Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.

What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write!
In this article, we explain how to write a thesis statement in the best way possible. We look at what to include and the steps to take for writing your own, along with plenty of thesis statement examples to guide you.
Here’s a tip: Want to make sure your writing shines? Grammarly can check your spelling and save you from grammar and punctuation mistakes. It even proofreads your text, so your work is polished wherever you write.
Your writing, at its best Grammarly helps you communicate confidently Write with Grammarly
Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, how to write a thesis statement: basics, what to include in a thesis statement (with examples), how to write a thesis statement in 3 steps.
The goal of a thesis statement is to let your reader know what your paper or essay is about. It helps your reader understand the greater context and scope of your topic, plus it lets your readers know what to expect from the rest of the work.
A secondary benefit of a thesis statement is that it makes it easier to search for papers on a particular topic, especially in the realm of academic writing like research papers and thesis papers (which are sometimes known as dissertations when written for doctoral degrees). For example, if you’re writing a paper of your own, you’ll want to look up other papers to use as evidence and sources . You can simply scan the thesis statements of several papers to see which match your topic and could be worthwhile sources to cite.
Before we get into details, here are the basic steps for how to write a thesis statement:
- Develop the best topic to cover in your paper
- Phrase your topic as a question-and-answer
- Add some polish
We ’ ll describe each of those steps in more detail below, but we wanted to share a quick guide. Also, we ’ ll provide some thesis statement examples and talk about how to write a thesis statement for different kinds of essays: persuasive, compare-and-contrast, expository, and argumentative essays.
The thesis statement is located at the beginning of a paper, in the opening paragraph, making it an essential way to start an essay . A thesis statement isn’t necessarily the first sentence in an essay; typically you’ll want to hook the reader in an engaging way in the opening sentence before inserting your central idea or argument later in the first paragraph. A thesis statement is often confused with a topic sentence , the first sentence in a paragraph, because they both introduce the central idea of what follows. You can think of thesis statements as the topic sentence of your entire paper.
Thesis statements are a necessary part of paper and essay writing , but different formats have different rules and best practices. Below, we break down how to write a thesis statement for the most common types of papers.
How to write a thesis statement for expository and argumentative essays
Expository and argumentative essays are some of the most common types of academic papers. Because they don’t have a formal abstract like research papers, they rely on their thesis statements to provide an overview of what’s discussed.
Thesis statements for argumentative and expository essays should use strong and decisive language; don’t be wishy-washy or uncertain. You want to take a stand right in the opening so that your readers understand what your paper is trying to show.
Moreover, thesis statements for these essays should be specific, with some minor details to hint at the rest of the paper. It’s not enough to merely make your point; you also want to provide some basic evidence or background context to paint a full picture.
If your paper dives into different subtopics or categories, try to fit them into the thesis statement if you can. You don’t have to get into details here, but it’s nice to mention the different sections at the top so that the reader knows what to expect.
Thesis statement examples
Despite the taboo, insects make an excellent food source and could stem humanity’s looming food shortage, based on both their protein output and the sustainability of farming them.
The backlash to rock ’n’ roll music in the ’50s by religious groups and traditionalists actually boosted the genre’s popularity instead of diminishing it as intended.
How to write a thesis statement for persuasive essays
Similar to argumentative essays, persuasive essays follow many of the same guidelines for their thesis statements: decisive language, specific details, and mentions of subtopics.
However, the main difference is that, while the thesis statements for argumentative and expository essays state facts, the thesis statements for persuasive essays state clear opinions . Still, the format is the same, and the opinions are often treated like facts, including conclusive language and citing evidence to support your claims.
Furthermore, unlike with other essays, it’s appropriate to make emotional connections in a thesis statement in persuasive essays. This can actually be a clever strategy to start your essay off on a more personal, impactful note.
Advertising should not be allowed in public schools because it’s a distraction from studies and may lead to misguided priorities among the school board, to say nothing of the materialist culture it promotes.
Exotic pets provide the same love and companionship as conventional pets, so the laws regulating which animals can and cannot be kept as pets should be more relaxed.
How to write a thesis statement for compare-and-contrast essays
Thesis statements for compare-and-contrast essays are tricky because you have at least two topics to touch on instead of just one. The same general guidelines apply (decisive language, details, etc.), but you need to give equal attention to both your topics—otherwise, your essay will seem biased from the start.
As always, your thesis statement should reflect what’s written in the rest of your essay. If your essay spends more time comparing than contrasting, your thesis statement should focus more on similarities than differences.
It sometimes helps to give specific examples as well, but keep them simple and brief. Save the finer details for the body of your essay.
Sean Connery and Daniel Craig are the two most popular actors to portray James Bond, but both have their own distinct and at times contradictory interpretations of the character.
Now that you know what you’re aiming for, it’s time to sit down and write your own thesis statement. To keep you on track, here are three easy steps to guide you.
1 Brainstorm the best topic for your essay
You can’t write a thesis statement until you know what your paper is about, so your first step is choosing a topic.
If the topic is already assigned, great ! That’s all for this step. If not, consider the tips below for choosing the topic that’s best for you:
- Pick a topic that you’re passionate about. Even if you don’t know much about it, it’ll be easier to learn about it while writing if you’re genuinely interested.
- Narrow down your topic to something specific; otherwise, your paper will be too broad and perhaps too long. Just make sure it’s not too specific, or you won’t have enough to write about. Try to find a happy medium.
- Check beforehand that there are enough strong, credible sources to use for research. You don’t want to run out of referential material halfway through.
Once you’ve chosen a topic—and the angle or stance you want to take—then it’s time to put the idea for your thesis sentence into words.
2 Phrase your topic as a question and then answer it
It’s not always easy to fit your entire thesis into just one sentence, let alone one that’s written clearly and eloquently. Here’s a quick technique to help you get started.
First, phrase your topic as a question. For example, if you want to write about Mahatma Gandhi’s legacy, ask yourself, “What influences did Gandhi have on society after his death?”
If you already know the answer, write it down—that’s a good start for your thesis statement. If you don’t know the answer, do some preliminary research to find out; you can certainly use what you discover as evidence and sources in your essay’s body paragraphs .
3 Add some polish
Chances are, your first attempt at a thesis statement won’t be perfect. To get it to its best, try revising , editing , and adding what’s missing.
Remember the core traits for thesis statements we mentioned above: decisive language, a happy medium of specific but not too specific details, and mention of subtopics. If you’re struggling to contain everything in a single sentence, feel free to move the secondary information to the following sentence. The thesis statement itself should only have what’s most necessary.
If you’re in doubt, read your thesis statement to a friend and ask them what they think your paper is about. If they answer correctly, your thesis statement does its job.
Next comes the hard part—writing the rest! While the bulk of the writing lies ahead, at least you’ve nailed down your central idea. To plot out your supporting argument, follow our advice on essay structure and let your ideas flow.

Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement
Learning objectives.
- Develop a strong, clear thesis statement with the proper elements.
- Revise your thesis statement.
Have you ever known a person who was not very good at telling stories? You probably had trouble following his train of thought as he jumped around from point to point, either being too brief in places that needed further explanation or providing too many details on a meaningless element. Maybe he told the end of the story first, then moved to the beginning and later added details to the middle. His ideas were probably scattered, and the story did not flow very well. When the story was over, you probably had many questions.
Just as a personal anecdote can be a disorganized mess, an essay can fall into the same trap of being out of order and confusing. That is why writers need a thesis statement to provide a specific focus for their essay and to organize what they are about to discuss in the body.
Just like a topic sentence summarizes a single paragraph, the thesis statement summarizes an entire essay. It tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point. It is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
Elements of a Thesis Statement
For every essay you write, you must focus on a central idea. This idea stems from a topic you have chosen or been assigned or from a question your teacher has asked. It is not enough merely to discuss a general topic or simply answer a question with a yes or no. You have to form a specific opinion, and then articulate that into a controlling idea —the main idea upon which you build your thesis.
Remember that a thesis is not the topic itself, but rather your interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic your professor gives you, you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful and confident.
A thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of your introduction. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
A Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement contains the following qualities.
Specificity. A thesis statement must concentrate on a specific area of a general topic. As you may recall, the creation of a thesis statement begins when you choose a broad subject and then narrow down its parts until you pinpoint a specific aspect of that topic. For example, health care is a broad topic, but a proper thesis statement would focus on a specific area of that topic, such as options for individuals without health care coverage.
Precision. A strong thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and to remain focused on the topic. If the specific topic is options for individuals without health care coverage, then your precise thesis statement must make an exact claim about it, such as that limited options exist for those who are uninsured by their employers. You must further pinpoint what you are going to discuss regarding these limited effects, such as whom they affect and what the cause is.
Ability to be argued. A thesis statement must present a relevant and specific argument. A factual statement often is not considered arguable. Be sure your thesis statement contains a point of view that can be supported with evidence.
Ability to be demonstrated. For any claim you make in your thesis, you must be able to provide reasons and examples for your opinion. You can rely on personal observations in order to do this, or you can consult outside sources to demonstrate that what you assert is valid. A worthy argument is backed by examples and details.
Forcefulness. A thesis statement that is forceful shows readers that you are, in fact, making an argument. The tone is assertive and takes a stance that others might oppose.
Confidence. In addition to using force in your thesis statement, you must also use confidence in your claim. Phrases such as I feel or I believe actually weaken the readers’ sense of your confidence because these phrases imply that you are the only person who feels the way you do. In other words, your stance has insufficient backing. Taking an authoritative stance on the matter persuades your readers to have faith in your argument and open their minds to what you have to say.
Even in a personal essay that allows the use of first person, your thesis should not contain phrases such as in my opinion or I believe . These statements reduce your credibility and weaken your argument. Your opinion is more convincing when you use a firm attitude.
On a separate sheet of paper, write a thesis statement for each of the following topics. Remember to make each statement specific, precise, demonstrable, forceful and confident.
- Texting while driving
- The legal drinking age in the United States
- Steroid use among professional athletes
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
Each of the following thesis statements meets several of the following requirements:
- Specificity
- Ability to be argued
- Ability to be demonstrated
- Forcefulness
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxon in the play Fences symbolize the challenge of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Shakespeare’s use of dramatic irony in Romeo and Juliet spoils the outcome for the audience and weakens the plot.
- J. D. Salinger’s character in Catcher in the Rye , Holden Caulfield, is a confused rebel who voices his disgust with phonies, yet in an effort to protect himself, he acts like a phony on many occasions.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
You can find thesis statements in many places, such as in the news; in the opinions of friends, coworkers or teachers; and even in songs you hear on the radio. Become aware of thesis statements in everyday life by paying attention to people’s opinions and their reasons for those opinions. Pay attention to your own everyday thesis statements as well, as these can become material for future essays.
Now that you have read about the contents of a good thesis statement and have seen examples, take a look at the pitfalls to avoid when composing your own thesis:
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak thesis statement: My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Weak thesis statement: Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Weak thesis statement: Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
Weak thesis statement: The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Read the following thesis statements. On a separate piece of paper, identify each as weak or strong. For those that are weak, list the reasons why. Then revise the weak statements so that they conform to the requirements of a strong thesis.
- The subject of this paper is my experience with ferrets as pets.
- The government must expand its funding for research on renewable energy resources in order to prepare for the impending end of oil.
- Edgar Allan Poe was a poet who lived in Baltimore during the nineteenth century.
- In this essay, I will give you lots of reasons why slot machines should not be legalized in Baltimore.
- Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation.
- Because many children’s toys have potential safety hazards that could lead to injury, it is clear that not all children’s toys are safe.
- My experience with young children has taught me that I want to be a disciplinary parent because I believe that a child without discipline can be a parent’s worst nightmare.
Writing at Work
Often in your career, you will need to ask your boss for something through an e-mail. Just as a thesis statement organizes an essay, it can also organize your e-mail request. While your e-mail will be shorter than an essay, using a thesis statement in your first paragraph quickly lets your boss know what you are asking for, why it is necessary, and what the benefits are. In short body paragraphs, you can provide the essential information needed to expand upon your request.
Thesis Statement Revision
Your thesis will probably change as you write, so you will need to modify it to reflect exactly what you have discussed in your essay. Remember from Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” that your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statement , an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing.
Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and form new opinions and reasons for those opinions. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
The best way to revise your thesis statement is to ask questions about it and then examine the answers to those questions. By challenging your own ideas and forming definite reasons for those ideas, you grow closer to a more precise point of view, which you can then incorporate into your thesis statement.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
1. Pinpoint and replace all nonspecific words, such as people , everything , society , or life , with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use and be appreciated for their talents.
The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard. The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard , the writer can better focus his or her research and gain more direction in his or her writing.
2. Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke . The writer should ask himself or herself questions similar to the 5WH questions. (See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information on the 5WH questions.) By incorporating the answers to these questions into a thesis statement, the writer more accurately defines his or her stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
3. Replace any linking verbs with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be , a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Working thesis: Kansas City schoolteachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are . Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions. The writer should ask himself or herself questions in order to replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement, one that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- What is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results
4. Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on MTV are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
In the first section of Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” , you determined your purpose for writing and your audience. You then completed a freewriting exercise about an event you recently experienced and chose a general topic to write about. Using that general topic, you then narrowed it down by answering the 5WH questions. After you answered these questions, you chose one of the three methods of prewriting and gathered possible supporting points for your working thesis statement.
Now, on a separate sheet of paper, write down your working thesis statement. Identify any weaknesses in this sentence and revise the statement to reflect the elements of a strong thesis statement. Make sure it is specific, precise, arguable, demonstrable, forceful, and confident.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
In your career you may have to write a project proposal that focuses on a particular problem in your company, such as reinforcing the tardiness policy. The proposal would aim to fix the problem; using a thesis statement would clearly state the boundaries of the problem and tell the goals of the project. After writing the proposal, you may find that the thesis needs revision to reflect exactly what is expressed in the body. Using the techniques from this chapter would apply to revising that thesis.
Key Takeaways
- Proper essays require a thesis statement to provide a specific focus and suggest how the essay will be organized.
- A thesis statement is your interpretation of the subject, not the topic itself.
- A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated.
- A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence.
- A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
- Depending on your topic, it may or may not be appropriate to use first person point of view.
- Revise your thesis by ensuring all words are specific, all ideas are exact, and all verbs express action.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
We apologize for any inconvenience as we update our site to a new look.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips
Published on July 24, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An argumentative essay expresses an extended argument for a particular thesis statement . The author takes a clearly defined stance on their subject and builds up an evidence-based case for it.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you write an argumentative essay, approaches to argumentative essays, introducing your argument, the body: developing your argument, concluding your argument, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about argumentative essays.
You might be assigned an argumentative essay as a writing exercise in high school or in a composition class. The prompt will often ask you to argue for one of two positions, and may include terms like “argue” or “argument.” It will frequently take the form of a question.
The prompt may also be more open-ended in terms of the possible arguments you could make.
Argumentative writing at college level
At university, the vast majority of essays or papers you write will involve some form of argumentation. For example, both rhetorical analysis and literary analysis essays involve making arguments about texts.
In this context, you won’t necessarily be told to write an argumentative essay—but making an evidence-based argument is an essential goal of most academic writing, and this should be your default approach unless you’re told otherwise.
Examples of argumentative essay prompts
At a university level, all the prompts below imply an argumentative essay as the appropriate response.
Your research should lead you to develop a specific position on the topic. The essay then argues for that position and aims to convince the reader by presenting your evidence, evaluation and analysis.
- Don’t just list all the effects you can think of.
- Do develop a focused argument about the overall effect and why it matters, backed up by evidence from sources.
- Don’t just provide a selection of data on the measures’ effectiveness.
- Do build up your own argument about which kinds of measures have been most or least effective, and why.
- Don’t just analyze a random selection of doppelgänger characters.
- Do form an argument about specific texts, comparing and contrasting how they express their thematic concerns through doppelgänger characters.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An argumentative essay should be objective in its approach; your arguments should rely on logic and evidence, not on exaggeration or appeals to emotion.
There are many possible approaches to argumentative essays, but there are two common models that can help you start outlining your arguments: The Toulmin model and the Rogerian model.
Toulmin arguments
The Toulmin model consists of four steps, which may be repeated as many times as necessary for the argument:
- Make a claim
- Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim
- Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim)
- Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives
The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays. You don’t have to use these specific terms (grounds, warrants, rebuttals), but establishing a clear connection between your claims and the evidence supporting them is crucial in an argumentative essay.
Say you’re making an argument about the effectiveness of workplace anti-discrimination measures. You might:
- Claim that unconscious bias training does not have the desired results, and resources would be better spent on other approaches
- Cite data to support your claim
- Explain how the data indicates that the method is ineffective
- Anticipate objections to your claim based on other data, indicating whether these objections are valid, and if not, why not.
Rogerian arguments
The Rogerian model also consists of four steps you might repeat throughout your essay:
- Discuss what the opposing position gets right and why people might hold this position
- Highlight the problems with this position
- Present your own position , showing how it addresses these problems
- Suggest a possible compromise —what elements of your position would proponents of the opposing position benefit from adopting?
This model builds up a clear picture of both sides of an argument and seeks a compromise. It is particularly useful when people tend to disagree strongly on the issue discussed, allowing you to approach opposing arguments in good faith.
Say you want to argue that the internet has had a positive impact on education. You might:
- Acknowledge that students rely too much on websites like Wikipedia
- Argue that teachers view Wikipedia as more unreliable than it really is
- Suggest that Wikipedia’s system of citations can actually teach students about referencing
- Suggest critical engagement with Wikipedia as a possible assignment for teachers who are skeptical of its usefulness.
You don’t necessarily have to pick one of these models—you may even use elements of both in different parts of your essay—but it’s worth considering them if you struggle to structure your arguments.
Regardless of which approach you take, your essay should always be structured using an introduction , a body , and a conclusion .
Like other academic essays, an argumentative essay begins with an introduction . The introduction serves to capture the reader’s interest, provide background information, present your thesis statement , and (in longer essays) to summarize the structure of the body.
Hover over different parts of the example below to see how a typical introduction works.
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts is on the rise, and its role in learning is hotly debated. For many teachers who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its critical benefits for students and educators—as a uniquely comprehensive and accessible information source; a means of exposure to and engagement with different perspectives; and a highly flexible learning environment.
The body of an argumentative essay is where you develop your arguments in detail. Here you’ll present evidence, analysis, and reasoning to convince the reader that your thesis statement is true.
In the standard five-paragraph format for short essays, the body takes up three of your five paragraphs. In longer essays, it will be more paragraphs, and might be divided into sections with headings.
Each paragraph covers its own topic, introduced with a topic sentence . Each of these topics must contribute to your overall argument; don’t include irrelevant information.
This example paragraph takes a Rogerian approach: It first acknowledges the merits of the opposing position and then highlights problems with that position.
Hover over different parts of the example to see how a body paragraph is constructed.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
An argumentative essay ends with a conclusion that summarizes and reflects on the arguments made in the body.
No new arguments or evidence appear here, but in longer essays you may discuss the strengths and weaknesses of your argument and suggest topics for future research. In all conclusions, you should stress the relevance and importance of your argument.
Hover over the following example to see the typical elements of a conclusion.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The majority of the essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Unless otherwise specified, you can assume that the goal of any essay you’re asked to write is argumentative: To convince the reader of your position using evidence and reasoning.
In composition classes you might be given assignments that specifically test your ability to write an argumentative essay. Look out for prompts including instructions like “argue,” “assess,” or “discuss” to see if this is the goal.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Write an Argumentative Essay | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved August 19, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/argumentative-essay/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, how to write an expository essay, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
50 Argumentative Essay Thesis Statement Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

A thesis statement in an argumentative essay needs to present a point of view . The biggest mistake you can make is to provide a thesis statement that doesn’t demonstrate what your argument will be. So, your thesis statement should set a clear argument, perspective, or position in relation to a debate. Check out the examples below.
Thesis Statements for Argumentative Essays
1. mandatory school uniforms.

For: “School uniforms should be mandatory as they promote equality and reduce distractions, fostering a better learning environment.”
Against: “Mandatory school uniforms infringe on students’ freedom of expression and fail to address the root causes of bullying and social stratification.”
Read More: School Uniform Pros and Cons
2. School Should Start Later

For: “Schools should start later in the morning to align with adolescents’ natural sleep cycles, resulting in improved mental health, increased academic performance, and better overall student well-being.”
Against: “Starting school later in the morning disrupts family routines, poses logistical challenges for after-school activities and transportation, and fails to prepare students for the traditional workday schedule.”
Read More: School Should Start Later Arguments | School Should Start Earlier Arguments
3. College Athletes Should be Paid

For: “College athletes should be compensated for their contributions to the multi-billion dollar collegiate sports industry, as their commitment and efforts generate significant revenue and marketing value for their institutions.”
Against: “Paying college athletes undermines the spirit of amateurism in collegiate sports, complicates the primary focus on education, and poses significant financial and regulatory challenges for universities.”
Read More: Why College Athletes Should be Paid
4. Homework should be Banned

For: “Excessive homework can lead to student burnout, reduce family time, and is not always effective in enhancing learning.”
Against: “Homework is essential for reinforcing learning, fostering independent study skills, and preparing students for academic challenges.”
Read More: 21 Reasons Homework Should be Banned
5. Nature is More Important than Nurture

For: “Genetic predispositions play a more critical role in shaping an individual than environmental factors, highlighting the importance of nature in personal development.”
Against: “Environmental factors and upbringing have a more significant impact on an individual’s development than genetic factors, emphasizing the role of nurture.”
Read More: Nature vs Nurture
6. The American Dream is Unattainable

For: “The American Dream is an outdated and unachievable concept for many, masked by systemic inequalities and economic barriers.”
Against: “The American Dream is still a relevant and attainable goal, symbolizing hope, opportunity, and hard work in a land of limitless potential.”
Read More: Examples of the American Dream
7. Social Media is Good for Society

For: “Social media is a vital tool for modern communication, fostering global connectivity and democratizing information dissemination.”
Against: “Social media platforms contribute to mental health issues, spread misinformation, and erode quality face-to-face interactions.”
Read More: Social Media Pros and Cons
8. Globalization has been Bad for Society

For: “Globalization leads to the exploitation of developing countries, loss of cultural identity, and increased income inequality.”
Against: “Globalization is beneficial, driving economic growth, cultural exchange, and technological advancement on a global scale.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons
9. Urbanization has been Good for Society

For: “Urbanization is a positive force for economic development and cultural diversity, offering improved opportunities and lifestyles.”
Against: “Rapid urbanization leads to environmental degradation, overpopulation, and heightened social inequalities.”
Read More: Urbanization Examples
10. Immigration is Good for Society

For: “Immigration enriches the social and economic fabric of the host country, bringing diversity and innovation.”
Against: “Uncontrolled immigration can strain public resources, disrupt local job markets, and lead to cultural clashes.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

11. Cultural Identity must be Preserved

For: “Maintaining cultural identity is essential to preserve historical heritage and promote diversity in a globalized world.”
Against: “Excessive emphasis on cultural identity can lead to isolationism and hinder integration and mutual understanding in multicultural societies.”
Read More: Cultural Identity Examples
12. Technology is Essential for Social Progress

For: “The advancement of technology is crucial for societal progress, improving efficiency, healthcare, and global communication.”
Against: “Over-dependence on technology leads to privacy concerns, job displacement, and a disconnection from the natural world.”
13. Capitalism is the Best Economic System

For: “Capitalism drives innovation, economic growth, and personal freedom, outperforming socialist systems in efficiency and prosperity.”
Against: “Capitalism creates vast inequalities and exploits workers and the environment, necessitating a shift towards socialist principles for a fairer society.”
14. Socialism is the Best Economic System

For: “Socialism promotes social welfare and equality, ensuring basic needs are met for all citizens, unlike the inequalities perpetuated by capitalism.”
Against: “Socialism stifles individual initiative and economic growth, often leading to governmental overreach and inefficiency.”
Read More: Socialism Pros and Cons
15. Pseudoscience has no Value to Society
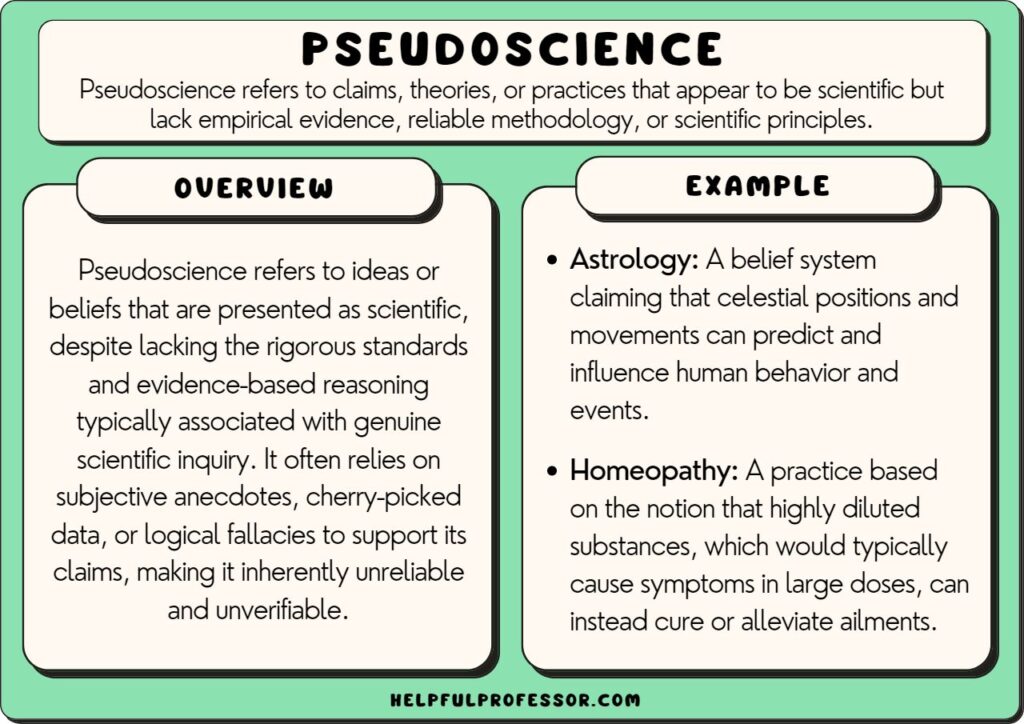
For: “Pseudoscience is harmful as it misleads people, often resulting in health risks and the rejection of scientifically proven facts.”
Against: “Pseudoscience, while not scientifically validated, can offer alternative perspectives and comfort to individuals where mainstream science has limitations.”
Read More: Pseudoscience Examples
16. Free Will is Real

For: “Individuals possess free will, enabling them to make autonomous choices that shape their lives and moral character, independent of genetic or environmental determinism.”
Against: “The concept of free will is an illusion, with human behavior being the result of genetic and environmental influences beyond personal control.”
Read More: Free Will Examples
17. Gender Roles are Outdated

For: “Rigid gender roles are outdated and limit individual freedom, perpetuating inequality and stereotyping.”
Against: “Traditional gender roles provide structure and clarity to societal functions and personal relationships.”
Read More: Gender Roles Examples
18. Work-Life Ballance is Essential for a Good Life

For: “Achieving a work-life balance is essential for mental health, productivity, and personal fulfillment.”
Against: “The pursuit of work-life balance can lead to decreased professional ambition and economic growth, particularly in highly competitive industries.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
19. Universal Healthcare
For: “Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right, ensuring equitable access to medical services for all individuals.”
Against: “Universal healthcare can be inefficient and costly, potentially leading to lower quality of care and longer wait times.”
Read More: Universal Healthcare Pros and Cons
20. Raising the Minimum Wage

For: “Raising the minimum wage is necessary to provide a living wage, reduce poverty, and stimulate economic growth.”
Against: “Increasing the minimum wage can lead to higher unemployment and negatively impact small businesses.”
Read More: Raising the Minimum Wage Pros and Cons
21. Charter Schools are Better than Public Schools

For: “Charter schools provide valuable alternatives to traditional public schools, often offering innovative educational approaches and higher standards.”
Against: “Charter schools can drain resources from public schools and lack the same level of accountability and inclusivity.”
Read More: Charter Schools vs Public Schools
22. The Internet has had a Net Positive Effect

For: “The internet is a transformative tool for education, communication, and business, making information more accessible than ever before.”
Against: “The internet can be a platform for misinformation, privacy breaches, and unhealthy social comparison, negatively impacting society.”
Read Also: Pros and Cons of the Internet
23. Affirmative Action is Fair and Just

For: “Affirmative action is necessary to correct historical injustices and promote diversity in education and the workplace.”
Against: “Affirmative action can lead to reverse discrimination and undermine meritocracy, potentially harming those it aims to help.”
Read More: Pros and Cons of Affirmative Action
24. Soft Skills are the Most Important Workforce Skills

For: “Soft skills like communication and empathy are crucial in the modern workforce, contributing to a collaborative and adaptable work environment.”
Against: “Overemphasis on soft skills can neglect technical proficiency and practical skills that are essential in many professional fields.”
Read More: Examples of Soft Skills
25. Freedom of the Press has gone Too Far

For: “Unregulated freedom of the press can lead to the spread of misinformation and biased reporting, influencing public opinion unfairly.”
Against: “Freedom of the press is essential for a democratic society, ensuring transparency and accountability in governance.”
Read More: Free Press Examples

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Inspiring & Fun Teacher Desk Setup Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 26 Dorm Room Decoration Ideas (for Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Study Desk Aesthetic Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Thoughtful Ways to Greet your Students
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

How To Create Rock Solid Arguments In Your Dissertation, Thesis Or Assignments
The 6 essential ingredients (with examples).
By: Derek Jansen | August 2017
Arguments happen all the time and that’s okay.
Whether we realise it or not, we have arguments every day. We may quarrel with a significant other over dirty dishes, disagree with an acquaintance over a political hot topic, or even argue with ourselves over the fact that we procrastinate too much. On a more serious note, we also face arguments in our professional and academic lives. For example:
- We debate in class or write assignments on how a company should resolve a particular crisis
- We propose and defend our theses, both orally and written
- We give a presentation to our boss(es) on how best to target a specific market segment
The point with arguments is that we try to convince someone (or ourselves) that we are right . So why don’t we always win our arguments? The art of persuasion is not a natural gift to all of us (it definitely isn’t for me). I’ve learned that I can’t stand on my passion and beliefs alone; I need cold hard facts to back me up.
This blog post will not make you an expert (and I do not claim to be an expert) at argument, but it will provide you with a framework and checklist to help you build strong arguments within your assignments, exams and dissertation or thesis. After all, strong, rigorous arguments are a mainstay of mark-earning work.

So, what do you need in an argument?
A strong argument has six essential ingredients:
- A clear, well-communicated objective/conclusion
- Premise(s) backed by relevant evidence
- Sound logic
- Clear qualifications
- Acknowledgement of counter-arguments
- Emotion and energy
Ingredient #1:
A clearly stated objective or conclusion.
First, an argument, just like any other assignment or research project, will go nowhere without an objective or conclusion. If you do not have a clear focus, you risk confusing yourself, your audience, and your marker. Therefore, you need to ensure that you are very clear about the point you are trying to make (your conclusion or objective). Sounds simple, but you’d be amazed just how many students are unclear about what their point is and, consequently, end up going nowhere slowly.
Throughout this post, I’ll use the example of Company X and its Product Z:
- Company X’s Product Z had great success in the UK, with over 100% ROI within the first two quarters.
- Strong demand for a product like Product Z exists in Germany, France, and Spain.
- Market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- Therefore, Company X will most likely launch product Z in Germany, France, and Spain.
The objective of my argument is to convince you that Company X will most likely successfully launch product Z in the targeted European countries. With this conclusion in focus, I will be able to identify and weigh my strategic options, and then articulate the best way to achieve the objective.
So, the ultimate goal of the argument is to convince someone to agree with your conclusion… but why? Why are you trying to change someone’s mind? It’s not just to get great marks. You must have reasons for your conclusion – these reasons are called premises .
Ingredient #2:
Well-grounded premises.
Once you have your objective, you need to clearly communicate your premises. Premises are the building blocks that underpin your conclusion (objective); they provide evidence to lead the audience to agree with your conclusion (Side note: I use proof and premise as synonyms so that I remember the importance of including premises in my arguments). While there can only be one conclusion in an argument, there can be one or (ideally) many premises to support the conclusion. For example, in the case of Company X and Product Z: the two premises are that demand exists in these target countries, and market competition is relatively low.
Great premises have (at least) two requirements:
- They must be backed by credible, verifiable data; and
- They must be relevant to the conclusion.
Data trumps gut
Strong arguments are not based on gut instinct. An argument without data-backed premises is, by definition, baseless. Let’s return to the above example: Demand exists in these target countries, and market competition is relatively low. To make these great premises, I need to add credible data points.
For example:
- An independent consulting firm conducted a market research study of 6,000 people in the targeted countries, and results revealed that high demand exists for a product like Product Z.
- The data collected from an independent consulting firm is a verifiable, citable source. Always double check your sources to make sure you understand and defend them.
Remember, data may not always come from an independent source – it may be outsourced/sponsored by a company, or a company may have an internal research arm. Be ready to ensure the credibility of the information if/when you are asked.
- IBISWorld’s latest industry report shows that market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- IBISWorld is a well-recognized provider of industry information and may be a source that your marker recommended. Similar to the point above, this data point is credible and can easily be verified.
To gather information, I suggest you prioritize using class- or school-prescribed sources first; use additional sources to complement, not replace, the class recommended sources.
Relevance is essential
While your premises must be data-backed, they must also be relevant to your conclusion. In other words, relevant premises have evidence that is clearly and logically linked to your conclusion. Be wary of following into the “my premise is true so it must be relevant” trap. If a premise is deemed irrelevant, your argument loses weight because you appear to lose focus.
For example: Company X recently built a state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in the United States.
Your marker will ask: how is this a manufacturing facility in the US connected to your conclusion? The answer is, that premise does not connect. Yes, it is true, but it does not seem logical that a manufacturing facility is strategically linked to a product launch in Europe. Use logic to make sure that your premises are relevant.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #3:
Ensuring that your arguments are underpinned by firm logic is… logical. You want to convince your audience, so you need to make sense when building and stating your argument. When making your argument, select your line of reasoning: deductive or inductive.
When making your argument, select your line of reasoning: deductive or inductive. Logically (pun intended), sound deductive reasoning means that your conclusion can be deducted from your valid premises; cogent inductive reasoning means that your conclusion can be inferred from your strong premises.
Deductive reasoning
In deductive reasoning, the premises are a series of consequential statements that lead to the conclusion. To form a conclusion through deduction, you use general premises to point to a specific conclusion. Deductive reasoning is typically focused on the past or present: the general premises have been tested and lead to a specific past or present conclusion.
To identify if an argument is sound, you first check whether the argument is valid. Then, assess if the premises are true or false. Here is an example of deductive reasoning:
- Premise : Most tech companies have a Chief Innovation Officer.
- Premise : Company X is a tech company.
- Conclusion : We may conclude that Company X has a Chief Innovation Officer.
In the above example, the premises start general and then get more specific as they get to the conclusion. Deductive arguments are classified as valid or invalid and deemed to be sound or unsound. To check the validity of the argument, ask this question:
Assuming that the premises are true, does it logically follow that this conclusion is also true?
If the answer is yes, like with the example above, then the argument is valid. It is important to note that the premises do not actually have to be true in order for an argument to be valid. For example, Company X could actually be a healthcare company. However, the argument is still valid because it makes sense that if Company X were hypothetically a tech company, it makes sense that it would have a CIO.
To see if the argument is sound, next check to see if the premises are actually true. An argument is not sound if it is based on false premises. Since in our example we have maintained that Company X is a tech company, we know that premise to be true. Based on other information, we also know that most tech companies have a Chief Innovation Officer. We have two true premises, so we have a sound argument. If Company X actually turned out to be a healthcare company, then we would have one false premise. The argument is therefore unsound because it is based on a false premise.
Inductive reasoning
Inductive reasoning is the opposite of deductive reasoning: specific premises infer a general conclusion. Inductive reasoning is typically geared towards conclusions that will happen in the future. In other words, the conclusion is a prediction that will be tested through future observation. The example we have been using throughout this post is an example of inductive reasoning:
- Premise : Company X’s Product Z had great success in the UK, with over 100% ROI within the first two quarters.
- Premise : An independent consulting firm conducted a survey of 6,000 people in Germany, France, and Spain, revealing a strong demand for Product Z.
- Premise : IBISWorld’s latest industry report shows that market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- Conclusion : Therefore, Company X will most likely successfully launch product Z in Germany, France, and Spain.
Inductive arguments are classified as strong or weak and deemed to be cogent or uncogent. In terms of the strength of an inductive argument, there is a little more grey area than when gauging the validity of a deductive argument. The validity of a deductive argument is pretty clear-cut: you assess if a conclusion from the past or present is either true or false. However, in an inductive argument, the conclusion is a prediction, so you cannot be 100% sure if it is actually true or false. Therefore, you ask:
Assuming that the premises are true, is there more than a 50% chance that the conclusion will actually happen?
If the answer is yes, like in the example above, then the argument is strong.
Just as with deductive arguments, the next step in assessing an inductive argument is evaluating the truth of its premises. A true premise is backed up with data. For example, in the above argument, the premises contain data. If, after verification that the data is true, then the argument is cogent. If it turns out that the data is false – for example, if market research reveals that there is not much demand for Product Z, then the argument is not cogent.
Pro tip: Look at the argument’s premise and conclusion indicator words to identify if or inductive reasoning was used. Words that refer to the past or present are used in deductive reasoning; words that refer to the future, or form a hypothesis , are used in inductive reasoning.
That was a lot of information to throw at you. Here are the main points to take away:
- In deductive reasoning, validity and soundness are different concepts. Validity refers to the feasibility of the conclusion; soundness refers to the truthfulness of the premises.
- In inductive reasoning, strength and cogency are different concepts. Strength refers to the feasibility of the conclusion; cogency refers to the truthfulness of the premises.

Ingredient #4:
The conclusions you draw in your argument are not universally applicable (surprise!); there will typically be limitations to the generalisability of your argument – in other words, it will not necessarily be a sound argument in all contexts (in fact, very little is every universally true or relevant). For example, it may only be true in a certain country, for certain people, in a specific organisation, at a certain time of year, etc.
Before finalising your assignment or dissertation and concluding that you have solved the world’s problems, consider the situations in which your arguments might not work. In doing so, you identify your argument’s qualifications.
Remember to use qualifying indicator words (such as “in many cases”, “most”, “predictably”) to help explain your conclusion. For example:
- Premise: Company X’s Product Z had great success in the UK, with over 100% ROI within the first two quarters.
- Premise: An independent consulting firm conducted a survey of 6,000 people in Germany, France, and Spain, revealing a strong demand for Product Z.
- Premise: IBISWorld’s latest industry report shows that market competition Product Z is relatively low in the targeted European countries.
- Conclusion: Therefore, Company X will most likely successfully launch product Z in Germany, France, and Spain.
- Qualification: However, Company X must consider cultural and importation barriers that can hinder the success of Product Z’s expansion.
Ingredient #5:
Acknowledgement of the counter-arguments.
Similarly to qualifying your argument, a good argument needs to anticipate the opposition. There will almost always be counter-arguments to any argument – very little is cut and dry. Therefore, analysing and addressing counter-arguments shows the marker that you have put in considerable time and thought to develop the best scenario.
Additionally, if you have a strong defence against an opposing view, you may very well be likely to turn naysayers into advocates. Potential challenges you can anticipate and address are:
- A different conclusion may be drawn using your own premises
- A question of the importance or validity of your premises
- There may be significant drawbacks to your conclusion
You have some options in addressing counter-arguments:
- Point out and prove errors in the counter-argument.
- Acknowledge the strength or validity of the counter-argument, but show why it is not as strong or valid as your original argument, or within your particular context (i.e. a specific industry or country)
- If the counter-argument points a flaw in one aspect of your conclusion, rewrite your conclusion in a more detailed manner.
Here’s an example:
- Counter argument: Product Z will face tremendous cultural and financial barriers if launched across Europe.
- Response to counter-argument: The launch will occur in phases. Company X will first beta test Product Z in order to understand how to tailor the product and better understand how to import and market the product.
Ingredient #6: Emotion and energy
Lastly, arguments need to do demonstrate a level of emotion in order to be convincing. This might seem contradictory to my previous point about arguments needing to be built on data-backed premises, but it’s not. Simply put, your argument needs to be fueled by data and demonstrated and communicated with emotion and energy.
Imagine standing up in front of your class and just saying, “We need to implement strategy X because we will increase our market share.” without intonation. No matter how great your prepared argument is, you will lose the attention of your audience if you do not exhibit emotion and energy. We’ve all had that one lecturer who drones on and on, and we quickly lose interest in the subject. Don’t be like that lecturer. Be you. I’m not saying to gesticulate wildly and shout at top volume; it is possible to be poised and passionate at the same time.
Remember: emotion can also be felt in writing. Think of your favorite author, journalist, or researcher. How does she write? She must show emotion in her writing in order to keep you engaged. Try to channel that passion/emulate her writing to make sure that your voice can be heard in your writing.
Wrapping up
In this post, I have discussed six elements of a good argument. Build your arguments using these ingredients and you will no doubt improve the quality of your academic work.
Here’s the checklist for quick reference – a good argument should have:
These elements will help you convey to your marker an articulate, sensible argument that was created after the consideration of several scenarios.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
I’ve never come across a much simpler explanation of the Inductive and Deductive concept. Thanks for this.
I concur. I love it when things are written in understandable language.
I enjoyed this article! Easily understandable.
Glad to hear that, Georgios!
This article is so helpful for me who is ready to write my postgrad dissertation! Thank you!
Great to hear that, Lizzy. Good luck with your dissertation!
Straightforward and to the point! I like that, especially since I don’t have time to beat around the bush.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

writingxhumanities
A "how to" guide for UC Berkeley writers

Making an Argument
Sometimes your instructor will give you a paper prompt. Here’s some advice on how to write in response to a prompt . And here are tips for responding to specific terms in prompts such as “analyze,” “compare,” “define.”
When your instructor doesn’t provide a detailed prompt, you will have to come up with a topic on your own. Are some topics better than others, and why? And what kinds of arguments do writers in the humanities make about those topics?
Arguments in the humanities are usually made in order to draw connections, whether these are connections between elements within a text, between texts, or between a text and one or more of its contexts.
- Within a text: how does some textual element (form, character, image, theme) contribute to the meaning of the work as a whole?
- Between texts: the classic format is “compare and contrast” (though you still need to make an argument based one or more elements of your comparison rather than simply identifying similarities and differences), but you might think also about how one text might influence, translate, or adapt another.
- Between a text and context: contexts might include one or more facets of the historical, social, political, economic, or even the biographical. Literary theories and critical methodologies might also provide interpretive contexts for your argument.
In most humanities essays, emphasis is placed on how these connections work, and why they are important for understanding a text. The most interesting questions, in other words, are not ones that can simply be answered “yes” or “no,” or “good” or “bad,” but ones that invite you to analyze how and why . Even when you are asked to evaluate a text as a work of art or an ethical performance, your evaluation must be based upon a considered discussion of the terms of your judgement and how the text you are discussing fulfills or falls short of these expectations.
You’ve probably heard of “writing as a process,” but this phrase can be used to mean different things. The writing process is often imagined as moving only in one direction: you read a text, come up with a thesis statement, gather evidence that proves that thesis, outline your essay, and then write that essay in a fixed five-paragraph structure, consisting of an introduction with a single-sentence thesis statement, three body paragraphs that contains your analysis of evidence you’ve found in your text, and a conclusion that restates your thesis statement.
This is sometimes the way that “writing as a process” is taught in high school. But at the college level, writing is best practiced as a recursive mode of inquiry. The process of writing shapes the way we think about and investigate our objects of study. Ideally, your thesis will deepen and develop over the course of writing a paper, becoming more nuanced as you return to the text again and again to consider additional evidence and further implications of—or perhaps objections to—your argument. Unlike in mathematics or logic, your goal when writing in the humanities is not to “prove” your argument, but to explore or examine an idea.
You might think of an essay in terms of the critical moves of its argument:
- Your essay should advance a single argument, which is also often called a thesis . Your thesis should be focused –if you’re analyzing a novel in a five-page paper, for example, you’ll need to focus on perhaps just a single scene, character, or repeated detail. Your thesis should be supportable —it has to rely on textual evidence rather than your subjective opinion or speculation. And your thesis should not be obvious -—it needs to be an argument about a text that you could imagine an intelligent reader disagreeing with.
- Your thesis is important not only as a statement that appears in your introduction, but also as the main claim that you make over the course of the entire essay. The supporting claims that you make in your body paragraphs may be able to stand on their own, but they should all be in service of the main claim. Hence, your main claim should not be limited to the initial form that it takes as the thesis statement in your introductory paragraph, but rather should evolve over the course of the paper as you establish your supporting claims.
- Then, there are the actions you take to make those supporting claims, which include summary , description , observation , contextualization , analysis , and interpretation . You’ll also want to think about the logic of the organization of these moves: how your sub-claims relate to your main claim. For more on working with textual evidence, see How can I use textual evidence to make an argument?
- To make your argument stronger and more complex, you may want to include counterclaims (claims that someone else might make against your argument), rebuttals (answering the questions raised in those counterclaims), and qualifications (acknowledging the limitations of your argument).
- One of the most challenging and crucial components of an argument is articulating what’s at stake. Sometimes the stakes of an argument are referred to as an answer to the question “so what?” Such significance will provoke your reader to think: “I see why this matters. I never thought of it that way”; or “You make a good, relevant point that enriches my reading of the text”; or even “I’m not entirely convinced, but you made me see this text in a new light.”
The most effective pieces of textual evidence are interpretively rich: they allow you to make compelling, unexpected, and nuanced claims that push your argument in new directions. (For more on using close reading to find those pieces of evidence, see Reading Between the Lines .) Depending on the particular focus of your paper, a good piece of evidence might exhibit some significant formal quality you want to draw attention to (things like alliteration, rhyme schemes, repetition, unexpected syntax, etc.) or reveal the psychology of a character. Avoid quoting textual evidence simply to summarize the plot, showcase general or widely known information about the text, or (of course) just to take up space in your 5-page paper requirement.
Some tips for using textual evidence to support an argument:
- Make sure to foreground your interpretation of the quoted material— sandwiching quotations in your own thought is a great way to do this.
- Quote only those textual details that exemplify the aspect of the text you are discussing.
- If you’re citing a written text, only give the most relevant bits of a quotations, using ellipses to “hide” irrelevant material within or between quoted sentences or lines. (Obviously, take care not to “hide” a part of the text that contradicts the quote you’ve chosen or the interpretation you are making about it!) Ellipses are just one way to handle that problem; click here for more on using quotations with clarity and style .
- It’s worth saying again: avoid using textual evidence to summarize the plot, to demonstrate general or widely known information about the text, or as filler to meet your minimum required word count!
For additional materials, go to Teaching Making an Argument in the For Instructors section of this website.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
3 Key Tips for How to Write an Argumentative Essay
General Education

If there’s one writing skill you need to have in your toolkit for standardized tests, AP exams, and college-level writing, it’s the ability to make a persuasive argument. Effectively arguing for a position on a topic or issue isn’t just for the debate team— it’s for anyone who wants to ace the essay portion of an exam or make As in college courses.
To give you everything you need to know about how to write an argumentative essay , we’re going to answer the following questions for you:
- What is an argumentative essay?
- How should an argumentative essay be structured?
- How do I write a strong argument?
- What’s an example of a strong argumentative essay?
- What are the top takeaways for writing argumentative papers?
By the end of this article, you’ll be prepped and ready to write a great argumentative essay yourself!
Now, let’s break this down.

What Is an Argumentative Essay?
An argumentative essay is a type of writing that presents the writer’s position or stance on a specific topic and uses evidence to support that position. The goal of an argumentative essay is to convince your reader that your position is logical, ethical, and, ultimately, right . In argumentative essays, writers accomplish this by writing:
- A clear, persuasive thesis statement in the introduction paragraph
- Body paragraphs that use evidence and explanations to support the thesis statement
- A paragraph addressing opposing positions on the topic—when appropriate
- A conclusion that gives the audience something meaningful to think about.
Introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion: these are the main sections of an argumentative essay. Those probably sound familiar. Where does arguing come into all of this, though? It’s not like you’re having a shouting match with your little brother across the dinner table. You’re just writing words down on a page!
...or are you? Even though writing papers can feel like a lonely process, one of the most important things you can do to be successful in argumentative writing is to think about your argument as participating in a larger conversation . For one thing, you’re going to be responding to the ideas of others as you write your argument. And when you’re done writing, someone—a teacher, a professor, or exam scorer—is going to be reading and evaluating your argument.
If you want to make a strong argument on any topic, you have to get informed about what’s already been said on that topic . That includes researching the different views and positions, figuring out what evidence has been produced, and learning the history of the topic. That means—you guessed it!—argumentative essays almost always require you to incorporate outside sources into your writing.

What Makes Argumentative Essays Unique?
Argumentative essays are different from other types of essays for one main reason: in an argumentative essay, you decide what the argument will be . Some types of essays, like summaries or syntheses, don’t want you to show your stance on the topic—they want you to remain unbiased and neutral.
In argumentative essays, you’re presenting your point of view as the writer and, sometimes, choosing the topic you’ll be arguing about. You just want to make sure that that point of view comes across as informed, well-reasoned, and persuasive.
Another thing about argumentative essays: they’re often longer than other types of essays. Why, you ask? Because it takes time to develop an effective argument. If your argument is going to be persuasive to readers, you have to address multiple points that support your argument, acknowledge counterpoints, and provide enough evidence and explanations to convince your reader that your points are valid.

Our 3 Best Tips for Picking a Great Argumentative Topic
The first step to writing an argumentative essay deciding what to write about! Choosing a topic for your argumentative essay might seem daunting, though. It can feel like you could make an argument about anything under the sun. For example, you could write an argumentative essay about how cats are way cooler than dogs, right?
It’s not quite that simple . Here are some strategies for choosing a topic that serves as a solid foundation for a strong argument.
Choose a Topic That Can Be Supported With Evidence
First, you want to make sure the topic you choose allows you to make a claim that can be supported by evidence that’s considered credible and appropriate for the subject matter ...and, unfortunately, your personal opinions or that Buzzfeed quiz you took last week don’t quite make the cut.
Some topics—like whether cats or dogs are cooler—can generate heated arguments, but at the end of the day, any argument you make on that topic is just going to be a matter of opinion. You have to pick a topic that allows you to take a position that can be supported by actual, researched evidence.
(Quick note: you could write an argumentative paper over the general idea that dogs are better than cats—or visa versa!—if you’re a) more specific and b) choose an idea that has some scientific research behind it. For example, a strong argumentative topic could be proving that dogs make better assistance animals than cats do.)
You also don’t want to make an argument about a topic that’s already a proven fact, like that drinking water is good for you. While some people might dislike the taste of water, there is an overwhelming body of evidence that proves—beyond the shadow of a doubt—that drinking water is a key part of good health.
To avoid choosing a topic that’s either unprovable or already proven, try brainstorming some issues that have recently been discussed in the news, that you’ve seen people debating on social media, or that affect your local community. If you explore those outlets for potential topics, you’ll likely stumble upon something that piques your audience’s interest as well.
Choose a Topic That You Find Interesting
Topics that have local, national, or global relevance often also resonate with us on a personal level. Consider choosing a topic that holds a connection between something you know or care about and something that is relevant to the rest of society. These don’t have to be super serious issues, but they should be topics that are timely and significant.
For example, if you are a huge football fan, a great argumentative topic for you might be arguing whether football leagues need to do more to prevent concussions . Is this as “important” an issue as climate change? No, but it’s still a timely topic that affects many people. And not only is this a great argumentative topic: you also get to write about one of your passions! Ultimately, if you’re working with a topic you enjoy, you’ll have more to say—and probably write a better essay .
Choose a Topic That Doesn’t Get You Too Heated
Another word of caution on choosing a topic for an argumentative paper: while it can be effective to choose a topic that matters to you personally, you also want to make sure you’re choosing a topic that you can keep your cool over. You’ve got to be able to stay unemotional, interpret the evidence persuasively, and, when appropriate, discuss opposing points of view without getting too salty.
In some situations, choosing a topic for your argumentative paper won’t be an issue at all: the test or exam will choose it for you . In that case, you’ve got to do the best you can with what you’re given.
In the next sections, we’re going to break down how to write any argumentative essay —regardless of whether you get to choose your own topic or have one assigned to you! Our expert tips and tricks will make sure that you’re knocking your paper out of the park.

The Thesis: The Argumentative Essay’s Backbone
You’ve chosen a topic or, more likely, read the exam question telling you to defend, challenge, or qualify a claim on an assigned topic. What do you do now?
You establish your position on the topic by writing a killer thesis statement ! The thesis statement, sometimes just called “the thesis,” is the backbone of your argument, the north star that keeps you oriented as you develop your main points, the—well, you get the idea.
In more concrete terms, a thesis statement conveys your point of view on your topic, usually in one sentence toward the end of your introduction paragraph . It’s very important that you state your point of view in your thesis statement in an argumentative way—in other words, it should state a point of view that is debatable.
And since your thesis statement is going to present your argument on the topic, it’s the thing that you’ll spend the rest of your argumentative paper defending. That’s where persuasion comes in. Your thesis statement tells your reader what your argument is, then the rest of your essay shows and explains why your argument is logical.
Why does an argumentative essay need a thesis, though? Well, the thesis statement—the sentence with your main claim—is actually the entire point of an argumentative essay. If you don’t clearly state an arguable claim at the beginning of your paper, then it’s not an argumentative essay. No thesis statement = no argumentative essay. Got it?
Other types of essays that you’re familiar with might simply use a thesis statement to forecast what the rest of the essay is going to discuss or to communicate what the topic is. That’s not the case here. If your thesis statement doesn’t make a claim or establish your position, you’ll need to go back to the drawing board.
Example Thesis Statements
Here are a couple of examples of thesis statements that aren’t argumentative and thesis statements that are argumentative
The sky is blue.
The thesis statement above conveys a fact, not a claim, so it’s not argumentative.
To keep the sky blue, governments must pass clean air legislation and regulate emissions.
The second example states a position on a topic. What’s the topic in that second sentence? The best way to keep the sky blue. And what position is being conveyed? That the best way to keep the sky blue is by passing clean air legislation and regulating emissions.
Some people would probably respond to that thesis statement with gusto: “No! Governments should not pass clean air legislation and regulate emissions! That infringes on my right to pollute the earth!” And there you have it: a thesis statement that presents a clear, debatable position on a topic.
Here’s one more set of thesis statement examples, just to throw in a little variety:
Spirituality and otherworldliness characterize A$AP Rocky’s portrayals of urban life and the American Dream in his rap songs and music videos.
The statement above is another example that isn’t argumentative, but you could write a really interesting analytical essay with that thesis statement. Long live A$AP! Now here’s another one that is argumentative:
To give students an understanding of the role of the American Dream in contemporary life, teachers should incorporate pop culture, like the music of A$AP Rocky, into their lessons and curriculum.
The argument in this one? Teachers should incorporate more relevant pop culture texts into their curriculum.
This thesis statement also gives a specific reason for making the argument above: To give students an understanding of the role of the American Dream in contemporary life. If you can let your reader know why you’re making your argument in your thesis statement, it will help them understand your argument better.

An actual image of you killing your argumentative essay prompts after reading this article!
Breaking Down the Sections of An Argumentative Essay
Now that you know how to pick a topic for an argumentative essay and how to make a strong claim on your topic in a thesis statement, you’re ready to think about writing the other sections of an argumentative essay. These are the parts that will flesh out your argument and support the claim you made in your thesis statement.
Like other types of essays, argumentative essays typically have three main sections: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Within those sections, there are some key elements that a reader—and especially an exam scorer or professor—is always going to expect you to include.
Let’s look at a quick outline of those three sections with their essential pieces here:
- Introduction paragraph with a thesis statement (which we just talked about)
- Support Point #1 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary (AKA, the fun part!)
- Support Point #2 with evidence
- Explain/interpret the evidence with your own, original commentary
- Support Point #3 with evidence
- New paragraph addressing opposing viewpoints (more on this later!)
- Concluding paragraph
Now, there are some key concepts in those sections that you’ve got to understand if you’re going to master how to write an argumentative essay. To make the most of the body section, you have to know how to support your claim (your thesis statement), what evidence and explanations are and when you should use them, and how and when to address opposing viewpoints. To finish strong, you’ve got to have a strategy for writing a stellar conclusion.
This probably feels like a big deal! The body and conclusion make up most of the essay, right? Let’s get down to it, then.

How to Write a Strong Argument
Once you have your topic and thesis, you’re ready for the hard part: actually writing your argument. If you make strategic choices—like the ones we’re about to talk about—writing a strong argumentative essay won’t feel so difficult.
There are three main areas where you want to focus your energy as you develop a strategy for how to write an argumentative essay: supporting your claim—your thesis statement—in your essay, addressing other viewpoints on your topic, and writing a solid conclusion. If you put thought and effort into these three things, you’re much more likely to write an argumentative essay that’s engaging, persuasive, and memorable...aka A+ material.
Focus Area 1: Supporting Your Claim With Evidence and Explanations
So you’ve chosen your topic, decided what your position will be, and written a thesis statement. But like we see in comment threads across the Internet, if you make a claim and don’t back it up with evidence, what do people say? “Where’s your proof?” “Show me the facts!” “Do you have any evidence to support that claim?”
Of course you’ve done your research like we talked about. Supporting your claim in your thesis statement is where that research comes in handy.
You can’t just use your research to state the facts, though. Remember your reader? They’re going to expect you to do some of the dirty work of interpreting the evidence for them. That’s why it’s important to know the difference between evidence and explanations, and how and when to use both in your argumentative essay.
What Evidence Is and When You Should Use It
Evidence can be material from any authoritative and credible outside source that supports your position on your topic. In some cases, evidence can come in the form of photos, video footage, or audio recordings. In other cases, you might be pulling reasons, facts, or statistics from news media articles, public policy, or scholarly books or journals.
There are some clues you can look for that indicate whether or not a source is credible , such as whether:
- The website where you found the source ends in .edu, .gov, or .org
- The source was published by a university press
- The source was published in a peer-reviewed journal
- The authors did extensive research to support the claims they make in the source
This is just a short list of some of the clues that a source is likely a credible one, but just because a source was published by a prestigious press or the authors all have PhDs doesn’t necessarily mean it is the best piece of evidence for you to use to support your argument.
In addition to evaluating the source’s credibility, you’ve got to consider what types of evidence might come across as most persuasive in the context of the argument you’re making and who your readers are. In other words, stepping back and getting a bird’s eye view of the entire context of your argumentative paper is key to choosing evidence that will strengthen your argument.
On some exams, like the AP exams , you may be given pretty strict parameters for what evidence to use and how to use it. You might be given six short readings that all address the same topic, have 15 minutes to read them, then be required to pull material from a minimum of three of the short readings to support your claim in an argumentative essay.
When the sources are handed to you like that, be sure to take notes that will help you pick out evidence as you read. Highlight, underline, put checkmarks in the margins of your exam . . . do whatever you need to do to begin identifying the material that you find most helpful or relevant. Those highlights and check marks might just turn into your quotes, paraphrases, or summaries of evidence in your completed exam essay.
What Explanations Are and When You Should Use Them
Now you know that taking a strategic mindset toward evidence and explanations is critical to grasping how to write an argumentative essay. Unfortunately, evidence doesn’t speak for itself. While it may be obvious to you, the researcher and writer, how the pieces of evidence you’ve included are relevant to your audience, it might not be as obvious to your reader.
That’s where explanations—or analysis, or interpretations—come in. You never want to just stick some quotes from an article into your paragraph and call it a day. You do want to interpret the evidence you’ve included to show your reader how that evidence supports your claim.
Now, that doesn’t mean you’re going to be saying, “This piece of evidence supports my argument because...”. Instead, you want to comment on the evidence in a way that helps your reader see how it supports the position you stated in your thesis. We’ll talk more about how to do this when we show you an example of a strong body paragraph from an argumentative essay here in a bit.
Understanding how to incorporate evidence and explanations to your advantage is really important. Here’s why: when you’re writing an argumentative essay, particularly on standardized tests or the AP exam, the exam scorers can’t penalize you for the position you take. Instead, their evaluation is going to focus on the way you incorporated evidence and explained it in your essay.

Focus Area 2: How—and When—to Address Other Viewpoints
Why would we be making arguments at all if there weren’t multiple views out there on a given topic? As you do research and consider the background surrounding your topic, you’ll probably come across arguments that stand in direct opposition to your position.
Oftentimes, teachers will ask you to “address the opposition” in your argumentative essay. What does that mean, though, to “ address the opposition ?”
Opposing viewpoints function kind of like an elephant in the room. Your audience knows they’re there. In fact, your audience might even buy into an opposing viewpoint and be waiting for you to show them why your viewpoint is better. If you don’t, it means that you’ll have a hard time convincing your audience to buy your argument.
Addressing the opposition is a balancing act: you don’t want to undermine your own argument, but you don’t want to dismiss the validity of opposing viewpoints out-of-hand or ignore them altogether, which can also undermine your argument.
This isn’t the only acceptable approach, but it’s common practice to wait to address the opposition until close to the end of an argumentative essay. But why?
Well, waiting to present an opposing viewpoint until after you’ve thoroughly supported your own argument is strategic. You aren’t going to go into great detail discussing the opposing viewpoint: you’re going to explain what that viewpoint is fairly, but you’re also going to point out what’s wrong with it.
It can also be effective to read the opposition through the lens of your own argument and the evidence you’ve used to support it. If the evidence you’ve already included supports your argument, it probably doesn’t support the opposing viewpoint. Without being too obvious, it might be worth pointing this out when you address the opposition.

Focus Area #3: Writing the Conclusion
It’s common to conclude an argumentative essay by reiterating the thesis statement in some way, either by reminding the reader what the overarching argument was in the first place or by reviewing the main points and evidence that you covered.
You don’t just want to restate your thesis statement and review your main points and call it a day, though. So much has happened since you stated your thesis in the introduction! And why waste a whole paragraph—the very last thing your audience is going to read—on just repeating yourself?
Here’s an approach to the conclusion that can give your audience a fresh perspective on your argument: reinterpret your thesis statement for them in light of all the evidence and explanations you’ve provided. Think about how your readers might read your thesis statement in a new light now that they’ve heard your whole argument out.
That’s what you want to leave your audience with as you conclude your argumentative paper: a brief explanation of why all that arguing mattered in the first place. If you can give your audience something to continue pondering after they’ve read your argument, that’s even better.
One thing you want to avoid in your conclusion, though: presenting new supporting points or new evidence. That can just be confusing for your reader. Stick to telling your reader why the argument you’ve already made matters, and your argument will stick with your reader.

A Strong Argumentative Essay: Examples
For some aspiring argumentative essay writers, showing is better than telling. To show rather than tell you what makes a strong argumentative essay, we’ve provided three examples of possible body paragraphs for an argumentative essay below.
Think of these example paragraphs as taking on the form of the “Argumentative Point #1 → Evidence —> Explanation —> Repeat” process we talked through earlier. It’s always nice to be able to compare examples, so we’ve included three paragraphs from an argumentative paper ranging from poor (or needs a lot of improvement, if you’re feeling generous), to better, to best.
All of the example paragraphs are for an essay with this thesis statement:
Thesis Statement: In order to most effectively protect user data and combat the spread of disinformation, the U.S. government should implement more stringent regulations of Facebook and other social media outlets.
As you read the examples, think about what makes them different, and what makes the “best” paragraph more effective than the “better” and “poor” paragraphs. Here we go:
A Poor Argument
Example Body Paragraph: Data mining has affected a lot of people in recent years. Facebook has 2.23 billion users from around the world, and though it would take a huge amount of time and effort to make sure a company as big as Facebook was complying with privacy regulations in countries across the globe, adopting a common framework for privacy regulation in more countries would be the first step. In fact, Mark Zuckerberg himself supports adopting a global framework for privacy and data protection, which would protect more users than before.
What’s Wrong With This Example?
First, let’s look at the thesis statement. Ask yourself: does this make a claim that some people might agree with, but others might disagree with?
The answer is yes. Some people probably think that Facebook should be regulated, while others might believe that’s too much government intervention. Also, there are definitely good, reliable sources out there that will help this writer prove their argument. So this paper is off to a strong start!
Unfortunately, this writer doesn’t do a great job proving their thesis in their body paragraph. First, the topic sentence—aka the first sentence of the paragraph—doesn’t make a point that directly supports the position stated in the thesis. We’re trying to argue that government regulation will help protect user data and combat the spread of misinformation, remember? The topic sentence should make a point that gets right at that, instead of throwing out a random fact about data mining.
Second, because the topic sentence isn’t focused on making a clear point, the rest of the paragraph doesn’t have much relevant information, and it fails to provide credible evidence that supports the claim made in the thesis statement. For example, it would be a great idea to include exactly what Mark Zuckerberg said ! So while there’s definitely some relevant information in this paragraph, it needs to be presented with more evidence.
A Better Argument
This paragraph is a bit better than the first one, but it still needs some work. The topic sentence is a bit too long, and it doesn’t make a point that clearly supports the position laid out in the thesis statement. The reader already knows that mining user data is a big issue, so the topic sentence would be a great place to make a point about why more stringent government regulations would most effectively protect user data.
There’s also a problem with how the evidence is incorporated in this example. While there is some relevant, persuasive evidence included in this paragraph, there’s no explanation of why or how it is relevant . Remember, you can’t assume that your evidence speaks for itself: you have to interpret its relevance for your reader. That means including at least a sentence that tells your reader why the evidence you’ve chosen proves your argument.
A Best—But Not Perfect!—Argument
Example Body Paragraph: Though Facebook claims to be implementing company policies that will protect user data and stop the spread of misinformation , its attempts have been unsuccessful compared to those made by the federal government. When PricewaterhouseCoopers conducted a Federal Trade Commission-mandated assessment of Facebook’s partnerships with Microsoft and the makers of the Blackberry handset in 2013, the team found limited evidence that Facebook had monitored or even checked that its partners had complied with Facebook’s existing data use policies. In fact, Facebook’s own auditors confirmed the PricewaterhouseCoopers findings, despite the fact that Facebook claimed that the company was making greater attempts to safeguard users’ personal information. In contrast, bills written by Congress have been more successful in changing Facebook’s practices than Facebook’s own company policies have. According to The Washington Post, The Honest Ads Act of 2017 “created public demand for transparency and changed how social media companies disclose online political advertising.” These policy efforts, though thus far unsuccessful in passing legislation, have nevertheless pushed social media companies to change some of their practices by sparking public outrage and negative media attention.
Why This Example Is The Best
This paragraph isn’t perfect, but it is the most effective at doing some of the things that you want to do when you write an argumentative essay.
First, the topic sentences get to the point . . . and it’s a point that supports and explains the claim made in the thesis statement! It gives a clear reason why our claim in favor of more stringent government regulations is a good claim : because Facebook has failed to self-regulate its practices.
This paragraph also provides strong evidence and specific examples that support the point made in the topic sentence. The evidence presented shows specific instances in which Facebook has failed to self-regulate, and other examples where the federal government has successfully influenced regulation of Facebook’s practices for the better.
Perhaps most importantly, though, this writer explains why the evidence is important. The bold sentence in the example is where the writer links the evidence back to their opinion. In this case, they explain that the pressure from Federal Trade Commission and Congress—and the threat of regulation—have helped change Facebook for the better.
Why point out that this isn’t a perfect paragraph, though? Because you won’t be writing perfect paragraphs when you’re taking timed exams either. But get this: you don’t have to write perfect paragraphs to make a good score on AP exams or even on an essay you write for class. Like in this example paragraph, you just have to effectively develop your position by appropriately and convincingly relying on evidence from good sources.

Top 3 Takeaways For Writing Argumentative Essays
This is all great information, right? If (when) you have to write an argumentative essay, you’ll be ready. But when in doubt, remember these three things about how to write an argumentative essay, and you’ll emerge victorious:
Takeaway #1: Read Closely and Carefully
This tip applies to every aspect of writing an argumentative essay. From making sure you’re addressing your prompt, to really digging into your sources, to proofreading your final paper...you’ll need to actively and pay attention! This is especially true if you’re writing on the clock, like during an AP exam.
Takeaway #2: Make Your Argument the Focus of the Essay
Define your position clearly in your thesis statement and stick to that position! The thesis is the backbone of your paper, and every paragraph should help prove your thesis in one way or another. But sometimes you get to the end of your essay and realize that you’ve gotten off topic, or that your thesis doesn’t quite fit. Don’t worry—if that happens, you can always rewrite your thesis to fit your paper!
Takeaway #3: Use Sources to Develop Your Argument—and Explain Them
Nothing is as powerful as good, strong evidence. First, make sure you’re finding credible sources that support your argument. Then you can paraphrase, briefly summarize, or quote from your sources as you incorporate them into your paragraphs. But remember the most important part: you have to explain why you’ve chosen that evidence and why it proves your thesis.
What's Next?
Once you’re comfortable with how to write an argumentative essay, it’s time to learn some more advanced tips and tricks for putting together a killer argument.
Keep in mind that argumentative essays are just one type of essay you might encounter. That’s why we’ve put together more specific guides on how to tackle IB essays , SAT essays , and ACT essays .
But what about admissions essays? We’ve got you covered. Not only do we have comprehensive guides to the Coalition App and Common App essays, we also have tons of individual college application guides, too . You can search through all of our college-specific posts by clicking here.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
SCOTT BOATWRIGHT , COO AND 7-YEAR CHIPOTLE VETERAN, NAMED INTERIM CEO
JACK HARTUNG TO REMAIN WITH COMPANY AS PRESIDENT, STRATEGY, FINANCE & SUPPLY CHAIN
NEWPORT BEACH, Calif. , Aug. 13, 2024 / PRNewswire / -- Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. (NYSE: CMG) today announced that Brian Niccol , Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, has accepted the role as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Starbucks and will be leaving the Company effective August 31, 2024 . Niccol has served as Chipotle's CEO since 2018 and as Chairman of the Board since 2020.
Chipotle's Board of Directors has appointed Scott Boatwright , Chief Operating Officer, as Interim CEO. Boatwright joined Chipotle in 2017 and has been instrumental in driving restaurant operations for the company's more than 120,000 employees and over 3,500 restaurants. He also led the integration of new technology into restaurants, built a strong culture aligned to the organization's values, and achieved industry-leading retention rates yielding impressive results and improvements in throughput and the overall guest experience. Boatwright played a critical role as part of the leadership team that created and executed the turnaround strategy that has delivered incredible results since it began in 2018. Boatwright and the esteemed leadership team will continue to execute the company's strategic plan without interruption.
In addition, Jack Hartung , who recently announced his retirement from Chipotle in 2025, has agreed to remain with the organization indefinitely as President of Strategy, Finance and Supply Chain to ensure a smooth transition. In this new role, Hartung will support Boatwright as Interim CEO, and continue his current oversight of Adam Rymer , Vice President of Finance and incoming CFO, as well as Carlos Londono , global head of Supply Chain.
With this leadership change, Scott Maw , Chipotle's Lead Independent Director, has been named Chairman of the Board, effective immediately. "Thanks to our robust talent planning process, we are well-prepared for events like this due to the deep bench within the organization," said Scott Maw , Chipotle's Chairman of the Board. "The board is excited to see other strong leaders expand their roles and provide growth and development for more people in the organization," added Maw.
"I'm incredibly proud of the work that has been accomplished since I joined Chipotle in 2018," said Brian Niccol . "The strategic priorities this team has put in place have positioned Chipotle to win today and enable future growth. It's hard to leave such a great company and all of the talented people I've had the pleasure to work with, but I depart knowing the business is in great shape and poised for growth with a strong, experienced leadership team."
Scott Boatwright added: "I have the utmost confidence in our five key strategies and I'm excited for the new opportunity to lead the business moving forward. We have a world-class organization full of talented leaders who are passionate about our brand and purpose and excited for the long-term opportunity to grow to 7,000 restaurants in North America and expand internationally."
About Chipotle Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. (NYSE: CMG ) is cultivating a better world by serving responsibly sourced, classically-cooked, real food with wholesome ingredients without artificial colors, flavors or preservatives. There are over 3,500 restaurants as of June 30, 2024, in the United States , Canada , the United Kingdom , France , Germany , and Kuwait and it is the only restaurant company of its size that owns and operates all its restaurants in North America and Europe . Chipotle is ranked on the Fortune 500 and is recognized on Fortune's Most Admired Companies 2024 list and Time Magazine's Most Influential Companies. With over 120,000 employees passionate about providing a great guest experience, Chipotle is a longtime leader and innovator in the food industry. Chipotle is committed to making its food more accessible to everyone while continuing to be a brand with a demonstrated purpose as it leads the way in digital, technology and sustainable business practices. For more information or to place an order online, visit Chipotle.com .
Forward-Looking Statements Certain statements in this press release are forward-looking statements as defined in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, including statements about Chipotle's future growth potential and statements that begin with words such as "anticipate", "believe", "could", "should", "may", and similar terms and phrases. The forward-looking statements in this press release are based on currently available operating, financial and competitive information available to us as of the date of this release and we assume no obligation to update these forward-looking statements. These statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those described in the statements, including but not limited to: increasing wage inflation, and the competitive labor market; the impact of any union organizing efforts and our responses to such efforts; increasing supply costs; risks of food safety incidents and food-borne illnesses; risks associated with our reliance on certain information technology systems and potential material failures, interruptions or outages; privacy and cyber security risks; the impact of competition, including from sources outside the restaurant industry; the impact of federal, state or local government regulations relating to our employees, employment practices, restaurant design and construction, and the sale of food or alcoholic beverages; our ability to achieve our planned growth, such as the costs and availability of suitable new restaurant sites, construction materials and contractors; the expected costs and risks related to our international expansion; increases in ingredient and other operating costs due to inflation, global conflicts, severe weather and climate change, our Food with Integrity philosophy, tariffs or trade restrictions; intermittent supply shortages; the uncertainty of our ability to achieve expected levels of comparable restaurant sales due to factors such as changes in guests' perceptions of our brand, including as a result of negative publicity or social media posts, decreased consumer spending, or the inability to increase menu prices or realize the benefits of menu price increases; risks associated with our digital business, including risks arising from our reliance on third party delivery services and the IT infrastructure; litigation risks, including possible governmental actions and potential class action litigation related to food safety incidents, cybersecurity incidents, employment or privacy laws, advertising claims, contract disputes or other matters; and other risk factors described from time to time in our SEC reports, including our annual report on Form 10-K and quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, all of which are available on the investor relations page of our website at ir.Chipotle.com .

SOURCE Chipotle Mexican Grill
- SI SWIMSUIT
- SI SPORTSBOOK
- TRANSACTIONS
Three New York Jets Players Who Have Most to Prove Against Carolina Panthers
Ralph ventre | aug 17, 2024.

- New York Jets
The New York Jets experienced an eventful joint practice against the Carolina Panthers on Thursday, and now it's time for the actual preseason game.
In their second of three August exhibitions, the Jets will clash in Carolina on Saturday, August 17 at 7 p.m. ET. Future Hall-of-Fame quarterback Aaron Rodgers won't play, but there will be plenty of meaningful reps to go around.
With players fighting for roster spots and trying to establish their roles, Saturday's preseason contest is important for so many young Jets. Here are three to watch in the Preseason Week 2 affair.
WR Malachi Corley
New York's offense is seemingly counting on contributions from the No. 65 overall draft pick this fall. Corley figures to see time in the slot as the Jets test the run-after-catch ability that made the Western Kentucky receiver such an attractive prospect to general manager Joe Douglas.
"What's been really good is we all know what he can do with the ball in his hands. We've been able to kind of manufacture some situations where he does get it, and he's as advertised when that ball's in his hands," said Saleh on Thursday in Charlotte.
Corley has flashed during training camp, but he's clearly in the midst of a major adjustment to the professional level.
"He's been growing. Still a long way to go with his route running and understanding the same thing that Garrett [Wilson] went through, just being where he needs to be as fast as he can get there," said Saleh.
Corley started the preseason opener against the Washington Commanders , totaling 18 offensive snaps. He caught 4 of 5 targets for 27 yards, a 6.8 ypc average. On special teams, he botched a punt return but looked electrifying on a 33-yard kickoff return.
TE Zack Kuntz
With presumed TE2 Jeremy Ruckert missing time due to a concussion, there's an opportunity for Kuntz to step up and earn a role. The 2023 seventh-round draft pick posses rare athletic attributes, but has yet to show his true potential in game situations. He spent the first 17 weeks of his rookie season on the Practice Squad and played only two snaps on offense during the finale.
Kuntz was on the field for 27 offensive snaps, the second most amongst Jets skill players, in the preseason opener, but he garnered zero targets as a receiver. Kuntz faces stiff competition to earn the spot behind Tyler Conklin and Ruckert. With Kenny Yeboah already in the mix, New York signed Anthony Firkser, who made one nine-yard reception last Saturday.
The 6-foot-7 Kuntz may be able to distinguish himself through special teams. He played 12 snaps on specials against the Commanders.
DL Leonard Taylor
The highly-touted undrafted rookie is making a legitimate push for a spot on the 53-man roster, but there's still a lot to prove before cutdown day.
"Now, he has got a long way to go and he knows that, we all know that, but it is really exciting to see some flashes early on here," said defensive coordinator Jeff Ulbrich earlier this week.
Taylor had a couple of dominant moments during his preseason debut. He blew up a first-half run play and added a fourth-quarter sack.
"He is starting to really figure out what attack means in our front. He has had all this ability in his body forever since he started playing ball I imagine," said Ulbrich.
RALPH VENTRE
Ralph, a former college football conference administrator, brings 20 years of media experience to the New York Jets beat. Prior to concentrating on Gang Green, he covered the NCAA Football Championship Subdivision for NFL Draft Bible on FanNation. Ventre remains as an official voter for the Stats Perform FCS Top 25 and the annual legacy awards. The Fordham University graduate is a member of the Pro Football Writers of America. The veteran sports media professional resides in his native state of New Jersey.

Solar energy breakthrough could reduce need for solar farms
Scientists at Oxford University Physics Department have developed a revolutionary approach which could generate increasing amounts of solar electricity without the need for silicon-based solar panels. Instead, their innovation works by coating a new power-generating material onto the surfaces of everyday objects such as rucksacks, cars, and mobile phones.

This ultra-thin material, using this so-called multi-junction approach, has now been independently certified to deliver over 27% energy efficiency, for the first time matching the performance of traditional, single-layer, energy-generating materials known as silicon photovoltaics. Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), gave its certification prior to publication of the researchers’ scientific study later this year.
‘During just five years experimenting with our stacking or multi-junction approach we have raised power conversion efficiency from around 6% to over 27%, close to the limits of what single-layer photovoltaics can achieve today,’ said Dr Shuaifeng Hu , Post Doctoral Fellow at Oxford University Physics. ‘We believe that, over time, this approach could enable the photovoltaic devices to achieve far greater efficiencies, exceeding 45%.’
This compares with around 22% energy efficiency from solar panels today (meaning they convert around 22% of the energy in sunlight), but the versatility of the new ultra-thin and flexible material is also key. At just over one micron thick, it is almost 150 times thinner than a silicon wafer. Unlike existing photovoltaics, generally applied to silicon panels, this can be applied to almost any surface.
‘By using new materials which can be applied as a coating, we’ve shown we can replicate and out-perform silicon whilst also gaining flexibility. This is important because it promises more solar power without the need for so many silicon-based panels or specially-built solar farms,’ said Dr Junke Wang , Marie Skłodowska Curie Actions Postdoc Fellow at Oxford University Physics.
The latest innovations in solar materials and techniques demonstrated in our labs could become a platform for a new industry, manufacturing materials to generate solar energy more sustainably and cheaply by using existing buildings, vehicles, and objects. Henry Snaith , Professor of Renewable Energy, Oxford University Physics Department.
The researchers believe their approach will continue to reduce the cost of solar and also make it the most sustainable form of renewable energy. Since 2010, the global average cost of solar electricity has fallen by almost 90%, making it almost a third cheaper than that generated from fossil fuels. Innovations promise additional cost savings as new materials, like thin-film perovskite, reduce the need for silicon panels and purpose-built solar farms.
‘We can envisage perovskite coatings being applied to broader types of surface to generate cheap solar power, such as the roof of cars and buildings and even the backs of mobile phones. If more solar energy can be generated in this way, we can foresee less need in the longer term to use silicon panels or build more and more solar farms’ Dr Wang added.
The researchers are among 40 scientists working on photovoltaics led by Professor of Renewable Energy Henry Snaith at Oxford University Physics Department. Their pioneering work in photovoltaics and especially the use of thin-film perovskite began around a decade ago and benefits from a bespoke, robotic laboratory.

Oxford PV, a UK company spun out of Oxford University Physics in 2010 by co-founder and chief scientific officer Professor Henry Snaith to commercialise perovskite photovoltaics, recently started large-scale manufacturing of perovskite photovoltaics at its factory in Brandenburg-an-der-Havel, near Berlin, Germany. This is the world’s first volume manufacturing line for ‘perovskite-on-silicon’ tandem solar cells.
‘We originally looked at UK sites to start manufacturing but the government has yet to match the fiscal and commercial incentives on offer in other parts of Europe and the United States,’ Professor Snaith said. ‘Thus far the UK has thought about solar energy purely in terms of building new solar farms, but the real growth will come from commercialising innovations – we very much hope that the newly-created British Energy will direct its attention to this.’
‘Supplying these materials will be a fast-growth new industry in the global green economy and we have shown that the UK is innovating and leading the way scientifically. However, without new incentives and a better pathway to convert this innovation into manufacturing the UK will miss the opportunity to lead this new global industry,’ Professor Snaith added.
DISCOVER MORE
- Support Oxford's research
- Partner with Oxford on research
- Study at Oxford
- Research jobs at Oxford
You can view all news or browse by category
Mpox cases are soaring in Africa – what must be done to prevent a global pandemic
Senior Lecturer in Biomedical Science, University of Hull
Disclosure statement
Cheryl Walter does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Hull provides funding as a member of The Conversation UK.
View all partners

Alarmed by the surge in mpox cases, the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention has taken the unprecedented step of declaring the outbreak sweeping through African countries a continental public health emergency. A day later, the World Health Organization declared that the outbreak constitutes a global health emergency.
These moves come after a virulent strain of the disease spread rapidly to 16 countries and six new countries were affected in 10 days.
There have been 15,132 mpox confirmed cases in Africa since the beginning of 2024. Some of the countries affected are Burundi, Cameroon, Congo, Ghana, Liberia, Nigeria, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of Congo, South Africa, Uganda and Kenya.
Virologist Cheryl Walter sets out some of the reasons the mpox outbreaks are so worrying.
How many strains of mpox are there and which ones should we be worried about?
Mpox is one species of pox virus, such as smallpox and cowpox, characterised by a rash followed by bumps that appear on the skin. With mpox the bumps then fill with liquid and eventually scab over.
As we’ve come to know through diseases such as COVID-19, viruses change genetically and mutate quite quickly.
Mpox is no different, although pox viruses typically mutate much more slowly compared to other viruses, such as HIV. HIV changes approximately every three times a single virus replicates.
There are two strains of mpox – clade I and clade II. Think of them as two big branches on a tree.
Until about five or six years ago these clades weren’t that diverse.
Something has changed. These branches are growing and the leaves on the branches are becoming more numerous. In fact, we have new subclades for both I and II, so two new offshoot branches have appeared.
Clade II is far less dangerous with a case fatality rate of about 0.1% . In other words, roughly one person in a thousand dies.
Now scientists are seeing thousands of cases of clade I being reported in 16 countries in Africa and a case fatality rate of anything from 3% to 4%. That means three or four people in a hundred die. Many cases are children.
Let’s use COVID-19 again as a comparison. It was declared an international public emergency from 30 January 2020 to 31 December 2021, with an estimated case fatality rate of 1.2% .
Mpox is a relatively understudied virus. Until recently there were a handful of confirmed cases every year. It occurred primarily in tropical rainforest areas of central and west Africa. There was very little opportunity for the virus to adapt to a human host.
We don’t understand if genetic changes are making these viruses spread more easily and if the variants in circulation are more dangerous.
We do know the virus is changing and moving through lots of people. Viruses can only mutate when they’re passing through a host such as a human.
The more people it passes through, the more opportunity it has to change and potentially become more virulent or more transmissible.
Now this virus is moving through lots of people, there are lots of these opportunities.
Read more: Mpox: what to watch out for, treatment and what to worry about
How does the disease spread to new areas?
The virus spreads through contact such as sharing utensils, plates, towels and bedding.
Women and children are disproportionately affected through skin-to-skin contact because they are close to each other every day. Children play games in schools and creches and touch objects and each other all the time.
Viruses also spread easily when people live in densely populated, low income areas and can’t isolate themselves because they have to bring in an income.
Two of the other other reasons mpox spreads quickly is the longer incubation period and vague symptoms.
The incubation period ranges quite widely from five to up to 21 days. A person can become infected with mpox during this period and travel to another country and transmit the disease to others.
The initial symptoms are vague and include swollen glands, fever and feeling a bit run down. It is estimated 10% of people infected with mpox are asymptomatic.
It’s only when the rash appears that it might become apparent that it’s not a cold or flu or COVID-19.
To add to that challenge, when children get those rashes they could be mistaken for chickenpox or one of the other childhood infectious diseases.
What emergency measures need to be put in place to ensure the outbreak doesn’t explode into a pandemic?
There are a couple of things stacked against African health agencies trying to contain the virus.
There are few resources to fight this disease and the shortage of vaccines is a major problem. The Africa Centres for Disease Control estimates there are only 200,000 doses available to African countries compared with a demand of at least 10 million.
However, there’s still a lot that can be done.
Testing: This is the number one tool in this fight. We need to know where these cases are and who in the community mpox is passing through. We also need to use this data to trace contacts. We can do this with simple lateral flow tests – using a swab of the nose and/or throat that can be done in the community and give results within 30 minutes.
Messaging: In the previous outbreak across the world, a lot of communications that were going out were aimed at sex workers and men who have sex with men. As a result, people may have thought that this is only a sexually transmitted disease. It’s not.
Now women and children are getting the virus, so communities need to be told what symptoms to look for and what action to take.
Vaccinating: Because mpox is so similar to smallpox, we can use that vaccine. However there are limited stockpiles and we can’t manufacture smallpox vaccines quickly enough. The WHO has called for vaccine candidates for fast approval and distribution.
These measures and others need to be taken urgently to contain and to repress this epidemic before it potentially becomes a global pandemic.
Read more: At what point is a disease deemed to be a global threat? Here's the answer
- World Health Organization (WHO)
- Global health emergency

Senior Student & Programs Coordinator

Casual Facilitator: GERRIC Student Programs - Arts, Design and Architecture

Senior Lecturer, Digital Advertising

Manager, Centre Policy and Translation

Newsletter and Deputy Social Media Producer
Statement by the Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator a.i. for Myanmar
19 August 2024
World Humanitarian Day 2024: Acting for Humanity
World Humanitarian Day is an occasion for us all to honor the courageous aid workers who are delivering humanitarian assistance to millions of people in need throughout Myanmar. Amid an expanding crisis, they are stepping up each day to get help where it is needed most.
Across Myanmar, people are facing the painful consequences of widespread conflict and devastating disaster. An estimated 18.6 million people urgently require humanitarian assistance, including 6 million children. The spiraling crisis has pushed many people into survival mode. With remarkable dedication, aid workers do their utmost to get people in need food, shelter, protection and other lifesaving assistance. In the first half of 2024, the humanitarian community reached 2.1 million people with support. This assistance was delivered despite significant funding challenges, with the 2024 Humanitarian Needs and Response Plan only 21 per cent funded.
Local and national humanitarian organizations are at the forefront of this response, showing tireless determination to help those in need. Alongside aid workers, host communities across Myanmar are providing crucial support to people in need. They are often the first responders in this crisis and a lifeline to affected people.
This year’s World Humanitarian Day calls on people around the world to #ActForHumanity. It aims to shine a light on the consequences of violations of International Humanitarian Law and confront the normalization of attacks on aid workers and civilians suffering from the impact of the conflict. In Myanmar, civilians and aid workers face risks each day as the conflict escalates. It is imperative that all parties to the conflict uphold their obligations under International Humanitarian Law to protect civilians and aid workers, ensuring sustained and unhindered humanitarian access to those in need.
Today, and every day, all who are working to help the most vulnerable people in Myanmar are deeply appreciated. Amid immense challenges, your unwavering support is a source of hope that together we can alleviate suffering and protect lives.
For more information on World Humanitarian Day please visit www.worldhumanitarianday.org .

Christina Powell

Lesly Lotha
Un entities involved in this initiative, goals we are supporting through this initiative.
Mobile Menu Overlay
The White House 1600 Pennsylvania Ave NW Washington, DC 20500
Statement from Vice President Kamala Harris on Lower Prescription Drug Prices
Every American should be able to access the health care they need no matter their income or wealth. That is why President Biden and I fought to lower the costs of health care with our Inflation Reduction Act, transformational legislation that I was proud to cast the tie-breaking vote on in the Senate. During the two years since President Biden signed this landmark bill into law, we have cut prescription drug costs, capped the cost of insulin at $35 a month, and lowered premiums for seniors and people with disabilities on Medicare – helping millions of families get the care they deserve. Today, we are building on our work to lower costs and increase access to affordable prescription drugs by announcing that the Biden-Harris Administration has reached agreements with all participating manufacturers to lower prices for the first 10 drugs selected for the Medicare price negotiation program – from those that treat cancer to those that treat diabetes, heart disease, and blood clots. Thanks to our historic work to allow Medicare to negotiate lower drug prices, millions of Americans who rely on these drugs will save on their out-of-pocket costs. While people enrolled in Medicare are expected to save $1.5 billion in 2026 alone, American taxpayers will also save an estimated $6 billion. Today’s announcement will be lifechanging for so many of our loved ones across the nation, and we are not stopping here. Additional prescription drugs will be selected each year as part of our Medicare drug price negotiation program. This includes up to 15 additional drugs covered under Medicare Part D for negotiation in 2025, up to an additional 15 Part B and Part D drugs in 2026, and up to 20 drugs every year after that. From my time as Attorney General of California and a U.S. Senator, I have consistently worked to lower the costs of prescription drugs and fought to protect patients. As Attorney General, I held Big Pharma accountable for their deceptive and illegal practices. The record-breaking settlements that I won – for the people – amounted to more than $7 billion against pharmaceutical companies for their unsafe and unfair tactics. President Biden and I will never stop fighting for the health, wellbeing, and financial stability of the American people.
Stay Connected
We'll be in touch with the latest information on how President Biden and his administration are working for the American people, as well as ways you can get involved and help our country build back better.
Opt in to send and receive text messages from President Biden.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Step 1: Start with a question. You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis, early in the writing process. As soon as you've decided on your essay topic, you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic.Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs your careful analysis of the evidence to understand how ...
How to write a thesis statement for compare-and-contrast essays. Thesis statements for compare-and-contrast essays are tricky because you have at least two topics to touch on instead of just one. The same general guidelines apply (decisive language, details, etc.), but you need to give equal attention to both your topics—otherwise, your essay will seem biased from the start.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following: Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences. Answer your project's main research question. Clearly state your position in relation to the topic. Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Working Thesis Statements. A strong thesis statement must have the following qualities: It must be arguable. A thesis statement must state a point of view or judgment about a topic. An established fact is not considered arguable. It must be supportable. The thesis statement must contain a point of view that can be supported with evidence ...
A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated. A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence. A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
A thesis statement is: The statement of the author's position on a topic or subject. Clear, concise, and goes beyond fact or observation to become an idea that needs to be supported (arguable). Often a statement of tension, where the author refutes or complicates an existing assumption or claim (counterargument).
The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper. 4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper. Thesis Statement Examples. Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
The thesis needs to be narrow. Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Make a claim. Provide the grounds (evidence) for the claim. Explain the warrant (how the grounds support the claim) Discuss possible rebuttals to the claim, identifying the limits of the argument and showing that you have considered alternative perspectives. The Toulmin model is a common approach in academic essays.
An argumentative thesis takes a position, asserting the writer's stance. Questions, vague statements, or quotations from others are not argumentative theses because they do not assert the writer's viewpoint. ... This is an argumentative thesis because it asserts a position that immigration enforcement law needs to be changed. Reasonable. An ...
A thesis statement is a one- to two-sentence statement that presents the main idea and makes an assertion about your issue. You may have a longer thesis for much longer essays, but one to two sentences is a good general guideline. And, remember, in an argumentative essay, the assertion you present in your thesis is going to be particularly ...
A thesis statement in an argumentative essay needs to present a point of view.The biggest mistake you can make is to provide a thesis statement that doesn't demonstrate what your argument will be. So, your thesis statement should set a clear argument, perspective, or position in relation to a debate. Check out the examples below.
Remember, the thesis statement is the driving force of organization in your essay, so each paragraph needs to have a specific purpose (topic sentence) in proving or explaining your thesis. Linking sentences complete this task within the body of each paragraph and create cohesion.
An academic argument asserts a claim and supports that claim with evidence. The goal of an argument is to convince readers that the writer's position is reasonable, valid, and worthy of consideration. Therefore, an argumentative thesis statement needs to be not only clear and focused, but also debatable, assertive, and reasoned. Additionally ...
Strong arguments are not based on gut instinct. An argument without data-backed premises is, by definition, baseless. Let's return to the above example: Demand exists in these target countries, and market competition is relatively low. To make these great premises, I need to add credible data points. For example:
You might think of an essay in terms of the critical moves of its argument: Your essay should advance a single argument, which is also often called a thesis. Your thesis should be focused-if you're analyzing a novel in a five-page paper, for example, you'll need to focus on perhaps just a single scene, character, or repeated detail. Your thesis should be supportable—it has to rely on ...
If your thesis statement doesn't make a claim or establish your position, you'll need to go back to the drawing board. Example Thesis Statements. Here are a couple of examples of thesis statements that aren't argumentative and thesis statements that are argumentative. The sky is blue.
SCOTT BOATWRIGHT, COO AND 7-YEAR CHIPOTLE VETERAN, NAMED INTERIM CEO. JACK HARTUNG TO REMAIN WITH COMPANY AS PRESIDENT, STRATEGY, FINANCE & SUPPLY CHAIN. NEWPORT BEACH, Calif., Aug. 13, 2024 /PRNewswire/ -- Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc. (NYSE: CMG) today announced that Brian Niccol, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, has accepted the role as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Starbucks ...
The New York Jets visit the Carolina Panthers for a Week 2 Preseason battle and three young players need to make a statement.
Scientists at Oxford University Physics Department have developed a revolutionary approach which could generate increasing amounts of solar electricity without the need for silicon-based solar panels. Instead, their innovation works by coating a new power-generating material onto the surfaces of everyday objects such as rucksacks, cars, and mobile phones.
These measures and others need to be taken urgently to contain and to repress this epidemic before it potentially becomes a global pandemic. Read more: At what point is a disease deemed to be a ...
Thesis Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs
Local and national humanitarian organizations are at the forefront of this response, showing tireless determination to help those in need. Alongside aid workers, host communities across Myanmar are providing crucial support to people in need. They are often the first responders in this crisis and a lifeline to affected people.
Every American should be able to access the health care they need no matter their income or wealth. That is why President Biden and I fought to lower the costs of health care with our Inflation ...
Harris unveils populist economic agenda Proposes ban for grocery price gouging Proposes $25,000 subsidy for first-time homebuyers Also wants to give a $6,000 tax credit for families of newborns