Paraphrasing Tool
Paraphrasing Tool in partnership with QuillBot. Paraphrase everywhere with the free Chrome Extension .
Try our other writing services


Avoid plagiarism in your paraphrased text

What is a paraphrasing tool?
This AI-powered paraphrasing tool lets you rewrite text in your own words. Use it to paraphrase articles, essays, and other pieces of text. You can also use it to rephrase sentences and find synonyms for individual words. And the best part? It’s all 100% free!
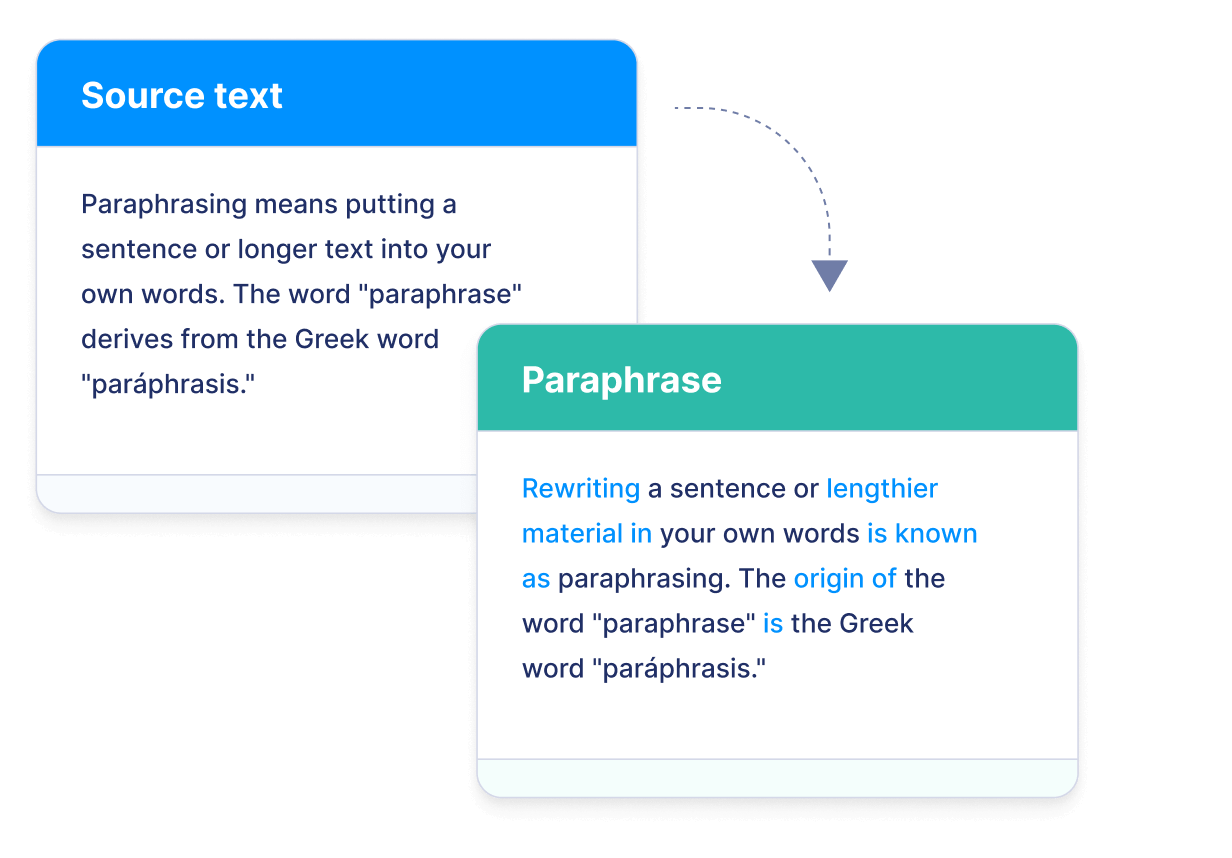
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing involves expressing someone else’s ideas or thoughts in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Paraphrasing tools can help you quickly reword text by replacing certain words with synonyms or restructuring sentences. They can also make your text more concise, clear, and suitable for a specific audience. Paraphrasing is an essential skill in academic writing and professional communication.
Why use this paraphrasing tool?
- Save time: Gone are the days when you had to reword sentences yourself; now you can rewrite an individual sentence or a complete text with one click.
- Improve your writing: Your writing will always be clear and easy to understand. Automatically ensure consistent language throughout.
- Preserve original meaning: Paraphrase without fear of losing the point of your text.
- No annoying ads: We care about the user experience, so we don’t run any ads.
- Accurate: Reliable and grammatically correct paraphrasing.
- No sign-up required: We don’t need your data for you to use our paraphrasing tool.
- Super simple to use: A simple interface even your grandma could use.
- It’s 100% free: No hidden costs, just unlimited use of a free paraphrasing tool.
People are in love with our paraphrasing tool
No Signup Needed
You don’t have to register or sign up. Insert your text and get started right away.

The Paraphraser is Ad-Free
Don’t wait for ads or distractions. The paraphrasing tool is ad-free!

Multi-lingual
Use our paraphraser for texts in different languages.
Features of the paraphrasing tool
Rephrase individual sentences
With the Scribbr Paraphrasing Tool, you can easily reformulate individual sentences.
- Write varied headlines
- Rephrase the subject line of an email
- Create unique image captions
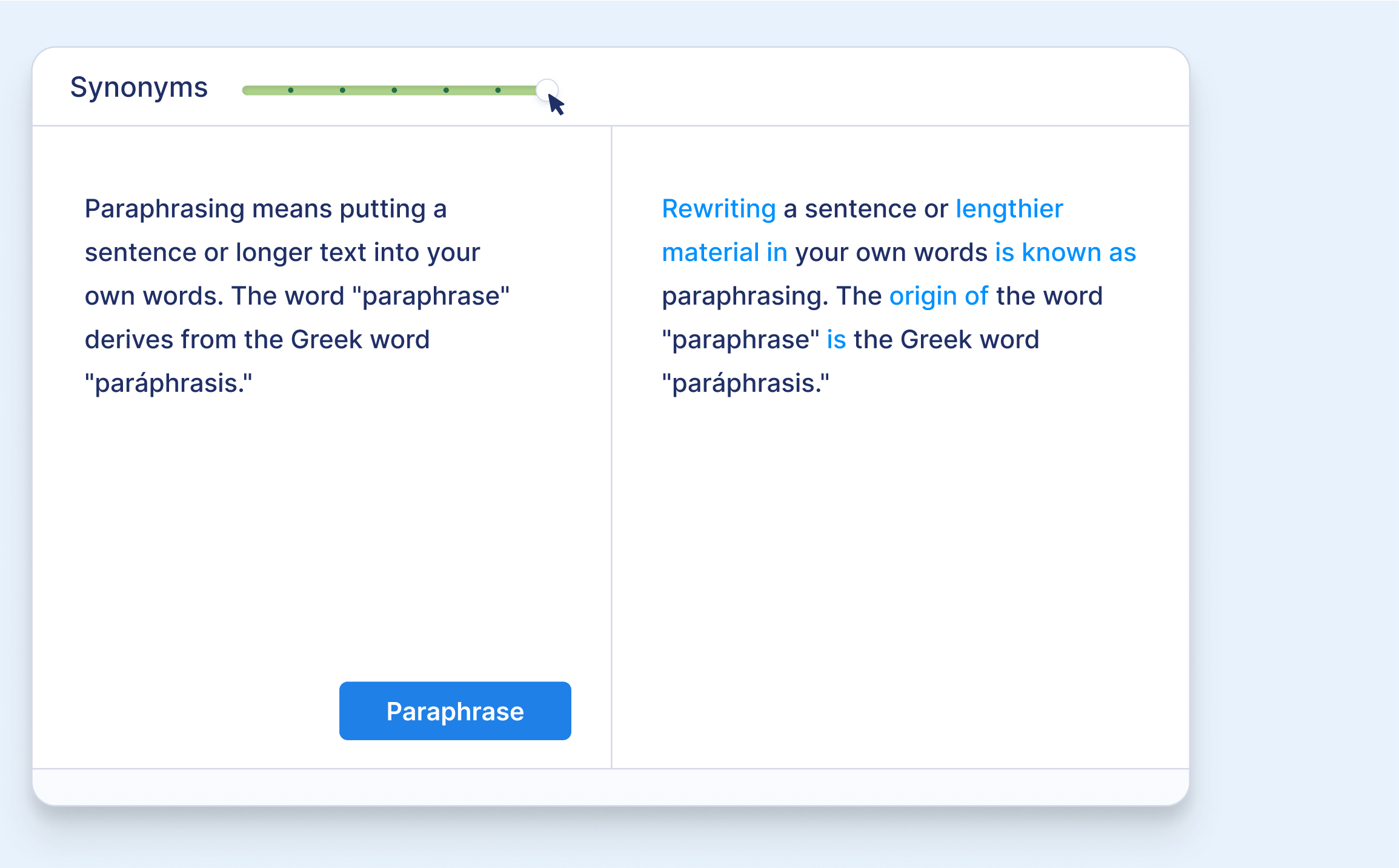
Paraphrase a whole text
Our paraphraser can also help with longer passages (up to 125 words per input). Upload your document or copy your text into the input field.
With one click, you can reformulate the entire text.
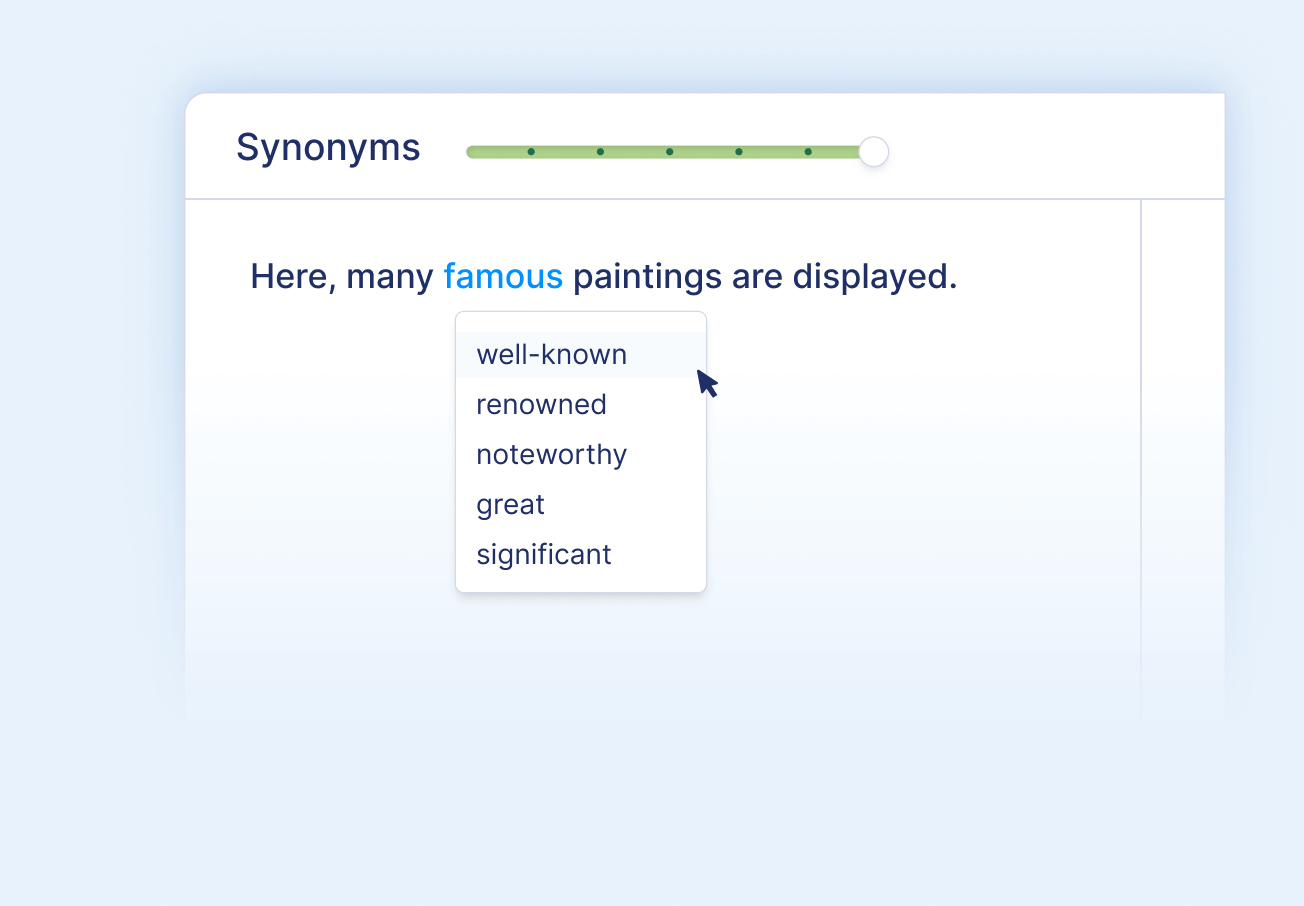
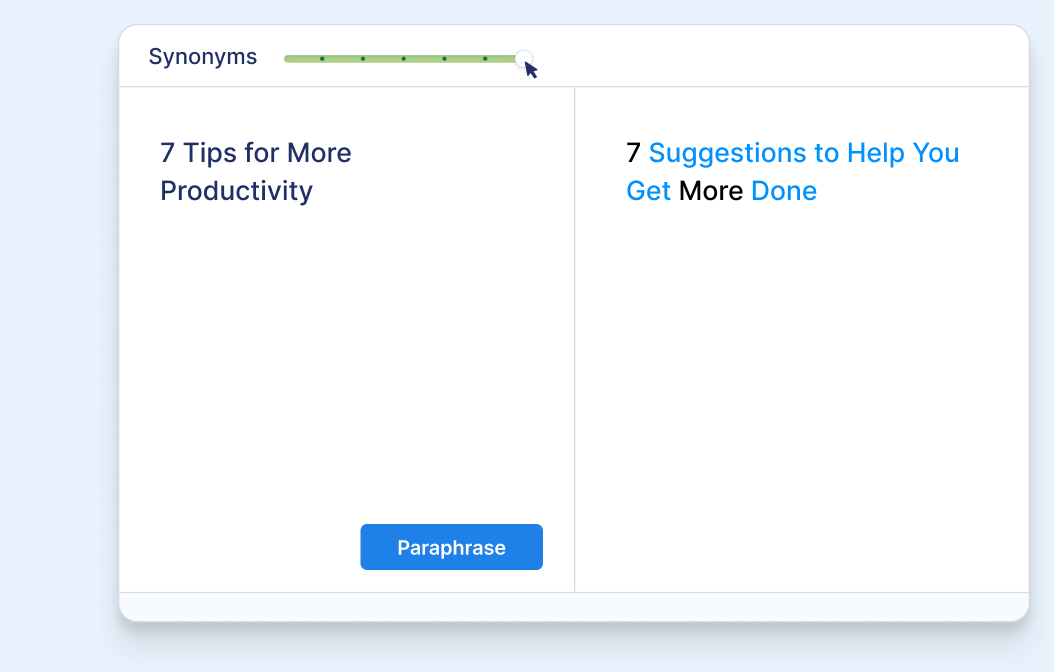
Find synonyms with ease
Simply click on any word to open the interactive thesaurus.
- Choose from a list of suggested synonyms
- Find the synonym with the most appropriate meaning
- Replace the word with a single click

Paraphrase in two ways
- Standard: Offers a compromise between modifying and preserving the meaning of the original text
- Fluency: Improves language and corrects grammatical mistakes

Upload different types of documents
Upload any Microsoft Word document, Google Doc, or PDF into the paraphrasing tool.
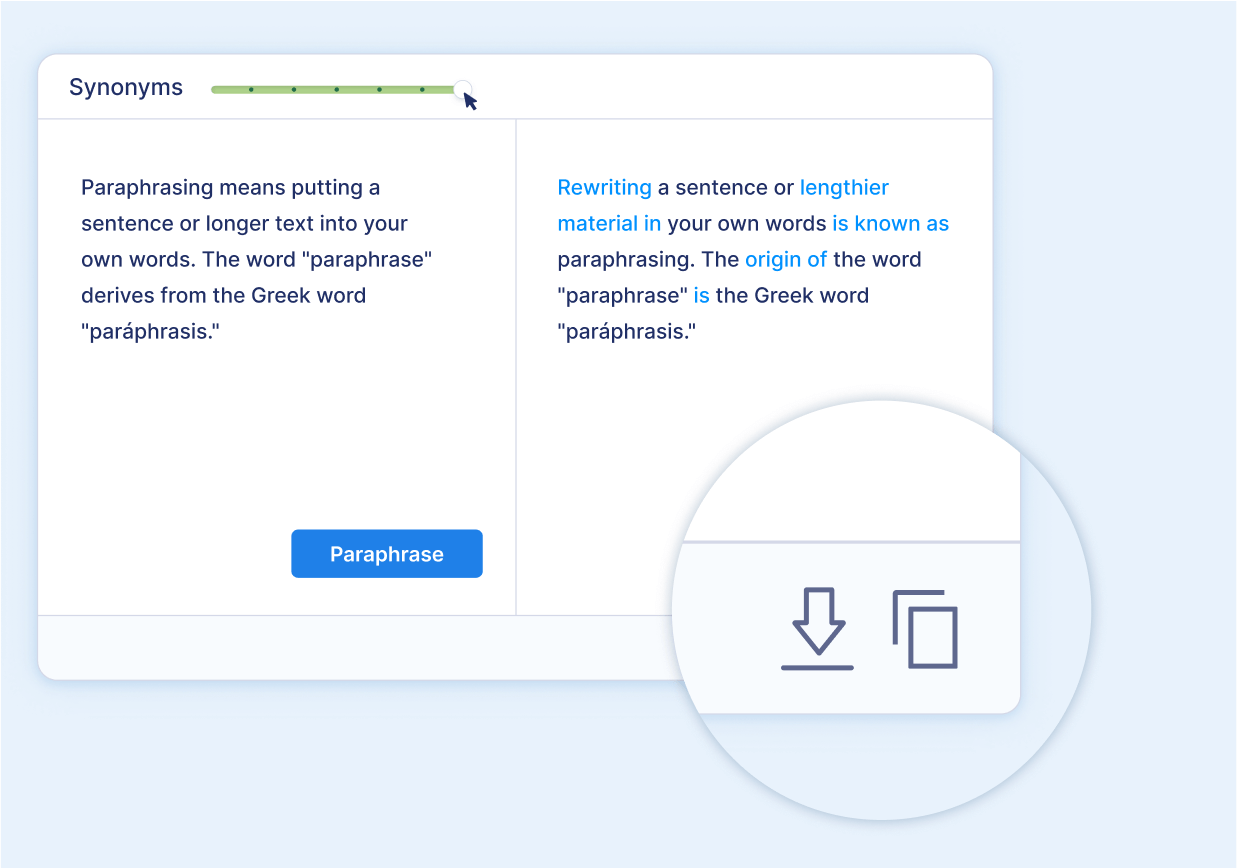
Download or copy your results
After you’re done, you can easily download or copy your text to use somewhere else.

Powered by AI
The paraphrasing tool uses natural language processing to rewrite any text you give it. This way, you can paraphrase any text within seconds.
Avoid accidental plagiarism
Want to make sure your document is plagiarism-free? In addition to our paraphrasing tool, which will help you rephrase sentences, quotations, or paragraphs correctly, you can also use our anti-plagiarism software to make sure your document is unique and not plagiarized.
Scribbr’s anti-plagiarism software enables you to:
- Detect plagiarism more accurately than other tools
- Ensure that your paraphrased text is valid
- Highlight the sources that are most similar to your text
Start for free
How does this paraphrasing tool work?
1. put your text into the paraphraser, 2. select your method of paraphrasing, 3. select the quantity of synonyms you want, 4. edit your text where needed, who can use this paraphrasing tool.

Paraphrasing tools can help students to understand texts and improve the quality of their writing.
Create original lesson plans, presentations, or other educational materials.

Researchers
Explain complex concepts or ideas to a wider audience.
Journalists
Quickly and easily rephrase text to avoid repetitive language.

Copywriters
By using a paraphrasing tool, you can quickly and easily rework existing content to create something new and unique.

Bloggers can rewrite existing content to make it their own.

Writers who need to rewrite content, such as adapting an article for a different context or writing content for a different audience.

A paraphrasing tool lets you quickly rewrite your original content for each medium, ensuring you reach the right audience on each platform.
The all-purpose paraphrasing tool
The Scribbr Paraphrasing Tool is the perfect assistant in a variety of contexts.

Brainstorming
Writer’s block? Use our paraphraser to get some inspiration.

Professional communication
Produce creative headings for your blog posts or PowerPoint slides.
Academic writing
Paraphrase sources smoothly in your thesis or research paper.

Social media
Craft memorable captions and content for your social media posts.
Paraphrase text online, for free
The Scribbr Paraphrasing Tool lets you rewrite as many sentences as you want—for free.
| 💶 100% free | Rephrase as many texts as you want |
|---|---|
| 🟢 No login | No registration needed |
| 📜 Sentences & paragraphs | Suitable for individual sentences or whole paragraphs |
| 🖍️ Choice of writing styles | For school, university, or work |
| ⭐️ Rating | based on 13,309 reviews |
Write with 100% confidence 👉
Scribbr & academic integrity.
Scribbr is committed to protecting academic integrity. Our plagiarism checker , AI Detector , Citation Generator , proofreading services , paraphrasing tool, grammar checker , summarizer , and free Knowledge Base content are designed to help students produce quality academic papers.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
The act of putting someone else’s ideas or words into your own words is called paraphrasing, rephrasing, or rewording. Even though they are often used interchangeably, the terms can mean slightly different things:
Paraphrasing is restating someone else’s ideas or words in your own words while retaining their meaning. Paraphrasing changes sentence structure, word choice, and sentence length to convey the same meaning.
Rephrasing may involve more substantial changes to the original text, including changing the order of sentences or the overall structure of the text.
Rewording is changing individual words in a text without changing its meaning or structure, often using synonyms.
It can. One of the two methods of paraphrasing is called “Fluency.” This will improve the language and fix grammatical errors in the text you’re paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing and using a paraphrasing tool aren’t cheating. It’s a great tool for saving time and coming up with new ways to express yourself in writing. However, always be sure to credit your sources. Avoid plagiarism.
If you don’t properly cite text paraphrased from another source, you’re plagiarizing. If you use someone else’s text and paraphrase it, you need to credit the original source. You can do that by using citations. There are different styles, like APA, MLA, Harvard, and Chicago. Find more information about citing sources here.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly cite the source . This means including an in-text citation and a full reference, formatted according to your required citation style .
As well as citing, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas in your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely in your own words and properly cite the source .
Try our services
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Paraphrase in 5 Simple Steps (Without Plagiarizing)

Krystal N. Craiker

Paraphrasing is a tricky balance between using your own words and still getting the original message across.
Understanding what paraphrasing is, and how to do it well, takes the challenge out of paraphrasing and makes it a more user-friendly skill.
What Is Paraphrasing?
How to paraphrase in 5 easy steps, paraphrasing different types of content, paraphrasing examples, want to improve your essay writing skills.
The word paraphrase can be used as a noun or a verb .
A paraphrase (noun) is a restatement of someone else’s words into other words . If you’re reading a paraphrase, you’re reading someone else’s rephrasing of the original.
To paraphrase (verb) is the act of rephrasing a statement into your own words . When you paraphrase, you are essentially borrowing someone else’s ideas and putting them into your own words. Since you’re borrowing and not creating those ideas, be certain to give credit to the original source.

Paraphrasing vs. Plagiarism
Plagiarism is when you steal someone’s words or ideas. Some people think that it’s only plagiarizing when you use the exact words.
Paraphrasing isn’t a way to steal someone’s ideas by putting it in your own words. If you’re paraphrasing someone else’s ideas, you must give them credit.
If you don’t acknowledge that source, you’ve plagiarized, which has serious ethical, and even legal, implications.
ProWritingAid can help you keep your work plagiarism-free with its plagiarism checker , and will never store or resell your work as some other plagiarism checking services sometimes do.
How to Paraphrase Properly
Why paraphrase when you could just use direct quotations? Direct quotes in academic writing and research papers do not demonstrate that you understand the original material.
Proper paraphrasing doesn’t mean rewriting the original passage word for word. It’s more than just pulling out a thesaurus. You are rewriting the ideas in your own words.
Just as you would provide the source of a direct quote, provide the source of paraphrased information according to whatever style guide you’re following (e.g. APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.) or by including the source within the paraphrase itself.
Typically, you’ll use an in-text citation alongside your paraphrased text, but sometimes you may use footnotes or endnotes.
When you use a direct quotation, it’s important to put the original passage or statement in quotation marks. But paraphrased text does not require quotation marks.
Paraphrasing is translating someone else’s words into your words. If you were to translate a sentence from one language into another going word-by-word, you’d end up with nonsense.
The same thing happens when you paraphrase. You’re performing a translation of sorts.
If you try to translate each word, you’ll end up with a paraphrase that reads more like a “word salad” than an intelligent rephrasing.
Why? When you isolate words, you take them out of their context.
The meaning of a word can change based on its context, so respect that context. Keep ideas whole to keep the original meanings intact.
Here’s what it looks like when you translate word for word.
Original Text: “Life expectancy isn’t set in stone: Both public policy and personal responsibility can tip the scales, experts said.” (Craig Schneider, Newsday)
If I paraphrase that text word-by-word, I could end up with something like this:
Word-by-Word Paraphrase: Human existences are not put in rocks. The pair of non-private systems and individual duty can point the measures, professionals uttered.
That makes no sense. Here’s a more effective paraphrase:
Proper Paraphrase: According to experts, public policy and individual choices can affect life expectancy.
This makes much more sense. Keep the entire context in mind when you paraphrase.

There are some practical steps you can follow to ensure skillful paraphrasing. It might take some practice at first.
As you become more experienced with paraphrasing, you’ll notice that you follow these steps naturally.
Step 1: Read, Reread, Then Read It Again
You can’t properly paraphrase if you don’t fully understand the original passage. For effective paraphrasing, reread the original text multiple times.
Pay attention to word choice and tone, as those contribute to the overarching message. Be sure that you know exactly what the original author was trying to get across before you move on.
Step 2: Determine the Big Idea
There’s a difference between paraphrasing and summarizing, but a quick summary is a great starting point for a paraphrase.
A summary is the main idea. What is the big idea of the original passage?
Try to sum up the big idea in one sentence using your own words.
If you’re only paraphrasing a short chunk of text, this might be the extent of your work and you can skip to step five. For longer quotes, start with the gist.
Step 3: Break It Down
Once you have the big idea, you can start looking at the individual ideas. A good paraphrase includes all the essential information. This is the step where you determine which pieces are essential.
You can start breaking it down sentence by sentence, but keep in mind that you’re really trying to understand it idea by idea.
There might be one idea in two or three sentences or two ideas in one long sentence!
Step 4: Rewrite, Idea by Idea
Once you know all the essential information, it’s time to rewrite. Use your own words and phrasing as much as possible.
Of course, sometimes you will have to use some of the same words. For example, if you’re paraphrasing a quote about the economy, you don’t need to find a new word for “economy.”
Plagiarism isn’t just the words you use, but also the order those words are in.
If you do use more than two of the same words as the original in a row, place them in quotation marks . Avoid this as much as possible for a good paraphrase.
Once you’ve rewritten each idea with the important information, it’s time to make sure your paraphrased version accurately expresses the intent of the original passage.
That leads us to the final step.
Step 5: Check and Cite
Have you ever heard the phrase “lost in translation?” It’s true for paraphrasing, too. Sometimes, when we rewrite something in our own words, we lose the intent and meaning of the original.
Reread what you’ve written and ask yourself the following questions:
- Does this portray the same big idea?
- Have I included all relevant information and ideas?
- Does my paraphrase maintain the integrity of the original’s intent?
- Are all sentences written in my own voice and my own words?
If you can answer yes to all four questions, you’ve successfully paraphrased! If not, return to the quoted material and go through each step again.
Finally, add your citation. Always credit the original source so you don’t plagiarize.

While the same basic steps apply no matter what you’re paraphrasing, it will look a little different depending on the type of text and why you’re paraphrasing.
Let’s take a look at three common situations that require paraphrasing.
How to Paraphrase in an Essay
Essays require paraphrases of many different quotes and sources.
While the occasional quote is fine, frequent direct quotes suggest that you don’t fully understand the material.
Your professor wants to know that you comprehend the subject and have thoughts of your own about it.
To paraphrase in an essay, start with a reasonable sized quote.
If the entire quotation is too long, your essay will become one giant paraphrase. You can always paraphrase another piece of the original text later in your paper.
Make sure the quote you are paraphrasing fits your thesis statement and is in the correct section of your essay.
Then, follow the five steps above to write a paraphrase. Don’t forget to cite your source material!
After you’ve paraphrased and cited the original text, offer your own commentary or thoughts.
How does that paraphrase answer the prompt of your research paper or support your argument? Original thoughts are crucial so your whole essay isn’t a paraphrase. That would be a form of plagiarism!
How to Paraphrase a Quote
Paraphrasing a quote requires you to pay special attention to the tone. Quoted material for academic writing often has a dry, informative tone. Spoken quotes usually don’t.
When you’re determining the big idea (step two), also determine the tone. You can note the tone in your paraphrase by saying the speaker was impassioned, angry, nostalgic, optimistic, etc.
When you move to step three and break down the ideas, pay attention to where the speaker placed emphasis. That’s a clue that you’ve found essential information to include in your paraphrase.
How to Paraphrase Complex Text
Complex and highly technical text can be difficult to paraphrase. All the same steps apply, but pay special attention to your words and sentence structure when you rewrite.

Whenever possible, simplify the complex text in your paraphrase.
Paraphrases are useful because they can make something easier to understand. Imagine that you are explaining the complex text to a middle school student.
Use simplified terms and explain any jargon in layman’s terms. Avoid clichés or idioms and focus only on the most essential pieces of information.
You can also use ProWritingAid’s editing tool to run a Jargon Report and a Cliché Report, as well as readability.
We use the Flesch-Kincaid Scale for readability , which is based on U.S. grade levels. You can see how old someone needs to be to understand your paraphrasing.
Your level of readability might change depending on the purpose of the paraphrase.
If you are paraphrasing complex text for a college-level essay, your readability score can be higher. If you are paraphrasing for a technical audience, some jargon is appropriate.
Let’s take a look at a couple of examples of properly paraphrased material.
Original Text : “Life expectancy isn’t set in stone: Both public policy and personal responsibility can tip the scales, experts said. Everyone can make choices that increase the odds of a longer life, said Cantor, of the Center for Socio-Economic Policy. Eating well, exercising, not smoking, getting enough sleep and staying in school are decisions made by each and every one of us, he said.” (Craig Schneider, Newsday )
Paraphrase: People do have some control over their life expectancy. While public policies matter, experts say personal choices can also affect how long you live and that making healthy lifestyle choices about food, sleep, education, and smoking is up to each individual.
Here’s another example from a speech.
Original Text: “We’ve got to accelerate the transition away from dirty energy. Rather than subsidize the past, we should invest in the future—especially in communities that rely on fossil fuels. That’s why I’m going to push to change the way we manage our oil and coal resources, so that they better reflect the costs they impose on taxpayers and our planet.” (President Barack Obama, State of the Union Address, January 12, 2016)
Paraphrase: President Obama emphasized the importance of investing in clean energy. He supports a shift in the way the country manages non-renewable resources to match the impact they have on both American citizens and the planet.
Remember, when you paraphrase, focus on the ideas, not rewriting word for word. Always cite your original source material even though you are using your own words.
(This article is an update to a previous version by Allison Bressmer.)
Use ProWritingAid!
Are your teachers always pulling you up on the same errors? Maybe you’re losing clarity by writing overly long sentences or using the passive voice too much.

Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Krystal N. Craiker is the Writing Pirate, an indie romance author and blog manager at ProWritingAid. She sails the seven internet seas, breaking tropes and bending genres. She has a background in anthropology and education, which brings fresh perspectives to her romance novels. When she’s not daydreaming about her next book or article, you can find her cooking gourmet gluten-free cuisine, laughing at memes, and playing board games. Krystal lives in Dallas, Texas with her husband, child, and basset hound.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
How to Paraphrase: Dos, Don'ts, and Strategies for Success
#scribendiinc
Written by Scribendi
Is It Considered Plagiarism If You Paraphrase?
How do i paraphrase a source without running the risk of plagiarizing, paraphrasing vs. quoting: what's the difference, paraphrasing vs. summarizing, how to paraphrase a sentence, direct quotation, omissions and editorial changes, paraphrasing, all you need to know about paraphrasing, when should you paraphrase information, what is the purpose of paraphrasing, understand the text you are paraphrasing, do paraphrases need to be cited, example of paraphrasing, how to cite a paraphrase, don't start paraphrasing by picking up a thesaurus , don't copy without quotation marks, paraphrase with a direct quote example, don't paraphrase too closely, example of paraphrases being too similar to their sources.
How to Paraphrase and Tips for Paraphrasing Correctly
Write Down Paraphrases of a Source on Notecards
Paraphrase from your own point-form notes on a source, how to paraphrase using plotnick's method, practice two-step paraphrasing: sentence structure and word choice, understand basic sentence structures, vary the use of active and passive voice, vary sentence length, vary word choice, citing a paraphrase in apa, mla, and chicago styles, how to paraphrase in apa, apa paraphrasing examples, how to paraphrase in mla, mla paraphrasing examples, how to cite a paraphrase in chicago style, chicago style paraphrasing examples, what is the meaning of paraphrase, how do you put things in your own words, what does it mean to paraphrase something.
As if the research process isn't hard enough already—finding relevant and reliable sources, reading and interpreting material, and selecting key quotations/information to support your findings/arguments are all essential when writing a research essay.
Academic writers and students face the additional stress of ensuring that they have properly documented their sources. Failure to do so, whether intentionally or unintentionally, could result in plagiarism, which is a serious academic offense.
That's why we've written this article: to provide tips for proper paraphrasing. We'll start with an overview of the difference between paraphrasing and quoting, and then we'll provide a list of paraphrasing dos and don'ts, followed by strategies for proper paraphrasing.
We will include paraphrasing examples throughout to illustrate best practices for paraphrasing and citing paraphrased material .
As mentioned in our previous article on plagiarism , "simply taking another writer's ideas and rephrasing them as one's own can be considered plagiarism as well."
Paraphrasing words is acceptable if you interpret and synthesize the information from your sources, rephrase the ideas in your own words, and add citations at the sentence level. It is NOT acceptable if you simply copy and paste large chunks of an original source and modify them slightly, hoping that your teacher, editor, or reviewer won't notice.
Passing off another's work as one's own is a form of intellectual theft, so researchers and students must learn how to paraphrase quotes and be scrupulous when reporting others' work.
You might be familiar with all this. Still, you might be concerned and find yourself asking, "How do I paraphrase a source correctly without running the risk of unintentional plagiarism?"
For many writers, especially those who are unfamiliar with the concepts of a particular field, learning how to paraphrase a source or sentence is daunting.
To avoid charges of plagiarism, you must not only document your sources correctly using an appropriate style guide (e.g., APA, Harvard, or Vancouver) for your reference list or bibliography but also handle direct quotations and paraphrasing correctly.

Quoting uses the exact words and punctuation from your source, whereas paraphrasing involves synthesizing material from the source and putting things in your own words. Citing paraphrases is just as necessary as citing quotations.
Even if you understand quoting versus paraphrasing, you might still need some additional paraphrasing help or guidance on how to paraphrase a quote.
Summarizing is when you're discussing the main point or overview of a piece, while paraphrasing is when you're translating a direct quote into language that will be easy for your readers to understand .
It's easy to see how the two are similar, given that the steps to paraphrasing and summarizing both include putting ideas into your own words.
But summarizing and paraphrasing are distinctly different. Paraphrasing highlights a certain perspective from a source, and summarizing offers more of an overview of an entire subject, theme, or book.
You can usually tell the difference between paraphrasing and summarizing by the length of what you're writing abore writing about. If you’re writing about a quote, that would be a smaller theme inside a larger work, so you'd paraphrase.
If you're writing about the themes or plot of an entire book, you'd summarize. Summaries are usually shorter than the original work.
Learn How to Format Quotation Marks here.
When learning how to paraphrase a quote, you first need to consider whether you should be paraphrasing a text or quoting it directly.
If you find the perfect quote from a reliable source that fits your main topic, supports your argument, and lends authority to your paper but is too long (40+ words) or complex, it should be paraphrased. Long/complex quotes can also be shortened with omissions and editorial changes (as discussed below).
Introduce the quote with a signal phrase (e.g., "According to Ahmad [2017] . . .") and insert the entire quotation, indicating the text with quotation marks or indentation (i.e., a block quote).
If you only need to use parts of a long quotation, you can insert an ellipsis (. . .) to indicate omissions. You can also make editorial changes in square brackets [like this].
Keep in mind that you need to reflect the author's intent accurately when using this strategy. Don't change important words in a quotation so that it better fits your argument, as this is a form of intellectual fraud.
Changes in square brackets should only be used to clarify the text without altering meaning in the context of the paper (e.g., clarifying antecedents and matching verb tense). They signal to the reader that these changes were made by the author of the essay and not by the author of the original text.
Paraphrasing
Demonstrate that you clearly understand the text by expressing the main ideas in your own unique style and language. Now, you might be asking yourself, "Do paraphrases need to be cited like quotes?" The answer is a resounding "yes."

When deciding whether to paraphrase or use a direct quote, it is essential to ask what is more important: the exact words of the source or the ideas.
If the former is important, consider quoting directly. If the latter is important, consider paraphrasing or summarizing.
Direct quotation is best for well-worded material that you cannot express any more clearly or succinctly in your own style. It's actually the preferred way of reporting sources in the arts, particularly in literary studies.
Shortening a long quote is a great way to retain the original phrasing while ensuring that the quote reads well in your paper. However, direct quotations are often discouraged in the sciences and social sciences, so keep that in mind when deciding whether to paraphrase or quote.
Paraphrasing is best used for long portions of text that you can synthesize into your own words. Think of paraphrasing as a form of translation; you are translating an idea in another "language" into your own language. The idea should be the same, but the words and sentence structure should be totally different.
The purpose of paraphrasing is to draw together ideas from multiple sources to convey information to your reader clearly and succinctly.
As a student or researcher, your job is to demonstrate that you understand the material you've read by expressing ideas from other sources in your own style, adding citations to the paraphrased material as appropriate.
If you think the purpose of paraphrasing is to help you avoid thinking for yourself, you are mistaken.
When you paraphrase, be sure that you understand the text clearly . The purpose of paraphrasing is to interpret the information you researched for your reader, explaining it as though you were speaking to a colleague or teacher. In short, paraphrasing is a skill that demonstrates one's comprehension of a text.
Yes, paraphrases always need to be cited. Citing paraphrased material helps you avoid plagiarism by giving explicit credit to the authors of the material you are discussing.
Citing your paraphrases ensures academic integrity. When you sit down to write your paper, however, you might find yourself asking these questions: "Do paraphrases need to be cited? How do I paraphrase?"
Here is a quick paraphrase example that demonstrates how to cite paraphrased ideas. The opening lines to one of Juliet's most famous speeches are "O Romeo, Romeo! Wherefore art thou Romeo? / Deny thy father and refuse thy name; / Or, if thou wilt not, be but sworn my love, / And I'll no longer be a Capulet" (Romeo and Juliet, 2.2.880–884).
If you needed to paraphrase these lines in an essay, you could do so as follows:
Juliet muses about why Romeo's family name is Montague and concludes that if either gave up their name (and thereby their family affiliations) for the other, they could be together (Romeo and Juliet, 2.2.880–884).
Generally speaking, you must include an in-text citation at the end of a paraphrased sentence.
However, if your paraphrased material is several sentences long, then you should check with your preferred style guide. Some style guides (such as APA) call for a paraphrase citation after the first paraphrased sentence. Other style guides (such as MLA) call for a paraphrase citation after the last paraphrased sentence.
Remember, no matter what style guide you use, it is not necessary to cite every single sentence of paraphrased material in a multi-sentence paraphrase.
Don't Start Paraphrasing by Picking Up a Thesaurus
This might shock you, but a thesaurus is NOT the answer to the problem of paraphrasing. Why? Using a thesaurus to swap out a few words here and there from an original source is a form of patchwriting, which is a type of plagiarism.
You shouldn't have to resort to a thesaurus unless you are completely unsure about what a word means—although, in that case, a dictionary might be a better tool. Ideally, you should be able to use clear, simple language that is familiar to you when reporting findings (or other information) from a study.
The problem with using a thesaurus is that you aren't really using your own words to paraphrase a text; you're using words from a book. Plus, if you're unfamiliar with a concept or if you have difficulty with English, you might choose the wrong synonym and end up with a paraphrase like this: "You may perhaps usage an erroneous word."
This is a common mistake among writers who are writing about a field with which they are unfamiliar or who do not have a thorough grasp of the English language or the purpose of paraphrasing.
If you choose to keep a few phrases from the original source but paraphrase the rest (i.e., combining quoting and paraphrasing), that's okay, but keep in mind that phrasing from the source text must be reproduced in an exact manner within quotation marks.
Direct quotations are more than three consecutive words copied from another source, and they should always be enclosed in quotation marks or offset as a block quotation.
A sentence that combines a direct quote with paraphrased material would look like this:
In "The Laugh of the Medusa," Cixous highlights women's writing as a specific feat and speaks "about what it will do" when it has the same formal recognition as men's writing (Cixous 875).
The paraphrased paragraph of Cixous' essay includes a direct quote and a paraphrase citation.
Did you know that copying portions of a quote without quotation marks (i.e., patchwriting) is a form of plagiarism—even if you provide an in-text citation? If you've reworded sections of a quote in your own style, simply enclose any direct quotations (three or more words) in quotation marks to indicate that the writing is not your own.
When learning how to paraphrase, you need to distinguish between appropriate and inappropriate forms of paraphrasing. The Office of Research and Integrity , a branch of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, puts it this way:
Taking portions of text from one or more sources, crediting the author/s, but only making 'cosmetic' changes to the borrowed material, such as changing one or two words, simply rearranging the order, voice (i.e., active vs. passive) and/or tense of the sentences is NOT paraphrasing.
What does paraphrasing too closely look like? Here is an overly close paraphrase example of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services' description of plagiarizing:
Using sections of a source, citing it, but only making surface-level changes to the language (such as changing a few words, the verb tense, the voice, or word order) fails as a paraphrase. True paraphrasing involves changing the words and syntactical structure of the original source. Keep reading for strategies for paraphrasing properly.
Get Help with Proper Paraphrasing
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample.
In an article on how to paraphrase , the Purdue University Online Writing Lab suggests that you read the source text carefully and write paraphrases on notecards. You can then compare your version with the original, ensuring that you've covered all the key information and noting any words or phrases that are too closely paraphrased.
Your notecards should be labeled with the author(s) and citation information of the source text so that you don't lose track of which source you used. You should also note how you plan to use the paraphrase in your essay.
If you are a visual learner, the benefit of this strategy is that you can visualize the content you intend to paraphrase.
Because a notecard is a tangible object, you can physically arrange it in an essay outline, moving the right information to the appropriate paragraph so that your essay flows well. (If you're not sure how to write an outline , check out our article.)
Plus, having a physical copy of paraphrased information makes it harder for you to accidentally plagiarize by copying and pasting text from an original source and forgetting to paraphrase or quote it properly. Writing out your paraphrase allows you to distance yourself from the source text and express the idea in your own unique style.
For more paraphrasing help, Jerry Plotnick from the University College Writing Centre at the University of Toronto provides a similar strategy for paraphrasing.
Plotnick advises that you take point-form notes of text that you want to use in your paper. Don't use full sentences, but instead "capture the original idea" in a few words and record the name of the source.
This strategy is similar to the notecard idea, but it adds another step. Instead of just reading the source carefully and writing your complete paraphrase on a notecard, Plotnick recommends using point-form notes while researching your sources. These notes can then be used to paraphrase the source text when you are writing your paper.
Like handwriting your paraphrases on notecards, taking notes and coming back to them later will help you distance yourself from the source, allowing you to forget the original wording and use your own style.
The Plotnick method above describes how to use point-form notes while researching a paper to keep your paraphrasing original. To paraphrase in your paper using Plotnick's method above, look at your sources and try the following:
Write down the basic point(s) you want to discuss on a notecard (in your own words).
Take your notecard points and turn them into sentences when you write your essay.
Add the reference for the source.
Compare your paraphrase to the original source to make sure your words are your own.
Practice Two-Step Paraphrasing: Sentence Structure and Word Choice
In an article on how to paraphrase by the Writing Center at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, the first two strategies are acknowledged—taking notes and looking away from the source before you write your paraphrase.
The authors then suggest another two-step strategy for paraphrasing: change the structure first and then change the words. Let's break down this process a bit further.
Sentences in English have two main components: a subject and a predicate . The subject is who or what is performing an action (i.e., a noun or pronoun), and the predicate is what the subject is doing (i.e., a verb). Sentences can be simple, compound, complex, or compound-complex.
Here are some paraphrase examples using different sentence structures:
Simple: It was difficult.
Compound: It was difficult, but she knew there was no going back.
Complex: Although it was difficult, she knew there was no going back.
Compound-complex: Although it was difficult, she knew there was no going back, so she kept calm and carried on.
Once you have identified the structure of the original sentence, you can reconstruct it using one of the different types of sentences illustrated above.
You can also change passive voice to active voice, or vice versa.
The active voice is structured like this: Subject + Verb + Object (e.g., She learned how to paraphrase.)
The passive voice is structured like this: Object + "To Be" Verb + Past Participle (e.g., How to paraphrase was learned by the girl.)
See how awkward the passive sentence example is? It's best not to force a sentence into an unnatural sentence structure.
Otherwise, you'll end up with Yoda-speak: "Forced to learn how to paraphrase a sentence, the girl was." (Did you like the unintentional "force" pun?)
Another way to distinguish your paraphrase from the original source is to use different sentence lengths. Often, scholarly articles are written using long, compound, complex, or compound-complex sentences. Use short sentences instead.
Break down complex ideas into easy-to-understand material. Alternatively, you can combine several ideas from the source text into one long sentence, synthesizing the material. Try to stick with your own style of writing so that the paraphrased text matches that of the rest of your document.
Once the paraphrased sentence structure is sufficiently different from the original sentence structure, you can replace the wording of the original text with words you understand and are comfortable with.
Paraphrasing isn't meant to hide the fact that you are copying someone else's idea using clever word-swapping techniques. Rather, it is meant to demonstrate that you are capable of explaining the text in your own language.
One handy article on word choice by the Writing Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill lists some strategies for successful word choice, such as eliminating jargon and simplifying unnecessary wordiness. While this applies to academic writing in general, the "questions to ask yourself" are also useful as great paraphrasing help.
Once you have completed a sentence-long paraphrase, you include an in-text citation at the end of that sentence. However, if your paraphrased material is several sentences long, then you should check with your preferred style guide.
Some style guides (such as APA) call for a paraphrase citation after the first paraphrased sentence. Other style guides (such as MLA) call for a paraphrase citation after the last paraphrased sentence.

To paraphrase properly, you need to explain a text in your own words without using a direct quote . Keep in mind, however, that different styles require different formats when it comes to documenting paraphrased sources. Some styles require a citation after the first paraphrased sentence, while others require a citation after the last.
For this reason, we've outlined examples of how to paraphrase in the APA, MLA, and Chicago styles below. Be sure to check with your professor to see which style your essay requires.
APA guidelines for paraphrasing include citing your source on the first mention in either the narrative or parenthetical format. Here's a refresher of both formats:
Narrative format: Koehler (2016) noted the dangers of false news.
Parenthetical format: The news can distort our perception of an issue (Koehler, 2016).
Here's an example of how to paraphrase from a primary source in APA:
Dudley (1999) states that "direct quote" or paraphrase (Page #).
Note: It's not always necessary to include the page number, but it's recommended if it'll help readers quickly find a passage in a book.
Below are a couple of examples of how to paraphrase in APA. Keep in mind that for longer paraphrases, you don't have to add the citation again if it's clear that the same work is being paraphrased.
Short paraphrase:
Stephenson (1992) outlined a case study of a young man who showed increasing signs of insecurity without his father (pp. 23–27).
Long paraphrase:
Johnson et al. (2013) discovered that for small-breed dogs of a certain age, possession aggression was associated with unstable living environments in earlier years, including fenced-in yards with multiple dogs all together for long periods of time. However, these effects were mediated over time. Additionally, with careful training, the dogs showed less possession aggression over time. These findings illustrate the importance of positive reinforcement over the length of a dog's life.
When paraphrasing in MLA, include an in-text citation at the end of the last paraphrased sentence.
Your in-text citation can be done either parenthetically or in prose, and it requires the last name of the cited author and the page number of the source you're paraphrasing from. Here are MLA citation examples :
Parenthetical:
Paraphrase (Author's Last Name Page #)
Author's Last Name states that paraphrase (Page #)
In addition to adding a short in-text citation to the end of your last paraphrased sentence, MLA requires that this source be included in your Works Cited page, so don't forget to add it there as well.
Here are two examples of how to paraphrase in MLA:
In an attempt to communicate his love for Elizabeth, all Mr. Darcy did was communicate the ways in which he fought to hide his true feelings (Austen 390).
Rowling explains how happy Harry was after being reunited with his friends when he thought all was lost (17).
Paraphrasing correctly in Chicago style depends on whether you're using the notes and bibliography system or the author-date system.
The notes and bibliography system includes footnotes or endnotes, whereas the author-date system includes in-text citations.
Below, you'll find the correct way to format citations when paraphrasing in both the notes and bibliography and author-date systems.
Notes and Bibliography
For the notes and bibliography system, add a superscript at the end of your paraphrase that corresponds to your footnote or endnote.
Johnson explains that there was no proof in the pudding. 1
Author-Date
For the author-date style, include the page number of the text you're referencing at the end of your paraphrase. If you mention the author, include the year the source was published.
Johnson (1995) explains that there was no proof in the pudding (21).
In summary, the purpose of paraphrasing is not to simply swap a few words; rather, it is to take ideas and explain them using an entirely different sentence structure and choice of words. It has a greater objective; it shows that you've understood the literature on your subject and are able to express it clearly to your reader.
In other words, proper paraphrasing shows that you are familiar with the ideas in your field, and it enables you to support your own research with in-text citations.
Knowing when to paraphrase or quote strengthens your research presentation and arguments. Asking for paraphrasing help before you accidentally plagiarize shows that you understand the value of academic integrity.
If you need help, you might consider an editing and proofreading service, such as Scribendi. While our editors cannot paraphrase your sources for you, they can check whether you've cited your sources correctly according to your target style guide via our Academic Editing service.
Even if you need more than just paraphrase citation checks, our editors can help you decide whether a direct quote is stronger as a paraphrase, and vice versa. Editors cannot paraphrase quotes for you, but they can help you learn how to paraphrase a quote correctly.
What Is the Meaning of "Paraphrase"?
Paraphrasing is when you write text from another source in your own words. It's a way of conveying to your reader or professor that you understand a specific source material well enough to describe it in your own style or language without quoting it directly.
Paraphrasing (and citing your paraphrases) allows you to explain and share ideas you've learned from other sources without plagiarizing them.
You can write things in your own words by taking original notes on the sources you're reading and using those notes to write your paraphrase while keeping the source material out of sight.
You can also practice putting things in your own words by changing sentences from passive to active, or vice versa, or by varying word choice and sentence length. You can also try Jeremy Plotnick's idea of paraphrasing from your own point-form notes.
When you're paraphrasing something, it means you are putting someone else's writing in your own words. You're not copying or quoting content directly. Instead, you are reading someone else's work and explaining their ideas in your own way.
Paraphrasing demonstrates that you understand the material you're writing about and gives your reader the opportunity to understand the material in a simplified way that is different from how the original author explained it.
About the Author

Scribendi's in-house editors work with writers from all over the globe to perfect their writing. They know that no piece of writing is complete without a professional edit, and they love to see a good piece of writing turn into a great one after the editing process. Scribendi's in-house editors are unrivaled in both experience and education, having collectively edited millions of words and obtained nearly 20 degrees collectively. They love consuming caffeinated beverages, reading books of various genres, and relaxing in quiet, dimly lit spaces.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

How Do I Know If I'm Plagiarizing?

Scribendi's Ultimate Essay Writing Guide

What is Plagiarism?
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
| File | Word Count | Include in Price? |
|---|
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Essay Tips: How to Paraphrase Effectively

- 5-minute read
- 25th December 2022
Writing an essay or research paper is no simple task. It’s hard enough to gather research and write your paper within a tight deadline, but you also have to ensure that you aren’t plagiarizing somebody else’s work. This means you’ll need to give credit to all sources that you used to support your claims with appropriate citations and references.
However, submitting a paper filled with citations isn’t the way to go. Many professors will reject papers with chunks of quoted sources – even if you cite them properly. Conversely, you can’t submit a paper without citations. A professor will either question your knowledge or accuse you of plagiarism.
Therefore, you need to have a healthy balance of your ideas and supporting claims (citations) in your paper. One way of doing this is by paraphrasing . However, many students don’t fully understand this concept or how to do it effectively. That’s where this post comes in!
What Is Paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is taking the ideas or research of other authors and putting them into your own words. It demonstrates your understanding of what you’ve read and helps you to ensure that your entire text is written in a cohesive style. Paraphrasing is a legitimate academic writing skill that can easily boost your grades when it’s done effectively. It’s better than quoting sources.
Check out the following tips for paraphrasing the right way . Once you finish reading this post, you’ll hopefully feel more confident in your paraphrasing ability and ready to tackle your next essay with ease!
1. Understand What You’ve Read
Make sure you understand the quotation or sentence you want to paraphrase. If there’s one thing we want you to remember from this post, it’s this! If you don’t fully understand it, you won’t be able to rewrite it in your own words .
Imagine having to explain the original passage to a friend. How would you tell them in your own words? We recommend reading the original sentence several times and even a few times aloud. We also recommend highlighting keywords, which are needed to ensure that the meaning remains the same. Let’s look at an example of a sentence that we want to paraphrase:
Notice that the bold words are necessary for the meaning, so in your paraphrase, you should use those exact words or synonyms of them. Try finding a few synonyms first, and then decide which one resonates with your own words.
2. Restructure the Sentence
Rewriting a sentence by changing one or two words isn’t proper paraphrasing. Many students erroneously use a “copy and paste” method to change a few words in their paraphrased version. However, you need to change the sentence structure as well.
It would also help if you did this without looking at the original text, which is why we encourage reading the original multiple times. Here is an example of paraphrasing the sentence from our first tip with bolded words as synonyms:
As you can see, the sentence has been restructured, making it significantly different from the original text. However, the meaning remains the same.
3. Compare Your Paraphrase with the Original Text
This might seem simple, but there are a few things to consider when comparing your paraphrase with the original sentence:
● Have you used synonyms for necessary words?
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
● Is the sentence structure significantly different?
● Is the basic meaning still the same?
The goal is to create a significantly different sentence structure while maintaining the original meaning. Of course, if you changed the meaning, you’ll need to correct the paraphrase!
4. Make Sure the Paraphrased Text Makes Sense
A common error associated with paraphrasing is an incoherent paraphrased text. This often happens because the writer hasn’t properly understood the original text or has used an online paraphrasing tool. Take this example of a paraphrase without a clear meaning:
The attempted paraphrase is entirely different from the original. The writer has likely used a thesaurus or paraphrasing tool to find a synonym for each word. Paraphrasing doesn’t mean substituting every word with a synonym!
Remember the following to ensure coherent paraphrasing:
● Focus on the overall point of the original text.
● Avoid using paraphrasing tools, as they often change the meaning of a text.
● Use simple language instead of complex words.
5. Cite and Reference the Original Text
Yes, you must provide an in-text citation and reference list entry for each paraphrased sentence or passage! Just because you have paraphrased an idea doesn’t mean you don’t have to provide a citation . Otherwise, you’ll be subjected to the perils of plagiarism ! Here is an example of a properly cited paraphrase:
Omitting citations can happen accidentally. For example, you might rush to finish the paper or be worried about citing a source too frequently. However, it’s important to know that many institutions use plagiarism detection software , and therefore, a paraphrased text without an in-text citation won’t go unnoticed. So, cite for your sake (and the sake of your grade).
Are you currently working on an essay or research paper? Don’t forget to proofread it once it’s done. Our team of experts can ensure perfect spelling, punctuation, and grammar. We can also check for proper citation and referencing. Submit a 500-word document today, and we’ll proofread it for free!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Academic Integrity at MIT
A handbook for students, search form, avoiding plagiarism - paraphrasing.
In writing papers, you will paraphrase more than you will quote. For a report or research paper, you may need to gather background information that is important to the paper but not worthy of direct quotation. Indeed, in technical writing direct quotation is rarely used.
Exactly what does "paraphrase" mean?
It means taking the words of another source and restating them, using your own vocabulary. In this way, you keep the meaning of the original text, but do not copy its exact wording.
| Original | Plagiarism | Paraphrasing |
|---|---|---|
| Because of their unique perspective, Americans fear globalization less than anyone else, and as a consequence they think about it less than anyone else. When Americans do think about globalization, they think of the global economy as an enlarged version of the American economy. (Source: Thurow, L. (1993). (p. 6). New York: Harper Collins.) | According to Lester Thurow (1993) Americans than people from other countries and spend less time . Indeed, Americans see globalization their own economy.
The writer has used Thurow's exact words without enclosing them in quotation marks. S/he has only substituted synonyms here and there. Even though Thurow is credited with a citation, this would be considered | Lester Thurow (1993) maintains that because Americans see globalization simply as a bigger form of their own economy, they are less concerned about it than is the rest of the world.
The writer has kept the meaning of the original passage without copying words or structure. Words like and are generic terms (i.e., terms that are commonly used for the concept they illustrate - it is difficult to find synonyms for them). Thus you may use these words without placing them in quotation marks. (Complete Thurow reference appears in bibliography) |
What strategies can I use to paraphrase?
Use synonyms for all words that are not generic. Words like world, food, or science are so basic to our vocabulary that is difficult to find a synonym.
Change the structure of the sentence.
Change the voice from active to passive and vice versa.
Change clauses to phrases and vice versa.
Change parts of speech.
| Original | ||
|---|---|---|
| Like drought, excess rainfall and flooding can also contribute to epidemics of waterborne infectious diseases, in this case due to poor sanitation resulting from runoff from overwhelmed sewage lines or the contamination of water by livestock. (Source: Shuman, E., M.D. (2010, March 25). Global climate change and infectious diseases. New England Journal of Medicine; 362, 12, 1061-1063. Retrieved from nejm.org at MIT Libraries.) |
rainfall can also infectious diseases water, usually as a result of and (Shuman, 2010). |
there is an overabundance of rainfall, : sewers can overflow and water can become polluted by the presence of livestock, outbreaks of waterborne diseases (Shuman, 2010). |
| Original | Acceptable Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| Current political and economic incentives favor industry and other interest groups at the expense of health: consider the subsidies paid for corn-based agriculture and mass-produced processed foods, the tobacco revenue generated in countries with a government-owned tobacco industry, industrial growth in the face of environmental pollution, and the spread of the sedentary automobile-and-television culture. (Source: Venkat Narayan, K.M., Ali, M.K., and Koplan, J. (2010, September 23). Global noncomunicable diseases – where worlds meet. The New England Journal of Medicine, 363; 13. 1196-1198. Retrieved from nejm.org at MIT Libraries.) | Changed Parts of Speech Researchers point out that in attempting to implement economic growth, industry is often favored over health: government may subsidize certain forms of agriculture and food production, contribute to tobacco consumption in nations where it owns the industry and otherwise promote growth of industries that pollute. (Venkat Narayan et. al, 2011). |
| Original | Acceptable Paraphrase: Changed Clause to Phrase |
|---|---|
| The prevalence and impact of non-communicable diseases continue to grow. Chronic diseases account for 60% of all deaths worldwide, and 80% of these deaths occur in low-or middle-income countries, where the toll is disproportionate during the prime productive years of youth and middle age. (Source: Venkat Narayan, K.M., , Ali, M.K., and Koplan, J. (2010, September 23). Global noncomunicable diseases – where worlds meet. The New England Journal of Medicine, 363; 13. 1196-1198. Retrieved from nejm.org at MIT Libraries.) | can be seen in figures that show these diseases are responsible for 60% of all deaths on the planet, and that in countries where the population is primarily of low or middle income, the impact is greatest, often focusing on those who are young or middle-aged (Venkat Narayan et. al, 2011). |
A good paraphrase combines a number of strategies: the goal is to rephrase the information so that it appears in your words, not those of the author.
Example 4: Using Multiple Strategies to Paraphrase
| Original | Acceptable Paraphrase #1 | Acceptable Paraphrase #2 |
|---|---|---|
| We do not yet understand all the ways in which brain chemicals are related to emotions and thoughts, but the salient point is that our state of mind has an immediate and direct effect on our state of body. (Source: Siegel, B. (1986). | Siegel (1986) writes that although the relationship between brain chemistry and thoughts and feelings is not fully understood, we do know that our psychological state affects our physical state.
Words like are generic and do not need to be changed. | Siegel (1986) writes that the relationship between the chemicals in the brain and our thoughts and feelings remains only partially understood. He goes on to say, however, that one thing is clear: our mental state affects our bodily state.
Words like and are generic and do not need to be changed. |
Example 5: Unacceptable Paraphrase
| Original | Unacceptable Paraphrase #1 | Unacceptable Paraphrase #2 |
|---|---|---|
| We do not yet understand all the ways in which brain chemicals are related to emotions and thoughts, but the salient point is that our state of mind has an immediate and direct effect on our state of body.
(Source: Siegel, B. (1986). | Siegel (1986) writes that still know brain chemistry is important mental state on our physical state.
. | According to Siegel (1986), our mind affects our body quickly and directly, although every aspect of
. |
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Paraphrase to Avoid Plagiarism
What is Paraphrasing?
“Paraphrasing” means expressing the meaning of someone else’s words in your own words instead of quoting directly. Paraphrasing is applied both by the author of the text and by editors during the proofreading process .
By paraphrasing the work and arguments of others effectively, you can:
- save space and keep your study more focused
- distill complex information into language that general readers can understand
- avoid plagiarism (including self-plagiarism ) and provide your own authorial voice in your paper
How to Paraphrase in Research
Direct Quote: simply a “copy-and-paste” of the original words and/or word order. In all research papers with formatting guidelines (APA, AMA, MLA, etc.), quoted text must be accompanied by quotation marks and in-text citations.
Paraphrasing: can include some key terms from the original work but must use new language to represent the original work—DO NOT COPY THE ORIGINAL WORK. When you paraphrase–that is, rewrite the text you want to use–you do not need to include quotation marks, but you must still cite the original work.
Paraphrasing Source Text
Step 1 : Read important parts of the source material until you fully understand its meaning.
Step 2 : Take some notes and list key terms of the source material.
Step 3: Write your own paragraph without looking at the source material, only using the key terms.
Step 4: Check to make sure your version captures important parts and intent of the source material.
Step 5: Indicate where your paraphrasing starts and ends using in-text citations.
When to Paraphrase vs Use Direct Quotes

Paraphrasing Examples in Research Writing
Use the following methods to make your paraphrases even stronger. Note that you should not apply only one of these rules in isolation—combine these techniques to reduce your chances of accidental plagiarism.
*Text in red indicates key changes from the source material.
Change the source text voice : active vs. passive voice
By changing the voice of the sentence (active voice to passive; passive voice to active—have a look at this article for details on the different roles of both voices in scientific writing), you can alter the general structure of your paraphrase and put it into words that are more your own.

Use a thesaurus to find synonyms and related terms
A thesaurus can be an excellent resource for finding terms that are synonymous with or similar to those in the original text, especially for non-native English speakers. However, be careful not to use terms that you don’t fully understand or that might not make sense in the context of your paper.
Include introductory phrases with signaling terms
Signaling terms (e.g., “they write ,” “Kim notes that…” “He believes that…”) help smoothly introduce the work of other studies and let the reader know where your own ideas end and where the cited information begins.

Use specific signaling verbs to show your position
Authors also show their positions regarding the original content by using verbs that are neutral , that show agreement , or that show disagreement . A relative pronoun (“that,” “how,” “if”) is also used in many instances. Include these terms to introduce your position in paraphrased content.

Merge multiple sentences into a one- or two-sentence paraphrase
One major reason for paraphrasing is to capture the main idea of the original text without using so many words. Use only one sentence or two in your paraphrase to capture the main idea—even if the original is an entire paragraph.
Original Source Text :
The journal primarily considers empirical and theoretical investigations that enhance understanding of cognitive, motivational, affective, and behavioral psychological phenomena in work and organizational settings, broadly defined. Those psychological phenomena can be at one or multiple levels — individuals, groups, organizations, or cultures; in work settings such as business, education, training, health, service, government, or military institutions; and in the public or private sector, for-profit or nonprofit organizations. (Source: Journal of Applied Psychology Website http://www.apa.org/pubs/journals/apl/ )
Paraphrased Source Text :
The Journal of Applied Psychology accepts studies that increase understanding of a broad range of psychological phenomena and that apply to a variety of settings and levels, not limited by subgroup, institution, or sector (JAP, 2015).
Combine quotes and paraphrased text in the same sentence
Too often, research writers separate information from the current work and information cited from earlier studies into completely different sentences. This limits the dialogue between the works, makes it boring for readers, and can even create issues of plagiarism if the paper is composed of too much quoted material. Include direct quotes within your paraphrased sentences to fix all of these issues and make your research writing much smoother and more natural.
Some details from the original source are quoted because they are taken directly from the text. They provide important information that readers might need to know and it thus makes more sense to use quotes here.
Cite your sources, create a References list, and copy your citations to MS Word using the following Wordvice Citation Generators:

Although paraphrasing can be very helpful in helping to reduce instances of plagiarism, writers still need to follow the rules of citation and referencing carefully. Here are a few rules to keep in mind when paraphrasing any original material, whether from someone else’s published work or your own work.
Here are a few things you must keep in mind when paraphrasing any original material, even your own earlier publications.
- When you paraphrase, use your own terms along with the key terms from the source material.
- Even when you paraphrase using your own terms, you still must provide in-text citations (according to the specific formatting requirements—APA, AMA, MLA , etc.).
- If you are quoting or paraphrasing your own previous work, treat it as another person’s work (i.e., you must still use quotation marks and/or citations).
Example of Plagiarism in Paraphrasing
The following example is an attempt to paraphrase the above source text taken from the Journal of Applied Psychology website . Note that the author does not follow the above-mentioned rules to avoid plagiarizing the work.
Plagiarized Source Text
The Journal of Applied Psychology (JAP 2015) accepts empirical and theoretical investigations that increase knowledge of motivational, affective, cognitive, and behavioral psychological phenomena in many settings, broadly conceived. These phenomena can be at several levels—individual, teams, or cultures; in professional settings like business, education, training, health, government, or military institutions; and in either public or private sector, in nonprofit or for-profit institutions.
Some of the source text words have been changed or removed, but the underlined terms are identical to the original; overall the meaning and even the grammar structures have been copied. Finally, quotation marks are missing. Do not copy passages like this unless you put quotation marks around the content.

Examples of Multiple Attribution Methods:
In this paraphrase example, the details in the source text and how they have been changed in the paraphrase are indicated in red. Note the usage of signaling terms in each version to introduce the author’s content.
Original Source Tex t:
Fully grown penguins generate pressures of around 74 mm Hg to excrete liquid material and 430 mm Hg to excrete material of higher viscosity similar to that of oil. ”
Direct Quote
In her study of Antarctic penguin defecation habits, Brooks (1995, p.4) wrote, “fully grown Chinstrap penguins generate pressures of around 74 mm Hg to excrete liquid material and 430 mm Hg to excrete material of higher viscosity similar to that of oil. ”
*Quotations around quotes; citations included; many details provided; a complete sentence is quoted.
Paraphrased Text
When studying Chinstrap penguin defecation habits, Brooks (1995, p.4) observed that fully grown penguins generate a much higher pressure when excreting more viscous fecal matter.
*No quotation marks; citations included; the most important data fact is highlighted: “Penguins use more pressure to excrete thicker poo.”
Quote/Paraphrase Combination
When studying penguin defecation habits, Brooks (1995, p.4) observed that fully grown penguins vary in how they excrete waste, generating “pressures of around 74 mm Hg to excrete liquid material and 430 mm Hg to excrete material of higher viscosity similar to that of oil .”
*Quotation marks only around directly quoted information; citations included; the most important data fact is paraphrased; additional details provided by direct quote.
More Paraphrasing Examples for Reference
The following paraphrasing examples do not include citations and are therefore better used for reference when learning how to paraphrase original text. Therefore, the tips mentioned earlier in this article should be applied when paraphrasing published academic work.
| “The author’s life spanned years of incredible changes for African Americans in society.” | DuBois lived through at least two eras of liberating reforms and advances for African Americans. |
| “Any trip to France should include a visit to Marseille to visit the old piers of the 17th century.” | Be sure to include a Marseille pier-watching experience when visiting the South of France. |
| “Koala bears eat solely eucalyptus leaves and can consume up to 4 kg per day. | Koalas eat multiple kilograms of eucalyptus leaves per day, their only source of food. |
| “The price of a cruise trip usually includes meals, drinks, and sleeping accommodations, which make your vacation dollar stretch further.” | Most cruise trips include expenses such as meals, drinks, and a room for sleeping in their overall package price. |
| “The average citizen of the UK throws away 20 kg of plastic per month.” | British citizens are among the biggest users of plastic in Europe, throwing away kilograms of plastic each month. |
Paraphrasing Checklist
- Write the paraphrased text in your own words.
- Always include a citation with a paraphrase—you are still using someone else’s ideas
- When you use a direct quote, be sure to clarify the quote to show why you have included it.
- Avoid using blocks of quoted text, especially in papers in the natural sciences. You can almost always use a paraphrase/quote combination instead.
- Overall, focus on your study first—any extra information should be used to enhance your arguments or clarify your research.
Wordvice Resources
After paraphrasing the source text in your research paper, be sure to use a plagiarism checker to make sure there are no overt similarities in your paper. And get English proofreading and academic editing for your journal manuscript or essay editing for your admissions essay to ensure that your writing is ready for submission to journals or schools. Finally, visit our academic resources pages to get more tips beyond how to paraphrase, including common academic phrases , the best transition words in academic papers, verbs for research writing , and many more articles on how to strengthen your academic writing skills.
Find and fix writing mistakes instantly
- Check for unintentional plagiarism
- Get instant grammar and style suggestions
How to Paraphrase in an Essay
When you learn how to paraphrase correctly, you become a more proficient writer. This is especially true if you’re referencing outside information and using supporting evidence for your claims. Paraphrasing is useful because it shows that you understand the key, underlying concepts behind a passage. By putting these ideas in your own words, you can show your instructor that you’re capable of more than just copying and pasting quotes.
Learning how to paraphrase is also useful when you want to clarify a concept and make it easier for the reader to understand. For example, perhaps you know that you’re writing to an audience with only a cursory understanding of the topic at hand. You may want to phrase complex concepts in simpler terms so that your writing is more accessible.
It’s always a good idea to paraphrase throughout your writing instead of relying on direct quotes. Quotes are only meant to be used sparingly throughout your text. When you learn how to paraphrase properly, you can reference other people’s work without your entire essay devolving into one long string of endless quotes.
What is paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing is when you rewrite another author’s text into your own words. A paraphrased passage can be shorter, longer, or the same length as the original text. After you learn how to paraphrase, you can help the reader understand a passage more clearly. This is especially true if you think the subject matter is too antiquated or complex for your readers.
How to paraphrase
In an academic setting, there are a number of specific rules and guidelines when it comes to paraphrasing. You can’t simply put someone else’s ideas in your own words and call it a day. For example, you must properly attribute the source material when paraphrasing. Although this process might seem daunting at first, it’s quite easy to learn how to paraphrase when you follow a few easy steps:
1. Read the text
First, you need to thoroughly read the text. The key to paraphrasing is developing a strong understanding of the ideas at play. Once you develop a firm grasp on the meaning behind the passage, you’ll find it much easier to paraphrase it effectively. Don’t be afraid to read the source material over three or four times and really think about what it all means.
2. Put the original text away and try to paraphrase by memory
Although it might seem tempting to constantly refer back to the original text while paraphrasing, it’s best to close the book or document and start from scratch. This ensures that you’re using your own unique language instead of being influenced too much by the source material. Remember, to paraphrase correctly you need to do more than simply change one or two words.
Once you’ve put the original text away, try to convey the same general message by memory alone. As you write, you’ll naturally express the passage in words that seem more familiar to you. You’ll likely end up with a paraphrase that seems clearer than the source material, and this is one of the main goals of paraphrasing.
3. Think about how you’re going to use your paraphrase
Context is important when paraphrasing. While you’re constructing your paraphrase, it’s always a good idea to think about how you’re going to use it in your own writing. Is there a specific point you want to make with this paraphrase? If you’re using the paraphrase as evidence of something, what purpose does the evidence need to serve?
If you keep these ideas in the back of your mind, you can create an effective paraphrase that fits with your writing. That being said, you can’t pick and choose certain parts of a passage when paraphrasing. Instead, you have to refer to all of the ideas in the passage without leaving anything out.
4. Check the original text
Once you’ve finished writing your paraphrase from memory alone, it’s time to check the original text to make sure that you’ve presented the ideas in an accurate manner. At this point, you should also make sure that your paraphrase is not too similar to the source material.
Unlike summaries, paraphrases are specific instead of selective. In other words, you need to say exactly the same thing as the original author when paraphrasing. This means that all of their key ideas must also be present in your paraphrase.
5. Acknowledge your source
Even though you’re not using a direct quote, you still need to attribute your source when paraphrasing. Essentially, you’re using other people’s ideas to make a point, so you need to give people credit for the concepts that you’re borrowing.
The exact format for source attribution will depend on your course, subject, or instructor. For example, MLA and Chicago style formats both have different paraphrasing requirements. If you’re not sure what format you need to adhere to, check with your instructor and ask how they’d like you to cite sources when paraphrasing.
If you’re looking for help creating a citation, check out www.CitationMachine.net !
When creating your paraphrase, you may decide that you want to keep one or two words from the source material. If you do this, it’s important to use quotation marks. This is helpful when you want to make use of powerful words in the original text. Alternatively, specific words may be important when using paraphrases as evidence.
Avoiding plagiarism
Even when you diligently follow all the steps for proper paraphrasing, it can be easy to accidentally plagiarize another work. The most common mistake is to unintentionally create paraphrases that are too similar to the source material. Sometimes, students do this on a subconscious level.
This is why it’s so important to rely on your memory when writing paraphrases. Not only that, but it’s also crucial to check the source material for overt similarities after you’ve written your paraphrase.
Another obvious tip for avoiding plagiarism is to cite your sources. It’s important to note that only 10% of your writing should contain other people’s work in the form of direct quotes. This is why paraphrases and summaries are so useful in academic writing.
Key takeaways
- Paraphrasing is useful because it shows that you understand the source material
- The goal of paraphrasing is to make ideas easier to understand
- Paraphrases can be longer, shorter, or the same length as the original passage
- Read the source material thoroughly
- Close the book or document and paraphrase from memory
- Check for similarities between your paraphrase and the source material
- Think about context
- Cite your sources properly
- You can’t just change one or two words and claim that you’re paraphrasing
Published October 29, 2020.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Paraphrasing in an Essay
3-minute read
- 22nd May 2018
Quoting sources in an essay is a bit like cutting your toenails: useful to do now and then, but you can definitely go too far. However, rather than leading to sore toes, excessive quoting can mean you lose marks on your work (which is arguably far worse). This is why paraphrasing is a crucial skill.
Paraphrase or Quote?
Paraphrasing and quoting are two ways of referring to someone else’s ideas in your writing. When we quote someone, we use their exact words and place them within quotation marks.
When we paraphrase something, on the other hand, we try to express the same idea in our own words. This offers a few advantages over quoting:
- It lets you demonstrate your understanding of the source.
- You can explain a complex idea in simple terms.
- You can focus on the parts of the source most relevant to your work.
As such, paraphrasing is usually a better choice than quoting a source at length . The only times you ever truly need to quote a source are when:
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
- Your argument depends on the wording of something (e.g. if your interpretation of a text depends on the exact words used).
- The original text expresses something in an especially useful way.
This is not to say that you can’t quote sources in other situations, but most of the document should be your own words. Whether you quote or paraphrase, though, you still need to give a citation .
5 Paraphrasing Tips
Hopefully, you’re now keen to start paraphrasing sources. But how should you do this? Check out the five tips below for some handy advice!
- Read the original source a few times to make sure you fully understand it.
- Choose whether to paraphrase the source in full (i.e. presenting all the information from the original passage in your own words) or summarise it (i.e. selecting the details most relevant to your own work).
- Think about how you would explain the passage to a friend who does not understand your subject area (you could even try this in real life).
- Write your paraphrased version of the passage, then compare it to the original to make sure you haven’t missed anything.
- If you use any exact phrases from the original text, put these in quotation marks and add the relevant page numbers to the citation.
Keep all of this in mind and you should be paraphrasing like a pro in no time!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Advanced Paraphrasing Tool
Elevate your writing with our free and ai-powered paraphraser. instantly correct or rephrase your sentences in different tones., paraphrasing tool, please rewrite my sentence, what is paraphrasing.
Paraphrasing is the art of rewriting text into other words. This includes using synonyms, restructuring phrases, and connecting ideas in different ways. A state-of-the-art paraphraser provides automatic and simple-to-use rephrasing of complete sentences.

Why Should I Paraphrase My Sentences?
By paraphrasing existing sentences, you can elevate your writing and achieve different goals as a writer. That’s why rephrasing is helpful in plenty of cases: rewriting citations, strengthening the message of your text, and rewording your ideas while improving style.

How Does Rephrasing Help Me Become a Better Writer?
This feature is highly customizable, meaning you’re in control. Choose from five different categories—general, formal, concise, fluent, or simple—to transform your writing to better suit the context and tone. Paraphrasing helps you by refining and perfecting your masterpieces.
Where Can I Use the Paraphrasing Tool?
Rephrasing is available wherever and whenever! All you need is a LanguageTool account and a stable internet connection to rewrite your sentences in almost all of LanguageTool's extensions. The feature is easily accessible for everyone that aims to improve their writing.
Thunderbird
What exactly does an online paraphraser do.
LanguageTool’s paraphrasing feature does so much more than just rewrite sentences. Not only does it check for stronger, more suitable word choice, but it also corrects your sentence as a whole to ensure high-quality writing. With its intuitive and user-friendly interface, everyone can leverage Artificial Intelligence to achieve the best results possible.

What Other Features Does LanguageTool’s Paraphraser Provide?
The best part of using A.I. to paraphrase your writing is that the suggested sentences come free of spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Want to also improve style? Simply go back to the general correction to view stylistic suggestions.

As multilingual as you
Make your text sound professional and avoid embarrassing style, punctuation, and grammar mistakes
It’s an online tool that rewrites texts in a new (stylistically different) way by using alternative wording and a rephrased sentence structure.
This function is recommended for all types of texts, including professional, academic, and creative writing. It’s available for all LanguageTool users, but unlimited paraphrasing is only available in Premium.
A paraphrasing tool can easily enhance your writing by improving the tone and style of your text. Moreover, it helps you avoid having to write direct citations by rewriting copy-and-pasted text.
Premium accounts offer even more useful and powerful features:
Only with Premium
Sentence correction of longer texts
Style guide for customizing individual rules
Team features for companies
More in-depth suggestions, especially for word choice and style
How Can I Effectively Use the Rephrasing Tool?
For basic users, the paraphrasing feature is limited to three times daily. If you need more rephrased sentences, you can upgrade to LanguageTool Premium to get access to unlimited paraphrasing in six languages and several English dialects. Remember: No personal data is stored (ever) and privacy guidelines are strictly followed (always).
Strengthen Your Communication Skills
Try out the best paraphrasing tool for free and discover how LanguageTool can elevate your writing.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Sample Essay for Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Quoting

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The following is a sample essay you can practice quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing. Examples of each task are provided at the end of the essay for further reference. Here is the citation for Sipher's essay:
Sipher, Roger. “So That Nobody Has to Go to School If They Don't Want To.” The New York Times , 19 Dec. 1977, p. 31.
So That Nobody Has To Go To School If They Don't Want To
by Roger Sipher
A decline in standardized test scores is but the most recent indicator that American education is in trouble.
One reason for the crisis is that present mandatory-attendance laws force many to attend school who have no wish to be there. Such children have little desire to learn and are so antagonistic to school that neither they nor more highly motivated students receive the quality education that is the birthright of every American.
The solution to this problem is simple: Abolish compulsory-attendance laws and allow only those who are committed to getting an education to attend.
This will not end public education. Contrary to conventional belief, legislators enacted compulsory-attendance laws to legalize what already existed. William Landes and Lewis Solomon, economists, found little evidence that mandatory-attendance laws increased the number of children in school. They found, too, that school systems have never effectively enforced such laws, usually because of the expense involved.
There is no contradiction between the assertion that compulsory attendance has had little effect on the number of children attending school and the argument that repeal would be a positive step toward improving education. Most parents want a high school education for their children. Unfortunately, compulsory attendance hampers the ability of public school officials to enforce legitimate educational and disciplinary policies and thereby make the education a good one.
Private schools have no such problem. They can fail or dismiss students, knowing such students can attend public school. Without compulsory attendance, public schools would be freer to oust students whose academic or personal behavior undermines the educational mission of the institution.
Has not the noble experiment of a formal education for everyone failed? While we pay homage to the homily, "You can lead a horse to water but you can't make him drink," we have pretended it is not true in education.
Ask high school teachers if recalcitrant students learn anything of value. Ask teachers if these students do any homework. Quite the contrary, these students know they will be passed from grade to grade until they are old enough to quit or until, as is more likely, they receive a high school diploma. At the point when students could legally quit, most choose to remain since they know they are likely to be allowed to graduate whether they do acceptable work or not.
Abolition of archaic attendance laws would produce enormous dividends.
First, it would alert everyone that school is a serious place where one goes to learn. Schools are neither day-care centers nor indoor street corners. Young people who resist learning should stay away; indeed, an end to compulsory schooling would require them to stay away.
Second, students opposed to learning would not be able to pollute the educational atmosphere for those who want to learn. Teachers could stop policing recalcitrant students and start educating.
Third, grades would show what they are supposed to: how well a student is learning. Parents could again read report cards and know if their children were making progress.
Fourth, public esteem for schools would increase. People would stop regarding them as way stations for adolescents and start thinking of them as institutions for educating America's youth.
Fifth, elementary schools would change because students would find out early they had better learn something or risk flunking out later. Elementary teachers would no longer have to pass their failures on to junior high and high school.
Sixth, the cost of enforcing compulsory education would be eliminated. Despite enforcement efforts, nearly 15 percent of the school-age children in our largest cities are almost permanently absent from school.
Communities could use these savings to support institutions to deal with young people not in school. If, in the long run, these institutions prove more costly, at least we would not confuse their mission with that of schools.
Schools should be for education. At present, they are only tangentially so. They have attempted to serve an all-encompassing social function, trying to be all things to all people. In the process they have failed miserably at what they were originally formed to accomplish.
Example Summary, Paraphrase, and Quotation from the Essay:
Example summary: Roger Sipher makes his case for getting rid of compulsory-attendance laws in primary and secondary schools with six arguments. These fall into three groups—first that education is for those who want to learn and by including those that don't want to learn, everyone suffers. Second, that grades would be reflective of effort and elementary school teachers wouldn't feel compelled to pass failing students. Third, that schools would both save money and save face with the elimination of compulsory-attendance laws.
Example paraphrase of the essay's conclusion: Roger Sipher concludes his essay by insisting that schools have failed to fulfill their primary duty of education because they try to fill multiple social functions (par. 17).
Example quotation: According to Roger Sipher, a solution to the perceived crisis of American education is to "[a]bolish compulsory-attendance laws and allow only those who are committed to getting an education to attend" (par. 3).
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
Published on 8 April 2022 by Courtney Gahan and Jack Caulfield. Revised on 15 May 2023.
Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas into your own words. Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning.
Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone’s exact words and putting them in quotation marks ). In academic writing, it’s usually better to paraphrase instead of quoting. It shows that you have understood the source, reads more smoothly, and keeps your own voice front and center.
Every time you paraphrase, it’s important to cite the source . Also take care not to use wording that is too similar to the original. Otherwise, you could be at risk of committing plagiarism .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to paraphrase in five easy steps, how to paraphrase correctly, examples of paraphrasing, how to cite a paraphrase, paraphrasing vs quoting, paraphrasing vs summarising, avoiding plagiarism when you paraphrase, frequently asked questions about paraphrasing.
If you’re struggling to get to grips with the process of paraphrasing, check out our easy step-by-step guide in the video below.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Putting an idea into your own words can be easier said than done. Let’s say you want to paraphrase the text below, about population decline in a particular species of sea snails.
Incorrect paraphrasing
You might make a first attempt to paraphrase it by swapping out a few words for synonyms .
Like other sea creatures inhabiting the vicinity of highly populated coasts, horse conchs have lost substantial territory to advancement and contamination , including preferred breeding grounds along mud flats and seagrass beds. Their Gulf home is also heating up due to global warming , which scientists think further puts pressure on the creatures , predicated upon the harmful effects extra warmth has on other large mollusks (Barnett, 2022).
This attempt at paraphrasing doesn’t change the sentence structure or order of information, only some of the word choices. And the synonyms chosen are poor:
- ‘Advancement and contamination’ doesn’t really convey the same meaning as ‘development and pollution’.
- Sometimes the changes make the tone less academic: ‘home’ for ‘habitat’ and ‘sea creatures’ for ‘marine animals’.
- Adding phrases like ‘inhabiting the vicinity of’ and ‘puts pressure on’ makes the text needlessly long-winded.
- Global warming is related to climate change, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing.
Because of this, the text reads awkwardly, is longer than it needs to be, and remains too close to the original phrasing. This means you risk being accused of plagiarism .
Correct paraphrasing
Let’s look at a more effective way of paraphrasing the same text.
Here, we’ve:
- Only included the information that’s relevant to our argument (note that the paraphrase is shorter than the original)
- Retained key terms like ‘development and pollution’, since changing them could alter the meaning
- Structured sentences in our own way instead of copying the structure of the original
- Started from a different point, presenting information in a different order
Because of this, we’re able to clearly convey the relevant information from the source without sticking too close to the original phrasing.
Explore the tabs below to see examples of paraphrasing in action.
- Journal article
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| ‘The current research extends the previous work by revealing that to moral dilemmas could elicit a FLE [foreign-language effect] in highly proficient bilinguals. … Here, it has been demonstrated that hearing a foreign language can even influence moral decision making, and namely promote more utilitarian-type decisions’ ( , p. 874). | The research of Brouwer (2019, p. 874) suggests that the foreign-language effect can occur even among highly proficient bilinguals, influencing their moral decision making, when auditory (rather than written) prompting is given. |
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| ‘The Environmental Protection Agency on Tuesday proposed to ban chrysotile asbestos, the most common form of the toxic mineral still used in the United States. … Chlorine manufacturers and companies that make vehicle braking systems and sheet gaskets still import chrysotile asbestos and use it to manufacture new products. ‘The proposed rule would ban all manufacturing, processing, importation and commercial distribution of six categories of products containing chrysotile asbestos, which agency officials said would cover all of its current uses in the United States’ ( ). | Chrysotile asbestos, which is used to manufacture chlorine, sheet gaskets, and braking systems, may soon be banned by the Environmental Protection Agency. The proposed ban would prevent it from being imported into, manufactured in, or processed in the United States (Phillips, 2022). |
| Source text | Paraphrase |
|---|---|
| ‘The concept of secrecy might evoke an image of two people in conversation, with one person actively concealing from the other. Yet, such concealment is actually uncommon. It is far more common to ruminate on our secrets. It is our tendency to mind-wander to our secrets that seems most harmful to well-being. Simply thinking about a secret can make us feel inauthentic. Having a secret return to mind, time and time again, can be tiring. When we think of a secret, it can make us feel isolated and alone’ ( ). | Research suggests that, while keeping secrets from others is indeed stressful, this may have little to do with the act of hiding information itself. Rather, the act of ruminating on one’s secrets is what leads to feelings of fatigue, inauthenticity, and isolation (Slepian, 2019). |
Once you have your perfectly paraphrased text, you need to ensure you credit the original author. You’ll always paraphrase sources in the same way, but you’ll have to use a different type of in-text citation depending on what citation style you follow.
| (Brouwer, 2019, p. 874) | |
| (1, p. 874) | |
| (Brouwer, 2019, p. 874) |
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
It’s a good idea to paraphrase instead of quoting in most cases because:
- Paraphrasing shows that you fully understand the meaning of a text
- Your own voice remains dominant throughout your paper
- Quotes reduce the readability of your text
But that doesn’t mean you should never quote. Quotes are appropriate when:
- Giving a precise definition
- Saying something about the author’s language or style (e.g., in a literary analysis paper)
- Providing evidence in support of an argument
- Critiquing or analysing a specific claim
A paraphrase puts a specific passage into your own words. It’s typically a similar length to the original text, or slightly shorter.
When you boil a longer piece of writing down to the key points, so that the result is a lot shorter than the original, this is called summarising .
Paraphrasing and quoting are important tools for presenting specific information from sources. But if the information you want to include is more general (e.g., the overarching argument of a whole article), summarising is more appropriate.
When paraphrasing, you have to be careful to avoid accidental plagiarism .
Students frequently use paraphrasing tools , which can be especially helpful for non-native speakers who might have trouble with academic writing. While these can be useful for a little extra inspiration, use them sparingly while maintaining academic integrity.
This can happen if the paraphrase is too similar to the original quote, with phrases or whole sentences that are identical (and should therefore be in quotation marks). It can also happen if you fail to properly cite the source.
To make sure you’ve properly paraphrased and cited all your sources, you could elect to run a plagiarism check before submitting your paper.
To paraphrase effectively, don’t just take the original sentence and swap out some of the words for synonyms. Instead, try:
- Reformulating the sentence (e.g., change active to passive , or start from a different point)
- Combining information from multiple sentences into one
- Leaving out information from the original that isn’t relevant to your point
- Using synonyms where they don’t distort the meaning
The main point is to ensure you don’t just copy the structure of the original text, but instead reformulate the idea in your own words.
Paraphrasing without crediting the original author is a form of plagiarism , because you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
However, paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you correctly reference the source . This means including an in-text referencing and a full reference , formatted according to your required citation style (e.g., Harvard , Vancouver ).
As well as referencing your source, make sure that any paraphrased text is completely rewritten in your own words.
Plagiarism means using someone else’s words or ideas and passing them off as your own. Paraphrasing means putting someone else’s ideas into your own words.
So when does paraphrasing count as plagiarism?
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if you don’t properly credit the original author.
- Paraphrasing is plagiarism if your text is too close to the original wording (even if you cite the source). If you directly copy a sentence or phrase, you should quote it instead.
- Paraphrasing is not plagiarism if you put the author’s ideas completely into your own words and properly reference the source .
To present information from other sources in academic writing , it’s best to paraphrase in most cases. This shows that you’ve understood the ideas you’re discussing and incorporates them into your text smoothly.
It’s appropriate to quote when:
- Changing the phrasing would distort the meaning of the original text
- You want to discuss the author’s language choices (e.g., in literary analysis )
- You’re presenting a precise definition
- You’re looking in depth at a specific claim
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Gahan, C. & Caulfield, J. (2023, May 15). How to Paraphrase | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/working-sources/paraphrasing/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, apa referencing (7th ed.) quick guide | in-text citations & references.

Capstone Form and Style
Evidence-based arguments: paraphrasing, basics of paraphrasing.
A successful paraphrase is your own explanation or interpretation of another person's ideas. Paraphrasing in academic writing is an effective way to restate, condense, or clarify another author's ideas while also providing credibility to your own argument or analysis. While successful paraphrasing is essential for strong academic writing, unsuccessful paraphrasing can result in unintentional plagiarism. Look through the paraphrasing strategies below to better understand what counts as an effective paraphrase.
Effective Paraphrasing Strategies
If you’re having trouble paraphrasing a text effectively, try following these steps:
- Reread the original passage you wish to paraphrase, looking up any words you do not recognize, until you think you understand the full meaning of and intention behind the author's words.
- Next, cover or hide the passage. Once the passage is hidden from view, write out the author's idea, in your own words, as if you were explaining it to your instructor or classmates.
Have I accurately addressed the author's ideas in a new way that is unique to my writing style and scholarly voice? Have I tried to replicate the author's idea or have I simply changed words around in his/her original sentence(s)?
- Last, include a citation, which should contain the author's name, the year, and the page or paragraph number (if available), directly following your paraphrase.
Examples of Paraphrasing
Here is the original source an author might use in a paper:
Differentiation as an instructional approach promotes a balance between a student's style and a student's ability. Differentiated instruction provides the student with options for processing and internalizing the content, and for constructing new learning in order to progress academically.
Here is an example of bad paraphrasing of the source. Even though the student is citing correctly, underlined words are simply synonyms of words used in the original source. You can also see how the sentence structure is the same for both the original source and this paraphrase.
Differentiation is a way to encourage equality between the approach and talent of the student (Thompson, 2009). This type of instruction gives students different ways to deal with and grasp information , and for establishing new learning to move on in education (Thompson, 2009).
Here is an example of a better way to paraphrase the source. In this example, the author has taken the essential ideas and information from the original source, but has worded it in her own way, using unique word choice and sentence structure. The author has condensed Thompson's (2009) information, including what is relevant to her paper, but leaving out extra details that she does not needed.
Teachers use differentiated instruction to help students learn, allowing the teacher to cater lessons to the way each student learns and each student's skill (Thompson, 2009).
- Previous Page: Home
- Next Page: Quoting
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- Utility Menu
fa3d988da6f218669ec27d6b6019a0cd
A publication of the harvard college writing program.
Harvard Guide to Using Sources
- The Honor Code
- Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Quoting
Depending on the conventions of your discipline, you may have to decide whether to summarize a source, paraphrase a source, or quote from a source.
When and how to summarize
When you summarize, you provide your readers with a condensed version of an author's key points. A summary can be as short as a few sentences or much longer, depending on the complexity of the text and the level of detail you wish to provide to your readers. You will need to summarize a source in your paper when you are going to refer to that source and you want your readers to understand the source's argument, main ideas, or plot (if the source is a novel, film, or play) before you lay out your own argument about it, analysis of it, or response to it.
Before you summarize a source in your paper, you should decide what your reader needs to know about that source in order to understand your argument. For example, if you are making an argument about a novel, you should avoid filling pages of your paper with details from the book that will distract or confuse your reader. Instead, you should add details sparingly, going only into the depth that is necessary for your reader to understand and appreciate your argument. Similarly, if you are writing a paper about a journal article, you will need to highlight the most relevant parts of the argument for your reader, but you should not include all of the background information and examples. When you have to decide how much summary to put in a paper, it's a good idea to consult your instructor about whether you are supposed to assume your reader's knowledge of the sources.
Guidelines for summarizing a source in your paper
- Identify the author and the source.
- Represent the original source accurately.
- Present the source’s central claim clearly.
- Don’t summarize each point in the same order as the original source; focus on giving your reader the most important parts of the source
- Use your own words. Don’t provide a long quotation in the summary unless the actual language from the source is going to be important for your reader to see.
Stanley Milgram (1974) reports that ordinarily compassionate people will be cruel to each other if they are commanded to be by an authority figure. In his experiment, a group of participants were asked to administer electric shocks to people who made errors on a simple test. In spite of signs that those receiving shock were experiencing great physical pain, 25 of 40 subjects continued to administer electric shocks. These results held up for each group of people tested, no matter the demographic. The transcripts of conversations from the experiment reveal that although many of the participants felt increasingly uncomfortable, they continued to obey the experimenter, often showing great deference for the experimenter. Milgram suggests that when people feel responsible for carrying out the wishes of an authority figure, they do not feel responsible for the actual actions they are performing. He concludes that the increasing division of labor in society encourages people to focus on a small task and eschew responsibility for anything they do not directly control.
This summary of Stanley Milgram's 1974 essay, "The Perils of Obedience," provides a brief overview of Milgram's 12-page essay, along with an APA style parenthetical citation. You would write this type of summary if you were discussing Milgram's experiment in a paper in which you were not supposed to assume your reader's knowledge of the sources. Depending on your assignment, your summary might be even shorter.
When you include a summary of a paper in your essay, you must cite the source. If you were using APA style in your paper, you would include a parenthetical citation in the summary, and you would also include a full citation in your reference list at the end of your paper. For the essay by Stanley Milgram, your citation in your references list would include the following information:
Milgram, S. (1974). The perils of obedience. In L.G. Kirszner & S.R. Mandell (Eds.), The Blair reader (pp.725-737).
When and how to paraphrase
When you paraphrase from a source, you restate the source's ideas in your own words. Whereas a summary provides your readers with a condensed overview of a source (or part of a source), a paraphrase of a source offers your readers the same level of detail provided in the original source. Therefore, while a summary will be shorter than the original source material, a paraphrase will generally be about the same length as the original source material.
When you use any part of a source in your paper—as background information, as evidence, as a counterargument to which you plan to respond, or in any other form—you will always need to decide whether to quote directly from the source or to paraphrase it. Unless you have a good reason to quote directly from the source , you should paraphrase the source. Any time you paraphrase an author's words and ideas in your paper, you should make it clear to your reader why you are presenting this particular material from a source at this point in your paper. You should also make sure you have represented the author accurately, that you have used your own words consistently, and that you have cited the source.
This paraphrase below restates one of Milgram's points in the author's own words. When you paraphrase, you should always cite the source. This paraphrase uses the APA in-text citation style. Every source you paraphrase should also be included in your list of references at the end of your paper. For citation format information go to the Citing Sources section of this guide.
Source material
The problem of obedience is not wholly psychological. The form and shape of society and the way it is developing have much to do with it. There was a time, perhaps, when people were able to give a fully human response to any situation because they were fully absorbed in it as human beings. But as soon as there was a division of labor things changed.
--Stanley Milgram, "The Perils of Obedience," p.737.
Milgram, S. (1974). The perils of obedience. In L.G. Kirszner & S.R. Mandell (Eds.), The Blair reader (pp.725-737). Prentice Hall.
Milgram (1974) claims that people's willingness to obey authority figures cannot be explained by psychological factors alone. In an earlier era, people may have had the ability to invest in social situations to a greater extent. However, as society has become increasingly structured by a division of labor, people have become more alienated from situations over which they do not have control (p.737).
When and how much to quote
The basic rule in all disciplines is that you should only quote directly from a text when it's important for your reader to see the actual language used by the author of the source. While paraphrase and summary are effective ways to introduce your reader to someone's ideas, quoting directly from a text allows you to introduce your reader to the way those ideas are expressed by showing such details as language, syntax, and cadence.
So, for example, it may be important for a reader to see a passage of text quoted directly from Tim O'Brien's The Things They Carried if you plan to analyze the language of that passage in order to support your thesis about the book. On the other hand, if you're writing a paper in which you're making a claim about the reading habits of American elementary school students or reviewing the current research on Wilson's disease, the information you’re providing from sources will often be more important than the exact words. In those cases, you should paraphrase rather than quoting directly. Whether you quote from your source or paraphrase it, be sure to provide a citation for your source, using the correct format. (see Citing Sources section)
You should use quotations in the following situations:
- When you plan to discuss the actual language of a text.
- When you are discussing an author's position or theory, and you plan to discuss the wording of a core assertion or kernel of the argument in your paper.
- When you risk losing the essence of the author's ideas in the translation from their words to your own.
- When you want to appeal to the authority of the author and using their words will emphasize that authority.
Once you have decided to quote part of a text, you'll need to decide whether you are going to quote a long passage (a block quotation) or a short passage (a sentence or two within the text of your essay). Unless you are planning to do something substantive with a long quotation—to analyze the language in detail or otherwise break it down—you should not use block quotations in your essay. While long quotations will stretch your page limit, they don't add anything to your argument unless you also spend time discussing them in a way that illuminates a point you're making. Unless you are giving your readers something they need to appreciate your argument, you should use quotations sparingly.
When you quote from a source, you should make sure to cite the source either with an in-text citation or a note, depending on which citation style you are using. The passage below, drawn from O’Brien’s The Things They Carried , uses an MLA-style citation.
On the morning after Ted Lavender died, First Lieutenant Jimmy Cross crouched at the bottom of his foxhole and burned Martha's letters. Then he burned the two photographs. There was a steady rain falling, which made it difficult, but he used heat tabs and Sterno to build a small fire, screening it with his body holding the photographs over the tight blue flame with the tip of his fingers.
He realized it was only a gesture. Stupid, he thought. Sentimental, too, but mostly just stupid. (23)
O'Brien, Tim. The Things They Carried . New York: Broadway Books, 1990.
Even as Jimmy Cross burns Martha's letters, he realizes that "it was only a gesture. Stupid, he thought. Sentimental too, but mostly just stupid" (23).
If you were writing a paper about O'Brien's The Things They Carried in which you analyzed Cross's decision to burn Martha's letters and stop thinking about her, you might want your reader to see the language O'Brien uses to illustrate Cross's inner conflict. If you were planning to analyze the passage in which O'Brien calls Cross's realization stupid, sentimental, and then stupid again, you would want your reader to see the original language.
- Locating Sources
- Evaluating Sources
- Sources and Your Assignment
- A Source's Role in Your Paper
- Choosing Relevant Parts of a Source
- The Nuts & Bolts of Integrating
PDFs for This Section
- Using sources
- Integrating Sources
- Online Library and Citation Tools

Paraphrasing
A paraphrase restates another’s idea (or your own previously published idea) in your own words. Paraphrasing allows you to summarize and synthesize information from one or more sources, focus on significant information, and compare and contrast relevant details.
Published authors paraphrase their sources most of the time, rather than directly quoting the sources; student authors should emulate this practice by paraphrasing more than directly quoting.
When you paraphrase, cite the original work using either the narrative or parenthetical citation format .
Although it is not required to provide a page or paragraph number in the citation, you may include one (in addition to the author and year) when it would help interested readers locate the relevant passage within a long or complex work (e.g., a book).
Webster-Stratton (2016) described a case example of a 4-year-old girl who showed an insecure attachment to her mother; in working with the family dyad, the therapist focused on increasing the mother’s empathy for her child (pp. 152–153).
These guidelines pertain to when you read a primary source and paraphrase it yourself. If you read a paraphrase of a primary source in a published work and want to cite that source, it is best to read and cite the primary source directly if possible; if not, use a secondary source citation .
Paraphrasing is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Sections 8.23 and 8.24 and the Concise Guide Sections 8.23 and 8.24
Related handout
- Paraphrasing and Citation Activities (PDF, 357KB)
Long paraphrases
A paraphrase may continue for several sentences. In such cases, cite the work being paraphrased on first mention. Once the work has been cited, it is not necessary to repeat the citation as long as the context of the writing makes it clear that the same work continues to be paraphrased.
Velez et al. (2018) found that for women of color, sexism and racism in the workplace were associated with poor work and mental health outcomes, including job-related burnout, turnover intentions, and psychological distress. However, self-esteem, person–organization fit, and perceived organizational support mediated these effects. Additionally, stronger womanist attitudes—which acknowledge the unique challenges faced by women of color in a sexist and racist society—weakened the association of workplace discrimination with psychological distress. These findings underscore the importance of considering multiple forms of workplace discrimination in clinical practice and research with women of color, along with efforts to challenge and reduce such discrimination.
If the paraphrase continues into a new paragraph, reintroduce the citation. If the paraphrase incorporates multiple sources or switches among sources, repeat the citation so the source is clear. Read your sentences carefully to ensure you have cited sources appropriately.
Play therapists can experience many symptoms of impaired wellness, including emotional exhaustion or reduced ability to empathize with others (Elwood et al., 2011; Figley, 2002), disruption in personal relationships (Elwood et al., 2011; Robinson-Keilig, 2014), decreased satisfaction with work (Elwood et al., 2011), avoidance of particular situations (Figley, 2002; O’Halloran & Linton, 2000), and feelings or thoughts of helplessness (Elwood et al., 2011; Figley, 2002; O’Halloran & Linton, 2000).
Get the Reddit app
The subreddit for discussion related to college and collegiate life.
53% plagiarism on my essay although I did not cheat at all
So I had to write a 7-page research paper for one of my history classes, containing a LOT of citations and sources (the professor said at least 12 sources). Meaning a big part of the essay should be quotes from different journals. I tried to make sure that the citations were made right, as I did not plagiarize at all of the essays.
When I turned it in nearly EVERY SINGLE quote on there that I cited counted as plagiarized for some reason. None of my own writing counted as copied only the quotes.
For example: According to " and then here is the quote from the journal". Would be totally counted as plagiarism.
Should I be worried that my essay still says 53 percent plagiarism although the only things copied were the quotes?
- Plagiarism Checker
- Paraphrasing
- Essay Generator
- Image To Text
Paraphrase Tool
Paraphrase your content by the paraphrase tool of Prepostseo to improve its overall quality.
Table of Contents
Paraphrasing Tool
Paraphrase Tool by Prepostseo is an online paraphraser that can help quickly rephrase your essays, articles, blogs, etc., without changing the actual meaning. Our paraphrasing tool uses advanced AI and large language models to accurately paraphrase your content into a fresh, more engaging, and plagiarism-free one.
What is Paraphrasing?
Paraphrasing refers to the process of expressing existing content in your own unique words and sentences, without altering the original meaning.
Paraphrasing is mainly done by using the below techniques;
Replacing original words with their suitable synonyms.
Changing sentence structures.
Altering the tone, tense, or voice of sentences in the original content.
And so on…
How to Use the Prepostseo Paraphrase Tool?
Our paraphrase online tool has a simple interface, you just follow these steps to paraphrase your content:
Enter the text that you want to rephrase into the input box of the paraphrasing tool.
Pick the “ Paraphrasing Mode ” such as; Standard, Academic, Fluency, etc., that matches your requirements.
Click the " Paraphrase ” button to start our paraphrase tool.
The paraphrase tool will quickly rephrase your content into a new one and highlight changes.
Review the changed text and “ Copy to Clipboard ” or “ Download ” it.
Free All-in-One Office Suite with PDF Editor
Edit Word, Excel, and PPT for FREE.
Read, edit, and convert PDFs with the powerful PDF toolkit.
Microsoft-like interface, easy to use.
Windows • MacOS • Linux • iOS • Android
Select areas that need to improve
- Didn't match my interface
- Too technical or incomprehensible
- Incorrect operation instructions
- Incomplete instructions on this function
Fields marked * are required please
Please leave your suggestions below
- Quick Tutorials
How to Write an Essay in MLA Format | For Students
Starting from when I entered high school, the importance of submitting assignments in a particular format became a top priority. I quickly realized the significance of adhering to these guidelines, as they remained essential throughout my academic journey. You never know when the need for proper formatting will arise. At first, it may seem overwhelming, but in this simple guide, I'll show you how to write an essay in MLA format [For Students].
When is MLA format used?
MLA format is created by the Modern Language Association which is a standardized way to format academic papers and cite sources. It’s mainly used for subjects in the humanities, like literature, philosophy, and the arts. Unlike APA or Chicago formats, which are used for social sciences and history, MLA puts a strong emphasis on the authorship of sources.
Most students will need to use MLA format at some point, especially in humanities courses. It’s essential for essays, research papers, and other assignments in these subjects.
General Guidelines/ Rules of MLA Formatting
The first step to learning how to write an essay in MLA format for students is to get familiar with the general guidelines. It's all about following the rules to get your paper formatted in the MLA style:
Margins and Font:
Set 1-inch margins on all sides.
Choose a readable font such as Times New Roman, 12-point size.
Double-space the entire document, including block quotes (quotes longer than four lines), notes, and the works cited page.
Paragraph Indentation:
Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches (press Tab key once).
Punctuation:
Utilize standard punctuation marks and maintain consistency with punctuation, italics, and quotation marks throughout your paper.
Quotations:
Use double quotation marks (" ") for direct quotes.
For quotes longer than four lines, format as a block quote: start on a new line, indent 0.5 inches from the left margin (without quotation marks), and keep double-spacing.
Here is an essay MLA format template for your reference:
How to Set up MLA Format Essay [Step-by-Step]
So we have seen the general guidelines in the above example and also saw an essay MLA format example/sample showing what our final MLA format will look like. However, going through guidelines is not enough when you're learning how to write an essay in MLA format in Word or PDF format. You need a professional writing software that not only provides the tools but also allows you to use them easily.
Therefore, I will be using WPS Writer as my partner in writing an essay in MLA format, and I would recommend students to download WPS Writer from their website so that you can easily follow this guide. And yes, it is completely free. So let's begin formatting an essay to MLA format in WPS Writer:
1. Page Margins
So the first step is to ensure that our page margins are set to 1 inch on every side. Setting the margins first would help you avoid any formatting errors if you do this at a later stage. To set page margins in WPS Writer:
Step 1: Open WPS Writer and visit the “Page Layout” tab in the toolbar.
Step 2: Find the Page Margin options on the far left of the Page Layout ribbon.
Step 3: Set all the margin fields—top, bottom, left, and right—to 1 inch.
2. Line Spacing
Next, we need to ensure that the line spacing is set to double spacing . This helps improve readability and ensures your paper meets MLA formatting standards. To set double line spacing in WPS Writer:
Step 1: In WPS Writer, go to the “Home” tab in the toolbar.
Step 2: Find and click the “Line Spacing” option in the Home ribbon.
Step 3: In the Line Spacing drop-down, click on More.
Step 4: The Paragraph window will pop up. Visit the Spacing section and in the Line Spacing field, select “Double”.
Step 5: After that, click on OK to exit the Paragraph window.
Note: We can also use the keyboard shortcut CTRL + 2 to quickly change the line spacing to double.
3. Header- In the Upper-Left Corner
After setting the page settings, let's move on to the content of the essay, starting with the header in the following order:
Student's Name
Professor's Name
Course and Course Code
Due Date in the format DD Month, Year
Step 1: Follow the order to enter the header into your essay.
Step 2: To make the Header left aligned, visit the Home tab and then click on the “Align Text Left” icon.
Step 3: After entering the header, make sure the Font is set to "Times New Roman" in the Fonts field in the Home ribbon.
Step 4: After the font, the font size should also be set to "12." Therefore, make the change in the "Font Size" field in the Home ribbon.
4. Last Name & Page Numbers- In the Upper-Right Corner
MLA Format requires a running header that includes your last name along with the page number on the top right corner of every page. Let's see how we can create our running header for the MLA Format:
Step 1: Double-click on the Header area to open the Header/Footer in WPS Writer.
Step 2: Now type your last name and set its alignment to right by clicking on the “Align Text Right” icon in the Home ribbon.
Step 3: To add the page number, click on the "Page Number" option in the Header/Footer ribbon and select the "Header right" option to insert a page number in the right corner.
Once the running header has been added, it is important to set the font size of the running header to 12 and the font to "Times New Roman".
Step 4: Simply select your running header and click on the Home tab.
Step 5: In the Home tab, change the Font to "Times New Roman" in the Fonts field.
Step 6: To change the font size, in the Home ribbon, enter "12" in the Font size field.
The last setting for the running header is to set the header margin to "0.5 inches":
Step 7: Head over to the Header/Footer tab.
Step 8: In the Header/Footer ribbon, enter "0.5 in" in the “Header Height” field to set the header margin to 0.5 inches.
5. Title of Essay- On the Line Below the Date
After the header and running header, let's begin our essay with the title of our essay. Remember the rules:
The title should be center aligned.
The title should not be bolded, italicized, or placed in quotation marks unless it includes the title of a source (e.g., a book or movie title).
Step 1: Insert the title right below the header and visit the Home tab.
Step 2: In the Home ribbon, click on the “Center” icon to center align the title.
6. Headings and Subheadings- Into Sections
Headings and subheadings are important as they give reference to the reader. There are no hard and fast rules for their formatting, except that they need to be center aligned. You can set the font style to bold to help the reader distinguish them.
Step 1: Enter your heading below the title of the essay and visit the Home tab.
Step 2: In the Home ribbon, click on “Center” to align the heading to the center.
Step 3: To change the font style to bold, in the Home ribbon, click on the “Bold” icon right below the font field.
7. In-text Citation
In MLA format, in-text citations use parenthetical references to indicate quotes or ideas from another author. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do in-text citations:
Step 1: When you quote or paraphrase from a source, use the author's last name and the page number where the information is found.
Step 2: After the quote or paraphrase, place the citation in parentheses. The citation should include the author's last name followed by the page number without a comma between them.
Step 3: The parenthetical citation should be placed before the period at the end of the sentence.
8. Works Cited Page
Finally, you will need to cite all the sources you took assistance from in writing your paper. Follow the following steps to understand how to cite your work in MLA format.
Step 1: Use a page break to start a fresh new page with the title "Works Cited." The heading "Works Cited" will follow similar heading guidelines as before.
Step 2: Double-space all entries and do not add extra spaces between entries.
Step 3: Use a hanging indent for each entry. The first line of each citation is flush with the left margin, and subsequent lines are indented by 0.5 inches simply using the “Tab” key..
Step 4: List entries in alphabetical order by the author's last name. If a work has no author, alphabetize it by the first significant word in the title.
Step 5: Format your sources as mentioned below for respective source medium:
Books Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of Publication.
Articles in Journals Format: Author's Last Name, First Name. "Title of Article." Title of Journal, vol. number, no. number, Year, pages.
Websites Format: Author's Last Name, First Name (if available). "Title of Webpage." Title of Website, Publisher, Date of Publication, URL.
Bonus Tips: How to Convert Word to PDF without losing Format
Once you finish writing your essay, the next challenge is converting it from Microsoft Word to PDF without losing formatting. This can be frustrating because sometimes the formatting doesn't stay the same.
To avoid this issue, use WPS Office . It offers strong PDF features and keeps APA and MLA formatting intact. On the other hand, Microsoft Word 365, though widely used, may occasionally struggle to keep formatting consistent when converting to PDF. It's important to choose tools that prioritize preserving the look and structure of your academic work.
Here is how you can use WPS PDF to convert your essay documents to PDF without compromising on the quality:
Step 1: On WPS Writer, click on the Menu button on the top left corner of the screen.
Step 2: Now simply click on the “Export to PDF” option in the Menu.
Step 3: The Export to PDF window will open. Here, you can alter a few settings such as the output path. After going through the settings, simply click on Export to PDF to save the essay document as a PDF.
FAQs about writing an essay in MLA format
1. how to cite an image in mla.
To cite an image in MLA style, you need to format the citation based on where the image was viewed. For online images, the citation should follow this structure:
MLA format:
Creator’s last name, First name. “Image Title” or Description of the image. Website Name in italics, Day Month Year, URL.
MLA Works Cited entry:
Smith, Jamie. “Vintage Cars.” Travel With Us, 15 Mar. 2023, www.travelwithus.com/vintage-cars.
MLA in-text citation:
(Smith) Note: If you discover an image through a search engine such as Google, ensure that you credit and link to the website that hosts the image, rather than the search engine.
2. Do I need to include a title page in my MLA essay?
In most instances, an MLA-formatted essay does not necessitate a separate title page unless instructed otherwise by your instructor. Instead, begin your essay with a header and center the title on the subsequent line.
3. How to Cite a Website in MLA?
To cite a website in MLA style, you should include the author’s name (if known), the title of the page in quotation marks, the name of the website in italics, the publication date, and the URL without "https://". If the identity of the author is not known, start with the title of the page. If the publication date is unavailable or if there's a possibility of content modifications, include an access date at the end.
Author’s last name, First name. “Title of Page.” Website Name, Day Month Year, URL.
Adams, John. "Explore with us." Random Discoveries, 15 Sept. 2023, www.randomdiscoveries.com/explore-with-us.
Write Your Essays in Comfort With WPS Office
It’s so easy! The great thing about MLA format is that it’s not vastly different from APA and Chicago formats. There are only a few distinctions, and once you learn how to write an essay in MLA format [For Students], everything will become much easier for your academic life. Also, WPS Office is an incredibly handy tool for students. Not only can you format comfortably, but it’s also designed to be student-friendly, avoiding complex procedures. Simple yet advanced, and best of all, free. Get WPS Office today and write essays with ease and comfort!
- 1. How to Remove Page Breaks in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
- 2. Top 10 Best Introduce Yourself Essay Sample Words
- 3. How to Double Space in Word for Your Essay: A Guide for Students
- 4. How to Do Hanging Indent in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
- 5. How to Make MLA Format Heading and Header in WPS Office (Step-by-Step)
- 6. How to Use Track Changes in Word for Your Essay? [For Students]
15 years of office industry experience, tech lover and copywriter. Follow me for product reviews, comparisons, and recommendations for new apps and software.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Should Biden Heed Calls to Drop Out?
Readers offer a range of views after an editorial that called on the president to leave the race after his poor debate performance.

To the Editor:
Re “ To Serve His Country, President Biden Should Leave the Race ” (editorial, June 30):
Joe Biden is an extraordinary person, with a track record of service to this country he loves so much to prove it. Being its president has clearly been the pinnacle of that service.
But it is time for Mr. Biden to have a heart-to-heart with his ego and recognize that the same altruism and passion that brought him to the White House must now guide him to the sidelines of this election. The stakes are too high, and his candidacy is too risky.
To stay is to repeat the tragic miscalculation of another soldier for the good, Ruth Bader Ginsburg.
Don’t lose your faith now, Joe. Do the right thing for democracy.
Alison Daley Stevenson Waldoboro, Maine
To paraphrase the great Mark Twain, your report of President Biden’s cognitive demise is greatly exaggerated. Not to mention premature.
The president is probably one of the worst extemporaneous public speakers to hold his office. Age has made his lack of skill in this area worse, but that does not mean it has impaired his intellectual capacity.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Source text Paraphrase "The current research extends the previous work by revealing that listening to moral dilemmas could elicit a FLE [foreign-language effect] in highly proficient bilinguals. … Here, it has been demonstrated that hearing a foreign language can even influence moral decision making, and namely promote more utilitarian-type decisions" (Brouwer, 2019, p. 874).
Paraphrasing involves expressing someone else's ideas or thoughts in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Paraphrasing tools can help you quickly reword text by replacing certain words with synonyms or restructuring sentences. They can also make your text more concise, clear, and suitable for a specific audience.
To paraphrase in an essay, start with a reasonable sized quote. If the entire quotation is too long, your essay will become one giant paraphrase. You can always paraphrase another piece of the original text later in your paper. Make sure the quote you are paraphrasing fits your thesis statement and is in the correct section of your essay.
It helps you control the temptation to quote too much. The mental process required for successful paraphrasing helps you to grasp the full meaning of the original. 6 Steps to Effective Paraphrasing. Reread the original passage until you understand its full meaning. Set the original aside, and write your paraphrase on a note card.
To paraphrase in your paper using Plotnick's method above, look at your sources and try the following: Write down the basic point (s) you want to discuss on a notecard (in your own words). Take your notecard points and turn them into sentences when you write your essay. Add the reference for the source.
Try finding a few synonyms first, and then decide which one resonates with your own words. 2. Restructure the Sentence. Rewriting a sentence by changing one or two words isn't proper paraphrasing. Many students erroneously use a "copy and paste" method to change a few words in their paraphrased version.
Avoiding Plagiarism - Paraphrasing. In writing papers, you will paraphrase more than you will quote. For a report or research paper, you may need to gather background information that is important to the paper but not worthy of direct quotation. Indeed, in technical writing direct quotation is rarely used.
Paraphrasing Source Text. Step 1: Read important parts of the source material until you fully understand its meaning. Step 2: Take some notes and list key terms of the source material. Step 3: Write your own paragraph without looking at the source material, only using the key terms.
1. Read the text. First, you need to thoroughly read the text. The key to paraphrasing is developing a strong understanding of the ideas at play. Once you develop a firm grasp on the meaning behind the passage, you'll find it much easier to paraphrase it effectively.
AI Paraphrasing Tool. Your words matter, and our paraphrasing tool is designed to ensure you use the right ones. With unlimited Custom modes and 9 predefined modes, Paraphraser lets you rephrase text countless ways. Our product will improve your fluency while also ensuring you have the appropriate vocabulary, tone, and style for any occasion.
Practice summarizing the essay found here, using paraphrases and quotations as you go. It might be helpful to follow these steps: Read the entire text, noting the key points and main ideas. Summarize in your own words what the single main idea of the essay is. Paraphrase important supporting points that come up in the essay.
Check out the five tips below for some handy advice! Read the original source a few times to make sure you fully understand it. Choose whether to paraphrase the source in full (i.e. presenting all the information from the original passage in your own words) or summarise it (i.e. selecting the details most relevant to your own work).
Strengthen Your Communication Skills. Try out the best paraphrasing tool for free and discover how LanguageTool can elevate your writing. Enhance your writing with LanguageTool's free AI paraphrasing tool. Discover a smarter way to rewrite and refine your text for improved clarity and uniqueness.
The following strategy will make the job of paraphrasing a lot easier: 1. When you are at the note-taking stage, and you come across a passage that may be useful for your essay, do not copy the passage verbatim unless you think you will want to quote it. 2. If you think you will want to paraphrase the passage, make a note only of the author's ...
The following is a sample essay you can practice quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing. Examples of each task are provided at the end of the essay for further reference. ... "You can lead a horse to water but you can't make him drink," we have pretended it is not true in education. Ask high school teachers if recalcitrant students learn ...
Example Paraphrase 7. "Over-the-top international fast-food items". Original source: "For some reason, cheese-topped donuts are quite popular in Indonesia, and in September 2013 KFC decided to get in on the action, offering a glazed donut topped with shredded Swiss and cheddar cheese.".
Paraphrasing means putting someone else's ideas into your own words. Paraphrasing a source involves changing the wording while preserving the original meaning. Paraphrasing is an alternative to quoting (copying someone's exact words and putting them in quotation marks ). In academic writing, it's usually better to paraphrase instead of ...
Basics of Paraphrasing. A successful paraphrase is your own explanation or interpretation of another person's ideas. Paraphrasing in academic writing is an effective way to restate, condense, or clarify another author's ideas while also providing credibility to your own argument or analysis. While successful paraphrasing is essential for strong ...
Scholars in the humanities tend to summarize, paraphrase, and quote texts; social scientists and natural scientists rely primarily on summary and paraphrase. When you summarize, you provide your readers with a condensed version of an author's key points. A summary can be as short as a few sentences or much longer, depending on the complexity of ...
Paraphrasing. A paraphrase restates another's idea (or your own previously published idea) in your own words. Paraphrasing allows you to summarize and synthesize information from one or more sources, focus on significant information, and compare and contrast relevant details. Published authors paraphrase their sources most of the time, rather ...
The subreddit for discussion related to college and collegiate life. 53% plagiarism on my essay although I did not cheat at all. So I had to write a 7-page research paper for one of my history classes, containing a LOT of citations and sources (the professor said at least 12 sources). Meaning a big part of the essay should be quotes from ...
Paraphrasing Tool. Paraphrase Tool by Prepostseo is an online paraphraser that can help quickly rephrase your essays, articles, blogs, etc., without changing the actual meaning. Our paraphrasing tool uses advanced AI and large language models to accurately paraphrase your content into a fresh, more engaging, and plagiarism-free one.
For example, in a short paper like an essay, you can complete each of the steps above in just a sentence or two. But in a longer one, such as a dissertation, each step may take a couple of paragraphs. In a sense, the intro is a summary of the rest of the paper, and summarizing is all about prioritizing.
It assists you in crafting high-quality documents, reports, and essays, ensuring your writing is clear and concise, even when you're not connected to the internet. ... With it, you can paraphrase 125 words. It provides Standard and Fluency modes with limited use of the Synonym Slider. Moreover, you can summarize up to 1,200 words through the ...
If you're looking to expand your vocabulary, you can learn languages online with Preply, from conversational English to classic Spanish lessons. Take French lessons with confidence or learn a business language in our courses. Methodology. We have collected 12,346 student-written essays from the platform IvyPanda.
Step 2: After the quote or paraphrase, place the citation in parentheses. The citation should include the author's last name followed by the page number without a comma between them. ... Here is how you can use WPS PDF to convert your essay documents to PDF without compromising on the quality: Step 1: On WPS Writer, click on the Menu button on ...
To paraphrase the great Mark Twain, your report of President Biden's cognitive demise is greatly exaggerated. Not to mention premature. The president is probably one of the worst extemporaneous ...