Is Psychology a Science?
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Psychology is a science because it employs systematic methods of observation, experimentation, and data analysis to understand and predict behavior and mental processes, grounded in empirical evidence and subjected to peer review.
Science uses an empirical approach. Empiricism (founded by John Locke) states that the only source of knowledge is our senses – e.g., sight, hearing, etc.
In psychology, empiricism refers to the belief that knowledge is derived from observable, measurable experiences and evidence, rather than from intuition or speculation.
This was in contrast to the existing view that knowledge could be gained solely through the powers of reason and logical argument (known as rationalism). Thus, empiricism is the view that all knowledge is based on or may come from experience.
Through gaining knowledge through experience, the empirical approach quickly became scientific and greatly influenced the development of physics and chemistry in the 17th and 18th centuries.
The idea that knowledge should be gained through experience, i.e., empirically, turned into a method of inquiry that used careful observation and experiments to gather facts and evidence.
The nature of scientific inquiry may be thought of at two levels:
1. That to do with theory and the foundation of hypotheses. 2. And actual empirical methods of inquiry (i.e. experiments, observations)
The prime empirical method of inquiry in science is the experiment.
The key features of the experiment are control over variables ( independent, dependent , and extraneous ), careful, objective measurement, and establishing cause and effect relationships.

Features of Science
Empirical evidence.
- Refers to data being collected through direct observation or experiment.
- Empirical evidence does not rely on argument or belief.
- Instead, experiments and observations are carried out carefully and reported in detail so that other investigators can repeat and attempt to verify the work.
Objectivity
- Researchers should remain value-free when studying; they should try to remain unbiased in their investigations. I.e., Researchers are not influenced by personal feelings and experiences.
- Objectivity means that all sources of bias are minimized and that personal or subjective ideas are eliminated. The pursuit of science implies that the facts will speak for themselves, even if they differ from what the investigator hoped.
- All extraneous variables need to be controlled to establish the cause (IV) and effect (DV).
Hypothesis testing
- E.g., a statement made at the beginning of an investigation that serves as a prediction and is derived from a theory. There are different types of hypotheses (null and alternative), which need to be stated in a form that can be tested (i.e., operationalized and unambiguous).
Replication
- This refers to whether a particular method and finding can be repeated with different/same people and/or on different occasions to see if the results are similar.
- If a dramatic discovery is reported, but other scientists cannot replicate it, it will not be accepted.
- If we get the same results repeatedly under the same conditions, we can be sure of their accuracy beyond a reasonable doubt.
- This gives us confidence that the results are reliable and can be used to build up a body of knowledge or a theory: which is vital in establishing a scientific theory.
Predictability
- We should aim to be able to predict future behavior from the findings of our research.
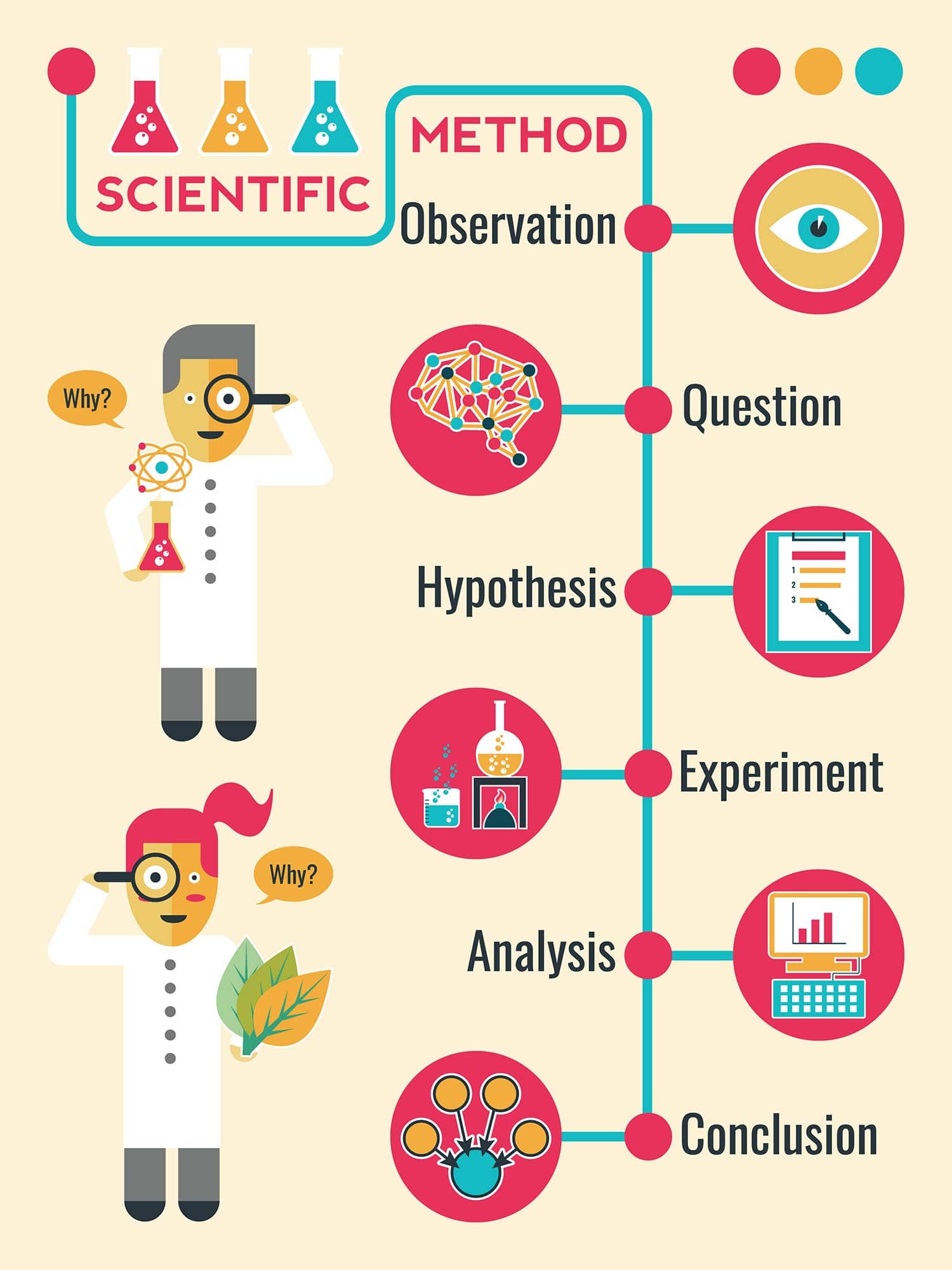
The Scientific Process
Before the twentieth century, science largely used induction principles – making discoveries about the world through accurate observations, and formulating theories based on the regularities observed.
Newton’s Laws are an example of this. He observed the behavior of physical objects (e.g., apples) and produced laws that made sense of what he observed.
The scientific process is now based on the hypothetico-deductive model proposed by Karl Popper (1935). Popper suggested that theories/laws about the world should come first, and these should be used to generate expectations/hypotheses, which observations and experiments can falsify.
As Popper pointed out, falsification is the only way to be certain: ‘No amount of observations of white swans can allow the conclusion that all swans are white, but the observation of a single black swan is sufficient to refute that conclusion.
Darwin’s theory of evolution is an example of this. He formulated a theory and tested its propositions by observing animals in nature. He specifically sought to collect data to prove his theory / disprove it.
Thomas Kuhn argued that science does not evolve gradually towards truth, science has a paradigm that remains constant before going through a paradigm shift when current theories can’t explain some phenomenon, and someone proposes a new theory. Science tends to go through these shifts; therefore, psychology is not a science as it has no agreed paradigm.
There are many conflicting approaches, and the subject matter of Psychology is so diverse; therefore, researchers in different fields have little in common.
Psychology is really a very new science, with most advances happening over the past 150 years or so. However, it can be traced back to ancient Greece, 400 – 500 years BC. The emphasis was a philosophical one, with great thinkers such as Socrates influencing Plato, who in turn influenced Aristotle.
Plato argued that there was a clear distinction between body and soul, believed very strongly in the influence of individual differences on behavior, and played a key role in developing the notion of “mental health,” believing that the mind needed stimulation from the arts to keep it alive.
Aristotle firmly believed that the body strongly affected the mind – you might say he was an early biopsychologist.
Psychology as a science took a “back seat” until Descartes (1596 – 1650) wrote in the 17th century. He believed strongly in the concept of consciousness, maintaining that it was that that separated us from animals.
He did, however, believe that our bodies could influence our consciousness and that the beginnings of these interactions were in the pineal gland – we know now that this is probably NOT the case!
From this influential work came other important philosophies about psychology, including the work by Spinoza (1632 – 1677) and Leibnitz (1646 – 1716). But there still was no single, scientific, unified psychology as a separate discipline (you could certainly argue that there still isn’t”t!).
When asked, “Who is the parent of psychology?” many people answer, “Freud.” Whether this is the case or not is open to debate, but if we were to ask who the parent of experimental psychology is, few would likely respond similarly. So, where did modern experimental psychology come from, and why?
Psychology took so long to emerge as a scientific discipline because it needed time to consolidate. Understanding behavior, thoughts, and feelings are not easy, which may explain why it was largely ignored between ancient Greek times and the 16th century.
But tired of years of speculation, theory, and argument, and bearing in mind Aristotle’s plea for scientific investigation to support the theory, psychology as a scientific discipline began to emerge in the late 1800s.
Wilheim Wundt developed the first psychology lab in 1879. Introspection was used, but systematically (i.e., methodologically). It was really a place from which to start thinking about how to employ scientific methods to investigate behavior.
The classic movement in psychology to adopt these strategies was the behaviorists, who were renowned for relying on controlled laboratory experiments and rejecting any unseen or subconscious forces as causes of behavior.
And later, cognitive psychologists adopted this rigorous (i.e., careful), scientific, lab-based approach.
Psychological Approaches
Psychoanalysis has great explanatory power and understanding of behavior. Still, it has been accused of only explaining behavior after the event, not predicting what will happen in advance, and being unfalsifiable.
Some have argued that psychoanalysis has approached the status more of a religion than a science. Still, it is not alone in being accused of being unfalsifiable (evolutionary theory has, too – why is anything the way it is? Because it has evolved that way!), and like theories that are difficult to refute – the possibility exists that it is actually right.
Kline (1984) argues that psychoanalytic theory can be broken down into testable hypotheses and tested scientifically. For example, Scodel (1957) postulated that orally dependent men would prefer larger breasts (a positive correlation) but, in fact, found the opposite (a negative correlation).
Although Freudian theory could be used to explain this finding (through reaction formation – the subject showing exactly the opposite of their unconscious impulses!), Kline has nevertheless pointed out that no significant correlation would have refuted the theory.
Behaviorism has parsimonious (i.e., economic / cost-cutting) theories of learning, using a few simple principles (reinforcement, behavior shaping, generalization, etc.) to explain a wide variety of behavior from language acquisition to moral development.
It advanced bold, precise, and refutable hypotheses (such as Thorndike’s law of effect ) and possessed a hard core of central assumptions such as determinism from the environment (it was only when this assumption faced overwhelming criticism by the cognitive and ethological theorists that the behaviorist paradigm/model was overthrown).
Behaviorists firmly believed in the scientific principles of determinism and orderliness. They thus came up with fairly consistent predictions about when an animal was likely to respond (although they admitted that perfect prediction for any individual was impossible).
The behaviorists used their predictions to control the behavior of both animals (pigeons trained to detect life jackets) and humans (behavioral therapies), and indeed Skinner , in his book Walden Two (1948), described a society controlled according to behaviorist principles.
Cognitive psychology – adopts a scientific approach to unobservable mental processes by advancing precise models and conducting experiments on behavior to confirm or refute them.
Full understanding, prediction, and control in psychology are probably unobtainable due to the huge complexity of environmental, mental, and biological influences upon even the simplest behavior (i.e., all extraneous variables cannot be controlled).
You will see, therefore, that there is no easy answer to the question, “is psychology a science?”. But many approaches of psychology do meet the accepted requirements of the scientific method, whilst others appear to be more doubtful in this respect.
Alternatives
However, some psychologists argue that psychology should not be a science. There are alternatives to empiricism, such as rational research, argument, and belief.
The humanistic approach (another alternative) values private, subjective conscious experience and argues for the rejection of science.
The humanistic approach argues that objective reality is less important than a person’s subjective perception and subjective understanding of the world. Because of this, Carl Rogers and Maslow placed little value on scientific psychology, especially using the scientific laboratory to investigate human and other animal behavior.
A person’s subjective experience of the world is an important and influential factor in their behavior. Only by seeing the world from the individual’s point of view can we really understand why they act the way they do. This is what the humanistic approach aims to do.
Humanism is a psychological perspective that emphasizes the study of the whole person. Humanistic psychologists look at human behavior not only through the eyes of the observer but through the eyes of the person doing the behavior. Humanistic psychologists believe that an individual’s behavior is connected to his inner feelings and self-image.
The humanistic approach in psychology deliberately steps away from a scientific viewpoint, rejecting determinism in favor of free will, aiming to arrive at a unique and in-depth understanding. The humanistic approach does not have an orderly set of theories (although it does have some core assumptions).
It is not interested in predicting and controlling people’s behavior – the individuals themselves are the only ones who can and should do that.
Miller (1969), in “Psychology as a Means of Promoting Human Welfare,” criticizes the controlling view of psychology, suggesting that understanding should be the main goal of the subject as a science since he asks who will do the controlling and whose interests will be served by it?
Humanistic psychologists rejected a rigorous scientific approach to psychology because they saw it as dehumanizing and unable to capture the richness of conscious experience.
In many ways, the rejection of scientific psychology in the 1950s, 1960s, and 1970s was a backlash to the dominance of the behaviorist approach in North American psychology.
Common Sense Views of Behavior
In certain ways, everyone is a psychologist. This does not mean that everyone has been formally trained to study and be trained in psychology.
People have common sense views of the world, of other people, and of themselves. These common-sense views may come from personal experience, from our upbringing as a child, and through culture, etc.
People have common-sense views about the causes of their own and other people’s behavior, personality characteristics they and others possess, what other people should do, how to bring up your children, and many more aspects of psychology.
Informal psychologists acquire common-sense knowledge in a rather subjective (i.e., unreliable) and anecdotal way. Common-sense views about people are rarely based on systematic (i.e., logical) evidence and are sometimes based on a single experience or observation.
Racial or religious prejudices may reflect what seems like common sense within a group of people. However, prejudicial beliefs rarely stand up to what is actually the case.
Common sense, then, is something that everybody uses in their day-to-day lives, guides decisions and influences how we interact with one another.
However, because it is not based on systematic evidence or derived from scientific inquiry, it may be misleading and lead to one group of people treating others unfairly and in a discriminatory way.
Limitations of Scientific Psychology
Despite having a scientific methodology worked out (we think), some further problems and arguments doubt psychology is ever a science.
Limitations may refer to the subject matter (e.g., overt behavior versus subjective, private experience), objectivity, generality, testability, ecological validity, ethical issues, and philosophical debates, etc.
Science assumes that there are laws of human behavior that apply to each person. Therefore, science takes both a deterministic and reductionist approach.
Science studies overt behavior because overt behavior is objectively observable and can be measured, allowing different psychologists to record behavior and agree on what has been observed. This means that evidence can be collected to test a theory about people.
Scientific laws are generalizable, but psychological explanations are often restricted to specific times and places. Because psychology studies (mostly) people, it studies (indirectly) the effects of social and cultural changes on behavior.
Psychology does not go on in a social vacuum. Behavior changes over time and in different situations. These factors, and individual differences, make research findings reliable for a limited time only.
Are traditional scientific methods appropriate for studying human behavior? When psychologists operationalize their IV, it is highly likely that this is reductionist, mechanistic, subjective, or just wrong.
Operationalizing variables refers to how you will define and measure a specific variable as it is used in your study. For example, a biopsychologist may operationalize stress as an increased heart rate. Still, it may be that in doing this, we are removed from the human experience of what we are studying. The same goes for causality.
Experiments are keen to establish that X causes Y, but taking this deterministic view means that we ignore extraneous variables and the fact that at a different time, in a different place, we probably would not be influenced by X. There are so many variables that influence human behavior that it is impossible to control them effectively. The issue of ecological validity ties in really nicely here.
Objectivity is impossible. It is a huge problem in psychology, as it involves humans studying humans, and it is very difficult to study people’s behavior in an unbiased fashion.
Moreover, in terms of a general philosophy of science, we find it hard to be objective because a theoretical standpoint influences us (Freud is a good example). The observer and the observed are members of the same species are this creates problems of reflectivity.
A behaviorist would never examine a phobia and think in terms of unconscious conflict as a cause, just like Freud would never explain it as a behavior acquired through operant conditioning.
This particular viewpoint that a scientist has is called a paradigm (Kuhn, 1970). Kuhn argues that most scientific disciplines have one predominant paradigm that the vast majority of scientists subscribe to.
Anything with several paradigms (e.g., models – theories) is a pre-science until it becomes more unified. With a myriad of paradigms within psychology, it is not the case that we have any universal laws of human behavior. Kuhn would most definitely argue that psychology is not a science.
Verification (i.e., proof) may be impossible. We can never truly prove a hypothesis; we may find results to support it until the end of time, but we will never be 100% confident that it is true.
It could be disproved at any moment. The main driving force behind this particular grumble is Karl Popper, the famous philosopher of science and advocator of falsificationism.
Take the famous Popperian example hypothesis: “All swans are white.” How do we know for sure that we will not see a black, green, or hot pink swan in the future? So even if there has never been a sighting of a non-white swan, we still haven’t really proven our hypothesis.
Popper argues that the best hypotheses are those which we can falsify – disprove. If we know something is not true, then we know something for sure.
Testability: much of the subject matter in psychology is unobservable (e.g., memory) and, therefore, cannot be accurately measured. The fact that there are so many variables that influence human behavior that it is impossible to control the variables effectively.
So, are we any closer to understanding a) what science is and b) if psychology is a science? Unlikely. There is no definitive philosophy of science and no flawless scientific methodology.
When people use the term “Scientific,” we all have a general schema of what they mean, but when we break it down in the way that we just have done, the picture is less certain. What is science? It depends on your philosophy. Is psychology a science? It depends on your definition. So – why bother, and how do we conclude all this?
Slife and Williams (1995) have tried to answer these two questions:
1) We must at least strive for scientific methods because we need a rigorous discipline. If we abandon our search for unified methods, we’ll lose a sense of what psychology is (if we knew it in the first place).
2) We need to keep trying to develop scientific methods that are suitable for studying human behavior – it may be that the methods adopted by the natural sciences are not appropriate for us.
Further Information
- Psychology as a Science (PDF)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Psychology’s Status as a Science: Peculiarities and Intrinsic Challenges. Moving Beyond its Current Deadlock Towards Conceptual Integration
School of Human Sciences, University of Greenwich, Old Royal Naval College, Park Row, London, SE10 9LS UK
Psychology holds an exceptional position among the sciences. Yet even after 140 years as an independent discipline, psychology is still struggling with its most basic foundations. Its key phenomena, mind and behaviour, are poorly defined (and their definition instead often delegated to neuroscience or philosophy) while specific terms and constructs proliferate. A unified theoretical framework has not been developed and its categorisation as a ‘soft science’ ascribes to psychology a lower level of scientificity. The article traces these problems to the peculiarities of psychology’s study phenomena, their interrelations with and centrality to everyday knowledge and language (which may explain the proliferation and unclarity of terms and concepts), as well as to their complex relations with other study phenomena. It shows that adequate explorations of such diverse kinds of phenomena and their interrelations with the most elusive of all—immediate experience—inherently require a plurality of epistemologies, paradigms, theories, methodologies and methods that complement those developed for the natural sciences. Their systematic integration within just one discipline, made necessary by these phenomena’s joint emergence in the single individual as the basic unit of analysis, makes psychology in fact the hardest science of all. But Galtonian nomothetic methodology has turned much of today’s psychology into a science of populations rather than individuals, showing that blind adherence to natural-science principles has not advanced but impeded the development of psychology as a science. Finally, the article introduces paradigmatic frameworks that can provide solid foundations for conceptual integration and new developments.
Psychology’s Status as a Discipline
Psychology holds an exceptional position among the sciences—not least because it explores the very means by which any science is made, for it is humans who perceive, conceive, define, investigate, analyse and interpret the phenomena of the world. Scientists have managed to explore distant galaxies, quantum particles and the evolution of life over 4 billion years—phenomena inaccessible to the naked eye or long deceased. Yet, psychology is still struggling with its most basic foundations. The phenomena of our personal experience, directly accessible to everyone in each waking moment of life, remain challenging objects of research. Moreover, psychical phenomena are essential for all sciences (e.g., thinking). But why are we struggling to scientifically explore the means needed to first make any science? Given the successes in other fields, is this not a contradiction in itself?
This article outlines three key problems of psychology (poor definitions of study phenomena, lack of unified theoretical frameworks, and an allegedly lower level of scientificity) that are frequently discussed and at the centre of Zagaria, Andò and Zennaro’s ( 2020 ) review. These problems are then traced to peculiarities of psychology’s study phenomena and the conceptual and methodological challenges they entail. Finally, the article introduces paradigmatic frameworks that can provide solid foundations for conceptual integration and new developments.
Lack of Proper Terms and Definitions of Study Phenomena
Introductory text books are supposed to present the corner stones of a science’s established knowledge base. In psychology, however, textbooks present definitions of its key phenomena—mind (psyche) and behaviour—that are discordant, ambiguous, overlapping, circular and context-dependent, thus inconclusive (Zagaria et al. 2020 ). Tellingly, many popular text books define ‘mind’ exclusively as ‘brain activity’, thus turning psychology’s central object of research into one of neuroscience. What then is psychology as opposed to neuroscience? Some even regard the definition of mind as unimportant and leave it to philosophers, thus categorising it as a philosophical phenomenon and shifting it again out of psychology’s own realm. At the same time, mainstream psychologists often proudly distance themselves from philosophers (Alexandrova & Haybron, 2016 ), explicitly referring to the vital distinction between science and philosophy. Behaviour, as well, is commonly reduced to ill-defined ‘activities’, ‘actions’ and ‘doings’ and, confusingly, often even equated with mind (psyche), such as in concepts of ‘inner and outer behaviours’ (Uher 2016b ). All this leaves one wonder what psychology is actually about.
As if to compensate the unsatisfactory definitional and conceptual status of its key phenomena in general, psychology is plagued with a chaotic proliferation of terms and constructs for specific phenomena of mind and behaviour (Zagaria et al. 2020 ). This entails that different terms can denote the same concept (jangle-fallacies; Kelley 1927 ) and the same terms different concepts (jingle-fallacies; Thorndike 1903 ). Even more basically, many psychologists struggle to explain what their most frequent study phenomena—constructs—actually are (Slaney and Garcia 2015 ). These deficiencies and inconsistencies involve a deeply fragmented theoretical landscape.
Lack of Conceptual Integration Into Overarching Frameworks
Like no other science, psychology embraces an enormous diversity of established epistemologies, paradigms, theories, methodologies and methods. Is that a result of the discipline’s unparalleled complexity and the therefore necessary scientific pluralism (Fahrenberg 2013 ) or rather an outcome of mistaking this pluralism for the unrestrained proliferation of perspectives (Zagaria et al. 2020 )?
The lack of a unified theory in psychology is widely lamented. Many ‘integrative theories’ were proposed as overarching frameworks, yet without considering contradictory presuppositions underlying different theories. Such integrative systems merely provide important overviews of the essential plurality of research perspectives and methodologies needed in the field (Fahrenberg 2013 ; Uher 2015b ). Zagaria and colleagues ( 2020 ) suggested evolutionary psychology could provide the much-needed paradigmatic framework. This field, however, is among psychology’s youngest sub-disciplines and its most speculative ones because (unlike biological phenomena) psychical, behavioural and social phenomena leave no fossilised traces in themselves. Their possible ancestral forms can only be reconstructed indirectly from archaeological findings and investigations of today’s humans, making evolutionary explorations prone to speculations and biases (e.g., gender bias in interpretations of archaeological findings; Ginge 1996 ). Cross-species comparative psychology offers important correctives through empirical studies of today’s species with different cognitive, behavioural, social and ecological systems and different degrees of phylogenetic relatedness to humans. This enables comparisons and hypothesis testing not possible when studying only humans but still faces limitations given human ancestors’ unavailability for direct study (Uher 2020a ).
But most importantly, evolutionary psychology does not provide consistent terms and concepts either; its key constructs ‘psychological adaptations’ and ‘evolved psychological mechanisms’ are as vague, ambiguous and ill-defined as ‘mind’ and ‘behaviour’. Moreover, the strong research heuristic formulated in Tinbergen’s four questions on the causation, function, development and evolution of behaviour is not an achievement of evolutionary psychology but originates from theoretical biology, thus again from outside of psychology.
Psychology—a ‘Soft Science’ in Pre-scientific Stage?
The pronounced inconsistencies in psychology’s terminological, conceptual and theoretical landscape have been likened to the pre-scientific stage of emerging sciences (Zagaria et al. 2020 ). Psychology was therefore declared a ‘soft science’ that can never achieve the status of the ‘hard sciences’ (e.g., physics, chemistry). This categorisation implies the belief that some sciences have only minor capacities to accumulate secured knowledge and lower abilities to reach theoretical and methodological consensus (Fanelli and Glänzel 2013 ; Simonton 2015 ). In particular, soft sciences would have only limited abilities to apply ‘the scientific method’, the general set of principles involving systematic observation, experimentation and measurement as well as deduction and testing of hypotheses that guide scientific practice (Gauch 2015 ). The idea of the presumed lack of methodological rigor and exactitude of ‘soft sciences’ goes back to Kant ( 1798 / 2000 ) and is fuelled by recurrent crises of replication, generalisation, validity, and other criteria considered essential for all sciences.
But classifying sciences into ‘hard’ and ‘soft’, implying some would be more scientific than others, is ill-conceived and misses the point why there are different sciences at all. Crucially, the possibilities for implementing particular research practices are not a matter of scientific discipline or their ascribed level of scientificity but solely depend on the particular study phenomena and their properties (Uher 2019 ). For study phenomena that are highly context-dependent and continuously changing in themselves, such as those of mind, behaviour and society, old knowledge cannot have continuing relevance as this is the case for (e.g., non-living) phenomena and properties that are comparably invariant in themselves. Instead, accurate and valid investigations require that concepts, theories and methods must be continuously adapted as well (Uher 2020b ).
The classification of sciences by the degree to which they can implement ‘the scientific method’ as developed for the natural sciences is a reflection of the method-centrism that has taken hold of psychology over the last century, when the craft of statistical analysis became psychologists’ dominant activity (Lamiell 2019 ; Valsiner 2012 ). The development of ever more sophisticated tools for statistical analysis as well as of rating scales enabling the efficient generation of allegedly quantitative data for millions of individuals misled psychologists to adapt their study phenomena and research questions to their methods, rather than vice versa (Omi 2012 ; Toomela and Valsiner 2010 ; Uher 2013 ). But methods are just a means to an end. Sciences must be phenomenon-centred and problem-centred, and they must develop epistemologies, theories, methodologies and methods that are suited to explore these phenomena and the research problems in their field.
Psychology’s Study Phenomena and Intrinsic Challenges
Psychology’s exceptional position among the sciences and its key problems can be traced to its study phenomena’s peculiarities and the conceptual and methodological challenges they entail.
Experience: Elementary to All Empirical Sciences
Experience is elementary to all empirical sciences, which are experience-based by definition (from Greek empeiria meaning experience). The founder of psychology, Wilhelm Wundt, already highlighted that every concrete experience has always two aspects, the objective content given and individuals’ subjective apprehension of it—thus, the objects of experience in themselves and the subjects experiencing them. This entails two fundamental ways in which experience is treated in the sciences (Wundt 1896a ).
Natural sciences explore the objective contents mediated by experience that can be obtained by subtracting from the concrete experience the subjective aspects always contained in it. Hence, natural scientists consider the objects of experience in their properties as conceived independently of the subjects experiencing them, using the perspective of mediate experience (mittelbare Erfahrung; Wundt 1896a ). Therefore, natural scientists develop theories, approaches and technologies that help minimise the involvement of human perceptual and conceptual abilities in research processes and filter out their effects on research outcomes. This approach is facilitated by the peculiarities of natural-science study phenomena (of the non-living world, in particular), in which general laws, immutable relationships and natural constants can be identified that remain invariant across time and space and that can be measured and mathematically formalised (Uher 2020b ).
Psychologists, in turn, explore the experiencing subjects and their understanding and interpretation of their experiential contents and how this mediates their concrete experience of ‘reality’. This involves the perspective of immediate experience (unmittelbare Erfahrung), with immediate indicating absence of other phenomena mediating their perception (Wundt 1896a ). Immediate experience comprises connected processes, whereby every process has an objective content but is, at the same time, also a subjective process. Inner experience, Wundt highlighted, is not a special part of experience but rather constitutes the entirety of all immediate experience; thus, inner and outer experience do not constitute separate channels of information as often assumed (Uher 2016a ). That is, psychology deals with the entire experience in its immediate subjective reality. The inherent relation to the perceiving and experiencing subject— subject reference —is therefore a fundamental category in psychology. Subjects are feeling and thinking beings capable of intentional action who pursue purposes and values. This entails agency, volition, value orientation and teleology. As a consequence, Wundt highlighted, research on these phenomena can determine only law-like generalisations that allow for exceptions and singularities (Fahrenberg 2019 ). Given this, it is meaningless to use theories-to-laws ratios as indicators of scientificity (e.g., in Simonton 2015 ; Zagaria et al. 2020 ).
Constructs: Concepts in Science AND Everyday Psychology
The processual and transient nature of immediate experience (and many behaviours) imposes further challenges because, of processual entities, only a part exists at any moment (Whitehead 1929 ). Experiential phenomena can therefore be conceived only through generalisation and abstraction from their occurrences over time, leading to concepts, beliefs and knowledge about them , which are psychical phenomena in themselves as well but different from those they are about (reflected in the terms experien cing versus experien ce ; Erleben versus Erfahrung; Uher 2015b , 2016a ). Abstract concepts, because they are theoretically constructed, are called constructs (Kelly 1963 ). All humans implicitly develop constructs (through abduction, see below) to describe and explain regularities they observe in themselves and their world. They use constructs to anticipate the unknown future and to choose among alterative actions and responses (Kelly 1963 ; Valsiner 2012 ).
Constructs about experiencing, experience and behaviour form important parts of our everyday knowledge and language. This entails intricacies because psychologists cannot simply put this everyday psychology aside for doing their science, even more so as they are studying the phenomena that are at the centre of everyday knowledge and largely accessible only through (everyday) language. Therefore, psychologists cannot invent scientific terms and concepts that are completely unrelated to those of everyday psychology as natural scientists can do (Uher 2015b ). But this also entails that, to first delineate their study phenomena, psychologists need not elaborate scientific definitions because everyday psychology already provides some terms, implicit concepts and understanding—even if these are ambiguous, discordant, circular, overlapping, context-dependent and biased. This may explain the proliferation of terms and concepts and the lack of clear definitions of key phenomena in scientific psychology.
Constructs and language-based methods entail further challenges. The construal of constructs allowed scientists to turn abstract ideas into entities, thereby making them conceptually accessible to empirical study. But this entification misguides psychologists to overlook their constructed nature (Slaney and Garcia 2015 ) by ascribing to constructs an ontological status (e.g., ‘traits’ as psychophysical mechanisms; Uher 2013 ). Because explorations of many psychological study phenomena are intimately bound to language, psychologists must differentiate their study phenomena from the terms, concepts and methods used to explore them, as indicated by the terms psych ical versus psych ological (from Greek -λογία, -logia for body of knowledge)—differentiations not commonly made in the English-language publications dominating in contemporary psychology (Lewin 1936 ; Uher 2016a ).
Psychology’s Exceptional Position Among the Sciences and Philosophy
The concepts of mediate and immediate experience illuminate psychology’s special interrelations with the other sciences and philosophy. Wundt conceived the natural sciences (Naturwissenschaften; e.g., physics, physiology) as auxiliary to psychology and psychology, in turn, as supplementary to the natural sciences “in the sense that only together they are able to exhaust the empirical knowledge accessible to us“ (Fahrenberg 2019 ; Wundt 1896b , p. 102). By exploring the universal forms of immediate experience and the regularities of their connections, psychology is also the foundation of the intellectual sciences (Geisteswissenschaften, commonly (mis)translated as humanities; e.g., philology, linguistics, law), which explore the actions and effects emerging from humans’ immediate experiences (Fahrenberg 2019 ). Psychology also provides foundations for the cultural and social sciences (Kultur- und Sozialwissenschaften; e.g., sociology; anthropology), which explore the products and processes emerging from social and societal interactions among experiencing subjects who are thinking and intentional agents pursuing values, aims and purposes. Moreover, because psychology considers the subjective and the objective as the two fundamental conditions underlying theoretical reflection and practical action and seeks to determine their interrelations, Wundt regarded psychology also a preparatory empirical science for philosophy (especially epistemology and ethics; Fahrenberg 2019 ).
Psychology’s exceptional position at the intersection with diverse sciences and with philosophy is reflected in the extremely heterogeneous study phenomena explored in its diverse sub-disciplines, covering all areas of human life. Some examples are individuals’ sensations and perceptions of physical phenomena (e.g., psychophysics, environmental psychology, engineering psychology), biological and pathological phenomena associated with experience and behaviour (e.g., biopsychology, neuropsychology, clinical psychology), individuals’ experience and behaviour in relation to others and in society (e.g., social psychology, personality psychology, cultural psychology, psycholinguistics, economic psychology), as well as in different periods and domains of life (e.g., developmental psychology, educational psychology, occupational psychology). No other science explores such a diversity of study phenomena. Their exploration requires a plurality of epistemologies, methodologies and methods, which include experimental and technology-based investigations (e.g., neuro-imaging, electromyography, life-logging, video-analyses), interpretive and social-science investigations (e.g., of texts, narratives, multi-media) as well as investigations involving self-report and self-observation (e.g., interviews, questionnaires, guided introquestion).
All this shows that psychology cannot be a unitary science. Adequate explorations of so many different kinds of phenomena and their interrelations with the most elusive of all—immediate experience—inherently require a plurality of epistemologies, paradigms, theories, methodologies and methods that complement those developed for the natural sciences, which are needed as well. Their systematic integration within just one discipline, made necessary by these phenomena’s joint emergence in the single individual as the basic unit of analysis, makes psychology in fact the hardest science of all.
Idiographic and Nomothetic Strategies of Knowledge Generation
Immediate experience, given its subjective, processual, context-dependent, and thus ever-changing nature, is always unique and unprecedented. Exploring such particulars inherently requires idiographic strategies, in which local phenomena of single cases are modelled in their dynamic contexts to create generalised knowledge from them through abduction. In abduction, scientists infer from observations of surprising facts backwards to a possible theory that, if it were true, could explain the facts observed (Peirce 1901 ; CP 7.218). Abduction leads to the creation of new general knowledge, in which theory and data are circularly connected in an open-ended cycle, allowing to further generalise, extend and differentiate the new knowledge created. By generalising from what was once and at another time as well, idiographic approaches form the basis of nomothetic approaches, which are aimed at identifying generalities common to all particulars of a class and at deriving theories or laws to account for these generalities. This Wundtian approach to nomothetic research, because it is case-by-case based , allows to create generalised knowledge about psychical processes and functioning, thus building a bridge between the individual and theory development (Lamiell 2003 ; Robinson 2011 ; Salvatore and Valsiner 2010 ).
But beliefs in the superiority of natural-science principles misled many psychologists to interpret nomothetic strategies solely in terms of the Galtonian methodology, in which many cases are aggregated and statistically analysed on the sample-level . This limits research to group-level hypothesis testing and theory development to inductive generalisation, which are uninformative about single cases and cannot reveal what is, indeed, common to all (Lamiell 2003 ; Robinson 2011 ). This entails numerous fallacies, such as the widespread belief between-individual structures would be identical to and even reflect within-individual structures (Molenaar 2004 ; Uher 2015d ). Galtonian nomothetic methodology has turned much of today’s psychology into a science exploring populations rather than individuals. That is, blind adherence to natural-science principles has not advanced but, instead, substantially impeded the development of psychology as a science.
Moving Psychology Beyond its Current Conceptual Deadlock
Wundt’s opening of psychology’s first laboratory marked its official start as an independent science. Its dynamic developments over the last 140 years testify to psychology’s importance but also to the peculiarities of its study phenomena and the intricate challenges that these entail for scientific explorations. Yet, given its history, it seems unlikely that psychology can finally pull itself out of the swamps of conceptual vagueness and theoretical inconsistencies using just its own concepts and theories, in a feat similar to that of the legendary Baron Münchhausen. Psychology can, however, capitalise on its exceptional constellation of intersections with other sciences and philosophy that arises from its unique focus on the individual. Although challenging, this constitutes a rich source for perspective-taking and stimulation of new developments that can meaningfully complement and expand its own genuine achievements as shown in the paradigm outlined now.
The Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals (TPS-Paradigm)
The Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals ( TPS-Paradigm 2 ) is targeted toward making explicit and scrutinising the most basic assumptions that different disciplines make about research on individuals to help scientists critically reflect on; discuss and refine their theories and practices; and to derive ideas for new developments (therefore philosophy-of–science ). It comprises a system of interrelated philosophical, metatheoretical and methodological frameworks that coherently build upon each other (therefore paradigm ). In these frameworks, concepts from various lines of thought, both historical and more recent, and from different disciplines (e.g., psychology, life sciences, social sciences, physical sciences, metrology, philosophy of science) that are relevant for exploring research objects in (relation to) individuals were systematically integrated, refined and complemented by novel ones, thereby creating unitary frameworks that transcend disciplinary boundaries (therefore transdisciplinary ; Uher 2015a , b , 2018c ).
The Philosophical Framework: Presuppositions About Research on Individuals
The philosophical framework specifies three sets of presuppositions that are made in the TPS-Paradigm about the nature and properties of individuals and the phenomena studied in (relations to) them as well as about the notions by which knowledge about them can be gained.
- All science is done by humans and therefore inextricably entwined with and limited by human’s perceptual and conceptual abilities. This entails risks for particular fallacies of the human mind (e.g., oversimplifying complexity, Royce 1891 ; reifying linguistic abstractions, Whitehead 1929 ). Scientists researching individuals face particular challenges because they are individuals themselves, thus inseparable from their research objects. This entails risks for anthropocentric, ethnocentric and egocentric biases influencing metatheories and methodologies (Uher 2015b ). Concepts from social, cultural and theoretical psychology, sociology, and other fields (e.g., Gergen 2001 ; Valsiner 1998 ; Weber 1949 ) were used to open up meta-perspectives on research processes and help scientists reflect on their own presuppositions, ideologies and language that may (unintentionally) influence their research.
- Individuals are complex living organisms , which can be conceived as open (dissipative) and nested systems. On each hierarchical level, they function as organised wholes from which new properties emerge not predictable from their constituents and that can feed back to the constituents from which they emerge, causing complex patterns of upward and downward causation. With increasing levels of organisation, ever more complex systems emerge that are less rule-bound, highly adaptive and historically unique. Therefore, dissecting systems into elements cannot reveal the processes governing their functioning and development as a whole; assumptions on universal determinism and reductionism must be rejected. Relevant concepts from thermodynamics, physics of life, philosophy, theoretical biology, medicine, psychology, sociology and other fields (e.g., Capra 1997 ; Hartmann 1964 ; Koffka 1935 ; Morin 2008 ; Prigogine and Stengers 1997 ; Varela et al. 1974 ; von Bertalanffy 1937 ) about dialectics, complexity and nonlinear dynamic systems were used to elaborate their relevance for research on individuals.
- The concept of complementarity is applied to highlight that, by using different methods, ostensibly incompatible information can be obtained about properties of the same object of research that are nevertheless all equally essential for an exhaustive account of it and that may therefore be regarded as complementary to one another. Applications of this concept, originating from physics (wave-particle dilemma in research on the nature of light; Bohr 1937 ; Heisenberg 1927 ), to the body-mind problem emphasise the necessity for a methodical dualism to account for observations of two categorically different realities that require different frames of reference, approaches and methods (Brody and Oppenheim 1969 ; Fahrenberg 1979 , 2013 ; Walach 2013 ). Complementarity was applied to specify the peculiarities of psychical phenomena and to derive methodological concepts (Uher, 2016a ). It was also applied to develop solutions for the nomothetic-idiographic controversy in ‘personality’ research (Uher 2015d ).
These presuppositions underlie the metatheoretical and the methodological framework.
Metatheoretical Framework
The metatheoretical framework formalises a phenomenon’s accessibility to human perception under everyday conditions using three metatheoretical properties: internality-externality, temporal extension, and spatiality conceived complementarily as physical (spatial) and “non-physical” (without spatial properties). The particular constellations of their forms in given phenomena were used to metatheoretically define and differentiate from one another various kinds of phenomena studied in (relation to) individuals: morphology, physiology, behaviour, psyche, semiotic representations (e.g., language), artificial outer-appearance modifications (e.g., clothing) and contexts (e.g., situations; Uher 2015b ).
These metatheoretical concepts allowed to integrate and further develop established concepts from various fields to elaborate the peculiarities of the phenomena of the psyche 3 and their functional connections with other phenomena (e.g., one-sided psyche-externality gap; Uher 2013 ), to trace their ontogenetic development and to explore the fundamental imperceptibility of others’ psychical phenomena and its role in the development of agency, language, instructed learning, culture, social institutions and societies in human evolution (Uher 2015a ). The metatheoretical definition of behaviour 4 enabled clear differentiations from psyche and physiology, and clarified when the content-level of language in itself constitutes behaviour, revealing how language extends humans’ behavioural possibilities far beyond all non-language behaviours (Uher 2016b ). The metatheoretical definition of ‘personality’ as individual-specificity in all kinds of phenomena studied in individuals (see above) highlighted the unique constellation of probabilistic, differential and temporal patterns that merge together in this concept, the challenges this entails and the central role of language in the formation of ‘personality’ concepts. This also enabled novel approaches for conceptual integrations of the heterogeneous landscape of paradigms and theories in ‘personality’ research (Uher 2015b , c , d , 2018b ). The semiotic representations concept emphasised the composite nature of language, comprising psychical and physical phenomena, thus both internal and external phenomena. Failure to consider the triadic relations among meaning, signifier and referent inherent to any sign system as well as their inseparability from the individuals using them was shown to underly various conceptual fallacies, especially regarding data generation and measurement (Uher 2018a , 2019 ).
Methodological Framework
The metatheoretical framework is systematically linked to the methodological framework featuring three main areas.
- General concepts of phenomenon-methodology matching . The three metatheoretical properties were used to derive implications for research methodology, leading to new concepts that help to identify fallacies and mismatches (e.g., nunc-ipsum methods for transient phenomena, intro questive versus extro questive methods to remedy methodological problems in previous concepts of introspection; Uher 2016a , 2019 ).
- Methodological concepts for comparing individuals within and across situations, groups and species were developed (Uher 2015e ). Approaches for taxonomising individual differences in various kinds of phenomena in human populations and other species were systematised on the basis of their underlying rationales. Various novel approaches, especially behavioural ones, were developed to systematically test and complement the widely-used lexical models derived from everyday language (Uher 2015b , c , d , 2018b , c ).
- Theories and practices of data generation and measurement from psychology, social sciences and metrology, the science of measurement and foundational to the physical sciences, were scrutinised and compared. These transdisciplinary analyses identified two basic methodological principles of measurement underlying metrological concepts that are also applicable to psychological and social-science research (data generation traceability, numerical traceability; Uher 2020b ). Further analyses explored the involvement of human abilities in data generation across the empirical sciences (Uher 2019 ) and raters’ interpretation and use of standardised assessment scales (Uher 2018a ).
Empirical demonstrations of these developments and analyses in various empirical studies involving humans of different sociolinguistic backgrounds as well as several nonhuman primate species (e.g., Uher 2015e , 2018a ; Uher et al. 2013a , b ; Uher and Visalberghi 2016 ) show the feasibility of this line of research. Grounded in established concepts from various disciplines, it offers many possibilities for fruitful cross-scientific collaborations waiting to be explored in order to advance the fascinating science of individuals.
Author Contributions
I declare I am the sole creator of this research.
Funding Information
This research was conducted without funding.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
I declare to have no conflicting or competing interests.
2 http://researchonindividuals.org .
3 The psyche is defined as the “entirety of the phenomena of the immediate experiential reality both conscious and non-conscious of living organisms” (Uher 2015c , p. 431, derived from Wundt 1896a ).
4 Behaviours are defined as the “external changes or activities of living organisms that are functionally mediated by other external phenomena in the present moment” (Uher 2016b , p. 490).
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Alexandrova, A., & Haybron, D. M. (2016). Is construct validation valid? Philosophy of Science, 83(5), 1098–1109. 10.1086/687941
- Bohr N. Causality and complementarity. Philosophy of Science. 1937; 4 (3):289–298. doi: 10.1086/286465. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brody N, Oppenheim P. Application of Bohr’s principle of complementarity to the mind-body problem. Journal of Philosophy. 1969; 66 (4):97–113. doi: 10.2307/2024529. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Capra F. The web of life: A new synthesis of mind and matter. New York: Anchor Books; 1997. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fahrenberg, J. (1979). The complementarity principle in psychophysiological research and somatic medicine. Zeitschrift für Klinische Psychologie und Psychotherapie, 27 (2), 151–167. [ PubMed ]
- Fahrenberg J. Zur Kategorienlehre der Psychologie: Komplementaritätsprinzip; Perspektiven und Perspektiven-Wechsel. Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers; 2013. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fahrenberg, J. (2019). Wilhelm Wundt (1832 – 1920). Introduction, quotations, reception, commentaries, attempts at reconstruction . Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers.
- Fanelli D, Glänzel W. Bibliometric evidence for a hierarchy of the sciences. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8 (6):e66938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066938. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gauch, H. G. J. (2015). Scientific method in practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Gergen, K. J. (2001). Psychological science in a postmodern context. American Psychologist, 56(10) , 803–813. 10.1037/0003-066X.56.10.803. [ PubMed ]
- Ginge, B. (1996). Identifying gender in the archaeological record: Revising our stereotypes. Etruscan Studies, 3, Article 4.
- Hartmann N. Der Aufbau der realen Welt. Grundriss der allgemeinen Kategorienlehre (3. Aufl.) Berlin: Walter de Gruyter; 1964. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heisenberg, W. (1927). Über den anschaulichen Inhalt der quantentheoretischen Kinematik und Mechanik. Zeitschrift für Physik, 43 (3–4), 172–198. 10.1007/BF01397280.
- Kant, I. (1798/2000). Anthropologie in pragmatischer Hinsicht (Reinhard Brandt, ed.). Felix Meiner.
- Kelley TL. Interpretation of educational measurements. Yonkers: World; 1927. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kelly, G. (1963). A theory of personality: The psychology of personal constructs . W.W. Norton.
- Koffka K. Principles of Gestalt psychology. New York: Harcourt, Brace, & World; 1935. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamiell, J. (2003). Beyond individual and group differences: Human individuality, scientific psychology, and William Stern’s critical personalism . Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publications. 10.4135/9781452229317.
- Lamiell, J. (2019). Psychology’s misuse of statistics and persistent dismissal of its critics . Springer International. 10.1007/978-3-030-12131-0.
- Lewin K. Principles of topological psychology. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1936. [ Google Scholar ]
- Molenaar PCM. A manifesto on psychology as idiographic science: Bringing the person back into scientific psychology, this time forever. Measurement: Interdisciplinary Research & Perspective. 2004; 2 (4):201–218. doi: 10.1207/s15366359mea0204_1. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morin E. On complexity. Cresskill: Hampton Press; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Omi Y. Tension between the theoretical thinking and the empirical method: Is it an inevitable fate for psychology? Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science. 2012; 46 (1):118–127. doi: 10.1007/s12124-011-9185-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Peirce, C. S. (1901/1935). Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce (CP 7.218—1901, On the logic of drawing history from ancient documents especially from testimonies) . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Prigogine, I., & Stengers, I. (1997). The end of certainty: Time, chaos, and the new laws of nature . Free Press.
- Robinson OC. The idiographic/nomothetic dichotomy: Tracing historical origins of contemporary confusions. History & Philosophy of Psychology. 2011; 13 :32–39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Royce, J. (1891). The religious aspect of philosophy: A critique of the bases of conduct and of faith. Boston: Houghton, Mifflin.
- Salvatore S, Valsiner J. Between the general and the unique. Theory & Psychology. 2010; 20 :817–833. doi: 10.1177/0959354310381156. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simonton DK. Psychology as a science within Comte’s hypothesized hierarchy: Empirical investigations and conceptual implications. Review of General Psychology. 2015; 19 (3):334–344. doi: 10.1037/gpr0000039. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slaney KL, Garcia DA. Constructing psychological objects: The rhetoric of constructs. Journal of Theoretical and Philosophical Psychology. 2015; 35 (4):244–259. doi: 10.1037/teo0000025. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorndike EL. Notes on child study. 2. New York: Macmillan; 1903. [ Google Scholar ]
- Toomela, A., & Valsiner, J. (2010). Methodological thinking in psychology: 60 years gone astray? Information Age Publishing.
- Uher J. Personality psychology: Lexical approaches, assessment methods, and trait concepts reveal only half of the story-Why it is time for a paradigm shift. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science. 2013; 47 (1):1–55. doi: 10.1007/s12124-013-9230-6. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher, J. (2015a). Agency enabled by the psyche: Explorations using the Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals. In C. W. Gruber, M. G. Clark, S. H. Klempe, & J. Valsiner (Eds.), Constraints of agency: Explorations of theory in everyday life. Annals of Theoretical Psychology (Vol. 12) (pp. 177–228). 10.1007/978-3-319-10130-9_13.
- Uher J. Conceiving “personality”: Psychologist’s challenges and basic fundamentals of the Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science. 2015; 49 (3):398–458. doi: 10.1007/s12124-014-9283-1. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher J. Developing “personality” taxonomies: Metatheoretical and methodological rationales underlying selection approaches, methods of data generation and reduction principles. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science. 2015; 49 (4):531–589. doi: 10.1007/s12124-014-9280-4. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher J. Interpreting “personality” taxonomies: Why previous models cannot capture individual-specific experiencing, behaviour, functioning and development. Major taxonomic tasks still lay ahead. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science. 2015; 49 (4):600–655. doi: 10.1007/s12124-014-9281-3. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher, J. (2015e). Comparing individuals within and across situations, groups and species: Metatheoretical and methodological foundations demonstrated in primate behaviour. In D. Emmans & A. Laihinen (Eds.), Comparative Neuropsychology and Brain Imaging (Vol. 2), Series Neuropsychology: An Interdisciplinary Approach (pp. 223–284). 10.13140/RG.2.1.3848.8169
- Uher, J. (2016a). Exploring the workings of the Psyche: Metatheoretical and methodological foundations. In J. Valsiner, G. Marsico, N. Chaudhary, T. Sato & V. Dazzani (Eds.), Psychology as the science of human being: The Yokohama Manifesto (pp. 299–324). 10.1007/978-3-319-21094-0_18.
- Uher J. What is behaviour? And (when) is language behaviour? A metatheoretical definition. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour. 2016; 46 (4):475–501. doi: 10.1111/jtsb.12104. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher J. Quantitative data from rating scales: An epistemological and methodological enquiry. Frontiers in Psychology. 2018; 9 :2599. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02599. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher J. Taxonomic models of individual differences: A guide to transdisciplinary approaches. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 2018; 373 (1744):20170171. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0171. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher, J. (2018c). The Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals: Foundations for the science of personality and individual differences. In V. Zeigler-Hill & T. K. Shackelford (Eds.), The SAGE Handbook of Personality and Individual Differences: Volume I: The science of personality and individual differences (pp. 84–109). 10.4135/9781526451163.n4.
- Uher J. Data generation methods across the empirical sciences: differences in the study phenomena’s accessibility and the processes of data encoding. Quality & Quantity. International Journal of Methodology. 2019; 53 (1):221–246. doi: 10.1007/s11135-018-0744-3. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher J. Human uniqueness explored from the uniquely human perspective: Epistemological and methodological challenges. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour. 2020; 50 :20–24. doi: 10.1111/jtsb.12232. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher, J. (2020b). Measurement in metrology, psychology and social sciences: data generation traceability and numerical traceability as basic methodological principles applicable across sciences. Quality & Quantity. International Journal of Methodology, 54 , 975-1004. 10.1007/s11135-020-00970-2.
- Uher J, Addessi E, Visalberghi E. Contextualised behavioural measurements of personality differences obtained in behavioural tests and social observations in adult capuchin monkeys (Cebus apella) Journal of Research in Personality. 2013; 47 (4):427–444. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2013.01.013. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher J, Visalberghi E. Observations versus assessments of personality: A five-method multi-species study reveals numerous biases in ratings and methodological limitations of standardised assessments. Journal of Research in Personality. 2016; 61 :61–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2016.02.003. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Uher J, Werner CS, Gosselt K. From observations of individual behaviour to social representations of personality: Developmental pathways, attribution biases, and limitations of questionnaire methods. Journal of Research in Personality. 2013; 47 (5):647–667. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2013.03.006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Valsiner, J. (1998). The guided mind : A sociogenetic approach to personality. Harvard University Press.
- Valsiner J. A guided science: History of psychology in the mirror of its making. New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Varela FG, Maturana HR, Uribe R. Autopoiesis: The organization of living systems, its characterization and a model. BioSystems. 1974; 5 (4):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90031-8. [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- von Bertalanffy L. Das Gefüge des Lebens. Leipzig: Teubner; 1937. [ Google Scholar ]
- Walach, H. (2013). Psychologie: Wissenschaftstheorie, Philosophische Grundlagen und Geschichte (3. Aufl.) . Stuttgart: Kohlhammer.
- Weber, M. (1949). On the methodology of the social sciences (E. Shils & H. Finch, Eds.). New York: Free Press.
- Whitehead AN. Process and reality. New York: Harper; 1929. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wundt, W. (1896a). Grundriss der Psychologie . Stuttgart: Körner. Retrieved from https://archive.org/ .
- Wundt W. Über die Definition der Psychologie. Philosophische Studien. 1896; 12 :9–66. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zagaria, A., Andò, A., & Zennaro, A. (2020). Psychology: A giant with feet of clay. Integrative Psychological & Behavioral Science. 10.1007/s12124-020-09524-5. [ PubMed ]

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1.1 Psychology as a Science
Learning objectives.
- Explain why using our intuition about everyday behavior is insufficient for a complete understanding of the causes of behavior.
- Describe the difference between values and facts and explain how the scientific method is used to differentiate between the two.
Despite the differences in their interests, areas of study, and approaches, all psychologists have one thing in common: They rely on scientific methods. Research psychologists use scientific methods to create new knowledge about the causes of behavior, whereas psychologist-practitioners , such as clinical, counseling, industrial-organizational, and school psychologists, use existing research to enhance the everyday life of others. The science of psychology is important for both researchers and practitioners.
In a sense all humans are scientists. We all have an interest in asking and answering questions about our world. We want to know why things happen, when and if they are likely to happen again, and how to reproduce or change them. Such knowledge enables us to predict our own behavior and that of others. We may even collect data (i.e., any information collected through formal observation or measurement ) to aid us in this undertaking. It has been argued that people are “everyday scientists” who conduct research projects to answer questions about behavior (Nisbett & Ross, 1980). When we perform poorly on an important test, we try to understand what caused our failure to remember or understand the material and what might help us do better the next time. When our good friends Monisha and Charlie break up, despite the fact that they appeared to have a relationship made in heaven, we try to determine what happened. When we contemplate the rise of terrorist acts around the world, we try to investigate the causes of this problem by looking at the terrorists themselves, the situation around them, and others’ responses to them.
The Problem of Intuition
The results of these “everyday” research projects can teach us many principles of human behavior. We learn through experience that if we give someone bad news, he or she may blame us even though the news was not our fault. We learn that people may become depressed after they fail at an important task. We see that aggressive behavior occurs frequently in our society, and we develop theories to explain why this is so. These insights are part of everyday social life. In fact, much research in psychology involves the scientific study of everyday behavior (Heider, 1958; Kelley, 1967).
The problem, however, with the way people collect and interpret data in their everyday lives is that they are not always particularly thorough. Often, when one explanation for an event seems “right,” we adopt that explanation as the truth even when other explanations are possible and potentially more accurate. For example, eyewitnesses to violent crimes are often extremely confident in their identifications of the perpetrators of these crimes. But research finds that eyewitnesses are no less confident in their identifications when they are incorrect than when they are correct (Cutler & Wells, 2009; Wells & Hasel, 2008). People may also become convinced of the existence of extrasensory perception (ESP), or the predictive value of astrology, when there is no evidence for either (Gilovich, 1993). Furthermore, psychologists have also found that there are a variety of cognitive and motivational biases that frequently influence our perceptions and lead us to draw erroneous conclusions (Fiske & Taylor, 2007; Hsee & Hastie, 2006). In summary, accepting explanations for events without testing them thoroughly may lead us to think that we know the causes of things when we really do not.
Research Focus: Unconscious Preferences for the Letters of Our Own Name
A study reported in the Journal of Consumer Research (Brendl, Chattopadhyay, Pelham, & Carvallo, 2005) demonstrates the extent to which people can be unaware of the causes of their own behavior. The research demonstrated that, at least under certain conditions (and although they do not know it), people frequently prefer brand names that contain the letters of their own name to brand names that do not contain the letters of their own name.
The research participants were recruited in pairs and were told that the research was a taste test of different types of tea. For each pair of participants, the experimenter created two teas and named them by adding the word stem “oki” to the first three letters of each participant’s first name. For example, for Jonathan and Elisabeth, the names of the teas would have been Jonoki and Elioki.
The participants were then shown 20 packets of tea that were supposedly being tested. Eighteen packets were labeled with made-up Japanese names (e.g., “Mataku” or “Somuta”), and two were labeled with the brand names constructed from the participants’ names. The experimenter explained that each participant would taste only two teas and would be allowed to choose one packet of these two to take home.
One of the two participants was asked to draw slips of paper to select the two brands that would be tasted at this session. However, the drawing was rigged so that the two brands containing the participants’ name stems were always chosen for tasting. Then, while the teas were being brewed, the participants completed a task designed to heighten their needs for self-esteem, and that was expected to increase their desire to choose a brand that had the letters of their own name. Specifically, the participants all wrote about an aspect of themselves that they would like to change.
After the teas were ready, the participants tasted them and then chose to take a packet of one of the teas home with them. After they made their choice, the participants were asked why they chose the tea they had chosen, and then the true purpose of the study was explained to them.
The results of this study found that participants chose the tea that included the first three letters of their own name significantly more frequently (64% of the time) than they chose the tea that included the first three letters of their partner’s name (only 36% of the time). Furthermore, the decisions were made unconsciously; the participants did not know why they chose the tea they chose. When they were asked, more than 90% of the participants thought that they had chosen on the basis of taste, whereas only 5% of them mentioned the real cause—that the brand name contained the letters of their name.
Once we learn about the outcome of a given event (e.g., when we read about the results of a research project), we frequently believe that we would have been able to predict the outcome ahead of time. For instance, if half of a class of students is told that research concerning attraction between people has demonstrated that “opposites attract” and the other half is told that research has demonstrated that “birds of a feather flock together,” most of the students will report believing that the outcome that they just read about is true, and that they would have predicted the outcome before they had read about it. Of course, both of these contradictory outcomes cannot be true. (In fact, psychological research finds that “birds of a feather flock together” is generally the case.) The problem is that just reading a description of research findings leads us to think of the many cases we know that support the findings, and thus makes them seem believable. The tendency to think that we could have predicted something that has already occurred that we probably would not have been able to predict is called the hindsight bias , or the tendency to think that we could have predicted something that has already occurred that we probably would not have been able to predict.
Why Psychologists Rely on Empirical Methods
All scientists, whether they are physicists, chemists, biologists, sociologists, or psychologists, use empirical methods to study the topics that interest them. Empirical methods include the processes of collecting and organizing data and drawing conclusions about those data. The empirical methods used by scientists have developed over many years and provide a basis for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data within a common framework in which information can be shared. We can label the scientific method as the set of assumptions, rules, and procedures that scientists use to conduct empirical research .
Psychologists use a variety of techniques to measure and understand human behavior.
Tim Sheerman-Chase – “Volunteer Duty” Psychology Testing – CC BY 2.0 CAFNR – CC BY-NC 2.0
Although scientific research is an important method of studying human behavior, not all questions can be answered using scientific approaches. Statements that cannot be objectively measured or objectively determined to be true or false are not within the domain of scientific inquiry. Scientists therefore draw a distinction between values and facts. Values are personal statements such as “Abortion should not be permitted in this country,” “I will go to heaven when I die,” or “It is important to study psychology.” Facts are objective statements determined to be accurate through empirical study. Examples are “There were more than 21,000 homicides in the United States in 2009,” or “Research demonstrates that individuals who are exposed to highly stressful situations over long periods of time develop more health problems than those who are not.”
Because values cannot be considered to be either true or false, science cannot prove or disprove them. Nevertheless, as shown in Table 1.1 “Examples of Values and Facts in Scientific Research” , research can sometimes provide facts that can help people develop their values. For instance, science may be able to objectively measure the impact of unwanted children on a society or the psychological trauma suffered by women who have abortions. The effect of capital punishment on the crime rate in the United States may also be determinable. This factual information can and should be made available to help people formulate their values about abortion and capital punishment, as well as to enable governments to articulate appropriate policies. Values also frequently come into play in determining what research is appropriate or important to conduct. For instance, the U.S. government has recently supported and provided funding for research on HIV, AIDS, and terrorism, while denying funding for research using human stem cells.
Although scientists use research to help establish facts, the distinction between values and facts is not always clear-cut. Sometimes statements that scientists consider to be factual later, on the basis of further research, turn out to be partially or even entirely incorrect. Although scientific procedures do not necessarily guarantee that the answers to questions will be objective and unbiased, science is still the best method for drawing objective conclusions about the world around us. When old facts are discarded, they are replaced with new facts based on newer and more correct data. Although science is not perfect, the requirements of empiricism and objectivity result in a much greater chance of producing an accurate understanding of human behavior than is available through other approaches.
Levels of Explanation in Psychology
The study of psychology spans many different topics at many different levels of explanation which are the perspectives that are used to understand behavior . Lower levels of explanation are more closely tied to biological influences, such as genes, neurons, neurotransmitters, and hormones, whereas the middle levels of explanation refer to the abilities and characteristics of individual people, and the highest levels of explanation relate to social groups, organizations, and cultures (Cacioppo, Berntson, Sheridan, & McClintock, 2000).
The same topic can be studied within psychology at different levels of explanation, as shown in Figure 1.3 “Levels of Explanation” . For instance, the psychological disorder known as depression affects millions of people worldwide and is known to be caused by biological, social, and cultural factors. Studying and helping alleviate depression can be accomplished at low levels of explanation by investigating how chemicals in the brain influence the experience of depression. This approach has allowed psychologists to develop and prescribe drugs, such as Prozac, which may decrease depression in many individuals (Williams, Simpson, Simpson, & Nahas, 2009). At the middle levels of explanation, psychological therapy is directed at helping individuals cope with negative life experiences that may cause depression. And at the highest level, psychologists study differences in the prevalence of depression between men and women and across cultures. The occurrence of psychological disorders, including depression, is substantially higher for women than for men, and it is also higher in Western cultures, such as in the United States, Canada, and Europe, than in Eastern cultures, such as in India, China, and Japan (Chen, Wang, Poland, & Lin, 2009; Seedat et al., 2009). These sex and cultural differences provide insight into the factors that cause depression. The study of depression in psychology helps remind us that no one level of explanation can explain everything. All levels of explanation, from biological to personal to cultural, are essential for a better understanding of human behavior.
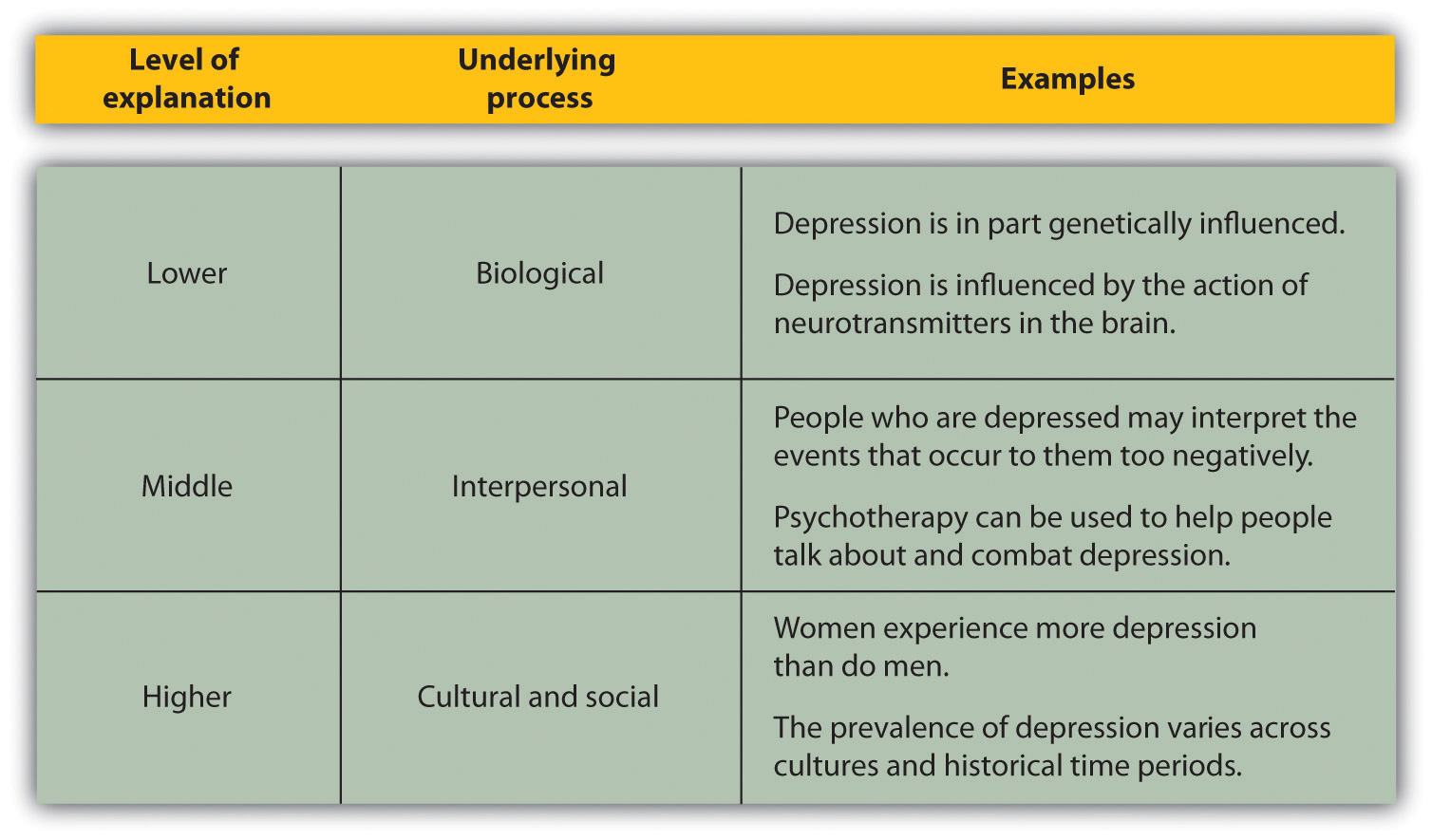
Figure 1.3 Levels of Explanation
The Challenges of Studying Psychology
Understanding and attempting to alleviate the costs of psychological disorders such as depression is not easy, because psychological experiences are extremely complex. The questions psychologists pose are as difficult as those posed by doctors, biologists, chemists, physicists, and other scientists, if not more so (Wilson, 1998).
A major goal of psychology is to predict behavior by understanding its causes. Making predictions is difficult in part because people vary and respond differently in different situations. Individual differences are the variations among people on physical or psychological dimensions. For instance, although many people experience at least some symptoms of depression at some times in their lives, the experience varies dramatically among people. Some people experience major negative events, such as severe physical injuries or the loss of significant others, without experiencing much depression, whereas other people experience severe depression for no apparent reason. Other important individual differences that we will discuss in the chapters to come include differences in extraversion, intelligence, self-esteem, anxiety, aggression, and conformity.
Because of the many individual difference variables that influence behavior, we cannot always predict who will become aggressive or who will perform best in graduate school or on the job. The predictions made by psychologists (and most other scientists) are only probabilistic. We can say, for instance, that people who score higher on an intelligence test will, on average, do better than people who score lower on the same test, but we cannot make very accurate predictions about exactly how any one person will perform.
Another reason that it is difficult to predict behavior is that almost all behavior is multiply determined , or produced by many factors. And these factors occur at different levels of explanation. We have seen, for instance, that depression is caused by lower-level genetic factors, by medium-level personal factors, and by higher-level social and cultural factors. You should always be skeptical about people who attempt to explain important human behaviors, such as violence, child abuse, poverty, anxiety, or depression, in terms of a single cause.
Furthermore, these multiple causes are not independent of one another; they are associated such that when one cause is present other causes tend to be present as well. This overlap makes it difficult to pinpoint which cause or causes are operating. For instance, some people may be depressed because of biological imbalances in neurotransmitters in their brain. The resulting depression may lead them to act more negatively toward other people around them, which then leads those other people to respond more negatively to them, which then increases their depression. As a result, the biological determinants of depression become intertwined with the social responses of other people, making it difficult to disentangle the effects of each cause.
Another difficulty in studying psychology is that much human behavior is caused by factors that are outside our conscious awareness, making it impossible for us, as individuals, to really understand them. The role of unconscious processes was emphasized in the theorizing of the Austrian neurologist Sigmund Freud (1856–1939), who argued that many psychological disorders were caused by memories that we have repressed and thus remain outside our consciousness. Unconscious processes will be an important part of our study of psychology, and we will see that current research has supported many of Freud’s ideas about the importance of the unconscious in guiding behavior.
Key Takeaways
- Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior.
- Though it is easy to think that everyday situations have commonsense answers, scientific studies have found that people are not always as good at predicting outcomes as they think they are.
- The hindsight bias leads us to think that we could have predicted events that we actually could not have predicted.
- People are frequently unaware of the causes of their own behaviors.
- Psychologists use the scientific method to collect, analyze, and interpret evidence.
- Employing the scientific method allows the scientist to collect empirical data objectively, which adds to the accumulation of scientific knowledge.
- Psychological phenomena are complex, and making predictions about them is difficult because of individual differences and because they are multiply determined at different levels of explanation.
Exercises and Critical Thinking
- Can you think of a time when you used your intuition to analyze an outcome, only to be surprised later to find that your explanation was completely incorrect? Did this surprise help you understand how intuition may sometimes lead us astray?
- Describe the scientific method in a way that someone who knows nothing about science could understand it.
- Consider a behavior that you find to be important and think about its potential causes at different levels of explanation. How do you think psychologists would study this behavior?
Brendl, C. M., Chattopadhyay, A., Pelham, B. W., & Carvallo, M. (2005). Name letter branding: Valence transfers when product specific needs are active. Journal of Consumer Research, 32 (3), 405–415.
Cacioppo, J. T., Berntson, G. G., Sheridan, J. F., & McClintock, M. K. (2000). Multilevel integrative analyses of human behavior: Social neuroscience and the complementing nature of social and biological approaches. Psychological Bulletin, 126 (6), 829–843.
Chen, P.-Y., Wang, S.-C., Poland, R. E., & Lin, K.-M. (2009). Biological variations in depression and anxiety between East and West. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 15 (3), 283–294.
Cutler, B. L., & Wells, G. L. (2009). Expert testimony regarding eyewitness identification. In J. L. Skeem, S. O. Lilienfeld, & K. S. Douglas (Eds.), Psychological science in the courtroom: Consensus and controversy (pp. 100–123). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Fiske, S. T., & Taylor, S. E. (2007). Social cognition: From brains to culture . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Gilovich, T. (1993). How we know what isn’t so: The fallibility of human reason in everyday life . New York, NY: Free Press.
Heider, F. (1958). The psychology of interpersonal relations . Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Hsee, C. K., & Hastie, R. (2006). Decision and experience: Why don’t we choose what makes us happy? Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10 (1), 31–37.
Kelley, H. H. (1967). Attribution theory in social psychology. In D. Levine (Ed.), Nebraska symposium on motivation (Vol. 15, pp. 192–240). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Nisbett, R. E., & Ross, L. (1980). Human inference: Strategies and shortcomings of social judgment . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Seedat, S., Scott, K. M., Angermeyer, M. C., Berglund, P., Bromet, E. J., Brugha, T. S.,…Kessler, R. C. (2009). Cross-national associations between gender and mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66 (7), 785–795.
Wells, G. L., & Hasel, L. E. (2008). Eyewitness identification: Issues in common knowledge and generalization. In E. Borgida & S. T. Fiske (Eds.), Beyond common sense: Psychological science in the courtroom (pp. 159–176). Malden, NJ: Blackwell.
Williams, N., Simpson, A. N., Simpson, K., & Nahas, Z. (2009). Relapse rates with long-term antidepressant drug therapy: A meta-analysis. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 24 (5), 401–408.
Wilson, E. O. (1998). Consilience: The unity of knowledge . New York, NY: Vintage Books
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Is Psychology a True Science? Essay
There is reasonable doubt as to the classification of psychology as a science in the minds of the lay person. This is mostly as a result of the overly simplified and logical manner in which psychology and indeed psychologists are represented by popular media.
As such, psychology is seen to be more of a subjective human-oriented art as opposed to an objective and exact science. This paper shall set out to make a case for psychology as a science. The arguments made by people who do not accept the status of psychology as a science shall also be presented and their due merits evaluated.
Science is defined as knowledge which emanates from factual evidence. This being the case, there are certain features which are fundamental to all sciences and they make up the scientific methods. They include the collecting of quantitative data under controlled conditions, objectivity as opposed to subjectivity and an establishment of general laws and theories after experimentation. An interesting consideration is that this laws apply universally and as such, there is the element of repeatability.
Proponents of psychology as a science contend that psychology uses the stated scientific methods to study both human and non-human behaviors in various settings. Studies such as the genetic theory of IQ involve carefully controlled scientific experiments which are not only objective but are also high reliable and verifiable.
As with other scientific experiment findings, psychology results are produced and made open to the public domain for the interest of furthering science. The findings are also presented over for peer review to ensure their critical analysis. This is in line with the requirements set forth for scientific findings.
There exist theories in the psychology field which have been proven time and time again. This is a concept that is common to science whereby prediction of future events can be made by derivations obtained from experimentation.
An example is the behaviourist theory of operant conditioning which proposes that behavior is learned through reinforcement. Since this theory is objective and quantifiable one can from this theory make predictions about learning. The concept of generalization which is core to science is therefore exhibited in psychology as well.
On the other hand the seeming lack of objectivity in most psychological endevour is advanced as the most common argument advanced by opponents of psychology as a science. This claim is affirmed by the labeling theory of schizophrenia which proposes that schizophrenia is not caused so much by biological factors but rather, diagnosis of the disease is a result of subjective factors. This is because the social construct and reality will play a big role in the diagnosis process therefore presenting psychology as a hugely subjective art.
Science requires that there by measurable concepts meaning that the phenomena should not only be perceivable through our senses but also quantifiable as data. Psychology fails in this count since unobservable behaviour such as feelings play a pivotal role in psychology. This is contrary to the methods of science which dictate that all data must be quantifiable.
This paper set out to reinforce the notion that psychology is a science. In light of the arguments presented in this paper, it can be stated that to some extent, those who propose that psychology is not a science are right in that psychology can never be an exact science given the dynamic nature of the human subject which psychology sets out to examine.
However, most of the other attributes of psychology reinforce the claim that psychology is indeed a fully-fledged science deserving the same merits as physics or any of the other “accepted” sciences. This being the case, we can authoritatively state that psychology is indeed a true science.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, February 7). Is Psychology a True Science? https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-psychology-a-true-science/
"Is Psychology a True Science?" IvyPanda , 7 Feb. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/is-psychology-a-true-science/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Is Psychology a True Science'. 7 February.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Is Psychology a True Science?" February 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-psychology-a-true-science/.
1. IvyPanda . "Is Psychology a True Science?" February 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-psychology-a-true-science/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Is Psychology a True Science?" February 7, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/is-psychology-a-true-science/.
- Experimentation on Animals
- Objectivity of Science
- Psychological Classification of Schizophrenia
- How Managers Can Positively Reinforce Desirable Behavior?
- Reinforce Training on a Horse
- Utilitarianism for Animals: Testing and Experimentation
- Ethics and Self-Experimentation Argument
- Mental Health: Analysis of Schizophrenia
- Schizophrenia in Young Men and Women
- Ethics Problems in Animal Experimentation
- Clinical Psychology, Its Methods and Approaches
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Developed in Repeated War Zones Deployment
- Towards Understanding Stress-Related Issues Affecting First Year Students on Their Transition Into University Culture
- Comparison of Normal and Abnormal Psychology
- Women in Psychology: Assessing the Contributions of Margaret Floy Washburn

Academic Degrees , Health Science News
How Is Psychology a Science: What You Should Know
Updated: July 11, 2022
Published: July 7, 2021

There’s been a long debate about the question: “Is psychology a science?” By defining what psychology is and looking at the ways in which academics have defined science, we can come to see how psychology is classified as a science.
To get to this endpoint, let’s explore the details about psychology and science.

What is Psychology?
The term psychology can be broken down into its root words that are Greek. Psyche means “mind” or “soul.” Logos means “the study of.” Psychology is the study of mental processes and human behavior.
Psychology consists of the following scientific steps:
- Collecting facts
- Developing theories and hypotheses to explain the facts
- Testing the theories
What Makes Psychology a Science?
Regardless of how you view psychology, it’s either going to be placed into the social sciences or science category. To support psychology as a science, we turn to the idea of empirical evidence. Empirical evidence is able to be supported and verified by way of observation and experience, as opposed to simply relying on logic or theory.
Through empirical evidence, psychologists can understand human behavior because of observation. Since the mind cannot be directly observed, it is through actions that psychologists are able to better grasp what may be happening in the mind.
Going deeper, psychology leverages the following:
- Reasoning: Psychologists rely on scientific reasoning to interpret and design psychological research and interpret phenomena.
- Discipline: At the core of psychology sits the scientific method. Psychologists conduct studies and contribute to research based on verifiable evidence.
- Research: Like traditional science, psychologists make use of quantitative and qualitative research methods that are necessary for performing analysis and drawing conclusions.
- Application: To practice psychology in a practical setting, students must complete further education beyond a bachelor’s degree. In most instances, a psychologist will need to obtain a PhD. This advanced education will consist of research skills and robust knowledge and application of the scientific method.
Key Characteristics of a Science
To define any field as a science, it generally will cover these key elements:
Objectivity
When conducting any study, researchers must remain unbiased and objective. They cannot let their own emotions and feelings enter the process. Additionally, while it’s not always possible to fully remove bias, it is necessary to minimize it as much as possible. That’s a main tenet of science.
Empirical evidence
Evidence is collected through experiments and observations. Again, this negates the entry of belief. While data is being collected, the information is diligently recorded so that other researchers can review the validity and the process.
In order to deduce cause and effect (independent variables and dependent variables), variables must be controlled.
Hypothesis testing
To start off the process, an observation is made. Then, scientists, academics, and researchers create their hypothesis, which is a prediction that’s rooted in theory. These hypotheses should be clearly stated and then tested through unbiased experiments.
Predictability
Based on the findings of research, scientists should technically be able to forecast and predict the future.
Replication
When scientists develop experiments, they should be able to be replicated to test if the outcomes are the same given different variables. When the same results occur based on the same conditions, then that provides credibility and accuracy to the findings, which can give way to the creation of a scientific theory or discovery.
Social Science: A Definition
It’s clear to see how psychology maintains the elements of science. However, the argument exists because it also can fall into the category of a social science based on the definition.
A social science is any academic study or science that looks at human behavior in a social and cultural aspect. Such studies include: sociology, anthropology, economics, political science, and for some, psychology.
Psychology as a Social Science
When it comes to studying psychology in college, most institutions will classify psychology under social science. As a student, you’ll study social behaviors, human development, and emotions, which all include social science methods. However, depending on the speciality of psychology you can pursue, some align more closely with hard science and others with social science.
For example, neuropsychology and biological psychology are closer to physical sciences. Social psychology, as you probably guessed, is closely aligned to the social sciences.

What Do Psychologists Do?
The main goal of a psychologist is to understand humans’ emotions, thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. In both the short term and long term, clinical psychologists work with patients to help them deal with and overcome their problems.
Psychologists have the opportunity to work in a variety of settings and study various sub disciplines. For example, a psychologist can work as a clinical psychologist, child psychologist, career counselor, professor, or neuropsychologist, to name a few.
Psychologists can be found working in private practice, rehabilitation facilities, schools, hospitals, clinics, corporations, sports teams, and other settings.
How to Become a Psychologist
To practice as a psychologist, you must complete the licensure process. Before becoming licensed, you’ll need to earn a degree.
Here are the basics steps you’ll need to follow to work in this rewarding field:
- Undergraduate Studies: Begin by earning your bachelor’s degree. You can do so in psychology or a related field like education, communication, or sociology, for example.
- Graduate Studies: To specialize, you’ll continue your formal education with a master’s, doctor of psychology (PsyD), PhD in Psychology, or education specialist (EdS) in Psychology.
- Intern: Based on your level of study, you’ll have to fulfill a specified number of hours working under a licensed psychologist and learning from them while completing projects.
- Licensure: To legally call yourself a psychologist and work as a psychologist, you’ll have to obtain licensure . The steps to do so will vary by state and location. However, the general idea is that you will have to pass national exams and work under supervision of a licensed psychologist. Some states also may require an oral examination or jurisprudence examination to understand the legal issues concerning psychology.
The Bottom Line
No matter how you look at it, the answer is yes to the question, “Is psychology a science?” While some people will argue that psychology is a social science, others will view it as a hard science.
Regardless of how you categorize the area of study and career, there are a variety of subspecialties and career paths to choose within the realm.
Related Articles

Is Psychology Really a Science?
Some people say no. are they right.
Posted October 6, 2017
I remember the first time I heard the words "physics envy." I was attending a lecture by a relatively famous psychologist who was up at the chalkboard explaining a complex theory. He had drawn an intricate network of boxes and arrows all looping back on one another. As he gesticulated toward each part of the diagram, mind-numbing jargon filled the air. After about 15 minutes, he must have been afraid that he was losing his audience, because he stepped back from the blackboard, scratched his chin, and made a joke.
"Sometimes I think psychologists use all this psychobabble because we have physics envy," he said, grinning. Everyone chuckled.
Though he clearly achieved his goal of lightening the mood, I found myself plagued by his curious turn of phrase. I wondered if psychologists might indeed be jealous of their physicist colleagues, whom nobody doubted were real scientists. To make themselves feel better, perhaps psychologists do compensate by using confusing technical terms. His apparently harmless joke seemed to imply that psychology was not a real science.
It's a question as old as the field itself: Is psychology a science or is it better classified as one of the humanities, like philosophy , theology, or literature? I have to admit it’s a bit of a sore spot. As a psychologist, I’ve been poked at more than once by would-be debaters hoping to start an argument. “You don’t really think psychology is a science, do you?” they ask, incredulously.
So let's take a moment to consider a couple of perspectives on what makes something scientific.
One view is that science involves measuring things with great precision. Biologists place cells under powerful microscopes, measuring them to the minutest detail. Astrophysicists measure the rate of expansion of the universe to astounding decimals. And chemists measure precisely what happens to molecules when exposed to heat, cold, or any number of other treatments. Judged from this perspective, psychology clearly falls short. To measure depression , the best we can often do is to use psychological tests that ask people perhaps a few dozens questions about their mood. But this method isn’t foolproof—people can lie or even be self- deceived . As an alternative, we might ask someone to submit to an fMRI or similar brain scan. But this is hardly a direct way of measuring depression. In order to know how the splotches of brain activity that appear on the screen translate into lived experience, we still need to ask the person. Like sociology, economics, and other social sciences, psychology necessarily relies on indirect measurements. But all of these fields are nonetheless known as sciences, even if we do put the word "social" in front of them. So accuracy of measurement may not be the best criterion by which to judge what is and what is not a science.
Perhaps the clearest definition of a “science” is any endeavor that uses the scientific method . Like all scientists, psychology researchers form hypotheses, devise experiments to gather data, and carefully analyze the results. Psychology journals are filled with such studies. Judged from this perspective, psychology is clearly a science. Though not every study is equally well done , of course, psychology investigators are increasingly held to higher and higher standards of evidence.
So why do people persist in questioning the field’s scientific chops?
The problem is that much of what is written about psychology in the popular press isn’t based on the science. Everyone seems to have an opinion about the way the human mind works, leading to a cacophony of conflicting ideas. Self-help books, podcasts, and web pages often propound notions that either have never been scientifically tested or have been tested without success. Though the academic field represented by most professional journals is overtly scientific, the ideas that make their way into public consciousness often are only tenuously related to that field. We psychologists deserve some of the blame for this. Sometimes out of laziness or honest mistakes, at least some psychologists prefer to communicate from the standpoint of personal experience, rather than to base what they teach on scientific findings.
Good science involves an attitude of skepticism, particularly about what we think we know from personal experience. Consider the commonly held belief that opposites attract, a so-called “fact” that I’ve seen many psychologists endorse. Though it may seem intuitively obvious that people with widely differing personalities and values would make good romantic partners, research generally shows just the opposite . In fact, the longest lasting relationships tend to be characterized by deep similarities. Every year, I mention this tidbit to students in one of my university courses. Invariably, whenever I share a counterintuitive finding like this one, someone raise his or her hand and says, “My partner and I are opposites, and we get along great. That proves the research is wrong!” But one person’s experience doesn’t prove or disprove anything. That’s because psychological science isn’t based on a single individual’s experience, but rather concerns what is true the majority of the time for the majority of people. There will always be exceptions to every rule. Though these exceptions are important to understand because every person matters, science is most concerned with figuring out what the general rules are first. So we should be very careful not to regard scientific findings as untrue just because they don't fit with what we think we already know from anecdotal experience.
So, is psychology a science? Yes, particularly if we base our judgment on the research that appears in scientific journals. But most people in the general public don’t read scientific journals. Instead, that research is often filtered through teachers in their classrooms, therapists in their clinics, self-help writers at their keyboards, podcasters at their microphones, and even what we tell one another. What happens to scientific findings after they leave the lab can be at least as important in influencing the public as the findings themselves.
We all share in that responsibility.
David B. Feldman is a Professor of Counseling Psychology at Santa Clara University. Listen to his podcast, “ Psychology in 10 Minutes ,” on any podcast app, through SoundCloud , iTunes , or by subscribing to the show’s RSS feed .

David B. Feldman, Ph.D. , is a professor in the department of counseling psychology at Santa Clara University.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Home — Essay Samples — Psychology — Social Psychology — Why Psychology Is Considered A Science
A Discussion of Whether Psychology is a Science
- Categories: Social Psychology
About this sample

Words: 496 |
Published: Dec 16, 2021
Words: 496 | Page: 1 | 3 min read
Works Cited
- Bunge, M. (2009). Is psychology a unified science? Cognitive Systems Research, 10(2), 162-176.
- Craver, C. F. (2007). Explaining the brain: Mechanisms and the mosaic unity of neuroscience. Oxford University Press.
- Fuchs, T., & Mahr, A. (2019). Psychology as science: The theoretical framework of psychology as a natural science. In The Routledge Handbook of Philosophy of Empathy (pp. 38-53). Routledge.
- Gergen, K. J. (2015). The science of psychology as methodologically embodied skepticism. In The Oxford Handbook of the History of Psychology: Global Perspectives (pp. 225-242). Oxford University Press.
- Kuhn, T. S. (2012). The structure of scientific revolutions. University of Chicago Press.
- Lambert, A. J. (2013). Toward a positive psychology of religion: Belief science in the postmodern era. Journal of Humanistic Psychology , 53(2), 195-215.
- Popper, K. R. (2002). The logic of scientific discovery. Routledge.
- Shadish, W. R., Cook, T. D., & Campbell, D. T. (2002). Experimental and quasi-experimental designs for generalized causal inference. Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
- Thagard, P. (2012). The cognitive science of science: Explanation, discovery, and conceptual change. MIT Press.
- Wundt, W. (1897). Outlines of Psychology. Wilhelm Engelmann.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Science Psychology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 662 words
2 pages / 853 words
2 pages / 938 words
1 pages / 671 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Social Psychology
Procrastination is a common issue amongst college students, which can greatly impact their academic performance and overall success. This informative speech will explore the causes and consequences of procrastination in college, [...]
The Role Of Humor In Society Humor is an essential aspect of human life, and its role in society is significant. From ancient times to the present day, humor has been used as a powerful tool for communication, social [...]
Racism is a deeply ingrained issue in society that continues to plague communities across the globe. While overt acts of racism are widely condemned, there exists a more insidious form of racism that often goes unnoticed: the [...]
Social pressure is a powerful force that can shape individuals' thoughts, behaviors, and decisions. It refers to the influence that society, peers, and other groups have on an individual's actions and beliefs. This pressure can [...]
What would come to students mind when they hear the team work at class or at university? Students may think that it is a bit of annoying or, for new comers it may seem as a disaster. Team work usually teaches students many [...]
Contentions in the psychological literature abound when it comes to intrapsychic phenomena, and self-deception is no exception. Self-deception is understandably difficult to measure, since it is difficult to discern whether a [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
The Study Blog

Term Paper Writing Help

If you aren't sure whether you are good at expressing yourself through writing, then if you find it difficult to do so (e.g., when trying to write an english essay), we can help you overcome those obstacles by assisting you in improving your communication through writing. We help students compose essays or other types of papers for their courses. Now is the time to come visit us!
How to Overcome the Complexity of a Nursing Essay
There aren't many alternatives for professional translations. Before writing a good summary of something, you need to know your subject well enough to be able to write an accurate one. A research paper requires mastery of research language, a deep understanding of their subjects to be able to write about them clearly, and a careful consideration of possible problems before proposing solutions. Students often have trouble understanding medical terminology when they first encounter it, because they have never heard of these words before. When writing a cohesive psychology essay, students must be familiar with some psychological concepts. We have a wealth of experience under our belt, so we know where they need help. Although you may be able to find better deals elsewhere, there is no way to tell if these sites offer superior customer service and top-quality results. Read customer reviews before making any online purchases. If you don't think there's a market for them, it's perhaps best to skip them.
Professional Help from Copywriters
If you would like us to write anything from an essay in history to a term paper for you, we’d be happy to oblige. When writing something, there's a precise formula for choosing the best word. You can rest assured that you'll receive an expertly written paper from those who know exactly what they're doing. No need to write anything down today; there are no reasons why you shouldn't let others edit your document for you. Don't waste your time trying to convince them to do it for you, instead, invest it in something more productive! Order term papers online and go there! Founded in a simple belief that we are capable of delivering top-quality content to you, we offer a range of guarantees. Test it out yourself! The results must be presented after all the research has been completed.
Cheap Business Essay Writing Services
Before being accepted into our company, we underwent extensive background checks. Check their credentials to confirm that they have been writing professionally for some time. If they are members of professional associations, check, for instance.

Fun Tips to Spend Orthodox Easter Away from Home
In "Student Life"
Welcome to the New Bloggers
In "Degree Essentials"
Mastering Warwick as a Postgraduate
In "Looking After You"
Comments are closed.
Copyright, 2023

- Environment
- Information Science
- Social Issues
- Argumentative
- Cause and Effect
- Classification
- Compare and Contrast
- Descriptive
- Exemplification
- Informative
- Controversial
- Exploratory
- What Is an Essay
- Length of an Essay
- Generate Ideas
- Types of Essays
- Structuring an Essay
- Outline For Essay
- Essay Introduction
- Thesis Statement
- Body of an Essay
- Writing a Conclusion
- Essay Writing Tips
- Drafting an Essay
- Revision Process
- Fix a Broken Essay
- Format of an Essay
- Essay Examples
- Essay Checklist
- Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Research Paper
- Write My Research Paper
- Write My Essay
- Custom Essay Writing Service
- Admission Essay Writing Service
- Pay for Essay
- Academic Ghostwriting
- Write My Book Report
- Case Study Writing Service
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Do My Assignment
- Buy College Papers
- Capstone Project Writing Service
- Buy Research Paper
- Custom Essays for Sale
Can’t find a perfect paper?
- Free Essay Samples
Is Psychology a Science?
Updated 12 December 2023
Downloads 58
Category Psychology , Science
There has been an argument on whether psychology is a science or pseudoscience. Psychology is the defined by the American Psychology Association as the study of the behavior and mind (Carlson, 2014). It studies how the mind works, and how it affects the behavior. Pseudoscience consists of observations or beliefs that are incorrectly considered to be founded on scientific methods (Armstrong, 2010). Scientific methods are the procedures that characterize natural science that is characterized by operationalizable definition, a measurement that is reliable, control conditions, and reliability (Armstrong, 2010). From these definitions characteristics, psychology can be argued to be a science.
Why psychology is a science
Psychology is science as because it is based on scientific process. The scientific process is founded on a hypothetico-deductive model formulated by Karl Popper (Sharma, 2006). He proposed that theories ought to be put first, which are then applied in the generation of hypotheses that are falsifiable through experiment and observation. Popper points out that falsification is the only way of being certain (Yearley, 1985). Classic Psychologists rely on laboratory controlled experiments and reject any invisible or hidden forces as influencing behavior (Dienes, 2008). The lab based approach is also adopted by cognitive psychologists (Carlson, 2014). Thus psychology can be regarded as science as uses experiments and observation to falsify theories.
Psychology is science as its theories can be falsified. According to Popper the typical method of pseudoscience is looking for verifications. If any behavior by an individual can be explained, then the theory cannot be criticized using observations. It means that it loses its empirical character. Theories can only be improved if they are criticized (Dienes, 2008). Popper was trying to differentiate science from non-science was not only on classification but also an analysis of how to grow knowledge. Regarding the growing knowledge the point is whether a theory is used in inspiring falsifiable predictions, which in turn are applied in the improvement of the theory. Psychology conducts observations and experiments with the aim of testing a theory. It thus means that psychological theories are falsifiable, creating room for criticism and verification. Psychological theories have an empirical character (L'Abate, 2014). However, it does not mean that it is all the psychological theories that have an empirical character. As Popper points out, the Freudian psychoanalysis theory is not falsifiable. That is contrary to the view of Grunbaum, who argued that the theory is falsifiable. He argues based on the fact that comprehensible projections can be drawn from the psychoanalysis theory account (Lack " Rousseau, 2016). Consequently, psychological theories are scientific as they contain prediction statements making psychology a science.
Psychology is a science because it uses scientific methods. Psychology shows characteristics of scientific methods. Psychology uses theories that generate hypotheses. The hypotheses are verified using empirical methods and observations. Psychology is also considered science due to its theories that can be criticized. Hence psychological theories have empirical character. Psychological theories such as the psychoanalysis theory have prediction statements that are verified through empirical methods to increase knowledge and grow the theory. From these arguments, it is evident that psychology can be classified as a science.
Armstrong, B. (2010). Scientific methods. British Journal of Occupational Therapy, 73, 7.
Carlson, N. R. (2014). Psychology: The science of behavior. Pearson.
Dienes, Z. (2008). Understanding psychology as a science: An introduction to scientific and statistical inference. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
L'Abate, L. (2014). Clinical psychology and psychotherapy as a science. Place of publication not identified: Springer.
Lack, C. W., " Rousseau, J. (2016). Critical thinking, science, and pseudoscience: Why we can't trust our brains. New York: Springer Publishing Company.
Sharma, A. (2006). Scientific methods. New Delhi: Vishvabharti Publications.
Yearley, S. (1985). Imputing intentionality: Popper, demarcation and Darwin, Freud and Marx. Studies in History and Philosophy of Science, 16, 4, 337-50.
Deadline is approaching?
Wait no more. Let us write you an essay from scratch
Related Essays
Related topics.
Find Out the Cost of Your Paper
Type your email
By clicking “Submit”, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy policy. Sometimes you will receive account related emails.
- 1(877)219-7556 1(877)733-3925
Fully unique works only
Your privacy is our concern
Writing that is plagiarism free
Free Is Psychology a Science? Essay Sample
The debate as to whether psychology is considered a science has drawn considerable attention since the inception of the discipline of psychology during the second half of the 19th century. Some have even stated that psychology is more than science. Other scholars have stated the debate is complicated because both psychology and science are multifaceted, and complex constructs; thus, a dichotomous approach to the issue involving yes and no answer to the issue is insufficient. This paper argues that psychology is not a science. To support this argument, the key elements of science are discussed, after which it is demonstrated that psychology fails to meet the criteria of a scientific discipline.
Attributes of Science
Redding outlined the key features associated with science, which include empirical evidence, objectivity, control, testing of hypothesis, replication, and predictability. Empirical evidence represents the data gathered using experiment or observation. Empirical evidence is not reliant on belief or argument; rather, observations and experiments are conducted cautiously and reported with sufficient detail to enable other investigators to repeat and validate the work. The objectivity criterion requires researchers to remain independent of their research, which demands that they should be wholly unbiased in their studies to ensure that the knowledge gained is not influenced by personal experiences and feelings. The control criteria requires the researcher to control all extraneous variables to be able to ascertain the cause and effect relationships. Hypothesis refers to a statement developed by a researcher prior to conducting an investigation to show the predicted outcomes based on existing theory. Replication denotes the degree to which a specific method can be replicated to ascertain whether the findings are consistent. The criterion of predictability requires scientists to have the ability to predict future behavioral patterns by relying on the findings reported in research.
{t_essay_order_type_0-0}
Psychology as not a Science
Whereas psychology has been frequently defined as the “scientific” study of mind processes and behavior, the raw data that psychologists rely on human behavior to illustrate the functioning of human brain. The fundamental criticism that scientists level against psychologists as being their peers is the fact that the discipline of psychology lacks direct observations. Mind represent the actions of brains. There are practical limitations when trying to observe the human mind and its functioning since the mind is an inaccessible aspect of nature. This implies that true physical evidence regarding the mind cannot be collected. As a result, practitioners in other scientific disciplines such as anatomy and medicine do not consider psychology to be in the same level as far as the merits of science are concerned.
Secondly, psychology is not considered a science because it does not satisfy the key requirements of scientific fields including a terminology that is clearly defined; experimental conditions that are extremely controlled; reproducibility/replication; quantifiability; and testability and predictability. A notable example indicating why psychology fails to meet this key requirements of science is happiness research. There are no exact definitions of happiness. The definition of happiness various between individuals and cultures. Additionally, it is extremely problematic to measure happiness. Psychologists cannot utilize a microscope or a ruler; thus, they rely in an arbitrary scale to measure ambiguous constructs in an attempt to achieve quantifiability. Failing to satisfy the requirements of quantifiability and clear terminology (needed to achieve scientific rigor) makes it nearly impossible for the psychological research on happiness to meet the requirements of extremely controlled experiments, testability and predictability, and replication. For instance, it is not possible for an experiment to report consistent findings using vague and unquantifiable terms. Additionally, it is impossible to reliably predict the behavior of humans. Meaningful predictions is a key tenet of science; however, psychology performs dismally in this aspect. Other limitations that arise when psychology is considered a science include problems applying a reductionist and deterministic approach in human behavior; inability to generalize psychological explanations since they are limited to particular places and times; and that objectivity is impossible when studying the behavior of humans.
To be reasonable, not all research in psychology is weak. Some scientifically rigorous research has been conducted in psychology and has been able to provide crucial insights; however, it is erroneous to state that it is science. Instead, psychologists are aiming at redefining science. When science is redefined, it ceases to be an empirical assessment of the physical world, which is a dangerous precedent since anything can merit to be considered science, which threatens the influence of science in provide unique explanations for truth. Various authors agree that redefining science to a level that it does not rely on time-tested criteria like predictability and testability is a dangerous trend. As a result, some authors have argued that psychology should not be classified as science, but instead be viewed as an alternative to science, just like belief, argument, and rational research. This means that psychology is in the same class as the humanistic approach that places considerable emphasis on the subjective conscious and advocates for rejecting science on grounds that objective reality is of less importance when compared to an individual’s subjective understanding and perception of the world. Consequently, some have proposed that psychology should cease using scientific methods in understanding and explaining human behavior since it is dehumanizing and cannot be effectively used to explore the richness associated with conscious experience.
It is evident that psychology fails to satisfy the requirements of a scientific discipline including empirical evidence, objectivity, control, testing of hypothesis, replication, and predictability. Even though psychology utilizes scientific methods, the subject of psychology (human behavior) cannot be studied scientifically. The rules of science are fundamentally inapplicable in the subjective nature of psychology. This has resulted in the proposition that psychology should cease using scientific methods, and instead focus on using humanistic and subjective approaches. Overall, psychology cannot be deemed a scientific discipline.

Have NO Inspiration to write your essay?
Ask for Professional help
Search Free Essay
Please note!
Some text in the modal.
Psychology’s Status as a Science: Peculiarities and Intrinsic Challenges. Moving Beyond its Current Deadlock Towards Conceptual Integration
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 17 June 2020
- Volume 55 , pages 212–224, ( 2021 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Jana Uher ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2450-4943 1
14k Accesses
13 Citations
65 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Psychology holds an exceptional position among the sciences. Yet even after 140 years as an independent discipline, psychology is still struggling with its most basic foundations. Its key phenomena, mind and behaviour, are poorly defined (and their definition instead often delegated to neuroscience or philosophy) while specific terms and constructs proliferate. A unified theoretical framework has not been developed and its categorisation as a ‘soft science’ ascribes to psychology a lower level of scientificity. The article traces these problems to the peculiarities of psychology’s study phenomena, their interrelations with and centrality to everyday knowledge and language (which may explain the proliferation and unclarity of terms and concepts), as well as to their complex relations with other study phenomena. It shows that adequate explorations of such diverse kinds of phenomena and their interrelations with the most elusive of all—immediate experience—inherently require a plurality of epistemologies, paradigms, theories, methodologies and methods that complement those developed for the natural sciences. Their systematic integration within just one discipline, made necessary by these phenomena’s joint emergence in the single individual as the basic unit of analysis, makes psychology in fact the hardest science of all. But Galtonian nomothetic methodology has turned much of today’s psychology into a science of populations rather than individuals, showing that blind adherence to natural-science principles has not advanced but impeded the development of psychology as a science. Finally, the article introduces paradigmatic frameworks that can provide solid foundations for conceptual integration and new developments.
Similar content being viewed by others

Research design: qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches / sixth edition
James P. Takona

Positive Psychology: An Introduction

Identity Theory
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Psychology’s Status as a Discipline
Psychology holds an exceptional position among the sciences—not least because it explores the very means by which any science is made, for it is humans who perceive, conceive, define, investigate, analyse and interpret the phenomena of the world. Scientists have managed to explore distant galaxies, quantum particles and the evolution of life over 4 billion years—phenomena inaccessible to the naked eye or long deceased. Yet, psychology is still struggling with its most basic foundations. The phenomena of our personal experience, directly accessible to everyone in each waking moment of life, remain challenging objects of research. Moreover, psychical phenomena are essential for all sciences (e.g., thinking). But why are we struggling to scientifically explore the means needed to first make any science? Given the successes in other fields, is this not a contradiction in itself?
This article outlines three key problems of psychology (poor definitions of study phenomena, lack of unified theoretical frameworks, and an allegedly lower level of scientificity) that are frequently discussed and at the centre of Zagaria, Andò and Zennaro’s ( 2020 ) review. These problems are then traced to peculiarities of psychology’s study phenomena and the conceptual and methodological challenges they entail. Finally, the article introduces paradigmatic frameworks that can provide solid foundations for conceptual integration and new developments.
Lack of Proper Terms and Definitions of Study Phenomena
Introductory text books are supposed to present the corner stones of a science’s established knowledge base. In psychology, however, textbooks present definitions of its key phenomena—mind (psyche) and behaviour—that are discordant, ambiguous, overlapping, circular and context-dependent, thus inconclusive (Zagaria et al. 2020 ). Tellingly, many popular text books define ‘mind’ exclusively as ‘brain activity’, thus turning psychology’s central object of research into one of neuroscience. What then is psychology as opposed to neuroscience? Some even regard the definition of mind as unimportant and leave it to philosophers, thus categorising it as a philosophical phenomenon and shifting it again out of psychology’s own realm. At the same time, mainstream psychologists often proudly distance themselves from philosophers (Alexandrova & Haybron, 2016 ), explicitly referring to the vital distinction between science and philosophy. Behaviour, as well, is commonly reduced to ill-defined ‘activities’, ‘actions’ and ‘doings’ and, confusingly, often even equated with mind (psyche), such as in concepts of ‘inner and outer behaviours’ (Uher 2016b ). All this leaves one wonder what psychology is actually about.
As if to compensate the unsatisfactory definitional and conceptual status of its key phenomena in general, psychology is plagued with a chaotic proliferation of terms and constructs for specific phenomena of mind and behaviour (Zagaria et al. 2020 ). This entails that different terms can denote the same concept (jangle-fallacies; Kelley 1927 ) and the same terms different concepts (jingle-fallacies; Thorndike 1903 ). Even more basically, many psychologists struggle to explain what their most frequent study phenomena—constructs—actually are (Slaney and Garcia 2015 ). These deficiencies and inconsistencies involve a deeply fragmented theoretical landscape.
Lack of Conceptual Integration Into Overarching Frameworks
Like no other science, psychology embraces an enormous diversity of established epistemologies, paradigms, theories, methodologies and methods. Is that a result of the discipline’s unparalleled complexity and the therefore necessary scientific pluralism (Fahrenberg 2013 ) or rather an outcome of mistaking this pluralism for the unrestrained proliferation of perspectives (Zagaria et al. 2020 )?
The lack of a unified theory in psychology is widely lamented. Many ‘integrative theories’ were proposed as overarching frameworks, yet without considering contradictory presuppositions underlying different theories. Such integrative systems merely provide important overviews of the essential plurality of research perspectives and methodologies needed in the field (Fahrenberg 2013 ; Uher 2015b ). Zagaria and colleagues ( 2020 ) suggested evolutionary psychology could provide the much-needed paradigmatic framework. This field, however, is among psychology’s youngest sub-disciplines and its most speculative ones because (unlike biological phenomena) psychical, behavioural and social phenomena leave no fossilised traces in themselves. Their possible ancestral forms can only be reconstructed indirectly from archaeological findings and investigations of today’s humans, making evolutionary explorations prone to speculations and biases (e.g., gender bias in interpretations of archaeological findings; Ginge 1996 ). Cross-species comparative psychology offers important correctives through empirical studies of today’s species with different cognitive, behavioural, social and ecological systems and different degrees of phylogenetic relatedness to humans. This enables comparisons and hypothesis testing not possible when studying only humans but still faces limitations given human ancestors’ unavailability for direct study (Uher 2020a ).
But most importantly, evolutionary psychology does not provide consistent terms and concepts either; its key constructs ‘psychological adaptations’ and ‘evolved psychological mechanisms’ are as vague, ambiguous and ill-defined as ‘mind’ and ‘behaviour’. Moreover, the strong research heuristic formulated in Tinbergen’s four questions on the causation, function, development and evolution of behaviour is not an achievement of evolutionary psychology but originates from theoretical biology, thus again from outside of psychology.
Psychology—a ‘Soft Science’ in Pre-scientific Stage?
The pronounced inconsistencies in psychology’s terminological, conceptual and theoretical landscape have been likened to the pre-scientific stage of emerging sciences (Zagaria et al. 2020 ). Psychology was therefore declared a ‘soft science’ that can never achieve the status of the ‘hard sciences’ (e.g., physics, chemistry). This categorisation implies the belief that some sciences have only minor capacities to accumulate secured knowledge and lower abilities to reach theoretical and methodological consensus (Fanelli and Glänzel 2013 ; Simonton 2015 ). In particular, soft sciences would have only limited abilities to apply ‘the scientific method’, the general set of principles involving systematic observation, experimentation and measurement as well as deduction and testing of hypotheses that guide scientific practice (Gauch 2015 ). The idea of the presumed lack of methodological rigor and exactitude of ‘soft sciences’ goes back to Kant ( 1798 / 2000 ) and is fuelled by recurrent crises of replication, generalisation, validity, and other criteria considered essential for all sciences.
But classifying sciences into ‘hard’ and ‘soft’, implying some would be more scientific than others, is ill-conceived and misses the point why there are different sciences at all. Crucially, the possibilities for implementing particular research practices are not a matter of scientific discipline or their ascribed level of scientificity but solely depend on the particular study phenomena and their properties (Uher 2019 ). For study phenomena that are highly context-dependent and continuously changing in themselves, such as those of mind, behaviour and society, old knowledge cannot have continuing relevance as this is the case for (e.g., non-living) phenomena and properties that are comparably invariant in themselves. Instead, accurate and valid investigations require that concepts, theories and methods must be continuously adapted as well (Uher 2020b ).
The classification of sciences by the degree to which they can implement ‘the scientific method’ as developed for the natural sciences is a reflection of the method-centrism that has taken hold of psychology over the last century, when the craft of statistical analysis became psychologists’ dominant activity (Lamiell 2019 ; Valsiner 2012 ). The development of ever more sophisticated tools for statistical analysis as well as of rating scales enabling the efficient generation of allegedly quantitative data for millions of individuals misled psychologists to adapt their study phenomena and research questions to their methods, rather than vice versa (Omi 2012 ; Toomela and Valsiner 2010 ; Uher 2013 ). But methods are just a means to an end. Sciences must be phenomenon-centred and problem-centred, and they must develop epistemologies, theories, methodologies and methods that are suited to explore these phenomena and the research problems in their field.
Psychology’s Study Phenomena and Intrinsic Challenges
Psychology’s exceptional position among the sciences and its key problems can be traced to its study phenomena’s peculiarities and the conceptual and methodological challenges they entail.
Experience: Elementary to All Empirical Sciences
Experience is elementary to all empirical sciences, which are experience-based by definition (from Greek empeiria meaning experience). The founder of psychology, Wilhelm Wundt, already highlighted that every concrete experience has always two aspects, the objective content given and individuals’ subjective apprehension of it—thus, the objects of experience in themselves and the subjects experiencing them. This entails two fundamental ways in which experience is treated in the sciences (Wundt 1896a ).
Natural sciences explore the objective contents mediated by experience that can be obtained by subtracting from the concrete experience the subjective aspects always contained in it. Hence, natural scientists consider the objects of experience in their properties as conceived independently of the subjects experiencing them, using the perspective of mediate experience (mittelbare Erfahrung; Wundt 1896a ). Therefore, natural scientists develop theories, approaches and technologies that help minimise the involvement of human perceptual and conceptual abilities in research processes and filter out their effects on research outcomes. This approach is facilitated by the peculiarities of natural-science study phenomena (of the non-living world, in particular), in which general laws, immutable relationships and natural constants can be identified that remain invariant across time and space and that can be measured and mathematically formalised (Uher 2020b ).
Psychologists, in turn, explore the experiencing subjects and their understanding and interpretation of their experiential contents and how this mediates their concrete experience of ‘reality’. This involves the perspective of immediate experience (unmittelbare Erfahrung), with immediate indicating absence of other phenomena mediating their perception (Wundt 1896a ). Immediate experience comprises connected processes, whereby every process has an objective content but is, at the same time, also a subjective process. Inner experience, Wundt highlighted, is not a special part of experience but rather constitutes the entirety of all immediate experience; thus, inner and outer experience do not constitute separate channels of information as often assumed (Uher 2016a ). That is, psychology deals with the entire experience in its immediate subjective reality. The inherent relation to the perceiving and experiencing subject— subject reference —is therefore a fundamental category in psychology. Subjects are feeling and thinking beings capable of intentional action who pursue purposes and values. This entails agency, volition, value orientation and teleology. As a consequence, Wundt highlighted, research on these phenomena can determine only law-like generalisations that allow for exceptions and singularities (Fahrenberg 2019 ). Given this, it is meaningless to use theories-to-laws ratios as indicators of scientificity (e.g., in Simonton 2015 ; Zagaria et al. 2020 ).
Constructs: Concepts in Science AND Everyday Psychology
The processual and transient nature of immediate experience (and many behaviours) imposes further challenges because, of processual entities, only a part exists at any moment (Whitehead 1929 ). Experiential phenomena can therefore be conceived only through generalisation and abstraction from their occurrences over time, leading to concepts, beliefs and knowledge about them , which are psychical phenomena in themselves as well but different from those they are about (reflected in the terms experien cing versus experien ce ; Erleben versus Erfahrung; Uher 2015b , 2016a ). Abstract concepts, because they are theoretically constructed, are called constructs (Kelly 1963 ). All humans implicitly develop constructs (through abduction, see below) to describe and explain regularities they observe in themselves and their world. They use constructs to anticipate the unknown future and to choose among alterative actions and responses (Kelly 1963 ; Valsiner 2012 ).
Constructs about experiencing, experience and behaviour form important parts of our everyday knowledge and language. This entails intricacies because psychologists cannot simply put this everyday psychology aside for doing their science, even more so as they are studying the phenomena that are at the centre of everyday knowledge and largely accessible only through (everyday) language. Therefore, psychologists cannot invent scientific terms and concepts that are completely unrelated to those of everyday psychology as natural scientists can do (Uher 2015b ). But this also entails that, to first delineate their study phenomena, psychologists need not elaborate scientific definitions because everyday psychology already provides some terms, implicit concepts and understanding—even if these are ambiguous, discordant, circular, overlapping, context-dependent and biased. This may explain the proliferation of terms and concepts and the lack of clear definitions of key phenomena in scientific psychology.
Constructs and language-based methods entail further challenges. The construal of constructs allowed scientists to turn abstract ideas into entities, thereby making them conceptually accessible to empirical study. But this entification misguides psychologists to overlook their constructed nature (Slaney and Garcia 2015 ) by ascribing to constructs an ontological status (e.g., ‘traits’ as psychophysical mechanisms; Uher 2013 ). Because explorations of many psychological study phenomena are intimately bound to language, psychologists must differentiate their study phenomena from the terms, concepts and methods used to explore them, as indicated by the terms psych ical versus psych ological (from Greek -λογία, -logia for body of knowledge)—differentiations not commonly made in the English-language publications dominating in contemporary psychology (Lewin 1936 ; Uher 2016a ).
Psychology’s Exceptional Position Among the Sciences and Philosophy
The concepts of mediate and immediate experience illuminate psychology’s special interrelations with the other sciences and philosophy. Wundt conceived the natural sciences (Naturwissenschaften; e.g., physics, physiology) as auxiliary to psychology and psychology, in turn, as supplementary to the natural sciences “in the sense that only together they are able to exhaust the empirical knowledge accessible to us“ (Fahrenberg 2019 ; Wundt 1896b , p. 102). By exploring the universal forms of immediate experience and the regularities of their connections, psychology is also the foundation of the intellectual sciences (Geisteswissenschaften, commonly (mis)translated as humanities; e.g., philology, linguistics, law), which explore the actions and effects emerging from humans’ immediate experiences (Fahrenberg 2019 ). Psychology also provides foundations for the cultural and social sciences (Kultur- und Sozialwissenschaften; e.g., sociology; anthropology), which explore the products and processes emerging from social and societal interactions among experiencing subjects who are thinking and intentional agents pursuing values, aims and purposes. Moreover, because psychology considers the subjective and the objective as the two fundamental conditions underlying theoretical reflection and practical action and seeks to determine their interrelations, Wundt regarded psychology also a preparatory empirical science for philosophy (especially epistemology and ethics; Fahrenberg 2019 ).
Psychology’s exceptional position at the intersection with diverse sciences and with philosophy is reflected in the extremely heterogeneous study phenomena explored in its diverse sub-disciplines, covering all areas of human life. Some examples are individuals’ sensations and perceptions of physical phenomena (e.g., psychophysics, environmental psychology, engineering psychology), biological and pathological phenomena associated with experience and behaviour (e.g., biopsychology, neuropsychology, clinical psychology), individuals’ experience and behaviour in relation to others and in society (e.g., social psychology, personality psychology, cultural psychology, psycholinguistics, economic psychology), as well as in different periods and domains of life (e.g., developmental psychology, educational psychology, occupational psychology). No other science explores such a diversity of study phenomena. Their exploration requires a plurality of epistemologies, methodologies and methods, which include experimental and technology-based investigations (e.g., neuro-imaging, electromyography, life-logging, video-analyses), interpretive and social-science investigations (e.g., of texts, narratives, multi-media) as well as investigations involving self-report and self-observation (e.g., interviews, questionnaires, guided introquestion).
All this shows that psychology cannot be a unitary science. Adequate explorations of so many different kinds of phenomena and their interrelations with the most elusive of all—immediate experience—inherently require a plurality of epistemologies, paradigms, theories, methodologies and methods that complement those developed for the natural sciences, which are needed as well. Their systematic integration within just one discipline, made necessary by these phenomena’s joint emergence in the single individual as the basic unit of analysis, makes psychology in fact the hardest science of all.
Idiographic and Nomothetic Strategies of Knowledge Generation
Immediate experience, given its subjective, processual, context-dependent, and thus ever-changing nature, is always unique and unprecedented. Exploring such particulars inherently requires idiographic strategies, in which local phenomena of single cases are modelled in their dynamic contexts to create generalised knowledge from them through abduction. In abduction, scientists infer from observations of surprising facts backwards to a possible theory that, if it were true, could explain the facts observed (Peirce 1901 ; CP 7.218). Abduction leads to the creation of new general knowledge, in which theory and data are circularly connected in an open-ended cycle, allowing to further generalise, extend and differentiate the new knowledge created. By generalising from what was once and at another time as well, idiographic approaches form the basis of nomothetic approaches, which are aimed at identifying generalities common to all particulars of a class and at deriving theories or laws to account for these generalities. This Wundtian approach to nomothetic research, because it is case-by-case based , allows to create generalised knowledge about psychical processes and functioning, thus building a bridge between the individual and theory development (Lamiell 2003 ; Robinson 2011 ; Salvatore and Valsiner 2010 ).
But beliefs in the superiority of natural-science principles misled many psychologists to interpret nomothetic strategies solely in terms of the Galtonian methodology, in which many cases are aggregated and statistically analysed on the sample-level . This limits research to group-level hypothesis testing and theory development to inductive generalisation, which are uninformative about single cases and cannot reveal what is, indeed, common to all (Lamiell 2003 ; Robinson 2011 ). This entails numerous fallacies, such as the widespread belief between-individual structures would be identical to and even reflect within-individual structures (Molenaar 2004 ; Uher 2015d ). Galtonian nomothetic methodology has turned much of today’s psychology into a science exploring populations rather than individuals. That is, blind adherence to natural-science principles has not advanced but, instead, substantially impeded the development of psychology as a science.
Moving Psychology Beyond its Current Conceptual Deadlock
Wundt’s opening of psychology’s first laboratory marked its official start as an independent science. Its dynamic developments over the last 140 years testify to psychology’s importance but also to the peculiarities of its study phenomena and the intricate challenges that these entail for scientific explorations. Yet, given its history, it seems unlikely that psychology can finally pull itself out of the swamps of conceptual vagueness and theoretical inconsistencies using just its own concepts and theories, in a feat similar to that of the legendary Baron Münchhausen. Psychology can, however, capitalise on its exceptional constellation of intersections with other sciences and philosophy that arises from its unique focus on the individual. Although challenging, this constitutes a rich source for perspective-taking and stimulation of new developments that can meaningfully complement and expand its own genuine achievements as shown in the paradigm outlined now.
The Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals (TPS-Paradigm)
The Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals ( TPS-Paradigm Footnote 1 ) is targeted toward making explicit and scrutinising the most basic assumptions that different disciplines make about research on individuals to help scientists critically reflect on; discuss and refine their theories and practices; and to derive ideas for new developments (therefore philosophy-of–science ). It comprises a system of interrelated philosophical, metatheoretical and methodological frameworks that coherently build upon each other (therefore paradigm ). In these frameworks, concepts from various lines of thought, both historical and more recent, and from different disciplines (e.g., psychology, life sciences, social sciences, physical sciences, metrology, philosophy of science) that are relevant for exploring research objects in (relation to) individuals were systematically integrated, refined and complemented by novel ones, thereby creating unitary frameworks that transcend disciplinary boundaries (therefore transdisciplinary ; Uher 2015a , b , 2018c ).
The Philosophical Framework: Presuppositions About Research on Individuals
The philosophical framework specifies three sets of presuppositions that are made in the TPS-Paradigm about the nature and properties of individuals and the phenomena studied in (relations to) them as well as about the notions by which knowledge about them can be gained.
All science is done by humans and therefore inextricably entwined with and limited by human’s perceptual and conceptual abilities. This entails risks for particular fallacies of the human mind (e.g., oversimplifying complexity, Royce 1891 ; reifying linguistic abstractions, Whitehead 1929 ). Scientists researching individuals face particular challenges because they are individuals themselves, thus inseparable from their research objects. This entails risks for anthropocentric, ethnocentric and egocentric biases influencing metatheories and methodologies (Uher 2015b ). Concepts from social, cultural and theoretical psychology, sociology, and other fields (e.g., Gergen 2001 ; Valsiner 1998 ; Weber 1949 ) were used to open up meta-perspectives on research processes and help scientists reflect on their own presuppositions, ideologies and language that may (unintentionally) influence their research.
Individuals are complex living organisms , which can be conceived as open (dissipative) and nested systems. On each hierarchical level, they function as organised wholes from which new properties emerge not predictable from their constituents and that can feed back to the constituents from which they emerge, causing complex patterns of upward and downward causation. With increasing levels of organisation, ever more complex systems emerge that are less rule-bound, highly adaptive and historically unique. Therefore, dissecting systems into elements cannot reveal the processes governing their functioning and development as a whole; assumptions on universal determinism and reductionism must be rejected. Relevant concepts from thermodynamics, physics of life, philosophy, theoretical biology, medicine, psychology, sociology and other fields (e.g., Capra 1997 ; Hartmann 1964 ; Koffka 1935 ; Morin 2008 ; Prigogine and Stengers 1997 ; Varela et al. 1974 ; von Bertalanffy 1937 ) about dialectics, complexity and nonlinear dynamic systems were used to elaborate their relevance for research on individuals.
The concept of complementarity is applied to highlight that, by using different methods, ostensibly incompatible information can be obtained about properties of the same object of research that are nevertheless all equally essential for an exhaustive account of it and that may therefore be regarded as complementary to one another. Applications of this concept, originating from physics (wave-particle dilemma in research on the nature of light; Bohr 1937 ; Heisenberg 1927 ), to the body-mind problem emphasise the necessity for a methodical dualism to account for observations of two categorically different realities that require different frames of reference, approaches and methods (Brody and Oppenheim 1969 ; Fahrenberg 1979 , 2013 ; Walach 2013 ). Complementarity was applied to specify the peculiarities of psychical phenomena and to derive methodological concepts (Uher, 2016a ). It was also applied to develop solutions for the nomothetic-idiographic controversy in ‘personality’ research (Uher 2015d ).
These presuppositions underlie the metatheoretical and the methodological framework.
Metatheoretical Framework
The metatheoretical framework formalises a phenomenon’s accessibility to human perception under everyday conditions using three metatheoretical properties: internality-externality, temporal extension, and spatiality conceived complementarily as physical (spatial) and “non-physical” (without spatial properties). The particular constellations of their forms in given phenomena were used to metatheoretically define and differentiate from one another various kinds of phenomena studied in (relation to) individuals: morphology, physiology, behaviour, psyche, semiotic representations (e.g., language), artificial outer-appearance modifications (e.g., clothing) and contexts (e.g., situations; Uher 2015b ).
These metatheoretical concepts allowed to integrate and further develop established concepts from various fields to elaborate the peculiarities of the phenomena of the psyche Footnote 2 and their functional connections with other phenomena (e.g., one-sided psyche-externality gap; Uher 2013 ), to trace their ontogenetic development and to explore the fundamental imperceptibility of others’ psychical phenomena and its role in the development of agency, language, instructed learning, culture, social institutions and societies in human evolution (Uher 2015a ). The metatheoretical definition of behaviour Footnote 3 enabled clear differentiations from psyche and physiology, and clarified when the content-level of language in itself constitutes behaviour, revealing how language extends humans’ behavioural possibilities far beyond all non-language behaviours (Uher 2016b ). The metatheoretical definition of ‘personality’ as individual-specificity in all kinds of phenomena studied in individuals (see above) highlighted the unique constellation of probabilistic, differential and temporal patterns that merge together in this concept, the challenges this entails and the central role of language in the formation of ‘personality’ concepts. This also enabled novel approaches for conceptual integrations of the heterogeneous landscape of paradigms and theories in ‘personality’ research (Uher 2015b , c , d , 2018b ). The semiotic representations concept emphasised the composite nature of language, comprising psychical and physical phenomena, thus both internal and external phenomena. Failure to consider the triadic relations among meaning, signifier and referent inherent to any sign system as well as their inseparability from the individuals using them was shown to underly various conceptual fallacies, especially regarding data generation and measurement (Uher 2018a , 2019 ).
Methodological Framework
The metatheoretical framework is systematically linked to the methodological framework featuring three main areas.
General concepts of phenomenon-methodology matching . The three metatheoretical properties were used to derive implications for research methodology, leading to new concepts that help to identify fallacies and mismatches (e.g., nunc-ipsum methods for transient phenomena, intro questive versus extro questive methods to remedy methodological problems in previous concepts of introspection; Uher 2016a , 2019 ).
Methodological concepts for comparing individuals within and across situations, groups and species were developed (Uher 2015e ). Approaches for taxonomising individual differences in various kinds of phenomena in human populations and other species were systematised on the basis of their underlying rationales. Various novel approaches, especially behavioural ones, were developed to systematically test and complement the widely-used lexical models derived from everyday language (Uher 2015b , c , d , 2018b , c ).
Theories and practices of data generation and measurement from psychology, social sciences and metrology, the science of measurement and foundational to the physical sciences, were scrutinised and compared. These transdisciplinary analyses identified two basic methodological principles of measurement underlying metrological concepts that are also applicable to psychological and social-science research (data generation traceability, numerical traceability; Uher 2020b ). Further analyses explored the involvement of human abilities in data generation across the empirical sciences (Uher 2019 ) and raters’ interpretation and use of standardised assessment scales (Uher 2018a ).
Empirical demonstrations of these developments and analyses in various empirical studies involving humans of different sociolinguistic backgrounds as well as several nonhuman primate species (e.g., Uher 2015e , 2018a ; Uher et al. 2013a , b ; Uher and Visalberghi 2016 ) show the feasibility of this line of research. Grounded in established concepts from various disciplines, it offers many possibilities for fruitful cross-scientific collaborations waiting to be explored in order to advance the fascinating science of individuals.
http://researchonindividuals.org .
The psyche is defined as the “entirety of the phenomena of the immediate experiential reality both conscious and non-conscious of living organisms” (Uher 2015c , p. 431, derived from Wundt 1896a ).
Behaviours are defined as the “external changes or activities of living organisms that are functionally mediated by other external phenomena in the present moment” (Uher 2016b , p. 490).
Alexandrova, A., & Haybron, D. M. (2016). Is construct validation valid? Philosophy of Science, 83(5), 1098–1109. https://doi.org/10.1086/687941
Bohr, N. (1937). Causality and complementarity. Philosophy of Science, 4 (3), 289–298.
Article Google Scholar
Brody, N., & Oppenheim, P. (1969). Application of Bohr’s principle of complementarity to the mind-body problem. Journal of Philosophy, 66 (4), 97–113. https://doi.org/10.2307/2024529 .
Capra, F. (1997). The web of life: A new synthesis of mind and matter . New York: Anchor Books.
Google Scholar
Fahrenberg, J. (1979). The complementarity principle in psychophysiological research and somatic medicine. Zeitschrift für Klinische Psychologie und Psychotherapie, 27 (2), 151–167.
Fahrenberg, J. (2013). Zur Kategorienlehre der Psychologie: Komplementaritätsprinzip; Perspektiven und Perspektiven-Wechsel . Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers.
Fahrenberg, J. (2019). Wilhelm Wundt (1832 – 1920). Introduction, quotations, reception, commentaries, attempts at reconstruction . Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers.
Fanelli, D., & Glänzel, W. (2013). Bibliometric evidence for a hierarchy of the sciences. PLoS ONE, 8 (6), e66938. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0066938 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gauch, H. G. J. (2015). Scientific method in practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gergen, K. J. (2001). Psychological science in a postmodern context. American Psychologist, 56(10) , 803–813. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.56.10.803 .
Ginge, B. (1996). Identifying gender in the archaeological record: Revising our stereotypes. Etruscan Studies, 3, Article 4.
Hartmann, N. (1964). Der Aufbau der realen Welt. Grundriss der allgemeinen Kategorienlehre (3. Aufl.) . Berlin: Walter de Gruyter.
Book Google Scholar
Heisenberg, W. (1927). Über den anschaulichen Inhalt der quantentheoretischen Kinematik und Mechanik. Zeitschrift für Physik, 43 (3–4), 172–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01397280 .
Kant, I. (1798/2000). Anthropologie in pragmatischer Hinsicht (Reinhard Brandt, ed.). Felix Meiner.
Kelley, T. L. (1927). Interpretation of educational measurements . Yonkers: World.
Kelly, G. (1963). A theory of personality: The psychology of personal constructs . W.W. Norton.
Koffka, K. (1935). Principles of Gestalt psychology . New York: Harcourt, Brace, & World.
Lamiell, J. (2003). Beyond individual and group differences: Human individuality, scientific psychology, and William Stern’s critical personalism . Thousand Oaks, California: Sage Publications. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781452229317 .
Lamiell, J. (2019). Psychology’s misuse of statistics and persistent dismissal of its critics . Springer International. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12131-0 .
Lewin, K. (1936). Principles of topological psychology . New York: McGraw-Hill.
Molenaar, P. C. M. (2004). A manifesto on psychology as idiographic science: Bringing the person back into scientific psychology, this time forever. Measurement: Interdisciplinary Research & Perspective, 2 (4), 201–218. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15366359mea0204_1 .
Morin, E. (2008). On complexity . Cresskill: Hampton Press.
Omi, Y. (2012). Tension between the theoretical thinking and the empirical method: Is it an inevitable fate for psychology? Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science, 46 (1), 118–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-011-9185-4 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Peirce, C. S. (1901/1935). Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce (CP 7.218—1901, On the logic of drawing history from ancient documents especially from testimonies) . Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Prigogine, I., & Stengers, I. (1997). The end of certainty: Time, chaos, and the new laws of nature . Free Press.
Robinson, O. C. (2011). The idiographic/nomothetic dichotomy: Tracing historical origins of contemporary confusions. History & Philosophy of Psychology, 13 , 32–39.
Royce, J. (1891). The religious aspect of philosophy: A critique of the bases of conduct and of faith. Boston: Houghton, Mifflin.
Salvatore, S., & Valsiner, J. (2010). Between the general and the unique. Theory & Psychology, 20 , 817–833. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959354310381156 .
Simonton, D. K. (2015). Psychology as a science within Comte’s hypothesized hierarchy: Empirical investigations and conceptual implications. Review of General Psychology, 19 (3), 334–344. https://doi.org/10.1037/gpr0000039 .
Slaney, K. L., & Garcia, D. A. (2015). Constructing psychological objects: The rhetoric of constructs. Journal of Theoretical and Philosophical Psychology, 35 (4), 244–259. https://doi.org/10.1037/teo0000025 .
Thorndike, E. L. (1903). Notes on child study (2nd ed.). New York: Macmillan.
Toomela, A., & Valsiner, J. (2010). Methodological thinking in psychology: 60 years gone astray? Information Age Publishing.
Uher, J. (2013). Personality psychology: Lexical approaches, assessment methods, and trait concepts reveal only half of the story-Why it is time for a paradigm shift. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science, 47 (1), 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-013-9230-6 .
Uher, J. (2015a). Agency enabled by the psyche: Explorations using the Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals. In C. W. Gruber, M. G. Clark, S. H. Klempe, & J. Valsiner (Eds.), Constraints of agency: Explorations of theory in everyday life. Annals of Theoretical Psychology (Vol. 12) (pp. 177–228). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10130-9_13 .
Uher, J. (2015b). Conceiving “personality”: Psychologist’s challenges and basic fundamentals of the Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science, 49 (3), 398–458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-014-9283-1 .
Uher, J. (2015c). Developing “personality” taxonomies: Metatheoretical and methodological rationales underlying selection approaches, methods of data generation and reduction principles. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science, 49 (4), 531–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-014-9280-4 .
Uher, J. (2015d). Interpreting “personality” taxonomies: Why previous models cannot capture individual-specific experiencing, behaviour, functioning and development. Major taxonomic tasks still lay ahead. Integrative Psychological and Behavioral Science, 49 (4), 600–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-014-9281-3 .
Uher, J. (2015e). Comparing individuals within and across situations, groups and species: Metatheoretical and methodological foundations demonstrated in primate behaviour. In D. Emmans & A. Laihinen (Eds.), Comparative Neuropsychology and Brain Imaging (Vol. 2), Series Neuropsychology: An Interdisciplinary Approach (pp. 223–284). https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.3848.8169
Uher, J. (2016a). Exploring the workings of the Psyche: Metatheoretical and methodological foundations. In J. Valsiner, G. Marsico, N. Chaudhary, T. Sato & V. Dazzani (Eds.), Psychology as the science of human being: The Yokohama Manifesto (pp. 299–324). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21094-0_18 .
Uher, J. (2016b). What is behaviour? And (when) is language behaviour? A metatheoretical definition. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour, 46 (4), 475–501. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsb.12104 .
Uher, J. (2018a). Quantitative data from rating scales: An epistemological and methodological enquiry. Frontiers in Psychology, 9 , 2599. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02599 .
Uher, J. (2018b). Taxonomic models of individual differences: A guide to transdisciplinary approaches. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 373 (1744), 20170171. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2017.0171 .
Uher, J. (2018c). The Transdisciplinary Philosophy-of-Science Paradigm for Research on Individuals: Foundations for the science of personality and individual differences. In V. Zeigler-Hill & T. K. Shackelford (Eds.), The SAGE Handbook of Personality and Individual Differences: Volume I: The science of personality and individual differences (pp. 84–109). https://doi.org/10.4135/9781526451163.n4 .
Uher, J. (2019). Data generation methods across the empirical sciences: differences in the study phenomena’s accessibility and the processes of data encoding. Quality & Quantity. International Journal of Methodology, 53 (1), 221–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-018-0744-3 .
Uher, J. (2020a). Human uniqueness explored from the uniquely human perspective: Epistemological and methodological challenges. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour, 50 , 20–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/jtsb.12232 .
Uher, J. (2020b). Measurement in metrology, psychology and social sciences: data generation traceability and numerical traceability as basic methodological principles applicable across sciences. Quality & Quantity. International Journal of Methodology, 54 , 975-1004. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-020-00970-2 .
Uher, J., Addessi, E., & Visalberghi, E. (2013). Contextualised behavioural measurements of personality differences obtained in behavioural tests and social observations in adult capuchin monkeys (Cebus apella). Journal of Research in Personality, 47 (4), 427–444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2013.01.013
Uher, J., & Visalberghi, E. (2016). Observations versus assessments of personality: A five-method multi-species study reveals numerous biases in ratings and methodological limitations of standardised assessments. Journal of Research in Personality, 61 , 61–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2016.02.003 .
Uher, J., Werner, C. S., & Gosselt, K. (2013). From observations of individual behaviour to social representations of personality: Developmental pathways, attribution biases, and limitations of questionnaire methods. Journal of Research in Personality, 47 (5), 647–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrp.2013.03.006
Valsiner, J. (1998). The guided mind : A sociogenetic approach to personality. Harvard University Press.
Valsiner, J. (2012). A guided science: History of psychology in the mirror of its making . New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers.
Varela, F. G., Maturana, H. R., & Uribe, R. (1974). Autopoiesis: The organization of living systems, its characterization and a model. BioSystems, 5 (4), 187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/0303-2647(74)90031-8 .
von Bertalanffy, L. (1937). Das Gefüge des Lebens . Leipzig: Teubner.
Walach, H. (2013). Psychologie: Wissenschaftstheorie, Philosophische Grundlagen und Geschichte (3. Aufl.) . Stuttgart: Kohlhammer.
Weber, M. (1949). On the methodology of the social sciences (E. Shils & H. Finch, Eds.). New York: Free Press.
Whitehead, A. N. (1929). Process and reality . New York: Harper.
Wundt, W. (1896a). Grundriss der Psychologie . Stuttgart: Körner. Retrieved from https://archive.org/ .
Wundt, W. (1896b). Über die Definition der Psychologie. Philosophische Studien, 12 , 9–66.
Zagaria, A., Andò, A., & Zennaro, A. (2020). Psychology: A giant with feet of clay. Integrative Psychological & Behavioral Science. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-020-09524-5 .
Download references
This research was conducted without funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Human Sciences, University of Greenwich, Old Royal Naval College, Park Row, London, SE10 9LS, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
I declare I am the sole creator of this research.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jana Uher .
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests.
I declare to have no conflicting or competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Uher, J. Psychology’s Status as a Science: Peculiarities and Intrinsic Challenges. Moving Beyond its Current Deadlock Towards Conceptual Integration. Integr. psych. behav. 55 , 212–224 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-020-09545-0
Download citation
Published : 17 June 2020
Issue Date : March 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12124-020-09545-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Terminology
- Soft Science
- Integrative framework
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
Is a Psychology Degree Worth It?

Know before you read At SNHU, we want to make sure you have the information you need to make decisions about your education and your future—no matter where you choose to go to school. That's why our informational articles may reference careers for which we do not offer academic programs, along with salary data for those careers. Cited projections do not guarantee actual salary or job growth.
If you're interested in the human mind, you might want to pursue a psychology degree. But you may also be wondering how you might use a psychology degree and if it’ll be worth it in the end.
Can a Psychology Degree Be Useful?
There are a few different types of psychology degrees you may consider pursuing, depending on your interests and career goals.
A few of those include:
- Associate of Arts (AA) in Psychology (Not currently offered at SNHU)
- Bachelor of Arts (BA) in Psychology
- Master of Science (MS) in Psychology
- Doctor of Philosophy in Psychology (PhD-PSY) (Not currently offered at SNHU)
- Doctor of Psychology (PsyD) (Not currently offered at SNHU)

Dr. Leslie Buddington , an online adjunct psychology instructor at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU), suggested a master’s degree in industrial-organizational psychology degree if you’d like to apply psychology concepts to the workplace.
Although there are several different areas you can focus on, most psychology programs have some common skills you can learn.
According to Buddington, while pursuing a psychology degree, you may learn about:
- Applying research
- Conducting experiments
- Data analysis and research methods
- Individual differences
- Making measurable changes in an environment
- Social justice and inequities
“Those are incredible skills that are useful in any future career,” said Buddington.
Many employers look for individuals with those kinds of skills, across a variety of fields. According to Buddington, psychology is a well-rounded field that demonstrates that you understand people, how situations contribute to behavior, how to predict and change behaviors and how to apply that information in order to make changes to a system. “That is going to help you stand out as a job candidate in multiple careers," she said.
Exploring experiential learning opportunities can help you to stand out even further, providing real-world experience while you're a student. Buddington noted that you can also work with your school's career center to find an internship. “An internship or experiential learning opportunity is definitely worthwhile to pursue," she said.
Find Your Program
How hard is a psychology degree.
"Because in psychology there are multiple perspectives (cognitive, developmental, behavioral, evolutionary and so forth), there is often no one ‘correct’ answer,” said Buddington. “Sometimes the fact that an answer is not just black or white doesn’t fit with how some people think.”
Buddington also said that students can sometimes be surprised by the amount of statistics and research work a psychology program involves.
The course load and program requirements may vary from school to school. Taking the time to research and ask questions about the programs you’re interested in can give you a better idea of what to expect while pursuing a psychology degree.
“I don’t necessarily think a psychology degree is hard, but it can sometimes be different from what you are expecting,” said Buddington.
Is a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology Worth It?
Buddington said that a BA in Psychology can allow you to work in many careers. Some options you may consider include:
- Data analysis
- Human resources
- Law enforcement
- Sports coaching
“I think because the principles you are learning apply to people, situations, behavior, society, as well as data analysis, they are universal skills that are needed across multiple career fields,” said Buddington.
And the reasons for entering this field of study are just as varied.
.ashx?h=220&w=220&hash=18D49708A4D50D402698767722F33743)
With her degree, Molinari hopes to work at a healthcare organization. She wants to help anyone who needs discretion, empathy and care, such as those transitioning or those who don’t have healthcare.
“I would just like to lend a helping hand to anybody who needs it,” she said.
A psychology degree can also help you to change careers.

“I always had an interest in the human mind,” said Parker. Psychology was the obvious choice when choosing his major.
After working 14-hour shifts, traveling all over the country, he would start doing his schoolwork. Since earning his degree, he now works as an HR business partner.
“It’s amazing, the job opportunities you can get with a psychology degree,” said Parker.
Is a Master of Science in Psychology Worth It?
“With an MS in Psychology, you are able to concentrate more fully on a field,” said Buddington.
You might become a therapist or forensic psychologist, according to Buddington. She said that a master’s degree may also allow you to teach at some community colleges.
Parker said that his degree has already opened doors for him, including the opportunity to pursue further education. He’s currently enrolled in the MA in Clinical Mental Health Counseling program at SNHU. (SNHU is not currently enrolling new students in the graduate counseling program.)
“My ultimate goal is to go back into drug and alcohol counseling, try to help people who suffer with addiction,” he said.
Are Psychologists in Demand?
“Post-pandemic there is more need than ever for psychologists,” said Buddington.
Becoming a psychologist typically requires a master's degree or higher, and licensing requirements vary by state. BLS predicts that job growth for psychologists will grow by 6% through 2032.*
“Teletherapy allows more individuals to have access to therapy that they otherwise may not have had,” said Buddington.
For example, people living in rural areas might not have therapists available nearby. Teletherapy allows those individuals to have access to therapy, said Buddington. “The fact that you can become teletherapy certified is an equity and inclusion triumph,” she said.
Like most fields, psychology is open to more diverse and inclusive perspectives. A psychology degree can provide you with the ability to better understand those from different backgrounds from you.
According to a study on diverse populations by the American Psychiatric Association, people from racial or ethnic minority groups are less likely to receive mental health care ( American Psychiatric Association PDF Source ). Some factors contributing to this include:
- Lack of diversity among mental health providers
- Language barriers
- Mental health stigma
Psychologists with unique cultural perspectives can help more people to feel understood.
A degree can change your life. Find the SNHU psychology program that can best help you meet your career goals.
*Cited job growth projections may not reflect local and/or short-term economic or job conditions and do not guarantee actual job growth. Actual salaries and/or earning potential may be the result of a combination of factors including, but not limited to: years of experience, industry of employment, geographic location, and worker skill.
Ashleigh Worley '22 is a writer at Southern New Hampshire University, where she earned her Bachelor of Arts in English. She is currently pursuing a Master of Fine Arts in Creative Writing at SNHU. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

How to Become a Social Worker

What is Political Science All About?

SNHU Spotlight: Mellissa Honings, BA in Psychology Grad
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.
- International edition
- Australia edition
- Europe edition

Behavioural scientist Michael Norton: ‘When a tennis player ties their shoes in a particular way, they feel they can play at Wimbledon’
The Harvard professor reveals how everyday rituals can help us cope with pressure, unlock our emotions and define our identities – but can also become unhelpful and divisive
M ichael Norton studied psychology and was a fellow at the MIT Media Lab before becoming professor of business administration at Harvard Business School. Known for his research on behavioural economics and wellbeing, Norton published his first book, Happy Money: The New Science of Smarter Spending , with Elizabeth Dunn , in 2013. For his latest, The Ritual Effect: The Transformative Power of Our Everyday Actions , out on 18 April, Norton spent more than a decade surveying thousands of people about the role of ritual in their lives.
Rituals seem a tricky subject for scientific study. How do you categorise them and measure their effect? It felt very daunting at first, because you can’t randomly assign people to families and have them do different rituals, then follow up in 12 years. At first I was going to study obvious things like weddings and funerals, but when we surveyed people, we found that they had all these other things they made up – in their families, with a significant other, with people at work. That opened it up a lot. We could look at these kinds of rituals and see when people do them. We could measure their emotions, we could really start to get traction on what these things are doing in our lives.
So what are they doing? What is the “ritual effect”, as you call it? One of the things that rituals do is help us to unlock emotions that may otherwise be hard to unlock. You can experience awe or wonder if you go to the Grand Canyon, for example, but it’s hard to go there every day. And so we use these rituals to help us feel in different ways. We use them to cope with grief, to amp ourselves up, to calm ourselves down, or whatever we need in the moment.
Is that what distinguishes rituals from habits – the emotional component? That’s a big part of it. We describe habits as the “what”, as the thing that you’re doing, whereas rituals are what you’re building around it. Take a mundane action like tying your shoes. It’s boring, and yet when a tennis player does it in a particular way, they feel like they can go out and play at Wimbledon. So rituals bring emotion and meaning.
You write that rituals can also reinforce or even create a sense of identity. Think about families at dinner. At a very basic level, they’re putting calories in their faces. But when families are eating a cake that their great-grandmother made, it’s a connection to the past and a sense of “who we are as a family”.
Do you think there’s something deep in the human brain that attracts us to ritual? There is some neuroscience on this, but from my perspective as a behavioural scientist there are very few things that humans use in every situation, in response to various problems, and ritual is one of them. I think that suggests there’s something inside us that turns to ritual. Go back thousands of years and you can find evidence that we were doing them then too – ceremonial burials, for example.
Why do so many top athletes and musicians rely on rituals before they perform? This is one of the most fun things to study. There is research showing that, as things become more stressful, we’re more likely to behave in ritualistic ways. I have stress in my life, but not like Beyoncé has stress, and I’d look very strange if I did her elaborate rituals before teaching a class. Culturally, we allow people who are doing very stressful things to do elaborate rituals without really judging them. Research shows that they also help us to be a little less reactive to our errors during a performance.
From your research, how important are rituals in romantic relationships? Sometimes people ask: “What’s your favourite ritual that you’ve ever come across?” And there are lots, but my favourite is this couple who said they clink forks three times before they eat. If I say that to an audience, there’s an instantaneous “ Awwwww ”. We do see in our research that rituals serve as a signal of commitment (we don’t know fully whether couples who already love each other are more likely to engage in rituals – the causal arrows are hard to tease apart). You can get married and sign papers to show that you’re committed, but day to day it’s these little actions that we’ve been doing for years that signal “we’re in this, this is us, we’re going to keep doing this”. And when couples stop clinking forks, it’s often very upsetting.
What about rituals in family relationships? Families that report having rituals around holidays are more likely to say that they feel close to one another, and they’re more likely to get together for those holidays. So there’s a cementing function that draws us back. As with couples, we don’t know if families that love each other are more likely to develop rituals, but there is something there.
Rituals aren’t always beneficial, they can be damaging at both individual and societal levels. On the individual level, if a ritual gets interrupted, it can really throw us off. And as rituals become too central, they can start to interfere. And that’s where we see issues such as obsessive compulsive disorder, where the ritual itself becomes the goal. Instead of checking the door is locked so you can get on with your day, the checking itself becomes the goal and you don’t end up doing the thing you had to do.
On a societal level, rituals can divide as well as unite. I taught a class the other day, and I often do this thing where I have everybody stand up and perform a made-up ritual that involves clapping, and it’s very fun, but if somebody claps at the wrong time, people look really annoyed. If that happens with a made-up ritual, you can see how, at a broader level, when history and culture and tradition come into play, even minor differences can become a real point of contention.
What do you hope people get out of the book? I really love when people notice the things they’re already doing. It’s almost like you laugh at yourself a bit, but from then on, when you do it, it has a different resonance because you owned it – it’s your ritual. And I want to encourage people to experiment. If you don’t do a ritual before your big stressful presentation, try something out. If it doesn’t work for you, that’s fine, but I like the idea of having these tools that we can experiment with and see if they can help us.
The Ritual Effect: The Transformative Power of Our Everyday Actions by Michael Norton is published by Penguin (£20). To support the Guardian and Observer order your copy at guardianbookshop.com . Delivery charges may apply
- The Observer
- Science and nature books
Comments (…)
Most viewed.
April 2, 2024
Eclipse Psychology: When the Sun and Moon Align, So Do We
How a total solar eclipse creates connection, unity and caring among the people watching
By Katie Weeman

Students observing a partial solar eclipse on June 21, 2020, in Lhokseumawe, Aceh Province, Indonesia.
NurPhoto/Getty Images
This article is part of a special report on the total solar eclipse that will be visible from parts of the U.S., Mexico and Canada on April 8, 2024.
It was 11:45 A.M. on August 21, 2017. I was in a grassy field in Glendo, Wyo., where I was surrounded by strangers turned friends, more than I could count—and far more people than had ever flocked to this town, population 210 or so. Golden sunlight blanketed thousands of cars parked in haphazard rows all over the rolling hills. The shadows were quickly growing longer, the air was still, and all of our faces pointed to the sky. As the moon progressively covered the sun, the light melted away, the sky blackened, and the temperature dropped. At the moment of totality, when the moon completely covered the sun , some people around me suddenly gasped. Some cheered; some cried; others laughed in disbelief.
Exactly 53 minutes later, in a downtown park in Greenville, S.C., the person who edited this story and the many individuals around him reacted in exactly the same ways.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
When a total solar eclipse descends—as one will across Mexico, the U.S. and Canada on April 8—everyone and everything in the path of totality are engulfed by deep shadow. Unlike the New Year’s Eve countdown that lurches across the globe one blocky time zone after another, the shadow of totality is a dark spot on Earth that measures about 100 miles wide and cruises steadily along a path, covering several thousand miles in four to five hours. The human experiences along that path are not isolated events any more than individual dominoes are isolated pillars in a formation. Once that first domino is tipped, we are all linked into something bigger—and unstoppable. We all experience the momentum and the awe together.
When this phenomenon progresses from Mexico through Texas, the Great Lakes and Canada on April 8, many observers will describe the event as life-changing, well beyond expectations. “You feel a sense of wrongness in those moments before totality , when your surroundings change so rapidly,” says Kate Russo, an author, psychologist and eclipse chaser. “Our initial response is to ask ourselves, ‘Is this an opportunity or a threat?’ When the light changes and the temperature drops, that triggers primal fear. When we have that threat response, our whole body is tuned in to taking in as much information as possible.”
Russo, who has witnessed 13 total eclipses and counting, has interviewed eclipse viewers from around the world. She continues to notice the same emotions felt by all. They begin with that sense of wrongness and primal fear as totality approaches. When totality starts, we feel powerful awe and connection to the world around us. A sense of euphoria develops as we continue watching, and when it’s over, we have a strong desire to seek out the next eclipse.
“The awe we feel during a total eclipse makes us think outside our sense of self. It makes you more attuned to things outside of you,” says Sean Goldy, a postdoctoral fellow at the department of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins University.
Goldy and his team analyzed Twitter data from nearly 2.9 million people during the 2017 total solar eclipse. They found that people within the path of totality were more likely to use not only language that expressed awe but also language that conveyed being unified and affiliated with others. That meant using more “we” words (“us” instead of “me”) and more humble words (“maybe” instead of “always”).
“During an eclipse, people have a broader, more collective focus,” Goldy says. “We also found that the more people expressed awe, the more likely they were to use those ‘we’ words, indicating that people who experience this emotion feel more connected with others.”
This connectivity ties into a sociological concept known as “collective effervescence,” Russo and Goldy say. When groups of humans come together over a shared experience, the energy is greater than the sum of its parts. If you’ve ever been to a large concert or sporting event, you’ve felt the electricity generated by a hive of humans. It magnifies our emotions.
I felt exactly that unified feeling in the open field in Glendo, as if thousands of us were breathing as one. But that’s not the only way people can experience a total eclipse.
During the 2008 total eclipse in Mongolia “I was up on a peak,” Russo recounts. “I was with only my husband and a close friend. We had left the rest of our 25-person tour group at the bottom of the hill. From that vantage point, when the shadow came sweeping in, there was not one man-made thing I could see: no power lines, no buildings or structures. Nothing tethered me to time: It could have been thousands of years ago or long into the future. In that moment, it was as if time didn’t exist.”
Giving us the ability to unhitch ourselves from time—to stop dwelling on time is a unique superpower of a total eclipse. In Russo’s work as a clinical psychologist, she notices patterns in our modern-day mentality. “People with anxiety tend to spend a lot of time in the future. And people with depression spend a lot of time in the past,” she says. An eclipse, time and time again, has the ability to snap us back into the present, at least for a few minutes. “And when you’re less anxious and worried, it opens you up to be more attuned to other people, feel more connected, care for others and be more compassionate,” Goldy says.
Russo, who founded Being in the Shadow , an organization that provides information about total solar eclipses and organizes eclipse events around the world, has experienced this firsthand. Venue managers regularly tell her that eclipse crowds are among the most polite and humble: they follow the rules; they pick up their garbage—they care.
Eclipses remind us that we are part of something bigger, that we are connected with something vast. In the hours before and after totality you have to wear protective glasses to look at the sun, to prevent damage to your eyes. But during the brief time when the moon blocks the last of the sun’s rays, you can finally lower your glasses and look directly at the eclipse. It’s like making eye contact with the universe.
“In my practice, usually if someone says, ‘I feel insignificant,’ that’s a negative thing. But the meaning shifts during an eclipse,” Russo says. To feel insignificant in the moon’s shadow instead means that your sense of self shrinks, that your ego shrinks, she says.
The scale of our “big picture” often changes after witnessing the awe of totality, too. “When you zoom out—really zoom out—it blows away our differences,” Goldy says. When you sit in the shadow of a celestial rock blocking the light of a star 400 times its size that burns at 10,000 degrees Fahrenheit on its surface, suddenly that argument with your partner, that bill sitting on your counter or even the differences among people’s beliefs, origins or politics feel insignificant. When we shift our perspective, connection becomes boundless.
You don’t need to wait for the next eclipse to feel this way. As we travel through life, we lose our relationship with everyday awe. Remember what that feels like? It’s the way a dog looks at a treat or the way my toddler points to the “blue sky!” outside his car window in the middle of rush hour traffic. To find awe, we have to surrender our full attention to the beauty around us. During an eclipse, that comes easily. In everyday life, we may need to be more intentional.
“Totality kick-starts our ability to experience wonder,” Russo says. And with that kick start, maybe we can all use our wonderment faculties more—whether that means pausing for a moment during a morning walk, a hug or a random sunset on a Tuesday. In the continental U.S., we won’t experience another total eclipse until 2044. Let’s not wait until then to seek awe and connection.
A Psychologist Explains Four Reasons the Internet Feels So Broken Plain English with Derek Thompson
- News Commentary
Jay Van Bavel is a professor of psychology and neural science at New York University. His lab has published papers on how the internet became a fun-house mirror of extreme political opinions, why the news media has a strong negativity bias, why certain emotions go viral online, why tribalism is inflamed by online activity, and how the internet can make us seem like the worst versions of ourselves. At the same time, Van Bavel emphasizes that many of the group psychology dynamics that can make social media seem like a dumpster fire are also core to what makes humankind such a special and ingenious species. We discuss the four dark laws of online engagement and the basics of group psychology. If you have questions, observations, or ideas for future episodes, email us at [email protected]. Host: Derek Thompson Guest: Jay Van Bavel Producer: Devon Baroldi Learn more about your ad choices. Visit podcastchoices.com/adchoices
- More Episodes
- © All rights reserved.
A Solar Eclipse Means Big Science
By Katrina Miller April 1, 2024
- Share full article

On April 8, cameras all over North America will make a “megamovie” of the sun’s corona, like this one from the 2017 eclipse. The time lapse will help scientists track the behavior of jets and plumes on the sun’s surface.
There’s more science happening along the path of totality →
An app named SunSketcher will help the public take pictures of the eclipse with their phones.
Scientists will use these images to study deviations in the shape of the solar surface , which will help them understand the sun’s churning behavior below.
The sun right now is approaching peak activity. More than 40 telescope stations along the eclipse’s path will record totality.
By comparing these videos to what was captured in 2017 — when the sun was at a lull — researchers can learn how the sun’s magnetism drives the solar wind, or particles that stream through the solar system.
Students will launch giant balloons equipped with cameras and sensors along the eclipse’s path.
Their measurements may improve weather forecasting , and also produce a bird’s eye view of the moon’s shadow moving across the Earth.
Ham radio operators will send signals to each other across the path of totality to study how the density of electrons in Earth’s upper atmosphere changes .
This can help quantify how space weather produced by the sun disrupts radar communication systems.
(Animation by Dr. Joseph Huba, Syntek Technologies; HamSCI Project, Dr. Nathaniel Frissell, the University of Scranton, NSF and NASA.)
NASA is also studying Earth’s atmosphere, but far from the path of totality.
In Virginia, the agency will launch rockets during the eclipse to measure how local drops in sunlight cause ripple effects hundreds of miles away . The data will clarify how eclipses and other solar events affect satellite communications, including GPS.
Biologists in San Antonio plan to stash recording devices in beehives to study how bees orient themselves using sunlight , and how the insects respond to the sudden atmospheric changes during a total eclipse.
Two researchers in southern Illinois will analyze social media posts to understand tourism patterns in remote towns , including when visitors arrive, where they come from and what they do during their visits.
Results can help bolster infrastructure to support large events in rural areas.
Read more about the eclipse:

Advertisement

2024 Ethics Essay Contest winners announced
Claire Martino , a junior from New Berlin, Wis., majoring in applied mathematics and data science, is the winner of the 2024 Ethics Essay Contest for the essay "Artificial Intelligence Could Probably Write This Essay Better than Me."
The second place entry was from Morgan J. Janes , a junior from Rock Island, Ill., majoring in biology, for the essay "The Relevant History and Medical and Ethical Future Viability of Xenotransplantation."
Third place went to Alyssa Scudder , a senior from Lee, Ill., majoring in biology, for the essay "The Ethicality of Gene Alteration in Human Embryos."
Dr. Dan Lee announced the winners on behalf of the board of directors of the Augustana Center for the Study of Ethics, sponsor of the contest. The winner will receive an award of $100, the second-place winner an award of $50, and the third-place winner an award of $25.
Honorable mentions went to Grace Palmer , a senior art and accounting double major from Galesburg, Ill., for the essay "The Ethiopian Coffee Trade: Is Positive Change Brewing?" and Sarah Marrs , a sophomore from Carpentersville, Ill., majoring in political science and women, gender and sexuality studies, for the essay "Dating Apps as an Outlet to Promote Sexual Autonomy among Disabled Individuals: an Intersectional Approach to Change."
The winning essays will be published in Augustana Digital Commons .
The Augustana Center for the Study of Ethics was established to enrich the teaching-learning experiences for students by providing greater opportunities for them to meet and interact with community leaders and to encourage discussions of issues of ethical significance through campus programs and community outreach.
Dr. Lee, whose teaching responsibilities since joining the Augustana faculty in 1974 have included courses in ethics, serves as the center's director.
If you have news, send it to [email protected] ! We love hearing about the achievements of our alumni, students and faculty.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
On This Page: Psychology is a science because it employs systematic methods of observation, experimentation, and data analysis to understand and predict behavior and mental processes, grounded in empirical evidence and subjected to peer review. Science uses an empirical approach. Empiricism (founded by John Locke) states that the only source of ...
Defining Psychology as a Science. Let's turn from defining science to defining psychology. In what follows, I will be referring to psychology as it is presented in the academy, such as in Psych ...
Psychology is the scientific study of the human mind and behavior. It seeks to understand and explain thoughts, emotions, and actions through systematic observation, measurement, and analysis. While some may argue that psychology is not a science due to its subjective nature, the field has made significant strides in establishing itself as a ...
But Galtonian nomothetic methodology has turned much of today's psychology into a science of populations rather than individuals, showing that blind adherence to natural-science principles has not advanced but impeded the development of psychology as a science. ... Collected papers of Charles Sanders Peirce (CP 7.218—1901, On the logic of ...
The science of psychology is important for both researchers and practitioners. In a sense all humans are scientists. We all have an interest in asking and answering questions about our world. We want to know why things happen, when and if they are likely to happen again, and how to reproduce or change them. Such knowledge enables us to predict ...
However, most of the other attributes of psychology reinforce the claim that psychology is indeed a fully-fledged science deserving the same merits as physics or any of the other "accepted" sciences. This being the case, we can authoritatively state that psychology is indeed a true science. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder: Definition, Types ...
The term psychology can be broken down into its root words that are Greek. Psyche means "mind" or "soul.". Logos means "the study of.". Psychology is the study of mental processes and human behavior. Psychology consists of the following scientific steps: Collecting facts. Developing theories and hypotheses to explain the facts.
Understanding psychology involves mastering writing methods for essays. It's about communicating complex scientific ideas clearly and concisely. Psychology research can shed light on common mistakes in foreign university applications, such as cultural misunderstandings or misinterpretation of academic norms.
The short answer is yes, but the long answer is much more expansive and flexible. Psychology begins with the scientific method, and researchers employ many of the same methods as their colleagues in the natural and physical sciences, but psychology also calls for a deep understanding of human behavior that goes beyond science alone.
Perhaps the clearest definition of a "science" is any endeavor that uses the scientific method. Like all scientists, psychology researchers form hypotheses, devise experiments to gather data ...
The British Psychological Society states that 'Psychology is the scientific study of people, the mind and behaviour' (BPS). In this essay I will be discussing what is actually meant by this and whether psychology fits into both the traditional views of a science, as well as more contemporary perspectives. It is widely suggested that ...
The question of what makes a given discipline a science is complex (see Chalmers, 2013, for an excellent discussion).Nonetheless, while it is possible to establish a list of reasonable criteria that define science (e.g., Coyne, 2015), it is highly unlikely that people do so in order to determine whether or not psychology is a science.Considering that people typically act like "cognitive ...
The need for a critical psychology, or simply a responsible, real science, that treats itself as part of the problem, and not solely as an exclusive part of the solution, is therefore greater than ...
The question - 'Is psychology a science' has always been debatable, however, before jumping to conclusions it is important to consider the definition of science. Science originates from the Latin, meaning 'knowledge', therefore it can have reference to something that we know to be true rather than what we believe to be true. Science ...
However, the view that psychology must be approached as a science has become ingrained in the field over time, and critically discussing the implications of this notion has turned into a taboo. In this article, I examine the benefits and limitations of applying the scientific paradigm to psychology, and I propose when it is not optimal to ...
Wilhelm Wundt, who noted psychology as a science, was important because he separated psychology from philosophy by studying the workings of the mind in a more structured way, with more focus being on objective measurement and control. This is known as the empirical method, which uses "verifiable" evidence by observing a subject in a ...
It appears that whether or not psychology is a science depends on one's own philosophical point of view. It is also important to point out that there is no definitive philosophy of science or perfect research methodology. Slife and Williams (1997) argue that psychology should not give up on striving for scientific methods if the discipline is ...
When writing a cohesive psychology essay, students must be familiar with some psychological concepts. We have a wealth of experience under our belt, so we know where they need help. Although you may be able to find better deals elsewhere, there is no way to tell if these sites offer superior customer service and top-quality results. ...
Psychology is a science because it uses scientific methods. Psychology shows characteristics of scientific methods. Psychology uses theories that generate hypotheses. The hypotheses are verified using empirical methods and observations. Psychology is also considered science due to its theories that can be criticized.
Psychology as not a Science. Whereas psychology has been frequently defined as the "scientific" study of mind processes and behavior, the raw data that psychologists rely on human behavior to illustrate the functioning of human brain. The fundamental criticism that scientists level against psychologists as being their peers is the fact that ...
4. This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Cite This Essay. Download. On the off chance that one is a science or even has a passing enthusiasm for the field, one has likely experienced the inquiry regarding whether psychology is really a ...
Psychology holds an exceptional position among the sciences. Yet even after 140 years as an independent discipline, psychology is still struggling with its most basic foundations. Its key phenomena, mind and behaviour, are poorly defined (and their definition instead often delegated to neuroscience or philosophy) while specific terms and constructs proliferate. A unified theoretical framework ...
PSY 101. There seem to be two ways to look at psychology. Some experts and scholars claim that psychology is without question a science. There are also those that argue it is not an exact science, but rather concepts of common sense in a well arranged package. In this essay, I will attempt to argue both sides of the debate and conclude with my ...
A psychology degree can help prepare you for higher education or provide you with skills applicable in any field. If you are interested in a career working with people, such as education, human resources or counseling, a psychology degree might be worth it for you. Ashleigh Worley. Apr 10, 2024. Explore Psychology.
Essay Example: Stages skeleton analysis three is a basic concept in well-assorted disciplines so as for example terms, sociology, psychology, and political science international. It offers the access structured despite understanding difficult appearances, breaks them in legible three : stages.
M ichael Norton studied psychology and was a fellow at the MIT Media Lab before ... The New Science of Smarter Spending, with ... You can get married and sign papers to show that you're ...
This article is part of a special report on the total solar eclipse that will be visible from parts of the U.S., Mexico and Canada on April 8, 2024. It was 11:45 A.M. on August 21, 2017. I was in ...
Jay Van Bavel is a professor of psychology and neural science at New York University. His lab has published papers on how the internet became a fun-house mirror of extreme political opinions, why the news media has a strong negativity bias, why certain emotions go viral online, why tribalism is inflamed by online activity, and how the internet can make us seem like the worst versions of ourselves.
A Solar Eclipse Means Big Science. On April 8, cameras all over North America will make a "megamovie" of the sun's corona, like this one from the 2017 eclipse. The time lapse will help ...
Claire Martino, a junior from New Berlin, Wis., majoring in applied mathematics and data science, is the winner of the 2024 Ethics Essay Contest for the essay "Artificial Intelligence Could Probably Write This Essay Better than Me.". The second place entry was from Morgan J. Janes, a junior from Rock Island, Ill., majoring in biology, for the essay "The Relevant History and Medical and Ethical ...