
Peer Recognized
Make a name in academia

How to Write a Research Paper: the LEAP approach (+cheat sheet)
In this article I will show you how to write a research paper using the four LEAP writing steps. The LEAP academic writing approach is a step-by-step method for turning research results into a published paper .
The LEAP writing approach has been the cornerstone of the 70 + research papers that I have authored and the 3700+ citations these paper have accumulated within 9 years since the completion of my PhD. I hope the LEAP approach will help you just as much as it has helped me to make an real, tangible impact with my research.
What is the LEAP research paper writing approach?
I designed the LEAP writing approach not only for merely writing the papers. My goal with the writing system was to show young scientists how to first think about research results and then how to efficiently write each section of the research paper.
In other words, you will see how to write a research paper by first analyzing the results and then building a logical, persuasive arguments. In this way, instead of being afraid of writing research paper, you will be able to rely on the paper writing process to help you with what is the most demanding task in getting published – thinking.
The four research paper writing steps according to the LEAP approach:

I will show each of these steps in detail. And you will be able to download the LEAP cheat sheet for using with every paper you write.
But before I tell you how to efficiently write a research paper, I want to show you what is the problem with the way scientists typically write a research paper and why the LEAP approach is more efficient.
How scientists typically write a research paper (and why it isn’t efficient)
Writing a research paper can be tough, especially for a young scientist. Your reasoning needs to be persuasive and thorough enough to convince readers of your arguments. The description has to be derived from research evidence, from prior art, and from your own judgment. This is a tough feat to accomplish.
The figure below shows the sequence of the different parts of a typical research paper. Depending on the scientific journal, some sections might be merged or nonexistent, but the general outline of a research paper will remain very similar.

Here is the problem: Most people make the mistake of writing in this same sequence.
While the structure of scientific articles is designed to help the reader follow the research, it does little to help the scientist write the paper. This is because the layout of research articles starts with the broad (introduction) and narrows down to the specifics (results). See in the figure below how the research paper is structured in terms of the breath of information that each section entails.
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach
For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
For example, it might feel intimidating to start writing a research paper by explaining your research’s global significance in the introduction, while it is easy to plot the figures in the results. When plotting the results, there is not much room for wiggle: the results are what they are.
Starting to write a research papers from the results is also more fun because you finally get to see and understand the complete picture of the research that you have worked on.
Most importantly, following the LEAP approach will help you first make sense of the results yourself and then clearly communicate them to the readers. That is because the sequence of writing allows you to slowly understand the meaning of the results and then develop arguments for presenting to your readers.
I have personally been able to write and submit a research article in three short days using this method.
Step 1: Lay Out the Facts

You have worked long hours on a research project that has produced results and are no doubt curious to determine what they exactly mean. There is no better way to do this than by preparing figures, graphics and tables. This is what the first LEAP step is focused on – diving into the results.
How to p repare charts and tables for a research paper
Your first task is to try out different ways of visually demonstrating the research results. In many fields, the central items of a journal paper will be charts that are based on the data generated during research. In other fields, these might be conceptual diagrams, microscopy images, schematics and a number of other types of scientific graphics which should visually communicate the research study and its results to the readers. If you have reasonably small number of data points, data tables might be useful as well.
Tips for preparing charts and tables
- Try multiple chart types but in the finished paper only use the one that best conveys the message you want to present to the readers
- Follow the eight chart design progressions for selecting and refining a data chart for your paper: https://peerrecognized.com/chart-progressions
- Prepare scientific graphics and visualizations for your paper using the scientific graphic design cheat sheet: https://peerrecognized.com/tools-for-creating-scientific-illustrations/
How to describe the results of your research
Now that you have your data charts, graphics and tables laid out in front of you – describe what you see in them. Seek to answer the question: What have I found? Your statements should progress in a logical sequence and be backed by the visual information. Since, at this point, you are simply explaining what everyone should be able to see for themselves, you can use a declarative tone: The figure X demonstrates that…
Tips for describing the research results :
- Answer the question: “ What have I found? “
- Use declarative tone since you are simply describing observations
Step 2: Explain the results

The core aspect of your research paper is not actually the results; it is the explanation of their meaning. In the second LEAP step, you will do some heavy lifting by guiding the readers through the results using logic backed by previous scientific research.
How to define the Message of a research paper
To define the central message of your research paper, imagine how you would explain your research to a colleague in 20 seconds . If you succeed in effectively communicating your paper’s message, a reader should be able to recount your findings in a similarly concise way even a year after reading it. This clarity will increase the chances that someone uses the knowledge you generated, which in turn raises the likelihood of citations to your research paper.
Tips for defining the paper’s central message :
- Write the paper’s core message in a single sentence or two bullet points
- Write the core message in the header of the research paper manuscript
How to write the Discussion section of a research paper
In the discussion section you have to demonstrate why your research paper is worthy of publishing. In other words, you must now answer the all-important So what? question . How well you do so will ultimately define the success of your research paper.
Here are three steps to get started with writing the discussion section:
- Write bullet points of the things that convey the central message of the research article (these may evolve into subheadings later on).
- Make a list with the arguments or observations that support each idea.
- Finally, expand on each point to make full sentences and paragraphs.
Tips for writing the discussion section:
- What is the meaning of the results?
- Was the hypothesis confirmed?
- Write bullet points that support the core message
- List logical arguments for each bullet point, group them into sections
- Instead of repeating research timeline, use a presentation sequence that best supports your logic
- Convert arguments to full paragraphs; be confident but do not overhype
- Refer to both supportive and contradicting research papers for maximum credibility
How to write the Conclusions of a research paper
Since some readers might just skim through your research paper and turn directly to the conclusions, it is a good idea to make conclusion a standalone piece. In the first few sentences of the conclusions, briefly summarize the methodology and try to avoid using abbreviations (if you do, explain what they mean).
After this introduction, summarize the findings from the discussion section. Either paragraph style or bullet-point style conclusions can be used. I prefer the bullet-point style because it clearly separates the different conclusions and provides an easy-to-digest overview for the casual browser. It also forces me to be more succinct.
Tips for writing the conclusion section :
- Summarize the key findings, starting with the most important one
- Make conclusions standalone (short summary, avoid abbreviations)
- Add an optional take-home message and suggest future research in the last paragraph
How to refine the Objective of a research paper
The objective is a short, clear statement defining the paper’s research goals. It can be included either in the final paragraph of the introduction, or as a separate subsection after the introduction. Avoid writing long paragraphs with in-depth reasoning, references, and explanation of methodology since these belong in other sections. The paper’s objective can often be written in a single crisp sentence.
Tips for writing the objective section :
- The objective should ask the question that is answered by the central message of the research paper
- The research objective should be clear long before writing a paper. At this point, you are simply refining it to make sure it is addressed in the body of the paper.
How to write the Methodology section of your research paper
When writing the methodology section, aim for a depth of explanation that will allow readers to reproduce the study . This means that if you are using a novel method, you will have to describe it thoroughly. If, on the other hand, you applied a standardized method, or used an approach from another paper, it will be enough to briefly describe it with reference to the detailed original source.
Remember to also detail the research population, mention how you ensured representative sampling, and elaborate on what statistical methods you used to analyze the results.
Tips for writing the methodology section :
- Include enough detail to allow reproducing the research
- Provide references if the methods are known
- Create a methodology flow chart to add clarity
- Describe the research population, sampling methodology, statistical methods for result analysis
- Describe what methodology, test methods, materials, and sample groups were used in the research.
Step 3: Advertize the research
Step 3 of the LEAP writing approach is designed to entice the casual browser into reading your research paper. This advertising can be done with an informative title, an intriguing abstract, as well as a thorough explanation of the underlying need for doing the research within the introduction.

How to write the Introduction of a research paper
The introduction section should leave no doubt in the mind of the reader that what you are doing is important and that this work could push scientific knowledge forward. To do this convincingly, you will need to have a good knowledge of what is state-of-the-art in your field. You also need be able to see the bigger picture in order to demonstrate the potential impacts of your research work.
Think of the introduction as a funnel, going from wide to narrow, as shown in the figure below:
- Start with a brief context to explain what do we already know,
- Follow with the motivation for the research study and explain why should we care about it,
- Explain the research gap you are going to bridge within this research paper,
- Describe the approach you will take to solve the problem.
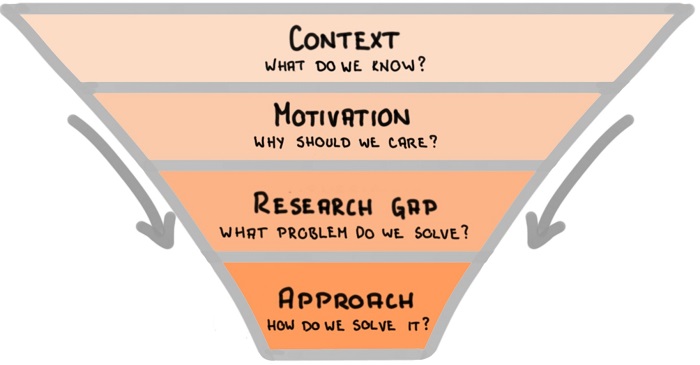
Tips for writing the introduction section :
- Follow the Context – Motivation – Research gap – Approach funnel for writing the introduction
- Explain how others tried and how you plan to solve the research problem
- Do a thorough literature review before writing the introduction
- Start writing the introduction by using your own words, then add references from the literature
How to prepare the Abstract of a research paper
The abstract acts as your paper’s elevator pitch and is therefore best written only after the main text is finished. In this one short paragraph you must convince someone to take on the time-consuming task of reading your whole research article. So, make the paper easy to read, intriguing, and self-explanatory; avoid jargon and abbreviations.
How to structure the abstract of a research paper:
- The abstract is a single paragraph that follows this structure:
- Problem: why did we research this
- Methodology: typically starts with the words “Here we…” that signal the start of own contribution.
- Results: what we found from the research.
- Conclusions: show why are the findings important
How to compose a research paper Title
The title is the ultimate summary of a research paper. It must therefore entice someone looking for information to click on a link to it and continue reading the article. A title is also used for indexing purposes in scientific databases, so a representative and optimized title will play large role in determining if your research paper appears in search results at all.
Tips for coming up with a research paper title:
- Capture curiosity of potential readers using a clear and descriptive title
- Include broad terms that are often searched
- Add details that uniquely identify the researched subject of your research paper
- Avoid jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords as title extension (instead of duplicating the words) to increase the chance of appearing in search results
How to prepare Highlights and Graphical Abstract
Highlights are three to five short bullet-point style statements that convey the core findings of the research paper. Notice that the focus is on the findings, not on the process of getting there.
A graphical abstract placed next to the textual abstract visually summarizes the entire research paper in a single, easy-to-follow figure. I show how to create a graphical abstract in my book Research Data Visualization and Scientific Graphics.
Tips for preparing highlights and graphical abstract:
- In highlights show core findings of the research paper (instead of what you did in the study).
- In graphical abstract show take-home message or methodology of the research paper. Learn more about creating a graphical abstract in this article.
Step 4: Prepare for submission

Sometimes it seems that nuclear fusion will stop on the star closest to us (read: the sun will stop to shine) before a submitted manuscript is published in a scientific journal. The publication process routinely takes a long time, and after submitting the manuscript you have very little control over what happens. To increase the chances of a quick publication, you must do your homework before submitting the manuscript. In the fourth LEAP step, you make sure that your research paper is published in the most appropriate journal as quickly and painlessly as possible.
How to select a scientific Journal for your research paper
The best way to find a journal for your research paper is it to review which journals you used while preparing your manuscript. This source listing should provide some assurance that your own research paper, once published, will be among similar articles and, thus, among your field’s trusted sources.
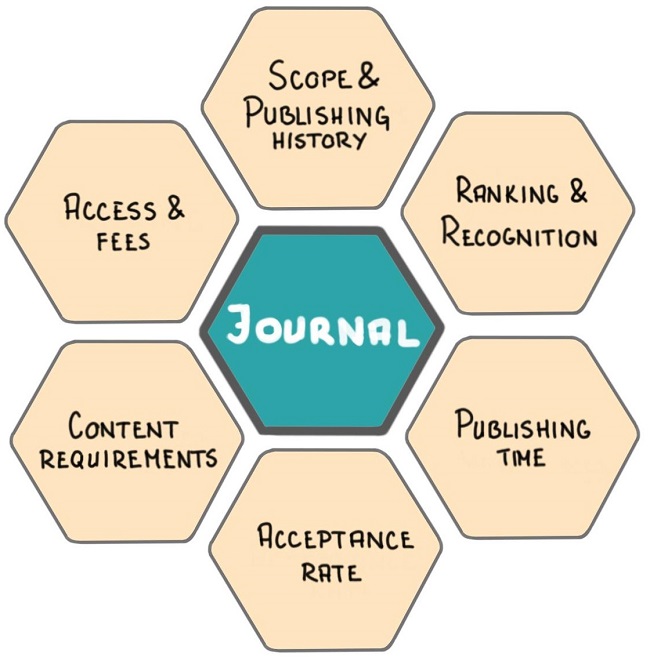
After this initial selection of hand-full of scientific journals, consider the following six parameters for selecting the most appropriate journal for your research paper (read this article to review each step in detail):
- Scope and publishing history
- Ranking and Recognition
- Publishing time
- Acceptance rate
- Content requirements
- Access and Fees
How to select a journal for your research paper:
- Use the six parameters to select the most appropriate scientific journal for your research paper
- Use the following tools for journal selection: https://peerrecognized.com/journals
- Follow the journal’s “Authors guide” formatting requirements
How to Edit you manuscript
No one can write a finished research paper on their first attempt. Before submitting, make sure to take a break from your work for a couple of days, or even weeks. Try not to think about the manuscript during this time. Once it has faded from your memory, it is time to return and edit. The pause will allow you to read the manuscript from a fresh perspective and make edits as necessary.
I have summarized the most useful research paper editing tools in this article.
Tips for editing a research paper:
- Take time away from the research paper to forget about it; then returning to edit,
- Start by editing the content: structure, headings, paragraphs, logic, figures
- Continue by editing the grammar and language; perform a thorough language check using academic writing tools
- Read the entire paper out loud and correct what sounds weird
How to write a compelling Cover Letter for your paper
Begin the cover letter by stating the paper’s title and the type of paper you are submitting (review paper, research paper, short communication). Next, concisely explain why your study was performed, what was done, and what the key findings are. State why the results are important and what impact they might have in the field. Make sure you mention how your approach and findings relate to the scope of the journal in order to show why the article would be of interest to the journal’s readers.
I wrote a separate article that explains what to include in a cover letter here. You can also download a cover letter template from the article.
Tips for writing a cover letter:
- Explain how the findings of your research relate to journal’s scope
- Tell what impact the research results will have
- Show why the research paper will interest the journal’s audience
- Add any legal statements as required in journal’s guide for authors
How to Answer the Reviewers
Reviewers will often ask for new experiments, extended discussion, additional details on the experimental setup, and so forth. In principle, your primary winning tactic will be to agree with the reviewers and follow their suggestions whenever possible. After all, you must earn their blessing in order to get your paper published.
Be sure to answer each review query and stick to the point. In the response to the reviewers document write exactly where in the paper you have made any changes. In the paper itself, highlight the changes using a different color. This way the reviewers are less likely to re-read the entire article and suggest new edits.
In cases when you don’t agree with the reviewers, it makes sense to answer more thoroughly. Reviewers are scientifically minded people and so, with enough logical and supported argument, they will eventually be willing to see things your way.
Tips for answering the reviewers:
- Agree with most review comments, but if you don’t, thoroughly explain why
- Highlight changes in the manuscript
- Do not take the comments personally and cool down before answering
The LEAP research paper writing cheat sheet
Imagine that you are back in grad school and preparing to take an exam on the topic: “How to write a research paper”. As an exemplary student, you would, most naturally, create a cheat sheet summarizing the subject… Well, I did it for you.
This one-page summary of the LEAP research paper writing technique will remind you of the key research paper writing steps. Print it out and stick it to a wall in your office so that you can review it whenever you are writing a new research paper.

Now that we have gone through the four LEAP research paper writing steps, I hope you have a good idea of how to write a research paper. It can be an enjoyable process and once you get the hang of it, the four LEAP writing steps should even help you think about and interpret the research results. This process should enable you to write a well-structured, concise, and compelling research paper.
Have fund with writing your next research paper. I hope it will turn out great!
Learn writing papers that get cited
The LEAP writing approach is a blueprint for writing research papers. But to be efficient and write papers that get cited, you need more than that.
My name is Martins Zaumanis and in my interactive course Research Paper Writing Masterclass I will show you how to visualize your research results, frame a message that convinces your readers, and write each section of the paper. Step-by-step.
And of course – you will learn to respond the infamous Reviewer No.2.

Hey! My name is Martins Zaumanis and I am a materials scientist in Switzerland ( Google Scholar ). As the first person in my family with a PhD, I have first-hand experience of the challenges starting scientists face in academia. With this blog, I want to help young researchers succeed in academia. I call the blog “Peer Recognized”, because peer recognition is what lifts academic careers and pushes science forward.
Besides this blog, I have written the Peer Recognized book series and created the Peer Recognized Academy offering interactive online courses.
Related articles:
One comment
- Pingback: Research Paper Outline with Key Sentence Skeleton (+Paper Template)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
I want to join the Peer Recognized newsletter!
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Copyright © 2024 Martins Zaumanis
Contacts: [email protected]
Privacy Policy
Writing an Introduction for a Scientific Paper
Dr. michelle harris, dr. janet batzli, biocore.
This section provides guidelines on how to construct a solid introduction to a scientific paper including background information, study question , biological rationale, hypothesis , and general approach . If the Introduction is done well, there should be no question in the reader’s mind why and on what basis you have posed a specific hypothesis.
Broad Question : based on an initial observation (e.g., “I see a lot of guppies close to the shore. Do guppies like living in shallow water?”). This observation of the natural world may inspire you to investigate background literature or your observation could be based on previous research by others or your own pilot study. Broad questions are not always included in your written text, but are essential for establishing the direction of your research.
Background Information : key issues, concepts, terminology, and definitions needed to understand the biological rationale for the experiment. It often includes a summary of findings from previous, relevant studies. Remember to cite references, be concise, and only include relevant information given your audience and your experimental design. Concisely summarized background information leads to the identification of specific scientific knowledge gaps that still exist. (e.g., “No studies to date have examined whether guppies do indeed spend more time in shallow water.”)
Testable Question : these questions are much more focused than the initial broad question, are specific to the knowledge gap identified, and can be addressed with data. (e.g., “Do guppies spend different amounts of time in water <1 meter deep as compared to their time in water that is >1 meter deep?”)
Biological Rationale : describes the purpose of your experiment distilling what is known and what is not known that defines the knowledge gap that you are addressing. The “BR” provides the logic for your hypothesis and experimental approach, describing the biological mechanism and assumptions that explain why your hypothesis should be true.
The biological rationale is based on your interpretation of the scientific literature, your personal observations, and the underlying assumptions you are making about how you think the system works. If you have written your biological rationale, your reader should see your hypothesis in your introduction section and say to themselves, “Of course, this hypothesis seems very logical based on the rationale presented.”
- A thorough rationale defines your assumptions about the system that have not been revealed in scientific literature or from previous systematic observation. These assumptions drive the direction of your specific hypothesis or general predictions.
- Defining the rationale is probably the most critical task for a writer, as it tells your reader why your research is biologically meaningful. It may help to think about the rationale as an answer to the questions— how is this investigation related to what we know, what assumptions am I making about what we don’t yet know, AND how will this experiment add to our knowledge? *There may or may not be broader implications for your study; be careful not to overstate these (see note on social justifications below).
- Expect to spend time and mental effort on this. You may have to do considerable digging into the scientific literature to define how your experiment fits into what is already known and why it is relevant to pursue.
- Be open to the possibility that as you work with and think about your data, you may develop a deeper, more accurate understanding of the experimental system. You may find the original rationale needs to be revised to reflect your new, more sophisticated understanding.
- As you progress through Biocore and upper level biology courses, your rationale should become more focused and matched with the level of study e ., cellular, biochemical, or physiological mechanisms that underlie the rationale. Achieving this type of understanding takes effort, but it will lead to better communication of your science.
***Special note on avoiding social justifications: You should not overemphasize the relevance of your experiment and the possible connections to large-scale processes. Be realistic and logical —do not overgeneralize or state grand implications that are not sensible given the structure of your experimental system. Not all science is easily applied to improving the human condition. Performing an investigation just for the sake of adding to our scientific knowledge (“pure or basic science”) is just as important as applied science. In fact, basic science often provides the foundation for applied studies.
Hypothesis / Predictions : specific prediction(s) that you will test during your experiment. For manipulative experiments, the hypothesis should include the independent variable (what you manipulate), the dependent variable(s) (what you measure), the organism or system , the direction of your results, and comparison to be made.
|
|
We hypothesized that reared in warm water will have a greater sexual mating response. (The dependent variable “sexual response” has not been defined enough to be able to make this hypothesis testable or falsifiable. In addition, no comparison has been specified— greater sexual mating response as compared to what?) | We hypothesized that ) reared in warm water temperatures ranging from 25-28 °C ( ) would produce greater ( ) numbers of male offspring and females carrying haploid egg sacs ( ) than reared in cooler water temperatures of 18-22°C. |
If you are doing a systematic observation , your hypothesis presents a variable or set of variables that you predict are important for helping you characterize the system as a whole, or predict differences between components/areas of the system that help you explain how the system functions or changes over time.
|
|
We hypothesize that the frequency and extent of algal blooms in Lake Mendota over the last 10 years causes fish kills and imposes a human health risk. (The variables “frequency and extent of algal blooms,” “fish kills” and “human health risk” have not been defined enough to be able to make this hypothesis testable or falsifiable. How do you measure algal blooms? Although implied, hypothesis should express predicted direction of expected results [ , higher frequency associated with greater kills]. Note that cause and effect cannot be implied without a controlled, manipulative experiment.) | We hypothesize that increasing ( ) cell densities of algae ( ) in Lake Mendota over the last 10 years is correlated with 1. increased numbers of dead fish ( ) washed up on Madison beaches and 2. increased numbers of reported hospital/clinical visits ( .) following full-body exposure to lake water. |
Experimental Approach : Briefly gives the reader a general sense of the experiment, the type of data it will yield, and the kind of conclusions you expect to obtain from the data. Do not confuse the experimental approach with the experimental protocol . The experimental protocol consists of the detailed step-by-step procedures and techniques used during the experiment that are to be reported in the Methods and Materials section.
Some Final Tips on Writing an Introduction
- As you progress through the Biocore sequence, for instance, from organismal level of Biocore 301/302 to the cellular level in Biocore 303/304, we expect the contents of your “Introduction” paragraphs to reflect the level of your coursework and previous writing experience. For example, in Biocore 304 (Cell Biology Lab) biological rationale should draw upon assumptions we are making about cellular and biochemical processes.
- Be Concise yet Specific: Remember to be concise and only include relevant information given your audience and your experimental design. As you write, keep asking, “Is this necessary information or is this irrelevant detail?” For example, if you are writing a paper claiming that a certain compound is a competitive inhibitor to the enzyme alkaline phosphatase and acts by binding to the active site, you need to explain (briefly) Michaelis-Menton kinetics and the meaning and significance of Km and Vmax. This explanation is not necessary if you are reporting the dependence of enzyme activity on pH because you do not need to measure Km and Vmax to get an estimate of enzyme activity.
- Another example: if you are writing a paper reporting an increase in Daphnia magna heart rate upon exposure to caffeine you need not describe the reproductive cycle of magna unless it is germane to your results and discussion. Be specific and concrete, especially when making introductory or summary statements.
Where Do You Discuss Pilot Studies? Many times it is important to do pilot studies to help you get familiar with your experimental system or to improve your experimental design. If your pilot study influences your biological rationale or hypothesis, you need to describe it in your Introduction. If your pilot study simply informs the logistics or techniques, but does not influence your rationale, then the description of your pilot study belongs in the Materials and Methods section.
from an Intro Ecology Lab: Researchers studying global warming predict an increase in average global temperature of 1.3°C in the next 10 years (Seetwo 2003). are small zooplankton that live in freshwater inland lakes. They are filter-feeding crustaceans with a transparent exoskeleton that allows easy observation of heart rate and digestive function. Thomas et al (2001) found that heart rate increases significantly in higher water temperatures are also thought to switch their mode of reproduction from asexual to sexual in response to extreme temperatures. Gender is not mediated by genetics, but by the environment. Therefore, reproduction may be sensitive to increased temperatures resulting from global warming (maybe a question?) and may serve as a good environmental indicator for global climate change. In this experiment we hypothesized that reared in warm water will switch from an asexual to a sexual mode of reproduction. In order to prove this hypothesis correct we observed grown in warm and cold water and counted the number of males observed after 10 days. Comments: Background information · Good to recognize as a model organism from which some general conclusions can be made about the quality of the environment; however no attempt is made to connect increased lake temperatures and gender. Link early on to increase focus. · Connection to global warming is too far-reaching. First sentence gives impression that Global Warming is topic for this paper. Changes associated with global warming are not well known and therefore little can be concluded about use of as indicator species. · Information about heart rate is unnecessary because heart rate in not being tested in this experiment. Rationale · Rationale is missing; how is this study related to what we know about D. magna survivorship and reproduction as related to water temperature, and how will this experiment contribute to our knowledge of the system? · Think about the ecosystem in which this organism lives and the context. Under what conditions would D. magna be in a body of water with elevated temperatures? Hypothesis · Not falsifiable; variables need to be better defined (state temperatures or range tested rather than “warm” or “cold”) and predict direction and magnitude of change in number of males after 10 days. · It is unclear what comparison will be made or what the control is · What dependent variable will be measured to determine “switch” in mode of reproduction (what criteria are definitive for switch?) Approach · Hypotheses cannot be “proven” correct. They are either supported or rejected. | Introduction are small zooplankton found in freshwater inland lakes and are thought to switch their mode of reproduction from asexual to sexual in response to extreme temperatures (Mitchell 1999). Lakes containing have an average summer surface temperature of 20°C (Harper 1995) but may increase by more than 15% when expose to warm water effluent from power plants, paper mills, and chemical industry (Baker et al. 2000). Could an increase in lake temperature caused by industrial thermal pollution affect the survivorship and reproduction of ? The sex of is mediated by the environment rather than genetics. Under optimal environmental conditions, populations consist of asexually reproducing females. When the environment shifts may be queued to reproduce sexually resulting in the production of male offspring and females carrying haploid eggs in sacs called ephippia (Mitchell 1999). The purpose of this laboratory study is to examine the effects of increased water temperature on survivorship and reproduction. This study will help us characterize the magnitude of environmental change required to induce the onset of the sexual life cycle in . Because are known to be a sensitive environmental indicator species (Baker et al. 2000) and share similar structural and physiological features with many aquatic species, they serve as a good model for examining the effects of increasing water temperature on reproduction in a variety of aquatic invertebrates. We hypothesized that populations reared in water temperatures ranging from 24-26 °C would have lower survivorship, higher male/female ratio among the offspring, and more female offspring carrying ephippia as compared with grown in water temperatures of 20-22°C. To test this hypothesis we reared populations in tanks containing water at either 24 +/- 2°C or 20 +/- 2°C. Over 10 days, we monitored survivorship, determined the sex of the offspring, and counted the number of female offspring containing ephippia. Comments: Background information · Opening paragraph provides good focus immediately. The study organism, gender switching response, and temperature influence are mentioned in the first sentence. Although it does a good job documenting average lake water temperature and changes due to industrial run-off, it fails to make an argument that the 15% increase in lake temperature could be considered “extreme” temperature change. · The study question is nicely embedded within relevant, well-cited background information. Alternatively, it could be stated as the first sentence in the introduction, or after all background information has been discussed before the hypothesis. Rationale · Good. Well-defined purpose for study; to examine the degree of environmental change necessary to induce the Daphnia sexual life |
How will introductions be evaluated? The following is part of the rubric we will be using to evaluate your papers.
0 = inadequate (C, D or F) | 1 = adequate (BC) | 2 = good (B) | 3 = very good (AB) | 4 = excellent (A) | |
Introduction BIG PICTURE: Did the Intro convey why experiment was performed and what it was designed to test?
| Introduction provides little to no relevant information. (This often results in a hypothesis that “comes out of nowhere.”) | Many key components are very weak or missing; those stated are unclear and/or are not stated concisely. Weak/missing components make it difficult to follow the rest of the paper. e.g., background information is not focused on a specific question and minimal biological rationale is presented such that hypothesis isn’t entirely logical
| Covers most key components but could be done much more logically, clearly, and/or concisely. e.g., biological rationale not fully developed but still supports hypothesis. Remaining components are done reasonably well, though there is still room for improvement. | Concisely & clearly covers all but one key component (w/ exception of rationale; see left) clearly covers all key components but could be a little more concise and/or clear. e.g., has done a reasonably nice job with the Intro but fails to state the approach OR has done a nice job with Intro but has also included some irrelevant background information
| Clearly, concisely, & logically presents all key components: relevant & correctly cited background information, question, biological rationale, hypothesis, approach. |

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
What is a "good" introduction?
Citing sources in the introduction, "introduction checklist" from: how to write a good scientific paper. chris a. mack. spie. 2018..
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is where you describe briefly and clearly why you are writing the paper. The introduction supplies sufficient background information for the reader to understand and evaluate the experiment you did. It also supplies a rationale for the study.
- Present the problem and the proposed solution
- Presents nature and scope of the problem investigated
- Reviews the pertinent literature to orient the reader
- States the method of the experiment
- State the principle results of the experiment
It is important to cite sources in the introduction section of your paper as evidence of the claims you are making. There are ways of citing sources in the text so that the reader can find the full reference in the literature cited section at the end of the paper, yet the flow of the reading is not badly interrupted. Below are some example of how this can be done: "Smith (1983) found that N-fixing plants could be infected by several different species of Rhizobium." "Walnut trees are known to be allelopathic (Smith 1949, Bond et al. 1955, Jones and Green 1963)." "Although the presence of Rhizobium normally increases the growth of legumes (Nguyen 1987), the opposite effect has been observed (Washington 1999)." Note that articles by one or two authors are always cited in the text using their last names. However, if there are more than two authors, the last name of the 1st author is given followed by the abbreviation et al. which is Latin for "and others".
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-reports-introductions
- Indicate the field of the work, why this field is important, and what has already been done (with proper citations).
- Indicate a gap, raise a research question, or challenge prior work in this territory.
- Outline the purpose and announce the present research, clearly indicating what is novel and why it is significant.
- Avoid: repeating the abstract; providing unnecessary background information; exaggerating the importance of the work; claiming novelty without a proper literature search.
- << Previous: ABSTRACT
- Next: METHODS >>
- Last Updated: Sep 27, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
This page has been archived and is no longer updated
Effective Writing
To construct sentences that reflect your ideas, focus these sentences appropriately. Express one idea per sentence. Use your current topic — that is, what you are writing about — as the grammatical subject of your sentence (see Verbs: Choosing between active and passive voice ). When writing a complex sentence (a sentence that includes several clauses), place the main idea in the main clause rather than a subordinate clause. In particular, focus on the phenomenon at hand, not on the fact that you observed it.
Constructing your sentences logically is a good start, but it may not be enough. To ensure they are readable, make sure your sentences do not tax readers' short-term memory by obliging these readers to remember long pieces of text before knowing what to do with them. In other words, keep together what goes together. Then, work on conciseness: See whether you can replace long phrases with shorter ones or eliminate words without loss of clarity or accuracy.
The following screens cover the drafting process in more detail. Specifically, they discuss how to use verbs effectively and how to take care of your text's mechanics.
Shutterstock. Much of the strength of a clause comes from its verb. Therefore, to express your ideas accurately, choose an appropriate verb and use it well. In particular, use it in the right tense, choose carefully between active and passive voice, and avoid dangling verb forms.
Verbs are for describing actions, states, or occurrences. To give a clause its full strength and keep it short, do not bury the action, state, or occurrence in a noun (typically combined with a weak verb), as in "The catalyst produced a significant increase in conversion rate." Instead write, "The catalyst increased the conversion rate significantly." The examples below show how an action, state, or occurrence can be moved from a noun back to a verb.
Using the right tense
In your scientific paper, use verb tenses (past, present, and future) exactly as you would in ordinary writing. Use the past tense to report what happened in the past: what you did, what someone reported, what happened in an experiment, and so on. Use the present tense to express general truths, such as conclusions (drawn by you or by others) and atemporal facts (including information about what the paper does or covers). Reserve the future tense for perspectives: what you will do in the coming months or years. Typically, most of your sentences will be in the past tense, some will be in the present tense, and very few, if any, will be in the future tense.
Work done We collected blood samples from . . . Groves et al. determined the growth rate of . . . Consequently, astronomers decided to rename . . . Work reported Jankowsky reported a similar growth rate . . . In 2009, Chu published an alternative method to . . . Irarrázaval observed the opposite behavior in . . . Observations The mice in Group A developed , on average, twice as much . . . The number of defects increased sharply . . . The conversion rate was close to 95% . . .
Present tense
General truths Microbes in the human gut have a profound influence on . . . The Reynolds number provides a measure of . . . Smoking increases the risk of coronary heart disease . . . Atemporal facts This paper presents the results of . . . Section 3.1 explains the difference between . . . Behbood's 1969 paper provides a framework for . . .
Future tense
Perspectives In a follow-up experiment, we will study the role of . . . The influence of temperature will be the object of future research . . .
Note the difference in scope between a statement in the past tense and the same statement in the present tense: "The temperature increased linearly over time" refers to a specific experiment, whereas "The temperature increases linearly over time" generalizes the experimental observation, suggesting that the temperature always increases linearly over time in such circumstances.
In complex sentences, you may have to combine two different tenses — for example, "In 1905, Albert Einstein postulated that the speed of light is constant . . . . " In this sentence, postulated refers to something that happened in the past (in 1905) and is therefore in the past tense, whereas is expresses a general truth and is in the present tense.
Choosing between active and passive voice
In English, verbs can express an action in one of two voices. The active voice focuses on the agent: "John measured the temperature." (Here, the agent — John — is the grammatical subject of the sentence.) In contrast, the passive voice focuses on the object that is acted upon: "The temperature was measured by John." (Here, the temperature, not John, is the grammatical subject of the sentence.)
To choose between active and passive voice, consider above all what you are discussing (your topic) and place it in the subject position. For example, should you write "The preprocessor sorts the two arrays" or "The two arrays are sorted by the preprocessor"? If you are discussing the preprocessor, the first sentence is the better option. In contrast, if you are discussing the arrays, the second sentence is better. If you are unsure what you are discussing, consider the surrounding sentences: Are they about the preprocessor or the two arrays?
The desire to be objective in scientific writing has led to an overuse of the passive voice, often accompanied by the exclusion of agents: "The temperature was measured " (with the verb at the end of the sentence). Admittedly, the agent is often irrelevant: No matter who measured the temperature, we would expect its value to be the same. However, a systematic preference for the passive voice is by no means optimal, for at least two reasons.
For one, sentences written in the passive voice are often less interesting or more difficult to read than those written in the active voice. A verb in the active voice does not require a person as the agent; an inanimate object is often appropriate. For example, the rather uninteresting sentence "The temperature was measured . . . " may be replaced by the more interesting "The measured temperature of 253°C suggests a secondary reaction in . . . ." In the second sentence, the subject is still temperature (so the focus remains the same), but the verb suggests is in the active voice. Similarly, the hard-to-read sentence "In this section, a discussion of the influence of the recirculating-water temperature on the conversion rate of . . . is presented " (long subject, verb at the end) can be turned into "This section discusses the influence of . . . . " The subject is now section , which is what this sentence is really about, yet the focus on the discussion has been maintained through the active-voice verb discusses .
As a second argument against a systematic preference for the passive voice, readers sometimes need people to be mentioned. A sentence such as "The temperature is believed to be the cause for . . . " is ambiguous. Readers will want to know who believes this — the authors of the paper, or the scientific community as a whole? To clarify the sentence, use the active voice and set the appropriate people as the subject, in either the third or the first person, as in the examples below.
Biologists believe the temperature to be . . . Keustermans et al. (1997) believe the temperature to be . . . The authors believe the temperature to be . . . We believe the temperature to be . . .
Avoiding dangling verb forms
A verb form needs a subject, either expressed or implied. When the verb is in a non-finite form, such as an infinitive ( to do ) or a participle ( doing ), its subject is implied to be the subject of the clause, or sometimes the closest noun phrase. In such cases, construct your sentences carefully to avoid suggesting nonsense. Consider the following two examples.
To dissect its brain, the affected fly was mounted on a . . . After aging for 72 hours at 50°C, we observed a shift in . . .
Here, the first sentence implies that the affected fly dissected its own brain, and the second implies that the authors of the paper needed to age for 72 hours at 50°C in order to observe the shift. To restore the intended meaning while keeping the infinitive to dissect or the participle aging , change the subject of each sentence as appropriate:
To dissect its brain, we mounted the affected fly on a . . . After aging for 72 hours at 50°C, the samples exhibited a shift in . . .
Alternatively, you can change or remove the infinitive or participle to restore the intended meaning:
To have its brain dissected , the affected fly was mounted on a . . . After the samples aged for 72 hours at 50°C, we observed a shift in . . .
In communication, every detail counts. Although your focus should be on conveying your message through an appropriate structure at all levels, you should also save some time to attend to the more mechanical aspects of writing in English, such as using abbreviations, writing numbers, capitalizing words, using hyphens when needed, and punctuating your text correctly.
Using abbreviations
Beware of overusing abbreviations, especially acronyms — such as GNP for gold nanoparticles . Abbreviations help keep a text concise, but they can also render it cryptic. Many acronyms also have several possible extensions ( GNP also stands for gross national product ).
Write acronyms (and only acronyms) in all uppercase ( GNP , not gnp ).
Introduce acronyms systematically the first time they are used in a document. First write the full expression, then provide the acronym in parentheses. In the full expression, and unless the journal to which you submit your paper uses a different convention, capitalize the letters that form the acronym: "we prepared Gold NanoParticles (GNP) by . . . " These capitals help readers quickly recognize what the acronym designates.
- Do not use capitals in the full expression when you are not introducing an acronym: "we prepared gold nanoparticles by… "
- As a more general rule, use first what readers know or can understand best, then put in parentheses what may be new to them. If the acronym is better known than the full expression, as may be the case for techniques such as SEM or projects such as FALCON, consider placing the acronym first: "The FALCON (Fission-Activated Laser Concept) program at…"
- In the rare case that an acronym is commonly known, you might not need to introduce it. One example is DNA in the life sciences. When in doubt, however, introduce the acronym.
In papers, consider the abstract as a stand-alone document. Therefore, if you use an acronym in both the abstract and the corresponding full paper, introduce that acronym twice: the first time you use it in the abstract and the first time you use it in the full paper. However, if you find that you use an acronym only once or twice after introducing it in your abstract, the benefit of it is limited — consider avoiding the acronym and using the full expression each time (unless you think some readers know the acronym better than the full expression).
Writing numbers
In general, write single-digit numbers (zero to nine) in words, as in three hours , and multidigit numbers (10 and above) in numerals, as in 24 hours . This rule has many exceptions, but most of them are reasonably intuitive, as shown hereafter.
Use numerals for numbers from zero to nine
- when using them with abbreviated units ( 3 mV );
- in dates and times ( 3 October , 3 pm );
- to identify figures and other items ( Figure 3 );
- for consistency when these numbers are mixed with larger numbers ( series of 3, 7, and 24 experiments ).
Use words for numbers above 10 if these numbers come at the beginning of a sentence or heading ("Two thousand eight was a challenging year for . . . "). As an alternative, rephrase the sentence to avoid this issue altogether ("The year 2008 was challenging for . . . " ) .
Capitalizing words
Capitals are often overused. In English, use initial capitals
- at beginnings: the start of a sentence, of a heading, etc.;
- for proper nouns, including nouns describing groups (compare physics and the Physics Department );
- for items identified by their number (compare in the next figure and in Figure 2 ), unless the journal to which you submit your paper uses a different convention;
- for specific words: names of days ( Monday ) and months ( April ), adjectives of nationality ( Algerian ), etc.
In contrast, do not use initial capitals for common nouns: Resist the temptation to glorify a concept, technique, or compound with capitals. For example, write finite-element method (not Finite-Element Method ), mass spectrometry (not Mass Spectrometry ), carbon dioxide (not Carbon Dioxide ), and so on, unless you are introducing an acronym (see Mechanics: Using abbreviations ).
Using hyphens
Punctuating text.
Punctuation has many rules in English; here are three that are often a challenge for non-native speakers.
As a rule, insert a comma between the subject of the main clause and whatever comes in front of it, no matter how short, as in "Surprisingly, the temperature did not increase." This comma is not always required, but it often helps and never hurts the meaning of a sentence, so it is good practice.
In series of three or more items, separate items with commas ( red, white, and blue ; yesterday, today, or tomorrow ). Do not use a comma for a series of two items ( black and white ).
In displayed lists, use the same punctuation as you would in normal text (but consider dropping the and ).
The system is fast, flexible, and reliable.
The system is fast, flexible, reliable.
This page appears in the following eBook
Topic rooms within Scientific Communication

Within this Subject (22)
- Communicating as a Scientist (3)
- Papers (4)
- Correspondence (5)
- Presentations (4)
- Conferences (3)
- Classrooms (3)
Other Topic Rooms
- Gene Inheritance and Transmission
- Gene Expression and Regulation
- Nucleic Acid Structure and Function
- Chromosomes and Cytogenetics
- Evolutionary Genetics
- Population and Quantitative Genetics
- Genes and Disease
- Genetics and Society
- Cell Origins and Metabolism
- Proteins and Gene Expression
- Subcellular Compartments
- Cell Communication
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division
© 2014 Nature Education
- Press Room |
- Terms of Use |
- Privacy Notice |

Visual Browse
- Access through your organization
- Patient Access
Article preview
Section snippets, references (8), cited by (25).

European Geriatric Medicine
Research paper writing a scientific article: a step-by-step guide for beginners, getting started: things to do before you write a word, what are the main sections of a scientific article, disclosure of interest, authors’ contributions, preparing reports for publication and responding to reviewers’ comments, j clin epidemiol, writing for publication: pressures, barriers and support strategies, nurse educ today, writing for publication: a pratical six-step approach, int j orthop trauma nurs, writing and publishing scientific papers, gastroenterology, bibliometric review of prefabricated and modular timber construction from 1990 to 2023: evolution, trends, and current challenges, the influence of indonesian instructional books with a scientific approach on students’ learning outcomes in scientific writing, scientific writing and publishing for early-career researchers from the perspective of young chemists, effects of synchronized and asynchronized e-feedback interactions on academic writing, achievement motivation and critical thinking, improving students' scientific writing ability through blended learning-based collaborative learning, successful scientific writing and publishing: a step-by-step approach.

Writing the Scientific Paper
When you write about scientific topics to specialists in a particular scientific field, we call that scientific writing. (When you write to non-specialists about scientific topics, we call that science writing.)
The scientific paper has developed over the past three centuries into a tool to communicate the results of scientific inquiry. The main audience for scientific papers is extremely specialized. The purpose of these papers is twofold: to present information so that it is easy to retrieve, and to present enough information that the reader can duplicate the scientific study. A standard format with six main part helps readers to find expected information and analysis:
- Title--subject and what aspect of the subject was studied.
- Abstract--summary of paper: The main reason for the study, the primary results, the main conclusions
- Introduction-- why the study was undertaken
- Methods and Materials-- how the study was undertaken
- Results-- what was found
- Discussion-- why these results could be significant (what the reasons might be for the patterns found or not found)
There are many ways to approach the writing of a scientific paper, and no one way is right. Many people, however, find that drafting chunks in this order works best: Results, Discussion, Introduction, Materials & Methods, Abstract, and, finally, Title.
The title should be very limited and specific. Really, it should be a pithy summary of the article's main focus.
- "Renal disease susceptibility and hypertension are under independent genetic control in the fawn hooded rat"
- "Territory size in Lincoln's Sparrows ( Melospiza lincolnii )"
- "Replacement of deciduous first premolars and dental eruption in archaeocete whales"
- "The Radio-Frequency Single-Electron Transistor (RF-SET): A Fast and Ultrasensitive Electrometer"
This is a summary of your article. Generally between 50-100 words, it should state the goals, results, and the main conclusions of your study. You should list the parameters of your study (when and where was it conducted, if applicable; your sample size; the specific species, proteins, genes, etc., studied). Think of the process of writing the abstract as taking one or two sentences from each of your sections (an introductory sentence, a sentence stating the specific question addressed, a sentence listing your main techniques or procedures, two or three sentences describing your results, and one sentence describing your main conclusion).
Example One
Hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia are risk factors for life-threatening complications such as end-stage renal disease, coronary artery disease and stroke. Why some patients develop complications is unclear, but only susceptibility genes may be involved. To test this notion, we studied crosses involving the fawn-hooded rat, an animal model of hypertension that develops chronic renal failure. Here, we report the localization of two genes, Rf-1 and Rf-2 , responsible for about half of the genetic variation in key indices of renal impairment. In addition, we localize a gene, Bpfh-1 , responsible for about 26% of the genetic variation in blood pressure. Rf-1 strongly affects the risk of renal impairment, but has no significant effect on blood pressure. Our results show that susceptibility to a complication of hypertension is under at least partially independent genetic control from susceptibility to hypertension itself.
Brown, Donna M, A.P. Provoost, M.J. Daly, E.S. Lander, & H.J. Jacob. 1996. "Renal disease susceptibility and hypertension are under indpendent genetic control in the faun-hooded rat." Nature Genetics , 12(1):44-51.
Example Two
We studied survival of 220 calves of radiocollared moose ( Alces alces ) from parturition to the end of July in southcentral Alaska from 1994 to 1997. Prior studies established that predation by brown bears ( Ursus arctos ) was the primary cause of mortality of moose calves in the region. Our objectives were to characterize vulnerability of moose calves to predation as influenced by age, date, snow depths, and previous reproductive success of the mother. We also tested the hypothesis that survival of twin moose calves was independent and identical to that of single calves. Survival of moose calves from parturition through July was 0.27 ± 0.03 SE, and their daily rate of mortality declined at a near constant rate with age in that period. Mean annual survival was 0.22 ± 0.03 SE. Previous winter's snow depths or survival of the mother's previous calf was not related to neonatal survival. Selection for early parturition was evidenced in the 4 years of study by a 6.3% increase in the hazard of death with each daily increase in parturition date. Although there was no significant difference in survival of twin and single moose calves, most twins that died disappeared together during the first 15 days after birth and independently thereafter, suggesting that predators usually killed both when encountered up to that age.
Key words: Alaska, Alces alces , calf survival, moose, Nelchina, parturition synchrony, predation
Testa, J.W., E.F. Becker, & G.R. Lee. 2000. "Temporal patterns in the survival of twin and single moose ( alces alces ) calves in southcentral Alaska." Journal of Mammalogy , 81(1):162-168.
Example Three
We monitored breeding phenology and population levels of Rana yavapaiensis by use of repeated egg mass censuses and visual encounter surveys at Agua Caliente Canyon near Tucson, Arizona, from 1994 to 1996. Adult counts fluctuated erratically within each year of the study but annual means remained similar. Juvenile counts peaked during the fall recruitment season and fell to near zero by early spring. Rana yavapaiensis deposited eggs in two distinct annual episodes, one in spring (March-May) and a much smaller one in fall (September-October). Larvae from the spring deposition period completed metamorphosis in earlv summer. Over the two years of study, 96.6% of egg masses successfully produced larvae. Egg masses were deposited during periods of predictable, moderate stream flow, but not during seasonal periods when flash flooding or drought were likely to affect eggs or larvae. Breeding phenology of Rana yavapaiensis is particularly well suited for life in desert streams with natural flow regimes which include frequent flash flooding and drought at predictable times. The exotic predators of R. yavapaiensis are less able to cope with fluctuating conditions. Unaltered stream flow regimes that allow natural fluctuations in stream discharge may provide refugia for this declining ranid frog from exotic predators by excluding those exotic species that are unable to cope with brief flash flooding and habitat drying.
Sartorius, Shawn S., and Philip C. Rosen. 2000. "Breeding phenology of the lowland leopard frog ( Rana yavepaiensis )." Southwestern Naturalist , 45(3): 267-273.
Introduction
The introduction is where you sketch out the background of your study, including why you have investigated the question that you have and how it relates to earlier research that has been done in the field. It may help to think of an introduction as a telescoping focus, where you begin with the broader context and gradually narrow to the specific problem addressed by the report. A typical (and very useful) construction of an introduction proceeds as follows:
"Echimyid rodents of the genus Proechimys (spiny rats) often are the most abundant and widespread lowland forest rodents throughout much of their range in the Neotropics (Eisenberg 1989). Recent studies suggested that these rodents play an important role in forest dynamics through their activities as seed predators and dispersers of seeds (Adler and Kestrell 1998; Asquith et al 1997; Forget 1991; Hoch and Adler 1997)." (Lambert and Adler, p. 70)
"Our laboratory has been involved in the analysis of the HLA class II genes and their association with autoimmune disorders such as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. As part of this work, the laboratory handles a large number of blood samples. In an effort to minimize the expense and urgency of transportation of frozen or liquid blood samples, we have designed a protocol that will preserve the integrity of lymphocyte DNA and enable the transport and storage of samples at ambient temperatures." (Torrance, MacLeod & Hache, p. 64)
"Despite the ubiquity and abundance of P. semispinosus , only two previous studies have assessed habitat use, with both showing a generalized habitat use. [brief summary of these studies]." (Lambert and Adler, p. 70)
"Although very good results have been obtained using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of DNA extracted from dried blood spots on filter paper (1,4,5,8,9), this preservation method yields limited amounts of DNA and is susceptible to contamination." (Torrance, MacLeod & Hache, p. 64)
"No attempt has been made to quantitatively describe microhabitat characteristics with which this species may be associated. Thus, specific structural features of secondary forests that may promote abundance of spiny rats remains unknown. Such information is essential to understand the role of spiny rats in Neotropical forests, particularly with regard to forest regeneration via interactions with seeds." (Lambert and Adler, p. 71)
"As an alternative, we have been investigating the use of lyophilization ("freeze-drying") of whole blood as a method to preserve sufficient amounts of genomic DNA to perform PCR and Southern Blot analysis." (Torrance, MacLeod & Hache, p. 64)
"We present an analysis of microhabitat use by P. semispinosus in tropical moist forests in central Panama." (Lambert and Adler, p. 71)
"In this report, we summarize our analysis of genomic DNA extracted from lyophilized whole blood." (Torrance, MacLeod & Hache, p. 64)
Methods and Materials
In this section you describe how you performed your study. You need to provide enough information here for the reader to duplicate your experiment. However, be reasonable about who the reader is. Assume that he or she is someone familiar with the basic practices of your field.
It's helpful to both writer and reader to organize this section chronologically: that is, describe each procedure in the order it was performed. For example, DNA-extraction, purification, amplification, assay, detection. Or, study area, study population, sampling technique, variables studied, analysis method.
Include in this section:
- study design: procedures should be listed and described, or the reader should be referred to papers that have already described the used procedure
- particular techniques used and why, if relevant
- modifications of any techniques; be sure to describe the modification
- specialized equipment, including brand-names
- temporal, spatial, and historical description of study area and studied population
- assumptions underlying the study
- statistical methods, including software programs
Example description of activity
Chromosomal DNA was denatured for the first cycle by incubating the slides in 70% deionized formamide; 2x standard saline citrate (SSC) at 70ºC for 2 min, followed by 70% ethanol at -20ºC and then 90% and 100% ethanol at room temperature, followed by air drying. (Rouwendal et al ., p. 79)
Example description of assumptions
We considered seeds left in the petri dish to be unharvested and those scattered singly on the surface of a tile to be scattered and also unharvested. We considered seeds in cheek pouches to be harvested but not cached, those stored in the nestbox to be larderhoarded, and those buried in caching sites within the arena to be scatterhoarded. (Krupa and Geluso, p. 99)
Examples of use of specialized equipment
- Oligonucleotide primers were prepared using the Applied Biosystems Model 318A (Foster City, CA) DNA Synthesizer according to the manufacturers' instructions. (Rouwendal et al ., p.78)
- We first visually reviewed the complete song sample of an individual using spectrograms produced on a Princeton Applied Research Real Time Spectrum Analyzer (model 4512). (Peters et al ., p. 937)
Example of use of a certain technique
Frogs were monitored using visual encounter transects (Crump and Scott, 1994). (Sartorius and Rosen, p. 269)
Example description of statistical analysis
We used Wilcox rank-sum tests for all comparisons of pre-experimental scores and for all comparisons of hue, saturation, and brightness scores between various groups of birds ... All P -values are two-tailed unless otherwise noted. (Brawner et al ., p. 955)
This section presents the facts--what was found in the course of this investigation. Detailed data--measurements, counts, percentages, patterns--usually appear in tables, figures, and graphs, and the text of the section draws attention to the key data and relationships among data. Three rules of thumb will help you with this section:
- present results clearly and logically
- avoid excess verbiage
- consider providing a one-sentence summary at the beginning of each paragraph if you think it will help your reader understand your data
Remember to use table and figures effectively. But don't expect these to stand alone.
Some examples of well-organized and easy-to-follow results:
- Size of the aquatic habitat at Agua Caliente Canyon varied dramatically throughout the year. The site contained three rockbound tinajas (bedrock pools) that did not dry during this study. During periods of high stream discharge seven more seasonal pools and intermittent stretches of riffle became available. Perennial and seasonal pool levels remained stable from late February through early May. Between mid-May and mid-July seasonal pools dried until they disappeared. Perennial pools shrank in surface area from a range of 30-60 m² to 3-5- M². (Sartorius and Rosen, Sept. 2000: 269)
Notice how the second sample points out what is important in the accompanying figure. It makes us aware of relationships that we may not have noticed quickly otherwise and that will be important to the discussion.
A similar test result is obtained with a primer derived from the human ß-satellite... This primer (AGTGCAGAGATATGTCACAATG-CCCC: Oligo 435) labels 6 sites in the PRINS reaction: the chromosomes 1, one pair of acrocentrics and, more weakly, the chromosomes 9 (Fig. 2a). After 10 cycles of PCR-IS, the number of sites labeled has doubled (Fig. 2b); after 20 cycles, the number of sites labeled is the same but the signals are stronger (Fig. 2c) (Rouwendal et al ., July 93:80).
Related Information: Use Tables and Figures Effectively
Do not repeat all of the information in the text that appears in a table, but do summarize it. For example, if you present a table of temperature measurements taken at various times, describe the general pattern of temperature change and refer to the table.
"The temperature of the solution increased rapidly at first, going from 50º to 80º in the first three minutes (Table 1)."
You don't want to list every single measurement in the text ("After one minute, the temperature had risen to 55º. After two minutes, it had risen to 58º," etc.). There is no hard and fast rule about when to report all measurements in the text and when to put the measurements in a table and refer to them, but use your common sense. Remember that readers have all that data in the accompanying tables and figures, so your task in this section is to highlight key data, changes, or relationships.
In this section you discuss your results. What aspect you choose to focus on depends on your results and on the main questions addressed by them. For example, if you were testing a new technique, you will want to discuss how useful this technique is: how well did it work, what are the benefits and drawbacks, etc. If you are presenting data that appear to refute or support earlier research, you will want to analyze both your own data and the earlier data--what conditions are different? how much difference is due to a change in the study design, and how much to a new property in the study subject? You may discuss the implication of your research--particularly if it has a direct bearing on a practical issue, such as conservation or public health.
This section centers on speculation . However, this does not free you to present wild and haphazard guesses. Focus your discussion around a particular question or hypothesis. Use subheadings to organize your thoughts, if necessary.
This section depends on a logical organization so readers can see the connection between your study question and your results. One typical approach is to make a list of all the ideas that you will discuss and to work out the logical relationships between them--what idea is most important? or, what point is most clearly made by your data? what ideas are subordinate to the main idea? what are the connections between ideas?
Achieving the Scientific Voice
Eight tips will help you match your style for most scientific publications.
- Develop a precise vocabulary: read the literature to become fluent, or at least familiar with, the sort of language that is standard to describe what you're trying to describe.
- Once you've labeled an activity, a condition, or a period of time, use that label consistently throughout the paper. Consistency is more important than creativity.
- Define your terms and your assumptions.
- Include all the information the reader needs to interpret your data.
- Remember, the key to all scientific discourse is that it be reproducible . Have you presented enough information clearly enough that the reader could reproduce your experiment, your research, or your investigation?
- When describing an activity, break it down into elements that can be described and labeled, and then present them in the order they occurred.
- When you use numbers, use them effectively. Don't present them so that they cause more work for the reader.
- Include details before conclusions, but only include those details you have been able to observe by the methods you have described. Do not include your feelings, attitudes, impressions, or opinions.
- Research your format and citations: do these match what have been used in current relevant journals?
- Run a spellcheck and proofread carefully. Read your paper out loud, and/ or have a friend look over it for misspelled words, missing words, etc.
Applying the Principles, Example 1
The following example needs more precise information. Look at the original and revised paragraphs to see how revising with these guidelines in mind can make the text clearer and more informative:
Before: Each male sang a definite number of songs while singing. They start with a whistle and then go from there. Each new song is always different, but made up an overall repertoire that was completed before starting over again. In 16 cases (84%), no new songs were sung after the first 20, even though we counted about 44 songs for each bird.
After: Each male used a discrete number of song types in his singing. Each song began with an introductory whistle, followed by a distinctive, complex series of fluty warbles (Fig. 1). Successive songs were always different, and five of the 19 males presented their entire song repertoire before repeating any of their song types (i.e., the first IO recorded songs revealed the entire repertoire of 10 song types). Each song type recurred in long sequences of singing, so that we could be confident that we had recorded the entire repertoire of commonly used songs by each male. For 16 of the 19 males, no new song types were encountered after the first 20 songs, even though we analyzed and average of 44 songs/male (range 30-59).
Applying the Principles, Example 2
In this set of examples, even a few changes in wording result in a more precise second version. Look at the original and revised paragraphs to see how revising with these guidelines in mind can make the text clearer and more informative:
Before: The study area was on Mt. Cain and Maquilla Peak in British Columbia, Canada. The study area is about 12,000 ha of coastal montane forest. The area is both managed and unmanaged and ranges from 600-1650m. The most common trees present are mountain hemlock ( Tsuga mertensiana ), western hemlock ( Tsuga heterophylla ), yellow cedar ( Chamaecyparis nootkatensis ), and amabilis fir ( Abies amabilis ).
After: The study took place on Mt. Cain and Maquilla Peak (50'1 3'N, 126'1 8'W), Vancouver Island, British Columbia. The study area encompassed 11,800 ha of coastal montane forest. The landscape consisted of managed and unmanaged stands of coastal montane forest, 600-1650 m in elevation. The dominant tree species included mountain hemlock ( Tsuga mertensiana ), western hemlock ( Tsuga heterophylla ), yellow cedar ( Chamaecyparis nootkatensis ), and amabilis fir ( Abies amabilis ).
Two Tips for Sentence Clarity
Although you will want to consider more detailed stylistic revisions as you become more comfortable with scientific writing, two tips can get you started:
First, the verb should follow the subject as soon as possible.
Really Hard to Read : "The smallest of the URF's (URFA6L), a 207-nucleotide (nt) reading frame overlapping out of phase the NH2- terminal portion of the adenosinetriphosphatase (ATPase) subunit 6 gene has been identified as the animal equivalent of the recently discovered yeast H+-ATPase subunit gene."
Less Hard to Read : "The smallest of the UR-F's is URFA6L, a 207-nucleotide (nt) reading frame overlapping out of phase the NH2-terminal portion of the adenosinetriphosphatase (ATPase) subunit 6 gene; it has been identified as the animal equivalent of the recently discovered yeast H+-ATPase subunit 8 gene."
Second, place familiar information first in a clause, a sentence, or a paragraph, and put the new and unfamiliar information later.
More confusing : The epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutaneous layer are the three layers of the skin. A layer of dead skin cells makes up the epidermis, which forms the body's shield against the world. Blood vessels, carrying nourishment, and nerve endings, which relay information about the outside world, are found in the dermis. Sweat glands and fat cells make up the third layer, the subcutaneous layer.
Less confusing : The skin consists of three layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the subcutaneous layer. The epidermis is made up of dead skin cells, and forms a protective shield between the body and the world. The dermis contains the blood vessels and nerve endings that nourish the skin and make it receptive to outside stimuli. The subcutaneous layer contains the sweat glands and fat cells which perform other functions of the skin.
Bibliography
- Scientific Writing for Graduate Students . F. P. Woodford. Bethesda, MD: Council of Biology Editors, 1968. [A manual on the teaching of writing to graduate students--very clear and direct.]
- Scientific Style and Format . Council of Biology Editors. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1994.
- "The science of scientific writing." George Gopen and Judith Swann. The American Scientist , Vol. 78, Nov.-Dec. 1990. Pp 550-558.
- "What's right about scientific writing." Alan Gross and Joseph Harmon. The Scientist , Dec. 6 1999. Pp. 20-21.
- "A Quick Fix for Figure Legends and Table Headings." Donald Kroodsma. The Auk , 117 (4): 1081-1083, 2000.
Wortman-Wunder, Emily, & Kate Kiefer. (1998). Writing the Scientific Paper. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/resources/writing/guides/.
Call/Text/Whatsapp:
+1 (888-687-4420)
24/7/365 Available
- College Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Expository Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Scholarship Essay
- Admission Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Nursing Essay
- Economics Essay
Assignments
- Term Papers
- Research Papers
- Case Studies
- Dissertation
- Presentation
- Editing Help
- Cheap Essay Writing
- How to Order
Science Essay
Learn How to Write an A+ Science Essay
11 min read

People also read
150+ Engaging Science Essay Topics To Hook Your Readers
Read 13 Impressive Science Essay Examples And Get Inspired
Science Fiction Essay: Examples & Easy Steps Guide
Essay About Science and Technology| Tips & Examples
Essay About Science in Everyday Life - Samples & Writing Tips
Check Out 5 Impressive Essay About Science Fair Examples
Did you ever imagine that essay writing was just for students in the Humanities? Well, think again!
For science students, tackling a science essay might seem challenging, as it not only demands a deep understanding of the subject but also strong writing skills.
However, fret not because we've got your back!
With the right steps and tips, you can write an engaging and informative science essay easily!
This blog will take you through all the important steps of writing a science essay, from choosing a topic to presenting the final work.
So, let's get into it!
- 1. What Is a Science Essay?
- 2. How To Write a Science Essay?
- 3. How to Structure a Science Essay?
- 4. Science Essay Examples
- 5. How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
- 6. Science Essay Topics
- 7. Science Essay Writing Tips
What Is a Science Essay?
A science essay is an academic paper focusing on a scientific topic from physics, chemistry, biology, or any other scientific field.
Science essays are mostly expository. That is, they require you to explain your chosen topic in detail. However, they can also be descriptive and exploratory.
A descriptive science essay aims to describe a certain scientific phenomenon according to established knowledge.
On the other hand, the exploratory science essay requires you to go beyond the current theories and explore new interpretations.
So before you set out to write your essay, always check out the instructions given by your instructor. Whether a science essay is expository or exploratory must be clear from the start. Or, if you face any difficulty, you can take help from a science essay writer as well.
Moreover, check out this video to understand scientific writing in detail.
Now that you know what it is, let's look at the steps you need to take to write a science essay.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How To Write a Science Essay?
Writing a science essay is not as complex as it may seem. All you need to do is follow the right steps to create an impressive piece of work that meets the assigned criteria.
Here's what you need to do:
Choose Your Topic
A good topic forms the foundation for an engaging and well-written essay. Therefore, you should ensure that you pick something interesting or relevant to your field of study.
To choose a good topic, you can brainstorm ideas relating to the subject matter. You may also find inspiration from other science essays or articles about the same topic.
Conduct Research
Once you have chosen your topic, start researching it thoroughly to develop a strong argument or discussion in your essay.
Make sure you use reliable sources and cite them properly . You should also make notes while conducting your research so that you can reference them easily when writing the essay. Or, you can get expert assistance from an essay writing service to manage your citations.
Create an Outline
A good essay outline helps to organize the ideas in your paper. It serves as a guide throughout the writing process and ensures you don’t miss out on important points.
An outline makes it easier to write a well-structured paper that flows logically. It should be detailed enough to guide you through the entire writing process.
However, your outline should be flexible, and it's sometimes better to change it along the way to improve your structure.
Start Writing
Once you have a good outline, start writing the essay by following your plan.
The first step in writing any essay is to draft it. This means putting your thoughts down on paper in a rough form without worrying about grammar or spelling mistakes.
So begin your essay by introducing the topic, then carefully explain it using evidence and examples to support your argument.
Don't worry if your first draft isn't perfect - it's just the starting point!
Proofread & Edit
After finishing your first draft, take time to proofread and edit it for grammar and spelling mistakes.
Proofreading is the process of checking for grammatical mistakes. It should be done after you have finished writing your essay.
Editing, on the other hand, involves reviewing the structure and organization of your essay and its content. It should be done before you submit your final work.
Both proofreading and editing are essential for producing a high-quality essay. Make sure to give yourself enough time to do them properly!
After revising the essay, you should format it according to the guidelines given by your instructor. This could involve using a specific font size, page margins, or citation style.
Most science essays are written in Times New Roman font with 12-point size and double spacing. The margins should be 1 inch on all sides, and the text should be justified.
In addition, you must cite your sources properly using a recognized citation style such as APA , Chicago , or Harvard . Make sure to follow the guidelines closely so that your essay looks professional.
Following these steps will help you create an informative and well-structured science essay that meets the given criteria.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
How to Structure a Science Essay?
A basic science essay structure includes an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Let's look at each of these briefly.
- Introduction
Your essay introduction should introduce your topic and provide a brief overview of what you will discuss in the essay. It should also state your thesis or main argument.
For instance, a thesis statement for a science essay could be,
"The human body is capable of incredible feats, as evidenced by the many athletes who have competed in the Olympic games."
The body of your essay will contain the bulk of your argument or discussion. It should be divided into paragraphs, each discussing a different point.
For instance, imagine you were writing about sports and the human body.
Your first paragraph can discuss the physical capabilities of the human body.
The second paragraph may be about the physical benefits of competing in sports.
Similarly, in the third paragraph, you can present one or two case studies of specific athletes to support your point.
Once you have explained all your points in the body, it’s time to conclude the essay.
Your essay conclusion should summarize the main points of your essay and leave the reader with a sense of closure.
In the conclusion, you reiterate your thesis and sum up your arguments. You can also suggest implications or potential applications of the ideas discussed in the essay.
By following this structure, you will create a well-organized essay.
Check out a few example essays to see this structure in practice.
Science Essay Examples
A great way to get inspired when writing a science essay is to look at other examples of successful essays written by others.
Here are some examples that will give you an idea of how to write your essay.
Science Essay About Genetics - Science Essay Example
Environmental Science Essay Example | PDF Sample
The Science of Nanotechnology
Science, Non-Science, and Pseudo-Science
The Science Of Science Education
Science in our Daily Lives
Short Science Essay Example
Let’s take a look at a short science essay:
As we step into the 21st century, it is evident that the chalkboard and textbook are no longer the sole tools of education. Technology has fundamentally reshaped education by offering improved learning experiences, enhancing accessibility, and equipping students with essential digital skills. Technology enhances learning experiences by providing interactive and engaging educational content. Digital platforms offer multimedia resources, simulations, and virtual laboratories, enabling students to grasp complex concepts more effectively. For example, in the field of science, students can virtually dissect organisms, observe chemical reactions, and explore outer space—all from the comfort of their devices. These immersive experiences not only make learning more enjoyable but also deepen understanding and retention of the subject matter. Lastly, technology equips students with essential digital skills vital for success in the modern workforce. Proficiency in using digital tools, software, and online research is becoming increasingly necessary in almost every career path. By incorporating technology into education, students not only acquire subject-specific knowledge but also develop crucial digital literacy and problem-solving skills that are highly sought after by employers. In conclusion, technology's impact on modern education cannot be overstated. It enhances learning experiences, broadens access to education, and equips students with the digital skills they need to thrive in today's interconnected world. While traditional teaching methods still hold value, integrating technology into education is essential to prepare students for the challenges and opportunities of the digital age. As we move forward, it is crucial to strike a balance between technology and traditional pedagogy to provide a well-rounded education that prepares students for a diverse and dynamic future. |
Want to read more essay examples? Here, you can find more science essay examples to learn from.
How to Choose the Right Science Essay Topic
Choosing the right science essay topic is a critical first step in crafting a compelling and engaging essay. Here's a concise guide on how to make this decision wisely:
- Consider Your Interests: Start by reflecting on your personal interests within the realm of science. Selecting a topic that genuinely fascinates you will make the research and writing process more enjoyable and motivated.
- Relevance to the Course: Ensure that your chosen topic aligns with your course or assignment requirements. Read the assignment guidelines carefully to understand the scope and focus expected by your instructor.
- Current Trends and Issues: Stay updated with the latest scientific developments and trends. Opting for a topic that addresses contemporary issues not only makes your essay relevant but also demonstrates your awareness of current events in the field.
- Narrow Down the Scope: Science is vast, so narrow your topic to a manageable scope. Instead of a broad subject like "Climate Change," consider a more specific angle like "The Impact of Melting Arctic Ice on Global Sea Levels."
- Available Resources: Ensure that there are sufficient credible sources and research materials available for your chosen topic. A lack of resources can hinder your research efforts.
- Discuss with Your Instructor: If you're uncertain about your topic choice, don't hesitate to consult your instructor or professor. They can provide valuable guidance and may even suggest specific topics based on your academic goals.
Science Essay Topics
Choosing an appropriate topic for a science essay is one of the first steps in writing a successful paper.
Here are a few science essay topics to get you started:
- How space exploration affects our daily lives?
- How has technology changed our understanding of medicine?
- Are there ethical considerations to consider when conducting scientific research?
- How does climate change affect the biodiversity of different parts of the world?
- How can artificial intelligence be used in medicine?
- What impact have vaccines had on global health?
- What is the future of renewable energy?
- How do we ensure that genetically modified organisms are safe for humans and the environment?
- The influence of social media on human behavior: A social science perspective
- What are the potential risks and benefits of stem cell therapy?
Important science topics can cover anything from space exploration to chemistry and biology. So you can choose any topic according to your interests!
Need more topics? We have gathered 100+ science essay topics to help you find a great topic!
Continue reading to find some tips to help you write a successful science essay.
Science Essay Writing Tips
Once you have chosen a topic and looked at examples, it's time to start writing the science essay.
Here are some key tips for a successful essay:
- Research thoroughly
Make sure you do extensive research before you begin writing your paper. This will ensure that the facts and figures you include are accurate and supported by reliable sources.
- Use clear language
Avoid using jargon or overly technical language when writing your essay. Plain language is easier to understand and more engaging for readers.
- Referencing
Always provide references for any information you include in your essay. This will demonstrate that you acknowledge other people's work and show that the evidence you use is credible.
Make sure to follow the basic structure of an essay and organize your thoughts into clear sections. This will improve the flow and make your essay easier to read.
- Ask someone to proofread
It’s also a good idea to get someone else to proofread your work as they may spot mistakes that you have missed.
These few tips will help ensure that your science essay is well-written and informative!
You've learned the steps to writing a successful science essay and looked at some examples and topics to get you started.
Make sure you thoroughly research, use clear language, structure your thoughts, and proofread your essay. With these tips, you’re sure to write a great science essay!
Do you still need expert help writing a science essay? Our science essay writing service is here to help. With our team of professional writers, you can rest assured that your essay will be written to the highest standards.
Ask us to ' help me do my essay ' now to get started!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Betty is a freelance writer and researcher. She has a Masters in literature and enjoys providing writing services to her clients. Betty is an avid reader and loves learning new things. She has provided writing services to clients from all academic levels and related academic fields.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading
- For Authors
- Collaboration
- Privacy Policy

- Conferences & Symposiums
Tools & Methods
How to successfully write a scientific essay.
Posted by Cody Rhodes
If you are undertaking a course which relates to science, you are more or less apt to write an essay on science. You need to know how to write a science essay irrespective of whether your professor gives you a topic or you come up with one. Additionally, you need to have an end objective in mind. Writing a science essay necessitates that you produce an article which has all the details and facts about the subject matter and it ought to be to the point. Also, you need to know and understand that science essays are more or less different from other types of essays. They require you to be analytical and precise when answering questions. Hence, this can be quite challenging and tiresome. However, that should not deter you from learning how to write your paper. You can always inquire for pre-written research papers for sale from writing services like EssayZoo.
Also, you can read other people’s articles and find out how they produce and develop unique and high-quality papers. Moreover, this will help you understand how to approach your essays in different ways. Nonetheless, if you want to learn how to write a scientific paper in a successful manner, consider the following tips.

Select a topic for your article Like any other type of essay, you need to have a topic before you start the actual writing process. Your professor or instructor may give you a science essay topic to write about or ask you to come up with yours. When selecting a topic for your paper, ensure that you choose one you can write about. Do not pick a complex topic which can make the writing process boring and infuriating for you. Instead, choose one that you are familiar with. Select a topic you will not struggle gathering information about. Also, you need to have an interest in it. If you are unable to come up with a good topic, trying reading other people’s articles. This will help you develop a topic with ease.
Draft a plan After selecting a topic, the next step is drafting a plan or an outline. An outline is fundamental in writing a scientific essay as it is the foundation on which your paper is built. Additionally, it acts as a road map for your article. Hence, you need to incorporate all the thoughts and ideas you will include in your essay in the outline. You need to know what you will include in the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Drafting a plan helps you save a lot of time when writing your paper. Also, it helps you to keep track of the primary objective of your article.
Start writing the article After drafting a plan, you can begin the writing process. Writing your paper will be smooth and easier as you have an outline which helps simplify the writing process. When writing your article, begin with a strong hook for your introduction. Dictate the direction your paper will take. Provide some background information and state the issue you will discuss as well as the solutions you have come up with. Arrange the body of your article according to the essay structure you will use to guide you. Also, ensure that you use transitory sentences to show the relationship between the paragraphs of your article. Conclude your essay by summarizing all the key points. Also, highlight the practical potential of our findings and their impacts.
Proofread and check for errors in the paper Before submitting or forwarding your article, it is fundamental that you proofread and correct all the errors that you come across. Delivering a paper that is full of mistakes can affect your overall performance in a negative manner. Thus, it is essential you revise your paper and check for errors. Correct all of them. Ask a friend to proofread your paper. He or she may spot some of the mistakes you did not come across.
In conclusion, writing a scientific essay differs from writing other types of papers. A scientific essay requires you to produce an article which has all the information and facts about the subject matter and it ought to be to the point. Nonetheless, the scientific essay formats similar to the format of any other essay: introduction, body, and conclusion. You need to use your outline to guide you through the writing process. To learn how to write a scientific essay in a successful manner, consider the tips above.

Related Articles:
| In recent years, nitrogen pollution, especially nitrate is an important problem faced by lots of reservoirs. Excessive nitrogen levels can cause water eutrophication, resulting in deterioration of water quality by… | |
| Born from the wreckage of the Titanic, used in the marine then industry, ultrasound impacted medicine in the 50s. However, the lung has always been considered as not accessible to… | |
| Patients and staff should expect privacy in emergency departments and should not be recorded without giving their consent in advance. Emergency departments (ED) use audiovisual recordings to document clinical information… | |
| Public perception of pharmacists might be limited to dispensing medications. However, pharmacists are trained to deliver patient care to help patients improve their health-related outcomes and achieve their goals. Recognizing… | |
| Fatalists aside, who doesn't want to live longer and in good health? But, obviously, to live longer it would be nonsense to put our health at risk. Yet, since we… | |
| Sleep abnormalities are commonly observed in individuals with schizophrenia and related psychotic disorders. Research shows that over half of people with these conditions have trouble sleeping. Poor sleep also often… |
2 Responses to How to successfully write a scientific essay
Hai…you have posted great article, it really helpful to us.. I will refer this page to my friends; I hope you will like to read – scientific research paper writing service
Nice concentration on education blogs. Such a great work regarding education and online study to gain knowledge and time.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Top Keywords
Diabetes | Alzheimer’s disease Cancer | Breast cancer | Tumor Blood pressure | Heart Brain | Kidney | Liver | Lung Stress | Pain | Therapy Infection | Inflammation | Injury DNA | RNA | Receptor | Nanoparticles Bacteria | Virus | Plant
See more …

Proofread or Perish: Editing your scientific writing for successful publication

Lab Leader makes software applications for experiment design in life science

Cyagen Biosciences – Helping you choose the right animal model for your research
Labcollector lims and eln for improving productivity in the lab.

Image Cytometer – NucleoCounter® NC-3000™
Recent posts.
- Unlocking new treatments for bone diseases: using PEPITEM to strengthen bones and prevent loss
- The Manikin Challenge: manikin-based simulation in the psychiatry clerkship
- Does UV-B radiation modify gene expression?
- Ferrate technology: an innovative solution for sustainable sewer and wastewater management
- Sleep abnormalities in different clinical stages of psychosis
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 | ||||||

Essay and dissertation writing skills
Planning your essay
Writing your introduction
Structuring your essay
- Writing essays in science subjects
- Brief video guides to support essay planning and writing
- Writing extended essays and dissertations
- Planning your dissertation writing time
Structuring your dissertation
- Top tips for writing longer pieces of work
Advice on planning and writing essays and dissertations
University essays differ from school essays in that they are less concerned with what you know and more concerned with how you construct an argument to answer the question. This means that the starting point for writing a strong essay is to first unpick the question and to then use this to plan your essay before you start putting pen to paper (or finger to keyboard).
A really good starting point for you are these short, downloadable Tips for Successful Essay Writing and Answering the Question resources. Both resources will help you to plan your essay, as well as giving you guidance on how to distinguish between different sorts of essay questions.
You may find it helpful to watch this seven-minute video on six tips for essay writing which outlines how to interpret essay questions, as well as giving advice on planning and structuring your writing:
Different disciplines will have different expectations for essay structure and you should always refer to your Faculty or Department student handbook or course Canvas site for more specific guidance.
However, broadly speaking, all essays share the following features:
Essays need an introduction to establish and focus the parameters of the discussion that will follow. You may find it helpful to divide the introduction into areas to demonstrate your breadth and engagement with the essay question. You might define specific terms in the introduction to show your engagement with the essay question; for example, ‘This is a large topic which has been variously discussed by many scientists and commentators. The principal tension is between the views of X and Y who define the main issues as…’ Breadth might be demonstrated by showing the range of viewpoints from which the essay question could be considered; for example, ‘A variety of factors including economic, social and political, influence A and B. This essay will focus on the social and economic aspects, with particular emphasis on…..’
Watch this two-minute video to learn more about how to plan and structure an introduction:
The main body of the essay should elaborate on the issues raised in the introduction and develop an argument(s) that answers the question. It should consist of a number of self-contained paragraphs each of which makes a specific point and provides some form of evidence to support the argument being made. Remember that a clear argument requires that each paragraph explicitly relates back to the essay question or the developing argument.
- Conclusion: An essay should end with a conclusion that reiterates the argument in light of the evidence you have provided; you shouldn’t use the conclusion to introduce new information.
- References: You need to include references to the materials you’ve used to write your essay. These might be in the form of footnotes, in-text citations, or a bibliography at the end. Different systems exist for citing references and different disciplines will use various approaches to citation. Ask your tutor which method(s) you should be using for your essay and also consult your Department or Faculty webpages for specific guidance in your discipline.
Essay writing in science subjects
If you are writing an essay for a science subject you may need to consider additional areas, such as how to present data or diagrams. This five-minute video gives you some advice on how to approach your reading list, planning which information to include in your answer and how to write for your scientific audience – the video is available here:
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.
Short videos to support your essay writing skills
There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing, including:
- Approaching different types of essay questions
- Structuring your essay
- Writing an introduction
- Making use of evidence in your essay writing
- Writing your conclusion
Extended essays and dissertations
Longer pieces of writing like extended essays and dissertations may seem like quite a challenge from your regular essay writing. The important point is to start with a plan and to focus on what the question is asking. A PDF providing further guidance on planning Humanities and Social Science dissertations is available to download.
Planning your time effectively
Try not to leave the writing until close to your deadline, instead start as soon as you have some ideas to put down onto paper. Your early drafts may never end up in the final work, but the work of committing your ideas to paper helps to formulate not only your ideas, but the method of structuring your writing to read well and conclude firmly.
Although many students and tutors will say that the introduction is often written last, it is a good idea to begin to think about what will go into it early on. For example, the first draft of your introduction should set out your argument, the information you have, and your methods, and it should give a structure to the chapters and sections you will write. Your introduction will probably change as time goes on but it will stand as a guide to your entire extended essay or dissertation and it will help you to keep focused.
The structure of extended essays or dissertations will vary depending on the question and discipline, but may include some or all of the following:
- The background information to - and context for - your research. This often takes the form of a literature review.
- Explanation of the focus of your work.
- Explanation of the value of this work to scholarship on the topic.
- List of the aims and objectives of the work and also the issues which will not be covered because they are outside its scope.
The main body of your extended essay or dissertation will probably include your methodology, the results of research, and your argument(s) based on your findings.
The conclusion is to summarise the value your research has added to the topic, and any further lines of research you would undertake given more time or resources.
Tips on writing longer pieces of work
Approaching each chapter of a dissertation as a shorter essay can make the task of writing a dissertation seem less overwhelming. Each chapter will have an introduction, a main body where the argument is developed and substantiated with evidence, and a conclusion to tie things together. Unlike in a regular essay, chapter conclusions may also introduce the chapter that will follow, indicating how the chapters are connected to one another and how the argument will develop through your dissertation.
For further guidance, watch this two-minute video on writing longer pieces of work .
Systems & Services
Access Student Self Service
- Student Self Service
- Self Service guide
- Registration guide
- Libraries search
- OXCORT - see TMS
- GSS - see Student Self Service
- The Careers Service
- Oxford University Sport
- Online store
- Gardens, Libraries and Museums
- Researchers Skills Toolkit
- LinkedIn Learning (formerly Lynda.com)
- Access Guide
- Lecture Lists
- Exam Papers (OXAM)
- Oxford Talks
Latest student news
CAN'T FIND WHAT YOU'RE LOOKING FOR?
Try our extensive database of FAQs or submit your own question...
Ask a question
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
The PMC website is updating on October 15, 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Sports Phys Ther
- v.7(5); 2012 Oct
HOW TO WRITE A SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE
Barbara j. hoogenboom.
1 Grand Valley State University, Grand Rapids, MI, USA
Robert C. Manske
2 University of Wichita, Wichita, KS, USA
Successful production of a written product for submission to a peer‐reviewed scientific journal requires substantial effort. Such an effort can be maximized by following a few simple suggestions when composing/creating the product for submission. By following some suggested guidelines and avoiding common errors, the process can be streamlined and success realized for even beginning/novice authors as they negotiate the publication process. The purpose of this invited commentary is to offer practical suggestions for achieving success when writing and submitting manuscripts to The International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy and other professional journals.
INTRODUCTION
“The whole of science is nothing more than a refinement of everyday thinking” Albert Einstein
Conducting scientific and clinical research is only the beginning of the scholarship of discovery. In order for the results of research to be accessible to other professionals and have a potential effect on the greater scientific community, it must be written and published. Most clinical and scientific discovery is published in peer‐reviewed journals, which are those that utilize a process by which an author's peers, or experts in the content area, evaluate the manuscript. Following this review the manuscript is recommended for publication, revision or rejection. It is the rigor of this review process that makes scientific journals the primary source of new information that impacts clinical decision‐making and practice. 1 , 2
The task of writing a scientific paper and submitting it to a journal for publication is a time‐consuming and often daunting task. 3 , 4 Barriers to effective writing include lack of experience, poor writing habits, writing anxiety, unfamiliarity with the requirements of scholarly writing, lack of confidence in writing ability, fear of failure, and resistance to feedback. 5 However, the very process of writing can be a helpful tool for promoting the process of scientific thinking, 6 , 7 and effective writing skills allow professionals to participate in broader scientific conversations. Furthermore, peer review manuscript publication systems requiring these technical writing skills can be developed and improved with practice. 8 Having an understanding of the process and structure used to produce a peer‐reviewed publication will surely improve the likelihood that a submitted manuscript will result in a successful publication.
Clear communication of the findings of research is essential to the growth and development of science 3 and professional practice. The culmination of the publication process provides not only satisfaction for the researcher and protection of intellectual property, but also the important function of dissemination of research results, new ideas, and alternate thought; which ultimately facilitates scholarly discourse. In short, publication of scientific papers is one way to advance evidence‐based practice in many disciplines, including sports physical therapy. Failure to publish important findings significantly diminishes the potential impact that those findings may have on clinical practice. 9
BASICS OF MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION & GENERAL WRITING TIPS
To begin it might be interesting to learn why reviewers accept manuscripts! Reviewers consider the following five criteria to be the most important in decisions about whether to accept manuscripts for publication: 1) the importance, timeliness, relevance, and prevalence of the problem addressed; 2) the quality of the writing style (i.e., that it is well‐written, clear, straightforward, easy to follow, and logical); 3) the study design applied (i.e., that the design was appropriate, rigorous, and comprehensive); 4) the degree to which the literature review was thoughtful, focused, and up‐to‐date; and 5) the use of a sufficiently large sample. 10 For these statements to be true there are also reasons that reviewers reject manuscripts. The following are the top five reasons for rejecting papers: 1) inappropriate, incomplete, or insufficiently described statistics; 2) over‐interpretation of results; 3) use of inappropriate, suboptimal, or insufficiently described populations or instruments; 4) small or biased samples; and 5) text that is poorly written or difficult to follow. 10 , 11 With these reasons for acceptance or rejection in mind, it is time to review basics and general writing tips to be used when performing manuscript preparation.
“Begin with the end in mind” . When you begin writing about your research, begin with a specific target journal in mind. 12 Every scientific journal should have specific lists of manuscript categories that are preferred for their readership. The IJSPT seeks to provide readership with current information to enhance the practice of sports physical therapy. Therefore the manuscript categories accepted by IJSPT include: Original research; Systematic reviews of literature; Clinical commentary and Current concept reviews; Case reports; Clinical suggestions and unique practice techniques; and Technical notes. Once a decision has been made to write a manuscript, compose an outline that complies with the requirements of the target submission journal and has each of the suggested sections. This means carefully checking the submission criteria and preparing your paper in the exact format of the journal to which you intend to submit. Be thoughtful about the distinction between content (what you are reporting) and structure (where it goes in the manuscript). Poor placement of content confuses the reader (reviewer) and may cause misinterpretation of content. 3 , 5
It may be helpful to follow the IMRaD format for writing scientific manuscripts. This acronym stands for the sections contained within the article: Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Each of these areas of the manuscript will be addressed in this commentary.
Many accomplished authors write their results first, followed by an introduction and discussion, in an attempt to “stay true” to their results and not stray into additional areas. Typically the last two portions to be written are the conclusion and the abstract.
The ability to accurately describe ideas, protocols/procedures, and outcomes are the pillars of scientific writing . Accurate and clear expression of your thoughts and research information should be the primary goal of scientific writing. 12 Remember that accuracy and clarity are even more important when trying to get complicated ideas across. Contain your literature review, ideas, and discussions to your topic, theme, model, review, commentary, or case. Avoid vague terminology and too much prose. Use short rather than long sentences. If jargon has to be utilized keep it to a minimum and explain the terms you do use clearly. 13
Write with a measure of formality, using scientific language and avoiding conjunctions, slang, and discipline or regionally specific nomenclature or terms (e.g. exercise nicknames). For example, replace the term “Monster walks” with “closed‐chain hip abduction with elastic resistance around the thighs”. You may later refer to the exercise as “also known as Monster walks” if you desire.
Avoid first person language and instead write using third person language. Some journals do not ascribe to this requirement, and allow first person references, however, IJSPT prefers use of third person. For example, replace “We determined that…” with “The authors determined that….”.
For novice writers, it is really helpful to seek a reading mentor that will help you pre‐read your submission. Problems such as improper use of grammar, tense, and spelling are often a cause of rejection by reviewers. Despite the content of the study these easily fixed errors suggest that the authors created the manuscript with less thought leading reviewers to think that the manuscript may also potentially have erroneous findings as well. A review from a second set of trained eyes will often catch these errors missed by the original authors. If English is not your first language, the editorial staff at IJSPT suggests that you consult with someone with the relevant expertise to give you guidance on English writing conventions, verb tense, and grammar. Excellent writing in English is hard, even for those of us for whom it is our first language!
Use figures and graphics to your advantage . ‐ Consider the use of graphic/figure representation of data and important procedures or exercises. Tables should be able to stand alone and be completely understandable at a quick glance. Understanding a table should not require careful review of the manuscript! Figures dramatically enhance the graphic appeal of a scientific paper. Many formats for graphic presentation are acceptable, including graphs, charts, tables, and pictures or videos. Photographs should be clear, free of clutter or extraneous background distractions and be taken with models wearing simple clothing. Color photographs are preferred. Digital figures (Scans or existing files as well as new photographs) must be at least 300dpi. All photographs should be provided as separate files (jpeg or tif preferred) and not be embedded in the paper. Quality and clarity of figures are essential for reproduction purposes and should be considered before taking images for the manuscript.
A video of an exercise or procedure speaks a thousand words. Please consider using short video clips as descriptive additions to your paper. They will be placed on the IJSPT website and accompany your paper. The video clips must be submitted in MPEG‐1, MPEG‐2, Quicktime (.mov), or Audio/Video Interface (.avi) formats. Maximum cumulative length of videos is 5 minutes. Each video segment may not exceed 50 MB, and each video clip must be saved as a separate file and clearly identified. Formulate descriptive figure/video and Table/chart/graph titles and place them on a figure legend document. Carefully consider placement of, naming of, and location of figures. It makes the job of the editors much easier!
Avoid Plagiarism and inadvertent lack of citations. Finally, use citations to your benefit. Cite frequently in order to avoid any plagiarism. The bottom line: If it is not your original idea, give credit where credit is due . When using direct quotations, provide not only the number of the citation, but the page where the quote was found. All citations should appear in text as a superscripted number followed by punctuation. It is the authors' responsibility to fully ensure all references are cited in completed form, in an accurate location. Please carefully follow the instructions for citations and check that all references in your reference list are cited in the paper and that all citations in the paper appear correctly in the reference list. Please go to IJSPT submission guidelines for full information on the format for citations.
Sometimes written as an afterthought, the abstract is of extreme importance as in many instances this section is what is initially previewed by readership to determine if the remainder of the article is worth reading. This is the authors opportunity to draw the reader into the study and entice them to read the rest of the article. The abstract is a summary of the article or study written in 3 rd person allowing the readers to get a quick glance of what the contents of the article include. Writing an abstract is rather challenging as being brief, accurate and concise are requisite. The headings and structure for an abstract are usually provided in the instructions for authors. In some instances, the abstract may change slightly pending content revisions required during the peer review process. Therefore it often works well to complete this portion of the manuscript last. Remember the abstract should be able to stand alone and should be as succinct as possible. 14
Introduction and Review of Literature
The introduction is one of the more difficult portions of the manuscript to write. Past studies are used to set the stage or provide the reader with information regarding the necessity of the represented project. For an introduction to work properly, the reader must feel that the research question is clear, concise, and worthy of study.
A competent introduction should include at least four key concepts: 1) significance of the topic, 2) the information gap in the available literature associated with the topic, 3) a literature review in support of the key questions, 4) subsequently developed purposes/objectives and hypotheses. 9
When constructing a review of the literature, be attentive to “sticking” or “staying true” to your topic at hand. Don't reach or include too broad of a literature review. For example, do not include extraneous information about performance or prevention if your research does not actually address those things. The literature review of a scientific paper is not an exhaustive review of all available knowledge in a given field of study. That type of thorough review should be left to review articles or textbook chapters. Throughout the introduction (and later in the discussion!) remind yourself that a paper, existing evidence, or results of a paper cannot draw conclusions, demonstrate, describe, or make judgments, only PEOPLE (authors) can. “The evidence demonstrates that” should be stated, “Smith and Jones, demonstrated that….”
Conclude your introduction with a solid statement of your purpose(s) and your hypothesis(es), as appropriate. The purpose and objectives should clearly relate to the information gap associated with the given manuscript topic discussed earlier in the introduction section. This may seem repetitive, but it actually is helpful to ensure the reader clearly sees the evolution, importance, and critical aspects of the study at hand See Table 1 for examples of well‐stated purposes.
Examples of well-stated purposes by submission type.
| Type of Submission | Example purpose |
|---|---|
| Original Research | Therefore, the purpose of this study was to describe the volume of pitching for pitchers from multiple college teams at the Division I level. |
| Systematic Review of the Literature | Therefore, the purpose of this systematic review was to investigate the association between training characteristics and running related injuries. |
| Clinical Commentary/Current Concepts Report | The purpose of this clinical commentary is to examine the risk factors contributing to the high recurrence rate of hamstring injuries, and propose a unique rehabilitation strategy addressing these factors in order to decrease the rate of reinjury. |
| Case Report | The purpose of this case report is to describe the non-surgical management of a professional athlete with the characteristic signs and symptoms of a sports hernia. |
| Clinical Suggestion | The purpose of this clinical commentary is to review types of integumentary wounds that may occur in sport, and their acute management. |
The methods section should clearly describe the specific design of the study and provide clear and concise description of the procedures that were performed. The purpose of sufficient detail in the methods section is so that an appropriately trained person would be able to replicate your experiments. 15 There should be complete transparency when describing the study. To assist in writing and manuscript preparation there are several checklists or guidelines that are available on the IJSPT website. The CONSORT guidelines can be used when developing and reporting a randomized controlled trial. 16 The STARD checklist was developed for designing a diagnostic accuracy study. 17 The PRISMA checklist was developed for use when performing a meta‐analyses or systematic review. 18 A clear methods section should contain the following information: 1) the population and equipment used in the study, 2) how the population and equipment were prepared and what was done during the study, 3) the protocol used, 4) the outcomes and how they were measured, 5) the methods used for data analysis. Initially a brief paragraph should explain the overall procedures and study design. Within this first paragraph there is generally a description of inclusion and exclusion criteria which help the reader understand the population used. Paragraphs that follow should describe in more detail the procedures followed for the study. A clear description of how data was gathered is also helpful. For example were data gathered prospectively or retrospectively? Who if anyone was blinded, and where and when was the actual data collected?
Although it is a good idea for the authors to have justification and a rationale for their procedures, these should be saved for inclusion into the discussion section, not to be discussed in the methods section. However, occasionally studies supporting components of the methods section such as reliability of tests, or validation of outcome measures may be included in the methods section.
The final portion of the methods section will include the statistical methods used to analyze the data. 19 This does not mean that the actual results should be discussed in the methods section, as they have an entire section of their own!
Most scientific journals support the need for all projects involving humans or animals to have up‐to‐date documentation of ethical approval. 20 The methods section should include a clear statement that the researchers have obtained approval from an appropriate institutional review board.
Results, Discussion, and Conclusions
In most journals the results section is separate from the discussion section. It is important that you clearly distinguish your results from your discussion. The results section should describe the results only. The discussion section should put those results into a broader context. Report your results neutrally, as you “found them”. Again, be thoughtful about content and structure. Think carefully about where content is placed in the overall structure of your paper. It is not appropriate to bring up additional results, not discussed in the results section, in the discussion. All results must first be described/presented and then discussed. Thus, the discussion should not simply be a repeat of the results section. Carefully discuss where your information is similar or different from other published evidence and why this might be so. What was different in methods or analysis, what was similar?
As previously stated, stick to your topic at hand, and do not overstretch your discussion! One of the major pitfalls in writing the discussion section is overstating the significance of your findings 4 or making very strong statements. For example, it is better to say: “Findings of the current study support….” or “these findings suggest…” than, “Findings of the current study prove that…” or “this means that….”. Maintain a sense of humbleness, as nothing is without question in the outcomes of any type of research, in any discipline! Use words like “possibly”, “likely” or “suggests” to soften findings. 12
Do not discuss extraneous ideas, concepts, or information not covered by your topic/paper/commentary. Be sure to carefully address all relevant results, not just the statistically significant ones or the ones that support your hypotheses. When you must resort to speculation or opinion, be certain to state that up front using phrases such as “we therefore speculate” or “in the authors' opinion”.
Remember, just as in the introduction and literature review, evidence or results cannot draw conclusions, just as previously stated, only people, scientists, researchers, and authors can!
Finish with a concise, 3‐5 sentence conclusion paragraph. This is not just a restatement of your results, rather is comprised of some final, summative statements that reflect the flow and outcomes of the entire paper. Do not include speculative statements or additional material; however, based upon your findings a statement about potential changes in clinical practice or future research opportunities can be provided here.
CONCLUSIONS
Writing for publication can be a challenging yet satisfying endeavor. The ability to examine, relate, and interlink evidence, as well as to provide a peer‐reviewed, disseminated product of your research labors can be rewarding. A few suggestions have been offered in this commentary that may assist the novice or the developing writer to attempt, polish, and perfect their approach to scholarly writing.
How to Write a Scientific Essay

When writing any essay it’s important to always keep the end goal in mind. You want to produce a document that is detailed, factual, about the subject matter and most importantly to the point.
Writing scientific essays will always be slightly different to when you write an essay for say English Literature . You need to be more analytical and precise when answering your questions. To help achieve this, you need to keep three golden rules in mind.
- Analysing the question, so that you know exactly what you have to do
Planning your answer
- Writing the essay
Now, let’s look at these steps in more detail to help you fully understand how to apply the three golden rules.
Analysing the question
- Start by looking at the instruction. Essays need to be written out in continuous prose. You shouldn’t be using bullet points or writing in note form.
- If it helps to make a particular point, however, you can use a diagram providing it is relevant and adequately explained.
- Look at the topic you are required to write about. The wording of the essay title tells you what you should confine your answer to – there is no place for interesting facts about other areas.
The next step is to plan your answer. What we are going to try to do is show you how to produce an effective plan in a very short time. You need a framework to show your knowledge otherwise it is too easy to concentrate on only a few aspects.
For example, when writing an essay on biology we can divide the topic up in a number of different ways. So, if you have to answer a question like ‘Outline the main properties of life and system reproduction’
The steps for planning are simple. Firstly, define the main terms within the question that need to be addressed. Then list the properties asked for and lastly, roughly assess how many words of your word count you are going to allocate to each term.
Writing the Essay
The final step (you’re almost there), now you have your plan in place for the essay, it’s time to get it all down in black and white. Follow your plan for answering the question, making sure you stick to the word count, check your spelling and grammar and give credit where credit’s (always reference your sources).
How Tutors Breakdown Essays
An exceptional essay
- reflects the detail that could be expected from a comprehensive knowledge and understanding of relevant parts of the specification
- is free from fundamental errors
- maintains appropriate depth and accuracy throughout
- includes two or more paragraphs of material that indicates greater depth or breadth of study
A good essay
An average essay
- contains a significant amount of material that reflects the detail that could be expected from a knowledge and understanding of relevant parts of the specification.
In practice this will amount to about half the essay.
- is likely to reflect limited knowledge of some areas and to be patchy in quality
- demonstrates a good understanding of basic principles with some errors and evidence of misunderstanding
A poor essay
- contains much material which is below the level expected of a candidate who has completed the course
- Contains fundamental errors reflecting a poor grasp of basic principles and concepts
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Write Like a Scientist
A Guide to Scientific Communication
What is scientific writing ?
Scientific writing is a technical form of writing that is designed to communicate scientific information to other scientists. Depending on the specific scientific genre—a journal article, a scientific poster, or a research proposal, for example—some aspects of the writing may change, such as its purpose , audience , or organization . Many aspects of scientific writing, however, vary little across these writing genres. Important hallmarks of all scientific writing are summarized below. Genre-specific information is located here and under the “By Genre” tab at the top of the page.
What are some important hallmarks of professional scientific writing?
1. Its primary audience is other scientists. Because of its intended audience, student-oriented or general-audience details, definitions, and explanations — which are often necessary in lab manuals or reports — are not terribly useful. Explaining general-knowledge concepts or how routine procedures were performed actually tends to obstruct clarity, make the writing wordy, and detract from its professional tone.
2. It is concise and precise . A goal of scientific writing is to communicate scientific information clearly and concisely. Flowery, ambiguous, wordy, and redundant language run counter to the purpose of the writing.
3. It must be set within the context of other published work. Because science builds on and corrects itself over time, scientific writing must be situated in and reference the findings of previous work . This context serves variously as motivation for new work being proposed or the paper being written, as points of departure or congruence for new findings and interpretations, and as evidence of the authors’ knowledge and expertise in the field.
All of the information under “The Essentials” tab is intended to help you to build your knowledge and skills as a scientific writer regardless of the scientific discipline you are studying or the specific assignment you might be working on. In addition to discussions of audience and purpose , professional conventions like conciseness and specificity, and how to find and use literature references appropriately, we also provide guidelines for how to organize your writing and how to avoid some common mechanical errors .
If you’re new to this site or to professional scientific writing, we recommend navigating the sub-sections under “The Essentials” tab in the order they’re provided. Once you’ve covered these essentials, you might find information on genre- or discipline-specific writing useful.

How to Write a Standout Conclusion in UPSC Essays for Better Scores
In the competitive world of UPSC examinations, essay writing plays a crucial role in showcasing not only a candidate’s knowledge but also their analytical and structured thinking. A well-structured essay can set you apart, but what often leaves a lasting impression on the examiner is the conclusion. A strong conclusion not only ties your argument together but reinforces your key points effectively. In this blog, we’ll break down how to craft a standout conclusion in UPSC essays to elevate your score.
1. Why Is the Conclusion Important?
The conclusion of an essay is like the final bow in a performance—it is the last thing your reader remembers. For UPSC essays, a standout conclusion shows the examiner that you can summarize complex arguments succinctly, create closure, and give weight to the points you have raised. A poorly written conclusion, on the other hand, can diminish the strength of an otherwise excellent essay. Hence, learning how to write a standout conclusion in UPSC essays is essential for securing higher marks.
2. Summarize, Don’t Repeat
A common mistake candidates make is repeating what they’ve already said in the body of the essay. To write a standout conclusion in UPSC essays, ensure that you’re summarizing your main points but not merely regurgitating them. Instead, rephrase the core ideas in a way that links them logically and draws out their significance.
For instance, if you’re writing on a topic like “Environmental Policies in India,” your conclusion should reiterate the main challenges and successes but present them in a way that emphasizes their relevance to India’s future sustainable development.
3. Provide Closure with a Broader Perspective
While it’s important to reiterate your key arguments, a standout conclusion in UPSC essays must also provide closure by reflecting on the broader significance of the topic. You could link it to current affairs, global developments, or long-term policy implications. This demonstrates your ability to think critically and holistically, a trait valued in UPSC exams.
If you’re writing an essay on “India’s Demographic Dividend,” you could end by linking your discussion to global trends in aging populations or the potential for India to shape future global economic policies. This adds depth to your conclusion and makes it stand out.
4. End with a Forward-Looking Statement
Another way to ensure a standout conclusion in UPSC essays is to finish with a forward-looking statement or solution. This gives your essay a sense of direction and optimism. It signals that you’re not only capable of analyzing a situation but also thinking proactively about solutions.
For an essay on “Agricultural Reforms in India,” your conclusion could suggest forward-thinking measures, like emphasizing sustainable farming techniques or integrating technology with agriculture to solve future challenges.
5. Avoid Ending with Questions
Ending your essay with a question might seem like a good way to provoke thought, but it often leaves your reader (examiner) with a sense of incompleteness. For a standout conclusion in UPSC essays, focus on providing definitive closure rather than open-ended questions.
What to Avoid:
Don’t end with statements like, “So, where does India’s economy go from here?” Instead, make a strong assertion: “With continued focus on reforms and innovation, India’s economy is poised to become a global powerhouse.”
6. Use Quotes or Data Wisely
While it’s common to start an essay with a quote, using a quote in the conclusion can be just as effective if done correctly. A quote can lend authority to your conclusion, provided it aligns with your argument. However, don’t rely on it too heavily—your voice should remain central.
For an essay on “Inclusive Education in India,” you could conclude with a quote from an educationist like Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam to reinforce the importance of educational reforms.
7. Stay Neutral but Firm
Remember, UPSC essays are evaluated for your balanced views. A standout conclusion in UPSC essays is not overly biased but presents a well-reasoned, objective viewpoint. Ensure that while you’re summarizing, you’re also leaving room for nuance and complexity.
For a topic on “Caste and Politics in India,” your conclusion should acknowledge both the positive role of reservation in empowering marginalized communities and the potential downsides if not implemented effectively. This shows a balanced and mature outlook.
8. Practice Crafting Conclusions in Mock Essays
Like any other skill, writing a standout conclusion in UPSC essays improves with practice. One of the best ways to hone this skill is by writing mock essays and focusing particularly on the conclusion. Sleepy Classes offers a range of essay courses where experienced mentors guide students through essay writing strategies, including how to end essays powerfully.
Other platforms like Vision IAS and ForumIAS also provide mock essay writing tests where you can practice and get feedback.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion (pun intended), the secret to writing a standout conclusion in UPSC essays is to be clear, concise, and forward-looking. A strong conclusion leaves the examiner with a positive impression, increases the weight of your arguments, and reinforces the purpose of your essay. Practice summarizing complex ideas without repetition, stay neutral in your tone, and ensure you’re linking your conclusion to broader themes or solutions.
With consistent practice, mock essay writing, and guidance from coaching platforms like Sleepy Classes, you can master the art of crafting standout conclusions for UPSC essays and boost your scores significantly.
- Sleepy Classes: Essay Writing Course
- Vision IAS: Essay Writing Test Series
- ForumIAS: Essay Mains Guidance Program
By integrating these tips and utilizing available resources, you’ll be well-equipped to write a standout conclusion in your UPSC essays that leaves a lasting impact on your examiners.
Previous Post The Role of Globalization in Indian Society for UPSC Sociology Optional
Next post how to tackle reading comprehension in csat with limited time, similar posts, how to use scholarly journals for psir optional preparation.
The Role of Globalization in Indian Society for UPSC Sociology Optional

How to Tackle Reading Comprehension in CSAT with Limited Time
Browse our content, information.
- Disclaimer
- Privacy Policy
- Refund & Cancellation
- General Studies
- Monday – Saturday (9AM – 5PM)
- [email protected]
- 1800-890-3043
- Sleepy Edusolutions Private Limited
- GST No.- 03ABDCS3013L1ZN
- Plot No. E-42, Phase 8, Industrial Area, Sahibzada Ajit Singh Nagar, Punjab 160071
© 2024 Sleepy Classes IAS.
- General Studies 2025
- Sociology 2025
- Political Science & IR 2025
- Political Science & International Relations
- Essay Courses
- Psychological Counselling
- Prelims Courses
- Political Science & IR
- NCERT Batch
- Current Affairs

- Uttar Pradesh PSC Courses
- Jammu & Kashmir PCS Courses
- Punjab PSC Courses
- Bihar PSC Courses
- Haryana PSC Courses
- Himachal Pradesh PSC Courses
- Odisha PSC Courses
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- UPSC Previous Year Papers
- PSIR Optional – Syllabus & PYQs
- Haryana PCS
- Himachal Pradesh PCS
- Jammu & Kashmir PCS
- Uttar Pradesh PCS
- Recommended Books For UPSC
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Our Toppers
Fill the Form to Register
Which Year are You Targeting to Crack the UPSC Exam? —Please choose an option— Preparing for UPSC 2024 Preparing for UPSC 2025 Beyond That Preparing for State PSC
Do You Require Coaching? —Please choose an option— Yes No Joined Sleepy Classes Joined Some Other Coaching
Which Optional are You Preparing For? Sociology Political Science & International Relations Others
Which Year are You Targeting to Crack the UPSC Exam? Preparing for UPSC 2024 Preparing for UPSC 2025 Beyond That Preparing for State PSC
Do You Require Coaching? Yes No Joined Sleepy Classes Joined Some Other Coaching
Fill the Form to Get State PYQs
Which State PCS Are You Preparing For? Select Your State Uttar Pradesh Bihar Punjab Haryana Himachal Pradesh Jammu and Kashmir Other
Do You Require Coaching? Looking for Coaching Preparing by Yourself Already Joined Coaching
Fill Your Details to Register
Fill the form to download your files.
What is Your UPSC Optional —Please choose an option— Sociology Political Science & IR Others
Year of Attempt UPSC 2024 UPSC 2025 Beyond that
Are You Preparing On Your Own? —Please choose an option— Yes No Joined Sleepy Classes Joined Some Other Coaching Looking for Mentorship Only
Fill the Form to Download Your File
Are You Preparing On Your Own? Yes I have already joined Coaching I am looking for Coaching I am looking for Mentorship
Fill Your Details to Register for the IGP 2023
Roll Number
What is Your Optional?
Preferred Mode for Mock Interview —Please choose an option— Online Offline – Delhi Offline – Chandigarh
Marks in Previous Interview (if applicable)
Date of UPSC Interview (if applicable)
Home State & Other States (if any)
Academic Qualifications
Upload DAF-I
Upload DAF-II
Upload Passport-Size Photograph
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
Lab Report Format

The Ultimate Guide to Lab Report Format: Simple Steps to Follow
12 min read
Published on: Sep 28, 2024
Last updated on: Sep 28, 2024

People also read
Write Your Lab Report Like a Pro with this Helpful Guide
Share this article
Ever found yourself staring at a blank page, wondering how to start your lab report? It’s a common struggle, especially when you’re unsure of the right format to follow.
This confusion can lead to frustration, as you know that a poorly structured report could affect your grades or the clarity of your findings.
But don’t worry—getting your lab report format right doesn’t have to be a headache. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the essential elements of a lab report format, so you can tackle your next assignment with confidence.
Ready to dive in? Let's start by understanding what a lab report actually is.
On This Page On This Page -->
What Is A Lab Report? - A Simple Definition
A lab report is a detailed document that explains an experiment you've conducted in a scientific setting. It serves as a record of what you did, how you did it, what you observed, and what your results mean.
The main purpose of a lab report is to communicate your findings clearly and logically, so others can understand your process and replicate your experiment if needed. It typically includes sections like the introduction, methods, results, and discussion, each serving a specific role in telling the story of your experiment.
In essence, a lab report is your way of sharing scientific knowledge in a structured format, making your research accessible and understandable to others.
Lab Report Format Template
When it comes to writing a lab report, following a clear and organized format is essential. Each section of your report serves a specific purpose and helps present your experiment and findings in a logical manner.
Below, we'll break down each component of a lab report, so you know exactly what to include and how to structure your work. By following this format, youâll ensure that your report is comprehensive and easy to understand.
The title page is the first impression of your report. It should include the title of your experiment, your name, the date, and any other relevant information like your instructorâs name or course details. Keep it simple and professional.
The abstract is a brief summary of your entire report, usually no more than 100-200 words. It highlights the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of your experiment. Think of it as a snapshot that gives readers a quick overview of what to expect.
Introduction
In the introduction, you provide background information on the experiment, state the problem youâre investigating, and explain why itâs important. This section sets the stage for the reader, offering context and defining the scope of your report.
Your hypothesis is an educated guess about the outcome of your experiment. It should be clear, testable, and based on existing knowledge or theories. This section outlines what you aim to prove or disprove through your conducted experiment.
Materials and Methods (Procedures and Equipment)
This section details the materials, tools, and methods you used in your experiment. Itâs important to be precise so that someone else can replicate your experiment based on your description. Include step-by-step procedures and a list of equipment.
Experimental Design
Here, you explain how you structured your experiment, including the variables you tested and the controls you used. This section should clarify how you ensured the reliability and accuracy of your results.
Results/Data Analysis
In the results section, you present the data you collected during your experiment. Use tables, infographics, and charts to make your findings clear and easy to interpret. Avoid drawing conclusions hereâjust present the raw data.
Calculations
If your experiment involves calculations, this section is where you'll show your work. Include all formulas and steps used to arrive at your results. Clear and accurate calculations are crucial for supporting your findings.
This is where you interpret your results and explain what they mean. Here, you'll compare your findings with your hypothesis and discuss any anomalies or unexpected outcomes. The discussion section allows you to explore the implications of your results.
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of your experiment and their significance. Restate whether your hypothesis was supported and suggest any further research that could be conducted. This section should neatly wrap up your report
Documentation
If your experiment involved specific protocols, safety measures, or compliance with regulations, detail them in the documentation section. This ensures transparency and adherence to standards.
The references section lists all the sources you cited in your report. Use the appropriate citation style as required by your instructor or field of study. Proper citation and referencing adds credibility to your work.
The appendix includes any additional material that supports your report, such as raw data, detailed calculations, or supplementary information. Itâs a useful place to include material that is too lengthy or detailed to fit in the main sections.
By following this structured format, your lab report will be well-organized and easy to follow. Next, we'll walk through a complete lab report example that incorporates all these sections, so you can see how it all comes together in practice.
Lab Report Format Example
Understanding the format of a lab report is essential, but seeing an example in action can be even more helpful. Here, we'll walk through a complete lab report, section by section, using a simple experiment as an example.
This example will show you how to apply the format we discussed earlier, ensuring that your report is clear, detailed, and easy to follow.
: The Effect of Light on Plant Growth |
This experiment aimed to determine the effect of different light conditions on the growth of bean plants. Three groups of plants were exposed to full sunlight, partial sunlight, and no light over two weeks. The growth was measured by height and leaf count. Results showed that plants in full sunlight grew the most, while those in no light showed minimal growth. The conclusion supports the hypothesis that light is essential for optimal plant growth. |
Plants rely on light for photosynthesis, the process that allows them to produce energy. This experiment investigates how varying light levels affect the growth of bean plants. Understanding the relationship between light and plant growth is crucial for optimizing agricultural practices. The experiment will test the hypothesis that more light results in greater plant growth, providing insights into how light influences plant health. |
The hypothesis for this experiment is that bean plants exposed to full sunlight will grow taller and develop more leaves than those exposed to partial sunlight or no light. |
: : |
The experiment was designed to test the effect of light on plant growth by controlling the light exposure for three groups of bean plants. The independent variable was the light condition (full sunlight, partial sunlight, no light), while the dependent variables were plant height and leaf count. Each group contained three plants to account for variability and increase reliability. |
: Average height 15 cm, average leaf count 10. Average height 10 cm, average leaf count 7. Average height 2 cm, average leaf count 2.: The data showed a clear trend where plants exposed to more light grew taller and developed more leaves. The full sunlight group had the most growth, while the no light group showed stunted growth. |
: (15 cm - 5 cm) / 14 days = 0.71 cm/day (10 cm - 5 cm) / 14 days = 0.36 cm/day (2 cm - 5 cm) / 14 days = -0.21 cm/day |
The experimentâs results support the hypothesis that light significantly influences plant growth. Plants in full sunlight showed the highest growth rate, confirming that light is crucial for photosynthesis and energy production. The stunted growth in the no-light group highlights the importance of light in maintaining plant health. Unexpectedly, the partial sunlight group showed less growth than anticipated, suggesting that light intensity might also play a role. Further research could explore the effects of different light wavelengths on plant growth. |
In conclusion, this experiment demonstrates that light is a vital factor in plant growth, with full sunlight leading to the most significant growth. The hypothesis was supported by the data, confirming that light exposure directly impacts plant development. This information could be useful in agricultural practices where light conditions can be controlled to optimize growth. |
All safety protocols were followed during the experiment, including proper handling of plants and equipment. The experiment was conducted in a controlled environment, ensuring accurate results. |
|
: Raw data tables for plant height and leaf count. |
Now that youâve seen a complete lab report example, you can better understand how to apply this format to your own work. In the next section, weâll provide different detailed lab report format examples, showing how all these elements come together in a real-world scenario.
Additional Lab Report Format PDF Examples
Sometimes, seeing multiple examples can make all the difference in mastering the structure and format of a lab report. In this section, weâll provide links to a variety of PDF examples that showcase different types of lab reports across various scientific disciplines.
Lab Report Format Chemistry
Lab Report Format Physics
Pathology Lab Report Format
Medical Lab Report Format
Lab Report Format University
College Lab Report Format
APA Lab Report Format
MLA Lab Report Format
Best Practices For Writing A Lab Report That Stands Out
Here are some practical tips to help you write an outstanding lab report:
- Plan and Prepare Thoroughly: Before you start writing, make sure you understand the experiment and the requirements of the report. Gather all relevant data, notes, and observations. Creating an outline can help you organize your thoughts and ensure you cover all necessary sections systematically.
- Use Third-Person Pronoun: Write your report in the third person to maintain a formal and objective tone. Avoid using first-person pronouns like "I" or "we". For example, instead of saying " We conducted the experiment, " write " The experiment was conducted ".
- Employ Past-Passive Tense: Use the past passive tense to describe the procedures and results. This approach helps to focus on the actions and results rather than the researcher. For instance, instead of " We mixed the solutions ," write " The solutions were mixed ".
- Be Clear and Concise: Ensure that your writing is clear and to the point. Avoid unnecessary jargon and complex sentences that might confuse the reader. Each section of your report should be straightforward and focused on conveying the relevant information.
- Follow a Structured Format: Adhere to the standard lab report structure: Title Page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusion, References, and Appendices. Consistent formatting helps readers follow your report easily and understand your findings.
- Include Accurate Data and Analysis: Present your data clearly using tables, graphs, or charts as needed. Ensure that your analysis is accurate and directly addresses the research question. Discuss the significance of your results and how they relate to your hypothesis.
- Review and Revise: Proofread your lab report to correct any grammatical errors, typos, or inconsistencies. Revising your report helps to ensure clarity and accuracy. Consider having a peer review of your work to get additional feedback.
By applying these tips, you can enhance the quality of your lab report and effectively communicate your research findings. Following a structured approach and focusing on transparency and precision will help you produce a professional and credible report.
Writing a well-structured and insightful lab report is essential for communicating your research effectively. By following the outlined format, you can ensure your report is comprehensive and professionally presented.
Moreover, adhering to the tips and techniques mentioned will further enhance the clearness and impact of your report. Selecting a relevant and engaging topic will help in producing a report that is both informative and compelling. Remember, the key to a successful lab report lies in its ability to purely convey the objectives, methods, and findings of your research.
If you need further assistance with the ' write my lab report' task, or if you're looking for help with other academic writing tasks, our expert essay writing service is here to support you 24/7. Reach out to us to ensure your work meets the highest standards of excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do a lab report and a research paper differ.
A lab report is a detailed document that describes the process and results of an experiment, focusing on practical aspects and procedures. In contrast, a research paper is a more comprehensive analysis that includes a literature review, methodology, results, and discussion, often aiming to contribute new knowledge or insights to a field.
What distinguishes the results section from the discussion section inside a lab report?
In a lab report, the results section presents the raw data and findings from the experiment or investigation, while the discussion section interprets these results, exploring their significance, implications, and how they fit with other research or theories.
Which format, MLA or APA, is commonly used for lab reports?
Lab reports can be written in either APA or MLA style, depending on the instructor's preference or the specific requirements of the course. Both styles are suitable for lab reports, but APA is more commonly used in scientific disciplines for its emphasis on data presentation and clarity.
What is the typical length of a lab report?
The length of a lab report can vary depending on the complexity of the experiment and the instructor’s requirements, but it typically ranges from 5 to 10 pages. This includes sections such as the introduction, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion.
Cathy A. (Marketing, Literature)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Home > Blog > How To Write an Essay Introduction: A Step-by-Step Guide

How To Write an Essay Introduction: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Smodin Editorial Team
- Published: September 24, 2024
- Step-by-Step Instructions for Writing
- Student Guide for Writing
Do you want to learn how to write an essay introduction to get the best results? Then you’ll love the tips in this article to help you get your essay off to the right start. You’ll see that there’s a recipe for success whether you’re writing an expository essay introduction or a literary analysis essay introduction.
Furthermore, we’ll share the top reasons why your essay introductions are important and why you need to get them right. Keep reading to discover how to write an introductory paragraph that will grab your readers’ attention.

5 Reasons Why the Essay Introduction Is Important
Are you not sure why focusing on your essay introduction is a vital step of the overall essay-writing process? Then by the end of this section, you’ll see that it’s one of the more important aspects of your essay.
These are some of the reasons why a great introduction makes it easier to create the rest of your content.
1. Grabs the Reader’s Attention
The introduction serves as the first impression of your essay and can capture the reader’s attention immediately. Also, a well-crafted introduction can raise interest and make the reader want to continue exploring your ideas.
Here are a few best practices for grabbing the reader’s attention with an introduction:
- Start with a question: Ask a provocative or thought-provoking question that encourages the reader to think deeply or consider their own experiences. This instantly engages them as they seek answers or connect with the topic on a personal level.
- Use a surprising fact or statistic: Present an unexpected or shocking fact that challenges the reader’s assumptions. This creates curiosity and a sense of urgency to learn more, which compels them to keep reading.
- Tell an anecdote: Begin with a brief and vivid story that relates to your topic. A personal or relatable narrative can draw readers in emotionally, thereby making them more invested in what follows. Make sure that it relates to your thesis statement in your essay introductions.
- Open with a bold statement: Make a strong and opinionated claim or a bold declaration that challenges the status quo. This can provoke interest and even disagreement, which prompts the reader to continue reading to see your perspective.
- Set the scene: Create a sensory-rich description of a situation or environment. Generally, painting a vivid picture with words immerses the reader in the setting. This in turn makes them curious about what will happen next.
2. Provides Context and Background Information
The introduction establishes the context for your essay by providing essential background information. It helps the reader understand the topic, the significance of the issue, and the broader framework within which your argument is situated.
This context is crucial for readers unfamiliar with the subject, as it prepares them to grasp the subsequent points you will make. For example, when writing an argumentative essay introduction, you may want to provide context for the point you will make.

3. States the Thesis or Central Argument
A key function of the introduction is to present the thesis statement , the central argument or claim of your essay. This thesis acts as the guiding thread for the entire essay by providing direction and focus.
Adding a clear thesis statement helps the reader understand the purpose and scope of your essay. Furthermore, it also allows the reader to anticipate the structure of your argument and the points you will address.
4. Sets the Tone and Style
The introduction not only introduces the content of the essay but also establishes the tone and style. This includes essays that are formal, informal, serious, or humorous. Furthermore, the introduction sets the reader’s expectations for how the topic will be addressed.
Also, the language, sentence structure, and overall approach in the introduction can signal to the reader what kind of essay they are about to read. Hence, by setting the appropriate tone, the introduction aligns the reader’s mindset with the essay’s objectives.
5. Outlines the Structure of the Essay
An effective introduction often provides a concise summary of the essay’s structure. This includes outlining the main point or areas that will be covered. This roadmap helps the reader understand how your argument will be developed and what to expect in each section of the essay.
Additionally, previewing the essay’s outline and the introduction makes it easier for the reader to follow the logical flow of ideas. This structural outline is particularly important in longer essays, where it serves as a guide that helps the reader navigate the complexities of your argument.

Can I Use AI Tools To Write Essay Introduction Paragraphs?
Using AI tools to write an essay introduction offers several advantages that enhance both the writing process and the final output. First, AI can help generate creative and engaging hooks, which are crucial for capturing the reader’s attention.
These tools also provide suggestions for structuring the introduction, which ensures that essential elements like background information and the thesis statement are effectively presented. You may struggle to complete this step on your own, or it will take a lot of time.
Additionally, AI can assist in refining language, improving clarity, and maintaining the appropriate tone, making the introduction more impactful. Tools like Smodin’s Advanced AI Essay Writer will help you with this, which is also great for overcoming writer’s block.
Moreover, AI tools can help ensure that the introduction is concise, focused, and aligned with the essay’s overall direction. Ultimately, AI tools serve as valuable aids for essays that also help you understand how to produce better-quality work in the future.

How To Write an Essay Introduction: Step-By-Step
Now let’s focus on the step-by-step process for essay academic writing. You’ll see that there is a method that will ensure you get the right result. This process is what most teachers expect you to use to get the best results.
1. Start With a Hook
Write a hook as the first sentence of your essay to grab the reader’s attention and encourage them to continue reading. Also, the hook should be relevant to your topic and can take many forms. Top examples include a surprising fact, an interesting question, a brief anecdote, or a bold statement.
The key is to intrigue your reader right away. For example, if your essay is about climate change, then write a startling statistic like “The last decade was the hottest on record.” This could draw readers in and make them curious about what your essay will explore.
2. Provide Background Information
After your hook, provide some background information to give context to your essay. This section should briefly introduce the topic and any key terms or issues your reader needs to understand before delving into your main argument.
The background sets the stage for your thesis and helps your readers follow the upcoming discussion. For instance, if your essay is about the influence of social media on youth, you might briefly discuss the rise of social media and its widespread use among teenagers. It can give your readers a basic understanding of why this topic is significant.
3. Define the Purpose of Your Essay
Clearly defining the purpose of your essay lets your readers know what to expect. In this section, you state the focus of your essay, which could involve arguing a point, analyzing a concept, comparing ideas, or exploring an issue.
This purpose statement provides direction and prepares your readers for the argument or analysis you’ll develop. Imagine that you’re writing about renewable energy. In this instance, you could define your essay’s purpose as examining the benefits and challenges of transitioning to sustainable energy sources.
4. Clearly State Your Thesis Statement
Your thesis statement is the central argument or point of your essay and is essential to your introduction. It should be specific, concise, and clearly express your position or the main idea you’ll be arguing or exploring in your essay. Also, a strong thesis statement guides your writing and informs your reader about the essay’s focus.
For example, if you’re writing about the effects of social media on communication, your thesis might be: “While social media fosters global connections, it also diminishes face-to-face interactions and spreads misinformation, challenging the quality of our communications.”
5. Outline the Structure
Providing an outline of your essay’s structure within the introduction can help guide your reader through the content. This section briefly summarizes the main points or sections you’ll cover, thereby giving your reader a roadmap to follow. While this step is optional, it can be particularly helpful for longer or more complex essays. Also, it will help you write better sentences as you have more structure.
For instance, if you’re writing about the impacts of climate change, you might outline that your essay will first discuss the causes. Then you can cover the effects on different ecosystems and the potential solutions. This is an excellent way to give your reader a preview of what’s to come.
6. Finalize With a Transition Sentence
The last part of your introduction should include a transition sentence that smoothly connects your introduction to the first body paragraph. This sentence helps maintain the flow of your essay and ensures that your reader is not caught off guard by the shift in focus. A good transition sentence hints at what’s coming next without fully diving into the details.
Let’s look at an example of a well-executed transition sentence if you’re discussing the positive aspects of social media: “Understanding the widespread use of social media is essential to grasp its influence on modern communication practices.”

Frequently Asked Questions
How long should an essay introduction be.
An essay introduction should typically be about 10% of the total essay length. For shorter essays, a single paragraph may suffice, while longer essays may require two or three paragraphs. The specifics typically depend on the nature of your assignment.
The key is to be concise yet informative and ensure that you cover the essential elements. This typically includes a hook, background information, and a thesis statement. However, make sure you don’t overwhelm the reader by providing too much detail prematurely.
What makes a good hook in an introduction?
A good hook is engaging, relevant, and thought-provoking. For example, you can use a surprising fact, a rhetorical question, a quote, or a brief anecdote that draws the reader in. Also, the hook should relate directly to the essay’s topic and smoothly lead into the background information and thesis statement.
Where should the thesis statement be placed in the introduction?
The thesis statement should typically be placed at the end of the introduction. This placement allows you to first provide a hook and background information. Then you can gradually lead the reader to your main argument.
Furthermore, by positioning the thesis at the end, you effectively transition into the body of the essay. This will seem more natural and improve the writing flow.
Can I outline the structure of my essay in the introduction?
Yes, outlining the structure in the introduction can be helpful, especially in longer essays. Therefore, a brief overview of the key points or sections helps the reader understand how the essay will develop.
This roadmap provides clarity and ensures that the reader can follow your argument’s progression. However, keep it concise to maintain the introduction’s focus on the thesis.
What common mistakes should I avoid in an essay introduction?
Common mistakes to avoid in your essay introduction include being too vague, overly detailed, or off-topic. Additionally, avoid generic statements, unnecessary background information, and long-winded explanations.
Don’t forget to include a clear thesis statement, as this guides the essay. You’ll also want to follow the best practices for writing and coming up with a thesis statement to ensure you get the best results.

Write Top Essay Introductions With Smodin AI
Writing an essay introduction paragraph is straightforward when you follow the best practices in this article. Make sure that you select a topic that you’re enthusiastic about. This allows you to naturally be curious about the topic and want to research on a deeper level.
Now that you understand how to write an essay introduction apply the tips to your next project. Practice makes perfect, so it may take a few tries and editing to get it right. Finally, use the structural suggestions in this article to ensure you don’t miss any important points.
Do you need further help with your essay writing? Then check out Smodin AI now ! Our tools can support you with every aspect of your essay, including the introduction.
Try the Smodin AI Writer today to boost the performance of your essay writing and impress your readers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tutorial Essays for Science Subjects. This guide is designed to provide help and advice on scientific writing. Although students studying Medical and Life Sciences are most likely to have to write essays for tutorials at Oxford, it is important all scientists learn to write clearly and concisely to present their data and conclusions.
This guide was inspired by Joshua Schimel's Writing Science: How to Write Papers that Get Cited and Proposals that Get Funded—an excellent book about scientific writing for graduate students and professional scientists—but designed to address undergraduate students. While the guide was written by a group of ecologists and evolutionary ...
How to write a research paper according to the LEAP approach. For a scientist, it is much easier to start writing a research paper with laying out the facts in the narrow sections (i.e. results), step back to describe them (i.e. write the discussion), and step back again to explain the broader picture in the introduction.
In each paragraph, the first sentence defines the context, the body contains the new idea and the final sentence offers a conclusion. For the whole paper, the introduction sets the context, the ...
of scientific work . 2. State. where your work could be extended or improved . 1. Clear. Citation . 2. Complete. Reference list . 3. Accepted . Style . 4. Accurately . reproduced . Acknowledge . work of other researchers so that readers can see how your point of view developed
Dr. Michelle Harris, Dr. Janet Batzli,Biocore. This section provides guidelines on how to construct a solid introduction to a scientific paper including background information, study question, biological rationale, hypothesis, and general approach. If the Introduction is done well, there should be no question in the reader's mind why and on ...
Follow: 1. Context — your introduction. 2. Content — your results. 3. Conclusion — your discussion. Plan your paper carefully and decide where each point will sit within the framework before ...
The introduction supplies sufficient background information for the reader to understand and evaluate the experiment you did. It also supplies a rationale for the study. Goals: Present the problem and the proposed solution. Presents nature and scope of the problem investigated. Reviews the pertinent literature to orient the reader.
Take concise notes while reading, focusing on information relevant to the essay. Identify the most crucial information and examples that support the argument. Begin writing the essay, considering starting with the middle sections for clarity. Circle back to the introduction and conclusion once the main body is outlined.
They are best rewritten in a simpler way. Effective writing is readable — that is, clear, accurate, and concise. When you are writing a paper, try to get your ideas across in such a way that the ...
We describe here the basic steps to follow in writing a scientific article. We outline the main sections that an average article should contain; the elements that should appear in these sections, and some pointers for making the overall result attractive and acceptable for publication. 1. Background.
Introduction. Publishing in the peer-reviewed literature is essential to advancing science and its translation to practice in public health (1,2).The public health workforce is diverse and practices in a variety of settings ().For some public health professionals, writing and publishing the results of their work is a requirement.
Title--subject and what aspect of the subject was studied. There are many ways to approach the writing of a scientific paper, and no one way is right. Many people, however, find that drafting chunks in this order works best: Results, Discussion, Introduction, Materials & Methods, Abstract, and, finally, Title.
Continue reading to find some tips to help you write a successful science essay. Science Essay Writing Tips. Once you have chosen a topic and looked at examples, it's time to start writing the science essay. Here are some key tips for a successful essay: Research thoroughly; Make sure you do extensive research before you begin writing your paper.
Conclude your essay by summarizing all the key points. Also, highlight the practical potential of our findings and their impacts. Proofread and check for errors in the paper. Before submitting or forwarding your article, it is fundamental that you proofread and correct all the errors that you come across.
A PDF providing further guidance on writing science essays for tutorials is available to download.. Short videos to support your essay writing skills. There are many other resources at Oxford that can help support your essay writing skills and if you are short on time, the Oxford Study Skills Centre has produced a number of short (2-minute) videos covering different aspects of essay writing ...
When we do discuss writing with students, trainees, and peers, we emphasize the mechanics: how to structure a manuscript, the style conventions of scientific writing, and the submission process (Guilford 2001, Turbek et al. 2016). As a scientific community, we rarely discuss the actual act of scientific writing itself.
The task of writing a scientific paper and submitting it to a journal for publication is a time‐consuming and often daunting task. 3,4 Barriers to effective writing include lack of experience, poor writing habits, writing anxiety, unfamiliarity with the requirements of scholarly writing, lack of confidence in writing ability, fear of failure ...
Writing scientific essays will always be slightly different to when you write an essay for say English Literature. You need to be more analytical and precise when answering your questions. ... A good essay. reflects the detail that could be expected from a comprehensive knowledge and understanding of relevant parts of the specification;
It is concise and precise. A goal of scientific writing is to communicate scientific information clearly and concisely. Flowery, ambiguous, wordy, and redundant language run counter to the purpose of the writing. 3. It must be set within the context of other published work. Because science builds on and corrects itself over time, scientific ...
📌Sign Up for my Essay Writing Masterclass: https://www.doctorshaene.com/essay-masterclassIn this video I run through how to structure a scientific/medical e...
Tips for Writing a Science Essay. Writing a science essay can be challenging, especially if you don't have much experience in writing academic papers. However, with the right approach and strategies, you can produce a high-quality science essays. Here are some tips to help you write a successful science essay:
How to Write a Good Hypothesis. Writing a good hypothesis is definitely a good skill to have in scientific research. But it is also one that you can definitely learn with some practice if you don't already have it. Just keep in mind that the hypothesis is what sets the stage for the entire investigation. It guides the methods and analysis.
How To Write a Good Hook for a College Essay. Learning how to write a good hook for a college essay is essential as a great hook can captivate your reader's attention from the start. Begin with a bold statement, a thought-provoking question, or a vivid scene. The goal is to intrigue your readers and make them want to read more.
With consistent practice, mock essay writing, and guidance from coaching platforms like Sleepy Classes, you can master the art of crafting standout conclusions for UPSC essays and boost your scores significantly. Resources: Sleepy Classes: Essay Writing Course; Vision IAS: Essay Writing Test Series; ForumIAS: Essay Mains Guidance Program
This essay will consider four writing techniques: his use of rhetorical questions, his structure in terms of problem-solution, his conversational style, and finally, his use of scientific support to shore up his argument. First, one of the key techniques Ball uses to engage the reader is the frequent use of rhetorical questions.
In essence, a lab report is your way of sharing scientific knowledge in a structured format, making your research accessible and understandable to others. ... our expert essay writing service is here to support you 24/7. Reach out to us to ensure your work meets the highest standards of excellence. Frequently Asked Questions.
Restating your thesis in the conclusion is a common practice in essay writing, and for good reason. It helps underscore how your understanding has deepened or shifted based on the evidence you provided. ... The following are two hypothetical thesis essays from the fields of science and literature. Science. Thesis Topic: The Impact of Climate ...
Writing an essay introduction paragraph is straightforward when you follow the best practices in this article. Make sure that you select a topic that you're enthusiastic about. This allows you to naturally be curious about the topic and want to research on a deeper level. Now that you understand how to write an essay introduction apply the ...