development, resources have been utilised to the point of depletion or deterioration. Additionally, the region has been polluted because of toxic discharge into the ecosystem.
Pollution comes in 4 different forms:
- The dumping of hazardous wastes into the earth pollutes the environment and renders the land unsuitable for agricultural use, leading to land pollution.
- Health issues, including hearing loss and mental illnesses, are brought on by noise pollution from industry and traffic.
- Industrial waste that is released through a pipe causes water pollution.
- Burning waste materials and vehicle exhaust fumes that emit dangerous gases into the environment are two factors that contribute to air pollution.
Q10. Describe how the labour movement has helped businesses in upholding their social obligations.
Answer. The labour movement has grown significantly in strength to secure benefits for the working class globally. Due to this, companies are now required to think about the well-being of their workers rather than using a “hire and fire” strategy.
Q11. Explain the various elements of business ethics.
Answer. A few elements of business ethics are:
- Top-tier managers, such as the CEO of a company, should carefully adhere to the ethical standards and mentor others to do the same.
- The code of conduct, which contains regulations about workplace safety, health, and other matters, must be retained in the form of written papers known as “code.”
- It is essential to have appropriate compliance systems that guarantee choices and the accompanying actions adhere to the firm’s ethical standards.
- The business must track whether its ethics programmes adhere to moral norms, evaluate their outcomes, and determine what course of action is necessary.
- Since workers are the ones who put ethical rules into practice, employees should be included in all levels of ethics programmes.
Q12. Discuss the forces responsible for increasing the concern of business enterprises toward social responsibility.
Answer. The following factors influence how much corporate firms care about their social responsibility:
Labour movement pressure:
- The labour movement has strengthened globally to secure benefits for the working class.
- Due to this, companies are now required to think about the well-being of their workers rather than following a “hire and fire” philosophy.
Effect of consumer awareness:
- The consumer is increasingly aware of his rights and abilities to influence market dynamics because of improvements in education and mass media and greater market competition.
- Businesses are starting to adopt a customer-centric strategy now that the consumer is king.
The threat of public regulation:
- Actions are made to regulate businesses that conduct themselves in a socially irresponsible way to protect the general public’s interests.
- The fear of government regulation is one of the critical causes of why corporations are worried about social responsibility.
Establishment of social standards for business:
- The economic activity of corporate enterprises is now recognised by new social criteria, but only if it also meets social needs.
- It is impossible to operate a business without interacting with the outside world.
The connection between business and social interest:
- Business firms claim that social and commercial objectives are no longer incompatible. They complement one another well.
- Providing high-quality service to society is how businesses may gain in the long run.
The emergence of the managerial and professional classes:
- A unique class of professionals has been created due to professional management education at universities and specialised management institutes.
- When successfully operating their enterprises, professional managers are more concerned with gratifying a range of social interest groups than only hitting profit objectives.
Improving business education:
- Public awareness of the company’s social mission has expanded with the expansion of business education and its substantial social responsibility element.
Q13. Why do enterprises need to adopt pollution control measures?
Answer. A corporate company must undertake pollution control measures for the following reasons:
- Environmental pollutants contribute to many consequences, including cancer, kidney and lung damage, respiratory illnesses, and cancer. A healthy environment on earth can be achieved through reducing or controlling pollution.
- Organisations can install pollution control equipment in their buildings to stop the harm that gases and solid wastes create.
- Utilising outmoded production methods generates excessive waste, harming the environment and people. As a result, newer, cleaner methods should be employed.
- An organization is regarded as a socially responsible business if it has an effective pollution control strategy in place.
- Effective pollution control methods also lower a company’s operational expenses while preserving the environment.
Q14. Briefly explain (a) Air Pollution, (b) Water Pollution, and ( c) Land Pollution.
Answer. The terms are briefly explained below:
- Air Pollution: Carbon monoxide emissions from autos, smoke, and other chemical emissions from manufacturing enterprises are the leading causes of air pollution. The pollution has caused a hole in the ozone layer, leading to significant global warming.
- Water Pollution: The major causes of water pollution are chemicals, industrial waste, and rubbish dumping. It has claimed the lives of several animals and seriously endangers human life.
- Land Pollution: When hazardous trash is placed on land, pollution occurs. This lowers the quality of the land, making it unsuitable for farming or planting.
Q15. Explain Discretionary responsibility?
Answer. Discretionary responsibility refers to the voluntary obligations met by the company.
Q16. What steps can an enterprise take to protect the environment from the dangers of pollution?
Answer. The actions that business enterprises may implement for environmental protection are:
- They are obeying the government’s laws and guidelines to prevent pollution.
- Taking part in government initiatives to plant trees, manage toxic chemicals, clean up filthy rivers, and avoid deforestation.
- Ensuring that all divisions and workers share the company’s commitment to environmental preservation.
- Creating specified plans and programmes for sourcing high-quality raw materials, employing innovative technology, implementing scientific waste disposal and treatment techniques, and developing staff skills to prevent pollution.
- A clear commitment from the company’s senior management to build, maintain and grow a work culture that fosters environmental protection and pollution prevention.
- Periodic review of pollution control initiatives regarding costs and benefits to enhance environmental protection efforts.
- Organising educational seminars and training materials to share technical knowledge and expertise with suppliers, dealers, and customers to involve them in pollution control activities.
Q17. What is business ethics? Mention the essential elements of business ethics.
Answer. Corporate ethics deals with values and rules controlling the behaviour of a person or an organisation and business actions that are viewed as pleasant from the societal standpoint. It aids managers and other workers in completing their jobs in a manner regarded as socially acceptable.
Elements of Business ethics include:
- Top management’s commitment
- Establishment of a “code.”
- Setting up a compliance system.
- Including staff members at all levels.
- Monitoring outcomes
Q18. Describe the idea of “Human Rights.” Mention any human rights cases as well.
Answer. In the interests of each person, human rights guarantee equality. Human rights essentially served as a justification for action, protection, and support. Human rights emphasise the idea of humanity. All significant corporations ought to support and uphold human rights.
Cases for human rights- In our culture, human rights are highly valued. Numerous movements have also emerged to get these rights.
The following arguments are in favour of human rights in society generally and specifically in business:
- Protection against human injustice: Businessmen typically don’t uphold governmental norms and set their own social and economic standards. Human rights are brought to light when individuals believe that injustice is being sustained.
- Respecting human values: Some human rights are seen as being fundamental. These rights are of more importance than other human rights and legal rights and give entitlements outside the purview of legal authority, and others should respect them.
- Provides benchmarks for law and land policies: Following independence, a few fundamental rights emerged that operate independently of all laws and policies. These rights are more important than any laws or norms a community may have established.
Human rights and legal rights are very different from one another. There may be a legal justification for doing anything cruel, but there is no justification for committing any act of humanity. Human rights are derived independently, whereas legal rights are derived from the constitution and policies. Human standards are the foundation of human rights. Independent of any specific legal system, a set of human norms can serve as the foundation for human rights entitlement. These rights forbid engaging in cruel behaviour.
The United Nations declares the following as Human Rights:
- Right to form and join trade unions.
- The right to work, free choice of employment, good working conditions, and right of protection against unemployment.
- Reasonable limits on working hours and periodic holidays with pay.
- Right of just or favourable remuneration.
Q19. ‘Business is essentially a social institution and not merely a profit-making activity. Explain?
Answer. Profit maximisation is a business’s primary goal. However, businesses are not solely for-profit entities. Because they were developed by society to meet the need for products, every firm uses both human and societal resources. Such social issues like unemployment and poverty influence businesses as well. Socially acceptable actions that enhance society’s image include generating employment and providing a healthy work environment, paying taxes, reducing pollution, and attending to consumer concerns. Here are a few instances that demonstrate how business is a social institution.
On the other hand, it is said that business enterprises are more than just profit-making entities for the following reasons:
- They are seen as social institutions since society plays a role in a company’s success.
- Waste of time, money, and labour should be kept to a minimum since every firm uses society’s physical and human capital.
- Since a business cannot function without customers, purchasing its goods and services depends on them. To do business effectively, it must keep a positive connection with its customers.
Considering this, businesses must give back to society. As a result, we talk of a corporate enterprise as a social institution instead of a for-profit business.
Q20. Why are businesses accountable for protecting the environment?
Answer. The environment is defined as the entirety of a person’s surroundings, including natural and artificial elements. Resources that are advantageous to human life are also present in these settings. Resources include both natural and artificial things. Natural resources include land, water, air, flora and fauna, and raw materials. Artificial resources include things like cultural heritage, socioeconomic institutions, and people.
Discharging hazardous substances into the environment is known as pollution, and industrial activities mostly bring it on. As the environment can only absorb so many pollutants, pollution alters air, land, and water’s physical, chemical, and biological aspects. Hazardous pollutants include toxic wastes, poisonous byproducts, and substances with harmful properties that the environment cannot metabolise. As a result, pollution puts human health, natural resources, and environmental quality at peril.
A company needs many environmental resources to operate, including raw materials, timber, air, and water. Therefore, it is only fitting that the company gives something back to society and the environment by safeguarding, preserving, and conserving it.
A business is accountable for creating, sustaining, and expanding a workplace culture that supports environmental preservation and pollution prevention through the dedication of the company’s senior management.
The above-stated section of Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 is a list of Important Questions covering the entire chapter.
Key Topics Covered in Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6
Social Responsibility
People in business have a duty to the community known as social responsibility. Businesspeople need to consider how their choices and activities may affect the other facets of society.
Need for Social Responsibilities
Due to the following reasons, business people are expected to fulfil their social obligations:
- Commitment to societal problems
- Resources used for moral justification
- Social influence
- Avoiding the involvement of government
- Public image
- Better environment for business
- Personal gain
The case against Social Responsibility
Some academics have criticised the idea of social responsibility; a few of the arguments presented below are against social responsibility:
- The motive of earning profit.
- Social skills deficit.
- It costs money to be socially responsible.
- Diluted main business objective.
- Business People lack morality.
- Decreased competitiveness
The reality of Social Responsibility
We may infer that business is not just an economic institution but also a social institution. Business people are the trustees of various social groups after understanding the arguments in favour of and against social obligations.
The fundamental causes and influences that have compelled businesspeople to think about their obligations to society are:
- The threat of government regulation
- Labour movement pressure
- Effect of consumer awareness
- Creation of social norms for business
- Social and commercial interests are related to one another.
- Growth of the professional-managerial class
Kinds of Social Responsibility
- Ethical Responsibility: While acting ethically, business people should refrain from engaging in adulteration, black marketing, etc. Ethics are much more than the law.
- Economic Responsibility: Businesses must provide things and services that society needs and values and sell them for a profit to fulfil their economic responsibilities.
- Discretionary Responsibility: This obligation is entirely optional. This involves charitable giving. Helping those impacted by floods, earthquakes, etc., by participating in social service programmes, establishing educational and training facilities, etc.
- Legal Responsibility: Every firm is expected to operate within our society’s legal framework. A business that follows the law is viewed as socially responsible and receives no interference from the government.
Social responsibility towards different interest groups
Responsibilities towards Consumers:
- Production of certain products while upholding quality requirements.
- Being sincere in marketing.
- Should adhere to fair trade principles.
Responsibilities towards Employees:
- Provide perks and remuneration that are just.
- Establishing favourable and secure working circumstances.
- To provide them with opportunities to take part in the decision-making
Responsibilities towards the Owners/Shareholders/Investors:
- To guarantee investment safety.
- To guarantee a just and consistent return on investment.
- To guarantee investment growth through efficient resource use.
Responsibilities towards Government:
- To follow the law, rules, and regulations.
- Must promptly pay all taxes and fees.
- To assist in resolving social issues.
Responsibilities towards the community:
- To defend the environment from contamination of all kinds.
- To increase the number of work options.
- To support society’s less fortunate groups.
Responsibilities towards Suppliers:
- To make sure that the provider is regularly paid.
- To conduct fair business with suppliers.
- By placing orders with them to defend and support small-scale suppliers.
Business and Environment protection
Causes of Environmental Pollution
The following factors contribute to environmental pollution:
- Land pollution
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
Need for Pollution Control
The following are the primary causes for pollution control:
- To guarantee safety
- To preserve the beauty of nature
- Economic losses
- To guarantee a healthy life
- To lead a comfortable life
Role of Business in Environmental Protection
Business people should take the following actions to control and check environmental pollution:
- Using environmentally sustainable production methods.
- Industrial waste recycling.
- We are using technology to treat garbage before dumping it on land or releasing it into the sea.
- Utilise eco-marks by making environmentally beneficial items.
Business Ethics
It refers to the collection of moral principles that guide a businessperson’s actions. What is good and wrong are defined by ethics.
Elements of Business Ethics
The following are some fundamental principles of conducting business ethically:
- The construction of a compliance system
- Publication of a ‘code.’
- Engaging workers at all levels
- Top management commitment
- Result measurement
In the above section of Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 , all the critical topics covered have been discussed.
Benefits of Solving Business Studies Class 11 Chapter 6 Important Questions
As mentioned earlier, Business Studies is a subject that requires constant reading and revising of each chapter on a regular basis. Its fundamentals are introduced in Class 11 with a more detailed explanation in Class 12. Class 11 students are advised to go through Extramarks Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 . These critical questions make comprehension much easier for the students.
Following are some benefits of solving Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6:
- Business Studies comprises a vast syllabus —all the intricacies of the chapters are adequately explained through these crucial questions by Extramarks. Students and teachers have unshakable trust and faith in Extramarks resources.
- Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 covers the concepts of the entire chapter- Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics. These questions are prepared by subject matter ex perts who provide system atic and well-laid-out balanced study plans that boost their performance naturally and effortlessly.
- Important Questions are curated keeping in mind all the guidelines laid by CBSE , so that students can study independently without any further assistance.
Extramarks provides comprehensive learning solutions for students from Class 1 to Class 12. As reiterated earlier, Extramarks has abundant resources available on their website, along with essential questions and solutions. Students can click on the links given below to access some of these resources:
- NCERT books
- CBSE syllabus
- CBSE sample papers
- CBSE previous year’s question papers
- Important formulas
- CBSE extra questions
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
Q.1 A business is essentially a social institution and not merely a profit making activity. Do you think this statement is correct Give arguments in favour of the statement.
Marks: 6 Ans
The statement A business is essentially a social institution and not merely a profit making activity is correct and can be justified with following arguments:
i) Existence and Growth of Business : The prosperity and growth is possible only through continuous service to society. Profit motive is an important justification for a business and it is an outcome of satisfactory services to people. Therefore, satisfying the customers through social responsibility is necessary for the existence and growth of business.
ii) Avoidance of Government Intervention : Governmental intervention is undesirable for smooth running of a business as it limits the freedom of activities. If the firms voluntarily adopt social responsibility programmes, they can avoid this problem.
iii) Creating Opportunities : The business institutions have valuable financial and human resources which can be effectively used for solving problems. In this way they can convert risky situations into profitable deals, create new opportunities as well as solve social problems.
iv) Long Term Interest of Business : It is in the long term interest of the business to fulfill its social responsibility. The public image of the firm would improve when it supports social goals. If the firm fails to do so, the members of the society feel that business is not serving its best interest and they tend to withdraw their cooperation to the enterprise.
v) Creating Better Business Environment : A firm cannot do better in a society which is full of complicated problems. If the society has fewer problems, it will provide better environment for a firm to conduct its business. Therefore, it is in the interest of the business firms to take steps to minimise the problems of the society by acknowledging their responsibility towards them.
vi) Moral Obligation of Business : Most of the social problems have either been created or perpetuated by business enterprises themselves such as environmental pollution, unsafe workplaces, corruption in public institutions and discriminatory practices in employment. Hence, it becomes the moral obligation of business firms to get involved in solving these problems.
Q.2 Suggest the steps which can be taken by business organisations for environmental protection.
Following steps can be taken by business enterprises for environmental protection:
i) Commitment by Management : Top management should take the commitment to create, maintain and develop work culture to enhance environment protection. All measures should be taken to prevent any type of pollution.
ii) Involvement of All : All departments and employees should be involved in environment protection programmes. It would be helpful to achieve the desired result, if efforts are made jointly.
iii) Developing Policies : Business firms should make policies for purchasing good quality raw materials using superior technology and scientific techniques of disposal and treatment of wastes. Efforts should be made to develop employee skills for the purpose of pollution control.
iv) Complying with Laws : The business organisations must comply with the laws, acts and regulations enacted by the government for prevention of pollution. It should be the duty of all business firms to participate in government programmes relating to management of hazardous substances, clearing up of polluted rivers etc.
v) Periodical Assessment : Regular assessment of pollution control programmes in terms of cost benefit analysis should be done to ensure that they progress in the right direction.
vi) Arranging Workshops : To involve all stakeholders such as suppliers, consumers, employees etc., workshops or seminars should be organised. Through these workshops or seminars, education and training related to environment protection can be provided easily.
Q.3 Explain the basic elements of business ethics which can be taken care of while running an enterprise.
Marks: 5 Ans
The basic elements of business ethics which should be taken care of while running an enterprise are as follows:
i) Role of Top Management : To achieve good results in terms of business ethics, the top management of the firm needs to be openly and strongly committed to ethical conduct of the business. The top management must give continuous leadership for developing and upholding the values of the organisation.
ii) Involvement of Employees : Whatever the policies are framed for ethical conduct of the business, are implemented by the employees working at different levels of the organisation. Therefore, it is necessary that all employees of the firm should be involved in ethical conduct of the business.
iii) Publication of a Code : Business organisations publish a written document containing the principles of conduct for the whole organisation, called Code. This code covers the areas of honesty, product safety, fairness of selling practices etc.
iv) Compliance Mechanisms : To ensure that the conduction of business and actions comply with the ethical standards set up by the firm, it is necessary to establish appropriate mechanisms.
v) Measuring Results : It is difficult to accurately measure the results of ethical programmes. However, the firms can certainly audit to monitor compliance with ethical standards.
Q.4 Aarav works as a whole time director and legal consultant in a large manufacturing organisation. The top management decided to expand their operations and open a new unit. Aarav along with other managers decided to establish an advanced pollution control device for the new unit so that there is less possibility of damage to nearby areas and avoidance of government regulations with respect to pollution control measures. Also, workers living in nearby areas were hired and given fair amount of wages so that their standard of living can be improved.
- Installation of pollution control device can be categorised under which type of social responsibility
- Also, identify the concept that involves adhering to moral practices and following fair business practices in the interest of people.
Marks: 4 Ans
(i) Installation of pollution control unit can be categorised under Legal responsibility of a business as there are laws and measures imposed by government with respect to industrial units that can create pollution and to avoid breaking of such laws, companies install pollution control devices.
Legal responsibility is to operate business within the laws of the country and be a law abiding enterprise. A business needs to comply with the provisions of law.
(ii) The concept that involves adhering to moral practices and following fair business practices in the interest of people is known as Business ethics.
Business ethics is an act, decision or behavior that is in agreement with the prevailing norms of the society. Every business is expected to carry its operations in an ethical manner. It is different from law. Ethics means the business practices which are desirable from the point of view of the society.
Examples of business ethics will be: charging fair prices from customers, giving fair treatment to workers, earning reasonable profits etc. On the other hand, malpractices such as adulteration, hoarding, black-marketing etc. are not desirable from the point of view of the society and so are termed as unethical.
Please register to view this section
Cbse class 11 business studies important questions, chapter 1 - business, trade and commerce.

Chapter 2 - Forms of Business Organisation
Chapter 3 - private, public and global enterprises, chapter 4 - business services, chapter 5 - emerging modes of business, chapter 7 - formation of a company, chapter 8 - sources of business finance, chapter 9 - small business, chapter 10 - internal trade, chapter 11 - international business, faqs (frequently asked questions), 1. where can a student easily find important questions class 11 business studies chapter 6.
Students can easily register with Extramarks and gain access to Important Questions Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 . These critical questions cover the entire chapter. Prepared by subject matter experts, these questions and their solutions are authentic and exclusive. This encourages the student to master the topic and help students achieve better grades in their examinations.
2. How many books are assigned for Class 11 Business Studies?
The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) only suggests one Class 11 Business Studies book. As a result, this book—available in both Hindi and English—was published by the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT). There are 10 chapters in this book, which are divided into two parts. Part A includes – Foundation of Business comprises six chapters while part B has Finance and Trade comprises four chapters.
CBSE Related Links

Fill this form to view question paper
Otp verification.
- List of Commerce Articles
- Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities Of Business And Business Ethics
Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics creates awareness amongst companies about the social responsibilities of trade. The concept explains different aspects of social responsibility of business, arguments for social responsibility, arguments against social responsibility, the reality of social responsibility, kinds of social responsibility.
Many factors can have a positive impact on the business while delivering social responsibilities. Let us understand and get more insight into various phases of Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics.
- Social Responsibilities of a Business
For more concepts and study materials of Class 11 Business Studies, visit BYJU’S or download the app for the best learning experience.
| COMMERCE Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

NCERT Solutions for Class 11th: Ch 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
Ncert solutions for class 11th: ch 6 social responsibilities of business and business ethics business studies, contact form.

COMMENTS
3. Avoidance of government regulations: Business can avoid the problem of government regulations by voluntarily assuming social responsibilities. 4. Availability of resources with business: Business has valuable financial and human resources which can be effectively used for solving problems of the society. 5.
Vedantu's revision notes in PDF format for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - "Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics" is an invaluable resource for students. These notes offer a condensed yet comprehensive overview of the critical concepts, principles, and practices related to business ethics and social responsibility.
develops the understanding that it is possible for a business enterprise to be socially responsible and ethically upright and, at the same time, be highly profitable. He then gets busy with studying more about the social responsibility of business and business ethics. Chapter 6.indd 134 9/2/2022 2:11:36 PM 2024-25
NCERT Solution For Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics includes all the questions provided in NCERT Books for 11th Class Business Studies subject. At BYJU'S, students have an option to download for free.
Free PDF download of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics solved by Expert Teachers as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter wise Questions with Solutions to help you to revise complete Syllabus and Score More marks in your examinations.
CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Revision Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics. SelfStudys provides chapter-wise Business Studies Revision Notes and short key notes for the CBSE board examination in free downloadable PDF format so students can practice it for their studies and get better in their board examinations.
Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics Class 11 Notes: Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has altered its syllabus for the current academic session 2023-2024.As a process ...
A Brief Overview of Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibility of Business and Business Ethics. Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 solutions explain how business ethics is the knowledge of appropriate business strategies and practices concerning potentially controversial matters, including corporate governance, internal trading ...
Learn CBSE Business Studies Index Terms for Class 11, Chapter 6 Including Definitions and Meanings. 1. Social Responsibility - Social responsibility is a moral obligation on a company or an individual to make decisions or actions that is in favour and useful to society. Social responsibility in business is commonly known as Corporate Social ...
NCERT solutions for Mathematics Class 11 Business Studies CBSE 6 (Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
So if you are in 11th standard, and studying Business Studies textbook (named Business Studies), then you can read Ch 6 here and afterwards use NCERT Solutions to solve questions answers of Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics. NCERT Book Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics
Class 11 business studies Chapter 6 SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITIES OF BUSINESS AND BUSINESS ETHICS Business is an integral part of society; so it must fulfill social responsibility. It can't exist without the support of the society.
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 11 Business Studies Subject - Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
Frequently asked Questions on CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Notes Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business Ethics Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics is a chapter that creates a sense of awareness among students with regards to the societal responsibilities of trade.
The compilation of important questions for CBSE Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 - "Social Responsibilities of Business and Ethics" is a significant asset for students. These thoughtfully selected questions cover essential topics related to ethical business practices and corporate social responsibility, offering a focused approach to exam ...
In this chapter, we will discuss on social responsibilities of business and business ethics class 11 notes. We will begin with the explanation of the concept of social responsibility. Then, we will understand the need for social responsibility. Also, we will discuss the arguments for and against social responsibility.
1. Existence and growth - Prosperity and growth of business is possible only through rendering continuous service to society. 2. Long term interest of the firm - A firm and its image stands to gain more profits in the long run when it accepts service as the highest goal. Supporting social goals enhances. public image of any firm.
Explain business ethics as explained in Class 11. Business ethics are the moral principles and standards of behaviour that a company must uphold in order to carry out only those deeds that are beneficial to society. The purpose of business ethics is to direct a company's management and employees towards polite behaviour.
Given below are a few Important Questions from Class 11 Business Studies Chapter 6 and their solutions:. Q1. State the meaning of Corporate Social Responsibility as per the Companies Act 2013. Answer. Corporate social responsibility refers to the obligation businesses have to play in achieving social development goals and maintaining a balance between environmental preservation, social ...
Chapter 6 Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics. There are many factors that can have a positive impact on the business while delivering social responsibilities. ... For more concepts and study materials of Class 11 Business Studies, visit BYJU'S or download the app for the best learning experience. COMMERCE Related Links ...
Learn the concepts of Class 11 Business Studies Social Responsibilities of Business and Business Ethics with Videos and Stories. Compare Ethics versus Laws Solve Study Textbooks Guides
1. Social responsibility is. 2. If business is to operate in a society which is full of diverse and complicated problems, it may have. 3. Business people have the skills to solve. 4. That an enterprise must behave as a good citizen is an example of its responsibilities towards. 5.