

Manufacturing Business Plan PDF Example
- May 7, 2024
- Business Plan

Creating a comprehensive business plan is crucial for launching and running a successful manufacturing business. This plan serves as your roadmap, detailing your vision, operational strategies, and financial plan. It helps establish your manufacturing business’s identity, navigate the competitive market, and secure funding for growth.
This article not only breaks down the critical components of a manufacturing business plan, but also provides an example of a business plan to help you craft your own.
Whether you’re an experienced entrepreneur or new to the manufacturing industry, this guide, complete with a business plan example, lays the groundwork for turning your manufacturing business concept into reality. Let’s dive in!
Our manufacturing business plan covers all essential aspects necessary for a comprehensive strategy. It details operations, marketing strategy , market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts.
- Executive Summary : Provides an overview of the manufacturing company’s business concept, market analysis , management, and financial strategy.
- Facilities & Equipment: Describes the facility’s capabilities, machinery, and technological advancements.
- Operations & Supply: Outlines the production processes, supply chain logistics, and inventory management.
- Key Stats: Offers data on industry size , growth trends, and market positioning.
- Key Trends: Highlights significant trends impacting the industry, such as automation and localization.
- Key Competitors : Analyzes primary competitors and differentiates the company from these rivals.
- SWOT: Analyzes strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Marketing Plan : Outlines tactics for attracting new contracts and maintaining client relationships.
- Timeline : Sets out key milestones from inception through the first year of operations.
- Management: Information on the management team and their roles within the company.
- Financial Plan: Projects the company’s financial performance over the next five years, detailing revenue, profits, and anticipated expenses.

Manufacturing Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Executive Summary
The Executive Summary introduces your manufacturing business plan, offering a concise overview of your manufacturing facility and its products. It should detail your market positioning, the range of products manufactured, the production process, its location, size, and an outline of day-to-day operations.
This section should also explore how your manufacturing business will integrate into the local and broader markets, including the number of direct competitors within the area, identifying who they are, along with your business’s unique selling points that differentiate it from these competitors.
Furthermore, you should include information about the management and co-founding team, detailing their roles and contributions to the business’s success. Additionally, a summary of your financial projections, including revenue and profits over the next five years, should be presented here to provide a clear picture of your business’s financial plan.
Make sure to cover here _ Business Overview _ Market Overview _ Management Team _ Financial Plan
Dive deeper into Executive Summary
Business Overview
Facilities & equipment.
Describe your manufacturing facility. Highlight its design, capacity, and technology. Mention the location, emphasizing accessibility to transport routes. Discuss advantages for efficiency and cost management. Detail essential equipment and its capabilities.
Operations & Supply Chain
Detail product range. Outline your operations strategy for efficiency and scalability. Discuss supply chain management. Highlight sourcing of materials, inventory control, and logistics. Emphasize strong partnerships with suppliers and distributors.
Make sure to cover here _ Facilities & Equipment _ Operations & Supplies

Market Overview
Industry size & growth.
Start by examining the size of the manufacturing industry relevant to your products and its growth potential. This analysis is crucial for understanding the market’s scope and identifying expansion opportunities.
Key Market Trends
Proceed to discuss recent market trends , such as the increasing demand for sustainable manufacturing processes, automation, and advanced materials. For example, highlight the demand for products that utilize eco-friendly materials or energy-efficient production techniques, alongside the rising popularity of smart manufacturing.
Key Competitors
Then, consider the competitive landscape, which includes a range of manufacturers from large-scale enterprises to niche firms. For example, emphasize what makes your business distinctive, whether it’s through advanced technology, superior product quality, or specialization in certain manufacturing niches. This section will help articulate the demand for your products, the competitive environment, and how your business is positioned to thrive within this dynamic market.
Make sure to cover here _ Industry size & growth _ Key competitors _ Key market trends

Dive deeper into Key competitors
First, conduct a SWOT analysis for your manufacturing business. Highlight Strengths such as advanced production technology and a skilled workforce. Address Weaknesses, including potential supply chain vulnerabilities or high production costs. Identify Opportunities like emerging markets for your products or potential for innovation in production processes. Consider Threats such as global competition or economic downturns that may impact demand for your products.
Marketing Plan
Next, develop a marketing strategy that outlines how to attract and retain customers through targeted advertising, trade shows, digital marketing, and strategic partnerships. Emphasize the importance of showcasing product quality and technological advantages to differentiate your business in the market.
Finally, create a detailed timeline that outlines critical milestones for your manufacturing business’s launch, marketing initiatives, customer acquisition, and expansion goals. Ensure the business progresses with clear direction and purpose, setting specific dates for achieving key operational and sales targets.
Make sure to cover here _ SWOT _ Marketing Plan _ Timeline

Dive deeper into SWOT
Dive deeper into Marketing Plan
The Management section focuses on the manufacturing business’s management and their direct roles in daily operations and strategic direction. This part is crucial for understanding who is responsible for making key decisions and driving the manufacturing business toward its financial and operational goals.
For your manufacturing business plan, list the core team members, their specific responsibilities, and how their expertise supports the business.

Financial Plan
The Financial Plan section is a comprehensive analysis of your financial projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability. It lays out your manufacturing business’s approach to securing funding, managing cash flow, and achieving breakeven.
This section typically includes detailed forecasts for the first 5 years of operation, highlighting expected revenue, operating costs and capital expenditures.
For your manufacturing business plan, provide a snapshot of your financial statement (profit and loss, balance sheet, cash flow statement), as well as your key assumptions (e.g. number of customers and prices, expenses, etc.).
Make sure to cover here _ Profit and Loss _ Cash Flow Statement _ Balance Sheet _ Use of Funds

Related Posts

Outdoor Sports Gear Store Business Plan PDF Example
- May 29, 2024

Shoe Store Business Plan PDF Example

Auto Parts Store Business Plan PDF Example
Privacy overview.
Manufacturing Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Manufacturing Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Manufacturing business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Manufacturing companies.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Manufacturing business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Perfect Snacks, located in Lincoln, Nebraska, is a food manufacturing company that specializes in the production of snack foods and packaged goods. We manufacture an extensive line of snack products, including trail mix, gummies, and chocolate. Our company focuses on quality and only uses the best natural ingredients in our products. We will primarily sell our products to grocery stores and other establishments that sell snacks, but will also sell bulk orders to individual customers through our website.
Perfect Snacks was founded by Joe Boseley. Joe has been working on the manufacturing company concept over the past few years and began networking with grocery store clients and locating the land to build his manufacturing and distribution center. As a line manager that oversaw dozens of employees, Joe has the proper knowledge and experience to own, manage, and operate his own manufacturing company.
Product Offering
Perfect Snacks will manufacture an extensive list of sweet, salty, and healthy snacks. Some of our initial products will include:
We will primarily sell our products to grocery stores, recreation centers, and other businesses that sell snacks in bulk. Consumers can find our products in stores or buy them in bulk on our website.
Customer Focus
Perfect Snacks will primarily serve the residents of Lincoln, Nebraska. The community has a large population of families and children, who are the primary consumers of snack foods. Therefore, we will market our products to recreational centers, schools, grocery stores, and other establishments that sell snacks to children and their parents.
Management Team
Perfect Snacks is owned by Joe Boseley, a local entrepreneur who has worked in various warehouses and manufacturing companies in Lincoln, Nebraska. Working in the manufacturing industry and in warehouses, Joe is very familiar with the processing and distribution of packaged foods. As a line manager that oversaw dozens of employees, Joe has the proper knowledge and experience to own, manage, and operate his own manufacturing company.
Joe will utilize his past experience with developing staff roles and functions. He is also very familiar with the manufacturing equipment and plans to purchase the latest technology that is efficient and cost effective. His contacts have allowed him to gain concrete Letters of Intent from local supermarket chains to have his manufactured goods in their stores.
Success Factors
Perfect Snacks will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Taste: Perfect Snacks’ snack products will be made with the highest quality ingredients and offer quality over quantity.
- Price: Perfect Snacks is able to offer the highest quality snacks at a competitive price point.
- Community Relations: Perfect Snacks will be a pillar in the community and be heavily involved in family-related activities in the area. It will sponsor events, provide snacks for schools and daycares at a discounted price, and donate a portion of its proceeds to area family-related charities and organizations.
- Proprietary Technology: Perfect Snacks will invest heavily on the latest technology to manufacture the snack foods for distribution. It will ensure the food products are made safely and free from any harmful chemicals and ingredients.
Financial Highlights
Perfect Snacks is seeking a total funding of $1,200,000 of debt capital to open its manufacturing company. The capital will be used for funding capital expenditures, salaries, marketing expenses, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Manufacturing facility design/build-out: $400,000
- Equipment and supplies: $375,000
- Initial inventory: $100,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $250,000
- Marketing costs: $50,000
- Working capital: $25,000
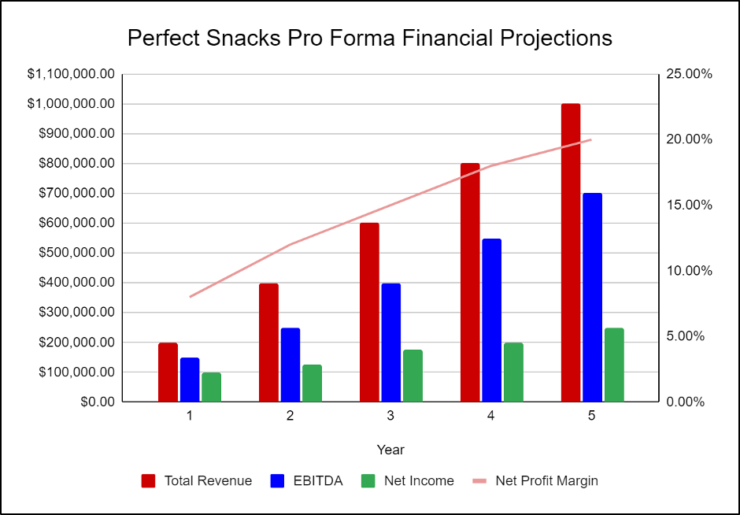
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Perfect Snacks.
Company Overview
Who is perfect snacks, perfect snacks history.
After conducting a market analysis, Joe Boseley began surveying the local vacant warehouse space and decided on a parcel of land to construct the warehouse and distribution center. Joe incorporated Perfect Snacks as a Limited Liability Corporation on January 1st, 2023.
Once the land is acquired for the warehouse space, construction can begin to build-out the manufacturing facility.
Since incorporation, the Company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located a vacant lot that would be ideal for a manufacturing facility
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Hired a general contractor and architect for the build-out of the warehouse, small office, and distribution area
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Determined beginning inventory
- Attained Letters of Intent from supermarket clients
- Began recruiting key employees
Perfect Snacks Services
Industry analysis.
The Manufacturing sector’s performance is largely attributable to the value of the US dollar, commodity prices, policy decisions and US manufacturing capacity. Food manufacturing has a history of success as it produces a basic human need. According to Grand View Research, the industry is currently valued at $121 billion and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate of 9.5% from now until 2030.
Commodity prices are currently stabilizing from coronavirus-induced volatility and renewed demand, both in the United States and global economies, which is anticipated to facilitate revenue expansion for manufacturers. Moreover, shifting technological change in the Manufacturing sector is anticipated to benefit large, developed economies, such as the United States. Therefore, now is a great time to start a new food manufacturing company in the U.S.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Perfect Snacks will serve the community residents of Lincoln, Nebraska and its surrounding areas. The community of Lincoln, Nebraska has thousands of households that have children. Statistics show that the main consumers of snack products are children of all ages. They are regularly placed in school lunchboxes, afterschool snacks and programs, and at weekend sporting events. Therefore, we will market to locations where snacks are bought by children or their parents, such as grocery stores, recreational centers, and schools.
The precise demographics Lincoln, Nebraska is as follows:
Customer Segmentation
Perfect Snacks will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Grocery stores and recreational centers
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Perfect Snacks will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Snacks N More
Snacks N More is another local manufacturing company that provides snack food to the immediate area. Established over thirty years ago, the company has the knowledge and expertise in food processing, commercialization, and packaging. They are known as a recognized ingredient supplier for the foodservice industry. Their portfolio of products include a variety of nuts, snacks, confections, and dry-blend ingredients. As a private label manufacturer, Snack’s More produces a full line of non-chocolate candy, nuts, and fruit-flavored snacks. The company is known for their fruit flavored snacks, dried raisins, nut mixes, and producing ingredients for local restaurants and establishments. Their line of nuts and dried fruits are often used for baking purposes.
Jaxon’s Candy
Jaxon’s Candy is a manufacturer of all things candy related. As a contract manufacturer, the company works with many companies to create their custom designed confections. Their large 50,000 square foot facility produces over 300,000 pounds of candy every month. All of the products are highly concentrated either in sugar or chocolate, or both. Jaxon’s Candy also designs and manufactures their own custom packaging. The candy produced is also kosher certified, gluten free, peanut free, and non-GMO.
Jaxon’s Candy currently manufactures candy for the following brands – Tommy Candy, Laffy Town, Chocowhoawhoa, Jellylicious, Healthee Candeee, and Sticky Teeth. Jaxon’s Candy can be found in grocery stores and convenient stores along the west coast of the United States.
Gimmy Candy
Gimmy Candy is located in the midwestern portion of the United States and boasts a facility of over 1 million square feet. Their fleet of transportation trucks distributes throughout the continental United States and is considered one of the largest candy manufacturers in the country. Their product portfolio includes assorted chocolates, gummy candy, hard candy, fruit candy, as well as gums and mints. Gimmy Candy was established in 1947 and has grown to be a model of manufacturing companies the industry uses as a model of sustainability and profitability. Their lineup of candy products can be found in every single grocery store and convenient store in the country. Gimmy Candy is considering expanding its distribution globally and start exporting its candy products to Asia, Canada, Europe, and South America. As one of the largest privately held companies in the United States, Gimmy Candy is also considered a top employer in the country and offers its employees a generous benefits package.
Competitive Advantage
Perfect Snacks will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Perfect Snacks will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Fresh and comforting taste
- Community family advocate
- Developed with proprietary technology
- Manufactured with fresh, quality ingredients
- Affordable price
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Perfect Snacks is as follows:
Social Media
Perfect Snacks will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media accounts. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
Perfect Snacks will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of the snack products. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Major Publications
We will also invest in advertising in selected larger publications until we have achieved significant brand awareness. Advertisements such as billboards and commercials will be shown during peak tv watching time and the billboards will be placed in highly trafficked areas.
Sponsorships
Perfect Snacks will also invest in sponsoring certain athletic and school events so that their banners and collateral material are displayed all over the event where numerous parents and children are at.
Perfect Snacks’s pricing will be moderate so consumers feel they receive great value when purchasing our snack products.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Perfect Snacks.
Operation Functions:
- Joe Boseley will be the CEO of Perfect Snacks. He will oversee the general operations and executive aspects of the business.
- Joe is joined by Candace Smith who will act as the warehouse manager. She will train and manage the staff as well as oversee general production of our products.
- Joe will hire an Administrative Assistant, Marketing Manager, and Accountant, to handle the administrative, marketing, and bookkeeping functions of the company.
- Joe will also hire several employees to manufacture our products and maintain the equipment and machinery.
Milestones:
Perfect Snacks will have the following milestones complete in the next six months.
- 02/202X Finalize lease agreement
- 03/202X Design and build out Perfect Snacks
- 04/202X Hire and train initial staff
- 05/202X Kickoff of promotional campaign
- 06/202X Launch Perfect Snacks
- 07/202X Reach break-even
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Perfect Snacks’s revenues will come primarily from its snack food sales. The company will sell the packaged snacks in local grocery stores, convenience stores, and other locations. As the company’s revenues increase, it will look to gain a wider distribution area.
The land purchase, equipment, supplies, opening inventory, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of Perfect Snacks. Other cost drivers include taxes, business insurance, and marketing expenditures.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Average order value: $250
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, manufacturing business plan faqs, what is a manufacturing business plan.
A manufacturing business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your manufacturing business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Manufacturing business plan using our Manufacturing Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Manufacturing Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of manufacturing businesses , some examples include: Garment manufacturing, Food product manufacturing, Diaper manufacturing, Tile manufacturing, and Toy manufacturing.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Manufacturing Business Plan?
Manufacturing businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Manufacturing Business?
Starting a manufacturing business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Manufacturing Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed manufacturing business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your manufacturing business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your manufacturing business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Manufacturing Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your manufacturing business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your manufacturing business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Manufacturing Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your manufacturing business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your manufacturing business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Getting started: A guide to creating a manufacturing business plan
What is a manufacturing business plan.

A manufacturing business plan is a formal document that outlines the goals and objectives of your business. It includes detailed information about your:
- Products or services
- Target market
- Marketing strategy
- Financial projections
- Operational details
The purpose of a business plan is to give you a roadmap to follow as you build and grow your business. It forces you to think through every aspect of your venture and identify potential problems or roadblocks before they happen.
Manufacturing business plans can also be used to attract investors or secure funding from lenders. If you are looking for outside financing, your business plan needs to be even more detailed and include information on your management team, financial history, and expected growth.
Ideally, you should update your business plan yearly to ensure that it remains relevant and accurate. As your business grows and changes, so too should your plan.
Why does a manufacturing company need a business plan?

No matter how simple or complex your ideas may be, you need a plan, or they will never become a reality. A business plan will clearly understand your costs, competition, and target market. It will also help you to set realistic goals and track your progress over time.
Let’s look at a manufacturing strategy example. You have a great idea that you think will revolutionize the automotive industry . Your new safety harness will be made from a lightweight, yet incredibly strong, material that cannot be cut or torn. You are confident that your product will be in high demand and generate a lot of revenue.
But before you walk into Ford or Toyota to try and get a purchase order , you need to have a plan. You must know:
- How much will it cost to produce your product
- How many units do you need to sell to break even
- Who is your target market is
- What is your competition selling
- How will you reach your target market
You also need to clearly understand the regulatory landscape and what it takes to bring a new product to market. All of this information (and more) should be included in your business plan.
This is not just a document that you create and forget about. It is a living, breathing tool that should be used to guide your actions as you build and grow your business.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Every manufacturing business plan will be different, but almost always, they will include the same five components:
Executive summary
Company description, products and services, market analysis.
- Financial plan
Let’s take a closer look.
The executive summary is the first section of your business plan, but it is typically written last. This is because it should be a concise overview of everything that follows, and you can only do that once you have completed the rest of your plan.
Include the following in your executive summary:
- The problem that your product or service solves
- Your target market
- Your unique selling proposition (what makes you different from your competitors?)
- Your manufacturing business model (how will you make money?)
- Your sales and marketing strategy
- A brief overview of your financial projections
Someone should be able to quickly scan through your executive summary and have a pretty good understanding of what your business is and how it plans to be successful.
This is where you can get a bit more creative, explaining your company’s history, mission, and values. You will also include information on your team or management structure.
It can be simple but should inspire faith in your ability to execute your business plan.
You will need to provide a detailed description of your product or service, as well as any unique features or benefits that it offers. You should also include information on your manufacturing process and quality control procedures.
If you have any patents or proprietary technology, they should be listed here as significant assets for your business.
For example, let’s say you are planning on creating a brand-new line of disposable coffee cups. The dimensions, materials, and other specifications would be listed here, along with any unique benefits (such as being made from recycled materials).
You might also include information on your manufacturing process, such as the fact that the cups will be produced in a certified clean room or that you will employ workers local to where the product is sold.
Chances are, you started down this path because you realized that there was a market opportunity for your product or service. In this section, you will need to provide detailed information on the opening, as well as the analysis that convinced you to pursue it.
This should include:
- Market size (current and projected)
- Key market segments
- Customer needs and wants
- Competitive landscape
This is where you will need to do your homework, as you will be justifying your business decision to enter this particular market. The more data and analysis you can provide, the better.
For our coffee cup example, the market analysis might include:
- Information on how many cups are used every day
- Projected growth
- Key segments (such as office workers or on-the-go consumers)
- Customer needs (such as convenience or sustainability)
It would also examine the competitive landscape, including both direct and indirect competitors.
Financial plan
You’re in this to make money, and so are your potential investors. In this section, you will need to provide detailed information on your manufacturing business model and how it will generate revenue. This should include:
- Initial investment
- Sales forecast
- Carrying costs
- Pricing strategy
- Expense budget
You will also need to provide information on your long-term financial goals, such as profitability or break-even point. Discuss production line details, inventory management strategies , and other factors impacting your bottom line.
How to write a business plan for a manufacturing company

The process of creating a business plan for a manufacturing company is similar to any other type of business. However, there are some key considerations to keep in mind.
First, you need to understand your industry and what it will take to be successful in it. This includes understanding the competitive landscape, the costs of goods sold , and the margins you can expect to achieve.
You also need to have a clear understanding of your target market and what needs or wants your product or service will address. This market analysis should include information on your target customer’s demographics, psychographics, and buying habits.
While there will be many things specific to your company, here are five questions to answer for each of the sections listed above.
Executive summary:
- What is the problem that your company will solve?
- How will your company solve that problem?
- Who are your target customers?
- What are your key competitive advantages?
- What is your business model?
Company description:
- What is the legal structure of your company?
- What are your company’s core values?
- What is your company’s history?
- Who are the key members of your management team?
- Where is your manufacturing facility located?
Products and services:
- What product or service does your company offer?
- How does your product or service solve the problem that your target market has?
- What are the key features and benefits of your product or service?
- How is your product or service unique from your competitors?
- What is the production process for your product or service?
Market analysis:
- Who is your target market?
- What needs or wants does your target market have that your product or service will address?
- What is the size of your target market?
- How do you expect the needs of your target market to change in the future?
- Who are your key competitors, and how do they serve the needs of your target market?
Financial plan:
- What are the start-up costs for your company?
- How will you finance your start-up costs?
- What are your monthly operating expenses?
- What is your sales forecast for the first year, and how does that compare to your industry’s average sales growth rate?
- What are your gross margin and profit targets?
Even if you do nothing but answer these questions, you’ll be well on your way to creating a thorough manufacturing business plan.
How to stabilize your growth
When getting started, managing your business with spreadsheets might be okay. But, once sales and manufacturing orders start to increase, the inefficiencies of manually managing your business come to light. That’s why many turn to automation to keep their manufacturing on track.
Common mistakes to avoid
However, new manufacturing entrepreneurs often fall into a handful of traps when creating their business plans.
- Not doing enough research – You can’t know everything about your industry, but you should do your best to understand as much as you can before writing your business plan. This means talking to experts, reading trade publications, and studying the competition
- Not being realistic – It’s important to be optimistic when starting a new business, but you also need to be realistic. This is especially true when it comes to financial projections. Don’t overestimate the amount of revenue you will generate or underestimate the costs of goods sold
- Not having a clear understanding of your target market – You need to know who you are selling to and what needs or wants your product or service will address. This market analysis should include information on your target customer’s demographics, psychographics, and buying habits
- Failing to understand your competition – You need to know who your competitors are, what they are offering, and how you can differentiate yourself. This information will be critical in developing your marketing strategy
- Not having a clear vision for the future – Your manufacturing business plan should include a section on your long-term goals and objectives. What does your company hope to achieve in the next five years? Ten years? Twenty years?
Creating a business plan for manufacturing can be simple. It can be quite simple if you break it down into smaller pieces.
Once you have it in place, staying on track can be quite a bit more difficult. By using ERP software like Katana , you can track all of your key metrics in real time, avoid any potential issues, and make course corrections as needed.
To start following your plan and creating a successful manufacturing company, get a Katana demo today.
Table of contents
Manufacturing guide.
1. What is manufacturing
1. 1. Production vs. manufacturing
1.2. Production scheduling software
1.3. Production tracking software
2. How to start a manufacturing business
2.1.How to manufacture a product
2.2. Manufacturing best practice
2.3. A guide to creating a manufacturing business plan
2.4. Manufacturer ecommerce
2.5. Marketing for manufacturers
2.6. Manufacturing business processes
2.7. Food manufacturing
2.8. Small business manufacturing software
3. Manufacturing processes
3.1. Job shop manufacturing
3.2. Production quality control checklist
4. Lean manufacturing principles
4.1. Just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing
4.2. Tips to reduce manufacturing waste
4.3. Manufacturing KPIs
5. Light manufacturing
6. Advanced manufacturing
7. IoT in manufacturing
8. Manufacturing challenges
9. Total manufacturing cost
9.1. Manufacturing overhead formula
9.2. Manufacturing inventory software
10. Good manufacturing practices
11. MRP systems
11.1. MRP in supply chain management
11.2. Best MRP software
12. Manufacturing ERP systems
12.1. Best ERP software for manufacturing
12.2. Manufacturing execution systems (MES)
More guides from Katana

Get visibility over your sales and stock
Wave goodbye to uncertainty by using Katana Cloud Inventory for total inventory control

Manufacturing Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Manufacturing Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 7,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their manufacturing businesses. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a manufacturing business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Manufacturing Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your manufacturing business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Manufacturing Company
If you’re looking to start a new manufacturing business, or grow your existing manufacturing business, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your manufacturing business in order to improve your chances of success. Your business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Manufacturing Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a manufacturing business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans and angel investors. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business.
Personal savings is the other most common form of funding for a manufacturing business. Venture capitalists will usually not fund a manufacturing business. They might consider funding a manufacturing business with a national presence, but never an individual location. This is because most venture capitalists are looking for millions of dollars in return when they make an investment, and an individual location could never achieve such results. With that said, personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for manufacturing businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a manufacturing company.
If you want to start a manufacturing business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below we detail what you should include in each section of your own business plan:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of manufacturing business you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a manufacturing business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of manufacturing businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the manufacturing industry. Discuss the type of manufacturing business you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target market. Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of business you are operating.
There are many types of manufacturing businesses, such as:
- Clothing manufacturing
- Garment manufacturing
- Food product manufacturing
- Diaper manufacturing
- Tile manufacturing
- Toy manufacturing
- Soap and detergent manufacturing
- Mobile accessories manufacturing
- Mattress manufacturing
- Bicycle manufacturing
- Pillow manufacturing
- Brick manufacturing
- Toilet paper manufacturing
- Furniture manufacturing
- Peanut butter manufacturing
- Cosmetics manufacturing
- Footwear manufacturing
In addition to explaining the type of manufacturing business you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of customers served, number of positive reviews, number of wholesale contracts, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the manufacturing industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the manufacturing industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section:
- How big is the manufacturing industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your manufacturing business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of target market segments: wholesalers, other manufacturers, exports, retailers.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of manufacturing business you operate. Clearly, retailers would respond to different marketing promotions than export markets, for example.
Try to break out your target market in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most manufacturing businesses primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Manufacturing Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other manufacturing businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes manufacturers in other niches, as well as those vertically integrated businesses that make their own product. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other manufacturing businesses with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be house flippers located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of products do they manufacture?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide high quality manufacturing practices?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a manufacturing business, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of manufacturing company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to manufacturing, will you provide R&D, design, prototyping or any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your manufacturing company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your manufacturing business located near a distribution hub, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your manufacturing business, including sourcing inputs, designing processes, managing production, coordinating logistics and meeting with potential buyers.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to secure your 1,000 th contract, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your manufacturing business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your manufacturing business’ ability to succeed, a strong team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing manufacturing businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in manufacturing or successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you offer short-run production, or will you focus strictly on long-run? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your manufacturing business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a manufacturing business:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of equipment and supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your production facility blueprint, or capabilities specifications.
Putting together a business plan for your manufacturing business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will really understand the manufacturing industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful manufacturing business.
Manufacturing Business Plan FAQs
What is the easiest way to complete my manufacturing business plan.
Growthink's Ultimate Business Plan Template allows you to quickly and easily complete your Manufacturing Business Plan.
What is the Goal of a Business Plan's Executive Summary?
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of manufacturing business you are operating and the status; for example, are you a startup, do you have a manufacturing business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of manufacturing businesses?
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Manufacturing business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook
Starting a manufacturing business is an exciting endeavor, but it can be daunting to know where to start. Fortunately, the #1 Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook provides entrepreneurs and businesses with a detailed roadmap for success. With this template and guidebook, you will have the guidance you need to plan for success and develop a comprehensive business plan that outlines your vision and strategy.

Get worry-free services and support to launch your business starting at $0 plus state fees.
- How to Start a Profitable Manufacturing Business [11 Steps]
- 10+ Best & Profitable Manufacturing Business Ideas [2023]
- 25 Catchy Manufacturing Business Names:
- List of the Best Marketing Ideas For Your Manufacturing Business:
How to Write a Manufacturing Business Plan in 7 Steps:
1. describe the purpose of your manufacturing business..
The first step to writing your business plan is to describe the purpose of your manufacturing business. This includes describing why you are starting this type of business, and what problems it will solve for customers. This is a quick way to get your mind thinking about the customers’ problems. It also helps you identify what makes your business different from others in its industry.
It also helps to include a vision statement so that readers can understand what type of company you want to build.
Here is an example of a purpose mission statement for a manufacturing business:
Our mission at [Company Name] is to be the premier provider of innovative, high-quality manufacturing solutions that meet our customers' needs, while delivering superior customer service and providing a safe and rewarding workplace for our employees.

2. Products & Services Offered by Your Manufacturing Business.
The next step is to outline your products and services for your manufacturing business.
When you think about the products and services that you offer, it's helpful to ask yourself the following questions:
- What is my business?
- What are the products and/or services that I offer?
- Why am I offering these particular products and/or services?
- How do I differentiate myself from competitors with similar offerings?
- How will I market my products and services?
You may want to do a comparison of your business plan against those of other competitors in the area, or even with online reviews. This way, you can find out what people like about them and what they don’t like, so that you can either improve upon their offerings or avoid doing so altogether.

3. Build a Creative Marketing Stratgey.
If you don't have a marketing plan for your manufacturing business, it's time to write one. Your marketing plan should be part of your business plan and be a roadmap to your goals.
A good marketing plan for your manufacturing business includes the following elements:
Target market
- Who is your target market?
- What do these customers have in common?
- How many of them are there?
- How can you best reach them with your message or product?
Customer base
- Who are your current customers?
- Where did they come from (i.e., referrals)?
- How can their experience with your manufacturing business help make them repeat customers, consumers, visitors, subscribers, or advocates for other people in their network or industry who might also benefit from using this service, product, or brand?
Product or service description
- How does it work, what features does it have, and what are its benefits?
- Can anyone use this product or service regardless of age or gender?
- Can anyone visually see themselves using this product or service?
- How will they feel when they do so? If so, how long will the feeling last after purchasing (or trying) the product/service for the first time?
Competitive analysis
- Which companies are competing with yours today (and why)?
- Which ones may enter into competition with yours tomorrow if they find out about it now through word-of-mouth advertising; social media networks; friends' recommendations; etc.)
- What specific advantages does each competitor offer over yours currently?
Marketing channels
- Which marketing channel do you intend to leverage to attract new customers?
- What is your estimated marketing budget needed?
- What is the projected cost to acquire a new customer?
- How many of your customers do you instead will return?
Form an LLC in your state!

4. Write Your Operational Plan.
Next, you'll need to build your operational plan. This section describes the type of business you'll be running, and includes the steps involved in your operations.
In it, you should list:
- The equipment and facilities needed
- Who will be involved in the business (employees, contractors)
- Financial requirements for each step
- Milestones & KPIs
- Location of your business
- Zoning & permits required for the business
What equipment, supplies, or permits are needed to run a manufacturing business?
- Manufacturing equipment
- Raw materials
- Safety equipment and supplies
- Labor and skilled workers
- Legal permits and licensing as required by local ordinance
5. Management & Organization of Your Manufacturing Business.
The second part of your manufacturing business plan is to develop a management and organization section.
This section will cover all of the following:
- How many employees you need in order to run your manufacturing business. This should include the roles they will play (for example, one person may be responsible for managing administrative duties while another might be in charge of customer service).
- The structure of your management team. The higher-ups like yourself should be able to delegate tasks through lower-level managers who are directly responsible for their given department (inventory and sales, etc.).
- How you’re going to make sure that everyone on board is doing their job well. You’ll want check-ins with employees regularly so they have time to ask questions or voice concerns if needed; this also gives you time to offer support where necessary while staying informed on how things are going within individual departments too!
6. Manufacturing Business Startup Expenses & Captial Needed.
This section should be broken down by month and year. If you are still in the planning stage of your business, it may be helpful to estimate how much money will be needed each month until you reach profitability.
Typically, expenses for your business can be broken into a few basic categories:
Startup Costs
Startup costs are typically the first expenses you will incur when beginning an enterprise. These include legal fees, accounting expenses, and other costs associated with getting your business off the ground. The amount of money needed to start a manufacturing business varies based on many different variables, but below are a few different types of startup costs for a manufacturing business.
Running & Operating Costs
Running costs refer to ongoing expenses related directly with operating your business over time like electricity bills or salaries paid out each month. These types of expenses will vary greatly depending on multiple variables such as location, team size, utility costs, etc.
Marketing & Sales Expenses
You should include any costs associated with marketing and sales, such as advertising and promotions, website design or maintenance. Also, consider any additional expenses that may be incurred if you decide to launch a new product or service line. For example, if your manufacturing business has an existing website that needs an upgrade in order to sell more products or services, then this should be listed here.
7. Financial Plan & Projections
A financial plan is an important part of any business plan, as it outlines how the business will generate revenue and profit, and how it will use that profit to grow and sustain itself. To devise a financial plan for your manufacturing business, you will need to consider a number of factors, including your start-up costs, operating costs, projected revenue, and expenses.
Here are some steps you can follow to devise a financial plan for your manufacturing business plan:
- Determine your start-up costs: This will include the cost of purchasing or leasing the space where you will operate your business, as well as the cost of buying or leasing any equipment or supplies that you need to start the business.
- Estimate your operating costs: Operating costs will include utilities, such as electricity, gas, and water, as well as labor costs for employees, if any, and the cost of purchasing any materials or supplies that you will need to run your business.
- Project your revenue: To project your revenue, you will need to consider the number of customers you expect to have and the average amount they will spend on each visit. You can use this information to estimate how much money you will make from selling your products or services.
- Estimate your expenses: In addition to your operating costs, you will need to consider other expenses, such as insurance, marketing, and maintenance. You will also need to set aside money for taxes and other fees.
- Create a budget: Once you have estimated your start-up costs, operating costs, revenue, and expenses, you can use this information to create a budget for your business. This will help you to see how much money you will need to start the business, and how much profit you can expect to make.
- Develop a plan for using your profit: Finally, you will need to decide how you will use your profit to grow and sustain your business. This might include investing in new equipment, expanding the business, or saving for a rainy day.
Frequently Asked Questions About Manufacturing Business Plans:
Why do you need a business plan for a manufacturing business.
A business plan for a manufacturing business is essential because it serves as a guide to help the business plan its activities and reach its desired goals. It provides important information such as market analysis, strategy, financial projections, and operational plans. Additionally, it can serve as an important tool to attract potential investors or lenders and help secure funding.
Who should you ask for help with your manufacturing business plan?
You should consult a qualified business consultant, accountant, and/or lawyer who specialise in assisting companies with their manufacturing business plans. Additionally, it is a good idea to reach out to trade organisations, industry bodies, and experts in the manufacturing sector for guidance.
Can you write a manufacturing business plan yourself?
Yes, you can write a manufacturing business plan yourself. Depending on the complexity of your plan, you may want to research best practices and consult experts in the field if necessary. When writing a manufacturing business plan, it is important to include a market analysis, competitive analysis, operations plan, financial projections, and strategic plan. Additionally, you should also include key objectives, milestones and management strategies.
Related Business Plans

Home Inventory Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Inspection Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Home Decor Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Health And Wellness Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hauling Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hardware Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handyman Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Hair Extension Business Plan Template & Guidebook

Handbag Business Plan Template & Guidebook
I'm Nick, co-founder of newfoundr.com, dedicated to helping aspiring entrepreneurs succeed. As a small business owner with over five years of experience, I have garnered valuable knowledge and insights across a diverse range of industries. My passion for entrepreneurship drives me to share my expertise with aspiring entrepreneurs, empowering them to turn their business dreams into reality.
Through meticulous research and firsthand experience, I uncover the essential steps, software, tools, and costs associated with launching and maintaining a successful business. By demystifying the complexities of entrepreneurship, I provide the guidance and support needed for others to embark on their journey with confidence.
From assessing market viability and formulating business plans to selecting the right technology and navigating the financial landscape, I am dedicated to helping fellow entrepreneurs overcome challenges and unlock their full potential. As a steadfast advocate for small business success, my mission is to pave the way for a new generation of innovative and driven entrepreneurs who are ready to make their mark on the world.

Manufacturing Business Plan Template

What is a Manufacturing Business Plan?
A manufacturing business plan outlines the objectives, initiatives, and goals of a manufacturing business. It is used to guide the development and execution of a business strategy and to monitor progress towards achieving desired goals. The plan should address all aspects of the business, including marketing, production, personnel, operations, and financials.
What's included in this Manufacturing Business Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Manufacturing Business Plan template for?
This Manufacturing Business Plan template is designed to help manufacturers of all sizes and industries create a plan to launch, run and grow their business. It provides a framework to clearly define and measure the objectives, actions, and measurements that are necessary for success.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is an area of your business that requires extra attention in order to achieve success. Examples of focus areas can include increasing operational efficiency, improving product quality, or strengthening financial management.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
An objective is a goal that you want to achieve within a specific focus area. For example, under the focus area of operational efficiency, the objective could be to reduce shipping wait time.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
KPIs, or key performance indicators, are metrics that help to measure the success of the objectives. For example, to measure the success of the objective to reduce shipping wait time, the KPI would be to decrease the average shipping wait time by 30%.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects, or actions, are the steps necessary to achieve the KPIs. For example, to achieve the KPI of reducing the average shipping wait time, the action would be to analyze the current shipping process.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
Cascade is a strategy execution platform that makes it easy to plan, implement, and track progress towards achieving your manufacturing business plan. With Cascade, you can create strategies, assign tasks, track progress, and quickly see the results of your efforts.

Manufacturing Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
Manufacturing Business Plan Template
If you want to start a Manufacturing business or expand your current Manufacturing company, you need a business plan.
The following Manufacturing business plan template gives you the key elements to include in a winning Manufacturing business plan.
You can download our business plan template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Below are links to each of the key sections of a sample manufacturing business plan. Once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors.
I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan
Comments are closed.
Manufacturing Business Plan Home I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan

Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a manufacturing company can be an exciting but challenging endeavor. To ensure success, you need a solid business plan that covers all the essential aspects of your operations. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Companies comes in!
Our template provides a comprehensive framework for outlining your company's goals, conducting market analysis, projecting finances, and strategizing your operations. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be able to:
- Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and objectives
- Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand your target audience and competitors
- Develop financial projections and budgets to secure funding and attract investors
- Create operational strategies to optimize production, logistics, and quality control
Whether you're a seasoned entrepreneur or just starting out, our Business Plan Template will guide you through the process of building a successful manufacturing company. Don't miss out on the opportunity to turn your vision into reality—get started with ClickUp today!
Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company Benefits
Creating a solid business plan is crucial for success in the manufacturing industry. By using the Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company, you can:
- Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and goals
- Conduct a thorough market analysis to identify target customers and competitors
- Develop a comprehensive financial plan, including revenue projections and cost analysis
- Outline your manufacturing processes, supply chain management, and quality control measures
- Present a professional and well-structured document to potential investors and lenders
- Guide strategic decision-making and ensure alignment with your long-term objectives
- Monitor and track progress towards your business milestones and objectives
Main Elements of Manufacturing Company Business Plan Template
When it comes to creating a comprehensive business plan for your manufacturing company, ClickUp has you covered with its Business Plan Template. Here are the main elements you'll find in this template:
- Custom Statuses: Keep track of the progress of different sections of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Add important details to your business plan using custom fields such as Reference, Approved, and Section, allowing you to easily organize and categorize information.
- Custom Views: Access different perspectives of your business plan using views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide, making it easy to navigate and present your plan effectively.
- Document Collaboration: Collaborate with your team in real-time using ClickUp's Docs feature to work together on your business plan.
- Task Management: Break down your business plan into actionable tasks, assign them to team members, set due dates, and track progress using ClickUp's powerful task management features.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
If you're looking to create a business plan for your manufacturing company, follow these 6 steps using ClickUp's Business Plan Template:
1. Define your company's mission and vision
Start by clearly defining the mission and vision of your manufacturing company. What do you aim to achieve and how do you plan to do it? This will serve as the guiding principles for your business plan.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to outline your company's mission and vision statements.
2. Conduct market research
Thorough market research is essential to understand your target audience, competitors, and industry trends. Identify your niche, analyze customer needs, and assess the competitive landscape. This will help you position your manufacturing company effectively.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to compile and analyze market data, including customer demographics, competitor analysis, and industry trends.
3. Develop your product offerings
Outline the products and services your manufacturing company will offer. Determine the unique selling points of your offerings and how they address customer needs. Consider factors such as pricing, quality, and delivery timelines.
Use tasks in ClickUp to create a product development plan and assign tasks to team members responsible for designing, manufacturing, and testing the products.
4. Create a marketing and sales strategy
Define your marketing and sales strategies to promote your manufacturing company. Identify the channels and tactics you will use to reach your target audience. This may include digital marketing, trade shows, partnerships, or direct sales.
Use Goals in ClickUp to set specific marketing and sales objectives, such as lead generation targets or revenue goals.
5. Establish operational processes
Develop a plan for your manufacturing processes, including procurement, production, quality control, and logistics. Define the roles and responsibilities of your team members and ensure smooth coordination across departments.
Use Automations in ClickUp to streamline your operational processes by automating repetitive tasks and setting up notifications for key milestones.
6. Create financial projections
Project your financials, including revenue, expenses, and cash flow projections for the next few years. Consider factors such as production costs, pricing, sales volume, and market demand. This will help you assess the viability and profitability of your manufacturing company.
Use Dashboards in ClickUp to track and visualize your financial projections, allowing you to monitor your company's performance and make informed decisions.
By following these steps and utilizing ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be well-equipped to create a comprehensive and effective business plan for your manufacturing company.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company
Entrepreneurs and business owners in the manufacturing industry can use the Business Plan Template for Manufacturing Company to create a comprehensive plan for their business.
First, hit "Add Template" to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you'd like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a solid business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize the different sections of your business plan, such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Financial Projections, and Operational Strategies.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and visualize the timeline for completing each section of your business plan.
- Use the Business Plan View to have a comprehensive overview of your entire plan, with all the sections and details in one place.
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide you with step-by-step instructions and tips on how to effectively use the template and create a successful business plan.
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to provide additional information and track important details.
- Update statuses and custom fields as you make progress and receive feedback from stakeholders.
- Monitor and analyze your business plan to ensure it aligns with your goals and attracts investors.
- Business Plan Template for Distance Learning
- Business Plan Template for Medication Errors
- Business Plan Template for Little Caesars
- Business Plan Template for Technology
- Business Plan Template for Gym Owners
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide
Check out everything that is new in the latest version of Visual Components!
December 28, 2021
How to Plan & Design a Manufacturing Plant Layout? (Video Examples Included)
Our experts at Visual Components discuss how to plan and design a manufacturing plant layout with a simulation case. We review the benefits, process, and necessity for a high-quality plant layout in your business organization.
Discover the essentials of factory layout design using advanced simulation and CAD technology. This approach aims to optimize space and efficiency, catering to each factory’s unique needs. Learn about creating lean layouts that streamline production and enhance workflow. Gain insights into how strategic planning can lead to cost savings and increased productivity. Explore the steps from concept to execution, including real-world examples, demonstrating the benefits of effective layout planning for manufacturing success.
Share this article
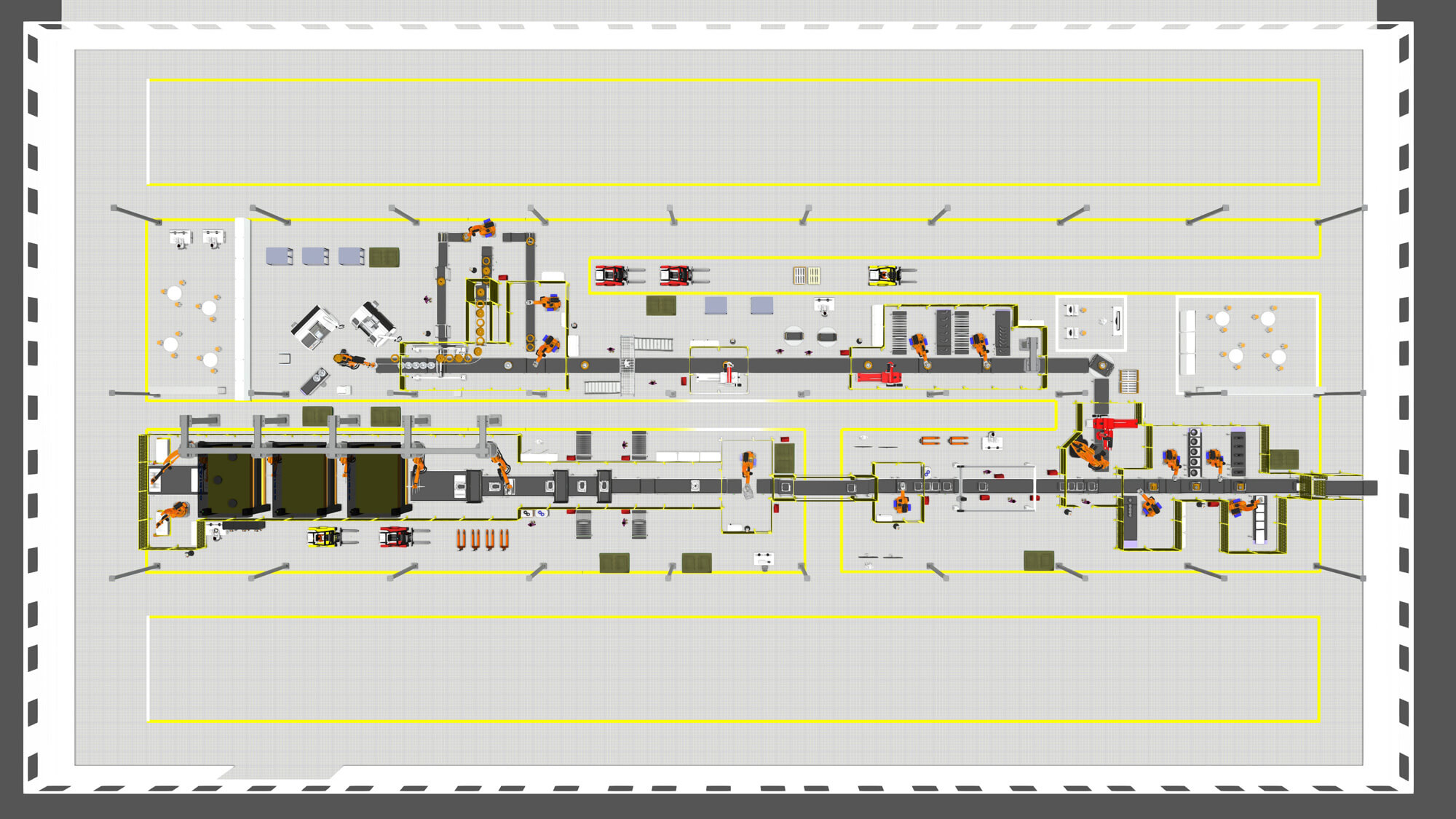
When it comes to running a manufacturing facility, there are a lot of things to consider. As an owner or manager, you’re probably looking for ways to speed up your process, improve your yield, and increase your profit. Did you know that a simple plant layout can achieve all three of these goals?
Layouts are often overlooked, despite their huge money-saving potential.
In this piece, we’ll discuss what is meant by a plant layout, some benefits of a layout, an example, and our step-by-step process for laying out a plant.
These are the topics we’ll cover. You can also jump to the part that interests you the most 🏃🏻
- What is meant by a plant layout?
- What is a lean plant layout?
- What are the characteristics of a good plant layout?
- Plant layout design benefits
Plant layout example
- Step-by-step plant layout design process
- Case: tire assembly and warehousing layout
Let’s go!
What is meant by a plant layout?
The plant layout definition is simple: it’s a way to draw your facility’s building, equipment, and major components on paper. It’s typically done through 2D CAD (2-dimensional Computer-Aided Drafting and Design) software.
The designer will use real-world dimensions of your equipment and facility and layout a scaled model of your plant. Without using real dimensions, the final layout won’t be as helpful for your plant.
In a lot of cases, the designer will submit a final layout that allows the viewer to fly through the building, seeing the equipment in motion and observing how the process looks. Since everything is a scale model, the viewer can find out how much distance there is between equipment, for walkways, and so on.
Since it’s all done on paper, this can be done before getting equipment or before having a warehouse. It also allows the designer to change the layout as much as they’d like.
The layout includes a lot of different features:
- How product moves through your building
- Equipment
- Building floorplan
- Dimensional distances between everything
- Visualization of your process
What is a lean plant layout?
If you take the concept one step further, you can start optimizing everything. In a lean plant layout, the designer will start incorporating lean principles into the floorplan.
A big principle in lean layouts is adding sections for different operations. If your process has multiple steps, like cutting, organizing, and packing your product, then it will be broken into different physical areas.
Cutting will be done in one zone, organizing in another, and packing in a third. This also groups together the required machinery and personnel to expedite the process.
Why does this work? Material and people travel shorter distances, the layout is more compact, and everything is streamlined.
There are a lot of other concepts that go into lean principles (a lean layout). For the sake of brevity, we’ll leave it there.
What are the characteristics of a good plant layout?
Knowing whether a plant layout is good or not really depends on your operations and needs. In general, there are a few characteristics to look for:
- Effectively uses the space . One of the limiting factors in your operation is how much space you have. You can’t just invent new space, so you have to get creative with the space you have. A good plant layout effectively uses every square inch of operation space.
- Accessible design . At the end of the day, there should be enough space between items for the full floorplan to be accessible. This means that material handlers need enough space for themselves as well as the product they’re carrying around the building.
- Flexibility for future growth . Make sure that the floorplan isn’t going to constrict your operation. A lot of manufacturing plants benefit by adding a potential for 20-40% growth. This doesn’t mean that you have to predict exactly how much you’ll grow in a decade, just design with future growth in mind.
- Has your operation in mind . You need a layout that works for your individual operation. There are very few cookie-cutter solutions that fit the needs of your business — your layout is the same way. A good plant layout is specialized to what your business needs.
If you want to oversimplify this idea, a good plant layout is one that achieves the goals of your operation while optimizing every possible parameter.
Plant layout design benefits
Why do people spend so much time putting together a plant layout? There are a number of benefits. Let’s quickly review some of the top reasons why people opt for a plant layout in their business organization.
Reduce cycle time
Cycle time is a term that quantifies how long it takes a business to make a product. It’s the combination of every process step that’s required to make your end product.
With a good plant layout, everything is set up with the operation in mind. As a result, businesses will see a reduced cycle time.
Increase Operational Speed
On top of an overall speed increase, you’ll find speed increases in every step of the process. This goes back to the idea of splitting your operation into different zones.
Rather than an operator walking across your warehouse to perform a task, everything will be centralized. Think of it as storing the knives next to the cutting board in your kitchen.
Maximize Your Square Footage
Depending on where you’re located, the price of your land could be your biggest expense. Due to that fact, most people want to maximize their square footage.
With a manufacturing plant layout, you have the ability to move equipment around on paper in order to maximize your square footage.
The designer can do things like relocating, rotating, and reorienting equipment to see which option makes the most sense for your facility. Clearly, this is a lot faster and less expensive than physically changing around equipment and testing the new layout.
Visualize and Tweak Your Operational Process
Once things are laid out, it might help you to see a potential shortcut in your operation. Maybe you can save time and money by moving one step of your process to another part of the cycle.
This is highly dependent on your operation, but we’ve seen it happen in the past: a company thinks their operation is optimized until they do a plant layout and notice some shortcomings.
Maximize Profits
When you combine all of these factors, you’re left with one big benefit: maximized profits. This is the major reason why a lot of businesses opt for putting together a plant layout.
You save time, space, and create more products each year. That should sound like millions of dollar signs annually.
To help illustrate this idea, let’s look at an example. Our team at Visual Components lead the design for a company called Midea.
Here’s a case study of one of our previous clients, Midea . They’re the world’s largest producer of major appliances. Before adding a new, high-end production line, they decided to get a plant layout.
Our simulation looked at the real-world size and operational speed of their different machines. We worked closely with their team to understand how the process works, what the limiting factors were, and what kind of flow their operation had.
This video cannot be displayed unless all necessary Cookies are accepted. Youtube uses three cookies that are VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE, CONSENT, YSC and they all live in targeting cookies category Accept all Cookie settings
After we produced some rounds of layouts, we arrived at, what both parties deemed to be, the best possible arrangement. We saved their operation a lot:
- Floor space used was reduced by 10%
- Production capacity increased 10%
- Reduced product defects by 10x
- Construction schedule expedited 20%
- Total project cost savings: $879,000, roughly 15%
- Long-term labor cost reduction, operational efficiency increase, and projected profit increase
This project for Midea shows the importance of lean plant layouts. We foresee an increase in their profits year over year — this isn’t just a short-term, upfront cost saving. The future of their operation will benefit thanks to an initial plant layout.
Step-by-step plant layout design process with a case example
Curious about what the plant layout design process looks like? Here’s a step-by-step process that we typically follow for our clients. Here’s our workflow for planning and building a plant layout:
1. Understanding clients’ needs
It all starts with understanding our clients’ needs. Before a plant layout can be generated, some information about the operation needs to be explored.
This entails a few conversations going over some basics like floor space, equipment, flow, and more.
For example, our customer Firac received a clear request from their client — to automate a manual screw tightening process. Read the whole story.
2. Planning manufacturing system design
Now it’s time to start drafting. Different companies will opt for different manufacturing programs in this step.
Some companies will only provide a 2D layout with no motion included. Others will use a 3D layout that shows how the equipment will move and how the product goes through the cycle.
At Visual Components, we typically use a 2D layout for the building and add a static 3D layout on top. This overlay ensures dimensional accuracy which is paramount in making a plant layout.
3. Equipment selection
Now it’s time to select and add equipment. This will go right into our static 3D layout, so it can be changed later.
Things like the overall size, motion constraints, and equipment parameters will be inputted during this step. This is done to ensure the model is precise and accurate.
As you probably noticed from our Midea case study, the equipment physically moves and operates in our model. During this step, we’re making sure our clients get the best visual of their potential layout.
To help our clients save time on equipment selection, we offer ready-made components. Visual Components eCatalog has a library of virtual models of robots, machines, and equipment from dozens of leading brands in industrial automation. We have over 1,500 pre-defined and ready-to-use components, to be exact.
4. Layout design
Once the equipment is selected, the designer can start moving around components. This is part of the optimization process where items are moved around until they’re in the perfect place.
Since the equipment and building are already drawn on the computer, this step is more of a “drag and drop” process. On the computer, the designer will move around equipment, change its orientation, and find the best place for the physical pieces.
Jump to 2:34-5:50 in the video below to see how it works in practice.
5. Define the flow
In step 5, we’ll start optimizing the flow. There are three major parts of this step:
- Defining the products
- Defining the processes
- Defining the process flow
There’s some overlap between this and the first step on the list. However, this step focuses on optimizing everything from a layout perspective.
This might mean changing the location of equipment, storage, and walkways to improve the overall process.
The flow is how the material cycle looks in your operation. In other words, when you trace the product from raw material to shipment, that’s the flow.
Jump to 6:43-9:22 in the same video below to see how it works in practice.
6. Simulation
With all of these parameters in mind, our team is ready to put together a simulation. The simulation will show the material and how it physically moves down the line.
A simulation is a 3D video that shows a flyby through your facility. It shows how the equipment and product move throughout. The Midea video discussed earlier is a great example of a simulation that our team makes.
However, this isn’t the final stage. Part of the simulation entails finding bottlenecks. This is where your operation is slowing down and hurting the production speed.
After finding a bottleneck, our team will work to alleviate them. Removing even one bottleneck in your operation can result in a huge performance improvement.
Some of our design software comes with plant layout analysis that aides us in targeting and alleviating these bottlenecks. This is another benefit of using computer-based plant layouts.
7. Modify And Validate the Changes
The final stage is all about making changes to improve the design. We typically target metrics when it comes to the use of space, operation cycle time, and the ability for product defects.
These changes result in faster speeds and more room for profit within your business on an annual scale.
If this layout is done before construction, you’ll also find some construction cost savings built into this step.
The validation stage involves our clients and getting valuable feedback from you.
Case: Tire Assembly and Warehousing Layout
Let’s discuss a case where the task was to design, simulate, analyze and optimize a manufacturing and warehousing system based on predefined production and layout goals.
This case is about a tire assembly and warehousing facility that is capable of handling a certain number of tires before they are supplied to a downstream assembly line. We can assume that the downstream is a car manufacturing plant.
Products and product variants
The product that we had to work with in this case was tires however there were many product variants.
First, we had three tires types meaning tires in three different materials.
Next, we had five tire sizes in the three tire types. These sizes are represented in different colors of tire rims.

So including all the product variants, we had to design a system that could handle 15 different tires.
Production goals
Once the products and product variants were clear, the next step was to evaluate the pre-defined goals. Here’s the list of the production goals that we had to meet,
- The customer needed a setup that was capable of handling all these tires in batches of 4.
- The downstream assembly required that this tire plant could supply 720 tires per hour regardless of how many it can store. The main objective was to have a functional system that provides uninterrupted supply to the downstream assembly regardless of how many tires it could store.
- Since we were working with batches of 4, 720 tires per hour meant that the goal was to supply 3 sets of tires per minute.
Layout Goals
Based on the production goals, there were also some layout goals,
- There must be enough buffer to recover from possible machine downtime.
- There must be enough warehouse to store tires for 5 hours of production meaning 900 sets in 5 hours and they must be available at all times to ensure any downtime does not interrupt the downstream supply.
- Also, in addition to storage, we needed to ensure that we had enough conveyor capacity to handle this amount and variety of products.
Layout Overview and Functionality
There layout was then designed based on the given production and layout goals. Here is a video for a closer look at the layout design and functionality of different sections,
1. The tire types are fed to the robot cell as a batch of 4.
2. Next, Tire rims which represent different sizes of the tires are incoming through conveyors behind the robot cell.
3. The robot cell is designed with 4 assembly lines. Each of these has a Yaskawa HP20RD robot on top of a smart pedestal with a tire tool. This tire tool helps to pick the tire type, lubricate it and assemble it with the rim.
4. Once Assembled, these tires go through a different set of machines where they are fixed and balanced before they are ready to be stored in the warehouse.
5. The tires are then sent towards the warehousing side with five storage sections, one for each tire size and four cartesian robots.
6. Each of these robots has certain tasks assigned to them shortly explained here,
- The first red cartesian robot sorts the tires by sizes onto their specific conveyors
- The second dark grey cartesian robot picks one stack of tires at a time and places them in their relevant tire size storage section.
- The third dark grey cartesian robot with beige pillars stores the tires by their sizes in the storage section and also supplies the sets forward when needed.
- The fourth steel-blue robot that is closer to the entrance of the warehousing collects the supplied stacks of tires released by the previous robot and places them in the rack. These racks are then picked and stored by the forklift in the next storage area.
7. From the last storage, the tires are then supplied to the downstream assembly as they’re needed.
Performance evaluation of the designed systems
Initially, two scenarios were designed and their simulation performance was evaluated.
The first scenario consisted of 4 robot assembly lines.
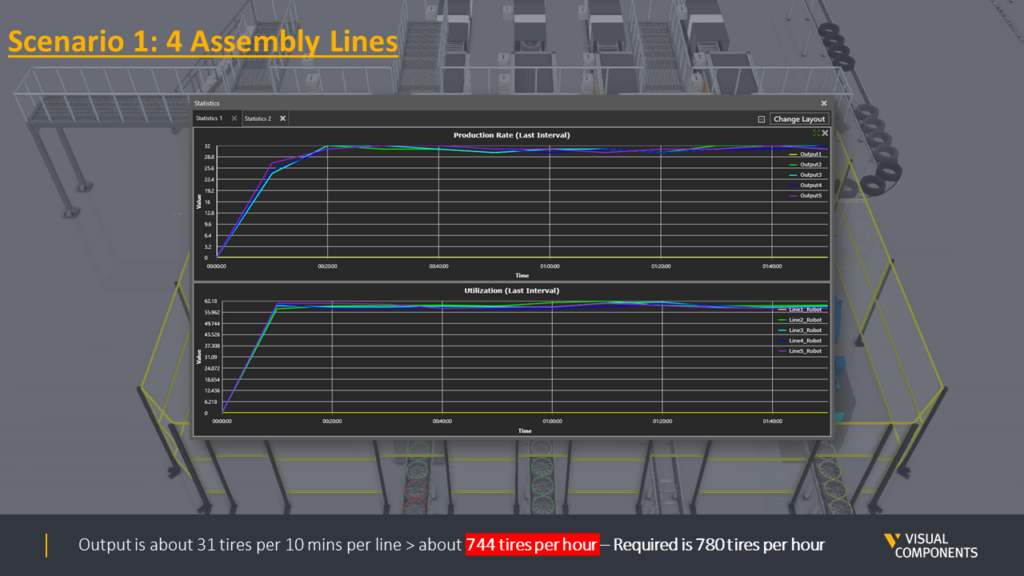
The second one had 5 robots assembly lines.
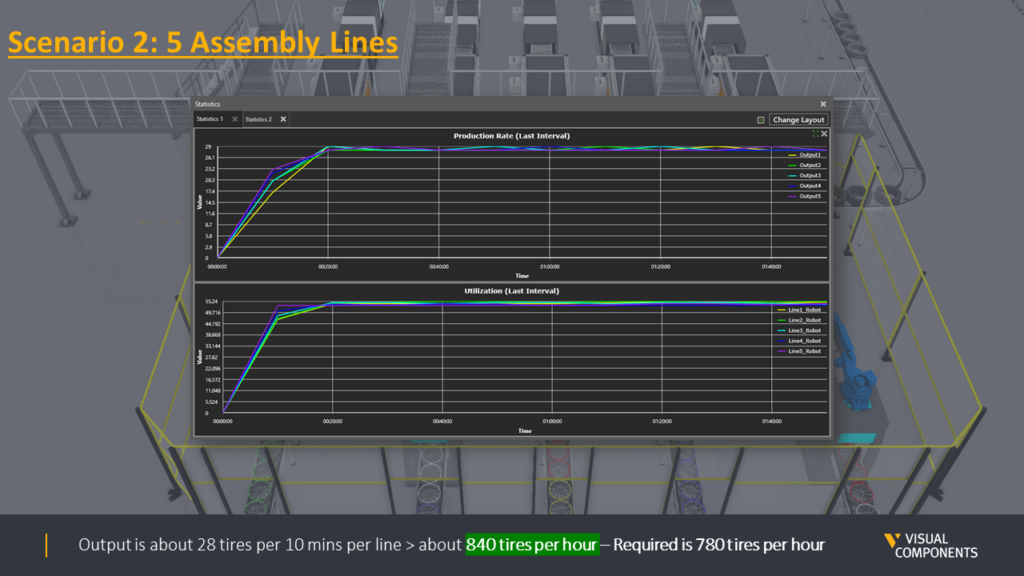
Later, we realized that machine breakdowns are not taken into account in the first two scenarios. Machine breakdowns could be due to many reasons but the most common reason for a production stoppage is usually Maintenance. So, the Maintenance times or Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) averaging 150 seconds were added to the machines in the robot cell. Also, the maintenance cycle was defined which meant the machine maintenance had to be carried out after every 30 tires were produced.
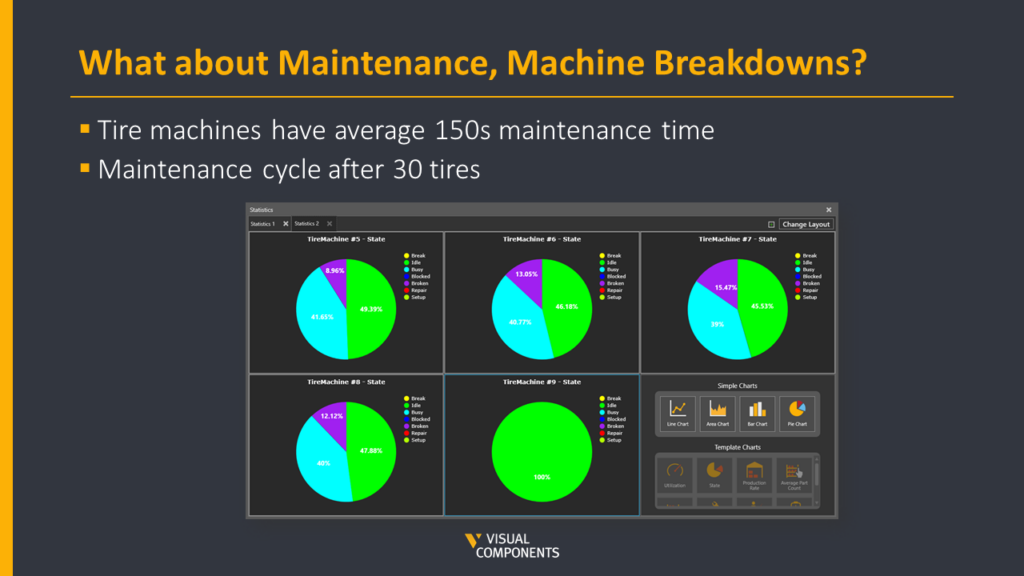
After these metrics were clear and defined, two more scenarios were built, basically, the same and 1st and 2nd scenarios but now with MTBF values included.
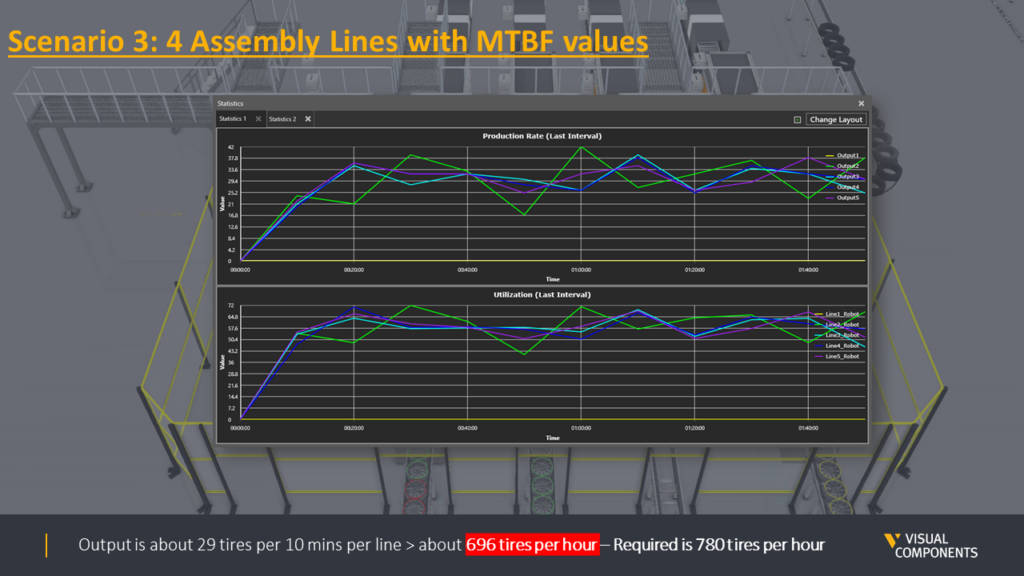
Overall, four scenarios were designed and simulated. Here is the summary of all scenarios with their production output.
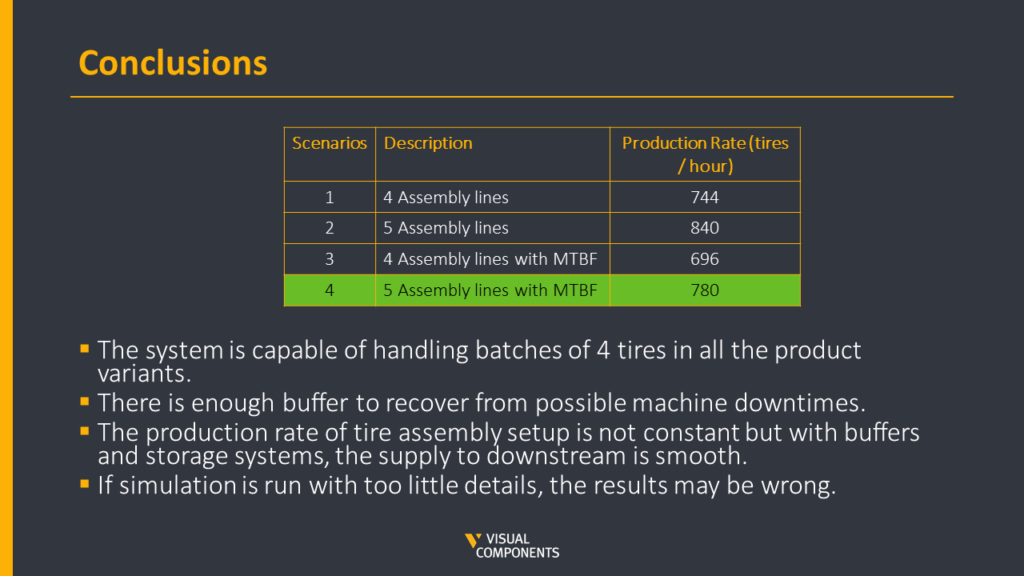
The difference in the production output is quite clear between scenarios where MTBF values were not considered and once they were. Based on the scenarios, it was safe to say that Scenario four with five assembly lines was able to generate the required goal of 780 tires per hour. This scenario was then locked as the final design for this case.
Summary of case results
Some important conclusions of this case were,
- The designed system was capable of handling batches of four tires in all the product variants.
- There was enough buffer to recover from possible machine downtimes.
- The production rate of tire assembly was not constant after the maintenance times were added but with enough buffers and storage systems, the supply to downstream was smooth.
- The last but one of the most important lessons to learn from this case was if the simulation is run with too few details, the results may be wrong like the clear difference between the production outputs in the first two scenarios compared to the last two.
Conclusion
We just reviewed how to plan and design a manufacturing plant layout. Now, you should know the benefits and process that goes into making a layout for your plant. With Visual Components , designing a plant layout is more logical, visual, and easier to do. Contact us today to get started. We’ll show you how your operation can save time and money thanks to our services.
Curious to learn more on the topic? Be sure to download our eBook about planning and optimizing your manufacturing plant layout.
Further reading
Boosting Production Line Efficiency: A Guide on Improving Production Output
Blog | March 27, 2024 Industry
An Introduction to Virtual Commissioning
Blog | February 22, 2024 Industry
Are Manufacturers Really Ready for the Digital Era? (Survey Results)
Blog | October 16, 2023 Industry
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)

Stage of Development Section
Production process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section.
You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan.
Key Takeaways
- The operations plan section should include general operational details that help investors understand the physical details of your vision.
- Details in the operations plan include information about any physical plants, equipment, assets, and more.
- The operations plan can also serve as a checklist for startups; it includes a list of everything that must be done to start turning a profit.
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process.
Keeping focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan.
Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included:
Production Workflow
A high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and disposed.
Industry Association Memberships
Show your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry.
Supply Chains
An explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down.
Quality Control
An explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this.
While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process.
When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business.
Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so.
The Physical Plant
Describe the type, site, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business.
The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements.
Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset.
Special Requirements
If your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions.
State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers.
Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders.
Explain how you'll keep track of inventory .
Feasibility
Describe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service.
Give details of product cost estimates.
Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystalize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes.
What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?
The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success.
Want to read more content like this? Sign up for The Balance's newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning!

How To Write a Business Plan for Cement Manufacturing Plant in 9 Steps: Checklist
By henry sheykin, resources on cement manufacturing plant.
- Financial Model
- Business Plan
- Value Proposition
- One-Page Business Plan
- SWOT Analysis
- Business Model
- Marketing Plan
- Bundle Business Plan & Fin Model
Welcome to our blog post on how to write a business plan for a cement manufacturing plant in 9 steps. With the construction industry on the rise, the demand for cement products is growing rapidly. In fact, the global cement market is projected to reach a market size of $725 billion by 2027, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.1% during the forecast period.
A cement manufacturing plant that produces sustainable yet high-quality cement products at competitive prices can tap into this lucrative market. By offering an alternative to traditional manufacturing practices, this plant aims to reduce environmental impact through resource conservation while delivering top-notch materials to customers.
So, how can you develop a comprehensive business plan for your cement manufacturing plant? Let's dive into the 9 crucial steps that will guide you through the process.
- Conduct market research
- Identify target market
- Analyze competition
- Determine the financial requirements
- Secure funding sources
- Assess legal and regulatory requirements
- Identify and select the location
- Develop a production plan
- Outline marketing and sales strategies
By following these steps, you'll be able to lay a strong foundation for a successful cement manufacturing plant. Let's get started!
Conduct Market Research
Market research is a crucial step in the process of starting a cement manufacturing plant. It provides valuable insights into the industry, market trends, customer preferences, and potential demand for your products. By conducting thorough market research, you can make informed decisions and develop a solid business plan. Here are the key steps to follow:
- Identify the target market: Determine who your primary customers will be. Are you targeting construction companies, developers, or individual consumers? Understand their needs, preferences, and purchasing behaviors.
- Analyze the competition: Identify your direct and indirect competitors in the market. Assess their strengths, weaknesses, market share, pricing strategies, and product offerings. This will help you position your cement manufacturing plant effectively.
- Assess market demand: Determine the current and future demand for cement products in your target market. Consider factors such as population growth, infrastructure projects, and construction activity. This information will guide you in estimating your potential market share and setting realistic production goals.
Tips for Market Research:
- Utilize online databases, industry reports, and trade publications to gather market data and insights.
- Conduct surveys and interviews with potential customers to understand their needs and preferences.
- Visit trade shows, seminars, and conferences related to the cement industry to stay updated on the latest trends and innovations.
- Engage with industry experts and consultants who can provide valuable guidance and insights.
- Keep track of government policies, regulations, and environmental standards that may impact the cement industry.
By conducting thorough market research, you will gain a deep understanding of the industry, market dynamics, and customer expectations. This knowledge will enable you to develop a targeted business strategy and position your cement manufacturing plant for success in the competitive marketplace.
Identify Target Market
Identifying the target market is a crucial step in developing a business plan for a cement manufacturing plant. Understanding who your customers are and what their needs and preferences are is essential for creating a successful and profitable operation. Here are some steps to help you identify your target market:
- Research the demand: Begin by conducting market research to determine the demand for cement products in your target region. Look for data on construction projects, infrastructure development, and trends in the cement industry.
- Segmentation: Once you have gathered the necessary data, segment your market based on various factors such as geographical location, customer demographics, and industry type. This will help you tailor your marketing efforts and product offerings to specific customer groups.
- Customer needs and preferences: Analyze the key needs and preferences of each customer segment. Consider factors such as the quality and durability requirements, price sensitivity, sustainability concerns, and any other relevant factors that may influence their purchasing decisions.
- Competitive analysis: Evaluate the existing competition in the market. Identify their strengths and weaknesses and determine how your plant can differentiate itself and fill any gaps in the market.
- Market size and growth potential: Assess the size of your target market and its growth potential. This will help you determine the scalability of your operation and forecast future demand for your cement products.
Tips for Identifying Target Market:
- Engage with potential customers: Talk to contractors, construction companies, and other industry stakeholders to gain insights into their needs and preferences.
- Utilize market research tools: Take advantage of market research tools and resources to gather accurate data about your target market.
- Stay updated on industry trends: Keep abreast of industry news and trends to identify emerging customer demands and preferences.
- Consider niche markets: Explore niche markets that may have specific cement requirements and tailor your offerings accordingly.
By thoroughly identifying your target market and understanding their needs, preferences, and the dynamics of the market, you can develop a business plan that positions your cement manufacturing plant for success.
Analyze Competition
One of the crucial steps in developing a business plan for a cement manufacturing plant is analyzing the competition. Understanding your competitors and their strategies will provide valuable insights for positioning your plant in the market.
Start by identifying the key players in the cement manufacturing industry. Research and gather information on their production capacity, product range, pricing strategies, market share, and distribution channels. This will help you assess the competitive landscape and determine where your plant can carve out a niche.
Important points to consider:
- Examine the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors. Identify areas where your plant can differentiate itself and offer unique value to customers.
- Study their marketing and sales strategies to understand how they target their customer base. This will help you develop effective strategies to attract and retain customers.
- Analyze their pricing structure and determine if your plant can offer competitive prices without compromising on quality.
- Identify any gaps in the market that your plant can fill. This could be related to product innovation, sustainability practices, or customer service.
- Consider the market trends and future growth potential to stay ahead of the competition. Look for opportunities to leverage new technologies or offer innovative solutions.
Tips for analyzing competition:
- Use online resources, industry reports, and trade publications to gather information about your competitors.
- Visit trade shows and conferences to network with industry professionals and gain insights into the latest trends and developments in the cement manufacturing sector.
- Consider conducting customer surveys or interviews to understand their preferences and experiences with existing cement products in the market.
- Establish strategic partnerships or collaborations with complementary businesses to enhance your competitive advantage.
- Regularly monitor and evaluate your competitors' activities to stay informed about any changes or new entrants in the market.
By thoroughly analyzing the competition, you will be able to develop a strong business strategy that differentiates your cement manufacturing plant and positions it for success in the market.
Determine The Financial Requirements
When starting a cement manufacturing plant, determining the financial requirements is crucial to ensure the success of your venture. This step involves assessing the funds needed to cover various aspects of the business, such as infrastructure, equipment, raw materials, labor, marketing, and working capital.
To determine the financial requirements, start by creating a detailed budget that outlines all the anticipated costs associated with setting up and running a cement manufacturing plant. This includes expenses for land acquisition, construction or renovation of the plant, procurement of machinery and equipment, installation, utilities, staffing, and training.
Create a comprehensive budget:
Consider industry benchmarks:, seek expert advice:, explore funding options:, create a contingency plan:.
By determining the financial requirements early on in the process, you can effectively plan and allocate resources to ensure the smooth operation and growth of your cement manufacturing plant.
Secure Funding Sources
Securing funding for your cement manufacturing plant is a crucial step in turning your business idea into a reality. Here are some important considerations to ensure you have the necessary financial resources:
1. Assess your financial needs: Before approaching potential funders, determine how much capital you require to establish and operate your cement manufacturing plant. This includes costs for land acquisition, construction, machinery, raw materials, labor, and marketing. Having a clear understanding of your financial needs will help you determine the type and amount of funding you should pursue.
2. Explore different funding sources: There are various funding options available for a cement manufacturing plant, including bank loans, government grants and subsidies, venture capital, angel investors, and crowdfunding. Research each option to understand the requirements, terms, and conditions, as well as the potential benefits and drawbacks.
3. Prepare a comprehensive business plan: A well-structured business plan is essential for attracting funding. It should clearly outline your plant's mission, vision, and objectives, as well as provide a detailed financial projection, market analysis, competitive advantage, and growth strategy. A strong and compelling business plan will help convince potential funders of the viability and profitability of your cement manufacturing plant.
4. Network and build relationships: Networking is crucial in securing funding. Attend industry events, join relevant associations, and connect with individuals who have experience in the cement manufacturing sector. Building positive relationships with potential investors, lenders, and other stakeholders can help open doors and create opportunities for funding.
Some tips to consider:
- Seek advice from professionals: Consult with accountants, financial advisors, and lawyers who specialize in business funding to ensure you are making informed decisions.
- Consider alternative financing options: In addition to traditional funding sources, explore alternative financing options such as grants, incubator programs, and partnerships with established companies in the industry.
- Showcase your sustainability initiatives: Emphasize the eco-friendly and sustainable aspects of your cement manufacturing plant, as this may attract investors interested in supporting environmentally responsible businesses.
- Be prepared for due diligence: Potential funders will conduct thorough due diligence on your business, so ensure that your financial records, permits, and legal documentation are up to date and readily available.
Securing funding for your cement manufacturing plant may require persistence, patience, and a well-thought-out strategy. By thoroughly evaluating your financial needs, exploring different funding sources, and building strong relationships with potential investors, you increase your chances of securing the necessary funds to bring your business plan to life.
Assess Legal And Regulatory Requirements
Before starting a cement manufacturing plant, it is crucial to assess the legal and regulatory requirements that must be followed. Compliance with these requirements ensures that the plant operates within the boundaries of the law and avoids any potential legal issues or penalties.
1. Research and understand local laws: Familiarize yourself with the laws and regulations that govern the establishment and operation of cement manufacturing plants in your specific location. This includes zoning regulations, environmental laws, labor laws, and any other industry-specific regulations. Consult with legal professionals or industry experts to gain a clear understanding of these requirements.
2. Obtain necessary permits and licenses: Identify the permits and licenses that are required to operate a cement manufacturing plant. This may include environmental permits, building permits, operational permits, and licenses specific to the cement industry. Ensure that all necessary documentation is obtained before starting the plant.
3. Comply with health and safety regulations: Cement manufacturing involves various health and safety risks. It is important to have robust safety protocols in place to protect employees and comply with health and safety regulations. Implement safety training programs, provide necessary personal protective equipment, and maintain a safe working environment.
4. Understand environmental regulations: Cement manufacturing can have a significant environmental impact. It is essential to understand and comply with regulations related to air and water pollution, waste management, and resource conservation. Implement measures to minimize environmental impact, such as using green production processes and adhering to emission standards.
5. Ensure compliance with labor laws: Be aware of labor laws that govern employment practices, including hours of work, wages, benefits, and employee rights. Comply with these laws to maintain a fair and lawful workplace.
- Engage with local regulatory authorities early in the process to understand their requirements and build a positive relationship.
- Seek legal advice to ensure full compliance with all laws and regulations.
- Maintain up-to-date documentation of permits, licenses, and compliance records to demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
By thoroughly assessing and complying with legal and regulatory requirements , you can establish a cement manufacturing plant that operates smoothly, avoids legal complications, and gains the trust of stakeholders.
Identify And Select The Location
Choosing the right location for your cement manufacturing plant is crucial to the success of your business. The location should meet certain criteria to ensure efficient operations, accessibility to markets, and compliance with regulations. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Proximity to raw materials: Look for a location that is close to sources of limestone, clay, and other necessary raw materials. This will help reduce transportation costs and ensure a steady supply of materials.
- Transportation infrastructure: Consider the availability of transportation networks such as roads, railways, and ports. A well-connected location will enable you to efficiently ship finished products to customers.
- Market proximity: Analyze the target market and select a location that is close to your customer base. This will reduce delivery times and transportation expenses, giving you a competitive advantage.
- Utilities and services: Ensure that the location has access to necessary utilities like water, electricity, and gas. Check if the area offers additional services such as waste management, telecommunications, and skilled labor.
- Consider conducting a feasibility study to evaluate different locations and compare their advantages and disadvantages.
- Engage with local authorities to understand zoning regulations, environmental restrictions, and other relevant requirements.
- Assess the potential impact of the cement manufacturing plant on the local community, including noise, dust, and other emissions. Address any concerns proactively.
By carefully evaluating and selecting the right location for your cement manufacturing plant, you can position your business for success, optimize operational efficiencies, and build strong relationships with customers and suppliers.
Develop A Production Plan
Developing a production plan is a crucial step in establishing and running a cement manufacturing plant. This plan outlines the processes and strategies that will be implemented to ensure a smooth and efficient production process.
Here are key points to consider when developing your production plan:
- Identify the required resources: Determine the materials, equipment, and technologies needed for the production process. This includes raw materials such as limestone, clay, and gypsum, as well as machinery and tools required for crushing, grinding, and mixing.
- Optimize resource utilization: Design the production process to optimize the use of resources, such as energy and water. This can be achieved through the implementation of energy-efficient technologies, recycling systems, and water conservation practices.
- Establish production targets: Set production targets based on market demand and operational capabilities. These targets should be realistic and achievable, taking into account factors such as manpower, equipment capacity, and raw material availability.
- Develop a production schedule: Create a detailed schedule that outlines the production activities, including the timing and sequence of each process. This will help ensure a smooth flow of production and minimize downtime.
- Implement quality control measures: Develop quality control procedures to ensure that the cement products meet the required standards. This can include sampling and testing procedures, as well as regular inspections and audits.
- Ensure safety and compliance: Incorporate safety measures and compliance with relevant regulations into the production plan. This includes ensuring the use of personal protective equipment, implementing proper waste management practices, and adhering to environmental regulations.
Tips for Developing an Effective Production Plan:
- Collaborate with experts: Seek input from industry experts and consultants who have experience in cement manufacturing. Their insights and recommendations can help optimize your production plan.
- Continuously assess and improve: Regularly review and evaluate your production plan to identify areas for improvement. This can involve analyzing production data, seeking feedback from employees, and staying updated on industry trends.
- Train and educate employees: Invest in training programs to ensure that your workforce is equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge for efficient production. This can contribute to higher productivity and quality output.
Remember, a well-developed production plan is essential for the success of your cement manufacturing plant. It will help streamline operations, enhance resource utilization, and ensure the production of high-quality and sustainable cement products.
Outline Marketing And Sales Strategies
Effective marketing and sales strategies are crucial for the success of any business, including a cement manufacturing plant. To promote your sustainable and high-quality cement products, you need to develop a comprehensive marketing and sales plan. Here are some essential steps to consider:
1. Define your target customers: Clearly identify the industries, construction companies, and individuals who are likely to be interested in your sustainable cement products. Understand their needs, preferences, and buying behavior to tailor your marketing efforts.
2. Create a strong brand image: Develop a compelling brand image that emphasizes the eco-friendly and efficient qualities of your cement products. Design a visually appealing and professional logo, website, and marketing materials that reflect your commitment to sustainability and quality.
3. Utilize online and offline marketing channels: Implement a multi-channel marketing approach to reach your target audience effectively. Use digital marketing strategies such as search engine optimization (SEO), social media marketing, and email marketing to generate awareness and drive traffic to your website. Additionally, leverage traditional marketing channels like print ads, trade shows, and industry publications to expand your reach.
4. Build partnerships and collaborations: Establish strategic partnerships with contractors, builders, architects, and other industry stakeholders to increase your visibility and credibility. Collaborate with them on joint marketing initiatives, such as co-hosting workshops or participating in industry events, to showcase the benefits of your sustainable cement products.
5. Provide exceptional customer service: Focus on delivering excellent customer service to build trust and loyalty. Train your sales team to provide accurate information about your cement products, address customer concerns, and offer personalized solutions. Encourage customer feedback and continuously improve your processes based on their suggestions.
- Offer product demonstrations and samples to potential customers to showcase the quality and environmental benefits of your cement.
- Develop case studies and testimonials from satisfied customers to build credibility and persuade new prospects.
- Invest in search engine optimization (SEO) to ensure your website ranks high in related searches and attracts organic traffic.
- Consider hosting webinars or online workshops to educate customers about the advantages of using sustainable cement products.
By outlining comprehensive marketing and sales strategies, you can effectively position your cement manufacturing plant as a sustainable and competitive solution in the market. Continuously evaluate and adjust your strategies based on market trends and customer feedback to ensure long-term success.
In conclusion, writing a business plan for a cement manufacturing plant requires thorough research and careful consideration of various factors. By following the nine steps outlined in this checklist, entrepreneurs can ensure that their business plan covers all the essential aspects of starting and managing a successful cement manufacturing plant.
Conducting market research enables entrepreneurs to identify the target market and analyze competition, helping them formulate effective strategies for sustainable growth. Determining the financial requirements and securing funding sources are crucial steps in ensuring the plant's financial stability and success.
Assessing legal and regulatory requirements is essential to ensure compliance and avoid any legal complications. Identifying and selecting the location, developing a production plan, and outlining marketing and sales strategies are key elements of a comprehensive business plan.
By investing in modern technology, clean energy, and state-of-the-art production techniques, cement manufacturing plants can reduce their environmental impact and optimize resource utilization. Building partnerships with suppliers and local stakeholders ensures a steady supply of raw materials and access to qualified personnel.
Finally, marketing the plant as an eco-friendly and efficient alternative to competitors emphasizes its unique selling points and attracts customers. With a well-developed business plan, entrepreneurs can lay a solid foundation for a successful cement manufacturing plant that delivers sustainable and high-quality products at competitive prices.

$169.00 $99.00 Get Template
Related Blogs
- Starting a Business
- KPI Metrics
- Running Expenses
- Startup Costs
- Pitch Deck Example
- Increasing Profitability
- Sales Strategy
- Rising Capital
- Valuing a Business
- How Much Makes
- Sell a Business
- Business Idea
- How To Avoid Mistakes
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Please note, comments must be approved before they are published
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Production Planning 101: Making a Production Plan (Example Included)

As the creation of products and services has become more extensive and varied, the manufacturing industry has become more competitive. There are many things to keep an eye on such as material requirements planning, supply chain management and inventory control. Operations continue to become more complex, meaning manufacturing companies require more thorough production planning.
A production plan is the best way to guarantee you deliver high-quality products or services as efficiently as possible.
What Is Production Planning?
Production planning is the process of deciding how a product or service will be manufactured before the manufacturing process begins. In other words, it’s how you plan to manage your supply chain, raw materials, employees and the physical space where the manufacturing process occurs.
Production planning is important for manufacturers as it affects other important aspects of their business such as:
- Supply chain management
- Production scheduling
- Material requirements planning
- Production lead time
- Capacity planning
ProjectManager is project management software that helps manufacturers cover every aspect of production planning. Plan with Gantt charts, execute with kanban boards and manage resources along the way. No other software offers sophisticated project and resource management features in one intuitive package. Get started today for free.
Why Is Production Planning Important?
If a manufacturing operation wishes to expand, that evolution demands careful production planning and scheduling. Someone must take on the responsibility of managing resources and deciding how they’ll be allocated. This process is a big part of capacity planning —how much can be made in a certain period, with the available resources?
Without production planning, it’s easy to use too much of a resource for one product and not leave enough for another, or fail to schedule your resources properly, which results in delays that affect your overall production management process. It’s just as easy to let resources go to waste. These issues indicate a lack of efficiency in your production planning process.
Production planning is the best way to ensure resources are used appropriately, products and services are high-quality and nothing goes over budget . In most organizations, a production manager manages the production planning process.
What Does a Production Planner Do?
A production planner is a team leader who oversees the production planning process, which defines how an organization will approach major areas of production management such as production scheduling, resource capacity planning, production control and production budgeting to manufacture products.
To better understand what a production planner does and the importance of this role in any manufacturing organization, let’s dive into each of the steps of the production planning process.
10 Steps of the Production Planning Process
The production planning process consists of an organization’s actions to make a production strategy that allows it to manufacture products most efficiently and profitably. Here are 10 key steps you should follow when planning your production process.
1. Use Production Forecasting Methods for Estimating Customer Demand
The first step of the production planning process is to forecast the customer demand for your product for a future period like a year or a quarter. To do so, manufacturers rely on quantitative and qualitative techniques such as Delphi method, historical analogy method, moving average method and the analysis of business data and sales forecasts.
This process is known as demand planning , which helps manufacturers be better prepared to meet the demand for their products and manufacture the right quantity so they can minimize production and operational costs.
2. Gauge Your Production Capacity
The term production capacity refers to the maximum quantity of product a manufacturing company can produce based on its available production resources such as raw materials, labor, equipment and machinery.
Once you better understand the customer demand for your product, you’ll need to gauge the total quantity of product that needs to be manufactured and then evaluate if your production capacity is sufficient.
3. Map Out the Shop Floor Layout
Now think about the steps of the production process itself. Outline the production tasks that must be executed to transform raw materials, parts and components into a final product and the physical route that those elements will follow to move across the shop floor. This will allow you to pick a production floor layout that minimizes the time and effort required from your employees.
4. Make a Production Budget to Find the Optimal Production Volume
The next challenge in the production planning process is determining the exact number of units to manufacture to keep up with customer demand and maintain your desired stock levels.
This requires a production budget , a document used to calculate the number of units that should be produced by a company to meet the customer demand for a period such as a month, quarter or even a year.
Creating a production budget involves assessing the current product inventory, the production capacity, sales forecasts and the ending inventory that should remain at the end of the period. Once you analyze these variables and use the production budgeting formula, you’ll know the required production level for a given time.
5. Choose a Production Costing Technique
Choose a costing method for your production process such as activity-based costing, process costing, job costing or simply standard costing. Each has its pros and cons depending on your organization’s particular characteristics.
6. Create a Production Schedule
Now it’s time to make a production schedule that allows your organization to create a stock inventory, deliver products to distribution channels, fulfill customer orders and meet the obligations of any manufacturing contracts the organization has in place for the production timeline you’re planning for.
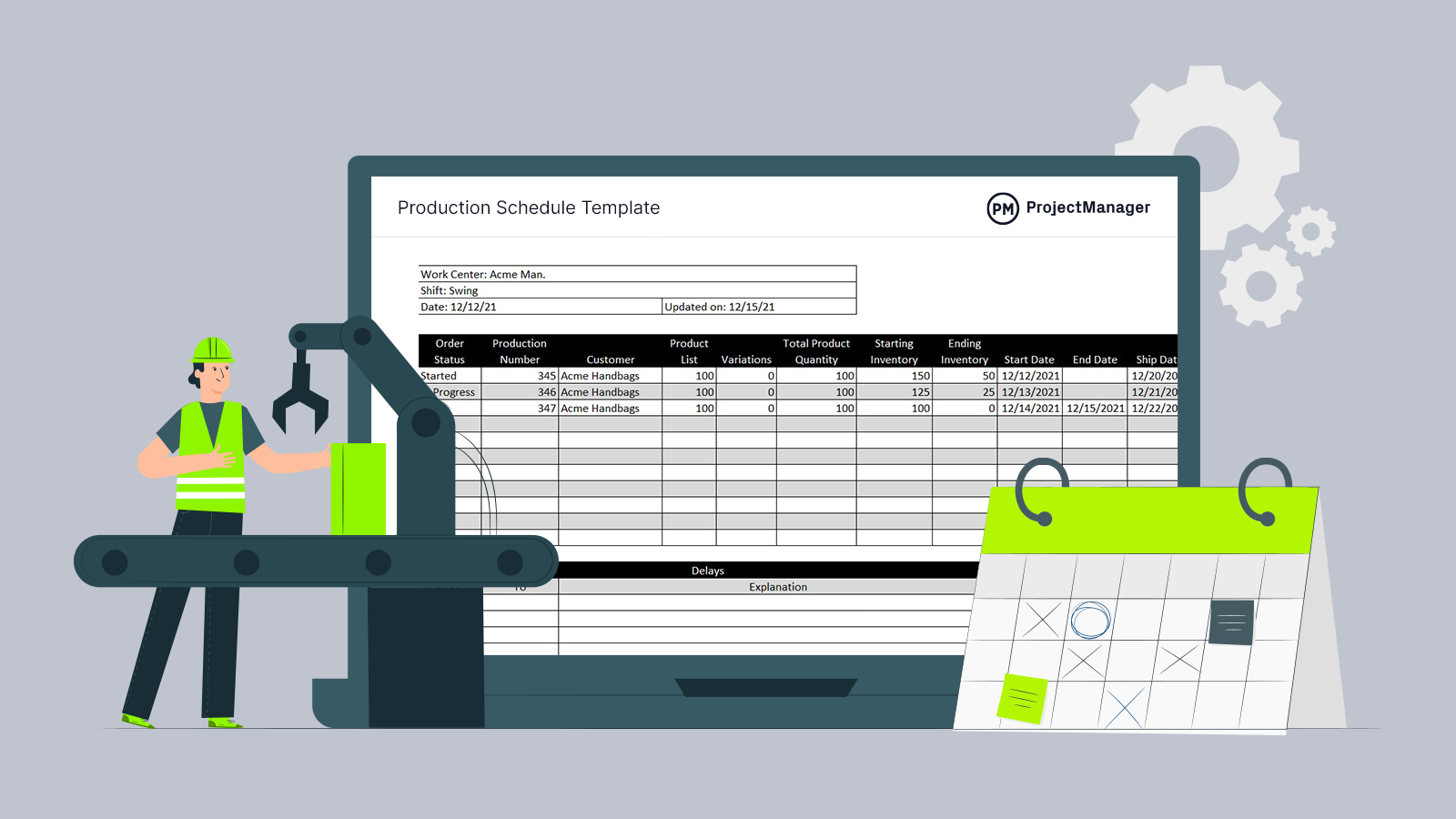
Get your free
- Production Schedule Template
Use this free Production Schedule Template for Excel to manage your projects better.
7. Establish a Production Control System
Next, it’s important to establish standard operating procedures and key performance indicators and use a variety of production control tools to create a system that allows you to track the production process to ensure your products meet quality standards and are manufactured on time and under budget.
8. Set Production Reporting Guidelines
After you’ve decided what KPIs will be used to monitor the efficiency of your production process, you’ll need to determine what types of reports will be used to communicate these metrics with stakeholders and the frequency in which they’ll be produced.
The documentation from each of these production planning stages, such as the production budget and production schedule are gathered in a larger document called the production plan.
What Is a Production Plan?
A production plan is a document that describes how production processes will be executed, and it’s the outcome of the production planning process. It describes the human resources, raw materials and equipment needed and the production schedule that will be followed.
The person responsible for production planning must also be very familiar with the operation’s inner workings, project resources and the products/services they produce. This usually entails collaborating with people on the floor, in the field or in different departments to create products and deliver services.
Production Plan Example
The best way to illustrate this process is through an example. When you set out to create a production plan, make sure to follow these steps to make it as robust as possible.
Sales Forecast
Making a sales forecast greatly helps you decide which product planning method is best for your operation given your production capacity. You’ll need to use diverse sales forecasting techniques to better understand what will be the future demand for your product. From here, you can estimate which resources are required and how they’ll be used in the manufacturing process to begin the production capacity planning process.
Inventory Management Plan
Accessing inventory is about more than simply taking stock: you should make an inventory management plan for your production inventory and work-in-progress inventory so that you don’t experience shortages that might halt production or let things go to waste. For this step, focus on the inventory control and inventory management techniques you can use to handle inventory in the most efficient way possible.
Production Budget
Most manufacturers use the production budgeting formula below to make a production budget that indicates the ideal production volume based on a starting inventory, sales forecasts, production capacity and expected ending inventory levels.
Required Production = Sales Forecast Expected Units + Desired Ending Inventory – Beginning Inventory
Resource Plan
A successful production plan requires you to be familiar with the resource planning details of the manufacturing process, which is why you’ll need to make a resource plan that outlines what resources such as labor, raw materials, equipment and any other capital assets are available for production and when they’re scheduled to be utilized.
Production Cost Estimate
Once you’ve determined what the required level of production is and the resources that will be needed, you’ll need to estimate the cost of production . It’s important to ensure the production process will be profitable before creating a production schedule.
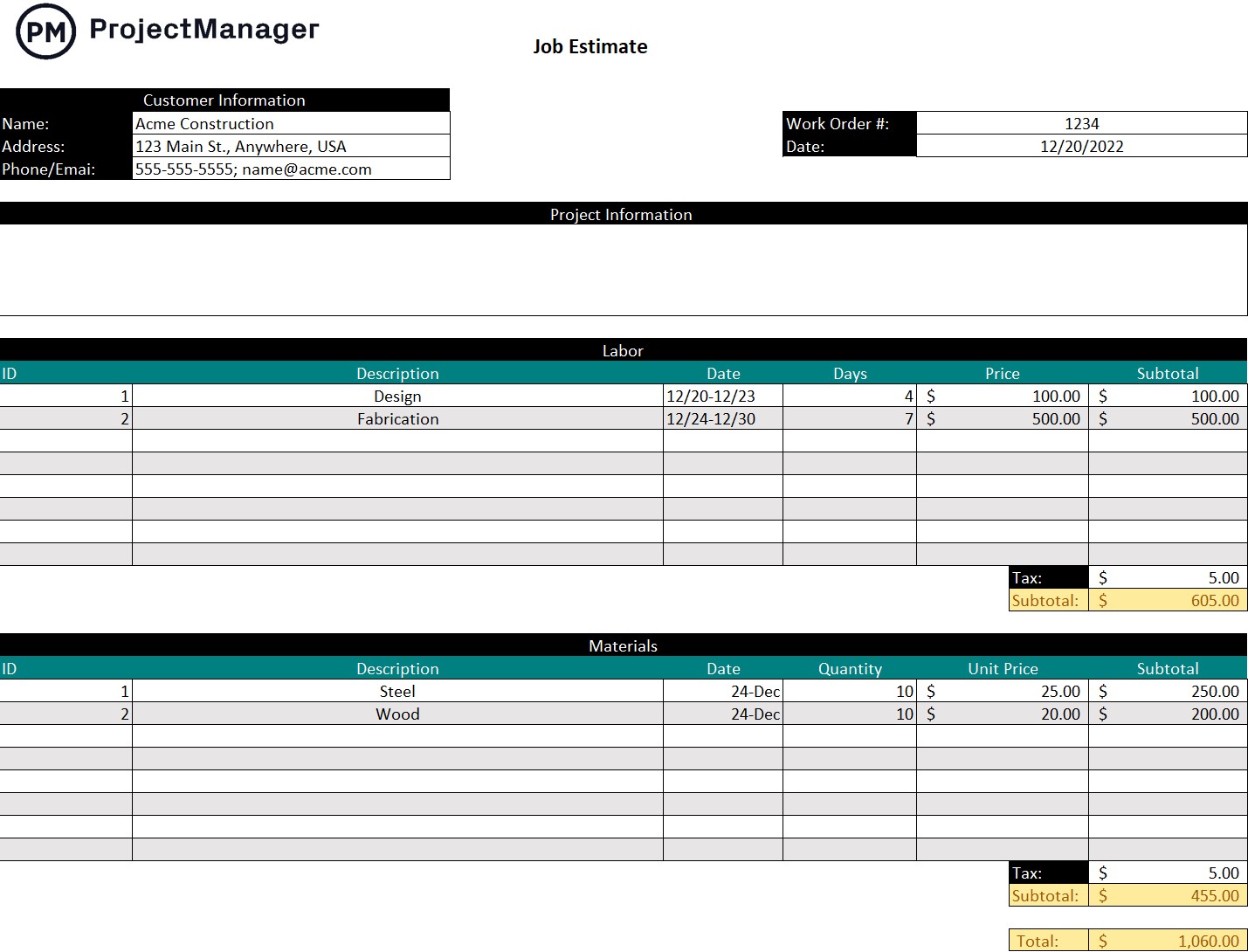
Production Schedule
As stated above, a production schedule is key to making sure your manufacturing team delivers products on time, but also guides efforts in other areas such as supply chain management and logistics management.
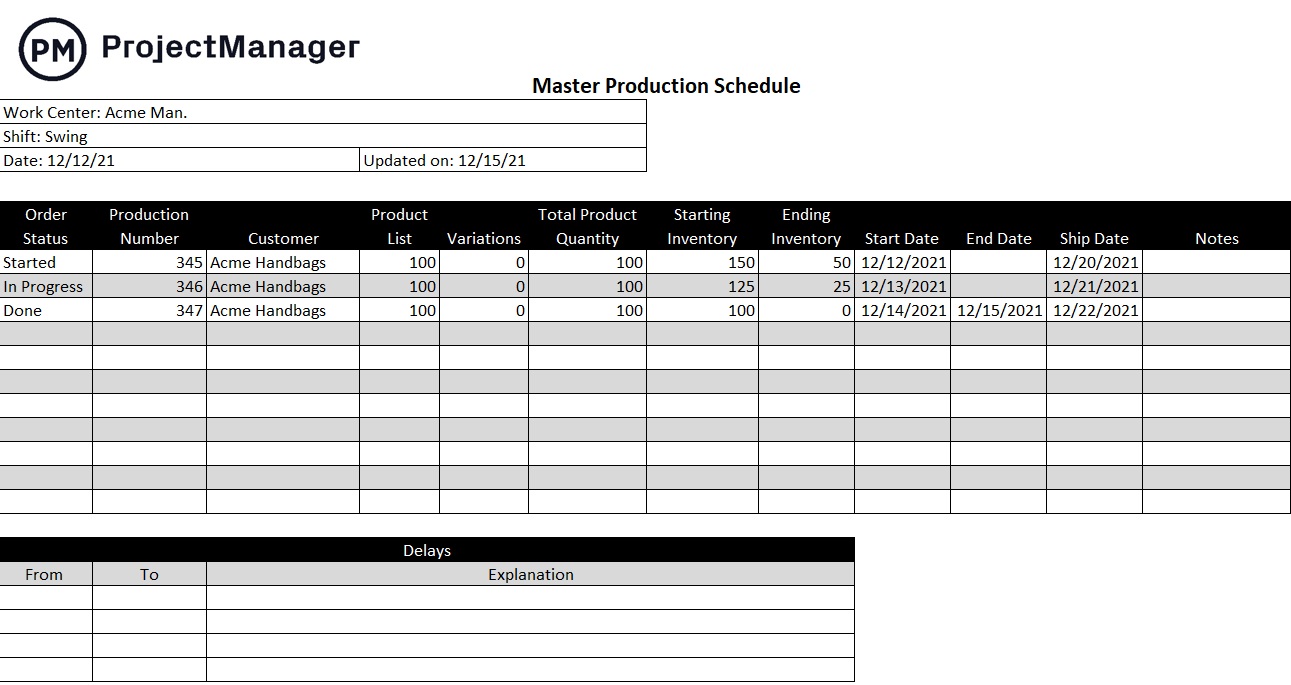
Production Control Plan
A production control plan should describe all the metrics, procedures, guidelines and tools that will be utilized to monitor how the results compare to the production schedule and resource management projections. This is something that should continually take place and be documented during the production process.
Types of Production Planning
Every operation is unique, and the same production plan isn’t right for everyone. To get the most from project planning, you decide which method is best for your manufacturing process. Here’s a quick intro to the different types of production planning.
The job method is often used when manufacturing a single product, for which a unique production plan is created. This production planning method is generally used in smaller-scale productions, but it can also be applied to larger manufacturing facilities. The job method is especially advantageous when a production order requires specific customizations.
Batch Production Method
Batch production consists of manufacturing goods in groups, instead of being produced individually or through continuous production . This method is useful when manufacturing products on a large scale.
Flow Method
The flow method is a demand-based manufacturing model that minimizes the production lead time by speeding up the production line. The manufacturing process starts based on work orders, and once it starts, it doesn’t stop until all finished goods are produced. This is called continuous production and it’s achieved by using machinery and little intervention to minimize waiting time.
Process Method
The process method is more or less what most people picture when they think about production—an assembly line. With the process method, there will generally be different types of machinery that complete separate tasks to put together the finished goods.
Mass Production Method
The mass production method primarily focuses on creating a continuous flow of identical products. It’s similar to the flow method, but at a much bigger scale, which cuts production costs. When uniformity is just as critical as efficiency, use “standardized processes” to guarantee all products look the same.

Production Planning Best Practices
No matter what product or service is being manufactured, there are many tried-and-true best practices to increase your operational efficiency . When creating a production plan, keep these two in mind.
Make Accurate Forecasts
When you don’t properly estimate the demand for your product or service, it’s impossible to create a detailed production plan. Demand planning is never static. Consider buying trends from previous years, changes in demographics, changes in resource availability and many other factors. These demand planning forecasts are the foundation of skillful production planning.
Know Your Capacity
Capacity planning means knowing the maximum capacity your operation can manage—the absolute most of a product or service it can offer during a period of time. This is the only way to anticipate how much of each resource you need to create X amount of products.
When you don’t know the production capacity, your production planning is like taking a shot in the dark.
Common Production Planning Mistakes
Stay vigilant of common missteps as you go through the production planning process. Here are three mistakes often made during production planning. Luckily, they can be prevented.
Not Expecting the Unexpected
This means having risk management strategies in place if things go awry. The goal is to never have to employ them, of course, but it’s better to have them and not need them. Production planning is incomplete if it doesn’t anticipate risks, issues and changes. When you plan for them, you’re ready to problem-solve if and when they happen.
Getting Stuck Behind the Desk
You should work with intelligent production planning tools, but that doesn’t mean you should only rely on enterprise resource planning software for production planning and not oversee resources and manufacturing operations in person. When production planning is only done from behind a screen, the result won’t be as informed as it could be. The best production planning is active and collaborative.
Neglecting Equipment
To get the most from your equipment, you need to take care of it. This means tracking usage and keeping up with regular maintenance. This looks different depending on the industry and product or service, but the principle is the same: continually take care of your equipment before it becomes a problem that slows down production.
Use ProjectManager for Production Planning and Scheduling
As the nature of manufacturing goods and services changes, you need modern tools to plan production and make schedules. ProjectManager is award-winning project management software that offers all the tools you need for excellent production planning and scheduling. With it, you can plan projects, create schedules, manage resources and track changes with one tool.
Plan With Gantt Charts
Manage your product manufacturing across a timeline with our Gantt chart view. With it, you can view your resources to help you track your cost of production to ensure you’re never overspending. You can then link any dependent tasks to avoid bottlenecks in your manufacturing.
Get a Bird’s-Eye View
To keep your production plan on track, you need a high-level view to pinpoint setbacks before or as they occur. Our real-time dashboard collects data and converts it into colorful graphs and charts that give you at-a-glance analytics.
Easily Measure and Report Your Progress
Any operation will have stakeholders who want to be kept in the loop. ProjectManager’s project status reports make it easy to share key data points. They can be generated in a single click, making it simple to generate them before important meetings.
Related Production Planning Content
The production planning process involves many different activities such as estimating the quantity of goods to be produced, the resources needed, the production schedule and much more. That’s why we’ve created dozens of blogs, guides and templates on production management topics. Here are some of them.
- Production vs. Manufacturing
- How to Make a Production Flow Chart for Manufacturing
- Best Production Scheduling Software Rankings
- How to Create a Master Production Schedule (MPS)
Manage every detail of your operation with ProjectManager’s powerful online project management tools. Our suite of tools is trusted by tens of thousands of teams, from NASA to Volvo, to aid them in the planning, scheduling, tracking and reporting on the progress and performance of their production plans. Our software lets you get out from behind your desk and make adjustments on the go. Try it for yourself for free for 30 days!

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.

Stellar Food for Thought
[Infographic] 4 Steps in Developing a Manufacturing Plan
- Food process & packaging engineering
- Strategic planning
![manufacturing plant in business plan [Infographic] 4 Steps in Developing a Manufacturing Plan: Strategic planning for food processors series](https://stellarfoodforthought.net/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/4-steps-in-developing-a-manufacturing-plan.jpg)
A manufacturing plan is a key piece of your food business’ overall strategic plan. Your manufacturing plan is a clear set of actions driven by gaps and discoveries from your manufacturing analysis, or the analysis of your business’ manufacturing processes.
It defines what your manufacturing strategy will look like in the future, whether it’s multiple facilities, renovations or even consolidating operations or products.
The goal is to ensure the appropriate technology is in place and to optimize current production practices to meet your sales goals. Developing the manufacturing plan helps identify where constraints exist and highlights areas to improve production efficiency.
![manufacturing plant in business plan [Infographic] 4 Steps in Developing a Manufacturing Plan: Strategic planning for food processors series](https://stellarfoodforthought.net/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/4-steps-in-developing-a-manufacturing-plan-822x1024.jpg)
To learn more about strategic planning, download our e-book The Strategic Planning Guide for Food Processors.

Conversation Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Post Comment

Syringe Manufacturing Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans » Manufacturing Sector
Do you want to start a syringe production company? If YES, here is a sample syringe & needle manufacturing business plan template & FREE feasibility report.
Just like most businesses, syringe manufacturing is pretty open to as many people that are interested in the industry as long as they have the required capital, experience and qualifications. Below is a sample syringe manufacturing business plan template that will help you successfully write yours with little effort.
A Sample Syringe Manufacturing Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Syringe manufacturing business is under the Syringes and Injection Needle manufacturing industry and players in this industry manufacture a variety of syringes and injection needles, including hypodermic syringes, medical bulb syringes, blood collection syringes and fountain syringes.
Typically, industry products include a barrel, plunger, needle and cap. This industry excludes syringes used for nonmedical purposes.
The Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing industry revenue has increased steadily as in the united states, due to demand for syringes and injection needles. Rising product prices have also supported industry growth. Revenue is projected to rise over the five years to 2022 as healthcare providers continue to invest in new equipment to keep up with growing demand for healthcare services.
In the United States of America, the industry generates over $4 billion annually from more than 48 syringes and injection needle manufacturing companies and the industry is responsible for the employment of over 9,068 people.
Experts projected that the industry will grow at a 3.6 percent annual rate between 2014 and 2019. The establishment in this industry that has dominant market shares in the United States of America are Becton, Dickinson and Company and Medtronic PLC.
A recent report published by IBISWORLD shows that the Syringes and Injection Needle manufacturing industry has experienced steady growth over the five years to 2019 as a result of favorable demographic shifts, increased health insurance coverage and strong sales abroad.
Furthermore, US total health expenditure has been on the rise, particularly government spending on healthcare. Increased public spending has recently bolstered demand for industry products but also served as a lifeline for the industry during the downturn and early recovery.
With national health expenditure expected to reach $3.4 trillion in 2019, IBISWorld estimates industry revenue will increase 2.6 percent over the year. As a result, industry revenue is expected to rise at an annualized rate of 3.6 percent to $3.8 billion within the next five years.
The syringe and injection needle manufacturing business is profitable and it is open for any aspiring entrepreneur to come in and establish his or her business.
2. Executive Summary
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. is a standard and registered syringes and injection needle manufacturing business that will be located in one of the industrial estates in West Palm Beach – Florida, United States of America. We have been able to lease a facility that is big enough to fit into the kind of standard syringe and injection needle manufacturing company that we intend launching.
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will manufacture a variety of syringes and injection needles, including hypodermic syringes, medical bulb syringes, blood collection syringes and fountain syringes. We are set to sell our products to a wide range of clientele not just in the United States of America, but also all across the world.
We spent time and resources to conduct a thorough feasibility studies and market survey so as to be well positioned to favorably compete with all our competitors. We will ensure that we engage in continuous improvement of our products so as to suite the ever – changing trends in the healthcare industry .
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will ensure that all our customers are given first class treatment whenever they purchase any of our products. We have a CRM software that will enable us manage a one on one relationship with our customers no matter how large they may grow to. We will ensure that we get our customers involved in our product conception and also when making some business decisions.
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will at all times demonstrate her commitment to sustainability, both individually and as a firm, by actively participating in our communities and integrating sustainable business practices wherever possible.
We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our customers’ needs precisely and completely whenever they patronize our products. Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. is owned by Billy Jones.
He has a B.Eng. in Production Engineering, with over 15 years’ experience in the syringes and injection needle manufacturing industry working for some of the leading brands in the United States. Although the business is launching out with just one outlet in West Palm Beach – Florida, but we will ensure that we distribute our products all across the United States of America and other countries of the world.
3. Our Products and Services
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will sell products to a wide range of clients which is why we will design, develop and manufacture various types of syringes and injection needles. Our product offerings are listed below;
- Standard disposable and reusable syringes
- Prefilled syringes, pens and auto injectors
- All Other including safety syringes
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to become one of the leading brands in the syringes and injection needle manufacturing industry in the United States of America and Canada.
- Our mission is to establish a world – class syringes and injection needle manufacturing company that will manufacture a wide range of syringes and injection needles and build a brand that will become a known brand not just in the United States of America, but also other parts of the world.
Our Business Structure
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. knows the standards expected from companies that are into the manufacturing of syringes hence the need for us to conform to industrial best practices. We will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, honest, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all the stake holders.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of ten years or more. In view of that, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Executive Officer (Owner)
- Production Manager
- Human Resources and Admin Manager
Production Engineers
Sales and Marketing Manager
- Accountants/Cashiers
- Customer Services Executive
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results
- Creating, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Reports to the board
Admin and HR Manager
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carrying out induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily office activities.
Production Manager:
- In charge of approving designs for the organization
- Responsible for managing the daily activities in the production facility
- Ensure that the production facility is in tip top shape and goods are properly arranged and easy to locate
- Control syringes and injection needle manufacturing, distribution and supply chain inventory
- Manage external research and coordinate all the internal sources of information to retain the organizations’ best customers and attract new ones
- Model demographic information and analyze the volumes of transactional data generated by customer purchases
- Identify, prioritize, and reach out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Document all customer contact and information
- Represent the company in strategic meetings
- Help increase sales and growth for the company
Accountant/Cashier:
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the organization
- Serves as internal auditor for the organization
- Responsible for designing, fabricating, developing and manufacturing a variety of syringes and injection needles
- Responsible for maintenance of equipment and instruments in the production plant.
Client Service Executive
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with customers on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the human resources and admin manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the organizations’ products to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to customers when they make enquiries
- Make suggestions and encourage purchase of products
6. SWOT Analysis
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. is in business to become one of the leading syringe manufacturing companies in the United States of America and we are fully aware that it will take the right business concept, management and organizational structure to achieve our goal.
We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be equipped to confront our threats.
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in manufacturing to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives.
This is the summary of the SWOT analysis that was conducted for Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc.;
Our core strength lies in the high quality of our finished syringes and injection needles, the power of our team and the state of the art and well – equipped plant that we own.
We have a team of highly trained and experienced engineers and support staff members that can produce top notch syringes and injection needles. We are well positioned in the heart of West Palm Beach – Florida and we know we will attract loads of clients from the first day we open our company for business.
A major weakness that may count against us is the fact that we are a new syringes and injection needle manufacturing company and we don’t have the financial capacity to compete with multi – million dollar companies such as Becton, Dickinson and Company and Medtronic PLC when it comes to manufacturing and selling syringes and injection needle at a rock bottom prices. So also, we may not have enough cash reserve to promote our brand the way we would want to do.
- Opportunities:
The fact that we are going to be operating our syringes and injection needle manufacturing company in West Palm Beach – Florida provides us with unlimited opportunities to sell our products to a large number of hospitals, pharmaceutical stores and health facilities.
We have been able to conduct thorough feasibility studies and market survey and we know what our potential clients will be looking for when they visit our show room and production plant; we are well positioned to take on the opportunities that will come our way.
Just like any other business, one of the major threats that we are likely going to face is economic downturn. It is a fact that economic downturn affects purchasing/spending power. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a new syringes and injection needle manufacturing company in same location where ours is located. So also, unfavorable government policies may also pose a threat for businesses such as ours.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
If you keep tabs with happening in the syringes and injection needle manufacturers industry, you will agree that technological advances, the legislative expansion of healthcare access and the improving economy have stimulated demand for syringes over the last five years, and the aging US population has further contributed to revenue growth, due to the high incidence of health issues requiring syringes and injection needle among the elderly.
A report published by IBISWorld shows that over the next five years, demographic shifts and higher demand for medical services will continue to favor industry operators. Despite being a fairly mature industry, product innovation and the emergence of prefilled syringes will boost demand in emerging markets.
Nevertheless, of all demand-related factors affecting the industry, the rising average age of the US population will have the largest effect on future demand. Demographic and products shift The US population is expected to continue growing older over the next five years.
So also, technological advances, expansion of healthcare and the improving economy have stimulated demand. Industry operators often have the weak hand in price negotiations and recent healthcare legislation has created a degree of uncertainty for syringes and injection needle manufacturing companies.
Lastly, as part of marketing strategies, syringes and injection needle manufacturing companies now ensure that they have showrooms at different locations where they display their products.
As a matter of fact, it is even cheaper to purchase directly from these showrooms established by syringes and injection needle manufacturing companies as against purchasing from pharmaceutical retail stores. It is a strategy that helps them increase sales and income for their business.
8. Our Target Market
We have positioned our syringes and injection needle manufacturing company to service businesses in the healthcare industry in and around West Palm Beach – Florida and every other location where our show rooms will be located.
We have conducted our market research and feasibility studies and we have ideas of what our target market would be expecting from us. We are in business to design, develop and manufacture a wide range of syringes and injection needle for the following customers;
- Pharmaceutical stores
- Medical laboratories
- Medical colleges
- Dental clinics
- Optical centers
Our Competitive Advantage
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. is launching a standard syringes and injection needle manufacturing company that will indeed become the preferred choice for hospitals and other healthcare facilities in the United States of America and other countries of the world.
One thing is certain; we will ensure that we design, develop and manufacture a wide range of medical equipment and instruments that are in high demand in the healthcare industry. We will also ensure that we work with some of our high – profile clients in designing, developing and manufacturing of syringes and injection needles.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our aims and objectives. We will also give good working conditions and commissions to freelance sales agents that we will recruit from time to time.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. is in business to design, develop and manufacture a wide range of syringes and injection needles. We are in the syringes and injection needle manufacturing industry to maximize profits and we are going to go all the way out to ensure that we achieve or business goals and objectives.
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will generate income by selling the following products;
- Others including safety syringes
10. Sales Forecast
We are well positioned to take on the available market in the United States of America and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income/profits from the first six months of operation and grow the business and our clientele base.
We have been able to examine the syringes and injection needle manufacturing industry, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast.
Below are the sales projections for Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. it is based on the location of our business and other factors as it relates to syringes and injection needle manufacturing companies startups in the United States;
- First Fiscal Year (FY1): $350,000
- Second Fiscal Year (FY2): $750,000
- Third Fiscal Year (FY3): $1.9 Million
N.B: This projection was done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and there won’t be any major competitor manufacturing same syringes and injection needles as we do within same location. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
Before choosing a location for Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. we conducted a thorough market survey and feasibility studies in order for us to penetrate the available market and become the preferred choice for hospitals, pharmaceutical stores and healthcare facilities in and around West Palm Beach – Florida.
We have detailed information and data that we were able to utilize to structure our business to attract the number of customers we want.
We hired experts who have good understanding of the syringes and injection needle manufacturing industry to help us develop marketing strategies that will help us achieve our business goal of winning a larger percentage of the available market in the United States of America.
In summary, Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will adopt the following sales and marketing approach to win customers over;
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to hospitals, pharmaceutical stores, dental clinics, optical centers, medical laboratories and key stake holders in the United States of America
- Ensure that we design, develop and manufacture a wide range of syringes and injection needle needed in the healthcare sector.
- Make use of attractive hand bills to create awareness and also to give direction to our show rooms
- Position our signage / flexi banners at strategic places around West Palm Beach – Florida
- Position our greeters to welcome and direct potential customers
- Create a loyalty plan that will enable us reward our regular customers
- List our business and products on yellow pages ad (local directories)
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Engage in direct marketing and sales
- Encourage the use of Word of mouth marketing (referrals)
- Join local chambers of commerce and industries to network and market our products
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Despite the fact that our syringes and injection needle manufacturing plant is well located, we will still go ahead to intensify publicity for the business.
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. has a long-term plan of exporting our syringes and injection needle to other countries of the world and to become a household name in the healthcare industry which is why we will deliberately build our brand to be well accepted in West Palm Beach – Florida before venturing out.
Here are the platforms we intend leveraging on to promote and advertise Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc.;
- Place adverts on community based newspapers, radio and TV stations.
- Encourage the use of word of mouth publicity from our loyal customers
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Snapchat, Google+ and other platforms to promote our business.
- Ensure that our we position our banners and billboards in strategic positions all around West Palm Beach – Florida
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas in and around our neighborhood
- Advertise our medical equipment and instruments in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site
- Brand all our official cars and vans and ensure that all our staff members and management staff wear our branded shirt or cap at regular intervals.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Aside from quality, pricing is one of the key factors that gives leverage to players in the syringes and injection needle manufacturing industry, it is normal for customers to go to places where they can get quality syringes and injection needles at cheaper price which is why big players in the industry like Becton, Dickinson and Company and Medtronic PLC et al will attract loads of clients.
We know we don’t have the capacity to compete with market leaders in the industry, but we will ensure that the prices and quality of all the syringes we manufacture are competitive with what is obtainable amongst companies within our level.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Billy Jones is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment via credit cards/Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via mobile money transfer
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our clients make payment for all purchases without any stress on their part.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
In setting up any business, the amount or cost will depend on the approach and scale you want to undertake. If you intend to go big by renting/leasing a big facility, then you would need a good amount of capital as you need to ensure that your facility is conducive enough for workers to be creative and productive.
The tools and equipment that will be used are nearly the same cost everywhere, and any difference in prices would be minimal and can be overlooked. As for the detailed cost analysis of starting a syringes and injection needle manufacturing business; it might differ in other countries due to the value of their money.
These are the key areas where we will spend our startup capital on;
- The total fee for registering the business in the United States of America – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) – $3,300.
- Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580.
- The total cost for hiring Business Consultant – $2,500.
- The total cost for payment of insurance policy covers (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $9,400.
- The total cost for long – term leasing of a standard warehouse and showroom – $250,000
- The total cost for remodeling the production facility and showroom – $20,000.
- Other start-up expenses including stationery ($500) and phone and utility deposits – ($2,500).
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $60,000
- The total cost for Start-up inventory (purchase of syringes and injection needle making tools and equipment and the purchase of raw materials inclusive) – $250,000
- The total cost for store equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) – $13,750
- The total cost for the purchase and installation of CCTVs – $10,000
- The cost for the purchase of office furniture and gadgets (Computers, Printers, Telephone, TVs, Sound System, tables and chairs et al) – $4,000.
- The total cost of launching a Website – $600
- Miscellaneous – $10,000
We would need an estimate of five hundred and fifty thousand dollars ($550,000) to successfully set up our syringes and injection needle development plant in West Palm Beach – Florida.
Generating Funds/Startup Capital for Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc.
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. is a private registered business that is solely owned and financed by Engr. Billy Jones. He has decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital to 3 major sources.
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from the bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $150,000 (Personal savings $100,000 and soft loan from family members $50,000) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $400,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited with the amount.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
Part of the plans we have in place to sustain Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. is to ensure that we continue to make available different sizes of high – quality syringes and injection needles, deliver quality services, improvise on how to do things faster and cheaper. We are not going to relent in providing conducive environment for our workers and also the required trainings that will help them deliver excellent services at all times.
We are quite aware that our customers are key component to the growth and survival of our business hence we are going to continuously engage them to give us ideas on how to serve them better and the products they want to see in our store. We will not waste time in adopting new technology, best practices and diversifying our services.
Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner.
We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check : Completed
- Business Registration: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Securing Point of Sales (POS) Machines: Completed
- Opening Mobile Money Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of facility and remodeling the production plant: In Progress
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating capital from family members: Completed
- Applications for Loan from the bank: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents and other relevant Legal Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Printing of Packaging and Promotional Materials: In Progress
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed production equipment and machines, tools, furniture, racks, shelves, computers, electronic appliances, office appliances and CCTV: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business both online and around the community: In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement (License): Secured
- Compilation of our list of products that will be producing: Completed
- Establishing business relationship with vendors – In Progress
Related Posts:
- Ice Block Making Business Plan [Sample Template]
- LED Bulb Assembling Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Paper Cup Manufacturing Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Paper Mill Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Agriculture Equipment Manufacturing Business Plan [Sample Template]
Are you signed up for the Tuesday Business Report?
This new weekly digest of our business and development reporting is your must-read newsletter for local business news.

San Antonio Report
Nonprofit journalism for an informed community

Equipment maker JCB breaks ground on its Southside manufacturing plant

Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
Local officials took up gold-tinted shovels Tuesday, joining the leaders of one of the world’s largest equipment makers in a groundbreaking ceremony for what some are calling the biggest deal in San Antonio business since Toyota.
The Great Britain-based JCB marked the start of construction on its major manufacturing plant with the traditional turning of dirt, fireworks and a backhoe loader demonstration on its 400-acre site at Palo Alto Road and South Zarzamora Street on the South Side.
San Antonio businessman Graham Weston said the Bamfords are longtime family friends, and Weston called the JCB investment the biggest deal since Toyota. “We don’t know JCB very well in the U.S. but they’re one of the largest companies in the world,” he said. “San Antonio is going to be key to their attack in the U.S. market.”
JCB makes more than 300 types of construction and agricultural equipment in its trademark marigold-yellow, including backhoes, excavators, tractors, skid-steer loaders and forklifts.
“It’s a very exciting milestone in my family’s history,” said Alice Bamford, granddaughter of Joseph Cyril Bamford, who started the family-owned JCB in 1945. The founder’s son, Lord Anthony Bamford, succeeded his father as chairman in 1975.
“We’re not just going to be American-made, we’re going to be Texas-made,” Alice Bamford said. “For the next 80 years we’re writing the next chapters from here in America, where we sell a quarter of our machines from around the world … and it’s going to be a lot more.”

The company operates manufacturing plants in Great Britain, India, Brazil and China, and has its North American headquarters in Savannah, Georgia.
The 720,000-square-foot San Antonio facility will produce lift and access equipment, such as mobile elevating work platforms and telescopic handles. Though the Southside site has been cleared, a general contractor has not been selected for the San Antonio factory.
Manufacturing at the plant is expected to begin in 2026 and its product line could be expanded to include more types of equipment, said Richard Fox-Marrs, president and CEO of JCB.
“At JCB, we always have a long-term vision, we’re always looking to the future,” he said. “And whilst we must start with those two products, this 400-acre site gives us the scope to grow much greater in the future and create real long sustainable opportunity for JCB and for San Antonio.”
JCB jobs in San Antonio
The plant will employ 1,500 workers within five years, jobs that pay an hourly wage of at least $20.54, which is the minimum set by the City of San Antonio as a qualification for economic development incentives. Job openings will be posted to the JCB website .
In April, the City Council approved tax abatements and incentives worth $13.74 million. Bexar County also provided a package valued at roughly $12 million.
Fox-Marrs said the San Antonio plant is the “single biggest investment the company has ever made.” When the company announced its plans in October , it estimated spending $265.7 million by the end of 2028.
On Tuesday, he said, “By the time this facility is completed, we will have invested $500 million.”
Bexar County Commissioner Rebeca Clay-Flores, who represents Precinct 1, where the plant is being built, said the JCB facility represents new resources for the South Side — a “part of the county that has been left behind.”

“JCB being built here is helping to change educational trajectories, because more taxes … in our schools means more funding opportunities like the one I had when I went to [the University of] Oxford,” she said. “But there are still parts of the county that need a lot more work.”
Councilwoman Adriana Rocha Garcia (D4) attended the event representing Mayor Ron Nirenberg. She said it is estimated JCB will have a $30 billion economic impact on the city over the next decade.
“I’m thrilled to see you here to celebrate our newest manufacturing employer, which I know will have a profound impact on our community,” she said.
Greater:SATX Chief Economic Development Officer Sarah Carabias Rush said the JCB plant is already creating opportunities for suppliers in the South Texas region and in Mexico, which could mean more manufacturing plants setting up operations in San Antonio.
The Toyota Motor Manufacturing Texas plant, which opened in 2006, has at least 20 on-site suppliers and is credited with attracting other related manufacturers to the region.
You’re local, we’re local.
If you’d like to read more of our South Side reporting, sign up for our daily newsletters about San Antonio business, arts, culture — and more.
Toyota is currently in talks with local officials regarding economic incentives as it plans a $500 million expansion to its Southside plant.
The British billionaire Lord Bamford also attended the event and reminisced about his ancestors, who were once farmers and blacksmiths. He said Texas feels like home.
“I also enjoyed meeting the great and the good businessmen and politicians and I’m very impressed with their warmth, their approach and honesty about sort of the warts and all, which I think is very good,” he said. “I love that about Texas.”
Lord Bamford added that wherever JCB builds a plant, “we are good neighbors, not only in training, but also in charities.”
SOUTH SIDE LATEST

Can VIA’s public transportation infrastructure keep pace with Southside growth?

New nonprofit coalition will aim to break cycles of disease, starting in South San Antonio
More from san antonio report, 26 rescued at ‘miserable’ human smuggling scene in south bexar county, greater san antonio chamber launches initiative to support military families, ‘waking nightmare’: neisd trustees face looming deficit in budget talks, shari biediger.
Shari Biediger has been covering business and development for the San Antonio Report since 2017. A graduate of St. Mary’s University, she has worked in the corporate and nonprofit worlds in San Antonio... More by Shari Biediger
- WEATHER ALERT Excessive Heat Warning Full Story
- Action News Accuweather Forecast Watch Now
Ruiz Foods closing manufacturing plant in Tulare after 20 years

TULARE, Calif. (KFSN) -- Ruiz Foods in Tulare is closing its doors after near 20 years in business.
The closure will impact more than 200 employees.
The company says some employees have been given the chance to transfer to the plant in Dinuba.
The business was founded in 1964 and is the country's largest manufacturer of Mexican food.
Last year, Ruiz Foods announced Dinuba and Frisco, Texas would be co-headquarters.
The company says the Tulare manufacturing facility will close as an active production site later this year.
Related Topics
Top stories.

Paco Balderrama investigated for 'inappropriate off-duty relationship'
- 2 hours ago

Suspect in Fresno County crash that killed couple pleads not guilty

Central Valley to see 1st stretch of triple-digit temperatures in 2024

1 killed in single-vehicle crash in Fresno County, CHP says

Arsonist wanted for setting grass fires across Fresno, officials say
Buchanan graduate earns associate's degrees before high school diploma
Woman suffers broken leg in central Fresno hit-and-run, police say
Residents working to rebuild after fire rips through Fresno home
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
Eli Lilly beefs up plan to expand manufacturing for popular drugs Zepbound, Mounjaro
FILE - A sign for Eli Lilly & Co. sits outside their corporate headquarters in Indianapolis on April 26, 2017. Eli Lilly will spend more than $5 billion to expand an Indiana manufacturing site and eventually make more doses of its hot-selling weight-loss and diabetes treatments, Zepbound and Mounjaro. The drugmaker said Friday, May 24, 2024 that it was more than doubling its investment in a site near its Indianapolis headquarters. (AP Photo/Darron Cummings, File)
- Copy Link copied
Eli Lilly will spend more than $5 billion to expand an Indiana manufacturing site and eventually make more doses of its popular weight-loss and diabetes treatments, Zepbound and Mounjaro.
The drugmaker said Friday that it was more than doubling its investment in a site near its Indianapolis headquarters. But it will take time for the location to start producing.
The company broke ground for its Lebanon, Indiana, manufacturing plant last year and expects to start making products there near the end of 2026. Production will then increase through 2028.
Lilly said it would add $5.3 billion to the $3.7 billion it had already slated for the site. Company officials said in a statement that this amounts to the largest manufacturing investment in the company’s history, which dates back to the 19th century.
The site will make tirzepatide, the main ingredient behind both Mounjaro and Zepbound.
Zepbound, the weight-loss treatment, received U.S. regulatory approval last fall. The two drugs combined to generate more than $2 billion sales in this year’s first quarter.
But Lilly has struggled to make enough supply to keep up with the growing demand, as has its rival, the Danish drugmaker Novo Nordisk, which makes the popular weight-loss drug Wegovy.
Company officials have said they expected some manufacturing increases to occur starting in the back half of this year.
Analysts expect Zepbound and Mounjaro to eventually generate well over $30 billion in combined annual sales for Lilly, according to the data firm FactSet.
Shares of Eli Lilly and Co. rose slightly to $809.70 Friday morning, in line with the S&P 500 index.
Campbell to Cut 415 Jobs as It Restructures Its Manufacturing Plants

The logo and ticker for Campbell Soup Co. are displayed on a screen on the floor of the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) in New York, U.S., May 18, 2018. REUTERS/Brendan McDermid
(Reuters) - Campbell Soup on Tuesday said it plans to reduce the size of its Jeffersonville, Indiana site and close Tualatin, Oregon site, leading to 415 job cuts.
It added these changes are part of its ongoing efforts to strengthen growth, improve return on invested capital and boost manufacturing and distribution network.
The Goldfish crackers owner said it will close the Oregon facility in phases and expects to stop its operations by July 2026, with the first phase in August this year to impact 120 of its 330 employees.
The company said the Indiana plant will specialize in the Late July brand of tortilla chips and the production of kettle potato chips will be moved to its Charlotte plant in North Carolina and Hanover plant in Pennsylvania, which would lead to about 85 of 230 employees losing jobs after the change comes into effect in July this year.
Campbell also said it is making capital investments of about $230 million through fiscal 2026 at newer, more adaptable and efficient facilities in its network, which is expected to create 210 new jobs across the company.
Last year in July, the company announced plans to expand production of Goldfish crackers at its Richmond, Utah plant that is expected to be operational by the end of 2024.
Shares of the company, which had about 14,500 employees as of July 30 last year, were down about 2% in the morning trade.
(Reporting by Anuja Bharat Mistry in Bengaluru; Editing by Vijay Kishore)
Copyright 2024 Thomson Reuters .
Tags: United States
The Best Financial Tools for You
Credit Cards

Personal Loans

Comparative assessments and other editorial opinions are those of U.S. News and have not been previously reviewed, approved or endorsed by any other entities, such as banks, credit card issuers or travel companies. The content on this page is accurate as of the posting date; however, some of our partner offers may have expired.

Subscribe to our daily newsletter to get investing advice, rankings and stock market news.
See a newsletter example .
You May Also Like
Top income investments in 2024.
Kate Stalter June 6, 2024

7 High-Yield Dividend Stocks to Buy
Glenn Fydenkevez June 6, 2024

Lock In High Yield Before Rate Cuts

9 Best Cheap Stocks to Buy Under $5
Ian Bezek June 6, 2024

7 Best ETFs to Buy Now
Jeff Reeves June 5, 2024

Investments by Elon Musk and Tesla
Brian O'Connell June 5, 2024

9 of the Best REITs to Buy for 2024
Wayne Duggan June 5, 2024

9 of the Best Bond ETFs to Buy Now
Tony Dong June 5, 2024

8 Best Defense Stocks to Buy Now
Wayne Duggan June 4, 2024

7 Best Vanguard Funds to Buy and Hold
Tony Dong June 4, 2024

Can AI Pick Stocks?
Marc Guberti June 4, 2024

How Inflation Affects Investments
Rachel McVearry June 4, 2024

6 Best Cryptocurrencies to Buy
John Divine June 4, 2024

7 High-Yield Covered Call ETFs
Tony Dong June 3, 2024

Is Gold a Good Investment Right Now?
Rachel McVearry and Matt Whittaker June 3, 2024

6 of the Best AI ETFs to Buy Now

2024's 10 Best-Performing Stocks
Wayne Duggan June 3, 2024

Fidelity vs. Charles Schwab
Marc Guberti May 31, 2024

7 Best Oil and Gas Stocks to Buy in 2024
Matt Whittaker May 31, 2024

Testing Dave Ramsey's Investing Advice
Wayne Duggan May 31, 2024

Hino Motors closing Arkansas plant, 1,300 workers affected. Here's what we know.

Japanese-based Hino Motors is shutting down its Mid-South manufacturing center, its largest facility in the United States.
On Friday, May 31, Hino Motors announced it would withdraw the parts business from Hino Motors Manufacturing U.S.A. Inc. at its Marion, Arkansas, plant. The decision affects 1,300 employees and almost 70% of the Hino Motors workforce in the United States. The decision was made by the company's board of directors, according to a news release.
The Marion plant, located at 100 Hino Blvd., opened in October 2006. The plant closure will be completed by 2027.
Hino Motors Manufacturing U.S.A. Inc. has been in operation since 1994 and has approximately 1,900 employees. The Marion facility is the largest arm in the company, with approximately 200 employees at its headquarters in Detroit and 400 at its heavy-duty truck manufacturing plant in West Virginia.
Hino Motors is a subsidiary of Toyota. The Arkansas plant has produced axles and truck frames for Toyota and Hino trucks and vehicles .
Neil Strebig is a journalist with The Commercial Appeal. He can be reached at [email protected] , 901-426-0679 or via X/Twitter, @neilStrebig .
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Pallet Manufacturer Business Plan
Start your own pallet manufacturer business plan
Advanced Technology Pallets
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
The scrap tire recycling industry has been around for many years, but uses for recycled scrap tire rubber are in the initial stage, as less than 20% of scrap tires are processed. Approximately 10% are incinerated, generally for power generation, although air quality issues are always a concern as scrap tires, like coal, are dirty fuel. Approximately 4% of our scrap tires are exported to other countries where the casings are used in retread plants or the used tires are sold as is. Currently about 2% are processed into crumb rubber and used in molded products and for modified rubberized asphalt applications, which provides a longer lasting and more durable asphalt surface.
Stockpiles of scrap tires create health problems as they become breeding grounds for rodents, snakes, and mosquitoes, and also are serious fire hazards. With approximately 250 million scrap tires being generated annually in the United States and the existing piles estimated at between 2-3 billion, this represents a serious problem.
ATP-Advanced Technology Pallets a Nevada Corporation (ATP), is proud to present its unique and patented product the RST-PAL Pallet, a new pallet made from recycled scrap tire rubber. The “RST-PAL Pallet” is strong, durable and reusable, providing an alternative to wooden pallets and the expense associated with replacing, repairing and discarding wooden pallets. RST-PAL Pallets might be serial numbered and bar-coded to insure tracking and retrieval so that they can be used over and over again for many years.
The inventor, Dan Radke, has assigned to ATP all patent rights (to the approved and issued patent USPTO # 08/680,476) to manufacture and market the RST-PAL pallets worldwide, in perpetuity.
OUR MISSION
To provide cost effective and durable pallets to all industries and manufacturing.
THE EXISTING PROBLEM
- Wood and plastic pallet life cycle is short and the cost is very high.
- Wood pallets break and need repair or replacement every one or two trips.
- Wood absorbs liquids, gains weight, breaks and splinters, and is difficult to clean.
- Industries demand more durable and long lasting pallets.
- Scrap tire stockpiles are an environmental hazard.
- Current pallets made of wood, are consuming over 3.5 million trees annually.
THE SOLUTION
- RST-PAL pallets are less costly to buy and maintain.
- RST-PAL pallets are more durable and indestructible.
- RST-PAL pallets can support 15 times the load of a similar wooden pallet.
- RST-PAL pallets are rackable, stackable, more durable and longer lasting.
- RST-PAL pallets are unique, made from recycled scrap tire rubber using a newly patented process that includes rubber, recycled plastics and a binder system.
- RST-PAL pallets are guaranteed for years.
- RST-PAL pallets have no competition worldwide.
TECHNOLOGY AND PROCESS
- The materials process and the manufacturing of pallets are based on an approved and issued patent (USPTO # 08/680,476).
- International (PCT) patent protection filed.
- Production line machinery is available and has been sourced.
- Raw materials are readily available and have been sourced.
- Flexible production line allows for building various pallet sizes, with high yield and quality.
- Product is production “ready”. All R&D and qualification complete.
- Process based on modular capacity that allows for quick manufacturing expansion.
- Factory is environmentally “clean” with no waste stream.
- Prototypes have been built, tested, and qualified.
- U.S. consumption of pallets is 800 million a year (National Wooden Pallet and Container Association, NWPCA).
- RST-PAL pallets have the lowest life cycle cost compared to wood, aluminum, and plastic.
- Global Pallets-leasing options available.
- Marketing to focus on both closed and open loop distribution systems.
- Worldwide markets and licensing opportunities (Internationally protected patents).
- U.S. Government Agencies and Contractors markets.
- U.S. government has mandated product replacement with recycled products first.
MARKET QUOTATIONS
- “Quality, reusable multi-trip pallets instead of poorly constructed single user pallets” is needed ASAP. (Reference: NWPCA)
- Contractors doing business with the government are required to purchase “environmentally friendly” and “recycled products” products first. (Reference: President Clinton Executive order)
- Prototypes were evaluated by different industries, including military and government agencies with positive feedback.
- Potential sales pending investment and production ramp up.
- Environmental incentives to certain markets (Government sub-contractors).
- All licenses, permits, governmental agencies acquired and in support of project.
PALLET COST COMPARISON – OVER FIVE YEARS
- Use of RST-PAL pallets demonstrates substantial savings, $22 for RST-PAL pallet vs. $133 for total cost for wooden pallet, over 5 years. (See Topic 4.2 and 4.3.1).
INVESTMENT REQUIRED AND USE OF FUNDS
- $6M investment for 35% ownership estimated to reach profitability within 12-18 months.
- From the second year forward, 50% of the net profit after tax will be distributed as dividends to the shareholders (as long as it will not affect the planned expansion). The other 50% will be dedicated to growth.
- Funds raised will be used for plant setup, operations, equipment, marketing and sales.
First year operation with two production lines is expected to produce 1,137,000 units, with a projected net profit of over $8 million.
INVESTOR DISCUSSION
- Projections reflect the return of the original investment in less than two years.
- Approximately six times valuation, based on discounting of five years of net earnings to present value.
- Present Value of five years of projected net earnings at a 25% discount (incl. risk factor) is $98 million.
- Reaching less than 1% of the market share with five plants within five years.
- Projected revenue of approximately $402 million.
- Projected net profit (before taxes) of approximately $178 million.
- Management Team – Strong and professional with highly specialized consultants.
- Exit Strategy alternatives: (a) IPO after two years; (b) Acquisition; (c) Private ownership with a long horizon of profits.
RST-PAL Pallets — MANUFACTURED FROM RECYCLED SCRAP TIRE RUBBER
HELPING TO CLEAN UP AMERICA’S SCRAP TIRES
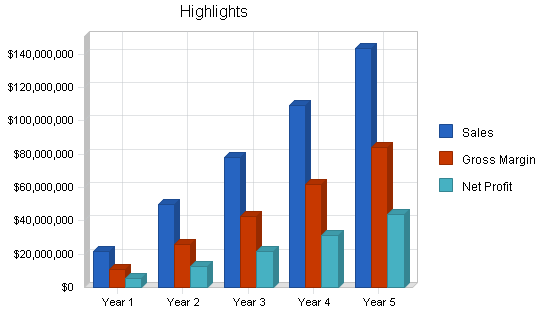
1.1 Mission
ATP is a manufacturing and marketing company dedicated to providing to all industries cost effective and durable pallets made from recycled scrap tires. The manufacturing process and the product are patent protected worldwide with no existing competition.
Pallet users, both manufacturers of commodities and industries that use pallets for their main distribution, demand a more durable and longer lasting pallet to replace wooden pallets that require constant repairing, replacing and discarding. The National Wooden Pallet and Container Association states that a wooden pallet gives service for only one to two trips before having to be repaired or replaced. Because of the short life cycle of wood (and plastic) pallets, pallet users are forced to purchase pallets more often.
Scrap tire stockpiles throughout the United States represent dangerous environmental hazards as they are breeding grounds for mosquitoes, rodents, and snakes, and create potential hazards for fires, which are extremely dangerous and expensive to extinguish.
ATP will reduce scrap tire stockpiles hazards and will help to conserve some of the 3.5 million trees harvested each year to manufacture wooden pallets. ATP will locate its manufacturing plants in rural towns, near large metropolitan areas, where employment is needed the most.
ATP will earn profits and provide excellent return to its investors while at the same time financing an aggressive growth of the company to increase production each year. ATP will also maintain a friendly, fair, and creative work environment, which respects diversity, product improvement, and hard work.
1.2 Objectives
- To establish two production lines at the first plant in Stamford, Texas in order to produce 1.2 million pallets annually, with projected net income (before taxes) in excess of $8 million.
- To expand production annually by opening a plant with two additional lines of production each year for years two through five.
- Achieve targeted market share of 0.15% in the first production year to 0.75% by the end of year five. (800 million pallets are manufactured and sold annually in the U.S.)
- First year projected market share of 0.15% is expected to bring net profits of $8 million (before taxes), and 0.75% of the market share in year five is projected to bring net profits of $66 million. Accumulated profits (before taxes) are projected to be $173 million for the first five years of production.
- ATP will take advantage of the acute need for solutions to America’s scrap tire problems, and establish plants in different locations where scrap tires are abundantly available, while taking advantage of benefits and subsidies offered by different State Government programs for the remediation of scrap tires.
- Develop foreign markets, through licensing agreements, especially in Europe and the Far East, where similar acute problems of scrap tires exist.
1.3 Keys to Success

- An existing pallet market in the U.S. of over 800 million pallets sold annually. It is estimated that approximately 60% are hardwood pallets; these users are ATP’s targeted customers.
- RST-PAL pallets have the lowest life cycle costs compared to wooden or plastic pallets.
- RST-PAL pallets are patent protected, are durable and virtually indestructible, and can carry in excess of 15 times the load of wooden pallets.
- Pallets are a well-known, necessary and established product; therefore there is no need to penetrate the market with a totally new product. In fact, RST-PAL pallets are not a new product at all, but are far superior, durable and longer lasting than anything comparable in the market place. The advertising and marketing costs will remain low as the RST-PAL pallets are introduced to pallet users through trade shows and conventions, with ATP’s sales representatives located in targeted marketing regions. The first targeted marketing region is Dallas/Fort Worth, Texas, near the first plant in Stamford, Texas.
- The U.S. government has mandated, through an executive order, a “buy recycled first” for all government agencies and contractors, including the Department of Defense and Department of Transportation. ATP will target federal and state agencies to market RST-PAL pallets.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
A.T.P.-Advanced Technology Pallets (ATP) a Nevada Corporation was formed to create a joint venture with the participation of the new investors and the current owners: RST Manufacturing LLC and Elie Banensohn, ATP’s Vice President.
ATP will manufacture and market worldwide the RST-PAL Pallet, made from a patent protected new material that includes the use of recycled scrap tire rubber. The pallet will be an affordable alternative to the high cost of purchasing, repairing, replacing, and discarding wooden pallets. Pallet users purchasing RST-PAL pallets will realize substantial savings in their pallet costs.
ATP is a new entity with RST Manufacturing LLC, becoming a shareholder. RST Manufacturing has invested in excess of $1 million to date, to complete research and development, prototypes, and pre-production marketing of the pallets. Plant property in Stamford, Texas, initial machinery, materials and supplies were purchased to bring the project to where it is today so that we can move into production and marketing of the RST-PAL Pallets through ATP. RST will transfer all assets to ATP. These efforts include the issuance of USPTO #08/680,476 in July 2002, a Utility Patent that will protect the unique material, and the product, RST-PAL Pallets.
All patent rights to manufacture and market the RST-PAL Pallets worldwide, are assigned in perpetuity to ATP by the inventor and ATP’s president, Dan Radke.
The Company’s was formed as a Standard C Corporation under the laws of the State of Nevada. The principal offices are presently located in Las Vegas, NV.
2.1 Company Ownership
Upon completion of the offering ATP a Nevada Corporation, will be owned by:
- The new investors (up to) – 35%
ATP is offering 35% of its shares to raise $6 million as additional capital needed for starting the first plant (with two production lines), in Stamford, Texas. ATP National Headquarters is in Las Vegas, Nevada and sales representatives will be positioned in targeted marketing areas.
The majority owner of RST Manufacturing LLC, is the inventor of the new material and the RST-PAL pallet, Mr. Dan R. Radke, the President of ATP.
The inventor, Dan Radke, has assigned all patent rights to ATP to manufacture and market the RST-PAL pallets worldwide in perpetuity.
2.2 Start-up Summary
The following summary table shows the projected start-up costs during the seven months needed to get into production. It includes the supply of specific machinery and equipment needed for the production lines. The start-up costs are to be financed by the money raised through this Private Placement Memorandum Offer.
The funds sought for opening the plant with two production lines is $6 million with projected net profits, in the first year of over $7 million. Alternatively, as a minimum plan, we could open with one line of production with funds of $4 million. In this case, the projected net profit, in the first year is over $3 million. In either case, about $750,000 will be available as working capital for the first six months of operations (after the plant is in production).
Management expects to begin production in approximately 180-200 days from funding as detailed in the Start-Up table.
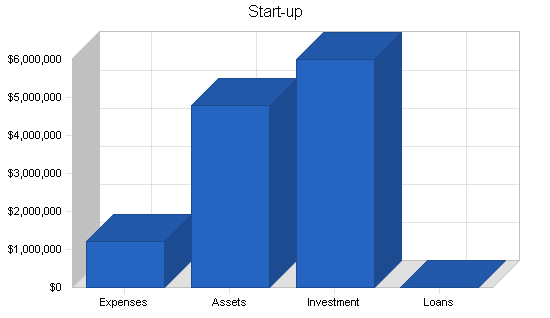
ATP’s product – the RST-PAL pallet is a unique and revolutionary pallet made from a new, patent protected, material of recycled scrap tires, a small amount of recycled plastic and a bonding process. The function specifications of our pallets are identical to the existing wooden pallets (e.g. sizes, four ways entry, upper deck coverage etc.) except that RST-PAL pallets are much more durable and longer lasting which makes penetration into the existing markets less difficult. The patented process and product gives our RST-PAL pallets the following advantages over the existing pallets:
- RST-PAL pallets carry 15 times the load of a similar wood pallet.
- RST-PAL pallets are rackable, stackable, and longer lasting than wooden pallets.
- RST-PAL pallets do not absorb liquids and are easy to clean.
- RST-PAL pallets have NO competition.
- RST-PAL pallets are environmentally friendly and are, themselves, a recyclable product.
- RST-PAL pallets are made of recycled scrap tire rubber material using a newly patented process which includes rubber, recycled plastics, and a binder system.
It is a rare occasion when a company can make a significant contribution to our environment as well as create an important long awaited product that will provide substantial cost savings for its users and allow them the opportunity to use and promote environmentally friendly, recycled products.
According to the National Wooden Pallet Container Association (NWPCA), its Strategic Planning Committee suggests that its members educate pallet users toward using higher quality, reusable multi-trip pallets instead of cheaper single use pallets. From a list of 62 potential threats to the wooden pallet industry, the committee chose lumber supply/raw material availability as the top threat. Other top threats identified by the committee include frozen thinking on the part of the industry, demonstrated by an unwillingness to recognize or adapt to the new realities of the marketplace, and environmentalists, a threat recently demonstrated by the draft Executive Order which would have banned wood pallets from use by the Federal Government.
A Clinton Administration Executive Order entitled “Federal Recycling, Acquisition and Use of Environmentally Preferable Products and Services” requires government agencies and those doing business under government contract to begin using “environmentally preferable” products made from recycled materials.
Paul Evanko, principal and vice president, St. Orge Company, York, PA, stated, “Pallets must adhere to a high quality standard”. “Poor quality pallets carry a hidden cost beyond the price paid and customers should be encouraged to purchase the best quality they can”. “Alternative materials including plastic, recycled and composite materials will emerge and pallet users will seek these pallets because of limited storage space, efficient handling weight and full four-way entry,” Evanko contends. “Wood will still be predominant,” Evanko said, “but there is a niche for alternative materials in the distribution flows”.
The Earth Works Group, Berkeley, CA states; “U.S. companies could be spending up to $1.75 billion dollars a year just to throw wooden pallets into landfills”. The Pallet Container Research Laboratory at Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA states “calculations show the annual wooden pallet production in the U.S. is using in excess of 3.5 million trees”.
3.1 Innovative Technology
Background (*) A major technological obstacle, which the recycled rubber market must overcome, is the nature of the rubber itself. Rubber used in the manufacturing of tires is vulcanized (rubber + sulfur) combined in the presence of heat and thermo set (formed into shape by steam and pressure – also referred to as a “cured” product). To date, no technology has been able to devulcanize rubber (break the carbon-sulfur bonds).
As such, thermo set rubber cannot chemically bond with any other polymer (rubber or plastic) to a degree anywhere approaching the uncured rubber. If, however current research is able to remove this obstacle, a very significant market will be opened.
(*) Scrap Tire Management Council, 1400 K Street, Washington, D.C.
Current usage Today’s usage of scrap tire rubber reaches about 7% of the annually accumulated scrap tires. Each year, about 250 million scrap tires accumulate throughout the U.S. This quantity of tires represents 3.75 billion pounds of crumb rubber from which only 262 million pounds (7%) are recycled and another 187 million pounds (5%) are used as tire derived fuel (TDF), which is a dirty fuel like coal, and requires strict EPA controls, is only being burned in a few states.
According to the Scrap Tire Management Council there were seven markets listed for recycled scrap tire rubber. These markets without exception utilize crumb rubber with all of the steel, wire, and textile removed, as an additive to rubber-modified asphalt (25%); pneumatic tires (25%); athletic fields (20%); bound rubber products (15%); friction material (5%); molded rubber products (5%); and molded rubber/plastic products (5%).
The new technology and the patent Mr. Dan Radke has overcome the obstacle mentioned in the article, (para.1) above. Mr. Radke’s invention of this “unique new material” through formulation and different particle sized recycled scrap tire rubber has created a tough, durable, hard and rigid material from which RST-PAL pallets are manufactured. The process is absolutely unique as proven by the issue of the utility patent protecting the pallet and process of making thereof. This unique and strong material and the usage of it for making pallets will save pallet users throughout the world millions of dollars annually in costs associated with purchasing, repairing, replacing and discarding broken wooden pallets.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
U.S. yearly consumption of pallets is 800 million a year, costing over $10 billion (according to National Wooden Pallet and Container Association). Our first market will be a 200 miles radius area around Dallas/Fort Worth in which the yearly consumption is 60 million pallets. Our markets for the RST-PAL pallets are all industries and users of pallets. About 300 interested users for our RST-PAL pallets (each of them buying over 100,000 pallets/yr) were contacted.
- RST-PAL pallets have the lowest life cycle cost compared to hard wood and plastic.
- Global Pallets leasing.
- Closed and open loop systems.
- Worldwide markets and licensing opportunities (Internationally patent protection filed).
- U.S. Defense and Transportation Departments market. U.S. government has mandated product replacement with recycled products.
ATP’s target in the first year is to produce 1.14 million pallets with two lines of production (constitutes 0.15% of the market), reach sales of $22 million, and ATP projects to earn profits of over $8 million (before tax).
The growth projection for the next five years is to add a new plant with two lines each year, reaching production in excess of six million pallets by the fifth year, (0.75% of the market), with sales projected at $143 million and profits before taxes of over $66 million.
4.1 Market Segmentation
Due to the fact that ATP’s projected plan is to open a new plant each year over the next five years, and to capture 0.15% to 0.75% of the U.S. pallet market, our main growth problem will be the limited abilities to supply the potential demand. Although we segmented the market into six groups we cannot indicate the percentage of growth for each segment, as the growth is not linear. The percentage represents our relative emphasis of this segment.
Yearly Pallet Users – Potential Customers
Total: Five year production =18,410,112. % of the pallet market =0.46
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
The following table demonstrates the cost savings that will be realized when a company converts its wooden pallet inventory to RST-PAL pallets.
Currently new hardwood pallets, (example: 40″x48″, four-way entry, 80% top deck coverage) are sold from $12 to $24 per pallet depending on the geographical area where you are purchasing your pallets, and the always fluctuating cost of hardwood. For the purpose of this chart we show the lowest price for large quantities of hardwood pallets at $10.
CHEP Pallet, Inc., the largest pallet leasing company in the world currently pays $23.50 to construct its pallets.
A pallet user of 100,000 new pallets per year will be saving over $3 million within 5 years using our RST-PAL pallets.
The table demonstrates that big users will realize huge savings. For example, one poultry processing plant that purchases one million pallets per year (about the production of one ATP plant) will realize savings of over $31 million within five years which will encourage them to convert their wooden pallet inventory to RST-PAL pallets.
4.2.1 Sample of Advertisment Content
RST-PAL PALLETS
COMING SOON
THE NEW SOLUTION TO COSTLY
REPAIRS AND REPLACEMENT OF
WOODEN PALLETS
RST-PAL pallets are not affected by heat or cold. Won’t rot, split or mildew STRONG & IMPACT RESISTANT, No more rusty nails, splinters, broken boards and runners RST-PAL PALLETS are 100% Recyclable, made from post consumer waste. No disposal costs
RST-PAL pallets, offering a new solution to an old problem
- RST-PAL pallets made from new tough materials = virtually indestructible.
- RST-PAL pallets are tougher, longer lasting pallets.
- Many years of repeated usage make RST-PAL pallets the best buy.
- Close your pallet repair facilities, our pallets don’t break.
- Stronger and more durable than wood or plastic.
- Easily trackable with bar coding or electronic chip.
RECYCLE / RE-USE of RST-PAL pallets represents a great innovation to the pallet industry with a major cost savings.
RST-PAL pallets address important environmental issues; help clean up America’s growing scrap tire problem and conserve valuable timber resources by using old tires to transport America’s commodities to consumers.
4.3 Industry Analysis
The pallet industry’s computation of the cost of a pallet includes the costs of production, maintenance and repairs, and discarding of the broken pallet. In the last decade, materials other than wood were introduced to the pallet industry like plastic, metal and corrugated cardboard, but still over 90% remain wood.
More than eight hundred million wooden pallets are constructed each year in the U.S., according to the National Wooden Pallet and Container Association (NWPCA). Most wooden pallets must be replaced or repaired after only one to two trips. It is estimated that over 3.5 million trees are used each year for pallet production, and most of these pallets end up in landfills, burned, or composted.
For years pallet users have been asking NWPCA members to build stronger and more durable pallets that would last longer, but nothing has changed. Pallet manufacturers favor the ongoing replacement prevalent in the industry.
The Recycled Scrap Tire industry generates more than two hundred fifty million scrap tires annually in the United States, one scrap tire for every American. These scrap tires are piling up, adding to the existing stockpile of an estimated two to three billion scrap tires located across the nation causing dangerous environmental hazards. Most states have adopted emergency scrap tire programs to help solve the growing problem of accumulations of scrap tires. The state of Texas has a scrap tire program; collecting and processing more than two hundred thousand tons of scrap tire rubber annually. Currently Texas has more than three million tons of shredded scrap tire rubber on the ground, available to end-users.
ATP with its RST-PAL pallet product will utilize Texas’ scrap tires to manufacture pallets at its first plant in Stamford, TX. The RST-PAL pallets will provide tough and durable pallets to pallet users while helping clean up the scrap tire problem.
ATP’s patented material and the manufacturing process to make pallets from scrap tires is the ultimate solution to the problems presented above: a) stronger and more durable pallets; b) reducing scrap tire stockpiles; c) saving trees. The use of RST-PAL pallets provides an excellent cost effective price, competitive to hardwood pallet prices.
The table in Topic 4.2 demonstrates the savings for a pallet user that purchases 100,000 pallets annually, when converting from wood to RST-PAL pallets. It shows savings over a five year period of more than $3 million. This saving comes on top of other benefits of using the RST-PAL pallets including: more durable and indestructible, carries 15 times the load of wooden pallets, rackable and stackable, will not absorb liquids (can be stored outside), and guaranteed for years. ATP’s first plant is located in Stamford, Texas, a rural community that is badly in need of economic development and new jobs. Stamford is approximately 150 miles from our first targeted marketing area the Dallas/Ft.Worth Metroplex.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
There is NO direct competition to RST-PAL pallets and no similar pallets exist today. The inventor, Dan Radke, has granted, in perpetuity, to ATP Corp the sole rights of utilizing the patent worldwide. This patent (USPTO # 08/680,476) gives very wide protection to the revolutionary invention of special material and to the process of making pallets.
The “competition” comes from pallets made of other materials like wood and plastic. Pallet users that use hardwood pallets do not use pallets made of corrugated cardboard. The table below demonstrates the cost comparison among the different pallets:
PALLET COST COMPARISONS – OVER 5 YEARS (in USD)
(*) Six repairs per year costing $4 each x 5 years.
The table clearly shows that costs over five years of the hardwood pallet is almost ten times that of RST-PAL pallets. In addition to the savings, there are other advantages such as the guarantee, no need to repair, can be stored outside (no liquids are absorbed), washable (important in the food industry), rackable and stackable, strong and indestructible. Bar-coding and electronic chips can be molded into the pallet to allow for specific inventory information regarding what is loaded on the pallet and for tracking.
There is no competition to RST-PAL pallets. There is no competitor making pallets from recycled rubber. ATP anticipates that our limited production will cause our five years expansion plan to be revised in order to meet the demand. Our first plant is expected to produce approximately 1.14 million pallets in the first year and 1.23 million from the second year forward. While the market for pallets is in excess of 800 million annually, ATP expects to capture about 0.15% of the market in the first year, and 0.75% after five years to meet our projections. This takes a great part of the risk out of the project.
ATP has already explored opening a subsidiary company that will lease or lease to own pallets to companies. This will enable ATP to compete with CHEP Pallet Corporation, which leases wooden pallets. CHEP has about 300 branches in the U.S. and also operates in foreign countries. Leasing RST-PAL pallets would be very profitable, as our pallets do not require repairs.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
Due to the increased lifecycle and interchangeability of the RST-PAL pallets with existing wooden pallets, ATP’s customers derive value from utilizing these innovative products in a number of ways. First and foremost, using and replacing the user’s wooden pallet inventory with RST-PAL pallets eliminates ongoing maintenance and replacement costs.
Another value is the longevity RST-PAL pallets offer. RST-PAL pallets have the longest life-cycle regardless of hot, cold, or wet climates or in environments where maintenance is difficult. RST-PAL Pallets will not rot, which is a common problem for wooden pallets.
RST-PAL pallets are manufactured from recycled materials mainly scrap automotive tires. Each 1,000 pallets use 25 tons of scrap tires from landfills, (31,000 tons or 62,000 pounds per plant per year).
RST-PAL pallets will help save hardwood forests currently used to manufacture wooden pallets, reduce greenhouse gases, use significant amounts of waste plastics and scrap tires from landfills and storage facilities, and reduce pallet users costs while increasing profits.
5.1 Competitive Edge
ATP’s most important competitive edge is based on the unique and patented material used to manufacture the RST-PAL pallets. The process, the unique material, and the use of the material to manufacture pallets are protected by the issued utility patent that will prevent duplication or “copycat” competition.
RST-PAL pallets are manufactured from recycled scrap tires. Federal law and most State Governments require agencies and contractors to purchase recycled products first, as mandated by “buy recycled products first”. ATP has already presented RST-PAL pallets to the Army, Air Force Exchange System, (AAFES) located in Texas and throughout the Pacific Rim, and AAFES is interested in purchasing pallets, which will increase their pallet lifecycle, which in the long run is less costly than wooden pallets. We will focus on different government agencies including the Department of Defense and Department of Transportation to introduce and market RST-PAL pallets.
RST-PAL pallets can be power washed or steam cleaned which is a critical factor in the food industry, such as in poultry and meat processing plants, which must maintain sanitized production areas. RST-PAL pallets do not absorb liquids as wooden pallets and they can be stored outside without occupying expensive indoor space.
The RST-PAL pallets are a “triple green” product. They are manufactured from recycled materials, and can be recycled in the event they ever wear out, and they will help conserve our nation’s forests while helping clean up America’s scrap tire problems.
The RST-PAL pallets will be the best cost/performance pallets in the market. The summary of advantages that our pallets have in comparison to existing material pallets such as hardwood, plastic, corrugated cardboard, and aluminum, are:
- An electronic chip for pallet identification and load identification will be available with RST-PAL pallets, and this can be done because of the strength and rigidity of the pallet, which is practically indestructible.
5.2 Marketing Strategy
The RST-PAL pallet is positioned uniquely as all industries and manufacturers use pallets to transport everything from commodities to equipment and parts. The main segmentation among the users is found in how they use pallets. The Power industry uses in excess of twenty million pallets annually, government owned poultry processing plants use more than ten million pallets annually, 3M Corporation purchased seven million pallets in one year alone, and the beverage industry uses in excess of fifty million pallets annually. There are also thousands of companies using anywhere from hundreds of thousands to millions of pallets annually including, chemical companies, bag cement, building materials, grocery, paint companies, and many others.
Our first targeted customers are those that use a “closed loop” distribution system, where they manufacture and/or distribute products using their own fleet, where loaded pallets can be dropped and returned when unloaded, to be utilized over and over again. We also will target government entities, agencies, and contractors both Federal and State.
Our marketing strategy is based on informing and introducing the RST-PAL pallet to pallet buyers across the country and in different industries. We can accomplish this at a rapid pace by showcasing the pallets at selected trade shows and conventions. Samples will be available as well as brochures and videotapes explaining the benefits of the RST-PAL pallet. Our first targeted marketing territory will be the Dallas/Ft.Worth Metroplex, concentrating on those companies using a “closed loop” system for distribution.
The marketing will convey the advantages, benefits and the quality of our product in every picture, every promotion, and every publication. Pallet users have been screaming for years for the wooden pallet industry to make a longer lasting more durable pallet, but their request has fallen on deaf ears, as the pallet builders would rather build a less sturdy pallet so that it will fail after only a few trips, requiring the customer to purchase more pallets. The RST-PAL pallet is a solution to the high cost of purchasing, maintaining and discarding wooden pallets. Our marketing efforts will not only focus on educating purchasing agents of companies, but also in making presentations to company board of directors, demonstrating the cost savings and benefits of using RST-PAL pallets. As was shown in a previous example, a company purchasing 100,000 pallets per year when converting to RST-PAL pallets will save in excess of $3 million over five years. With such convincing statistics, we anticipate universal acceptance of RST-PAL pallets.
5.3 Sales Strategy
As stated, ATP will sell pallets as they are manufactured. Pre-production marketing efforts have been on going for the last year. We have established a sales plan, however our production will dictate how quickly our sales team will expand. One company we have contacted expects to purchase 22 million pallets during the next two years. If we were to capture a large contract, our production schedule would be sold out for a number of years. Another sales company that markets products exclusively to the power industry, would like to have an exclusive to sell our pallets to power companies, and they estimate they can sell a minimum of 1.2 million pallets annually. We have approached many companies on the benefits of using RST-PAL pallets, including; 3-M Corporation, Coca-Cola, Pepsi, Snapple, Anhauser Busch, Hunts Wesson, Kraft Foods, S.E. Rycoff, Albertsons, Kroger Foods, Associated Foods, H.E.B. Foods, Purina Pet Foods, manufacturers of charcoal briquettes, flour and cereal mills, salt processors, building materials, including bagged sand and cement, plaster and even chemical companies.
Our concept is to introduce the RST-PAL pallets to many industries, and ATP will do that from our National Marketing Headquarters in Las Vegas, Nevada. The Las Vegas Visitors and Convention Authority will provide a great arena in which to showcase and demonstrate the RST-PAL pallets, as virtually every important convention and trade show now meets in Las Vegas.
This business plan calls for the company to grow itself. The Texas plant will be the first, and we expect new plants to be opened in years two, three, four and five. Some future plant site work has been completed, however we will locate the plants in States with positive scrap tire programs, some of which may provide subsidies for using scrap tire rubber to manufacture new products. In addition, our company policy will be to establish plants near massive scrap tire piles, and in rural communities where a good labor force exists but jobs are not plentiful and economic development will benefit the community.
ATP Corp. is the worldwide licensee to manufacture and market pallets. We have already had several foreign entities show interest in either becoming distributors or manufacturers through a foreign license arrangement. We have held discussions with a group from China, Japan, Taiwan and South Africa and are in contact with a group in Spain that is interested in our technology.
It is our intent to move our Stamford, TX plant into full production, and utilize the same team of key employees and consultants to open new plants over the next five years. Whereas our Business Plan provides for future plants being financed internally from company profits, additional capital can be raised through the licensing of foreign companies wishing to manufacture and market pallets in those countries.
5.3.1 Sales Forecast
Our sales forecast is based on the following assumptions. We expect our production will be sold as soon as it is ready, as the forecasted production is much less than the anticipated demand. Our product is not seasonal and will be continually manufactured throughout the year. We will operate in three shifts (except during training in first two months).
Our sales force will start taking orders sixty days prior to production. The initial selling price is low in order to introduce the pallets to many different manufacturers and industries. However we expect to raise prices at the rate of 5% per year (which is less than the rate of increase of the wooden pallets).
Regarding the “direct cost of sales” (COG), we assume the costs of materials will remain the same for us, due to discounts we will receive for the quantities of materials that we consume which should offset rising costs. We can also reduce our costs by doing some manufacturing processes ourselves, such as mixing and batching the binders at our plant, and by cutting the scrap tire rubber from chips to our required specifications.
We’ve calculated production labor costs, including salaries, taxes, and benefits to be $1.31 per pallet. The break down of production personnel is presented in the Personnel table, Production Personnel category, and the resultant figures appear in the Profit and Loss table under Sales, Production Payroll.
The Sales Forecast table for the first 12 months appears in the appendix.
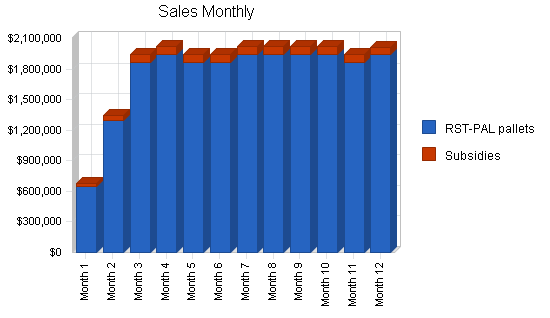
5.3.2 Pallet Users
PALLET USERS, Dallas / FT. Worth Area ANNUAL PALLET USAGE. The following list of pallet users was contacted and the new RST-PAL Pallet was introduced to each user, receiving excellent interest. Another 22 users were also visited. The Total yearly estimated usage of pallets in the DFW area is 60 million.
PALLET USERS, HOUSTON Area
5.4 Milestones
The following table lists important project milestones during the pre-production start-up period, with dates and managers in charge, and budgets for each milestone. The milestone schedule indicates our emphasis on planning for implementation.
The production schedule is based on three shifts. During the first month only one shift will be in operation, in the second month, two shifts, and from the third month, a full three shifts of production. During the start-up period, the employees will be located and trained.
The municipality of Stamford, Texas will assist us in recruiting about seventy employees. There is an adequate work force within the surrounding communities, which will enable us to choose quality people.
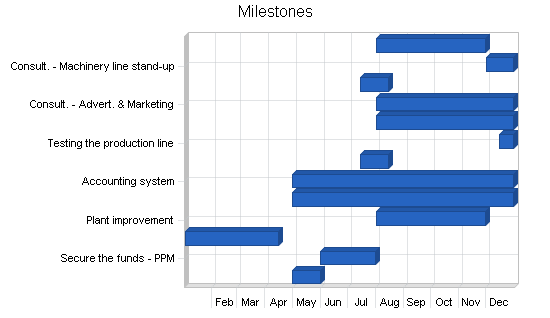
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
THE MANAGEMENT TEAM ATP’s management team and its consultants are qualified professionals with vast experience with plant installation and operations, purchasing and marketing. ATP’s consultants will be employed during the start-up period (see Start-up table). ATP welcomes any additional person from our investor’s group that can contribute to the success of the company.
Dan R. Radke, President: SUMMARY OF QUALIFICATIONS
- Dan Radke, the inventor of the unique material for making the RST-PAL Pallets, has been involved in scrap tire recycling issues for ten years by offering his expertise to government agencies, municipalities, individuals and companies wishing to enter the emerging scrap tire recycling industry, Radke has earned a reputation for his knowledge of the scrap tire industry. Assisted States, Counties and Municipalities to remediate scrap tire problems. Contributed to California Integrated Waste Management Board to develop rules, regulations and guidelines for the States scrap tire program.
- Process, technology inventor, business owner and manager, sales, marketing, production line machinery and equipment, business operations, training and management
- More than 30 years owning and operating start-up companies.
- Three years, international business transactions, as a consultant bringing American Companies to Eastern Europe, primarily Hungary to form U.S./Hungarian Joint Ventures.
- Authored the Hungarian Small Business Foundation to establish loan guarantees for privatization and start up Hungarian Small Businesses, working directly with the Hungarian Banks and Government.
Eliezer Banensohn, Vice President: SUMMARY OF QUALIFICATIONS
- Aeronautical Engineer – B.Sc. degree. Experience in R & D for new products.
- 12 years extensive experience as an expert in marketing of new and revolutionary products in new markets.
- Eight years experience as a specialist in putting up new franchise organizations and licensing operations.
- Won prizes for best business in South-Africa and Argentina (as VP Marketing & Engineering).
- Participated, in engineering capacity, in the development and marketing of revolutionary advanced building system – “Domecrete” in many countries worldwide.
- Participated, in engineering capacity, in the development of Hi-Tech product (Baby-Sense S.I.D.S. detector, medical industry).
- Plant design and Manufacturing experience in plastic, rubber, and metal products, injection molds and machinery. Inventor and patent owner for the product “non-electrical hand operated washing machine”.
- 25 years experience as computer software and hardware analyst.
- 15 years experience in marketing software and hardware computer systems.
- Owned several computer service bureaus using IBM mainframe
Shayne Del Cohen, (Consultant) Public Relations, Government Affairs
- Business and economic development, government relations, grant writing, bid preparation, business trade representations, lobbying, employee relations, training and staff planning.
Gene Pitzer, (Consultant) Machinery & Equipment Acquisitions
- Contract acquisition for machinery and equipment for Stamford, Texas plant, 25 years experience, retired No.1 tool and die manager for General Motors, Owner; Tool Consulting Corporation, developed tire recycling machinery.
Steven Garbukas, (Consultant) Chemical, Epoxy Binder Systems Acquisitions
- Contract acquisition for all special binder systems developed by Dan Radke and Steven Garbukas, source and supply plants with materials at best possible price, provide all injection and delivery systems to material during batching.
Richard Turner, (Consultant) Machinery and Equipment Line Standup, Plant Engineer
- Supervise and install all production line machinery and equipment at the first plant, in Stamford, Texas and all subsequent plants. Initial plant manager, over production and safety, will train employees, including plant manager.
Layne T. Rushforth, (Attorney)
Richard Dickinson, (CPA)
* (Resumes of any of the above people are available on request.)
6.1 Personnel Plan
Our first plant will be located in Stamford, Texas, a rural area close to a large metropolitan city, where large scrap tire stockpiles are located within less than one mile of our plant. The area has a large workforce in desperate need of jobs, which will help ATP recruit qualified and devoted workers, that will be paid more than the average wages for this area, which are less than in more populated areas. The direct labor cost shows that each plant will require approximately 70 workers in three shifts.
The team for the first manufacturing plant is currently being interviewed with the help of Stamford’s Mayor and City Manager. The Personnel table shows the position and salary of the 68 employees that will work in three shifts of eight hours each. Production is based on seven working hours with one hour budgeted for maintenance and crew change. To facilitate training, during the first month one shift will be in operation, in the second month, two shifts and from the third month forward the plant will operate at full production capacity with three shifts.
The Profit & Loss table shows the payroll burden as 23% of the salary, which covers the taxes and benefits for the employees. No increase in wages and salaries have been forecasted, however, it is assumed that as the company grows, employees will receive increases in their wages, salaries and benefits.
The Personnel table shows the direct and active involvement of the company President (the inventor) and the V.P. in all stages of the start up, purchasing of the machinery and running the business. The team includes highly qualified professionals as consultants in different areas that will enable a smooth and efficient entry to production. As the projected expansion takes place, ATP will begin a search for highly qualified management candidates that will manage the company in the future.
ATP will also investigate foreign licensing that will bring additional revenue streams to the company. ATP’s V.P. has already made contacts with foreign entities and has found great interest from foreign companies. Elie (VP) spearheads negotiations for foreign licensing and manufacturing.
The Personnel table for the first 12 months appears in the appendix.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The projected financial plan is very sound. The one-time investment gives ATP the ability to take 50% of the profits (after tax) as dividends at the end of year two and to self fund expansion by one additional plant per year. The projected cash flow is outstanding and will enable ATP to be even more aggressive in our expansion plans.
As mentioned throughout this Business Plan, each plant will produce a maximum of 100,000 pallets per month, which is very low in comparison to the demand for pallets. (800 million pallets divide by 12 gives approximately an average of 67 million pallets per month sold in the U.S.)
In addition to the expansion within the U.S., overseas licensing projects will be developed, from which we will create additional revenue streams through licensing fees, royalties, and other contractual payments.
ATP may also enter into other joint ventures or partnerships to license other entities to manufacture and market RST-PAL pallets not only in the U.S. but also worldwide.
The last two sources of income are not included in the financial forecast and do not appear in the tables.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The financial plan based on important assumptions, detailed in the following statements:
- Due to the initial limited production in comparison to the market size, ATP assumes that even a slow-growth economy, will not affect our plan for the next five years.
- ATP forecasts that there would be no unforeseen changes in technology to make our products obsolete. Pallet buyers are looking for cost effective solutions for replacing the high cost of purchasing, repairing, and discarding wooden pallets and RST-PAL pallets offer the solution by providing a longer lasting more durable pallet.
- Cash flow is not expected to be a problem, with most pallets being paid for on delivery. There will be exceptions for specific customers, as an example, the U.S. Government, based on the quantity of pallets that are ordered, but generally, payments for pallets will be paid in full upon delivery.
- ATP’s growth is based on internal financial resources. ATP will budget 50% for growth and 50% from the profits as dividends after taxes (from year two forward and as long as it does not affect the planned growth of the company).
- The source of raw material (scrap tires) is virtually endless as long as cars continue to roll on tires. Presently, 250 million tires are added each year to scrap tire stockpiles all over the country.
- ATP assumes a short holding of inventory beyond the curing time of the pallets and transportation arrangements.
- ATP assumes a 5% annual raise in our selling price, which is comparable to the wooden pallet industry and fluctuating lumber costs.
- ATP assumes no raise in our material costs, because the quantities we purchase will increase, and ATP anticipates discounts to offset any increased costs.
- ATP assumes an average sales price per pallet in the first year of production to be $18.50, which is significantly less costly than hardwood pallets whose entire cost includes purchase, repair, maintenance, and discard/disposal.
7.2 Break-even Analysis
This break-even analysis shows that ATP has budgeted fixed costs and projects sufficient sales to maintain good cash flow balances. This projection is based on two production lines.
The essential insight here is that ATP’s projected sales levels will be running comfortably above the break-even point.
7.3 Projected Profit and Loss
NOTES TO PROJECTED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
NOTE 1 – MATERIALS COST The raw materials, recycled scrap tire rubber, will be provided on an as needed basis. No large stockpiles of material or inventories of recycled rubber shall be stored at the manufacturing site.
The main ingredient of an RST-PAL pallet is recycled scrap tire rubber that has been processed to specific dimensions. There is three million tons of scrap tire shredded rubber on the ground in Texas with ten permitted processors or tire shredders, which want to provide material to ATP.
ATP will purchase scrap tire rubber from a Stamford, Texas processor, and has estimated the cost of material at $1.25/pallet ($50 per ton). It should be noted that ATP is working closely with the Texas Natural Resource and Conservation Commission and ATP may even have an opportunity to acquire surplus scrap tire rubber for less costs. Texas now produces approximately 200,000 tons of scrap tire rubber annually. In addition, the current Texas Legislature is considering paying manufacturers of products using recycled scrap tire rubber, $0.75 per pallet ($30 per ton) as an incentive to increase production of products using scrap tire rubber.
A small amount of recycled plastic is utilized in the formula and its cost is estimated at $0.90 per pallet. In addition a secret formulated binder, developed by the inventor Dan Radke, is used in the manufacture of the pallets, estimated to cost $6.50 per pallet.
NOTE 2 – DIRECT LABOR (Production Payroll) and PAYROLL BURDEN Projected Direct Labor includes the salary and wages for those employees directly involved in the pallet production process in the plant and is reflected in Topic 6.1. Payroll burden is estimated at 23% (FICA 6.20%; Medicare 1.45%; FUTA .80%; State Unemployment 3.00%; Workers Compensation and Employee Health Benefits 11.55%).
The total Direct Labor cost includes payroll burden and other direct costs such as utilities, building repairs and maintenance, plus plant supplies estimated at 5%. The total for direct labor cost and payroll burden per pallet is estimated at $1.31.
NOTE 3 – ROYALTIES The Licensing Agreement requires payment of 5% of gross sales to Mr. Radke, the inventor, as royalties. This may be paid quarterly or monthly (5% has been used throughout these projections). There will be no royalties for the first six months of production to help the cash flow of the company.
NOTE 4 -GENERAL & ADMINISTRATIVE WAGES AND PAYROLL BURDEN The company will employ Management and clerical staff as appears in the Personnel table, Topic 6.1. Additional management members and marketing representatives will be added as needed throughout the growth of the company. Payroll burden estimated at 23% including taxes, W/C, health and employee benefits. During the six-month start-up phase and thereafter, the company will employ experts in the industry as consultants.
NOTE 5 – DEPRECIATION Machinery and equipment is being depreciated over 10 years, property over 30 years.
NOTE 6 – OFFICE EXPENSES Provision has been made for estimated general office expenses. Computers and office equipment costing $15,000 is included in the initial start-up budget and Expensed Equipment. The amount budgeted for Year One is $12,000, which will increase at the rate of $12,000 per year with each additional plant.
NOTE 7 – MARKETING and SALES Management anticipates strong demand for the RST-PAL pallets creating a real challenge for production to keep up with the demand. Back orders are expected and sales on advanced production should drive expansion. With many potential pallet users identified, who currently use from 100,000 to 7 million pallets annually, we will approach the expansion of our national sales force, carefully. ATP does not want a large sales force with production sold out for months in advance. A budget in this category will be used for sales representatives or commissions on sales and is budgeted at $73,000 during year one. Based on attendance at conventions and trade shows it is anticipated that our targeted Dallas – Fort Worth Metropolis, Houston, San Antonio and the rest of Texas will absorb all our production for many years.
A Marketing Director shall develop goals and strategies with the board of directors. ATP plans to hire a qualified director in year one. Sales representatives will be hired and it is anticipated they will receive a base salary with commissions of ten cents per pallet sold. The budget takes these assumptions into consideration.
NOTE 8 – MACHINERY MAINTENANCE The initial production line machinery will be in good working order, nevertheless, ATP will plan for parts maintenance and replacement. This budget grows as more machinery and plants are established.
NOTE 9 – TAXES The “taxes incurred” appearing in the P&L represents State of Texas Franchise taxes and Federal Income Taxes for a total of 34%.
The Profit and Loss table for the first 12 months appears in the appendix.
7.4 Projected Cash Flow
The table presents our projected cash flow balances. The critical first year reflects positive cash flow. Monthly cash flow is positive and more important the balances are positive, which indicates adequate financial reserves and correct planning of the required working capital. The estimated results permit a margin of error and still appear strong, even though the numbers remain conservative.
ATP intends to distribute dividends to its shareholders in a way that will enable the continuation of the expansion of the company according to this Business Plan. ATP estimates that from year two forward 50% of the profit (after tax) will be distributed to the shareholders. The Board of Directors will determine any other distributions to be made on an annual basis.
The following chart shows the cash availability for the next 12 months. The bar labeled “Cash Balance” shows our projected cash balance for the first 12 months of the project and it is adequate (above zero). The second set of bars, labeled “Net Cash Flow”, indicates the change in the Cash Balance for each month.
7.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The Projected annual financial balances are shown in the following table. The balances for the first 12 months are presented in the appendix.
7.6 Business Ratios
Business ratios for the years of this plan are shown below. Industry profile ratios based on the Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) code 2448, Wood Pallets and Skids, are the closest available and are shown for comparison. ATP’s patented technologies are so new, that there is no SIC code that directly applies.
7.7 Long-term Plan
In addition to the enclosed financial information contained in this Business Plan, ATP would like to make the following observations that were not emphasized in this Business Plan:
The Business Plan covers five years of activities. We consider the financial projections in the Business Plan as conservative. As an example; since July 2002, (the date the patent was issued), ATP’s Vice President, Elie Banensohn has traveled to several European countries and has met with representatives of companies from the Far East. These companies recognize the value of RST-PAL pallets and have shown an interest in licensing the technology in order to manufacture and market the pallets in their countries (in some cases with our participation). The Business Plan does not include any income from licensing fees or royalties from foreign entities. Scrap tire problems exists everywhere and is even more acute in Europe and the Far East as they have less space for storage and less scrap tire processing technology than the U.S.
Revenues include some benefits from State or Federal level subsidies or grants for helping to clean up scrap tire problems, which are available. There are States that are offering participation in funding new companies using scrap tire rubber. ATP and its Board of Directors believe that demand for RST-PAL pallets may cause expansion plans to be reviewed and changed, assuming demand will be high. After initial exposure of RST-PAL pallets to the market, additional plants may need to be installed sooner than the company growth plan calls for.
As previously mentioned, a division or subsidiary of ATP will be proposed to manage the pallet leasing aspect of sales, which will afford pallet users the option to change over their entire inventories of wooden pallets to RST pallets on a “lease to purchase” plan. ATP anticipates substantial revenues and success in the pallet leasing market.
1. Why did you choose Stamford, Texas as your first location?
- One of the largest piles of shredded scrap tires in Texas is located in Stamford. The quantities of raw material in this pile are enough for ten years of full production.
- The state of Texas pays for making final products from the scrapped tires about $30 per ton (approximately $0.75 per pallet).
- In the area of DFW (about a radius of 150 miles around) the yearly consumption of new pallets is about sixty million.
- The local municipality is very helpful. Rural America has unemployment problems. Therefore the local authorities have offered to subsidize the plant for our production lines, by enabling us to use a new existing building of 60,000 sq.ft. with all the facilities including: offices, rest rooms, electricity, air conditioning, boiler system etc. and the property is located on seven acres with the building which can be used for storing and loading pallets and employee parking, all offered with great terms and conditions.
- The location of this plant is less than one mile from the scrap tire pile.
2. If your plant is in Texas why is your headquarters is in Las Vegas? As can be seen from our Business Plan, ATP expects to open four plants in the next five years. These plants will be in different states. Las Vegas was chosen as our corporate headquarters because of the following reasons:
- Las Vegas is also a popular tourist destination for business people throughout the world. Vegas has excellent airline connections, which offers a real opportunity to bring executives to visit and learn more about RST-PAL pallets and how it will positively affect their company profits.
3. Is there any financial help from the State administration in putting up the plant in their State? There are several States, among them Louisiana and New Jersey that are giving up to 80% of the capital cost of putting up a plant that will utilize scrap tires. The problem of scrap tires is enormous and exists in most states. Most states have scrap tire programs to deal with the remediation of scrap tires.
4. Are there any federal laws regarding the use of recycled products? Yes, all Federal Agencies, including the Department of Defense and Department of Transportation are mandated to use “recycled products first”. Our product is made from recycled materials and is very strong and durable and is acceptable for Government use due to its life cycle being much longer than a traditional wooden pallet, and the price of a RST-PAL pallets is very competitive.
5. How does the production of pallets made from scrap tires helps the ecology? The RST-PAL pallet is an environmentally correct product made from recycled materials that can be recycled itself, making it a “triple green product”. First, according to statistics published by NWPCA (National Wooden Pallet and Container Association) the U.S. consumption of pallets is 800 million per year. To make this huge quantity of pallets, 3.5 million trees are cut every year. Every RST-PAL pallet sold will help to save our forests, allowing hardwoods to be used for more important and valuable uses other than pallets.
Second, getting rid of the scrap tire piles is a worldwide problem. This problem is even more acute in Europe and the Far East. Each year in the U.S. 250-280 million tires are added to the existing stockpiles of scrap tires. These piles are environmental hazards as they can become disastrous tire fires and are breeding grounds for mosquitoes (which bring diseases such as the West Nile Virus), rodents, snakes, and other vermin.
6. Are the projections in ATP’s Business Plan “Too good to be true”? ATP believes that the projections, although they are very positive, are conservative. We also believe our biggest challenge will be keeping up with the production needed to meet the demand for our pallets. When a company evaluates the annual cost of their wooden pallets, including; purchase, repair, replacement, and discarding costs versus the one time purchase price of RST-PAL pallets, they will see tremendous savings in buying and using RST-PAL pallets.
Regarding the financial forecasts, ATP has purposely left out several positive issues. For example, the cost of recycled rubber (cut and prepared for our use) is $1.25/pallet. This cost can be reduced drastically by purchasing a special machine (Grizli) and cutting the tire shreds to our specific dimensions. The price of the machine can be recovered within one year of production. Additionally, the most expensive cost in making our pallets is the binder system, $6.50/pallet. Our projections do not take into consideration the savings of using even less binder per pallet which will be achieved by utilizing the new production line machinery, with a different delivery system. We estimate a minimum saving of 25% on our projected costs when we will buy the raw material and batch it ourselves.
Additional savings will be achieved by getting larger discounts as the volume of materials purchased increases.
Other potential revenue streams that are not projected include licensing ATP technology to foreign countries to manufacture and market RST-PAL pallets. In addition ATP anticipates opening a subsidiary company to provide pallet leasing or a lease to purchase program for our customers to enable them the opportunity to convert their wooden pallet inventory to RST-PAL pallets at an accelerated pace.
7. How are the scrap tires used today? Only a small portion of scrap tires are recycled or used today. The main use (about 30%) is adding crumb rubber to asphalt for making roads. Other products that are made of scrap tires are: car floor mats, playground filler, floor tiles and some other soft products which do not need strength or rigidity of the final material. Scrap tire piles continue to accumulate all over the country and constitute dangerous environmental hazards.
8.What is the real market potential and what is the risk if the users do not accept the pallets? As previously stated, of the 800 million pallets manufactured each year, about 60% are made from hardwood. Our product replaces the hardwood pallets, and if you look at our 5-year projection, we will produce approximately 19 million pallets while in the same 5 years the pallets industry will produce 2.4 billion hardwood pallets, which means we will capture, within 5 years, about 0.8% (less than 1%) of the total pallet market.
ATP surveyed the acceptance of RST-PAL pallets through pre-production marketing efforts and it was excellent. We visited 62 pallet users in the DFW area. All of the companies were impressed with the RST-PAL pallets made from this unique and patented “new material” from recycled scrap tires. Many stated that they would use the pallets once we had a production facility. They were especially impressed that our pallets were stronger and more durable than wooden pallets and would perform much longer than wooden pallets. NWPCA states, “wooden pallets last from 1.5 to 2 trips before having to be repaired or replaced.” We also visited with the buyer of pallets for 3M company in Minneapolis, and the buyer was very eager to use RST-PAL pallets. 3M purchases more than 7 million pallets in just one year. ATP also contacted, through the Department of Defense, the Army, Air Force PX and Exchange, AAFAS. They actually wanted us to deliver 50,000 pallets as an initial order but unfortunately we were not in production.
9.Can you show us orders from companies that were interested in using your pallet? No. As we have not begun production, we cannot guarantee that ATP will be able to deliver pallets on a specific date, and so we have not accepted any orders. As the projected calculation shows tremendous savings to the user, and as RST-PAL pallets have so many advantages in comparison to wooden pallets and at a competitive price, ATP believes that when production commences, pallets will be immediately accepted. Some of the users we visited were surprised that the price was so low in relation to the performances of RST-PAL pallets.
10. What are the technical properties of the pallets and which tests have already done? The technical data and the tests results are as follows:
- RST-PAL pallets are both rackable and stackable, and pass ISO standards.
- The RST-PAL pallets have the same parameters as hardwood pallets, including two or four way entry, and meet GMA pallet standards.
- Weight: 40″x48″, four way GMA pallet, hardwood=65 lbs; RST-PAL=71 lbs. The difference in weight disappears after the wood starts absorbing water/liquids.
- The deflection of a pallet with our material, according to ISO when R=1500KG, is about zero (actually equal to the deflection of metal under the same load).
- A test was conducted with 3 concrete beams weighing 25 tons (51,000 lbs), which were loaded and lifted onto an RST-PAL pallet. In comparison, wooden pallets have a static weight load of 2,500 pounds.
In conclusion, this is not a high precision, high tech product — it is a strong and durable pallet with excellent material qualities and is offered to pallet users at a very competitive price, which will save pallet buyers bottom line profits.
11. Usually, as production increases, the price normally decreases (mainly because of competition). In your B.P. the price is increased. Please explain? Actually, part of the answer is in the question. There is no competition. Hardwood is a commodity and its price changes constantly with lumber prices (which continue to increase annually). Our increase in price takes this fact into account. The raise in prices, as appears in our projections, of 25% during the next five years is probably less than the increase in the cost of hardwood. Another reason is that our initial price is very low, designed so that ATP can penetrate different markets rapidly.
Most key pallet purchasers that we talk with, think we are vastly under priced for a pallet that is so durable and lasts so long. Some believe RST-PAL pallets should be in the $39.00-$59.00 price range (similar to plastic pallets), and not just a few dollars more than hardwood pallets. ATP assumes that for many years (due to patent protection) RST-PAL pallets will not have competitors, which can often drive the price down. The assumption is that the advantages of RST-PAL pallets over hardwood pallets will cause pallet users to purchase RST-PAL pallets to lower their pallet costs. Following RST-PAL pallets becoming established in the market place, the advantages and the savings will be widely recognized and there will be justification for further price increases.
The opening price of $18.50 is an average price and not applicable to all sizes nor to all customers. Certainly, a customer purchasing 500,000 pallets per year will be given a discount different from a customer purchasing 1,000 pallets.
The Board of Directors will re-visit the $18.50 price as sales develop. Our projected low price is intended to introduce the pallet to many different manufacturers and industries that use pallets, targeting those companies with a closed loop system that can use, retrieve and use over and over again the same durable pallets.
12. Everything seems so good, what is the down side to this project? ATP believes that according to the projections, the only downside is our start-up production capacity. ATP knows that it will capture the small percentage of less than 1% of the total market demand. The projection shows that this 1% of the market will enable both growth from profits to fund expansion and a good return in the form of dividends for its investors.
RST-PAL pallets are heavier, by about 8 lbs, than the equivalent size pallet made of hardwood. This is true only at the beginning of the lifecycle of a wooden pallet as wood absorbs water and other liquids and can become even heavier than RST-PAL pallets. An average 40′ truck trailer carries about 22 loaded pallets, and by using RST-PAL pallets the total added weight is less than 200 lbs, which is not significant.
13. Is your patent defendable and what does it actually protect? The patent was approved and issued in July 2002. It took about five years to perfect and to reach the utmost protection possible. It protects any product made from recycled scrap tire rubber using a plurality of sizes with or without other materials like plastic, adhesives etc.
14. Who has the exclusivity to utilize this patent? The total and irrevocable exclusivity was granted to ATP Corporation, which consists of the new investors and the existing partners. This exclusivity includes licensing to other parties worldwide for the manufacturing and marketing of RST-PAL pallets.
15. It appears that you are looking for investment of $4M to $6M. Elaborate. These two numbers express the difference between starting with one line of production vs. two lines. The basic set of machines needed for production can be extended to two lines with addition of some machines. By starting with two lines, the production capacity is doubled to 1.2M pallets per year with net profit projected of over $8M versus $3.2M if ATP opens with a single line.
16. How will the investor’s capital be used? A detailed start-up expenses and funding table can be found in Topic 2.2. The main expense item is for machinery and in both cases about $750,000 remains as working capital.
17. What equity percentage are you offering for the investment? The calculation of the present value of the company based on the projections appears in the business plan. The present value of five years of net earnings at 25% discount is over $100 million. We deliberately took an unreasonably high discount rate to avoid any disputes.
We value our company at “present value” of just over $17M. Hence, for the $6 million investment; we offer 35% of the company with all its rights.
18. Is there any other way of financing the project? Yes. We would accept a loan, secured by the assets and rights of ATP, which will carry interest of 5% for a period of ten years starting (the repayment) at the beginning of the second year. The return can be accelerated.
In addition to the secured note, the lender will be offered 17.5% equity interest for a loan of $6 million.
19. Who is ATP’s management team? See Chapter 6.0 of the Business Plan. Each member of the team along with our consultants, are highly qualified professionals with vast and proven experience in their fields (e.g. plant installation and operations, purchasing and marketing). ATP is also open to investor participation both in the company and on the Board of Directors.
The financial projections that appear in this Business Plan are estimated revenues, expenses, and cash flow, which are based on research and the assumptions discussed throughout this Business Plan. They represent the best of management’s knowledge and belief and also are based on actual operations in the pilot plant in Stamford, Texas. The Company’s expected revenues, expenses, and cash flow for the projected periods are subject to the Company’s ability to develop sales and production levels at the price and costs estimated by management. Accordingly, these projections reflect management’s estimates as of January-June 2003, and its expected course of action if such sales and production levels are attained at the price and costs anticipated.
These projected financial statements are for the purpose of providing updated information to existing and new investors. These projected financial statements should not be considered to be a presentation to forecast future results. Accordingly, these projections may not be useful for other purposes.
The assumptions disclosed herein are those that management believes are significant to the projections. Furthermore, even if the sales and production levels as well as the projected price and costs are attained, there will usually be differences between projected and actual results because events and circumstances frequently do not occur as expected, and those differences may be material.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Titus Mold Manufacturing, Inc. is located in Molder, Missouri. Our company designs and manufactures prototypes and molds for use in casting metals or forming other materials, such as plastics, glass or rubber. Our business operates within the manufacturing industry and is classified under NAICS code 333511 - industrial mold manufacturing.
The Plan. Our manufacturing business plan covers all essential aspects necessary for a comprehensive strategy. It details operations, marketing strategy, market environment, competitors, management team, and financial forecasts. Executive Summary: Provides an overview of the manufacturing company's business concept, market analysis ...
The capital will be used for funding capital expenditures, salaries, marketing expenses, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows: Manufacturing facility design/build-out: $400,000. Equipment and supplies: $375,000. Initial inventory: $100,000. Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $250,000.
A manufacturing business plan is a formal document that outlines the goals and objectives of your business. It includes detailed information about your: The purpose of a business plan is to give you a roadmap to follow as you build and grow your business. It forces you to think through every aspect of your venture and identify potential ...
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a manufacturing business, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of manufacturing company that you documented in your Company Analysis.
If you are planning to start a new manufacturing, fabrication, or production business, the first thing you will need is a business plan.Use our business plan example created using upmetrics business plan software to start writing your business plan in no time.. Before you start writing your business plan for your new manufacturing business, spend as much time as you can reading through some ...
If you're planning to start a manufacturing, fabrication, or production business you'll need a business plan to do it. To help you get started, check out our library of sample plans to be sure you're covering everything from sourcing your raw materials to budgeting for plant and equipment.
Fortunately, the #1 Manufacturing Business Plan Template & Guidebook provides entrepreneurs and businesses with a detailed roadmap for success. With this template and guidebook, you will have the guidance you need to plan for success and develop a comprehensive business plan that outlines your vision and strategy. Written by:
Manufacturing A Company Of Quality Business Plan [YEAR] John Doe 10200 Bolsa Ave, Westminster, CA, 92683 (650) 359-3153 [email protected] https://upmetrics.co
This Manufacturing Business Plan template is designed to help manufacturers of all sizes and industries create a plan to launch, run and grow their business. It provides a framework to clearly define and measure the objectives, actions, and measurements that are necessary for success. 1. Define clear examples of your focus areas.
Here are some streamlined steps to organize your ideas a how to start a manufacturing business from scratch: 1. Target Products and By-Products. The first and obvious step is to narrow down what exactly you want to manufacture and sell. If you're reading this, you most likely have a product or niche in mind already.
3. Pick a name and create a logo. Now it's time to start legitimizing your business. When it comes to manufacturer branding, your name and your logo are going to be part of what defines you. In the world of business, together, your name and logo make your dream venture into a "real business" — it authenticates you.
Below are links to each of the key sections of a sample manufacturing business plan. Once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors. I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team
Our template provides a comprehensive framework for outlining your company's goals, conducting market analysis, projecting finances, and strategizing your operations. With ClickUp's Business Plan Template, you'll be able to: Clearly define your company's vision, mission, and objectives. Conduct a thorough market analysis to understand your ...
Since the equipment and building are already drawn on the computer, this step is more of a "drag and drop" process. On the computer, the designer will move around equipment, change its orientation, and find the best place for the physical pieces. Jump to 2:34-5:50 in the video below to see how it works in practice. 5.
Tracking Device Maker Business Plan. RQM Technologies (RQM) is a start-up company which will develop and distribute miniaturized Personal Locator Devices. There are plenty of emerging and traditional industries in need of equipment manufacturers. Companies that can do it better, faster, cheaper, or more specifically to suit their needs.
By. Susan Ward. Updated on September 13, 2022. Fact checked by David Rubin. In This Article. How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan. Stage of Development Section. Production Process Section. The Bottom Line.
Analyze Competition. One of the crucial steps in developing a business plan for a cement manufacturing plant is analyzing the competition. Understanding your competitors and their strategies will provide valuable insights for positioning your plant in the market. Start by identifying the key players in the cement manufacturing industry.
The production planning process consists of an organization's actions to make a production strategy that allows it to manufacture products most efficiently and profitably. Here are 10 key steps you should follow when planning your production process. 1. Use Production Forecasting Methods for Estimating Customer Demand.
This plan will result in sales revenues growing to almost $420,000 by Year 3. The Pasta Tree is located in a 3,000 square feet facility that operates as a storefront and a production facility. With the expansion, 3/4 of the area will be dedicated to production. The preparation of the new production space will cost $10,000.
A manufacturing plan is a key piece of your food business' overall strategic plan. Your manufacturing plan is a clear set of actions driven by gaps and discoveries from your manufacturing analysis, or the analysis of your business' manufacturing processes. It defines what your manufacturing strategy will look like in the future, whether it ...
Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Billy Jones® Syringes and Injection Needle Manufacturing, Inc. in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580. The total cost for hiring Business Consultant - $2,500.
Equipment maker JCB breaks ground on its Southside manufacturing plant. Local officials took up gold-tinted shovels Tuesday, joining the leaders of one of the world's largest equipment makers in a groundbreaking ceremony for what some are calling the biggest deal in San Antonio business since Toyota. The Great Britain-based JCB marked the ...
The company says some employees have been given the chance to transfer to the plant in Dinuba. The business was founded in 1964 and is the country's largest manufacturer of Mexican food.
FILE - A sign for Eli Lilly & Co. sits outside their corporate headquarters in Indianapolis on April 26, 2017. Eli Lilly will spend more than $5 billion to expand an Indiana manufacturing site and eventually make more doses of its hot-selling weight-loss and diabetes treatments, Zepbound and Mounjaro. The drugmaker said Friday, May 24, 2024 ...
REUTERS/Brendan McDermid. (Reuters) - Campbell Soup on Tuesday said it plans to reduce the size of its Jeffersonville, Indiana site and close Tualatin, Oregon site, leading to 415 job cuts. It ...
Tesla broke ground on a new manufacturing plant in Shanghai on Thursday, just weeks after CEO Elon Musk made a surprise visit to China in a bid to shore up the carmaker's slumping sales.
The Marion plant, located at 100 Hino Blvd., opened in October 2006. The plant closure will be completed by 2027. Hino Motors Manufacturing U.S.A. Inc. has been in operation since 1994 and has ...
The team for the first manufacturing plant is currently being interviewed with the help of Stamford's Mayor and City Manager. The Personnel table shows the position and salary of the 68 employees that will work in three shifts of eight hours each. ... As mentioned throughout this Business Plan, each plant will produce a maximum of 100,000 ...
June 06, 2024 12:11 PM. A Spanish chemical company is investing $30.5 million to open its first U.S. manufacturing plant, a move that will bring 100 jobs to Union County. Briolf USA, a U.S ...